Datasheet SMJ4C1024-10FQ, SMJ4C1024-10HJ, SMJ4C1024-10HK, SMJ4C1024-10HL, SMJ4C1024-10JD Datasheet (Texas Instruments)
...Page 1
SMJ4C1024
1048576 BY 1-BIT
DYNAMIC RANDOM-ACCESS MEMORY
SGMS023E – DECEMBER 1988 – REVISED MARCH 1996
D
Organization...1048576 × 1-Bit
D
Processed to MIL-STD-883, Class B
D
Single 5-V Supply (10% Tolerance)
D
Performance Ranges:
ACCESS ACCESS ACCESS READ
TIME TIME TIME OR
t
a(R)
(t
RAC
(MAX) (MAX) (MAX) (MIN)
’4C1024-80 80 ns 20 ns 40 ns 150 ns
’4C1024-10 100 ns 25 ns 45 ns 190 ns
’4C1024-12 120 ns 30 ns 55 ns 220 ns
’4C1024-15 150 ns 40 ns 70 ns 260 ns
D
Enhanced Page-Mode Operation for Faster
t
a(C)ta(CA)
)(t
CAC
) (tAA) CYCLE
Memory Access
– Higher Data Bandwidth Than
Conventional Page Mode Parts
– Random Single-Bit Access Within a Row
With a Column Address
D
One of TI’s CMOS Megabit Dynamic
Random-Access Memory (DRAM) Family
Including SMJ44C256 — 256K × 4
Enhanced Page Mode
D
CAS-Before-RAS (CBR) Refresh
D
Long Refresh Period
512-Cycle Refresh in 8 ms (Max)
D
3-State Unlatched Output
D
Low Power Dissipation
D
All Inputs/Outputs and Clocks Are
TTL-Compatible
D
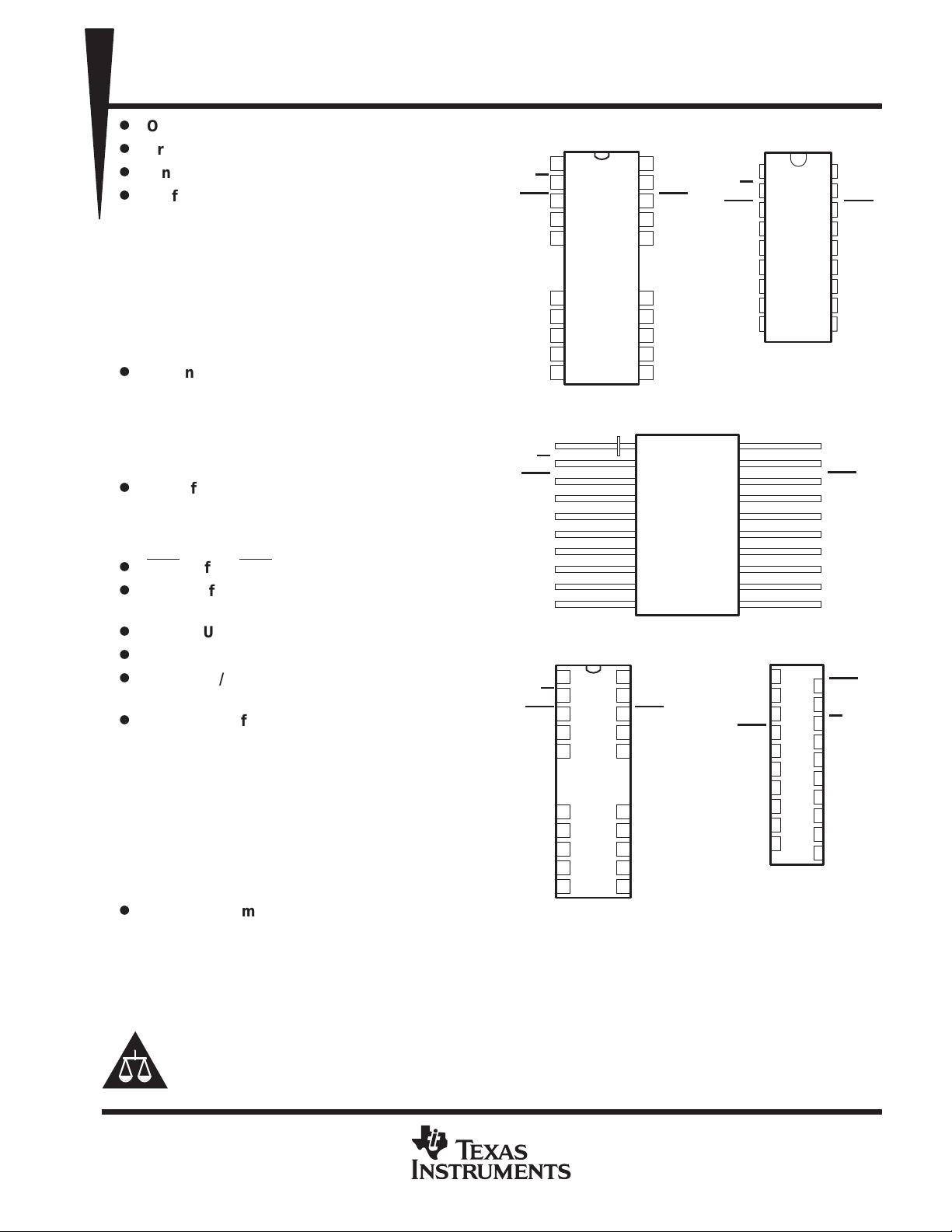
Packaging Offered:
– 20/26-Pin J-Leaded Ceramic Surface
Mount Package (HJ Suffix)
– 18-Pin 300-Mil Ceramic Dual-In-Line
Package (JD Suffix)
– 20-Pin Ceramic Flatpack (HK Suffix)
– 20/26-Terminal Leadless Ceramic
Surface Mount Package (FQ/HL Suffixes)
– 20-Pin Ceramic Zig-Zag In-Line Package
(SV Suffix)
D
Operating Temperature Range
– 55°C to 125°C
WRITE
HJ PACKAGE
(TOP VIEW)
D
1
2
W
RAS
V
TF
NC
A0
A1
A2
A3
CC
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
D
W
RAS
TF
NC
A0
A1
A2
A3
V
CC
FQ/HL PACKAGES
(TOP VIEW)
D
10
11
9
W
RAS
TF
NC
A0
A1
A2
A3
V
CC
12
8
13
7
14
6
15
5
16
4
17
3
18
2
19
1
20
V
20
19
Q
CAS
18
NC
17
16
A9
A8
15
A7
14
A6
13
A5
12
A4
11
HK PACKAGE
(TOP VIEW)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
V
SS
Q
CAS
NC
A9
A8
A7
A6
A5
A4
SS
RAS
V
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
D
W
TF
A0
A1
A2
A3
CC
A9
RAS
NC
A0
A2
V
CC
A5
A7
JD PACKAGE
(TOP VIEW)
1
18
2
17
3
16
4
15
5
14
6
13
7
12
8
11
9
10
SV PACKAGE
(SIDE VIEW)
1
3
5
7
9
11
13
15
17
19
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
20
Q
D
V
SS
Q
CAS
NC
A9
A8
A7
A6
A5
A4
CAS
V
SS
W
TF
NC
A1
A3
A4
A6
A8
V
SS
Q
CAS
A9
A8
A7
A6
A5
A4
Please be aware that an important notice concerning availability, standard warranty, and use in critical applications of
Texas Instruments semiconductor products and disclaimers thereto appears at the end of this data sheet.
PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date.
Products conform to specifications per the terms of Texas Instruments
standard warranty. Production processing does not necessarily include
testing of all parameters.
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251–1443
Copyright 1996, Texas Instruments Incorporated
1
Page 2

