Page 1

S
R
C
4
1
9
2
S
R
C
4
1
9
3
192kHz Stereo Asynchronous
Sample Rate Converters
SRC4192
SRC4193
SBFS022A – JULY 2003
(1)
(1)
FEATURES
● AUTOMATIC SENSING OF THE INPUT-TO-
OUTPUT SAMPLING RATIO
● WIDE INPUT-TO-OUTPUT SAMPLING RANGE:
16:1 to 1:16
● SUPPORTS INPUT & OUTPUT SAMPLING
RATES UP TO 212kHz
● DYNAMIC RANGE: 144dB (-60dbFS input,
BW = 20Hz to fS/2, A-Weighted)
● THD+N: -140dB (0dbFS input, BW = 20Hz to
fS/2)
● ATTENUATES SAMPLING AND REFERENCE
CLOCK JITTER
● HIGH PERFORMANCE, LINEAR PHASE
DIGITAL FILTERING WITH BETTER THAN
140dB OF STOP BAND ATTENUATION
● FLEXIBLE AUDIO SERIAL PORTS:
Master or Slave Mode Operation
Supports I2S, Left Justified, Right Justified, and
TDM Data Formats
Supports 16, 18, 20, or 24-Bit Audio Data
TDM Mode allows daisy chaining of up to eight
devices
● SUPPORTS 24-, 20-, 18-, or 16-BIT INPUT AND
OUTPUT DATA
All output data is dithered from the internal
28-Bit data path
● LOW GROUP DELAY OPTION FOR INTERPO-
LATION FILTER
● DIRECT DOWNSAMPLING OPTION FOR
DECIMATION FILTER (SRC4193 ONLY)
● SPI PORT PROVIDES ACCESS TO INTERNAL
CONTROL REGISTERS (SRC4193 ONLY)
● SOFT MUTE FUNCTION
● BYPASS MODE
● PROGRAMMABLE DIGITAL OUTPUT
ATTENUATION (SRC4193 ONLY)
256 steps: 0dB to –127.5dB, 0.5dB/step
(1) Patents Pending.
(2) Refer to the Applications Information section of this data sheet for details.
● POWER DOWN MODE
● OPERATES FROM A SINGLE +3.3 VOLT
POWER SUPPLY
● SMALL 28-LEAD SSOP PACKAGE
● PIN COMPATIBLE WITH THE AD1896
(SRC4192 ONLY)
(2)
APPLICATIONS
● DIGITAL MIXING CONSOLES
● DIGITAL AUDIO WORKSTATIONS
● AUDIO DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS
● BROADCAST STUDIO EQUIPMENT
● HIGH-END A/V RECEIVERS
● GENERAL DIGITAL AUDIO PROCESSING
DESCRIPTION
The SRC4192 and SRC4193 are asynchronous sample rate
converters designed for professional and broadcast audio
applications. The SRC4192 and SRC4193 combine a wide
input-to-output sampling ratio with outstanding dynamic range
and ultra low distortion. Input and output serial ports support
standard audio formats, as well as a Time Division Multiplexed (TDM) mode. Flexible audio interfaces allow the
SRC4192 and SRC4193 to connect to a wide range of audio
data converters, digital audio receivers and transmitters, and
digital signal processors.
The SRC4192 is a standalone pin programmed device, with
control pins for mode, data format, mute, bypass, and low
group delay functions. The SRC4193 is a software-controlled
device featuring a serial peripheral interface (SPI) port, which
is utilized to program all functions via internal control registers.
The SRC4192 and SRC4193 may be operated from a single
+3.3V power supply. A separate digital I/O supply (V
operates over the +1.65V to +3.6V supply range, allowing
greater flexibility when interfacing to current and future generation signal processors and logic devices. Both the
SRC4192 and SRC4193 are available in a 28-lead SSOP
package.
IO
)
Please be aware that an important notice concerning availability, standard warranty, and use in critical applications of
Texas Instruments semiconductor products and disclaimers thereto appears at the end of this data sheet.
All trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date.
Products conform to specifications per the terms of Texas Instruments
standard warranty. Production processing does not necessarily include
testing of all parameters.
Copyright © 2003, Texas Instruments Incorporated
www.ti.com
Page 2
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Supply Voltage, VDD.......................................................... –0.3V to +4.0V
Supply Voltage, V
Digital Input Voltage .......................................................... –0.3V to +4.0V
Operating Temperature Range ........................................–45°C to +85°C
Storage Temperature Range ......................................... –65°C to +150°C
NOTE: (1) Stresses above these ratings may cause permanent damage.
Exposure to absolute maximum conditions for extended periods may degrade device reliability. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those specified is
not implied.
........................................................... –0.3V to +4.0V
IO
(1)
ELECTROSTATIC
DISCHARGE SENSITIVITY
This integrated circuit can be damaged by ESD. Texas Instruments recommends that all integrated circuits be handled with
appropriate precautions. Failure to observe proper handling
and installation procedures can cause damage.
ESD damage can range from subtle performance degradation
to complete device failure. Precision integrated circuits may be
more susceptible to damage because very small parametric
changes could cause the device not to meet its published
specifications.
PACKAGE/ORDERING INFORMATION
PRODUCT PACKAGE-LEAD DESIGNATOR
PACKAGE TEMPERATURE PACKAGE ORDERING TRANSPORT
SRC4192 SSOP-28 DB –45°C to +85°C SRC4192I SRC4192IDB Rails, 50
(1)
SPECIFIED
RANGE MARKING NUMBER MEDIA, QUANTITY
" """"SRC4192IDBR Tape and Reel, 2000
SRC4193 SSOP-28 DB –45°C to +85°C SRC4193I SRC4193IDB Rails, 50
" """"SRC4193IDBR Tape and Reel, 2000
NOTE: (1) For the most current specifications and package information, refer to our web site at www.ti.com.
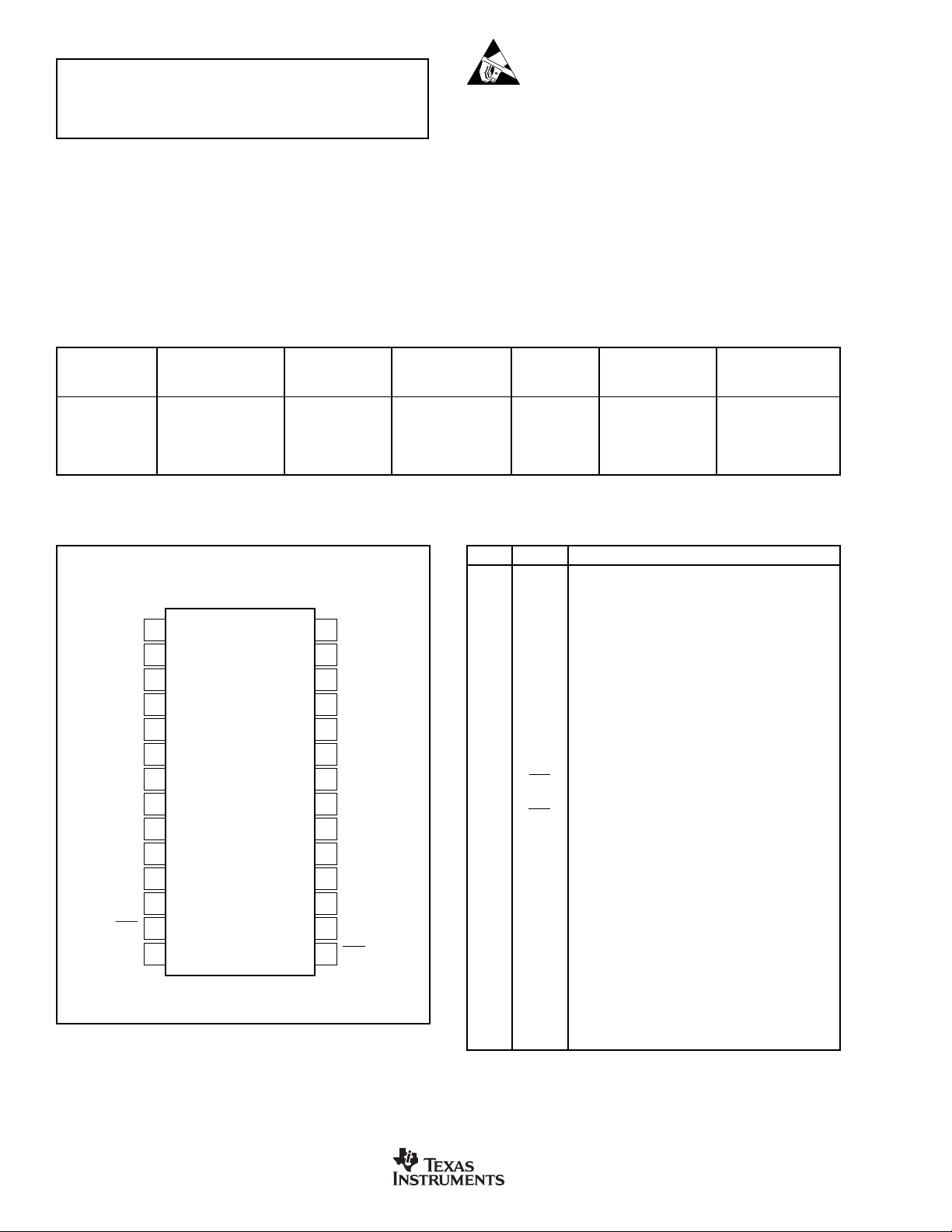
PIN CONFIGURATION (SRC4192)
Top View
LGRP
1
RCKI
2
NC
3
SDIN
4
BCKI
5
LRCKI
DGND
BYPAS
IFMT0
IFMT1
IFMT2
VIO
RST
MUTE
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
SRC4192
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
MODE2
MODE1
MODE0
BCKO
LRCKO
SDOUT
VDD
DGND
TDMI
OFMT0
OFMT1
OWL0
OWL1
RDY
PIN DESCRIPTIONS (SRC4192)
PIN# NAME DESCRIPTION
1 LGRP Low Group Delay Control Input (Active High)
2 RCKI Reference Clock Input
3 N.C. No Connection
4 SDIN Audio Serial Data Input
5 BCKI Input Port Bit Clock I/O
6 LRCKI Input Port Left/Right Word Clock I/O
7V
8 DGND Digital Ground
9 BYPAS ASRC Bypass Control Input (Active High)
10 IFMT0 Input Port Data Format Control Input
11 IFMT1 Input Port Data Format Control Input
12 IFMT2 Input Port Data Format Control Input
13 RST Reset Input (Active Low)
14 MUTE Output Mute Control Input (Active High)
