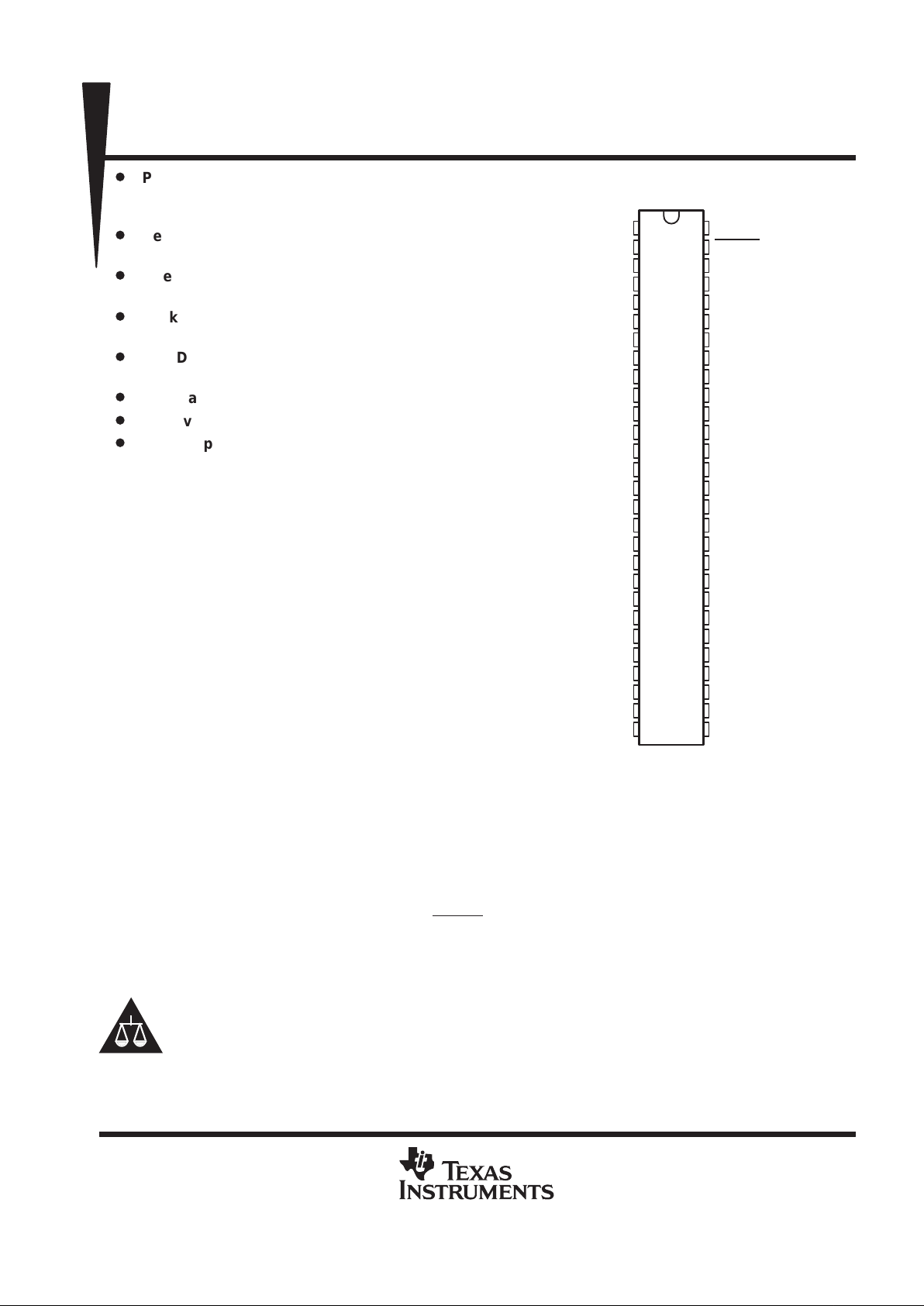
SN75LBC971A
SCSI DIFFERENTIAL CONVERTER-DATA
SLLS186B – OCTOBER 1994 – REVISED JUL Y 1997
1
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
D
Provides Differential SCSI From
Single-Ended Controller When Used With
the SN75LBC970A Control Transceiver
D
Designed to Operate at Fast-SCSI Speed of
Ten Million Data Transfers per Second
D
Meets or Exceeds the Requirements of EIA
Standard RS-485 and ISO-8482 Standards
D
Packaged in Shrink Small-Outline Package
With 25-Mil Terminal Pitch
D
Low Disabled-Supply Current
23 mA Typ
D
Thermal Shutdown Protection
D
Positive- and Negative-Current Limiting
D
Power-Up/-Down Glitch Protection
description
The SN75LBC971A SCSI differential converter-data is
an adaptation of the industry’s first 9-channel RS-485
transceiver, the SN75LBC976. When used in conjunction with its companion control transceiver, the
SN75LBC970A, the resulting chip set provides the
superior electrical performance of differential SCSI
from a single-ended SCSI bus or controller. A 16-bit
SCSI bus can be implemented with just three devices
(two data and one control) in the space efficient, 56-pin,
shrink small-outline package (SSOP) and a few
external components. An 8-bit SCSI bus requires only
one data and one control transceiver.
