Page 1

SRC4382EVM-PDK and SRC4392EVM-PDK User's Guide
This user’s guide provides a reference document for the SRC4382EVM-PDK and
SRC4392EVM-PDK product development kits. The kits include either an SRC4382EVM
or an SRC4392EVM daughterboard, as well as a DAIMB motherboard. Together, the
daughter and mother boards form a modular platform for evaluating the function and
performance of the Texas Instruments’ SRC4382 and SRC4392 integrated circuits.
Applications software is provided with the PDK for writing and reading registers and
data buffers integral to the SRC4382 and SRC4392 devices. The software
communicates with the device under test using the USB slave interface on the DAIMB
board. The software requires a host PC running the Microsoft Windows™ 2000 or XP
operating system.
Throughout this document, the acronym EVM and the phrase evaluation module are
synonymous with the SRC4382EVM and SRC4392EVM. The acronym PDK refers to
the daughterboard EVM and DAIMB motherboard combination. This document includes
information regarding absolute operating conditions, hardware configuration, and
software installation and operation. Complete electrical schematics and a bill of
materials for both the EVM and the DAIMB boards are also included.
User's Guide
SBOU038 – April 2006
1 Introduction .......................................................................................... 2
2 Quick Start ........................................................................................... 3
3 Software Overview, Installation, and Operation ................................................ 9
4 Hardware Reference .............................................................................. 14
1 Illustration of the PDK Platform Utilizing a DAIMB Motherboard and a
Daughterboard EVM ............................................................................... 2
2 Power-Supply Jumper Configuration (DAIMB Motherboard) ................................. 5
3 PDK Power, Host, and Input/Output Connections ............................................. 8
4 Applications Software Window (USB Serial Commander) ................................... 10
5 Example of a Readback Display and Break Message in the USB Serial Commander
Application ......................................................................................... 12
6 Electrical Schematic: SRC4382/92EVM Daughterboard ..................................... 15
7 Electrical Schematic: DAIMB Motherboard, Page 1 .......................................... 16
8 Electrical Schematic: DAIMB Motherboard, Page 2 .......................................... 17
1 Absolute Operating Conditions ................................................................... 4
2 Jumper JMP3 Configuration (EVM Daughterboard) ........................................... 5
3 Jumper JMP4 Configuration (EVM Daughterboard) ........................................... 5
4 Jumper JMP5 Configuration (EVM Daughterboard) ........................................... 5
5 Jumper JMP1, RX4 Input Selection (EVM Daughterboard) ................................... 6
6 Audio Serial Port Slave/Master Switch Configuration (DAIMB Motherboard) .............. 6
I2C, I2S are trademarks of Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V.
Windows is a trademark of Microsoft Corporation.
SPI is a trademark of Motorola, Inc.
NI-VISA is a trademark of National Instruments.
WinZip is a trademark of WinZip International, LLC.
All trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Contents
List of Figures
List of Tables
SBOU038 – April 2006 SRC4382EVM-PDK and SRC4392EVM-PDK User's Guide 1
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 2
www.ti.com
PORT C
PORT D
TX1
110W
Power
Adapter
+5V VIO EXT SPI EXT I C and DIO2USB
PORT A
PORT B
RX1
110W
RX1
75W
RX2
75W
RX3
75W
RX4
75W
OPTICALINLOGICINEXT
MCLK1
EXT
MCLK2
LOGIC
OUT
OPTICAL
OUT
TX1
75W
75W
TX2
TX3
75W
TX4
75W
DAIMB
(Motherboard)
EVM
(Daughterboard)
J1
J2
J5
J6
J7
J8
J9
U9
J10
J17
J18
J3
J4
J12
J13
J14
J15
J11
J16
U13
J19
J20
J21 J22
J23
J24
JA JB
JC
JD
JF
HOST I/O
PORTS
A and B
PORTS
C and D
DAI
IN
DAI
OUT
JE
POWER
Introduction
7 USB SPI PortConfiguration (DAIMB Motherboard) ............................................ 6
8 MCLK1 Clock Source Selection (DAIMB Daughterboard) .................................... 7
9 MCLK2 Clock Source Selection (DAIMB Daughterboard) .................................... 7
10 SRC Output Mute Configuration (EVM Daughterboard) ....................................... 7
11 SRC4382/4392 Control Port Mode Configuration (EVM Daughterboard) ................... 7
12 I
2
C 7-Bit Slave Address Configuration (EVM Daughterboard) ................................ 8
13 SPI Command Syntax ............................................................................ 12
14 I
2
C Command Syntax ............................................................................. 13
15 Bill of Materials for the SRC4382/92EVM ..................................................... 18
16 Bill of Materials for the DAIMB .................................................................. 19
1 Introduction
The SRC4382EVM-PDK and the SRC4392EVM-PDK provide a modular solution for evaluating the
function and performance of the SRC4382 and SRC4392 devices from Texas Instruments. The PDK
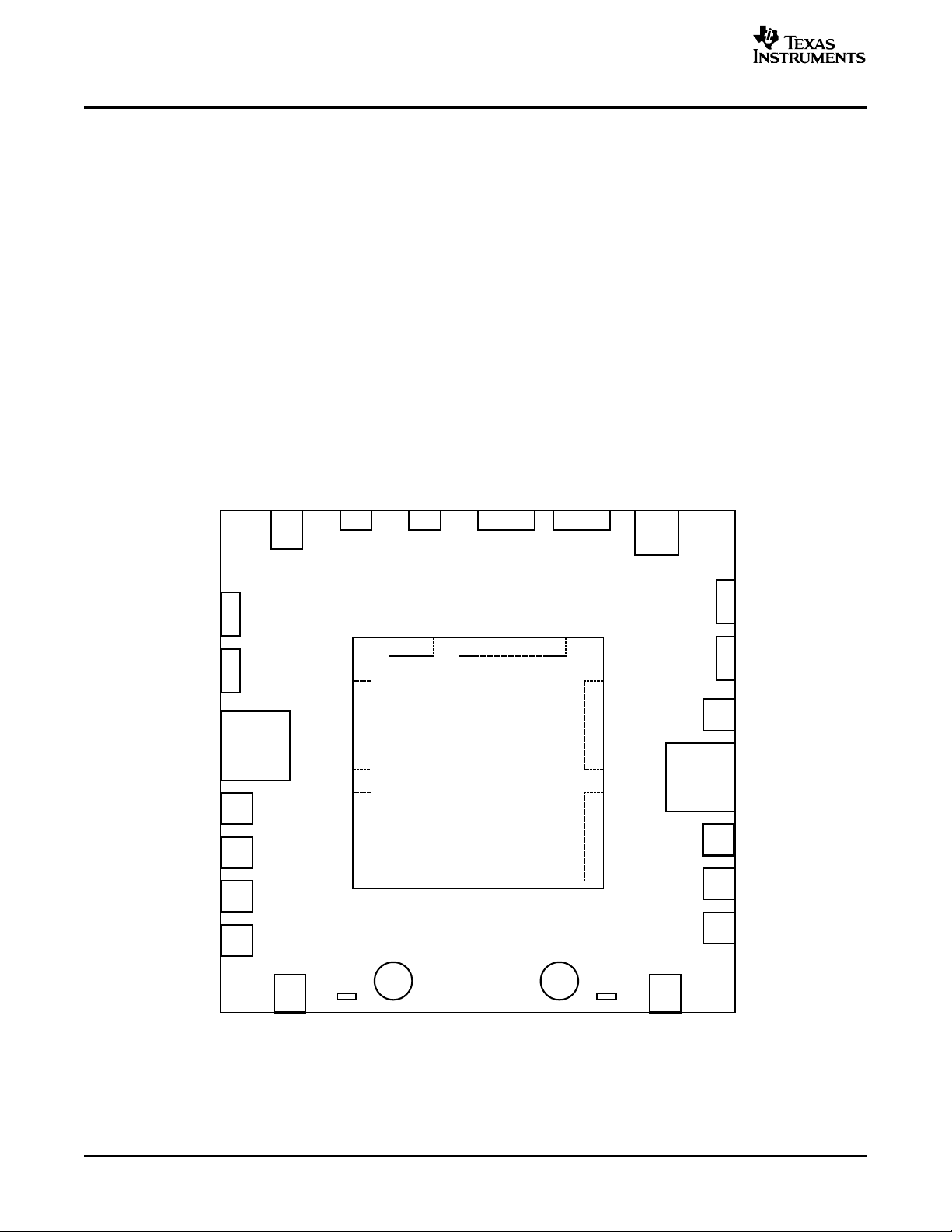
includes a motherboard (the DAIMB) and a daughterboard (the EVM). Figure 1 depicts the modular
platform concept, with the EVM plugged into the DAIMB board. Connectors are indicated and labeled for
ease of identification.
Figure 1. Illustration of the PDK Platform Utilizing a DAIMB Motherboard and a Daughterboard EVM
2 SRC4382EVM-PDK and SRC4392EVM-PDK User's Guide SBOU038 – April 2006
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 3
www.ti.com
Quick Start
The modular design allows for common functions to be integrated onto the DAIMB motherboard, while
device-specific functions are integrated onto the daughterboard EVM. The modular platform supports a
variety of digital audio interface devices by simply replacing the daughterboard EVM shipped with the
product specific PDK. Texas Instruments products supported by this modular platform include digital audio
interface receivers, transmitters, transceivers, and combination SRC/transceiver products.
The primary features of the SRC4382EVM-PDK and SRC4392EVM-PDK include:
• A USB slave interface, implemented with a Texas Instruments TAS1020B USB controller, and
supported by computers running Microsoft Windows 2000 or XP. The USB interface supports bus or
self-powered operation, and communicates with the EVM daugther board via an SPI™ or I2C™
interface.
• Buffered headers support up to four audio serial port interfaces, compatible with I2S™-style or
time-division multiplexed (TDM) data formats. Only two of these ports are utilized for the
SRC4382EVM and SRC4392EVM.
• Six digital audio input ports support AES3 balanced inputs, S/PDIF coaxial and optical sources, and
CMOS logic level inputs.
• Six digital audio output ports support AES3 balanced, S/PDIF coaxial and optical, and CMOS logic
level outputs. Three of the ports are utilized for the SRC4382EVM and SRC4392EVM.
• Flexible reference and master clock generation are supported, using either onboard oscillators or
external clock sources.
• Power may be provided from a wall adapter (included), or an external +5V regulated power supply. An
optional external logic I/O (or VIO) supply connection is also supported.
• Onboard linear regulators derive +1.8V, +3.3V, and +5V power supplies from the supplied power
adapter, external supplies, and/or the USB bus connection.
• LED indicators are provided for DIR Lock and SRC Ready output flags.
• Applications software provides functions for writing and reading the on-chip registers and data buffers.
The applications software is compatible with personal computers with at least one USB 1.x or 2.0 port
running the Microsoft Windows 2000 or XP operating systems.
2 Quick Start
This section provides information regarding handling, package contents, and the absolute operating
conditions for the SRC4392/82EVM.
2.1 Electrostatic Discharge Warning
Failure to observe proper ESD handling precautions may result in
damage to EVM components.
Many of the components used in the assembly of the PDK are susceptible to damage by electrostatic
discharge (ESD). Customers are advised to observe proper ESD handling procedure when unpacking and
handling the PDK components. All handling should be performed at an approved ESD workstation or test
bench, using a grounded wrist strap. Failure to observe proper handling procedure may result in damage
to EVM components.
WARNING
