Texas Instruments SN74LVTH18502APM, SN74LVTH18502APMR, SN74LVTH182502APM, SNJ54LVTH18502AHV Datasheet
D
Members of the Texas Instruments
SCOPE
D
Members of the Texas Instruments
Widebus
D
State-of-the-Art 3.3-V ABT Design Supports
Mixed-Mode Signal Operation (5-V Input
and Output Voltages With 3.3-V V
D
Support Unregulated Battery Operation
Down to 2.7 V
D
UBT
Combines D-Type Latches and D-Type
Flip-Flops for Operation in Transparent,
Latched, or Clocked Mode
D
Bus Hold on Data Inputs Eliminates the
Need for External Pullup Resistors
D
B-Port Outputs of ’LVTH182502A Devices
Have Equivalent 25-Ω Series Resistors, So
No External Resistors Are Required
SN54LVTH18502A, SN54LVTH182502A, SN74LVTH18502A, SN74LVTH182502A
Family of Testability Products
Family
(Universal Bus Transceiver)
CC
3.3-V ABT SCAN TEST DEVICES
WITH 18-BIT UNIVERSAL BUS TRANSCEIVERS
SCBS668B – JULY 1996 – REVISED MARCH 1999
D
Compatible With the IEEE Standard
1149.1-1990 (JTAG) Test Access Port and
Boundary-Scan Architecture
D
SCOPE
– IEEE Standard 1149.1-1990 Required
)
– Parallel-Signature Analysis at Inputs
– Pseudorandom Pattern Generation From
– Sample Inputs/Toggle Outputs
– Binary Count From Outputs
– Device Identification
– Even-Parity Opcodes
D
Packaged in 64-Pin Plastic Thin Quad Flat
(PM) Packages Using 0.5-mm
Center-to-Center Spacings and 68-Pin
Ceramic Quad Flat (HV) Packages Using
25-mil Center-to-Center Spacings
Instruction Set
Instructions and Optional CLAMP and
HIGHZ
Outputs
description
The ’LVTH18502A and ’L VTH182502A scan test devices with 18-bit universal bus transceivers are members
of the Texas Instruments SCOPE testability integrated-circuit family. This family of devices supports IEEE
Standard 1 149.1-1990 boundary scan to facilitate testing of complex circuit-board assemblies. Scan access to
the test circuitry is accomplished via the 4-wire test access port (TAP) interface.
Additionally, these devices are designed specifically for low-voltage (3.3-V) V
capability to provide a TTL interface to a 5-V system environment.
In the normal mode, these devices are 18-bit universal bus transceivers that combine D-type latches and D-type
flip-flops to allow data flow in transparent, latched, or clocked modes. They can be used either as two 9-bit
transceivers or one 18-bit transceiver. The test circuitry can be activated by the TAP to take snapshot samples
of the data appearing at the device pins or to perform a self test on the boundary-test cells. Activating the TAP
in the normal mode does not affect the functional operation of the SCOPE universal bus transceivers.
Data flow in each direction is controlled by output-enable (OEAB
and clock (CLKAB and CLKBA) inputs. For A-to-B data flow, the device operates in the transparent mode when
LEAB is high. When LEAB is low , the A-bus data is latched while CLKAB is held at a static low or high logic level.
Otherwise, if LEAB is low, A-bus data is stored on a low-to-high transition of CLKAB. When OEAB
B outputs are active. When OEAB
similar to A-to-B data flow, but uses the OEBA
In the test mode, the normal operation of the SCOPE universal bus transceivers is inhibited, and the test
circuitry is enabled to observe and control the I/O boundary of the device. When enabled, the test circuitry
performs boundary-scan test operations according to the protocol described in IEEE Standard 1149.1-1990.
is high, the B outputs are in the high-impedance state. B-to-A data flow is
, LEBA, and CLKBA inputs.
and OEBA), latch-enable (LEAB and LEBA),
operation, but with the
CC
is low, the
Please be aware that an important notice concerning availability, standard warranty, and use in critical applications of
Texas Instruments semiconductor products and disclaimers thereto appears at the end of this data sheet.
SCOPE, Widebus, and UBT are trademarks of Texas Instruments Incorporated.
UNLESS OTHERWISE NOTED this document contains PRODUCTION
DATA information current as of publication date. Products conform to
specifications per the terms of Texas Instruments standard warranty.
Production processing does not necessarily include testing of all
parameters.
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
Copyright 1999, Texas Instruments Incorporated
1
SN54LVTH18502A, SN54LVTH182502A, SN74LVTH18502A, SN74LVTH182502A
3.3-V ABT SCAN TEST DEVICES
WITH 18-BIT UNIVERSAL BUS TRANSCEIVERS
SCBS668B – JULY 1996 – REVISED MARCH 1999
description (continued)
Four dedicated test pins are used to observe and control the operation of the test circuitry: test data input (TDI),
test data output (TDO), test mode select (TMS), and test clock (TCK). Additionally, the test circuitry performs
other testing functions such as parallel-signature analysis (PSA) on data inputs and pseudo-random pattern
generation (PRPG) from data outputs. All testing and scan operations are synchronized to the T AP interface.
Active bus-hold circuitry is provided to hold unused or floating data inputs at a valid logic level.
The B-port outputs of ’L VTH182502A, which are designed to source or sink up to 12 mA, include 25- Ω series
resistors to reduce overshoot and undershoot.
The SN54LVTH18502A and SN54LVTH182502A are characterized for operation over the full military
temperature range of –55°C to 125°C. The SN74L VTH18502A and SN74LVTH182502A are characterized for
operation from –40°C to 85°C.
