查询CDC921DL供应商
CDC921
133-MHz CLOCK SYNTHESIZER/DRIVER FOR PC MOTHERBOARDS
WITH 3-STATE OUTPUTS
SCAS623 –MA Y 27, 1999
D
Generates Clocks for Pentium III Class
Microprocessors
D
Supports a Single Pentium III
Microprocessor
D
Uses a 14.318 MHz Crystal Input to
Generate Multiple Output Frequencies
D
Includes Spread Spectrum Clocking (SSC),
0.5% Downspread for Reduced EMI
Performance
D
Power Management Control Terminals
D
Low Output Skew and Jitter for Clock
Distribution
D
Operates from Dual 2.5-V and 3.3-V
Supplies
D
Generates the Following Clocks:
– 3 CPU (2.5 V, 100/133 MHz)
– 10 PCI (3.3 V, 33.3 MHz)
– 1 CPU/2 (2.5 V, 50/66 MHz)
– 1 APIC (2.5 V, 16.67 MHz)
– 3 3V66 (3.3 V, 66 MHz)
– 2 REF (3.3 V, 14.318 MHz)
– 1 48MHz (3.3 V, 48 MHz)
D
Packaged in 48-Pin SSOP Package
D
Designed for Use with TI’s Direct Rambus
Clock Generators (CDCR81, CDCR82,
CDCR83)
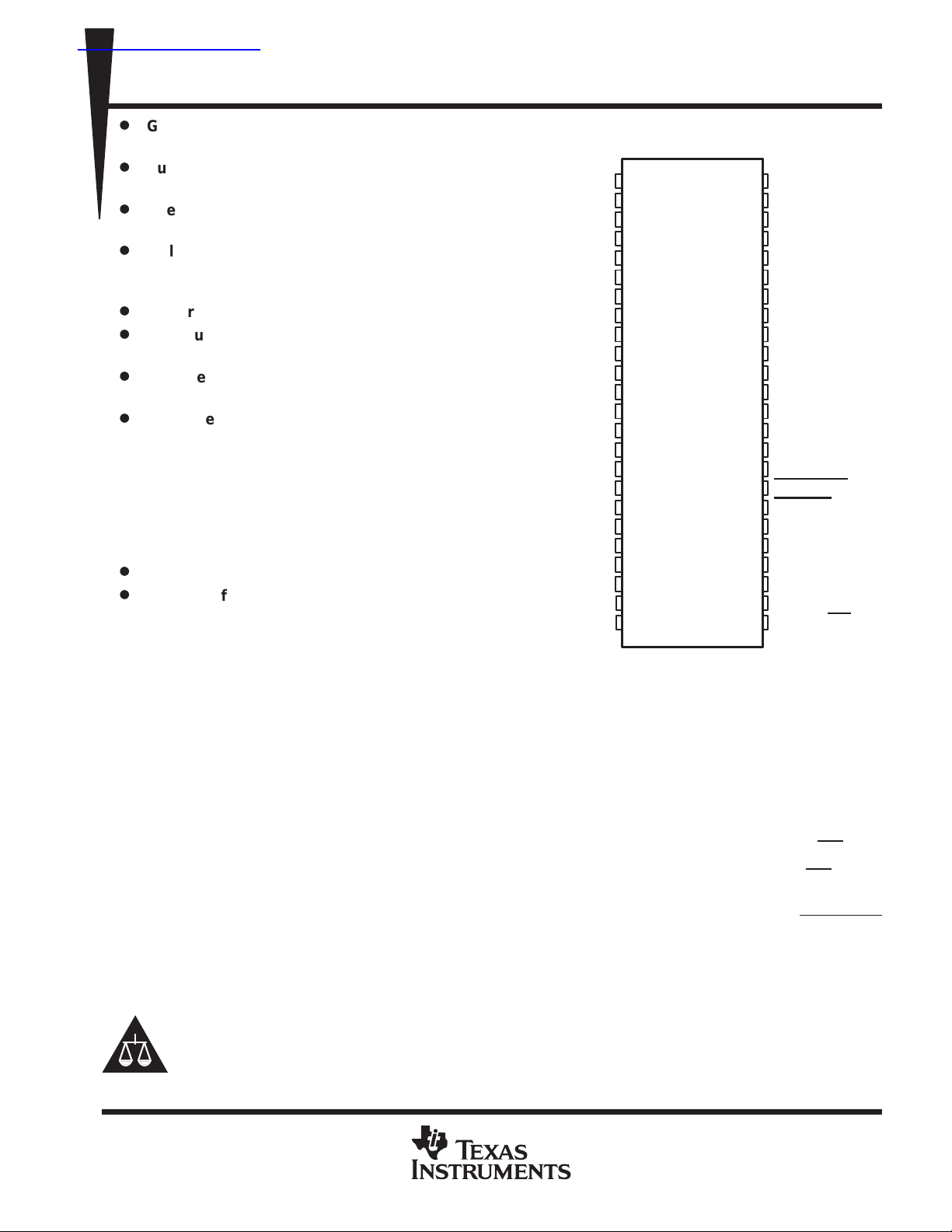
description
REF0
REF1
3.3V
V
DD
XOUT
GND
PCI0
PCI1
3.3V
V
DD
PCI2
PCI3
PCI4
PCI5
GND
PCI6
PCI7
3.3V
V
DD
PCI8
PCI9
GND
3V66(0)
3V66(1)
3V66(2)
V
3.3V
DD
XIN
DL PACKAGE
(TOP VIEW)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
GND
48
V
47
APIC
46
GND
45
V
44
CPU_DIV2
43
GND
42
VDD2.5V
41
40
CPU2
39
GND
38
VDD2.5V
37
CPU1
36
CPU0
35
GND
34
V
33
GND
32
PWR_DWN
31
SPREAD
30
SEL1
29
SEL0
28
V
27
48MHz
26
GND
25
SEL133/100
DD
DD
DD
DD
2.5V
2.5V
3.3V
3.3V
The CDC921 is a clock synthesizer/driver that generates CPU, CPU_DIV2, 3V66, PCI, APIC, 48MHz, and REF
system clock signals to support computer systems with a single Pentium III class microprocessor.
All output frequencies are generated from a 14.318-MHz crystal input. Instead of a crystal, a reference clock
input can be provided at the XIN input. Two phase-locked loops (PLLs) are used to generate the host
frequencies and the 48-MHz clock frequency . On-chip loop filters and internal feedback eliminate the need for
external components.