SBOU038 – April 2006 SRC4382EVM-PDK and SRC4392EVM-PDK User's Guide 3
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 4
www.ti.com
Quick Start
2.2 Product Development Kit (PDK) Package Contents
Either the SRC4382EVM or SRC4392EVM is included as part of a complete evaluation module package,
referred to as a Product Development Kit, or PDK. Each PDK package includes:
• One SRC4382EVM or SRC4392EVM board, depending upon the PDK ordered.
• One DAIMB board.
• One printed copy of this SRC4382EVM-PDK and SRC4392EVM-PDK User’s Guide.
• One printed copy of the SRC4382 or SRC4392 datasheet, depending upon the PDK ordered.
• One power supply for powering the PDK.
• One USB cable (Type A to Type B male plugs).
• One CD-ROM containing the EVM applications software, support files, and documentation.
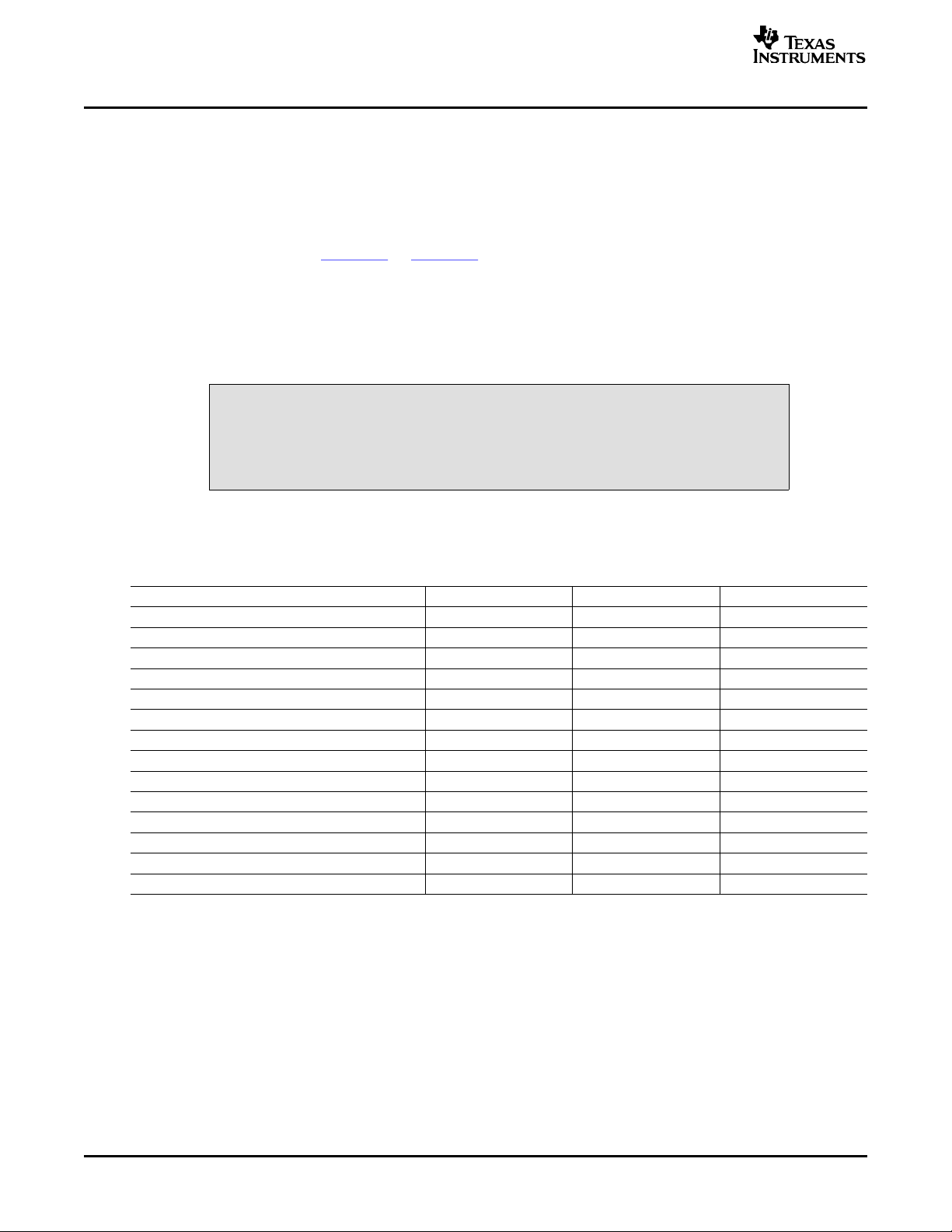
2.3 Absolute Operating Conditions
Exceeding the absolute operating conditions may result in improper EVM
operation or damage to the evaluation module and/or the equipment connected
to it.
The user should be aware of the absolute operating conditions for the PDK. Table 1 summarizes these
conditions.
CAUTION
Table 1. Absolute Operating Conditions
Min Max Units
Power Supplies
Power Adapter (J19) +6.0 +10.0 VDC
EXT +5V (J20) –0.3 +5.5 VDC
EXT VIO –0.3 +3.6 VDC
Digital Input Voltage Range
daughterboard Connectors (JA–JD,JF) –0.3 +3.6 V
PORT A through PORT D (J1–J4) –0.3 +3.6 V
EXT SPI and EXT I2C & DIO (J22 and J23) –0.3 +3.6 V
RX1 Balanced Input (J5), measured differentially — 7.2 V
RX1 Unbalanced Input (J6) — 3.6 V
RX2 through RX4 (J7–J9) — 3.6 V
EXT MCLK1 and EXT MCLK2 (J17 and J18) –0.3 +3.6 V
LOGIC INPUT (J10) –0.3 +5.5 V
PDK Operating Temperature 0 +70 ° C
PP
PP
PP
2.4 Jumper Configuration
This sub-section provides an overview of the required jumper configuration for both the DAIMB
motherboard and EVM daughterboard. Refer to the electrical schematics included in Section 4 of this
document for connection details, as well as jumper functions that may not be discussed in this section.
4 SRC4382EVM-PDK and SRC4392EVM-PDK User's Guide SBOU038 – April 2006
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 5
www.ti.com
External +5V (J20)
Power Adapter (U17)
1
2
3
4
JMP1
EXT
+5V
ADAPTER
External VIO (J21)
+1.8V (U18)
JMP2
1
2
3
4
VIO
+3.3V (U19)
5
6
+5V (selected by JMP1)
+5V from USB Port (J24)
1
2
3
4
JMP3
SELF
To Input
of U20
BUS
2.4.1 Power Supply Jumpers
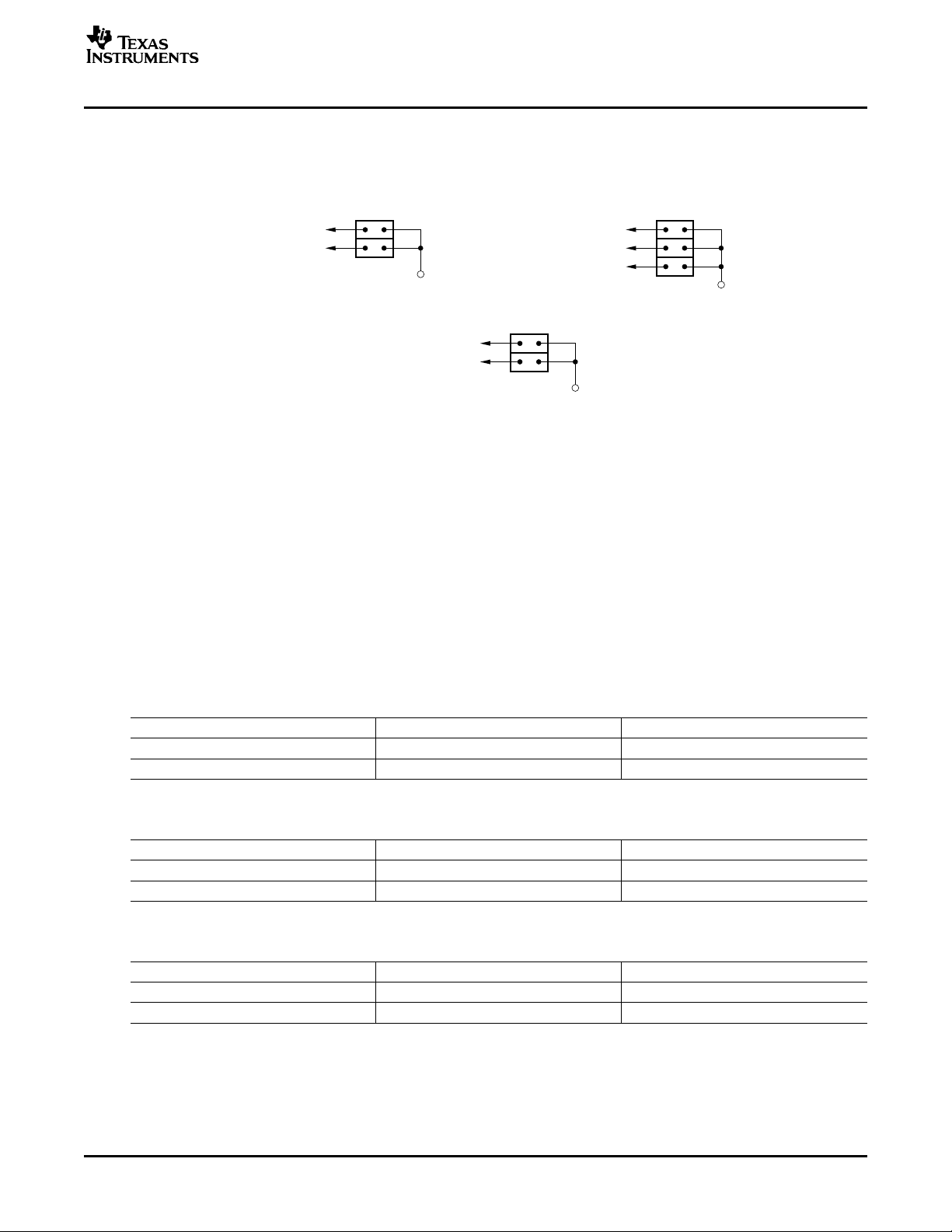
Power-supply configuration for the PDK is set up using jumpers JMP1 through JMP3, located on the
DAIMB motherboard. Figure 2 illustrates the options for each of these jumpers.
By default, jumper JMP1 is configured for Power Adapter input at J19, jumper JMP2 is set up for a +3.3V
logic I/O (or VIO) supply, and jumper JMP3 is set up for Bus power operation (+5V from connector J24).
The +3.3V logic I/O supply is required in this case to maintain logic level compatibility with the USB slave
interface circuitry.
Jumpers JMP6 through JMP9 on the EVM daughterboard are provided for measuring power-supply
current. By default, these jumpers are shorted with bus wire, soldered during assembly of the board.
Quick Start
Figure 2. Power-Supply Jumper Configuration (DAIMB Motherboard)
2.4.2 SPI and I2C Jumpers
SBOU038 – April 2006 SRC4382EVM-PDK and SRC4392EVM-PDK User's Guide 5
Submit Documentation Feedback
Jumpers JMP3 through JMP5, located on the EVM daughterboard, are utilized to select SPI or I2C host
interface connections for the SRC4382EVM or SRC4392EVM. Refer to Table 2 through Table 4 for
jumper configuration.
Table 2. Jumper JMP3 Configuration (EVM Daughterboard)
JMP3 Pins 1–2 JMP3 Pins 3–4 Host Interface Selection
OPEN SHORT SPI
SHORT OPEN I2C
Table 3. Jumper JMP4 Configuration (EVM Daughterboard)
JMP4 Pins 1–2 JMP4 Pins 3–4 Host Interface Selection
OPEN SHORT SPI
SHORT OPEN I2C
Table 4. Jumper JMP5 Configuration (EVM Daughterboard)
JMP5 Pins 1-2 JMP5 Pins 3-4 Host Interface Selection
OPEN OPEN SPI
SHORT SHORT I2C
Page 6
www.ti.com
Quick Start
2.4.3 RX4 Receiver Input Jumper
Jumper JMP1, located on the EVM daughterboard, is utilized to select the input source for the RX4 line
receiver inputs. Selection options are shown in Table 5 .
Table 5. Jumper JMP1, RX4 Input Selection (EVM Daughterboard)
JMP1 Pins JMP1 Pins JMP1 Pins JMP1 Pins
1-2 3-4 5-6 7-8 RX4 Input Source
SHORT SHORT OPEN OPEN RX4 Unbalanced 75 Ω Input (DAIMB connector J9)
OPEN SHORT SHORT OPEN Optical Input Receiver (DAIMB U9)
OPEN SHORT OPEN SHORT Logic Level Input (DAIMB header J10)
2.5 Switch Configuration
This sub-section provides an overview of the DIP switch configuration for both the DAIMB motherboard
and EVM daughterboard.
2.5.1 Audio Serial Port Slave/Master Configuration
The audio serial ports for the SRC4382 or SRC4392 may operate in either Slave or Master mode.
Switches SW1 and SW2 must be configured to match the programmed register configurations for the Port
A and Port B audio serial ports on the SRC4382 or SRC4392.
Port A of the SRC4382 or SRC4392 is connected to Port D (or header J4) on the DAIMB motherboard,
while Port B is connected to Port B (or header J2) on the motherboard. Switch SW1 must be set to match
the Port B slave/master configuration, while switch SW2 must be set to match the Port A slave/master
configuration. Switch configuration is summarized in Table 6 , where x = B for Port B, and x = D for Port A.
Table 6. Audio Serial Port Slave/Master Switch Configuration (DAIMB Motherboard)
Switch SW1 or SW2, x_S/M Port Configuration
LO Master
HI Slave
2.5.2 USB Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) Port Configuration
When the I2C bus is utilized for host communications, the USBSPI switch must
be set to HI.
For the DAIMB motherboard, the USBSPI switch on SW5 is utilized to enable or disable the tri-state
buffers for the USB controller SPI port connections. Table 7 summarizes the USBSPI switch settings.
Table 7. USB SPI PortConfiguration (DAIMB Motherboard)
Switch SW5, USBSPI USB-based SPI Interface
LO Enabled; the SPI port may be utilized for SRC4382/4392 host
HI Disabled; the SPI port outputs are set to a high-impedance
CAUTION
communications.
state.
SRC4382EVM-PDK and SRC4392EVM-PDK User's Guide6 SBOU038 – April 2006
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 7
www.ti.com
When the USB controller SPI interface is disabled, an external SPI host may be connected via header
J22. Refer to the DAIMB electrical schematics in Section 4 of this document for the header pin
configuration.
2.5.3 MCLK1 and MCLK2 Clock Configuration
The DAIMB board supports both onboard and external clock generation for two clocks, referred to as
MCLK1 and MCLK2. The MCLK1 clock source is buffered and routed to the RXCKI input (pin 13) of the
SRC4382 or SCR4392 on the EVM daughterboard. The MCLK2 source is buffered and routed to the
MCLK input (pin 25) of the SRC4382 or SRC4392 on the EVM daughterboard.
Switch SW3 selects the clock source for the MCLK1 (that is, RXCKI) clock, while SW4 selects the clock
source for MCLK2 (that is, MCLK). Table 8 and Table 9 summarize the SW3 and SW4 switch settings.
Switch SW3, Switch SW3,
OSC2 OSC1 MCLK1 (or RXCKI) Source Selection
LO LO External clock source at BNC connector J17 (X1 and X2 are disabled)
LO HI Oscillator X1, 24.576MHz ± 50ppm
HI LO Oscillator X2, 22.5792MHz ± 50ppm
HI HI Not allowed due to Oscillator X1 and X2 output contention.
Switch SW4, Switch SW4,
OSC4 OSC3 MCLK2 (or MCLK) Source Selection
LO LO External clock source at BNC connector J18 (X3 and X4 are disabled)
LO HI Oscillator X3, 24.576MHz ± 50ppm
HI LO Oscillator X4, 22.5792MHz ± 50ppm
HI HI Not allowed due to Oscillator X3 and X4 output contention.
Quick Start
Table 8. MCLK1 Clock Source Selection (DAIMB Daughterboard)
Table 9. MCLK2 Clock Source Selection (DAIMB Daughterboard)
2.5.4 Host Interface and SRC Output Mute Configuration
For the EVM daughterboard, DIP switch SW1 is utilized to manually select the SRC4382 or SRC4392
control port mode via the CPM input (pin 18), and to manually control the mute input, MUTE (pin 14). Bits
A0 and A1 for the SRC4382 or SRC4392 I2C slave address may also be configured using this switch.
Table 10 through Table 12 summarize the operation of the SW1 switches.
Table 10. SRC Output Mute Configuration (EVM Daughterboard)
Switch SW1, MUTE SRC Output Mute
LO Disabled; the SRC data output operates normally.
HI Enabled; the SRC data output is forced low.
Table 11. SRC4382/4392 Control Port Mode Configuration (EVM Daughterboard)
Switch SW1, CPM SPI or I2C
LO SPI
HI I2C
SBOU038 – April 2006 SRC4382EVM-PDK and SRC4392EVM-PDK User's Guide 7
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 8