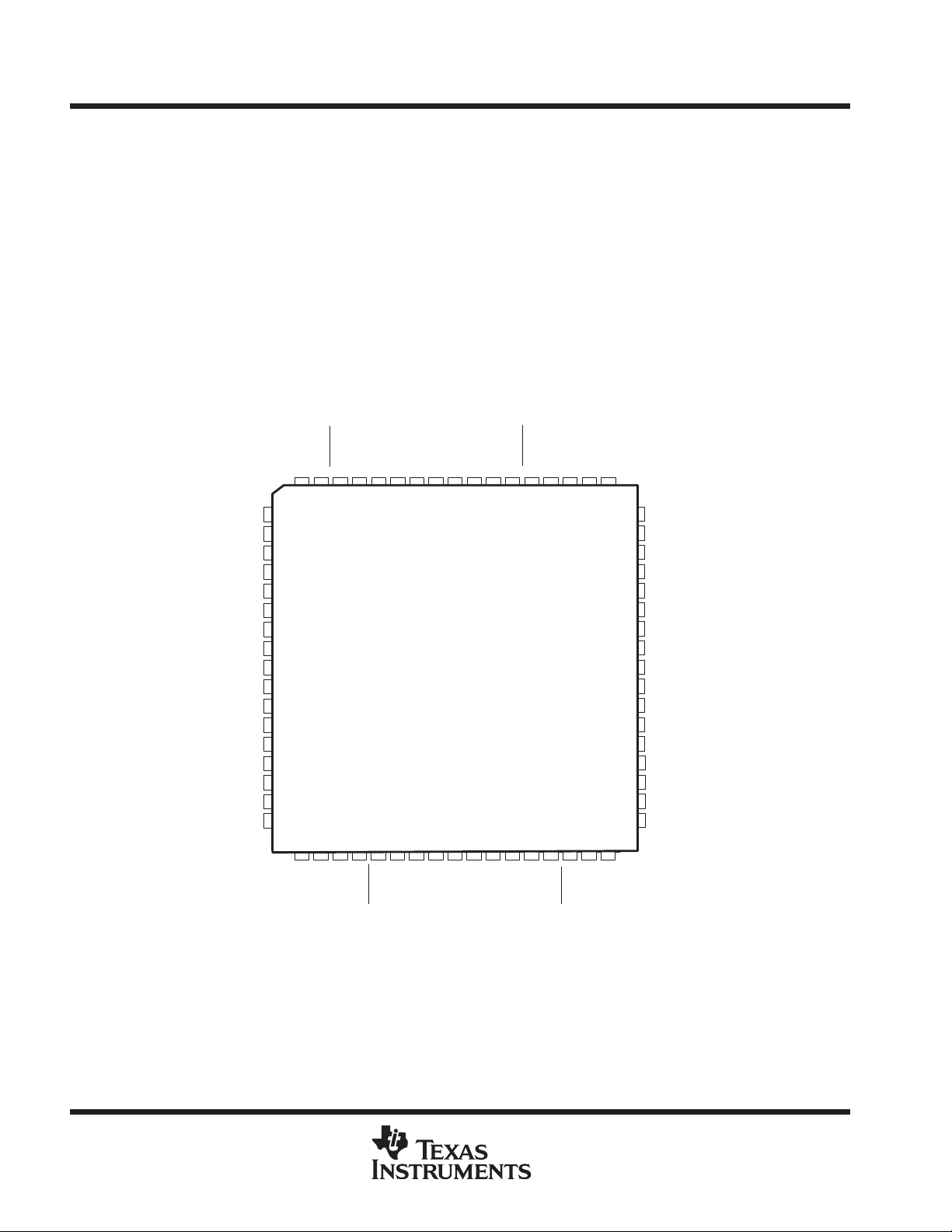
SN54LVTH18502A, SN54LVTH182502A. . . HV PACKAGE
1A2
1A1
1OEAB
GND
1LEAB
1CLKAB
(TOP VIEW)
CC
VNCTMS
TDO
1CLKBA
1LEBA
1OEBA
GND
1B1
1B2
1B3
87 65493168672
1A3
1A4
1A5
GND
1A6
1A7
1A8
1A9
V
2A1
2A2
2A3
GND
2A4
2A5
2A6
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
NC
18
19
CC
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
28 29 30 31 32 33 34
2A9
2A7
2A8
NC – No internal connection
GND
2LEAB
2OEAB
35 36 37 38 39
NC
TDI
2CLKAB
66 652764 63 62 61
CC
V
TCK
2LEBA
2CLKBA
40 41 42 43
2B9
GND
2OEBA
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
2B8
1B4
1B5
1B6
GND
1B7
1B8
1B9
V
CC
NC
2B1
2B2
2B3
2B4
GND
2B5
2B6
2B7
2
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
SN54LVTH18502A, SN54LVTH182502A, SN74LVTH18502A, SN74LVTH182502A
3.3-V ABT SCAN TEST DEVICES
WITH 18-BIT UNIVERSAL BUS TRANSCEIVERS
SCBS668B – JULY 1996 – REVISED MARCH 1999
1A3
1A4
1A5
GND
1A6
1A7
1A8
1A9
V
CC
2A1
2A2
2A3
GND
2A4
2A5
2A6
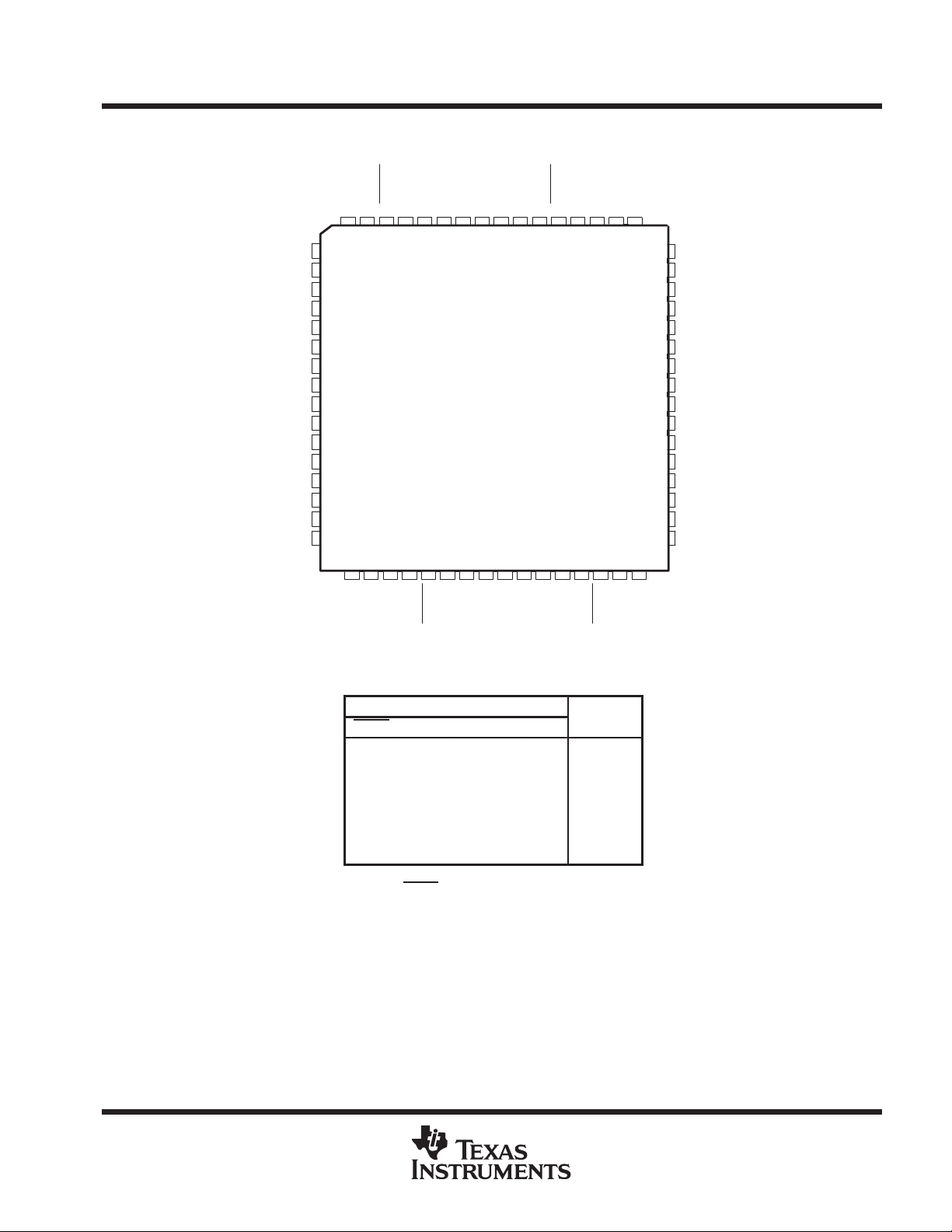
SN74LVTH18502A, SN74LVTH182502A. . . PM PACKAGE
1OEAB
1A1
GND
20
1A2
63 62 61 60 5964 58 56 55 5457
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
18 19
17
(TOP VIEW)
1CLKAB