SMJ4C1024
1048576 BY 1-BIT
DYNAMIC RANDOM-ACCESS MEMORY
SGMS023E – DECEMBER 1988 – REVISED MARCH 1996
PIN NOMENCLATURE
A0–A9 Address Inputs
CAS
D Data In
NC No Internal Connection
Q Data Out
RAS
TF Test Function
V
CC
V
SS
W
description
The SMJ4C1024 is a 1048576-bit DRAM organized as 1048576 words of one bit each. It employs technology
for high performance, reliability, and low power at a low cost.
Column Address Strobe
Row Address Strobe
5-V Supply
Ground
Write Enable
This device features maximum RAS
access times of 80 ns, 100 ns, 120 ns, and 150 ns. Maximum power
dissipation is as low as 305 mW operating and 16.5 mW standby on 150-ns devices.
peaks are typIcally 140 mA and a –1 V input voltage undershoot can be tolerated, minimizing system noise.
I
DD
All inputs and outputs, including clocks, are compatible with series 54 TTL. All addresses and data-in lines are
latched on-chip to simplify system design. Data out is unlatched to allow greater system flexibility.
The SMJ4C1024 is offered in an 18-pin ceramic dual-in-line package (JD suffix), a 20 /26-terminal leadless
ceramic carrier package (FQ/HL suffixes), a 20/26-pin J-leaded carrier package (HJ suffix), a 20-pin flatpack
(HK suffix), and a 20-pin ceramic zig-zag in-line package (SV suffix). They are characterized for operation from
– 55°C to 125°C.
2
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251–1443
Page 3
SMJ4C1024
1048576 BY 1-BIT
DYNAMIC RANDOM-ACCESS MEMORY
SGMS023E – DECEMBER 1988 – REVISED MARCH 1996
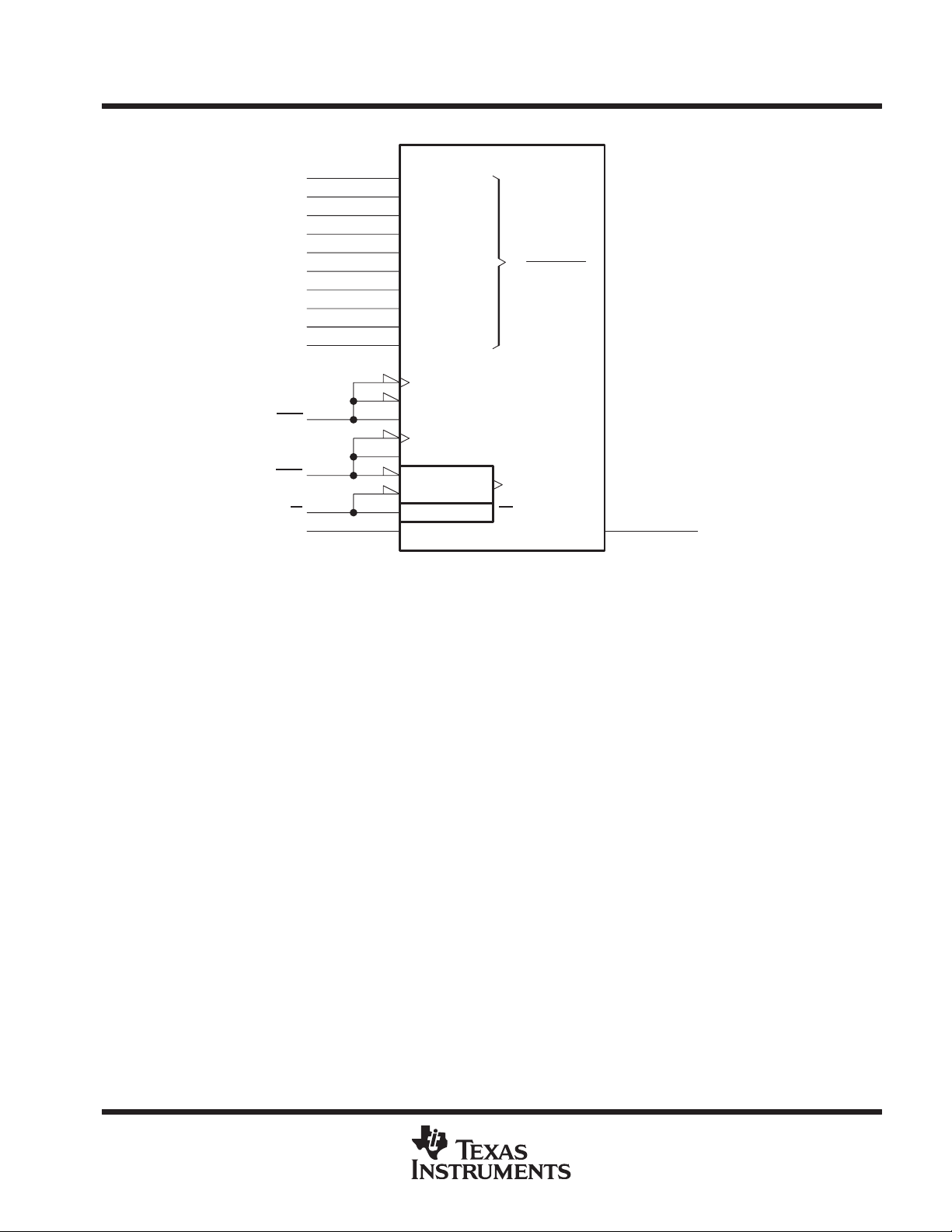
logic symbol
†
This symbol is in accordance with ANSI/IEEE Std. 91-1984 and IEC Publication 617-12.
The pin numbers shown are for the 18-pin JD package.
†
RAM 1024K × 1
&
A
1 048 575
23C22
EN
0
A0
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
RAS
CAS
W
5
6
7
8
10
11
12
13
14
15
3
16
2
1
D
20D10/21D0
20D19/21D9
C20 [ROW]
G23 [REFRESH ROW]
24 [PWR DWN]
C21 [COL]
G24
23,21D 24
A, 22D
A∇ Q
17
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251–1443
3
Page 4
SMJ4C1024
1048576 BY 1-BIT
DYNAMIC RANDOM-ACCESS MEMORY
SGMS023E – DECEMBER 1988 – REVISED MARCH 1996
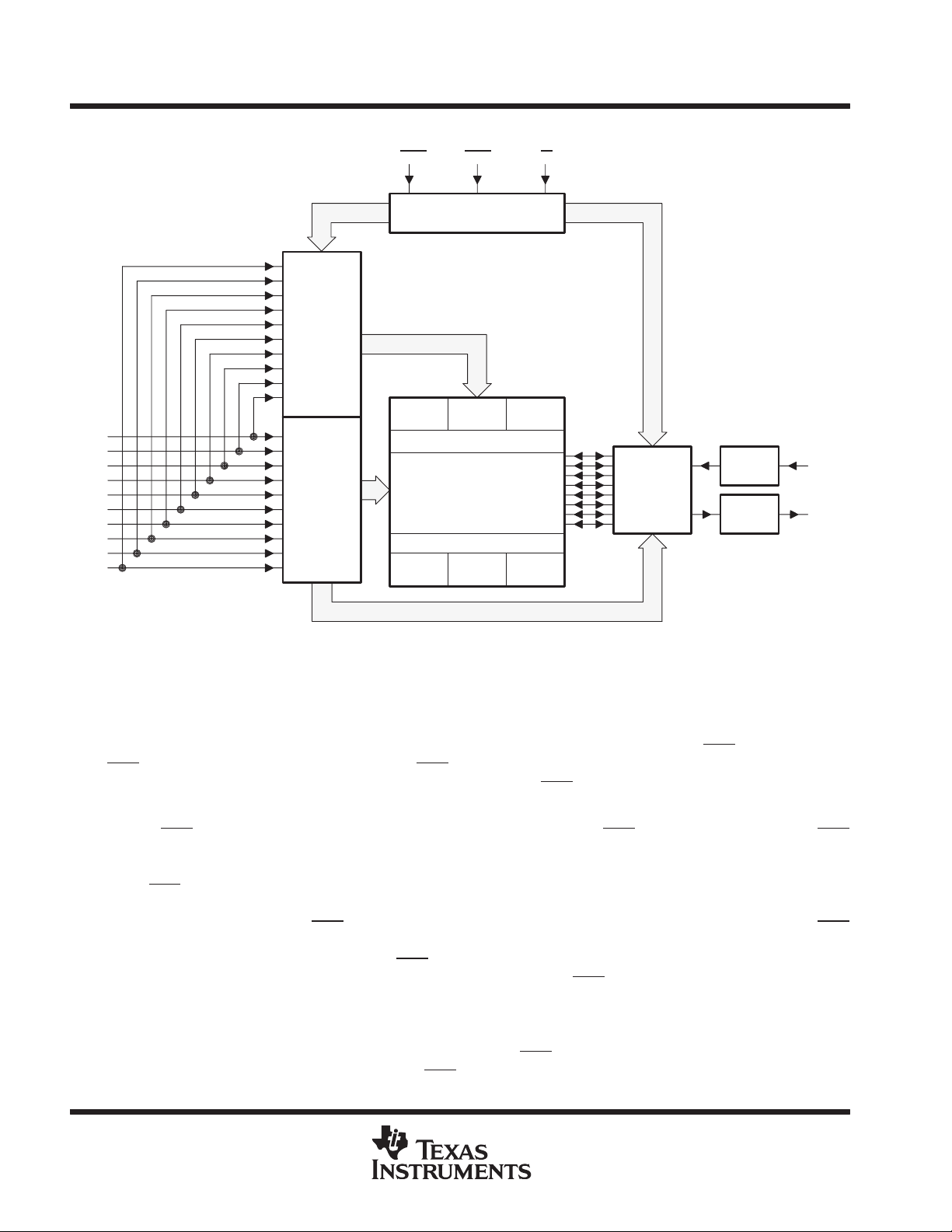
functional block diagram
Row
Address
Buffers
(10)
RAS CAS W
Timing and Control
A0
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
256K
Array
Column
Address
Buffers
(10)
256K
Array
Row
Decode
Sense Amplifiers
Column Decode
Sense Amplifiers
Row
Decode
256K
Array
256K
Array
I/O
Buffers
1 of 8
Selection
Data In
Reg.
Data
Out Reg.
operation
enhanced page mode
Enhanced page-mode operation allows faster memory access by keeping the same row address while selecting
random column addresses. The time for row-address setup and hold and for address multiplexing is eliminated.
The maximum number of columns that can be accessed is determined by the maximum RAS
CAS
page-cycle time used. With minimum CAS page-cycle time, all 1 024 columns specified by column
addresses A0 through A9 can be accessed without intervening RAS
cycles.
Unlike conventional page-mode DRAMs, the column-address buffers in this device are activated on the falling
edge of RAS
. The buffers act as transparent or flow-through latches while CAS is high. The falling edge of CAS
latches the column addresses. This feature lets the SMJ4C1024 operate at a higher data bandwidth than
conventional page-mode parts, since data retrieval begins as soon as the column address is valid rather than
when CAS
goes low. This performance improvement is referred to as enhanced page mode. A valid column
address can be presented immediately after the row-address hold time has been satisfied, usually well in
advance of the falling edge of CAS
low) if t
maximum (access time from column address) has been satisfied. If the column addresses for the
a(CA)
next page cycle are valid at the same time CAS
later occurrence of t
a(CA)
or t
. In this case, data is obtained after t
goes high, access time for the next cycle is determined by the
(access time from rising edge of CAS).
a(CP)
maximum (access time from CAS
a(C)
address (A0–A9)
low time and the
D
Q
Twenty address bits are required to decode one of 1048576 storage cell locations. Ten row-address bits are
set up on inputs A0 through A9 and latched onto the chip by RAS
pins A0 through A9 and latched onto the chip by CAS
4
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251–1443
. All addresses must be stable on or before the falling edges
. The ten column-address bits are set up on
Page 5
address (A0–A9) (continued)
SMJ4C1024
1048576 BY 1-BIT
DYNAMIC RANDOM-ACCESS MEMORY
SGMS023E – DECEMBER 1988 – REVISED MARCH 1996
of RAS
decoder. CAS
and CAS. RAS is similar to a chip enable in that it activates the sense amplifiers as well as the row
is used as a chip select to activate the output buffer as well as to latch the address bits into the
column-address buffer.
write enable (W
The read or write mode is selected through W
)
. A logic high on the W input selects the read mode and a logic
low selects the write mode. The write-enable pin can be driven from standard TTL circuits without a pullup
resistor. The data input is disabled when the read mode is selected. When W
goes low prior to CAS (early write),
data out remains in the high-impedance state for the entire cycle, permitting common input/output operation.
data in (D)
Data-in is written during a write or a read-modify-write cycle. Depending on the mode of operation, the falling
edge of CAS
and the data is strobed in by CAS
read-modify-write cycle, CAS
or W strobes data into the on-chip latch. In an early-write cycle, W is brought low prior to CAS,
