1
Data sheet acquired from Harris Semiconductor
SCHS177
CD74HC297,
CD74HCT297
High-Speed CMOS Logic
Digital Phase-Locked-Loop
Features
• Digital Design Avoids Analog Compensation Errors
• Easily Cascadable for Higher Order Loops
• Useful Frequency Range
- K-Clock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .DC to 55MHz (Typ)
- I/D-Clock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . DC to 35MHz (Typ)
• Dynamically Variable Bandwidth
• Very Narrow Bandwidth Attainable
• Power-On Reset
• Output Capability
- Standard. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . XORPD
OUT
, ECPD
OUT
- Bus Driver. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . I/D
OUT
• Fanout (Over Temperature Range)
- Standard Outputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 LSTTL Loads
- Bus Driver Outputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15 LSTTL Loads
• Balanced Propagation Delay and Transition Times
• Significant Power Reduction Compared to LSTTL
Logic ICs
• CD74HC297 Types
- Operation Voltage. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 to 6V
- High Noise ImmunityN
IL
= 30%, NIH= 30% of VCC at 5V
• CD74HCT297 Types
- Operation Voltage. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.5 to 5.5V
- Direct LSTTL Input Logic Compatibility
V
IL
= 0.8V (Max), VIH= 2V (Min)
- CMOS Input Compatibility I
I
≤ 1µA at VOL, V
OH
Description
The Harris CD74HC297 and CD74HCT297 are high-speed
silicon gate CMOS devices that are pin-compatible with low
power Schottky TTL (LSTTL).
These devices are designed to provide a simple, cost-effective solution to high-accuracy,digital, phase-locked-loop applications. The y contain all the necessary circuits, with the
exception of the divide-by-N counter, to build first-order
phase-locked-loops.
Both EXCLUSIVE-OR (XORPD) and edge-controlled phase
detectors (ECPD) are provided for maximum flexibility. The
input signals for the EXCLUSIVE-OR phase detector must
have a 50% duty factor to obtain the maxim um loc k-range .
Proper partitioning of the loop function, with many of the building blocks external to the package, makes it easy for the
designer to incorporate ripple cancellation (see Figure 2) or to
cascade to higher order phase-locked-loops.
The length of the up/down K-counter is digitally programmable
according to the K-counter function table. With A, B, C and D
all LOW,the K-counter is disabled. With A HIGH and B, C and
D LOW,the K-counter is only three stages long, which widens
the bandwidth or capture range and shortens the lock time of
the loop. When A, B, C and D are all programmed HIGH, the
K-counter becomes sev enteen stages long, which narrows
the bandwidth or capture range and lengthens the lock time.
Real-time control of loop bandwidth by manipulating the A to
D inputs can maximize the overall performance of the digital
phase-locked-loop.
The CD74HC297 and CD74HCT297 can perform the classic
first order phase-locked-loop function without using analog
components. The accuracy of the digital phase-locked-loop
(DPLL) is not affected by V
CC
and temperature variations but
depends solely on accuracies of the K-clock and loop propagation delays.
Pinout
CD74HC297, CD74HCT297 (PDIP)
TOP VIEW
Ordering Information
PART NUMBER TEMP.RANGE(oC) PACKAGE
PKG.
NO.
CD74HC297E -55 to 125 16 Ld PDIP E16.3
CD74HCT297E -55 to 125 16 Ld PDIP E16.3
NOTES:
1. When ordering, use the entire part number. Add the suffix 96 to
obtain the variant in the tape and reel.
2. Wafer or diefor thispartnumber isavailablewhich meetsallelectrical specifications. Please contact your local sales office or
Harris customer service for ordering information.
14
15
16
9
13
12
11
10
1
2
3
4
5
7
6
8
B
A
EN
CTR
K
CP
I/D
CP
D/U
GND
I/D
OUT
V
CC
D
φA
2
ECPD
OUT
XORPD
OUT
φB
φA
1
C
November 1997
CAUTION: These devices are sensitive to electrostatic discharge. Users should follow proper IC Handling Procedures.
