Page 1
SN74GTLPH1655
16-BIT LVTTL-TO-GTL+ ADJUSTABLE-EDGE-RATE
UNIVERSAL BUS TRANSCEIVER
SCES294 – OCTOBER 1999
D
UBT
(Universal Bus Transceiver)
Combines D-Type Latches and D-Type
Flip-Flops for Operation in Transparent,
Latched, or Clocked Mode
D
Bidirectional Interface Between GTL+
Signal Levels and LVTTL Logic Levels
D
Partitioned as Two 8-Bit Transceivers With
Individual Latch Timing and Output Control
but With a Common Clock
D
LVTTL Interfaces Are 5-V Tolerant
D
High-Drive GTL+ Outputs (100 mA)
D
LVTTL Outputs (–24 mA/24 mA)
D
Variable Edge-Rate Control (ERC) Input
Selects GTL+ Rise and Fall Times for
Optimal Data-Transfer Rate and Signal
Integrity
D
I
, Power-Up 3-State, and BIAS V
off
Support Live Insertion
D
Bus Hold on A-Port Data Inputs
D
Distributed VCC and GND-Pin Configuration
Minimizes High-Speed Switching Noise
D
Package Option Includes Plastic Thin
Shrink Small-Outline Package
description
The SN74GTLPH1655 is a high-drive 16-bit
universal bus transceiver (UBT) that provides
LVTTL-to-GTL+ and GTL+-to-LVTTL signal-level
translation. It is partitioned as two 8-bit
transceivers and allows for transparent, latched,
and clocked modes of data transfer similar to the
’16501 function. The device provides a
high-speed interface between cards operating at
LVTTL logic levels and a backplane operating at
GTL+ signal levels. High-speed (about two times
faster than standard LVTTL or TTL) backplane
operation is a direct result of GTLP’s reduced
output swing (<1 V), reduced input threshold
levels, improved differential input, and output
edge control (OEC). Improved GTLP OEC
circuits minimize bus settling time and have been
designed and tested using several backplane
models. The high drive is suitable for driving
double-terminated low-impedance backplanes
using incident-wave switching.
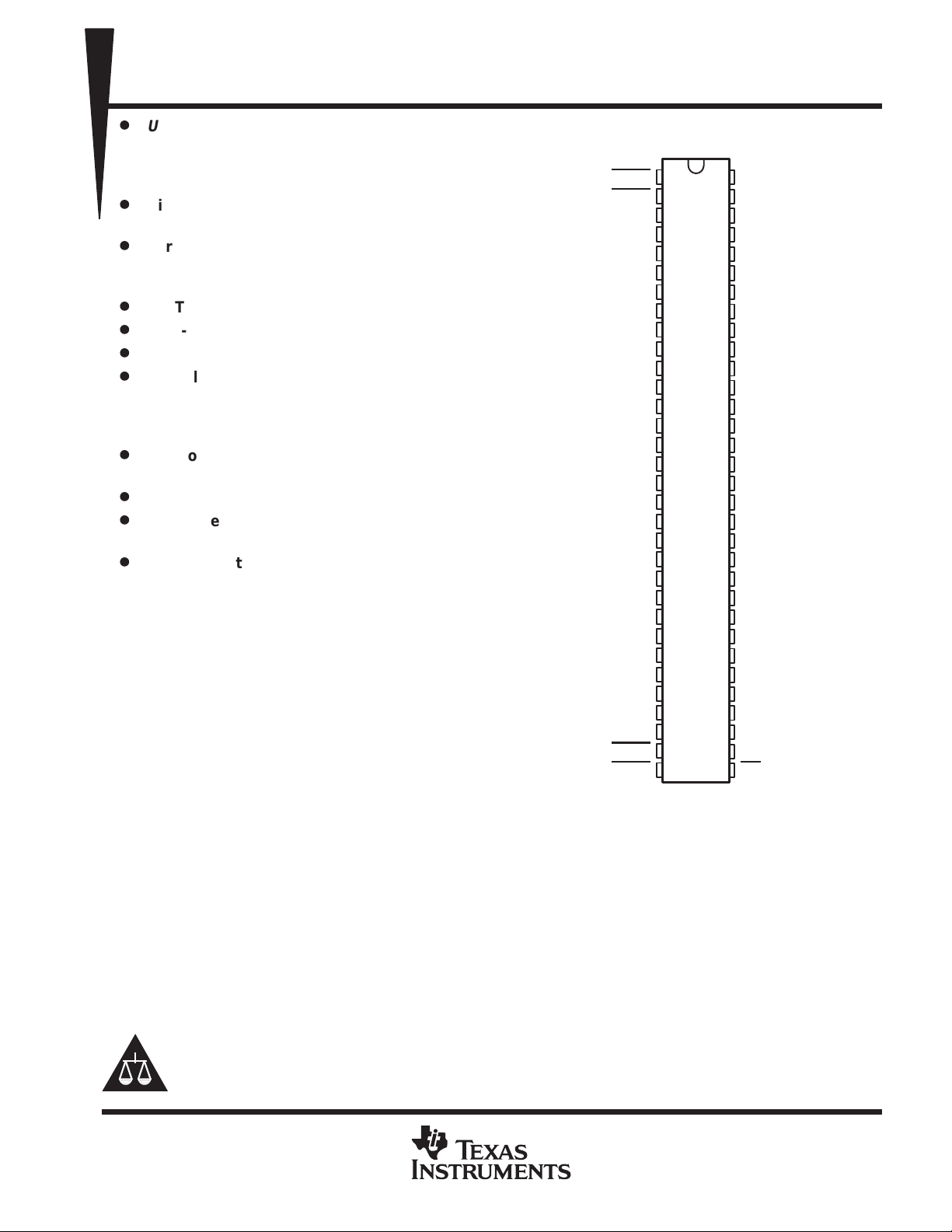
CC
1OEAB
1OEBA
V
CC
1A1
GND
1A2
1A3
GND
1A4
GND
1A5
GND
1A6
1A7
V
CC
1A8
2A1
GND
2A2
2A3
GND
2A4
2A5
GND
2A6
GND
2A7
V
CC
2A8
GND
2OEAB
2OEBA
DGG PACKAGE
(TOP VIEW)
1
64
2
63
3
62
4
61
5
60
6
59
7
58
8
57
9
56
10
55
11
54
12
53
13
52
14
51
15
50
16
49
17
48
18
47
19
46
20
45
21
44
22
43
23
42
24
41
25
40
26
39
27
38
28
37
29
36
30
35
31
34
32
33
CLK
1LEAB
1LEBA
ERC
GND
1B1
1B2
GND
1B3
1B4
1B5
GND
1B6
1B7
V
CC
1B8
2B1
GND
2B2
2B3
GND
2B4
2B5
V
REF
2B6
GND
2B7
2B8
BIAS V
2LEAB
2LEBA
OE
CC
PRODUCT PREVIEW
Please be aware that an important notice concerning availability, standard warranty, and use in critical applications of
Texas Instruments semiconductor products and disclaimers thereto appears at the end of this data sheet.
OEC and UBT are trademarks of Texas Instruments Incorporated.
PRODUCT PREVIEW information concerns products in the formative or
design phase of development. Characteristic data and other