15 RDY ASRC Ready Status Output (Active Low)
16 OWL1 Output Port Data Word Length Control Input
17 OWL0 Output Port Data Word Length Control Input
18 OFMT1 Output Port Data Format Control Input
19 OFMT0 Output Port Data Format Control Input
20 TDMI TDM Data Input (Connect to DGND when not in use)
21 DGND Digital Ground
22 V
23 SDOUT Audio Serial Data Output
24 LRCKO Output Port Left/Right Word Clock I/O
25 BCKO Output Port Bit Clock I/O
26 MODE0 Serial Port Mode Control Input
27 MODE1 Serial Port Mode Control Input
28 MODE2 Serial Port Mode Control Input
Digital I/O Supply, +1.65V to V
IO
Digital Core Supply, +3.3V
DD
DD
2
www.ti.com
SRC4192, SRC4193
SBFS022A
Page 3
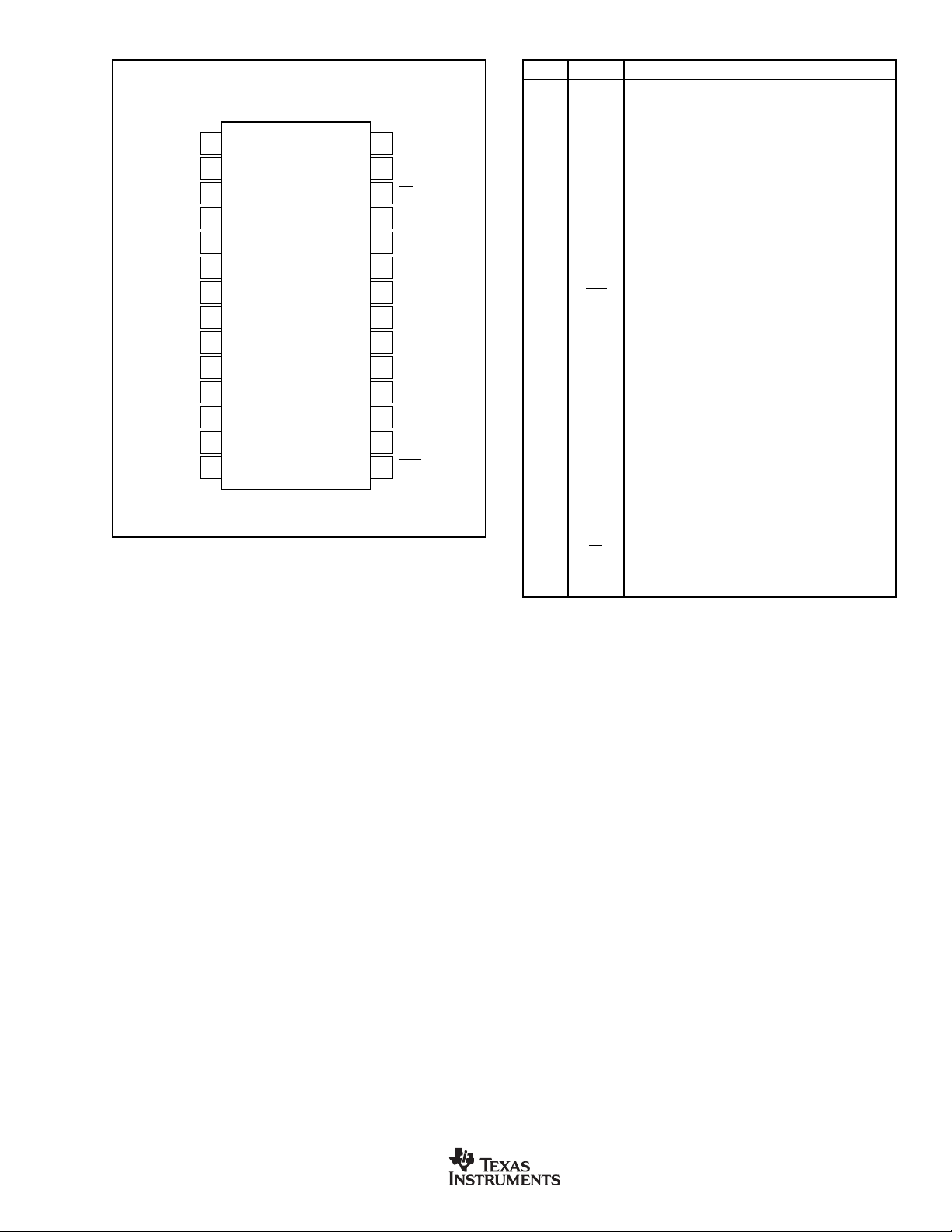
PIN CONFIGURATION (SRC4193)
Top View
RCKI
1
NC
2
NC
3
SDIN
4
BCKI
5
LRCKI
6
VIO
DGND
BYPAS
NC
NC
NC
RST
MUTE
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
SRC4193
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
CDATA
CCLK
CS
BCKO
LRCKO
SDOUT
V
DD
DGND
TDMI
NC
NC
NC
RATIO
RDY
PIN DESCRIPTIONS (SRC4193)
PIN# NAME DESCRIPTION
1 RCKI Reference Clock Input
2 N.C. No Connection
3 N.C. No Connection
4 SDIN Audio Serial Data Input
5 BCKI Input Port Bit Clock I/O
6 LRCKI Input Port Left/Right Word Clock I/O
7V
8 DGND Digital Ground
9 BYPAS ASRC Bypass Control Input (Active High)
10 N.C. No Connection
11 N.C. No Connection
12 N.C. No Connection
13 RST Reset Input (Active Low)
14 MUTE Output Mute Control Input (Active High)
15 RDY ASRC Ready Status Output (Active Low)
16 RATIO Input-to-Output Ratio Flag Output
17 N.C. No Connection
18 N.C. No Connection
19 N.C. No Connection
20 TDMI TDM Data Input (Connect to DGND when not in use)
21 DGND Digital Ground
22 V
23 SDOUT Audio Serial Data Output
24 LRCKO Output Port Left/Right Word Clock I/O
25 BCKO Output Port Bit Clock I/O
26 CS SPI Port Chip Select Input (Active Low)
27 CCLK SPI Port Data Clock Input
28 CDATA SPI Port Serial Data Input
Digital I/O Supply, +1.65V to V
IO
Low output denotes Output rate lower than Input rate.
High output denotes Output rate higher than Input rate.
Digital Core Supply, +3.3V
DD
DD
SRC4192, SRC4193
SBFS022A
www.ti.com
3
Page 4
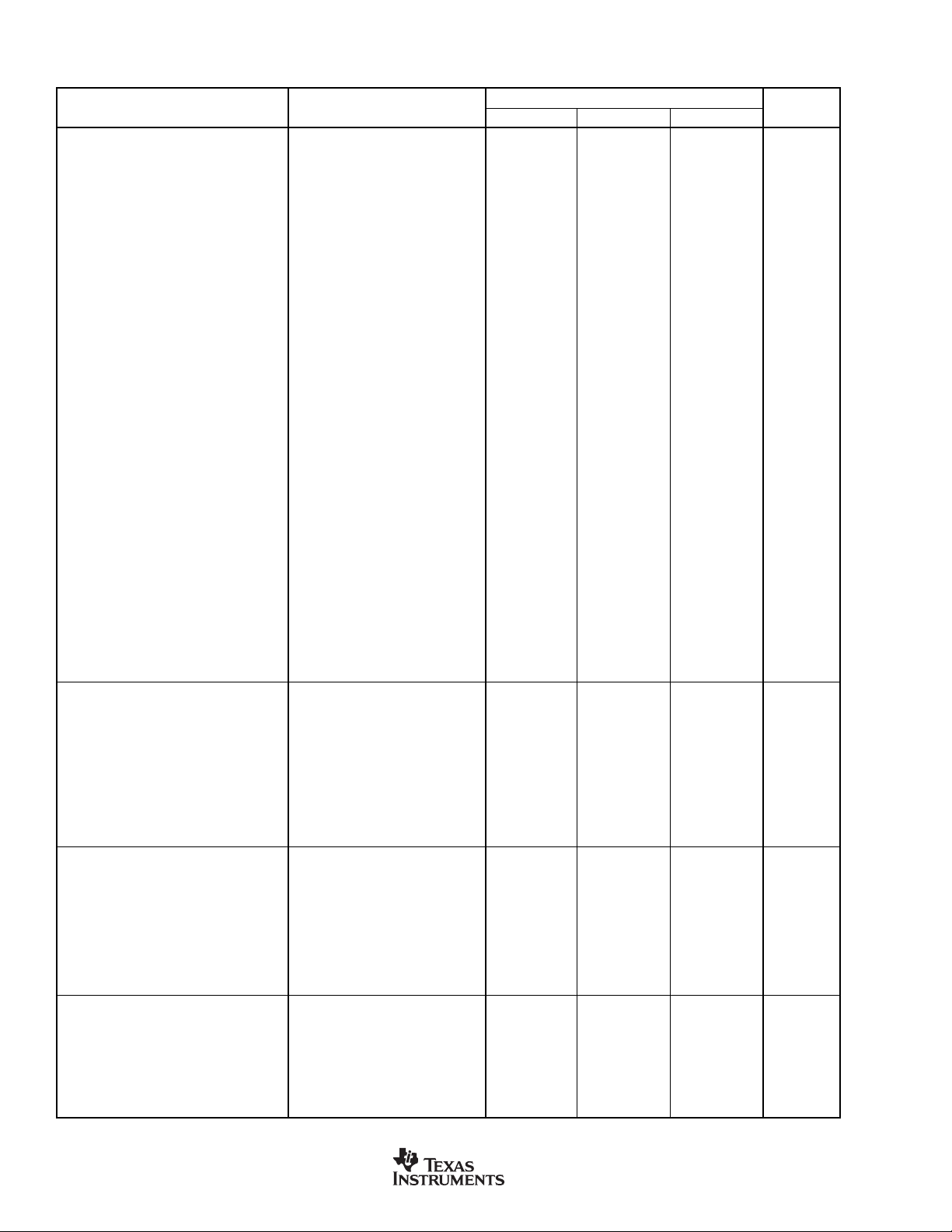
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
All parameters specified with TA = +25°C, V
PARAMETER CONDITION MIN TYP MAX UNITS
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE
(1)
Resolution 24 Bits
Input Sampling Frequency f
Output Sampling Frequency f
Input: Output Sampling Ratio
Upsampling 1:16
Downsampling 16:1
Dynamic Range BW = 20Hz to f
44.1kHz; 48kHz 140 dB
48kHz; 44.1kHz 140 dB
48kHz; 96kHz 140 dB
44.1kHz; 192kHz 138 dB
96kHz; 48kHz 141 dB
192kHz; 12kHz 141 dB
192kHz; 32kHz 141 dB
192kHz; 48kHz 141 dB
32kHz; 48kHz 140 dB
12kHz; 192kHz 138 dB
Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise BW = 20Hz to f
44.1kHz; 48kHz –140 dB
48kHz; 44.1kHz –140 dB
48kHz; 96kHz –140 dB
44.1kHz; 192kHz –137 dB
96kHz; 48kHz –140 dB
192kHz; 12kHz –140 dB
192kHz; 32kHz –141 dB
192kHz; 48kHz –141 dB
32kHz; 48kHz –140 dB
12kHz; 192kHz –137 dB
Interchannel Gain Mismatch 0dB
Interchannel Phase Deviation 0 Degrees
Digital Attenuation SRC4193 Only
Minimum 0dB
Maximum –127.5 dB
Step Size 0.5 dB
Mute Attenuation 24-Bit Word Length, A-weighted –144 dB
DIGITAL INTERPOLATION FILTER
CHARACTERISTICS
Passband 0.4535 x f
Passband Ripple ±0.007 dB
Transition Band 0.4535 x f
Stop Band 0.5465 x f
Stop Band Attenuation –144 dB
Normal Group Delay (LGRP = 0) Decimation Filter On (DFLT = 0) 102.53125/f
Normal Group Delay (LGRP = 0) Decimation Filter Off (DFLT = 1) 102/f
Low Group Delay (LGRP = 1) Decimation Filter On (DFLT = 0) 70.53125/f
Low Group Delay (LGRP = 1) Decimation Filter Off (DFLT = 1) 70/f
DIGITAL DECIMATION FILTER
CHARACTERISTICS
Passband 0.4535 x f
Passband Ripple ±0.008 dB
Transition Band 0.4535 x f
Stop Band 0.5465 x f
Stop Band Attenuation –143 dB
Group Delay
Decimation Filter DFLT = 0 for SRC4193 36.46875/f
Direct Down-Sampling SRC4193 Only, DFLT = 1 0 Seconds
DIGITAL I/O CHARACTERISTICS
High-Level Input Voltage V
Low Level Input Voltage V
High-Level Input Current I
Low-Level Input Current I
High-Level Output Voltage V
Low-Level Output Voltage V
Input Capacitance C
= +3.3V, and V
DD
SIN
SOUT
(add 3dB to spec for A-weighted result)
IH
IL
IH
IL
OH
OL
IN
= +3.3V, unless otherwise noted.
IO
/2, –60dBFS Input
SOUT
f
= 1kHz, Unweighted
IN
/2, 0dBFS Input
SOUT
f
= 1kHz, Unweighted
IN
IO = –4mA 0.8 x V
IO = +4mA 0 0.2 x V
SRC4192, SRC4193
4 212 kHz
4 212 kHz
SIN
SIN
SIN
0.5465 x f
0.5465 x f
V
IO
SIN
SOUT
SOUT
IO
SIN
SIN
SIN
SIN
SOUT
SOUT
SOUT
0.7 x V
IO
0 0.3 x V
0.5 10 µA
0.5 10 µA
IO
3pF
V
IO
IO
Hz
Hz
Hz
Seconds
Seconds
Seconds
Seconds
Hz
Hz
Hz
Seconds
V
V
V
V
4
www.ti.com
SRC4192, SRC4193
SBFS022A
Page 5
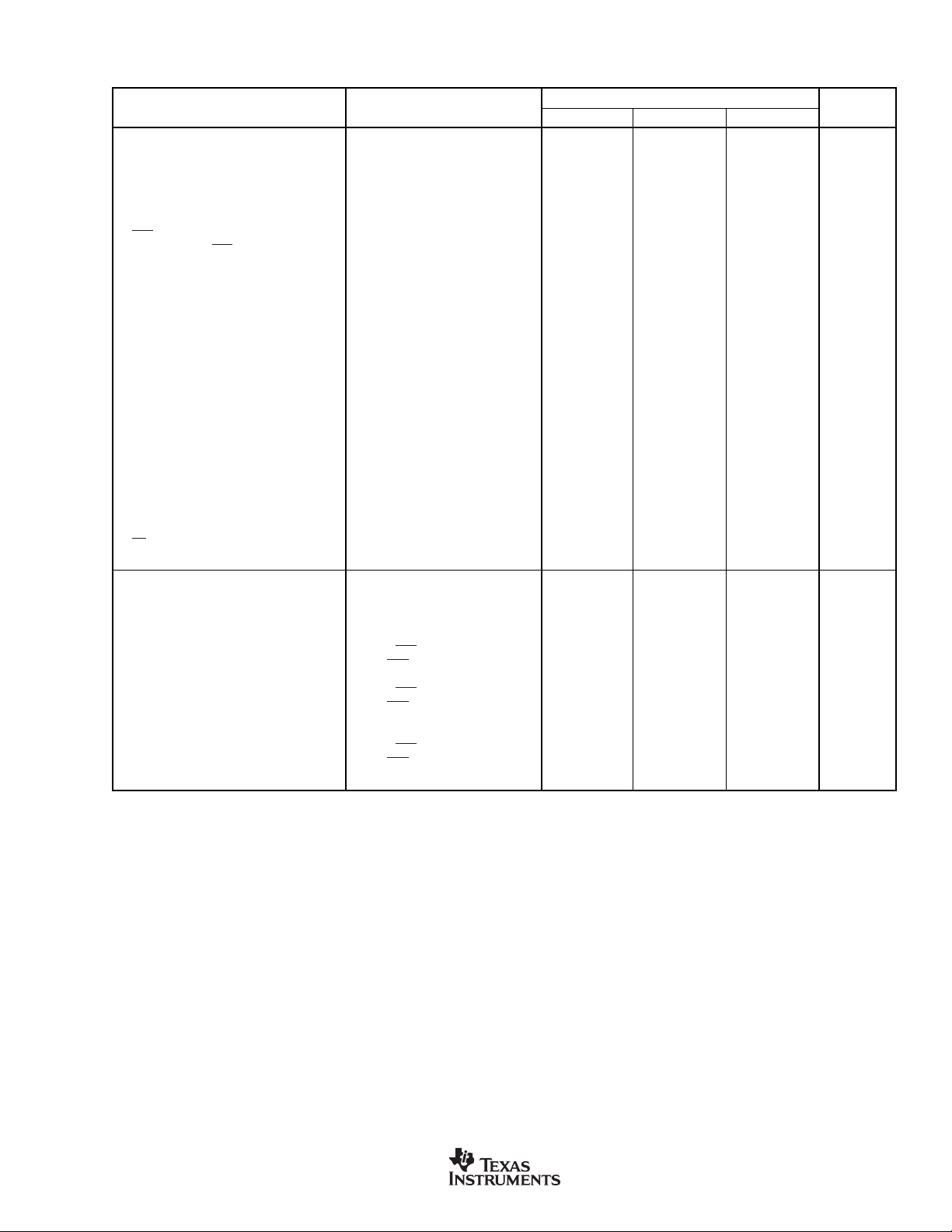
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (Cont.)
All parameters specified with TA = +25°C, V
PARAMETER CONDITION MIN TYP MAX UNITS
SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS
Reference Clock Timing
RCKI Frequency
(2), (3)
RCKI Period t
RCKI Pulsewidth High t
RCKI Pulsewidth Low t
Reset Timing
Pulse Width Low t
RST
Delay Following
Rising Edge SRC4193 Only 500 µs
RST
Input Serial Port Timing
LRCKI to BCKI Setup Time t
BCKI Pulsewidth High t
BCKI Pulsewidth Low t
SDIN Data Setup Time t
SDIN Data Hold Time t
Output Serial Port Timing
SDOUT Data Delay Time t
SDOUT Data Hold Time t
BCKO Pulsewidth High t
BCKO Pulsewidth Low t
TDM Mode Timing
LRCKO Setup Time t
LRCKO Hold Time t
TDMI Data Setup Time t
TDMI Data Hold Time t
SPI Timing
CCLK Frequency 25 MHz
CDATA Setup Time t
CDATA Hold Time t
Falling to CCLK Rising t
CS
CCLK Falling to CS Rising t
POWER SUPPLIES
Operating Voltage
V
DD
V
IO
Supply Current V
I
, Power Down
DD
I
, Power Down (SRC4193 only)
DD
I
, Dynamic f
DD
I
, Power Down
IO
I
, Power Down (SRC4193 only)
IO
I
, Dynamic f
IO
Total Power Dissipation V
P
, Power Down
D
P
, Power Down (SRC4193)
D
P
, Dynamic f
D
NOTES: (1) Dynamic performance measured with an Audio Precision System Two Cascade or Cascade Plus.
(2) f
(3) f
SMIN
SMAX
= min (f
= max (f
SIN
SIN
, f
).
SOUT
, f