Copyright
© Harris Corporation 1997
File Number 1852.1
[ /Title
(CD74
HC297
,
CD74
HCT29
7)
/
Sub-
j
ect
(HighSpeed
CMOS
Logic
Digital
PhaseLocked
2
The phase detector generates an error signal waveform that,
at zero phase error, is a 50% duty factor square wave. At the
limits of linear operation, the phase detector output will be
either HIGH or LOW all of the time depending on the direction
of the phase error (φIN - φOUT). Within these limits the phase
detector output varies linearly with the input phase error
according to the gain K
d
, which is expressed in terms of
phase detector output per cycle or phase error. The phase
detector output can be defined to vary between ±1 according
to the relation:
The output of the phase detector will be K
dφe
, where the
phase error φ
e
= φIN - φOUT.
EXCLUSIVE-OR phase detectors (XORPD) and edge-controlled phase detectors (ECPD) are commonly used digital
types. The ECPD is more complex than the XORPD logic
function but can be described generally as a circuit that
changes states on one of the transitions of its inputs. The gain
(K
d
) for an XORPD is 4 because its output remains HIGH
(XORPD
OUT
= 1) for a phase error of one quarter cycle.
Similarly , K
d
for the ECPD is 2 since its output remains HIGH
for a phase error of one half cycle. The type of phase detector
will determine the zero-phase-error point, i.e., the phase separation of the phase detector inputs for a φe defined to be
zero. For the basic DPLL system of Figure 3, φe = 0 when the
phase detector output is a square wave.
The XORPD inputs are one quarter cycle out-of-phase for
zero phase error. For the ECPD, φe = 0 when the inputs are
one half cycle out of phase.
The phase detector output controls the up/down input to the
K-counter. The counter is clocked by input frequency Mf
c
which is a multiple M of the loop center frequency fc. When
the K-counter recycles up, it generates a carry pulse. Recycling while counting down generates a borrow pulse. If the
carry and the borrow outputs are conceptually combined into
one output that is positive for a carry and negative for a borrow, and if the K-counter is considered as a frequency divider
with the ratio Mf
c
/K, the output of the K-counter will equal the
input frequency multiplied by the division ratio. Thus the output from the K-counter is (K
dφeMfc
)/K.
The carry and borrow pulses go to the increment/decrement
(I/D) circuit which, in the absence of any carry or borrow
pulses has an output that is one half of the input clock (I/D
CP
).
The input clock is just a multiple, 2N, of the loop center frequency. In response to a carry of borrow pulse, the I/D circuit
will either add or delete a pulse at I/D
OUT
. Thus the output of
the I/D circuit will be Nf
c
+ (KdφeMfc)/2K.
The output of the N-counter (or the output of the phaselocked-loop) is thus: fo = fc + (KdφeMfc)/2KN.
If this result is compared to the equation for a first-order analog phase-locked-loop, the digital equivalent of the gain of the