specifications are design goals. Texas Instruments reserves the right to
change or discontinue these products without notice.
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
Copyright 1999, Texas Instruments Incorporated
1
Page 2
SN74GTLPH1655
16-BIT LVTTL-TO-GTL+ ADJUSTABLE-EDGE-RATE
UNIVERSAL BUS TRANSCEIVER
SCES294 – OCTOBER 1999
description (continued)
GTL+ is the Texas Instruments derivative of the Gunning transceiver logic (GTL) JEDEC standard JESD 8-3.
The AC specification of the SN74GTLPH1655 is given only at the preferred higher noise margin GTL+, but the
user has the flexibility of using this device at either GTL (VTT = 1.2 V and V
and V
= 1 V) signal levels.
REF
Normally, the B port operates at GTL or GTL+ levels, while the A-port and control inputs are compatible with
LVTTL logic levels and are 5-V tolerant. V
This device is fully specified for live-insertion applications using I
is the reference input voltage for the B port.
REF
, power-up 3-state, and BIAS VCC. The I
off
circuitry disables the outputs, preventing damaging current backflow through the device when it is powered
down. The power-up 3-state circuitry places the outputs in the high-impedance state during power up and power
down, which prevents driver conflict. The BIAS VCC circuitry precharges and preconditions the B-port
input/output connections, preventing disturbance of active data on the backplane during card insertion or
removal, and permits true live-insertion capability.
High-drive GTLP backplane interface devices feature adjustable edge-rate control (ERC). Changing the ERC
input voltage between GND and VCC adjusts the B-port output rise and fall times. This allows the designer to
optimize system data-transfer rate and signal integrity to the backplane load.
Active bus-hold circuitry holds unused or undriven L VTTL inputs at a valid logic state. Use of pullup or pulldown
resistors with the bus-hold circuitry is not recommended.
= 0.8 V) or GTL+ (VTT = 1.5 V
REF
off
When VCC is between 0 and 1.5 V , the device is in the high-impedance state during power up or power down.
However, to ensure the high-impedance state above 1.5 V, the output-enable (OE) input should be tied to V
through a pullup resistor; the minimum value of the resistor is determined by the current-sinking capability of
the driver.
The SN74GTLPH1655 is characterized for operation from –40°C to 85°C.
functional description
The SN74GTLPH1655 is a high-drive (100 mA) 16-bit UBT containing D-type latches and D-type flip-flops for
data-path operation in transparent, latched, or clocked modes and is similar to a ’16501 function. The device
is uniquely partitioned as two 8-bit transceivers with individual latch timing and output signals and a common
PRODUCT PREVIEW
clock for both transceiver words. It can replace any of the functions shown in Table 1.
