
CC2640R2L SimpleLink™ Bluetooth®5.1 Low Energy Wireless MCU
1 Device Overview
1.1 Features
1
• Microcontroller
– Powerful Arm®Cortex®-M3
– EEMBC CoreMark®score: 142
– Up to 48-MHz clock speed
– 275KB of nonvolatile memory including 128KB
of in-system programmable flash
– Up to 28KB of system SRAM, of which 20KB is
ultra-low leakage SRAM
– 8KB of SRAM for cache or system RAM use
– 2-pin cJTAG and JTAG debugging
– Supports over-the-air upgrade (OTA)
• Efficient code size architecture, placing drivers, TIRTOS, and Bluetooth®software in ROM to make
more Flash available for the application
• RoHS-compliant packages
– 5‑mm × 5‑mm RHB VQFN32 (15 GPIOs)
– 7‑mm × 7‑mm RGZ VQFN48 (31 GPIOs)
• Peripherals
– All digital peripheral pins can be routed to any
GPIO
– Four general-purpose timer modules (eight 16-
bit or four 32-bit timers, PWM each)
– 12-bit ADC, 200-ksamples/s, 8-channel analog
MUX
– UART, I2C, and I2S
– 2× SSI (SPI, MICROWIRE, TI)
– Real-time clock (RTC)
– AES-128 security module
– True random number generator (TRNG)
– Integrated temperature sensor
• External system
– On-chip internal DC/DC converter
– Seamless integration with CC2590 and CC2592
range extenders
– Very few external components
– Pin compatible with the SimpleLink™ CC2640,
CC2640R2F, and CC2650 devices in 5‑mm ×
5‑mm and 7‑mm x 7‑mm VQFN packages
CC2640R2L
SWRS250 –JUNE 2020
– Pin compatible with the SimpleLink™ CC2642R
and CC2652R devices in 7‑mm x 7‑mm VQFN
packages
– Pin compatible with the SimpleLink™ CC1350
device in 5‑mm × 5‑mm VQFN packages
• Low power
– Wide supply voltage range
– Normal operation: 1.8 to 3.8 V
– External regulator mode: 1.7 to 1.95 V
– Active-mode RX: 5.9 mA
– Active-mode TX at 0 dBm: 6.1 mA
– Active-mode TX at +5 dBm: 9.1 mA
– Active-mode MCU: 61 µA/MHz
– Active-mode MCU: 48.5 CoreMark/mA
– Standby: 1.5 µA (RTC running and RAM/CPU
retention)
– Shutdown: 100 nA (wake up on external events)
• RF section
– 2.4-GHz RF transceiver compatible with
Bluetooth low energy 5.1 and earlier LE
specifications
– Excellent receiver sensitivity (–97 dBm for BLE),
selectivity, and blocking performance
– Link budget of 102 dB for BLE
– Programmable output power up to +5 dBm
– Single-ended or differential RF interface
– Suitable for systems targeting compliance with
worldwide radio frequency regulations
– ETSI EN 300 328 (Europe)
– EN 300 440 Class 2 (Europe)
– FCC CFR47 Part 15 (US)
– ARIB STD-T66 (Japan)
• Development Tools and Software
– Full-feature development kits
– Multiple reference designs
– SmartRF™ Studio
– IAR Embedded Workbench®for Arm
®
– Code Composer Studio™ Integrated
Development Environment (IDE)
– Code Composer Studio™ Cloud IDE
1
An IMPORTANT NOTICE at the end of this data sheet addresses availability, warranty, changes, use in safety-critical applications,
intellectual property matters and other important disclaimers. PRODUCTION DATA.