In a typical differential SCSI node, the SCSI controller
provides an enable for each external RS-485
transceiver channel. This could require as many as 27
extra terminals for a 16-bit differential bus controller or
relegate a 16-bit, single-ended controller to only an
8-bit differential bus. Using the standard nine SCSI
control signals, the SN75LBC970A control transceiver decodes the state of the bus and enables the
SN75LBC971A data transceiver to transmit the single-ended SCSI input signals (A side) differentially to the
cable or receive the differential cable signals (B side) and drive the single-ended outputs to the controller.
A reset function, which disables all outputs and clears internal latches, can be accomplished from two external
inputs and two internally-generated signals. RESET
(reset) and DSENS (differential sense) are available to
external circuits for a bus reset or to disable all outputs should a single-ended cable be inadvertently connected
to a differential connector . Internally-generated power-up and thermal-shutdown signals have the same affect
when the supply voltage is below approximately 3.5 V or the junction temperature exceeds 175°C.
Please be aware that an important notice concerning availability, standard warranty, and use in critical applications of
Texas Instruments semiconductor products and disclaimers thereto appears at the end of this data sheet.
Copyright 1997, Texas Instruments Incorporated
PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date.
Products conform to specifications per the terms of Texas Instruments
standard warranty. Production processing does not necessarily include
testing of all parameters.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
SDB
DRVBUS
GND
ADBP–
NC
ADB7–
NC
ADB6–
NC
ADB5–
NC
V
CC
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
V
CC
ABD4–
NC
ADB3–
NC
ADB2–
NC
ADB1–
NC
ADB0–
NC
DSENS
RESET
GND
BDBP–
BDBP+
BDB7–
BDB7+
BDB6–
BDB6+
BDB5–
BDB5+
V
CC
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
V
CC
BDB4–
BDB4+
BDB3–
BDB3+
BDB2–
BDB2+
BDB1–
BDB1+
BDB0–
BDB0+
DL PACKAGE
(TOP VIEW)
NC – No internal connection
Pins 13 – 17 and 40 – 44 are connected
together to the package lead frame and
to signal ground.
SN75LBC971A
SCSI DIFFERENTIAL CONVERTER-DATA
SLLS186B – OCTOBER 1994 – REVISED JUL Y 1997
2
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
description (continued)
The SCSI, differential, converter-data chip operates in two modes depending on the state of the DRVBUS input.
With DRVBUS low , a bidirectional latch circuit sets the direction of data transfer. Each data bit has its own latch,
and each bit’s direction is independent of all other bits. When neither the single-ended nor the differential sides
are asserted, the latch disables both A- and B-side output drivers. When the input to either side is asserted, the
latch enables the opposite side’s driver and sets data flow from the asserted input to the opposite side of the
device. When the input deasserts, the latch maintains the direction until the receiver on the enabled driver
detects a deassertion. The latch then returns to the initial state. No parity checking is done by this device; the
parity signal passes through the device like other data signals do.
When DRVBUS is high, direction is determined by the SDB signal. However , a change in SDB does not always
immediately change the direction. When DRVBUS first asserts, the direction indicated by SDB is latched and
takes effect immediately . When SDB changes while DRVBUS is high, the drivers that were on immediately turn
off. However , the other driver set does not turn on until the receivers sense a deasserted state on all nine data
lines. This is done to prevent the active drivers from turning on until all other drivers are off and the terminators
pull the lines to a deasserted state.
The single-ended SCSI bus interface consists of CMOS, bidirectional inputs and outputs. The drivers are rated
to ±16 mA of output current. The receiver inputs are pulled high with approximately 4 mA to eliminate the need
for external pullup resistors for the open-drain outputs of most single-ended SCSI controllers. The single-ended
side of the device is not intended to drive the SCSI bus directly.
The differential SCSI bus interface consists of bipolar , bidirectional inputs and outputs that meet or exceed the
requirements of EIA-485 and ISO 8482-1982/TIA TR30.2 referenced by American National Standard of
Information Systems (ANSI) X3.131-1994 Small Computer System Interface-2 (SCSI-2).
The SN75LBC971A is characterized for operation over the temperature range of 0°C to 70°C.