The host and PCI clock outputs provide low-skew and low-jitter clock signals for reliable clock operation. All
outputs have 3-state capability, which can be selected via control inputs SEL0, SEL1, and SEL133/100
The 48MHz clock can be independently disabled via the control inputs SEL0, SEL1, and SEL133/100
state, the 48-MHz PLL is disabled and the 48MHz clock is driven to high impedance to reduce component jitter.
The outputs are either 3.3-V or 2.5-V single-ended CMOS buffers. With a logic high-level on the PWR_DWN
terminal, the device operates normally, but when a logical low-level input is applied, the device powers down
completely with the outputs in a low-level output state.
Please be aware that an important notice concerning availability, standard warranty, and use in critical applications of
Texas Instruments semiconductor products and disclaimers thereto appears at the end of this data sheet.
Intel and Pentium III are trademarks of Intel Corporation.
Direct Rambus and Rambus are trademarks of Rambus Inc.
PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date.
Products conform to specifications per the terms of Texas Instruments
standard warranty. Production processing does not necessarily include
testing of all parameters.
Copyright 1999, Texas Instruments Incorporated
.
. In this
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
1
CDC921
133-MHz CLOCK SYNTHESIZER/DRIVER FOR PC MOTHERBOARDS
WITH 3-STATE OUTPUTS
SCAS623 –MA Y 27, 1999
description (continued)
The CPU bus can operate at 100 MHz or 133 MHz. Output frequency selection is done with corresponding
setting for SEL133/100
Since the CDC921 is based on PLL circuitry, it requires a stabilization time to achieve phase lock of the PLL.
This stabilization time is required after power up or after changes to the SEL inputs are made. With use of an
external reference clock, this signal must be fixed-frequency and fixed-phase before the stabilization time starts.
INPUTS
SEL133/
100
SEL1 SEL0 CPU CPU_DIV2 3V66 PCI 48MHz REF APIC
L L L Hi-Z Hi-Z Hi-Z Hi-Z Hi-Z Hi-Z Hi-Z 3-state
L L H N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A Reserved
L H L 100 MHz 50 MHz 66 MHz 33 MHz Hi-Z 14.318 MHz 16.67 MHz 48-MHz PLL off
L H H 100 MHz 50 MHz 66 MHz 33 MHz 48 MHz 14.318 MHz 16.67 MHz 48-MHz PLL on
H L L TCLK/2 TCLK/4 TCLK/4 TCLK/8 TCLK/2 TCLK TCLK/16 Test
H L H N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A Reserved
H H L 133 MHz 66 MHz 66 MHz 33 MHz Hi-Z 14.318 MHz 16.67 MHz 48-MHz PLL off
H H H 133 MHz 66 MHz 66 MHz 33 MHz 48 MHz 14.318 MHz 16.67 MHz 48-MHz PLL on
control input. The PCI bus frequency is fixed to 33 MHz.
Function Tables
SELECT FUNCTIONS
OUTPUTS
FUNCTION
ENABLE FUNCTIONS
INPUTS
PWR_DWN CPU CPU_DIV2 APIC 3V66 PCI
L L L L L L L Off Off
H On On On On On On On On
OUTPUT BUFFER SPECIFICATIONS
BUFFER NAME
CPU, CPU_DIV2, APIC 2.375 – 2.625 13.5 – 45 TYPE 1
48MHz, REF 3.135 – 3.465 20 – 60 TYPE 3
PCI, 3V66 3.135 – 3.465 12 – 55 TYPE 5
VDD RANGE
OUTPUTS INTERNAL
(V)
REF,
48MHz
IMPEDANCE
(Ω)
CRYSTAL VCOs
BUFFER TYPE
2
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
I/O
DESCRIPTION
133-MHz CLOCK SYNTHESIZER/DRIVER FOR PC MOTHERBOARDS
WITH 3-STATE OUTPUTS
Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
3V66 [0–2] 21–23 O 3.3 V, Type 5, 66-MHz clock outputs
48MHz 27 O 3.3 V, Type 3, 48-MHz clock output