CC2640R2L
SWRS250 –JUNE 2020
1.2 Applications
• Home and Building Automation
– Connected appliances
– Lighting
– Smart locks
– Gateways
– Security Systems
• Industrial
– Factory automation
– Asset tracking and management
– HMI
– Access control
• Electronic Point Of Sale (EPOS)
– Electronic Shelf Label (ESL)
1.3 Description
www.ti.com
• Health and Medical
– Electronic thermometers
– SpO2
– Blood glucose monitors and blood pressure
monitors
– Weigh scales
– Hearing aids
• Sports and Fitness
– Wearable fitness and activity monitors
– Smart trackers
– Patient monitors
– Fitness machines
• HID
– Gaming
– Pointing devices (wireless keyboard and
mouse)
The CC2640R2L device is a 2.4 GHz wireless microcontroller (MCU) supporting Bluetooth®5.1 Low
Energy and Proprietary 2.4 GHz applications. The device is optimized for low-power wireless
communication and advanced sensing in building security systems, HVAC, asset tracking, and medical
markets, and applications where industrial performance is required. The highlighted features of this device
include:
• Support for Bluetooth®5.1 features: LE Coded PHYs (Long Range), LE 2-Mbit PHY (High Speed),
Advertising Extensions, Multiple Advertisement Sets, as well as backwards compatibility and support
for key features from the Bluetooth®5.0 and earlier Low Energy specifications.
• Fully-qualified Bluetooth®5.1 software protocol stack included with the SimpleLink™ CC2640R2
Software Development Kit (SDK) for developing applications on the powerful Arm®Cortex®-M3
processor.
• Longer battery life wireless applications with low standby current of 1.5 µA with full RAM retention.
• Dedicated software controlled radio controller (Arm®Cortex®-M0) providing flexible low-power RF
transceiver capability to support multiple physical layers and RF standards, such as real-time
localization (RTLS) technologies.
• Excellent radio sensitivity and robustness (selectivity and blocking) performance for Bluetooth®Low
Energy (-103 dBm for 125-kbps LE Coded PHY).
The CC2640R2L device is part of the SimpleLink™ microcontroller (MCU) platform, which consists of WiFi®, Bluetooth Low Energy, Thread, ZigBee®, Sub-1 GHz MCUs, and host MCUs that all share a common,
easy-to-use development environment with a single core software development kit (SDK) and rich tool set.
A one-time integration of the SimpleLink™ platform enables you to add any combination of the portfolio’s
devices into your design, allowing 100 percent code reuse when your design requirements change. For
more information, visit SimpleLink™ MCU platform.
PART NUMBER PACKAGE BODY SIZE (NOM)
CC2640R2LRGZ VQFN (48) 7.00 mm × 7.00 mm
CC2640R2LRHB VQFN (32) 5.00 mm × 5.00 mm
(1) For more information, see Section 9.
2
Device Overview Copyright © 2020, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Device Information
Submit Documentation Feedback
(1)
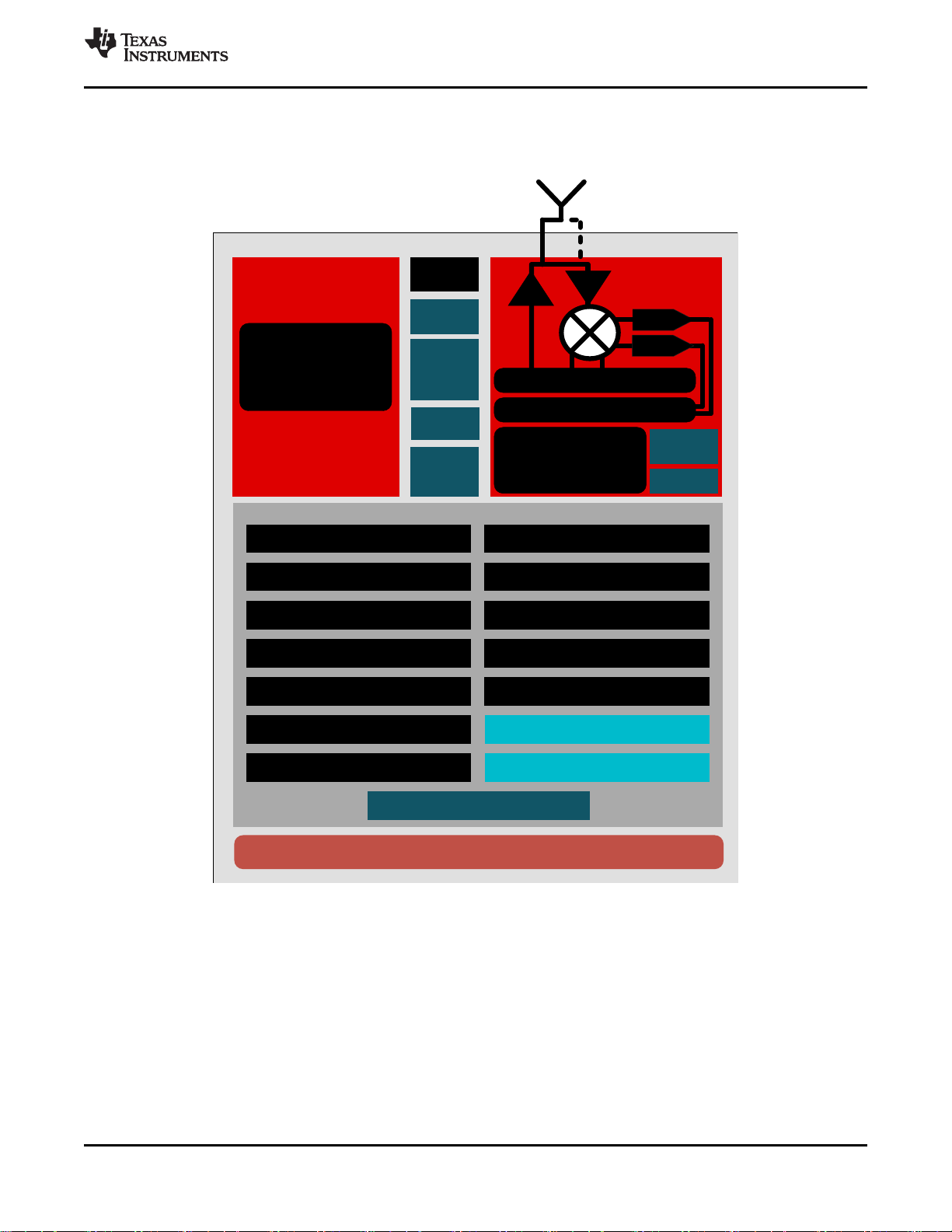
SimpleLink CC2640R2L Wireless MCU
Main CPU
128-KB
Flash
cJTAG
20-KB
SRAM
ROM
ARM
Cortex-M3
DC-DC Converter
RF Core
ARM
Cortex-M0
DSP modem
4-KB
SRAM
ROM
General Peripherals / Modules
4× 32-bit Timers
2× SSI (SPI, µW, TI)
Watchdog Timer
Temperature and Battery Monitor
RTC
I2C
UART
I2S
15 / 31 GPIOs
AES 32-channel µDMA
ADC
Digital PLL
Up to 48 MHz
61 µA/MHz
TRNG
ADC
8-KB
cache
12-bit ADC, 200 ksps
Time-to-Digital Converter
2-KB AUX RAM
www.ti.com
1.4 Functional Block Diagram
Figure 1-1 shows a block diagram for the CC2640R2L device.
CC2640R2L
SWRS250 –JUNE 2020
Figure 1-1. Block Diagram
Submit Documentation Feedback
Device OverviewCopyright © 2020, Texas Instruments Incorporated
3
CC2640R2L
SWRS250 –JUNE 2020
www.ti.com
Table of Contents
1 Device Overview ......................................... 1
1.1 Features .............................................. 1
1.2 Applications........................................... 2
1.3 Description............................................ 2
1.4 Functional Block Diagram ............................ 3
2 Revision History ......................................... 4
3 Device Comparison ..................................... 5
3.1 Related Products ..................................... 5
4 Terminal Configuration and Functions.............. 6
4.1 Pin Diagram – RGZ Package ........................ 6
4.2 Signal Descriptions – RGZ Package ................. 7
4.3 Pin Diagram – RHB Package ........................ 9
4.4 Signal Descriptions – RHB Package................ 10
5 Specifications........................................... 11
5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings......................... 11
5.2 ESD Ratings ........................................ 11
5.3 Recommended Operating Conditions............... 11
5.4 Power Consumption Summary...................... 12
5.5 General Characteristics ............................. 13
5.6 125-kbps Coded (Bluetooth 5) – RX ................ 14
5.7 125-kbps Coded (Bluetooth 5) – TX ................ 15
5.8 500-kbps Coded (Bluetooth 5) – RX ................ 15
5.9 500-kbps Coded (Bluetooth 5) – TX ................ 16
5.10 1-Mbps GFSK (Bluetooth low energy) – RX ........ 16
5.11 1-Mbps GFSK (Bluetooth low energy) – TX ........ 17
5.12 2-Mbps GFSK (Bluetooth 5) – RX .................. 17
5.13 2-Mbps GFSK (Bluetooth 5) – TX................... 18
5.14 24-MHz Crystal Oscillator (XOSC_HF) ............. 18
5.15 32.768-kHz Crystal Oscillator (XOSC_LF).......... 19
5.16 48-MHz RC Oscillator (RCOSC_HF) ............... 19
5.17 32-kHz RC Oscillator (RCOSC_LF)................. 19
5.18 ADC Characteristics................................. 19
5.19 Temperature Sensor ................................ 20
5.20 Battery Monitor...................................... 21
5.21 Synchronous Serial Interface (SSI) ................ 21
5.22 DC Characteristics .................................. 23
5.23 Thermal Resistance Characteristics ................ 24
5.24 Timing Requirements ............................... 24
5.25 Switching Characteristics ........................... 24
5.26 Typical Characteristics .............................. 25
6 Detailed Description ................................... 29
6.1 Overview ............................................ 29
6.2 Functional Block Diagram........................... 29
6.3 Main CPU ........................................... 30
6.4 RF Core ............................................. 30
6.5 Memory.............................................. 30
6.6 Debug ............................................... 31
6.7 Power Management................................. 31
6.8 Clock Systems ...................................... 32
6.9 General Peripherals and Modules .................. 32
6.10 Voltage Supply Domains............................ 33
6.11 System Architecture................................. 33
7 Application, Implementation, and Layout ......... 34
7.1 Application Information.............................. 34
7.2 5 × 5 External Differential (5XD) Application Circuit
...................................................... 36
8 Device and Documentation Support ............... 38
8.1 Device Nomenclature ............................... 38
8.2 Tools and Software ................................. 39
8.3 Documentation Support ............................. 39
8.4 Support Resources.................................. 39
8.5 Trademarks.......................................... 40
8.6 Electrostatic Discharge Caution..................... 40
8.7 Export Control Notice ............................... 40
8.8 Glossary............................................. 40
9 Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable
Information .............................................. 41
2 Revision History
DATE REVISION NOTES
June 2020 * Initial Release
4
Revision History Copyright © 2020, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
CC2640R2L
www.ti.com
SWRS250 –JUNE 2020
3 Device Comparison
Table 3-1. Device Family Overview
Device PHY Support Flash (KB) RAM (KB) GPIO Package
CC2640R2Lxxx
CC2640R2Fxxx
CC2640F128xxx Bluetooth low energy (Normal) 128 20 31, 15, 10 RGZ, RHB, RSM
CC2650F128xxx Multi-Protocol
CC2630F128xxx IEEE 802.15.4 (ZigBee/6LoWPAN) 128 20 31, 15, 10 RGZ, RHB, RSM
CC2620F128xxx IEEE 802.15.4 (RF4CE) 128 20 31, 10 RGZ, RSM
(1) The package designator replaces the xxx in device name to form a complete device name, RGZ is 7-mm × 7-mm VQFN48, RHB is 5-
mm × 5-mm VQFN32, RSM is 4-mm × 4-mm VQFN32, and YFV is 2.7-mm × 2.7-mm DSBGA.
(2) CC2640R2L devices contain Bluetooth Low Energy Host and Controller libraries in ROM, leaving more of the 128KB Flash memory
available for the customer application when used with supported BLE-Stack software protocol stack releases. Actual use of ROM and
Flash memory by the protocol stack may vary depending on device software configuration. See www.ti.com for more details.
(3) The CC2650 device supports all PHYs and can be reflashed to run all the supported standards.
(2)
(2)
Bluetooth low energy
(Normal, High Speed, Long Range)
Bluetooth low energy
(Normal, High Speed, Long Range)
(3)
128 20 31, 15 RGZ, RHB
128 20 31, 15, 14, 10 RGZ, RHB, YFV, RSM
128 20 31, 15, 10 RGZ, RHB, RSM
3.1 Related Products
TI's Wireless Connectivity
The wireless connectivity portfolio offers a wide selection of low-power RF solutions suitable
for a broad range of applications. The offerings range from fully customized solutions to turn
key offerings with pre-certified hardware and software (protocol).
TI's SimpleLink™ Sub-1 GHz Wireless MCUs
Long-range, low-power wireless connectivity solutions are offered in a wide range of
Sub-1 GHz ISM bands.
Companion Products
Review products that are frequently purchased or used in conjunction with this product.
SimpleLink™ CC2640R2 Wireless MCU LaunchPad™ Development Kit
The CC2640R2 LaunchPad ™ development kit brings easy Bluetooth®low energy (BLE)
connection to the LaunchPad ecosystem with the SimpleLink ultra-low power CC26xx family
of devices. Compared to the CC2650 LaunchPad, the CC2640R2 LaunchPad provides the
following:
• More free flash memory for the user application in the CC2640R2 wireless MCU
• Out-of-the-box support for Bluetooth 4.2 specification
• 4× faster Over-the-Air download speed compared to Bluetooth 4.1
SimpleLink™ Bluetooth low energy/Multi-standard SensorTag
The new SensorTag IoT kit invites you to realize your cloud-connected product idea. The
new SensorTag now includes 10 low-power MEMS sensors in a tiny red package. And it is
expandable with DevPacks to make it easy to add your own sensors or actuators.
Reference Designs Find reference designs leveraging the best in TI technology to solve your system-
level challenges
(1)
Submit Documentation Feedback
Device ComparisonCopyright © 2020, Texas Instruments Incorporated
5
40
39
DIO_25 38
DIO_24 37
21
22
23
24
DCDC_SW33
DIO_18
34
RESET_N35
DIO_2336
X32K_Q2 4
X32K_Q1 3
RF_N 2
RF_P 1
DIO_2232
DIO_2131
DIO_2030
DIO_1929
DIO_0 5
DIO_1 6
DIO_2 7
8
28
27
26
JTAG_TCKC25
9
10
11
12
41
42
43
44
20
DIO_15
19
DIO_14
18
17
VDDR 45
46
47
VDDR_RF 48
16
15
14
13
DIO_17
DIO_16
VDDS_DCDC
DIO_26
DIO_12
DIO_13
VDDS2
DIO_11
DIO_10
DIO_5
DIO_6
DIO_7
DIO_3
DIO_4
X24M_P
X24M_N
DIO_8
DIO_9
DIO_28
VDDS3
DCOUPL
JTAG_TMSC
DIO_29
DIO_30
DIO_27
VDDS
CC2640R2L
SWRS250 –JUNE 2020
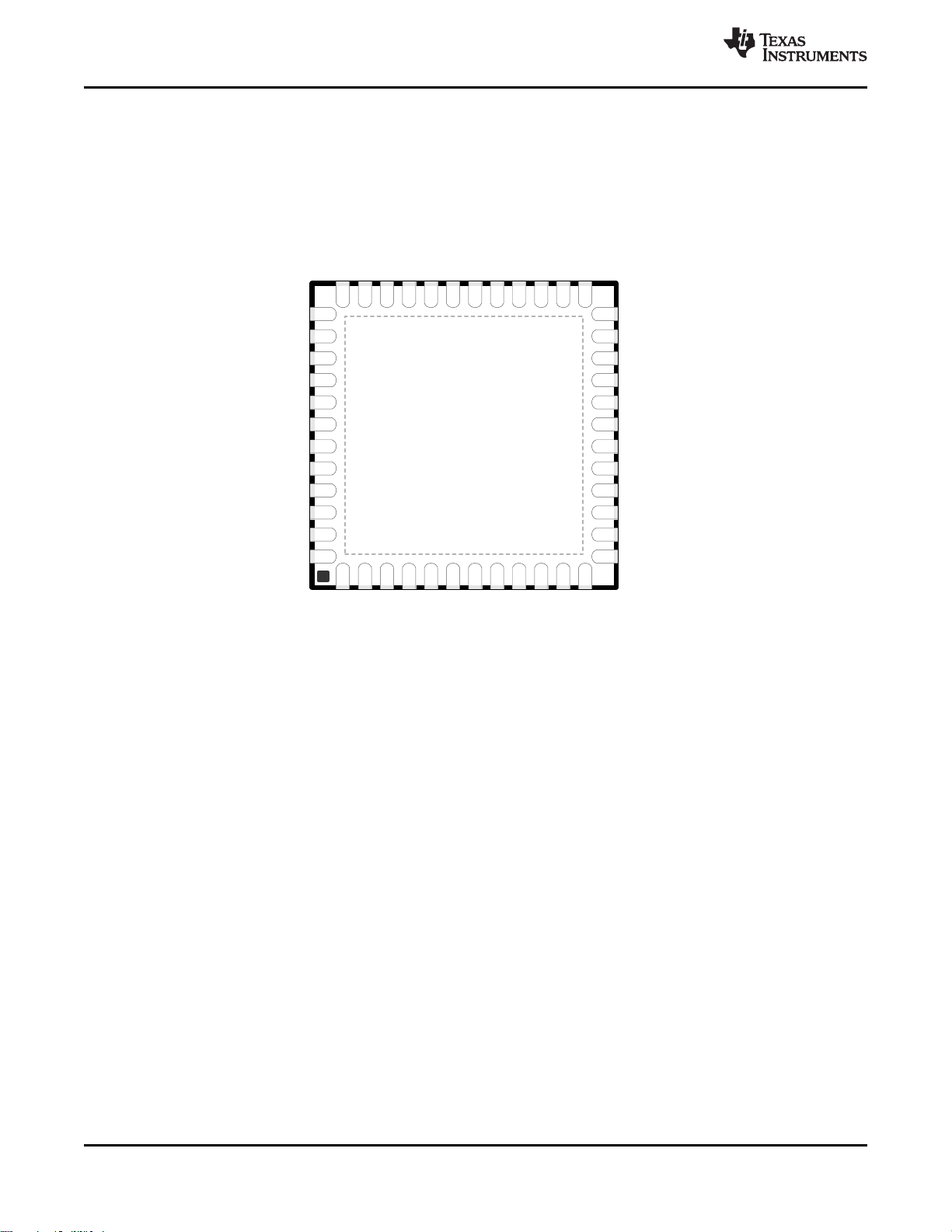
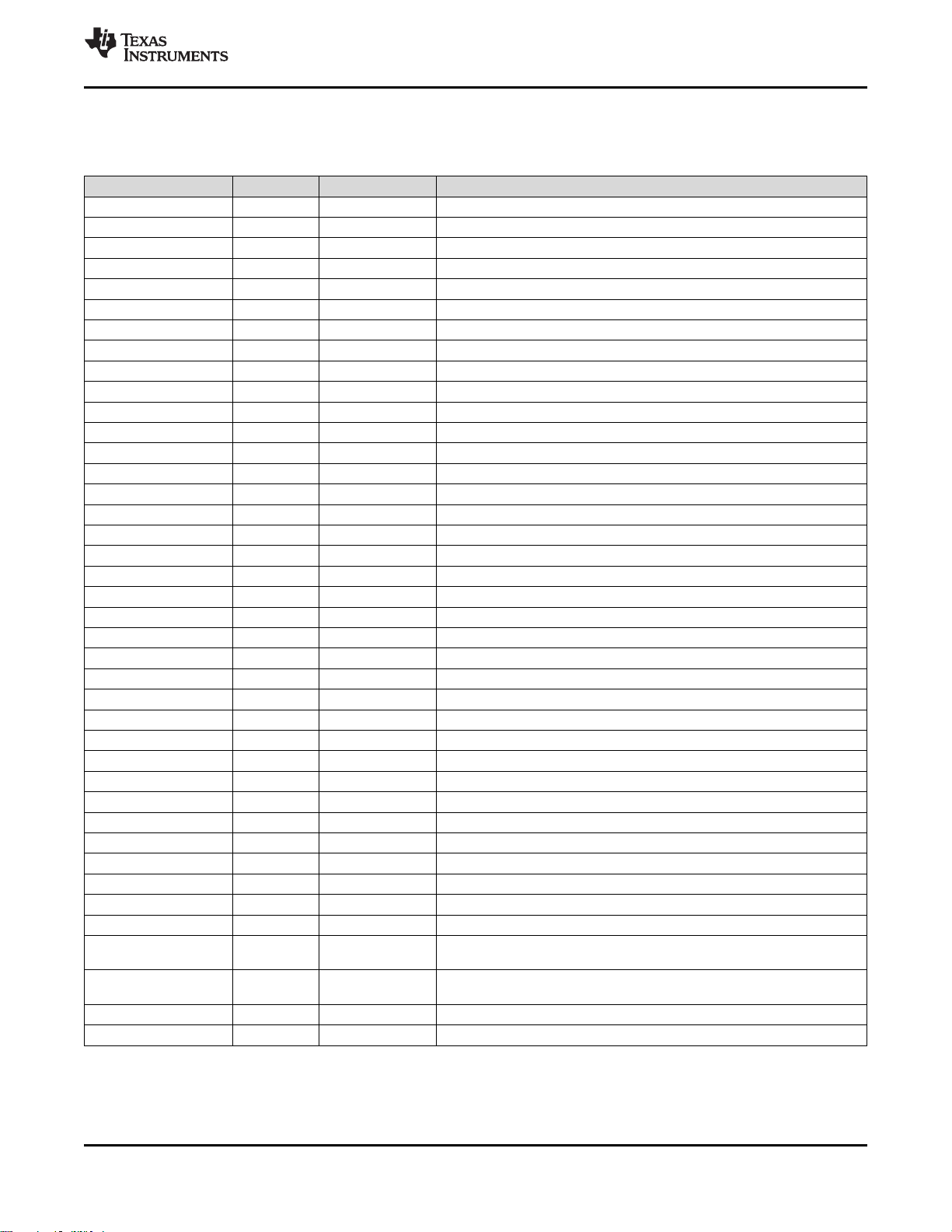
4 Terminal Configuration and Functions
4.1 Pin Diagram – RGZ Package
www.ti.com
Figure 4-1. RGZ Package
48-Pin VQFN
(7-mm × 7-mm) Pinout, 0.5-mm Pitch
I/O pins marked in Figure 4-1 in bold have high-drive capabilities; they are the following:
• Pin 10, DIO_5
• Pin 11, DIO_6
• Pin 12, DIO_7
• Pin 24, JTAG_TMSC
• Pin 26, DIO_16
• Pin 27, DIO_17
I/O pins marked in Figure 4-1 in italics have analog capabilities; they are the following:
• Pin 36, DIO_23
• Pin 37, DIO_24
• Pin 38, DIO_25
• Pin 39, DIO_26
• Pin 40, DIO_27
• Pin 41, DIO_28
• Pin 42, DIO_29
• Pin 43, DIO_30
6
Terminal Configuration and Functions Copyright © 2020, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
CC2640R2L
www.ti.com
SWRS250 –JUNE 2020
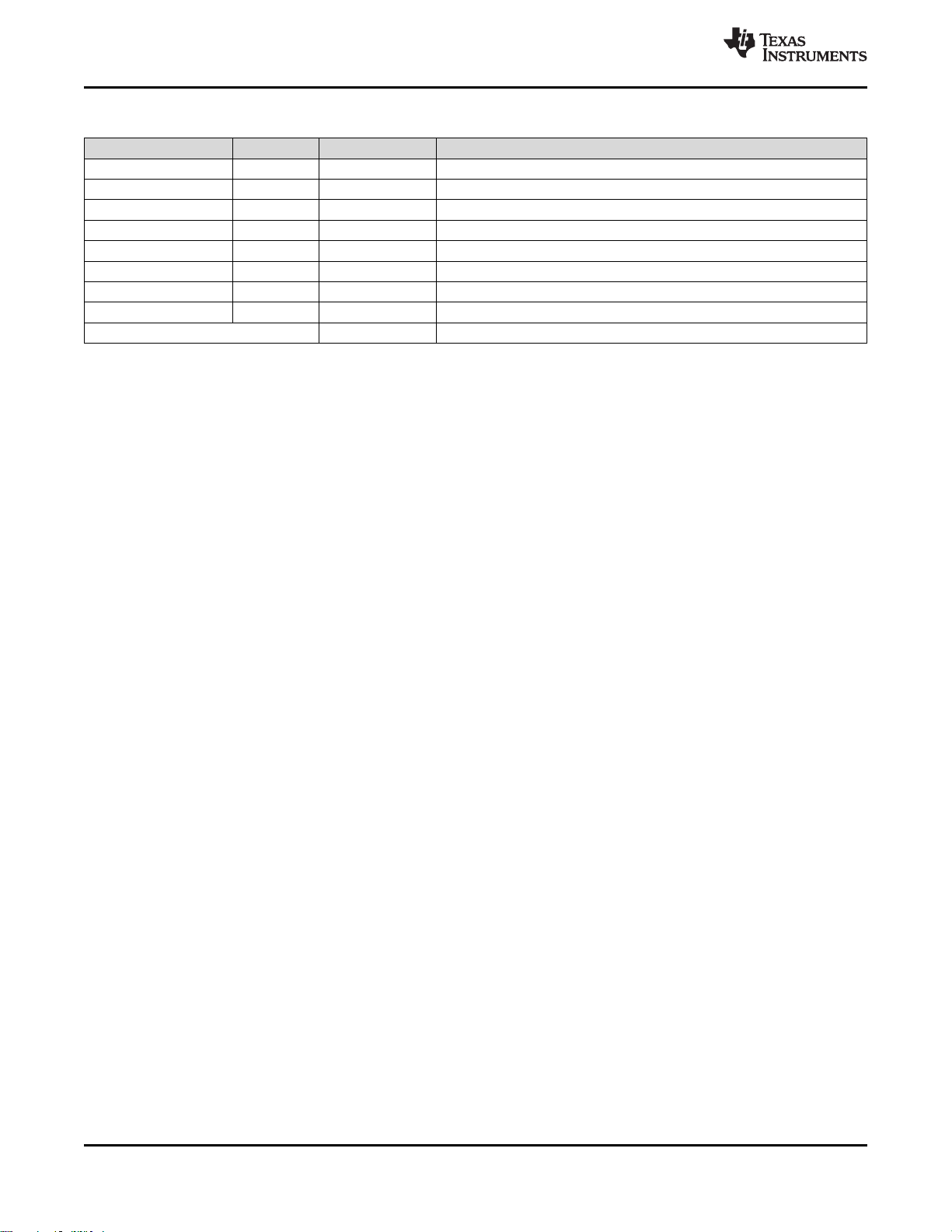
4.2 Signal Descriptions – RGZ Package
Table 4-1. Signal Descriptions – RGZ Package
NAME NO. TYPE DESCRIPTION
DCDC_SW 33 Power Output from internal DC/DC
DCOUPL 23 Power 1.27-V regulated digital-supply decoupling capacitor
DIO_0 5 Digital I/O GPIO
DIO_1 6 Digital I/O GPIO
DIO_2 7 Digital I/O GPIO
DIO_3 8 Digital I/O GPIO
DIO_4 9 Digital I/O GPIO
DIO_5 10 Digital I/O GPIO, high-drive capability
DIO_6 11 Digital I/O GPIO, high-drive capability
DIO_7 12 Digital I/O GPIO, high-drive capability
DIO_8 14 Digital I/O GPIO
DIO_9 15 Digital I/O GPIO
DIO_10 16 Digital I/O GPIO
DIO_11 17 Digital I/O GPIO
DIO_12 18 Digital I/O GPIO
DIO_13 19 Digital I/O GPIO
DIO_14 20 Digital I/O GPIO
DIO_15 21 Digital I/O GPIO
DIO_16 26 Digital I/O GPIO, JTAG_TDO, high-drive capability
DIO_17 27 Digital I/O GPIO, JTAG_TDI, high-drive capability
DIO_18 28 Digital I/O GPIO
DIO_19 29 Digital I/O GPIO
DIO_20 30 Digital I/O GPIO
DIO_21 31 Digital I/O GPIO
DIO_22 32 Digital I/O GPIO
DIO_23 36 Digital/Analog I/O GPIO, Analog
DIO_24 37 Digital/Analog I/O GPIO, Analog
DIO_25 38 Digital/Analog I/O GPIO, Analog
DIO_26 39 Digital/Analog I/O GPIO, Analog
DIO_27 40 Digital/Analog I/O GPIO, Analog
DIO_28 41 Digital/Analog I/O GPIO, Analog
DIO_29 42 Digital/Analog I/O GPIO, Analog
DIO_30 43 Digital/Analog I/O GPIO, Analog
JTAG_TMSC 24 Digital I/O JTAG TMSC, high-drive capability
JTAG_TCKC 25 Digital I/O JTAG TCKC
(3)
RESET_N 35 Digital input Reset, active-low. No internal pullup.
RF_P 1 RF I/O
RF_N 2 RF I/O
Positive RF input signal to LNA during RX
Positive RF output signal to PA during TX
Negative RF input signal to LNA during RX
Negative RF output signal to PA during TX
VDDR 45 Power 1.7-V to 1.95-V supply, typically connect to output of internal DC/DC
VDDR_RF 48 Power 1.7-V to 1.95-V supply, typically connect to output of internal DC/DC
(1) For more details, see the technical reference manual (listed in Section 8.3).
(2) Do not supply external circuitry from this pin.
(3) For design consideration regarding noise immunity for this pin, see the JTAG Interface chapter in the CC13x0, CC26x0 SimpleLink™
Wireless MCU Technical Reference Manual
(4) If internal DC/DC is not used, this pin is supplied internally from the main LDO.
(5) If internal DC/DC is not used, this pin must be connected to VDDR for supply from the main LDO.
(1)
(2)
(2)(4)
(2)(5)
Submit Documentation Feedback
Terminal Configuration and FunctionsCopyright © 2020, Texas Instruments Incorporated
7
CC2640R2L
SWRS250 –JUNE 2020
Table 4-1. Signal Descriptions – RGZ Package (continued)
NAME NO. TYPE DESCRIPTION
VDDS 44 Power 1.8-V to 3.8-V main chip supply
VDDS2 13 Power 1.8-V to 3.8-V DIO supply
VDDS3 22 Power 1.8-V to 3.8-V DIO supply
VDDS_DCDC 34 Power 1.8-V to 3.8-V DC/DC supply
X32K_Q1 3 Analog I/O 32-kHz crystal oscillator pin 1
X32K_Q2 4 Analog I/O 32-kHz crystal oscillator pin 2
X24M_N 46 Analog I/O 24-MHz crystal oscillator pin 1
X24M_P 47 Analog I/O 24-MHz crystal oscillator pin 2
EGP Power Ground – Exposed Ground Pad
(1)
(1)
www.ti.com
(1)
8
Terminal Configuration and Functions Copyright © 2020, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
28
29
27
30
212022
19
18
13
12
14
11
453
6
7
26 15
25 16
31 10
32 9
232
241
178
DIO_10
DIO_7
DIO_9
DIO_8
DCDC_SW
RESET_N
VDDS_DCDC
DIO_11
VDDR_RF
X24M_N
X24M_P
VDDR
VDDS
DIO_13
DIO_14
DIO_12
DIO_3
JTAG_TMSC
DIO_4
DCOUPL
VDDS2
JTAG_TCKC
DIO_5
DIO_6
RF_P
RF_N
RX_TX
DIO_0
DIO_1
DIO_2
X32K_Q1
X32K_Q2
www.ti.com
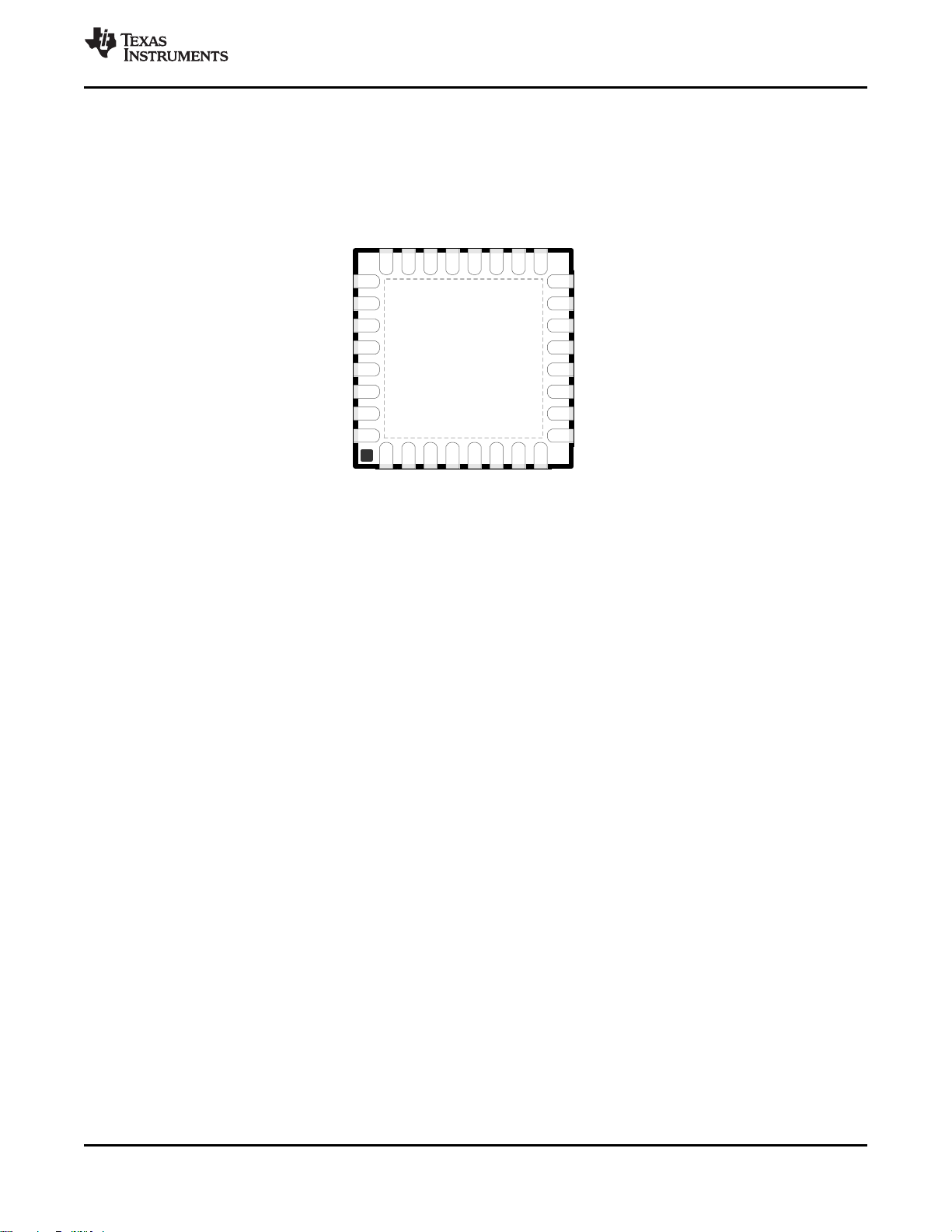
4.3 Pin Diagram – RHB Package
CC2640R2L
SWRS250 –JUNE 2020
I/O pins marked in Figure 4-2 in bold have high-drive capabilities; they are the following:
• Pin 8, DIO_2
• Pin 9, DIO_3
• Pin 10, DIO_4
• Pin 13, JTAG_TMSC
• Pin 15, DIO_5
• Pin 16, DIO_6
I/O pins marked in Figure 4-2 in italics have analog capabilities; they are the following:
• Pin 20, DIO_7
• Pin 21, DIO_8
• Pin 22, DIO_9
• Pin 23, DIO_10
• Pin 24, DIO_11
• Pin 25, DIO_12
• Pin 26, DIO_13
• Pin 27, DIO_14
Figure 4-2. RHB Package
32-Pin VQFN
(5-mm × 5-mm) Pinout, 0.5-mm Pitch
Submit Documentation Feedback
Terminal Configuration and FunctionsCopyright © 2020, Texas Instruments Incorporated
9
CC2640R2L
SWRS250 –JUNE 2020
www.ti.com
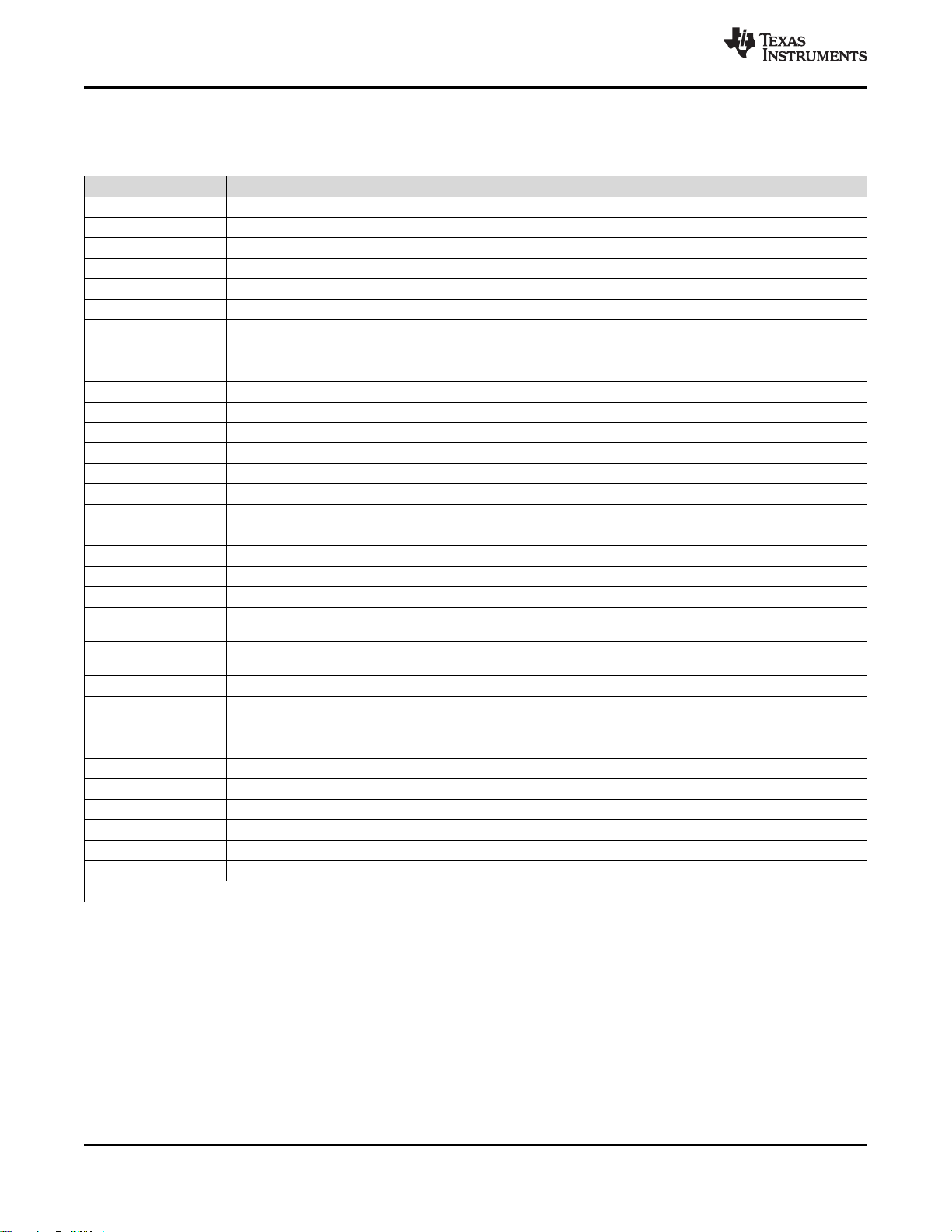
4.4 Signal Descriptions – RHB Package
Table 4-2. Signal Descriptions – RHB Package
NAME NO. TYPE DESCRIPTION
DCDC_SW 17 Power Output from internal DC/DC
DCOUPL 12 Power 1.27-V regulated digital-supply decoupling
DIO_0 6 Digital I/O GPIO
DIO_1 7 Digital I/O GPIO
DIO_2 8 Digital I/O GPIO, high-drive capability
DIO_3 9 Digital I/O GPIO, high-drive capability
DIO_4 10 Digital I/O GPIO, high-drive capability
DIO_5 15 Digital I/O GPIO, High drive capability, JTAG_TDO
DIO_6 16 Digital I/O GPIO, High drive capability, JTAG_TDI
DIO_7 20 Digital/Analog I/O GPIO, Analog
DIO_8 21 Digital/Analog I/O GPIO, Analog
DIO_9 22 Digital/Analog I/O GPIO, Analog
DIO_10 23 Digital/Analog I/O GPIO, Analog
DIO_11 24 Digital/Analog I/O GPIO, Analog
DIO_12 25 Digital/Analog I/O GPIO, Analog
DIO_13 26 Digital/Analog I/O GPIO, Analog
DIO_14 27 Digital/Analog I/O GPIO, Analog
JTAG_TMSC 13 Digital I/O JTAG TMSC, high-drive capability
JTAG_TCKC 14 Digital I/O JTAG TCKC
(3)
RESET_N 19 Digital input Reset, active-low. No internal pullup.
RF_N 2 RF I/O
RF_P 1 RF I/O
Negative RF input signal to LNA during RX,
Negative RF output signal to PA during TX
Positive RF input signal to LNA during RX,
Positive RF output signal to PA during TX
RX_TX 3 RF I/O Optional bias pin for the RF LNA
VDDR 29 Power 1.7-V to 1.95-V supply, typically connect to output of internal DC/DC
VDDR_RF 32 Power 1.7-V to 1.95-V supply, typically connect to output of internal DC/DC
VDDS 28 Power 1.8-V to 3.8-V main chip supply
VDDS2 11 Power 1.8-V to 3.8-V GPIO supply
VDDS_DCDC 18 Power 1.8-V to 3.8-V DC/DC supply
X32K_Q1 4 Analog I/O 32-kHz crystal oscillator pin 1
X32K_Q2 5 Analog I/O 32-kHz crystal oscillator pin 2
X24M_N 30 Analog I/O 24-MHz crystal oscillator pin 1
X24M_P 31 Analog I/O 24-MHz crystal oscillator pin 2
EGP Power Ground – exposed ground pad
(1) See technical reference manual (listed in Section 8.3) for more details.
(2) Do not supply external circuitry from this pin.
(3) For design consideration regarding noise immunity for this pin, see the JTAG Interface chapter in the CC13x0, CC26x0 SimpleLink™
Wireless MCU Technical Reference Manual
(4) If internal DC/DC is not used, this pin is supplied internally from the main LDO.
(5) If internal DC/DC is not used, this pin must be connected to VDDR for supply from the main LDO.
(1)
(2)
(4)(2)
(2)(5)
(1)
(1)
10
Terminal Configuration and Functions Copyright © 2020, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
CC2640R2L
www.ti.com
SWRS250 –JUNE 2020
5 Specifications
5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)
Supply voltage (VDDS, VDDS2,
and VDDS3)
Supply voltage (VDDS
VDDR)
Voltage on any digital pin
Voltage on crystal oscillator pins, X32K_Q1, X32K_Q2, X24M_N and X24M_P –0.3 VDDR + 0.3, max 2.25 V
Voltage on ADC input (Vin)
Input RF level 5 dBm
T
stg
(1) All voltage values are with respect to ground, unless otherwise noted.
(2) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings
only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating
Conditions is not implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
(3) In external regulator mode, VDDS2 and VDDS3 must be at the same potential as VDDS.
(4) Including analog-capable DIO.
(5) Each pin is referenced to a specific VDDSx (VDDS, VDDS2 or VDDS3). For a pin-to-VDDS mapping table, see Table 6-2.
(3)
and
(4)(5)
VDDR supplied by internal DC/DC regulator or
internal GLDO. VDDS_DCDC connected to VDDS on
PCB
External regulator mode (VDDS and VDDR pins
connected on PCB)
Voltage scaling enabled –0.3 VDDS
Voltage scaling disabled, VDDS as reference –0.3 VDDS / 2.9
Storage temperature –40 150 °C
(1)(2)
MIN MAX UNIT
–0.3 4.1 V
–0.3 2.25 V
–0.3 VDDSx + 0.3, max 4.1 V
VVoltage scaling disabled, internal reference –0.3 1.49
5.2 ESD Ratings
VALUE UNIT
Human body model (HBM), per
V
ESD
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
Electrostatic discharge
(RHB and RGZ packages)
ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS001
Charged device model (CDM), per JESD22-
(2)
C101
(1)
All pins ±2500
RF pins ±500
Non-RF pins ±500
5.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)
MIN MAX UNIT
Ambient temperature –40 85 °C
Operating supply
voltage (VDDS and
VDDR), external
regulator mode
Operating supply
voltage VDDS
Operating supply
voltages VDDS2 and
VDDS3
Operating supply
voltages VDDS2 and
VDDS3
For operation in 1.8-V systems
(VDDS and VDDR pins connected on PCB, internal DC/DC cannot be used)
For operation in battery-powered and 3.3-V systems
(internal DC/DC can be used to minimize power consumption)
VDDS < 2.7 V 1.8 3.8 V
VDDS ≥ 2.7 V 1.9 3.8 V
1.7 1.95 V
1.8 3.8 V
V
Submit Documentation Feedback
SpecificationsCopyright © 2020, Texas Instruments Incorporated
11
CC2640R2L
SWRS250 –JUNE 2020
5.4 Power Consumption Summary
Measured on the TI CC2650EM-5XD reference design with Tc= 25°C, V
otherwise noted.
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Reset. RESET_N pin asserted or VDDS below
Power-on-Reset threshold
Shutdown. No clocks running, no retention 150
Standby. With RTC, CPU, RAM and (partial)
register retention. RCOSC_LF
Standby. With RTC, CPU, RAM and (partial)
register retention. XOSC_LF
Standby. With Cache, RTC, CPU, RAM and
(partial) register retention. RCOSC_LF
I
core
Core current consumption
Peripheral Current Consumption (Adds to core current I
Peripheral power domain Delta current with domain enabled 50 µA
Serial power domain Delta current with domain enabled 13 µA
RF Core
µDMA Delta current with clock enabled, module idle 165 µA
I
peri
Timers Delta current with clock enabled, module idle 113 µA
I2C Delta current with clock enabled, module idle 12 µA
I2S Delta current with clock enabled, module idle 36 µA
SSI Delta current with clock enabled, module idle 93 µA
UART Delta current with clock enabled, module idle 164 µA
(1) Single-ended RF mode is optimized for size and power consumption. Measured on CC2650EM-4XS.
(2) Differential RF mode is optimized for RF performance. Measured on CC2650EM-5XD.
(3) I
is not supported in Standby or Shutdown.
peri
Standby. With Cache, RTC, CPU, RAM and
(partial) register retention. XOSC_LF
Idle. Supply Systems and RAM powered. 650
Active. Core running CoreMark
Radio RX
Radio RX
Radio TX, 0-dBm output power
Radio TX, 0-dBm output power
Radio TX, 5-dBm output power
(1)
(2)
(1)
(2)
(2)
for each peripheral unit activated)
core
Delta current with power domain enabled, clock
enabled, RF core idle
= 3.0 V with internal DC/DC converter, unless
DDS
(3)
100
1.5
1.7
6
6.2
1.45 mA +
31 µA/MHz
5.9
6.1
6.1
7.0
9.1
237 µA
www.ti.com
nA
µA
mA
12
Specifications Copyright © 2020, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
CC2640R2L
www.ti.com
SWRS250 –JUNE 2020
5.5 General Characteristics
Tc= 25°C, V
FLASH MEMORY
Supported flash erase cycles before
(1)
failure
Maximum number of write operations
per row before erase
Flash retention 105°C 11.4
Flash page/sector erase current Average delta current 12.6 mA
Flash page/sector size 4 KB
Flash write current Average delta current, 4 bytes at a time 8.15 mA
Flash page/sector erase time
Flash write time
(1) Aborting flash during erase or program modes is not a safe operation.
(2) Each row is 2048 bits (or 256 Bytes) wide.
(3) This number is dependent on Flash aging and will increase over time and erase cycles.
= 3.0 V, unless otherwise noted.
DDS
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
100 k Cycles
write
(2)
83
operations
Years at
105°C
(3)
(3)
4 bytes at a time 8 µs
8 ms
Submit Documentation Feedback
SpecificationsCopyright © 2020, Texas Instruments Incorporated
13
CC2640R2L
SWRS250 –JUNE 2020
www.ti.com
5.6 125-kbps Coded (Bluetooth 5) – RX
Measured on the TI CC2650EM-5XD reference design with Tc= 25°C, V
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Receiver sensitivity
Receiver saturation
Frequency error tolerance
Data rate error tolerance
Data rate error tolerance
Co-channel rejection
Selectivity, ±1 MHz
Selectivity, ±2 MHz
Selectivity, ±3 MHz
Selectivity, ±4 MHz
Selectivity, ±6 MHz
Alternate channel rejection,
(1)
±7 MHz
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
Selectivity, image frequency
Selectivity, image frequency
(1)
±1 MHz
Blocker rejection, ±8 MHz and
(1)
above
Out-of-band blocking
(3)
Out-of-band blocking 2003 MHz to 2399 MHz –19 dBm
Out-of-band blocking 2484 MHz to 2997 MHz –22 dBm
Intermodulation
(1) Numbers given as I/C dB.
(2) X / Y, where X is +N MHz and Y is –N MHz.
(3) Excluding one exception at F
Differential mode. Measured at the CC2650EM-5XD
SMA connector, BER = 10
Differential mode. Measured at the CC2650EM-5XD
SMA connector, BER = 10
–3
–3
Difference between the incoming carrier frequency
and the internally generated carrier frequency
Difference between incoming data rate and the
internally generated data rate (37-byte packets)
Difference between incoming data rate and the
internally generated data rate (255-byte packets)
Wanted signal at –79 dBm, modulated interferer in
channel, BER = 10
Wanted signal at –79 dBm, modulated interferer at
±1 MHz, BER = 10
–3
–3
Wanted signal at –79 dBm, modulated interferer at
±2 MHz, Image frequency is at –2 MHz, BER = 10
Wanted signal at –79 dBm, modulated interferer at
±3 MHz, BER = 10
Wanted signal at –79 dBm, modulated interferer at
±4 MHz, BER = 10
Wanted signal at –79 dBm, modulated interferer at
±6 MHz, BER = 10
Wanted signal at –79 dBm, modulated interferer at ≥
±7 MHz, BER = 10
Wanted signal at –79 dBm, modulated interferer at
(1)
image frequency, BER = 10
–3
–3
–3
–3
–3
Note that Image frequency + 1 MHz is the Cochannel –1 MHz. Wanted signal at –79 dBm,
modulated interferer at ±1 MHz from image
frequency, BER = 10
Wanted signal at –79 dBm, modulated interferer at
±8 MHz and above, BER = 10
–3
–3
30 MHz to 2000 MHz –40 dBm
Wanted signal at 2402 MHz, –76 dBm. Two
interferers at 2405 and 2408 MHz respectively, at
the given power level
/ 2, per Bluetooth Specification.
wanted
= 3.0 V, fRF= 2440 MHz, unless otherwise noted.
DDS
–103 dBm
>5 dBm
–260 310 kHz
–260 260 ppm
–140 140 ppm
–3 dB
(2)
9 / 5
(2)
–3
43 / 32
47 / 42
46 / 47
49 / 46
50 / 47
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
32 dB
(2)
5 / 32
>46 dB
–42 dBm
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
14
Specifications Copyright © 2020, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
CC2640R2L
www.ti.com
SWRS250 –JUNE 2020
5.7 125-kbps Coded (Bluetooth 5) – TX
Measured on the TI CC2650EM-5XD reference design with Tc= 25°C, V
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Output power, highest setting
Output power, highest setting
Output power, lowest setting Delivered to a single-ended 50-Ω load through a balun –21 dBm
Spurious emission conducted
measurement
(1)
(1) Suitable for systems targeting compliance with worldwide radio-frequency regulations ETSI EN 300 328 and EN 300 440 Class 2
(Europe), FCC CFR47 Part 15 (US), and ARIB STD-T66 (Japan).
Differential mode, delivered to a single-ended 50-Ω load
through a balun
Measured on CC2650EM-4XS, delivered to a single-ended
50-Ω load
f < 1 GHz, outside restricted bands –43 dBm
f < 1 GHz, restricted bands ETSI –65 dBm
f < 1 GHz, restricted bands FCC –71 dBm
f > 1 GHz, including harmonics –46 dBm
= 3.0 V, fRF= 2440 MHz, unless otherwise noted.
DDS
5 dBm
2 dBm
5.8 500-kbps Coded (Bluetooth 5) – RX
Measured on the TI CC2650EM-5XD reference design with Tc= 25°C, V
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Receiver sensitivity
Receiver saturation
Frequency error tolerance
Data rate error tolerance
Data rate error tolerance
Co-channel rejection
Selectivity, ±1 MHz
Selectivity, ±2 MHz
Selectivity, ±3 MHz
Selectivity, ±4 MHz
Selectivity, ±6 MHz
Alternate channel rejection,
(1)
±7 MHz
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
Selectivity, image frequency
Selectivity, image frequency
(1)
±1 MHz
Blocker rejection, ±8 MHz and
(1)
above
Out-of-band blocking
(3)
Out-of-band blocking 2003 MHz to 2399 MHz –19 dBm
Out-of-band blocking 2484 MHz to 2997 MHz –19 dBm
Differential mode. Measured at the CC2650EM-5XD
SMA connector, BER = 10
Differential mode. Measured at the CC2650EM-5XD
SMA connector, BER = 10
–3
–3
Difference between the incoming carrier frequency
and the internally generated carrier frequency
Difference between incoming data rate and the
internally generated data rate (37-byte packets)
Difference between incoming data rate and the
internally generated data rate (255-byte packets)
Wanted signal at –72 dBm, modulated interferer in
channel, BER = 10
Wanted signal at –72 dBm, modulated interferer at
±1 MHz, BER = 10
–3
–3
Wanted signal at –72 dBm, modulated interferer at
±2 MHz, Image frequency is at –2 MHz, BER = 10
Wanted signal at –72 dBm, modulated interferer at
±3 MHz, BER = 10
Wanted signal at –72 dBm, modulated interferer at
±4 MHz, BER = 10
Wanted signal at –72 dBm, modulated interferer at
±6 MHz, BER = 10
Wanted signal at –72 dBm, modulated interferer at
≥ ±7 MHz, BER = 10
Wanted signal at –72 dBm, modulated interferer at
(1)
image frequency, BER = 10
–3
–3
–3
–3
–3
Note that Image frequency + 1 MHz is the Cochannel –1 MHz. Wanted signal at –72 dBm,
modulated interferer at ±1 MHz from image
frequency, BER = 10
Wanted signal at –72 dBm, modulated interferer at
±8 MHz and above, BER = 10
–3
–3
30 MHz to 2000 MHz –35 dBm
= 3.0 V, fRF= 2440 MHz, unless otherwise noted.
DDS
–101 dBm
>5 dBm
–240 240 kHz
–500 500 ppm
–310 330 ppm
–5 dB
(2)
9 / 5
(2)
–3
41 / 31
44 / 41
44 / 44
44 / 44
44 / 44
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
31 dB
(2)
5 / 41
44 dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
(1) Numbers given as I/C dB.
(2) X / Y, where X is +N MHz and Y is –N MHz.
(3) Excluding one exception at F
/ 2, per Bluetooth Specification.
wanted
Submit Documentation Feedback
SpecificationsCopyright © 2020, Texas Instruments Incorporated
15
CC2640R2L
SWRS250 –JUNE 2020
www.ti.com
500-kbps Coded (Bluetooth 5) – RX (continued)
Measured on the TI CC2650EM-5XD reference design with Tc= 25°C, V
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Intermodulation
Wanted signal at 2402 MHz, –69 dBm. Two
interferers at 2405 and 2408 MHz respectively, at
the given power level
= 3.0 V, fRF= 2440 MHz, unless otherwise noted.
DDS
–37 dBm
5.9 500-kbps Coded (Bluetooth 5) – TX
Measured on the TI CC2650EM-5XD reference design with Tc= 25°C, V
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Output power, highest setting
Output power, highest setting
Output power, lowest setting Delivered to a single-ended 50-Ω load through a balun –21 dBm
Spurious emission conducted
measurement
(1)
(1) Suitable for systems targeting compliance with worldwide radio-frequency regulations ETSI EN 300 328 and EN 300 440 Class 2
(Europe), FCC CFR47 Part 15 (US), and ARIB STD-T66 (Japan).
Differential mode, delivered to a single-ended 50-Ω load
through a balun
Measured on CC2650EM-4XS, delivered to a single-ended
50-Ω load
f < 1 GHz, outside restricted bands –43 dBm
f < 1 GHz, restricted bands ETSI –65 dBm
f < 1 GHz, restricted bands FCC –71 dBm
f > 1 GHz, including harmonics –46 dBm
= 3.0 V, fRF= 2440 MHz, unless otherwise noted.
DDS
5 dBm
2 dBm
5.10 1-Mbps GFSK (Bluetooth low energy) – RX
Measured on the TI CC2650EM-5XD reference design with Tc= 25°C, V
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Receiver sensitivity
Receiver sensitivity
Receiver saturation
Receiver saturation
Frequency error tolerance
Data rate error tolerance
Co-channel rejection
Selectivity, ±1 MHz
Selectivity, ±2 MHz
Selectivity, ±3 MHz
Selectivity, ±4 MHz
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
Selectivity, ±5 MHz or more
Selectivity, image frequency
Selectivity, image frequency
(1)
±1 MHz
Differential mode. Measured at the CC2650EM-5XD
SMA connector, BER = 10
Single-ended mode. Measured on CC2650EM-4XS,
at the SMA connector, BER = 10
Differential mode. Measured at the CC2650EM-5XD
SMA connector, BER = 10
Single-ended mode. Measured on CC2650EM-4XS,
at the SMA connector, BER = 10
–3
–3
–3
–3
Difference between the incoming carrier frequency
and the internally generated carrier frequency
Difference between incoming data rate and the
internally generated data rate
Wanted signal at –67 dBm, modulated interferer in
channel, BER = 10
Wanted signal at –67 dBm, modulated interferer at
±1 MHz, BER = 10
Wanted signal at –67 dBm, modulated interferer at
±2 MHz, BER = 10
Wanted signal at –67 dBm, modulated interferer at
±3 MHz, BER = 10
Wanted signal at –67 dBm, modulated interferer at
±4 MHz, BER = 10
Wanted signal at –67 dBm, modulated interferer at
(1)
≥ ±5 MHz, BER = 10
Wanted signal at –67 dBm, modulated interferer at
(1)
image frequency, BER = 10
–3
–3
–3
–3
–3
–3
–3
Wanted signal at –67 dBm, modulated interferer at
±1 MHz from image frequency, BER = 10
–3
= 3.0 V, fRF= 2440 MHz, unless otherwise noted.
DDS
–97 dBm
–96 dBm
4 dBm
0 dBm
–350 350 kHz
–750 750 ppm
–6 dB
(2)
7 / 3
(2)
34 / 25
(2)
38 / 26
(2)
42 / 29
32 dB
25 dB
(2)
3 / 26
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
(1) Numbers given as I/C dB.
(2) X / Y, where X is +N MHz and Y is –N MHz.
16
Specifications Copyright © 2020, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
CC2640R2L
www.ti.com
SWRS250 –JUNE 2020
1-Mbps GFSK (Bluetooth low energy) – RX (continued)
Measured on the TI CC2650EM-5XD reference design with Tc= 25°C, V
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Out-of-band blocking
Out-of-band blocking 2003 MHz to 2399 MHz –5 dBm
Out-of-band blocking 2484 MHz to 2997 MHz –8 dBm
Out-of-band blocking 3000 MHz to 12.75 GHz –10 dBm
Intermodulation
Spurious emissions,
30 to 1000 MHz
Spurious emissions,
1 to 12.75 GHz
RSSI dynamic range 70 dB
RSSI accuracy ±4 dB
(3) Excluding one exception at F
(3)
30 MHz to 2000 MHz –20 dBm
Wanted signal at 2402 MHz, –64 dBm. Two
interferers at 2405 and 2408 MHz respectively, at
the given power level
Conducted measurement in a 50-Ω single-ended
load. Suitable for systems targeting compliance with
EN 300 328, EN 300 440 class 2, FCC CFR47, Part
15 and ARIB STD-T-66
Conducted measurement in a 50-Ω single-ended
load. Suitable for systems targeting compliance with
EN 300 328, EN 300 440 class 2, FCC CFR47, Part
15 and ARIB STD-T-66
/ 2, per Bluetooth Specification.
wanted
= 3.0 V, fRF= 2440 MHz, unless otherwise noted.
DDS
–34 dBm
–71 dBm
–62 dBm
5.11 1-Mbps GFSK (Bluetooth low energy) – TX
Measured on the TI CC2650EM-5XD reference design with Tc= 25°C, V
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Output power, highest setting
Output power, highest setting
Output power, lowest setting Delivered to a single-ended 50-Ω load through a balun –21 dBm
Spurious emission conducted
measurement
(1)
(1) Suitable for systems targeting compliance with worldwide radio-frequency regulations ETSI EN 300 328 and EN 300 440 Class 2
(Europe), FCC CFR47 Part 15 (US), and ARIB STD-T66 (Japan).
Differential mode, delivered to a single-ended 50-Ω load
through a balun
Measured on CC2650EM-4XS, delivered to a single-ended
50-Ω load
f < 1 GHz, outside restricted bands –43 dBm
f < 1 GHz, restricted bands ETSI –65 dBm
f < 1 GHz, restricted bands FCC –71 dBm
f > 1 GHz, including harmonics –46 dBm
= 3.0 V, fRF= 2440 MHz, unless otherwise noted.
DDS
5 dBm
2 dBm
5.12 2-Mbps GFSK (Bluetooth 5) – RX
Measured on the TI CC2650EM-5XD reference design with Tc= 25°C, V
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Receiver sensitivity
Receiver saturation
Frequency error tolerance
Data rate error tolerance
Co-channel rejection
Selectivity, ±2 MHz
(1)
(1)
Differential mode. Measured at the CC2650EM-5XD
SMA connector, BER = 10
Differential mode. Measured at the CC2650EM-5XD
SMA connector, BER = 10
–3
–3
Difference between the incoming carrier frequency and
the internally generated carrier frequency
Difference between incoming data rate and the
internally generated data rate
Wanted signal at –67 dBm, modulated interferer in
channel, BER = 10
–3
Wanted signal at –67 dBm, modulated interferer at
±2 MHz, Image frequency is at –2 MHz BER = 10
= 3.0 V, fRF= 2440 MHz, unless otherwise noted.
DDS
–90 dBm
3 dBm
–300 500 kHz
–1000 1000 ppm
–7 dB
(2)
–3
8 / 4
dB
(1) Numbers given as I/C dB.
(2) X / Y, where X is +N MHz and Y is –N MHz.
Submit Documentation Feedback
SpecificationsCopyright © 2020, Texas Instruments Incorporated
17

