Texas Instruments MSP430F247TPM, MSP430F233TRGC, MSP430F247TRGC, MSP430F2471TRGC, MSP430F2471TPM User Manual
...Page 1

MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
www.ti.com
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
1
FEATURES
23
• Low Supply-Voltage Range, 1.8 V to 3.6 V
• Ultra-Low Power Consumption • Supply Voltage Supervisor/Monitor With
– Active Mode: 270 µA at 1 MHz, 2.2 V
– Standby Mode (VLO): 0.3 µA
– Off Mode (RAM Retention): 0.1 µA
• Ultra-Fast Wake-Up From Standby Mode in
Less Than 1 µs
• 16-Bit RISC Architecture, 62.5-ns Instruction
Cycle Time
• Basic Clock Module Configurations:
– Internal Frequencies up to 16 MHz
– Internal Very Low-Power LF Oscillator
– 32-kHz Crystal
– Internal Frequencies up to 16 MHz With
Four Calibrated Frequencies to ±1% – 2KB RAM
– Resonator – MSP430F247, MSP430F2471
– External Digital Clock Source – 32KB+256B Flash Memory
– External Resistor – 4KB RAM
• 12-Bit Analog-to-Digital (A/D) Converter With – MSP430F248, MSP430F2481
Internal Reference, Sample-and-Hold, and
Autoscan Feature
• 16-Bit Timer_A With Three Capture/Compare
Registers
• 16-Bit Timer_B With Seven Capture/Compare
With Shadow Registers
• Four Universal Serial Communication
Interfaces (USCI)
– USCI_A0 and USCI_A1
– Enhanced UART Supporting Auto-Baudrate
Detection
– IrDA Encoder and Decoder
– Synchronous SPI
– USCI_B0 and USCI_B1
– I2C™
– Synchronous SPI implemented on the MSP430F24x1.
• On-Chip Comparator
Programmable Level Detection
• Brownout Detector
• Bootstrap Loader
• Serial Onboard Programming, No External
Programming Voltage Needed, Programmable
Code Protection by Security Fuse
• Family Members Include:
– MSP430F233
– 8KB+256B Flash Memory,
– 1KB RAM
– MSP430F235
– 16KB+256B Flash Memory
(1)
– 48KB+256B Flash Memory
– 4KB RAM
– MSP430F249, MSP430F2491
– 60KB+256B Flash Memory
– 2KB RAM
– MSP430F2410
– 56KB+256B Flash Memory
– 4KB RAM
• Available in 64-Pin QFP and 64-Pin QFN
Packages (See Available Options)
• For Complete Module Descriptions, See
MSP430x2xx Family User’s Guide (SLAU144)
(1) The MSP430F24x1 devices are identical to the MSP430F24x
devices, with the exception that the ADC12 module is not
1
Please be aware that an important notice concerning availability, standard warranty, and use in critical applications of
Texas Instruments semiconductor products and disclaimers thereto appears at the end of this data sheet.
2MSP430 is a trademark of Texas Instruments.
3All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date.
Products conform to specifications per the terms of the Texas
Instruments standard warranty. Production processing does not
necessarily include testing of all parameters.
Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 2

MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
This integrated circuit can be damaged by ESD. Texas Instruments recommends that all integrated circuits be handled with
appropriate precautions. Failure to observe proper handling and installation procedures can cause damage.
ESD damage can range from subtle performance degradation to complete device failure. Precision integrated circuits may be more
susceptible to damage because very small parametric changes could cause the device not to meet its published specifications.
DESCRIPTION
The Texas Instruments MSP430™ family of ultra-low power microcontrollers consists of several devices featuring
different sets of peripherals targeted for various applications. The architecture, combined with five low-power
modes, is optimized to achieve extended battery life in portable measurement applications. The device features a
powerful 16-bit RISC CPU, 16-bit registers, and constant generators that contribute to maximum code efficiency.
The calibrated digitally controlled oscillator (DCO) allows wake-up from low-power modes to active mode in less
than 1 µs.
The MSP430F23x, MSP430F24x(1), and MSP430F2410 series are microcontroller configurations with two builtin 16-bit timers, a fast 12-bit A/D converter (not MSP430F24x1), a comparator, four (two in MSP430F23x)
universal serial communication interface (USCI) modules, and up to 48 I/O pins. The MSP430F24x1 devices are
identical to the MSP430F24x devices, with the exception that the ADC12 module is not implemented. The
MSP430F23x devices are identical to the MSP430F24x devices, with the exception that a reduced Timer_B, one
USCI module, and less RAM are integrated.
Typical applications include sensor systems, industrial control applications, and hand-held meters.
www.ti.com
Table 1. Available Options
T
A
-40°C to 105°C MSP430F248TPM MSP430F248TRGC
(1) For the most current package and ordering information, see the Package Option Addendum at the end
of this document, or see the TI web site at www.ti.com.
(2) Package drawings, thermal data, and symbolization are available at www.ti.com/packaging.
PLASTIC 64-PIN QFP (PM) PLASTIC 64-PIN QFN (RGC)
MSP430F233TPM MSP430F233TRGC
MSP430F235TPM MSP430F235TRGC
MSP430F247TPM MSP430F247TRGC
MSP430F2471TPM MSP430F2471TRGC
MSP430F2481TPM MSP430F2481TRGC
MSP430F249TPM MSP430F249TRGC
MSP430F2491TPM MSP430F2491TRGC
MSP430F2410TPM MSP430F2410TRGC
PACKAGED DEVICES
(1)(2)
Development Tool Support
All MSP430 microcontrollers include an Embedded Emulation Module (EEM) allowing advanced debugging and
programming through easy to use development tools. Recommended hardware options include the following:
• Debugging and Programming Interface
– MSP-FET430UIF (USB)
– MSP-FET430PIF (Parallel Port)
• Debugging and Programming Interface with Target Board
– MSP-FET430U64 (PM package)
• Standalone Target Board
– MSP-TS430PM64 (PM package)
• Production Programmer
– MSP-GANG430
2 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 3
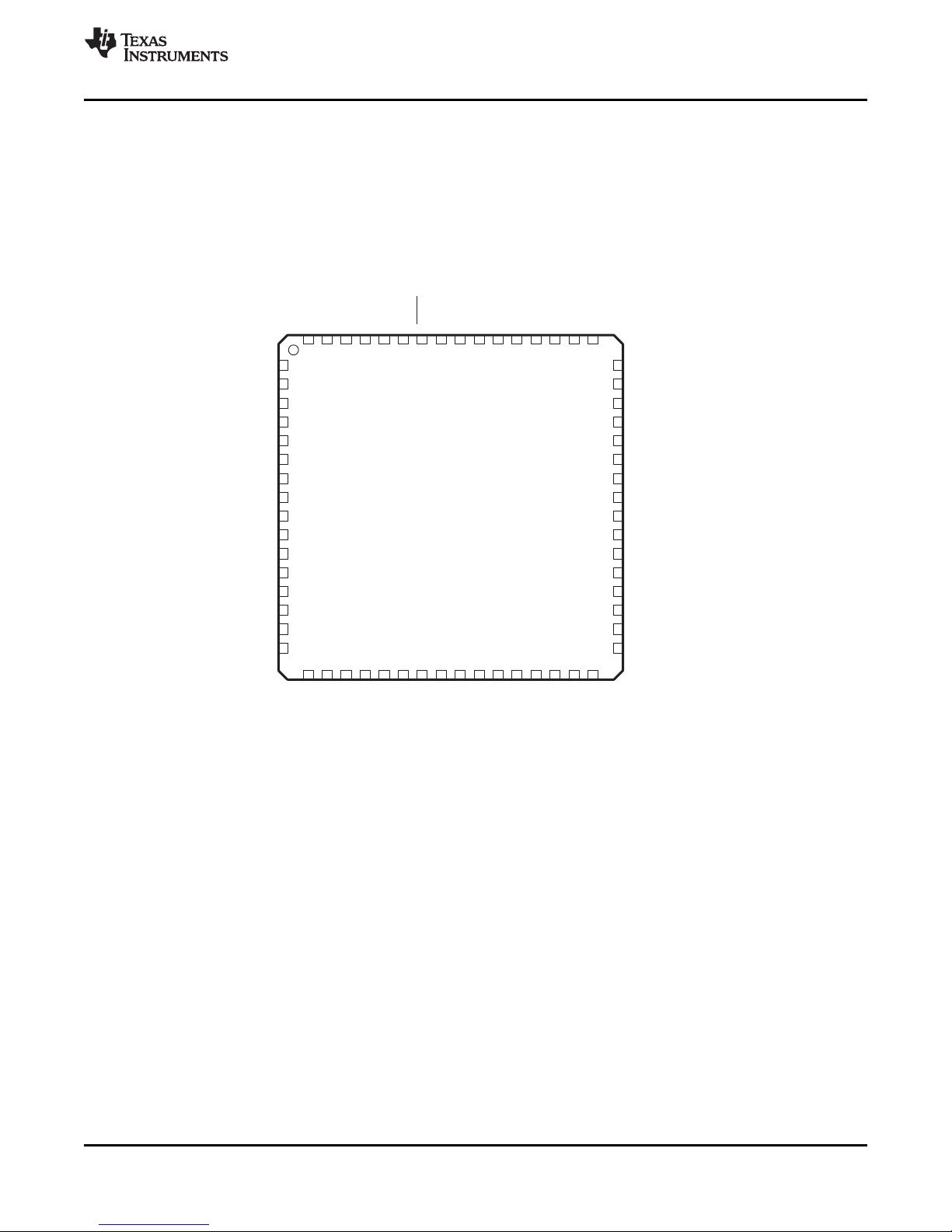
P1.7/TA2
AV
SS
P6.2/A2
P2.0/ACLK/CA2
P6.1/A1
P2.1/TAINCLK/CA3
P6.0/A0
P2.2/CAOUT/TA0/CA4
RST/NMI
P2.3/CA0/TA1
TCK
P2.4/CA1/TA2
TDO/TDI
P2.7/TA0/CA7
TDI/TCLK
P2.6/ADC12CLK/CA6
XT2IN
P3.0/UCB0STE/UCA0CLK
XT2OUT
P5.7/TBOUTH/SVSOUT
P3.2/UCB0SOMI/UCB0SCL
P5.6/ACLK
P3.3/UCB0CLK/UCA0STE
P5.5/SMCLK
P3.4/UCA0TXD/UCA0SIMO
P4.4
XOUT
P5.3
P6.3/A3
P5.4/MCLK
DV
CC
P5.2
P6.4/A4
P4.7/TBCLK
P6.7/A7/SVSIN
P5.1
P6.5/A5
P5.0
P6.6/A6
P4.6
V
REF+
P4.5XIN
P4.1/TB1P1.0/TACLK/CAOUT
P4.3Ve
REF+
P4.2/TB2V /Ve
REF- REF-
P4.0/TB0P1.1/TA0
P3.7P1.2/TA1
P3.5/UCA0RXD/UCA0SOMIP1.4/SMCLK
P3.6P1.3/TA2
TMS
P2.5/R /CA5
OSC
P1.6/TA1
DV
SS
P1.5/TA0
AV
CC
1962206121602259235824
57
27
54
2655285329523051315032
49
409
472
48
1
463
436
45
4
44
5
42
7
41
8
37
12
3910
38
11
3613
35
14
3316
3415
25
56
18
63
17
64
PM OR RGC PACKAGE
(TOP VIEW)
MSP430F23x
www.ti.com
Device Pinout, MSP430F23x
MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 3
Page 4

P1.7/TA2
AV
SS
P6.2/A2
P2.0/ACLK/CA2
P6.1/A1
P2.1/TAINCLK/CA3
P6.0/A0
P2.2/CAOUT/TA0/CA4
RST/NMI
P2.3/CA0/TA1
TCK
P2.4/CA1/TA2
TDO/TDI
P2.7/TA0/CA7
TDI/TCLK
P2.6/ADC12CLK/CA6
XT2IN
P3.0/UCB0STE/UCA0CLK
XT2OUT
P5.7/TBOUTH/SVSOUT
P3.2/UCB0SOMI/UCB0SCL
P5.6/ACLK
P3.3/UCB0CLK/UCA0STE
P5.5/SMCLK
P3.4/UCA0TXD/UCA0SIMO
P4.4/TB4
XOUT
P5.3/UCB1CLK/UCA1STE
P6.3/A3
P5.4/MCLK
DV
CC
P5.2/UCB1SOMI/UCB1SCL
P6.4/A4
P4.7/TBCLK
P6.7/A7/SVSIN
P5.1/UCB1SIMO/UCB1SDA
P6.5/A5
P5.0/UCB1STE/UCA1CLK
P6.6/A6
P4.6/TB6
V
REF+
P4.5/TB5XIN
P4.1/TB1P1.0/TACLK/CAOUT
P4.3/TB3Ve
REF+
P4.2/TB2V /Ve
REF- REF-
P4.0/TB0P1.1/TA0
P3.7/UCA1RXD/UCA1SOMIP1.2/TA1
P3.5/UCA0RXD/UCA0SOMIP1.4/SMCLK
P3.6/UCA1TXD/UCA1SIMO
P1.3/TA2
TMS
P2.5/R /CA5
OSC
P1.6/TA1
DV
SS
P1.5/TA0
AV
CC
1962206121602259235824
57
27
54
2655285329523051315032
49
409
472
48
1
463
436
45
4
44
5
42
7
41
8
37
12
3910
38
11
3613
35
14
3316
3415
25
56
18
63
17
64
PM OR RGC PACKAGE
(TOP VIEW)
MSP430F2410,
MSP430F24x
MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Device Pinout, MSP430F24x, MSP430F2410
www.ti.com
4 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 5

P1.7/TA2
AV
SS
P6.2
P2.0/ACLK/CA2
P6.1
P2.1/TAINCLK/CA3
P6.0
P2.2/CAOUT/TA0/CA4
RST/NMI
P2.3/CA0/TA1
TCK
P2.4/CA1/TA2
TDO/TDI
P2.7/TA0/CA7
TDI/TCLK
P2.6/ADC12CLK/CA6
XT2IN
P3.0/UCB0STE/UCA0CLK
XT2OUT
P5.7/TBOUTH/SVSOUT
P3.2/UCB0SOMI/UCB0SCL
P5.6/ACLK
P3.3/UCB0CLK/UCA0STE
P5.5/SMCLK
P3.4/UCA0TXD/UCA0SIMO
P4.4/TB4
XOUT
P5.3/UCB1CLK/UCA1STE
P6.3
P5.4/MCLK
DV
CC
P5.2/UCB1SOMI/UCB1SCL
P6.4
P4.7/TBCLK
P6.7/A7/SVSIN
P5.1/UCB1SIMO/UCB1SDA
P6.5
P5.0/UCB1STE/UCA1CLK
P6.6
P4.6/TB6
V
REF+
P4.5/TB5XIN
P4.1/TB1P1.0/TACLK/CAOUT
P4.3/TB3DV
SS
P4.2/TB2DV
SS
P4.0/TB0P1.1/TA0
P3.7/UCA1RXD/UCA1SOMIP1.2/TA1
P3.5/UCA0RXD/UCA0SOMIP1.4/SMCLK
P3.6/UCA1TXD/UCA1SIMO
P1.3/TA2
TMS
P2.5/R /CA5
OSC
P1.6/TA1
DV
SS
P1.5/TA0
AV
CC
1962206121602259235824
57
27
54
2655285329523051315032
49
409
472
48
1
463
436
45
4
44
5
42
7
41
8
37
12
3910
38
11
3613
35
14
3316
3415
25
56
18
63
17
64
PM OR RGC PACKAGE
(TOP VIEW)
MSP430F24x1
www.ti.com
Device Pinout, MSP430F24x1
MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 5
Page 6

Oscillators
Basic Clock
System+
RAM
2kB
1kB
BOR
SVS/SVM
RST/NMI
DVCC
DVSS
MCLK
Watchdog
WDT+
15/16-Bit
Timer_A3
3 CC
Registers
16MHz
CPU
incl. 16
Registers
Emulation
XOUT/
XT2OUT
JTAG
Interface
Ports
P1/P2
2x8 I/O
Interrupt
capability
USCI A0
UART/LIN,
IrDA, SPI
USCI B0
SPI, I2C
Comp_A+
Flash
16kB
8kB
Timer_B3
3 CC
Registers,
Shadow
Reg
ADC12
12-Bit
8
Channels
Ports
P3/P4
P5/P6
4x8 I/O
AVCC
AVSS
P1.x/P2.x
2x8
P3.x/P4.x
P5.x/P6.x
4x8
XIN/
XT2IN
22
SMCLK
ACLK
MDB
MAB
Hardware
Multiplier
MPY,
MPYS,
MAC,
MACS
MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Functional Block Diagram, MSP430F23x
www.ti.com
6 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 7

Oscillators
Basic Clock
System+
RAM
2kB
4kB
4kB
4kB
BOR
SVS/SVM
RST/NMI
DVCC
DVSS
MCLK
Watchdog
WDT+
15/16-Bit
Timer_A3
3 CC
Registers
16MHz
CPU
incl. 16
Registers
Emulation
XOUT/
XT2OUT
JTAG
Interface
Ports
P1/P2
2x8 I/O
Interrupt
capability
USCI A0
UART/LIN,
IrDA, SPI
USCI B0
SPI, I2C
Comp_A+
Flash
60kB
56kB
48kB
32kB
Timer_B7
7 CC
Registers,
Shadow
Reg
ADC12
12-Bit
8
Channels
Ports
P3/P4
P5/P6
4x8 I/O
AVCC
AVSS
P1.x/P2.x
2x8
P3.x/P4.x
P5.x/P6.x
4x8
XIN/
XT2IN
22
SMCLK
ACLK
MDB
MAB
Hardware
Multiplier
MPY,
MPYS,
MAC,
MACS
USCI A1
UART/LIN,
IrDA, SPI
USCI B1
SPI, I2C
www.ti.com
Functional Block Diagram, MSP430F24x, MSP430F2410
MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 7
Page 8

Oscillators
Basic Clock
System+
RAM
2kB
4kB
4kB
BOR
SVS/SVM
RST/NMI
DVCC
DVSS
MCLK
Watchdog
WDT+
15/16-Bit
Timer_A3
3 CC
Registers
16MHz
CPU
incl. 16
Registers
Emulation
XOUT/
XT2OUT
JTAG
Interface
Ports
P1/P2
2x8 I/O
Interrupt
capability
USCI A0
UART/LIN,
IrDA, SPI
USCI B0
SPI, I2C
Comp_A+
Flash
60kB
48kB
32kB
Timer_B7
7 CC
Registers,
Shadow
Reg
Ports
P3/P4
P5/P6
4x8 I/O
AVCC
AVSS
P1.x/P2.x
2x8
P3.x/P4.x
P5.x/P6.x
4x8
XIN/
XT2IN
22
SMCLK
ACLK
MDB
MAB
Hardware
Multiplier
MPY,
MPYS,
MAC,
MACS
USCI A1
UART/LIN,
IrDA, SPI
USCI B1
SPI, I2C
MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Functional Block Diagram, MSP430F24x1
www.ti.com
8 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 9

MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
www.ti.com
Table 2. Terminal Functions, MSP430F23x
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
AV
CC
AV
SS
DV
CC
DV
SS
P1.0/TACLK/CAOUT 12 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_A, clock signal TACLK input/Comparator_A output
P1.1/TA0 13 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_A, capture: CCI0A input, compare: Out0 output/BSL transmit
P1.2/TA1 14 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_A, capture: CCI1A input, compare: Out1 output
P1.3/TA2 15 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_A, capture: CCI2A input, compare: Out2 output
P1.4/SMCLK 16 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / SMCLK signal output
P1.5/TA0 17 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_A, compare: Out0 output
P1.6/TA1 18 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_A, compare: Out1 output
P1.7/TA2 19 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_A, compare: Out2 output
P2.0/ACLK/CA2 20 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / ACLK output/Comparator_A input
P2.1/TAINCLK/CA3 21 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_A, clock signal at INCLK
P2.2/CAOUT/TA0/CA4 22 I/O
P2.3/CA0/TA1 23 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_A, compare: Out1 output/Comparator_A input
P2.4/CA1/TA2 24 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_A, compare: Out2 output/Comparator_A input
P2.5/R
P2.6/ADC12CLK/CA6 26 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / conversion clock - 12-bit ADC/Comparator_A input
P2.7/TA0/CA7 27 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_A, compare: Out0 output/Comparator_A input
P3.0/UCB0STE/ UCA0CLK 28 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / USCI_B0 slave transmit enable/USCI A0 clock input/output
P3.1/UCB0SIMO/UCB0SDA 29 I/O
P3.2/UCB0SOMI/ UCB0SCL 30 I/O
P3.3/UCB0CLK/UCA0STE 31 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / USCI_B0 clock input/output, USCI A0 slave transmit enable
P3.4/UCA0TXD/ UCA0SIMO 32 I/O
P3.5/UCA0RXD/ General-purpose digital I/O / USCI_A0 receive data input in UART mode, slave data out/master in in SPI
UCA0SOMI mode
P3.6 34 I/O General-purpose digital I/O
P3.7 35 I/O General-purpose digital I/O
P4.0/TB0 36 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_B, capture: CCI0A/B input, compare: Out0 output
P4.1/TB1 37 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_B, capture: CCI1A/B input, compare: Out1 output
P4.2/TB2 38 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_B, capture: CCI2A/B input, compare: Out2 output
P4.3 39 I/O General-purpose digital I/O
P4.4 40 I/O General-purpose digital I/O
P4.5 41 I/O General-purpose digital I/O
P4.6 42 I/O General-purpose digital I/O
P4.7/TBCLK 43 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_B, clock signal TBCLK input
P5.0 44 I/O General-purpose digital I/O
P5.1 45 I/O General-purpose digital I/O
P5.2 46 I/O General-purpose digital I/O
P5.3 47 I/O General-purpose digital I/O
P5.4/MCLK 48 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / main system clock MCLK output
P5.5/SMCLK 49 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / submain system clock SMCLK output
P5.6/ACLK 50 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / auxiliary clock ACLK output
P5.7/TBOUTH/SVSOUT 51 I/O
P6.0/A0 59 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / analog input A0 - 12-bit ADC
P6.1/A1 60 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / analog input A1 - 12-bit ADC
P6.2/A2 61 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / analog input A2 - 12-bit ADC
/CA5 25 I/O
OSC
64 Analog supply voltage, positive. Supplies only the analog portion of ADC12.
62 Analog supply voltage, negative. Supplies only the analog portion of ADC12.
63 Digital supply voltage, negative. Supplies all digital parts.
33 I/O
I/O DESCRIPTION
1 Digital supply voltage, positive. Supplies all digital parts.
General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_A, capture: CCI0B input/Comparator_A output/BSL
receive/Comparator_A input
General-purpose digital I/O / input for external resistor defining the DCO nominal frequency/Comparator_A
input
General-purpose digital I/O / USCI_B0 slave in/master out in SPI mode, SDA I2C data in I2C mode
General-purpose digital I/O / USCI_B0 slave out/master in in SPI mode, SCL I2C clock in I2C mode
General-purpose digital I/O / USCI_A0 transmit data output in UART mode, slave data in/master out in SPI
mode
General-purpose digital I/O / switch all PWM digital output ports to high impedance - Timer_B TB0 to
TB6/SVS comparator output
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 9
Page 10

MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Table 2. Terminal Functions, MSP430F23x (continued)
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
P6.3/A3 2 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / analog input A3 - 12-bit ADC
P6.4/A4 3 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / analog input A4 - 12-bit ADC
P6.5/A5 4 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / analog input A5 - 12-bit ADC
P6.6/A6 5 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / analog input A6 - 12-bit ADC
P6.7/A7/SVSIN 6 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / analog input A7 - 12-bit ADC/SVS input
XT2OUT 52 O Output terminal of crystal oscillator XT2
XT2IN 53 I Input port for crystal oscillator XT2
RST/NMI 58 I Reset input, nonmaskable interrupt input, or bootstrap loader start (in flash devices)
TCK 57 I Test clock (JTAG). TCK is the clock input port for device programming test and bootstrap loader start.
TDI/TCLK 55 I Test data input or test clock input. The device protection fuse is connected to TDI/TCLK.
TDO/TDI 54 I/O Test data output. TDO/TDI data output or programming data input terminal.
TMS 56 I Test mode select. TMS is used as an input port for device programming and test.
V
eREF+
V
REF+
V
REF-/VeREF-
XIN 8 I Input for crystal oscillator XT1. Standard or watch crystals can be connected.
XOUT 9 O Output for crystal oscillator XT1. Standard or watch crystals can be connected.
QFN Pad NA NA QFN package pad connection to DVSSrecommended
10 I Input for an external reference voltage
11 I
I/O DESCRIPTION
7 O Output of positive terminal of the reference voltage in the ADC12
Negative terminal for the reference voltage for both sources, the internal reference voltage, or an external
applied reference voltage
www.ti.com
10 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 11

MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
www.ti.com
Table 3. Terminal Functions, MSP430F24x, MSP430F2410
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
AV
CC
AV
SS
DV
CC
DV
SS
P1.0/TACLK/CAOUT 12 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_A, clock signal TACLK input/Comparator_A output
P1.1/TA0 13 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_A, capture: CCI0A input, compare: Out0 output/BSL transmit
P1.2/TA1 14 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_A, capture: CCI1A input, compare: Out1 output
P1.3/TA2 15 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_A, capture: CCI2A input, compare: Out2 output
P1.4/SMCLK 16 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / SMCLK signal output
P1.5/TA0 17 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_A, compare: Out0 output
P1.6/TA1 18 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_A, compare: Out1 output
P1.7/TA2 19 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_A, compare: Out2 output
P2.0/ACLK/CA2 20 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / ACLK output/Comparator_A input
P2.1/TAINCLK/CA3 21 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_A, clock signal at INCLK
P2.2/CAOUT/TA0/CA4 22 I/O
P2.3/CA0/TA1 23 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_A, compare: Out1 output / Comparator_A input
P2.4/CA1/TA2 24 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_A, compare: Out2 output / Comparator_A input
P2.5/R
P2.6/ADC12CLK/CA6 26 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Conversion clock - 12-bit ADC / Comparator_A input
P2.7/TA0/CA7 27 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_A, compare: Out0 output / Comparator_A input
P3.0/UCB0STE/ UCA0CLK 28 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / USCI_B0 slave transmit enable / USCI A0 clock input/output
P3.1/UCB0SIMO/UCB0SDA 29 I/O
P3.2/UCB0SOMI/ UCB0SCL 30 I/O
P3.3/UCB0CLK/UCA0STE 31 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / USCI_B0 clock input/output, USCI A0 slave transmit enable
P3.4/UCA0TXD/UCA0SIMO 32 I/O
P3.5/UCA0RXD/ General-purpose digital I/O / USCI_A0 receive data input in UART mode, slave data out/master in in SPI
UCA0SOMI mode
P3.6/UCA1TXD/UCA1SIMO 34 I/O
P3.7/UCA1RXD/ General-purpose digital I/O / USCI_A1 receive data input in UART mode, slave data out/master in in SPI
UCA1SOMI mode
P4.0/TB0 36 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_B, capture: CCI0A/B input, compare: Out0 output
P4.1/TB1 37 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_B, capture: CCI1A/B input, compare: Out1 output
P4.2/TB2 38 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_B, capture: CCI2A/B input, compare: Out2 output
P4.3/TB3 39 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_B, capture: CCI3A/B input, compare: Out3 output
P4.4/TB4 40 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_B, capture: CCI4A/B input, compare: Out4 output
P4.5/TB5 41 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_B, capture: CCI5A/B input, compare: Out5 output
P4.6/TB6 42 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_B, capture: CCI6A input, compare: Out6 output
P4.7/TBCLK 43 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_B, clock signal TBCLK input
P5.0/UCB1STE/UCA1CLK 44 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / USCI_B1 slave transmit enable / USCI_A1 clock input/output
P5.1/UCB1SIMO/UCB1SDA 45 I/O
P5.2/UCB1SOMI/UCB1SCL 46 I/O
P5.3/UCB1CLK/UCA1STE 47 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / USCI_B1 clock input/output, USCI_A1 slave transmit enable
P5.4/MCLK 48 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / main system clock MCLK output
P5.5/SMCLK 49 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / submain system clock SMCLK output
P5.6/ACLK 50 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / auxiliary clock ACLK output
P5.7/TBOUTH/SVSOUT 51 I/O
P6.0/A0 59 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / analog input A0 - 12-bit ADC
/CA5 25 I/O
OSC
64 Analog supply voltage, positive terminal. Supplies only the analog portion of ADC12.
62 Analog supply voltage, negative terminal. Supplies only the analog portion of ADC12.
63 Digital supply voltage, negative terminal. Supplies all digital parts.
33 I/O
35 I/O
I/O DESCRIPTION
1 Digital supply voltage, positive terminal. Supplies all digital parts.
General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_A, capture: CCI0B input / Comparator_A output/BSL
receive/Comparator_A input
General-purpose digital I/O / Input for external resistor defining the DCO nominal frequency / Comparator_A
input
General-purpose digital I/O / USCI_B0 slave in/master out in SPI mode, SDA I2C data in I2C mode
General-purpose digital I/O / USCI_B0 slave out/master in in SPI mode, SCL I2C clock in I2C mode
General-purpose digital I/O / USCI_A- transmit data output in UART mode, slave data in/master out in SPI
mode
General-purpose digital I/O / USCI_A1 transmit data output in UART mode, slave data in/master out in SPI
mode
General-purpose digital I/O / USCI_B1 slave in/master out in SPI mode, SDA I2C data in I2C mode
General-purpose digital I/O / USCI_B1 slave out/master in in SPI mode, SCL I2C clock in I2C mode
General-purpose digital I/O / switch all PWM digital output ports to high impedance - Timer_B TB0 to
TB6/SVS comparator output
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 11
Page 12

MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Table 3. Terminal Functions, MSP430F24x, MSP430F2410 (continued)
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
P6.1/A1 60 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / analog input A1 - 12-bit ADC
P6.2/A2 61 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / analog input A2 - 12-bit ADC
P6.3/A3 2 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / analog input A3 - 12-bit ADC
P6.4/A4 3 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / analog input A4 - 12-bit ADC
P6.5/A5 4 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / analog input A5 - 12-bit ADC
P6.6/A6 5 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / analog input A6 - 12-bit ADC
P6.7/A7/SVSIN 6 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / analog input A7 - 12-bit ADC/SVS input
XT2OUT 52 O Output of crystal oscillator XT2
XT2IN 53 I Input for crystal oscillator XT2
RST/NMI 58 I Reset input, nonmaskable interrupt input, or bootstrap loader start (in flash devices)
TCK 57 I Test clock (JTAG). TCK is the clock input port for device programming test and bootstrap loader start.
TDI/TCLK 55 I Test data input or test clock input. The device protection fuse is connected to TDI/TCLK.
TDO/TDI 54 I/O Test data output. TDO/TDI data output or programming data input terminal.
TMS 56 I Test mode select. TMS is used as an input port for device programming and test.
V
eREF+
V
REF+
V
REF-/VeREF-
XIN 8 I Input for crystal oscillator XT1. Standard or watch crystals can be connected.
XOUT 9 O Output for crystal oscillator XT1. Standard or watch crystals can be connected.
QFN Pad NA NA QFN package pad connection to DVSSrecommended (RGC package only)
10 I Input for an external reference voltage
11 I
I/O DESCRIPTION
7 O Positive output of the reference voltage in the ADC12
Negative input for the reference voltage for both sources, the internal reference voltage, or an external
applied reference voltage
www.ti.com
12 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 13

MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
www.ti.com
Table 4. Terminal Functions, MSP430F24x1
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
AV
CC
AV
SS
DV
CC
DV
SS
P1.0/TACLK/CAOUT 12 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_A, clock signal TACLK input / Comparator_A output
P1.1/TA0 13 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_A, capture: CCI0A input, compare: Out0 output / BSL transmit
P1.2/TA1 14 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_A, capture: CCI1A input, compare: Out1 output
P1.3/TA2 15 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_A, capture: CCI2A input, compare: Out2 output
P1.4/SMCLK 16 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / SMCLK signal output
P1.5/TA0 17 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_A, compare: Out0 output
P1.6/TA1 18 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_A, compare: Out1 output
P1.7/TA2 19 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_A, compare: Out2 output
P2.0/ACLK/CA2 20 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / ACLK output/Comparator_A input
P2.1/TAINCLK/CA3 21 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_A, clock signal at INCLK
P2.2/CAOUT/TA0/CA4 22 I/O
P2.3/CA0/TA1 23 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_A, compare: Out1 output / Comparator_A input
P2.4/CA1/TA2 24 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_A, compare: Out2 output / Comparator_A input
P2.5/R
P2.6/ADC12CLK/CA6 26 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / conversion clock - 12-bit ADC / Comparator_A input
P2.7/TA0/CA7 27 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_A, compare: Out0 output/Comparator_A input
P3.0/UCB0STE/ UCA0CLK 28 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / USCI_B0 slave transmit enable/USCI A0 clock input/output
P3.1/UCB0SIMO/UCB0SDA 29 I/O
P3.2/UCB0SOMI/ UCB0SCL 30 I/O
P3.3/UCB0CLK/UCA0STE 31 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / USCI_B0 clock input/output, USCI A0 slave transmit enable
P3.4/UCA0TXD/UCA0SIMO 32 I/O
P3.5/UCA0RXD/ General-purpose digital I/O / USCI_A0 receive data input in UART mode, slave data out/master in in SPI
UCA0SOMI mode
P3.6/UCA1TXD/UCA1SIMO 34 I/O
P3.7/UCA1RXD/ General-purpose digital I/O / USCI_A1 receive data input in UART mode, slave data out/master in in SPI
UCA1SOMI mode
P4.0/TB0 36 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_B, capture: CCI0A/B input, compare: Out0 output
P4.1/TB1 37 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_B, capture: CCI1A/B input, compare: Out1 output
P4.2/TB2 38 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_B, capture: CCI2A/B input, compare: Out2 output
P4.3/TB3 39 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_B, capture: CCI3A/B input, compare: Out3 output
P4.4/TB4 40 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_B, capture: CCI4A/B input, compare: Out4 output
P4.5/TB5 41 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_B, capture: CCI5A/B input, compare: Out5 output
P4.6/TB6 42 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_B, capture: CCI6A input, compare: Out6 output
P4.7/TBCLK 43 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_B, clock signal TBCLK input
P5.0/UCB1STE/UCA1CLK 44 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / USCI_B1 slave transmit enable/USCI_A1 clock input/output
P5.1/UCB1SIMO/UCB1SDA 45 I/O
P5.2/UCB1SOMI/UCB1SCL 46 I/O
P5.3/UCB1CLK/UCA1STE 47 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / USCI_B1 clock input/output, USCI_A1 slave transmit enable
P5.4/MCLK 48 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / main system clock MCLK output
P5.5/SMCLK 49 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / submain system clock SMCLK output
P5.6/ACLK 50 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / auxiliary clock ACLK output
P5.7/TBOUTH/SVSOUT 51 I/O
P6.0 59 I/O General-purpose digital I/O
/CA5 25 I/O
OSC
64 Analog supply voltage, positive. Supplies only the analog portion of ADC12.
62 Analog supply voltage, negative. Supplies only the analog portion of ADC12.
63 Digital supply voltage, negative. Supplies all digital parts.
33 I/O
35 I/O
I/O DESCRIPTION
1 Digital supply voltage, positive. Supplies all digital parts.
General-purpose digital I/O / Timer_A, capture: CCI0B input / Comparator_A output/BSL
receive/Comparator_A input
General-purpose digital I/O / input for external resistor defining the DCO nominal frequency / Comparator_A
input
General-purpose digital I/O / USCI_B0 slave in/master out in SPI mode, SDA I2C data in I2C mode
General-purpose digital I/O / USCI_B0 slave out/master in in SPI mode, SCL I2C clock in I2C mode
General-purpose digital I/O / USCI_A0 transmit data output in UART mode, slave data in/master out in SPI
mode
General-purpose digital I/O / USCI_A1 transmit data output in UART mode, slave data in/master out in SPI
mode
General-purpose digital I/O / USCI_B1 slave in/master out in SPI mode, SDA I2C data in I2C mode
General-purpose digital I/O / USCI_B1 slave out/master in in SPI mode, SCL I2C clock in I2C mode
General-purpose digital I/O / switch all PWM digital output ports to high impedance - Timer_B TB0 to
TB6/SVS comparator output
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 13
Page 14

MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Table 4. Terminal Functions, MSP430F24x1 (continued)
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
P6.1 60 I/O General-purpose digital I/O
P6.2 61 I/O General-purpose digital I/O
P6.3 2 I/O General-purpose digital I/O
P6.4 3 I/O General-purpose digital I/O
P6.5 4 I/O General-purpose digital I/O
P6.6 5 I/O General-purpose digital I/O
P6.7/SVSIN 6 I/O General-purpose digital I/O / SVS input
XT2OUT 52 O Output terminal of crystal oscillator XT2
XT2IN 53 I Input port for crystal oscillator XT2
RST/NMI 58 I Reset input, nonmaskable interrupt input, or bootstrap loader start (in flash devices).
TCK 57 I Test clock (JTAG). TCK is the clock input for device programming test and bootstrap loader start.
TDI/TCLK 55 I Test data input or test clock input. The device protection fuse is connected to TDI/TCLK.
TDO/TDI 54 I/O Test data output. TDO/TDI data output or programming data input terminal.
TMS 56 I Test mode select. TMS is used as an input port for device programming and test.
DV
SS
Reserved 7 O Reserved, do not connect externally
DV
SS
XIN 8 I Input for crystal oscillator XT1. Standard or watch crystals can be connected.
XOUT 9 O Output for crystal oscillator XT1. Standard or watch crystals can be connected.
QFN Pad NA NA QFN package pad connection to DVSSrecommended (RGC package only)
10 I Connected to DV
11 I Connected to DV
I/O DESCRIPTION
SS
SS
www.ti.com
14 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 15

General-Purpose Register
Program Counter
Stack Pointer
Status Register
Constant Generator
General-Purpose Register
General-Purpose Register
General-Purpose Register
PC/R0
SP/R1
SR/CG1/R2
CG2/R3
R4
R5
R12
R13
General-Purpose Register
General-Purpose Register
R6
R7
General-Purpose Register
General-Purpose Register
R8
R9
General-Purpose Register
General-Purpose Register
R10
R11
General-Purpose Register
General-Purpose Register
R14
R15
www.ti.com
SHORT-FORM DESCRIPTION
CPU
The MSP430 CPU has a 16-bit RISC architecture
that is highly transparent to the application. All
operations, other than program-flow instructions, are
performed as register operations in conjunction with
seven addressing modes for source operand and four
addressing modes for destination operand.
The CPU is integrated with 16 registers that provide
reduced instruction execution time. The register-toregister operation execution time is one cycle of the
CPU clock.
Four of the registers, R0 to R3, are dedicated as
program counter, stack pointer, status register, and
constant generator, respectively. The remaining
registers are general-purpose registers.
Peripherals are connected to the CPU using data,
address, and control buses, and can be handled with
all instructions.
MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Instruction Set
The instruction set consists of 51 instructions with
three formats and seven address modes. Each
instruction can operate on word and byte data.
Table 5 shows examples of the three types of
instruction formats; Table 6 shows the address
modes.
Dual operands, source-destination ADD R4,R5 R4 + R5 → R5
Single operands, destination only CALL R8 PC → (TOS), R8 → PC
Relative jump, unconditional/conditional JNE Jump-on-equal bit = 0
ADDRESS MODE S
Register ✓ ✓ MOV Rs,Rd MOV R10,R11 R10 → R11
Indexed ✓ ✓ MOV X(Rn),Y(Rm) MOV 2(R5),6(R6) M(2+R5) → M(6+R6)
Symbolic (PC relative) ✓ ✓ MOV EDE,TONI M(EDE) → M(TONI)
Absolute ✓ ✓ MOV &MEM,&TCDAT M(MEM) → M(TCDAT)
Indirect ✓ MOV @Rn,Y(Rm) MOV @R10,Tab(R6) M(R10) → M(Tab+R6)
Indirect autoincrement ✓ MOV @Rn+,Rm MOV @R10+,R11
Immediate ✓ MOV #X,TONI MOV #45,TONI #45 → M(TONI)
(1) S = source
(2) D = destination
Table 5. Instruction Word Formats
INSTRUCTION FORMAT EXAMPLE OPERATION
(1)
Table 6. Address Mode Descriptions
(2)
D
SYNTAX EXAMPLE OPERATION
M(R10) → R11
R10 + 2 → R10
Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 15
Page 16

MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Operating Modes
The MSP430 has one active mode and five software-selectable low-power modes of operation. An interrupt
event can wake up the device from any of the five low-power modes, service the request, and restore back to the
low-power mode on return from the interrupt program.
The following six operating modes can be configured by software:
• Active mode (AM)
– All clocks are active.
• Low-power mode 0 (LPM0)
– CPU is disabled.
– ACLK and SMCLK remain active. MCLK is disabled.
• Low-power mode 1 (LPM1)
– CPU is disabled ACLK and SMCLK remain active. MCLK is disabled.
– DCO dc-generator is disabled if DCO not used in active mode.
• Low-power mode 2 (LPM2)
– CPU is disabled.
– MCLK and SMCLK are disabled.
– DCO dc-generator remains enabled.
– ACLK remains active.
• Low-power mode 3 (LPM3)
– CPU is disabled.
– MCLK and SMCLK are disabled.
– DCO dc-generator is disabled.
– ACLK remains active.
• Low-power mode 4 (LPM4)
– CPU is disabled.
– ACLK is disabled.
– MCLK and SMCLK are disabled.
– DCO dc-generator is disabled.
– Crystal oscillator is stopped.
www.ti.com
16 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 17

MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
www.ti.com
Interrupt Vector Addresses
The interrupt vectors and the power-up starting address are located in the address range 0xFFFF to 0xFFC0.
The vector contains the 16-bit address of the appropriate interrupt-handler instruction sequence. If the reset
vector (0xFFFE) contains 0xFFFF (for example, if flash is not programmed) the CPU enters LPM4 after powerup.
Table 7. Interrupt Vector Addresses
INTERRUPT SOURCE INTERRUPT FLAG SYSTEM INTERRUPT WORD ADDRESS PRIORITY
Power-up PORIFG
External reset WDTIFG
Watchdog RSTIFG Reset 0xFFFE 31, highest
Flash key violation KEYV
PC out of range
NMI NMIIFG (Non)maskable
Oscillator fault OFIFG (Non)maskable 0xFFFC 30
Flash memory access violation ACCVIFG
Timer_B7
Timer_B7
Comparator_A+ CAIFG Maskable 0xFFF6 27
Watchdog timer+ WDTIFG Maskable 0xFFF4 26
Timer_A3 TACCR0 CCIFG
Timer_A3 Maskable 0xFFF0 24
USCI_A0/USCI_B0 receive
USCI_B0 I2C status
USCI_A0/USCI_B0 transmit
USCI_B0 I2C receive / transmit
ADC12
I/O port P2 (eight flags) P2IFG.0 to P2IFG.7
I/O port P1 (eight flags) P1IFG.0 to P1IFG.7
USCI_A1/USCI_B1 receive
USCI_B1 I2C status
USCI_A1/USCI_B1 transmit
USCI_B1 I2C receive / transmit
Reserved
(1) A reset is generated if the CPU tries to fetch instructions from within the module register memory address range (0x0000 to 0x01FF) or
from within unused address range.
(2) Multiple source flags
(3) (Non)maskable: The individual interrupt-enable bit can disable an interrupt event, but the general-interrupt enable cannot.
(4) Timer_B7 in MSP430F24x(1)/MSP430F2410 family has seven CCRs, Timer_B3 in MSP430F23x family has three CCRs. In Timer_B3,
there are only interrupt flags TBCCR0 CCIFG, TBCCR1 CCIFG, and TBCCR2 CCIFG, and the interrupt enable bits TBCCTL0 CCIE,
TBCCTL1 CCIE, and TBCCTL2 CCIE.
(5) Interrupt flags are located in the module.
(6) In SPI mode: UCB0RXIFG. In I2C mode: UCALIFG, UCNACKIFG, ICSTTIFG, UCSTPIFG.
(7) In UART/SPI mode: UCB0TXIFG. In I2C mode: UCB0RXIFG, UCB0TXIFG.
(8) ADC12 is not implemented in the MSP430F24x1 family.
(9) The address 0xFFDE is used as bootstrap loader security key (BSLSKEY). A 0xAA55 at this location disables the BSL completely. A
zero disables the erasure of the flash if an invalid password is supplied.
(10) The interrupt vectors at addresses 0xFFDE to 0xFFC0 are not used in this device and can be used for regular program code if
necessary.
(4)
(4)
(8)
(9)(10)
(1)
TBCCR0 CCIFG
TBCCR1 to TBCCR6 CCIFGs,
TACCR1 CCIFG
TACCR2 CCIFG TAIFG
UCA0RXIFG, UCB0RXIFG
UCA0TXIFG, UCB0TXIFG
ADC12IFG
UCA1RXIFG, UCB1RXIFG
UCA1TXIFG, UCB1TXIFG
(see
TBIFG
(2)
)
(2)(3)
(2)(5)
(2)(5)
(5)
(5)
(2)(5)
(2)(5)
(2)(5)
(2)(6)
(2)(7)
(2)(6)
(2)(7)
(Non)maskable
Maskable 0xFFFA 29
Maskable 0xFFF8 28
Maskable 0xFFF2 25
Maskable 0xFFEE 23
Maskable 0xFFEC 22
Maskable 0xFFEA 21
Maskable 0xFFE6 19
Maskable 0xFFE4 18
Maskable 0xFFE2 17
Maskable 0xFFE0 16
Reserved 0xFFDE to 0xFFC0 15 to 0, lowest
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
0xFFE8 20
Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 17
Page 18

MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Special Function Registers
Most interrupt enable bits are collected in the lowest address space. Special-function register bits not allocated to
a functional purpose are not physically present in the device. This arrangement provides simple software access.
Legend
rw Bit can be read and written.
rw-0, 1 Bit can be read and written. It is Reset or Set by PUC.
rw-(0), (1) Bit can be read and written. It is Reset or Set by POR.
SFR bit is not present in device.
Table 8. Interrupt Enable 1
Address 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
00h ACCVIE NMIIE OFIE WDTIE
rw-0 rw-0 rw-0 rw-0
www.ti.com
WDTIE Watchdog timer interrupt enable. Inactive if watchdog mode is selected. Active if watchdog timer is configured in interval
OFIE Oscillator fault interrupt enable
NMIIE (Non)maskable interrupt enable
ACCVIE Flash access violation interrupt enable
timer mode.
Table 9. Interrupt Enable 2
Address 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
01h UCB0TXIE UCB0RXIE UCA0TXIE UCA0RXIE
rw-0 rw-0 rw-0 rw-0
UCA0RXIE USCI_A0 receive-interrupt enable
UCA0TXIE USCI_A0 transmit-interrupt enable
UCB0RXIE USCI_B0 receive-interrupt enable
UCB0TXIE USCI_B0 transmit-interrupt enable
Table 10. Interrupt Flag Register 1
Address 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
02h NMIIFG RSTIFG PORIFG OFIFG WDTIFG
rw-0 rw-(0) rw-(1) rw-1 rw-(0)
WDTIFG Set on watchdog timer overflow (in watchdog mode) or security key violation.
Reset on VCCpower-up or a reset condition at RST/NMI pin in reset mode.
OFIFG Flag set on oscillator fault
RSTIFG External reset interrupt flag. Set on a reset condition at RST/NMI pin in reset mode. Reset on VCCpower up.
PORIFG Power-on reset interrupt flag. Set on VCCpower up.
NMIIFG Set via RST/NMI pin
Address 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
03h UCB0TXIFG UCB0RXIFG UCA0TXIFG UCA0RXIFG
UCA0RXIFG USCI_A0 receive-interrupt flag
UCA0TXIFG USCI_A0 transmit-interrupt flag
UCB0RXIFG USCI_B0 receive-interrupt flag
UCB0TXIFG USCI_B0 transmit-interrupt flag
18 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Table 11. Interrupt Flag Register 2
rw-1 rw-0 rw-1 rw-0
Page 19

MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
www.ti.com
Memory Organization
Table 12. Memory Organization
MSP430F233 MSP430F235
Memory Size 8KB 16KB 60KB
Main: interrupt vector Flash 0xFFFF to 0xFFC0 0xFFFF to 0xFFC0 0xFFFF to 0xFFC0
Main: code memory Flash 0xFFFF to 0xE000 0xFFFF to 0xC000 0xFFFF to 0x1100
RAM (Total) Size 1KB 2KB 2KB
0x05FF to 0x0200 0x09FF to 0x0200 0x09FF to 0x0200
Information memory Size 256 Byte 256 Byte 256 Byte
Flash 0x10FF to 0x1000 0x10FF to 0x1000 0x10FF to 0x1000
Boot memory Size 1KB 1KB 1KB
ROM 0x0FFF to 0x0C00 0x0FFF to 0x0C00 0x0FFF to 0x0C00
RAM Size 1KB 2KB 2KB
0x05FF to 0x0200 0x09FF to 0x0200 0x09FF to 0x0200
Peripherals 16 bit 0x01FF to 0x0100 0x01FF to 0x0100 0x01FF to 0x0100
8 bit 0x00FF to 0x0010 0x00FF to 0x0010 0x00FF to 0x0010
SFR 0x000F to 0x0000 0x000F to 0x0000 0x000F to 0x0000
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
MSP430F249
MSP430F2491
MSP430F247 MSP430F248
MSP430F2471 MSP430F2481
Memory Size 32KB 48KB 56KB
Main: interrupt vector Flash 0xFFFF to 0xFFC0 0xFFFF to 0xFFC0 0xFFFF to 0xFFC0
Main: code memory Flash 0xFFFF to 0x8000 0xFFFF to 0x4000 0xFFFF to 0x2100
RAM (total) Size 4KB 4KB 4KB
0x20FF to 0x1100 0x20FF to 0x1100 0x20FF to 0x1100
Extended Size 2KB 2KB 2KB
0x20FF to 0x1900 0x20FF to 0x1900 0x20FF to 0x1900
Mirrored Size 2KB 2KB 2KB
0x18FF to 0x1100 0x18FF to 0x1100 0x18FF to 0x1100
Information memory Size 256 Byte 256 Byte 256 Byte
Flash 0x10FF to 0x1000 0x10FF to 0x1000 0x10FF to 0x1000
Boot memory Size 1KB 1KB 1KB
ROM 0x0FFF to 0x0C00 0x0FFF to 0x0C00 0x0FFF to 0x0C00
RAM (mirrored at Size 2KB 2KB 2KB
0x18FF to 0x1100) 0x09FF to 0x0200 0x09FF to 0x0200 0x09FF to 0x0200
Peripherals 16 bit 0x01FF to 0x0100 0x01FF to 0x0100 0x01FF to 0x0100
8 bit 0x00FF to 0x0010 0x00FF to 0x0010 0x00FF to 0x0010
SFR 0x000F to 0x0000 0x000F to 0x0000 0x000F to 0x0000
MSP430F2410
Bootstrap Loader (BSL)
The MSP430 bootstrap loader (BSL) enables users to program the flash memory or RAM using a UART serial
interface. Access to the MSP430 memory via the BSL is protected by user-defined password. For complete
description of the features of the BSL and its implementation, see the MSP430 Programming Via the Bootstrap
Loader User’s Guide (SLAU319).
Flash Memory
The flash memory can be programmed via the JTAG port, the bootstrap loader, or in-system by the CPU. The
CPU can perform single-byte and single-word writes to the flash memory. Features of the flash memory include:
• Flash memory has n segments of main memory and four segments of information memory (A to D) of
Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 19
Table 13. BSL Function Pins
BSL FUNCTION PM, RGC PACKAGE PINS
Data transmit 13 - P1.1
Data receive 22 - P2.2
Page 20

MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
64 bytes each. Each segment in main memory is 512 bytes in size.
• Segments 0 to n may be erased in one step, or each segment may be individually erased.
• Segments A to D can be erased individually, or as a group with segments 0 to n.
Segments A to D are also called information memory.
• Segment A contains calibration data. After reset, segment A is protected against programming and erasing. It
can be unlocked, but care should be taken not to erase this segment if the device-specific calibration data is
required.
www.ti.com
20 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 21

MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
www.ti.com
Peripherals
Peripherals are connected to the CPU through data, address, and control buses and can be handled using all
instructions. For complete module descriptions, see the MSP430x2xx Family User's Guide (SLAU144).
Oscillator and System Clock
The clock system is supported by the basic clock module that includes support for a 32768-Hz watch crystal
oscillator, an internal very-low-power low-frequency oscillator, an internal digitally-controlled oscillator (DCO), and
a high-frequency crystal oscillator. The basic clock module is designed to meet the requirements of both low
system cost and low power consumption. The internal DCO provides a fast turn-on clock source and stabilizes in
less than 1 µs. The basic clock module provides the following clock signals:
• Auxiliary clock (ACLK), sourced from a 32768-Hz watch crystal, a high-frequency crystal, or the internal verylow-power LF oscillator.
• Main clock (MCLK), the system clock used by the CPU.
• Sub-Main clock (SMCLK), the sub-system clock used by the peripheral modules.
Calibration Data Stored in Information Memory Segment A
Calibration data is stored for the DCO and for the ADC12. It is organized in a tag-length-value (TLV) structure.
Table 14. Tags Used by the ADC Calibration Tags
NAME ADDRESS VALUE DESCRIPTION
TAG_DCO_30 0x10F6 0x01 DCO frequency calibration at VCC= 3 V andTA= 25°C at calibration
TAG_ADC12_1 0x10DA 0x10 ADC12_1 calibration tag
TAG_EMPTY - 0xFE Identifier for empty memory areas
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Table 15. Labels Used by the ADC Calibration Tags
LABEL CONDITION AT CALIBRATION / DESCRIPTION SIZE ADDRESS OFFSET
CAL_ADC_25T85 INCHx = 0x1010, REF2_5 = 1, TA= 85°C word 0x000E
CAL_ADC_25T30 INCHx = 0x1010, REF2_5 = 1, TA= 30°C word 0x000C
CAL_ADC_25VREF_FACTOR REF2_5 = 1, TA= 30°C, I
CAL_ADC_15T85 INCHx = 0x1010, REF2_5 = 0, TA= 85°C word 0x0008
CAL_ADC_15T30 INCHx = 0x1010, REF2_5 = 0, TA= 30°C word 0x0006
CAL_ADC_15VREF_FACTOR REF2_5 = 0, TA= 30°C, I
CAL_ADC_OFFSET External Vref = 1.5 V, f
CAL_ADC_GAIN_FACTOR External Vref = 1.5 V, f
CAL_BC1_1MHZ - byte 0x0007
CAL_DCO_1MHZ - byte 0x0006
CAL_BC1_8MHZ - byte 0x0005
CAL_DCO_8MHZ - byte 0x0004
CAL_BC1_12MHZ - byte 0x0003
CAL_DCO_12MHZ - byte 0x0002
CAL_BC1_16MHZ - byte 0x0001
CAL_DCO_16MHZ - byte 0x0000
ADC12CLK
ADC12CLK
= 1.0 mA word 0x000A
VREF+
= 0.5 mA word 0x0004
VREF+
= 5 MHz word 0x0002
= 5 MHz word 0x0000
Brownout, Supply Voltage Supervisor (SVS)
The brownout circuit is implemented to provide the proper internal reset signal to the device during power on and
power off. The SVS circuitry detects if the supply voltage drops below a user-selectable level and supports both
supply voltage supervision (the device is automatically reset) and supply voltage monitoring (SVM, the device is
not automatically reset).
The CPU begins code execution after the brownout circuit releases the device reset. However, VCCmay not have
ramped to V
reaches V
Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 21
CC(min)
at that time. The user must ensure that the default DCO settings are not changed until V
CC(min)
. If desired, the SVS circuit can be used to determine when VCCreaches V
CC(min)
.
CC
Page 22

MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Digital I/O
There are up to six 8-bit I/O ports implemented—ports P1 through P6:
• All individual I/O bits are independently programmable.
• Any combination of input, output, and interrupt condition is possible.
• Edge-selectable interrupt input capability for all eight bits of port P1 and P2.
• Read/write access to port-control registers is supported by all instructions.
• Each I/O has an individually programmable pullup/pulldown resistor.
Watchdog Timer (WDT+)
The primary function of the WDT+ module is to perform a controlled system restart after a software problem
occurs. If the selected time interval expires, a system reset is generated. If the watchdog function is not needed
in an application, the module can be disabled or configured as an interval timer and can generate interrupts at
selected time intervals.
Hardware Multiplier
The multiplication operation is supported by a dedicated peripheral module. The module performs 16x16, 16x8,
8x16, and 8x8 bit operations. The module is capable of supporting signed and unsigned multiplication as well as
signed and unsigned multiply and accumulate operations. The result of an operation can be accessed
immediately after the operands have been loaded into the peripheral registers. No additional clock cycles are
required.
www.ti.com
Timer_A3
Timer_A3 is a 16-bit timer/counter with three capture/compare registers. Timer_A3 can support multiple
capture/compares, PWM outputs, and interval timing. Timer_A3 also has extensive interrupt capabilities.
Interrupts may be generated from the counter on overflow conditions and from each of the capture/compare
registers.
Table 16. Timer_A3 Signal Connections
INPUT PIN NUMBER MODULE BLOCK
12 - P1.0 TACLK TACLK
21 - P2.1 TAINCLK INCLK
13 - P1.1 TA0 CCI0A 13 - P1.1
22 - P2.2 TA0 CCI0B 17 - P1.5
14 - P1.2 TA1 CCI1A 14 - P1.2
15 - P1.3 TA2 CCI2A 15 - P1.3
(1) Not available in the MSP430F24x1 devices.
DEVICE INPUT MODULE INPUT MODULE OUTPUT OUTPUT PIN
SIGNAL NAME SIGNAL NUMBER
ACLK ACLK
SMCLK SMCLK
DV
SS
DV
CC
CAOUT (internal) CCI1B 18 - P1.6
DV
SS
DV
CC
ACLK (internal) CCI2B 19 - P1.7
DV
SS
DV
CC
GND 27 - P2.7
V
CC
GND 23 - P2.3
V
CC
GND 24 - P2.4
V
CC
Timer NA
CCR0 TA0
CCR1 TA1
CCR2 TA2
ADC12
(1)
(internal)
22 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 23

MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
www.ti.com
Timer_B7 (MSP430F24x(1) and MSP430F2410 Devices)
Timer_B7 is a 16-bit timer/counter with seven capture/compare registers. Timer_B7 can support multiple
capture/compares, PWM outputs, and interval timing. Timer_B7 also has extensive interrupt capabilities.
Interrupts may be generated from the counter on overflow conditions and from each of the capture/compare
registers.
Table 17. Timer_B7 Signal Connections
INPUT PIN NUMBER MODULE BLOCK
43 - P4.7 TBCLK TBCLK
43 - P4.7 TBCLK INCLK
36 - P4.0 TB0 CCI0A 36 - P4.0
36 - P4.0 TB0 CCI0B ADC12
37 - P4.1 TB1 CCI1A 37 - P4.1
37 - P4.1 TB1 CCI1B ADC12
38 - P4.2 TB2 CCI2A 38 - P4.2
38 - P4.2 TB2 CCI2B
39 - P4.3 TB3 CCI3A 39 - P4.3
39 - P4.3 TB3 CCI3B
40 - P4.4 TB4 CCI4A 40 - P4.4
40 - P4.4 TB4 CCI4B
41 - P4.5 TB5 CCI5A 41 - P4.5
41 - P4.5 TB5 CCI5B
42 - P4.6 TB6 CCI6A 42 - P4.6
(1) Not available in the MSP430F24x1 devices.
(2) Not available in the MSP430F24x1 devices.
DEVICE INPUT MODULE INPUT MODULE OUTPUT OUTPUT PIN
SIGNAL NAME SIGNAL NUMBER
ACLK ACLK
SMCLK SMCLK
DV
DV
DV
DV
DV
DV
DV
DV
DV
DV
DV
DV
SS
CC
SS
CC
SS
CC
SS
CC
SS
CC
SS
CC
GND
V
CC
GND
V
CC
GND
V
CC
GND
V
CC
GND
V
CC
GND
V
CC
ACLK (internal) CCI6B
DV
DV
SS
CC
GND
V
CC
Timer NA
CCR0 TB0
CCR1 TB1
CCR2 TB2
CCR3 TB3
CCR4 TB4
CCR5 TB5
CCR6 TB6
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
(1)
(internal)
(2)
(internal)
Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 23
Page 24

MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Timer_B3 (MSP430F23x Devices)
Timer_B3 is a 16-bit timer/counter with three capture/compare registers. Timer_B3 can support multiple
capture/compares, PWM outputs, and interval timing. Timer_B3 also has extensive interrupt capabilities.
Interrupts may be generated from the counter on overflow conditions and from each of the capture/compare
registers.
Table 18. Timer_B3 Signal Connections
INPUT PIN NUMBER MODULE BLOCK
43 - P4.7 TBCLK TBCLK
43 - P4.7 TBCLK INCLK
36 - P4.0 TB0 CCI0A 36 - P4.0
36 - P4.0 TB0 CCI0B ADC12 (internal)
37 - P4.1 TB1 CCI1A 37 - P4.1
37 - P4.1 TB1 CCI1B ADC12 (internal)
38 - P4.2 TB2 CCI2A 38 - P4.2
38 - P4.2 TB2 CCI2B
DEVICE INPUT MODULE INPUT MODULE OUTPUT OUTPUT PIN
SIGNAL NAME SIGNAL NUMBER
ACLK ACLK
SMCLK SMCLK
DV
DV
DV
DV
DV
DV
SS
CC
SS
CC
SS
CC
GND
V
CC
GND
V
CC
GND
V
CC
Timer NA
CCR0 TB0
CCR1 TB1
CCR2 TB2
www.ti.com
Universal Serial Communications Interface (USCI)
The USCI modules are used for serial data communication. The USCI module supports synchronous
communication protocols, such as SPI (3 or 4 pin) or I2C, and asynchronous combination protocols, such as
UART, enhanced UART with automatic baudrate detection (LIN), and IrDA.
The USCI A module provides support for SPI (3 or 4 pin), UART, enhanced UART, and IrDA.
The USCI B module provides support for SPI (3 or 4 pin) and I2C.
Comparator_A+
The primary function of the comparator_A+ module is to support precision slope analog-to-digital conversions,
battery-voltage supervision, and monitoring of external analog signals.
ADC12 (MSP430F23x, MSP430F24x, and MSP430F2410 Devices)
The ADC12 module supports fast, 12-bit analog-to-digital conversions. The module implements a 12-bit SAR
core, sample select control, reference generator, and a 16-word conversion-and-control buffer. The conversionand-control buffer allows up to 16 independent ADC samples to be converted and stored without any CPU
intervention.
24 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 25

MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
www.ti.com
Peripheral File Map
Table 19. Peripheral File Map
MODULE REGISTER NAME SHORT FORM ADDRESS
ADC12 Interrupt-vector-word register ADC12IV 0x01A8
(MSP430F24x,
MSP430F2410, and
MSP430F23x)
Interrupt-enable register ADC12IE 0x01A6
Interrupt-flag register ADC12IFG 0x01A4
Control register 1 ADC12CTL1 0x01A2
Control register 0 ADC12CTL0 0x01A0
Conversion memory 15 ADC12MEM15 0x015E
Conversion memory 14 ADC12MEM14 0x015C
Conversion memory 13 ADC12MEM13 0x015A
Conversion memory 12 ADC12MEM12 0x0158
Conversion memory 11 ADC12MEM11 0x0156
Conversion memory 10 ADC12MEM10 0x0154
Conversion memory 9 ADC12MEM9 0x0152
Conversion memory 8 ADC12MEM8 0x0150
Conversion memory 7 ADC12MEM7 0x014E
Conversion memory 6 ADC12MEM6 0x014C
Conversion memory 5 ADC12MEM5 0x014A
Conversion memory 4 ADC12MEM4 0x0148
Conversion memory 3 ADC12MEM3 0x0146
Conversion memory 2 ADC12MEM2 0x0144
Conversion memory 1 ADC12MEM1 0x0142
Conversion memory 0 ADC12MEM0 0x0140
ADC memory-control register15 ADC12MCTL15 0x008F
ADC memory-control register14 ADC12MCTL14 0x008E
ADC memory-control register13 ADC12MCTL13 0x008D
ADC memory-control register12 ADC12MCTL12 0x008C
ADC memory-control register11 ADC12MCTL11 0x008B
ADC memory-control register10 ADC12MCTL10 0x008A
ADC memory-control register9 ADC12MCTL9 0x0089
ADC memory-control register8 ADC12MCTL8 0x0088
ADC memory-control register7 ADC12MCTL7 0x0087
ADC memory-control register6 ADC12MCTL6 0x0086
ADC memory-control register5 ADC12MCTL5 0x0085
ADC memory-control register4 ADC12MCTL4 0x0084
ADC memory-control register3 ADC12MCTL3 0x0083
ADC memory-control register2 ADC12MCTL2 0x0082
ADC memory-control register1 ADC12MCTL1 0x0081
ADC memory-control register0 ADC12MCTL0 0x0080
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 25
Page 26

MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Table 19. Peripheral File Map (continued)
MODULE REGISTER NAME SHORT FORM ADDRESS
Timer_B7 Capture/compare register 6 TBCCR6 0x019E
(MSP430F24x(1) and
MSP430F2410)
Timer_B3 Capture/compare register 2 TBCCR2 0x0196
(MSP430F23x)
Timer_A3 Capture/compare register 2 TACCR2 0x0176
Hardware Multiplier Sum extend SUMEXT 0x013E
Capture/compare register 5 TBCCR5 0x019C
Capture/compare register 4 TBCCR4 0x019A
Capture/compare register 3 TBCCR3 0x0198
Capture/compare register 2 TBCCR2 0x0196
Capture/compare register 1 TBCCR1 0x0194
Capture/compare register 0 TBCCR0 0x0192
Timer_B register TBR 0x0190
Capture/compare control 6 TBCCTL6 0x018E
Capture/compare control 5 TBCCTL5 0x018C
Capture/compare control 4 TBCCTL4 0x018A
Capture/compare control 3 TBCCTL3 0x0188
Capture/compare control 2 TBCCTL2 0x0186
Capture/compare control 1 TBCCTL1 0x0184
Capture/compare control 0 TBCCTL0 0x0182
Timer_B control TBCTL 0x0180
Timer_B interrupt vector TBIV 0x011E
Capture/compare register 1 TBCCR1 0x0194
Capture/compare register 0 TBCCR0 0x0192
Timer_B register TBR 0x0190
Capture/compare control 2 TBCCTL2 0x0186
Capture/compare control 1 TBCCTL1 0x0184
Capture/compare control 0 TBCCTL0 0x0182
Timer_B control TBCTL 0x0180
Timer_B interrupt vector TBIV 0x011E
Capture/compare register 1 TACCR1 0x0174
Capture/compare register 0 TACCR0 0x0172
Timer_A register TAR 0x0170
Reserved 0x016E
Reserved 0x016C
Reserved 0x016A
Reserved 0x0168
Capture/compare control 2 TACCTL2 0x0166
Capture/compare control 1 TACCTL1 0x0164
Capture/compare control 0 TACCTL0 0x0162
Timer_A control TACTL 0x0160
Timer_A interrupt vector TAIV 0x012E
Result high word RESHI 0x013C
Result low word RESLO 0x013A
Second operand OP2 0x0138
Multiply signed + accumulate/operand1 MACS 0x0136
Multiply + accumulate/operand1 MAC 0x0134
Multiply signed/operand1 MPYS 0x0132
Multiply unsigned/operand1 MPY 0x0130
www.ti.com
26 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 27
MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
www.ti.com
Table 19. Peripheral File Map (continued)
MODULE REGISTER NAME SHORT FORM ADDRESS
Flash Flash control 4 FCTL4 0x01BE
Flash control 3 FCTL3 0x012C
Flash control 2 FCTL2 0x012A
Flash control 1 FCTL1 0x0128
Watchdog Watchdog Timer control WDTCTL 0x0120
USCI A0/B0 USCI A0 auto baud rate control UCA0ABCTL 0x005D
USCI A0 transmit buffer UCA0TXBUF 0x0067
USCI A0 receive buffer UCA0RXBUF 0x0066
USCI A0 status UCA0STAT 0x0065
USCI A0 modulation control UCA0MCTL 0x0064
USCI A0 baud rate control 1 UCA0BR1 0x0063
USCI A0 baud rate control 0 UCA0BR0 0x0062
USCI A0 control 1 UCA0CTL1 0x0061
USCI A0 control 0 UCA0CTL0 0x0060
USCI A0 IrDA receive control UCA0IRRCTL 0x005F
USCI A0 IrDA transmit control UCA0IRTCLT 0x005E
USCI B0 transmit buffer UCB0TXBUF 0x006F
USCI B0 receive buffer UCB0RXBUF 0x006E
USCI B0 status UCB0STAT 0x006D
USCI B0 I2C Interrupt enable UCB0CIE 0x006C
USCI B0 baud rate control 1 UCB0BR1 0x006B
USCI B0 baud rate control 0 UCB0BR0 0x006A
USCI B0 control 1 UCB0CTL1 0x0069
USCI B0 control 0 UCB0CTL0 0x0068
USCI B0 I2C slave address UCB0SA 0x011A
USCI B0 I2C own address UCB0OA 0x0118
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 27
Page 28

MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Table 19. Peripheral File Map (continued)
MODULE REGISTER NAME SHORT FORM ADDRESS
USCI A1/B1 USCI A1 auto baud rate control UCA1ABCTL 0x00CD
(MSP430F24x(1) and
MSP430F2410)
Comparator_A+ Comparator_A port disable CAPD 0x005B
Basic Clock Basic clock system control3 BCSCTL3 0x0053
Brownout, SVS SVS control register (reset by brownout signal) SVSCTL 0x0055
Port P6 Port P6 resistor enable P6REN 0x0013
Port P5 Port P5 resistor enable P5REN 0x0012
Port P4 Port P4 resistor enable P4REN 0x0011
USCI A1 transmit buffer UCA1TXBUF 0x00D7
USCI A1 receive buffer UCA1RXBUF 0x00D6
USCI A1 status UCA1STAT 0x00D5
USCI A1 modulation control UCA1MCTL 0x00D4
USCI A1 baud rate control 1 UCA1BR1 0x00D3
USCI A1 baud rate control 0 UCA1BR0 0x00D2
USCI A1 control 1 UCA1CTL1 0x00D1
USCI A1 control 0 UCA1CTL0 0x00D0
USCI A1 IrDA receive control UCA1IRRCTL 0x00CF
USCI A1 IrDA transmit control UCA1IRTCLT 0x00CE
USCI B1 transmit buffer UCB1TXBUF 0x00DF
USCI B1 receive buffer UCB1RXBUF 0x00DE
USCI B1 status UCB1STAT 0x00DD
USCI B1 I2C Interrupt enable UCB1CIE 0x00DC
USCI B1 baud rate control 1 UCB1BR1 0x00DB
USCI B1 baud rate control 0 UCB1BR0 0x00DA
USCI B1 control 1 UCB1CTL1 0x00D9
USCI B1 control 0 UCB1CTL0 0x00D8
USCI B1 I2C slave address UCB1SA 0x017E
USCI B1 I2C own address UCB1OA 0x017C
USCI A1/B1 interrupt enable UC1IE 0x0006
USCI A1/B1 interrupt flag UC1IFG 0x0007
Comparator_A control2 CACTL2 0x005A
Comparator_A control1 CACTL1 0x0059
Basic clock system control2 BCSCTL2 0x0058
Basic clock system control1 BCSCTL1 0x0057
DCO clock frequency control DCOCTL 0x0056
Port P6 selection P6SEL 0x0037
Port P6 direction P6DIR 0x0036
Port P6 output P6OUT 0x0035
Port P6 input P6IN 0x0034
Port P5 selection P5SEL 0x0033
Port P5 direction P5DIR 0x0032
Port P5 output P5OUT 0x0031
Port P5 input P5IN 0x0030
Port P4 selection P4SEL 0x001F
Port P4 direction P4DIR 0x001E
Port P4 output P4OUT 0x001D
Port P4 input P4IN 0x001C
www.ti.com
28 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 29

MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
www.ti.com
Table 19. Peripheral File Map (continued)
MODULE REGISTER NAME SHORT FORM ADDRESS
Port P3 Port P3 resistor enable P3REN 0x0010
Port P3 selection P3SEL 0x001B
Port P3 direction P3DIR 0x001A
Port P3 output P3OUT 0x0019
Port P3 input P3IN 0x0018
Port P2 Port P2 resistor enable P2REN 0x002F
Port P2 selection P2SEL 0x002E
Port P2 interrupt enable P2IE 0x002D
Port P2 interrupt-edge select P2IES 0x002C
Port P2 interrupt flag P2IFG 0x002B
Port P2 direction P2DIR 0x002A
Port P2 output P2OUT 0x0029
Port P2 input P2IN 0x0028
Port P1 Port P1 resistor enable P1REN 0x0027
Port P1 selection P1SEL 0x0026
Port P1 interrupt enable P1IE 0x0025
Port P1 interrupt-edge select P1IES 0x0024
Port P1 interrupt flag P1IFG 0x0023
Port P1 direction P1DIR 0x0022
Port P1 output P1OUT 0x0021
Port P1 input P1IN 0x0020
Special Functions SFR interrupt flag2 IFG2 0x0003
SFR interrupt flag1 IFG1 0x0002
SFR interrupt enable2 IE2 0x0001
SFR interrupt enable1 IE1 0x0000
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 29
Page 30