APIC 46 O 2.5 V, Type 2, APIC clock output at 16.67 MHz
CPU [0–2] 36, 37, 40 O 2.5 V, Type 1, CPU clock outputs
CPU_DIV2 43 O 2.5 V, Type 1, CPU_DIV2 clock output
GND 6, 14, 20, 26,
PCI [0–9] 7, 8, 10–13,
PWR_DWN 32 I Power down for complete device with outputs forced low
REF0, REF1 1, 2 O 3.3 V, Type 3, 14.318-MHz reference clock outputs
SEL0, SEL1 29, 30 I LVTTL level logic select terminals for function selection
SEL133/100 25 I LVTTL level logic select terminal for enabling 100/133 MHz
SPREAD 31 I Disables SSC function
VDD2.5V 38, 41, 44, 47 Power for CPU, CPU_DIV2, and APIC outputs
VDD3.3V 3, 9, 17, 24,
XIN 4 I Crystal input – 14.318 MHz
XOUT 5 O Crystal output – 14.318 MHz
33, 35, 39, 42,
45, 48
O 3.3 V, Type 5, 33-MHz PCI clock outputs
15, 16, 18, 19
28, 34
Ground for PCI, 3V66, 48MHz, CPU, CPU_DIV2, APIC, REF [0–1] outputs and CORE
Power for the REF, PCI, 3V66, 48MHz outputs and CORE
CDC921
SCAS623 –MA Y 27, 1999
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
3
CDC921
133-MHz CLOCK SYNTHESIZER/DRIVER FOR PC MOTHERBOARDS
WITH 3-STATE OUTPUTS
SCAS623 –MA Y 27, 1999
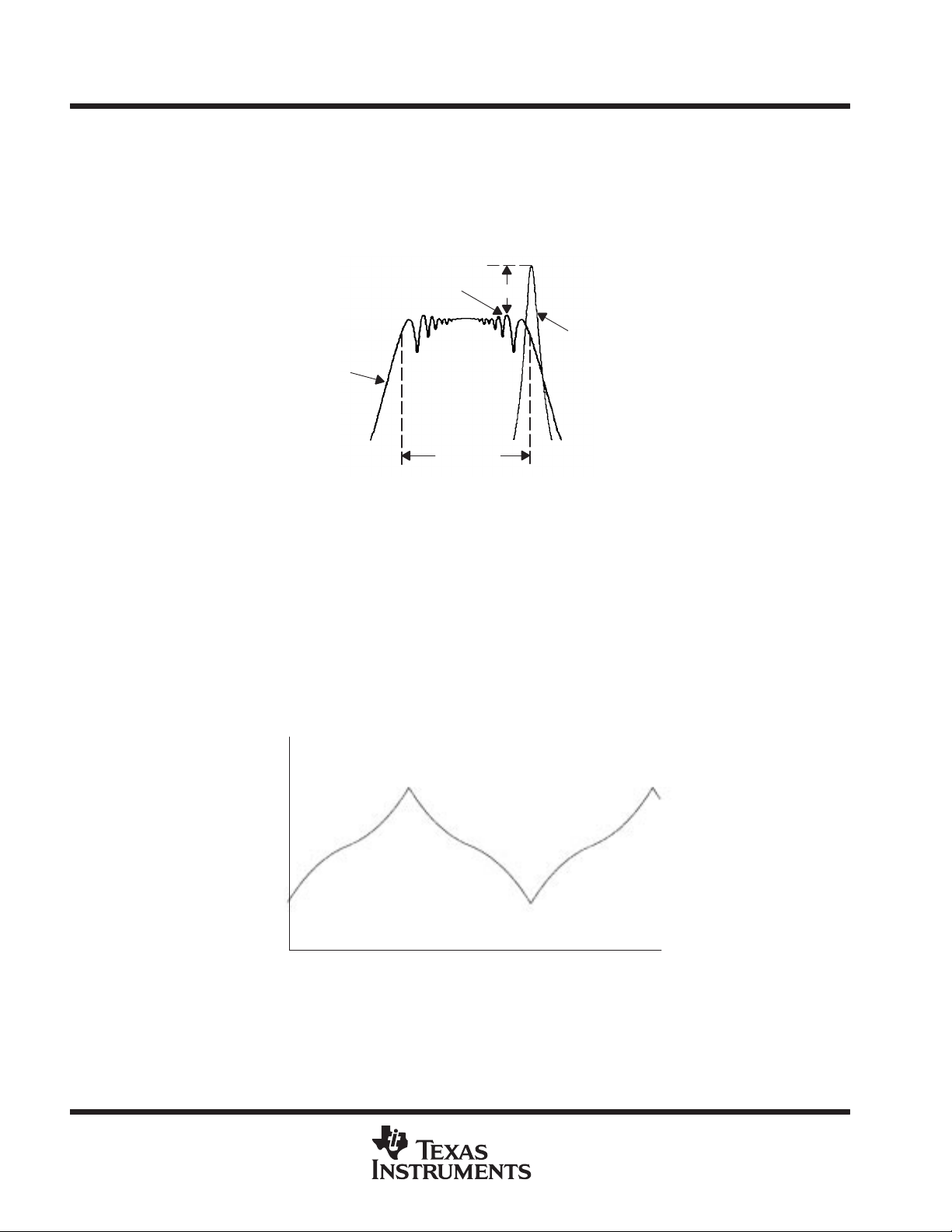
spread spectrum clock (SSC) implementation for CDC921
Simultaneously switching at fixed frequency generates a significant power peak at the selected frequency,
which in turn will cause EMI disturbance to the environment. The purpose of the internal frequency modulation
of the CPU–PLL allows to distribute the energy to many different frequencies which reduces the power peak.
A typical characteristic for a single frequency spectrum and a frequency modulated spectrum is shown in
Figure 1.
Highest Peak
SSC
δ of f
nom
∆
Non-SSC
f
nom
Figure 1. Frequency Power Spectrum With and Without the Use of SSC
The modulated spectrum has its distribution left hand to the single frequency spectrum which indicates a
“down-spread modulation”.
The peak reduction depends on the modulation scheme and modulation profile. System performance and timing
requirements are the limiting factors for actual design implementations. The implementation was driven to keep
the average clock frequency closed to its upper specification limit. The modulation amount was set to
approximately –0.5%.
In order to allow a downstream PLL to follow the frequency modulated signal, the bandwidth of the modulation
signal is limited in order to minimize SSC induced tracking skew jitter. The ideal modulation profile used for
CDC921 is shown in Figure 2.
10.03
10.02
10.01
10
9.99
9.98
9.97
Period of Output Frequency – ns
51015202530354045
Period of Modulation Signal – µs
Figure 2. SSC Modulation Profile
4
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
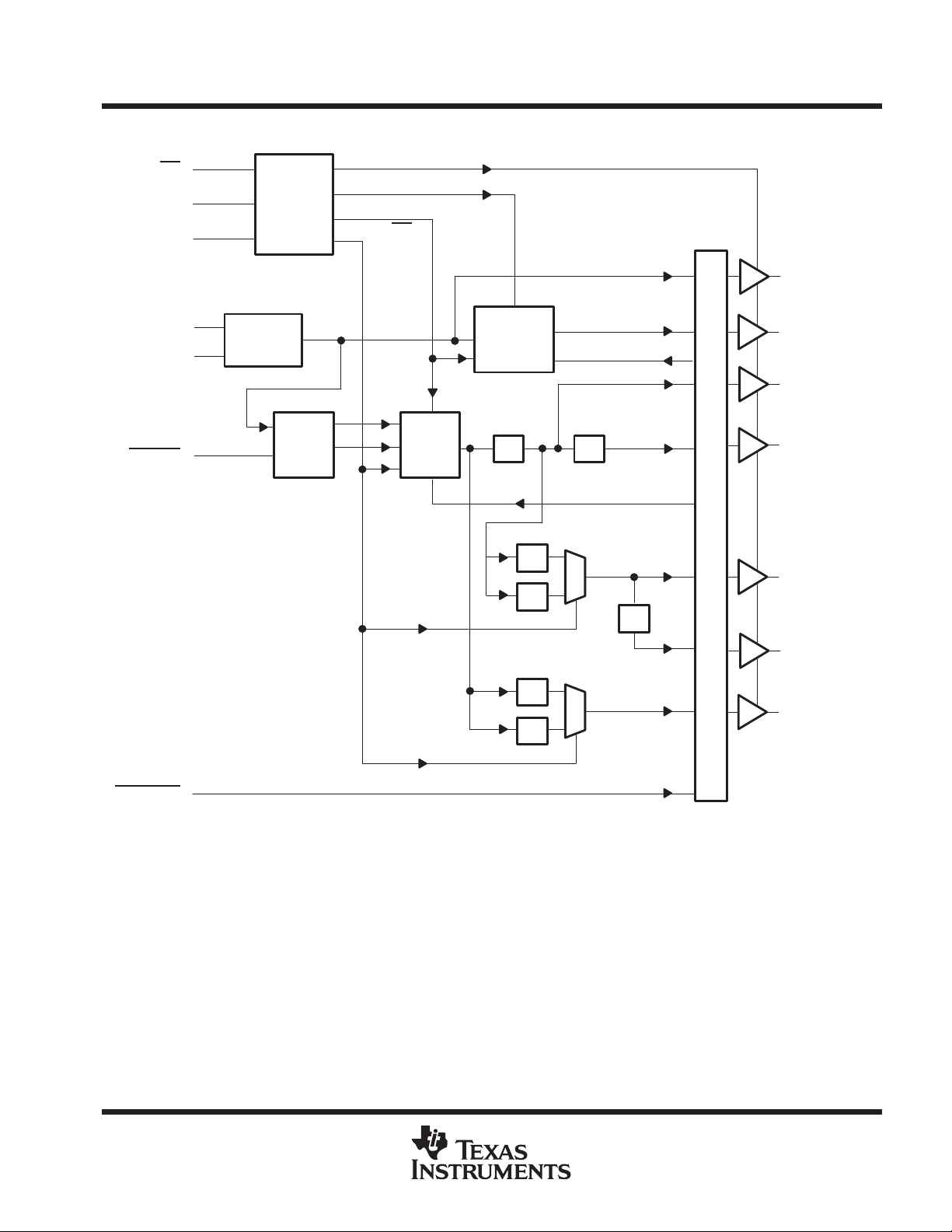
functional block diagram
CDC921
133-MHz CLOCK SYNTHESIZER/DRIVER FOR PC MOTHERBOARDS
WITH 3-STATE OUTPUTS
SCAS623 –MA Y 27, 1999
SEL133/100
SEL0
SEL1
XIN
XOUT
SPREAD
25
29
30
4
5
31
Control
Xtal
Oscillator
Logic
Spread
Logic
3-State
48-MHz Inactive
Test
SEL 133/100
CPU
PLL
48 MHz
PLL
/2 /2
/3
/4
/3
/4
2*REF
14.318 MHz
(1,2)
1*48MHz
48 MHz
(27)
3*CPU
100/133 MHz
(36,37,40)
1*CPU_DIV2
50/66 MHz
(43)
10*PCI
33 MHz
(7,8,10,11,12,
13,15,16,18,19)
/2
Sync Logic & Power Down Logic
1*APIC
16.67 MHz
(46)
3*AGP (3V66)
66 MHz
(21,22,23)
PWR_DWN
32
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
5

CDC921
†
PACKAGE
A
A
A
Suppl
oltage, V
V
High-level output current, I
mA