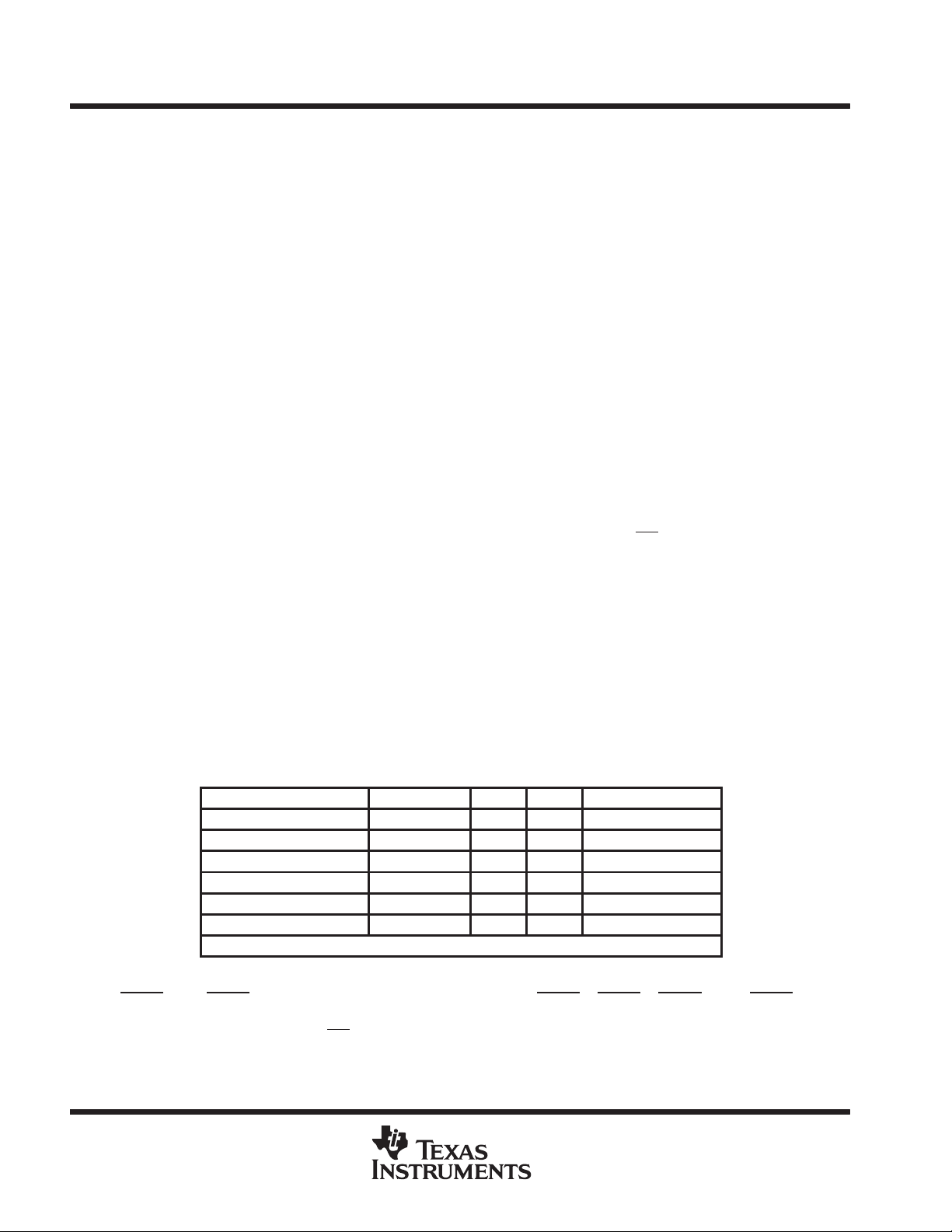
Table 1. SN74GTLPH1655 UBT Replacement Functions
FUNCTION 8 BIT 9 BIT 10 BIT 16 BIT
Transceiver ’245, ’623, ’645 ’863 ’861 ’16245, ’16623
Buffer/driver ’241, ’244, ’541 ’827 ’16241, ’16244, ’16541
Latched transceiver ’543 ’16543
Latch ’373, ’573 ’843 ’841 ’16373
Registered transceiver ’646, ’652 ’16646, ’16652
Flip-flop ’374, ’574 ’821 ’16374
CC
SN74GTLPH1655 UBT replaces all above functions
Data flow for each word is determined by the respective latch enables (xLEAB and xLEBA), output enables
(xOEAB
and xOEBA), and clock (CLK). The output enables (1OEAB, 1OEBA, 2OEAB, and 2OEBA) control
byte 1 and byte 2 data for the A-to-B and B-to-A directions, respectively. Note that CLK is common to both
directions and both 8-bit words. OE also is common and disables all I/O ports simultaneously.
2
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
Page 3
MODE
SN74GTLPH1655
16-BIT LVTTL-TO-GTL+ ADJUSTABLE-EDGE-RATE
UNIVERSAL BUS TRANSCEIVER
SCES294 – OCTOBER 1999
functional description (continued)
For A-to-B data flow, the devices operate in the transparent mode when LEAB is high. When LEAB transitions
low, the A data is latched independent of CLK high or low. If LEAB is low, the A data is registered on the CLK
low-to-high transition. When OEAB is low, the outputs are active. With OEAB high, the outputs are in the
high-impedance state.