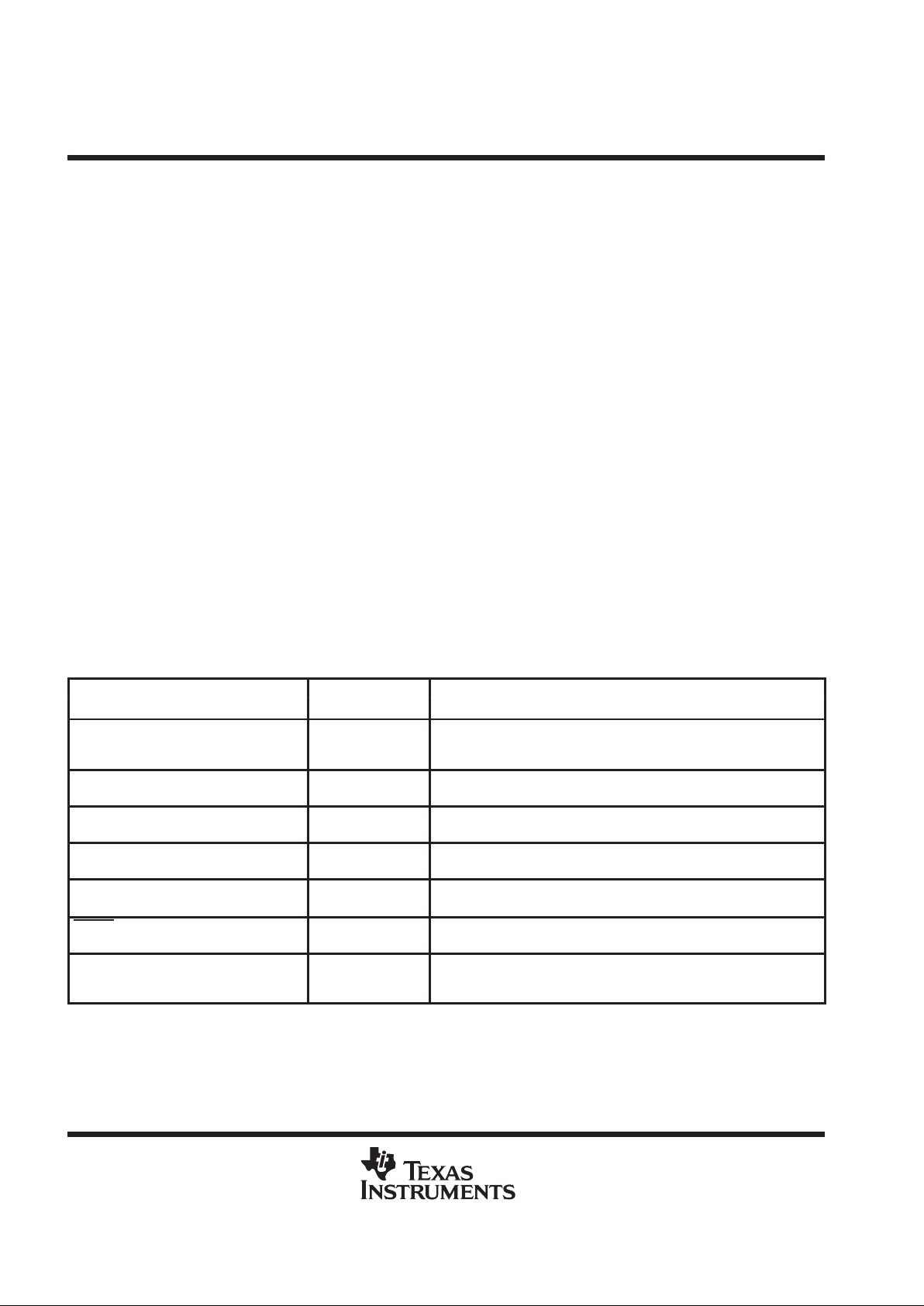
TERMINAL FUNCTION
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
I/O
DESCRIPTION
ADBn–, where
n = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,P}
4, 6, 8, 10, 19,
21, 23, 25, 27
I/O, Single-ended
SCSI voltage levels,
Strong pullup
Bidirectional I/O for data and parity bits to and from the single-ended SCSI
controller. As outputs, these terminals can source or sink 16 mA. As inputs,
they are pulled up with about 4-mA to eliminate external resistors.
BDBn+, where
n = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,P}
29, 31, 33, 35,
37, 46, 48, 50, 52
I/O, RS-485,
Weak pulldown
Bidirectional I/O for data and parity to and from the differential SCSI bus.
BDBn–, where
n = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,P}
30, 32, 34, 36,
38,47, 49, 51, 53
I/O, RS-485,
Weak pulldown
Bidirectional I/O for the complement of data and parity to and from the
differential SCSI bus.
DRVBUS 2 Input, TTL levels,
Weak pulldown
A high-level logic signal from the control transceiver enables either the
single-ended or differential drivers as directed by SDB.
DSENS 56 Input, TTL levels,
Weak pullup
A low-level input initializes the internal latches and disables all drivers.
RESET 55 Input, TTL levels,
Weak pullup
A low-level input initializes the internal latches and disables all drivers.
SDB 1 Input, TTL levels,
Weak pulldown
A high-level logic signal from the control transceiver sends data from the
differential bus to the single-ended bus. A low-level signal reverses the
flow.