Low-level output current, I
mA
133-MHz CLOCK SYNTHESIZER/DRIVER FOR PC MOTHERBOARDS
WITH 3-STATE OUTPUTS
SCAS623 –MA Y 27, 1999
absolute maximum ratings over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)
Supply voltage range, V
Input voltage range, V
Voltage range applied to any output in the high-impedance state or power-off state,
V
(see Note 1) –0.5 V to VDD + 0.5 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
O
Current into any output in the low state, I
Input clamp current, I
Output clamp current, I
Operating free-air temperature range, T
Storage temperature range, T
Lead temperature 1,6 mm (1/16 inch) from case for 10 seconds 260°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
†
Stresses beyond those listed under “absolute maximum ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and
functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under “recommended operating conditions” is not
implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
NOTE 1: The input and output negative-voltage ratings may be exceeded if the input and output clamp-current ratings are observed.
DL 1315.7 mW 10.53 mW/°C 842.1 mW 684.2 mW
†
This is the inverse of the traditional junction-to-case thermal resistance (R
at 95°C/W.
–0.5 V to 4.6 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DD
(see Note 1) –0.5 V to 4.6 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
I
2 × I
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
(V
< 0) –18 mA. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
IK
I
(V
< 0) –50 mA. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
OK
POWER RATNG ABOVE TA = 25°C
O
–65°C to 150°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
stg
T
≤ 25°C DERATING FACTOR
O
–0°C to 85°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
A
DISSIPATION RATING TABLE
T
= 70°C T
POWER RATING
) and uses a board-mounted device
θJA
= 85°C
POWER RATING
recommended operating conditions (see Note 2)
MIN NOM
pp
y v
High-level input voltage, V
Low-level input voltage, V
Input voltage, V
Reference frequency, f
Crystal frequency, f
Operating free-air temperature, T
NOTE 2: Unused inputs must be held high or low to prevent them from floating.
†
All nominal values are measured at their respective nominal VDD values.
‡
Reference frequency is a test clock driven on the XIN input during the device test mode and normal mode. In test mode, XIN can be driven
externally up to f
§
This is a series fundamental crystal with fO = 14.31818 MHz.
p
p
DD
IH
IL
I
OH
OL
‡
(XTAL)
§
(XTAL)
A
= 130 MHz. If XIN is driven externally, XOUT is floating.
(XTAL)
3.3 V 3.135 3.465
2.5 V 2.375 2.625
2
GND –
0.3 V
0 V
CPUx, CPU_DIV2 –12
APIC –12
48MHz, REFx –14
PCIx, PCI_F, 3V66x –18
CPUx, CPU_DIV2 12
APIC 12
48MHz, REFx 9
PCIx, PCI_F, 3V66x 12
Test mode 130 MHz
Normal mode 13.8 14.318 14.8 MHz
0 85 °C
†
VDD +
MAX UNIT
0.3 V
0.8 V
DD
V
V
†
OL
6
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265

IH
g
IL
IDDSupply current
I
gy
mA
Dynamic I
L
mA
CDC921
133-MHz CLOCK SYNTHESIZER/DRIVER FOR PC MOTHERBOARDS
WITH 3-STATE OUTPUTS
SCAS623 –MA Y 27, 1999
electrical characteristics over recommended operating free-air temperature range (unless
otherwise noted)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP†MAX UNIT
V
R
I
I
I
OZ
DD(Z)
C
†
All typical values are measured at their respective nominal VDD values.
