Datasheet LM3674MF, LM3674MF-1.2, LM3674MF-1.5, LM3674MF-1.8, LM3674MF-1.875 Datasheet (Texas Instruments) [ru]
...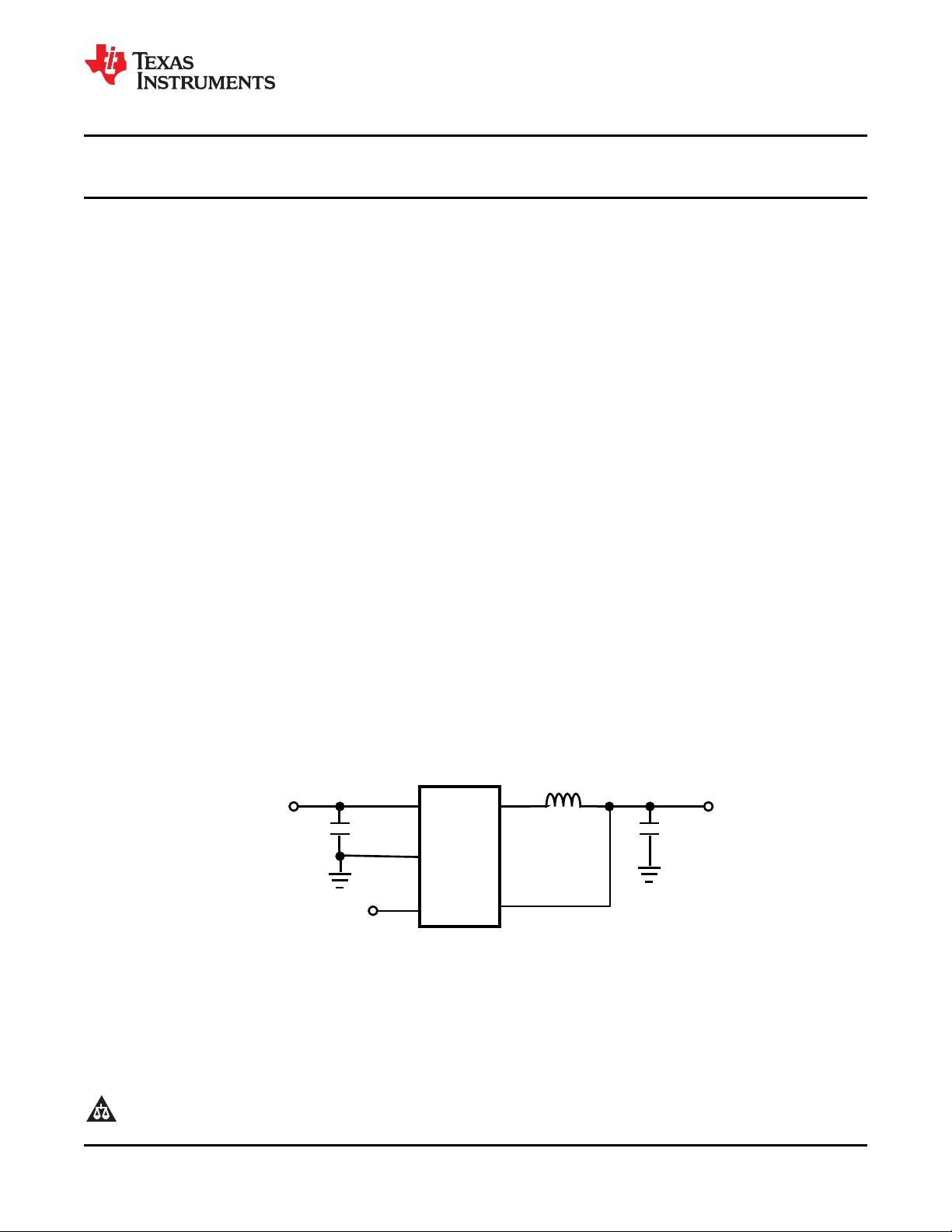
1
2
5
4
3
V
IN
SW
FB
EN
GND
L1:2.2 PH
V
OUT
C
OUT
10 PF
C
IN
4.7 PF
LM3674
V
IN
2.7V to 5.5V
LM3674
www.ti.com
LM3674 2MHz, 600mA Step-Down DC-DC Converter in SOT-23
Check for Samples: LM3674
1
FEATURES
2
• 600mA Max Load Current
• Input Voltage Range from 2.7V to 5.5V
• Available in Fixed and Adjustable Output
Voltages Ranging from 1.0V to 3.3V
• Operates from a Single Li-Ion Cell Battery
• Internal Synchronous Rectification for High
Efficiency
• Internal Soft Start
• 0.01 µA Typical Shutdown Current
• 2 MHz PWM Fixed Switching Frequency (typ)
• 5-Pin SOT-23 Package
• Current Overload Protection and Thermal
Shutdown Protection
APPLICATIONS
• Mobile Phones
• PDAs
• MP3 Players
• Portable Instruments
• W-LAN
• Digital Still Cameras
• Portable Hard Disk Drives
SNVS405F –DECEMBER 2005–REVISED MAY 2013
DESCRIPTION
The LM3674 step-down DC-DC converter is
optimized for powering low voltage circuits from a
single Li-Ion cell battery and input voltage rails from
2.7V to 5.5V. It provides up to 600mA load current,
over the entire input voltage range. There are several
fixed output voltages and adjustable output voltage
versions.
The device offers superior features and performance
for mobile phones and similar portable systems.
During PWM mode, the device operates at a fixedfrequency of 2 MHz (typ). Internal synchronous
rectification provides high efficiency during Pulse
Width Modulation (PWM) mode operation. In
shutdown mode, the device turns off and reduces
battery consumption to 0.01 µA (typ).
The LM3674 is available in a 5-pin SOT-23 package
in leaded (PB) and lead-free (NO PB) versions. A
high switching frequency of 2 MHz (typ) allows use of
only three tiny external surface-mount components,
an inductor and two ceramic capacitors.
TYPICAL APPLICATION CIRCUITS
Figure 1. Typical Application Circuit
1
2All trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date.
Products conform to specifications per the terms of the Texas
Instruments standard warranty. Production processing does not
necessarily include testing of all parameters.
Please be aware that an important notice concerning availability, standard warranty, and use in critical applications of
Texas Instruments semiconductor products and disclaimers thereto appears at the end of this data sheet.
Copyright © 2005–2013, Texas Instruments Incorporated
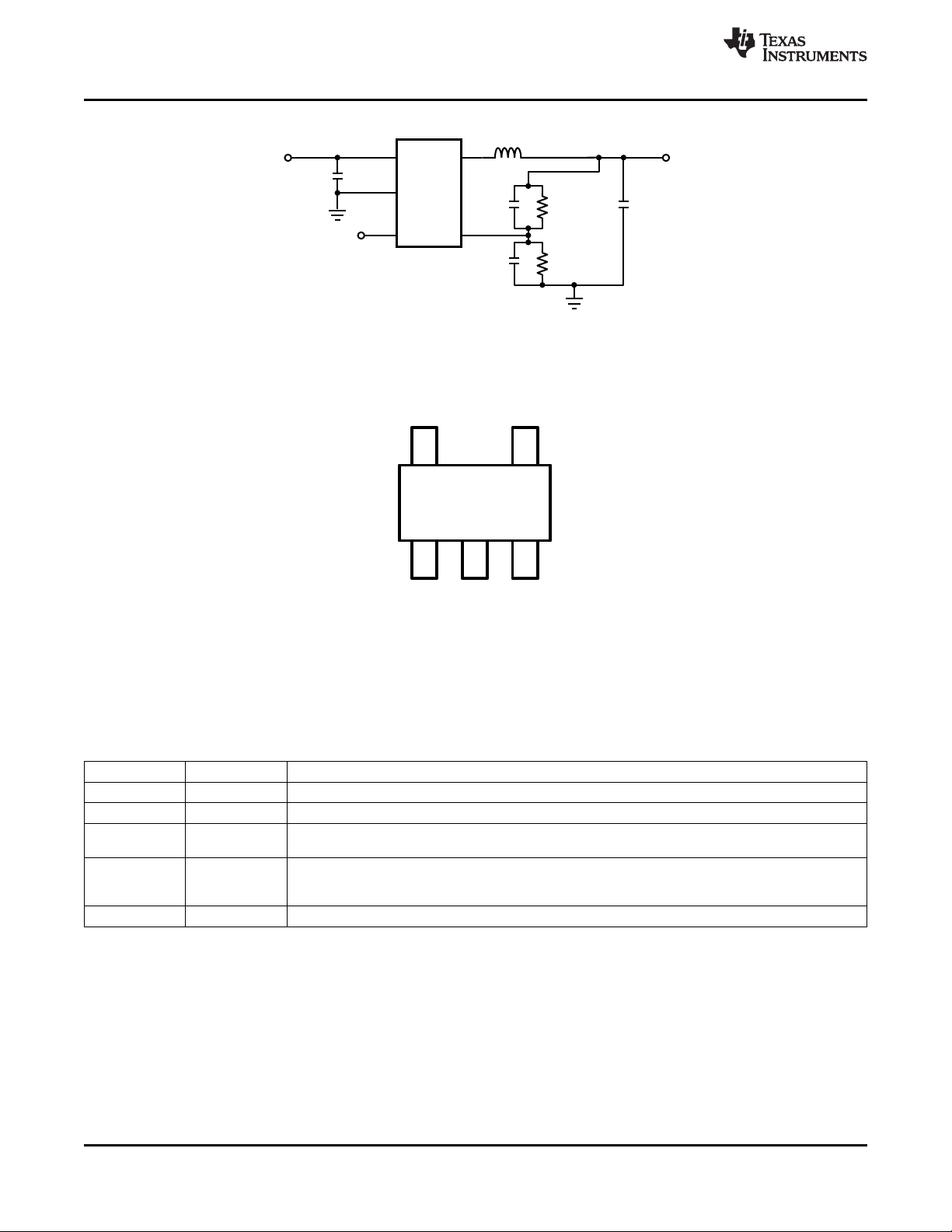
V
IN
1
GND
2
EN
3
FB
4
SW
5
1
2
5
43
V
IN
SW
FB
EN
GND
L1: 2.2 PH
V
OUT
C
OUT
: 10 PF
CIN: 4.7 PF
LM3674-
ADJ
V
IN
2.7V to 5.5V
C
1
C
2
R
1
R
2
LM3674
SNVS405F –DECEMBER 2005–REVISED MAY 2013
Figure 2. Typical Application Circuit for Adjustable Voltage Option
www.ti.com
PIN DIAGRAM
Figure 3. Top View
5-Pin SOT-23 Package
See Package Number DBV0005A
Note: The actual physical placement of the package marking will vary from part to part.
PIN DESCRIPTIONS
Pin Number Name Description
1 V
IN
2 GND Ground pin.
3 EN
4 FB version external resistor dividers are required ( Figure 2). The internal resistor dividers are disabled for
5 SW Switching node connection to the internal PFET switch and NFET synchronous rectifier.
2 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2005–2013, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Power supply input. Connect to the input filter capacitor ( Figure 1).
Enable input. The device is in shutdown mode when voltage to this pin is <0.4V and enable when
>1.0V. Do not leave this pin floating.
Feedback analog input. Connect to the output filter capacitor for fixed voltage versions. For adjustable
the adjustable version.
Product Folder Links: LM3674
LM3674
www.ti.com
These devices have limited built-in ESD protection. The leads should be shorted together or the device placed in conductive foam
during storage or handling to prevent electrostatic damage to the MOS gates.
ORDERING INFORMATION
LM3674 (5 Pin SOT-23)
Ordering Information Voltage Option (V)
LM3674MF-1.2
LM3674MFX-1.2
LM3674MF-1.2/NOPB
LM3674MFX-1.2/NOPB
LM3674MF-1.5
LM3674MFX-1.5
LM3674MF-1.5/NOPB
LM3674MFX-1.5/NOPB
LM3674MF-1.6
LM3674MFX-1.6
LM3674MF-1.6/NOPB
LM3674MFX-1.6/NOPB
LM3674MF-1.8
LM3674MFX-1.8
LM3674MF-1.8/NOPB
LM3674MFX-1.8/NOPB
LM3674MF-1.875
LM3674MFX-1.875
LM3674MF-1.875/NOPB
LM3674MFX-1.875/NOPB
LM3674MF-2.8
LM3674MFX-2.8
LM3674MF-2.8/NOPB
LM3674MFX-2.8/NOPB
LM3674MF-ADJ
LM3674MFX-ADJ
LM3674MF-ADJ/NOPB
LM3674MFX-ADJ/NOPB
(1) For the most current package and ordering information, see the Package Option Addendum at the end of this document, or see the TI
web site at www.ti.com.
(2) Package drawings, thermal data, and symbolization are available at www.ti.com/packaging.
SNVS405F –DECEMBER 2005–REVISED MAY 2013
(1)(2)
1.2
1.5
1.6
1.8
1.875
2.8
Adjustable
Copyright © 2005–2013, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 3
Product Folder Links: LM3674
LM3674
SNVS405F –DECEMBER 2005–REVISED MAY 2013
Absolute Maximum Ratings
(1)(2)
www.ti.com
VINPin: Voltage to GND −0.2V to 6.0V
EN, FB, SW Pin: (GND−0.2V) to
(VIN+ 0.2V)
Continuous Power Dissipation
Junction Temperature (T
(3)
) +125°C
J-MAX
Internally Limited
Storage Temperature Range −65°C to +150°C
Maximum Lead Temperature 260°C
(Soldering, 10 sec.)
ESD Rating
(4)
2 kV
Human Body model: All Pins
Machine Model: All Pins 200V
(1) Absolute Maximum Ratings indicate limits beyond which damage to the device may occur. Operating Ratings are conditions under
which operation of the device is ensured. Operating Ratings may not imply performance limits. For performance limits and associated
test conditions, see the Electrical Characteristics tables.
(2) If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required, please contact the TI Sales Office/Distributors for availability and specifications.
(3) In Applications where high power dissipation and /or poor package resistance is present, the maximum ambient temperature may have
to be derated. Maximum ambient temperature (T
maximum power dissipation of the device in the application (P
in the application, as given by the following equation: T
at different ambient temperatures.
) is dependent on the maximum operating junction temperature (T
A-MAX
A-MAX
) and the junction to ambient thermal resistance of the package (θJA)
D-MAX
= T
J-MAX
- (θJAx P
). Refer to Dissipation ration table for P
D-MAX
J-MAX
D-MAX
), the
values
(4) The Human body model is a 100 pF capacitor discharged through a 1.5 kΩ resistor into each pin. The machine model is a 200 pF
capacitor discharged directly into each pin (MIL-STD-883 3015.7). National Semiconductor recommends that all intergrated circuits be
handled with appropriate precautions. Failure to observe proper ESD handling techniques can result in damage.
(4)
(1)(2)(3)
2.7V to 5.5V
Operating Ratings
Input Voltage Range
Recommended Load Current 0A to 600 mA
Junction Temperature (TJ) Range −30°C to +125°C
Ambient Temperature (TA) Range −30°C to +85°C