SN75LBC971A
SCSI DIFFERENTIAL CONVERTER-DATA
SLLS186B – OCTOBER 1994 – REVISED JUL Y 1997
3
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
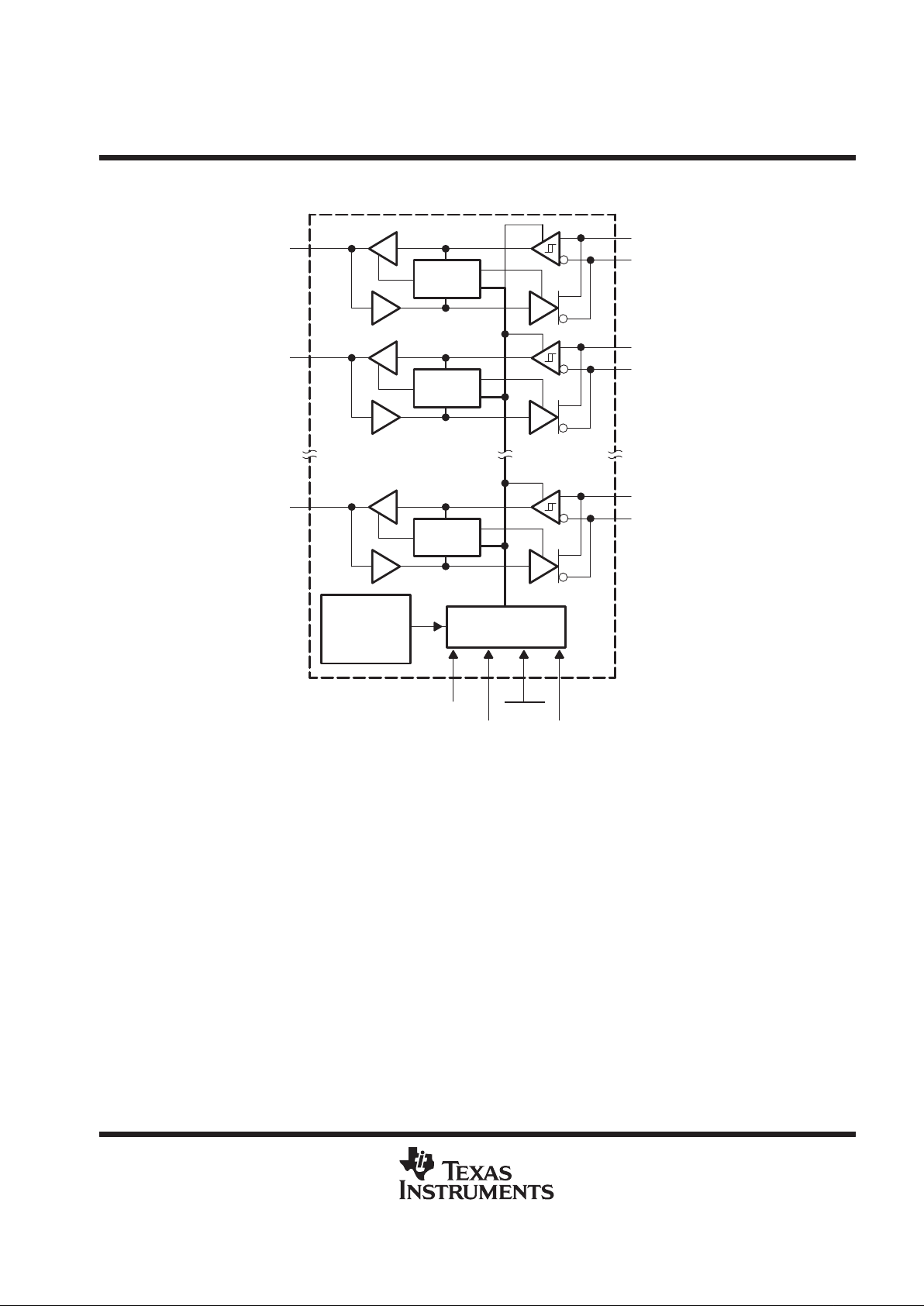
functional block diagram
Control
Latch
Control
Latch
Control
Latch
Steering and
Control Logic
Power-Up
and Thermal
Shut-Down
Circuits
ADBP–
ADB7–
ADB0–
BDBP–
BDBP+
BDB7–
BDB7+
BDB0–
BDB0+
SN75LBC971A
DRVBUS
SDB
RESET
DSENS
4
6
27
53
52
51
50
30
29
(6 Identical Channels
Not Shown)
2 1 55 56
SN75LBC971A
SCSI DIFFERENTIAL CONVERTER-DATA
SLLS186B – OCTOBER 1994 – REVISED JUL Y 1997
4
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
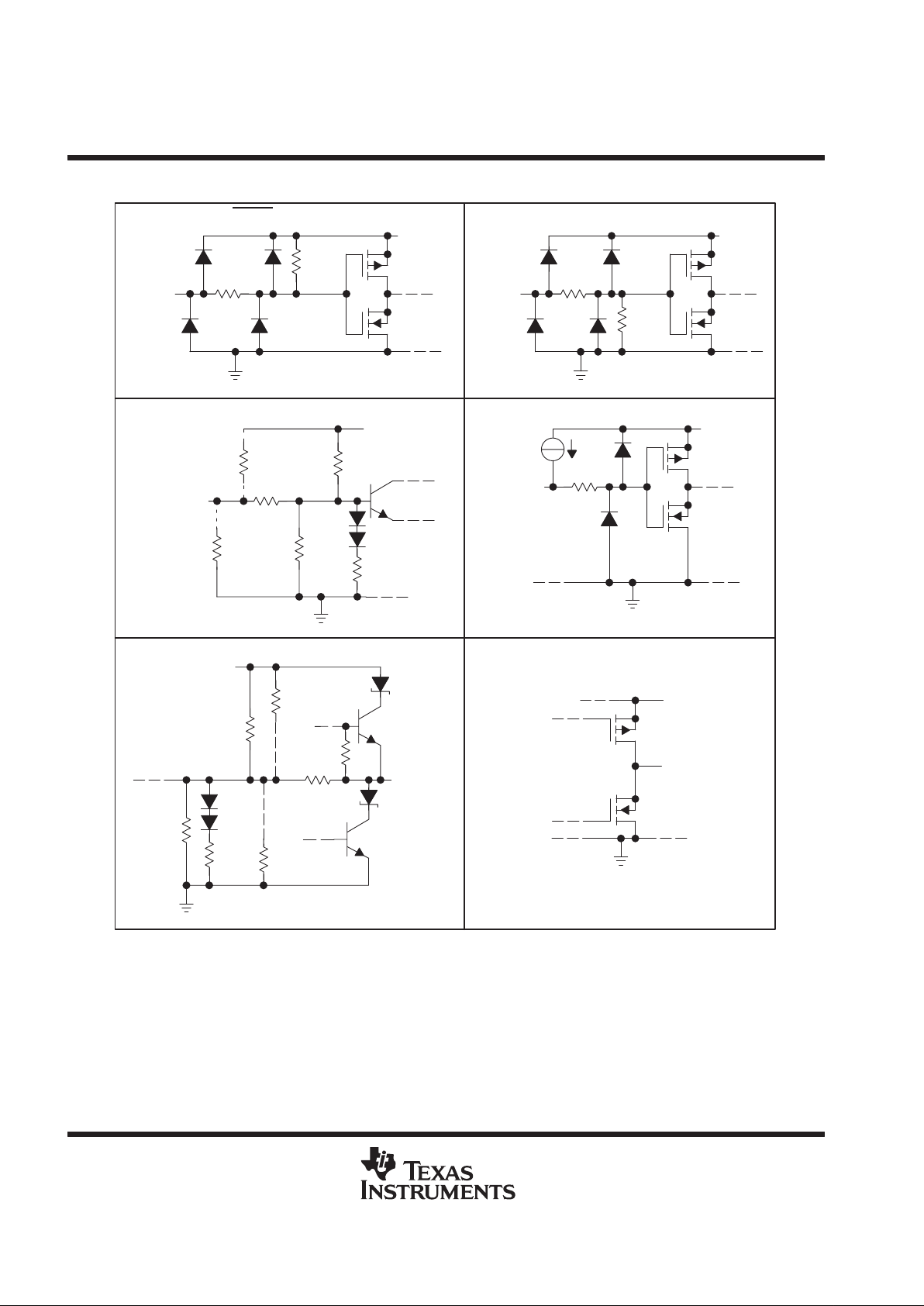
schematics of inputs and outputs
22 kΩ
200 Ω
Input
V
CC
RESET
, AND DSENS
50 kΩ
200 Ω
Input
V
CC
SDB AND DRVBUS
200 Ω
Input
V
CC
A
3 kΩ
12 kΩ
1 kΩ
100 kΩ
(B– Pin Only)
100 kΩ
(B+ Pin Only)
