Texas Instruments CD74HCT4046AE, CD74HCT4046AM96, CD74HCT4046AM, CD74HC4046APWR, CD74HC4046AM96 Datasheet
...
CD74HC4046A,
[ /Title
(CD74
HC404
6A,
CD74
HCT40
46A)
/Subject
(HighSpeed
CMOS
Data sheet acquired from Harris Semiconductor
SCHS204
February 1998
Features
• Operating Frequency Range
- Up to 18MHz (Typ) at V
- Minimum Center Frequency of 12MHz at V
• Choice of Three Phase Comparators
- EXCLUSIVE-OR
- Edge-Triggered JK Flip-Flop
- Edge-Triggered RS Flip-Flop
• Excellent VCO Frequency Linearity
• VCO-Inhibit Control for ON/OFF Keying and for Low
Standby Power Consumption
• Minimal Frequency Drift
• Operating Power Supply Voltage Range
- VCO Section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3V to 6V
- Digital Section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2V to 6V
• Fanout (Over Temperature Range)
- Standard Outputs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 LSTTL Loads
- Bus Driver Outputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15 LSTTL Loads
• Wide Operating Temperature Range . . . -55
• Balanced Propagation Delay and Transition Times
• Significant Power Reduction Compared to LSTTL
Logic ICs
• HC Types
- 2V to 6V Operation
- High Noise Immunity: N
at VCC = 5V
• HCT Types
- 4.5V to 5.5V Operation
- Direct LSTTL Input Logic Compatibility,
V
= 0.8V (Max), VIH = 2V (Min)
IL
- CMOS Input Compatibility, I
= 5V
CC
o
= 30%, NIH = 30% of V
IL
≤ 1µA at VOL, V
l
C to 125oC
CC
OH
= 4.5V
CC
CD74HCT4046A
High-Speed CMOS Logic
Phase-Locked-Loop with VCO
Description
The Harris CD74HC4046A and CD74HCT4046A are highspeed silicon-gate CMOS devicesthat are pin compatible with
the CD4046B of the “4000B” series. They are specified in
compliance with JEDEC standard number 7.
The CD74HC4046A and CD74HCT4046A are phase-lockedloop circuits that contain a linear voltage-controlled oscillator
(VCO) and three different phase comparators (PC1, PC2 and
PC3). A signal input and a comparator input are common to
each comparator.
The signal input can be directly coupled to large voltage signals, or indirectly coupled (with a series capacitor) to small
voltage signals. A self-bias input circuit keeps small voltage
signals within the linear region of the input amplifiers. With a
passive low-pass filter, the 4046A forms a second-order loop
PLL. The excellent VCO linearity is achieved by the use of linear op-amp techniques.
Ordering Information
TEMP.
PART NUMBER
CD74HC4046AE -55 to 125 16 Ld PDIP E16.3
CD74HCT4046AE -55 to 125 16 Ld PDIP E16.3
CD74HC4046AM -55 to 125 16 Ld SOIC M16.15
CD74HCT4046AM -55 to 125 16 Ld SOIC M16.15
NOTES:
1. When ordering, use the entire partnumber. Add the suffix 96 to
obtain the variant in the tape and reel.
2. Wafer and die for this part number is available which meets all
electrical specifications. Please contact your local sales office or
Harris customer service for ordering information.
RANGE (oC) PACKAGE
Applications
• FM Modulation and Demodulation
• Frequency Synthesis and Multiplication
• Frequency Discrimination
PKG.
NO.
• Tone Decoding
• Data Synchronization and Conditioning
• Voltage-to-Frequency Conversion
• Motor-Speed Control
CAUTION: These devices are sensitive to electrostatic discharge. Users should follow proper IC Handling Procedures.
Copyright
© Harris Corporation 1998
1
File Number 1854.1
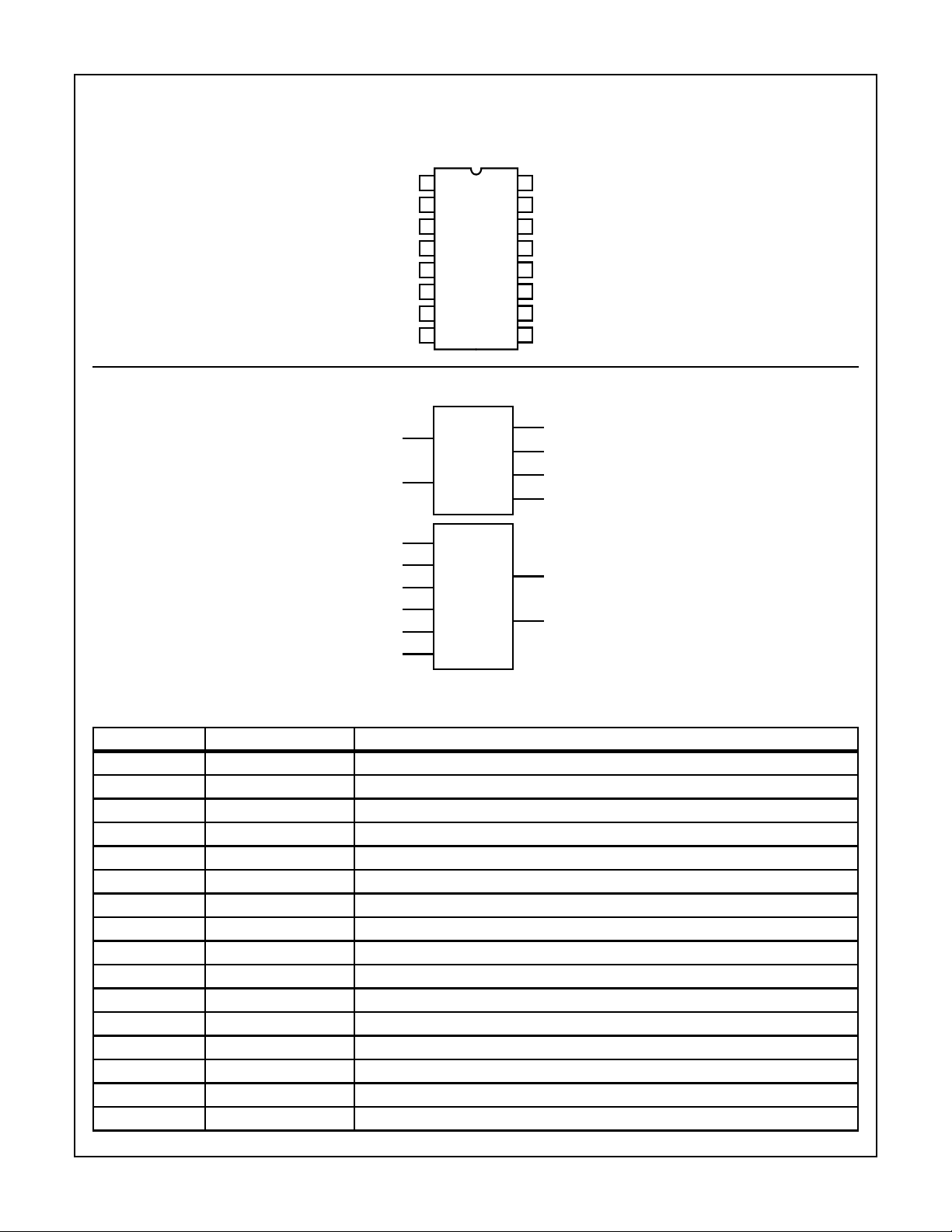
Pinout
Functional Diagram
CD74HC4046A, CD74HCT4046ACD74HC4046A, CD74HCT4046A
CD74HC4046A, CD74HCT4046A
(PDIP, SOIC)
TOP VIEW
16
PCP
PC1
COMP
VCO
COMP
SIG
OUT
OUT
OUT
INH
C1
C1
GND
IN
IN
1
2
3
IN
4
5
6
A
7
B
8
3
14
φ
V
CC
15
PC3
OUT
14
SIG
IN
13
PC2
OUT
12
R
2
11
R
1
10
DEM
OUT
9
VCO
IN
2
PC1
PC3
PC2
PCP
OUT
OUT
OUT
OUT
15
13
1
6
C1
A
VCO
C1
INH
7
B
11
R
1
12
R
2
IN
VCO
9
5
4
VCO
OUT