(1) In Applications where high power dissipation and /or poor package resistance is present, the maximum ambient temperature may have
to be derated. Maximum ambient temperature (T
maximum power dissipation of the device in the application (P
in the application, as given by the following equation: T
at different ambient temperatures.
) is dependent on the maximum operating junction temperature (T
A-MAX
A-MAX
) and the junction to ambient thermal resistance of the package (θJA)
D-MAX
= T
J-MAX
- (θJAx P
). Refer to Dissipation ration table for P
D-MAX
J-MAX
D-MAX
), the
values
(2) Absolute Maximum Ratings indicate limits beyond which damage to the device may occur. Operating Ratings are conditions under
which operation of the device is ensured. Operating Ratings may not imply performance limits. For performance limits and associated
test conditions, see the Electrical Characteristics tables.
(3) All voltages are with respect to the potential at the GND pin.
(4) Input voltage range recommended for ideal applications performance for the specified output voltages are given below
VIN= 2.7V to 5.5V for 1.0V ≤ V
VIN= ( V
OUT
+ V
DROP OUT
Thermal Properties
) to 5.5V for 1.8 ≤ V
(1)
OUT
< 1.8V
≤ 3.3V Where V
OUT
DROP OUT
= I
LOAD
* (R
DSON (P)
+ R
INDUCTOR
)
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)
Junction-to-Ambient Thermal Resistance (θJA) (SOT-23) for a 2 layer board
Junction-to-Ambient Thermal Resistance (θJA) (SOT-23) for a 4 layer board
(1) Internal thermal shutdown circuitry protects the device from permanent damage. Thermal shutdown engages at TJ= 150°C (typ.) and
disengages at TJ= 130°C
(2) Junction to ambient thermal resistance (θJA) is highly application and board layout dependent. In applications where high power
dissipation exists, special care must be given to thermal dissipation issues in board design. Value specified here 250°C/W is based on
measurement results using a 2 layer, 4" X 3", 2 oz. Cu board as per JEDEC standards. The θJAis 130°C/W if a 4 layer, 4" X 3", 2/1/1/2
oz. Cu board as per JEDEC standards is used.
(2)
(2)
250°C/W
130°C/W
4 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2005–2013, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Links: LM3674
LM3674
www.ti.com
Electrical Characteristics
(1)(2)(3)
SNVS405F –DECEMBER 2005–REVISED MAY 2013
Limits in standard typeface are for TJ= 25°C. Limits in boldface type apply over the full operating junction temperature range
(−30°C ≤ TJ≤ 125°C). Unless otherwise noted, specifications apply to the LM3674 with VIN= EN = 3.6V
Parameter Test Condition Min Typ Max Units
V
FB
Feedback Voltage
Line Regulation 2.7V ≤ VIN≤ 5.5V 0.083 %/V
Load Regulation 100 mA ≤ IO≤ 600 mA 0.0010 %/mA
V
REF
I
SHDN
I
Q
R
DSON (P)
R
DSON (N)
I
LIM
V
IH
V
IL
I
EN
F
OSC
Internal Reference Voltage See
Shutdown Supply Current EN = 0V 0.01 1 µA
DC Bias Current into V
Pin-Pin Resistance for PFET ISW= 200mA 380 500 mΩ
Pin-Pin Resistance for NFET ISW= 200mA 250 400 mΩ
Switch Peak Current Limit Open Loop
Logic High Input 1.0 V
Logic Low Input 0.4 V
Enable (EN) Input Current 0.01 1 µA
Internal Oscillator Frequency PWM Mode 1.6 2 2.6 MHz
(1) All voltages are with respect to the potential at the GND pin.
(2) Min and Max limits are specified by design, test or statistical analysis. Typical numbers represent the most likely norm.
(3) The parameters in the electrical characteristic table are tested at VIN= 3.6V unless otherwise specified. For performance over the input
voltage range refer to datasheet curves.
(4) ADJ configured to 1.5V output.
(5) For V
(6) For the ADJ version the resistor dividers should be selected such that at the desired output voltage, the voltage at the FB pin is 0.5V.
less than 2.5V, VIN= 3.6V, for V
OUT
(7) Refer to datasheet curves for closed loop data and its variation with regards to supply voltage and temperature. Electrical Characteristic
table reflects open loop data (FB=0V and current drawn from SW pin ramped up until cycle by cycle current limit is activated). Closed
loop current limit is the peak inductor current measured in the application circuit by increasing output current until output voltage drops
by 10%.
(4)(5)
IO= 10mA -4 +4 %
IO= 100 mA
VIN= 3.6V
(6)
IN
No load, device is not switching 300 600 µA
(FB=0V)
(7)
greater than or equal to 2.5V, VIN= V
OUT
OUT
830 1020 1200 mA
+1.
0.5 V
Dissipation Rating
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)
θ
JA
250°C/W (2 layer board) 400mW 260mW 160mW
130°C/W (4 layer board) 770mW 500mW 310mW
TA≤ 25°C (Power Rating) TA= 60°C (Power Rating) TA= 85°C (Power Rating)
Copyright © 2005–2013, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 5
Product Folder Links: LM3674
+
-
2 MHz
Oscillator
Soft
Start
Ramp
Generator
+
-
Thermal
Shutdown
Undervoltage
Lockout
V
REF
+
-
0.5V
Error
Amp
Control Logic Driver
Current Limit
Comparator
Ref1
SW
FB
EN
V
IN
PWM Comparator
GND
Bandgap
+
-
Vcomp
1.0V
Frequency
Compensation
Adjustable Version
Fixed Version
LM3674
SNVS405F –DECEMBER 2005–REVISED MAY 2013
www.ti.com
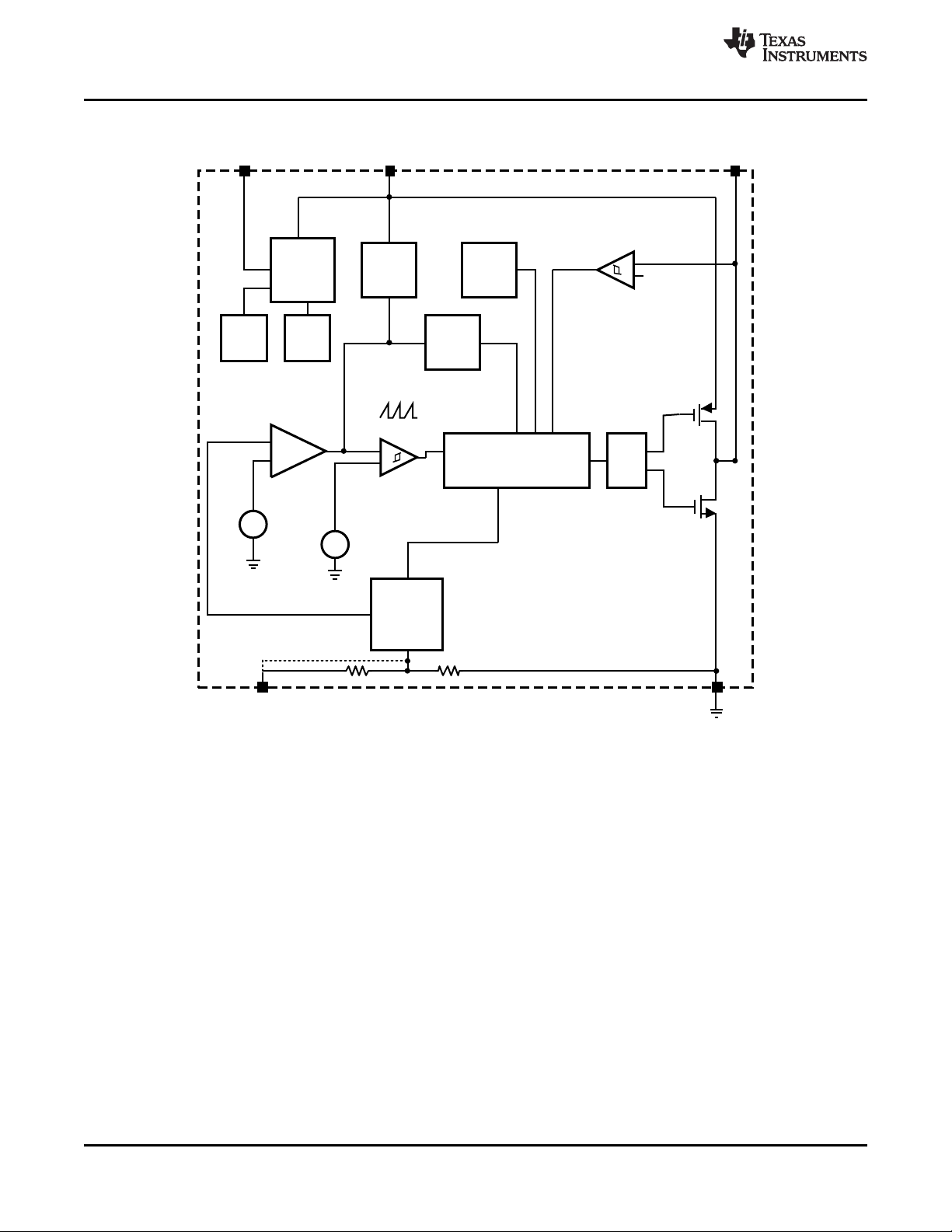
Block Diagram
Figure 4. Simplified Functional Block Diagram
6 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2005–2013, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Links: LM3674
-10 10 30 50 70 90
TEMPERATURE (°C)
0.00
0.05
0.10
0.15
0.20
0.25
0.30
0.35
0.40
SHUTDOWN CURRENT (
PA)
-30
EN = GND
VIN = 3.6V
VIN = 2.7V
VIN = 5.5V
LM3674
www.ti.com
SNVS405F –DECEMBER 2005–REVISED MAY 2013
Typical Performance Characteristics
(unless otherwise stated: VIN= 3.6V, V
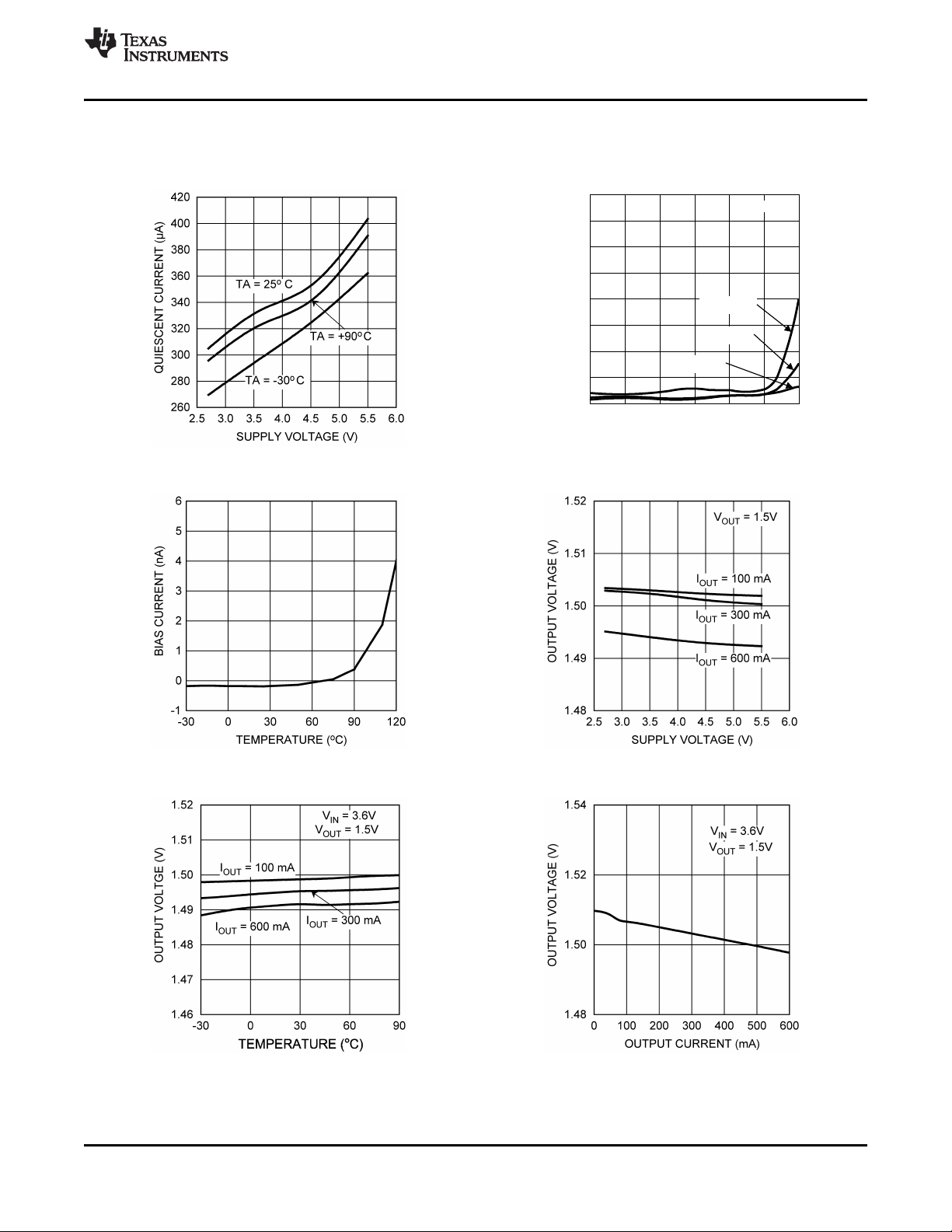
Quiescent Current vs. Supply Voltage
(FB = 0V, No Switching) IQShutdown vs. Temp
Figure 5. Figure 6.
Feedback Bias Current vs. Temp Output Voltage vs. Supply Voltage
= 1.5V, TA= 25°C)
OUT
Figure 7. Figure 8.
Output Voltage vs. Temperature Output Voltage vs. Output Current
Copyright © 2005–2013, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 7
Figure 9. Figure 10.
Product Folder Links: LM3674
-30
-
10
_
10
_
30
50_70_90
_
TEMPERATURE (°C)
1.88
_
1.90
_
1.92
_
1.94
_
1.96
_
1.98
_
2.00
FREQUENCY (MHz)
VIN = 2.7V
VIN = 4.5V
VIN = 3.6V
I
OUT
= 300 mA
-10 10 30 50 70 90 110
TEMPERATURE (°C)
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
500
550
600
R
DS(ON)
(
m:)
-30
NFET
VIN = 4.5V
PFET
VIN = 2.7V
VIN = 4.5V
VIN = 3.6V
VIN = 3.6V
VIN = 2.7V
LM3674
SNVS405F –DECEMBER 2005–REVISED MAY 2013
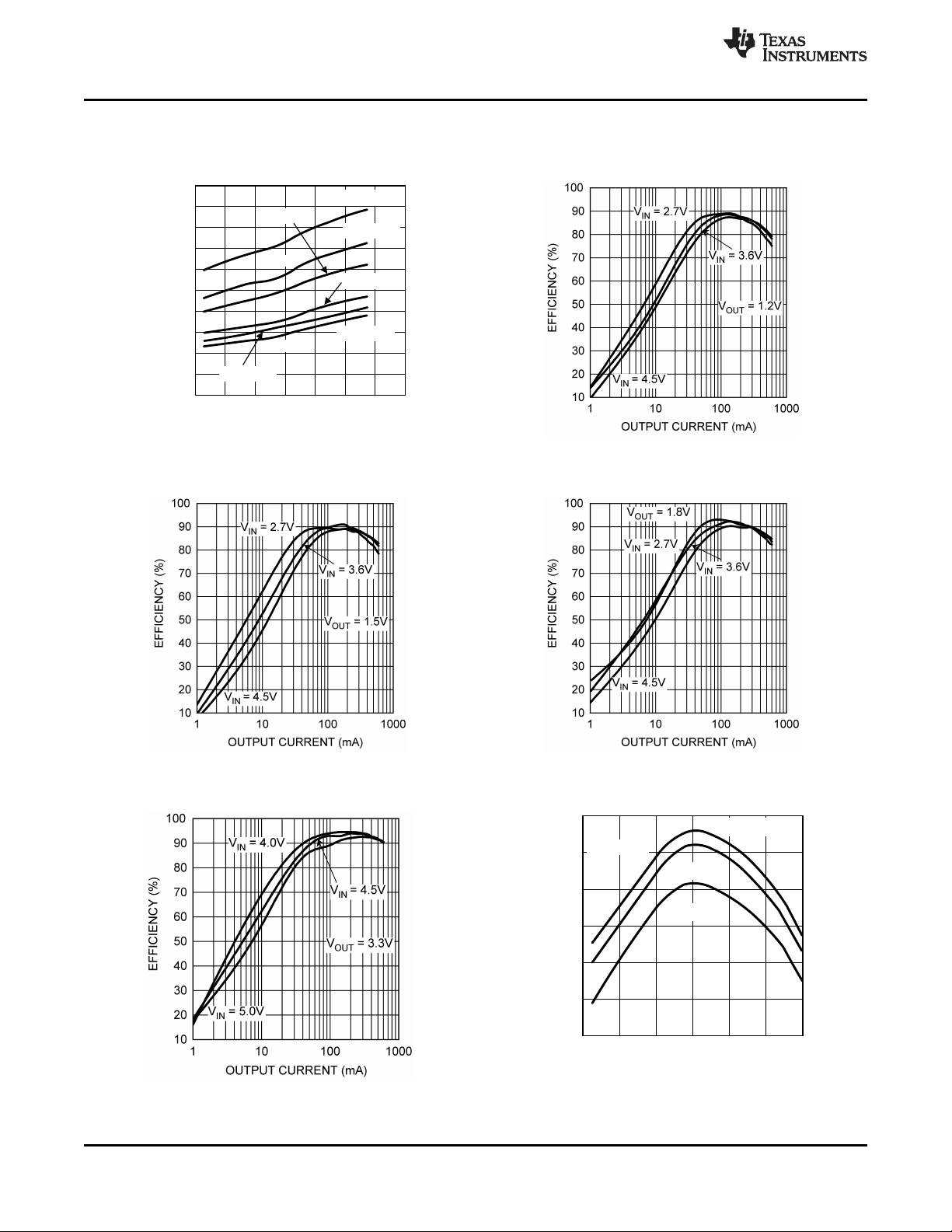
Typical Performance Characteristics (continued)
(unless otherwise stated: VIN= 3.6V, V
R
vs. Temperature (V
DSON
Figure 11. Figure 12.
Efficiency vs. Output Current Efficiency vs. Output Current
(V
= 1.5V, L = 2.2uH, DCR = 200mΩ) (V
OUT
OUT
= 1.5V, TA= 25°C)
Efficiency vs. Output Current
= 1.2V, L = 2.2uH, DCR = 200mΩ)
OUT
= 1.8V, L = 2.2uH, DCR = 200mΩ)
OUT
www.ti.com
Figure 13. Figure 14.
Efficiency vs. Output Current
(V
= 3.3V, L = 2.2uH, DCR = 200mΩ) Switching Frequency vs. Temperature
OUT
8 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2005–2013, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Figure 15. Figure 16.
Product Folder Links: LM3674