4.15 MHz
12 MHz
16 MHz
1.8 V 2.2 V 2.7 V 3.3 V 3.6 V
Supply Voltage −V
System Frequency −MHz
Supply voltage range
during flash memory
programming
Supply voltage range
during program execution
Legend:
7.5 MHz
MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Voltage applied at VCCto V
Voltage applied to any pin
SS
(2)
(1)
-0.3 V to 4.1 V
-0.3 V to VCC+ 0.3 V
Diode current at any device terminal ±2 mA
Storage temperature, T
stg
(3)
Unprogrammed device -55°C to 150°C
Programmed device -55°C to 150°C
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under absolute maximum ratingsmay cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings
only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under recommended operating
conditionsis not implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
(2) All voltages referenced to VSS. The JTAG fuse-blow voltage, VFB, is allowed to exceed the absolute maximum rating. The voltage is
applied to the TEST pin when blowing the JTAG fuse.
(3) Higher temperature may be applied during board soldering process according to the current JEDEC J-STD-020 specification with peak
reflow temperatures not higher than classified on the device label on the shipping boxes or reels.
www.ti.com
Recommended Operating Conditions
(1)(2)
Typical values are specified at VCC= 3.3 V and TA= 25°C (unless otherwise noted)
MIN NOM MAX UNIT
During program
V
CC
Supply voltage
(3)
AVCC= DVCC= V
CC
execution
During program or erase
flash memory
V
SS
T
A
f
SYSTEM
Supply voltage AVSS= DVSS= V
Operating free-air temperature °C
Processor frequency
(maximum MCLK frequency)
(see Figure 1)
VCC= 1.8 V, Duty cycle = 50% ± 10% dc 4.15
(1)(2)
VCC= 2.7 V, Duty cycle = 50% ± 10% dc 12 MHz
VCC≥ 3.3 V, Duty cycle = 50% ± 10% dc 16
SS
I version -40 85
T version -40 105
(1) The MSP430 CPU is clocked directly with MCLK. Both the high and low phase of MCLK must not exceed the pulse duration of the
specified maximum frequency.
(2) Modules might have a different maximum input clock specification. See the specification of the respective module in this data sheet.
(3) It is recommended to power AVCCand DVCCfrom the same source. A maximum difference of 0.3 V between AVCCand DVCCcan be
tolerated during power-up.
1.8 3.6 V
2.2 3.6 V
0 V
NOTE: Minimum processor frequency is defined by system clock. Flash program or erase operations require a minimum V
of 2.2 V.
30 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Figure 1. Operating Area
CC
Page 31
www.ti.com
Active Mode Supply Current (Into DVCCand AVCC) Excluding External Current
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
(1)(2)
over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air temperature (unless otherwise noted)
I
AM,1MHz
I
AM,1MHz
I
AM,4kHz
I
AM,100kHz
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS T
f
= f
= f
MCLK
= 32768 Hz,
Active mode (AM)
current (1 MHz)
DCO
f
ACLK
Program executes in flash,
BCSCTL1 = CALBC1_1MHZ, µA
DCOCTL = CALDCO_1MHZ,
CPUOFF = 0, SCG0 = 0, SCG1 = 0,
OSCOFF = 0
f
= f
= f
MCLK
= 32768 Hz,
Active mode (AM)
current (1 MHz)
DCO
f
ACLK
Program executes in RAM,
BCSCTL1 = CALBC1_1MHZ, µA
DCOCTL = CALDCO_1MHZ,
CPUOFF = 0, SCG0 = 0, SCG1 = 0,
OSCOFF = 0
f
= f
MCLK
SMCLK
32768 Hz/8 = 4096 Hz,
f
= 0 Hz,
Active mode (AM) Program executes in flash,
DCO
= 1 MHz, -40°C to 85°C 275 312
SMCLK
105°C 295 318
-40°C to 85°C 386 445
105°C 417 449
= 1 MHz, -40°C to 85°C 230 261
SMCLK
105°C 248 267
-40°C to 85°C 321 366
105°C 344 370
= f
= -40°C to 85°C 1.5 3.8
ACLK
105°C 6 10.5
-40°C to 85°C 2 4.7
current (4 kHz) SELMx = 11, SELS = 1,
DIVMx = DIVSx = DIVAx = 11,
CPUOFF = 0, SCG0 = 1, SCG1 = 0,
105°C 7 12.2
OSCOFF = 0
-40°C to 85°C 55 72
105°C 70 81
-40°C to 85°C 67 89
105°C 84 100
Active mode (AM)
current (100 kHz)
f
= f
MCLK
f
= 0 Hz,
ACLK
Program executes in flash, µA
SMCLK
= f
DCO(0, 0)
≈ 100 kHz,
RSELx = 0, DCOx = 0, CPUOFF = 0,
SCG0 = 0, SCG1 = 0, OSCOFF = 1
A
V
CC
2.2 V
3 V
2.2 V
3.3 V
2.2 V
3 V
2.2 V
3 V
MIN TYP MAX UNIT
MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
µA
(1) All inputs are tied to 0 V or VCC. Outputs do not source or sink any current.
(2) The currents are characterized with a Micro Crystal CC4V-T1A SMD crystal with a load capacitance of 9 pF. The internal and external
load capacitance is chosen to closely match the required 9 pF.
Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 31
Page 32

0.0
1.0
2.0
3.0
4.0
5.0
6.0
7.0
8.0
1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0
VCC− Supply Voltage − V
Active Mode Current − mA
f
DCO
= 1 MHz
f
DCO
= 8 MHz
f
DCO
= 12 MHz
f
DCO
= 16 MHz
0.0
1.0
2.0
3.0
4.0
5.0
0.0 4.0 8.0 12.0 16.0
f
DCO
− DCO Frequency − MHz
Active Mode Current − mA
TA= 25 °C
TA= 85 °C
VCC= 2.2 V
VCC= 3 V
TA= 25 °C
TA= 85 °C
MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Typical Characteristics - Active-Mode Supply Current (Into DVCCand AVCC)
ACTIVE-MODE CURRENT
vs ACTIVE-MODE CURRENT
SUPPLY VOLTAGE vs
TA= 25°C DCO FREQUENCY
www.ti.com
Figure 2. Figure 3.
32 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 33

www.ti.com
Low-Power-Mode Supply Currents (Into VCC) Excluding External Current
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
(1)(2)
over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air temperature (unless otherwise noted)
I
LPM0,1MHz
I
LPM0,100kHz
I
LPM2
I
LPM3,LFXT1
I
LPM3,VLO
I
LPM4
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS T
f
= 0 MHz, -40°C to 85°C 60 65
MCLK
f
= f
= 1 MHz,
DCO
= 32768 Hz,
105°C 63 72
-40°C to 85°C 75 90
105°C 80 95
= 0 MHz, -40°C to 85°C 33 38
= f
DCO(0, 0)
= 0 Hz,
≈ 100 kHz,
105°C 36 43
-40°C to 85°C 36 42
105°C 40 47
= f
= 32768 Hz,
= 0 MHz, -40°C to 85°C 20 25
SMCLK
105°C 25 30
-40°C to 85°C 23 30
105°C 28 35
Low-power mode 0
(LPM0) current
Low-power mode 0 f
(LPM0) current
Low-power mode 2
(LPM2) current
(3)
(3)
(4)
SMCLK
f
ACLK
BCSCTL1 = CALBC1_1MHZ, µA
DCOCTL = CALDCO_1MHZ,
CPUOFF = 1, SCG0 = 0, SCG1 = 0,
OSCOFF = 0
f
MCLK
f
SMCLK
ACLK
RSELx = 0, DCOx = 0,
CPUOFF = 1, SCG0 = 0, SCG1 = 0,
OSCOFF = 1
f
MCLK
f
= 1 MHz,
DCO
f
ACLK
BCSCTL1 = CALBC1_1MHZ, µA
DCOCTL = CALDCO_1MHZ,
CPUOFF = 1, SCG0 = 0, SCG1 = 1,
OSCOFF = 0
-40°C 0.8 1.2
25°C 0.9 1.3
85°C 2.4 3
105°C 6 13
-40°C 0.9 1.3
25°C 1 1.4
Low-power mode 3 f
(LPM3) current
(4)
f
= f
DCO
ACLK
CPUOFF = 1, SCG0 = 1, SCG1 = 1,
= f
MCLK
= 32768 Hz,
SMCLK
= 0 MHz,
OSCOFF = 0
85°C 3.9 4.3
105°C 10 15
-40°C 0.3 0.9
25°C 0.3 0.9
85°C 1.8 2.4
105°C 5.5 13
-40°C 0.4 1
25°C 0.4 1
Low-power mode 3
current, (LPM3)
(4)
f
= f
DCO
f
ACLK
(VLO), µA
= f
MCLK
from internal LF oscillator
SMCLK
= 0 MHz,
CPUOFF = 1, SCG0 = 1, SCG1 = 1,
OSCOFF = 0
85°C 2 3
105°C 9 15
-40°C 0.1 0.5
25°C 0.1 0.5
85°C 1.6 2.5
105°C 6.5 13
Low-power mode 4 f
(LPM4) current
(5)
f
= f
MCLK
= 0 Hz,
= f
DCO
ACLK
CPUOFF = 1, SCG0 = 1, SCG1 = 1,
SMCLK
= 0 MHz,
OSCOFF = 1
A
V
CC
MIN TYP MAX UNIT
2.2 V
3 V
2.2 V
3 V
2.2 V
3 V
2.2 V
3 V
2.2 V
3 V
2.2 V, 3 V µA
MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
µA
µA
(1) All inputs are tied to 0 V or VCC. Outputs do not source or sink any current.
(2) The currents are characterized with a Micro Crystal CC4V-T1A SMD crystal with a load capacitance of 9 pF. The internal and external
load capacitance is chosen to closely match the required 9 pF.
(3) Current for Brownout and WDT+ is included. The WDT+ is clocked by SMCLK.
(4) Current for Brownout and WDT+ is included. The WDT+ is clocked by ACLK.
(5) Current for Brownout is included.
Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 33
Page 34

0.0
1.0
2.0
3.0
4.0
5.0
6.0
7.0
8.0
9.0
10.0
−40.0 −20.0 0.0 20.0 40.0 60.0 80.0 100.0 120.0
TA− Temperature − °C
VCC= 3.6 V
I − Low−power mode current − µALPM4
Vcc = 1.8 V
VCC= 3 V
Vcc = 2.2V
MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Typical Characteristics - LPM4 Current
www.ti.com
LPM4 CURRENT
vs
TEMPERATURE
Figure 4.
34 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 35

www.ti.com
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Schmitt-Trigger Inputs (Ports P1, P2, P3, P4, P5, P6, RST/NMI, JTAG, XIN, XT2IN)
over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air temperature (unless otherwise noted)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS V
V
Positive-going input threshold voltage 2.2 V 1 1.65 V
IT+
CC
3 V 1.35 2.25
V
Negative-going input threshold voltage 2.2 V 0.55 1.20 V
IT-
3 V 0.75 1.65
V
Input voltage hysteresis (V
hys
R
Pullup/pulldown resistor 3 V 20 35 50 kΩ
Pull
C
Input capacitance VIN= VSSor V
I
- V
) V
IT+
IT-
For pullup: VIN= VSS,
For pulldown: VIN= V
CC
CC
2.2 V 0.2 1
3 V 0.3 1
MIN TYP MAX UNIT
0.45 V
CC
0.25 V
CC
Inputs (Ports P1, P2)
over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air temperature (unless otherwise noted)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS V
t
t
f
f
f
f
External interrupt timing 2.2 V, 3 V 20 ns
(int)
Timer_A Timer_B capture timing ns
cap
, Timer_A, Timer_B clock frequency
TAext
externally applied to pin
TBext
,
TAint
Timer_A, Timer_B clock frequency SMCLK or ACLK signal selected MHz
TBint
Port P1, P2: P1.x to P2.x, External trigger
pulse width to set interrupt flag
(1)
TA0, TA1, TA2 2.2 V 62
TB0, TB1, TB2, TB3, TB4, TB5, TB6 3 V 50
TACLK, TBCLK, INCLK: t
(H)
= t
(L)
(1) An external signal sets the interrupt flag every time the minimum interrupt pulse width t
shorter than t
(int)
.
is met. It may be set even with trigger signals
(int)
CC
2.2 V 8
3 V 10
2.2 V 8
3 V 10
MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
0.75 V
CC
0.55 V
CC
5 pF
MIN MAX UNIT
MHz
Leakage Current (Ports P1, P2, P3, P4, P5, P6)
over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air temperature (unless otherwise noted)
I
lkg(Px.y)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS V
High-impedance leakage current See
(1) (2)
CC
2.2 V, 3 V ±50 nA
(1) The leakage current is measured with VSSor VCCapplied to the corresponding pins, unless otherwise noted.
(2) The leakage of the digital port pins is measured individually. The port pin is selected for input and the pullup/pulldown resistor is
disabled.
MIN MAX UNIT
Standard Inputs (RST/NMI)
over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air temperature (unless otherwise noted)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS V
V
V
Low-level input voltage 2.2 V, 3 V VSSVSS+ 0.6 V
IL
High-level input voltage 2.2 V, 3 V 0.8 V
IH
CC
MIN MAX UNIT
CC
V
CC
V
Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 35
Page 36

MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Outputs (Ports P1, P2, P3, P4, P5, P6)
over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air temperature (unless otherwise noted)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS V
V
V
High-level output voltage V
OH
Low-level output voltage V
OL
(1) The maximum total current, I
specified.
(2) The maximum total current, I
specified.
OH(max)
OH(max)
I
OH(max)
I
OH(max)
I
OH(max)
I
OH(max)
I
OL(max)
I
OL(max)
I
OL(max)
I
OL(max)
and I
and I
= -1.5 mA
= -6 mA
= -1.5 mA
= -6 mA
= 1.5 mA
= 6 mA
= 1.5 mA
= 6 mA
OL(max)
OL(max)
(1)
(2)
(1)
(2)
(1)
(2)
(1)
(2)
, for all outputs combined, should not exceed ±12 mA to hold the maximum voltage drop
, for all outputs combined, should not exceed ±48 mA to hold the maximum voltage drop
CC
2.2 V
3 V
2.2 V
3 V
Output Frequency (Ports P1, P2, P3, P4, P5, P6)
over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air temperature (unless otherwise noted)
f
Px.y
f
Port°CLK
t
(Xdc)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS V
Port output 2.2 V DC 10
frequency with P1.4/SMCLK, CL= 20 pF, RL= 1 kΩ
(1)(2)
load
Clock output
frequency
P2.0/ACLK/CA2, P1.4/SMCLK, CL= 20 pF
(2)
P1.0/TACLK/CAOUT, CL= 20 pF, LF mode 30% 50% 70%
P1.0/TACLK/CAOUT, CL= 20 pF, XT1 mode 40% 50% 60%
Duty cycle of
output frequency
P1.1/TA0, CL= 20 pF, XT1 mode 40% 60%
P1.1/TA0, CL= 20 pF, DCO 50% – 15 ns 50% 50% + 15 ns
P1.4/SMCLK, CL= 20 pF, XT2 mode 40% 60%
P1.4/SMCLK, CL= 20 pF, DCO 50% – 15 ns 50% + 15 ns
CC
3 V DC 12
2.2 V DC 12
3 V DC 16
MIN MAX UNIT
VCC- 0.25 V
VCC- 0.6 V
VCC- 0.25 V
VCC- 0.6 V
V
SSVSS
V
SS
V
SSVSS
V
SS
MIN TYP MAX UNIT
www.ti.com
CC
CC
CC
CC
+ 0.25
VSS+ 0.6
+ 0.25
VSS+ 0.6
MHz
MHz
(1) A resistive divider with two 0.5-kΩ resistors between VCCand VSSis used as load. The output is connected to the center tap of the
divider.
(2) The output voltage reaches at least 10% and 90% VCCat the specified toggle frequency.
36 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 37

VOH− High-Level Output Voltage − V
−25.0
−20.0
−15.0
−10.0
−5.0
0.0
0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5
VCC= 2.2 V
P4.5
TA= 25°C
TA= 85°C
OH
I − Typical High-Level Output Current − mA
VOH− High-Level Output Voltage − V
−50.0
−40.0
−30.0
−20.0
−10.0
0.0
0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5
VCC= 3 V
P4.5
TA= 25°C
TA= 85°C
OH
I − Typical High-Level Output Current − mA
VOL− Low-Level Output Voltage − V
0.0
5.0
10.0
15.0
20.0
25.0
0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5
VCC= 2.2 V
P4.5
TA= 25°C
TA= 85°C
OL
I − Typical Low-Level Output Current − mA
VOL− Low-Level Output Voltage − V
0.0
10.0
20.0
30.0
40.0
50.0
0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5
VCC= 3 V
P4.5
TA= 25°C
TA= 85°C
OL
I − Typical Low-Level Output Current − mA
www.ti.com
MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Typical Characteristics - Outputs
One output loaded at a time.
TYPICAL LOW-LEVEL OUTPUT CURRENT TYPICAL LOW-LEVEL OUTPUT CURRENT
vs vs
LOW-LEVEL OUTPUT VOLTAGE LOW-LEVEL OUTPUT VOLTAGE
Figure 5. Figure 6.
TYPICAL HIGH-LEVEL OUTPUT CURRENT TYPICAL HIGH-LEVEL OUTPUT CURRENT
vs vs
HIGH-LEVEL OUTPUT VOLTAGE HIGH-LEVEL OUTPUT VOLTAGE
Figure 7. Figure 8.
Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 37
Page 38

0
1
t
d(BOR)
V
CC
V
(B_IT−)
V
hys(B_IT−)
V
CC(star t)
MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
is ≤ 1.8 V.
CC(min)
(1)(2)
, where V
CC
MIN TYP MAX UNIT
2.2 V, 3 V 2 µs
after VCC= V
is the minimum supply voltage for the desired operating frequency.
CC(min)
d(BOR)
(B_IT-)
+ V
hys(B_IT-)
. The default DCO settings
POR and Brownout Reset (BOR)
over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air temperature (unless otherwise noted)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS V
V
CC(start)
V
(B_IT-)
V
hys(B_IT-)
t
d(BOR)
t
(reset)
(1) The current consumption of the brownout module is already included in the ICCcurrent consumption data.
The voltage level V
(2) During power up, the CPU begins code execution following a period of t
must not be changed until VCC≥ V
Operating voltage dVCC/dt ≤ 3 V/s 0.7 × V
Negative going VCCreset threshold voltage dVCC/dt ≤ 3 V/s 1.71 V
VCCreset threshold hysteresis dVCC/dt ≤ 3 V/s 70 130 210 mV
BOR reset release delay time 2000 µs
Pulse duration needed at RST/NMI pin to
accepted reset internally
+ V
(B_IT-)
hys(B_IT-)
www.ti.com
(B_IT-)
V
Figure 9. POR/Brownout Reset (BOR) vs Supply Voltage
38 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 39

V
CC
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
V
CC(drop)
t
pw
tpw− Pulse Width − µs
V
CC(drop)
− V
3 V
0.001 1 1000
t
f
t
r
tpw− Pulse Width − µs
tf= t
r
Typical Conditions
VCC= 3 V
V
CC(drop)
V
CC
3 V
t
pw
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
0.001 1 1000
Typical Conditions
1 ns 1 ns
tpw− Pulse Width − µs
V
CC(drop)
− V
tpw− Pulse Width − µs
VCC= 3 V
www.ti.com
MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Typical Characteristics - POR/Brownout Reset (BOR)
Figure 10. V
Figure 11. V
Level With a Square Voltage Drop to Generate a POR/Brownout Signal
CC(drop)
Level With a Triangle Voltage Drop to Generate a POR/Brownout Signal
CC(drop)
Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 39
Page 40

MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
SVS (Supply Voltage Supervisor and Supply Voltage Monitor)
over recommended operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
t
(SVSR)
t
d(SVSon)
t
settle
V
(SVSstart)
V
hys(SVS_IT-)
V
(SVS_IT-)
(3)
I
CC(SVS)
(1) t
is the settling time that the comparator output needs to have a stable level after VLD is switched from VLD ≠ 0 to a different VLD
settle
value somewhere between 2 and 15. The overdrive is assumed to be > 50 mV.
(2) The recommended operating voltage range is limited to 3.6 V.
(3) The current consumption of the SVS module is not included in the ICCcurrent consumption data.
dVCC/dt > 30 V/ms (see Figure 12) 1 150
dVCC/dt ≤ 30 V/ms 2000
SVSon, switch from VLD = 0 to VLD ≠ 0, VCC= 3 V 150 300 µs
(1)
VLD ≠ 0
VLD ≠ 0, VCC/dt ≤ 3 V/s (see Figure 12) 1.55 1.7 V
VLD = 1 70 120 155 mV
VCC/dt ≤ 3 V/s (see Figure 12)
VCC/dt ≤ 3 V/s (see Figure 12), external voltage
applied on A7
VLD = 2 to 14
VLD = 15 4.4 20 mV
0.001 × 0.016 ×
V
(SVS_IT-)
VLD = 1 1.8 1.9 2.05
VLD = 2 1.94 2.1 2.25
VLD = 3 2.05 2.2 2.37
VLD = 4 2.14 2.3 2.48
VLD = 5 2.24 2.4 2.6
VLD = 6 2.33 2.5 2.71
VCC/dt ≤ 3V/s (see Figure 12 and Figure 13)
VLD = 7 2.46 2.65 2.86
VLD = 8 2.58 2.8 3
VLD = 9 2.69 2.9 3.13
VLD = 10 2.83 3.05 3.29
VLD = 11 2.94 3.2 3.42
VLD = 12 3.11 3.35 3.61
VLD = 13 3.24 3.5 3.76
(2)
VCC/dt ≤ 3 V/s (see Figure 12 and Figure 13),
external voltage applied on A7
VLD = 14 3.43 3.7
VLD = 15 1.1 1.2 1.3
VLD ≠ 0, VCC= 2.2 V, 3 V 10 15 µA
V
(SVS_IT-)
3.99
www.ti.com
12 µs
(2)
(2)
(2)
µs
V
40 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 41

0
0.5
1
1.5
2
V
CC
V
CC
1 ns 1 ns
V
CC(min)
t
pw
tpw− Pulse Width − µs
V
CC(min)
− V
3 V
1 10 1000
t
f
t
r
t − Pulse Width − µs
100
t
pw
3 V
tf= t
r
Rectangular Drop
Triangular Drop
V
CC(min)
V
CC(start)
AV
CC
V
(B_IT−)
Brownout
Region
V
(SVSstart)
V
(SVS_IT−)
Software sets VLD >0:
SVS is active
t
d(SVSR)
undefined
V
hys(SVS_IT−)
0
1
t
d(BOR)
Brownout
0
1
t
d(SVSon)
t
d(BOR)
0
1
Set POR
Brown-
out
Region
SVS Circuit is Active From VLD > to VCC< V(
B_IT−)
SVS out
V
hys (B_IT−)
www.ti.com
MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Figure 12. SVS Reset (SVSR) vs Supply Voltage
Figure 13. V
Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 41
: Square Voltage Drop and Triangle Voltage Drop to Generate an SVS Signal (VLD = 1)
CC(min)
Page 42