10
DEM
OUT
Pin Descriptions
PIN NUMBER SYMBOL NAME AND FUNCTION
1 PCP
2 PC1
3 COMP
4 VCO
OUT
OUT
IN
OUT
5 INH Inhibit Input
6C1
7C1
A
B
8 GND Ground (0V)
9 VCO
10 DEM
11 R
12 R
13 PC2
14 SIG
15 PC3
16 V
IN
OUT
1
2
OUT
IN
OUT
CC
Phase Comparator Pulse Output
Phase Comparator 1 Output
Comparator Input
VCO Output
Capacitor C1 Connection A
Capacitor C1 Connection B
VCO Input
Demodulator Output
Resistor R1 Connection
Resistor R2 Connection
Phase Comparator 2 Output
Signal Input
Phase Comparator 3 Output
Positive Supply Voltage
2
R2
R1
R5
CD74HC4046A, CD74HCT4046ACD74HC4046A, CD74HCT4046A
C1
674314
C1
C1
V
REF
R2
12
+
-
R1
11
10
DEM
OUT
-
+
B
A
VCO
-
+
INH
59
VCO
COMP
OUT
VCO
IN
SIG
IN
IN
PC1
OUT
2
PC2
PC3
OUT
PCP
OUT
V
CC
GND
p
n
OUT
15
13
1
R3
C2
S
D
Q
Q
R
D
CC
V
V
CC
D
CP
D
CP
UP
Q
Q
R
D
Q
DOWN
Q
R
D
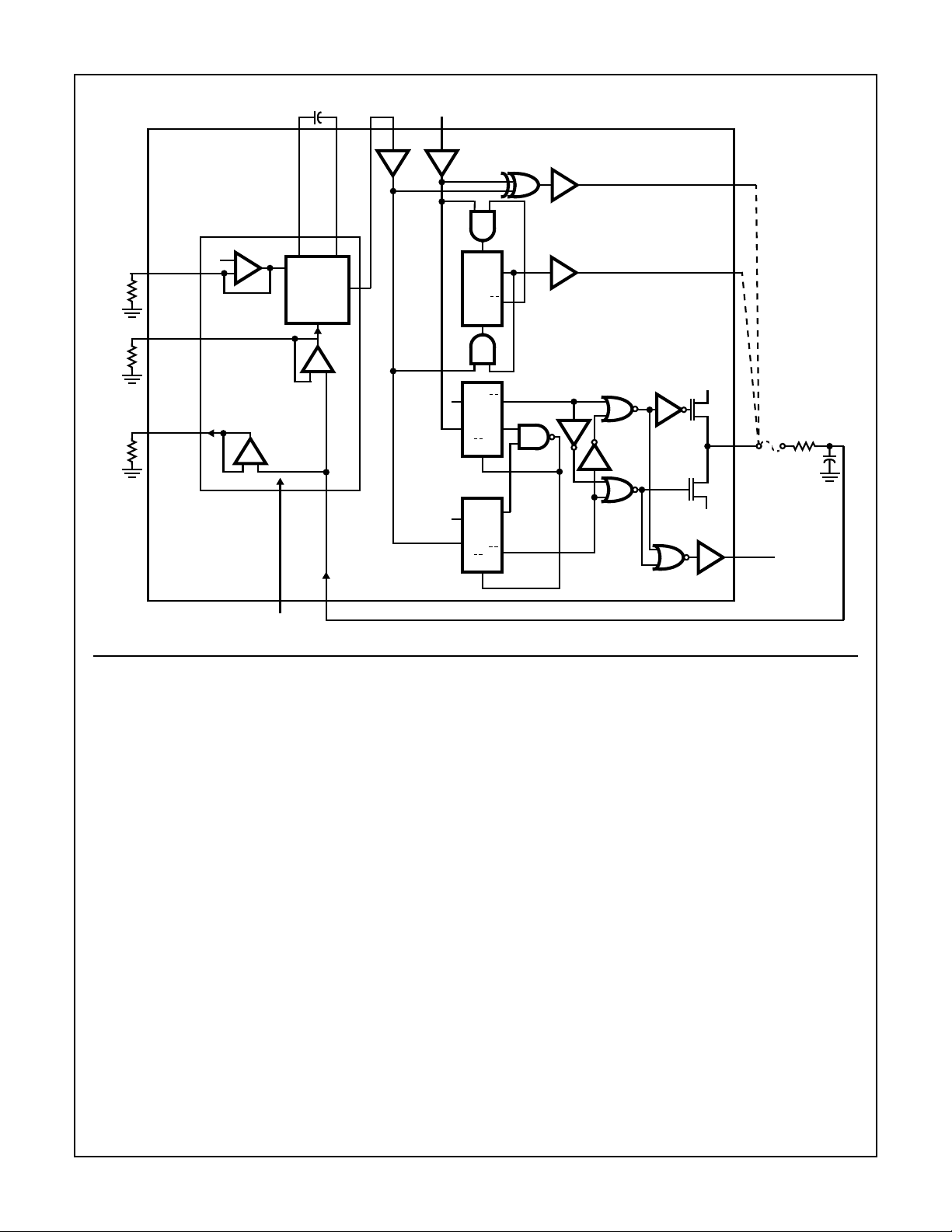
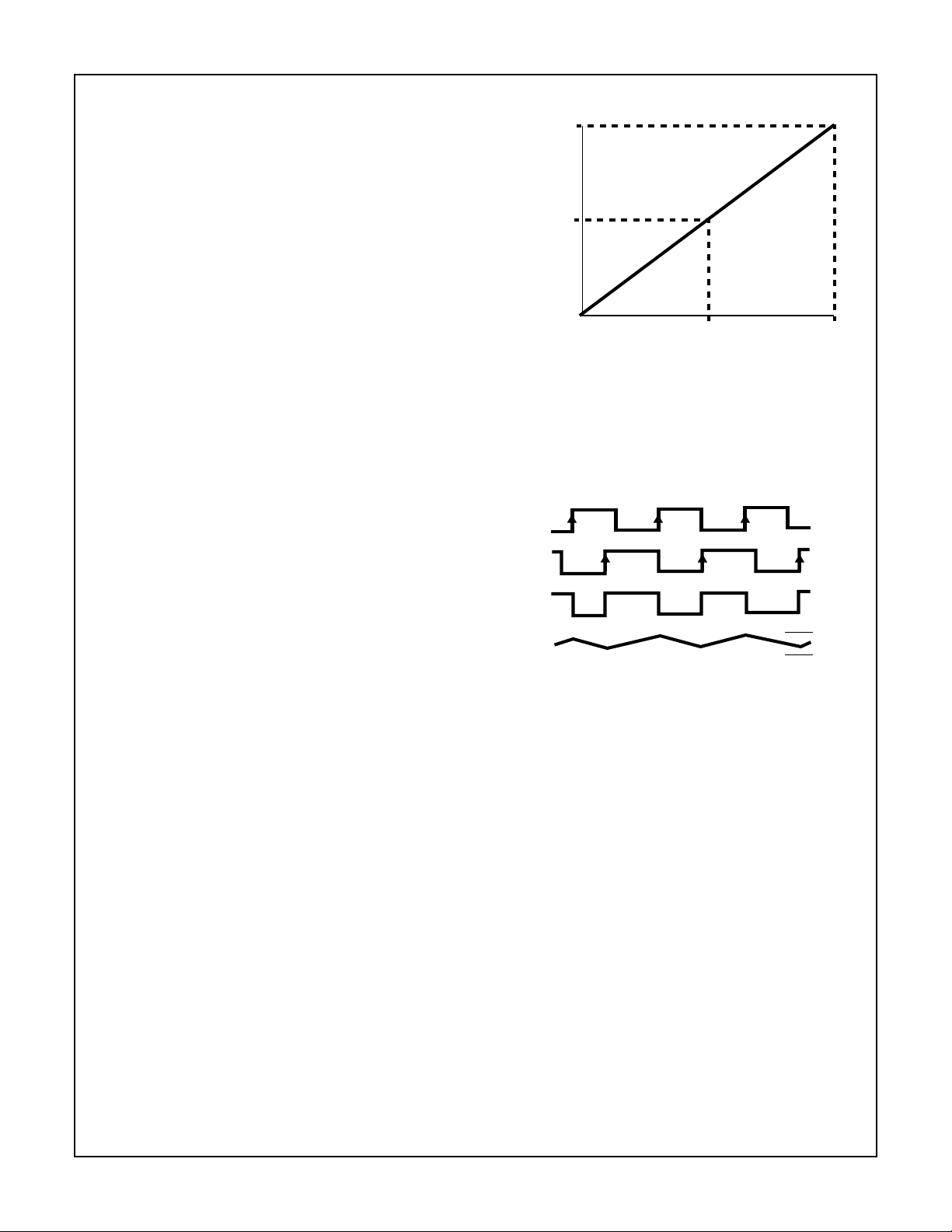
FIGURE 1. LOGIC DIAGRAM
General Description
VCO
The VCO requires one external capacitor C1 (between C1
and C1B) and one external resistor R1 (between R1and
GND) or two external resistors R1 and R2 (between R
GND, and R
and GND). Resistor R1 and capacitor C1
2
determine the frequency range of the VCO. Resistor R2
enables the VCO to have a frequency offset if required. See
logic diagram, Figure 1.
The high input impedance of the VCO simplifies the design
of low-pass filters by giving the designer a wide choice of
resistor/capacitor ranges. In order not to load the low-pass
filter, a demodulator output of the VCO input voltage is provided at pin 10 (DEM
niques where the DEM
lower than the VCO input voltage, here the DEM
equals that of the VCO input. If DEM
resistor (R
unused, DEM
(VCO
input (COMP
) should be connected from DEM
S
OUT
) can be connected directly to the comparator
OUT
), or connected via a frequency-divider. The
IN
). In contrast to conventional tech-
OUT
voltage is one threshold voltage
OUT
OUT
is used, a load
OUT
OUT
should be left open. The VCO output
VCO output signal has a guaranteed duty factor of 50%. A
LOW level at the inhibit input (INH) enables the VCO and
demodulator, while a HIGH level turns both off to minimize
standby power consumption.
and
1
voltage
to GND; if
Phase Comparators
The signal input (SIG
A
) can be directly coupled to the self-
IN
biasing amplifier at pin 14, provided that the signal swing is
between the standard HC family input logic levels. Capacitive coupling is required for signals with smaller swings.
Phase Comparator 1 (PC1)
This is an Exclusive-OR network. The signal and comparator
input frequencies (f
) must have a 50% duty factor to obtain
i
the maximum locking range. The transfer characteristic of
PC1, assuming ripple (f
V
DEMOUT
=(VCC/π)(φSIGIN- φCOMPIN) where V
is the demodulator output at pin 10; V
= 2fi) is suppressed, is:
r
DEMOUT=VPC1OUT
(via low-pass filter).
The average output voltage from PC1, fed to the VCO input
via the low-pass filter and seen at the demodulator output at
pin 10 (V
DEMOUT
of signals (SIG
shown in Figure 2. The average of V
), is the resultant of the phase differences
) and the comparator input (COMPIN)as
IN
is equal to 1/2 V
DEM
when there is no signal or noise at SIGIN, and with this input
the VCO oscillates at the center frequency (f
forms for the PC1 loop locked at f
are shown in Figure 3.
o
). Typical wave-
o
DEMOUT
CC
3
CD74HC4046A, CD74HCT4046ACD74HC4046A, CD74HCT4046A
The frequency capture range (2f
) is defined as the fre-
C
quency range of input signals on which the PLL will lock if it
was initially out-of-lock. The frequency lock range (2f
)is
L
defined as the frequency range of input signals on which the
loop will stay locked if it was initially in lock. The capture
range is smaller or equal to the lock range.