www.ti.com
Power
Supply
( nclui ded)
D O =I 1 G O1P
D O =I 2 G O2P
D O =I 3 G O3P
D O =I 4 G O4P
DI 5 =O BLS
D O =I 6 S NCY
J19 J24
J2 J4
J5
J6
J7
J8
J9
U9 U13
J12
J11
J17 J18
PC
W 2Kin /XP
U B oS P rt
RX 11: 10 BalanceW d XLR
RX1: 75W Unbala cen d RCA
RX2: 75W Unbala cen d RCA
RX3: 75W Unbala cen d RCA
RX4: 75W Unbala cen d RCA
TX 5: 7 W Unbalanced RCA
TX: 110 BalancedW XLR
RX4: TOSLINK Optical Input
TM
AE TS UO : TOSLINK Optical Output
TM
MCLK1 = RXCKI
Ext Clock Input
MCLK2 = MCLK
Ext Clock Input
1 2
J2
S OUTBD
S BDIN
L BRCK
BCKB
TP4
J23
2 1
J4
RXCKO
SDINA
SDOUTA
BCKA
LRCKA
Quick Start
Table 12. I2C 7-Bit Slave Address Configuration (EVM Daughterboard)
Switch SW1, Switch SW1,
A1 A0 7-bit Slave Address (Binary) Slave Address for Command Files (Hex)
LO LO 1110000 E0
LO HI 1110001 E2
HI LO 1110010 E4
HI HI 1110011 E6
2.6 Audio, Power, and Logic I/O Connections
Figure 3 illustrates the power, USB, and primary audio input/output connections for the PDK. Headers J2
and J4 provide access to the SRC4382 or SRC4392 audio serial ports, Port A (J4) and Port B (J2), as
well as the DIR recovered clock output, RXCKO (pin 12). The pin assignments for the headers are shown
in Figure 3 . Connectors J5 through J9, as well as optical receiver U9, provide the inputs for AES3 and
S/PDIF digital audio sources. Connectors J11 and J12, along with optical transmitter U13, provide the
AES3-encoded digital outputs for connection to external audio systems and test equipment. The J17 and
J18 BNC connectors allow connection to external clock sources when the on board oscillators are
disabled. General purpose outputs, as well as the DIT block start (BLS) and DIT internal frame
synchronization (SYNC) clocks, are made available at header J23. The power adapter provided with the
PDK is connected to the DAIMB motherboard at power jack J19. The host PC is connected to the PDK via
the supplied USB cable, with connector J24 providing access to the DAIMB motherboard USB slave
interface.
Figure 3. PDK Power, Host, and Input/Output Connections
8 SRC4382EVM-PDK and SRC4392EVM-PDK User's Guide SBOU038 – April 2006
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 9