DCO(RSEL,DCO) DCO(RSEL,DCO+1)
average
DCO(RSEL,DCO) DCO(RSEL,DCO+1)
32 × f × f
f =
MOD × f + (32 – MOD) × f
MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Main DCO Characteristics
• All ranges selected by RSELx overlap with RSELx + 1: RSELx = 0 overlaps RSELx = 1, ... RSELx = 14
overlaps RSELx = 15.
• DCO control bits DCOx have a step size as defined by parameter S
• Modulation control bits MODx select how often f
cycles. The frequency f
DCO(RSEL,DCO)
is used for the remaining cycles. The frequency is an average equal to:
DCO(RSEL,DCO+1)
.
DCO
is used within the period of 32 DCOCLK
DCO Frequency
over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air temperature (unless otherwise noted)
V
CC
f
DCO(0,0)
f
DCO(0,3)
f
DCO(1,3)
f
DCO(2,3)
f
DCO(3,3)
f
DCO(4,3)
f
DCO(5,3)
f
DCO(6,3)
f
DCO(7,3)
f
DCO(8,3)
f
DCO(9,3)
f
DCO(10,3)
f
DCO(11,3)
f
DCO(12,3)
f
DCO(13,3)
f
DCO(14,3)
f
DCO(15,3)
f
DCO(15,7)
S
RSEL
S
DCO
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS V
CC
RSELx < 14 1.8 3.6
Supply voltage range RSELx = 14 2.2 3.6 V
RSELx = 15 3.0 3.6
DCO frequency (0, 0) RSELx = 0, DCOx = 0, MODx = 0 2.2 V, 3 V 0.06 0.14 MHz
DCO frequency (0, 3) RSELx = 0, DCOx = 3, MODx = 0 2.2 V, 3 V 0.07 0.17 MHz
DCO frequency (1, 3) RSELx = 1, DCOx = 3, MODx = 0 2.2 V, 3 V 0.10 0.20 MHz
DCO frequency (2, 3) RSELx = 2, DCOx = 3, MODx = 0 2.2 V, 3 V 0.14 0.28 MHz
DCO frequency (3, 3) RSELx = 3, DCOx = 3, MODx = 0 2.2 V, 3 V 0.20 0.40 MHz
DCO frequency (4, 3) RSELx = 4, DCOx = 3, MODx = 0 2.2 V, 3 V 0.28 0.54 MHz
DCO frequency (5, 3) RSELx = 5, DCOx = 3, MODx = 0 2.2 V, 3 V 0.39 0.77 MHz
DCO frequency (6, 3) RSELx = 6, DCOx = 3, MODx = 0 2.2 V, 3 V 0.54 1.06 MHz
DCO frequency (7, 3) RSELx = 7, DCOx = 3, MODx = 0 2.2 V, 3 V 0.80 1.50 MHz
DCO frequency (8, 3) RSELx = 8, DCOx = 3, MODx = 0 2.2 V, 3 V 1.10 2.10 MHz
DCO frequency (9, 3) RSELx = 9, DCOx = 3, MODx = 0 2.2 V, 3 V 1.60 3.00 MHz
DCO frequency (10, 3) RSELx = 10, DCOx = 3, MODx = 0 2.2 V, 3 V 2.50 4.30 MHz
DCO frequency (11, 3) RSELx = 11, DCOx = 3, MODx = 0 2.2 V, 3 V 3.00 5.50 MHz
DCO frequency (12, 3) RSELx = 12, DCOx = 3, MODx = 0 2.2 V, 3 V 4.30 7.30 MHz
DCO frequency (13, 3) RSELx = 13, DCOx = 3, MODx = 0 2.2 V, 3 V 6.00 9.60 MHz
DCO frequency (14, 3) RSELx = 14, DCOx = 3, MODx = 0 2.2 V, 3 V 8.60 13.9 MHz
DCO frequency (15, 3) RSELx = 15, DCOx = 3, MODx = 0 3 V 12.0 18.5 MHz
DCO frequency (15, 7) RSELx = 15, DCOx = 7, MODx = 0 3 V 16.0 26.0 MHz
Frequency step between range
RSEL and RSEL+1
Frequency step between tap DCO
and DCO+1
S
S
= f
RSEL
DCO(RSEL+1,DCO)/fDCO(RSEL,DCO)
= f
DCO
DCO(RSEL,DCO+1)/fDCO(RSEL,DCO)
2.2 V, 3 V 1.55 ratio
2.2 V, 3 V 1.05 1.08 1.12 ratio
Duty cycle Measured at P1.4/SMCLK 2.2 V, 3 V 40 50 60 %
MIN TYP MAX UNIT
www.ti.com
42 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 43

www.ti.com
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Calibrated DCO Frequencies - Tolerance at Calibration
over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air temperature (unless otherwise noted)
f
CAL(1MHz)
f
CAL(8MHz)
f
CAL(12MHz)
f
CAL(16MHz)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS T
Frequency tolerance at calibration 25°C 3 V -1 ±0.2 +1 %
BCSCTL1 = CALBC1_1MHZ,
1-MHz calibration value DCOCTL = CALDCO_1MHZ, 25°C 3 V 0.990 1 1.010 MHz
Gating time: 5 ms
BCSCTL1 = CALBC1_8MHZ,
8-MHz calibration value DCOCTL = CALDCO_8MHZ, 25°C 3 V 7.920 8 8.080 MHz
Gating time: 5 ms
BCSCTL1 = CALBC1_12MHZ,
12-MHz calibration value DCOCTL = CALDCO_12MHZ, 25°C 3 V 11.88 12 12.12 MHz
Gating time: 5 ms
BCSCTL1 = CALBC1_16MHZ,
16-MHz calibration value DCOCTL = CALDCO_16MHZ, 25°C 3 V 15.84 16 16.16 MHz
Gating time: 2 ms
V
A
CC
MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Calibrated DCO Frequencies - Tolerance Over Temperature 0°C to 85°C
over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air temperature (unless otherwise noted)
f
CAL(1MHz)
f
CAL(8MHz)
f
CAL(12MHz)
f
CAL(16MHz)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS T
1-MHz tolerance over
temperature
8-MHz tolerance over
temperature
12-MHz tolerance over
temperature
16-MHz tolerance over
temperature
A
0°C to 85°C 3 V -2.5 ±0.5 2.5 %
0°C to 85°C 3 V -2.5 ±1.0 2.5 %
0°C to 85°C 3 V -2.5 ±1.0 2.5 %
0°C to 85°C 3 V -3 ±2.0 3 %
BCSCTL1 = CALBC1_1MHZ,
1-MHz calibration value DCOCTL = CALDCO_1MHZ, 0°C to 85°C 3 V 0.975 1 1.025 MHz
Gating time: 5 ms
BCSCTL1 = CALBC1_8MHZ,
8-MHz calibration value DCOCTL = CALDCO_8MHZ, 0°C to 85°C 3 V 7.8 8 8.2 MHz
Gating time: 5 ms
BCSCTL1 = CALBC1_12MHZ,
12-MHz calibration value DCOCTL = CALDCO_12MHZ, 0°C to 85°C 3 V 11.64 12 12.36 MHz
Gating time: 5 ms
BCSCTL1 = CALBC1_16MHZ, 3 V 15.52 16 16.48
16-MHz calibration value DCOCTL = CALDCO_16MHZ, 0°C to 85°C MHz
Gating time: 2 ms
V
CC
MIN TYP MAX UNIT
2.2 V 0.97 1 1.03
3.6 V 0.97 1 1.03
2.2 V 7.76 8 8.4
3.6 V 7.6 8 8.24
2.2 V 11.64 12 12.36
3.6 V 11.64 12 12.36
3.6 V 15 16 16.48
MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 43
Page 44

MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
www.ti.com
Calibrated DCO Frequencies - Tolerance Over Supply Voltage V
CC
over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air temperature (unless otherwise noted)
f
CAL(1MHz)
f
CAL(8MHz)
f
CAL(12MHz)
f
CAL(16MHz)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS T
1-MHz tolerance over V
8-MHz tolerance over V
12-MHz tolerance over V
16-MHz tolerance over V
CC
CC
CC
CC
A
25°C 1.8 V to 3.6 V -3 ±2 +3 %
25°C 1.8 V to 3.6 V -3 ±2 +3 %
25°C 2.2 V to 3.6 V -3 ±2 +3 %
25°C 3 V to 3.6 V -6 ±2 +3 %
BCSCTL1 = CALBC1_1MHZ,
1-MHz calibration value DCOCTL = CALDCO_1MHZ, 25°C 1.8 V to 3.6 V 0.97 1 1.03 MHz
Gating time: 5 ms
BCSCTL1 = CALBC1_8MHZ,
8-MHz calibration value DCOCTL = CALDCO_8MHZ, 25°C 1.8 V to 3.6 V 7.76 8 8.24 MHz
Gating time: 5 ms
BCSCTL1 = CALBC1_12MHZ,
12-MHz calibration value DCOCTL = CALDCO_12MHZ, 25°C 2.2 V to 3.6 V 11.64 12 12.36 MHz
Gating time: 5 ms
BCSCTL1 = CALBC1_16MHZ,
16-MHz calibration value DCOCTL = CALDCO_16MHZ, 25°C 3 V to 3.6 V 15 16 16.48 MHz
Gating time: 2 ms
V
CC
MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Calibrated DCO Frequencies - Overall Tolerance
over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air temperature (unless otherwise noted)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS T
1-MHz tolerance
overall
8-MHz tolerance
overall
12-MHz
tolerance overall
16-MHz
tolerance overall
f
CAL(1MHz)
f
CAL(8MHz)
f
CAL(12MHz)
f
CAL(16MHz)
1-MHz
calibration value
8-MHz
calibration value
12-MHz
calibration value
16-MHz
calibration value
BCSCTL1 = CALBC1_1MHZ,
DCOCTL = CALDCO_1MHZ, -40°C to 105°C 1.8 V to 3.6 V 0.95 1 1.05 MHz
Gating time: 5 ms
BCSCTL1 = CALBC1_8MHZ,
DCOCTL = CALDCO_8MHZ, -40°C to 105°C 1.8 V to 3.6 V 7.6 8 8.4 MHz
Gating time: 5 ms
BCSCTL1 = CALBC1_12MHZ,
DCOCTL = CALDCO_12MHZ, -40°C to 105°C 2.2 V to 3.6 V 11.4 12 12.6 MHz
Gating time: 5 ms
BCSCTL1 = CALBC1_16MHZ,
DCOCTL = CALDCO_16MHZ, -40°C to 105°C 3 V to 3.6 V 15 16 17 MHz
Gating time: 2 ms
A
-40°C to 105°C 1.8 V to 3.6 V -5 ±2 +5 %
-40°C to 105°C 1.8 V to 3.6 V -5 ±2 +5 %
-40°C to 105°C 2.2 V to 3.6 V -5 ±2 +5 %
-40°C to 105°C 3 V to 3.6 V -6 ±3 +6 %
V
CC
MIN TYP MAX UNIT
44 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 45
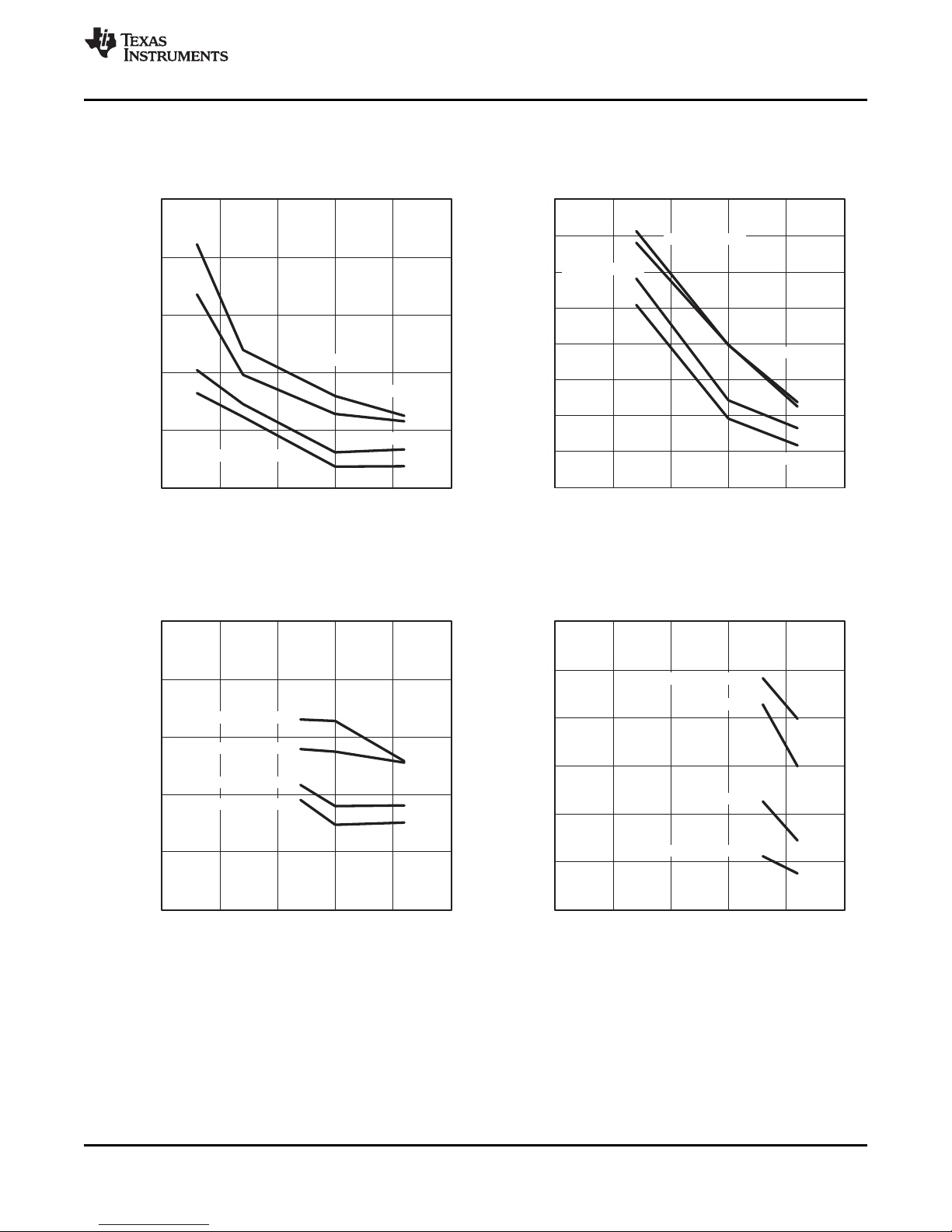
VCC− Supply Voltage − V
11.5
11.7
11.9
12.1
12.3
12.5
1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0
Frequency − MHz
TA= −40 °C
TA= 25 °C
TA= 85 °C
TA= 105 °C
VCC− Supply Voltage − V
15.5
15.6
15.7
15.8
15.9
16.0
16.1
1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0
Frequency − MHz
TA= −40 °C
TA= 25 °C
TA= 85 °C
TA= 105 °C
VCC− Supply Voltage − V
0.99
1.00
1.01
1.02
1.03
1.04
1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0
Frequency − MHz
TA= −40 °C
TA= 25 °C
TA= 85 °C
TA= 105 °C
VCC− Supply Voltage − V
7.80
7.85
7.90
7.95
8.00
8.05
8.10
8.15
8.20
1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0
Frequency − MHz
TA= −40 °C
TA= 25 °C
TA= 85 °C
TA= 105 °C
www.ti.com
MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Typical Characteristics - Calibrated DCO Frequency
CALIBRATED 1-MHz FREQUENCY CALIBRATED 8-MHz FREQUENCY
vs vs
SUPPLY VOLTAGE SUPPLY VOLTAGE
Figure 14. Figure 15.
CALIBRATED 12-MHz FREQUENCY CALIBRATED 16-MHz FREQUENCY
vs vs
SUPPLY VOLTAGE SUPPLY VOLTAGE
Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 45
Figure 16. Figure 17.
Page 46

DCO Frequency − MHz
0.10
1.00
10.00
0.10 1.00 10.00
RSELx = 0 to 11
DCO Wake Time − µs
RSELx = 12 to 15
MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Wake-Up From Lower-Power Modes (LPM3/4)
over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air temperature (unless otherwise noted)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS V
BCSCTL1 = CALBC1_1MHZ,
DCOCTL = CALDCO_1MHZ
BCSCTL1 = CALBC1_8MHZ,
t
DCO,LPM3/4
t
CPU,LPM3/4
(1) The DCO clock wake-up time is measured from the edge of an external wake-up signal (for example, a port interrupt) to the first clock
edge observable externally on a clock pin (MCLK or SMCLK).
(2) Parameter applicable only if DCOCLK is used for MCLK.
DCO clock wake-up time
from LPM3/4
CPU wake-up time from 1 / f
LPM3/4
(1)
(2)
DCOCTL = CALDCO_8MHZ
BCSCTL1 = CALBC1_12MHZ,
DCOCTL = CALDCO_12MHZ
BCSCTL1 = CALBC1_16MHZ,
DCOCTL = CALDCO_16MHZ
CC
2.2 V, 3 V 1.5
3 V 1
MIN TYP MAX UNIT
MCLK
t
Clock,LPM3/4
Typical Characteristics - DCO Clock Wake-Up Time From LPM3/4
CLOCK WAKE-UP TIME FROM LPM3
vs
DCO FREQUENCY
www.ti.com
2
µs
1
+
46 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Figure 18.
Page 47

0.00
0.25
0.50
0.75
1.00
1.25
1.50
1.75
2.00
2.25
2.50
−50.0 −25.0 0.0 25.0 50.0 75.0 100.0
TA− Temperature − C
DCO Frequency − MHz
R
OSC
= 100k
R
OSC
= 270k
R
OSC
= 1M
0.00
0.25
0.50
0.75
1.00
1.25
1.50
1.75
2.00
2.25
2.50
2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0
VCC− Supply Voltage − V
DCO Frequency − MHz
R
OSC
= 100k
R
OSC
= 270k
R
OSC
= 1M
0.01
0.10
1.00
10.00
10.00 100.00 1000.00 10000.00
R
OSC
− External Resistor − kW
DCO Frequency − MHz
RSELx = 4
0.01
0.10
1.00
10.00
10.00 100.00 1000.00 10000.00
R
OSC
− External Resistor − kW
DCO Frequency − MHz
RSELx = 4
www.ti.com
DCO With External Resistor R
OSC
(1)
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air temperature (unless otherwise noted)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS V
f
DCO,ROSC
D
T
D
V
DCO output frequency with R
OSC
Temperature drift 2.2 V, 3 V ±0.1 %/°C
Drift with V
CC
DCOR = 1, 2.2 V 1.8
RSELx = 4, DCOx = 3, MODx = 0, MHz
TA= 25°C
3 V 1.95
DCOR = 1,
RSELx = 4, DCOx = 3, MODx = 0
DCOR = 1,
RSELx = 4, DCOx = 3, MODx = 0
2.2 V, 3 V 10 %/V
MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
CC
TYP UNIT
(1) R
= 100 kΩ. Metal film resistor, type 0257, 0.6 W with 1% tolerance and TK= ±50 ppm/°C.
OSC
Typical Characteristics - DCO With External Resistor R
DCO FREQUENCY DCO FREQUENCY
vs vs
R
VCC= 2.2 V, TA= 25°C VCC= 3 V, TA= 25°C
DCO FREQUENCY DCO FREQUENCY
OSC
Figure 19. Figure 20.
vs vs
TEMPERATURE SUPPLY VOLTAGE
VCC= 3 V TA= 25°C
OSC
R
OSC
Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 47
Figure 21. Figure 22.
Page 48
MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Crystal Oscillator LFXT1, Low-Frequency Mode
over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air temperature (unless otherwise noted)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS V
f
LFXT1,LF
f
LFXT1,LF,logic
OA
LF
C
L,eff
f
Fault,LF
(1) To improve EMI on the XT1 oscillator, the following guidelines should be observed.
(a) Keep the trace between the device and the crystal as short as possible.
(b) Design a good ground plane around the oscillator pins.
(c) Prevent crosstalk from other clock or data lines into oscillator pins XIN and XOUT.
(d) Avoid running PCB traces underneath or adjacent to the XIN and XOUT pins.
(e) Use assembly materials and praxis to avoid any parasitic load on the oscillator XIN and XOUT pins.
(f) If conformal coating is used, ensure that it does not induce capacitive or resistive leakage between the oscillator pins.
(g) Do not route the XOUT line to the JTAG header to support the serial programming adapter as shown in other documentation. This
signal is no longer required for the serial programming adapter.
(2) Includes parasitic bond and package capacitance (approximately 2 pF per pin).
Because the PCB adds additional capacitance, it is recommended to verify the correct load by measuring the ACLK frequency. For a
correct setup, the effective load capacitance should always match the specification of the crystal that is used.
(3) Frequencies below the MIN specification set the fault flag. Frequencies above the MAX specification do not set the fault flag.
Frequencies in between might set the flag.
(4) Measured with logic-level input frequency but also applies to operation with crystals.
LFXT1 oscillator crystal
frequency, LF mode 0, 1
XTS = 0, LFXT1Sx = 0 or 1 1.8 V to 3.6 V 32768 Hz
LFXT1 oscillator logic level
square wave input frequency, XTS = 0, LFXT1Sx = 3, XCAPx = 0 1.8 V to 3.6 V 10000 32768 50000 Hz
LF mode
XTS = 0, LFXT1Sx = 0,
Oscillation allowance for
LF crystals
f
XTS = 0, LFXT1Sx = 0,
f
LFXT1,LF
LFXT1,LF
= 32768 Hz, C
= 32768 Hz, C
XTS = 0, XCAPx = 0 1
Integrated effective load
capacitance, LF mode
(2)
XTS = 0, XCAPx = 1 5.5
XTS = 0, XCAPx = 2 8.5
XTS = 0, XCAPx = 3 11
Duty cycle, LF mode 2.2 V, 3 V 30 50 70 %
Oscillator fault frequency,
LF mode
(3)
XTS = 0, Measured at P2.0/ACLK,
f
LFXT1,LF
= 32768 Hz
XTS = 0, LFXT1Sx = 3, XCAPx = 0
(1)
L,eff
L,eff
= 6 pF
= 12 pF
CC
MIN TYP MAX UNIT
500
200
(4)
2.2 V, 3 V 10 10000 Hz
www.ti.com
kΩ
pF
Internal Very-Low-Power Low-Frequency Oscillator (VLO)
over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air temperature (unless otherwise noted)
PARAMETER V
f
VLO
df
/dT VLO frequency temperature drift
VLO
df
/dV
VLO
CC
VLO frequency 2.2 V, 3 V 4 12 20 kHz
VLO frequency supply voltage drift
(1)
(2)
CC
2.2 V, 3 V 0.5 %/°C
1.8 V to 3.6 V 4 %/V
(1) Calculated using the box method:
I version: (MAX(-40 to 85°C) - MIN(-40 to 85°C))/MIN(-40 to 85°C)/(85°C - (-40°C))
T version: (MAX(-40 to 105°C) - MIN(-40 to 105°C))/MIN(-40 to 105°C)/(105°C - (-40°C))
(2) Calculated using the box method: (MAX(1.8 to 3.6 V) - MIN(1.8 to 3.6 V))/MIN(1.8 to 3.6 V)/(3.6 V - 1.8 V)
48 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated
MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Page 49

www.ti.com
Crystal Oscillator LFXT1, High-Frequency Mode
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS V
f
LFXT1,HF0
f
LFXT1,HF1
f
LFXT1,HF2
f
LFXT1,HF,logic
OA
HF
C
L,eff
f
Fault,HF
LFXT1 oscillator crystal
frequency, HF mode 0
LFXT1 oscillator crystal
frequency, HF mode 1
LFXT1 oscillator crystal
frequency, HF mode 2
XTS = 1, LFXT1Sx = 0, XCAPx = 0 1.8 V to 3.6 V 0.4 1 MHz
XTS = 1, LFXT1Sx = 1, XCAPx = 0 1.8 V to 3.6 V 1 4 MHz
XTS = 1, LFXT1Sx = 2, XCAPx = 0 2.2 V to 3.6 V 2 12 MHz
LFXT1 oscillator logic-level
square-wave input XTS = 1, LFXT1Sx = 3, XCAPx = 0 2.2 V to 3.6 V 0.4 12 MHz
frequency, HF mode
XTS = 1, XCAPx = 0, LFXT1Sx = 0,
Oscillation allowance for HF
crystals (see Figure 23 and 800 Ω
Figure 24)
XTS = 1, XCAPx = 0, LFXT1Sx = 1,
f
f
LFXT1,HF
LFXT1,HF
= 1 MHz, C
= 4 MHz, C
XTS = 1, XCAPx = 0, LFXT1Sx = 2,
Integrated effective load
capacitance, HF mode
f
XTS = 1, XCAPx = 0
(2)
LFXT1,HF
= 16 MHz, C
XTS = 1, XCAPx = 0,
Measured at P1.4/SMCLK, 40 50 60
Duty cycle, HF mode 2.2 V, 3 V %
f
XTS = 1, XCAPx = 0,
LFXT1,HF
= 10 MHz
Measured at P1.4/SMCLK, 40 50 60
Oscillator fault frequency
f
(4)
XTS = 1, LFXT1Sx = 3, XCAPx = 0
LFXT1,HF
= 16 MHz
(1)
L,eff
L,eff
(3)
= 15 pF
= 15 pF
L,eff
= 15 pF
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
CC
1.8 V to 3.6 V 2 10
3 V to 3.6 V 2 16
1.8 V to 3.6 V 0.4 10
3 V to 3.6 V 0.4 16
(5)
2.2 V, 3 V 30 300 kHz
MIN TYP MAX UNIT
2700
300
1 pF
MSP430F23x
(1) To improve EMI on the XT2 oscillator the following guidelines should be observed:
(a) Keep the trace between the device and the crystal as short as possible.
(b) Design a good ground plane around the oscillator pins.
(c) Prevent crosstalk from other clock or data lines into oscillator pins XIN and XOUT.
(d) Avoid running PCB traces underneath or adjacent to the XIN and XOUT pins.
(e) Use assembly materials and praxis to avoid any parasitic load on the oscillator XIN and XOUT pins.
(f) If conformal coating is used, ensure that it does not induce capacitive or resistive leakage between the oscillator pins.
(g) Do not route the XOUT line to the JTAG header to support the serial programming adapter as shown in other documentation. This
signal is no longer required for the serial programming adapter.
(2) Includes parasitic bond and package capacitance (approximately 2 pF per pin). Because the PCB adds additional capacitance, it is
recommended to verify the correct load by measuring the ACLK frequency. For a correct setup, the effective load capacitance should
always match the specification of the used crystal.
(3) Requires external capacitors at both terminals. Values are specified by crystal manufacturers.
(4) Frequencies below the MIN specification set the fault flag, frequencies above the MAX specification do not set the fault flag, and
frequencies in between might set the flag.
(5) Measured with logic-level input frequency, but also applies to operation with crystals.
Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 49
Page 50

0.0
100.0
200.0
300.0
400.0
500.0
600.0
700.0
800.0
900.0
1000.0
1100.0
1200.0
1300.0
1400.0
1500.0
1600.0
0.0 4.0 8.0 12.0 16.0 20.0
Crystal Frequency − MHz
XT Oscillator Supply Current − µA
LFXT1Sx = 0
LFXT1Sx = 2
LFXT1Sx = 1
Crystal Frequency − MHz
10.00
100.00
1000.00
10000.00
100000.00
0.10 1.00 10.00 100.00
Oscillation Allowance − W
LFXT1Sx = 0
LFXT1Sx = 2
LFXT1Sx = 1
MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Typical Characteristics - LFXT1 Oscillator in HF Mode (XTS = 1)
OSCILLATION ALLOWANCE
vs
CRYSTAL FREQUENCY
C
= 15 pF, TA= 25°C
L,eff
www.ti.com
50 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Figure 23.
OSCILLATOR SUPPLY CURRENT
vs
CRYSTAL FREQUENCY
C
= 15 pF, TA= 25°C
L,eff
Figure 24.
Page 51

MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
www.ti.com
Crystal Oscillator XT2
(1)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS V
f
XT2
f
XT2
f
XT2
f
XT2
OA 800 Ω
C
L,eff
XT2 oscillator crystal frequency,
mode 0
XT2 oscillator crystal frequency,
mode 1
XT2 oscillator crystal frequency,
mode 2
XT2 oscillator logic-level square-wave
input frequency
XT2Sx = 0 1.8 V to 3.6 V 0.4 1 MHz
XT2Sx = 1 1.8 V to 3.6 V 1 4 MHz
XT2Sx = 2 2.2 V to 3.0 V 2 12 MHz
XT2Sx = 3 2.2 V to 3.0 V 0.4 12 MHz
XT2Sx = 0, f
C
= 15 pF
L,eff
Oscillation allowance (see Figure 25 XT2Sx = 1, f
and Figure 26) C
L,eff
= 15 pF
XT2Sx = 2, f
C
= 15 pF
L,eff
Integrated effective load capacitance,
HF mode
(2)
See
(3)
= 1 MHz,
XT2
= 4 MHz,
XT2
= 16 MHz,
XT2
Measured at P1.4/SMCLK,
f
= 10 MHz
XT2
Measured at P1.4/SMCLK,
f
= 16 MHz
XT2
(4)
XT2Sx = 3
(5)
f
Fault
Duty cycle 2.2 V, 3 V %
Oscillator fault frequency, HF mode
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
CC
MIN TYP MAX UNIT
1.8 V to 2.2 V 2 10
3.0 V to 3.6 V 2 16
1.8 V to 2.2 V 0.4 10
3.0 V to 3.6 V 0.4 16
2700
300
1 pF
40 50 60
40 50 60
2.2 V, 3 V 30 300 kHz
(1) To improve EMI on the XT2 oscillator the following guidelines should be observed:
(a) Keep the trace between the device and the crystal as short as possible.
(b) Design a good ground plane around the oscillator pins.
(c) Prevent crosstalk from other clock or data lines into oscillator pins XT2IN and XT2OUT.
(d) Avoid running PCB traces underneath or adjacent to the XT2IN and XT2OUT pins.
(e) Use assembly materials and praxis to avoid any parasitic load on the oscillator XT2IN and XT2OUT pins.
(f) If conformal coating is used, ensure that it does not induce capacitive or resistive leakage between the oscillator pins.
(2) Includes parasitic bond and package capacitance (approximately 2 pF per pin). Because the PCB adds additional capacitance, it is
recommended to verify the correct load by measuring the ACLK frequency. For a correct setup, the effective load capacitance should
always match the specification of the used crystal.
(3) Requires external capacitors at both terminals. Values are specified by crystal manufacturers.
(4) Frequencies below the MIN specification set the fault flag, frequencies above the MAX specification do not set the fault flag, and
frequencies in between might set the flag.
(5) Measured with logic-level input frequency, but also applies to operation with crystals.
Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 51
Page 52

0.0
100.0
200.0
300.0
400.0
500.0
600.0
700.0
800.0
900.0
1000.0
1100.0
1200.0
1300.0
1400.0
1500.0
1600.0
0.0 4.0 8.0 12.0 16.0 20.0
Crystal Frequency − MHz
XT Oscillator Supply Current − µA
XT2Sx = 0
XT2Sx = 2
XT2Sx = 1
Crystal Frequency − MHz
10.00
100.00
1000.00
10000.00
100000.00
0.10 1.00 10.00 100.00
Oscillation Allowance − W
XT2Sx = 0
XT2Sx = 2
XT2Sx = 1
MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Typical Characteristics - XT2 Oscillator
OSCILLATION ALLOWANCE
vs
CRYSTAL FREQUENCY
C
= 15 pF, TA= 25°C
L,eff
www.ti.com
52 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Figure 25.
OSCILLATOR SUPPLY CURRENT
vs
CRYSTAL FREQUENCY
C
= 15 pF, TA= 25°C
L,eff
Figure 26.
Page 53

www.ti.com
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Timer_A
over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air temperature (unless otherwise noted)
f
TA
t
TA,cap
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS V
Internal: SMCLK, ACLK 2.2 V 10
Timer_A clock frequency External: TACLK, INCLK MHz
Duty cycle = 50% ± 10%
Timer_A capture timing TA0, TA1, TA2 2.2 V, 3 V 20 ns
CC
3 V 16
MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Timer_B
over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air temperature (unless otherwise noted)
f
TB
t
TB,cap
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS V
Internal: SMCLK, ACLK 2.2 V 10
Timer_B clock frequency External: TACLK, INCLK MHz
Duty cycle = 50% ± 10%
Timer_B capture timing TB0, TB1, TB2 2.2 V, 3 V 20 ns
CC
3 V 16
MIN TYP MAX UNIT
MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 53
Page 54

MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
USCI (UART Mode)
over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air temperature (unless otherwise noted)
PARAMETER CONDITIONS V
CC
Internal: SMCLK, ACLK
f
USCI
f
BITCLK
t
τ
USCI input clock frequency External: UCLK f
Duty cycle = 50% ± 10%
BITCLK clock frequency
(equals baud rate in MBaud)
UART receive deglitch time
(1)
(2)
2.2 V, 3 V 1 MHz
2.2 V 50 150
3 V 50 100
(1) The DCO wake-up time must be considered in LPM3/4 for baudrates above 1 MHz.
(2) Pulses on the UART receive input (UCxRX) shorter than the UART receive deglitch time are suppressed.
MIN TYP MAX UNIT
www.ti.com
SYSTEM
MHz
ns
USCI (SPI Master Mode)
(1)
over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air temperature (unless otherwise noted)
(see Figure 27 and Figure 28)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS V
f
USCI
t
SU,MI
t
HD,MI
t
VALID,MO
(1) f
For the slave's parameters t
USCI input clock frequency f
SOMI input data setup time ns
SOMI input data hold time ns
SIMO output data valid time ns
UCxCLK
= 1/2t
LO/HI
with t
LO/HI
USCI (SPI Slave Mode)
≥ max(t
SU,SI(Slave)
(1)
VALID,MO(USCI)
and t
VALID,SO(Slave)
SMCLK, ACLK
Duty cycle = 50% ± 10%
UCLK edge to SIMO valid,
CL= 20 pF
+ t
SU,SI(Slave)
, t
SU,MI(USCI)
, see the SPI parameters of the attached slave.
+ t
VALID,SO(Slave)
CC
2.2 V 110
3 V 75
2.2 V 0
3 V 0
2.2 V 30
3 V 20
).
MIN TYP MAX UNIT
over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air temperature (unless otherwise noted)
(see Figure 29 and Figure 30)
t
STE,LEAD
t
STE,LAG
t
STE,ACC
t
STE,DIS
t
SU,SI
t
HD,SI
t
VALID,SO
(1) f
For the master's parameters t
STE lead time, STE low to clock 2.2 V, 3 V 50 ns
STE lag time, Last clock to STE high 2.2 V, 3 V 10 ns
STE access time, STE low to SOMI data out 2.2 V, 3 V 50 ns
STE disable time, STE high to SOMI high
impedance
SIMO input data setup time ns
SIMO input data hold time ns
SOMI output data valid time ns
= 1/2t
UCxCLK
LO/HI
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS V
2.2 V, 3 V 50 ns
UCLK edge to SOMI valid,
CL= 20 pF
with t
LO/HI
≥ max(t
VALID,MO(Master)
SU,MI(Master)
and t
VALID,MO(Master)
+ t
SU,SI(USCI)
, t
SU,MI(Master)
see the SPI parameters of the attached slave.
+ t
VALID,SO(USCI)
CC
2.2 V 20
3 V 15
2.2 V 10
3 V 10
2.2 V 75 110
3 V 50 75
).
MIN TYP MAX UNIT
SYSTEM
MHz
54 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 55

UCLK
CKPL=0
CKPL=1
SIMO
1/f
UCxCLK
t
LO/HItLO/HI
SOMI
t
SU,MI
t
HD,MI
t
VALID,MO
UCLK
CKPL=0
CKPL=1
SIMO
1/f
UCxCLK
t
LO/HItLO/HI
SOMI
t
SU,MI
t
HD,MI
t
VALID,MO
www.ti.com
MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Figure 27. SPI Master Mode, CKPH = 0
Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 55
Figure 28. SPI Master Mode, CKPH = 1
Page 56

STE
UCLK
CKPL=0
CKPL=1
t
STE,LEAD
t
STE,LAG
t
STE,ACC
t
STE,DIS
t
LO/HItLO/HI
t
SU,SI
t
HD,SI
t
VALID,SO
SOMI
SIMO
1/f
UCxCLK
STE
UCLK
CKPL=0
CKPL=1
SOMI
t
STE,ACC
t
STE,DIS
1/f
UCxCLK
t
LO/HItLO/HI
SIMO
t
SU,SI
t
HD,SI
t
VALID,SO
t
STE,LEAD
t
STE,LAG
MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
www.ti.com
Figure 29. SPI Slave Mode, CKPH = 0
Figure 30. SPI Slave Mode, CKPH = 1
56 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 57

SDA
SCL
1/f
SCL
t
HD,DAT
t
SU,DAT
t
HD,STA
t
SU,STAtHD,STA
t
SU,STO
t
SP
MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
www.ti.com
USCI (I2C Mode)
over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air temperature (unless otherwise noted) (see Figure 31)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS V
f
USCI
f
SCL
t
HD,STA
t
SU,STA
t
HD,DAT
t
SU,DAT
t
SU,STO
t
SP
USCI input clock frequency External: UCLK f
SCL clock frequency 2.2 V, 3 V 0 400 kHz
Hold time (repeated) START 2.2 V, 3 V µs
Setup time for a repeated START 2.2 V, 3 V µs
Data hold time 2.2 V, 3 V 0 ns
Data setup time 2.2 V, 3 V 250 ns
Setup time for STOP 2.2 V, 3 V 4 µs
Pulse width of spikes suppressed by input filter ns
Internal: SMCLK, ACLK
Duty cycle = 50% ± 10%
f
≤ 100 kHz 4
SCL
f
> 100 kHz 0.6
SCL
f
≤ 100 kHz 4.7
SCL
f
> 100 kHz 0.6
SCL
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
CC
MIN TYP MAX UNIT
SYSTEM
2.2 V 50 150 600
3 V 50 100 600
MHz
Figure 31. I2C Mode Timing
Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 57
Page 58

MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Comparator_A+
(1)
over recommended operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS V
I
(DD)
I
(Refladder/RefDiode)
V
IC
V
(Ref025)
V
(Ref050)
V
(RefVT)
V
(offset)
V
hys
Common-mode input
voltage range
Voltage at 0.25 V
node / V
Voltage at 0.5 VCCnode / PCA0 = 1, CARSEL = 1, CAREF = 2,
V
See Figure 36 and
Figure 37
Offset voltage
Input hysteresis CAON = 1 2.2 V, 3 V 0 0.7 1.4 mV
Response time 3 V 70 120 240
t
(response)
(low-to-high and high-tolow)
CC
CC
CC
(2)
CAON = 1, CARSEL = 0, CAREF = 0 µA
CAON = 1, CARSEL = 0, CAREF = 1/2/3,
No load at P2.3/CA0/TA1 and P2.4/CA1/TA2
CAON = 1 2.2 V, 3 V 0 VCC- 1 V
PCA0 = 1, CARSEL = 1, CAREF = 1,
No load at P2.3/CA0/TA1 and P2.4/CA1/TA2
No load at P2.3/CA0/TA1 and P2.4/CA1/TA2
PCA0 = 1, CARSEL = 1, CAREF = 3, 2.2 V 390 480 540
No load at P2.3/CA0/TA1 and P2.4/CA1/TA2, mV
TA= 85°C
TA= 25°C, Overdrive 10 mV, 2.2 V 80 165 300
Without filter: CAF = 0
(3)
(see Figure 32 and Figure 33)
TA= 25°C, Overdrive 10 mV, 2.2 V 1.4 1.9 2.8
Without filter: CAF = 1
(3)
(see Figure 32 and Figure 33)
(1) The leakage current for the Comparator_A+ terminals is identical to I
(2) The input offset voltage can be cancelled by using the CAEX bit to invert the Comparator_A+ inputs on successive measurements. The
lkg(Px.y)
specification.
CC
2.2 V 25 40
3 V 45 60
2.2 V 30 50
3 V 45 71
2.2 V, 3 V 0.23 0.24 0.25
2.2 V, 3 V 0.47 0.48 0.5
3 V 400 490 550
2.2 V, 3 V -30 30 mV
3 V 0.9 1.5 2.2
two successive measurements are then summed together.
(3) The response time is measured at P2.2/CAOUT/TA0/CA4 with an input voltage step, with Comparator_A+ already enabled (CAON = 1).
If CAON is set at the same time, a settling time of up to 300 ns is added to the response time.
MIN TYP MAX UNIT
www.ti.com
µA
ns
µs
58 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 59

CASHORT
1
Comparator_A+
CASHORT = 1
CA1CA0
V
IN
+
−
I
OUT
= 10µA
Overdrive
V
CAOUT
t
(respons e)
V+
V−
400 mV
_
+
CAON
0
1
V+
0
1
CAF
Low Pass Filter
τ ≈ 2.0 µs
To Internal
Modules
Set CAIFG
Flag
CAOUT
V−
V
CC
1
0 V
0
www.ti.com
MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Figure 32. Comparator_A+ Block Diagram
Figure 33. Comparator_A+ Overdrive Definition
Figure 34. Comparator_A+ Short Resistance Test Condition
Figure 35. Comparator_A+ Short Resistance Test Condition
Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 59
Page 60
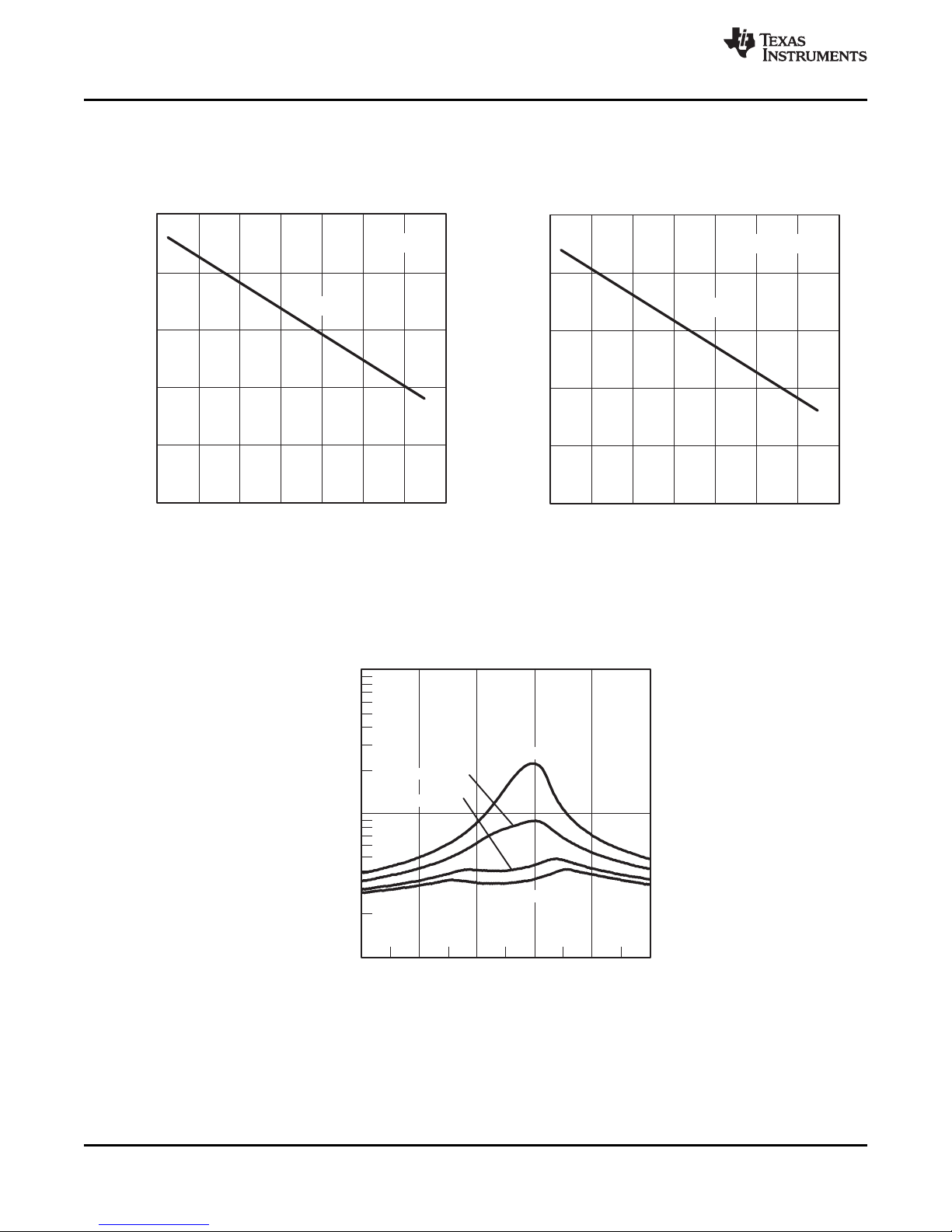
VIN/VCC− Normalized Input Voltage − V/V
1.00
10.00
100.00
0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0
VCC= 1.8 V
VCC= 3.6 V
VCC= 2.2V
VCC= 3 V
Short Resistance − kW
TA− Free-Air Temperature − °C
400
450
500
550
600
650
−45 −25 −5 15 35 55 75 95
VCC= 3 V
Figure 1. V
(RefVT)
vs Temperature, VCC= 3 V
V
(REFVT)
− Reference Volts −mV
Typical
TA− Free-Air Temperature − °C
400
450
500
550
600
650
−45 −25 −5 15 35 55 75 95
VCC= 2.2 V
V
(REFVT)
− Reference Volts −mV
Typical
MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Typical Characteristics, Comparator_A+
www.ti.com
V
(RefVT)
vs vs
TEMPERATURE TEMPERATURE
(VCC= 3 V) (VCC= 2.2 V)
Figure 36. Figure 37.
V
(RefVT)
SHORT RESISTANCE
vs
VIN/V
CC
Figure 38.
60 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 61

MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
www.ti.com
12-bit ADC, Power Supply and Input Range Conditions
(1)
over recommended operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS V
AV
CC
V
(P6.x/Ax)
I
ADC12
I
REF+
C
I
R
I
Analog supply voltage AVSSand DVSSare connected together 2.2 3.6 V
Analog input voltage selected in ADC12MCTLx register,
(2)
range
Operating supply current
into AVCCterminal
Operating supply current
into AVCCterminal
Input capacitance
Input MUX ON
resistance
(3)
(4)
(5)
(5)
(1) The leakage current is defined in the leakage current table with P6.x/Ax parameter.
(2) The analog input voltage range must be within the selected reference voltage range VR+to VR–for valid conversion results.
(3) The internal reference supply current is not included in current consumption parameter I
(4) The internal reference current is supplied via terminal AVCC. Consumption is independent of the ADC12ON control bit, unless a
conversion is active. The REFON bit enables settling of the built-in reference before starting an A/D conversion.
(5) Not production tested, limits verified by design.
AVCCand DVCCare connected together
V
(AVSS)
= V
(DVSS)
= 0 V
All P6.0/A0 to P6.7/A7 terminals, Analog inputs
P6Sel.x = 1, 0 ≤ × ≤ 7,
V
≤ V
(AVSS)
f
ADC12CLK
ADC12ON = 1, REFON = 0, mA
≤ V
P6.x/Ax
(AVCC)
= 5 MHz, 2.2 V 0.65 0.8
SHT0 = 0, SHT1 = 0, ADC12DIV = 0
f
ADC12CLK
ADC12ON = 0, REFON = 1, REF2_5V = 1
f
ADC12CLK
ADC12ON = 0, REFON = 1, REF2_5V = 0
= 5 MHz,
= 5 MHz,
Only one terminal can be selected at one time,
P6.x/Ax
0 V ≤ VAx≤ V
AVCC
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
CC
MIN TYP MAX UNIT
0 V
AVCC
3 V 0.8 1
3 V 0.5 0.7 mA
2.2 V 0.5 0.7
3 V 0.5 0.7
2.2 V 40 pF
3 V 2000 Ω
.
ADC12
V
mA
12-Bit ADC, External Reference
(1)
over recommended operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)
V
eREF+
V
REF–/VeREF–
(V
–
eREF+
V
REF–/VeREF–
I
VeREF+
I
VREF–/VeREF–
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS V
Positive external reference voltage input V
Negative external reference voltage input V
Differential external reference voltage input V
)
Static leakage current 0 V ≤ V
Static leakage current 0 V ≤ V
eREF+
eREF+
eREF+
> V
REF–/VeREF–
> V
REF–/VeREF–
> V
REF–/VeREF–
eREF+
eREF–
≤ V
≤ V
(2)
(3)
(4)
AVCC
AVCC
CC
2.2 V, 3 V ±1 µA
2.2 V, 3 V ±1 µA
(1) The external reference is used during conversion to charge and discharge the capacitance array. The input capacitance, CI, is also the
dynamic load for an external reference during conversion. The dynamic impedance of the reference supply should follow the
recommendations on analog-source impedance to allow the charge to settle for 12-bit accuracy.
(2) The accuracy limits the minimum positive external reference voltage. Lower reference voltage levels may be applied with reduced
accuracy requirements.
(3) The accuracy limits the maximum negative external reference voltage. Higher reference voltage levels may be applied with reduced
accuracy requirements.
(4) The accuracy limits minimum external differential reference voltage. Lower differential reference voltage levels may be applied with
reduced accuracy requirements.
MIN MAX UNIT
1.4 V
AVCC
V
0 1.2 V
1.4 V
AVCC
V
Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 61
Page 62

C
VREF+
1 µF
0
1 ms
10 ms
100 ms t
REFON
t
REFON
≈ .66 x C
VREF+
[ms] with C
VREF+
in µF
100 µF
10 µF
MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
12-Bit ADC, Built-In Reference
over recommended operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)
V
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS T
REF2_5V = 1 for 2.5 V,
REF+
Positive built-in
reference voltage V
output
I
VREF+
max ≤ I
VREF+
≤ I
REF2_5V = 0 for 1.5 V,
I
VREF+
max ≤ I
VREF+
≤ I
VREF+
VREF+
min
min
A
-40°C to 85°C 2.4 2.5 2.6
105°C 2.37 2.5 2.64
-40°C to 85°C 1.44 1.5 1.56
105°C 1.42 1.5 1.57
REF2_5V = 0, 2.2
I
AV
CC(min)
I
VREF+
I
L(VREF)+
max ≤ I
AVCCminimum
VREF+
voltage, positive REF2_5V = 1, 2.8
built-in reference -0.5 mA ≤ I
active
REF2_5V = 1, 2.9
-1 mA ≤ I
VREF+
VREF+
Load current out of
V
terminal
REF+
I
= 500 µA ± 100 µA, 2.2 V ±2
VREF+
Load-current 3 V ±2
regulation, V
terminal
REF+
(1)
Analog input voltage ≈ 0.75 V, LSB
REF2_5V = 0
I
= 500 µA ± 100 µA,
VREF+
Analog input voltage ≈ 1.25 V, 3 V ±2 LSB
VREF+
≤ I
≤ I
VREF+
≤ I
VREF+
VREF+
min
min
min
REF2_5V = 1
I
DL(VREF) +
C
VREF+
T
REF+
Load current I
regulation, V
terminal
Capacitance at pin REFON = 1,
V
REF+
REF+
(2)
(3)
Temperature
coefficient of built-in 2.2 V, 3 V ±100 ppm/°C
reference
(2)
= 100 µA → 900 µA,
VREF+
C
= 5 µF, ax ≈ 0.5 × V
VREF+
Error of conversion result ≤ 1 LSB
0 mA ≤ I
I
VREF+
0 mA ≤ I
≤ I
VREF+
VREF+
is a constant in the range of
≤ 1 mA
VREF+
REF+
max
, 3 V 20 ns
Settle time of
t
REFON
internal reference I
voltage (see V
Figure 39 )
(4) (2)
VREF+
REF+
= 0.5 mA, C
= 1.5 V, V
VREF+
AVCC
= 10 µF,
= 2.2 V
(1) Not production tested, limits characterized.
(2) Not production tested, limits verified by design.
(3) The internal buffer operational amplifier and the accuracy specifications require an external capacitor. All INL and DNL tests uses two
capacitors between pins V
(4) The condition is that the error in a conversion started after t
capacitive load.
and AVSSand V
REF+
REF-–/VeREF–
and AVSS: 10 µF tantalum and 100 nF ceramic.
is less than ±0.5 LSB. The settling time depends on the external
REFON
V
CC
MIN NOM MAX UNIT
3 V
2.2 V, 3 V
2.2 V 0.01 -0.5
3 V 0.01 -1
2.2 V, 3 V 5 10 µF
2.2 V 17 ms
www.ti.com
V
mA
Figure 39. Typical Settling Time of Internal Reference t
62 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated
vs External Capacitor on V
REFON
REF+
Page 63

+
−
10 µF 100 nF
AV
SS
+
−
10 µF 100 nF
AV
CC
10 µF 100 nF
DV
SS
DV
CC
From Power Supply
+
−
Apply External Reference [V ]
or Use Internal Reference [V ]
eREF+
REF+
V
REF+
or V
eREF+
V
REF−/VeREF−
Reference Is Internally
Switched to AVSS
+
−
10 µF 100 nF
AV
SS
+
−
+
−
10 µF 100 nF
10 µF 100 nF
AV
CC
10 µF 100 nF
DV
SS
DV
CC
From Power Supply
Apply External Reference
+
−
Apply External Reference [V ]
or Use Internal Reference [V ]
eREF+
REF+
V
REF+
or V
eREF+
V
REF
−/V
eREF−
www.ti.com
MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Figure 40. Supply Voltage and Reference Voltage Design V
Figure 41. Supply Voltage and Reference Voltage Design V
REF–/VeREF–
REF–/VeREF–
External Supply
= AVSS, Internally Connected
Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 63
Page 64

MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
12-Bit ADC, Timing Parameters
over recommended operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS V
f
ADC12CLK
f
ADC12OSC
t
CONVERT
t
ADC12ON
t
Sample
Internal ADC12 oscillator 2.2 V, 3 V 3.7 5 6.3 MHz
Conversion time
Turn-on settling time of the
(1)
ADC
Sampling time
(1)
(1) Limits verified by design
(2) The condition is that the error in a conversion started after t
settled.
(3) Approximately ten Tau (τ) are needed to get an error of less than ±0.5 LSB:
t
Sample
= ln(2
n+1
) × (RS+ RI) × CI+ 800 ns, where n = ADC resolution = 12, RS= external source resistance
For specified performance of ADC12
linearity parameters
ADC12DIV = 0,
f
ADC12CLK
C
VREF+
f
ADC12OSC
External f
or SMCLK, ADC12DIV × µs
= f
ADC12OSC
≥ 5 µF, Internal oscillator,
= 3.7 MHz to 6.3 MHz
ADC12CLK
from ACLK, MCLK, 13 ×
ADC12SSEL ≉ 0 1/f
(2)
See
RS= 400 Ω,RI= 1000 Ω, CI= 30 pF,
τ = [RS+RI] × C
(3)
I
ADC12ON
is less than ±0.5 LSB. The reference and input signal are already
www.ti.com
CC
MIN NOM MAX UNIT
2.2 V, 3 V 0.45 5 6.3 MHz
2.2 V, 3 V 2.06 3.51 µs
ADC12CLK
100 ns
3 V 1220
2.2 V 1400
ns
12-Bit ADC, Linearity Parameters
over recommended operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS V
Integral linearity
E
I
error
Differential linearity (V
E
D
error C
E
Offset error Internal impedance of source RS < 100 Ω, 2.2 V, 3 V ±2 ±4 LSB
O
E
Gain error 2.2 V, 3 V ±1.1 ±2 LSB
G
Total unadjusted (V
E
T
error C
1.4 V ≤ (V
1.6 V < (V
eREF+
VREF+
(V
eREF+
C
VREF+
(V
eREF+
C
VREF+
eREF+
VREF+
– V
eREF+
eREF+
– V
= 10 µF (tantalum) and 100 nF (ceramic)
– V
REF–/VeREF–
– V
REF–/VeREF–
REF–/VeREF–
REF–/VeREF–
) min ≤ 1.6 V ±2
) min ≤ V
) min ≤ (V
) min ≤ (V
eREF+
eREF+
AVCC
– V
REF–/VeREF–
– V
REF–/VeREF–
= 10 µF (tantalum) and 100 nF (ceramic)
– V
REF–/VeREF–
= 10 µF (tantalum) and 100 nF (ceramic)
-– V
REF–/VeREF–
= 10 µF (tantalum) and 100 nF (ceramic)
)min ≤ (V
)min ≤ (V
– V
eREF+
REF–/VeREF–
eREF+–VREF–/VeREF–
),
),
),
),
CC
2.2 V, 3 V LSB
MIN NOM MAX UNIT
±1.7
2.2 V, 3 V ±1 LSB
2.2 V, 3 V ±2 ±5 LSB
64 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 65

www.ti.com
MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
12-Bit ADC, Temperature Sensor and Built-In V
MID
over recommended operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS V
I
SENSOR
V
TC
t
I
V
(2)(3)
SENSOR
(3)
SENSOR
SENSOR(sample)
VMID
MID
current into AV
(1)
terminal
Sample time 2.2 V 30
(3)
required if channel µs
10 is selected
Current into divider
at channel 11
AVCCdivider at ADC12ON = 1, INCH = 0Bh,
channel 11 V
Sample time 2.2 V 1400
Operating supply 2.2 V 40 120
t
VMID(sample)
(1) The sensor current I
high). Therefore it includes the constant current through the sensor and the reference.
required if channel ns
11 is selected
is consumed if (ADC12ON = 1 and REFON = 1), or (ADC12ON = 1 AND INCH = 0Ah and sample signal is
SENSOR
REFON = 0, INCH = 0Ah,
CC
ADC12ON = 1, TA= 25°C
ADC12ON = 1, INCH = 0Ah, TA= 0°C mV
ADC12ON = 1, INCH = 0Ah mV/°C
ADC12ON = 1, INCH = 0Ah,
Error of conversion result ≤ 1 LSB
(4)
ADC12ON = 1, INCH = 0Bh µA
(5)
is ~0.5 × V
MID
AVCC
ADC12ON = 1, INCH = 0Bh,
Error of conversion result ≤ 1 LSB
(6)
CC
3V 60 160
2.2 V 986
3V 986
2.2 V 3.55 3.55 ± 3%
3V 3.55 3.55 ± 3%
3V 30
2.2 V NA
3V NA
2.2 V 1.1 1.1 ± 0.04
3V 1.5 1.5 ± 0.04
3 V 1220
(2) The temperature sensor offset can be as much as ±20°C. A single-point calibration is recommended to minimize the offset error of the
built-in temperature sensor.
(3) Limits characterized
(4) The typical equivalent impedance of the sensor is 51 kΩ. The sample time required includes the sensor-on time t
(5) No additional current is needed. The V
(6) The on-time t
is included in the sampling time t
VMID(on)
is used during sampling.
MID
VMID(sample)
, no additional on time is needed.
MIN TYP MAX UNIT
µA
V
SENSOR(on)
Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 65
Page 66

MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Flash Memory
over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air temperature (unless otherwise noted)
V
CC (PGM/ERASE)
f
FTG
I
PGM
I
ERASE
t
CPT
t
CMErase
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS V
Program and erase supply voltage 2.2 3.6 V
Flash timing generator frequency 257 476 kHz
Supply current from VCCduring program 2.2 V/3.6 V 1 5 mA
Supply current from VCCduring erase 2.2 V/3.6 V 1 7 mA
Cumulative program time
(1)
Cumulative mass erase time 2.2 V/3.6 V 20 ms
CC
2.2 V/3.6 V 10 ms
Program/Erase endurance 10
t
Retention
t
Word
t
Block, 0
t
Block, 1-63
t
Block, End
t
Mass Erase
t
Seg Erase
Data retention duration TJ= 25°C 100 years
Word or byte program time
Block program time for first byte or word
Block program time for each additional
byte or word
Block program end-sequence wait time
Mass erase time
Segment erase time
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
(1) The cumulative program time must not be exceeded when writing to a 64-byte flash block. This parameter applies to all programming
methods: individual word/byte write and block write modes.
(2) These values are hardwired into the flash controller's state machine (t
FTG
= 1/f
FTG
).
MIN TYP MAX UNIT
4
10
5
30 t
25 t
18 t
6 t
10593 t
4819 t
www.ti.com
cycles
FTG
FTG
FTG
FTG
FTG
FTG
RAM
over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air temperature (unless otherwise noted)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN MAX UNIT
V
(RAMh)
RAM retention supply voltage
(1) This parameter defines the minimum supply voltage VCCwhen the data in RAM remains unchanged. No program execution should
happen during this supply voltage condition.
(1)
CPU halted 1.6 V
JTAG Interface
over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air temperature (unless otherwise noted)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS V
f
TCK
R
Internal
(1) f
(2) TMS, TDI/TCLK, and TCK pullup resistors are implemented in all versions.
JTAG Fuse
TCK input frequency See
Internal pulldown resistance on TEST See
may be restricted to meet the timing requirements of the module selected.
TCK
(1)
(1)
(2)
CC
2.2 V 0 5
3 V 0 10
2.2 V, 3 V 25 60 90 kΩ
over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air temperature (unless otherwise noted)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN MAX UNIT
V
CC(FB)
V
FB
I
FB
t
FB
Supply voltage during fuse-blow condition TA= 25°C 2.5 V
Voltage level on TEST for fuse blow 6 7 V
Supply current into TEST during fuse blow 100 mA
Time to blow fuse 1 ms
MIN TYP MAX UNIT
MHz
(1) Once the fuse is blown, no further access to the JTAG/Test, Spy-Bi-Wire, and emulation feature is possible, and JTAG is switched to
bypass mode.
66 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 67

Direction
0: Input
1: Output
P1SEL.x
P1DIR.x
P1IN.x
P1IRQ.x
D
EN
Module X IN
Module X OUT
P1OUT.x
Interrupt
Edge
Select
Q
EN
Set
P1SEL.x
P1IES.x
P1IFG.x
P1IE.x
P1.0/TACLK
P1.1/TA0
P1.2/TA1
P1.3/TA2
P1.4/SMCLK
P1.5/TA0
P1.6/TA1
P1.7/TA2
DVSS
DVCC
Pad Logic
1
1
0
1
0
1
0
P1REN.x
www.ti.com
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
APPLICATION INFORMATION
Port P1 Pin Schematic: P1.0 to P1.7, Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 67
Page 68

MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Table 20. Port P1.0 to P1.7 Pin Functions
PIN NAME (P1.x) x FUNCTION
P1.0 (I/O) I: 0; O: 1 0
P1.0/TACLK 0 Timer_A3.TACLK 0 1
CAOUT 1 1
P1.1 (I/O) I: 0; O: 1 0
P1.1/TA0 1 Timer_A3.CCI0A 0 1
Timer_A3.TA0 1 1
P1.2 (I/O) I: 0; O: 1 0
P1.2/TA1 2 Timer_A3.CCI1A 0 1
Timer_A3.TA1 1 1
P1.3 (I/O) I: 0; O: 1 0
P1.3/TA2 3 Timer_A3.CCI2A 0 1
Timer_A3.TA2 1 1
P1.4/SMCLK 4
P1.5/TA0 5
P1.6/TA1 6
P1.7/TA2 7
P1.4 (I/O) I: 0; O: 1 0
SMCLK 1 1
P1.5 (I/O) I: 0; O: 1 0
Timer_A3.TA0 1 1
P1.6 (I/O) I: 0; O: 1 0
Timer_A3.TA1 1 1
P1.7 (I/O) I: 0; O: 1 0
Timer_A3.TA2 1 1
CONTROL BITS / SIGNALS
P1DIR.x P1SEL.x
www.ti.com
68 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 69

P2.0/ACLK/CA2
P2.1/TAINCLK/CA3
P2.2/CAOUT/TA0/CA4
P2.3/CA0/TA1
P2.4/CA1/TA2
P2.6/ADC12CLK/CA6
P2.7/TA0/CA7
Direction
0: Input
1: Output
P2SEL.x
P2DIR.x
P2IN.x
P2IRQ.x
D
EN
Module X IN
Module X OUT
P2OUT.x
Interrupt
Edge
Select
Q
EN
Set
P2SEL.x
P2IES.x
P2IFG.x
P2IE.x
DVSS
DVCC
P2REN.x
Pad Logic
1
1
0
1
0
1
0
Bus
Keeper
EN
CAPD.x
From
Comparator_A
To
Comparator_A
MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
www.ti.com
Port P2 Pin Schematic: P2.0 to P2.4, P2.6, and P2.7, Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 69
Page 70

MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Table 21. Port P2.0 to P2.4, P2.6, and P2.7 Pin Functions
PIN NAME (P2.x) x FUNCTION
0 P2.0 (I/O) 0 I: 0; O: 1 0
P2.0/ACLK/CA2 ACLK 0 1 1
CA2 1 X X
1 P2.1 (I/O) 0 I: 0; O: 1 0
P2.1/TAINCLK/CA3
P2.2/CAOUT/TA0/CA4
P2.3/CA0/TA1 Timer_A3.TA1 0 1 1
P2.4/CA1/TA2 Timer_A3.TA2 0 1 X
P2.6/ADC12CLK
P2.7/TA0/CA7 Timer_A3.TA0 0 1 1
(1) X = Don't care
(2) MSP430F24x and MSP430F23x devices only
(2)
/CA6 ADC12CLK
Timer_A3.INCLK 0 0 1
DV
SS
CA3 1 X X
2 P2.2 (I/O) 0 I: 0; O: 1 0
CAOUT 0 1 1
TA0 0 0 1
CA4 1 X X
3 P2.3 (I/O) 0 I: 0; O: 1 0
CA0 1 X X
4 P2.4 (I/O) 0 I: 0; O: 1 0
CA1 1 X 1
6 P2.6 (I/O) 0 I: 0; O: 1 0
(2)
CA6 1 X X
7 P2.7 (I/O) 0 I: 0; O: 1 0
CA7 1 X X
CONTROL BITS / SIGNALS
CAPD.x P2DIR.x P2SEL.x
0 1 1
0 1 1
www.ti.com
(1)
70 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 71

Direction
0: Input
1: Output
P2SEL.5
P2DIR.5
P2IN.5
P2IRQ.5
D
EN
Module X IN
Module X OUT
P2OUT.5
Interrupt
Edge
Select
Q
EN
Set
P2SEL.5
P2IES.5
P2IFG.5
P2IE.5
P2.5/ROSC/CA5
DVSS
DVCC
1
1
0
1
0
1
0
Bus
Keeper
EN
DCOR
To DCO
Pad Logic
From Comparator
To Comparator
CAPD.5
in DCO
P2REN.5
www.ti.com
Port P2 Pin Schematic: P2.5, Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
(1) X = Don't care
Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 71
PIN NAME (P2.x) x FUNCTION
P2.5 (I/O) 0 0 I: 0; O: 1 0
P2.5/R
/CA5 5
OSC
R
OSC
DV
SS
CA5 1 or selected 0 X X
Table 22. Port P2.5 Pin Functions
CAPD DCOR P2DIR.5 P2SEL.5
0 1 X X
0 0 1 1
CONTROL BITS / SIGNALS
(1)
Page 72

Direction
0: Input
1: Output
P3SEL.x
P3DIR.x
P3IN.x
D
EN
Module X IN
Module X OUT
P3OUT.x
DVSS
DVCC
Pad Logic
1
1
0
1
0
1
0
P3.0/UCB0STE/UCA0CLK
P3.1/UCB0SIMO/UCB0SDA
P3.2/UCB0SOMI/UCB0SCL
P3.3/UCB0CLK/UCA0STE
P3.4/UCA0TXD/UCA0SIMO
P3.5/UCA0RXD/UCA0SOMI
P3.6/UCA1TXD/UCA1SIMO
P3.7/UCA1RXD/UCA1SOMI
P3REN.x
Module direction
MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Port P3 Pin Schematic: P3.0 to P3.7, Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
www.ti.com
Table 23. Port P3.0 to P3.7 Pin Functions
CONTROL BITS /
PIN NAME (P3.x) x FUNCTION
SIGNALS
P3DIR.x P3SEL.x
P3.0/UCB0STE/UCA0CLK 0
P3.1/UCB0SIMO/UCB0SDA 1
P3.2/UCB0SOMI/UCB0SCL 2
P3.3/UCB0CLK/UCA0STE 3
P3.4/UCA0TXD/UCA0SIMO 4
P3.5/UCA0RXD/UCA0SOMI 5
P3.6/UCA1TXD
P3.7/UCA1RXD
(5)
/UCA1SIMO
(5)
/UCA1SOMI
(5)
(5)
P3.0 (I/O) I: 0; O: 1 0
UCB0STE/UCA0CLK
(2)(3)
X 1
P3.1 (I/O) I: 0; O: 1 0
UCB0SIMO/UCB0SDA
(2)(4)
X 1
P3.2 (I/O) I: 0; O: 1 0
UCB0SOMI/UCB0SCL
(2)(4)
X 1
P3.3 (I/O) I: 0; O: 1 0
UCB0CLK/UCA0STE
(2)
X 1
P3.4 (I/O) I: 0; O: 1 0
UCA0TXD/UCA0SIMO
(2)
X 1
P3.5 (I/O) I: 0; O: 1 0
UCA0RXD/UCA0SOMI
P3.6 (I/O) I: 0; O: 1 0
6
UCA1TXD
P3.7 (I/O) I: 0; O: 1 0
7
UCA1RXD
(5)
/UCA1SIMO
(5)
/UCA1SOMI
(2)
(5)(2)
(5)(2)
X 1
X 1
X 1
(1) X = Don't care
(2) The pin direction is controlled by the USCI module.
(3) UCA0CLK function takes precedence over UCB0STE function. If the pin is required as UCA0CLK input or output, USCI A/B0 is forced to
3-wire SPI mode if 4-wire SPI mode is selected.
(4) If I2C functionality is selected, the output drives only the logical 0 to VSSlevel.
(5) MSP430F24x and MSP430F24x1 devices only
(1)
72 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 73

P4.0/TB0
P4.1/TB1
P4.2/TB2
P4.3/TB3
P4.4/TB4
P4.5/TB5
P4.6/TB6
P4.7/TBCLK
Direction
0: Input
1: Output
D
EN
DVSS
DVCC
Pad Logic
1
1
0
1
0
1
0
P4SEL.x
P4DIR.x
P4IN.x
Module X IN
Module X OUT
P4OUT.x
P4REN.x
MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
www.ti.com
Port P4 Pin Schematic: P4.0 to P4.7, Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
Table 24. Port P4.0 to P4.7 Pin Functions
PIN NAME (P4.x) x FUNCTION
P4.0 (I/O) I: 0; O: 1 0
P4.0/TB0 0 Timer_B7.CCI0A and Timer_B7.CCI0B 0 1
Timer_B7.TB0 1 1
P4.1 (I/O) I: 0; O: 1 0
P4.1/TB1 1 Timer_B7.CCI1A and Timer_B7.CCI1B 0 1
Timer_B7.TB1 1 1
P4.2 (I/O) I: 0; O: 1 0
P4.2/TB2 2 Timer_B7.CCI2A and Timer_B7.CCI2B 0 1
Timer_B7.TB2 1 1
P4.3 (I/O) I: 0; O: 1 0
P4.3/TB3
(1)
3 Timer_B7.CCI3A and Timer_B7.CCI3B
Timer_B7.TB3
P4.4 (I/O) I: 0; O: 1 0
P4.4/TB4
(1)
4 Timer_B7.CCI4A and Timer_B7.CCI4B
Timer_B7.TB4
P4.5 (I/O) I: 0; O: 1 0
P4.5/TB5
(1)
5 Timer_B7.CCI5A and Timer_B7.CCI5B
Timer_B7.TB5
P4.6 (I/O) I: 0; O: 1 0
P4.6/TB6
(1)
6 Timer_B7.CCI6A and Timer_B7.CCI6B
Timer_B7.TB6
P4.7/TBCLK 7
(1) MSP430F24x and MSP430F24x1 devices only
P4.7 (I/O) I: 0; O: 1 0
Timer_B7.TBCLK 0 1
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
CONTROL BITS / SIGNALS
P4DIR.x P4SEL.x
0 1
1 1
0 1
1 1
0 1
1 1
0 1
1 1
Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 73
Page 74

P5SEL.x
P5DIR.x
P5IN.x
Module X IN
Module X OUT
P5OUT.x
P5REN.x
P5.0/UCB1STE/UCA1CLK
P5.1/UCB1SIMO/UCB1SDA
P5.2/UCB1SOMI/UCB1SCL
P5.3/UCB1CLK/UCA1STE
Direction
0: Input
1: Output
D
EN
DVSS
DVCC
Pad Logic
1
1
0
1
0
1
0
Module Direction
MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Port P5 Pin Schematic: P5.0 to P5.3, Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
Table 25. Port P5.0 to P5.3 Pin Functions
CONTROL BITS /
PIN NAME (P5.x) x FUNCTION
P5.0/UCB1STE
P5.1/UCB1SIMO
P5.2/UCB1SOMI
P5.3/UCB1CLK
(2)
/UCA1CLK
(2)
/UCB1SDA
(2)
/UCB1SCL
(2)
/UCA1STE
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
0 P5.0 (I/O) I: 0; O: 1 0
UCB1STE
(2)
/UCA1CLK
(2)(3)(4)
1 P5.1 (I/O) I: 0; O: 1 0
UCB1SIMO
(2)
/UCB1SDA
(2)(3)(5)
2 P5.2 (I/O) I: 0; O: 1 0
UCB1SOMI
(2)
/UCB1SCL
(2)(3)(5)
3 P5.3 (I/O) I: 0; O: 1 0
UCB1CLK
(2)
/UCA1STE
(2)(3)
(1) X = Don't care
(2) MSP430F24x and MSP430F24x1 devices only
(3) The pin direction is controlled by the USCI module.
(4) UCA0CLK function takes precedence over UCB0STE function. If the pin is required as UCA0CLK input or output, USCI A/B0 is forced to
3-wire SPI mode if 4-wire SPI mode is selected.
(5) If I2C functionality is selected, the output drives only the logical 0 to VSSlevel.
SIGNALS
P5DIR.x P5SEL.x
X 1
X 1
X 1
X 1
www.ti.com
(1)
74 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 75

P5SEL.x
P5DIR.x
P5IN.x
Module X IN
Module X OUT
P5OUT.x
P5REN.x
P5.4/MCLK
P5.5/SMCLK
P5.6/ACLK
P5.7/TBOUTH/SVSOUT
Direction
0: Input
1: Output
D
EN
DVSS
DVCC
Pad Logic
1
1
0
1
0
1
0
MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
www.ti.com
Port P5 Pin Schematic: P5.4 to P5.7, Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
Table 26. Port P5.4 to P5.7 Pin Functions
PIN NAME (P5.x) x FUNCTION
P5.4/MCLK 4
P5.5/SMCLK 5
P5.6/ACLK 6
P5.7/TBOUTH/SVSOUT 7 Timer_B7.TBOUTH 0 1
P5.4 (I/O) I: 0; O: 1 0
MCLK 1 1
P5.5 (I/O) I: 0; O: 1 0
SMCLK 1 1
P5.6 (I/O) I: 0; O: 1 0
ACLK 1 1
P5.7 (I/O) I: 0; O: 1 0
SVSOUT 1 1
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
CONTROL BITS / SIGNALS
P5DIR.x P5SEL.x
Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 75
Page 76

Direction
0: Input
1: Output
P6SEL.x
P6DIR.x
P6IN.x
D
EN
Module X IN
Module X OUT
P6OUT.x
P6.0/A0
P6.1/A1
P6.2/A2
P6.3/A3
P6.4/A4
P6.5/A5
P6.6/A6
DVSS
DVCC
Pad Logic
1
1
0
1
0
1
0
Bus
Keeper
EN
ADC12 Ax
P6REN.x
From ADC12
MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Port P6 Pin Schematic: P6.0 to P6.6, Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
www.ti.com
Table 27. Port P6.0 to P6.6 Pin Functions
PIN NAME (P6.x) x FUNCTION
(2)
P6.0/A0
(2)
P6.1/A1
(2)
P6.2/A2
(2)
P6.3/A3
(2)
P6.4/A4
(2)
P6.5/A5
(2)
P6.6/A6
(1) X = Don't care
(2) MSP430F24x and MSP430F23x devices only
P5.0 (I/O) I: 0; O: 1 0
0
(2)
A0
P5.1 (I/O) I: 0; O: 1 0
1
(2)
A1
P5.2 (I/O) I: 0; O: 1 0
2
(2)
A2
P5.3 (I/O) I: 0; O: 1 0
3
(2)
A3
P5.4 (I/O) I: 0; O: 1 0
4
(2)
A4
P5.5 (I/O) I: 0; O: 1 0
5
(2)
A5
P6.6 (I/O) I: 0; O: 1 0
6
(2)
A6
CONTROL BITS /
SIGNALS
(1)
P6DIR.x P6SEL.x
X 1
X 1
X 1
X 1
X 1
X 1
X 1
76 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 77

Direction
0: Input
1: Output
P6SEL.7
P6DIR.7
P6IN.7
D
EN
Module X IN
Module X OUT
P6OUT.7
P6.7/A7/SVSIN
DVSS
DVCC
P6REN.7
Pad Logic
1
1
0
1
0
1
0
Bus
Keeper
EN
ADC12 A7
VLD = 15
To SVS Mux
From ADC12
www.ti.com
Port P6 Pin Schematic: P6.7, Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Table 28. Port P6.7 Pin Functions
PIN NAME (P6.x) x FUNCTION
P6.7 (I/O) I: 0; O: 1 0 0
DV
P6.7/A7/SVSIN 7
(1) X = Don't care
(2) MSP430F24x and MSP430F23x devices only
SS
(2)
A7
SVSIN (VLD = 15) X X 1
CONTROL BITS / SIGNALS
P6DIR.x P6SEL.x INCHy
1 1 0
X X 1 (y = 7)
(1)
Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 77
Page 78

TDI
TDO
TMS
TCK
Test
JTAG
and
Emulation
Module
Burn & T est
Fuse
Controlled by JTAG
Controlled by JTAG
Controlled
by JTAG
DV
CC
DV
CC
DV
CC
During Programming Activity and
During Blowing of the Fuse, Pin
TDO/TDI Is Used to Apply the Test
Input Data for JTAG Circuitry
TDO/TDI
TDI/TCLK
TMS
TCK
Fuse
DV
CC
MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
JTAG Pins (TMS, TCK, TDI/TCLK, TDO/TDI), Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
www.ti.com
78 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 79