VCO is just Mf
c
/2KN or fc/K for M = 2N.
Thus, the simple first-order phase-locked-loop with an adjustable K-counter is the equivalent of an analog phase-lockedloop with a programmable VCO gain.
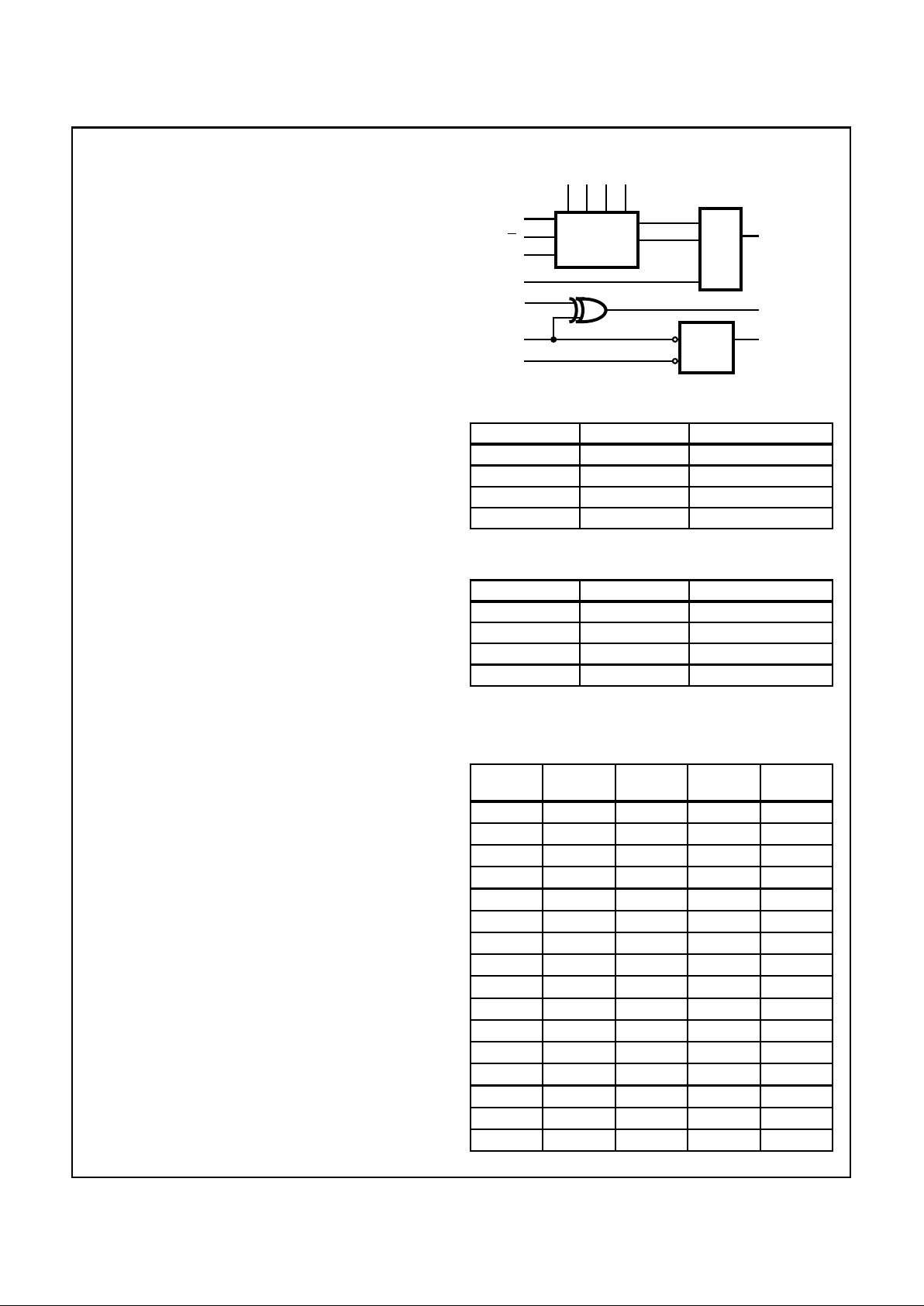
Functional Diagram
phase detector output =
%HIGH - %LOW
100
--------------------------------------------
FUNCTION TABLE
EXCLUSIVE-OR PHASE DETECTOR
φA
1
φB XORPD OUT
LL L
LH H
HL H
HH L
FUNCTION TABLE
EDGE-CONTROLLED PHASE DETECTOR
φA
2
φB ECPD OUT
H or L
↓
H
↓
H or L L
H or L ↑ No Change
↑ H or L No Change
H=Steady-State High Level,L= Steady-StateLowLevel, ↑=LOW
to HIGH φ Transition,↓ = HIGH to LOW φ Transition
K-COUNTER FUNCTION TABLE
(DIGITAL CONTROL)
DCBA
MODULO
(K)
LLLLInhibited
LLLH2
3
LLHL2
4
LLHH2
5
LHLL2
6
LHLH2
7
LHHL2
8
LHHH2
9
HLLL2
10
HLLH2
11
HLHL2
12
HLHH2
13
HHL L2
14
HHLH2
15
HHHL2
16
HHHH2
17
MODULO-K
COUNTER
K
CP
D/U
EN
CTR
4
6
3
5
9
10
13
14 15 1 2
CARRY
BORROW
I/D
CKT
DCBA
I/D
CP
φA
1
φB
φA
2
J
F/F
Q
K
7
11
12
I/D
OUT
XORPD
OUT
ECPD
OUT
CD74HC297, CD74HCT297CD74HC297, CD74HCT297
3
Absolute Maximum Ratings Thermal Information
DC Supply Voltage, VCC. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . -0.5V to 7V
DC Input Diode Current, I
IK
For VI < -0.5V or VI > VCC + 0.5V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .±20mA
DC Output Diode Current, I
OK
For VO < -0.5V or VO > VCC + 0.5V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .±20mA
DC Drain Current, per Output, I
O
For -0.5V < VO < VCC + 0.5V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .±25mA
DC Output Source or Sink Current per Output Pin, I
O
For VO > -0.5V or VO < VCC + 0.5V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .±25mA
DC VCC or Ground Current, ICC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .±50mA
Operating Conditions
Temperature Range, TA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . -55oC to 125oC
Supply Voltage Range, V
CC
HC Types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2V to 6V
HCT Types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4.5V to 5.5V
DC Input or Output Voltage, VI, VO . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0V to V
CC
Input Rise and Fall Time
2V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1000ns (Max)
4.5V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 500ns (Max)
6V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 400ns (Max)
Thermal Resistance (Typical, Note 2) θJA (oC/W)
PDIP Package. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Maximum Junction Temperature. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150oC
Maximum Storage Temperature Range . . . . . . . . . .-65oC to 150oC
Maximum Lead Temperature (Soldering 10s). . . . . . . . . . . . . 300oC
CAUTION: Stresses above those listed in “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress only rating and operation
of the device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the operational sections of this specification is not implied.