with setup and hold times referenced to this signal. In a delayed-write or a
is already low, and the data is strobed in by W with setup and hold times
referenced to this signal.
data out (Q)
The 3-state output buffers provide direct TTL compatibility (no pullup resistor required) with a fanout of two
series 54 TTL loads. Data out is the same polarity as data in. The output is in the high-impedance (floating) state
until CAS
from CAS
becomes valid after the access time has elapsed and remains valid while CAS
is brought low. In a read cycle, the output becomes valid after the access time t
low (t
) begins with the negative transition of CAS as long as t
a(C)
a(R)
and t
are satisfied. The output
a(CA)
is low; when CAS goes high, the
. The access time
a(C)
output returns to a high-impedance state. In a delayed-write or read-modify-write cycle, the output follows the
sequence for the read cycle.
refresh
A refresh operation must be performed at least once every 8 ms to retain data. This can be achieved by strobing
each of the 512 rows (A0–A8). A normal read or write cycle refreshes all bits in each selected row. A RAS
operation can be used by holding CAS
in the high-impedance state. Externally generated addresses must be used for a RAS
at the high (inactive) level, conserving power as the output buffer remains
-only refresh. Hidden
refresh can be performed while maintaining valid data at the output pin. This is accomplished by holding CAS
at VIL after a read operation and cycling RAS after a specified precharge period, similar to a RAS-only refresh
cycle.
CAS
-before-RAS (CBR) refresh
CBR refresh is used by bringing CAS
RAS
falls (parameter t
d(RLCH)R
low earlier than RAS (see parameter t
d(CLRL)R
) and holding it low after
). For successive CBR refresh cycles, CAS can remain low while cycling RAS.
The external address is ignored and the refresh address is generated internally. The external address is also
ignored during the hidden refresh cycles.
power up
T o achieve proper device operation, an initial pause of 200 µs followed by a minimum of eight initialization cycles
is required after full V
level is achieved.
CC
test function (TF) pin
During normal device operation, TF must be disconnected or biased at a voltage ≤ V
CC
.
-only
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251–1443
5
Page 6
SMJ4C1024
1048576 BY 1-BIT
DYNAMIC RANDOM-ACCESS MEMORY
SGMS023E – DECEMBER 1988 – REVISED MARCH 1996
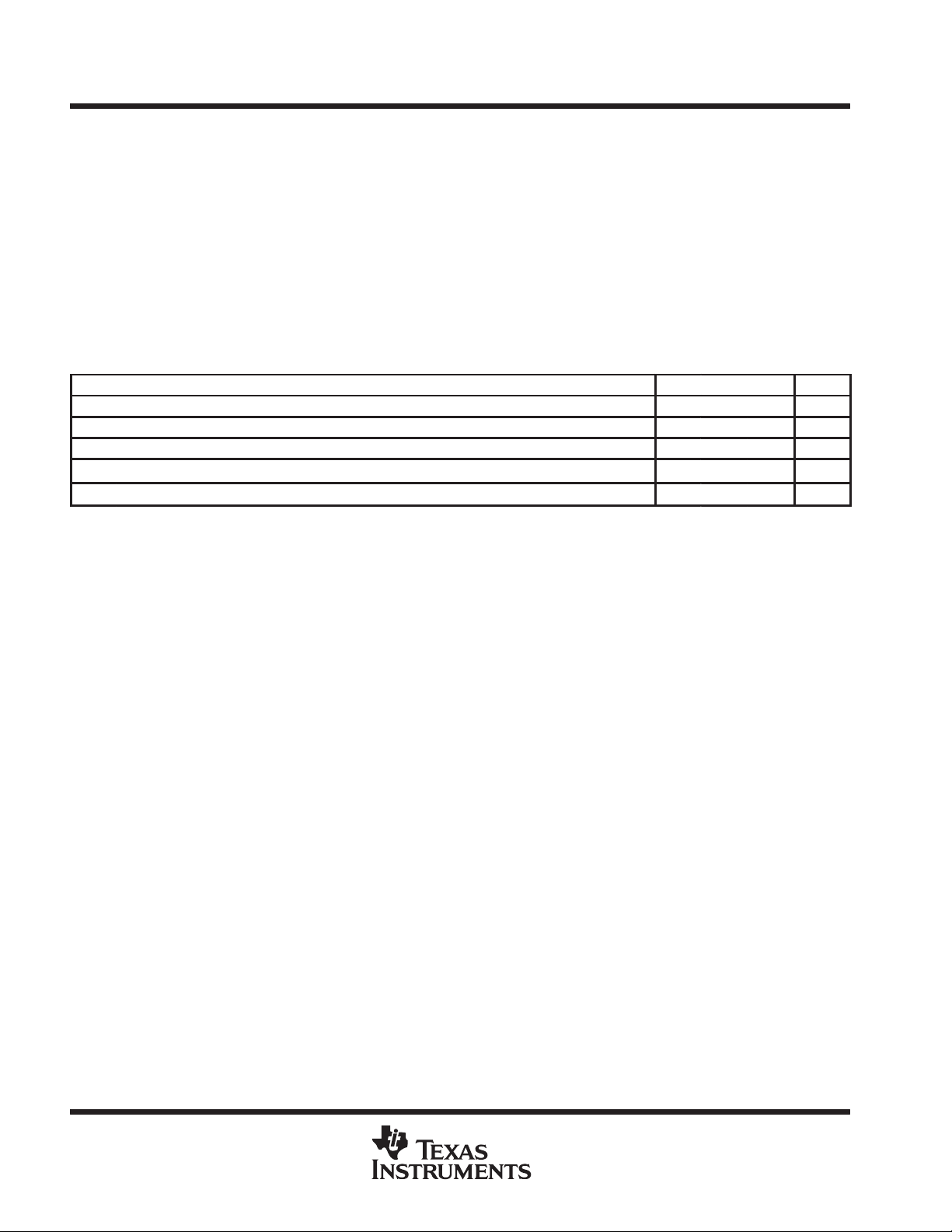
absolute maximum ratings over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)
†
Voltage range on any pin (see Note 1) – 1 V to 7 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Voltage range on V
Short-circuit output current, I
– 1 V to 7 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
CC
50 mA. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
OS
Power dissipation 1 W. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Operating free-air temperature range, T
Storage temperature range, T
†
Stresses beyond those listed under “absolute maximum ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and
functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under “recommended operating conditions” is not
implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
NOTE 1: All voltage values are with respect to VSS.
–65°C to 150°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
stg
– 55°C to 125°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
A
recommended operating conditions
MIN NOM MAX UNIT
V
Supply voltage 4.5 5 5.5 V
CC
V
High-level input voltage 2.4 6.5 V
IH
V
Low-level input voltage (see Note 2) –1 0.8 V
IL
T
Minimum operating free-air temperature – 55
A
T
Maximum operating case temperature 125
C
NOTE 2: The algebraic convention, where the more negative (less positive) limit is designated as minimum, is used for logic-voltage levels only.
°C
°C
6
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251–1443
Page 7
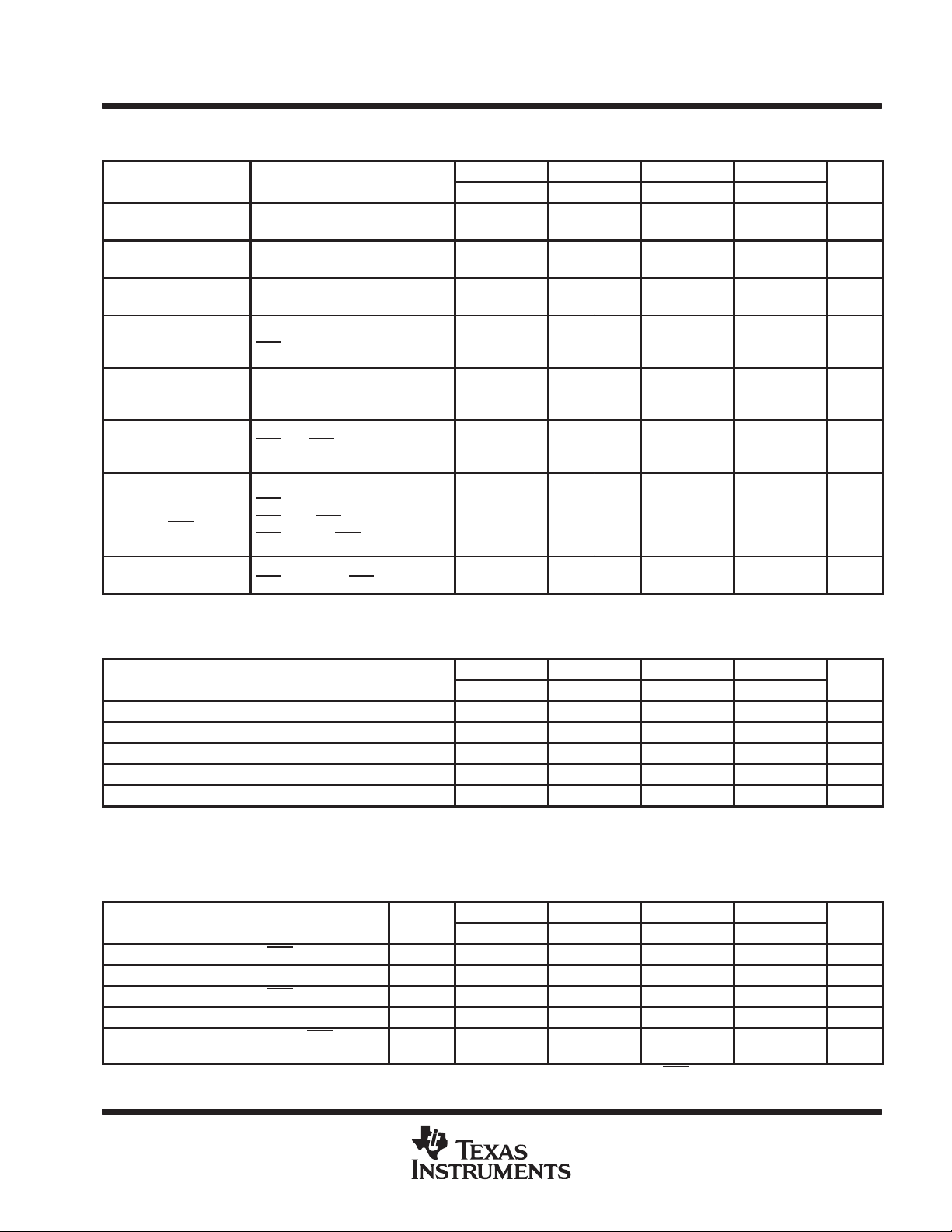
SMJ4C1024
PARAMETER
UNIT
PARAMETER
UNIT
PARAMETER
UNIT
1048576 BY 1-BIT
DYNAMIC RANDOM-ACCESS MEMORY
SGMS023E – DECEMBER 1988 – REVISED MARCH 1996
electrical characteristics over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air
temperature (unless otherwise noted)
’4C1024-80 ’4C1024-10 ’4C1024-12 ’4C1024-15
MIN MAX MIN MAX MIN MAX MIN MAX
± 10 ± 10 ± 10 ± 10 µA
± 10 ± 10 ± 10 ± 10 µA
3 3 3 3 mA
70 65 55 50 mA
50 45 35 30 mA
V
OH
V
OL
I
I
I
O
I
CC1
I
CC2
I
CC3
I
CC4
High-level
output voltage
Low-level
output voltage
Input current
(leakage)
Output
current
(leakage)
Read- or
write-cycle
current
Standby
current
Average
refresh
current
(RAS
only or
CBR)
Average page
current
TEST
CONDITIONS
IOH = – 5 mA 2.4 2.4 2.4 2.4 V
IOL = 4.2 mA 0.4 0.4 0.4 0.4 V
VCC = 5.5 V, VI = 0 V to 6.5 V,
All other pins = 0 V to V
VCC = 5.5 V, VO = 0 V to VCC,
high
CAS
VCC = 5.5 V, Minimum cycle 75 70 60 55 mA
After one memory cycle,
RAS
and CAS high,
VIH = 2.4 V
VCC = 5.5 V, Minimum cycle,
cycling,
RAS
high (RAS only),
CAS
low after CAS low (CBR)
RAS
VCC = 5.5 V, tPC = minimum,
low, CAS cycling
RAS
CC
capacitance over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air temperature,
f = 1 MHz (see Note 3)
HL/JD/FQ HJ HK SV
MIN MAX MIN MAX MIN MAX MIN MAX
C
i(A)
C
i(D)
C
i(RC)
C
i(W)
C
o
NOTE 3: Capacitance is sampled only at initial design and after any major change. Samples are tested at 0 V and 25°C with a 1-MHz signal
Input capacitance, address inputs 6 7 8 9 pF
Input capacitance, data input 5 5 6 7 pF
Input capacitance, strobe inputs 7 7 8 8 pF