CC2640R2L
SWRS250 –JUNE 2020
www.ti.com
2-Mbps GFSK (Bluetooth 5) – RX (continued)
Measured on the TI CC2650EM-5XD reference design with Tc= 25°C, V
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Selectivity, ±4 MHz
Selectivity, ±6 MHz
Alternate channel rejection,
(1)
±7 MHz
(1)
(1)
Selectivity, image frequency
Selectivity, image frequency
(1)
±2 MHz
Out-of-band blocking
(3)
Out-of-band blocking 2003 MHz to 2399 MHz –15 dBm
Out-of-band blocking 2484 MHz to 2997 MHz –12 dBm
Out-of-band blocking 3000 MHz to 12.75 GHz –10 dBm
Intermodulation
(3) Excluding one exception at F
Wanted signal at –67 dBm, modulated interferer at
±4 MHz, BER = 10
Wanted signal at –67 dBm, modulated interferer at
±6 MHz, BER = 10
Wanted signal at –67 dBm, modulated interferer at ≥
±7 MHz, BER = 10
Wanted signal at –67 dBm, modulated interferer at
(1)
image frequency, BER = 10
–3
–3
–3
–3
Note that Image frequency + 2 MHz is the Co-channel.
Wanted signal at –67 dBm, modulated interferer at
±2 MHz from image frequency, BER = 10
–3
30 MHz to 2000 MHz –33 dBm
Wanted signal at 2402 MHz, –64 dBm. Two interferers
at 2408 and 2414 MHz respectively, at the given power
level
/ 2, per Bluetooth Specification.
wanted
= 3.0 V, fRF= 2440 MHz, unless otherwise noted.
DDS
(2)
31 / 26
(2)
37 / 38
(2)
37 / 36
4 dB
(2)
–7 / 26
–45 dBm
dB
dB
dB
dB
5.13 2-Mbps GFSK (Bluetooth 5) – TX
Measured on the TI CC2650EM-5XD reference design with Tc= 25°C, V
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Output power, highest setting
Output power, highest setting
Output power, lowest setting Delivered to a single-ended 50-Ω load through a balun –21 dBm
Spurious emission conducted
measurement
(1)
(1) Suitable for systems targeting compliance with worldwide radio-frequency regulations ETSI EN 300 328 and EN 300 440 Class 2
(Europe), FCC CFR47 Part 15 (US), and ARIB STD-T66 (Japan).
Differential mode, delivered to a single-ended 50-Ω load
through a balun
Measured on CC2650EM-4XS, delivered to a single-ended
50-Ω load
f < 1 GHz, outside restricted bands –43 dBm
f < 1 GHz, restricted bands ETSI –65 dBm
f < 1 GHz, restricted bands FCC –71 dBm
f > 1 GHz, including harmonics –46 dBm
= 3.0 V, fRF= 2440 MHz, unless otherwise noted.
DDS
5 dBm
2 dBm
5.14 24-MHz Crystal Oscillator (XOSC_HF)
Tc= 25°C, V
= 3.0 V, unless otherwise noted.
DDS
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
ESR, Equivalent series resistance
ESR, Equivalent series resistance
LM, Motional inductance
CL, Crystal load capacitance
Crystal frequency
Crystal frequency tolerance
(2)
(2)(3)
(2)(4)
(2)(5)
(2)
(2)
6 pF < CL≤ 9 pF 20 60 Ω
5 pF < CL≤ 6 pF 80 Ω
Relates to load capacitance (CLin
Farads)
(1)
–24
< 1.6 × 10
/ C
2
L
H
5 9 pF
24 MHz
–40 40 ppm
(1) Probing or otherwise stopping the crystal while the DC/DC converter is enabled may cause permanent damage to the device.
(2) The crystal manufacturer's specification must satisfy this requirement
(3) Adjustable load capacitance is integrated into the device. External load capacitors are not required
(4) Measured on the TI CC2650EM-5XD reference design with Tc= 25°C, V
(5) Includes initial tolerance of the crystal, drift over temperature, ageing and frequency pulling due to incorrect load capacitance. As per
DDS
= 3.0 V
Bluetooth specification.
18
Specifications Copyright © 2020, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback

CC2640R2L
www.ti.com
SWRS250 –JUNE 2020
24-MHz Crystal Oscillator (XOSC_HF) (continued)
Tc= 25°C, V
= 3.0 V, unless otherwise noted.
DDS
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Start-up time
(4)(6)
(6) Kick-started based on a temperature and aging compensated RCOSC_HF using precharge injection.
(1)
150 µs
5.15 32.768-kHz Crystal Oscillator (XOSC_LF)
Tc= 25°C, V
Crystal frequency
Crystal frequency tolerance, Bluetooth low-
energy applications
ESR Equivalent series resistance
CLCrystal load capacitance
(1) The crystal manufacturer's specification must satisfy this requirement
(2) Includes initial tolerance of the crystal, drift over temperature, ageing and frequency pulling due to incorrect load capacitance. As per
Bluetooth specification.
= 3.0 V, unless otherwise noted.
DDS
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
(1)
(1)(2)
–500 500 ppm
(1)
(1)
32.768 kHz
30 100 kΩ
6 12 pF
5.16 48-MHz RC Oscillator (RCOSC_HF)
Measured on the TI CC2650EM-5XD reference design with Tc= 25°C, V
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Frequency 48 MHz
Uncalibrated frequency accuracy ±1%
Calibrated frequency accuracy
Start-up time 5 µs
(1) Accuracy relative to the calibration source (XOSC_HF).
(1)
= 3.0 V, unless otherwise noted.
DDS
±0.25%
5.17 32-kHz RC Oscillator (RCOSC_LF)
Measured on the TI CC2650EM-5XD reference design with Tc= 25°C, V
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Calibrated frequency
Temperature coefficient 80 ppm/°C
(1) The frequency accuracy of the Real Time Clock (RTC) is not directly dependent on the frequency accuracy of the 32-kHz RC Oscillator.
The RTC can be calibrated to an accuracy within ±500 ppm of 32.768 kHz by measuring the frequency error of RCOSC_LF relative to
XOSC_HF and compensating the RTC tick speed. The procedure is explained in Running Bluetooth® Low Energy on CC2640 Without
32 kHz Crystal.
(1)
= 3.0 V, unless otherwise noted.
DDS
32.8 kHz
5.18 ADC Characteristics
Tc= 25°C, V
= 3.0 V and voltage scaling enabled, unless otherwise noted.
DDS
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Input voltage range 0 VDDS V
Resolution 12 Bits
Sample rate 200 ksps
(2)
(2)
DNL
INL
Offset Internal 4.3-V equivalent reference
Gain error Internal 4.3-V equivalent reference
(3)
Differential nonlinearity >–1 LSB
(4)
Integral nonlinearity ±3 LSB
(1) Using IEEE Std 1241™-2010 for terminology and test methods.
(2) Input signal scaled down internally before conversion, as if voltage range was 0 to 4.3 V.
(3) No missing codes. Positive DNL typically varies from +0.3 to +3.5, depending on device (see Figure 5-21).
(4) For a typical example, see Figure 5-22.
Submit Documentation Feedback
(1)
2 LSB
2.4 LSB
SpecificationsCopyright © 2020, Texas Instruments Incorporated
19