18 kΩ
V
CC
Input
B+ AND B–
V
CC
Output
100 kΩ
(B– Pin Only)
100 kΩ
(B+ Pin Only)
3 kΩ
12 kΩ
V
CC
Output
A
B+ AND B–
4 mA
1 kΩ
18 kΩ
SN75LBC971A
SCSI DIFFERENTIAL CONVERTER-DATA
SLLS186B – OCTOBER 1994 – REVISED JUL Y 1997
5
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
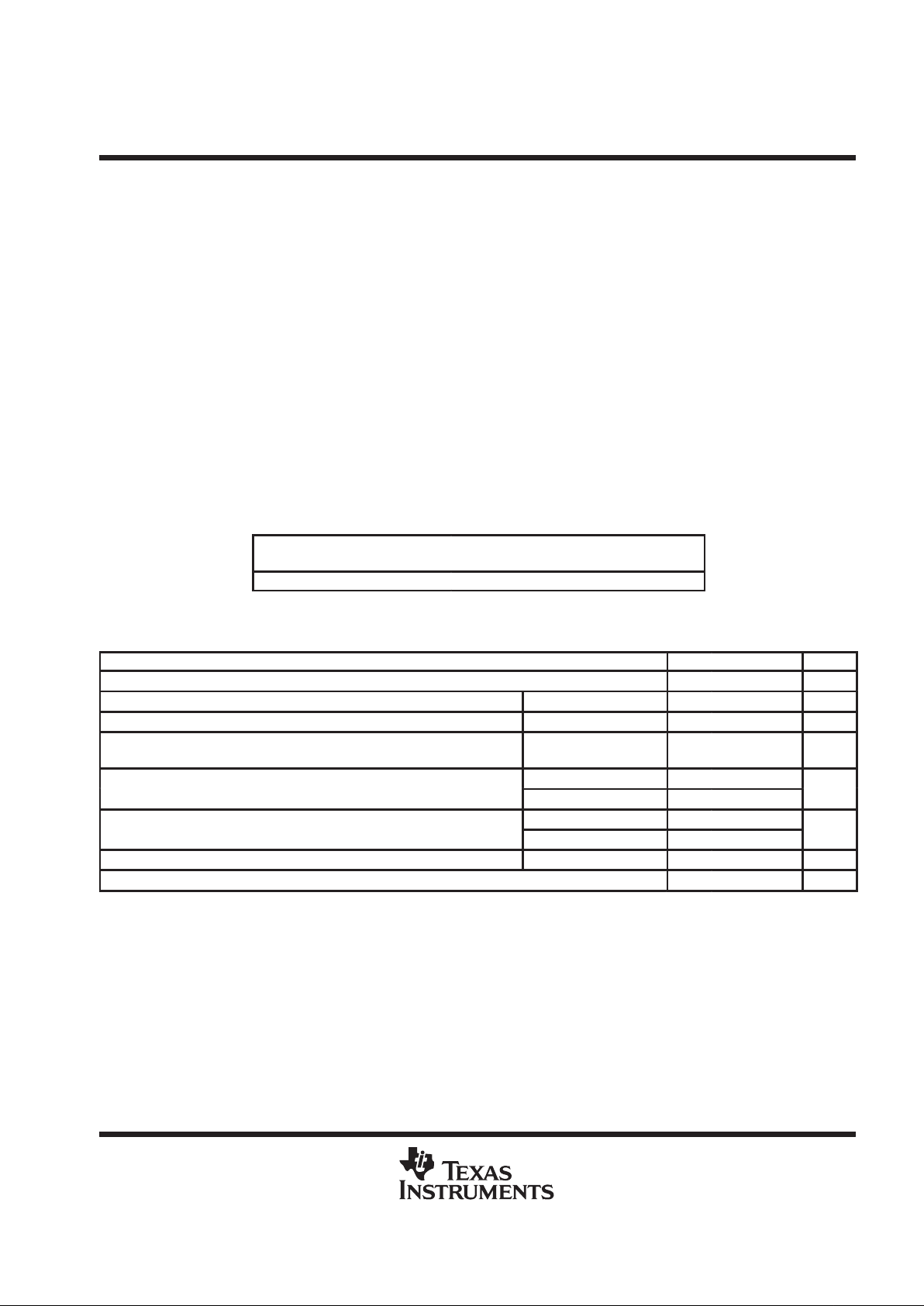
absolute maximum ratings over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)
†
Supply voltage range, V
CC
(see Note 1) –0.3 V to 7 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Differential bus voltage range (B side) –15 V to 15 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Single-ended bus voltage range (A side and control inputs) –0.3 V to 7 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Continuous total power dissipation (see Note 2) Internally Limited (see Dissipation Rating Table). . . . . . . . . .