Input capacitance, write-enable input 7 7 7 7 pF
Output capacitance 7 9 10 8 pF
applied to the pin under test. All other pins are open.
switching characteristics over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air
temperature (see Figure 1)
’4C1024-80 ’4C1024-10 ’4C1024-12 ’4C1024-15
MIN MAX MIN MAX MIN MAX MIN MAX
20 25 30 40 ns
40 45 55 70 ns
80 100 120 150 ns
40 40 60 75 ns
20 25 30 35 ns
t
a(C)
t
a(CA)
t
a(R)
t
a(CP)
t
dis(CH)
NOTE 4: t
ALT.
SYMBOL
Access time from CAS low t
Access time from column address t
Access time from RAS low t
Access time from column precharge t
Output disable time after CAS high
(see Note 4)
is specified when the output is no longer driven. The output is disabled by bringing CAS high.
dis(CH)
CAC
AA
RAC
CPA
t
OFF
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251–1443
7
Page 8
SMJ4C1024
UNIT
1048576 BY 1-BIT
DYNAMIC RANDOM-ACCESS MEMORY
SGMS023E – DECEMBER 1988 – REVISED MARCH 1996
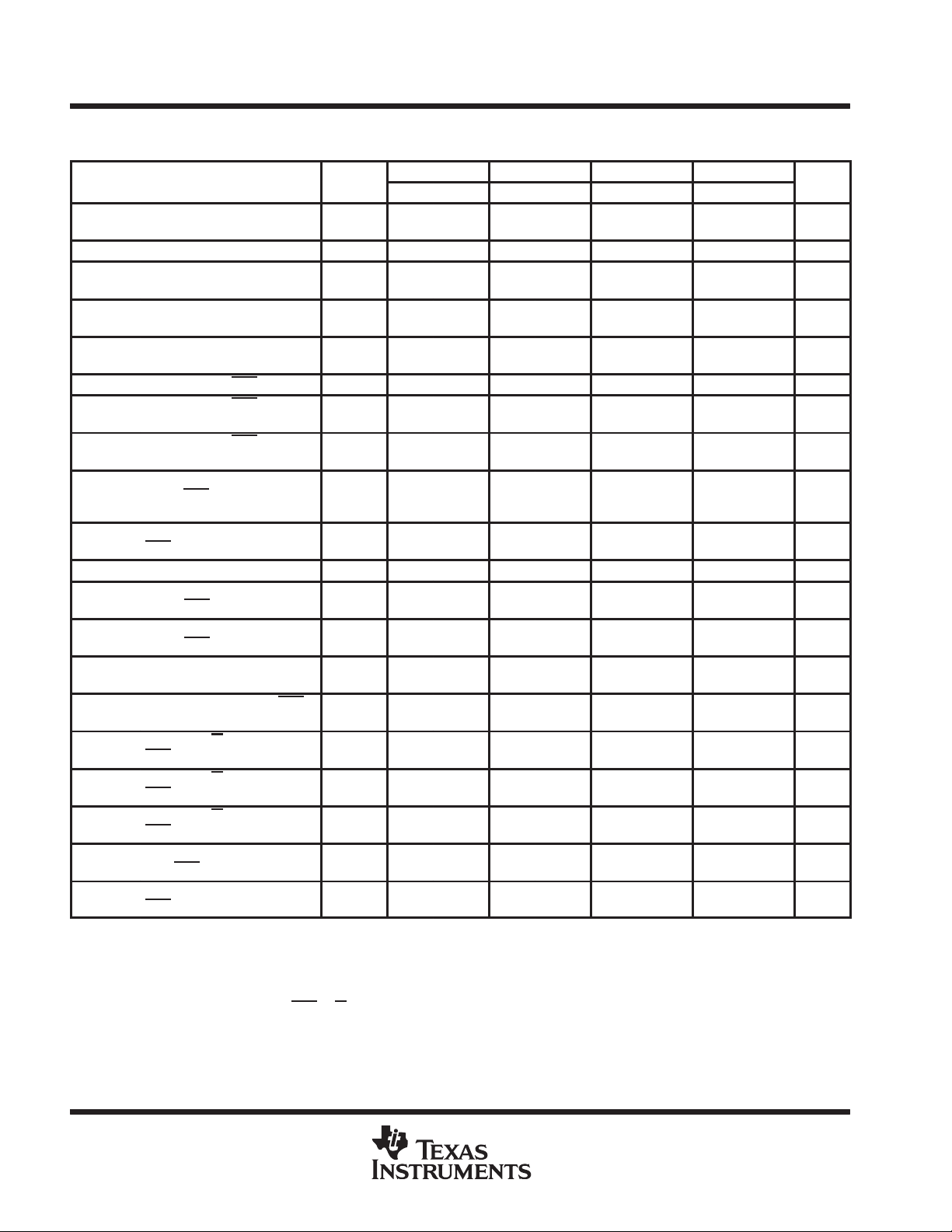
timing requirements over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air
temperature (see Note 5)
ALT.
SYMBOL
t
c(rd)
t
c(W)
t
c(rdW)
t
c(P)
t
c(PM)
t
w(CH)
t
w(CL)
t
w(RH)
t
w(RL)
t
w(RL)P
t
w(WL)
t
su(CA)
t
su(RA)
t
su(D)
t
su(rd)
t
su(WCL)
t
su(WCH)
t
su(WRH)
t
h(CA)
t
h(RA)
NOTES: 5. Timing measurements in this table are referenced to VIL max and VIH min.
Cycle time, read
(see Note 6)
Cycle time, write t
Cycle time,
read-write/read-modify-write
Cycle time, page-mode read
or write (see Note 7)
Cycle time, page-mode
read-modify-write
Pulse duration, CAS high t
Pulse duration, CAS low
(see Note 8)
Pulse duration, RAS high
(precharge)
Pulse duration, nonpage
mode, RAS
(see Note 9)
Pulse duration, page mode,
RAS
Pulse duration, write t
Setup time, column address
before CAS
Setup time, row address
before RAS
Setup time, data
(see Note 10)
Setup time, read before CAS
low
Setup time, W low before
CAS
Setup time, W low before
CAS
Setup time, W low before
RAS
Hold time, column address
after CAS
Hold time, row address after
RAS
6. All cycle times assume tt = 5 ns.
7. To assure t
8. In a read-modify-write cycle, t
9. In a read-modify-write cycle, t
10. Referenced to the later of CAS
11. Early write operation only
low
low (see Note 9)
low
low
low (see Note 11)
high
high
low
low
min, t
c(P)
su(CA)
should be ≥ t
t
RC
WC
t
RWC
t
PC
t
PRWC
CP
t
CAS
t
RP
t
RAS
t
RASP
WP
t
ASC
t
ASR
t
DS
t
RCS
t
WCS
t
CWL
t
RWL
t
CAH
t
RAH
d(CLWL)
d(RLWL)
or W in write operations
’4C1024-80 ’4C1024-10 ’4C1024-12 ’4C1024-15
MIN MAX MIN MAX MIN MAX MIN MAX
150 190 220 260 ns
150 190 220 260 ns
175 220 265 315 ns
50 55 65 80 ns
75 85 110 135 ns
10 10 15 25 ns
20 10000 25 10000 30 10000 40 10000 ns
60 80 90 100 ns
80 10000 100 10000 120 10000 150 10000 ns
80 100000 100 100000 120 100000 150 100000 ns
15 15 20 25 ns
0 3 3 3 ns
0 0 0 0 ns
0 0 0 0 ns
0 0 0 0 ns
0 0 0 0 ns
20 25 30 40 ns
20 25 30 40 ns
15 20 20 25 ns
12 15 15 20 ns
.
w(CH)
and t
and t
su(WCH)
su(WRH)
must be observed.
must be observed.
8
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251–1443
Page 9
SMJ4C1024
UNIT
1048576 BY 1-BIT
DYNAMIC RANDOM-ACCESS MEMORY
SGMS023E – DECEMBER 1988 – REVISED MARCH 1996
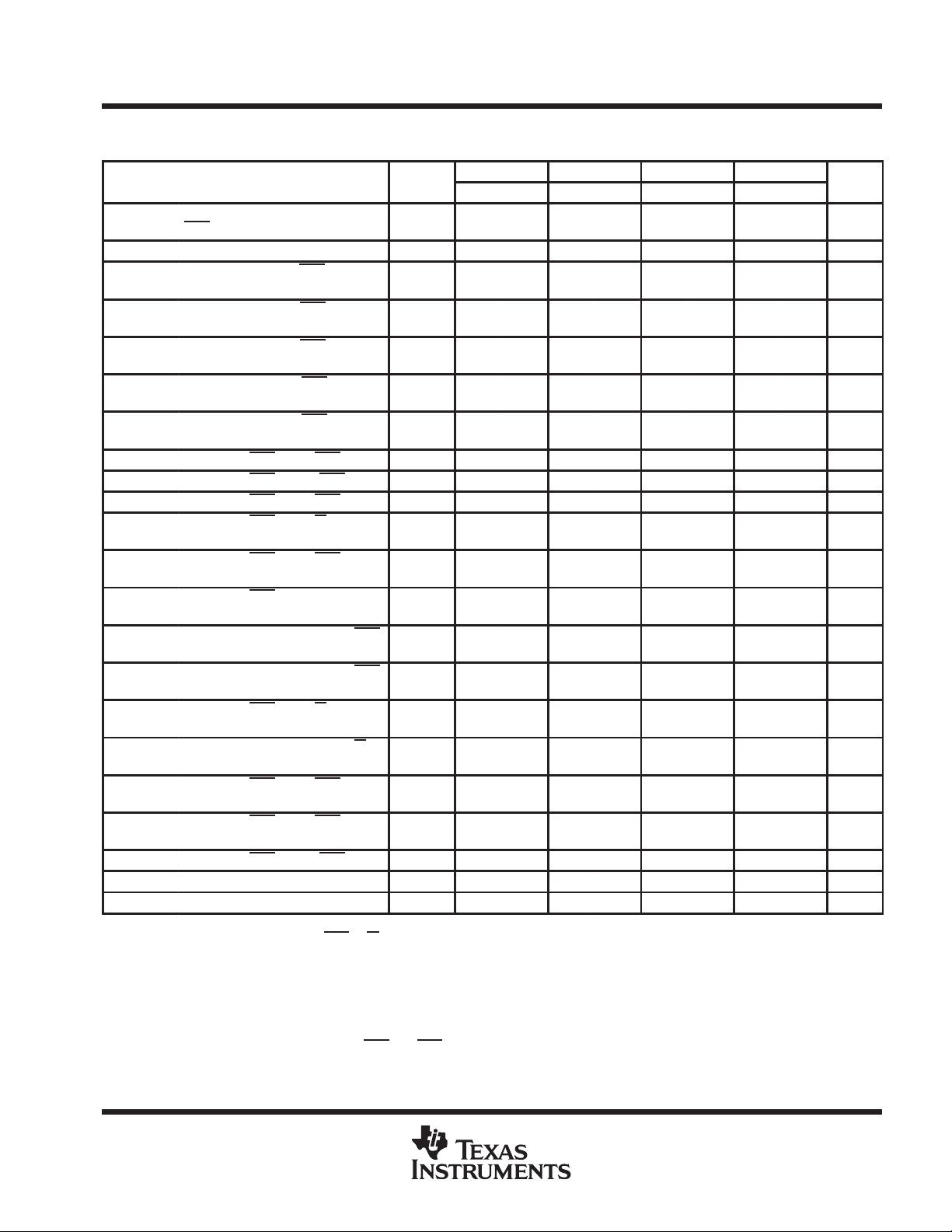
timing requirements over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air
temperature (see Note 5) (continued)
ALT.
SYMBOL
t
h(RLCA)
t
h(D)
t
h(RLD)
t
h(CHrd)
t
h(RHrd)
t
h(CLW)
t
h(RLW)
t
d(RLCH)
t
d(CHRL)
t
d(CLRH)
t
d(CLWL)
t
d(RLCL)
t
d(RLCA)
t
d(CARH)
t
d(CACH)
t
d(RLWL)
t
d(CAWL)
t
d(RLCH)R
t
d(CLRL)R
t
d(RHCL)R
t
rf
t
t
NOTES: 5. Timing measurements in this table are referenced to VIL max and VIH min.
Hold time, column address after
RAS
low (see Note 12)
Hold time, data (see Note 10) t
Hold time, data after RAS low
(see Note 12)
Hold time, read after CAS high
(see Note 13)
Hold time, read after RAS high
(see Note 13)
Hold time, write after CAS low
(see Note 11)
Hold time, write after RAS low
(see Note 12)
Delay time, RAS low to CAS high t
Delay time, CAS high to RAS low t
Delay time, CAS low to RAS high t
Delay time, CAS low to W low
(see Note 14)
Delay time, RAS low to CAS low
(see Note 15)
Delay time, RAS low to column
address (see Note 15)
Delay time, column address to RAS
high
Delay time, column address to CAS
high
Delay time, RAS low to W low
(see Note 14)
Delay time, column address to W
low (see Note 14)
Delay time, RAS low to CAS high
(see Note 16)
Delay time, CAS low to RAS low
(see Note 16)
Delay time, RAS high to CAS low t
Refresh time interval t
Transition time (see Note 17) — — — — — ns
10. Referenced to the later of CAS
11. Early-write operation only
12. The minimum value is measured when t
13. Either t
14. Read-modify-write operation only
15. Maximum value specified only to assure access time.
16. CBR refresh only
17. Transition times (rise and fall) for RAS
h(RHrd)
or t
h(CHrd)
or W in write operations.
must be satisfied for a read cycle.
t
AR
DH
t
DHR
t
RCH
t
RRH
t
WCH
t
WCR
CSH
CRP
RSH
t
CWD
t
RCD
t
RAD
t
RAL
t
CAL
t
RWD
t
AWD
t
CHR
t
CSR
RPC
REF
d(RLCL)
and CAS are to be minimum of 3 ns and a maximum of 50 ns.
’4C1024-80 ’4C1024-10 ’4C1024-12 ’4C1024-15
MIN MAX MIN MAX MIN MAX MIN MAX
60 70 80 100 ns
15 20 25 30 ns
60 70 85 110 ns
0 0 0 0 ns
10 10 10 10 ns
15 20 25 30 ns
60 70 85 100 ns
80 100 120 150 ns
0 0 0 0 ns
20 25 30 40 ns
20 25 40 50 ns
22 60 28 75 28 90 33 110 ns
17 40 20 55 20 65 25 80 ns
40 45 55 70 ns
40 45 55 70 ns
80 100 130 160 ns
40 45 65 80 ns
20 25 25 30 ns
10 10 10 15 ns
0 0 0 0 ns
8 8 8 8 ms
is set t
d(RLCL)
min as a reference.
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251–1443
9
Page 10