Input clamp voltage VDD = 3.135 V, II = –18 mA –1.2 V
IK
Input resistance XIN, XOUT VDD = 3.465 V, VI = VDD –0.5 V 80 350 kΩ
I
XOUT VDD = 3.135 V, VI = VDD –0.5 V 20 50 mA
SEL0, SEL1,
High-level input current
Low-level input current
High-impedance-state output current |VDD| = max, VO = VDD or GND ±10 µA
pp
High-impedance-state supply
current
DD
Input capacitance VDD = 3.3 V, VI = VDD or GND 3.3 5.8 pF
I
Crystal terminal capacitance VDD = 3.3 V, VI = 0.3 V 18 18.5 22.5 pF
SPREAD
PWR_DWN VDD = 3.465 V, VI = V
SEL133/100 VDD = 3.465 V, VI = V
XOUT VDD = 3.135 V, VI = 0 V –2 –5 mA
SEL0, SEL1,
SPREAD
PWR_DWN VDD = 3.465 V, VI = GND <10 –10 µA
SEL133/100 VDD = 3.465 V, VI = GND <10 –10 µA
VDD = 3.465 V, VI = V
VDD = 3.465 V, VI = GND <10 –10 µA
VDD = 2.625 V,
PWR_DWN
VDD = 2.625 V, All outputs = high <20 100 µA
VDD = 3.465 V,
PWR_DWN
VDD = 3.465 V, All outputs = high 12 37 mA
VDD = 2.625 V 1.4
VDD = 3.465 V
CL = 20 pF,
CPU = 133 MHz
= low
= low
DD
DD
DD
All outputs = low,
All outputs = low,
VDD = 3.465 V 114 156
VDD = 2.625 V 44 60
<10 10 µA
<10 10 µA
<10 10 µA
<20 100 µA
<50 200 µA
30
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
7

CDC921
OH
gg
VOLLow-level output voltage
V
ZOOutput impedance
Ω
OH
gg
VOLLow-level output voltage
V
ZOOutput impedance
Ω
133-MHz CLOCK SYNTHESIZER/DRIVER FOR PC MOTHERBOARDS
WITH 3-STATE OUTPUTS
SCAS623 –MA Y 27, 1999
electrical characteristics over recommended operating free-air temperature range (unless
otherwise noted) (continued)
CPUx, CPU_DIV2, APIC (Type 1)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP
V
High-level output voltage
p
I
High-level output current
OH
I
Low-level output current
OL
C
Output capacitance VDD = 3.3 V, VO = VDD or GND 5.8 8.5 pF
O
p
p
†
All typical values are measured at their respective nominal VDD values.
High state VO = 0.5 VDD, VO/I
Low state VO = 0.5 VDD, VO/I
VDD = min to max, IOH = –1 mA
VDD = 2.375 V, IOH = –12 mA 2
VDD = min to max, IOL = 1 mA 0.1
VDD = 2.375 V, IOL = 12 mA 0.18 0.4
VDD = 2.375 V, VO = 1 V –26 –42
VDD = 2.5 V,
VDD = 2.625 V, VO = 2.375 V –16 –27
VDD = 2.375 V, VO = 1.2 V 27 57
VDD = 2.5 V, VO = 1.25 V 63
VDD = 2.625 V, VO = 0.3 V 23 43
VDD –
0.1 V
VO = 1.25 V –46
OH
OL
13.5 27 45
13.5 20 45
†
MAX UNIT
V
mA
mA
48MHz, REFx (Type 3)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP
V
High-level output voltage
p
I
High-level output current
OH
I
Low-level output current
OL
C
Output capacitance VDD = 3.3 V, VO = VDD or GND 4.5 7 pF
O
p
p
†
All typical values are measured at their respective nominal VDD values.
High state VO = 0.5 VDD, VO/I
Low state VO = 0.5 VDD, VO/I
VDD = min to max, IOH = –1 mA
VDD = 3.135 V, IOH = –14 mA 2.4
VDD = min to max, IOL = 1 mA 0.1
VDD = 3.135 V, IOL = 9 mA 0.18 0.4
VDD = 3.135 V, VO = 1 V –27 –41
VDD = 3.3 V,
VDD = 3.465 V, VO = 3.135 V –12 –23
VDD = 3.135 V, VO = 1.95 V 29 50
VDD = 3.3 V, VO = 1.65 V 53
VDD = 3.465 V, VO = 0.4 V 20 37
VDD –
0.1 V
VO = 1.65 V –41
OH
OL
20 40 60
20 31 60
†
MAX UNIT
V
mA
mA
8
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265

OH
gg
VOLLow-level output voltage
V
ZOOutput impedance
Ω
Stabilization time
†
ms
CDC921
133-MHz CLOCK SYNTHESIZER/DRIVER FOR PC MOTHERBOARDS
WITH 3-STATE OUTPUTS
SCAS623 –MA Y 27, 1999
electrical characteristics over recommended operating free-air temperature range (unless
otherwise noted) (continued)
PCIx, 3V66x (Type 5)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP
V
High-level output voltage
p
I
High-level output current
OH
I
Low-level output current
OL
C
Output capacitance VDD = 3.3 V, VO = VDD or GND 4.5 7.5 pF
O
p
p
†
All typical values are measured at their respective nominal VDD values.