Data flow for the B-to-A direction is identical, but uses OEBA
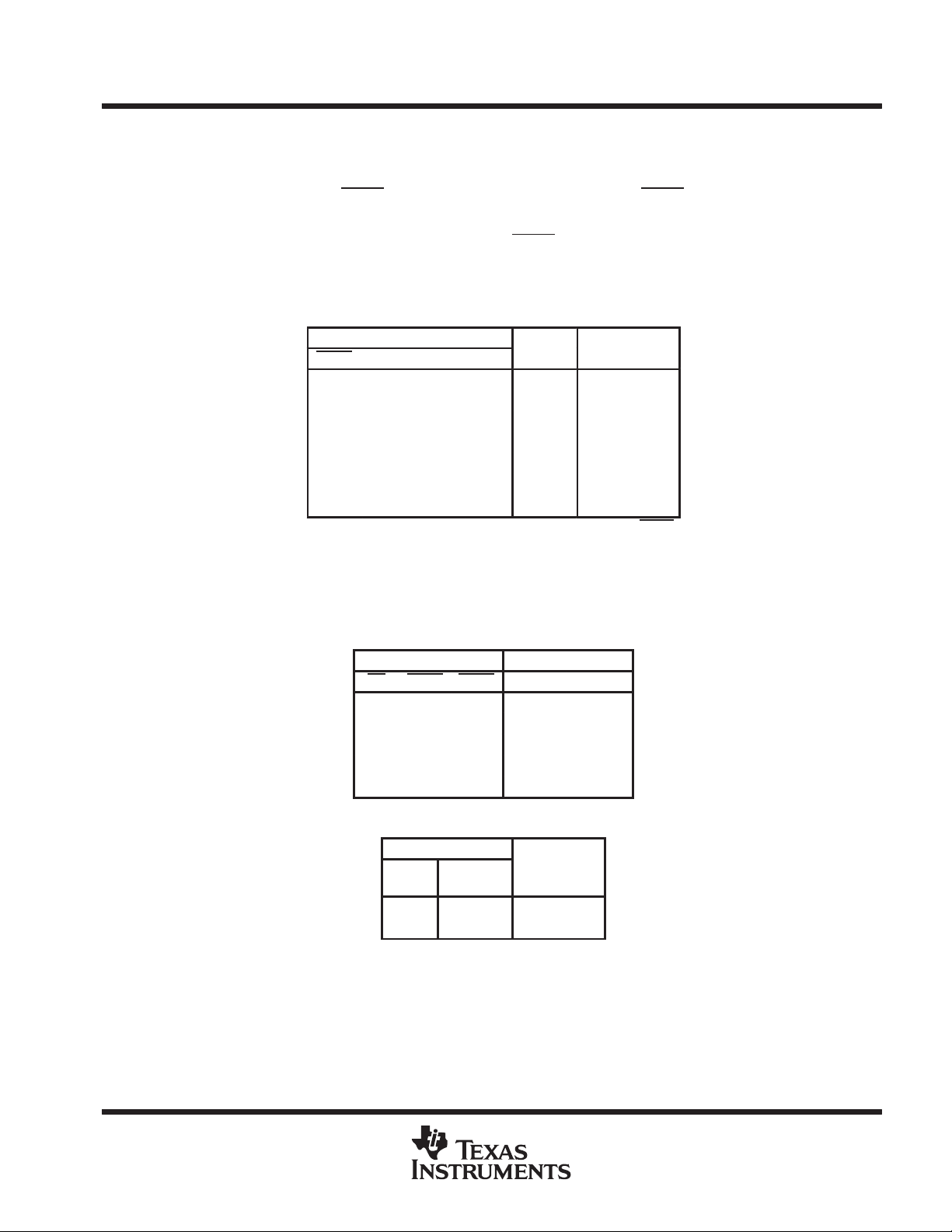
Function Tables
FUNCTION
INPUTS
OEAB LEAB CLK A
H X X X Z Isolation
L HXL L Transparent
L HXH H Transparent
L L ↑ LLRegistered
L L ↑ HH Registered
L LHXB
L L L X B
†
A-to-B data flow is shown. B-to-A flow is similar but uses OEBA,
LEBA, and CLK.
‡
Output level before the indicated steady-state input conditions were
established, provided that CLK was high before LEAB went low
§
Output level before the indicated steady-state input conditions were
established
OUTPUT ENABLE
INPUTS
OE OEAB OEBA A PORT B PORT
L L L Active Active
L LH ZActive
L H L Active Z
L HH Z Z
H X X Z Z
†
OUTPUT
B
0
0
OUTPUTS
, LEBA, and CLK.