TDO
1LEAB
21 22 23 24
CC
V
25 26 27 28 29
TMS
1CLKBA
1LEBA
53 52
1OEBA
GND
51 50 49
30 31 32
1B1
1B2
1B3
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
1B4
1B5
1B6
GND
1B7
1B8
1B9
V
CC
2B1
2B2
2B3
2B4
GND
2B5
2B6
2B7
CC
2LEAB
2CLKAB
TDI
V
TCK
2CLKBA
†
GND
2LEBA
OUTPUT
B
2OEBA
‡
0
2A9
2A7
2A8
GND
2OEAB
FUNCTION TABLE
(normal mode, each register)
INPUTS
OEAB LEAB CLKAB A
L L L X B
L L ↑ LL
LL↑HH
LHXLL
LHXHH
HXXXZ
†
A-to-B data flow is shown. B-to-A data flow is similar
but uses OEBA
‡
Output level before the indicated steady-state input
conditions are established
, LEBA, and CLKBA.
2B9
2B8
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
3
SN54LVTH18502A, SN54LVTH182502A, SN74LVTH18502A, SN74LVTH182502A
3.3-V ABT SCAN TEST DEVICES
WITH 18-BIT UNIVERSAL BUS TRANSCEIVERS
SCBS668B – JULY 1996 – REVISED MARCH 1999
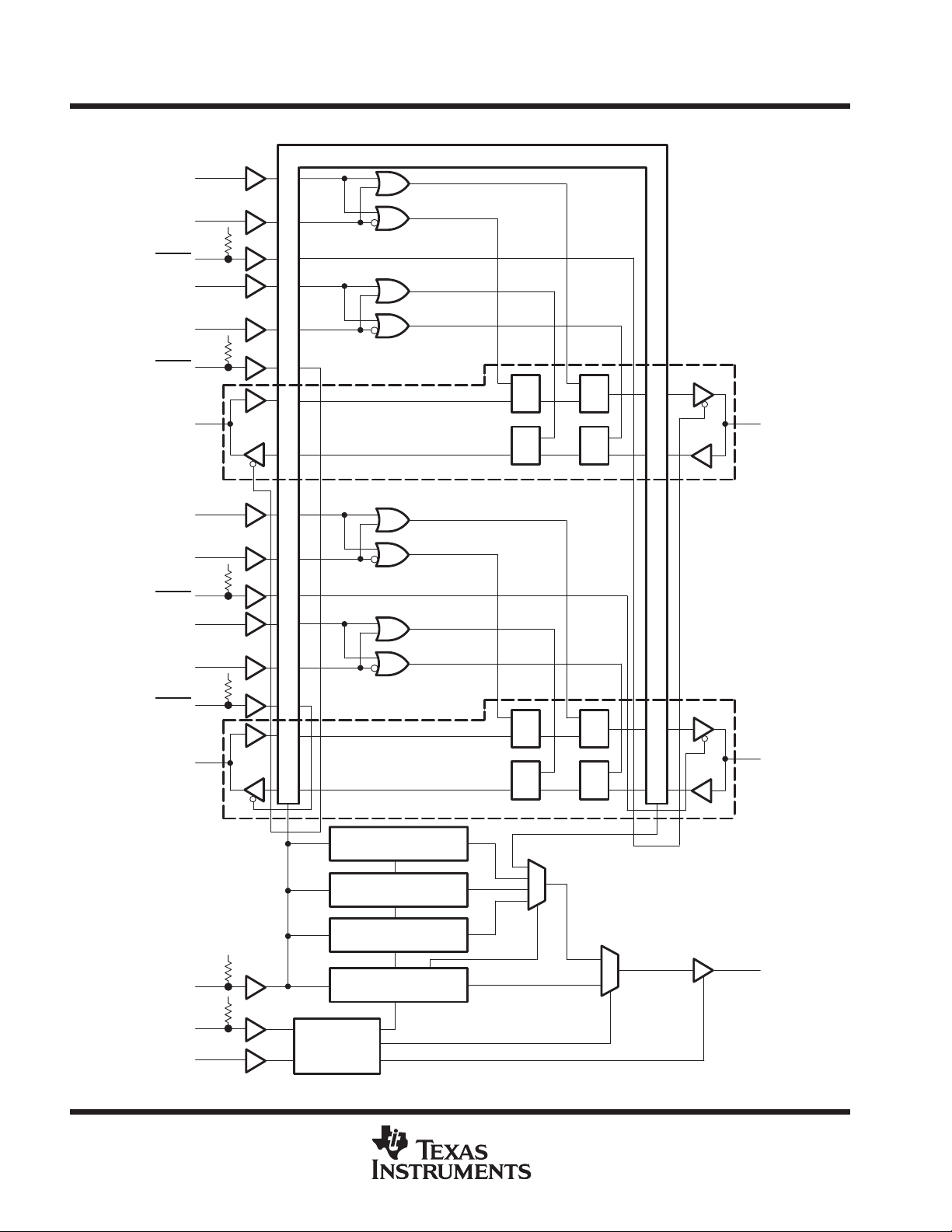
functional block diagram
1LEAB
1CLKAB
1OEAB
1LEBA
1CLKBA
1OEBA
1A1
2LEAB
2CLKAB
2OEAB
2LEBA
60
59
V
CC
62
54
55
V
CC
53
63
One of Nine Channels
22
23
V
CC
21
28
Boundary-Scan Register
C1
1D
C1
1D
C1
1D
C1
1D
51
1B1
2A1
TDI
TMS
TCK
27
V
CC
30
10
V
CC
24
V
CC
56
26
2CLKBA
2OEBA
Pin numbers shown are for the PM package.