SMJ4C1024
1048576 BY 1-BIT
DYNAMIC RANDOM-ACCESS MEMORY
SGMS023E – DECEMBER 1988 – REVISED MARCH 1996
PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION
V
IOH/I
OL
Output Under Test
CL = 80 pF
(see Note A)
(a) LOAD CIRCUIT
NOTE A: CL includes probe and fixture capacitance.
Figure 1. Load Circuits for Timing Parameters
1.31 V
RL = 218 Ω
Output Under Test
CL = 80 pF
(see Note A)
(b) ALTERNATE LOAD CIRCUIT
10
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251–1443
Page 11

RAS
DYNAMIC RANDOM-ACCESS MEMORY
SGMS023E – DECEMBER 1988 – REVISED MARCH 1996
PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION
t
c(rd)
t
w(RL)
SMJ4C1024
1048576 BY 1-BIT
t
w(CL)
t
su(CA)
t
d(CACH)
t
d(CARH)
t
d(CLRH)
t
h(CA)
t
a(C)
Don’t Care
t
t
t
d(RLCL)
t
d(RLCH)
CAS
t
d(RLCA)
t
h(RA)
t
su(RA)
t
h(RLCA)
A0–A9
W
Q
NOTE A: Output can go from the high-impedance state to an invalid-data state prior to the specified access time.
Row
Hi-Z
Column
t
su(rd)
See Note A
t
a(R)
t
a(CA)
t
w(RH)
t
d(CHRL)
t
dis(CH)
Valid
t
w(CH)
t
h(RHrd)
t
h(CHrd)
Don’t CareDon’t Care
Figure 2. Read-Cycle Timing
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251–1443
11
Page 12