Time TMS Goes Low After POR
TMS
I
TF
I
TDI/TCLK
MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
www.ti.com
JTAG Fuse Check Mode
MSP430 devices that have the fuse on the TEST terminal have a fuse check mode that tests the continuity of the
fuse the first time the JTAG port is accessed after a power-on reset (POR). When activated, a fuse check
current, ITF, of 1 mA at 3 V, 2.5 mA at 5 V can flow from the TEST pin to ground if the fuse is not burned. Care
must be taken to avoid accidentally activating the fuse check mode and increasing overall system power
consumption.
When the TEST pin is again taken low after a test or programming session, the fuse check mode and sense
currents are terminated.
Activation of the fuse check mode occurs with the first negative edge on the TMS pin after power up or if TMS is
being held low during power up. The second positive edge on the TMS pin deactivates the fuse check mode.
After deactivation, the fuse check mode remains inactive until another POR occurs. After each POR the fuse
check mode has the potential to be activated.
The fuse check current flows only when the fuse check mode is active and the TMS pin is in a low state (see
Figure 42). Therefore, the additional current flow can be prevented by holding the TMS pin high (default
condition).
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
Figure 42. Fuse Check Mode Current
NOTE
The CODE and RAM data protection is ensured if the JTAG fuse is blown and the 256-bit
bootloader access key is used. Also, see the Bootstrap Loader section for more
information.
Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 79
Page 80

MSP430F23x
MSP430F24x(1)
MSP430F2410
SLAS547I –JUNE 2007–REVISED DECEMBER 2012
www.ti.com
REVISION HISTORY
LITERATURE
NUMBER
SLAS547 Product Preview release
SLAS547A Production Data release
Corrected terminal names and descriptions for pins 34 and 35 in "Terminal Functions - MSP430F23x" (page 9)
Corrected terminal names for pins 13, 14, and 15 in "Terminal Functions - MSP430F24x1" (page 13)
SLAS547B Changed index values from 1-3 to 0-2 in Figures 23 to 26 (pages 52 and 54)
SLAS547C
SLAS547D Updated notes and t
SLAS547E Changed limits on t
SLAS547F
SLAS547G Changed T
SLAS547H
SLAS547I
Corrected interrupt source and flag entries for USCI_A1/USCI_B1 in "interrupt vector addresses" table (page 17)
Changed f
Corrected "Port P1.0 to P1.7 pin functions" table (page 72)
Removed incorrect CAPD.x column in "Port P6.0 to P6.6 pin functions" table (page 80)
Added Development Tool Support section (page 2)
Updated parametric values in "low-power mode supply current into VCCexcluding external current" table (page 34)
Changed "Port 6.0 to 6.6 Pin Functions" table (page 77)
Changed "Port 6.7 Pin Functions" table (page 78)
Corrected formatting error of TAcolumn in Active Mode Supply Current (both I
Mode Supply Currents (I
Corrected number of capture/compare registers in description in Timer_B3 (MSP430F23x Devices).
Added typical test conditions in Recommended Operating Conditions.
Removed "Timer_A3.CCIxA" entries from P1.5 through P1.7 in Table 20.
max,BITCLK
stg
and tτparameters in "USCI (UART mode)" table (page 56)
MIN value "flash memory" table (page 34)
CMErase
parameter (page 41)
d(SVSon)
, Programmed device, to -55°C to 150°C in Absolute Maximum Ratings
LPM0,1MHz
and I
LPM0,100kHz
SUMMARY
parameters)
parameters) and in Low-Power-
AM,1MHz
80 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2007–2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 81
PACKAGE OPTION ADDENDUM
www.ti.com
16-Nov-2013
Addendum-Page 1
PACKAGING INFORMATION
Orderable Device Status
(1)
Package Type Package
Drawing
Pins Package
Qty
Eco Plan
(2)
Lead/Ball Finish
(6)
MSL Peak Temp
(3)
Op Temp (°C) Device Marking
(4/5)
Samples
MSP430F233TPM ACTIVE LQFP PM 64 160 Green (RoHS
& no Sb/Br)
NIPDAU | CU NIPDAU Level-3-260C-168 HR -40 to 105 M430F233T
REV #
MSP430F233TPMR ACTIVE LQFP PM 64 1000 Green (RoHS
& no Sb/Br)
NIPDAU | CU NIPDAU Level-3-260C-168 HR -40 to 105 M430F233T
REV #
MSP430F233TRGC OBSOLETE VQFN RGC 64 TBD Call TI Call TI -40 to 105
MSP430F233TRGCR ACTIVE VQFN RGC 64 2500 Green (RoHS
& no Sb/Br)
CU NIPDAU Level-3-260C-168 HR -40 to 105 M430F233T
MSP430F233TRGCT ACTIVE VQFN RGC 64 250 Green (RoHS
& no Sb/Br)
CU NIPDAU Level-3-260C-168 HR -40 to 105 M430F233T
MSP430F235TPM ACTIVE LQFP PM 64 160 Green (RoHS
& no Sb/Br)
NIPDAU | CU NIPDAU Level-3-260C-168 HR -40 to 105 M430F235T
REV #
MSP430F235TPMR ACTIVE LQFP PM 64 1000 Green (RoHS
& no Sb/Br)
NIPDAU | CU NIPDAU Level-3-260C-168 HR -40 to 105 M430F235T
REV #
MSP430F235TRGC OBSOLETE VQFN RGC 64 TBD Call TI Call TI -40 to 105
MSP430F235TRGCR ACTIVE VQFN RGC 64 2500 Green (RoHS
& no Sb/Br)
CU NIPDAU Level-3-260C-168 HR -40 to 105 M430F235T
MSP430F235TRGCT ACTIVE VQFN RGC 64 250 Green (RoHS
& no Sb/Br)
CU NIPDAU Level-3-260C-168 HR -40 to 105 M430F235T
MSP430F2410TPM ACTIVE LQFP PM 64 160 Green (RoHS
& no Sb/Br)
NIPDAU | CU NIPDAU Level-3-260C-168 HR -40 to 105 M430F2410T
REV #
MSP430F2410TPMR ACTIVE LQFP PM 64 1000 Green (RoHS
& no Sb/Br)
NIPDAU | CU NIPDAU Level-3-260C-168 HR -40 to 105 M430F2410T
REV #
MSP430F2410TRGC OBSOLETE VQFN RGC 64 TBD Call TI Call TI -40 to 105
MSP430F2410TRGCR ACTIVE VQFN RGC 64 2500 Green (RoHS
& no Sb/Br)
CU NIPDAU Level-3-260C-168 HR -40 to 105 M430F2410T
MSP430F2410TRGCT ACTIVE VQFN RGC 64 250 Green (RoHS
& no Sb/Br)
CU NIPDAU Level-3-260C-168 HR -40 to 105 M430F2410T
MSP430F2471TPM ACTIVE LQFP PM 64 160 Green (RoHS
& no Sb/Br)
NIPDAU | CU NIPDAU Level-3-260C-168 HR -40 to 105 M430F2471T
REV #
MSP430F2471TPMR ACTIVE LQFP PM 64 1000 Green (RoHS
& no Sb/Br)
NIPDAU | CU NIPDAU Level-3-260C-168 HR -40 to 105 M430F2471T
REV #
MSP430F2471TRGC OBSOLETE VQFN RGC 64 TBD Call TI Call TI -40 to 105
MSP430F2471TRGCR ACTIVE VQFN RGC 64 2500 Green (RoHS
& no Sb/Br)
CU NIPDAU Level-3-260C-168 HR -40 to 105 M430F2471T
Page 82

PACKAGE OPTION ADDENDUM
www.ti.com
16-Nov-2013
Addendum-Page 2
Orderable Device Status
(1)
Package Type Package
Drawing
Pins Package
Qty
Eco Plan
(2)
Lead/Ball Finish
(6)
MSL Peak Temp
(3)
Op Temp (°C) Device Marking
(4/5)
Samples
MSP430F2471TRGCT ACTIVE VQFN RGC 64 250 Green (RoHS
& no Sb/Br)
CU NIPDAU Level-3-260C-168 HR -40 to 105 M430F2471T
MSP430F247TPM ACTIVE LQFP PM 64 160 Green (RoHS
& no Sb/Br)
NIPDAU | CU NIPDAU Level-3-260C-168 HR -40 to 105 M430F247T
REV #
MSP430F247TPMR ACTIVE LQFP PM 64 1000 Green (RoHS
& no Sb/Br)
NIPDAU | CU NIPDAU Level-3-260C-168 HR -40 to 105 M430F247T
REV #
MSP430F247TRGC OBSOLETE VQFN RGC 64 TBD Call TI Call TI -40 to 105
MSP430F247TRGCR ACTIVE VQFN RGC 64 2500 Green (RoHS
& no Sb/Br)
CU NIPDAU Level-3-260C-168 HR -40 to 105 M430F247T
MSP430F247TRGCT ACTIVE VQFN RGC 64 250 Green (RoHS
& no Sb/Br)
CU NIPDAU Level-3-260C-168 HR -40 to 105 M430F247T
MSP430F2481TPM ACTIVE LQFP PM 64 160 Green (RoHS
& no Sb/Br)
NIPDAU | CU NIPDAU Level-3-260C-168 HR -40 to 105 M430F2481T
REV #
MSP430F2481TPMR ACTIVE LQFP PM 64 1000 Green (RoHS
& no Sb/Br)
NIPDAU | CU NIPDAU Level-3-260C-168 HR -40 to 105 M430F2481T
REV #
MSP430F2481TRGC OBSOLETE VQFN RGC 64 TBD Call TI Call TI -40 to 105
MSP430F2481TRGCR ACTIVE VQFN RGC 64 2500 Green (RoHS
& no Sb/Br)
CU NIPDAU Level-3-260C-168 HR -40 to 105 M430F2481T
MSP430F2481TRGCT ACTIVE VQFN RGC 64 250 Green (RoHS
& no Sb/Br)
CU NIPDAU Level-3-260C-168 HR -40 to 105 M430F2481T
MSP430F248TPM ACTIVE LQFP PM 64 160 Green (RoHS
& no Sb/Br)
NIPDAU | CU NIPDAU Level-3-260C-168 HR -40 to 105 M430F248T
REV #
MSP430F248TPMR ACTIVE LQFP PM 64 1000 Green (RoHS
& no Sb/Br)
NIPDAU | CU NIPDAU Level-3-260C-168 HR -40 to 105 M430F248T
REV #
MSP430F248TRGC OBSOLETE VQFN RGC 64 TBD Call TI Call TI -40 to 105
MSP430F248TRGCR ACTIVE VQFN RGC 64 2500 Green (RoHS
& no Sb/Br)
CU NIPDAU Level-3-260C-168 HR -40 to 105 M430F248T
MSP430F248TRGCT ACTIVE VQFN RGC 64 250 Green (RoHS
& no Sb/Br)
CU NIPDAU Level-3-260C-168 HR -40 to 105 M430F248T
MSP430F2491TPM ACTIVE LQFP PM 64 160 Green (RoHS
& no Sb/Br)
NIPDAU | CU NIPDAU Level-3-260C-168 HR -40 to 105 M430F2491T
REV #
MSP430F2491TPMR ACTIVE LQFP PM 64 1000 Green (RoHS
& no Sb/Br)
NIPDAU | CU NIPDAU Level-3-260C-168 HR -40 to 105 M430F2491T
REV #
MSP430F2491TRGC OBSOLETE VQFN RGC 64 TBD Call TI Call TI -40 to 105
MSP430F2491TRGCR ACTIVE VQFN RGC 64 2500 Green (RoHS
& no Sb/Br)
CU NIPDAU Level-3-260C-168 HR -40 to 105 M430F2491T
Page 83

PACKAGE OPTION ADDENDUM
www.ti.com
16-Nov-2013
Addendum-Page 3
Orderable Device Status
(1)
Package Type Package
Drawing
Pins Package
Qty
Eco Plan
(2)
Lead/Ball Finish
(6)
MSL Peak Temp
(3)
Op Temp (°C) Device Marking
(4/5)
Samples
MSP430F2491TRGCT ACTIVE VQFN RGC 64 250 Green (RoHS
& no Sb/Br)
CU NIPDAU Level-3-260C-168 HR -40 to 105 M430F2491T
MSP430F249TPM ACTIVE LQFP PM 64 160 Green (RoHS
& no Sb/Br)
NIPDAU | CU NIPDAU Level-3-260C-168 HR -40 to 105 M430F249T
REV #
MSP430F249TPMR ACTIVE LQFP PM 64 1000 Green (RoHS
& no Sb/Br)
NIPDAU | CU NIPDAU Level-3-260C-168 HR -40 to 105 M430F249T
REV #
MSP430F249TRGC OBSOLETE VQFN RGC 64 TBD Call TI Call TI -40 to 105
MSP430F249TRGCR ACTIVE VQFN RGC 64 2500 Green (RoHS
& no Sb/Br)
CU NIPDAU Level-3-260C-168 HR -40 to 105 M430F249T
MSP430F249TRGCT ACTIVE VQFN RGC 64 250 Green (RoHS
& no Sb/Br)
CU NIPDAU Level-3-260C-168 HR -40 to 105 M430F249T
(1)
The marketing status values are defined as follows:
ACTIVE: Product device recommended for new designs.
LIFEBUY: TI has announced that the device will be discontinued, and a lifetime-buy period is in effect.
NRND: Not recommended for new designs. Device is in production to support existing customers, but TI does not recommend using this part in a new design.
PREVIEW: Device has been announced but is not in production. Samples may or may not be available.
OBSOLETE: TI has discontinued the production of the device.
(2)
Eco Plan - The planned eco-friendly classification: Pb-Free (RoHS), Pb-Free (RoHS Exempt), or Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br) - please check http://www.ti.com/productcontent for the latest availability
information and additional product content details.
TBD: The Pb-Free/Green conversion plan has not been defined.
Pb-Free (RoHS): TI's terms "Lead-Free" or "Pb-Free" mean semiconductor products that are compatible with the current RoHS requirements for all 6 substances, including the requirement that
lead not exceed 0.1% by weight in homogeneous materials. Where designed to be soldered at high temperatures, TI Pb-Free products are suitable for use in specified lead-free processes.
Pb-Free (RoHS Exempt): This component has a RoHS exemption for either 1) lead-based flip-chip solder bumps used between the die and package, or 2) lead-based die adhesive used between
the die and leadframe. The component is otherwise considered Pb-Free (RoHS compatible) as defined above.
Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br): TI defines "Green" to mean Pb-Free (RoHS compatible), and free of Bromine (Br) and Antimony (Sb) based flame retardants (Br or Sb do not exceed 0.1% by weight
in homogeneous material)
(3)
MSL, Peak Temp. - The Moisture Sensitivity Level rating according to the JEDEC industry standard classifications, and peak solder temperature.
(4)
There may be additional marking, which relates to the logo, the lot trace code information, or the environmental category on the device.
(5)
Multiple Device Markings will be inside parentheses. Only one Device Marking contained in parentheses and separated by a "~" will appear on a device. If a line is indented then it is a continuation
of the previous line and the two combined represent the entire Device Marking for that device.
(6)
Lead/Ball Finish - Orderable Devices may have multiple material finish options. Finish options are separated by a vertical ruled line. Lead/Ball Finish values may wrap to two lines if the finish
value exceeds the maximum column width.
Page 84

PACKAGE OPTION ADDENDUM
www.ti.com
16-Nov-2013
Addendum-Page 4
Important Information and Disclaimer:The information provided on this page represents TI's knowledge and belief as of the date that it is provided. TI bases its knowledge and belief on information
provided by third parties, and makes no representation or warranty as to the accuracy of such information. Efforts are underway to better integrate information from third parties. TI has taken and
continues to take reasonable steps to provide representative and accurate information but may not have conducted destructive testing or chemical analysis on incoming materials and chemicals.
TI and TI suppliers consider certain information to be proprietary, and thus CAS numbers and other limited information may not be available for release.
In no event shall TI's liability arising out of such information exceed the total purchase price of the TI part(s) at issue in this document sold by TI to Customer on an annual basis.
OTHER QUALIFIED VERSIONS OF MSP430F249 :
•
Enhanced Product: MSP430F249-EP
NOTE: Qualified Version Definitions:
•
Enhanced Product - Supports Defense, Aerospace and Medical Applications
Page 85

PACKAGE MATERIALS INFORMATION
www.ti.com 23-Jan-2014
TAPE AND REEL INFORMATION
*All dimensions are nominal
Device Package
MSP430F233TPMR LQFP PM 64 1000 330.0 24.4 13.0 13.0 2.1 16.0 24.0 Q2
MSP430F235TPMR LQFP PM 64 1000 330.0 24.4 13.0 13.0 2.1 16.0 24.0 Q2
MSP430F2410TPMR LQFP PM 64 1000 330.0 24.4 13.0 13.0 2.1 16.0 24.0 Q2
MSP430F2410TPMR LQFP PM 64 1000 330.0 24.4 13.0 13.0 2.1 16.0 24.0 Q2
MSP430F2471TPMR LQFP PM 64 1000 330.0 24.4 13.0 13.0 2.1 16.0 24.0 Q2
MSP430F2471TRGCT VQFN RGC 64 250 180.0 16.4 9.3 9.3 1.5 12.0 16.0 Q2
MSP430F247TPMR LQFP PM 64 1000 330.0 24.4 13.0 13.0 2.1 16.0 24.0 Q2
MSP430F247TPMR LQFP PM 64 1000 330.0 24.4 13.0 13.0 2.1 16.0 24.0 Q2
MSP430F2481TPMR LQFP PM 64 1000 330.0 24.4 13.0 13.0 2.1 16.0 24.0 Q2
MSP430F248TPMR LQFP PM 64 1000 330.0 24.4 13.0 13.0 2.1 16.0 24.0 Q2
MSP430F2491TPMR LQFP PM 64 1000 330.0 24.4 13.0 13.0 2.1 16.0 24.0 Q2
MSP430F2491TPMR LQFP PM 64 1000 330.0 24.4 13.0 13.0 2.1 16.0 24.0 Q2
MSP430F249TPMR LQFP PM 64 1000 330.0 24.4 13.0 13.0 2.1 16.0 24.0 Q2
MSP430F249TPMR LQFP PM 64 1000 330.0 24.4 13.0 13.0 2.1 16.0 24.0 Q2
Type
Package
Drawing
Pins SPQ Reel
Diameter
(mm)
Reel
Width
W1 (mm)
A0
(mm)B0(mm)K0(mm)P1(mm)W(mm)
Pin1
Quadrant
Pack Materials-Page 1
Page 86

PACKAGE MATERIALS INFORMATION
www.ti.com 23-Jan-2014
*All dimensions are nominal
Device Package Type Package Drawing Pins SPQ Length (mm) Width (mm) Height (mm)
MSP430F233TPMR LQFP PM 64 1000 336.6 336.6 41.3
MSP430F235TPMR LQFP PM 64 1000 336.6 336.6 41.3
MSP430F2410TPMR LQFP PM 64 1000 336.6 336.6 41.3
MSP430F2410TPMR LQFP PM 64 1000 367.0 367.0 45.0
MSP430F2471TPMR LQFP PM 64 1000 336.6 336.6 41.3
MSP430F2471TRGCT VQFN RGC 64 250 210.0 185.0 35.0
MSP430F247TPMR LQFP PM 64 1000 336.6 336.6 41.3
MSP430F247TPMR LQFP PM 64 1000 367.0 367.0 45.0
MSP430F2481TPMR LQFP PM 64 1000 336.6 336.6 41.3
MSP430F248TPMR LQFP PM 64 1000 336.6 336.6 41.3
MSP430F2491TPMR LQFP PM 64 1000 367.0 367.0 45.0
MSP430F2491TPMR LQFP PM 64 1000 336.6 336.6 41.3
MSP430F249TPMR LQFP PM 64 1000 367.0 367.0 45.0
MSP430F249TPMR LQFP PM 64 1000 336.6 336.6 41.3
Pack Materials-Page 2
Page 87

Page 88

Page 89

Page 90

MECHANICAL DATA
MTQF008A – JANUARY 1995 – REVISED DECEMBER 1996
PM (S-PQFP-G64) PLASTIC QUAD FLATPACK
49
64
0,50
48
0,27
0,17
33
1
7,50 TYP
10,20
SQ
9,80
12,20
SQ
11,80
16
0,08
32
17
M
0,05 MIN
0,13 NOM
Gage Plane
0,25
0°–7°
1,45
1,35
1,60 MAX
NOTES: A. All linear dimensions are in millimeters.
B. This drawing is subject to change without notice.
C. Falls within JEDEC MS-026
D. May also be thermally enhanced plastic with leads connected to the die pads.
0,75
0,45
Seating Plane
0,08
4040152/C 11/96
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
1
Page 91

Page 92

IMPORTANT NOTICE
Texas Instruments Incorporated and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make corrections, enhancements, improvements and other
changes to its semiconductor products and services per JESD46, latest issue, and to discontinue any product or service per JESD48, latest
issue. Buyers should obtain the latest relevant information before placing orders and should verify that such information is current and
complete. All semiconductor products (also referred to herein as “components”) are sold subject to TI’s terms and conditions of sale
supplied at the time of order acknowledgment.
TI warrants performance of its components to the specifications applicable at the time of sale, in accordance with the warranty in TI’s terms
and conditions of sale of semiconductor products. Testing and other quality control techniques are used to the extent TI deems necessary
to support this warranty. Except where mandated by applicable law, testing of all parameters of each component is not necessarily
performed.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or the design of Buyers’ products. Buyers are responsible for their products and
applications using TI components. To minimize the risks associated with Buyers’ products and applications, Buyers should provide
adequate design and operating safeguards.
TI does not warrant or represent that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any patent right, copyright, mask work right, or
other intellectual property right relating to any combination, machine, or process in which TI components or services are used. Information
published by TI regarding third-party products or services does not constitute a license to use such products or services or a warranty or
endorsement thereof. Use of such information may require a license from a third party under the patents or other intellectual property of the
third party, or a license from TI under the patents or other intellectual property of TI.
Reproduction of significant portions of TI information in TI data books or data sheets is permissible only if reproduction is without alteration
and is accompanied by all associated warranties, conditions, limitations, and notices. TI is not responsible or liable for such altered
documentation. Information of third parties may be subject to additional restrictions.
Resale of TI components or services with statements different from or beyond the parameters stated by TI for that component or service
voids all express and any implied warranties for the associated TI component or service and is an unfair and deceptive business practice.
TI is not responsible or liable for any such statements.
Buyer acknowledges and agrees that it is solely responsible for compliance with all legal, regulatory and safety-related requirements
concerning its products, and any use of TI components in its applications, notwithstanding any applications-related information or support
that may be provided by TI. Buyer represents and agrees that it has all the necessary expertise to create and implement safeguards which
anticipate dangerous consequences of failures, monitor failures and their consequences, lessen the likelihood of failures that might cause
harm and take appropriate remedial actions. Buyer will fully indemnify TI and its representatives against any damages arising out of the use
of any TI components in safety-critical applications.
In some cases, TI components may be promoted specifically to facilitate safety-related applications. With such components, TI’s goal is to
help enable customers to design and create their own end-product solutions that meet applicable functional safety standards and
requirements. Nonetheless, such components are subject to these terms.
No TI components are authorized for use in FDA Class III (or similar life-critical medical equipment) unless authorized officers of the parties
have executed a special agreement specifically governing such use.
Only those TI components which TI has specifically designated as military grade or “enhanced plastic” are designed and intended for use in
military/aerospace applications or environments. Buyer acknowledges and agrees that any military or aerospace use of TI components
which have not been so designated is solely at the Buyer's risk, and that Buyer is solely responsible for compliance with all legal and
regulatory requirements in connection with such use.
TI has specifically designated certain components as meeting ISO/TS16949 requirements, mainly for automotive use. In any case of use of
non-designated products, TI will not be responsible for any failure to meet ISO/TS16949.
Products Applications
Audio www.ti.com/audio Automotive and Transportation www.ti.com/automotive
Amplifiers amplifier.ti.com Communications and Telecom www.ti.com/communications
Data Converters dataconverter.ti.com Computers and Peripherals www.ti.com/computers
DLP® Products www.dlp.com Consumer Electronics www.ti.com/consumer-apps
DSP dsp.ti.com Energy and Lighting www.ti.com/energy
Clocks and Timers www.ti.com/clocks Industrial www.ti.com/industrial
Interface interface.ti.com Medical www.ti.com/medical
Logic logic.ti.com Security www.ti.com/security
Power Mgmt power.ti.com Space, Avionics and Defense www.ti.com/space-avionics-defense
Microcontrollers microcontroller.ti.com Video and Imaging www.ti.com/video
RFID www.ti-rfid.com
OMAP Applications Processors www.ti.com/omap TI E2E Community e2e.ti.com
Wireless Connectivity www.ti.com/wirelessconnectivity
Mailing Address: Texas Instruments, Post Office Box 655303, Dallas, Texas 75265
Copyright © 2014, Texas Instruments Incorporated
 Loading...
Loading...