V
OUT
40 Ps/DIV
3.6V
V
IN
3.0V
20 mV/DIV
AC Coupled
V
OUT
= 1.5V
I
OUT
= 400 mA
LM3674
www.ti.com
Typical Performance Characteristics (continued)
(unless otherwise stated: VIN= 3.6V, V
Open/Closed Loop Current Limit vs. Temperature Line Transient Response
Figure 17. Figure 18.
Load Transient (Output Current = 300mA)
= 1.5V, TA= 25°C)
OUT
SNVS405F –DECEMBER 2005–REVISED MAY 2013
Start Up
Figure 19. Figure 20.
(Output Current = 10mA)
Copyright © 2005–2013, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 9
Product Folder Links: LM3674
Start Up
Figure 21.

-V
OUT
VIN-V
OUT
LM3674
SNVS405F –DECEMBER 2005–REVISED MAY 2013
www.ti.com
OPERATION DESCRIPTION
DEVICE INFORMATION
The LM3674, a high efficiency step down DC-DC switching buck converter, delivers a constant voltage from a
single Li-Ion battery and input voltage rails from 2.7V to 5.5V to portable devices such as cell phones and PDAs.
Using a voltage mode architecture with synchronous rectification, the LM3674 has the ability to deliver up to 600
mA depending on the input voltage, output voltage, ambient temperature and the inductor chosen.
There are two modes of operation depending on the current required - Pulse Width Modulation (PWM), and
shutdown. The device operates in PWM throughout the I
the lowest current consumption (I
SHUTDOWN
= 0.01 µA typ).
range. Shutdown mode turns off the device, offering
OUT
Additional features include soft-start, under voltage protection, current overload protection, and thermal overload
protection. As shown in Figure 1, only three external power components are required for implementation.
The part uses an internal reference voltage of 0.5V. It is recommended to keep the part in shutdown until the
input voltage is 2.7V or higher.
CIRCUIT OPERATION
During the first portion of each switching cycle, the control block in the LM3674 turns on the internal PFET
switch. This allows current to flow from the input through the inductor to the output filter capacitor and load. The
inductor limits the current to a ramp with a slope of:
(1)
by storing energy in a magnetic field. During the second portion of each cycle, the controller turns the PFET
switch off, blocking current flow from the input, and then turns the NFET synchronous rectifier on. The inductor
draws current from ground through the NFET to the output filter capacitor and load, which ramps the inductor
current down with a slope of:
(2)
The output filter stores charge when the inductor current is high, and releases it when the inductor current is low,
smoothing the voltage across the load.
The output voltage is regulated by modulating the PFET switch on time to control the average current sent to the
load. The effect is identical to sending a duty-cycle modulated rectangular wave formed by the switch and
synchronous rectifier at the SW pin to a low-pass filter formed by the inductor and output filter capacitor. The
output voltage is equal to the average voltage at the SW pin.
PWM OPERATION
During Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) operation the converter operates as a voltage-mode controller with input
voltage feed forward. This allows the converter to achieve excellent load and line regulation. The DC gain of the
power stage is proportional to the input voltage. To eliminate this dependence, feed forward inversely
proportional to the input voltage is introduced.
While in PWM mode, the output voltage is regulated by switching at a constant frequency and then modulating
the energy per cycle to control power to the load. At the beginning of each clock cycle the PFET switch is turned
on and the inductor current ramps up until the comparator trips and the control logic turns off the switch.
The current limit comparator can also turn off the switch in case the current limit of the PFET is exceeded. Then
the NFET switch is turned on and the inductor current ramps down. The next cycle is initiated by the clock
turning off the NFET and turning on the PFET.
10 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2005–2013, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Links: LM3674
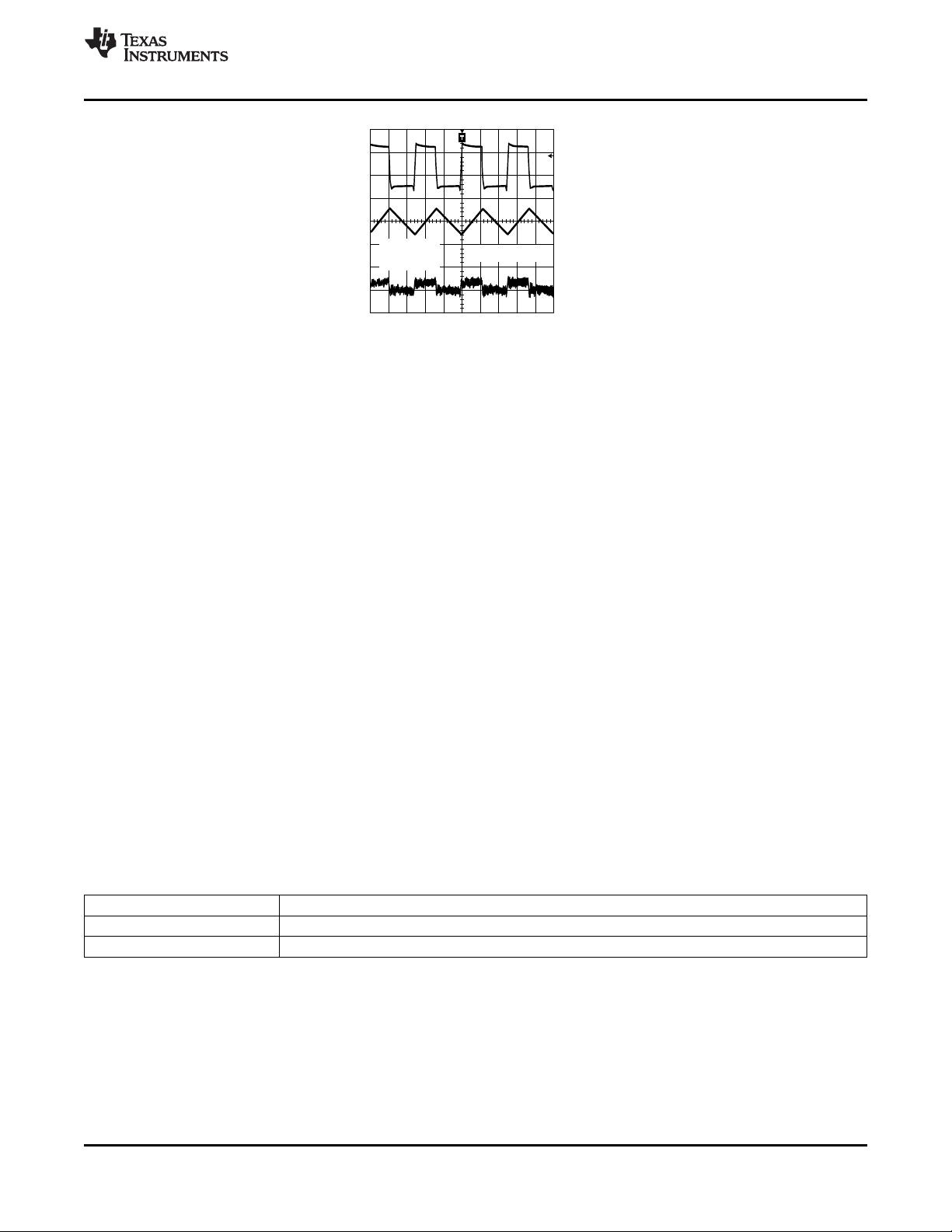
V
OUT
TIME (200 ns/DIV)
200 mA/DIV
I
L
V
SW
2V/DIV
10 mV/DIV
AC Coupled
VIN = 3.6V
V
OUT
= 1.5V
I
OUT
= 400 mA
LM3674
www.ti.com
SNVS405F –DECEMBER 2005–REVISED MAY 2013
Internal Synchronous Rectification
While in PWM mode, the LM3674 uses an internal NFET as a synchronous rectifier to reduce rectifier forward
voltage drop and associated power loss. Synchronous rectification provides a significant improvement in
efficiency whenever the output voltage is relatively low compared to the voltage drop across an ordinary rectifier
diode.
Current Limiting
A current limit feature allows the LM3674 to protect itself and external components during overload conditions.
PWM mode implements current limiting using an internal comparator that trips at 1020 mA (typ). If the output is
shorted to ground the device enters a timed current limit mode where the NFET is turned on for a longer duration
until the inductor current falls below a low threshold, ensuring inductor current has more time to decay, thereby
preventing runaway.
SOFT-START
The LM3674 has a soft-start circuit that limits in-rush current during start-up. During start-up the switch current
limit is increased in steps. Soft start is activated only if EN goes from logic low to logic high after Vin reaches
2.7V. Soft start is implemented by increasing switch current limit in steps of 70mA, 140mA, 280mA, and 1020mA
(typ. switch current limit). The start-up time thereby depends on the output capacitor and load current demanded
at start-up. Typical start-up times with 10µF output capacitor and 300mA load current is 350µs and with 10mA
load current is 240µs.
LDO - LOW DROP OUT OPERATION
The LM3674-ADJ can operate at 100% duty cycle (no switching, PMOS switch completely on) for low drop out
support of the output voltage. In this way the output voltage will be controlled down to the lowest possible input
voltage. When the device operates near 100% duty cycle, the output voltage supply ripple is slightly higher,
approximately 25mV.
The minimum input voltage needed to support the output voltage is:
V
= I
I
LOAD
R
DSON (P)
R
INDUCTOR
IN,MIN
LOAD
* (R
DSON (P)
+ R
INDUCTOR
Load current
Drain to source resistance of PFET switch in the triode region
Inductor resistance
) + V
OUT
(3)
APPLICATION INFORMATION
OUTPUT VOLTAGE SELECTION FOR ADJUSTABLE (LM3674-ADJ)
to FB then to GND. V
will be adjusted to make FB equal to 0.5V. The resistor from FB to GND (R2) should be
OUT
200 kΩ to keep the current drawn through this network small but large enough that it is not susceptible to noise.
If R2is 200KΩ, and given the VFBis 0.5V, then the current through the resistor feedback network will be 2.5µA.
The output voltage of the adjustable parts can be programmed through the resistor network connected from V
The output voltage formula is:
Copyright © 2005–2013, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 11
Product Folder Links: LM3674
OUT