One of Nine Channels
Bypass Register
Boundary-Control
Register
Identification
Register
Instruction
Register
TAP
Controller
C1
1D
C1
1D
C1
1D
C1
1D
40
58
2B1
TDO
4
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
SN54LVTH18502A, SN54LVTH182502A, SN74LVTH18502A, SN74LVTH182502A
WITH 18-BIT UNIVERSAL BUS TRANSCEIVERS
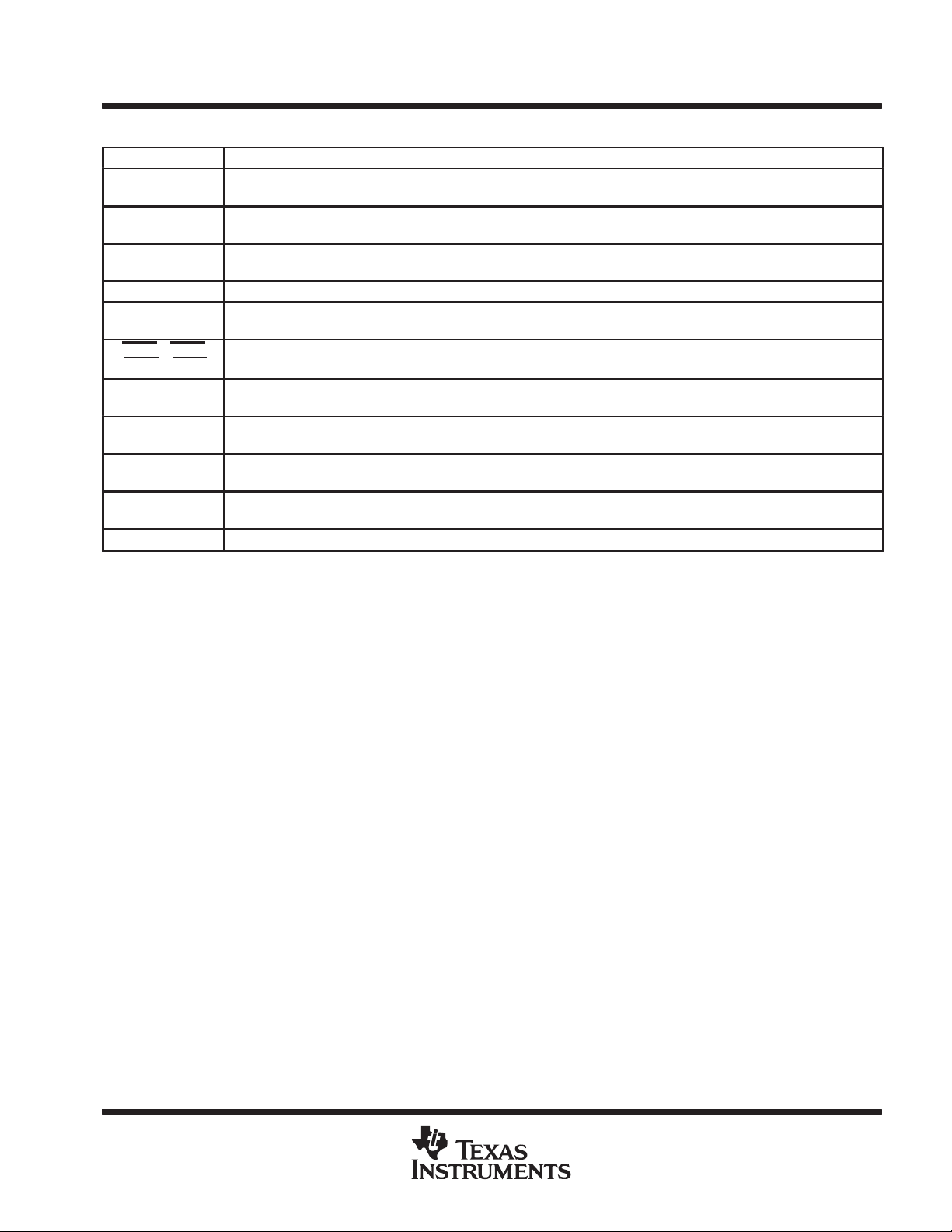
Terminal Functions
TERMINAL NAME DESCRIPTION
1A1–1A9,
2A1–2A9
1B1–1B9,
2B1–2B9
1CLKAB, 1CLKBA,
2CLKAB, 2CLKBA
GND Ground
1LEAB, 1LEBA,
2LEAB, 2LEBA
1OEAB, 1OEBA,
2OEAB
, 2OEBA
TCK
TDI
TDO
TMS
V
CC
Normal-function A-bus I/O ports. See function table for normal-mode logic.
Normal-function B-bus I/O ports. See function table for normal-mode logic.
Normal-function clock inputs. See function table for normal-mode logic.
Normal-function latch enables. See function table for normal-mode logic.
Normal-function output enables. See function table for normal-mode logic. An internal pullup at each terminal forces the
terminal to a high level if left unconnected.
T est clock. One of four terminals required by IEEE Standard 1149.1-1990. T est operations of the device are synchronous
to TCK. Data is captured on the rising edge of TCK and outputs change on the falling edge of TCK.
Test data input. One of four terminals required by IEEE Standard 1 149.1-1990. TDI is the serial input for shifting data
through the instruction register or selected data register. An internal pullup forces TDI to a high level if left unconnected.
T est data output. One of four terminals required by IEEE Standard 1 149.1-1990. TDO is the serial output for shifting data
through the instruction register or selected data register.
T est mode select. One of four terminals required by IEEE Standard 1149.1-1990. TMS directs the device through its T AP
controller states. An internal pullup forces TMS to a high level if left unconnected.