www.ti.com
3 Software Overview, Installation, and Operation
This section provides a discussion of the applications software that accompanies the PDK, including
system requirements, installation procedures, and software operating instructions.
3.1 Overview
The applications software provided with the PDK allows the user to program and read the contents of
SRC4382 or SRC4392 control and status registers, as well as the channel status and user data buffers for
both the DIR and DIT. The software is referred to as the USB Serial Commander, and is a product of
Texas Instruments (portions of the software are copyright by National Instruments). Refer to the End
Users License Agreement included with the software.
3.2 System Requirements
The applications software functions on computers that run the Microsoft Windows 2000 or XP operating
systems, and include at least one built-in USB 1.x or USB 2.0 port. A CD-ROM drive is also required for
software installation. A minimum of 256MB of system RAM is required, while 512MB of system RAM is
recommended. Installation of the applications software requires a minimum of 50MB of free hard disk
space.
3.3 Installation Procedure
The following steps are required to install the USB Serial Commander Software. It is assumed that the
user is familiar with the Windows 2000 or XP operating system, including window and menu navigation.
Step 1: Insert the accompanying CD-ROM into the PC CD-ROM drive.
Step 2: Go to the folder named usc_installer on the CD-ROM. Open the folder and double-click on the file
named setup.exe. Follow the instructions and prompts given by the installer program.
Step 3: When the main installation is complete, a dialog box will come up informing you about installing
NI-VISA™ 3.1 Runtime. This file is a self-extracting archive. Click OK to proceed. You will then be
presented with a WinZip™ dialog. Simply click Unzip; the archive self-extracts and automatically runs the
NI-VISA 3.1 Runtime installer.
Step 4: Follow the instructions in the NI-VISA 3.1 Runtime Installer. When prompted for which features to
install, do the following:
1. Click on the disk icon next to NI-VISA 3.1.
2. Select, Do not install this feature.
3. Click on the disk icon next to USB.
4. Select the option which installs this feature.
5. Click Next.
Step 5: Accept the license agreement, and continue the installation.
Step 6: When this completes, click Finish on the USB Serial Commander installer window.
Step 7: Restart your computer.
Step 8: When your computer is restarted, connect the SRC4382EVM-PDK or SRC4392EVM-PDK to the
host PC using the supplied a USB cable. Windows should recognize the new device as USB- MODEVM.
However, on some systems, it will be recognized as a USB Human Interface Device rather than an
NI-VISA USB device.
To check this configuration, go to Start --> Control Panel --> System --> Hardware --> Device Manager.
Look in the list and see if any NI-VISA USB Devices are shown. If so, the USB-MODEVM should be
included in the list of the NI-VISA USB devices, and you can proceed to Step 10.
Software Overview, Installation, and Operation
SBOU038 – April 2006 SRC4382EVM-PDK and SRC4392EVM-PDK User's Guide 9
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 10

www.ti.com
Software Overview, Installation, and Operation
If the USB-MODEVM appears instead under Human Interface Devices, right-click on the device and select
Update Driver... In the driver update screen, choose the option to select the driver from a list. When the
list is given, you should have the choice of either a Human Interface Device or the USB-MODEVM. Select
the USB-MODEVM and install the new driver.
If the USB-MODEVM does not appear as an option, go to the C:\Windows\inf directory and see if the
USB-MODEVM_WDM.inf file exists. If it does, right-click on the file and select Install... Repeat the Update
Driver … process described in the previous paragraph.
If the USB-MODEVM_WDM.inf file does not exist in the C:\Windows\inf directory, go to the CD-ROM and
locate the inf_file.zip archive. This archive contains the USB-MODEVM_WDM.inf file. Copy the archive to
your disk, unzip the archive, and move the USB-MODEVM_WDM.inf file to the C:\Windows\inf directory.
Once the file is moved, right-click on the file and select Install... Repeat the Update Driver … process
described previously in this section.
Step 9: Disconnect the USB_MODEVM hardware and reconnect to the USB cable. Repeat Step 8 to
check that it is now recognized as an NI-VISA USB Device. When the hardware is recognized and listed
as a NI-VISA USB device, proceed to Step 10.
Step 10: Installation is complete. You may now proceed with using the PDK software.
3.4 Operating the Applications Software
To start the applications software, click on the Start menu icon and navigate to Programs --> Texas
Instruments --> USB-SerialCommander. Click on the USB-SerialCommander to start the application. The
window shown in Figure 4 will appear. The Command Buffer text area will be empty when the application
initially launches.
Figure 4. Applications Software Window (USB Serial Commander)
The first order of business is to select the Interface, using one of the five radio buttons shown in the
Interface panel. For an I2C host interface configurations, either the I2C Standard Mode or I2C Fast Mode
may be selected. For an SPI host interface configuration, the SPI–16 bit register addresses mode must be
selected.
10 SRC4382EVM-PDK and SRC4392EVM-PDK User's Guide SBOU038 – April 2006
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 11

www.ti.com
On the CD-ROM accompanying the PDK, there is a folder named Sample Command Files. These files
have been written to exercise specific portions and functions of the SRC4382 or SRC4392. The sample
files also provide the user with code that can be copied and modified as needed, assisting the learning
process. Any standard text editor, such as Notepad, can be utilized to edit and create command files.
Click on the applications File menu. There is only one selection under the File menu: Open Command
File … Clicking on this menu selection displays an open file dialog, where sample command files may be
located and loaded.
Once a command file has been loaded, the Command Buffer text area will display the script code. You
may scroll through this code, as well as select and edit code as needed. The user can also select and
delete the contents of the Command Buffer and manually enter his or her own script code. Section 3.5
and Section 3.6 of this guide provide command syntax information for writing scripts. When you are ready
to execute the script code in the Command Buffer, simply click on the Execute Command Buffer button.
3.4.1 Error Indicators
There are three indicators below the Execute Command Buffer button. When a command buffer is
successfully executed, the req done indicator glows green. If a command request or an SPI/I
occurs, then the req error or bus error indicators glow red. Typical errors include selecting the wrong
interface mode for the given command buffer contents, running command syntax that is invalid, and bus
configuration or electrical errors.
3.4.2 Last Executed Command Field
This field is located below the error indicators, and contains the text of the last executed command (not
including Break commands).
Software Overview, Installation, and Operation
2
C bus error
3.4.3 Read Data Display
The Read Data display shows a list of hexadecimal values, with the first four values being program status
information, followed by the data bytes read from control or status registers using a Read command.
Figure 5 illustrates the results of an SPI read command. The Last Executed Command field shows that a
read command was executed. This information is reiterated in the text field to the left of the Read Data
display. Ignoring the first four bytes of the Read Data display, the last four bytes correspond to the data
located in the four register addresses referenced by the Read command.
SBOU038 – April 2006 SRC4382EVM-PDK and SRC4392EVM-PDK User's Guide 11
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 12