CC2640R2L
SWRS250 –JUNE 2020
ADC Characteristics (continued)
Tc= 25°C, V
ENOB Effective number of bits
THD Total harmonic distortion
SINAD,
SNDR
SFDR
(5) Applied voltage must be within absolute maximum ratings (Section 5.1) at all times.
= 3.0 V and voltage scaling enabled, unless otherwise noted.
DDS
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Internal 4.3-V equivalent reference
(2)
, 200 ksps,
9.6-kHz input tone
Internal 1.44-V reference, voltage scaling disabled,
32 samples average, 200 ksps, 300-Hz input tone
Internal 4.3-V equivalent reference
(2)
, 200 ksps,
9.6-kHz input tone
Internal 1.44-V reference, voltage scaling disabled,
32 samples average, 200 ksps, 300-Hz input tone
(2)
, 200 ksps,
Signal-to-noise
Internal 4.3-V equivalent reference
9.6-kHz input tone
and
Distortion ratio
Internal 1.44-V reference, voltage scaling disabled,
32 samples average, 200 ksps, 300-Hz input tone
Internal 4.3-V equivalent reference
(2)
, 200 ksps,
9.6-kHz input tone
Spurious-free dynamic
range
Internal 1.44-V reference, voltage scaling disabled,
32 samples average, 200 ksps, 300-Hz input tone
Conversion time Serial conversion, time-to-output, 24-MHz clock 50
Current consumption Internal 4.3-V equivalent reference
(2)
Current consumption VDDS as reference 0.75 mA
Equivalent fixed internal reference (input voltage scaling
Reference voltage
enabled). For best accuracy, the ADC conversion should
be initiated through the TIRTOS API in order to include the
gain/offset compensation factors stored in FCFG1.
Fixed internal reference (input voltage scaling disabled).
For best accuracy, the ADC conversion should be initiated
Reference voltage
through the TIRTOS API in order to include the gain/offset
compensation factors stored in FCFG1. This value is
derived from the scaled value (4.3 V) as follows:
Vref = 4.3 V × 1408 / 4095
Reference voltage
Reference voltage
VDDS as reference (Also known as RELATIVE) (input
voltage scaling enabled)
VDDS as reference (Also known as RELATIVE) (input
voltage scaling disabled)
200 ksps, voltage scaling enabled. Capacitive input, Input
Input impedance
impedance depends on sampling frequency and sampling
time
www.ti.com
(1)
9.8
BitsVDDS as reference, 200 ksps, 9.6-kHz input tone 10
11.1
–65
dBVDDS as reference, 200 ksps, 9.6-kHz input tone –69
–71
60
dBVDDS as reference, 200 ksps, 9.6-kHz input tone 63
69
67
dBVDDS as reference, 200 ksps, 9.6-kHz input tone 68
73
clockcycles
0.66 mA
(2)(5)
4.3
V
1.48 V
VDDS V
VDDS /
2.82
(5)
V
>1 MΩ
5.19 Temperature Sensor
Measured on the TI CC2650EM-5XD reference design with Tc= 25°C, V
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Resolution 4 °C
Range –40 85 °C
Accuracy ±5 °C
Supply voltage coefficient
(1) Automatically compensated when using supplied driver libraries.
20
Specifications Copyright © 2020, Texas Instruments Incorporated
(1)
Submit Documentation Feedback
= 3.0 V, unless otherwise noted.
DDS
3.2 °C/V

SSIClk
SSIFss
SSITx
SSIRx
MSB LSB
S2
S3
S1
4 to 16 bits
CC2640R2L
www.ti.com
SWRS250 –JUNE 2020
5.20 Battery Monitor
Measured on the TI CC2650EM-5XD reference design with Tc= 25°C, V
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Resolution 50 mV
Range 1.8 3.8 V
Accuracy 13 mV
= 3.0 V, unless otherwise noted.
DDS
5.21 Synchronous Serial Interface (SSI)
Tc= 25°C, V
(1)
S1
t
clk_per
(1)
S2
t
clk_high
(1)
S3
t
clk_low
S1 (TX only)
S1 (TX and RX)
(1)
S2
t
clk_high
(1)
S3
t
clk_low
(1) Refer to SSI timing diagrams Figure 5-1, Figure 5-2, and Figure 5-3.
= 3.0 V, unless otherwise noted.
DDS
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
(SSIClk period) Device operating as slave 12 65024
(SSIClk high time) Device operating as slave 0.5 t
(SSIClk low time) Device operating as slave 0.5 t
(1)
t
clk_per
(1)
t
clk_per
(SSIClk period)
(SSIClk period)
One-way communication to slave, device
operating as master
Normal duplex operation, device
operating as master
4 65024
8 65024
(SSIClk high time) Device operating as master 0.5 t
(SSIClk low time) Device operating as master 0.5 t
system
system
system
clocks
clk_per
clk_per
clocks
clocks
clk_per
clk_per
Figure 5-1. SSI Timing for TI Frame Format (FRF = 01), Single Transfer Timing Measurement
SpecificationsCopyright © 2020, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
21

SSIClk
(SPO = 1)
SSITx
(Master)
SSIRx
(Slave)
LSB
SSIClk
(SPO = 0)
S2
S1
SSIFss
LSB
S3
MSB
MSB
0
SSIClk
SSIFss
SSITx
SSIRx
MSB LSB
MSB LSB
S2
S3
S1
8-bit control
4 to 16 bits output data
CC2640R2L
SWRS250 –JUNE 2020
Figure 5-2. SSI Timing for MICROWIRE Frame Format (FRF = 10), Single Transfer
www.ti.com
22
Figure 5-3. SSI Timing for SPI Frame Format (FRF = 00), With SPH = 1
Specifications Copyright © 2020, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback

CC2640R2L
www.ti.com
SWRS250 –JUNE 2020
5.22 DC Characteristics
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
TA= 25°C, V
GPIO VOH at 8-mA load IOCURR = 2, high-drive GPIOs only 1.32 1.54 V
GPIO VOL at 8-mA load IOCURR = 2, high-drive GPIOs only 0.26 0.32 V
GPIO VOH at 4-mA load IOCURR = 1 1.32 1.58 V
GPIO VOL at 4-mA load IOCURR = 1 0.21 0.32 V
GPIO pullup current Input mode, pullup enabled, Vpad = 0 V 71.7 µA
GPIO pulldown current Input mode, pulldown enabled, Vpad = VDDS 21.1 µA
GPIO high/low input transition,
no hysteresis
GPIO low-to-high input transition,
with hysteresis
GPIO high-to-low input transition,
with hysteresis
IH = 0, transition between reading 0 and reading 1 0.88 V
IH = 1, transition voltage for input read as 0 → 1 1.07 V
IH = 1, transition voltage for input read as 1 → 0 0.74 V
GPIO input hysteresis IH = 1, difference between 0 → 1 and 1 → 0 points 0.33 V
TA= 25°C, V
GPIO VOH at 8-mA load IOCURR = 2, high-drive GPIOs only 2.68 V
GPIO VOL at 8-mA load IOCURR = 2, high-drive GPIOs only 0.33 V
GPIO VOH at 4-mA load IOCURR = 1 2.72 V
GPIO VOL at 4-mA load IOCURR = 1 0.28 V
TA= 25°C, V
GPIO pullup current Input mode, pullup enabled, Vpad = 0 V 277 µA
GPIO pulldown current Input mode, pulldown enabled, Vpad = VDDS 113 µA
GPIO high/low input transition,
no hysteresis
GPIO low-to-high input transition,
with hysteresis
GPIO high-to-low input transition,
with hysteresis
IH = 0, transition between reading 0 and reading 1 1.67 V
IH = 1, transition voltage for input read as 0 → 1 1.94 V
IH = 1, transition voltage for input read as 1 → 0 1.54 V
GPIO input hysteresis IH = 1, difference between 0 → 1 and 1 → 0 points 0.4 V
TA= 25°C
VIH
VIL
Lowest GPIO input voltage reliably interpreted as a
«High»
Highest GPIO input voltage reliably interpreted as a
«Low»
(1) Each GPIO is referenced to a specific VDDS pin. See the technical reference manual listed in Section 8.3 for more details.
DDS
DDS
DDS
= 1.8 V
= 3.0 V
= 3.8 V
0.8 VDDS
0.2 VDDS
(1)
(1)
Submit Documentation Feedback
SpecificationsCopyright © 2020, Texas Instruments Incorporated
23

CC2640R2L
SWRS250 –JUNE 2020
www.ti.com
5.23 Thermal Resistance Characteristics
NAME DESCRIPTION RHB (°C/W)
Rθ
Rθ
Rθ
Psi
Psi
Rθ
JA
JC(top)
JB
JT
JB
JC(bot)
Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance 32.8 29.6
Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance 24.0 15.7
Junction-to-board thermal resistance 6.8 6.2
Junction-to-top characterization parameter 0.3 0.3
Junction-to-board characterization parameter 6.8 6.2
Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance 1.9 1.9
(1) (2)
RGZ (°C/W)
(1) °C/W = degrees Celsius per watt.
(2) These values are based on a JEDEC-defined 2S2P system (with the exception of the Theta JC [RθJC] value, which is based on a
JEDEC-defined 1S0P system) and will change based on environment as well as application. For more information, see these
EIA/JEDEC standards:
• JESD51-2, Integrated Circuits Thermal Test Method Environmental Conditions - Natural Convection (Still Air).
• JESD51-3, Low Effective Thermal Conductivity Test Board for Leaded Surface Mount Packages.
• JESD51-7, High Effective Thermal Conductivity Test Board for Leaded Surface Mount Packages.
• JESD51-9, Test Boards for Area Array Surface Mount Package Thermal Measurements.
Power dissipation of 2 W and an ambient temperature of 70ºC is assumed.
(1) (2)
5.24 Timing Requirements
MIN NOM MAX UNIT
Rising supply-voltage slew rate 0 100 mV/µs
Falling supply-voltage slew rate 0 20 mV/µs
Falling supply-voltage slew rate, with low-power flash settings
Positive temperature gradient in standby
CONTROL INPUT AC CHARACTERISTICS
(2)
(3)
RESET_N low duration 1 µs
(1) For smaller coin cell batteries, with high worst-case end-of-life equivalent source resistance, a 22-µF VDDS input capacitor (see
Figure 7-1) must be used to ensure compliance with this slew rate.
(2) Applications using RCOSC_LF as sleep timer must also consider the drift in frequency caused by a change in temperature (see
Section 5.17).
(3) TA= –40°C to +85°C, V
= 1.7 V to 3.8 V, unless otherwise noted.
DDS
(1)
No limitation for negative
temperature gradient, or
outside standby mode
3 mV/µs
5 °C/s
5.25 Switching Characteristics
Measured on the TI CC2650EM-5XD reference design with Tc= 25°C, V
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
WAKEUP AND TIMING
Idle → Active 14 µs
Standby → Active 151 µs
Shutdown → Active 1015 µs
24
Specifications Copyright © 2020, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
= 3.0 V, unless otherwise noted.
DDS

VDDS (V)
Output power (dBm)
1.8 2.3 2.8 3.3 3.8
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
D003
5XD 5dBm Setting
4XS 2dBm Setting
Frequency (MHz)
Output Power (dBm)
2400 2410 2420 2430 2440 2450 2460 2470 2480
-1
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
D021
5-dBm setting (5XD)
0-dBm setting (4XS)
Frequency (MHz)
Sensitivity Level (dBm)
2400 2410 2420 2430 2440 2450 2460 2470 2480
-99
-98.5
-98
-97.5
-97
-96.5
-96
-95.5
-95
D020
Sensitivity 5XD
Sensitivity 4XS
Temperature (qC)
Output Power (dBm)
-40 -30 -20 -10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
4XS 2-dBm Setting
5XD 5-dBm Setting
VDDS (V)
Sensitivity (dBm)
1.8 2.3 2.8 3.3 3.8
-101
-100
-99
-98
-97
-96
-95
D004
BLE 5XD Sensitivity
BLE 4XS Sensitivity
Temperature (qC)
Sensitivity (dBm)
-40 -30 -20 -10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80
-99
-98
-97
-96
-95
-94
Sensitivity 4XS
Sensitivity 5XD
www.ti.com
5.26 Typical Characteristics
CC2640R2L
SWRS250 –JUNE 2020
Figure 5-4. BLE Sensitivity vs Temperature
Figure 5-6. BLE Sensitivity vs Channel Frequency
Figure 5-5. BLE Sensitivity vs Supply Voltage (VDDS)
Figure 5-7. TX Output Power vs Temperature
Figure 5-8. TX Output Power vs Supply Voltage (VDDS)
Submit Documentation Feedback
Figure 5-9. TX Output Power
vs Channel Frequency
SpecificationsCopyright © 2020, Texas Instruments Incorporated
25

Temperature (qC)
Active Mode Current Consumpstion (mA)
-40 -30 -20 -10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80
2.85
2.9
2.95
3
3.05
3.1
D006
Active Mode Current
VDDS (V)
Current Consumption (mA)
1.8 2.3 2.8 3.3 3.8
2
2.5
3
3.5
4
4.5
5
D007
Active Mode Current
Temperature (qC)
TX Current (mA)
-40 -30 -20 -10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
D002
5XD 5dBm Setting
4XS 2dBm Setting
Temperature (qC)
RX Current (mA)
-40 -30 -20 -10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80
5.6
5.8
6
6.2
6.4
6.6
6.8
7
D001
5XD RX Current
4XS RX Current
VDDS (V)
TX Current (mA)
1.8 2 2.2 2.4 2.6 2.8 3 3.2 3.4 3.6 3.8
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
D015
4XS 0-dBm Setting
4XS 2-dBm Setting
5XD 5-dBm Setting
Voltage (V)
Current Consumption (mA)
1.8 2.05 2.3 2.55 2.8 3.05 3.3 3.55 3.8
4
4.5
5
5.5
6
6.5
7
7.5
8
8.5
9
9.5
10
10.5
D016
4XS
5XD
CC2640R2L
SWRS250 –JUNE 2020
Typical Characteristics (continued)
www.ti.com
Figure 5-10. TX Current Consumption
vs Supply Voltage (VDDS)
Figure 5-12. RX Mode Current Consumption vs Temperature
Figure 5-11. RX Mode Current vs Supply Voltage (VDDS)
Figure 5-13. TX Mode Current Consumption vs Temperature
Figure 5-14. Active Mode (MCU Running, No Peripherals)
26
Current Consumption vs Temperature
Specifications Copyright © 2020, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Figure 5-15. Active Mode (MCU Running, No Peripherals) Current
Consumption vs Supply Voltage (VDDS)
Submit Documentation Feedback

Temperature (°C)
Standby Current (µA)
-20 -10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
3.5
4
4.5
5
D021
Temperature (qC)
ADC Code
-40 -30 -20 -10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80
1004.5
1005
1005.5
1006
1006.5
1007
1007.5
D013
Sampling Frequency (Hz)
ENOB
9.6
9.7
9.8
9.9
10
10.1
10.2
10.3
10.4
10.5
1k 10k 100k 200k
D009A
ENOB Internal Reference (No Averaging)
ENOB Internal Reference (32 Samples Averaging)
Input Frequency (Hz)
Effective Number of Bits
200300 500 1000 2000 5000 10000 20000 100000
9.4
9.6
9.8
10
10.2
10.4
10.6
10.8
11
11.2
11.4
D009
Fs= 200 kHz, No Averaging
Fs= 200 kHz, 32 samples averaging
VDDS (V)
ADC Code
1.8 2.3 2.8 3.3 3.8
1004.8
1005
1005.2
1005.4
1005.6
1005.8
1006
1006.2
1006.4
D012
www.ti.com
Typical Characteristics (continued)
CC2640R2L
SWRS250 –JUNE 2020
Figure 5-16. SoC ADC Effective Number of Bits vs Input
Frequency (Internal Reference, Scaling Enabled)
Figure 5-18. SoC ADC Output vs Temperature (Fixed Input,
Internal Reference)
Figure 5-17. SoC ADC Output vs Supply Voltage (Fixed Input,
Figure 5-19. SoC ADC ENOB vs Sampling Frequency
(Scaling Enabled, Input Frequency = FS / 10)
Internal Reference)
Figure 5-20. Standby Mode Supply Current vs Temperature
Submit Documentation Feedback
SpecificationsCopyright © 2020, Texas Instruments Incorporated
27

ADC Code
INL
0 200 400 600 80 0 1000 12 00 1400 1600 1800 2000 2200 2400 2600 2800 3000 3200 3400 3600 3800 4000 4200
-4
-3
-2
-1
0
1
2
3
D011
ADC Code
DNL
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
1400
1600
1800
2000
2200
2400
2600
2800
3000
3200
3400
3600
3800
4000
4200
-1.5
-1
-0.5
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
3.5
D010
CC2640R2L
SWRS250 –JUNE 2020
Typical Characteristics (continued)
Figure 5-21. SoC ADC DNL vs ADC Code (Internal Reference)
www.ti.com
Figure 5-22. SoC ADC INL vs ADC Code (Internal Reference)
28
Specifications Copyright © 2020, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback

SimpleLink CC2640R2L Wireless MCU
Main CPU
128-KB
Flash
cJTAG
20-KB
SRAM
ROM
ARM
Cortex-M3
DC-DC Converter
RF Core
ARM
Cortex-M0
DSP modem
4-KB
SRAM
ROM
General Peripherals / Modules
4× 32-bit Timers
2× SSI (SPI, µW, TI)
Watchdog Timer
Temperature and Battery Monitor
RTC
I2C
UART
I2S
15 / 31 GPIOs
AES 32-channel µDMA
ADC
Digital PLL
Up to 48 MHz
61 µA/MHz
TRNG
ADC
8-KB
cache
12-bit ADC, 200 ksps
Time-to-Digital Converter
2-KB AUX RAM
www.ti.com
6 Detailed Description
6.1 Overview
The core modules of the CC2640R2L MCU are shown in Section 6.2.
6.2 Functional Block Diagram
CC2640R2L
SWRS250 –JUNE 2020
Submit Documentation Feedback
Detailed DescriptionCopyright © 2020, Texas Instruments Incorporated
29

CC2640R2L
SWRS250 –JUNE 2020
6.3 Main CPU
The SimpleLink™ CC2640R2L Wireless MCU contains an Arm Cortex-M3 (CM3) 32-bit CPU, which runs
the application and the higher layers of the protocol stack.
The CM3 processor provides a high-performance, low-cost platform that meets the system requirements
of minimal memory implementation, and low-power consumption, while delivering outstanding
computational performance and exceptional system response to interrupts.
Arm Cortex-M3 features include:
• 32-bit Arm Cortex-M3 architecture optimized for small-footprint embedded applications
• Outstanding processing performance combined with fast interrupt handling
• Arm Thumb®-2 mixed 16- and 32-bit instruction set delivers the high performance expected of a 32-bit
Arm core in a compact memory size usually associated with 8- and 16-bit devices, typically in the
range of a few kilobytes of memory for microcontroller-class applications:
– Single-cycle multiply instruction and hardware divide
– Atomic bit manipulation (bit-banding), delivering maximum memory use and streamlined peripheral
control
– Unaligned data access, enabling data to be efficiently packed into memory
• Fast code execution permits slower processor clock or increases sleep mode time
• Harvard architecture characterized by separate buses for instruction and data
• Efficient processor core, system, and memories
• Hardware division and fast digital-signal-processing oriented multiply accumulate
• Saturating arithmetic for signal processing
• Deterministic, high-performance interrupt handling for time-critical applications
• Enhanced system debug with extensive breakpoint and trace capabilities
• Serial wire trace reduces the number of pins required for debugging and tracing
• Migration from the ARM7™ processor family for better performance and power efficiency
• Optimized for single-cycle flash memory use
• Ultra-low-power consumption with integrated sleep modes
• 1.25 DMIPS per MHz
www.ti.com
6.4 RF Core
The RF Core contains an Arm Cortex-M0 processor that interfaces the analog RF and base-band circuits,
handles data to and from the system side, and assembles the information bits in a given packet structure.
The RF core offers a high level, command-based API to the main CPU.
The RF core is capable of autonomously handling the time-critical aspects of the radio protocols
(Bluetooth low energy) thus offloading the main CPU and leaving more resources for the user application.
The RF core has a dedicated 4-KB SRAM block and runs initially from separate ROM memory. The Arm
Cortex-M0 processor is not programmable by customers.
6.5 Memory
The Flash memory provides nonvolatile storage for code and data. The Flash memory is in-system
programmable.
The SRAM (static RAM) can be used for both storage of data and execution of code and is split into two
4-KB blocks and two 6-KB blocks. Retention of the RAM contents in standby mode can be enabled or
disabled individually for each block to minimize power consumption. In addition, if flash cache is disabled,
the 8-KB cache can be used as a general-purpose RAM.
30
Detailed Description Copyright © 2020, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback

www.ti.com
The ROM provides preprogrammed embedded TI-RTOS kernel, Driverlib, and lower layer protocol stack
software (Bluetooth low energy controller). It also contains a bootloader that can be used to reprogram the
device using SPI or UART. For CC2640R2Lxxx devices, the ROM contains Bluetooth 4.2 low energy hostand controller software libraries, leaving more of the flash memory available for the customer application.
6.6 Debug
The on-chip debug support is done through a dedicated cJTAG (IEEE 1149.7) or JTAG (IEEE 1149.1)
interface.
6.7 Power Management
To minimize power consumption, the CC2640R2L MCU supports a number of power modes and power
management features (see Table 6-1).
CC2640R2L
SWRS250 –JUNE 2020
Table 6-1. Power Modes
MODE
CPU Active Off Off Off Off
Flash On Available Off Off Off
SRAM On On On Off Off
Radio Available Available Off Off Off
Supply System On On Duty Cycled Off Off
Current 1.45 mA + 31 µA/MHz 650 µA 1.5 µA 0.15 µA 0.1 µA
Wake-up Time to CPU Active
Register Retention Full Full Partial No No
SRAM Retention Full Full Full No No
High-Speed Clock
Low-Speed Clock
Peripherals Available Available Off Off Off
Wake up on RTC Available Available Available Off Off
Wake up on Pin Edge Available Available Available Available Off
Wake up on Reset Pin Available Available Available Available Available
Brown Out Detector (BOD) Active Active Duty Cycled Off N/A
Power On Reset (POR) Active Active Active Active N/A
(1) Not including RTOS overhead
(1)
ACTIVE IDLE STANDBY SHUTDOWN
XOSC_HF or
RCOSC_HF
XOSC_LF or
RCOSC_LF
SOFTWARE CONFIGURABLE POWER MODES
– 14 µs 151 µs 1015 µs 1015 µs
XOSC_HF or
RCOSC_HF
XOSC_LF or
RCOSC_LF
Off Off Off
XOSC_LF or
RCOSC_LF
Off Off
RESET PIN
HELD
In active mode, the application CM3 CPU is actively executing code. Active mode provides normal
operation of the processor and all of the peripherals that are currently enabled. The system clock can be
any available clock source (see Table 6-1).
In idle mode, all active peripherals can be clocked, but the Application CPU core and memory are not
clocked and no code is executed. Any interrupt event will bring the processor back into active mode.
In standby mode, only the always-on domain (AON) is active. An external wake-up event or RTC event is
required to bring the device back to active mode. MCU peripherals with retention do not need to be
reconfigured when waking up again, and the CPU continues execution from where it went into standby
mode. All GPIOs are latched in standby mode.
In shutdown mode, the device is turned off entirely, including the AON domain. The I/Os are latched with
the value they had before entering shutdown mode. A change of state on any I/O pin defined as a wake-
up from Shutdown pin wakes up the device and functions as a reset trigger. The CPU can differentiate
between a reset in this way, a reset-by-reset pin, or a power-on-reset by reading the reset status register.
The only state retained in this mode is the latched I/O state and the Flash memory contents.
Detailed DescriptionCopyright © 2020, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
31