SMJ4C1024
1048576 BY 1-BIT
DYNAMIC RANDOM-ACCESS MEMORY
SGMS023E – DECEMBER 1988 – REVISED MARCH 1996
PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION
t
RAS
t
t
t
d(RLCL)
w(RL)
t
d(RLCH)
t
t
d(CLRH)
t
w(CL)
c(W)
t
w(RH)
t
d(CHRL)
CAS
A0–A9
W
t
d(RLCA)
D
t
su(RA)
t
d(CACH)
t
h(RA)
t
h(RLCA)
Row
Don’t Care Don’t Care
t
su(D)
Column Don’t Care
t
h(RLW)
t
h(RLD)
Valid Data
t
su(CA)
t
t
su(WCL)
t
w(WL)
t
d(CARH)
t
h(CA)
su(WCH)
t
su(WRH)
t
h(CLW)
t
h(D)
Don’t Care
t
w(CH)
12
Q
Hi-Z
Figure 3. Early-Write-Cycle Timing
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251–1443
Page 13

RAS
DYNAMIC RANDOM-ACCESS MEMORY
SGMS023E – DECEMBER 1988 – REVISED MARCH 1996
PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION
t
c(W)
t
w(RL)
SMJ4C1024
1048576 BY 1-BIT
CAS
A0–A9
W
t
t
t
h(RA)
t
d(RLCA)
Row
t
su(CA)
t
su(RA)
t
d(RLCL)
t
h(RLCA)
t
su(D)
t
d(CLRH)
t
d(RLCH)
t
d(CACH)
Column Don’t Care
t
h(RLW)
t
h(RLD)
t
d(CARH)
t
h(CA)
t
t
w(WL)
t
h(D)
t
w(CL)
su(WCH)
t
su(WRH)
t
w(RH)
t
d(CHRL)
Don’t CareDon’t Care
t
w(CH)
D
Q
Don’t Care Don’t Care
Valid Data
t
dis(CH)
Not Valid
Figure 4. Write-Cycle Timing
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251–1443
13
Page 14