www.ti.com
Software Overview, Installation, and Operation
3.4.4 Command Script Paused Dialog
This dialog is presented when a Break command is executed in the Command Buffer, and is shown in
Figure 5 . The Break command pauses the Command Buffer execution until the OK button is clicked. Read
commands must always be followed by a Break command, so that the user may evaluate the Read Data
display results.
Figure 5. Example of a Readback Display and Break Message in the USB Serial Commander Application
3.5 Command Syntax for SPI Communications
Simple but strict command syntax is required for the command files utilized by the applications software.
The command syntax for SPI communications are summarized in Table 13 . Each command must be
terminated with a carriage return, and must fit on a single line.
Table 13. SPI Command Syntax
Command Syntax
Write w rr 00 dd
Read r rr 00 bb
Break b
Comment # write your comments here
Interface Mode i spi16
SRC4382EVM-PDK and SRC4392EVM-PDK User's Guide12 SBOU038 – April 2006
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 13

www.ti.com
Software Overview, Installation, and Operation
Where:
• rr = The register address (Hex)
• dd = The register data (Hex)
• bb = The number of bytes to be read (Hex)
For the SRC4382 and SRC4392, the SPI 16-bit address mode must always be utilized, as the second
byte (00) is interpreted as the second byte of the address by the USB Serial Commander. The first line of
the command file should always be the interface mode syntax shown in Table 13 .
When setting the register address for an SPI command, the most significant bit of the address is the
Read/Write bit. Set this bit to '0' for Write operations, and to '1' for Read operations.
Example 1.
# write register 01 to power-up all function blocks
w 01 00 3f
Example 2.
# read the Q sub code data registers and then break for read data display results
r 9f 00 0a
b
3.6 Command Syntax for I2C Communications
The command syntax for I2C communications are summarized in Table 14 . Each command must be
terminated with a carriage return, and must fit on a single line.
Where:
• ss = The I2C slave address for the SRC4382 or SRC4392 (Hex).
• rr = The register address byte (Hex)
• dd = The register data (Hex)
• bb = The number of bytes to be read (Hex)
For the SRC4382 and SRC4392, the I2C interface mode may be Slow or Fast. The first line of the
command file should always indicate the speed of the interface, and match the selection shown in the
Interface section of the USB Serial Commander window. Generally, the interface may be set to Fast mode
for all operations.
When setting the slave address, the R/W bit does not need to be included, as the Write or Read command
will set this bit automatically.
The most significant bit of the Register Address Byte is the INC, or auto-increment bit. When set to ‘0’,
auto-increment mode is disabled. When set to ‘1’, auto-increment mode is enabled. Refer to the datasheet
for additional information regarding auto-increment mode for I2C write and read operations.
Table 14. I2C Command Syntax
Command Syntax
Write w ss rr dd
Read r ss rr bb
Break b
Comment # write your comments here
Interface Mode (I2C Slow) i i2cslow
Interface Mode (I2C Fast) i i2cfast
SBOU038 – April 2006 SRC4382EVM-PDK and SRC4392EVM-PDK User's Guide 13
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 14

www.ti.com
Hardware Reference
4 Hardware Reference
Example 3.
# write register 01 to power up all function blocks
w e0 01 3f
Example 4.
# read the non pcm status register and then break for read data display results
r e0 12 01
b
Example 5.
# read the Q sub code data registers and then break for read data display results
# reading multiple registers requires that the auto increment bit be set to 1
r e0 9f 0a
b
This section includes schematics for the EVM and DAIMB boards, as well as a Bill of Materials for each
board.
14 SRC4382EVM-PDK and SRC4392EVM-PDK User's Guide SBOU038 – April 2006
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 15

www.ti.com
RN2
100
246
135
789
10
JE
POWER
+5V
VIO
+1.8V
+3.3V
246
135
78910111213141516171819
20
JA
PORTS A and B
246
135
78910111213141516171819
20
JB
PORTS C and D
246
135
78910111213141516171819
20
JC
DAI INPUT
246
135
78910111213141516171819
202224
26
212325
272829
30
JF
HOST I/O
246
135
78910111213141516171819
20
JD
DAI OUTPUT
DIO6
DIO5
DIO4
DIO3
DIO2
DIO1
DIO7
SDA
SCL
/RESET
/INT
CDOUT
CDIN
/CS
CCLK
SDINA
LRCKA
BCKA
SDOUTB
SDINB
SDOUTA
LRCKB
BCKB
SDINC
LRCKC
BCKC
CLKOUT1
SDOUTD
SDIND
SDOUTC
BCKD
CLKOUT2
LRCKD
RX1-
RX2+
RX2-
RX3+
RX3-
RX4+
RX1+
RX4-
LOGIC_IN
TOSLINK_IN
TX1-
TX2+
TX2-
TX3+
TX3-
TX4+
TX1+
TOSLINK_OUT
LOGIC_OUT
TX4-
TP1
TP2
MCLK1
MCLK2
RX1-
RX1+
RX2-
RX2+
RX3-
RX3+
RX4-
RX4+
R1
10
LED1
RX LOCK
VIO
TX+
32
AESOUT
34
BLS
35
SYNC
36
BCKA37SDINA39SDOUTB40NC41VIO42DGND343BGND44SDINB46LRCKB47BCKB48RX1+1RX2+3RX3+5RX3-6RX4+7VCC
9
RX2-
4
DGND1
16
GPO3
28
SDOUTB
45
AGND10/LOCK
11
LRCKA
38
RXCKO
12
CCLK(SCL)
20
CDOUT(SDA)
22
RXCKI
13
MUTE
14
/RDY
15
VDD18
17
CPM
18
/CS(A0)
19
RX1-
2
VDD33
33
CDIN(A1)
21
RX4-
8
/INT
23
/RST
24
MCLK25GPO126GPO2
27
GPO4
29
DGND2
30
TX-
31
U1
SRC4382IPFB
C5
0.1 Fm
C6
10 Fm
123
4
JMP4
+3.3V
1827364
5
SW1
1234567
8
JMP1
123
4
JMP3
12
JMP2
123
4
JMP5
1
2
JMP6
1
2
JMP9
1
2
JMP8
C3
0.1 Fm
C4
10 Fm
R2
10
LED2
SRC READY
VIO
RN3
10K
RN1
100
Daughter Board Connectors
C7
0.1 Fm
C8
10 Fm
+1.8V
R3 0
R6
2.7K
R5 0
R4
2.7K
VIO
VIO
VIO
C1
0.1 Fm
C2
10 Fm
1
2
JMP7
+3.3V
SDOUTD
SDIND
BCKD
LRCKD
SDOUTB
SDINB
LRCKB
BCKB
LOGIC_IN
TOSLINK_IN
CLKOUT2
DIO6
DIO5
DIO4
DIO3
DIO2
DIO1
SDA
SCL
/RESET
/INT
CDOUT
CDIN
/CS
CCLK
TX1-
TX1+
TOSLINK_OUT
LOGIC_OUT
MCLK2
MCLK1
CPM
A0
A1
MUTE
Hardware Reference
4.1 Schematics
The schematics for the EVM and DAIMB boards are shown in Figure 6 through Figure 8 .
Figure 6. Electrical Schematic: SRC4382/92EVM Daughterboard
SBOU038 – April 2006 SRC4382EVM-PDK and SRC4392EVM-PDK User's Guide 15
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 16