With PC1, the capture range depends on the low-pass filter
characteristics and can be made as large as the lock range.
This configuration retains lock behavior even with very noisy
input signals. Typical of this type of phase comparator is that
it can lock to input frequencies close to the harmonics of the
VCO center frequency.
V
CC
V
DEMOUT (AV)
1/2 V
CC
0
o
0
o
φ
90
DEMOUT
180
o
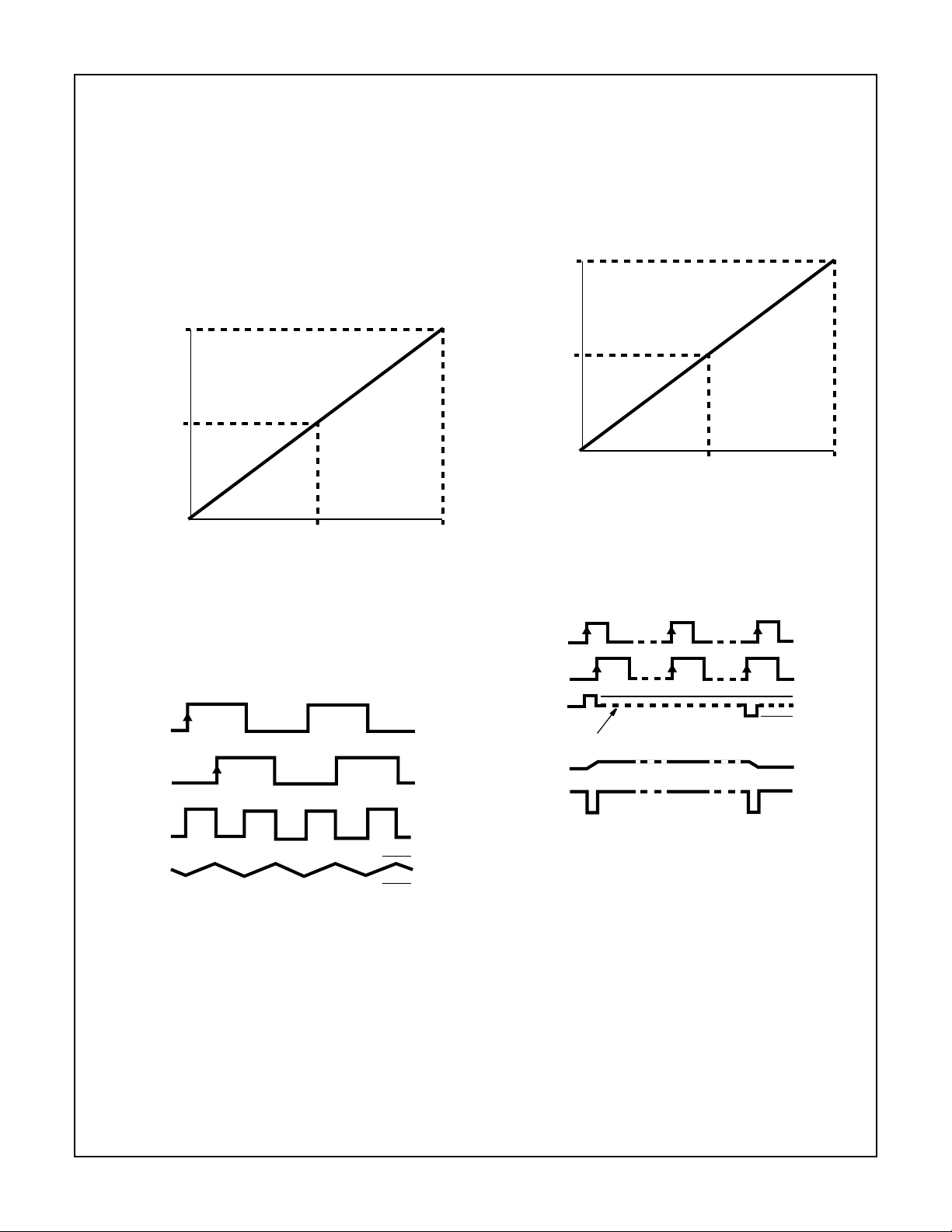
FIGURE 2. PHASE COMPARATOR1: AVERAGE OUTPUT
VOLTAGE vs INPUT PHASE DIFFERENCE:
SIG
COMP
VCO
PC1
VCO
OUT
OUT
IN
IN
IN
V
DEMOUT
PIN); φ
= V
DEMOUT
= (VCC/π) (φSIGIN - φCOM-
PC1OUT
=(φSIGIN - φCOMPIN)
V
CC
GND
FIGURE 3. TYPICAL WAVEFORMS FOR PLL USING PHASE
COMPARATOR 1, LOOP LOCKED AT f
o
Phase Comparator 2 (PC2)
This is a positive edge-triggered phase and frequency detector. When the PLL is using this comparator, the loop is controlled by positive signal transitions and the duty factors of
SIG
and COMPINare not important. PC2 comprises two
IN
D-type flip-flops, control-gating and a three-state output
stage. The circuit functions as an up-down counter (Figure
1) where SIG
count. The transfer function of PC2, assuming ripple (f
causes an up-count and COMPINa down-
IN
r=fi
is suppressed, is:
V
DEMOUT
MOUT
V
PC2OUT
=(VCC/4π)(φSIGIN- φCOMPIN) where V
is the demodulator output at pin 10; V
(via low-pass filter).
DEMOUT
The average output voltage from PC2, fed to the VCO via the
low-pass filter and seen at the demodulator output at pin 10
(V
DEMOUT
SIG
for the PC2 loop locked at f
V
DEMOUT (AV)
FIGURE 4. PHASE COMPARATOR 2: AVERAGE OUTPUT
FIGURE 5. TYPICAL WAVEFORMS FOR PLL USING PHASE
When the frequencies of SIG
the phase of SIG
driver at PC2
the phase difference (φ
), is the resultant of the phase differences of
and COMPINas shown in Figure 4. Typical waveforms
IN
COMP
VCO
PC2
PCP
V
CC
1/2 V
CC
0
o
-360
VOLTAGE vs INPUT PHASE DIFFERENCE:
V
DEMOUT
PIN); φ
DEMOUT
SIG
IN
IN
OUT
OUT
HIGH IMPEDANCE OFF - STATE
VCO
IN
OUT
COMPARATOR 2, LOOP LOCKED AT f
leads that of COMPIN, the p-type output
IN
is held “ON” for a time corresponding to
OUT
are shown in Figure 5.
o
0
= V
= (VCC/4π) (φSIGIN - φCOM-
PC2OUT
=(φSIGIN - φCOMPIN)
and COMPINare equal but
IN
DEMOUT
). When the phase of SIG
o
φ
DEMOUT
o
lags that of COMPIN, the n-type driver is held “ON”.
When the frequency of SIG
is higher than that of COMPIN,
IN
the p-type output driver is held “ON” for most of the input signal cycle time, and for the remainder of the cycle both n- and
p-type drivers are “OFF” (three-state). If the SIG
is lower than the COMP
frequency, then it is the n-type
IN
frequency
IN
driver that is held “ON” for most of the cycle. Subsequently,
the voltage at the capacitor (C2) of the low-pass filter connected to PC2
)
inputs are equal in both phase and frequency. At this stable
varies until the signal and comparator
OUT
V
CC
GND
360
DE-
=
o
IN
4
CD74HC4046A, CD74HCT4046A
point the voltage on C2 remains constant as the PC2 output
is in three-state and the VCO input at pin 9 is a high impedance. Also in this condition, the signal at the phase comparator pulse output (PCP
used for indicating a locked condition.
Thus, for PC2, no phase difference exists between SIG
and COMPINover the full frequency range of the VCO.
Moreover, the power dissipation due to the low-pass filter is
reduced because both p- and n-type drivers are “OFF” for
most of the signal input cycle. It should be noted that the
PLL lock range for this type of phase comparator is equal to
the capture range and is independent of the low-pass filter.
With no signal present at SIG
to its lowest frequency.
) is a HIGH level and so can be
OUT
, the VCO adjusts, via PC2,
IN
IN
V
DEMOUT (AV)
1/2 V
V
CC
CC
0
o
0
180
o
φ
DEMOUT
360
o
Phase Comparator 3 (PC3)
This is a positive edge-triggered sequential phase detector using an RS-type flip-flop. When the PLL is using this
comparator, the loop is controlled by positive signal transitions and the duty factors of SIG
and COMPINare not
IN
important. The transfer characteristic of PC3, assuming
ripple (f
V
MOUT
V
= fi) is suppressed, is:
r
DEMOUT
=(VCC/2p) (fSIGIN- fCOMPIN) where V
is the demodulator output at pin 10; V
PC3OUT
(via low-pass filter).
DE-
DEMOUT
The average output from PC3, fed to the VCO via the lowpass filter and seen at the demodulator at pin 10 (V
), is the resultant of the phase differences of SIG
MOUT
DE-
IN
and COMPINas shown in Figure 6. Typical waveforms for
the PC3 loop locked at f
are shown in Figure 7.
o
The phase-to-output response characteristic of PC3 (Figure
6) differs from that of PC2 in that the phase angle between
SIG
and COMPINvaries between 0oand 360oand is 180
IN
at the center frequency. Also PC3 gives a greater voltage
swing than PC2 for input phase differences but as a consequence the ripple content of the VCO input signal is higher.
With no signal present at SIG
, the VCO adjusts, via PC3,
IN
to its highest frequency.