SMJ4C1024
1048576 BY 1-BIT
DYNAMIC RANDOM-ACCESS MEMORY
SGMS023E – DECEMBER 1988 – REVISED MARCH 1996
PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION
RAS
t
CAS
t
t
d(RLCA)
t
h(RA)
t
su(RA)
t
d(RLCL)
t
h(RLCA)
t
su(CA)
t
w(RL)
t
c(rdW)
t
w(CL)
t
w(RH)
t
d(CHRL)
t
w(CH)
t
t
A0–A9
W
D
Q
NOTE A: Output can go from the high-impedance state to an invalid-data state prior to the specified access time.
Row
t
su(rd)
Don’t Care Don’t Care
t
d(RLWL)
Don’t Care Don’t Care
Hi-Z
See Note A
t
Column Don’t Care
a(R)
t
d(CAWL)
t
d(CLWL)
t
a(CA)
t
a(C)
Valid In
t
su(D)
t
t
su(WCH)
t
su(WRH)
w(WL)
t
h(CA)
t
h(D)
Valid Out
t
dis(CH)
14
Figure 5. Read-Write-/Read-Modify-Write-Cycle Timing
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251–1443
Page 15

RAS
CAS
t
su(RA)
DYNAMIC RANDOM-ACCESS MEMORY
PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION
t
w(RL)P
t
d(RLCL)
t
d(RLCH)
t
w(CL)
t
h(CA)
t
t
h(RA)
h(RLCA)
t
su(CA)
t
d(CACH)
SMJ4C1024
1048576 BY 1-BIT
SGMS023E – DECEMBER 1988 – REVISED MARCH 1996
t
w(RH)
t
t
c(P)
t
w(CH)
t
d(CARH)
t
d(CLRH)
d(CHRL)
A0–A9
W
Q
NOTES: A. Output can go from the high-impedance state to an invalid-data state prior to the specified access time.
B. A write cycle or a read-modify cycle can be mixed with the read cycles as long as the write and read-modify-write timing specifications
are not violated.
C. Access time is t
Row Column Column Don’t Care
t
t
d(RLCA)
t
su(rd)
a(CP)
or t
a(CA)
t
a(R)
dependent.
t
a(CA)
t
a(C)
See Note A
Valid
Out
See Note C
t
a(CA)
t
a(CP)
(see Note C)
h(RHrd)
See Note A
Figure 6. Enhanced-Page-Mode Read-Cycle Timing
t
h(CHrd)
t
dis(CH)
Valid
Out
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251–1443
15
Page 16

SMJ4C1024
1048576 BY 1-BIT
DYNAMIC RANDOM-ACCESS MEMORY
SGMS023E – DECEMBER 1988 – REVISED MARCH 1996
PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION
RAS
t
w(RL)P
t
w(RH)
CAS
A0–A9
W
t
d(RLCH)
t
h(RLCA)
t
h(RLD)
w(CL)
t
su(CA)
t
su(WCH)
t
w(WL)
t
h(D)
(see Note B)
t
h(D)
t
h(CA)
t
d(RLCL)
t
t
h(RA)
t
su(RA)
Row Column Column Don’t Care
t
d(RLCA)
t
h(RLW)
Don’t Care Don’t Care Don’t Care
t
su(D)
(see Note B)
t
su(D)
D
Valid Data In
t
c(P)
t
t
d(CACH)
t
su(WCH)
w(CH)
t
t
d(CARH)
Valid
In
d(CLRH)
t
su(WRH)
t
d(CHRL)
Don’t Care
Q
NOTES: A. A read cycle or a read-modify-write cycle can be intermixed with write cycles as long as read and read-modify-write timing
specifications are not violated.
B. Referenced to CAS
or W, whichever occurs last.
Hi-Z
Figure 7. Enhanced-Page-Mode Write-Cycle Timing
16
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251–1443
Page 17

RAS
CAS
t
su(CA)
t
su(RA)
DYNAMIC RANDOM-ACCESS MEMORY
PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION
t
w(RL)P
t
c(PM)
t
t
d(RLCL)
t
h(RA)
t
h(RLCA)
t
d(RLCA)
d(RLCH)
t
w(CL)
t
t
w(CH)
h(CA)
SMJ4C1024
1048576 BY 1-BIT
SGMS023E – DECEMBER 1988 – REVISED MARCH 1996
t
w(RH)
t
d(CLRH)
t
d(CHRL)
A0–A9
W
D
Q
NOTES: A. Output can go from high-impedance state to an invalid-data state prior to the specified access time.
Row
t
su(rd)
t
d(RLWL)
Don’t Care Don’t CareValid Valid
B. A read or a write cycle can be intermixed with read-modify-write cycles as long as the read and write timing specifications are
not violated.
Column Column Don’t Care
t
d(CLWL)
t
d(CAWL)
t
su(D)
t
a(C)
t
a(CA)
t
a(R)
See Note A See Note A
t
Valid
Out
h(D)
t
w(WL)
t
su(WCH)
t
a(CP)
t
su(WRH)
Don’t Care
t
dis(CH)
Valid
Out
Figure 8. Enhanced-Page-Mode Read-Modify-Write-Cycle Timing
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251–1443
17
Page 18

SMJ4C1024
1048576 BY 1-BIT
DYNAMIC RANDOM-ACCESS MEMORY
SGMS023E – DECEMBER 1988 – REVISED MARCH 1996
PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION
RAS
t
w(RL)
t
c(rd)
CAS
A0–A9
t
t
Don’t Care
su(RA)
Don’t Care Don’t Care
W
D
Q
Row Row
Don’t Care
Don’t Care
Hi-Z
t
d(RHCL)R
t
h(RA)
t
w(RH)
t
d(CHRL)t
Figure 9. RAS-Only Refresh-Cycle Timing
18
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251–1443
Page 19

DYNAMIC RANDOM-ACCESS MEMORY
SGMS023E – DECEMBER 1988 – REVISED MARCH 1996
PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION
SMJ4C1024
1048576 BY 1-BIT
RAS
CAS
t
su(RA)
A0–A9
W
t
h(RA)
t
su(rd)
Memory Cycle
t
w(RL)
Row Col
t
su(CA)
t
w(RH)
t
h(CA)
t
h(RHrd)
Refresh Cycle
t
w(RL)
t
w(CL)
t
Don’t Care
Don’t Care
Refresh Cycle
w(RH)
t
d(RLCH)R
D
t
a(C)
t
a(CA)
t
a(R)
Q
Don’t Care
Valid Data
t
dis(CH)
Figure 10. Hidden-Refresh-Cycle Timing
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251–1443
19
Page 20

SMJ4C1024
1048576 BY 1-BIT
DYNAMIC RANDOM-ACCESS MEMORY
SGMS023E – DECEMBER 1988 – REVISED MARCH 1996
PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION
t
w(RH)
RAS
t
d(CLRL)R
t
d(RHCL)R
t
CAS
t
t
c(rd)
t
d(RLCH)R
t
w(RL)
A0–A9
Don’t Care
D
Q
Don’t Care
Hi-Z
Figure 11. Automatic-CBR-Refresh-Cycle Timing
20
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251–1443
Page 21