NOTE:
3. θJA is measured with the component mounted on an evaluation PC board in free air.
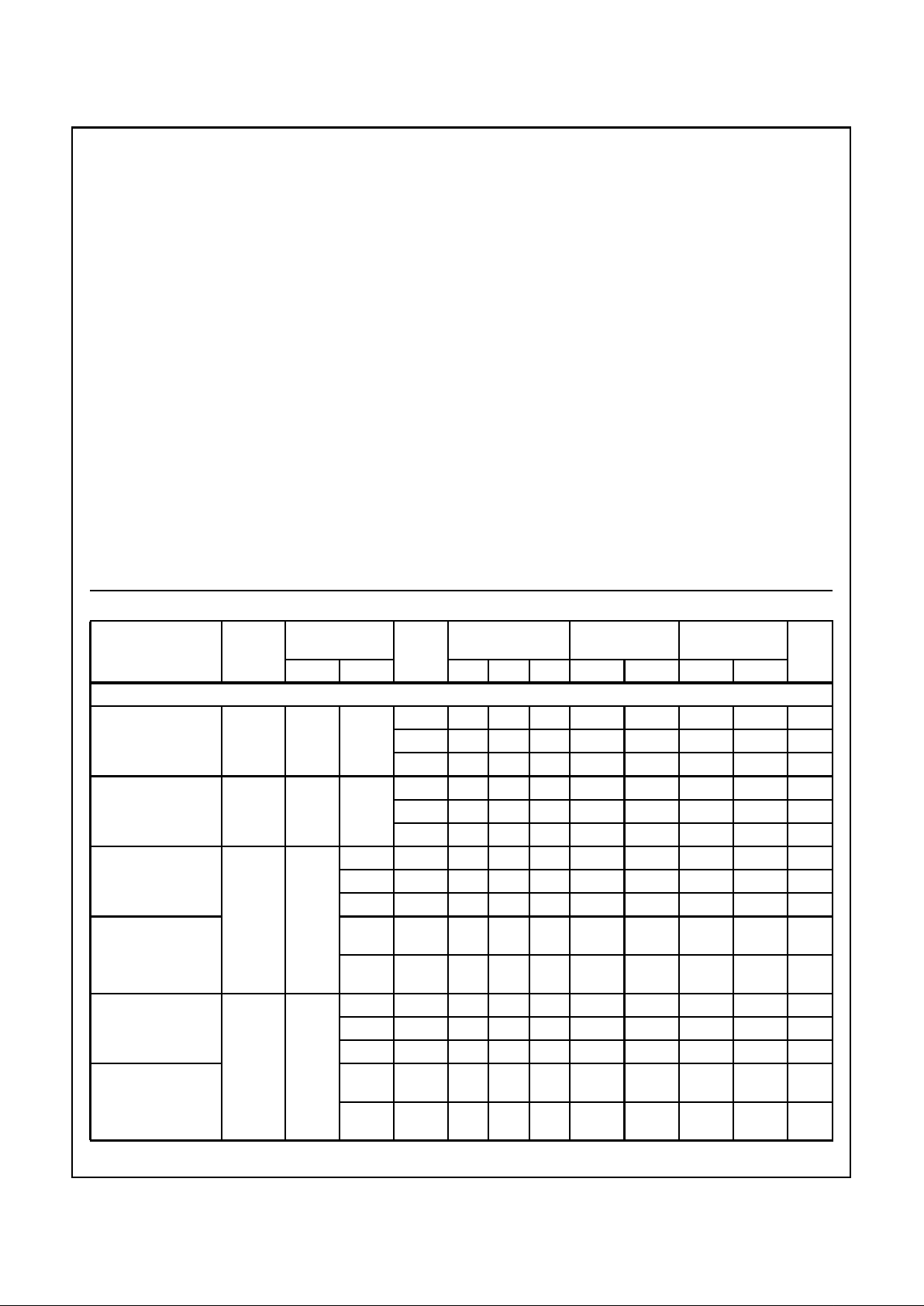
DC Electrical Specifications
PARAMETER SYMBOL
TEST
CONDITIONS
VCC (V)
25oC -40oC TO 85oC -55oC TO 125oC
UNITSVI(V) IO(mA) MIN TYP MAX MIN MAX MIN MAX
HC TYPES
High Level Input
Voltage
V
IH
- - 2 1.5 - - 1.5 - 1.5 - V
4.5 3.15 - - 3.15 - 3.15 - V
6 4.2 - - 4.2 - 4.2 - V
Low Level Input
Voltage
V
IL
- - 2 - - 0.5 - 0.5 - 0.5 V
4.5 - - 1.35 - 1.35 - 1.35 V
6 - - 1.8 - 1.8 - 1.8 V
High Level Output
Voltage
CMOS Loads
V
OH
VIH or
V
IL
-0.02 2 1.9 - - 1.9 - 1.9 - V
-0.02 4.5 4.4 - - 4.4 - 4.4 - V
-0.02 6 5.9 - - 5.9 - 5.9 - V
High Level Output
Voltage
TTL Loads
-6
(Note 4)
4.5 3.98 - - 3.84 - 3.7 - V
-7.8
(Note 4)
6 5.48 - - 5.34 - 5.2 - V
Low Level Output
Voltage
CMOS Loads
V
OL
VIH or
V
IL