I
RIPPLE
I
OUTMAX
+I
SAT
>
1
(2 * S * R1 * C1)
1
2 * S * (R1 R2) * (C1+C2)
C2 =
1
2 x S x R2 x 45 kHz
C1 =
1
2 x S x R1 x 45 kHz
OUT
=
R
1
R
VFB *
+ 1
( )
LM3674
SNVS405F –DECEMBER 2005–REVISED MAY 2013
www.ti.com
(4)
• V
= Output Voltage (V)
OUT
• VFB= Feedback Voltage (0.5V typ)
• R1= Resistor from V
OUT
to FB (Ω)
• R2= Resistor from FB to GND (Ω)
For any output voltage greater than or equal to 1.0V a frequency zero must be added at 45KHz for stability. The
formula is:
(5)
For output voltages greater than or equal to 2.5V, a pole must also be placed at 45KHz as well. If the pole and
zero are at the same frequency the formula for calculation of C2 is:
(6)
The formula for location of zero and pole frequency created by adding C1,C2 are given below. It can be seen
that by adding C1, a zero as well as a higher frequency pole is introduced.
(7)
See the LM3674-ADJ Configurations for Various V
table. Table 1
OUT
Table 1. Adjustable LM3674 Configurations for Various V
VOUT (V) R1 (KΩ) R2 (KΩ) C1 (pF) C2 (pF) L (µH) CIN (µF) COUT (µF)
1.0 200 200 18 None 2.2 4.7 10
1.1 191 158 18 None 2.2 4.7 10
1.2 280 200 12 None 2.2 4.7 10
1.5 357 178 10 None 2.2 4.7 10
1.6 442 200 8.2 None 2.2 4.7 10
1.7 432 178 8.2 None 2.2 4.7 10
1.8 464 178 8.2 None 2.2 4.7 10
1.875 523 191 6.8 None 2.2 4.7 10
2.5 402 100 8.2 None 2.2 4.7 10
2.8 464 100 8.2 33 2.2 4.7 10
3.3 562 100 6.8 33 2.2 4.7 10
OUT
INDUCTOR SELECTION
There are two main considerations when choosing an inductor: the inductor should not saturate, and the inductor
current ripple should be small enough to achieve the desired output voltage ripple. Different saturation current
rating specifications are followed by different manufacturers so attention must be given to details. Saturation
current ratings are typically specified at 25°C. However, ratings at the maximum ambient temperature of
application should be requested from the manufacturer. The minimum value of inductance to ensure good
performance is 1.76µH at I
(typ) dc current over the ambient temperature range. Shielded inductors
LIM
radiate less noise and should be preferred.
There are two methods to choose the inductor saturation current rating.
Method 1:
The saturation current is greater than the sum of the maximum load current and the worst case average to peak
inductor current. This can be written as:
12 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2005–2013, Texas Instruments Incorporated
(8)
Product Folder Links: LM3674