SMJ4C1024
1048576 BY 1-BIT
DYNAMIC RANDOM-ACCESS MEMORY
SGMS023E – DECEMBER 1988 – REVISED MARCH 1996
MECHANICAL DATA
HJ (R-CDCC-J20) J-LEADED CERAMIC CHIP CARRIER
0.685 (17,40)
0.665 (16,89)
0.608 (15,44)
20 11
0.048 (1,22)
0.028 (0,71)0.592 (15,04)
0.338 (8,59)
0.322 (8,18)
4 Places
110
0.056 (1,42)
0.044 (1,12)
0.050 (1,27)
NOTES: A. All linear dimensions are in inches (millimeters).
B. This drawing is subject to change without notice.
C. This package can be hermetically sealed with a metal lid.
D. The terminals will be gold plated.
0.022 (0,56)
0.012 (0,30)
0.035 (0,89)
0.025 (0,64)
0.102 (2,59)
0.080 (2,03)
Radius
0.010 (0,25)
0.006 (0,15)
0.137 (3,48)
0.114 (2,90)
0.308 (7,82)
0.264 (6,71)
4040144-2/B 10/94
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251–1443
21
Page 22

SMJ4C1024
1048576 BY 1-BIT
DYNAMIC RANDOM-ACCESS MEMORY
SGMS023E – DECEMBER 1988 – REVISED MARCH 1996
MECHANICAL DATA
HK (R-CDFP-F20) CERAMIC DUAL FLATPACK
0.035 (0,89)
0.025 (0,64)
0.010 (0,25)
0.004 (0,10)
0.095 (2,41)
0.075 (1,91)
0.680 (17,27)
0.660 (16,76)
Lid
10
0.310 (7,87)
0.290 (7,37)
0.120 (3,05)
0.090 (2,29)
1
0.390 (9,91) 0.315 (8,00)
20
0.050 (1,27)
0.021 (0,53)
0.015 (0,38)
11
0.295 (7,49)0.370 (9,40)
NOTES: A. All linear dimensions are in inches (millimeters).
22
B. This drawing is subject to change without notice.
C. This package can be hermetically sealed with a metal lid.
D. The terminals are gold plated.
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251–1443
4040174/C 08/95
Page 23

SMJ4C1024
1048576 BY 1-BIT
DYNAMIC RANDOM-ACCESS MEMORY
SGMS023E – DECEMBER 1988 – REVISED MARCH 1996
MECHANICAL DATA
FQ (R-CDCC-N20) LEADLESS CERAMIC CHIP CARRIER
0.685 (17,40)
0.665 (16,89)
0.357 (9,07)
0.343 (8,71)
10 11
0.608 (15,44)
0.592 (15,04)
1
0.090 (2,29) TYP 0.050 (1,27) TYP
NOTES: A. All linear dimensions are in inches (millimeters).
B. This drawing is subject to change without notice.
C. This package can be hermetically sealed with a metal lid.
D. The terminals are gold plated.
0.030 (0,76) MIN
0.092 (2,34)
0.069 (1,75)
0.028 (0,71)
0.022 (0,56)
0.008 (0,20) RAD TYP
0.050 (1,27)
20
4040143/B 10/94
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251–1443
23
Page 24

SMJ4C1024
1048576 BY 1-BIT
DYNAMIC RANDOM-ACCESS MEMORY
SGMS023E – DECEMBER 1988 – REVISED MARCH 1996
MECHANICAL DATA
HL (R-CDCC-N20/26) LEADLESS CERAMIC CHIP CARRIER
0.685 (17,40)
0.665 (16,89)
0.030 (0,76) MIN
0.357 (9,07)
0.343 (8,71)
0.080 (2,03)
0.065 (1,65)
10
0.608 (15,44)
0.592 (15,04)
1
0.090 (2,29) TYP
NOTES: A. All linear dimensions are in inches (millimeters).
B. This drawing is subject to change without notice.
C. This package can be hermetically sealed with a metal lid.
D. The terminals are gold plated.
11
0.028 (0,71)
0.022 (0,56)
0.008 (0,20) RAD TYP
0.050 (1,27)
20
0.050 (1,27) TYP
4040145/B 4/95
24
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251–1443
Page 25

SMJ4C1024
1048576 BY 1-BIT
DYNAMIC RANDOM-ACCESS MEMORY
SGMS023E – DECEMBER 1988 – REVISED MARCH 1996
MECHANICAL DATA
SV (R-CZIP-T**) CERAMIC ZIG-ZAG PACKAGE
20 PIN SHOWN
1
2 4
0.060 (1,52)
0.040 (1,02)
A
C
0.070 (1,78)
0.040 (1,02)
0.100 (2,54)
19
20181614121086
0.200 (5,08)
0.125 (3,18)
0.023 (0,58)
0.015 (0,38)
0.375 (9,53)
0.355 (9,02)
B
Seating Plane
0.050 (1,27)
0.015 (0,38)
DIM
PINS **
A MAX
A MIN
B MAX
B MIN
C MAX
C MIN
0.130 (3,30)
0.100 (2,54)
0.015 (0,38)
0.008 (0,20)
0.115 (2,92)
0.085 (2,16)
2420
1.065 1.265 1.465
(27,05)
1.035
(26,29)
0.380
(9,65)
0.355
(9,02)
0.910
(23,11)
0.890
(22,61)
(32,13)
1.235
(31,37)
0.465
(11,81)
0.440
(11,18)
1.110
(28,19)
1.090
(27,69)
28
(37,21)
1.435
(36,45)
0.465
(11,81)
0.440
(11,18)
1.310
(33,27)
1.290
(32,77)
NOTES: A. All linear dimensions are in inches (millimeters).
B. This drawing is subject to change without notice.
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251–1443
4040002/C 08/95
25
Page 26

SMJ4C1024
1048576 BY 1-BIT
DYNAMIC RANDOM-ACCESS MEMORY
SGMS023E – DECEMBER 1988 – REVISED MARCH 1996
MECHANICAL DATA
JD (R-CDIP-T**) CERAMIC SIDE-BRAZE DUAL-IN-LINE PACKAGE
20 PIN SHOWN
20
1
0.075 (1,91) MAX 4 Places
A
0.065 (1,65)
0.045 (1,14)
11
10
0.175 (4,45)
0.140 (3,56)
0.290 (7,37)
TYP
PINS **
DIM
A MAX
Seating Plane
0.020 (0,51) MIN
16 18 20
0.810
(20,57) (23,11)
0.910
0.320 (8,13)
0.290 (7,37)
1.010
(25,65)
24
1.100
(27,94)
0.100 (2,54)
0.021 (0,53)
0.015 (0,38)
NOTES: A. All linear dimensions are in inches (millimeters).
B. This drawing is subject to change without notice.
C. This package can be hermetically sealed with a metal lid.
D. The terminals are gold plated.
0.125 (3,18) MIN
0°–15°
0.012 (0,30)
0.008 (0,20)
4040086/C 08/95
26
POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251–1443
Page 27

IMPORTANT NOTICE
T exas Instruments and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make changes to their products or to discontinue
any product or service without notice, and advise customers to obtain the latest version of relevant information
to verify, before placing orders, that information being relied on is current and complete. All products are sold
subject to the terms and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgement, including those
pertaining to warranty, patent infringement, and limitation of liability.
TI warrants performance of its semiconductor products to the specifications applicable at the time of sale in
accordance with TI’s standard warranty. Testing and other quality control techniques are utilized to the extent
TI deems necessary to support this warranty . Specific testing of all parameters of each device is not necessarily
performed, except those mandated by government requirements.
CERT AIN APPLICATIONS USING SEMICONDUCTOR PRODUCTS MAY INVOLVE POTENTIAL RISKS OF
DEATH, PERSONAL INJURY, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE (“CRITICAL
APPLICATIONS”). TI SEMICONDUCTOR PRODUCTS ARE NOT DESIGNED, AUTHORIZED, OR
WARRANTED TO BE SUITABLE FOR USE IN LIFE-SUPPORT DEVICES OR SYSTEMS OR OTHER
CRITICAL APPLICA TIONS. INCLUSION OF TI PRODUCTS IN SUCH APPLICATIONS IS UNDERST OOD TO
BE FULLY AT THE CUSTOMER’S RISK.
In order to minimize risks associated with the customer’s applications, adequate design and operating
safeguards must be provided by the customer to minimize inherent or procedural hazards.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or customer product design. TI does not warrant or represent
that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any patent right, copyright, mask work right, or other
intellectual property right of TI covering or relating to any combination, machine, or process in which such
semiconductor products or services might be or are used. TI’s publication of information regarding any third
party’s products or services does not constitute TI’s approval, warranty or endorsement thereof.
Copyright 1998, Texas Instruments Incorporated
 Loading...
Loading...