‡
Previous state
§
Previous state
PRODUCT PREVIEW
B-PORT EDGE-RATE CONTROL (ERC)
INPUT ERC
LOGIC
LEVEL
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
NOMINAL
VOLTAGE
H V
L GND Fast
CC
OUTPUT
B-PORT
EDGE RATE
Slow
3
Page 4
SN74GTLPH1655
16-BIT LVTTL-TO-GTL+ ADJUSTABLE-EDGE-RATE
UNIVERSAL BUS TRANSCEIVER
SCES294 – OCTOBER 1999
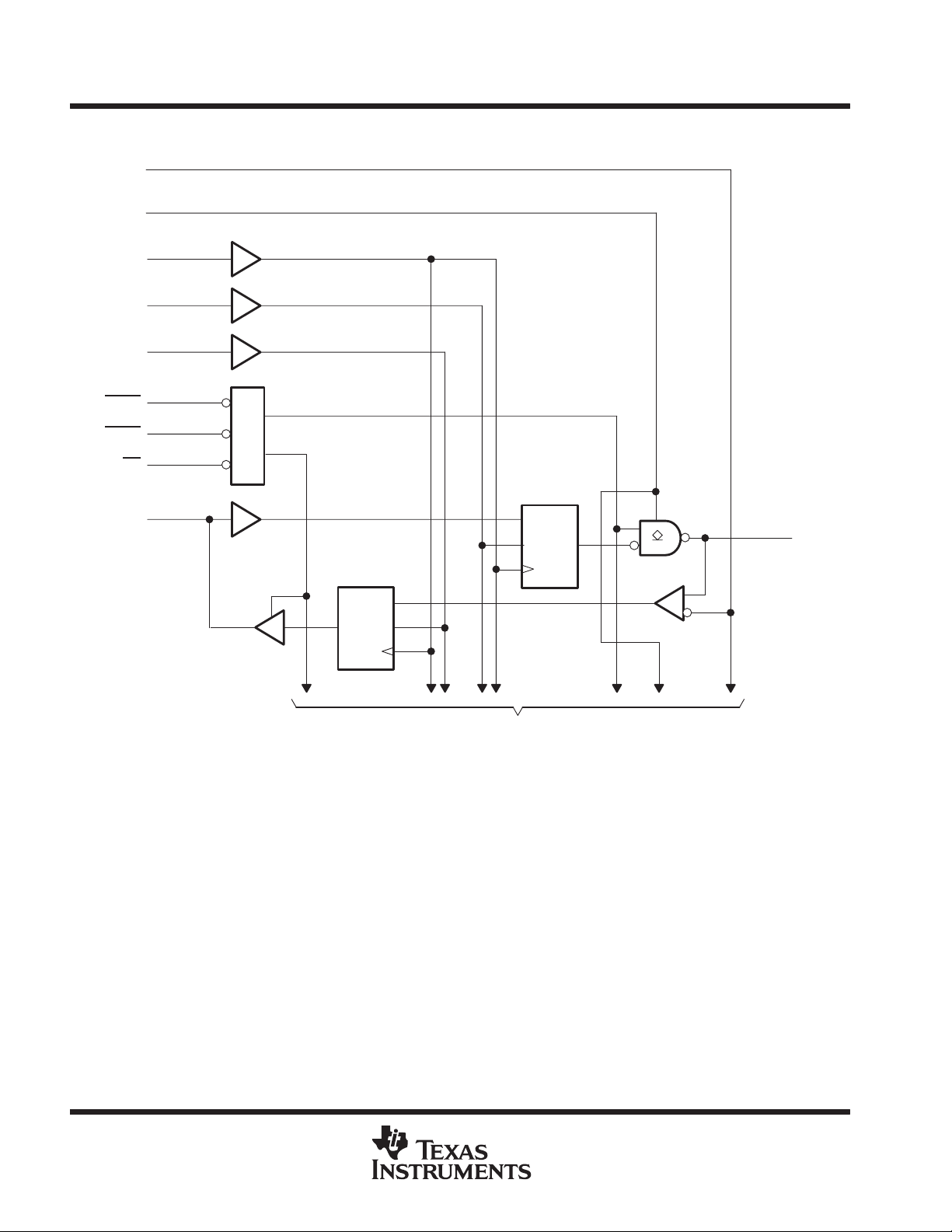
logic diagram (positive logic)
V
REF
ERC
CLK
1LEAB
1LEBA
1OEBA
1OEAB
OE
1A1
41
61
64
63
62
2
1
33
4
CLK
1D
C1
1D
C1
CLK
59
1B1
PRODUCT PREVIEW
To Seven Other Channels
4
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
Page 5

logic diagram (positive logic) (continued)
SN74GTLPH1655
16-BIT LVTTL-TO-GTL+ ADJUSTABLE-EDGE-RATE
UNIVERSAL BUS TRANSCEIVER
SCES294 – OCTOBER 1999
V
REF
ERC
CLK
2LEAB
2LEBA
2OEBA
2OEAB
OE
2A1
41
61
64
35
34
32
31
33
17
CLK
1D
C1
1D
C1
CLK
48
2B1
To Seven Other Channels
PRODUCT PREVIEW
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
5
Page 6

SN74GTLPH1655
16-BIT LVTTL-TO-GTL+ ADJUSTABLE-EDGE-RATE
UNIVERSAL BUS TRANSCEIVER
SCES294 – OCTOBER 1999
absolute maximum ratings over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)
Supply voltage range, VCC and BIAS VCC –0.5 V to 4.6 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Input voltage range, VI (see Note 1):A-port and control inputs –0.5 V to 7 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
B port, ERC, and V
Voltage range applied to any output in the high-impedance or power-off state, V
(see Note 1):A port –0.5 V to 7 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
B port –0.5 V to 4.6 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Voltage range applied to any output in the high or low state, V
(see Note 1):A port –0.5 V to VCC + 0.5 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
B port –0.5 V to 4.6 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Current into any output in the low state, IO: A port 48 mA. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
B port 200 mA. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Current into any A-port output in the high state, I
(see Note 2) 48 mA. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
O
Continuous current through each VCC or GND ±100 mA. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Input clamp current, I
Output clamp current, I
(V
< 0) –50 mA. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
IK
I
(V
< 0) –50 mA. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
OK
O
Package thermal impedance, θJA (see Note 3) 55°C/W. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Storage temperature range, T
†
Stresses beyond those listed under “absolute maximum ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and
functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under “recommended operating conditions” is not
implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
NOTES: 1. The input and output negative-voltage ratings may be exceeded if the input and output clamp-current ratings are observed.