www.ti.com
246
135
789
10
J1
PORTA
RN1
100
TP3
1OE11A122Y431A242Y351A362Y271A482Y19GND
10
2A1111Y4122A2131Y3142A3151Y2162A4171Y1
18
2OE
19
VCC
20
U1
SN74ALVC244PW
VIO
C1
0.1 Fm
SDOUTA
SDINA
LRCKA
BCKA
VIO
C2
0.1 Fm
A12A23A34A45A56A67A78A8
9
B118B217B316B415B514B613B712B8
11
GND
10
DIR
1
VCC
20
OE
19
U2
SN74ALVC245PW
RN2
10k
142
3
SW1
246
135
789
10
J2
PORT B
RN3
100
TP4
1OE11A122Y431A242Y351A362Y271A482Y19GND
10
2A1111Y4122A2131Y3142A3151Y2162A4171Y1
18
2OE
19
VCC
20
U3
SN74ALVC244PW
VIO
C3
0.1 Fm
SDOUTB
SDINB
LRCKB
BCKB
VIO
C4
0.1 Fm
A12A23A34A45A56A67A78A8
9
B118B217B316B415B514B613B712B8
11
GND
10
DIR
1
VCC
20
OE
19
U4
SN74ALVC245PW
246
135
789
10
J3
PORT C
RN4
100
1OE11A122Y431A242Y351A362Y271A482Y19GND
10
2A1111Y4122A2131Y3142A3151Y2162A4171Y1
18
2OE
19
VCC
20
U5
SN74ALVC244PW
VIO
C5
0.1 Fm
SDOUTC
SDINC
LRCKC
BCKC
VIO
C6
0.1 Fm
A12A23A34A45A56A67A78A8
9
B118B217B316B415B514B613B712B8
11
GND
10
DIR
1
VCC
20
OE
19
U6
SN74ALVC245PW
RN5
10K
142
3
SW2
246
135
789
10
J4
PORT D
RN6
100
1OE11A122Y431A242Y351A362Y271A482Y19GND
10
2A1111Y4122A2131Y3142A3151Y2162A4171Y1
18
2OE
19
VCC
20
U7
SN74ALVC244PW
VIO
C7
0.1 Fm
LRCKD
BCKD
VIO
C8
0.1 Fm
A12A23A34A45A56A67A78A8
9
B118B217B316B415B514B613B712B8
11
GND
10
DIR
1
VCC
20
OE
19
U8
SN74ALVC245PW
CLKOUT1
SDOUTD
SDIND
CLKOUT2
R1
75
R2
75
246
135
789
10
JE
POWER
+5V
VIO
+1.8V
+3.3V
246
135
78910111213141516171819
20
JA
PORTS A and B
246
135
78910111213141516171819
20
JB
PORTS C and D
246
135
78910111213141516171819
20
JC
DAI INPUT
246
135
78910111213141516171819
202224
26
212325
272829
30
JF
HOST I/O
246
135
78910111213141516171819
20
JD
DAI OUTPUT
DIO6
DIO5
DIO4
DIO3
DIO2
DIO1
DIO7
SDA
SCL
/RESET
/INT
CDOUT
CDIN
/CS
CCLK
SDINA
LRCKA
BCKA
SDOUTB
SDINB
SDOUTA
LRCKB
BCKB
SDINC
LRCKC
BCKC
CLKOUT1
SDOUTD
SDIND
SDOUTC
BCKD
CLKOUT2
LRCKD
RX1-
RX2+
RX2-
RX3+
RX3-
RX4+
RX1+
RX4-
LOGIC_IN
TOSLINK_IN
TX1-
TX2+
TX2-
TX3+
TX3-
TX4+
TX1+
TOSLINK_OUT
LOGIC_OUT
TX4-
TP1
TP2
MCLK1
MCLK2
C9
0.1 Fm
R5
110
J6
RX1 INPUT
75W
1
4
5
687
PRI
SEC 1
SEC 2
T1
SC939-06
+3.3V
2
4
1
53
U11
SN74LVC1G125DBV
C19
0.1 Fm
R30R4
0
C10
0.1 Fm
RX1-
RX1+
C11
0.1 Fm
R6
75
C12
0.1 Fm
RX2-
RX2+
J7
RX2 INPUT
75W
C13
0.1 Fm
R7
75
C14
0.1 Fm
RX3-
RX3+
J8
RX3 INPUT
75W
C15
0.1 Fm
R8
75
C16
0.1 Fm
RX4-
RX4+
J9
RX4 INPUT
75W
LOGIC_IN
+3.3V
2
4
1
53
U10
SN74LVC1G125DBV
C18
0.1 Fm
TOSLINK_IN
1
2
3
RX
U9
Optical Input
+5V
C17
0.1 Fm
L1
47 Hm
J11
TX1 OUTPUT
75W
1
4
5
687
PRI
SEC 1
SEC 2
T2
SC939-06
VIO
2
4
1
53
U14
SN74LVC1G125DBV
C26
0.1 Fm
R9
110
C20
0.1 Fm
TX1-
TX1+
C21
0.1 Fm
R10
150
TX2+
J13
TX2 OUTPUT
75W
C22
0.1 Fm
R11
150
TX3+
J14
TX3 OUTPUT
75W
C23
0.1 Fm
R12
150
TX4+
J15
TX4 OUTPUT
75W
LOGIC_OUT
+5V
2
4
1
53
U12
SN74AHCT1G125DBV
C25
0.1 Fm
TOSLINK_OUT
+5V
C24
0.1 Fm
1
2
3
TX
U13
Optical Output
Daughter Board Connectors
VIO
VIO
1
2
J10
LOGIC INPUT
1
2
J16
LOGIC OUTPUT
2
3
1
G
J12
TX1 OUTPUT
110
2
3
1
G
J5
RX1 OUTPUT
110
R28
150
R29
150
R30
150
Hardware Reference
16 SRC4382EVM-PDK and SRC4392EVM-PDK User's Guide SBOU038 – April 2006
Figure 7. Electrical Schematic: DAIMB Motherboard, Page 1
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 17

www.ti.com
TP11
SW6
MANUAL RESET
R18
2.7K
RN9
10K
VIO
1827364
5
SW5
/RESET
VIO
2
4
1
53
U23
SN74LVC1G125DBV
C48
0.1 Fm
USB33
A12A23A34A45A56A67A78A8
9
B118B217B316B415B514B613B712B8
11
GND
10
DIR
1
VCC
20
OE
19
U21
SN74ALVC245PW
C46
0.1 Fm
246
135
78910111213
14
J22 EXT SPI
123
4
JMP4
246
135
78910111213141516171819
20
J23
EXT I2C and DIO
CDOUT
CDIN
/CS
CCLK
/INT
VIO
2
4
1
53
U22
SN74LVC1G125DBV
C47
0.1 Fm
Q1
Q2
R16
2.7K
R17
2.7K
VIO
1 2
JMP5
1 2
JMP6
DIO6
DIO5
DIO4
DIO3
DIO2
DIO1
DIO7
EN
1
OUT
3
VCC4GND
2
X2
SM7745HSV-22.5792M
EN
1
OUT
3
VCC4GND
2
X1
SM7745HSV-24.576M
C28
0.01 Fm
C29
0.01 Fm
+3.3V
+3.3V
2
4
1
53
U15
SN74LVC1G125DBV
J17
EXTMCLK1
C27
0.1 Fm
VIO
RN7
10K
142
3
SW3
MCLK1 SELECT
MCLK1
+3.3V
EN
1
OUT
3
VCC4GND
2
X4
SM7745HSV-22.5792M
EN
1
OUT
3
VCC4GND
2
X3
SM7745HSV-24.576M
C31
0.01 Fm
C32
0.01 Fm
+3.3V
+3.3V
2
4
1
53
U16
SN74LVC1G125DBV
J18
EXT MCLK2
C30
0.1 Fm
VIO
RN8
10K
142
3
SW4
MCLK2 SELECT
MCLK2
+3.3V
CSCHNE
32
CRESET
34
CSYNC
35
CDATI
36
CSCLK
37
MCLKO139MCLKO2
40
RESET
41
VREN
42
SDA43SCL
44
XTALO
46
XTALI
47
PLLFILI
48
PLLFILO1MCLKI3PUR5DP6DM7MRESET
9
DVSS
4
DVSS
16
DVSS
28
AVSS
45
TEST10EXTEN
11
CDATO
38
RSTO
12
NC20NC
22
P3.013P3.114P3.2/XINT15P3.317P3.418P3.5
19
AVDD
2
DVDD
33
DVDD
21
DVDD
8
P1.023P1.1
24
P1.225P1.326P1.427P1.529P1.630P1.7
31
U24
TAS1020BPFB
R15
390
D4
USB ACTIVE
C49
33pF
R27
3.09K
R24
NI
Note: #3
USBVCC
X5
6.000MHz
VCC
1
D-
2
D+
3
GND
4
J24
USB PORT
R21 1.5K
R22 27.4
R23 27.4
C56
100pF
C50
33pF
C53
1.0 Fm
C52
1.0 Fm
C54
1.0 Fm
TP7
TP6
TP5
TP9
TP8
C55
0.001 Fm
C57
33pF
C58
33pF
TP10
C59
1.0 Fm
USB33
VDD
5
RESET
4
MR3CT1GND
2
U25
TPS3836
VCC
8
VSS
4
SDA5SCL
6
A01A12A2
3
WP
7
U26
24LC64
R25
NI
Note: #2
R26
NI
Note: #1
R19
2.7K
R20
2.7K
C51
0.1 Fm
C60
1.0 Fm
USB33
USB33
USB33
C33
0.01 Fm
C35
0.01 Fm
C34
100 Fm
C36
100 Fm
+3.3V
C39
10 Fm
123
4
JMP1
+5V SELECT
VIO
+5V
VIN
3
VOUT
2
GND
1
VOUT
4
U17
REG1117-5
1
2
J20
+5V SUPPLY
1
2
J21
VIO SUPPLY
C40
10 Fm
+1.8V
VIN
3
VOUT
2
GND
1
VOUT
4
U18
REG1117-1.8
R14
390
D2
MAIN POWER
C41
10 Fm
VIN
3
VOUT
2
GND
1
VOUT
4
U19
REG1117-3.3
C43
10 Fm
C42
10 Fm
12345
6
JMP2
VIO SELECT
J19
POWER ADAPTER
(6V-10V)
C37
0.1 Fm
D1
DL4001
USB33
VIN
3
VOUT
2
GND
1
VOUT
4
U20
REG1117-3.3
C45
10 Fm
C44
10 Fm
R13
390
D3
USB POWER
123
4
JMP3
USB POWER SELECT
SELF
BUS
USBVCC
C38
0.1 Fm
USB33
USB33
Note(s):
#1 - Install a 10K pull-up resistor
when using the TPS3838K33DBV.
#2 - Install a 0 ohm resistor for a
10ms reset pulse. Do not install this
resistor when using the 200ms reset
pulse.
#3 - Install a 0 ohm resistor for a
USB33
SDA
SCL
SBOU038 – April 2006 SRC4382EVM-PDK and SRC4392EVM-PDK User's Guide 17
Submit Documentation Feedback
Figure 8. Electrical Schematic: DAIMB Motherboard, Page 2
Hardware Reference
Page 18