Electrostatic discharge (see Note 3): Class 1 A (all pins) 500 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Class 1 B (all pins) 200 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Class 2 A (B-side and GND) 2 kV. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Class 2 B (B-side and GND) 200 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Operating free-air temperature range, T
A
0°C to 70°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Storage temperature range, T
stg
65°C to 150°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Lead temperature 1,6 mm (1/16 inch) from case for 10 seconds 260°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
†
Stresses beyond those listed under “absolute maximum ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and
functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under “recommended operating conditions” is not
implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
NOTES: 1. All voltage values are with respect to GND.
2. The maximum operating junction temperature is internally limited. Use the dissipation rating table to operate below this temperature.
3. This absolute maximum rating is tested in accordance with MIL-STD-883C, Method 3015.7.
DISSIPATION RATING TABLE
PACKAGE
TA ≤ 25°C
POWER RATING
DERATING FACTOR
‡
ABOVE TA = 25°C
TA = 70°C
POWER RATING
DL 2500 mW 20 mW/°C 1600 mW
‡
This is the inverse of the traditional junction-to-case thermal resistance (R
θJA
).
recommended operating conditions
MIN NOM MAX UNIT
Supply voltage, V
CC
4.75 5 5.25 V
High-level input voltage, V
IH
A side and control 2 V
Low-level input voltage, V
IL
A side and control 0.8 V
Voltage at any bus terminal (separately or common-mode), VO or V
I
B side
12
–7
V
p
B side –60
High-level output current, I
OH
A side –16
mA
p
B side 60
Low-level output current, I
OL
A side 16
mA
Operating case temperature, T
C
0 125 °C
Operating free-air temperature, T
A
0 70 °C

SN75LBC971A
SCSI DIFFERENTIAL CONVERTER-DATA
SLLS186B – OCTOBER 1994 – REVISED JUL Y 1997
6
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
electrical characteristics over recommended operating conditions (unless otherwise noted)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP†MAX UNIT
V
OD(H)
Driver high-level differential output voltage See Figure 1 1 1.8 V
V
OD(L)
Driver low-level differential output voltage See Figure 1 – 1 – 2.2 V
p
A side VID = –200 mV, IOH = –16 mA 2.5 4.2
VOHHigh-level output voltage
B side IOH = –60 mA 3.4
V
p
A side VID = 200 mV , IOL = 16 mA 0.4 0.8
VOLLow-level output voltage
B side IOL = 60 mA 1.6
V
V
IT+
Receiver positive-going
differential input
threshold voltage
IOH = –16 mA See Figure 2 0.2 V
V
IT–
Receiver negative-going
differential input
threshold voltage
B side
IOL = 16 mA See Figure 2 –0.2 V
V
hys
Receiver input hysteresis
voltage (V
IT+
– V
IT–
)
35 45 mV
V
= 12 V,
VCC = 5 V 0.6 1
p
I
,
Other input at 0 V
VCC = 0 0.7 1
mA
IIBus input current
B or B
V
= –7 V,
VCC = 5 V –0.5 –0.8
I
,
Other input at 0 V
VCC = 0 –0.4 –0.8
mA
A side –2.9 –5 –8 mA
I
IH
High-level input current
RESET
, DSENS
VIH = 2 V
–70 –100
SDB, DRVBUS 8 20
µ
A
A side –6 –8 mA
I
IL
Low-level input current
RESET
, DSENS
VIL = 0.8 V
–66 –100
SDB, DRVBUS ±1
µ
A
I
OS
Short-circuit output
current
B side VO = 5 V and 0 ±250 mA
High-impedance-state
A side See IIH and I
IL
I
OZ
g
output current
B side
See I
I
Disabled RESET at 0.8 V, Others open 23 33
I
CC
Supply current
B to A
Enabled
SDB and DRVBUS at 2 V,
All other inputs open,
VID = –1 V,
No load
36
mA
A to B
Enabled
SDB at 0.8 V ,
All other inputs open,
DRVBUS at 2 V,
No load
4 9
C
O
Output capacitance VI = 0.6 sin(2π × 106t) + 1.5 V, BDBn to GND 19 21 pF
p
p
B to A, One channel 100 pF
C
p
d
Power dissipation capacitance
‡
A to B, One channel 450 pF
†
All typical values are at VCC = 5 V, TA = 25°C.