The only difference between the HC and HCT versions is the
input level specification of the INH input. This input disables
the VCO section. The comparator’s sections are identical, so
that there is no difference in the SIG
(pin 14) or COMP
IN
IN
(pin 3) inputs between the HC and the HCT versions.
FIGURE 6. PHASE COMPARATOR3: AVERAGE OUTPUT
VOLTAGE vs INPUT PHASE DIFFERENCE:
V
DEMOUT
PIN); φ
=
o
SIG
IN
COMP
IN
VCO
OUT
PC3
OUT
VCO
IN
FIGURE 7. TYPICAL WAVEFORMS FOR PLL USING PHASE
COMPARATOR 3, LOOP LOCKED AT f
= V
DEMOUT
= (VCC/2π) (φSIGIN - φCOM-
PC3OUT
= (φSIGIN - φCOMPIN)
V
CC
GND
o
5
CD74HC4046A, CD74HCT4046ACD74HC4046A, CD74HCT4046A
Absolute Maximum Ratings Thermal Information
DC Supply Voltage, VCC. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . -0.5V to 7V
DC Input Diode Current, I
IK
For VI < -0.5V or VI > VCC + 0.5V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .±20mA
DC Output Diode Current, I
OK
For VO < -0.5V or VO > VCC + 0.5V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .±20mA
DC Drain Current, per Output, I
O
For -0.5V < VO < VCC + 0.5V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .±25mA
DC Output Source or Sink Current per Output Pin, I
O
For VO > -0.5V or VO < VCC + 0.5V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .±25mA
DC VCC or Ground Current, ICC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .±50mA
Operating Conditions
Temperature Range, TA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . -55oC to 125oC
Supply Voltage Range, V
HC Types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2V to 6V
HCT Types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4.5V to 5.5V
DC Input or Output Voltage, VI, VO . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0V to V
Input Rise and Fall Time
2V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1000ns (Max)
4.5V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 500ns (Max)
6V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 400ns (Max)
CAUTION: Stresses above those listed in “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress only rating and operation
of the device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the operational sections of this specification is not implied.
NOTE:
3. θJA is measured with the component mounted on an evaluation PC board in free air.
CC
Thermal Resistance (Typical, Note 3) θJA (oC/W)
PDIP Package. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
SOIC Package. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
Maximum Junction Temperature. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .150oC
Maximum Storage Temperature Range . . . . . . . . . .-65oC to 150oC
Maximum Lead Temperature (Soldering 10s). . . . . . . . . . . . .300oC
(SOIC - Lead Tips Only)
CC
DC Electrical Specifications
PARAMETER SYMBOL
HC TYPES
VCO SECTION
INH High Level Input
Voltage
INH Low Level Input
Voltage
VCO
High Level
OUT
Output Voltage
CMOS Loads
VCO
High Level
OUT
Output Voltage
TTL Loads
VCO
OUT
Low Level
Output Voltage
CMOS Loads
VCO
OUT
Low Level
Output Voltage
TTL Loads
C1A, C1B Low Level
Output Voltage
(Test Purposes Only)
V
IH
V
IL
V
OH
V
OL
V
OL
TEST
CONDITIONS
V
CC
(V)
25oC -40oC TO 85oC -55oCTO125oC
UNITSVI(V) IO(mA) MIN TYP MAX MIN MAX MIN MAX
- - 3 2.1 - - 2.1 - 2.1 - V
4.5 3.15 - - 3.15 - 3.15 - V
6 4.2 - - 4.2 - 4.2 - V
- - 3 - - 0.9 - 0.9 - 0.9 V
4.5 - - 1.35 - 1.35 - 1.35 V
6 - - 1.8 - 1.8 - 1.8 V
VIHor VIL-0.02 3 2.9 - - 2.9 - 2.9 - V
-0.02 4.5 4.4 - - 4.4 - 4.4 - V
-0.02 6 5.9 - - 5.9 - 5.9 - V
- - ---- - - - V
-4 4.5 3.98 - - 3.84 - 3.7 - V
-5.2 6 5.48 - - 5.34 - 5.2 - V
VIHor VIL0.02 2 - - 0.1 - 0.1 - 0.1 V
0.02 4.5 - - 0.1 - 0.1 - 0.1 V
0.02 6 - - 0.1 - 0.1 - 0.1 V
- - ---- - - - V
4 4.5 - - 0.26 - 0.33 - 0.4 V
5.2 6 - - 0.26 - 0.33 - 0.4 V
VILor V
4 4.5 - - 0.40 - 0.47 - 0.54 V
IH
5.2 6 - - 0.40 - 0.47 - 0.54 V
6
CD74HC4046A, CD74HCT4046A
DC Electrical Specifications (Continued)
TEST
PARAMETER SYMBOL
INH VCOIN Input
Leakage Current
CONDITIONS
I
VCC or
I
GND
V
CC
(V)
-6--±0.1 - ±1-±1µA
R1 Range (Note 4) - - - 4.5 3 - 300 - - - - kΩ
R2 Range (Note 4) - - - 4.5 3 - 300 - - - - kΩ
C1 Capacitance
Range
---3--No
4.5 - - - - - - pF
6-- ----pF
VCOIN Operating
Voltage Range
- Over the range
specified for R1 for
LinearitySeeFigure
10, and 35 - 38
3 1.1 - 1.9 - - - - V
4.5 1.1 - 3.2 - - - - V
6 1.1 - 4.6 - - - - V
(Note 5)
PHASE COMPARATOR SECTION
SIGIN, COMP
IN
DC Coupled
High-Level Input
Voltage
SIGIN, COMP
IN
DC Coupled
Low-Level Input
Voltage
PCP
, PCn OUT
OUT
High-Level Output
Voltage
CMOS Loads
PCP
, PCn OUT
OUT
High-Level Output
Voltage
V
IH
- - 2 1.5 - - 1.5 - 1.5 - V
4.5 3.15 - - 3.15 - 3.15 - V
6 4.2 - - 4.2 - 4.2 - V
V
IL
- - 2 - - 0.5 - 0.5 - 0.5 V
4.5 - - 1.35 - 1.35 - 1.35 V
6 - - 1.8 - 1.8 - 1.8 V
V
VILor VIH-0.02 2 1.9 - - 1.9 - 1.9 - V
OH
4.5 4.4 - - 4.4 - 4.4 - V
6 5.9 - - 5.9 - 5.9 - V
V
OH
VILor V
-4 4.5 3.98 - - 3.84 - 3.7 - V
IH
-5.2 6 5.48 - - 5.34 - 5.2 - V
TTL Loads
PCP
Low-Level Output
Voltage
CMOS Loads
PCP
Low-Level Output
Voltage
, PCn OUT
OUT
, PCn OUT
OUT
V
VILor VIH0.02 2 - - 0.1 - 0.1 - 0.1 V
OL
4.5 - - 0.1 - 0.1 - 0.1 V
6 - - 0.1 - 0.1 - 0.1 V
V
OL
VILor V
4 4.5 - - 0.26 - 0.33 - 0.4 V
IH
5.2 6 - - 0.26 - 0.33 - 0.4 V
TTL Loads
SIGIN, COMPINInput
Leakage Current
I
VCC or
I
GND
-2--±3-±4-±5µA
3--±7-±9-±11 µA
4.5 - - ±18 - ±23 - ±29 µA
6--±30 - ±38 - ±45 µA
PC2
Three-State
OUT
I
OZ
VILor V
-6--±0.5 - ±5-±10 µA
IH
Off-State Current
SIGIN, COMPINInput
Resistance
R
I
VI at Self-Bias
Operation Point:
∆VI, 0.5V,
See Figure 10
3 - 800 - - - - - kΩ
4.5 - 250 - - - - - kΩ