).
SOUT
= +3.3V, and V
DD
RCKIP
RCKIH
RCKIL
RSTL
LRIS
SIH
SIL
LDIS
LDIH
DOPD
DOH
SOH
SOL
LROS
LROH
TDMS
TDMH
CDS
CDH
CSCR
CFCS
= +3.3V, unless otherwise noted.
IO
SRC4192, SRC4193
128 x f
SMIN
20 1/(128 x f
0.4 x t
RCKIP
0.4 x t
RCKIP
50 MHz
)ns
SMIN
500 ns
10 ns
10 ns
10 ns
10 ns
10 ns
10 ns
2ns
10 ns
5ns
10 ns
10 ns
10 ns
10 ns
12 ns
8ns
15 ns
12 ns
3.0 +3.3 3.6 V
1.65 +3.3 3.6 V
= +3.3V, VIO = +3.3V
DD
= 0, No Clocks 100 µA
RST
Bit = 0, No Clocks 5 mA
PDN
= f
SIN
RST
PDN
SIN
DD
RST
PDN
SIN
= 192kHz 66 mA
sOUT
= 0, No Clocks 100 µA
Bit = 0, No Clocks 21 µA
= f
= 192kHz 2 mA
SOUT
= +3.3V, VIO = +3.3V
= 0, No Clocks 660 µW
Bit = 0, No Clocks 16.6 mW
= f
= 192kHz 225 mW
SOUT
ns
ns
SRC4192, SRC4193
SBFS022A
www.ti.com
5
Page 6
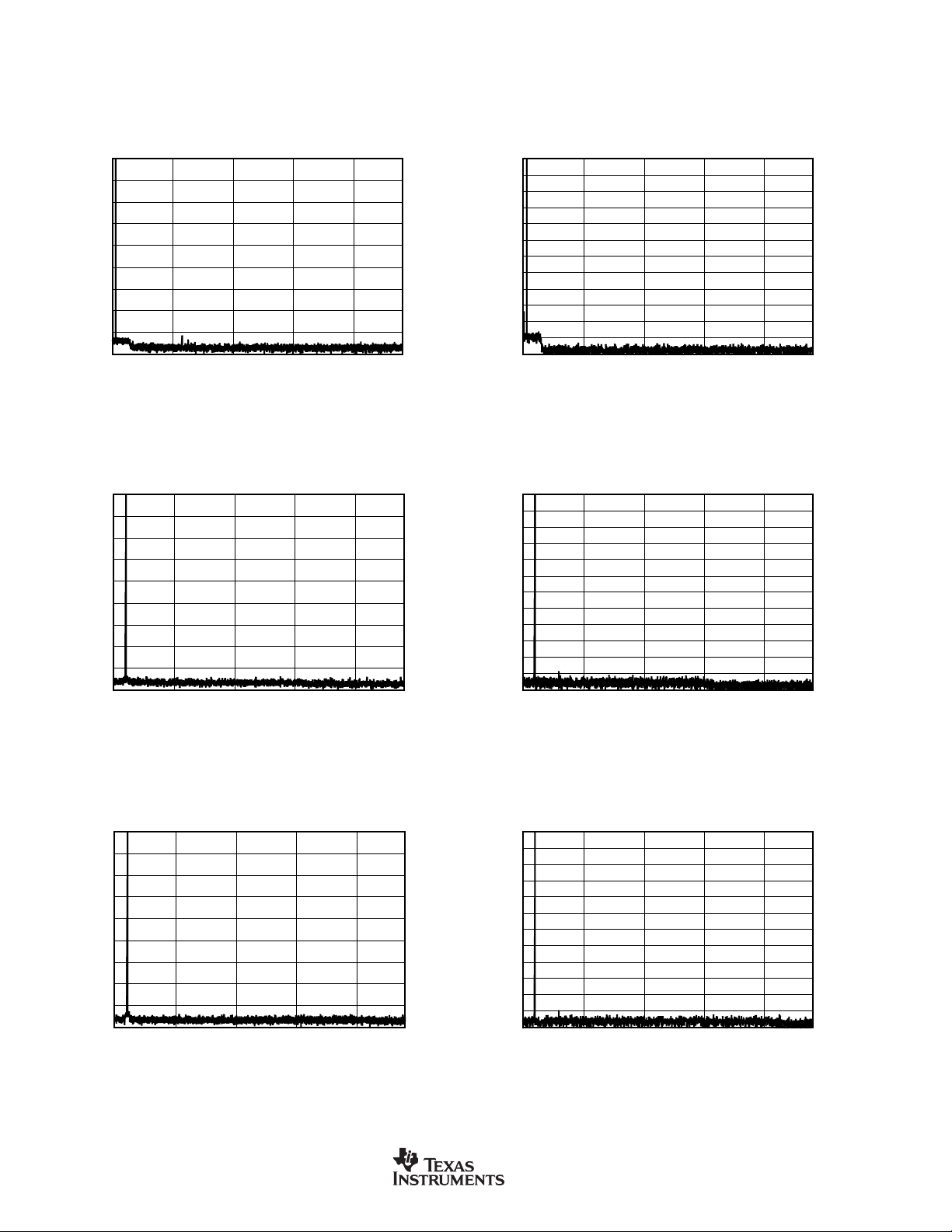
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
At TA = +25°C, VDD = +3.3V, and VIO = +3.3V, unless otherwise noted.
FFT with 1kHz INPUT TONE at 0dBFS
0
–20
–40
–60
–80
dBFS
–100
–120
–140
–160
–180
0 20k 40k 96k80k60k
FFT with 1kHz INPUT TONE at 0dBFS
0
–20
–40
–60
–80
dBFS
–100
–120
–140
–160
–180
0 5k 10k 24k20k15k
(12kHz:192kHz)
Frequency (Hz)
(32kHz:48kHz)
Frequency (Hz)
FFT with 1kHz INPUT TONE at –60dBFS
–60
–70
–80
–90
–100
–110
–120
dBFS
–130
–140
–150
–160
–170
–180
0 20k 40k 96k80k60k
FFT with 1kHz INPUT TONE at –60dBFS
–60
–70
–80
–90
–100
–110
–120
dBFS
–130
–140
–150
–160
–170
–180
0 5k 10k 24k20k15k
(12kHz:192kHz)
Frequency (Hz)
(32kHz:48kHz)
Frequency (Hz)
6
FFT with 1kHz INPUT TONE at 0dBFS
0
–20
–40
–60
–80
dBFS
–100
–120
–140
–160
–180
0 5k 10k 24k20k15k
(44.1kHz:48kHz)
Frequency (Hz)
www.ti.com
FFT with 1kHz INPUT TONE at –60dBFS
–60
–70
–80
–90
–100
–110
–120
dBFS
–130
–140
–150
–160
–170
–180
0 5k 10k 24k20k15k
(44.1kHz:48kHz)
Frequency (Hz)
SRC4192, SRC4193
SBFS022A
Page 7
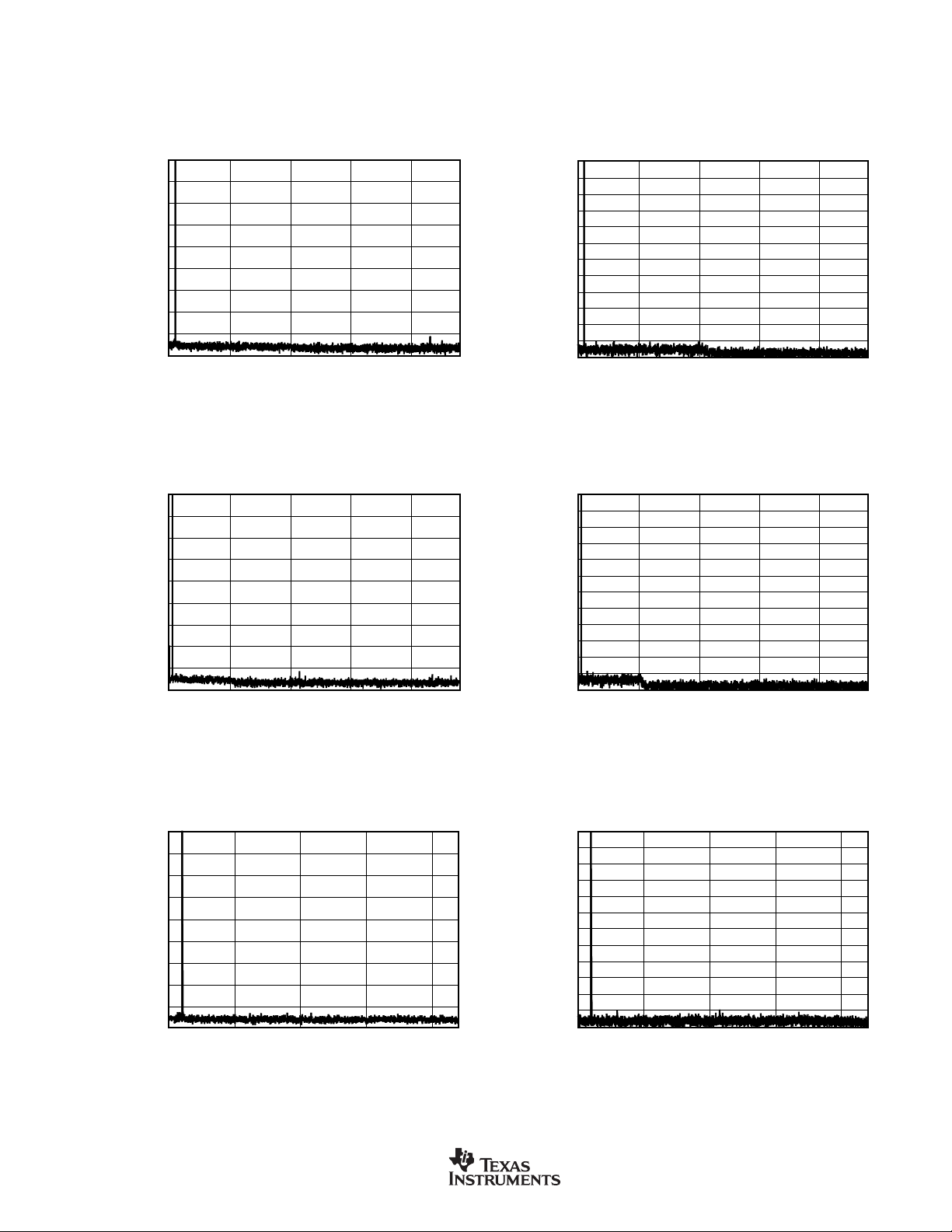
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS (Cont.)
At TA = +25°C, VDD = +3.3V, and VIO = +3.3V, unless otherwise noted.
FFT with 1kHz INPUT TONE at 0dBFS
0
–20
–40
–60
–80
dBFS
–100
–120
–140
–160
–180
0 10k 20k 48k40k30k
FFT with 1kHz INPUT TONE at 0dBFS
0
–20
–40
–60
–80
dBFS
–100
–120
–140
–160
–180
0 20k 40k 96k80k60k
(44.1kHz:96kHz)
Frequency (Hz)
(44.1kHz:192kHz)
Frequency (Hz)
FFT with 1kHz INPUT TONE at –60dBFS
–60
–70
–80
–90
–100
–110
–120
dBFS
–130
–140
–150
–160
–170
–180
0 10k 20k 48k40k30k
FFT with 1kHz INPUT TONE at –60dBFS
–60
–70
–80
–90
–100
–110
–120
dBFS
–130
–140
–150
–160
–170
–180
0 20k 40k 96k80k60k
(44.1kHz:96kHz)
Frequency (Hz)
(44.1kHz:192kHz)
Frequency (Hz)
FFT with 1kHz INPUT TONE at 0dBFS
0
–20
–40
–60
–80
dBFS
–100
–120
–140
–160
–180
0 5k 10k 22k20k15k
SRC4192, SRC4193
SBFS022A
(48kHz:44.1kHz)
Frequency (Hz)
www.ti.com
FFT with 1kHz INPUT TONE at –60dBFS
–60
–70
–80
–90
–100
–110
–120
dBFS
–130
–140
–150
–160
–170
–180
0 5k 10k 22k20k15k
(48kHz:44.1kHz)
Frequency (Hz)
7
Page 8
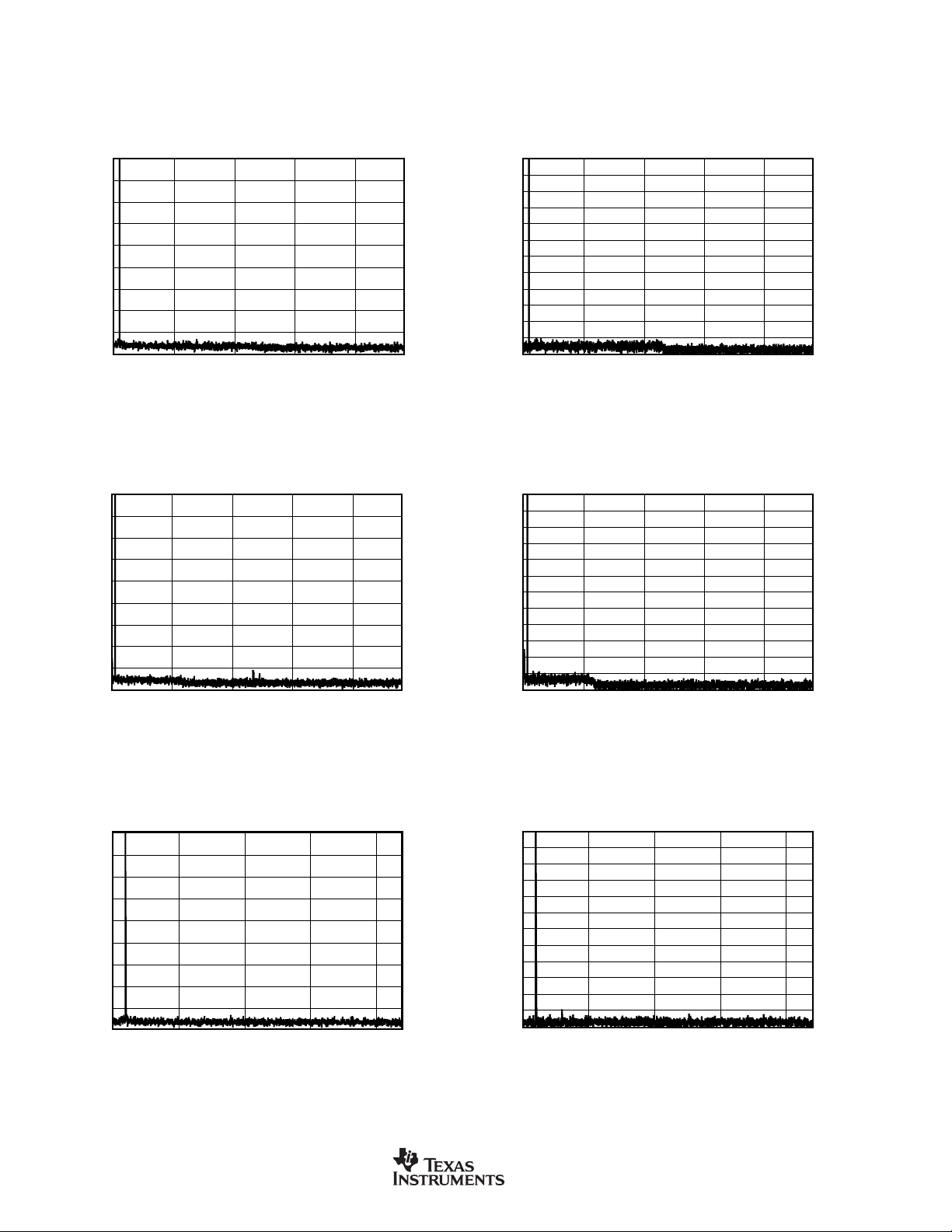
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS (Cont.)
At TA = +25°C, VDD = +3.3V, and VIO = +3.3V, unless otherwise noted.
FFT with 1kHz INPUT TONE at 0dBFS
0
–20
–40
–60
–80
dBFS
–100
–120
–140
–160
–180
0 10k 20k 48k40k30k
FFT with 1kHz INPUT TONE at 0dBFS
0
–20
–40
–60
–80
dBFS
–100
–120
–140
–160
–180
0 20k 40k 96k80k60k
(48kHz:96kHz)
Frequency (Hz)
(48kHz:192kHz)
Frequency (Hz)
FFT with 1kHz INPUT TONE at –60dBFS
–60
–70
–80
–90
–100
–110
–120
dBFS
–130
–140
–150
–160
–170
–180
0 10k 20k 48k40k30k
FFT with 1kHz INPUT TONE at –60dBFS
–60
–70
–80
–90
–100
–110
–120
dBFS
–130
–140
–150
–160
–170
–180
0 20k 40k 96k80k60k
(48kHz:96kHz)
Frequency (Hz)
(48kHz:192kHz)
Frequency (Hz)
8
FFT with 1kHz INPUT TONE at 0dBFS
0
–20
–40
–60
–80
dBFS
–100
–120
–140
–160
–180
0 5k 10k 22k20k15k
(96kHz:44.1kHz)
Frequency (Hz)
www.ti.com
FFT with 1kHz INPUT TONE at –60dBFS
–60
–70
–80
–90
–100
–110
–120
dBFS
–130
–140
–150
–160
–170
–180
0 5k 10k 22k20k15k
(96kHz:44.1kHz)
Frequency (Hz)
SRC4192, SRC4193
SBFS022A
Page 9
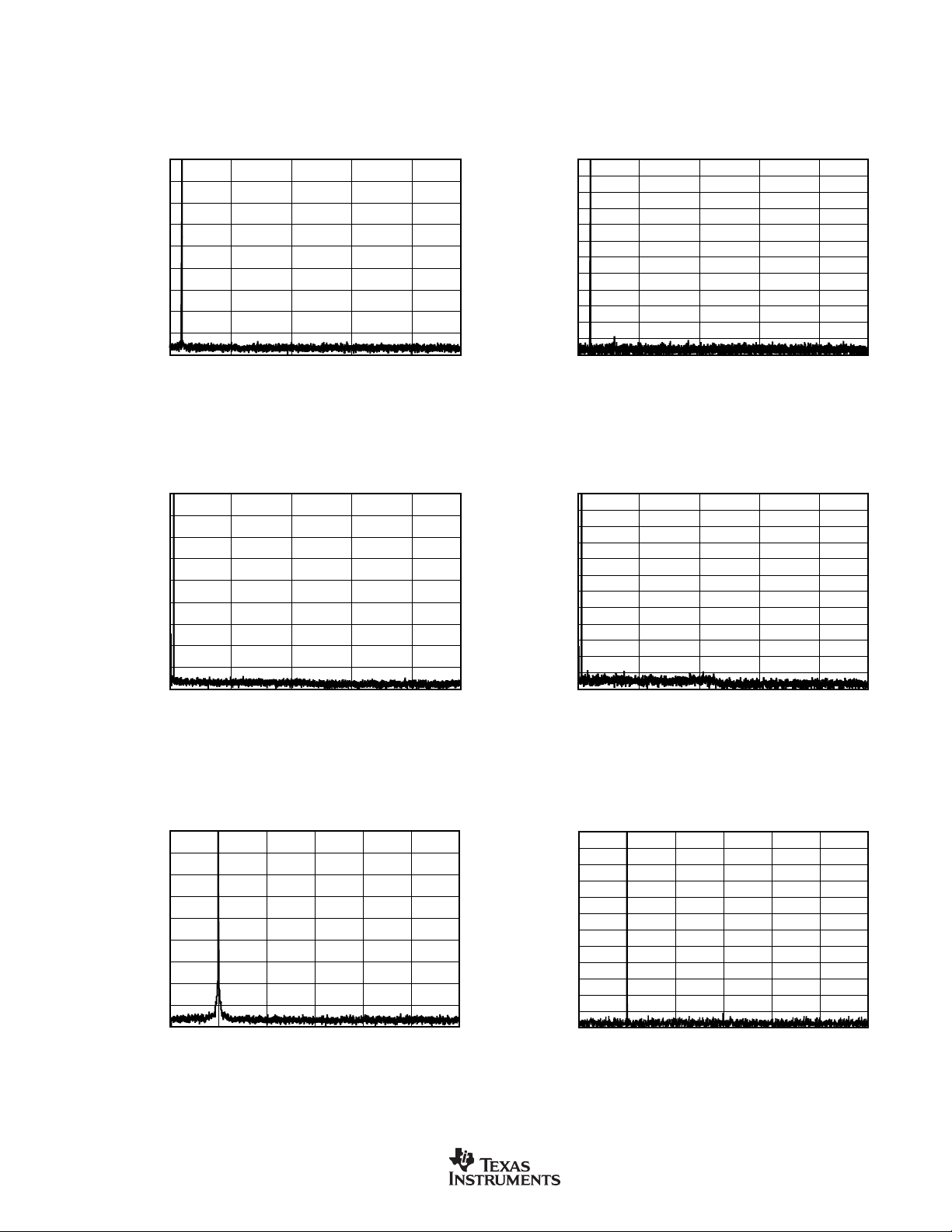
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS (Cont.)
–60
–70
–80
–90
–100
–110
–120
–130
–140
–150
–160
–170
–180
dBFS
FFT with 1kHz INPUT TONE at –60dBFS
(192kHz:12kHz)
01k2k3k4k 6k5k
Frequency (Hz)
At TA = +25°C, VDD = +3.3V, and VIO = +3.3V, unless otherwise noted.
FFT with 1kHz INPUT TONE at 0dBFS
0
–20
–40
–60
–80
dBFS
–100
–120
–140
–160
–180
0 5k 10k 24k20k15k
FFT with 1kHz INPUT TONE at 0dBFS
0
–20
–40
–60
–80
dBFS
–100
–120
–140
–160
–180
0 20k 40k 96k80k60k
(96kHz:48kHz)
Frequency (Hz)
(96kHz:192kHz)
Frequency (Hz)
FFT with 1kHz INPUT TONE at –60dBFS
–60
–70
–80
–90
–100
–110
–120
dBFS
–130
–140
–150
–160
–170
–180
0 5k 10k 24k20k15k
FFT with 1kHz INPUT TONE at –60dBFS
–60
–70
–80
–90
–100
–110
–120
dBFS
–130
–140
–150
–160
–170
–180
0 20k 40k 96k80k60k
(96kHz:48kHz)
Frequency (Hz)
(96kHz:192kHz)
Frequency (Hz)
0
–20
–40
–60
–80
dBFS
–100
–120
SRC4192, SRC4193
SBFS022A
–140
–160
–180
01k2k3k4k 6k5k
FFT with 1kHz INPUT TONE at 0dBFS
(192kHz:12kHz)
Frequency (Hz)
www.ti.com
9
Page 10
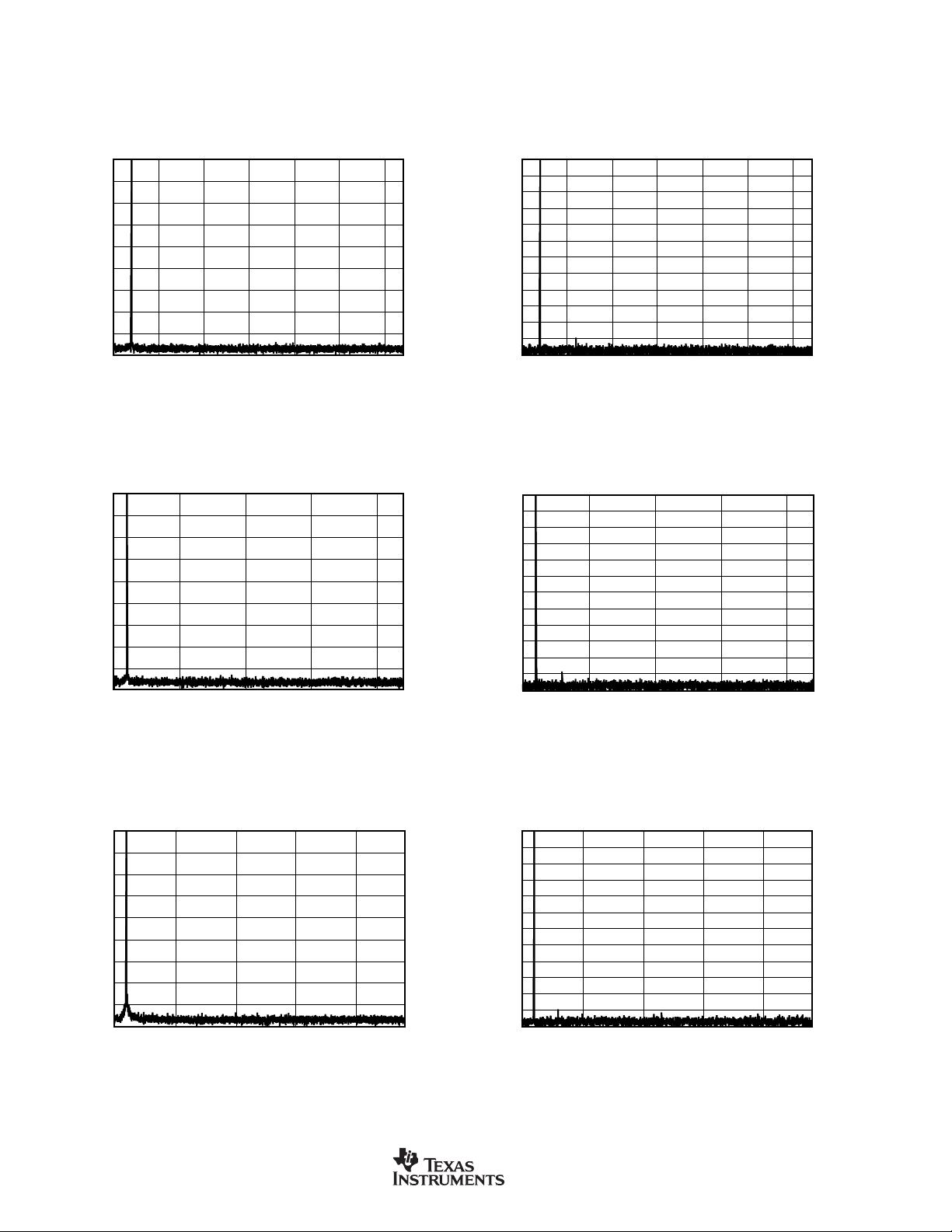
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS (Cont.)
At TA = +25°C, VDD = +3.3V, and VIO = +3.3V, unless otherwise noted.
FFT with 1kHz INPUT TONE at 0dBFS
0
–20
–40
–60
–80
dBFS
–100
–120
–140
–160
–180
0 2.5 5k 7.5k 10k 16k15k12.5k
FFT with 1kHz INPUT TONE at 0dBFS
0
–20
–40
–60
–80
dBFS
–100
–120
–140
–160
–180
0 5k 10k 22k20k15k
(192kHz:32kHz)
Frequency (Hz)
(192kHz:44.1kHz)
Frequency (Hz)
FFT with 1kHz INPUT TONE at –60dBFS
–60
–70
–80
–90
–100
–110
–120
dBFS
–130
–140
–150
–160
–170
–180
0 2.5k 5k 7.5k 10k 16k15k12.5k
FFT with 1kHz INPUT TONE at –60dBFS
–60
–70
–80
–90
–100
–110
–120
dBFS
–130
–140
–150
–160
–170
–180
0 5k 10k 22k20k15k
(192kHz:32kHz)
Frequency (Hz)
(192kHz:44.1kHz)
Frequency (Hz)
10
FFT with 1kHz INPUT TONE at 0dBFS
0
–20
–40
–60
–80
dBFS
–100
–120
–140
–160
–180
0 5k 10k 24k20k15k
(192kHz:48kHz)
Frequency (Hz)
www.ti.com
FFT with 1kHz INPUT TONE at –60dBFS
–60
–70
–80
–90
–100
–110
–120
dBFS
–130
–140
–150
–160
–170
–180
0 10k 20k 24k40k30k
(192kHz:48kHz)
Frequency (Hz)
SRC4192, SRC4193
SBFS022A
Page 11

TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS (Cont.)
At TA = +25°C, VDD = +3.3V, and VIO = +3.3V, unless otherwise noted.
FFT with 1kHz INPUT TONE at 0dBFS
0
–20
–40
–60
–80
dBFS
–100
–120
–140
–160
–180
0 10k 20k 48k40k30k
FFT with 20kHz INPUT TONE at 0dBFS
0
–20
–40
–60
–80
dBFS
–100
–120
–140
–160
–180
0 5k 10k 24k20k15k
(192kHz:96kHz)
Frequency (Hz)
(44.1kHz:48kHz)
Frequency (Hz)
FFT with 1kHz INPUT TONE at –60dBFS
–60
–70
–80
–90
–100
–110
–120
dBFS
–130
–140
–150
–160
–170
–180
0 10k 20k 48k40k30k
FFT with 20kHz INPUT TONE at 0dBFS
0
–20
–40
–60
–80
dBFS
–100
–120
–140
–160
–180
0 5k 10k 22k20k15k
(192kHz:96kHz)
Frequency (Hz)
(48kHz:44.1kHz)
Frequency (Hz)
FFT with 20kHz INPUT TONE at 0dBFS
0
–20
–40
–60
–80
dBFS
–100
–120
–140
–160
–180
0 5k 10k 24k20k15k
SRC4192, SRC4193
SBFS022A
(48kHz:48kHz)
Frequency (Hz)
www.ti.com
FFT with 20kHz INPUT TONE at 0dBFS
0
–20
–40
–60
–80
dBFS
–100
–120
–140
–160
–180
0 10k 20k 48k40k30k
(48kHz:96kHz)
Frequency (Hz)
11
Page 12

TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS (Cont.)
At TA = +25°C, VDD = +3.3V, and VIO = +3.3V, unless otherwise noted.
FFT with 20kHz INPUT TONE at 0dBFS
0
–20
–40
–60
–80
dBFS
–100
–120
–140
–160
–180
0 5k 10k 24k20k15k
THD+N vs INPUT AMPLITUDE fIN = 1kHz
–120
–125
–130
–135
–140
–145
–150
–155
Total Harmonic Distortion+Noise (dB)
–160
–140 –120 –100 –80 0–20–60 –40
(96kHz:48kHz)
Frequency (Hz)
(44.1kHz:48kHz)
Input Amplitude (dBFS)
FFT with 80kHz INPUT TONE at 0dBFS
0
–20
–40
–60
–80
dBFS
–100
–120
–140
–160
–180
0 20k 40k 96k80k60k
THD+N vs INPUT AMPLITUDE fIN = 1kHz
–120
–125
–130
–135
–140
–145
–150
–155
Total Harmonic Distortion+Noise (dB)
–160
–140 –120 –100 –80 0–20–60 –40
(192kHz:192kHz)
Frequency (Hz)
(48kHz:44.1kHz)
Input Amplitude (dBFS)
THD+N vs INPUT AMPLITUDE fIN = 1kHz
–120
–125
–130
–135
–140
–145
–150
–155
Total Harmonic Distortion+Noise (dB)
–160
–140 –120 –100 –80 0–20–60 –40
(48kHz:96kHz)
Input Amplitude (dBFS)
12
www.ti.com
THD+N vs INPUT AMPLITUDE fIN = 1kHz
–120
–125
–130
–135
–140
–145
–150
–155
Total Harmonic Distortion+Noise (dB)
–160
–140 –120 –100 –80 0–20–60 –40
(96kHz:48kHz)
Input Amplitude (dBFS)
SRC4192, SRC4193
SBFS022A
Page 13

TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS (Cont.)
–120
–125
–130
–135
–140
–145
–150
–155
–160
Total Harmonic Distortion+Noise (dB)
THD+N vs INPUT AMPLITUDE fIN = 1kHz
(192kHz:48kHz)
–140 –120 –100 –80 0–20–60 –40
Input Amplitude (dBFS)
–120
–125
–130
–135
–140
–145
–150
–155
–160
Total Harmonic Distortion+Noise (dB)
THD+N vs INPUT FREQUENCY, 0dBFS INPUT
(48kHz:44.1kHz)
0 5k 20k15k10k
Input Frequency (Hz)
–120
–125
–130
–135
–140
–145
–150
–155
–160
Total Harmonic Distortion+Noise (dB)
THD+N vs INPUT FREQUENCY, 0dBFS INPUT
(96kHz:48kHz)
0 5k 20k15k10k
Input Frequency (Hz)
At TA = +25°C, VDD = +3.3V, and VIO = +3.3V, unless otherwise noted.
THD+N vs INPUT AMPLITUDE fIN = 1kHz
–120
–125
–130
–135
–140
–145
–150
–155
Total Harmonic Distortion+Noise (dB)
–160
–140 –120 –100 –80 0–20–60 –40
THD+N vs INPUT FREQUENCY, 0dBFS INPUT
–120
–125
–130
–135
–140
–145
–150
–155
Total Harmonic Distortion+Noise (dB)
–160
0 5k 20k15k10k
(44.1kHz:192kHz)
Input Amplitude (dBFS)
(44.1kHz:48kHz)
Input Frequency (Hz)
–120
–125
–130
–135
–140
–145
–150
–155
Total Harmonic Distortion+Noise (dB)
–160
0 5k 20k15k10k
SRC4192, SRC4193
SBFS022A
THD+N vs INPUT FREQUENCY, 0dBFS INPUT
(48kHz:96kHz)
Input Frequency (Hz)
www.ti.com
13
Page 14

TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS (Cont.)
At TA = +25°C, VDD = +3.3V, and VIO = +3.3V, unless otherwise noted.
LINEARITY with fIN = 200Hz
0
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
–70
–80
–90
–100
Output Amplitude (dBFS)
–110
–120
–130
–140
–140 –130 –120 –110 –100 –90 –80 –70 –60 –50 0–40 –30 –20 –10
0
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
–70
–80
–90
–100
Output Amplitude (dBFS)
–110
–120
–130
–140
–140 –130 –120 –110 –100 –90 –80 –70 –60 –50 0–40 –30 –20 –10
(44.1kHz:48kHz)
Input Amplitude (dBFS)
LINEARITY with fIN = 200Hz
(48kHz:48kHz)
Input Amplitude (dBFS)
LINEARITY with fIN = 200Hz
0
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
–70
–80
–90
–100
Output Amplitude (dBFS)
–110
–120
–130
–140
–140 –130 –120 –110 –100 –90 –80 –70 –60 –50 0–40 –30 –20 –10
0
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
–70
–80
–90
–100
Output Amplitude (dBFS)
–110
–120
–130
–140
–140 –130 –120 –110 –100 –90 –80 –70 –60 –50 0–40 –30 –20 –10
(48kHz:44.1kHz)
Input Amplitude (dBFS)
LINEARITY with fIN = 200Hz
(48kHz:96kHz)
Input Amplitude (dBFS)
14
LINEARITY with fIN = 200Hz
0
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
–70
–80
–90
–100
Output Amplitude (dBFS)
–110
–120
–130
–140
–140 –130 –120 –110 –100 –90 –80 –70 –60 –50 0–40 –30 –20 –10
(96kHz:48kHz)
Input Amplitude (dBFS)
www.ti.com
LINEARITY with fIN = 200Hz
0
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
–70
–80
–90
–100
Output Amplitude (dBFS)
–110
–120
–130
–140
–140 –130 –120 –110 –100 –90 –80 –70 –60 –50 0–40 –30 –20 –10
(44.1kHz:192kHz)
Input Amplitude (dBFS)
SRC4192, SRC4193
SBFS022A
Page 15

TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS (Cont.)
0
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
–70
–80
–90
–100
–110
–120
–130
–140
–150
dBFS
FREQUENCY RESPONE with 0dBFS INPUT
0 10k 20k 30k 40k 60k50k
Frequency (Hz)
192kHz:32kHz
192kHz:48kHz
192kHz:96kHz
At TA = +25°C, VDD = +3.3V, and VIO = +3.3V, unless otherwise noted.
LINEARITY with fIN = 200Hz
0
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
–70
–80
–90
–100
Output Amplitude (dBFS)
–110
–120
–130
–140
–140 –130 –120 –110 –100 –90 –80 –70 –60 –50 0–40 –30 –20 –10
(192kHz:44.1kHz)
Input Amplitude (dBFS)
–0.004
–0.009
–0.014
–0.019
–0.024
dBFS
–0.029
–0.034
–0.039
–0.044
–0.049
PASS BAND RIPPLE
0
0 2k 4k 6k 8k 10k 12k 14k 16k 18k 22k20k
(48k:48k)
Frequency (Hz)
PASS BAND RIPPLE
0
–0.01
–0.02
(dBFS)
–0.03
–0.04
–0.05
0 5k 10k 15k 22k20k
(192k:48k)
Input Amplitude (dBFS)
SRC4192, SRC4193
SBFS022A
www.ti.com
15
Page 16