0.02 2 - - 0.1 - 0.1 - 0.1 V
0.02 4.5 - - 0.1 - 0.1 - 0.1 V
0.02 6 - - 0.1 - 0.1 - 0.1 V
Low Level Output
Voltage
TTL Loads
4
(Note 4)
4.5 - - 0.26 - 0.33 - 0.4 V
5.2
(Note 4)
6 - - 0.26 - 0.33 - 0.4 V
CD74HC297, CD74HCT297CD74HC297, CD74HCT297
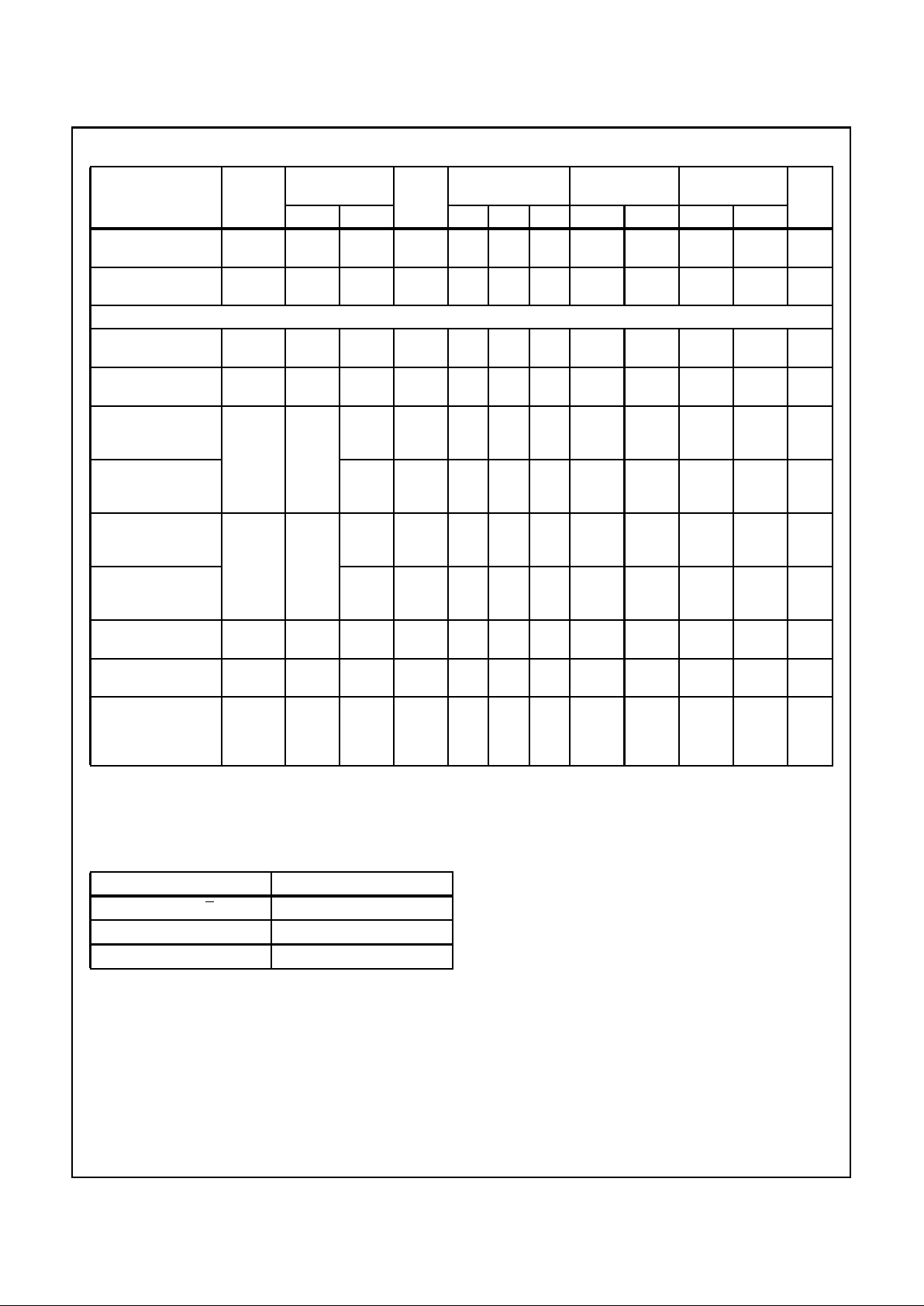
4
Input Leakage
Current
I
I
VCC or
GND
-6--±0.1 - ±1-±1 µA
Quiescent Device
Current
I
CC
VCC or
GND
0 6 - - 8 - 80 - 160 µA
HCT TYPES
High Level Input
Voltage
V
IH
- - 4.5 to
5.5
2-- 2 - 2 - V
Low Level Input
Voltage
V
IL
- - 4.5 to
5.5
- - 0.8 - 0.8 - 0.8 V
High Level Output
Voltage
CMOS Loads
V
OH
VIH or
V
IL
-0.02 4.5 4.4 - - 4.4 - 4.4 - V
High Level Output
Voltage
TTL Loads
-4 4.5 3.98 - - 3.84 - 3.7 - V
Low Level Output
Voltage
CMOS Loads
V
OL
VIH or
V
IL
0.02 4.5 - - 0.1 - 0.1 - 0.1 V
Low Level Output
Voltage
TTL Loads