‡
Cpd determines the no-load dynamic current consumption, IS = Cpd ×VCC ×f + ICC (ICC depends on the output states and load circuits and is
not necessarily the ICC specified in the Electrical Characteristics Table).

SN75LBC971A
SCSI DIFFERENTIAL CONVERTER-DATA
SLLS186B – OCTOBER 1994 – REVISED JUL Y 1997
7
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
switching characteristics over recommended of operating conditions (unless otherwise noted)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN MAX UNIT
See Figures 3 and 4 8.5 25.3 ns
td1, t
d2
Delay time, A to B, high- to low-level or
-
-
p
VCC = 5 V, TA = 25°C, See Figures 3 and 4 10 18
ns
low- to high-level out ut
VCC = 5 V, TA = 70°C, See Figures 3 and 4 12.5 20.5 ns
See Figures 5 and 6 21.5 36.2 ns
td3, t
d4
Delay time, B to A, high- to low-level or
-
-
p
VCC = 5 V, TA = 25°C, See Figures 5 and 6 23.6 32.6 ns
low- to high-level out ut
VCC = 5 V, TA = 70°C, See Figures 5 and 6 24.4 33.4 ns
A to B
†
See Figures 5 and 6 8 ns
t
s
k(lim)
Skew limit
B to A See Figures 5 and 6 9 ns
t
sk(p)
Pulse skew
‡
6 ns
t
dis1
Disable time, A to B See Figures 3 and 4 200 ns
t
dis2
Disable time, B to A See Figures 5 and 6 35 ns
t
en1
Enable time, A to B See Figures 3 and 4 65 ns
t
en2
Enable time, B to A See Figures 5 and 6 65 ns
t
en(TX)
Enable time, receive-to-transmit See Figure 7 142 ns
†
This parameter is applicable at one VCC and operating temperature within the recommended operating conditions and to any two devices.
‡
Pulse skew is the difference between the high-to-low and low-to-high propagation delay times of any single channel.

SN75LBC971A
SCSI DIFFERENTIAL CONVERTER-DATA
SLLS186B – OCTOBER 1994 – REVISED JUL Y 1997
8
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION
V
OD
75 Ω
VOH, V
OL
165 Ω
165 Ω
5 V
VIH, V
IL
ADBn–
BDBn–
BDBn+
2 V or 0.8 V
VOH, V
OL
NOTES: A. Resistance values are in ohms with a tolerance of ± 5%.
B. All input voltage levels are held to within 0.01 V.
C. The logical function is set with SDB at 0.8 V, DRVBUS at 3.5 V, and all others left open.
Figure 1. Differential Driver VOD, VOH, and VOL Test Circuit
BDBn–
BDBn+
ADBn–
IOH or I
OL
VOL or V
OL
VID or V
IT
I
I
V
I
NOTES: A. Resistance values are in ohms with a tolerance of ± 5%.
B. All input voltage levels are held to within 0.01 V.
C. The logical function is set with SDB and DRVBUS at 3.5 V , and all others left open.
Figure 2. Single-Ended Driver VOH, VOL, V
IT+
, and V
IT–
Test Circuit

SN75LBC971A
SCSI DIFFERENTIAL CONVERTER-DATA
SLLS186B – OCTOBER 1994 – REVISED JUL Y 1997
9
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION
75 Ω
165 Ω
165 Ω
5 V
Input (see Note A)
ADBn–
Output
50 pF
(see Note B)
50 pF
BDBn+
BDBn–
50%
V
OD(H)
~ –0.925 V
V
OD(L)
tent
d
tdt
dis
3 V
1.5 V
0 V
Input Output
0.5 V
t
0
t0or
NOTES: A. The input pulse is supplied by a generator having the following
characteristics: PRR ≤ 1 MHz, 45% < duty cycle < 50%, tr ≤ 6 ns, tf ≤ 6 ns,
ZO=50Ω.
B. CL includes probe and jig capacitance.
C. Resistance values are in ohms with a tolerance of ± 5%.
D. All input voltage levels are held to within 0.01 V.
Figure 3. A to B Propagation Delay Time Test Circuit
t
d1
t
d2
t
en1
t
dis1
SDB
DSENS
RESET
ADBn–
DRVBUS
BDBn–
BDBn+
V
OD
Figure 4. A to B Timing Waveforms

SN75LBC971A
SCSI DIFFERENTIAL CONVERTER-DATA
SLLS186B – OCTOBER 1994 – REVISED JUL Y 1997
10
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION
Input (see Note A)
BDBn–
Output
15 pF
(see Note B)
ADBn–
V
OH
~ 2.5 V
V
OL
t
entd
tdt
dis
3 V
1.5 V
0 V
Input Output
0.5 V
t
0
BDBn+
1.5 V
1.5 V
t0or
NOTES: A. The input pulse is supplied by a generator having the following
characteristics: PRR ≤ 1 MHz, 45% < duty cycle < 50%, tr ≤ 6 ns, tf ≤ 6 ns,
ZO=50Ω.