www.ti.com
Hardware Reference
4.2 Bills of Material
Table 15. Bill of Materials for the SRC4382/92EVM
QTY
REFERENCE PER
ITEM VALUE DESIGNATOR BOARD MFR MFR PART NUMBER DESCRIPTION
1 0 R3, R5 2 Panasonic ERJ-3GEY0R00V Resistor, 0 Ω , Size = 0603
2 10 R1, R2 2 Panasonic ERJ-3GEYJ100V Resistor, Thick Film Chip 10 Ω , 5%, 1/10W,
Size = 0603
3 2.7K R4, R6 2 Panasonic ERJ-3GEYJ272V Resistor, Thick Film Chip, 2.7k Ω , 5%, 1/10W
Size = 0603
4 100 RN1, RN2 2 CTS 742C083101J Thick Film Chip Resistor Array 100 Ω ,
8-Terminal, 4 Resistors, Isolated
5 10k RN3 1 CTS 742C163103J Thick Film Chip Resistor Array 10k Ω ,
16-Terminal, 8 Resistors, Isolated
6 0.1 µ F C1, C3, C5, C7 4 TDK C1608X7R1E104K Chip Capacitor, X7R Ceramic 0.1 µ F ± 10%,
25V, Size = 0603
7 10 µ F C2, C4, C6, C8 4 Kemet T491A106K010AS Chip Capacitor, Tantalum, 10 µ F ± 10%, 10V,
Size = A
8 U1 1 Texas SRC4382IPFB or 2-ch Asynchronous SRC with Integrated DIR
Instruments SRC4392IPFB and DIT
9 LED1, LED2 2 Lumex SML-LX0603GW-TR Green LED, SMT, Size = 0603
10 JA, JB, JC, JD 4 Samtec SSW-110-02-G-D Socket Strip, Dual Row, 10x2
11 JE 1 Samtec SSW-105-02-G-D Socket Strip, Dual Row, 5x2
12 JF 1 Samtec SSW-115-02-G-D Socket Strip, Dual Row, 15x2
13 JMP1 1 Samtec TSW-104-07-G-D Terminal Strip, Dual Row, 4x2
14 Not Installed JMP2 1 Samtec TSW-102-07-G-S Terminal Strip, 2x1
15 JMP3-JMP5 3 Samtec TSW-102-07-G-D Terminal Strip, Dual Row, 2x2
16 JMP6-JMP9 4 — — Bus Wire, 18 to 22 guage
17 SW1 1 ITT TDA04H0SK1 DIP Switch, 4-element, Half-pitch
Industries/C&K Surface-Mount, Tape Sealed
18 7 Samtec SNT-100-BK-G-H Shorting Blocks
19 PWB 1 Texas 6472598 SRC4382/92EVM Printed Circuit Board
Instruments
18 SRC4382EVM-PDK and SRC4392EVM-PDK User's Guide SBOU038 – April 2006
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 19

www.ti.com
Hardware Reference
Table 16. Bill of Materials for the DAIMB
ITEM VALUE DESIGNATOR BOARD MFR MFR PART NUMBER DESCRIPTION
1 0 R3, R4, R24 3 Panasonic ERJ-3GEY0R00V Resistor, 0 Ω , Size = 0603
2 Not Installed R25 1 Panasonic ERJ-3GEY0R00V Resistor, 0 Ω , Size = 0603
3 27.4 R22, R23 2 Panasonic ERJ-3EKF27R4V Resistor, Thick Film Chip 27.4 Ω , 1%,
4 75 R1, R2, R6–R8 5 Panasonic ERJ-3EKF75R0V Resistor, Thick Film Chip 75 Ω , 1%, 1/16W,
5 110 R5, R9 2 Panasonic ERJ-3EKF1100V Resistor, Thick Film Chip 110 Ω , 1%,
6 150 R10–R12,R28– 6 Panasonic ERJ-3EKF1500V Resistor, Thick Film Chip 150 Ω , 1%,
7 392 R13–R15 3 Panasonic ERJ-3EKF3920V Resistor, Thick Film Chip 392 Ω , 1%,
8 1.5K R21 1 Panasonic ERJ-3EKF1501V Resistor, Thick Film Chip 1.5k Ω , 1%,
9 2.7K R16–R20 5 Panasonic ERJ-3GEYJ272V Resistor, Thick Film Chip 2.7k Ω , 5%,
10 3.09K R27 1 Panasonic ERJ-3EKF3091V Resistor, Thick Film Chip 3.09k Ω , 1%,
11 Not Installed R26 1 Panasonic ERJ-3EKF1002V Resistor, Thick Film Chip 10k Ω , 1%,
12 100 RN1, RN3, 4 CTS 742C083101J Thick Film Chip Resistor Array 100 Ω ,
13 10k RN2, RN5, 5 CTS 742C083103J Thick Film Chip Resistor Array 10k Ω ,
14 33pF C49, C50, C57, 4 TDK C1608C0G1H330J Chip Capacitor, C0G Ceramic 33pF ± 5%,
15 100pF C56 1 TDK C1608C0G1H101J Chip Capacitor, C0G Ceramic 100pF ± 5%,
16 0.001 µ F C55 1 TDK C1608C0G1H102J Chip Capacitor, C0G Ceramic 0.001 µ F
17 0.01 µ F C28, C29, 6 TDK C1608X7R1H103K Chip Capacitor, X7R Ceramic 0.01 µ F
18 0.1 µ F C1–C27, C30, 33 TDK C1608X7R1E104K Chip Capacitor, X7R Ceramic 0.1 µ F ± 10%,
19 1 µ F C38, C52–C54, 6 TDK C1608X7R1C105K Chip Capacitor, X7R Ceramic 1 µ F ± 10%,
20 10 µ F C39–C45 7 Kemet T491A106K010AS Chip Capacitor, Tantalum, 10 µ F ± 10%,
21 100 µ F C34, C36 2 Panasonic EEV-FK1C101P Capacitor, Alum Elect, SMT, 100 µ F ± 20%,
22 47 µ H L1 1 Panasonic ELJ-FA470KF Inductor, SMT, 47 µ H ± 10%, Size = 1210
23 T1, T2 2 Scientific SC939-06 Dual Zo Digital Audio Transformer
24 U1, U3, U5, U7 4 Texas SN74ALVC244PWR Octal Buffer/Driver with Tri-State Outputs
25 U2, U4, U6, U8, 5 Texas SN74ALVC245PWR Octal Bus Transceiver with Tri-State
26 U9 1 Toshiba TORX179P TOSLINK Optical Receiver
27 U10, U11, 7 Texas SN74LVC1G125DBVR Single Buffer with Tri-State Output
28 U12 1 Texas SN74AHCT1G125DBVR Single Buffer with Tri-State Output and
29 U13 1 Toshiba TOTX179P TOSLINK Optical Transmitter
REFERENCE QTY PER
1/16W, Size = 0603
Size = 0603
1/16W, Size = 0603
R30 1/16W, Size = 0603
1/16W, Size = 0603
1/16W, Size = 0603
1/10W Size = 0603
1/16W, Size = 0603
1/16W, Size = 0603
RN4, RN6 8-Terminal, 4 Resistors, Isolated
RN7–RN9 8-Terminal, 4 Resistors, Isolated
C58 50V, Size = 0603
50V, Size = 0603
± 5%, 50V, Size = 0603
C31–C33,C35 ± 10%, 50V, Size = 0603
C37, C46–C48, 25V, Size = 0603
C51
C59, C60 16V, Size = 0603
10V, Size = A
16V, Size = D
Conversion
Instruments
U21 Instruments Outputs
or
TORX179PL TOSLINK Optical Receiver
U14–U16, U22, Instruments
U23
Instruments TTL Compatible Input
or
TOTX179PL TOSLINK Optical Transmitter
SBOU038 – April 2006 SRC4382EVM-PDK and SRC4392EVM-PDK User's Guide 19
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 20

www.ti.com
Hardware Reference
Table 16. Bill of Materials for the DAIMB (continued)
ITEM VALUE DESIGNATOR BOARD MFR MFR PART NUMBER DESCRIPTION
30 U17 1 Texas REG1117-5 Linear Voltage Regulator with +5V Fixed
31 U18 1 Texas REG1117A-1.8 Linear Voltage Regulator with +1.8V Fixed
32 U19, U20 2 Texas REG1117-3.3 Linear Voltage Regulator with +3.3V Fixed
33 U24 1 Texas TAS1020BPFB USB Streaming Controller
34 U25 1 Texas TPS3836K33DBVR Nanopower Supervisory Circuit with Active
35 U26 Microchip 24LC64I/SN
36 D1 Micro DL4001 Diode, 50V, 1A, MELF SMT
37 D2, D3 2 Lumex SML-LX0603GW-TR Green LED, SMT, Size = 0603
38 D4 1 Lumex SML-LX0603YW-TR Yellow LED, SMT, Size = 0603
39 Q1, Q2 2 Zetex ZXMN6A07F N-channel MOSFET, SMT
40 X1, X3 2 Pletronics SM7745HSV-24.576M +3.3V SMT Clock Oscillator with CMOS
41 X2, X4 2 Pletronics SM7745HSV-22.5792M +3.3V SMT Clock Oscillator with CMOS
42 X5 1 Citizen HCM49-6.000MABJT 6.000MHz Crystal, SMT
43 J1–J4, JE 5 Samtec TSW-105-07-G-D Terminal Strip, Dual Row, 5x2
44 J5 1 Neutrik NC3FAH2 3-pin Female XLR Chassis Connector,
45 J6–J9, J11, 8 CUI Stack RCJ-041 RCA Jack, PC Mount, Black
46 J10, J16, 4 Samtec TSW-102-07-G-S Terminal Strip, 2x1
47 J12 1 Neutrik NC3MAH-0 3-pin Male XLR Chassis Connector,
48 J17, J18 2 Tyco AMP 414305-1 BNC Connector, Female, PC Mount
49 J19 1 CUI Stack PJ-102BH 2.5mm Male Power Jack, PCB Mount,
50 J20, J21 2 Weidmuller 1699670000 Terminal Block, 2 poles, 3.5mm PCB
51 J22 1 Samtec TSW-107-07-G-D Terminal Strip, Dual Row, 7x2
52 J23, JA, JB, JC, 5 Samtec TSW-110-07-G-D Terminal Strip, Dual Row, 10x2
53 J24 1 Mill-Max 897-30-004-90-000000 USB Type B Receptable, Single,
54 JF 1 Samtec TSW-115-07-G-D Terminal Strip, Dual Row, 15x2
55 JMP1, JMP3 2 Samtec TSW-102-07-G-D Terminal Strip, Dual Row, 2x2
56 Not Installed JMP4 1 Samtec TSW-102-07-G-D Terminal Strip, Dual Row, 2x2
57 JMP2 1 Samtec TSW-103-07-G-D Terminal Strip, Dual Row, 3x2
58 SW1-SW4 4 ITT TDA02H0SK1 DIP Switch, 2-element, Half-pitch
REFERENCE QTY PER
Instruments Output
Instruments Output
Instruments Output
Instruments
Instruments Low Push-Pull Output
or
Texas TPS3838K33DBVR Nanopower Supervisory Circuit with Active
Instruments Low Open Drain Output (requires
installation of R26)
64k EEPROM with 2-wire I2C Serial
Interface
Commercial
Components
Output and Active High Enable 24.576MHz
± 50ppm
Output and Active High Enable
22.5792MHz ± 50ppm
or
Epson MA-505 6.000M-C0 6.000MHz Crystal, SMT
or
CTS ATS060SM-T 6.000MHz Crystal, SMT
Horizontal PC Mount with Latch
J13–J15
JMP5, JMP6
Horizontal PC Mount
Silver Plated
JD
Through-Hole
Industries/C&K Surface-Mount, Tape Sealed
20 SRC4382EVM-PDK and SRC4392EVM-PDK User's Guide SBOU038 – April 2006
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 21