4 4.5 - - 0.26 - 0.33 - 0.4 V
Input Leakage
Current
I
I
VCC to
GND
0 5.5 - - ±0.1 - ±1-±1 µA
Quiescent Device
Current
I
CC
VCC or
GND
0 5.5 - - 8 - 80 - 160 µA
Additional Quiescent
Device Current Per
Input Pin: 1 Unit Load
(Note 3)
∆I
CC
V
CC
-2.1
- 4.5 to
5.5
- 100 360 - 450 - 490 µA
NOTE:
4. For dual-supply systems theoretical worst case (VI = 2.4V, VCC = 5.5V) specification is 1.8mA.
5. XORPD, ECPD
DC Electrical Specifications (Continued)
PARAMETER SYMBOL
TEST
CONDITIONS
VCC (V)
25oC -40oC TO 85oC -55oC TO 125oC
UNITSVI(V) IO(mA) MIN TYP MAX MIN MAX MIN MAX
HCT Input Loading Table
INPUT UNIT LOADS
EN
CTR
, D/U 0.3
A, B, C, D, KCP, φA
2
0.6
I/DCP, φA1, φB 1.5
NOTE: Unit Load is ∆ICClimit specified in DC Electrical
Specifications table, e.g., 360µA max at 25oC.
CD74HC297, CD74HCT297CD74HC297, CD74HCT297
 Loading...
Loading...