Supply voltage
3.3-V ABT SCAN TEST DEVICES
SCBS668B – JULY 1996 – REVISED MARCH 1999
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
5
SN54LVTH18502A, SN54LVTH182502A, SN74LVTH18502A, SN74LVTH182502A
3.3-V ABT SCAN TEST DEVICES
WITH 18-BIT UNIVERSAL BUS TRANSCEIVERS
SCBS668B – JULY 1996 – REVISED MARCH 1999
test architecture
Serial-test information is conveyed by means of a 4-wire test bus or TAP, that conforms to IEEE Standard
1 149.1-1990. Test instructions, test data, and test control signals all are passed along this serial-test bus. The
TAP controller monitors two signals from the test bus, TCK and TMS. The TAP controller extracts the
synchronization (TCK) and state control (TMS) signals from the test bus and generates the appropriate on-chip
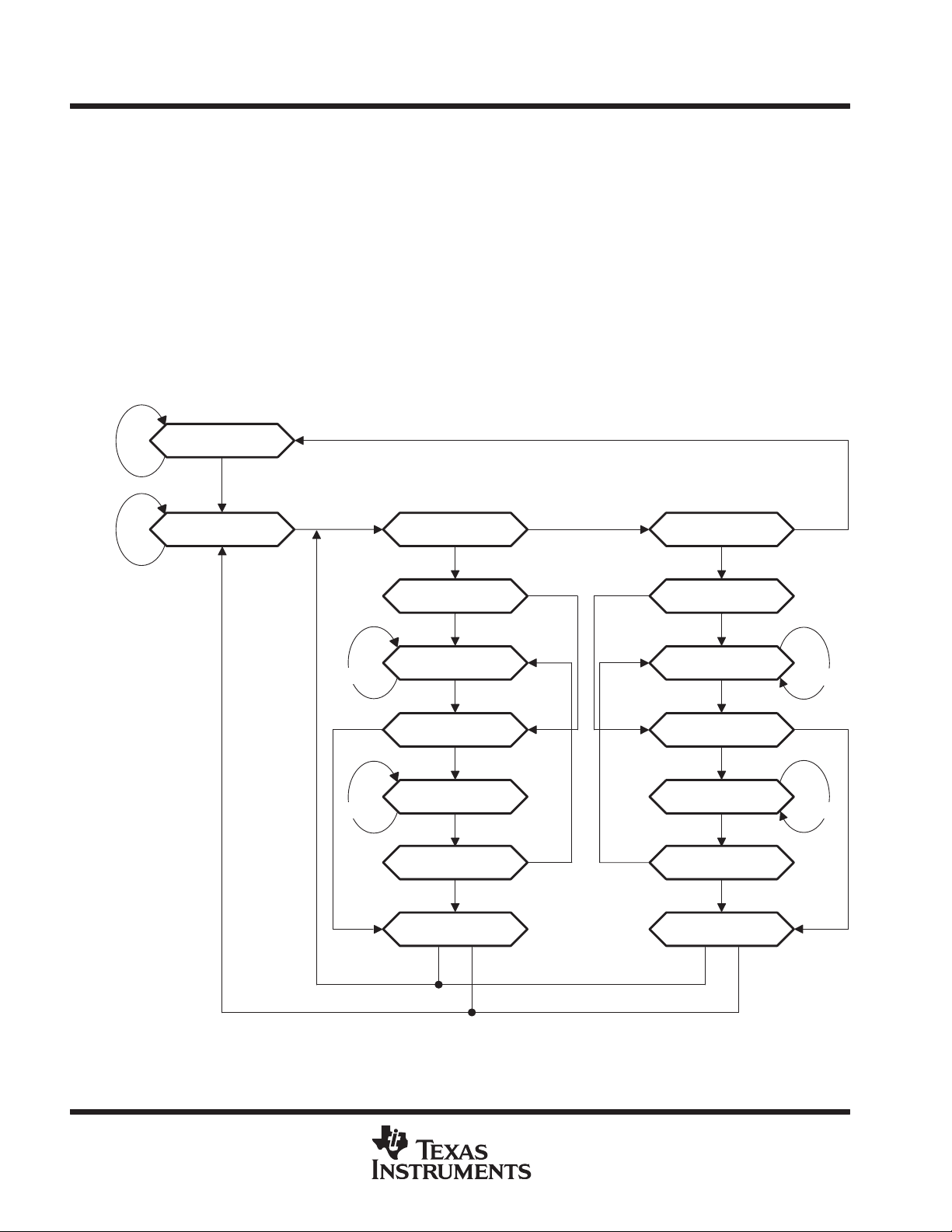
control signals for the test structures in the device. Figure 1 shows the TAP-controller state diagram.
The T AP controller is fully synchronous to the TCK signal. Input data is captured on the rising edge of TCK and
output data changes on the falling edge of TCK. This scheme ensures data to be captured is valid for fully
one-half of the TCK cycle.
The functional block diagram shows the IEEE Standard 1149.1-1990 4-wire test bus and boundary-scan
architecture and the relationship among the test bus, the T AP controller, and the test registers. As shown, the
device contains an 8-bit instruction register and four test-data registers: a 48-bit boundary-scan register, a 3-bit
boundary-control register, a 1-bit bypass register, and a 32-bit device identification register.
Test-Logic-Reset
TMS = H
TMS = L
TMS = L
Run-Test/Idle Select-DR-Scan
TMS = L
Capture-DR
TMS = L
Shift-DR
TMS = L
TMS = H
TMS = H
Exit1-DR
TMS = L
Pause-DR
TMS = L
TMS = H
Exit2-DR
TMS = H
TMS = HTMS = H
TMS = H TMS = H
TMS = L
TMS = L
Select-IR-Scan
TMS = H
TMS = L
Capture-IR
TMS = L
Shift-IR
TMS = L
TMS = H
TMS = H
Exit1-IR
TMS = L
Pause-IR
TMS = L
TMS = H
Exit2-IR
TMS = H
Update-DR
TMS = LTMS = H
Update-IR
TMS = LTMS = H
Figure 1. TAP-Controller State Diagram
6
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265

SN54LVTH18502A, SN54LVTH182502A, SN74LVTH18502A, SN74LVTH182502A
3.3-V ABT SCAN TEST DEVICES
WITH 18-BIT UNIVERSAL BUS TRANSCEIVERS
SCBS668B – JULY 1996 – REVISED MARCH 1999
state diagram description
The TAP controller is a synchronous finite-state machine that provides test control signals throughout the
device. The state diagram shown in Figure 1 is in accordance with IEEE Standard 1149.1-1990. The TAP
controller proceeds through its states based on the level of TMS at the rising edge of TCK.