6 - 150 - - - - - kΩ
DEMODULATOR SECTION
Resistor Range R
S
at RS > 300kΩ
Leakage Current
Can Influence
V
DEMOUT
3 50 - 300 - - - - kΩ
4.5 50 - 300 - - - - kΩ
6 50 - 300 - - - - kΩ
25oC -40oC TO 85oC -55oCTO125oC
UNITSVI(V) IO(mA) MIN TYP MAX MIN MAX MIN MAX
----pF
Limit
7

CD74HC4046A, CD74HCT4046A
DC Electrical Specifications (Continued)
TEST
PARAMETER SYMBOL
OffsetVoltage VCO
to V
DEM
IN
V
OFF
CONDITIONS
VI = V
V
VCO IN
CC
2
Values Taken Over
V
CC
(V)
=
3-±30 - - - - - mV
4.5 - ±20 - - - - - mV
6-±10 - - - - - mV
RS Range
See Figure 24
Dynamic Output
Resistance at
DEM
OUT
Quiescent Device
Current
I
R
CC
V
V
CC
DEMOUT
D
2
=3-25-----Ω
4.5 - 25 - - - - - Ω
6 - 25 - - - - - Ω
Pins 3, 5 and 14
6 - - 8 - 80 - 160 µA
at VCC Pin 9 at
GND, I1 at Pins 3
and 14 to be
excluded
HCT TYPES
VCO SECTION
INH High Level Input
Voltage
INH Low Level Input
Voltage
VCO
High Level
OUT
V
IH
- - 4.5 to
5.5
V
IL
- - 4.5 to
5.5
V
VIHor VIL-0.02 4.5 4.4 - - 4.4 - 4.4 - V
OH
Output Voltage
CMOS Loads
VCO
High Level
OUT
-4 4.5 3.98 - - 3.84 - 3.7 - V
Output Voltage
TTL Loads
VCO
OUT
Low Level
V
VIHor VIL0.02 4.5 - - 0.1 - 0.1 - 0.1 V
OL
Output Voltage
CMOS Loads
VCO
OUT
Low Level
4 4.5 - - 0.26 - 0.33 - 0.4 V
Output Voltage
TTL Loads
C1A, C1B Low Level
V
OL
VIHor V
4 4.5 - - 0.40 - 0.47 - 0.54 V
IL
Output Voltage
(Test Purposes Only)
INH VCOIN Input
Leakage Current
I
I
Any Voltage
Between VCC and
5.5 - ±0.1 - ±1-±1µA
GND
R1 Range (Note 4) - - - 4.5 3 - 300 - - - - kΩ
R2 Range (Note 4) - - - 4.5 3 - 300 - - - - kΩ
C1 Capacitance
- - - 4.5 0 - No
Range
VCOIN Operating
Voltage Range
- Over the range
specified for R1 for
4.5 1.1 - 3.2 - - - - V
LinearitySeeFigure
10, and 35 - 38
(Note 5)
PHASE COMPARATOR SECTION
SIGIN, COMP
DC Coupled
IN
V
IH
- - 4.5 to
5.5
High-Level Input
Voltage
25oC -40oC TO 85oC -55oCTO125oC
UNITSVI(V) IO(mA) MIN TYP MAX MIN MAX MIN MAX
2--2- 2 - V
- - 0.8 - 0.8 - 0.8 V
----pF
Limit
2--2- 2 - V
8

CD74HC4046A, CD74HCT4046A
DC Electrical Specifications (Continued)
TEST
PARAMETER SYMBOL
SIGIN, COMP
IN
DC Coupled
CONDITIONS
V
IL
- - 4.5 to
V
CC
(V)
5.5
Low-Level Input
Voltage
PCP
, PCn OUT
OUT
V
OH
VILor V
- 4.5 4.4 - - 4.4 - 4.4 - V
IH
High-Level Output
Voltage
CMOS Loads
PCP
, PCn OUT
OUT
V
OH
VILor V
- 4.5 3.98 - - 3.84 - 3.7 - V
IH
High-Level Output
Voltage
TTL Loads
PCP
, PCn OUT
OUT
V
OL
VILor V
- 4.5 - - 0.1 - 0.1 - 0.1 V
IH
Low-Level Output
Voltage
CMOS Loads
PCP
, PCn OUT
OUT
V
OL
VILor V
- 4.5 - - 0.26 - 0.33 - 0.4 V
IH
Low-Level Output
Voltage
TTL Loads
SIGIN, COMPINInput
Leakage Current
I
I
Any
- 5.5 - - ±30 ±38 ±45 µA
Voltage
Between
VCCand
GND
PC2
Three-State
OUT
I
OZ
VILor V
- 5.5 - - ±0.5 ±5- -±10 µA
IH
Off-State Current
SIGIN, COMPINInput
Resistance
R
I
VI at Self-Bias
4.5 - 250 - - - - - kΩ
Operation Point:
∆VI, 0.5V,
See Figure 10
DEMODULATOR SECTION
Resistor Range R
S
at RS > 300kΩ
4.5 5 - 300 - - - - kΩ
Leakage Current
Can Influence
V
DEM OUT
OffsetVoltage VCO
to V
DEM
V
IN
OFF
V
VI = V
CC
VCO IN
=
4.5 - ±20 - - - - - mV
2
Values tak en over
RS Range
See Figure 24
Dynamic Output
Resistance at
DEM
OUT
Quiescent Device
Current
Additional Quiescent
Device Current Per
Input Pin: 1 Unit Load
R
D
I
CC
∆I
CC
Note 6
V
DEM OUT
V
CC
2
VCC or
GND
V
CC
-2.1
Excluding
= 4.5 - 25 - - - - - Ω
- 5.5 - - 8 - 80 - 160 µA
- 4.5 to
5.5
Pin 5
NOTES:
4. The value for R1 and R2 in parallel should exceed 2.7kΩ.
5. The maximum operating voltage can be as high as VCC -0.9V, however, this may result in an increased offset voltage.
6. For dual-supply systems theoretical worst case (VI = 2.4V, VCC = 5.5V) specification is 1.8mA.
25oC -40oC TO 85oC -55oCTO125oC
- - 0.8 - 0.8 - 0.8 V
- 100 360 - 450 - 490 µA
UNITSVI(V) IO(mA) MIN TYP MAX MIN MAX MIN MAX
9

CD74HC4046A, CD74HCT4046A
HCT Input Loading Table
INPUT UNIT LOADS
INH 1
NOTE: Unit load is ∆ICClimit specific in DC Electrical Specifications
Table, e.g., 360µA max. at 25oC.
Switching Specifications C
PARAMETER SYMBOL
HC TYPES
PHASE COMPARATOR SECTION
Propagation Delay t
SIGIN, COMPIN to PCI
, COMPIN to PCP
SIG
IN
SIG
, COMPIN to PC3
IN
Output Transition Time t
Output Enable Time, SIG
COMPIN to PC2
OUT
Output Disable Time, SIG
COMPIN to PC2
OUT
ACCoupled Input Sensitivity (
) at SIGIN or COMP
P
VCO SECTION
Frequency Stability with
Temperature Change
Maximum Frequency f
OUT
OUT
OUT
,
IN
,
IN
P-
IN
= 50pF, Input tr, tf= 6ns
L
TEST
CONDITIONS VCC(V)
, t
PLH
PHL
, t
THL
TLH
t
, t
PZH
PZL
t
, t
PHZ
PLZ
V
I(P-P)
∆f
∆T
MAX
R1 = 100kΩ,
R
= ∞
2
C1 = 50pF
R1 = 3.5kΩ
R
= ∞
2
C
= 0pF
1
R1 = 9.1kΩ
R
= ∞
2
25
o
C
-40oC TO
85oC
-55oC TO
125oC
UNITSMIN TYP MAX MIN MAX MIN MAX
2 - - 200 - 250 - 300 ns
4.5 - - 40 - 50 - 60 ns
6 - - 34 - 43 - 51 ns
2 - - 300 - 375 - 450 ns
4.5 - - 60 - 75 - 90 ns
6 - - 51 - 64 - 77 ns
2 - - 245 - 305 - 307 ns
4.5 - - 49 - 61 - 74 ns
6 - - 42 - 52 - 63 ns
2 - - 75 - 95 - 110 ns
4.5 - - 15 - 19 - 22 ns
6 - - 13 - 16 - 19 ns
2 - - 265 - 330 - 400 ns
4.5 - - 53 - 66 - 80 ns
6 - - 45 - 56 - 68 ns
2 - - 315 - 395 - 475 ns
4.5 - - 63 - 79 - 95 ns
6 - - 54 - 67 - 81 ns
3 - 11 - - - - - mV
4.5 - 15 - - - - - mV
6 - 33 - - - - - mV
3 - - TYP
4.5 - - - - %/
0.11
--%/
6- - --%/
o
C
o
C
o
C
3 - 24 - - - - - MHz
4.5 - 24 - - - - - MHz
6 - 24 - - - - - MHz
3 - 38 - - - - - MHz
4.5 - 38 - - - - - MHz
6 - 38 - - - - - MHz
10

CD74HC4046A, CD74HCT4046A
Switching Specifications C
= 50pF, Input tr, tf= 6ns (Continued)
L
TEST
PARAMETER SYMBOL
CONDITIONS VCC(V)
Center Frequency C1 = 40pF
R1 = 3kΩ
R
= ∞
2
VCOIN =
VCC/2
Frequency Linearity ∆f
VCO
R1 = 100kΩ
R
= ∞
2
C1 = 100pF
Offset Frequency R
= 220kΩ
2