2. This current flows only when the output is in the high state and VO > VCC.
3. The package thermal impedance is calculated in accordance with JESD 51.
–65°C to 150°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
stg
–0.5 V to 4.6 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
REF
O
O
†
PRODUCT PREVIEW
6
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
Page 7

VTTTermination voltage
V
V
Suppl
oltage
V
VIInput voltage
V
IOLLow-level output current
mA
SN74GTLPH1655
16-BIT LVTTL-TO-GTL+ ADJUSTABLE-EDGE-RATE
UNIVERSAL BUS TRANSCEIVER
SCES294 – OCTOBER 1999
recommended operating conditions (see Notes 4 through 6)
MIN NOM MAX UNIT
VCC,
BIAS V
REF
V
IH
V
IL
I
IK
I
OH
T
A
NOTES: 4. All unused control and B-port inputs of the device must be held at VCC or GND to ensure proper device operation. Refer to the TI
Supply voltage 3.15 3.3 3.45 V
CC
GTL 1.14 1.2 1.26
GTL+ 1.35 1.5 1.65
pp
y v
p
High-level input voltage
Low-level input voltage
Input clamp current –18 mA
High-level output current A port –24 mA
p
Operating free-air temperature –40 85 °C
application report,
5. Normal connection sequence is GND first, BIAS VCC = 3.3 V second, and VCC = 3.3 V , I/O, control inputs, VTT and V
last. However, if the B-port I/O precharge is not required, the acceptable connection sequence is GND first and VCC = 3.3 V,
BIAS VCC = 3.3 V , I/O, control inputs, VTT and V
6. VTT and RTT can be adjusted to accommodate backplane impedances as long as they do not exceed the DC absolute IOL ratings.
Similarly , V
Implications of Slow or Floating CMOS Inputs
can be adjusted to optimize noise margins, but normally is 2/3 VTT.
REF
GTL 0.74 0.8 0.87
GTL+ 0.87 1 1.1
B port V
Except B port V
B port V
ERC
Except B port and ERC 2
B port V
ERC
Except B port and ERC 0.8
A port 24
B port 100
, literature number SCBA004.
(any order) last. When VCC is connected, the BIAS VCC circuitry is disabled.
REF
+0.05
REF
VCC–0.6 V
CC
GND 0.6
REF
TT
CC
–0.05
REF
V
V
(any order)
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
PRODUCT PREVIEW
7
Page 8

SN74GTLPH1655
V
3.15 V
V
V
V
V
‡
V
3.45 V
V
CC
I
O
C
pF
16-BIT LVTTL-TO-GTL+ ADJUSTABLE-EDGE-RATE
UNIVERSAL BUS TRANSCEIVER
SCES294 – OCTOBER 1999
electrical characteristics over recommended operating free-air temperature range for GTL+
(unless otherwise noted)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP†MAX UNIT
V
IK
V
OH
OL
I
I
I
BHL
I
BHH
I
BHLO
I
BHHO
I
CC
∆I
CC
C
i
io
†
All typical values are at VCC = 3.3 V, TA = 25°C.
‡
For I/O ports, the parameter II includes the off-state output leakage current.
§
PRODUCT PREVIEW
The bus-hold circuit can sink at least the minimum low sustaining current at VILmax. I
then raising it to VILmax.
¶
The bus-hold circuit can source at least the minimum high sustaining current at VIHmin. I
then lowering it to VIHmin.
#
An external driver must source at least I
||
An external driver must sink at least I
k
This is the increase in supply current for each input that is at the specified TTL voltage level rather than VCC or GND.
A port
A port
B port VCC = 3.15 V
B port
A-port and
control inputs
§
A port VCC = 3.15 V, VI = 0.8 V 75 µA
¶
A port VCC = 3.15 V, VI = 2 V –75 µA
#
A port VCC = 3.45 V, VI = 0 to V
||
A port VCC = 3.45 V, VI = 0 to V
A or B port
k
Control inputs VI = 3.15 V or 0 pF
A port VO = 3.15 V or 0
B port VO = 1.5 V or 0
VCC = 3.15 V, II = –18 mA –1.2 V
VCC = 3.15 V to 3.45 V, IOH = –100 µA VCC–0.2
=
CC
VCC = 3.15 V to 3.45 V, IOL = 100 µA 0.2
= 3.15
CC
VCC = 3.45 V, VI = 0 to 1.5 V ±10
=
CC
=
= 3.45 V,
VI (A-port or control input) = VCC or GND
VI (B port) = VTT or GND
VCC = 3.45 V, One A-port or control input at VCC – 0.6 V,
Other A-port or control inputs at VCC or GND
BHLO
BHHO
=
= 0,
to switch this node from low to high.
to switch this node from high to low.