High state VO = 0.5 VDD, VO/I
Low state VO = 0.5 VDD, VO/I
VDD = min to max, IOH = –1 mA
VDD = 3.135 V, IOH = –18 mA 2.4
VDD = min to max, IOL = 1 mA 0.1
VDD = 3.135 V, IOL = 12 mA 0.15 0.4
VDD = 3.135 V, VO = 1 V –33 –53
VDD = 3.3 V,
VDD = 3.465 V, VO = 3.135 V –16 –33
VDD = 3.135 V, VO = 1.95 V 30 67
VDD = 3.3 V, VO = 1.65 V 70
VDD = 3.465 V, VO = 0.4 V 27 49
VDD –
0.1 V
VO = 1.65 V –53
OH
OL
12 31 55
12 24 55
†
MAX UNIT
V
mA
mA
switching characteristics, VDD = 3.135 V to 3.465 V, TA = 0°C to 85°C
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Overshoot/undershoot GND – 0.7 V VDD + 0.7 V V
Ring back VIL – 0.1 V VIH + 0.1 V V
Stabilization time, PWR_DWN to PCIx f
t
Disable time, PWR_DWN to PCIx f
dis3
Stabilization time, PWR_DWN to CPUx f
t
Disable time, PWR_DWN to CPUx f
dis4
†
Stabilization time is the time required for the integrated PLL circuit to obtain phase lock of its feedback signal to its reference signal. In order for
phase lock to be obtained, a fixed-frequency, fixed-phase reference signal must be present at X1. Until phase lock is obtained, the specifications
for propagation delay and skew parameters given in the switching characteristics tables are not applicable. Stabilization time is defined as the
time from when VDD achieves its nominal operating level until the output frequency is stable and operating within specification.
= 133 MHz 0.05 3 ms
(CPU)
= 133 MHz 50 ns
(CPU)
= 133 MHz 0.03 3 ms
(CPU)
= 133 MHz 50 ns
(CPU)
After SEL1, SEL0 3
After power up 3
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
9

CDC921
t
CPU clock
d
†
tw1Pulse duration width, high
ns
tw2Pulse duration width, lo
ns
tcCPU_DIV2 clock period
†
tw1Pulse duration width, high
ns
tw2Pulse duration width, lo
ns
133-MHz CLOCK SYNTHESIZER/DRIVER FOR PC MOTHERBOARDS
WITH 3-STATE OUTPUTS
SCAS623 –MA Y 27, 1999
switching characteristics, VDD = 2.375 V to 2.625 V, TA = 0°C to 85°C (continued)
CPUx
PARAMETER
t
Output enable time SEL133/100 CPUx f
en1
t
Output disable time SEL133/100 CPUx f
dis1
c
Cycle to cycle jitter f
Duty cycle f
t
CPU bus skew CPUx CPUx f
sk(o)
t
CPU pulse skew CPUn CPUn f
sk(p)
t
CPU clock to APIC clock offset, rising edge 1.5 2.8 4 ns
(off)
t
CPU clock to 3V66 clock offset, rising edge 0 0.75 1.5 ns
(off)
t
Rise time VO = 0.4 V to 2.0 V 0.4 1.5 2.2 ns
r
t
Fall time VO = 0.4 V to 2.0 V 0.4 1.4 2 ns
f
†
The average over any 1-µs period of time is greater than the minimum specified period.
perio
w
FROM
(INPUT)TO(OUTPUT)
TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
= 100 or 133MHz 6 10 ns
(CPU)
= 100 or 133MHz 8 10 ns
(CPU)
f
= 100 MHz 10 10.04 10.2 ns
(CPU)
f
= 133 MHz 7.5 7.53 7.7 ns
(CPU)
= 100 or 133MHz 250 ps
(CPU)
= 100 or 133MHz 45 55 %
(CPU)
= 100 or 133MHz 50 175 ps
(CPU)
= 100 or 133MHz 2.2 ns
(CPU)
f
= 100 MHz 2.6 4.3
(CPU)
f
= 133 MHz 1.4 3.7
(CPU)
f
= 100 MHz 2.8 4.3
(CPU)
f
(CPU)
= 133 MHz
1.7 4
CPU_DIV2
PARAMETER
t
Output enable time SEL133/100 CPU_DIV2 f
en1
t
Output disable time SEL133/100 CPU_DIV2 f
dis1
p
Cycle to cycle jitter f
Duty cycle f
t
CPU_DIV2 pulse skew f
sk(p)
w
t
Rise time VO = 0.4 V to 2.0 V 0.4 1.4 2 ns
r
t
Fall time VO = 0.4 V to 2.0 V 0.4 1.3 1.8 ns
f
†
The average over any 1-µs period of time is greater than the minimum specified period.
FROM
(INPUT)TO(OUTPUT)
TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
(CPU)
(CPU)
f
(CPU)
f
(CPU)
(CPU)
(CPU)
(CPU)
f
(CPU)
f
(CPU)
f
(CPU)
f
(CPU)
= 100 or 133MHz 6 10 ns
= 100 or 133MHz 8 10 ns
= 100 MHz 20 20.08 20.4 ns
= 133 MHz 15 15.06 15.3 ns
= 100 or 133MHz 250 ps
= 100 or 133MHz 45 55 %
= 100 or 133MHz 1.6 ns
= 100 MHz 7.1
= 133 MHz 4.7
= 100 MHz 7.3 8.9
= 133 MHz
5 6.6
10
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265

133-MHz CLOCK SYNTHESIZER/DRIVER FOR PC MOTHERBOARDS
WITH 3-STATE OUTPUTS
switching characteristics, VDD = 2.375 V to 2.625 V, TA = 0°C to 85°C (continued)
APIC
PARAMETER
t
en1
t
dis1
t
c
t
sk(p)
t
(off)
t
w1
t
w2
t
r
t
f
†
The average over any 1-µs period of time is greater than the minimum specified period.
Output enable time SEL133/100 APIC f
Output disable time SEL133/100 APIC f
APIC clock period
Cycle to cycle jitter f
Duty cycle f
APIC pulse skew f
APIC clock to CPU clock offset,
rising edge
Pulse duration width, high f
Pulse duration width, low f
Rise time VO = 0.4 V to 2 V 0.4 1.6 2.1 ns
Fall time VO = 0.4 V to 2 V 0.4 1.2 1.7 ns
†
FROM
(INPUT)TO(OUTPUT)
APIC CPUx –1.5 –4 ns
TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
= 16.67 MHz 6 10 ns
(APIC)
= 16.67 MHz 8 10 ns
(APIC)
f
= 16.67 MHz 60 60.24 60.6 ns
(APIC)
= 100 or 133 MHz 400 ps
(CPU)
= 16.67 MHz 45 55 %
(APIC)
= 16.67 MHz 3 ns
(APIC)
= 16.67 MHz 25.5 28 ns
(APIC)
= 16.67 MHz 25.3 29.2 ns
(APIC)
CDC921
SCAS623 –MA Y 27, 1999
switching characteristics, VDD = 3.135 V to 3.465 V, TA = 0°C to 85°C
3V66
PARAMETER
t
en1
t
dis1
t
c
t
sk(o)
t
sk(p)
t
(off)
t
(off)
t
w1
t
w2
t
r
t
f
†
The average over any 1-µs period of time is greater than the minimum specified period.