PRODUCT OVERVIEW
The SRC4192 and SRC4193 are asynchronous sample rate
converters (ASRC) designed for professional audio applications. Operation at input and output sampling frequencies up
to 212kHz is supported, with an input/output sampling ratio
range of 16:1 to 1:16. Excellent dynamic range and Total
Harmonic Distortion + Noise (THD+N) are achieved by employing high performance, linear phase digital filtering with
better than 140dB of image rejection. Digital filtering options
allow for lower group delay processing. These include a low
group delay option for the interpolation and re-sampler function, as well as a direct down-sampling option for the decimation function (SRC4193 only).
The audio input and output ports support standard audio data
formats, as well as a TDM interface mode. Word lengths of
24-, 20-, 18-, and 16-bits are supported. Both ports may
operate in Slave mode, deriving their word and bit clocks
from external input and output devices. Alternatively, one
port may operate in Master mode while the other remains in
Slave mode. In Master mode, the LRCK and BCK clocks are
derived from the reference clock input, RCKI. The flexible
configuration of the input and output ports allows connection
to a wide variety of audio data converters, interface devices,
digital signal processors, and programmable logic.
A bypass mode is included, which allows audio data to be
passed directly from the input port to the output port, bypassing the ASRC function. The bypass option is useful for
passing through encoded or compressed audio data, or nonaudio control or status data.
A soft mute function is available on both the SRC4192 and
SRC4193. Digital output attenuation is available only for the
SRC4193. Both soft mute and digital attenuation functions
provide artifact-free operation, while allowing muting or level
adjustment of the audio output signal. The mute attenuation
is typically –144dB, while the digital attenuation control is
adjustable from 0dB to –127.5dB in 0.5dB steps.
The SRC4193 includes a three-wire SPI port, which is used
to access on-chip control registers for configuration of internal functions. The port can be easily interfaced to microprocessors or digital signal processors with synchronous serial
port peripherals.
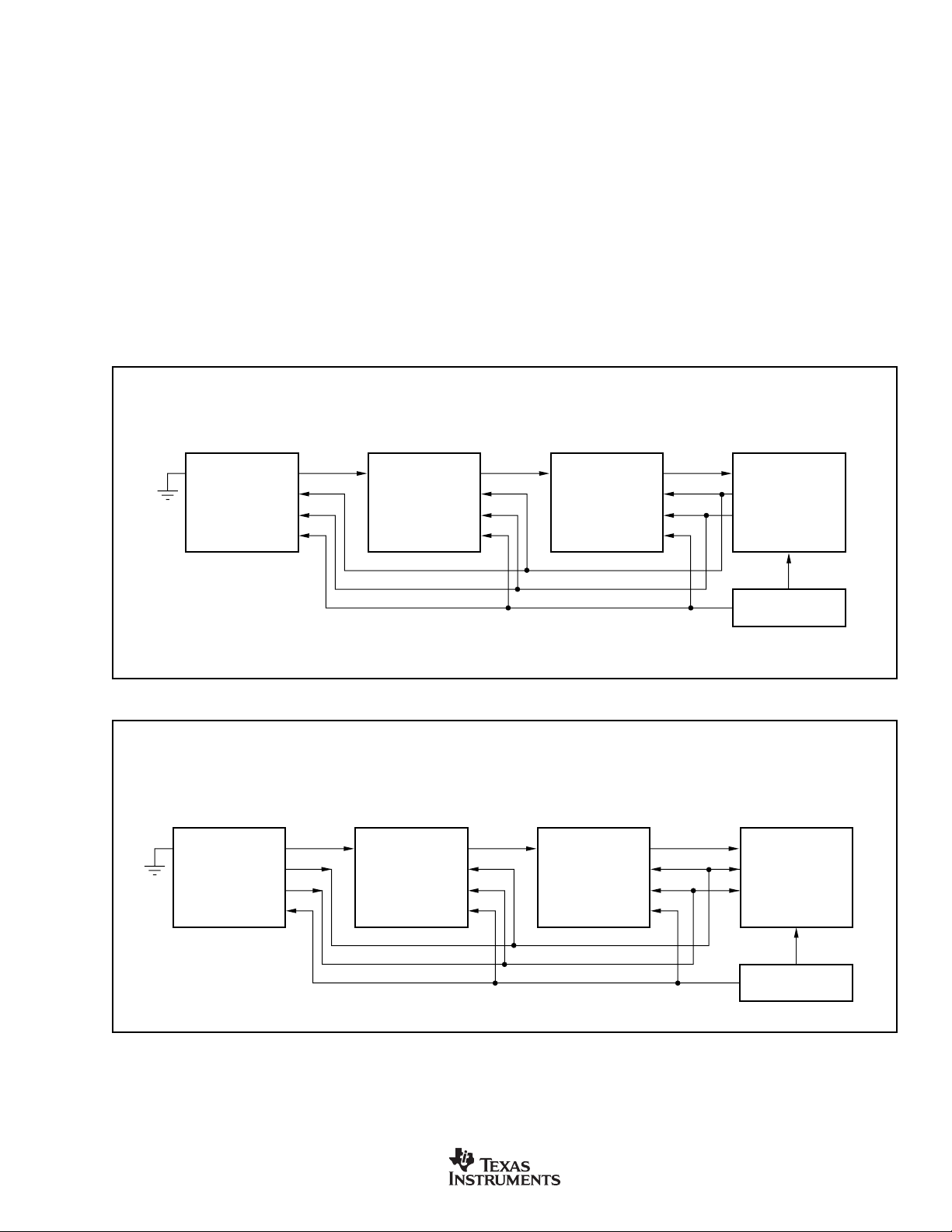
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
Figure 1 shows a functional block diagram of the SRC4192
and SRC4193. Audio data is received at the input port,
clocked by either the audio data source in Slave mode, or by
the SRC4192/4193 in Master mode. The output port data is
clocked by either the audio data source in Slave mode, or by
LRCKI
BCKI
SDIN
MODE [2:0]
IFMT [2:0
OFMT [1:0]
OWL [1:0]
MUTE
BYPAS
LGRP
RST
MUTE
BYPASS
RST
CS
CCLK
CDATA
LRCKO
BCKO
SDOUT
TDMI
RCKI REFCLK
Audio
Input
Port
Control
Logic
(SRC4192)
SPI and
Control Logic
(SRC4193)
Audio
Output
Port
Reference
Clock
LRCKI
LRCKO
Mux
Rate
Estimator
f
SIN
REFCLK
RDY
RATIO (SRC4193 only)
Interpolation
Filters
16f
f
SOUT
f
SOUT
SIN
Re-Sampler
Decimation
Filters
Direct
Down-Sampler
(SRC4193 only)
Power
16f
SOUT
V
DD
DGND
VIO
DGND
FIGURE 1. SRC4192/4193 Functional Block Diagram.
16
www.ti.com
SRC4192, SRC4193
SBFS022A
Page 17

the SRC4192/4193 in Master mode. The input data is passed
through interpolation filters which up-sample the data, which
is then passed on to the re-sampler. The rate estimator
compares the input and output sampling frequencies by
comparing LRCKI, LRCKO, and a reference clock. The
results include an offset for the FIFO pointer and the coefficients needed for re-sampling function.
The output of the re-sampler is passed on to either the
decimation filter or direct down-sampler function. The decimation filter performs down-sampling and anti-alias filtering
functions, and is required when the output sampling frequency is lower than the input sampling frequency. The
direct down-sampler function does not provide any filtering,
and may be used in cases when aliasing is not an issue. This
includes the case when the output sampling frequency is
equal to or greater than the input sampling frequency. The
advantage of direct down-sampling is a significant reduction
in the group delay associated with the decimation filter,
allowing lower latency sample rate conversion. The direct
down-sampler function is available only for the SRC4193.
REFERENCE CLOCK
The SRC4192 and SRC4193 require a reference clock for
operation. The reference clock is applied at the RCKI input
(pin 1 for the SRC4193, pin 2 for the SRC4192). Figure 2
illustrates the reference clock connections and requirements
for the SRC4192 and SRC4193. The reference clock may
operate at 128f
output sampling frequency. The maximum external reference
clock input frequency is 50 MHz.
, 256fS, or 512fS, where fS are the input or
S
RESET AND POWER DOWN OPERATION
The SRC4192 and SRC4193 may be reset using the
input (pin 13). There is no internal power on reset, so the
user should force a reset sequence after power up in order
to initialize the device. In order to force a reset, the reference
clock input must be active, with an external clock source
supplying a valid reference clock signal (refer to Figure 2).
The user must assert
nanoseconds and then bring
RST
low for a minimum of 500
RST
high again to force a reset.
Figure 3 shows the reset timing for the SRC4192 and
SRC4193.
For the SRC4193, there is an additional 500 microsecond
delay after the
RST
rising edge, due to internal logic requirements. The customer should wait at least 500 microseconds
after the
RST
rising edge before attempting to write to the
SPI port of the SRC4193.
The SRC4192 and SRC4193 also support a power-down
mode. Power-down mode may be set by either holding the
RST
input low (SRC4192 and SRC4193), or by setting the
PDN
bit in Control Register 1 to zero (SRC4193 only). The
SRC4193 will be in power-down mode by default after an
external reset has been issued. In order to enable normal
operation for the SRC4193, the customer must disable power
down mode by writing a 1 to the
Finally, for the SRC4193, when using the
PDN
bit in Control Register 1.
PDN
bit in Control
Register 1 to enable power-down mode, the current state
of the control registers is maintained through the power
down / power up transition.
RST
SRC4192
RCKI
2
RCKI
From External
Clock Source
50MHz max
t
RCKIH
t
RCKIP
t
RCKIL
From External
Clock Source
50MHz max
FIGURE 2. Reference Clock Input Connections and Timing Requirements.
RCKI
RST
t
> 500ns
RSTL
SRC4193
RCKI
1
t
t
t
RCKIP
RCKIH
RCKIL
> 20ns min
> 0.4 t
RCKIP
> 0.4 t
RCKIP
FIGURE 3. Reset Pulse Width Requirement.
SRC4192, SRC4193
SBFS022A
www.ti.com
17
Page 18

AUDIO PORT MODES
The SRC4192 and SRC4193 both support seven serial port
modes, which are shown in Table 1. For the SRC4192, the
audio port mode is selected using the MODE0 (pin 26),
MODE1 (pin 27), and MODE2 (pin 28) inputs. For the
SRC4193, the mode is selected using the MODE[2:0] bits in
Control Register 1. The default mode setting for the SRC4193
is both input and output ports set to Slave mode.
In Slave mode, the port LRCK and BCK clocks are configured as inputs, and receive their clocks from an external
audio device. In Master mode, the LRCK and BCK clocks are
configured as outputs, being derived from the reference
clock input (RCKI). Only one port can be set to Master mode
at any given time, as indicated in Table 1.
MODE2 MODE1 MODE0 SERIAL PORT MODE
0 0 0 Both Input and Output Ports are Slave mode
0 0 1 Output Port is Master mode with RCKI = 128f
0 1 0 Output Port is Master mode with RCKI = 512f
0 1 1 Output Port is Master mode with RCKI = 256f
1 0 0 Both Input and Output Ports are Slave Mode
1 0 1 Input Port is Master mode with RCKI = 128f
1 1 0 Input Port is Master mode with RCKI = 512f
1 1 1 Input Port is Master mode with RCKI = 256f
TABLE 1. Setting the Serial Port Modes.
S
S
S
INPUT PORT OPERATION
The audio input port is a three-wire synchronous serial
interface that may operate in either Slave or Master mode.
The SDIN input (pin 4) is the serial audio data input. Audio
data is input at this pin in one of three standard audio data
formats: Philips I
audio data word length may be up to 24-bits for I
Justified formats, while the Right Justified format supports
16-, 18-, 20-, or 24-bit data. The data formats are shown in
Figure 4, while critical timing parameters are shown in Figure
5 and listed in the Electrical Characteristics table.
LRCKI
BCKI
S
S
S
SDIN
FIGURE 5. Input Port Timing.
2
S, Left Justified, or Right Justified. The
t
LRIS
t
LDIS
t
LDIH
2
S and Left
t
SIH
t
SIL
LRCKO
BCKI
SDIN
LRCKI
BCKI
SDIN
LRCKI
BCKI
SDIN
Left Channel
MSB LSB LSBMSB
(a) Left Justified Data Format
MSB MSB LSBLSB
(b) Right Justified Data Format
MSB LSB MSB LSB
(c) I2S Data Format
Right Channel
FIGURE 4. Input Data Formats.
18
1/f
www.ti.com
S
SRC4192, SRC4193
SBFS022A
Page 19