I
RMS OUTMAX
x
x (1 -
V
OUT
V
IN
V
OUT
V
IN
= I
=
r
)
+
12
2
The worst case is when
OUT
V
V
IN
( )
OUT
V
V
IN
-
x
L
f
x
x x
V
IN
=
2 x
OUT
V
OUTMAX
I
V
IN
- V
OUT
2 x L
I
RIPPLE
=
V
OUT
V
1
f
¹·©
§
¹
·
©
§
¹
·
©
§
LM3674
www.ti.com
SNVS405F –DECEMBER 2005–REVISED MAY 2013
(9)
• I
• I
: average to peak inductor current
Ripple
: maximum load current (600mA)
outmax
• VIN: maximum input voltage in application
• L: min inductor value including worst case tolerances (30% drop can be considered for method 1)
• f: minimum switching frequency (1.6 MHz)
• V
: output voltage
OUT
Method 2:
A more conservative and recommended approach is to choose an inductor that has saturation current rating
greater than the max current limit of 1200 mA.
A 2.2 µH inductor with a saturation current rating of at least 1200 mA is recommended for most applications. The
inductor’s resistance should be less than around 0.3Ω for good efficiency. Table 2 lists suggested inductors and
suppliers. For low-cost applications, an unshielded bobbin inductor is suggested. For noise critical applications, a
toroidal or shielded-bobbin inductor should be used. A good practice is to lay out the board with overlapping
footprints of both types for design flexibility. This allows substitution of a low-noise toroidal inductor, in the event
that noise from low-cost bobbin models is unacceptable.
Table 2. Suggested Inductors and Their Suppliers
Model Vendor Dimensions LxWxH (mm) D.C.R (max)
DO3314-222MX Coilcraft 3.3 x 3.3 x 1.4 200 mΩ
LPO3310-222MX Coilcraft 3.3 x 3.3 x 1.0 150 mΩ
ELL5GM2R2N Panasonic 5.2 x 5.2 x 1.5 53 mΩ
CDRH2D14NP-2R2NC Sumida 3.2 x 3.2 x 1.55 94 mΩ
INPUT CAPACITOR SELECTION
A ceramic input capacitor of 4.7 µF, 6.3V is sufficient for most applications. Place the input capacitor as close as
possible to the VINpin of the device. A larger value may be used for improved input voltage filtering. Use X7R or
X5R types; do not use Y5V. DC bias characteristics of ceramic capacitors must be considered when selecting
case sizes like 0805 and 0603. The minimum input capacitance to ensure good performance is 2.2µF at 3V
dc bias; 1.5µF at 5V dc bias including tolerances and over ambient temperature range. The input filter
capacitor supplies current to the PFET switch of the LM3674 in the first half of each cycle and reduces voltage
ripple imposed on the input power source. A ceramic capacitor’s low ESR provides the best noise filtering of the
input voltage spikes due to this rapidly changing current. Select a capacitor with sufficient ripple current rating.
The input current ripple can be calculated as:
(10)
OUTPUT CAPACITOR SELECTION
A ceramic output capacitor of 10 µF, 6.3V is sufficient for most applications. Use X7R or X5R types; do not use
Y5V. DC bias characteristics of ceramic capacitors must be considered when selecting case sizes like 0805 and
0603. DC bias characteristics vary from manufacturer to manufacturer and dc bias curves should be requested
from them as part of the capacitor selection process.
The minimum output capacitance to ensure good performance is 5.75µF at 1.8V dc bias including
tolerances and over ambient temperature range. The output filter capacitor smoothes out current flow from
the inductor to the load, helps maintain a steady output voltage during transient load changes and reduces
output voltage ripple. These capacitors must be selected with sufficient capacitance and sufficiently low ESR to
perform these functions.
Product Folder Links: LM3674
Copyright © 2005–2013, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 13