Output enable time SEL133/100 3V66x f
Output disable time SEL133/100 3V66x f
3V66 clock period
Cycle to cycle jitter f
Duty cycle f
3V66 bus skew 3V66x 3V66x f
3V66 pulse skew 3V66n 3V66n f
3V66 clock to CPU clock offset 3V66x CPUx 0 –0.75 –1.5 ns
3V66 clock to PCI clock offset, rising edge 1.2 2.1 3 ns
Pulse duration width, high f
Pulse duration width, low f
Rise time VO = 0.4 V to 2 V 0.5 1.5 2 ns
Fall time VO = 0.4 V to 2 V 0.5 1.5 2 ns
†
FROM
(INPUT)TO(OUTPUT)
TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
= 66 MHz 6 10 ns
(3V66)
= 66 MHz 8 10 ns
(3V66)
f
= 66 MHz 15 15.06 15.3 ns
(3V66)
= 100 or 133 MHz 400 ps
(CPU)
= 66 MHz 45 55 %
(3V66)
= 66 MHz 50 150 ps
(3V66)
= 66 MHz 2.6 ns
(3V66)
= 66 MHz 5.2 ns
(3V66)
= 66 MHz 5 ns
(3V66)
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
11

CDC921
133-MHz CLOCK SYNTHESIZER/DRIVER FOR PC MOTHERBOARDS
WITH 3-STATE OUTPUTS
SCAS623 –MA Y 27, 1999
switching characteristics, VDD = 3.135 V to 3.465 V, TA = 0°C to 85°C (continued)
48MHz
PARAMETER
t
en1
t
dis1
t
c
t
sk(p)
t
w1
t
w2
t
r
t
f
†
The average over any 1-µs period of time is greater than the minimum specified period.
Output enable time SEL133/100 48MHz f
Output disable time SEL133/100 48MHz f
48MHz clock period
Cycle to cycle jitter f
Duty cycle f
48MHz pulse skew 48MHz 48MHz f
Pulse duration width, high f
Pulse duration width, low f
Rise time VO = 0.4 V to 2 V 1 2.1 2.8 ns
Fall time VO = 0.4 V to 2 V 1 1.9 2.8 ns
†
REF
PARAMETER
t
en1
t
dis1
t
c
t
sk(o)
t
sk(p)
t
w1
t
w2
t
r
t
f
†
The average over any 1-µs period of time is greater than the minimum specified period.
Output enable time SEL133/100 REFx f
Output disable time SEL133/100 REFx f
REF clock period
Cycle to cycle jitter f
Duty cycle f
REF bus skew REFx REFx f
REF pulse skew REFn REFn f
Pulse duration width, high f
Pulse duration width, low f
Rise time VO = 0.4 V to 2 V 1 2 2.8 ns
Fall time VO = 0.4 V to 2 V 1 1.9 2.8 ns
†
FROM
(INPUT)TO(OUTPUT)
FROM
(INPUT)TO(OUTPUT)
TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
(48MHz)
(48MHz)
f
(48MHz)
(CPU)
(48MHz)
(48MHz)
(48MHz)
(48MHz)
(REF)
(REF)
f
(REF)
(CPU)
(REF)
(REF)
(REF)
(REF)
(REF)
= 48 MHz 6 10 ns
= 48 MHz 8 10 ns
= 48 MHz 20.5 20.83 21.1 ns
= 100 or 133 MHz 500 ps
= 48 MHz 45 55 %
= 48 MHz 3 ns
= 48 MHz 7.8 ns
= 48 MHz 7.8 ns
TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
= 14.318 MHz 6 10 ns
= 14.318 MHz 8 10 ns
= 14.318 MHz 69.84 ns
= 100 or 133 MHz 700 ps
= 14.318 MHz 45 55 %
= 14.318 MHz 150 250 ps
= 14.318 MHz 2 ns
= 14.318 MHz 26.2 32.7 ns
= 14.318 MHz 26.2 31.2 ns
12
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265

133-MHz CLOCK SYNTHESIZER/DRIVER FOR PC MOTHERBOARDS
WITH 3-STATE OUTPUTS
switching characteristics, VDD = 3.135 V to 3.465 V, TA = 0°C to 85°C (continued)
PCI
PARAMETER
t
en1
t
dis1
t
c
t
sk(o)
t
sk(p)
t
(off)
t
w1
t
w2
t
r
t
f
†
The average over any 1-µs period of time is greater than the minimum specified period.
Output enable time SEL133/100 PCIx f
Output disable time SEL133/100 PCIx f
PCIx clock period
Cycle to cycle jitter f
Duty cycle f
PCIx bus skew PCIx PCIx f
PCIx pulse skew PCIn PCIn f
PCIx clock to 3V66 clock offset –1.2 –3 ns
Pulse duration width, high f
Pulse duration width, low f
Rise time VO = 0.4 V to 2 V 0.5 1.6 2 ns
Fall time VO = 0.4 V to 2 V 0.5 1.5 2 ns
†
FROM
(INPUT)TO(OUTPUT)
TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
= 33 MHz 6 10 ns
(PCI)
= 33 MHz 8 10 ns
(PCI)
f
= 33 MHz 30 30.12 30.5 ns
(PCI)
= 100 or 133 MHz 300 ps
(CPU)
= 33 MHz 45 55 %
(PCI)
= 33 MHz 70 300 ps
(PCI)
= 33 MHz 4 ns
(PCI)
= 33 MHz 12 ns
(PCI)
= 33 MHz 12 ns
(PCI)
CDC921
SCAS623 –MA Y 27, 1999
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
13

CDC921
133-MHz CLOCK SYNTHESIZER/DRIVER FOR PC MOTHERBOARDS
WITH 3-STATE OUTPUTS
SCAS623 –MA Y 27, 1999
PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION
Input
Output
From Output
Under Test
(see Note A)
From Output
Under Test
V
IH_REF
V
T_REF
V
IL_REF
t
r
t
w_high
t
w_low
RL = 500 Ω
C
L
LOAD CIRCUIT for tpd and t
LOAD CIRCUIT FOR tr and t
V
T_REF
t
PLH
RL = 500 Ω
C
L
(see Note A)
V
T_REF
t
PHL
V
OH
f
Test
Point
3 V
0 V
V
t
f
S1
sk
OL
V
O_REF
GND
Input
Output
Enable
(high-level
enabling)
Output
Waveform 1
S1 at 6 V
(see Note B)
Output
Waveform 2
S1 at GND
(see Note B)
OPEN
3 V
0 V
TEST S1
t
PLH/tPHL
t
PLZ/tPZL
t
PHZ/tPZH
VOLTAGE WAVEFORMS
V
T_REF
t
PZL
t
PZH
t
w
V
T_REF
V
T_REF
Open
V
O_REF
GND
V
T_REF
V
IH_REF
V
T_REF
V
IL_REF
t
PLZ
VOL + 0.3 V
t
PHZ
VOH – 0.3 V
V
DD
0 V
≈3 V
V
OL
V
OH
≈0 V
VOLTAGE WAVEFORMS
NOTES: A. CL includes probe and jig capacitance. CL = 20 pF (CPUx, APIC, 48MHz, REF), CL = 30 pF (PCIx)
B. Waveform 1 is for an output with internal conditions such that the output is low except when disabled by the output control.