The bit clock is either an input or output at BCKI (pin 5). In
slave mode, BCKI is configured as an input pin, and may
operate at rates from 32f
to 128fS,with a minimum of one
S
clock cycle per data bit. In Master mode, BCKI operates at a
fixed rate of 64f
.
S
The left/right word clock, LRCKI (pin 6), may be configured
as an input or output pin. In Slave mode, LRCKI is an input
pin, while in Master mode LRCKI is an output pin. In either
case, the clock rate is equal to f
, the input sampling
S
frequency. The LRCKI duty cycle is fixed to 50% for Master
mode operation.
Table 2 illustrates data format selection for the input port. For
the SRC4192, the IFMT0 (pin 10), IFMT1 (pin 11), and
IFMT2 (pin 12) inputs are utilized to set the input port data
format. For the SRC4193, the IFMT[2:0] bits in Control
Register 3 are used to select the data format.
OUTPUT PORT OPERATION
The audio output port is a four-wire synchronous serial
interface that may operate in either Slave or Master mode.
The SDOUT output (pin 23) is the serial audio data output.
Audio data is output at this pin in one of four data formats:
Philips I
data word length may be 16-, 18-, 20-, or 24-bits. For all word
lengths, the data is triangular PDF dithered from the internal
28-bit data path. The data formats (with the exception of
TDM mode) are shown in Figure 6, while critical timing
parameters are shown in Figure 7 and listed in the Electrical
Characteristics table. The TDM format and timing are shown
in Figures 14 and 15, respectively, while examples of standard TDM configurations are shown in Figures 16 and 17.
2
S, Left Justified, Right Justified, or TDM. The audio
IFMT2 IFMT1 IFMT0 INPUT PORT DATA FORMAT
0 0 0 24-Bit Left Justified
0 0 1 24-Bit I2S
0 1 0 Unused
0 1 1 Unused
1 0 0 16-Bit Right Justified
1 0 1 18-Bit Right Justified
1 1 0 20-Bit Right Justified
1 1 1 24-Bit Right Justified
TABLE 2. Input Port Data Format Selection.
Left Channel
LRCKO
BCKO
SDOUT
LRCKO
MSB LSB LSBMSB
LRCKO
BCKO
SDOUT
FIGURE 7. Output Port Timing.
(a) Left Justified Data Format
t
DOPD
Right Channel
t
DOH
t
SOH
t
SOL
BCKO
SDOUT
LRCKO
BCKO
SDOUT
FIGURE 6. Output Data Formats.
SRC4192, SRC4193
SBFS022A
MSB MSB LSBLSB
(b) Right Justified Data Format
MSB LSB MSB LSB
(c) I2S Data Format
1/f
S
www.ti.com
19
Page 20

The bit clock is either input or output at BCKO (pin 25). In
Slave mode, BCKO is configured as an input pin, and may
operate at rates from 32f
to 128fS, with a minimum of one
S
clock cycle for each data bit. The exception is the TDM
mode, where the BCKO must operate at N x 64f
, where N
S
is equal to the number of SRC4192 or SRC4193 devices
included on the TDM interface. In Master mode, BCKO
operates at a fixed rate of 64f
for all data formats except
S
TDM, where BCKO operates at the reference clock (RCKI)
frequency. Additional information regarding TDM mode operation is included in the Applications Information section
of this data sheet.
The left/right word clock, LRCKO (pin 24), may be configured
as an input or output pin. In Slave mode, LRCKO is an input
pin, while in Master mode it is an output pin. In either case,
the clock rate is equal to f
The clock duty cycle is fixed to 50% for I
, the output sampling frequency.
S
2
S, Left justified, and
Right Justified formats in Master mode. The LRCKO pulse
width is fixed to 32 BCKO cycles for the TDM format in
Master mode.
Table 3 illustrates data format selection for the output port.
For the SRC4192, the OFMT0 (pin 19), OFMT1 (pin 18),
OWL0 (pin 17), and OWL1 (pin 16) inputs are utilized to set
the output port data format and word length. For the SRC4193,
the OFMT[1:0] and OWL[1:0] bits in Control Register 3 are
used to select the data format and word length.
OFMT1 OFMT0 OUTPUT PORT DATA FORMAT
0 0 Left Justified
01 I
1 0 TDM
1 1 Right Justified
OWL1 OWL0 OUTPUT PORT DATA WORD LENGTH
0 0 24-Bits
0 1 20-Bits
1 0 18-Bits
1 1 16-Bits
2
S
TABLE 2. Output Port Data Format Selection.
BYPASS MODE
The SRC4192 and SRC4193 include a bypass function,
which routes the input port data directly to the output port,
bypassing the ASRC function. Bypass mode may be invoked
by forcing the BYPAS input (pin 9) high for either the
SRC4192 or SRC4193. For the SRC4193, the bypass mode
may also be accessed using the BYPAS bit in Control
Register 1. For normal ASRC operation, the BYPAS pin and
control bit should be set to 0.
No dithering is applied to the output data in bypass mode,
and the digital attenuation and mute functions are also
unavailable.
SOFT MUTE FUNCTION
The soft mute function of the SRC4192 and SRC4193 may
be invoked by forcing the MUTE input (pin 14) high. For the
SRC4193, the mute function may also be accessed using the
MUTE bit in Control Register 1. The Soft mute function slowly
attenuates the output signal level down to all zeroes plus
±1LSB of dither. This provides an artifact-free muting of the
audio output port.
DIGITAL ATTENUATION (SRC4193 ONLY)
The SRC4193 includes independent digital attenuation for
the Left and Right audio channels. The attenuation ranges
from 0dB (or unity) to -127.5dB in 0.5dB steps. The attenuation settings are programmed using Control Registers 4 and
5, corresponding to the Left and Right channels, respectively.
The TRACK bit in Control Register 1 is used to select
Independent or Tracking attenuation modes. When TRACK
= 0, the Left and Right channels are controlled independently. When TRACK = 1, the attenuation setting for the Left
channel is also used for the Right channel, and the Right
channel is said to track the Left channel attenuation setting.
READY OUTPUT
The SRC4192 and SRC4193 include an active low ready
output named
RDY
(pin 15). This is an output from the rate
estimator block, which indicates that the input-to-output sampling frequency ratio has been determined. The ready signal
can be used as a flag or indicator output. The ready signal
can also be connected to the active high MUTE input (pin 14)
to provide an auto-mute function, so that the output port is
muted when the rate estimator is in transition.
RATIO OUTPUT (SRC4193 ONLY)
The SRC4193 includes a simple ratio flag output named
RATIO (pin 16). When RATIO is low, it indicates that the
output sampling frequency is lower than the input sampling
frequency. When RATIO is high, it indicates that the output
sampling frequency is higher than the input sampling frequency. The ratio output can be used as an indicator or flag
output for an LED or host device.
SERIAL PERIPHERAL INTERFACE (SPI) PORT: SRC4193 ONLY
The SPI port is a three-wire synchronous serial interface
used to access the on-chip control registers of the SRC4193.
The interface is comprised of a serial data clock input, CCLK
(pin 27), a serial data input, CDATA (pin 28), and an active
low chip-select input,
protocol for writing control registers via the serial control port.
Figure 9 shows the critical timing parameters for the SPI port
interface, which are also listed in the Electrical Characteristics table.
CS
(pin 26). Figure 8 illustrates the
20
www.ti.com
SRC4192, SRC4193
SBFS022A
Page 21

Set CS = 1 here to write one register or buffer location.
CS
Keep CS = 0 to enable auto-increment mode.
CDIN
CCLK
BYTE DEFINITION
MSB LSB
BYTE 0:
00000A2A1A0
Byte 1: All 8 bits are Don’t Care. Set to 0 or 1.
Bytes 2 through N: Register Data.
All Bytes are written MSB first.
FIGURE 8. SPI Port Protocol.
CS
CCLK
Header
Byte 0 Byte 1
Register Address
Set to 0.
Set to 0.
t
CSCR
t
CDS
Register or Buffer Data
Byte 2 Byte 3
Byte N
t
CFCS
t
CDH
CDATA
FIGURE 9. SPI Port Timing.
Byte 0 indicates the address of the control register to be
written. The two most significant bits are set to 0, while the
six least significant bits contain the control register address.
Byte 1 is a
don’t care
byte. This byte is included in the
to be written. The address is automatically incremented by 1
after each byte is written as long as the
CS
input remains
low. This is referred to as auto-increment operation, and is
always enabled for the SPI port.
protocol in order to maintain compatibility with current and
future Texas Instruments’ digital audio products, including
the DIT4096 and DIT4192 digital audio transmitters. Byte 2
contains the 8-bit data for the control register addressed in
Byte 0.
As shown in Figure 8, a write sequence starts by bringing the
CS
input low. Bytes 0, 1, and 2 are then written to program
a single control register. Bringing the
third byte will write just one register. However, if
CS
input high after the
CS
remains
low after writing the first control byte, the port will auto-
CONTROL REGISTER MAP (SRC4193 ONLY)
The control register map for the SRC4193 is shown in Table
4. Register 0 is reserved for factory use and defaults to all
zeros upon reset. The user should avoid writing this register,
as unexpected operation may result if Register 0 is programmed to an arbitrary value. Registers 1 through 5 contain
control bits, which are used to configure the internal functions
of the SRC4193. All other register addresses are reserved
and should not be used in customer applications.
increment the address by 1, allowing successive addresses
Register Address D7 D0
(Dec/Hex) (MSB) D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 (LSB)
0 00 000000
1
2 0 0 0 0 0 0 DFLT LGRP
3 OWL1 OWL0 OFMT1 OFMT0 0 IFMT2 IFMT1 IFMT0
4 AL7 AL6 AL5 AL4 AL3 AL2 AL1 AL0
5 AR7 AR6 AR5 AR4 AR3 AR2 AR1 AR0
PDN
TRACK 0 MUTE BYPAS MODE2 MODE1 MODE0
TABLE 4. The SRC4193 Control Register Map.
SRC4192, SRC4193
SBFS022A
www.ti.com
21
Page 22

CONTROL REGISTER DEFINITIONS (SRC4193 ONLY)
This section contains detailed descriptions for each control register. Reset defaults are also defined for each register bit.
Register 1: System Control Register
Bit 7 (MSB) Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 (LSB)
PDN TRACK 0 MUTE BYPAS MODE2 MODE1 MODE0
MODE[2:0] Audio Serial Port Mode
MODE2 MODE1 MODE0 Audio Serial Port Mode
0 0 0 Both Serial Ports are in Slave Mode (Default)
0 0 1 Output Serial Port is Master with RCKI = 128fs
0 1 0 Output Serial Port is Master with RCKI = 512fs
0 1 1 Output Serial Port is Master with RCKI = 256fs
1 0 0 Both Serial Ports are in Slave Mode
1 0 1 Input Serial Port is Master with RCKI = 128fs
1 1 0 Input Serial Port is Master with RCKI = 512fs
1 1 1 Input Serial Port is Master with RCKI = 256fs
BYPAS Bypass Mode
This bit is logically OR’d with the BYPAS input (pin 9)
BYPAS Function
0 Bypass Mode Disabled with normal ASRC operation. (Default)
1 Bypass Mode Enabled with data routed directly from the input port to the output port,
bypassing the ARSC function.
MUTE Output Soft Mute
This bit is logically OR’d with the MUTE input (pin 14)
MUTE Output Mute Function
0 Soft Mute Disabled (Default)
1 Soft Mute Enabled with data attenuated to all 0’s
TRACK Digital Attenuation Tracking
TRACK Attenuation Tracking
0 Tracking Off: Attenuation for the Left and Right channels is controlled independently. (Default)
1 Tracking On: Left channel attenuation setting is used for both channels.
PDN
Power Down
Setting this bit to 0 will set the SRC4193 to the power-down state. All other register settings are preserved and
the SPI port remains active. (Default)
22
Setting this bit to 1 will power up the SRC4193 using the current register settings.
www.ti.com
SRC4192, SRC4193
SBFS022A
Page 23

Register 2: Filter Control Register
Bit 7 (MSB) Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 (LSB)
0 0 0 0 0 0 DFLT LGRP
LGRP Low Group Delay
This bit is used to select the number of input audio samples to be stored in the data buffer before the ASRC starts
processing the audio data.
LGRP Group Delay
0 Normal Delay, 64 samples. (Default)
1 Low Delay, 32 samples.
DFLT Decimation Filtering / Direct Down-Sampling
The DFLT bit is used to enable or disable the direct down-sampling function.
DFLT Decimation Filter Operation
0 Decimation Filter Enabled (Default)
(Must be used when f
1 Direct Down-Sampling enabled without filtering. (May be enabled when f
greater than f
sIN
)
is less than f
sOUT
sIN
)
is equal to or
sOUT
Register 3: Audio Data Format Register
Bit 7 (MSB) Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 (LSB)
OWL1 OWL0 OFMT1 OFMT0 0 IFMT2 IFMT1 IFMT0
IFMT[2:0] Input Port Data Format
IFMT2 IFMT1 IFMT0 Input Format
0 0 0 24-Bit Left Justified (Default)
0 0 1 24-Bit I
0 1 0 - Not Used 0 1 1 - Not Used 1 0 0 Right Justified, 16-Bit Data
1 0 1 Right Justified, 18-Bit Data
1 1 0 Right Justified, 20-Bit Data
1 1 1 Right Justified, 24-Bit Data
OFMT[1:0] Output Port Data Format
OFMT1 OFMT0 Output Format
0 0 Left Justified (Default)
2
01I
S
1 0 TDM
1 1 Right Justified
OWL[1:0] Output Port Data Word Length
OWL1 OWL0 Output Word Length
0 0 24-Bits (Default)
0 1 20-Bits
1 0 18-Bits
1 1 16-Bits
2
S
SRC4192, SRC4193
SBFS022A
www.ti.com
23
Page 24