V
PP-RMS
= V
PP-C
2
+ V
PP-ESR
2
OUT
=
V
PP-ESR
= IPP * R
ESR
V
PP-C
=
I
ripple
f x 4 x C
LM3674
SNVS405F –DECEMBER 2005–REVISED MAY 2013
The output voltage ripple is caused by the charging and discharging of the output capacitor and by the R
www.ti.com
and
ESR
can be calculated as:
Voltage peak-to-peak ripple due to capacitance can be expressed as follow:
(11)
Voltage peak-to-peak ripple due to ESR =
(12)
Because these two components are out of phase the rms value can be used to get an approximate value of
peak-to-peak ripple.
Voltage peak-to-peak ripple, root mean squared =
(13)
Note that the output ripple is dependent on the current ripple and the equivalent series resistance of the output
capacitor (R
The R
ESR
).
ESR
is frequency dependent (as well as temperature dependent); make sure the value used for calculations
is at the switching frequency of the part.
Table 3. Suggested Capacitors and Their Suppliers
Model Type Vendor Voltage Rating Case size inch (mm)
10 µF for C
GRM21BR60J106K Ceramic, X5R Murata 6.3V 0805 (2012)
4.7 µF for C
GRM21BR60J475K Ceramic, X5R Murata 6.3V 0805 (2012)
OUT
C2012X5R0J106K Ceramic, X5R TDK 6.3V 0805 (2012)
JMK212BJ106K Ceramic, X5R Taiyo-Yuden 6.3V 0805 (2012)
IN
JMK212BJ475K Ceramic, X5R Taiyo-Yuden 6.3V 0805 (2012)
C2012X5R0J475K Ceramic, X5R TDK 6.3V 0805 (2012)
BOARD LAYOUT CONSIDERATIONS
PC board layout is an important part of DC-DC converter design. Poor board layout can disrupt the performance
of a DC-DC converter and surrounding circuitry by contributing to EMI, ground bounce, and resistive voltage loss
in the traces. These can send erroneous signals to the DC-DC converter IC, resulting in poor regulation or
instability.
14 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2005–2013, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Links: LM3674