CC2640R2L
SWRS250 –JUNE 2020
6.8 Clock Systems
The CC2640R2L supports two external and two internal clock sources.
A 24-MHz crystal is required as the frequency reference for the radio. This signal is doubled internally to
create a 48-MHz clock.
The 32-kHz crystal is optional. Bluetooth low energy requires a slow-speed clock with better than
±500 ppm accuracy if the device is to enter any sleep mode while maintaining a connection. The internal
32-kHz RC oscillator can in some use cases be compensated to meet the requirements. The low-speed
crystal oscillator is designed for use with a 32-kHz watch-type crystal.
The internal high-speed oscillator (48-MHz) can be used as a clock source for the CPU subsystem.
The internal low-speed oscillator (32.768-kHz) can be used as a reference if the low-power crystal
oscillator is not used.
The 32-kHz clock source can be used as external clocking reference through GPIO.
6.9 General Peripherals and Modules
The I/O controller controls the digital I/O pins and contains multiplexer circuitry to allow a set of peripherals
to be assigned to I/O pins in a flexible manner. All digital I/Os are interrupt and wake-up capable, have a
programmable pullup and pulldown function and can generate an interrupt on a negative or positive edge
(configurable). When configured as an output, pins can function as either push-pull or open-drain. Five
GPIOs have high drive capabilities (marked in bold in Section 4).
www.ti.com
The SSIs are synchronous serial interfaces that are compatible with SPI, MICROWIRE, and Texas
Instruments synchronous serial interfaces. The SSIs support both SPI master and slave up to 4 MHz.
The UART implements a universal asynchronous receiver/transmitter function. It supports flexible baudrate generation up to a maximum of 3 Mbps .
Timer 0 is a general-purpose timer module (GPTM), which provides two 16-bit timers. The GPTM can be
configured to operate as a single 32-bit timer, dual 16-bit timers or as a PWM module.
Timer 1, Timer 2, and Timer 3 are also GPTMs. Each of these timers is functionally equivalent to Timer 0.
In addition to these four timers, the RF core has its own timer to handle timing for RF protocols; the RF
timer can be synchronized to the RTC.
The I2C interface is used to communicate with devices compatible with the I2C standard. The I2C interface
supports 100-kHz and 400-kHz operation, and can serve as both I2C master and I2C slave.
The TRNG module provides a true, nondeterministic noise source for the purpose of generating keys,
initialization vectors (IVs), and other random number requirements. The TRNG is built on 24 ring
oscillators that create unpredictable output to feed a complex nonlinear combinatorial circuit.
The watchdog timer is used to regain control if the system fails due to a software error after an external
device fails to respond as expected. The watchdog timer can generate an interrupt or a reset when a
predefined time-out value is reached.
The device includes a direct memory access (µDMA) controller. The µDMA controller provides a way to
offload data transfer tasks from the CM3 CPU, allowing for more efficient use of the processor and the
available bus bandwidth. The µDMA controller can perform transfer between memory and peripherals. The
µDMA controller has dedicated channels for each supported on-chip module and can be programmed to
automatically perform transfers between peripherals and memory as the peripheral is ready to transfer
more data. Some features of the µDMA controller include the following (this is not an exhaustive list):
• Highly flexible and configurable channel operation of up to 32 channels
32
Detailed Description Copyright © 2020, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback

www.ti.com
• Transfer modes:
• Data sizes of 8, 16, and 32 bits
The AON domain contains circuitry that is always enabled, except for in Shutdown (where the digital
supply is off). This circuitry includes the following:
• The RTC can be used to wake the device from any state where it is active. The RTC contains three
• The battery monitor and temperature sensor are accessible by software and give a battery status
The ADC is a 12-bit, 200 ksamples per second (ksps) ADC with eight inputs and a built-in voltage
reference. The ADC can be triggered by many different sources, including timers, I/O pins, software, and
the RTC.
CC2640R2L
SWRS250 –JUNE 2020
– Memory-to-memory
– Memory-to-peripheral
– Peripheral-to-memory
– Peripheral-to-peripheral
compare and one capture registers. With software support, the RTC can be used for clock and
calendar operation. The RTC is clocked from the 32-kHz RC oscillator or crystal. The RTC can also be
compensated to tick at the correct frequency even when the internal 32-kHz RC oscillator is used
instead of a crystal.
indication as well as a coarse temperature measure.
6.10 Voltage Supply Domains
The CC2640R2L device can interface to two or three different voltage domains depending on the package
type. On-chip level converters ensure correct operation as long as the signal voltage on each input/output
pin is set with respect to the corresponding supply pin (VDDS, VDDS2 or VDDS3). Table 6-2 lists the pinto-VDDS mapping.
Table 6-2. Pin Function to VDDS Mapping Table
(1)
VDDS
VDDS2 DIO 0–11
VDDS3
(1) VDDS_DCDC must be connected to VDDS on the PCB.
6.11 System Architecture
Depending on the product configuration, CC26xx can function either as a Wireless Network Processor
(WNP—an IC running the wireless protocol stack, with the application running on a separate MCU), or as
a System-on-Chip (SoC), with the application and protocol stack running on the Arm Cortex-M3 core
inside the device.
In the first case, the external host MCU communicates with the device using SPI or UART. In the second
case, the application must be written according to the application framework supplied with the wireless
protocol stack.
Package
VQFN 7 × 7 (RGZ) VQFN 5 × 5 (RHB)
DIO 23–30
Reset_N
DIO 12–22
JTAG
DIO 7–14
Reset_N
DIO 0–6
JTAG
N/A
Submit Documentation Feedback
Detailed DescriptionCopyright © 2020, Texas Instruments Incorporated
33

Antenna
(50 Ohm)
1 pF
1 pF
2.4 nH
2.4±2.7 nH
6.8 pF
6.2±6.8 nH
Antenna
(50 Ohm)
1.2 pF
15 nH
2 nH
1.2 pF
Antenna
(50 Ohm)
1.2 pF
2 nH
1.2 pF
Antenna
(50 Ohm)
1.2 pF
2 nH
1.2 pF
Pin 1 (RF P)
Pin 2 (RF N)
Pin 3 (RXTX)
Pin 1 (RF P)
Pin 2 (RF N)
Pin 1 (RF P)
Pin 2 (RF N)
Red = Not necessary if internal bias is used
Red = Not necessary if internal bias is used
Differential
operation
Single ended
operation
Single ended
operation with 2
antennas
Pin 3 (RXTX)
15 nH
15 nH
CC26xx
(GND exposed die
attached pad
)
Pin 3/4 (RXTX)
Pin 1 (RF P)
Pin 2 (RF N)
24MHz
XTAL
(Load caps
on chip)
10µF
10µH
Optional
inductor.
Only
needed for
DCDC
operation
12 pF
12 pF
12 pF
12 pF
2 nH 2 nH
1 pF
input
decoupling
10µF±22µF
To VDDR
pins
VDDS_DCDC
DCDC_SW
Red = Not necessary if internal bias is used
Copyright © 2016, Texas Instruments Incorporated
CC2640R2L
SWRS250 –JUNE 2020
7 Application, Implementation, and Layout
Information in the following applications sections is not part of the TI component
specification, and TI does not warrant its accuracy or completeness. TI's customers are
responsible for determining suitability of components for their purposes. Customers should
validate and test their design implementation to confirm system functionality.
7.1 Application Information
Very few external components are required for the operation of the CC2640R2L device. This section
provides some general information about the various configuration options when using the CC2640R2L in
an application, and then shows two examples of application circuits with schematics and layout. This is
only a small selection of the many application circuit examples available as complete reference designs
from the product folder on www.ti.com.
Figure 7-1 shows the various RF front-end configuration options. The RF front end can be used in
differential- or single-ended configurations with the options of having internal or external biasing. These
options allow for various trade-offs between cost, board space, and RF performance. Differential operation
with external bias gives the best performance while single-ended operation with internal bias gives the
least amount of external components and the lowest power consumption. Reference designs exist for
each of these options.
www.ti.com
NOTE
34
Figure 7-1. CC2640R2L Application Circuit
Application, Implementation, and Layout Copyright © 2020, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback

Internal DC-DC Regulator External RegulatorInternal LDO Regulator
(GND Exposed Die
Attached Pad)
Pin 3/4 (RXTX)
Pin 1 (RF P)
Pin 2 (RF N)
24-MHz XTAL
(Load Caps on Chip)
10 F
10 H
VDDS_DCDC
Input Decoupling
10 F±22 F
To All VDDR Pins
VDDS_DCDC Pin
DCDC_SW Pin
1.8 V±3.8 V
to All VDDS Pins
VDDR
VDDR
VDDS VDDS
CC26xx
(GND Exposed Die
Attached Pad)
Pin 3/4 (RXTX)
Pin 1 (RF P)
Pin 2 (RF N)
24-MHz XTAL
(Load Caps on Chip)
VDDS_DCDC
Input Decoupling
10 F±22 F
To All VDDR Pins
VDDS_DCDC Pin
NC
1.8 V±3.8 V
Supply Voltage
VDDR
VDDR
VDDS VDDS
CC26xx
10 F
To All VDDS Pins
(GND Exposed Die
Attached Pad)
Pin 3/4 (RXTX)
Pin 1 (RF P)
Pin 2 (RF N)
24-MHz XTAL
(Load Caps
on Chip)
VDDS_DCDC Pin
CC26xx
2.2 F
DCDC_SW Pin
1.7 V±1.95 V to All VDDR- and VDDS Pins Except VDDS_DCDC
Ext.
Regulator
Copyright © 2016, Texas Instruments Incorporated
www.ti.com
Figure 7-2 shows the various supply voltage configuration options. Not all power supply decoupling
capacitors or digital I/Os are shown. Exact pin positions will vary between the different package options.
For a detailed overview of power supply decoupling and wiring, see the TI reference designs and the
CC26xx technical reference manual (Section 8.3).
CC2640R2L
SWRS250 –JUNE 2020
Figure 7-2. Supply Voltage Configurations
Submit Documentation Feedback
Application, Implementation, and LayoutCopyright © 2020, Texas Instruments Incorporated
35

C12
DNM
C13
1 pF
L12
2 nH
1
2
L13
2 nH
1 2
VDDR Decoupling Capacitors
Pin 32
Pin 29
50-Ω
Antenna
VDDS
L1
10 uH
1
2
Y1
32.768 kHz
C18
12 pF
C17
12 pF
Place L1 and
C8 close to pin 17
C23
DNM
C22
DNM
C8
10 µF
C10
DNM
C16
100 nF
C6
10 µF
CC2650F128R HB
U1
VSS
33
DIO_0
6
DIO_1
7
DIO_2
8
DIO_3
9
DIO_4
10
DIO_5
15
DIO_6
16
DIO_7
20
DIO_8
21
DIO_9
22
DIO_10
23
DIO_11
24
DIO_12
25
DIO_13
26
DIO_14
27
VDDR
29
VDDR
32
VDDS
28
VDDS2
11
VDDS_D CDC
18
DCOU PL
12
RESET_N
19
JTAG_TMSC
13
JTAG_TCKC
14
X32K_Q1
4
X32K_Q2
5
X24M_N
30
X24M_P
31
RF_P
1
RF_N
2
RX_TX
3
DCD C_SW
17
Y2
24 MHz
1
2
4
3
C2
DNM
C11
1 pF
C21
1 pF
C20
100 nF
X24M_N
X24M_P
VDDS
VDDR
DCDC_SW
DCDC_SW
C31
6.8 pF
VDDS
nRESET
C19
1 µF
JTAG_TCK
JTA G_TMS
DIO_1
DIO_0
DIO_3
DIO_2
DIO_5/JTAG_TDO
DIO_4
DIO_7
DIO_6/JTAG_TDI
DIO_10
DIO_9
DIO_8
DIO_12
DIO_11
DIO_14
DIO_13
RX_TX
RFP
RFN
L11
2.7 nH
1 2
L21
2.4 nH
1
2
VDD_EB
FL1
BLM18HE152SN1
12
C9
100 nF
C3
100 nF
C4
100 nF
VDDS Decoupling Capacitors
Pin 18
Pin 28
Pin 11
C7
100 nF
L10
6.2 nH
1
2
R1
100 k
VDDR
Copyright © 2016, Texas Instruments Incorporated
CC2640R2L
SWRS250 –JUNE 2020
7.2 5 × 5 External Differential (5XD) Application Circuit
www.ti.com
Figure 7-3. 5 × 5 External Differential (5XD) Application Circuit
36
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2020, Texas Instruments IncorporatedApplication, Implementation, and Layout

www.ti.com
7.2.1 Layout
CC2640R2L
SWRS250 –JUNE 2020
Figure 7-4. 5 × 5 External Differential (5XD) Layout
Submit Documentation Feedback
Application, Implementation, and LayoutCopyright © 2020, Texas Instruments Incorporated
37