As shown, the T AP controller consists of 16 states. There are six stable states (indicated by a looping arrow in
the state diagram) and ten unstable states. A stable state is a state the T AP controller can retain for consecutive
TCK cycles. Any state that does not meet this criterion is an unstable state.
There are two main paths through the state diagram: one to access and control the selected data register and
one to access and control the instruction register. Only one register can be accessed at a time.
Test-Logic-Reset
The device powers up in the T est-Logic-Reset state. In the stable Test-Logic-Reset state, the test logic is reset
and is disabled so that the normal logic function of the device is performed. The instruction register is reset to
an opcode that selects the optional IDCODE instruction, if supported, or the BYP ASS instruction. Certain data
registers can also be reset to their power-up values.
The state machine is constructed such that the T AP controller returns to the Test-Logic-Reset state in no more
than five TCK cycles if TMS is left high. The TMS pin has an internal pullup resistor that forces it high if left
unconnected or if a board defect causes it to be open circuited.
For the ’L VTH18502A and ’L VTH182502A, the instruction register is reset to the binary value 10000001, which
selects the IDCODE instruction. Bits 47–44 in the boundary-scan register are reset to logic 1, ensuring that
these cells, which control A-port and B-port outputs, are set to benign values (i.e., if test mode were invoked
the outputs would be at the high-impedance state). Reset-value of other bits in the boundary-scan register
should be considered indeterminate. The boundary-control register is reset to the binary value 010, which
selects the PSA test operation.
Run-T est/Idle
The T AP controller must pass through the Run-T est/Idle state (from T est-Logic-Reset) before executing any test
operations. The Run-Test/Idle state also can be entered following data-register or instruction-register scans.
Run-Test/Idle is a stable state in which the test logic can be actively running a test or can be idle. The test
operations selected by the boundary-control register are performed while the TAP controller is in the
Run-Test/Idle state.
Select-DR-Scan, Select-lR-Scan
No specific function is performed in the Select-DR-Scan and Select-lR-Scan states, and the T AP controller exits
either of these states on the next TCK cycle. These states allow the selection of either data-register scan or
instruction-register scan.
Capture-DR
When a data-register scan is selected, the TAP controller must pass through the Capture-DR state. In the
Capture-DR state, the selected data register can capture a data value as specified by the current instruction.
Such capture operations occur on the rising edge of TCK, upon which the TAP controller exits the
Capture-DR state.
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
7

SN54LVTH18502A, SN54LVTH182502A, SN74LVTH18502A, SN74LVTH182502A
3.3-V ABT SCAN TEST DEVICES
WITH 18-BIT UNIVERSAL BUS TRANSCEIVERS
SCBS668B – JULY 1996 – REVISED MARCH 1999
Shift-DR
Upon entry to the Shift-DR state, the data register is placed in the scan path between TDI and TDO, and on the
first falling edge of TCK, TDO goes from the high-impedance state to an active state. TDO enables to the logic
level present in the least-significant bit of the selected data register.
While in the stable Shift-DR state, data is serially shifted through the selected data register on each TCK cycle.
The first shift occurs on the first rising edge of TCK after entry to the Shift-DR state (i.e., no shifting occurs during
the TCK cycle in which the T AP controller changes from Capture-DR to Shift-DR or from Exit2-DR to Shift-DR).
The last shift occurs on the rising edge of TCK, upon which the TAP controller exits the Shift-DR state.
Exit1-DR, Exit2-DR
The Exit1-DR and Exit2-DR states are temporary states that end a data-register scan. It is possible to return
to the Shift-DR state from either Exit1-DR or Exit2-DR without recapturing the data register. On the first falling
edge of TCK after entry to Exit1-DR, TDO goes from the active state to the high-impedance state.
Pause-DR
No specific function is performed in the stable Pause-DR state, in which the TAP controller can remain
indefinitely. The Pause-DR state suspends and resumes data-register scan operations without loss of data.
Update-DR
If the current instruction calls for the selected data register to be updated with current data, such update occurs
on the falling edge of TCK, following entry to the Update-DR state.
Capture-IR
When an instruction-register scan is selected, the TAP controller must pass through the Capture-IR state. In
the Capture-IR state, the instruction register captures its current status value. This capture operation occurs
on the rising edge of TCK, upon which the T AP controller exits the Capture-IR state. For the ’L VTH18502A and
’LVTH182502A, the status value loaded in the Capture-IR state is the fixed binary value 10000001.
Shift-IR
Upon entry to the Shift-IR state, the instruction register is placed in the scan path between TDI and TDO. On
the first falling edge of TCK, TDO goes from the high-impedance state to the active state. TDO enables to the
logic level present in the least-significant bit of the instruction register.
While in the stable Shift-IR state, instruction data is serially shifted through the instruction register on each TCK
cycle. The first shift occurs on the first rising edge of TCK after entry to the Shift-IR state (i.e., no shifting occurs
during the TCK cycle in which the TAP controller changes from Capture-IR to Shift-IR or from Exit2-IR to
Shift-IR). The last shift occurs on the rising edge of TCK, upon which the T AP controller exits the Shift-IR state.
Exit1-IR, Exit2-IR
The Exit1-IR and Exit2-IR states are temporary states that end an instruction-register scan. It is possible to
return to the Shift-IR state from either Exit1-IR or Exit2-IR without recapturing the instruction register. On the
first falling edge of TCK after entry to Exit1-IR, TDO goes from the active state to the high-impedance state.
Pause-IR
No specific function is performed in the stable Pause-IR state, in which the TAP controller can remain
indefinitely. The Pause-IR state suspends and resumes instruction-register scan operations without loss
of data.
Update-IR
The current instruction is updated and takes effect on the falling edge of TCK, following entry to the
Update-IR state.
8
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
SN54LVTH18502A, SN54LVTH182502A, SN74LVTH18502A, SN74LVTH182502A
3.3-V ABT SCAN TEST DEVICES
WITH 18-BIT UNIVERSAL BUS TRANSCEIVERS
SCBS668B – JULY 1996 – REVISED MARCH 1999
register overview
With the exception of the bypass and device-identification registers, any test register can be thought of as a
serial shift register with a shadow latch on each bit. The bypass and device-identification registers differ in that
they contain only a shift register. During the appropriate capture state (Capture-IR for instruction register,
Capture-DR for data registers), the shift register can be parallel loaded from a source specified by the current
instruction. During the appropriate shift state (Shift-IR or Shift-DR), the contents of the shift register are shifted
out from TDO while new contents are shifted in at TDI. During the appropriate update state (Update-IR or
Update-DR), the shadow latches are updated from the shift register.
instruction register description
The instruction register (IR) is eight bits long and tells the device what instruction is to be executed. Information
contained in the instruction includes the mode of operation (either normal mode, in which the device performs
its normal logic function, or test mode, in which the normal logic function is inhibited or altered), the test operation
to be performed, which of the four data registers is to be selected for inclusion in the scan path during
data-register scans, and the source of data to be captured into the selected data register during Capture-DR.