LM3674
www.ti.com
SNVS405F –DECEMBER 2005–REVISED MAY 2013
Figure 22. Board Layout Design Rules for the LM3674
Good layout for the LM3674 can be implemented by following a few simple design rules, as illustrated in .
1. Place the LM3674, inductor and filter capacitors close together and make the traces short. The traces
between these components carry relatively high switching currents and act as antennas. Following this rule
reduces radiated noise. Special care must by given to place the input filter capacitor very close to the VINand
GND pin.
2. Arrange the components so that the switching current loops curl in the same direction. During the first half of
each cycle, current flows from the input filter capacitor, through the LM3674 and inductor to the output filter
capacitor and back through ground, forming a current loop. In the second half of each cycle, current is pulled
up from ground, through the LM3674 by the inductor, to the output filter capacitor and then back through
ground, forming a second current loop. Routing these loops so the current curls in the same direction
prevents magnetic field reversal between the two half-cycles and reduces radiated noise.
3. Connect the ground pins of the LM3674, and filter capacitors together using generous component-side
copper fill as a pseudo-ground plane. Then, connect this to the ground-plane (if one is used) with several
vias. This reduces ground-plane noise by preventing the switching currents from circulating through the
ground plane. It also reduces ground bounce at the LM3674 by giving it a low-impedance ground connection.
4. Use wide traces between the power components and for power connections to the DC-DC converter circuit.
This reduces voltage errors caused by resistive losses across the traces.
5. Route noise sensitive traces, such as the voltage feedback path, away from noisy traces between the power
components. The voltage feedback trace must remain close to the LM3674 circuit and should be direct but
should be routed opposite to noisy components. This reduces EMI radiated onto the DC-DC converter’s own
voltage feedback trace. A good approach is to route the feedback trace on another layer and to have a
ground plane between the top layer and layer on which the feedback trace is routed. In the same manner for
the adjustable part it is desired to have the feedback dividers on the bottom layer.
6. Place noise sensitive circuitry, such as radio IF blocks, away from the DC-DC converter, CMOS digital blocks
and other noisy circuitry. Interference with noise-sensitive circuitry in the system can be reduced through
distance.
In mobile phones, for example, a common practice is to place the DC-DC converter on one corner of the board,
arrange the CMOS digital circuitry around it (since this also generates noise), and then place sensitive
preamplifiers and IF stages on the diagonally opposing corner. Often, the sensitive circuitry is shielded with a
metal pan and power to it is post-regulated to reduce conducted noise, using low-dropout linear regulators.
Copyright © 2005–2013, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 15
Product Folder Links: LM3674

LM3674
SNVS405F –DECEMBER 2005–REVISED MAY 2013
www.ti.com
REVISION HISTORY
Changes from Revision E (April 2013) to Revision F Page
• Changed layout of National Data Sheet to TI format .......................................................................................................... 15
16 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2005–2013, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Links: LM3674

PACKAGE OPTION ADDENDUM
www.ti.com
PACKAGING INFORMATION
Orderable Device Status
LM3674MF-1.2 ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 1000 TBD Call TI Call TI -30 to 85 SLRB
LM3674MF-1.2/NOPB ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 1000 Green (RoHS
LM3674MF-1.5 ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 1000 TBD Call TI Call TI -30 to 85 SLSB
LM3674MF-1.5/NOPB ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 1000 Green (RoHS
LM3674MF-1.8 ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 1000 TBD Call TI Call TI -30 to 85 SLHB
LM3674MF-1.8/NOPB ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 1000 Green (RoHS
LM3674MF-1.875 ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 1000 TBD Call TI Call TI -30 to 85 SNNB
LM3674MF-1.875/NOPB ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 1000 Green (RoHS
LM3674MF-2.8 ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 1000 TBD Call TI Call TI -30 to 85 SLZB
LM3674MF-2.8/NOPB ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 1000 Green (RoHS
LM3674MF-ADJ ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 1000 TBD Call TI Call TI -30 to 85 SLTB
Package Type Package
(1)
Drawing
Pins Package
Qty
Eco Plan
(2)
& no Sb/Br)
& no Sb/Br)
& no Sb/Br)
& no Sb/Br)
& no Sb/Br)
Lead/Ball Finish MSL Peak Temp
(3)
CU SN Level-1-260C-UNLIM -30 to 85 SLRB
CU SN Level-1-260C-UNLIM -30 to 85 SLSB
CU SN Level-1-260C-UNLIM -30 to 85 SLHB
CU SN Level-1-260C-UNLIM -30 to 85 SNNB
CU SN Level-1-260C-UNLIM -30 to 85 SLZB
Op Temp (°C) Top-Side Markings
2-May-2013
Samples
(4)
LM3674MF-ADJ/NOPB ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 1000 Green (RoHS
& no Sb/Br)
LM3674MFX-1.2 ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 TBD Call TI Call TI -30 to 85 SLRB
LM3674MFX-1.2/NOPB ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 Green (RoHS
& no Sb/Br)
LM3674MFX-1.5 ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 TBD Call TI Call TI -30 to 85 SLSB
LM3674MFX-1.5/NOPB ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 Green (RoHS
& no Sb/Br)
LM3674MFX-1.8 ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 TBD Call TI Call TI -30 to 85 SLHB
LM3674MFX-1.8/NOPB ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 Green (RoHS
& no Sb/Br)
LM3674MFX-1.875 ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 TBD Call TI Call TI -30 to 85 SNNB
Addendum-Page 1
CU SN Level-1-260C-UNLIM -30 to 85 SLTB
CU SN Level-1-260C-UNLIM -30 to 85 SLRB
CU SN Level-1-260C-UNLIM -30 to 85 SLSB
CU SN Level-1-260C-UNLIM -30 to 85 SLHB

PACKAGE OPTION ADDENDUM
www.ti.com
Orderable Device Status
LM3674MFX-1.875/NOPB ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 Green (RoHS
LM3674MFX-2.8 ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 TBD Call TI Call TI -30 to 85 SLZB
LM3674MFX-2.8/NOPB ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 Green (RoHS
LM3674MFX-ADJ ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 TBD Call TI Call TI -30 to 85 SLTB
LM3674MFX-ADJ/NOPB ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 Green (RoHS
(1)
The marketing status values are defined as follows:
ACTIVE: Product device recommended for new designs.
LIFEBUY: TI has announced that the device will be discontinued, and a lifetime-buy period is in effect.
NRND: Not recommended for new designs. Device is in production to support existing customers, but TI does not recommend using this part in a new design.
PREVIEW: Device has been announced but is not in production. Samples may or may not be available.
OBSOLETE: TI has discontinued the production of the device.
Package Type Package
(1)
Drawing
Pins Package
Qty
Eco Plan
(2)
& no Sb/Br)
& no Sb/Br)
& no Sb/Br)
Lead/Ball Finish MSL Peak Temp
(3)
CU SN Level-1-260C-UNLIM -30 to 85 SNNB
CU SN Level-1-260C-UNLIM -30 to 85 SLZB
CU SN Level-1-260C-UNLIM -30 to 85 SLTB
Op Temp (°C) Top-Side Markings
(4)
(2)
Eco Plan - The planned eco-friendly classification: Pb-Free (RoHS), Pb-Free (RoHS Exempt), or Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br) - please check http://www.ti.com/productcontent for the latest availability
information and additional product content details.
TBD: The Pb-Free/Green conversion plan has not been defined.
Pb-Free (RoHS): TI's terms "Lead-Free" or "Pb-Free" mean semiconductor products that are compatible with the current RoHS requirements for all 6 substances, including the requirement that
lead not exceed 0.1% by weight in homogeneous materials. Where designed to be soldered at high temperatures, TI Pb-Free products are suitable for use in specified lead-free processes.
Pb-Free (RoHS Exempt): This component has a RoHS exemption for either 1) lead-based flip-chip solder bumps used between the die and package, or 2) lead-based die adhesive used between
the die and leadframe. The component is otherwise considered Pb-Free (RoHS compatible) as defined above.
Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br): TI defines "Green" to mean Pb-Free (RoHS compatible), and free of Bromine (Br) and Antimony (Sb) based flame retardants (Br or Sb do not exceed 0.1% by weight
in homogeneous material)
(3)
MSL, Peak Temp. -- The Moisture Sensitivity Level rating according to the JEDEC industry standard classifications, and peak solder temperature.
(4)
Multiple Top-Side Markings will be inside parentheses. Only one Top-Side Marking contained in parentheses and separated by a "~" will appear on a device. If a line is indented then it is a
continuation of the previous line and the two combined represent the entire Top-Side Marking for that device.
Important Information and Disclaimer:The information provided on this page represents TI's knowledge and belief as of the date that it is provided. TI bases its knowledge and belief on information
provided by third parties, and makes no representation or warranty as to the accuracy of such information. Efforts are underway to better integrate information from third parties. TI has taken and
continues to take reasonable steps to provide representative and accurate information but may not have conducted destructive testing or chemical analysis on incoming materials and chemicals.
TI and TI suppliers consider certain information to be proprietary, and thus CAS numbers and other limited information may not be available for release.
In no event shall TI's liability arising out of such information exceed the total purchase price of the TI part(s) at issue in this document sold by TI to Customer on an annual basis.
2-May-2013
Samples
Addendum-Page 2