IOH = –12 mA 2.4
IOH = –24 mA 2
IOL = 12 mA 0.4
IOL = 24 mA 0.5
IOL = 10 mA 0.2
IOL = 64 mA 0.4
IOL = 100 mA 0.55
VI = 0 or V
VI = 5.5 V ±20
Outputs high 40
Outputs low 40
Outputs disabled 40
CC
CC
CC
should be measured after lowering VIN to GND and
BHL
should be measured after raising VIN to VCC and
BHH
±10
500 µA
–500 µA
1.5 mA
V
µA
mA
p
live-insertion specifications for A port over recommended operating free-air temperature range
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN MAX UNIT
I
off
I
OZPU
I
OZPD
8
VCC = 0, BIAS VCC = 0, VI or VO = 0 to 5.5 V 100 µA
VCC = 0 to 1.5 V, VO = 0.5 V to 3 V, OE = 0 ±100 µA
VCC = 1.5 V to 0, VO = 0.5 V to 3 V, OE = 0 ±100 µA
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
Page 9

I
(BIAS VCC)
BIAS V
V
port)
V
twPulse duration
ns
tsuSetup time
ns
thHold time
ns
SN74GTLPH1655
16-BIT LVTTL-TO-GTL+ ADJUSTABLE-EDGE-RATE
UNIVERSAL BUS TRANSCEIVER
SCES294 – OCTOBER 1999
live-insertion specifications for B port over recommended operating free-air temperature range
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN MAX UNIT
I
off
I
OZPU
I
OZPD
CC
V
O
I
O
timing requirements over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air
temperature, V
f
clock
Clock frequency MHz
VCC = 0, BIAS VCC = 0, VI or VO = 0 to 1.5 V 100 µA
VCC = 0 to 1.5 V, VO = 0.5 V to 1.5 V, OE = 0 ±100 µA
VCC = 1.5 V to 0, VO = 0.5 V to 1.5 V, OE = 0 ±100 µA
VCC = 0 to 3.15 V
VCC = 3.15 V to 3.45 V
VCC = 0, BIAS VCC = 3.3 V 0.95 1.05 V
VCC = 0, BIAS VCC = 3.15 V to 3.45 V, VO (B port) = 0.6 V –1 µA
= 1.5 V and V
TT
p
= 1 V for GTL+ (unless otherwise noted)
REF
= 3.15 V to 3.45 V,
CC
LEAB or LEBA high
CLK high or low
A before CLK
B before CLK
A before LEAB↓, CLK = don’t care
B before LEBA↓, CLK = don’t care
A after CLK
B after CLK
A after LEAB↓, CLK = don’t care
B after LEBA↓, CLK = don’t care
p
(B
O
= 0 to 1.5
MIN MAX UNIT
5 mA
10 µA
PRODUCT PREVIEW
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
9
Page 10

SN74GTLPH1655
A
B
tpdLEAB
B
ns
CLK
B
OE
B
Slo
ns
OE
B
Fast
ns
OEAB
B
Slo
ns
OEAB
B
Fast
ns
t
,
ns
t
,
ns
OE
A
ns
OEBA
A
ns
16-BIT LVTTL-TO-GTL+ ADJUSTABLE-EDGE-RATE
UNIVERSAL BUS TRANSCEIVER
SCES294 – OCTOBER 1999
switching characteristics over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air
temperature, V
PARAMETER
f
max
t
en
t
dis
t
en
t
dis
t
en
t
dis
t
en
t
dis
r
f
t
pd
t
en
t
dis
t
en
t
PRODUCT PREVIEW
†
Slow (ERC = VCC) and Fast (ERC = GND)
‡
All typical values are at VCC = 3.3 V, TA = 25°C.
dis
= 1.5 V and V
TT
REF
FROM
(INPUT)
Rise time, B outputs
(0.6 V to 1.3 V)
Fall time, B outputs
(1.3 V to 0.6 V)
B
LEBA
CLK
= 1 V for GTL+ (see Figure 1)
TO
(OUTPUT)
A ns
EDGE RATE
Slow
Fast
Slow
Fast
Slow
Fast
Slow
Fast
Slow
Fast
†
w
w
MIN TYP‡MAX UNIT
MHz
10
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
Page 11

SN74GTLPH1655
16-BIT LVTTL-TO-GTL+ ADJUSTABLE-EDGE-RATE
UNIVERSAL BUS TRANSCEIVER
SCES294 – OCTOBER 1999
PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION
From Output
Under Test
CL = 50 pF
(see Note A)
LOAD CIRCUIT FOR A OUTPUTS
Input
Input
t
PLH
Output
Input
t
PLH
Output
500 Ω
500 Ω
t
w
1.5 V 1.5 V
VOLTAGE WAVEFORMS
PULSE DURATION
1.5 V 1.5 V
1 V 1 V
VOLTAGE WAVEFORMS
PROPAGATION DELAY TIMES
(A port to B port)
1 V 1 V
1.5 V 1.5 V
VOLTAGE WAVEFORMS
PROPAGATION DELAY TIMES
(B port to A port)
S1
6 V
GND
t
PHL
t
PHL
Open
3 V
0 V
3 V
0 V
V
V
1.5 V
0 V
V
V
OH
OL
OH
OL
TEST
t
PLH/tPHL
t
PLZ/tPZL
t
PHZ/tPZH
Timing
Waveform 1
(see Note B)
Waveform 2
S1 at GND
(see Note B)
S1
Open
6 V
GND
Input
Data
Input
(VM = 1.5 V for A port and 1 V for B port)
(VH = 3 V for A port and 1.5 V for B port)
Output
Control
Output
S1 at 6 V
Output
V
M
VOLTAGE WAVEFORMS
SETUP AND HOLD TIMES
t
PZL
t
PZH
VOLTAGE WAVEFORMS
ENABLE AND DISABLE TIMES
From Output
Under Test
LOAD CIRCUIT FOR B OUTPUTS
1.5 V
t
su
1.5 V 1.5 V
1.5 V
1.5 V
(A port)
12.5 Ω
CL = 30 pF
(see Note A)
t
h
V
M
VOL + 0.3 V
VOH – 0.3 V
1.5 V
t
PLZ
t
PHZ
Test
Point
3 V
0 V
V
H
0 V
3 V
0 V
3 V
V
OL
V
OH
≈0 V
PRODUCT PREVIEW
NOTES: A. CL includes probe and jig capacitance.