C1 = 1nF
DEMODULATOR SECTION
V
OUT VS fIN
R1 = 100kΩ
R
= ∞
2
C1 = 100pF
RS = 10kΩ
R3 = 100kΩ
C2 = 100pF
HCT TYPES
PHASE COMPARATOR SECTION
Propagation Delay t
SIGIN, COMPIN to PCI
SIG
, COMPIN to PCP
IN
, COMPIN to PC3
SIG
IN
Output Transition Time t
Output Enable Time, SIG
COMPIN to PC2
OUT
IN
Output Disable Time, SIG
COMPIN to PCZ
OUT
AC Coupled Input Sensitivity
) at SIGIN or COMP
(
P-P
IN
PHL,tPLH
OUT
OUTtPHL,tPLH
OUTtPHL,tPLH
, t
TLH
,
t
, t
PZH
,
t
PHZ
, t
IN
CL = 50pF 4.5 - - 45 - 56 - 68 ns
CL = 50pF 4.5 - - 68 - 85 - 102 ns
CL = 50pF 4.5 - - 58 - 73 - 87 ns
THLCL
PZL
PLZ
= 50pF 4.5 - - 15 - 19 - 22 ns
CL = 50pF 4.5 - - 60 - 75 - 90 pF
CL = 50pF 4.5 - - 68 - 85 - 102 pF
V
I(P-P)
VCO SECTION
Frequency Stability with
Temperature Change
Maximum Frequency f
∆f
∆T
MAX
R1 = 100kΩ,
R
= ∞
2
C1 = 50pF
R1 = 3.5kΩ
R
= ∞
2
C
= 0pF
1
R1 = 9.1kΩ
R
= ∞
2
Center Frequency C
= 40pF
1
R1 = 3kΩ
R
= ∞
2
VCOIN =
VCC/2
25
o
C
-40oC TO
85oC
-55oC TO
125oC
UNITSMIN TYP MAX MIN MAX MIN MAX
3 7 10 - - - - - MHz
4.5 12 17 - - - - - MHz
6 14 21 - - - - - MHz
3 - 0.4 - - - - - %
4.5 - 0.4 - - - - - %
6 - 0.4 - - - - - %
3 - 400 - - - - - kHz
4.5 - 400 - - - - - kHz
6 - 400 - - - - - kHz
3 - - - - - - - mV/kHz
4.5 - 330 - - - - - mV/kHz
6 - - - - - - - mV/kHz
3 - 11 - - - - - mV
4.5 - 15 - - - - - mV
6 - 33 - - - - - mV
4.5 - 0.11 - - - - - %/oC
4.5 - 24 - - - - - MHz
4.5 - 38 - - - - - MHz
3 7 10 - - - - - MHz
4.5 12 17 - - - - - MHz
6 14 21 - - - - - MHz
11

CD74HC4046A, CD74HCT4046A
Switching Specifications C
= 50pF, Input tr, tf= 6ns (Continued)
L
PARAMETER SYMBOL
Frequency Linearity ∆f
VCO
Offset Frequency R
DEMODULATOR SECTION
V
OUT VS fIN
Test Circuits and Waveforms
SIGINCOMP
INPUTS
PCP
PC3
OUT
OUT
IN
PC1
OUT
OUTPUTS
t
TLH
t
PHL
V
S
V
S
TEST
CONDITIONS VCC(V)
R1 = 100kΩ
R
= ∞
2
4.5 - 0.4 - - - - - %
C1 = 100pF
= 220kΩ
2
4.5 - 400 - - - - - kHz
C1 = 1nF
R1 = 100kΩ
R
= ∞
2
4.5 - 330 - - - - - mV/kHz
C1 = 100pF
RS = 10kΩ
R3 = 100kΩ
C2 = 100pF
t
PHL
t
TLH
SIG
IN
INPUTS
COMP
INPUTS
PC2
OUT
OUTPUT
25
o
C
-40oC TO
85oC
-55oC TO
125oC
UNITSMIN TYP MAX MIN MAX MIN MAX
V
S
IN
t
PZH
V
S
t
PZH
90%
V
S
t
PZL
t
PZL
10%
FIGURE 8. INPUT TO OUTPUT PROPAGATION DELAYSAND
OUTPUT TRANSITION TIMES
Typical Performance Curves
I
I
∆V
I
SELF-BIAS OPERATING POINT
V
I
FIGURE 10. TYPICAL INPUT RESISTANCE CURVE AT SIGIN,
COMP
IN
FIGURE 9. THREE STATE ENABLE AND DISABLE TIMES FOR
PC2
OUT
800
700
600
500
(OHMS)
MIN
400
300
OR R2
MIN
200
R1
100
0
01 2 3 4 56
SUPPLY VOLTAGE, V
CC
(V)
FIGURE 11. HC/HCT4046A R1 (MIN) OR R2 (MIN) vs SUPPLY
VOLTAGE (VCC)
12

CD74HC4046A, CD74HCT4046A
Typical Performance Curves
8
10
7
10
6
10
5
10
4
10
3
10
2
10
CENTER FREQUENCY (Hz)
VCOIN = 0.5 V
10
VCC= 4.5V
1
110
CC
2
10
3
10
(Continued)
R1 = 2.2K
R1 = 22K
R1 = 220K
R1 = 2.2M
R1 = 11M
4
10
5
10
10
CAPACITANCE, C1 (pF)
FIGURE 12. HC4046A TYPICAL CENTER FREQUENCY vs R1,
C1 (VCC = 4.5V)
8
10
7
10
6
10
5
10
4
10
3
10
2
10
VCOIN = 0.5 V
CENTER FREQUENCY (Hz)
VCC= 3.0V
10
R2 = OPEN
1
110
CC
2
10
3
10
CAPACITANCE, C1 (pF)
10
4
R1 = 1.5K
R1 = 15K
R1 = 150K
R1 = 1.5M
R1 = 7.5M
5
10
10
8
10
7
10
6
10
5
10
4
10
3
10
2
10
CENTER FREQUENCY (Hz)
VCOIN = 0.5 V
10
CC
VCC= 6.0V
6
1
110
2
10
3
10
4
10
CAPACITANCE, C1 (pF)
FIGURE 13. HC4046A TYPICAL CENTER FREQUENCY vs R1,
C1 (VCC = 6V)
8
10
7
10
6
10
5
10
4
10
3
10
2
10
CENTER FREQUENCY (Hz)
VCOIN = 0.5 V
10
VCC= 4.5V
6
1
110
CC
2
10
3
10
CAPACITANCE, C1 (pF)
4
10
R1 =3K
R1 = 30K
R1 =330K
R1 = 3M
R1 = 15M
5
10
R1 = 2.2K
R1 = 22K
R1 = 220K
R1 = 2.2M
R1 = 11M
5
10
6
10
6
10
FIGURE 14. HC4046A TYPICAL CENTER FREQUENCY vs R1,
C1 (VCC = 3V, R2 = OPEN)
8
10
7
10
6
10
5
10
4
10
3
10
2
10
CENTER FREQUENCY (Hz)
VCOIN = 0.5 V
10
VCC= 5.5V
1
110
CC
2
10
3
10
10
4
R1 = 3K
R1 = 30K
R1 = 300K
R1 = 3M
R1 = 15M
5
10
10
CAPACITANCE, C1 (pF)
FIGURE 16. HCT4046A TYPICAL CENTER FREQUENCY vs R1,
C1 (VCC = 5.5V)
FIGURE 15. HCT4046A TYPICAL CENTER FREQUENCY vs R1,
C1 (VCC = 4.5V)
140
120
C1 = 50pF
R1 = 1.5M
VCC = 6V
100
VCC = 4.5V
80
60
VCO FREQUENCY (kHz)
40
6
20
01 2 3456
VCC = 3V
VCO
(V)
IN
FIGURE 17. HC4046A TYPICAL VCO FREQUENCY vs VCO
(R1 = 1.5MΩ, C1 = 50pF)
13
IN
CD74HC4046A, CD74HCT4046A
Typical Performance Curves
90
C1 = 0.1µF
80
R1 = 1.5M
70
60
50
40
30
VCO FREQUENCY (Hz)
20
10
01 23 45 6
VCC = 3V
VCC = 4.5V
VCO
IN
(Continued)
VCC = 6V
(V)
FIGURE 18. HC4046A TYPICAL VCO FREQUENCY vs VCO
(R1 = 1.5MΩ, C1 = 0.1µF)
18
C1 = 0.1µF
16
R1 = 5.6k
14
12
10
8
6
VCO FREQUENCY (kHz)
4
2
01 23 45 6
VCC = 3V
VCO
VCC = 4.5V
(V)
IN
VCC = 6V
FIGURE 20. HC4046A TYPICAL VCO FREQUENCY vs VCO
(R1 = 5.6kΩ, C1 = 0.1µF)
800
C1 = 0.1µF
R1 = 150K
700
600
500
400
300
VCO FREQUENCY (Hz)
200
100
01 23 45 6
IN
FIGURE 19. HC4046A TYPICAL VCO FREQUENCY vs VCO
VCC = 3V
VCC = 4.5V
(V)
VCO
IN
VCC = 6V
IN
(R1 = 150kΩ, C1 = 0.1µF)
1400
C1 = 50pF
R1 = 150K
1200
1000
800
VCC = 3V
600
VCO FREQUENCY (kHz)
400
200
01 23 45 6
IN
FIGURE 21. HC4046A TYPICAL VCO FREQUENCY vs VCO
VCC = 4.5V
VCO
IN
(V)
VCC = 6V
IN
(R1 = 150kΩ, C1 = 0.1µF)
24
C1 = 50pF
R1 = 5.6K
20
16
12
VCO FREQUENCY (MHz)
8
4
01 23 45 6
VCC = 3V
VCC = 4.5V
VCO
IN
(V)
VCC = 6V
FIGURE 22. HC4046A TYPICAL VCO FREQUENCY vs VCO
(R1 = 5.6kΩ, C1 = 50pF)
24
VCOIN = 0.5 V
20
C1 = 50pF, VCC = 3V
R2 = OPEN
16
12
8
4
0
-4
-8
VCO FREQUENCY CHANGE, ∆f (%)
-12
-16
-75 -50 -25 0 25 50 75
IN
FIGURE 23. HC4046A TYPICAL CHANGE IN VCO FREQUENCY
CC
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE, T
R1 = 1.5M
R1 = 150K
R1 = 3K
R1 = 1.5K
100 125 150
(oC)
A
vs AMBIENT TEMPERATURE AS A FUNCTION OF
R1 (VCC = 3V)
14

CD74HC4046A, CD74HCT4046A
Typical Performance Curves
VCOIN = 0.5 V
20