PACKAGE OPTION ADDENDUM
www.ti.com
2-May-2013
Addendum-Page 3

PACKAGE MATERIALS INFORMATION
www.ti.com 8-May-2013
TAPE AND REEL INFORMATION
*All dimensions are nominal
Device Package
Type
LM3674MF-1.2 SOT-23 DBV 5 1000 178.0 8.4 3.2 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q3
LM3674MF-1.2/NOPB SOT-23 DBV 5 1000 178.0 8.4 3.2 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q3
LM3674MF-1.5 SOT-23 DBV 5 1000 178.0 8.4 3.2 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q3
LM3674MF-1.5/NOPB SOT-23 DBV 5 1000 178.0 8.4 3.2 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q3
LM3674MF-1.8 SOT-23 DBV 5 1000 178.0 8.4 3.2 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q3
LM3674MF-1.8/NOPB SOT-23 DBV 5 1000 178.0 8.4 3.2 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q3
LM3674MF-1.875 SOT-23 DBV 5 1000 178.0 8.4 3.2 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q3
LM3674MF-1.875/NOPB SOT-23 DBV 5 1000 178.0 8.4 3.2 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q3
LM3674MF-2.8 SOT-23 DBV 5 1000 178.0 8.4 3.2 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q3
LM3674MF-2.8/NOPB SOT-23 DBV 5 1000 178.0 8.4 3.2 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q3
LM3674MF-ADJ SOT-23 DBV 5 1000 178.0 8.4 3.2 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q3
LM3674MF-ADJ/NOPB SOT-23 DBV 5 1000 178.0 8.4 3.2 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q3
LM3674MFX-1.2 SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 178.0 8.4 3.2 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q3
LM3674MFX-1.2/NOPB SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 178.0 8.4 3.2 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q3
LM3674MFX-1.5 SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 178.0 8.4 3.2 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q3
LM3674MFX-1.5/NOPB SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 178.0 8.4 3.2 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q3
LM3674MFX-1.8 SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 178.0 8.4 3.2 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q3
LM3674MFX-1.8/NOPB SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 178.0 8.4 3.2 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q3
Package
Drawing
Pins SPQ Reel
Diameter
(mm)
Reel
Width
W1 (mm)
A0
(mm)B0(mm)K0(mm)P1(mm)W(mm)
Quadrant
Pin1
Pack Materials-Page 1

PACKAGE MATERIALS INFORMATION
www.ti.com 8-May-2013
Device Package
Type
LM3674MFX-1.875 SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 178.0 8.4 3.2 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q3
LM3674MFX-1.875/NOPB SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 178.0 8.4 3.2 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q3
LM3674MFX-2.8 SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 178.0 8.4 3.2 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q3
LM3674MFX-2.8/NOPB SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 178.0 8.4 3.2 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q3
LM3674MFX-ADJ SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 178.0 8.4 3.2 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q3
LM3674MFX-ADJ/NOPB SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 178.0 8.4 3.2 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q3
Package
Drawing
Pins SPQ Reel
Diameter
(mm)
Reel
Width
W1 (mm)
A0
(mm)B0(mm)K0(mm)P1(mm)W(mm)
Pin1
Quadrant
*All dimensions are nominal
Device Package Type Package Drawing Pins SPQ Length (mm) Width (mm) Height (mm)
LM3674MF-1.2 SOT-23 DBV 5 1000 210.0 185.0 35.0
LM3674MF-1.2/NOPB SOT-23 DBV 5 1000 210.0 185.0 35.0
LM3674MF-1.5 SOT-23 DBV 5 1000 210.0 185.0 35.0
LM3674MF-1.5/NOPB SOT-23 DBV 5 1000 210.0 185.0 35.0
LM3674MF-1.8 SOT-23 DBV 5 1000 210.0 185.0 35.0
LM3674MF-1.8/NOPB SOT-23 DBV 5 1000 210.0 185.0 35.0
LM3674MF-1.875 SOT-23 DBV 5 1000 210.0 185.0 35.0
LM3674MF-1.875/NOPB SOT-23 DBV 5 1000 210.0 185.0 35.0
LM3674MF-2.8 SOT-23 DBV 5 1000 210.0 185.0 35.0
LM3674MF-2.8/NOPB SOT-23 DBV 5 1000 210.0 185.0 35.0
LM3674MF-ADJ SOT-23 DBV 5 1000 210.0 185.0 35.0
Pack Materials-Page 2

PACKAGE MATERIALS INFORMATION
www.ti.com 8-May-2013
Device Package Type Package Drawing Pins SPQ Length (mm) Width (mm) Height (mm)
LM3674MF-ADJ/NOPB SOT-23 DBV 5 1000 210.0 185.0 35.0
LM3674MFX-1.2 SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 210.0 185.0 35.0
LM3674MFX-1.2/NOPB SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 210.0 185.0 35.0
LM3674MFX-1.5 SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 210.0 185.0 35.0
LM3674MFX-1.5/NOPB SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 210.0 185.0 35.0
LM3674MFX-1.8 SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 210.0 185.0 35.0
LM3674MFX-1.8/NOPB SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 210.0 185.0 35.0
LM3674MFX-1.875 SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 210.0 185.0 35.0
LM3674MFX-1.875/NOPB SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 210.0 185.0 35.0
LM3674MFX-2.8 SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 210.0 185.0 35.0
LM3674MFX-2.8/NOPB SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 210.0 185.0 35.0
LM3674MFX-ADJ SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 210.0 185.0 35.0
LM3674MFX-ADJ/NOPB SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 210.0 185.0 35.0
Pack Materials-Page 3



IMPORTANT NOTICE
Texas Instruments Incorporated and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make corrections, enhancements, improvements and other
changes to its semiconductor products and services per JESD46, latest issue, and to discontinue any product or service per JESD48, latest
issue. Buyers should obtain the latest relevant information before placing orders and should verify that such information is current and
complete. All semiconductor products (also referred to herein as “components”) are sold subject to TI’s terms and conditions of sale
supplied at the time of order acknowledgment.
TI warrants performance of its components to the specifications applicable at the time of sale, in accordance with the warranty in TI’s terms
and conditions of sale of semiconductor products. Testing and other quality control techniques are used to the extent TI deems necessary
to support this warranty. Except where mandated by applicable law, testing of all parameters of each component is not necessarily
performed.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or the design of Buyers’ products. Buyers are responsible for their products and
applications using TI components. To minimize the risks associated with Buyers’ products and applications, Buyers should provide
adequate design and operating safeguards.
TI does not warrant or represent that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any patent right, copyright, mask work right, or
other intellectual property right relating to any combination, machine, or process in which TI components or services are used. Information
published by TI regarding third-party products or services does not constitute a license to use such products or services or a warranty or
endorsement thereof. Use of such information may require a license from a third party under the patents or other intellectual property of the
third party, or a license from TI under the patents or other intellectual property of TI.
Reproduction of significant portions of TI information in TI data books or data sheets is permissible only if reproduction is without alteration
and is accompanied by all associated warranties, conditions, limitations, and notices. TI is not responsible or liable for such altered
documentation. Information of third parties may be subject to additional restrictions.
Resale of TI components or services with statements different from or beyond the parameters stated by TI for that component or service
voids all express and any implied warranties for the associated TI component or service and is an unfair and deceptive business practice.
TI is not responsible or liable for any such statements.
Buyer acknowledges and agrees that it is solely responsible for compliance with all legal, regulatory and safety-related requirements
concerning its products, and any use of TI components in its applications, notwithstanding any applications-related information or support
that may be provided by TI. Buyer represents and agrees that it has all the necessary expertise to create and implement safeguards which
anticipate dangerous consequences of failures, monitor failures and their consequences, lessen the likelihood of failures that might cause
harm and take appropriate remedial actions. Buyer will fully indemnify TI and its representatives against any damages arising out of the use
of any TI components in safety-critical applications.
In some cases, TI components may be promoted specifically to facilitate safety-related applications. With such components, TI’s goal is to
help enable customers to design and create their own end-product solutions that meet applicable functional safety standards and
requirements. Nonetheless, such components are subject to these terms.
No TI components are authorized for use in FDA Class III (or similar life-critical medical equipment) unless authorized officers of the parties
have executed a special agreement specifically governing such use.
Only those TI components which TI has specifically designated as military grade or “enhanced plastic” are designed and intended for use in
military/aerospace applications or environments. Buyer acknowledges and agrees that any military or aerospace use of TI components
which have not been so designated is solely at the Buyer's risk, and that Buyer is solely responsible for compliance with all legal and
regulatory requirements in connection with such use.
TI has specifically designated certain components as meeting ISO/TS16949 requirements, mainly for automotive use. In any case of use of
non-designated products, TI will not be responsible for any failure to meet ISO/TS16949.
Products Applications
Audio www.ti.com/audio Automotive and Transportation www.ti.com/automotive
Amplifiers amplifier.ti.com Communications and Telecom www.ti.com/communications
Data Converters dataconverter.ti.com Computers and Peripherals www.ti.com/computers
DLP® Products www.dlp.com Consumer Electronics www.ti.com/consumer-apps
DSP dsp.ti.com Energy and Lighting www.ti.com/energy
Clocks and Timers www.ti.com/clocks Industrial www.ti.com/industrial
Interface interface.ti.com Medical www.ti.com/medical
Logic logic.ti.com Security www.ti.com/security
Power Mgmt power.ti.com Space, Avionics and Defense www.ti.com/space-avionics-defense
Microcontrollers microcontroller.ti.com Video and Imaging www.ti.com/video
RFID www.ti-rfid.com
OMAP Applications Processors www.ti.com/omap TI E2E Community e2e.ti.com
Wireless Connectivity www.ti.com/wirelessconnectivity
Mailing Address: Texas Instruments, Post Office Box 655303, Dallas, Texas 75265
Copyright © 2013, Texas Instruments Incorporated

 Loading...
Loading...