Register 4: Digital Attenuation Register – Left Channel
Bit 7 (MSB) Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 (LSB)
AL7 AL6 AL5 AL4 AL3 AL2 AL1 AL0
Register defaults to 00
Output Attenuation (dB) = (–N x 0.5), where N = AL[7:0]
, or 0dB (unity gain).
HEX
DEC
Register 5: Digital Attenuation Register – Right Channel
Bit 7 (MSB) Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 (LSB)
AR7 AR6 AR5 AR4 AR3 AR2 AR1 AR0
Register defaults to 00
Output Attenuation (dB) = (–N x 0.5), where N = AR[7:0]
, or 0dB (unity gain).
HEX
DEC
When the TRACK bit in Control Register 1 is set to 1, the Left Channel attenuation setting will be used for the Right Channel
attenuation.
APPLICATIONS INFORMATION
This section of the data sheet provides practical applications
information for hardware and systems engineers who will be
designing the SRC4192 and SRC4193 into their end equipment.
RECOMMENDED CIRCUIT CONFIGURATION
Typical connection diagrams for the SRC4192 and SRC4193
are shown in Figures 10 and 11, respectively. Recommended values for power supply bypass capacitors are
included. These capacitors should be placed as close to the
IC package as possible.
From
Control
Logic
Reference
Clock
From/To
Control
Logic
Audio Input
Device
V
= +1.65V to V
IO
SRC4192
V
TDMI
RDY
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
DD
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
V
0.1µF
DD
Audio Output
Device
= +3.3V
10µF
1
LGRP
2
RCKI
3
NC
4
SDIN
5
BCKI
6
LRCKI
7
VIO
8
DGND
9
BYPAS
10
IFMT0
11
IFMT1
12
IFMT2
13
RST
14
MUTE
DD
To Pin 7
0.1µF10µF
To Pin 8
MODE2
MODE1
MODE0
BCKO
LRCKO
SDOUT
DGND
OFMT0
OFMT1
OWL0
OWL1
To Pin 22
To Pin 21
FIGURE 10. Typical Connection Diagram for the SRC4192.
24
www.ti.com
SRC4192, SRC4193
SBFS022A
Page 25

Host
(MCU, DSP)
Reference
Clock
To/From
Host
Control
Logic
SRC4193
CS
V
TDMI
NC
NC
NC
RDY
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
DD
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
V
0.1µF
DD
Audio Output
Device
= +3.3V
10µF
1
RCKI
2
NC
3
NC
4
SDIN
Audio Input
Device
or
V
= +1.65V to V
IO
5
BCKI
6
LRCKI
7
VIO
8
DGND
9
BYPAS
10
NC
11
NC
12
NC
13
RST
14
MUTE
DD
To Pin 7
0.1µF10µF
To Pin 8
CDATA
CCLK
BCKO
LRCKO
SDOUT
DGND
RATIO
To Pin 22
To Pin 21
FIGURE 11. Typical Connection Diagram for the SRC4193.
INTERFACING TO DIGITAL AUDIO RECEIVERS AND TRANSMITTERS
The SRC4192 and SRC4193 input and output ports are
designed to interface to a variety of audio devices, including
receivers and transmitters commonly used for AES/EBU,
S/PDIF, and CP1201 communications.
Texas Instruments manufactures the DIR1703 digital audio
interface receiver and DIT4096/4192 digital audio transmitters to address these applications.
Figure 12 illustrates interfacing the DIR1703 to the SRC4192
or SRC4193 input port. The DIR1703 operates from a single
+3.3V supply, which requires the V
SRC4192 or SRC4193 to be set to +3.3V for interface
compatibility.
supply (pin 7) for the
IO
SRC4192, SRC4193
LRCKI
BCKI
SDIN
RCLI
Clock
Select
= +3.3V for SRC4192, SRC4293
AES3, S/PDIF
Input
RCV DIN
DIR1703
Clock
Generator
Assumes V
LRCKO
BCKO
DATA
SCKO
IO
FIGURE 12. Interfacing the SRC4193 to the DIR1703 Digital
Audio Interface Receiver.
SRC4192, SRC4193
SBFS022A
www.ti.com
25
Page 26

Figure 13 shows the interface between the SRC4192 or
SRC4193 output port and the DIT4096 or DIT4192 audio
serial port. Once again, the V
supplies for both the
IO
SRC4192/4193 and DIT4096/4192 are set to +3.3V for
compatibility.
SRC4192, SRC4193
LRCKO
BCKO
SDOUT
RCKI
REF Clock
Generator
DIT Clock
Generator
DIT4096, DIT4192
SYNC
SCLK
SDATA
MCLK
Clock
Select
TX+
TX–
AES3, S/PDIF
OUTPUT
Like the SRC4192 or SRC4193 output port, the DIT4096 and
DIT4192 audio serial port may be configured as a Master or
Slave. In cases where the SRC4192/4193 output port is set
to Master mode, it is recommended to use the reference
clock source (RCKI) as the master clock source (MCLK) for
the DIT4096/4192, to ensure that the transmitter is synchronized to the SRC4192/4193 output port data.
TDM APPLICATIONS
The SRC4192 and SRC4193 support a TDM output mode,
which allows multiple devices to be daisy-chained together
to create a serial frame. Each device occupies one subframe within a frame, and each sub-frame carries two channels (Left followed by Right). Each sub-frame is 64 bits long,
with 32 bits allotted for each channel. The audio data for
each channel is left justified within the allotted 32 bits. Figure
14 illustrates the TDM frame format, while Figure 15 shows
TDM input timing parameters, which are listed in the Electrical Characteristics table of this data sheet.
Assumes V
= +3.3V for SRC4192, SRC4293 and DIT4096, DIT4192
IO
FIGURE 13. Interfacing the SRC4193 to the DIT4096/4192
Digital Audio Interface Transmitter.
LRCKO
BCKO
SDOUT
Left Right
Sub-Frame 1 Sub-Frame 2 Sub-Frame N
N = Number of Daisy-Chained Devices
One Sub-Frame contains 64 bits, with 32 bits per channel.
For each channel, the audio data is left justified, MSB first format, with the word length determined by the OWL[1:0] pins/bits.
Left Right Left Right
One Frame = 1/f
s
FIGURE 14. TDM Frame Format.
LRCKO
BCKO
TDMI
FIGURE 15. Input Timing for TDM Mode.
26
t
LROS
t
TDMS
t
LROH
t
TDMH
www.ti.com
SRC4192, SRC4193
SBFS022A
Page 27
The frame rate is equal to the output sampling frequency, fs.
The BCKO frequency for the TDM interface is N*64f
, where
s
N is the number of devices included in the daisy chain. For
Master mode, the output BCKO frequency is fixed to the
reference clock (RCKI) input frequency. The number of
devices that can be daisy-chained in TDM mode is dependent upon the output sampling frequency and the BCKO
frequency, leading to the following numerical relationship:
Number of Daisy-Chained Devices = (f
BCKO
/ fs) / 64
Where:
= Output Port Bit Clock (BCKO), 27.648 MHz maximum
f
BCKO
= Output Port Sampling (or LRCKO) Frequency, 216kHz
f
s
maximum.
This relationship holds true for both Slave and Master modes.
Figures 16 and 17 show typical connection schemes for TDM
mode. Although the TMS320C671x DSP family is shown as
the audio processing engine in these figures, other TI digital
signal processors with a multi-channel buffered serial port
(McBSP
TM
) may also function with this arrangement. Interfacing to processors from other manufacturers is also possible. Refer to Figure 7 in this data sheet, along with the
equivalent serial port timing diagrams shown in the DSP data
sheet, to determine compatibility.
SRC4192, SRC4193
Slave #N
TDMI
SDOUT
LRCKO
BCKO
RCKI
SRC4192, SRC4193
Slave #2
TDMI
SDOUT
LRCKO
BCKO
RCKI
FIGURE 16. TDM Interface where all Devices are Slaves.
SRC4192, SRC4193
Master
TDMI
SDOUT
LRCKO
BCKO
RCKI
SRC4192, SRC4193
Slave #2
TDMI
SDOUT
LRCKO
BCKO
RCKI
SRC4192, SRC4193
Slave #1
TDMI
SRC4192, SRC4193
Slave #1
TDMI
SDOUT
LRCKO
BCKO
SDOUT
LRCKO
BCKO
RCKI
RCKI
TMS320C671x
McBSP
DRn
FSRn
CLKRn
CLKIN or CLKSn
DRn
FSRn
CLKRn
CLKIN or CLKSn
n = 0 or 1
Clock
Generator
TMS320C671x
McBSP
n = 0 or 1
FIGURE 17. TDM Interface where one Device is Master to Multiple Slaves.
SRC4192, SRC4193
SBFS022A
www.ti.com
Clock
Generator
27
Page 28

PIN COMPATIBILITY WITH THE ANALOG DEVICES AD1896 (SRC4192 ONLY)
The SRC4192 is pin-and function-compatible with the AD1896
when observing the guidelines indicated in the following
paragraphs.
Power Supplies. To ensure compatibility, the VDD_IO and
VDD_CORE supplies of the AD1896 must be set to +3.3V,
while the V
to +3.3V.
Crystal Oscillator. The SRC4192 does not have an on-chip
crystal oscillator. An external reference clock is required at
the RCKI input (pin 2).
Reference Clock Frequency. The reference clock input
frequency for the SRC4192 must be no higher than 30 MHz,
in order to match the master clock frequency specification of
the AD1896. In addition, the SRC4192 does not support the
768f
S
and VDD supplies of the SRC4192 must be set
IO
reference clock rate.
Master Mode Maximum Sampling Frequency. When the
input or output ports are set to Master mode, the maximum
sampling frequency must be limited to 96kHz in order to
support the AD1896 specification. This is despite the fact that
the SRC4192 supports a maximum sampling frequency of
212kHz in Master mode. The user should consider building
an option into his or her design to support the higher
sampling frequency of the SRC4192.
Matched Phase Mode. Due to the internal architecture of
the SRC4192, it does not require or support the matched
phase mode of the AD1896. Given multiple SRC4192 devices, if all reference clock (RCKI) inputs are driven from the
same clock source, the devices will be phase matched.
28
www.ti.com
SRC4192, SRC4193
SBFS022A
Page 29

PACKAGE DRAWING
DB (R-PDSO-G**) PLASTIC SMALL-OUTLINE
28 PINS SHOWN
0,65
28
1
2,00 MAX
0,38
0,22
15
14
A
0,05 MIN
0,15
5,60
5,00
M
8,20
7,40
Seating Plane
0,10
0,25
0,09
0°–8°
Gage Plane
0,25
0,95
0,55
PINS **
DIM
A MAX
A MIN
NOTES: A. All linear dimensions are in millimeters.
B. This drawing is subject to change without notice.
C. Body dimensions do not include mold flash or protrusion not to exceed 0,15.
D. Falls within JEDEC MO-150
14
6,50
6,50
5,905,90
2016
7,50
6,90
24
8,50
28
10,50
9,907,90
30
10,50
9,90
38
12,90
12,30
4040065 /E 12/01
SRC4192, SRC4193
SBFS022A
www.ti.com
29
Page 30

PACKAGE OPTION ADDENDUM
www.ti.com
3-Oct-2003
PACKAGING INFORMATION
ORDERABLE DEVICE STATUS(1) PACKAGE TYPE PACKAGE DRAWING PINS PACKAGE QTY
SRC4192IDB ACTIVE SSOP DB 28 50
SRC4192IDBR ACTIVE SSOP DB 28 2000
SRC4193IDB ACTIVE SSOP DB 28 50
SRC4193IDBR ACTIVE SSOP DB 28 2000
(1) The marketing status values are defined as follows:
ACTIVE: Product device recommended for new designs.
LIFEBUY: TI has announced that the device will be discontinued, and a lifetime-buy period is in effect.
NRND: Not recommended for new designs. Device is in production to support existing customers, but TI does not recommend using this part in
a new design.
PREVIEW: Device has been announced but is not in production. Samples may or may not be available.
OBSOLETE: TI has discontinued the production of the device.
Page 31

IMPORTANT NOTICE
Texas Instruments Incorporated and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make corrections, modifications,
enhancements, improvements, and other changes to its products and services at any time and to discontinue
any product or service without notice. Customers should obtain the latest relevant information before placing
orders and should verify that such information is current and complete. All products are sold subject to TI’s terms
and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgment.
TI warrants performance of its hardware products to the specifications applicable at the time of sale in
accordance with TI’s standard warranty . Testing and other quality control techniques are used to the extent TI
deems necessary to support this warranty . Except where mandated by government requirements, testing of all
parameters of each product is not necessarily performed.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or customer product design. Customers are responsible for
their products and applications using TI components. T o minimize the risks associated with customer products
and applications, customers should provide adequate design and operating safeguards.
TI does not warrant or represent that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any TI patent right,
copyright, mask work right, or other TI intellectual property right relating to any combination, machine, or process
in which TI products or services are used. Information published by TI regarding third-party products or services
does not constitute a license from TI to use such products or services or a warranty or endorsement thereof.
Use of such information may require a license from a third party under the patents or other intellectual property
of the third party , or a license from TI under the patents or other intellectual property of TI.
Reproduction of information in TI data books or data sheets is permissible only if reproduction is without
alteration and is accompanied by all associated warranties, conditions, limitations, and notices. Reproduction
of this information with alteration is an unfair and deceptive business practice. TI is not responsible or liable for
such altered documentation.
Resale of TI products or services with statements different from or beyond the parameters stated by TI for that
product or service voids all express and any implied warranties for the associated TI product or service and
is an unfair and deceptive business practice. TI is not responsible or liable for any such statements.
Following are URLs where you can obtain information on other Texas Instruments products and application
solutions:
Products Applications
Amplifiers amplifier.ti.com Audio www.ti.com/audio
Data Converters dataconverter.ti.com Automotive www.ti.com/automotive
DSP dsp.ti.com Broadband www.ti.com/broadband
Interface interface.ti.com Digital Control www.ti.com/digitalcontrol
Logic logic.ti.com Military www.ti.com/military
Power Mgmt power.ti.com Optical Networking www.ti.com/opticalnetwork
Microcontrollers microcontroller.ti.com Security www.ti.com/security
Telephony www.ti.com/telephony
Video & Imaging www.ti.com/video
Wireless www.ti.com/wireless
Mailing Address: Texas Instruments
Post Office Box 655303 Dallas, Texas 75265
Copyright 2003, Texas Instruments Incorporated
 Loading...
Loading...