C1 = 50pF, VCC = 4.5V
16
R2 = OPEN
12
8
4
0
-4
-8
VCO FREQUENCY CHANGE, ∆f (%)
-12
-75 -50 -25 0 25 50 75
CC
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE, TA (oC)
(Continued)
R1 = 2.2M
R1 = 220K
R1 = 2.2K
100 125 150
FIGURE 24. HC4046A TYPICAL CHANGE IN VCO FREQUENCY
vs AMBIENT TEMPERATURE AS A FUNCTION OF
R1 (VCC = 4.5V)
20
VCOIN = 0.5 V
C1 = 50pF, VCC = 5.5V
16
R2 = OPEN
12
8
4
0
-4
-8
VCO FREQUENCY CHANGE, ∆f (%)
-12
-75 -50 -25 0 25 50 75
CC
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE, T
R1 = 3M
R1 = 300K
R1 = 3K
100 125 150
(oC)
A
FIGURE 26. HCT4046A TYPICAL CHANGE IN VCO
FREQUENCY vs AMBIENT TEMPERATURE AS A
FUNCTION OF R1
VCOIN = 0.5 V
16
C1 = 50pF, VCC = 6.0V
12
R2 = OPEN
8
4
0
-4
-8
VCO FREQUENCY CHANGE, ∆f (%)
-12
-75 -50 -25 0 25 50 75
CC
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE, T
R1 = 3M
R1 = 300K
R1 = 3K
100 125 150
(oC)
A
FIGURE 25. HC4046A TYPICAL CHANGE IN VCO FREQUENCY
vs AMBIENT TEMPERATURE AS A FUNCTION OF
R1 (VCC = 6V)
VCOIN = 0.5 V
20
C1 = 50pF, VCC = 4.5V
16
R2 = OPEN
12
8
4
0
-4
-8
VCO FREQUENCY CHANGE, ∆f (%)
-12
-75 -50 -25 0 25 50 75
CC
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE, T
R1 = 2.2M
R1 = 220K
R1 = 2.2K
100 125 150
(oC)
A
FIGURE 27. HC4046A TYPICAL CHANGE IN VCO FREQUENCY
vs AMBIENT TEMPERATURE AS A FUNCTION OF
R1 (VCC = 4.5V)
15

CD74HC4046A, CD74HCT4046A
Typical Performance Curves
8
10
7
10
6
10
5
10
4
10
3
10
2
10
OFFSET FREQUENCY (Hz)
VCOIN = 0.5 V
10
VCC = 4.5V
1
110
CC
2
10
3
10
(Continued)
4
10
R2 = 2.2K
R2 = 22K
R2 = 220K
R2 = 2.2M
R2 = 11M
10
CAPACITANCE, C1 (pF)
FIGURE 28. HC4046A OFFSET FREQUENCY vs R2, C1
(VCC = 4.5V)
8
10
7
10
6
10
5
10
4
10
3
10
2
10
OFFSET FREQUENCY (Hz)
VCOIN = 0.5 V
10
VCC = 4.5V
1
110
CC
2
10
3
10
CAPACITANCE, C1 (pF)
10
R2 = 2.2K
R2 = 22K
R2 = 220K
R2 = 2.2M
R2 = 11M
4
10
8
10
7
10
6
10
5
10
4
10
3
10
2
10
OFFSET FREQUENCY (Hz)
VCOIN = 0.5 V
10
VCC = 3V
5
6
10
1
110
CC
2
10
3
10
10
4
R2 = 1.5K
R2 = 15K
R2 = 150K
R2 = 1.5M
R2 = 7.5M
5
10
6
10
CAPACITANCE, C1 (pF)
FIGURE 29. HC4046A OFFSET FREQUENCY vs R2, C1
(VCC = 3V)
8
10
7
10
6
10
5
10
4
10
3
10
2
10
OFFSET FREQUENCY (Hz)
VCOIN = 0.5 V
HC VCC = 6V
10
HCT V
5
6
10
1
110
CC
= 5.5V
CC
2
10
3
10
4
10
CAPACITANCE, C1 (pF)
R2 = 3K
R2 = 30K
R2 = 300K
R2 = 3M
R2 = 15M
5
10
6
10
FIGURE 30. HCT4046A OFFSET FREQUENCY vs R2, C1
(VCC = 4.5V)
PIN 9 = 0.95 VCC FOR f
PIN 9 = 0V FOR f
2
10
VCC = 3V, 4.5V, 6V
MIN
/f
10
MAX
f
0
-2
10
10
FIGURE 32. HC4046A f
-1
MIN
MIN/fMAX
MAX
1
10
R2/R1
vs R2/R1 (VCC = 3V, 4.5V, 6V) FIGURE 33. HCT4046A f
FIGURE 31. HC4046A AND HCT4046A OFFSET FREQUENCY
vs R2, C1 (VCC = 6V, VCC = 5.5V)
PIN 9 = 0.95 VCC FOR f
2
PIN 9 = 0V FOR f
10
VCC = 4.5V TO 5.5V
MIN
/f
10
MAX
f
0
2
10
-2
10
-1
10
MAX
MIN
MAX/fMIN
1
10
R2/R1
vs R2/R1 (VCC= 4.5V TO 5.5V)
2
10
16

CD74HC4046A, CD74HCT4046A
Typical Performance Curves
f
f
2
f
0
f
0
f
1
∆V
MIN MAX
1/2V
∆V
CC
∆V = 0.5V OVER THE VCC RANGE:
FOR VCO LINEARITY
= f1 + f
f’
o
LINEARITY =
V
VCOIN
(Continued)
2
2
8
C1 = 50pF
= 4.5V
V
6
CC
R2 = OPEN
4
2
0
-2
LINEARITY (%)
- f
f’
o
o
x 100%
f’
o
-4
-6
-8
1K 10K
VCOIN = 2.25V ± 1V
VCOIN = 2.25V ± 0.45V
100K 1M 10M
R1 (OHMS)
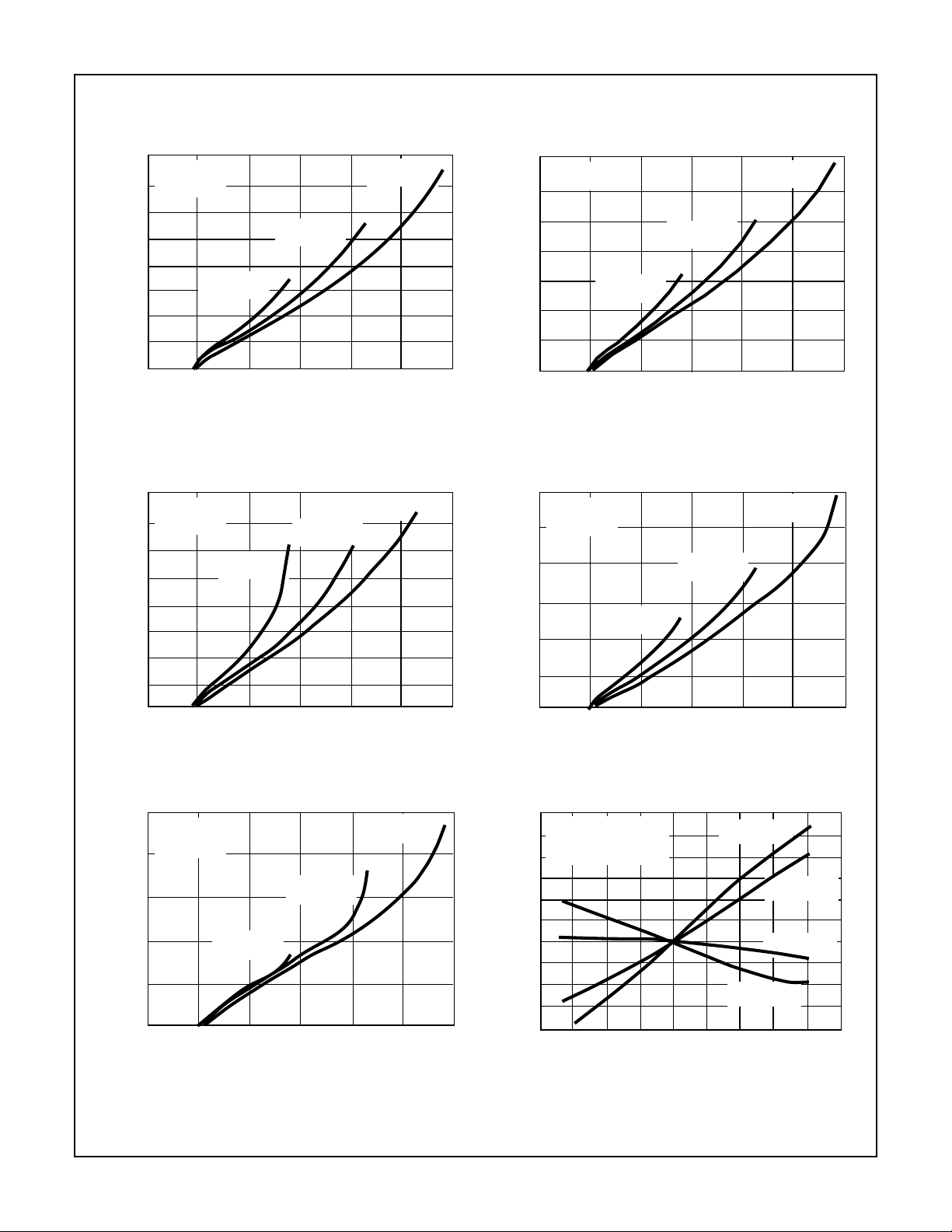
FIGURE 34. DEFINITION OF VCO FREQUENCY LINEARITY FIGURE 35. HC4046A VCO LINEARITY vs R1 (VCC = 4.5V)
8
C1 = 50pF
V
6
R2 = OPEN
4
2
CC
= 3V
VCOIN = 1.50V ± 0.4V
8
C1 = 50pF
V
6
R2 = OPEN
4
2
CC
= 6V
VCOIN = 3V ± 1.5V
0
-2
LINEARITY (%)
-4
-6
-8
1K 10K
VCOIN = 1.50V ± 0.3V
100K 1M 10M
R1 (OHMS)
0
-2
LINEARITY (%)
-4
-6
-8
1K 10K
VCOIN = 3V ± 0.6V
100K 1M 10M
R1 (OHMS)
FIGURE 36. HC4046A VCO LINEARITY vs R1 (VCC = 3V) FIGURE 37. HC4046A VCO LINEARITY vs R1 (VCC = 6V)
8
VCC = 5.5V,
VCOIN = 2.75V ±1.3V
6
= 4.5V,
V
CC
VCO
IN
4
2
0
-2
LINEARITY (%)
-4
-6
-8
1K 10K
= 2.25V ±1.0V
VCC = 5.5V,
= 2.75V ±0.55V
VCO
IN
V
= 4.5V,
CC
VCO
= 2.25V ±0.45V
IN
100K 1M 10M
R1 (OHMS)
C1 = 50pF
R2 = OPEN
4
10
(µW)
VCOIN = 0.5 V
D
3
10
2
10
10
1
1K 10K
DEMODULATOR POWER DISSIPATION, P
CC
VCC = 3V
RS (OHMS)
VCC = 6V
VCC = 4.5V
100K 1M
FIGURE 38. HCT4046A VCO LINEARITY vs R1 (VCC = 4.5V,
VCC = 5.5V)
FIGURE 39. HC4046A DEMODULATOR POWER DISSIPATION
vs RS (TYP) (VCC = 3V, 4.5V, 6V)
17

CD74HC4046A, CD74HCT4046A
Typical Performance Curves
4
10
(µW)
D
VCOIN = 0.5 V
CC
(Continued)
R1 = R2 = OPEN
3
10
2
10
VCC = 3V
VCC = 6V
VCC = 4.5V
10
1
DEMODULATOR POWER DISSIPATION, P
1K 10K
100K 1M
RS (OHMS)
FIGURE 40. HCT4046A DEMODULATOR POWER DISSIPATION
vs RS (TYP) (VCC = 3V, 4.5V, 6V)
6
10
(µW)
D
5
10
4
10
3
10
VCC = 4.5V
VCO POWER DISSIPATION, P
2
10
1K 10K
VCC = 6V
C1 = 50pF
C1 = 1µF
VCC = 6V
C1 = 1µF
R2 (OHMS)
VCOIN = 0V (AT f
MIN
R1 = RS = OPEN
= 50pF
C
L
VCC = 4.5V
C1 = 50pF
100K 1M
)
6
10
VCOIN = 0.5V
CC
R2 = RS = OPEN
C
= 50pF
(µW)
D
L
5
10
4
10
VCC = 6V
C1 = 50pF
VCC = 6V
C1 = 1µF
VCC = 4.5V
C1 = 50pF
VCC = 3V
C1 = 1µF
3
10
VCC = 3V
C1 = 50pF
VCO POWER DISSIPATION, P
2
10
1K 10K
VCC = 4.5V
C1 = 1µF
100K 1M
R1 (OHMS)
FIGURE 41. HC4046A VCO POWER DISSIPATION vs R1
(C1 = 50pF, 1µF)
6
10
(µW)
D
5
10
4
10
VCC = 5.5V
C1 = 1µF
3
10
VCO POWER DISSIPATION, P
2
10
1K 10K
VCC = 5.5V
C1 = 50pF
VCC = 4.5V
C1 = 1µF
R1 (OHMS)
VCOIN = 0.5V
R2 = RS = OPEN
VCC = 4.5V
C1 = 50pF
100K 1M
FIGURE 42. HCT4046A VCO POWER DISSIPATION vs R2
(C1 = 50pF, 1µF)
6
10
(µW)
D
5
10
4
10
VCC = 3V
C1 = 1µF
3
10
VCC = 3V
C1 = 50pF
VCO POWER DISSIPATION, P
2
10
1K 10K
FIGURE 44. HC4046A VCO POWER DISSIPATION vs R2 (C1 = 50pF, 1µF)
FIGURE 43. HCT4046A VCO POWER DISSIPATION vs R1
(C1 = 50pF, 1µF)
VCC = 6V
C1 = 50pF
VCC = 4.5V
C1 = 1µF
R2 (OHMS)
VCOIN = 0V (AT f
R1 = RS = OPEN
= 50pF
C
L
VCC = 4.5V
C1 = 50pF