Table 3 lists the instructions supported by the ’LVTH18502A and ’LVTH182502A. The even-parity feature
specified for SCOPE devices is supported in this device. Bit 7 of the instruction opcode is the parity bit. Any
instructions that are defined for SCOPE devices but are not supported by this device default to BYPASS.
During Capture-IR, the IR captures the binary value 10000001. As an instruction is shifted in, this value is shifted
out via TDO and can be inspected as verification that the IR is in the scan path. During Update-IR, the value
that has been shifted into the IR is loaded into shadow latches. At this time, the current instruction is updated
and any specified mode change takes effect. At power up or in the Test-Logic-Reset state, the IR is reset to the
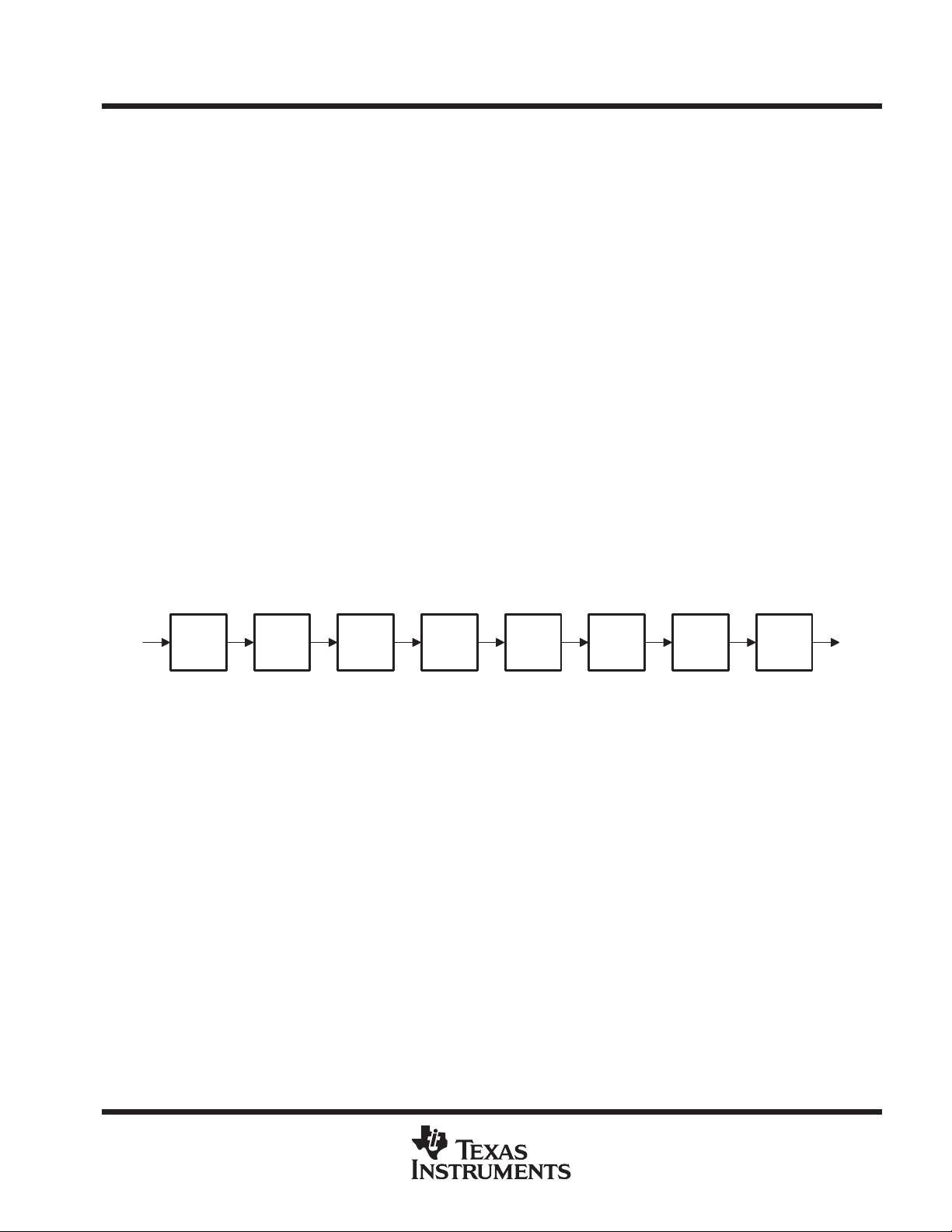
binary value 10000001, which selects the IDCODE instruction. The IR order of scan is shown in Figure 2.
Bit 7
Parity
(MSB)
Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1
Bit 0
(LSB)
TDOTDI
Figure 2. Instruction Register Order of Scan
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
9
SN54LVTH18502A, SN54LVTH182502A, SN74LVTH18502A, SN74LVTH182502A
3.3-V ABT SCAN TEST DEVICES
WITH 18-BIT UNIVERSAL BUS TRANSCEIVERS
SCBS668B – JULY 1996 – REVISED MARCH 1999
data register description
boundary-scan register
The boundary-scan register (BSR) is 48 bits long. It contains one boundary-scan cell (BSC) for each
normal-function input pin and one BSC for each normal-function I/O pin (one single cell for both input data and
output data). The BSR is used 1) to store test data that is to be applied externally to the device output pins,
and/or 2) to capture data that appears internally at the outputs of the normal on-chip logic and/or externally at
the device input pins.
The source of data to be captured into the BSR during Capture-DR is determined by the current instruction. The
contents of the BSR can change during Run-Test/Idle as determined by the current instruction. At power up or
in T est-Logic-Reset, BSCs 47–44 are reset to logic 1, ensuring that these cells, which control A-port and B-port
outputs are set to benign values (i.e., if test mode were invoked, the outputs would be at the high-impedance
state). Reset values of other BSCs should be considered indeterminate.
The BSR order of scan is from TDI through bits 47–0 to TDO. T able 1 shows the BSR bits and their associated
device pin signals.