Waveform 2 is for an output with internal conditions such that the output is high except when disabled by the output control.
C. All input pulses are supplied by generators having the following characteristics: PRR v 14.318 MHz, ZO = 50 Ω, tr ≤ 2.5 ns,
tf ≤ 2.5 ns.
D. The outputs are measured one at a time with one transition per measurement.
V
IH_REF
V
IL_REF
V
T_REF
V
O_REF
PARAMETER
High-level reference voltage 2.4 2 V
Low-level reference voltage 0.4 0.4 V
Input Threshold reference voltage 1.5 1.25 V
Off-state reference voltage 6 4.6 V
3.3-V INTERFACE 2.5-V INTERFACE UNIT
VOLTAGE WAVEFORMS
Figure 3. Load Circuit and Voltage Waveforms
14
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265

CDC921
133-MHz CLOCK SYNTHESIZER/DRIVER FOR PC MOTHERBOARDS
WITH 3-STATE OUTPUTS
SCAS623 –MA Y 27, 1999
PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION
V
CPUx or PCIx Clock
t
c
T_REF
CPUx or PCIx Clock
3V66 or CPUx
3V66, PCIx, or APIC
CPU
(internal)
t
sk(p)
+Ťt
PLH–tPHL
t
sk(o)
t
[3V66 to PCIx]
(off)
t
[CPUx to APIC]
(off)
t
[CPUx to 3V66]
(off)
Ť
t
(low)
t
(high)
Duty Cycle
t
(low)
+
t
c
Figure 4. Waveforms for Calculation of Skew, Offset, and Jitter
100
V
T_REF
VT_REF
VT_REF
PCI
(internal)
PWR_DWN
CPU
(external)
PCI
(external)
VCO
CRYSTAL
NOTE A: Shaded sections on the VCO and Crystal waveforms indicate that the VCO and crystal oscillators are active and there is a valid clock.
Figure 5. Power-Down Timing
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
15

CDC921
133-MHz CLOCK SYNTHESIZER/DRIVER FOR PC MOTHERBOARDS
WITH 3-STATE OUTPUTS
SCAS623 –MA Y 27, 1999
MECHANICAL DATA
DL (R-PDSO-G**) PLASTIC SMALL-OUTLINE PACKAGE
48-PIN SHOWN
0.025 (0,635)
48
1
0.110 (2,79) MAX
0.012 (0,305)
0.008 (0,203)
25
0.299 (7,59)
0.291 (7,39)
24
A
0.008 (0,20) MIN
0.005 (0,13)
0.420 (10,67)
0.395 (10,03)
Seating Plane
0.004 (0,10)
M
0.006 (0,15) NOM
Gage Plane
0.010 (0,25)
0°–8°
0.040 (1,02)
0.020 (0,51)
PINS **
DIM
A MAX
A MIN
NOTES: A. All linear dimensions are in inches (millimeters).
B. This drawing is subject to change without notice.
C. Body dimensions do not include mold flash or protrusion not to exceed 0.006 (0,15).
D. Falls within JEDEC MO-118
0.380
(9,65)
0.370
(9,40)
4828
0.630
(16,00)
0.620
(15,75)
56
0.730
(18,54)
0.720
(18,29)
4040048/D 08/97
16
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265

IMPORTANT NOTICE
T exas Instruments and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make changes to their products or to discontinue
any product or service without notice, and advise customers to obtain the latest version of relevant information
to verify, before placing orders, that information being relied on is current and complete. All products are sold
subject to the terms and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgement, including those
pertaining to warranty, patent infringement, and limitation of liability.
TI warrants performance of its semiconductor products to the specifications applicable at the time of sale in
accordance with TI’s standard warranty. Testing and other quality control techniques are utilized to the extent
TI deems necessary to support this warranty . Specific testing of all parameters of each device is not necessarily
performed, except those mandated by government requirements.
CERT AIN APPLICATIONS USING SEMICONDUCTOR PRODUCTS MAY INVOLVE POTENTIAL RISKS OF
DEATH, PERSONAL INJURY, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE (“CRITICAL
APPLICATIONS”). TI SEMICONDUCTOR PRODUCTS ARE NOT DESIGNED, AUTHORIZED, OR
WARRANTED TO BE SUITABLE FOR USE IN LIFE-SUPPORT DEVICES OR SYSTEMS OR OTHER
CRITICAL APPLICA TIONS. INCLUSION OF TI PRODUCTS IN SUCH APPLICATIONS IS UNDERST OOD TO
BE FULLY AT THE CUSTOMER’S RISK.
In order to minimize risks associated with the customer’s applications, adequate design and operating
safeguards must be provided by the customer to minimize inherent or procedural hazards.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or customer product design. TI does not warrant or represent
that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any patent right, copyright, mask work right, or other
intellectual property right of TI covering or relating to any combination, machine, or process in which such
semiconductor products or services might be or are used. TI’s publication of information regarding any third
party’s products or services does not constitute TI’s approval, warranty or endorsement thereof.
Copyright 1999, Texas Instruments Incorporated
 Loading...
Loading...