100K 1M
MIN
VCC = 6V
C1 = 1µF
)
18

CD74HC4046A, CD74HCT4046A
HC/HCT4046A C
PD
CHIP SECTION HC HCT UNIT
Comparator 1 48 50 pF
Comparators 2 and 3 39 48 pF
VCO 61 53 pF
Application Information
This information is a guide for the approximation of values of
external components to be used with the CD74HC4046A
and CD74HCT4046A in a phase-lock-loop system.
PHASE
SUBJECT
VCO Frequency
Without Extra Offset
COMPARATOR DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS
PC1, PC2 or PC3 VCO Frequency Characteristic
With R2 = ∞ and R1 within the range 3kΩ < R1 < 300kΩ, the characteristics of the VCO op-
erationwill beas shown in Figures 12 - 16. (Due to R1, C1 time constant a small offset remains
when R2 = ∞.)
f
f
References should be made to Figures 12 through 16 and
Figures 28 through 33 as indicated in the table.
Values of the selected components should be within the following ranges:
R1 Between 3kΩ and 300kΩ
R2 Between 3kΩ and 300kΩ
R1 + R2 Parallel Value > 2.7kΩ
C1 Greater Than 40pF
MAX
VCO
f
o
2f
L
VCO Frequency with
Extra Offset
f
MIN
MIN
FIGURE 45. FREQUENCY CHARACTERISTIC OF VCO OPERATING WITHOUT
OFFSET: fo = CENTER FREQUENCY: 2fL = FREQUENCY LOCK RANGE
PC1 Selection of R1 and C1
Given fo, determine the values of R1 and C1 using Figures 12 - 16.
PC2 or PC3 Given f
16. To obtain 2fL:2f
calculate foas f
MAX
≈1.2 (V
L
MAX
< VCC - 0.9V
PC1, PC2 or PC3 VCO Frequency Characteristic
With R1 and R2 within the ranges 3kΩ < R1 < 300kΩ,3kΩ, < R2 < 300kΩ, the characteristics
of the VCO operation will be as shown in Figures 28 - 33.
f
MAX
f
VCO
f
o
f
MIN
MIN
FIGURE 46. FREQUENCY CHARACTERISTIC OF VCO OPERATING WITH OFFSET:
fo = CENTER FREQUENCY: 2fL = FREQUENCY LOCK RANGE
V
1/2 V
CC
VCOIN
MAX
/2 and determine the values of R1 and C1 using Figures 12 -
- 1.8V)/(R1C1) where valid range of VCOINis 1.1V < VCO
CC
2f
L
CC
V
VCOIN
MAX
1/2 V
IN
PC1, PC2 or PC3 Selection of R1, R2 and C1
Given fo and fL, offset frequency, f
Obtain the values of C1 and R2 by using Figures 28 - 31.
Calculate the values of R1 from Figures 32 - 33.
19
, may be calculated from f
MIN
MIN
≈ f
- 1.6 fL.
o

SUBJECT
PLL Conditions with
No Signal at the
SIGIN Input
PLL Frequency
Capture Range
CD74HC4046A, CD74HCT4046A
PHASE
COMPARATOR DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS
PC1 VCO adjusts to fo with φ
PC2 VCO adjusts to f
PC3 VCO adjusts to f
MIN
MAX
DEMOUT
with φ
with φ
PC1, PC2 or PC3 Loop Filter Component Selection
R3
C2
INPUT OUTPUT
(A) τ = R3 x C2
A small capture range (2fc) is obtained if τ > 2f
FIGURE 47. SIMPLE LOOP FILTER FOR PLL WITHOUT OFFSET
R3
INPUT OUTPUT
R4
C2
= 90o and V
DEMOUT
DEMOUT
|F
= -360o and V
= 360o and V
|
(jω)
= 1/2 VCC (see Figure 2)
VCOIN
= 0V (see Figure 4)
VCOIN
= VCC (see Figure 6)
VCOIN
ω
(B) AMPLITUDE CHARACTERISTIC (C) POLE-ZERO DIAGRAM
≈ 1/π (2πf
c
|F
|
(jω)
m
m =
/τ.)
L
R4
R3 + R4
1/2
-1/
-1/
τ
-1/
2
3
τ
τ
PLL Locks on
Harmonics at Center
Frequency
Noise Rejection at
Signal Input
AC Ripple Content
when PLL is Locked
(A) τ1 = R3 x C2;
(B) AMPLITUDE CHARACTERISTIC (C) POLE-ZERO DIAGRAM
τ2 = R4 x C2;
τ3 = (R3 + R4) x C2
FIGURE 48. SIMPLE LOOP FILTER FOR PLL WITH OFFSET
PC1 or PC3 Yes
PC2 No
PC1 High
PC2 or PC3 Low
PC1 fr = 2fi, large ripple content at φ
PC2 fr = fi, small ripple content at φ
PC3 fr = fSIGIN, large ripple content at φ
DEMOUT
DEMOUT
= 90
= 0
DEMOUT
1/
τ
o
o
= 180
1/
3
ω
2
τ
o
20

IMPORTANT NOTICE
T exas Instruments and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make changes to their products or to discontinue
any product or service without notice, and advise customers to obtain the latest version of relevant information
to verify, before placing orders, that information being relied on is current and complete. All products are sold
subject to the terms and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgement, including those
pertaining to warranty, patent infringement, and limitation of liability.
TI warrants performance of its semiconductor products to the specifications applicable at the time of sale in
accordance with TI’s standard warranty. Testing and other quality control techniques are utilized to the extent
TI deems necessary to support this warranty . Specific testing of all parameters of each device is not necessarily
performed, except those mandated by government requirements.
CERT AIN APPLICATIONS USING SEMICONDUCTOR PRODUCTS MAY INVOLVE POTENTIAL RISKS OF
DEATH, PERSONAL INJURY, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE (“CRITICAL
APPLICATIONS”). TI SEMICONDUCTOR PRODUCTS ARE NOT DESIGNED, AUTHORIZED, OR
WARRANTED TO BE SUITABLE FOR USE IN LIFE-SUPPORT DEVICES OR SYSTEMS OR OTHER
CRITICAL APPLICA TIONS. INCLUSION OF TI PRODUCTS IN SUCH APPLICATIONS IS UNDERST OOD TO
BE FULLY AT THE CUSTOMER’S RISK.
In order to minimize risks associated with the customer’s applications, adequate design and operating
safeguards must be provided by the customer to minimize inherent or procedural hazards.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or customer product design. TI does not warrant or represent
that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any patent right, copyright, mask work right, or other
intellectual property right of TI covering or relating to any combination, machine, or process in which such
semiconductor products or services might be or are used. TI’s publication of information regarding any third
party’s products or services does not constitute TI’s approval, warranty or endorsement thereof.
Copyright 1999, Texas Instruments Incorporated
 Loading...
Loading...