Table 1. Boundary-Scan Register Configuration
BSR BIT
NUMBER
47 2OEAB 35 2A9-I/O 17 2B9-I/O
46 1OEAB 34 2A8-I/O 16 2B8-I/O
45 2OEBA 33 2A7-I/O 15 2B7-I/O
44 1OEBA 32 2A6-I/O 14 2B6-I/O
43 2CLKAB 31 2A5-I/O 13 2B5-I/O
42 1CLKAB 30 2A4-I/O 12 2B4-I/O
41 2CLKBA 29 2A3-I/O 11 2B3-I/O
40 1CLKBA 28 2A2-I/O 10 2B2-I/O
39 2LEAB 27 2A1-I/O 9 2B1-I/O
38 1LEAB 26 1A9-I/O 8 1B9-I/O
37 2LEBA 25 1A8-I/O 7 1B8-I/O
36 1LEBA 24 1A7-I/O 6 1B7-I/O
–– –– 23 1A6-I/O 5 1B6-I/O
–– –– 22 1A5-I/O 4 1B5-I/O
–– –– 21 1A4-I/O 3 1B4-I/O
–– –– 20 1A3-I/O 2 1B3-I/O
–– –– 19 1A2-I/O 1 1B2-I/O
–– –– 18 1A1-I/O 0 1B1-I/O
DEVICE
SIGNAL
BSR BIT
NUMBER
DEVICE
SIGNAL
BSR BIT
NUMBER
DEVICE
SIGNAL
10
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
SN54LVTH18502A, SN54LVTH182502A, SN74LVTH18502A, SN74LVTH182502A
3.3-V ABT SCAN TEST DEVICES
WITH 18-BIT UNIVERSAL BUS TRANSCEIVERS
SCBS668B – JULY 1996 – REVISED MARCH 1999
boundary-control register
The boundary-control register (BCR) is three bits long. The BCR is used in the context of the boundary-run test
(RUNT) instruction to implement additional test operations not included in the basic SCOPE instruction set.
Such operations include PRPG, PSA, and binary count up (COUNT). Table 4 shows the test operations that
are decoded by the BCR.
During Capture-DR, the contents of the BCR are not changed. At power up or in Test-Logic-Reset, the BCR is
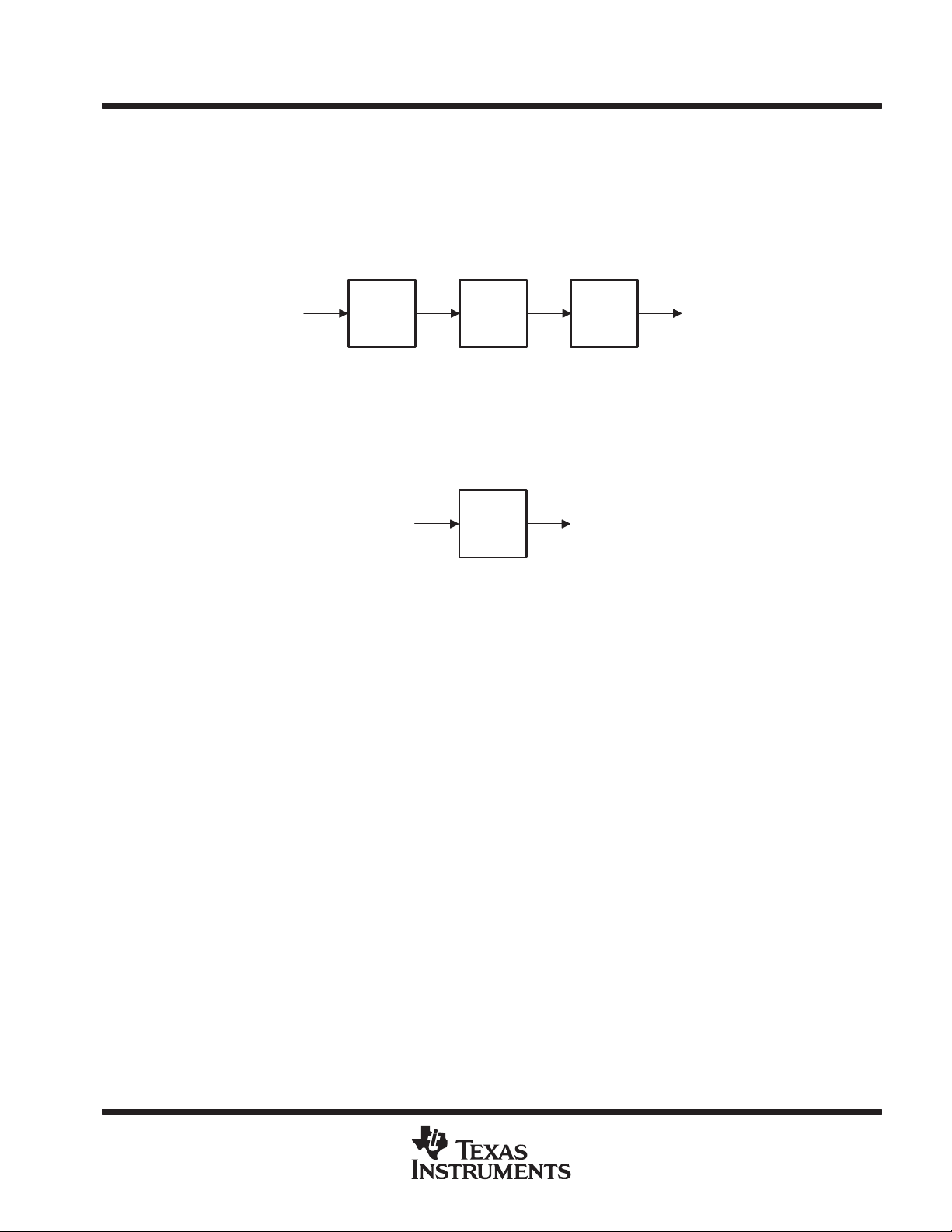
reset to the binary value 010, which selects the PSA test operation. The BCR order of scan is shown in Figure 3.
Bit 2
(MSB)
Bit 1
Bit 0
(LSB)
TDOTDI
Figure 3. Boundary-Control Register Order of Scan
bypass register
The bypass register is a 1-bit scan path that can be selected to shorten the length of the system scan path,
reducing the number of bits per test pattern that must be applied to complete a test operation. During
Capture-DR, the bypass register captures a logic 0. The bypass register order of scan is shown in Figure 4.
Bit 0
TDOTDI
Figure 4. Bypass Register Order of Scan
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
11
 Loading...
Loading...