www.ti.com
Hardware Reference
Table 16. Bill of Materials for the DAIMB (continued)
ITEM VALUE DESIGNATOR BOARD MFR MFR PART NUMBER DESCRIPTION
59 SW5 1 ITT TDA04H0SK1 DIP Switch, 4-element, Half-pitch
60 SW6 1 Omron B3S-1000 Momentary Tact Switch, SMT, Without
61 5 Samtec SNT-100-BK-G-H Shorting Blocks
62 5 3M Bumpon SJ-5003 Rubber Feet, Adhesive Backed
63 PWB 1 Texas 6472591 DAIMB Printed Circuit Board
REFERENCE QTY PER
Industries/C&K Surface-Mount, Tape Sealed
Ground Terminal
Instruments
SBOU038 – April 2006 SRC4382EVM-PDK and SRC4392EVM-PDK User's Guide 21
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 22

EVALUATION BOARD/KIT IMPORTANT NOTICE
Texas Instruments (TI) provides the enclosed product(s) under the following conditions:
This evaluation board/kit is intended for use for ENGINEERING DEVELOPMENT, DEMONSTRATION, OR EVALUATION
PURPOSES ONLY and is not considered by TI to be a finished end-product fit for general consumer use. Persons handling the
product(s) must have electronics training and observe good engineering practice standards. As such, the goods being provided are
not intended to be complete in terms of required design-, marketing-, and/or manufacturing-related protective considerations,
including product safety and environmental measures typically found in end products that incorporate such semiconductor
components or circuit boards. This evaluation board/kit does not fall within the scope of the European Union directives regarding
electromagnetic compatibility, restricted substances (RoHS), recycling (WEEE), FCC, CE or UL, and therefore may not meet the
technical requirements of these directives or other related directives.
Should this evaluation board/kit not meet the specifications indicated in the User’s Guide, the board/kit may be returned within 30
days from the date of delivery for a full refund. THE FOREGOING WARRANTY IS THE EXCLUSIVE WARRANTY MADE BY
SELLER TO BUYER AND IS IN LIEU OF ALL OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED, IMPLIED, OR STATUTORY, INCLUDING
ANY WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR ANY PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
The user assumes all responsibility and liability for proper and safe handling of the goods. Further, the user indemnifies TI from all
claims arising from the handling or use of the goods. Due to the open construction of the product, it is the user’s responsibility to
take any and all appropriate precautions with regard to electrostatic discharge.
EXCEPT TO THE EXTENT OF THE INDEMNITY SET FORTH ABOVE, NEITHER PARTY SHALL BE LIABLE TO THE OTHER
FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES.
TI currently deals with a variety of customers for products, and therefore our arrangement with the user is not exclusive.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance, customer product design, software performance, or infringement of
patents or services described herein.
Please read the User’s Guide and, specifically, the Warnings and Restrictions notice in the User’s Guide prior to handling the
product. This notice contains important safety information about temperatures and voltages. For additional information on TI’s
environmental and/or safety programs, please contact the TI application engineer or visit www.ti.com/esh .
No license is granted under any patent right or other intellectual property right of TI covering or relating to any machine, process, or
combination in which such TI products or services might be or are used.
FCC Warning
This evaluation board/kit is intended for use for ENGINEERING DEVELOPMENT, DEMONSTRATION, OR EVALUATION
PURPOSES ONLY and is not considered by TI to be a finished end-product fit for general consumer use. It generates, uses, and
can radiate radio frequency energy and has not been tested for compliance with the limits of computing devices pursuant to part 15
of FCC rules, which are designed to provide reasonable protection against radio frequency interference. Operation of this
equipment in other environments may cause interference with radio communications, in which case the user at his own expense
will be required to take whatever measures may be required to correct this interference.
EVM WARNINGS AND RESTRICTIONS
It is important to operate this EVM within the input voltage range of the Absolute Operating Conditions and the output voltage range
of the Absolute Operating Conditions (see Table 1 ).
Exceeding the specified input range may cause unexpected operation and/or irreversible damage to the EVM. If there are
questions concerning the input range, please contact a TI field representative prior to connecting the input power.
Applying loads outside of the specified output range may result in unintended operation and/or possible permanent damage to the
EVM. Please consult the EVM User's Guide prior to connecting any load to the EVM output. If there is uncertainty as to the load
specification, please contact a TI field representative.
During normal operation, some circuit components may have case temperatures greater than +37 ° C. The EVM is designed to
operate properly with certain components above +60 ° C as long as the input and output ranges are maintained. These components
include but are not limited to linear regulators, switching transistors, pass transistors, and current sense resistors. These types of
devices can be identified using the EVM schematic located in the EVM User's Guide. When placing measurement probes near
these devices during operation, please be aware that these devices may be very warm to the touch.
Mailing Address: Texas Instruments, Post Office Box 655303, Dallas, Texas 75265
Copyright © 2006, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 23

IMPORTANT NOTICE
Texas Instruments Incorporated and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make corrections, modifications, enhancements,
improvements, and other changes to its products and services at any time and to discontinue any product or service without notice.
Customers should obtain the latest relevant information before placing orders and should verify that such information is current and
complete. All products are sold subject to TI’s terms and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgment.
TI warrants performance of its hardware products to the specifications applicable at the time of sale in accordance with TI’s
standard warranty. Testing and other quality control techniques are used to the extent TI deems necessary to support this
warranty. Except where mandated by government requirements, testing of all parameters of each product is not necessarily
performed.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or customer product design. Customers are responsible for their products and
applications using TI components. To minimize the risks associated with customer products and applications, customers should
provide adequate design and operating safeguards.
TI does not warrant or represent that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any TI patent right, copyright, mask
work right, or other TI intellectual property right relating to any combination, machine, or process in which TI products or services
are used. Information published by TI regarding third-party products or services does not constitute a license from TI to use such
products or services or a warranty or endorsement thereof. Use of such information may require a license from a third party under
the patents or other intellectual property of the third party, or a license from TI under the patents or other intellectual property of TI.
Reproduction of information in TI data books or data sheets is permissible only if reproduction is without alteration and is
accompanied by all associated warranties, conditions, limitations, and notices. Reproduction of this information with alteration is an
unfair and deceptive business practice. TI is not responsible or liable for such altered documentation.
Resale of TI products or services with statements different from or beyond the parameters stated by TI for that product or service
voids all express and any implied warranties for the associated TI product or service and is an unfair and deceptive business
practice. TI is not responsible or liable for any such statements.
TI products are not authorized for use in safety-critical applications (such as life support) where a failure of the TI product would
reasonably be expected to cause severe personal injury or death, unless officers of the parties have executed an agreement
specifically governing such use. Buyers represent that they have all necessary expertise in the safety and regulatory ramifications
of their applications, and acknowledge and agree that they are solely responsible for all legal, regulatory and safety-related
requirements concerning their products and any use of TI products in such safety-critical applications, notwithstanding any
applications-related information or support that may be provided by TI. Further, Buyers must fully indemnify TI and its
representatives against any damages arising out of the use of TI products in such safety-critical applications.
TI products are neither designed nor intended for use in military/aerospace applications or environments unless the TI products are
specifically designated by TI as military-grade or "enhanced plastic." Only products designated by TI as military-grade meet military
specifications. Buyers acknowledge and agree that any such use of TI products which TI has not designated as military-grade is
solely at the Buyer's risk, and that they are solely responsible for compliance with all legal and regulatory requirements in
connection with such use.
TI products are neither designed nor intended for use in automotive applications or environments unless the specific TI products
are designated by TI as compliant with ISO/TS 16949 requirements. Buyers acknowledge and agree that, if they use any
non-designated products in automotive applications, TI will not be responsible for any failure to meet such requirements.
Following are URLs where you can obtain information on other Texas Instruments products and application solutions:
Products Applications
Amplifiers amplifier.ti.com Audio www.ti.com/audio
Data Converters dataconverter.ti.com Automotive www.ti.com/automotive
DSP dsp.ti.com Broadband www.ti.com/broadband
Interface interface.ti.com Digital Control www.ti.com/digitalcontrol
Logic logic.ti.com Military www.ti.com/military
Power Mgmt power.ti.com Optical Networking www.ti.com/opticalnetwork
Microcontrollers microcontroller.ti.com Security www.ti.com/security
RFID www.ti-rfid.com Telephony www.ti.com/telephony
Low Power www.ti.com/lpw Video & Imaging www.ti.com/video
Wireless
Wireless www.ti.com/wireless
Mailing Address: Texas Instruments, Post Office Box 655303, Dallas, Texas 75265
Copyright © 2007, Texas Instruments Incorporated
 Loading...
Loading...