B. Waveform 1 is for an output with internal conditions such that the output is low except when disabled by the output control.
Waveform 2 is for an output with internal conditions such that the output is high except when disabled by the output control.
C. All input pulses are supplied by generators having the following characteristics: PRR ≤ 10 MHz, ZO = 50 Ω, slew rate ≤ 1 V/ns.
D. The outputs are measured one at a time with one transition per measurement.
Figure 1. Load Circuits and Voltage Waveforms
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
11
Page 12

SN74GTLPH1655
A
B
tpdLEAB
B
ns
CLK
B
OE
B
Slo
ns
OE
B
Fast
ns
OEAB
B
Slo
ns
OEAB
B
Fast
ns
t
,
ns
t
ns
16-BIT LVTTL-TO-GTL+ ADJUSTABLE-EDGE-RATE
UNIVERSAL BUS TRANSCEIVER
SCES294 – OCTOBER 1999
DISTRIBUTED-LOAD BACKPLANE SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS
This data sheet is specified for and tested to the lump load shown in Figure 1. However, the designer probably uses
this GTLP device in a distributed load like that shown in Figure 2, in which actual B-port backplane switching
characteristics are different. Therefore, the device is modeled as shown in Figure 3, which very closely matches the
results obtained using Figure 2. Switching characteristics based on Figure 3 more closely match actual backplane
design requirements.
V
TT
TT
.25” .875”
R
.625” .625”
1” 1”
Figure 2. Test Backplane Model
.875” .25”
.625”.625”
Conn.
Drvr
Slot 1 Slot 2 Slot 15 Slot 16
Conn. Conn. Conn.
1”1”
Rcvr
Rcvr
Rcvr
V
TT
TT
R
1.5 V
14 Ω
Test
Point
CL = 13 pF
From Output
Under Test
LL = 21 nH
Figure 3. Distributed-Load Circuit for B Outputs
switching characteristics over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air
temperature, V
PARAMETER
f
max
PRODUCT PREVIEW
t
en
t
dis
t
en
t
dis
t
en
t
dis
t
en
t
dis
r
f
†
Slow (ERC = VCC) and Fast (ERC = GND)
‡
All typical values are at VCC = 3.3 V, TA = 25°C.
= 1.5 V and V
TT
REF
FROM
(INPUT)
Rise time, B outputs
(0.6 V to 1.3 V)
Fall time, B outputs
(1.3 V to 0.6 V)
= 1 V for GTL+ (see Figure 3)
TO
(OUTPUT)
EDGE RATE
Slow
Fast
Slow
Fast
Slow
Fast
Slow
Fast
Slow
Fast
†
w
w
MIN TYP‡MAX UNIT
MHz
12
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
Page 13

IMPORTANT NOTICE
T exas Instruments and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make changes to their products or to discontinue
any product or service without notice, and advise customers to obtain the latest version of relevant information
to verify, before placing orders, that information being relied on is current and complete. All products are sold
subject to the terms and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgement, including those
pertaining to warranty, patent infringement, and limitation of liability.
TI warrants performance of its semiconductor products to the specifications applicable at the time of sale in
accordance with TI’s standard warranty. Testing and other quality control techniques are utilized to the extent
TI deems necessary to support this warranty . Specific testing of all parameters of each device is not necessarily
performed, except those mandated by government requirements.
CERTAIN APPLICA TIONS USING SEMICONDUCT OR PRODUCTS MAY INVOLVE POTENTIAL RISKS OF
DEATH, PERSONAL INJURY, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE (“CRITICAL
APPLICATIONS”). TI SEMICONDUCTOR PRODUCTS ARE NOT DESIGNED, AUTHORIZED, OR
WARRANTED TO BE SUITABLE FOR USE IN LIFE-SUPPORT DEVICES OR SYSTEMS OR OTHER
CRITICAL APPLICA TIONS. INCLUSION OF TI PRODUCTS IN SUCH APPLICATIONS IS UNDERST OOD TO
BE FULLY AT THE CUSTOMER’S RISK.
In order to minimize risks associated with the customer’s applications, adequate design and operating
safeguards must be provided by the customer to minimize inherent or procedural hazards.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or customer product design. TI does not warrant or represent
that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any patent right, copyright, mask work right, or other
intellectual property right of TI covering or relating to any combination, machine, or process in which such
semiconductor products or services might be or are used. TI’s publication of information regarding any third
party’s products or services does not constitute TI’s approval, warranty or endorsement thereof.
Copyright 1999, Texas Instruments Incorporated
 Loading...
Loading...