B. CL includes probe and jig capacitance.
C. Resistance values are in ohms with a tolerance of ± 5%.
D. All input voltage levels are held to within 0.01 V.
Figure 5. B to A Propagation Delay Time Test Circuit
t
d3
t
d4
t
en2
t
dis2
SDB
DSENS
RESET
BDBn–
DRVBUS
ADBn–
Figure 6. B to A Timing Waveforms

SN75LBC971A
SCSI DIFFERENTIAL CONVERTER-DATA
SLLS186B – OCTOBER 1994 – REVISED JUL Y 1997
11
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION
Input
Output
0 V
1.5 V
V
OL
RESET
DRVBUS
SDB
1.5 V
ADB0–
t
en(TX)
BDB0+
BDB0–
BDB1,2,3,4,5,7+
ADB1,2,3,4,5,7–
and
BDB1,2,3,4,5,7–
ADB6–
BDB6+
BDB6–
V
OH
≈3 V
t
en(TX)
BDB0–
BDB6–
Output
OutputInput
Figure 7. Receive-to-Transmit (t
en(TX)
) Timing Waveforms

SN75LBC971A
SCSI DIFFERENTIAL CONVERTER-DATA
SLLS186B – OCTOBER 1994 – REVISED JUL Y 1997
12
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
APPLICATION INFORMATION
SN75LBC970A
DIFFSENS
6
±BSY
±SEL
±RST
8
±I/O
±MSG
±C/D
±REQ
4
±ATN
±ACK
TEST
CLK 40
(see Note A)
–BSY, –SEL, –I/O, –MSG,
–C/D, –REQ, –A TN, –ACK
8
–RST
RSTFLTR
RESET
(from system)
X1/CLK20
X2
optional
(see Note B)
V
CC
0.022 µF
205 kΩ
SCSI
Controller
2
16
8
2
16
8
±DB(7–0)
±DBP(0)
±DB(15–8)
±DBP(1)
DIFFSENS
DIFFSENS
–DB(7–0)
–DBP(0)
RESET
–DB(15–8)
–DBP(1)
RESET
SN75LBC971A
DRVBUS SDB
TIMEOUT
20 kΩ
0.1 µF
RESET
20 MHz
(see Note A)
BDBn
BDBP
DSENS
ADBn
ADBP–
RESET
SN75LBC971A
BDBn
BDBP
DSENS
ADBn
ADBP–
RESET
DRVBUS SDB
NOTES: A. When using the 40-MHz clock input, X1 must be connected to VCC.
B. The oscillator cell of the SN75LBC970A is for a series-resonant crystal and requires
approximately 10 pF (including fixture capacitance) from X1 and X2 to ground in order
to function.
Figure 8. Typical Application of the SN75LBC970A and SN75LBC971A

SN75LBC971A
SCSI DIFFERENTIAL CONVERTER-DATA
SLLS186B – OCTOBER 1994 – REVISED JUL Y 1997
13
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
MECHANICAL INFORMATION
DL (R-PDSO-G**) PLASTIC SMALL-OUTLINE PACKAGE
4040048/C 03/97
48 PIN SHOWN
56
0.730
(18,54)
0.720
(18,29)
4828
0.370
(9,40)
(9,65)
0.380
Gage Plane
DIM
0.420 (10,67)
0.395 (10,03)
A MIN
A MAX
0.006 (0,15) NOM
PINS **
0.630
(16,00)
(15,75)
0.620
0.010 (0,25)
Seating Plane
0.020 (0,51)
0.040 (1,02)
25
24
0.008 (0,203)
0.012 (0,305)
48
1
0.008 (0,20) MIN
A
0.110 (2,79) MAX
0.299 (7,59)
0.291 (7,39)
0.004 (0,10)
M
0.005 (0,13)
0.025 (0,635)
0°–8°
NOTES: E. All linear dimensions are in inches (millimeters).
F. This drawing is subject to change without notice.
G. Body dimensions do not include mold flash or protrusion not to exceed 0.006 (0,15).
H. Falls within JEDEC MO-118

IMPORTANT NOTICE
T exas Instruments and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make changes to their products or to discontinue
any product or service without notice, and advise customers to obtain the latest version of relevant information
to verify, before placing orders, that information being relied on is current and complete. All products are sold
subject to the terms and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgement, including those
pertaining to warranty, patent infringement, and limitation of liability.
TI warrants performance of its semiconductor products to the specifications applicable at the time of sale in
accordance with TI’s standard warranty. Testing and other quality control techniques are utilized to the extent
TI deems necessary to support this warranty. Specific testing of all parameters of each device is not necessarily
performed, except those mandated by government requirements.
CERT AIN APPLICATIONS USING SEMICONDUCTOR PRODUCTS MAY INVOLVE POTENTIAL RISKS OF
DEATH, PERSONAL INJURY, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE (“CRITICAL
APPLICATIONS”). TI SEMICONDUCTOR PRODUCTS ARE NOT DESIGNED, AUTHORIZED, OR
WARRANTED TO BE SUITABLE FOR USE IN LIFE-SUPPORT DEVICES OR SYSTEMS OR OTHER
CRITICAL APPLICATIONS. INCLUSION OF TI PRODUCTS IN SUCH APPLICA TIONS IS UNDERST OOD TO
BE FULLY AT THE CUSTOMER’S RISK.
In order to minimize risks associated with the customer’s applications, adequate design and operating
safeguards must be provided by the customer to minimize inherent or procedural hazards.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or customer product design. TI does not warrant or represent
that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any patent right, copyright, mask work right, or other
intellectual property right of TI covering or relating to any combination, machine, or process in which such
semiconductor products or services might be or are used. TI’s publication of information regarding any third
party’s products or services does not constitute TI’s approval, warranty or endorsement thereof.
Copyright 1998, Texas Instruments Incorporated
 Loading...
Loading...