SimpleLink™ Multistandard
Wireless MCU
"
DEVICE FAMILY
PREFIX
X = Experimental device
Blank = Qualified device
PACKAGE DESIGNATOR
RGZ = 48-pin VQFN (Very Thin Quad Flatpack No-Lead)
RHB = 32-pin VQFN (Very Thin Quad Flatpack No-Lead)
R = Large Reel
T = Small Reel
CC26 xx
zzz
(R/T)
yyy
ROM version
F128 = ROM version 1
R2 = ROM version 2
DEVICE
40 = Bluetooth
CC2640R2L
SWRS250 –JUNE 2020
8 Device and Documentation Support
8.1 Device Nomenclature
To designate the stages in the product development cycle, TI assigns prefixes to all pre-production part
numbers or date-code markings. Each device has one of three prefixes/identifications: X, P, or null (no
prefix) (for example, CC2640R2L is in production; therefore, no prefix/identification is assigned).
Device development evolutionary flow:
X Experimental device that is not necessarily representative of the final device's electrical
specifications and may not use production assembly flow.
P Prototype device that is not necessarily the final silicon die and may not necessarily meet
final electrical specifications.
null Production version of the silicon die that is fully qualified.
Production devices have been characterized fully, and the quality and reliability of the device have been
demonstrated fully. TI's standard warranty applies.
Predictions show that prototype devices (X or P) have a greater failure rate than the standard production
devices. Texas Instruments recommends that these devices not be used in any production system
because their expected end-use failure rate still is undefined. Only qualified production devices are to be
used.
www.ti.com
TI device nomenclature also includes a suffix with the device family name. This suffix indicates the
package type (for example, RGZ).
For orderable part numbers of the CC2640R2L device in the RHB and RGZ package types, see the
Package Option Addendum of this document, the TI website (www.ti.com), or contact your TI sales
representative.
Figure 8-1. Device Nomenclature
38
Device and Documentation Support Copyright © 2020, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback

www.ti.com
8.2 Tools and Software
TI offers an extensive line of development tools, including tools to evaluate the performance of the
processors, generate code, develop algorithm implementations, and fully integrate and debug software
and hardware modules.
The following products support development of the CC2640R2L device applications:
Software Tools
SmartRF Studio 7 is a PC application that helps designers of radio systems to easily evaluate the RF-IC
at an early stage in the design process.
• Test functions for sending and receiving radio packets, continuous wave transmit and receive
• Evaluate RF performance on custom boards by wiring it to a supported evaluation board or debugger
• Can also be used without any hardware, but then only to generate, edit and export radio configuration
settings
• Can be used in combination with several development kits for Texas Instruments’ CCxxxx RF-ICs
IDEs and Compilers
Code Composer Studio™ Integrated Development Environment (IDE)
• Integrated development environment with project management tools and editor
• Code Composer Studio (CCS) 7.0 and later has built-in support for the CC26xx device family
• Best support for XDS debuggers; XDS100v3, XDS110 and XDS200
• High integration with TI-RTOS with support for TI-RTOS Object View
IAR Embedded Workbench®for Arm
• Integrated development environment with project management tools and editor
• IAR EWARM 7.80.1 and later has built-in support for the CC26xx device family
• Broad debugger support, supporting XDS100v3, XDS200, IAR I-Jet and Segger J-Link
• Integrated development environment with project management tools and editor
• RTOS plugin available for TI-RTOS
CC2640R2L
SWRS250 –JUNE 2020
®
For a complete listing of development-support tools for the CC2640R2L platform, visit the Texas
Instruments website at www.ti.com. For information on pricing and availability, contact the nearest TI field
sales office or authorized distributor.
8.3 Documentation Support
To receive notification of documentation updates, navigate to the device product folder on ti.com
(CC2640R2L). In the upper right corner, click on Alert me to register and receive a weekly digest of any
product information that has changed. For change details, review the revision history included in any
revised document.
The current documentation that describes the CC2640R2L devices, related peripherals, and other
technical collateral is listed in the following.
Technical Reference Manual
CC13xx, CC26xx SimpleLink™ Wireless MCU Technical Reference Manual
Errata
CC2640R2L SimpleLink™ Wireless MCU Errata
8.4 Support Resources
TI E2E™ support forums are an engineer's go-to source for fast, verified answers and design help —
straight from the experts. Search existing answers or ask your own question to get the quick design help
you need.
Submit Documentation Feedback
Device and Documentation SupportCopyright © 2020, Texas Instruments Incorporated
39

CC2640R2L
SWRS250 –JUNE 2020
Linked content is provided "AS IS" by the respective contributors. They do not constitute TI specifications
and do not necessarily reflect TI's views; see TI's Terms of Use.
8.5 Trademarks
SmartRF, Code Composer Studio, LaunchPad, TI E2E are trademarks of Texas Instruments.
ARM7 is a trademark of Arm Limited (or its subsidiaries).
Arm, Cortex, Thumb are registered trademarks of Arm Limited (or its subsidiaries).
Bluetooth is a registered trademark of Bluetooth SIG Inc.
CoreMark is a registered trademark of Embedded Microprocessor Benchmark Consortium.
IAR Embedded Workbench is a registered trademark of IAR Systems AB.
IEEE Std 1241 is a trademark of Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Incorporated.
Wi-Fi is a registered trademark of Wi-Fi Alliance.
ZigBee is a registered trademark of ZigBee Alliance.
8.6 Electrostatic Discharge Caution
This integrated circuit can be damaged by ESD. Texas Instruments recommends that all integrated circuits be handled with
appropriate precautions. Failure to observe proper handling and installation procedures can cause damage.
ESD damage can range from subtle performance degradation to complete device failure. Precision integrated circuits may be more
susceptible to damage because very small parametric changes could cause the device not to meet its published specifications.
8.7 Export Control Notice
Recipient agrees to not knowingly export or re-export, directly or indirectly, any product or technical data
(as defined by the U.S., EU, and other Export Administration Regulations) including software, or any
controlled product restricted by other applicable national regulations, received from disclosing party under
nondisclosure obligations (if any), or any direct product of such technology, to any destination to which
such export or re-export is restricted or prohibited by U.S. or other applicable laws, without obtaining prior
authorization from U.S. Department of Commerce and other competent Government authorities to the
extent required by those laws.
www.ti.com
8.8 Glossary
TI Glossary This glossary lists and explains terms, acronyms, and definitions.
40
Device and Documentation Support Copyright © 2020, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback

www.ti.com
9 Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
The following pages include mechanical packaging and orderable information. This information is the most
current data available for the designated devices. This data is subject to change without notice and
revision of this document. For browser-based versions of this data sheet, refer to the left-hand navigation.
CC2640R2L
SWRS250 –JUNE 2020
Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable InformationCopyright © 2020, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
41

PACKAGE OPTION ADDENDUM
www.ti.com
27-Jun-2020
PACKAGING INFORMATION
Orderable Device Status
CC2640R2LRGZR ACTIVE VQFN RGZ 48 2500 Green (RoHS
CC2640R2LRHBR ACTIVE VQFN RHB 32 2500 Green (RoHS
(1)
The marketing status values are defined as follows:
ACTIVE: Product device recommended for new designs.
LIFEBUY: TI has announced that the device will be discontinued, and a lifetime-buy period is in effect.
NRND: Not recommended for new designs. Device is in production to support existing customers, but TI does not recommend using this part in a new design.
PREVIEW: Device has been announced but is not in production. Samples may or may not be available.
OBSOLETE: TI has discontinued the production of the device.
Package Type Package
(1)
Drawing
Pins Package
Qty
Eco Plan
(2)
& no Sb/Br)
& no Sb/Br)
Lead finish/
Ball material
(6)
NIPDAU Level-3-260C-168 HR -40 to 85 CC2640
NIPDAU Level-3-260C-168 HR -40 to 85 CC2640
MSL Peak Temp
(3)
Op Temp (°C) Device Marking
R2L
R2L
(4/5)
(2)
RoHS: TI defines "RoHS" to mean semiconductor products that are compliant with the current EU RoHS requirements for all 10 RoHS substances, including the requirement that RoHS substance
do not exceed 0.1% by weight in homogeneous materials. Where designed to be soldered at high temperatures, "RoHS" products are suitable for use in specified lead-free processes. TI may
reference these types of products as "Pb-Free".
RoHS Exempt: TI defines "RoHS Exempt" to mean products that contain lead but are compliant with EU RoHS pursuant to a specific EU RoHS exemption.
Green: TI defines "Green" to mean the content of Chlorine (Cl) and Bromine (Br) based flame retardants meet JS709B low halogen requirements of <=1000ppm threshold. Antimony trioxide based
flame retardants must also meet the <=1000ppm threshold requirement.
(3)
MSL, Peak Temp. - The Moisture Sensitivity Level rating according to the JEDEC industry standard classifications, and peak solder temperature.
(4)
There may be additional marking, which relates to the logo, the lot trace code information, or the environmental category on the device.
(5)
Multiple Device Markings will be inside parentheses. Only one Device Marking contained in parentheses and separated by a "~" will appear on a device. If a line is indented then it is a continuation
of the previous line and the two combined represent the entire Device Marking for that device.
(6)
Lead finish/Ball material - Orderable Devices may have multiple material finish options. Finish options are separated by a vertical ruled line. Lead finish/Ball material values may wrap to two
lines if the finish value exceeds the maximum column width.
Important Information and Disclaimer:The information provided on this page represents TI's knowledge and belief as of the date that it is provided. TI bases its knowledge and belief on information
provided by third parties, and makes no representation or warranty as to the accuracy of such information. Efforts are underway to better integrate information from third parties. TI has taken and
continues to take reasonable steps to provide representative and accurate information but may not have conducted destructive testing or chemical analysis on incoming materials and chemicals.
TI and TI suppliers consider certain information to be proprietary, and thus CAS numbers and other limited information may not be available for release.
In no event shall TI's liability arising out of such information exceed the total purchase price of the TI part(s) at issue in this document sold by TI to Customer on an annual basis.
Samples
Addendum-Page 1

PACKAGE OPTION ADDENDUM
www.ti.com
27-Jun-2020
Addendum-Page 2

PACKAGE MATERIALS INFORMATION
www.ti.com 13-Sep-2020
TAPE AND REEL INFORMATION
*All dimensions are nominal
Device Package
CC2640R2LRGZR VQFN RGZ 48 2500 330.0 16.4 7.3 7.3 1.1 12.0 16.0 Q2
CC2640R2LRGZR VQFN RGZ 48 2500 330.0 16.4 7.3 7.3 1.1 12.0 16.0 Q2
Type
Package
Drawing
Pins SPQ Reel
Diameter
(mm)
Reel
Width
W1 (mm)
A0
(mm)B0(mm)K0(mm)P1(mm)W(mm)
Pin1
Quadrant
Pack Materials-Page 1

PACKAGE MATERIALS INFORMATION
www.ti.com 13-Sep-2020
*All dimensions are nominal
Device Package Type Package Drawing Pins SPQ Length (mm) Width (mm) Height (mm)
CC2640R2LRGZR VQFN RGZ 48 2500 336.6 336.6 31.8
CC2640R2LRGZR VQFN RGZ 48 2500 367.0 367.0 35.0
Pack Materials-Page 2

GENERIC PACKAGE VIEW
VQFN - 1 mm max heightRHB 32
5 x 5, 0.5 mm pitch
PLASTIC QUAD FLATPACK - NO LEAD
Images above are just a representation of the package family, actual package may vary.
Refer to the product data sheet for package details.
www.ti.com
4224745/A

PACKAGE OUTLINE
PIN 1 INDEX AREA
1 MAX
0.05
0.00
28X 0.5
SCALE 3.000
VQFN - 1 mm max heightRHB0032E
PLASTIC QUAD FLATPACK - NO LEAD
A
9
8
5.1
4.9
2X 3.5
3.45 0.1
16
B
5.1
4.9
EXPOSED
THERMAL PAD
17
OPTIONAL METAL THICKNESS
C
SEATING PLANE
0.08 C
SEE SIDE WALL
DETAIL
(0.1)
SIDE WALL DETAIL
20.000
(0.2) TYP
2X
3.5
PIN 1 ID
(OPTIONAL)
33
1
32
SYMM
32X
25
0.5
0.3
SYMM
24
0.3
32X
0.2
0.1 C A B
0.05
C
4223442/B 08/2019
NOTES:
1. All linear dimensions are in millimeters. Any dimensions in parenthesis are for reference only. Dimensioning and tolerancing
per ASME Y14.5M.
2. This drawing is subject to change without notice.
3. The package thermal pad must be soldered to the printed circuit board for thermal and mechanical performance.
www.ti.com

32X (0.6)
32
EXAMPLE BOARD LAYOUT
VQFN - 1 mm max heightRHB0032E
PLASTIC QUAD FLATPACK - NO LEAD
( 3.45)
SYMM
25
32X (0.25)
28X (0.5)
( 0.2) TYP
(R0.05)
TYP
VIA
1
33
8
9
(4.8)
(1.475)
16
24
(1.475)
SYMM
(4.8)
17
LAND PATTERN EXAMPLE
SCALE:18X
0.07 MAX
ALL AROUND
METAL
SOLDER MASK
OPENING
NON SOLDER MASK
DEFINED
(PREFERRED)
0.07 MIN
ALL AROUND
SOLDER MASK
OPENING
METAL UNDER
SOLDER MASK
SOLDER MASK
DEFINED
SOLDER MASK DETAILS
4223442/B 08/2019
NOTES: (continued)
4. This package is designed to be soldered to a thermal pad on the board. For more information, see Texas Instruments literature
number SLUA271 (www.ti.com/lit/slua271).
5. Vias are optional depending on application, refer to device data sheet. If any vias are implemented, refer to their locations shown
on this view. It is recommended that vias under paste be filled, plugged or tented.
www.ti.com

(R0.05) TYP
32X (0.6)
32
EXAMPLE STENCIL DESIGN
VQFN - 1 mm max heightRHB0032E
PLASTIC QUAD FLATPACK - NO LEAD
4X ( 1.49)
(0.845)
25
32X (0.25)
28X (0.5)
METAL
TYP
1
33
8
9
SYMM
16
24
(0.845)
SYMM
(4.8)
17
(4.8)
SOLDER PASTE EXAMPLE
BASED ON 0.125 mm THICK STENCIL
EXPOSED PAD 33:
75% PRINTED SOLDER COVERAGE BY AREA UNDER PACKAGE
NOTES: (continued)
6. Laser cutting apertures with trapezoidal walls and rounded corners may offer better paste release. IPC-7525 may have alternate
design recommendations.
SCALE:20X
4223442/B 08/2019
www.ti.com

GENERIC PACKAGE VIEW
VQFN - 1 mm max heightRGZ 48
7 x 7, 0.5 mm pitch
PLASTIC QUADFLAT PACK- NO LEAD
Images above are just a representation of the package family, actual package may vary.
Refer to the product data sheet for package details.
www.ti.com
4224671/A

NOTES:
1. All linear dimensions are in millimeters. Any dimensions in parenthesis are for reference only. Dimensioning and tolerancing
per ASME Y14.5M.
2. This drawing is subject to change without notice.
3. The package thermal pad must be soldered to the printed circuit board for optimal thermal and mechanical performance.
PACKAGE OUTLINE
4219044/C 09/2020
www.ti.com
VQFN - 1 mm max height
PLASTIC QUADFLAT PACK- NO LEAD
RGZ0048A
A
0.08
C
0.1 C A B
0.05 C
B
SYMM
SYMM
PIN 1 INDEX AREA
7.1
6.9
7.1
6.9
1 MAX
0.05
0.00
SEATING PLANE
C
5.15±0.1
2X 5.5
2X
5.5
44X 0.5
48X
0.5
0.3
48X
0.30
0.18
PIN1 ID
(OPTIONAL)
(0.2) TYP
1
12
13
24
25
36
37
48
(0.1) TYP
SIDE WALL DETAIL
OPTIONAL METAL THICKNESS
SEE SIDE WALL
DETAIL
CHAMFERED LEAD
CORNER LEAD OPTION
(0.45) TYP
SEE LEAD OPTION

NOTES: (continued)
4. This package is designed to be soldered to a thermal pad on the board. For more information, see Texas Instruments literature
number SLUA271 (www.ti.com/lit/slua271)
.
5. Vias are optional depending on application, refer to device data sheet. If any vias are implemented, refer to their locations shown
on this view. It is recommended that vias under paste be filled, plugged or tented.
EXAMPLE BOARD LAYOUT
4219044/C 09/2020
www.ti.com
VQFN - 1 mm max height
RGZ0048A
PLASTIC QUADFLAT PACK- NO LEAD
SYMM
SYMM
LAND PATTERN EXAMPLE
SCALE: 15X
( 5.15)
2X (6.8)
2X
(6.8)
48X (0.6)
48X (0.24)
44X (0.5)
2X (5.5)
2X
(5.5)
21X (Ø0.2) VIA
TYP
(R0.05)
TYP
NON SOLDER MASK
DEFINED
(PREFERRED)
SOLDER MASK
DEFINED
METAL
SOLDER MASK
OPENING
EXPOSED METAL
SOLDER MASK DETAILS
SOLDER MASK
OPENING
METAL UNDER
SOLDER MASK
EXPOSED METAL
0.07 MAX
ALL AROUND
0.07 MIN
ALL AROUND
2X
(1.26)
2X (1.26)
2X (1.065)
2X
(1.065)
1
12
13
22
23
34
35
48

NOTES: (continued)
6. Laser cutting apertures with trapezoidal walls and rounded corners may offer better paste release. IPC-7525 may have alternate
design recommendations.
EXAMPLE STENCIL DESIGN
4219044/C 09/2020
www.ti.com
VQFN - 1 mm max height
RGZ0048A
PLASTIC QUADFLAT PACK- NO LEAD
SOLDER PASTE EXAMPLE
BASED ON 0.125 mm THICK STENCIL
EXPOSED PAD
67% PRINTED COVERAGE BY AREA
SCALE: 15X
SYMM
SYMM
( 1.06)
2X (6.8)
2X
(6.8)
48X (0.6)
48X (0.24)
44X (0.5)
2X (5.5)
2X
(5.5)
(R0.05)
TYP
2X
(0.63)
2X (0.63)
2X
(1.26)
2X
(1.26)

IMPORTANT NOTICE AND DISCLAIMER
TI PROVIDES TECHNICAL AND RELIABILITY DATA (INCLUDING DATASHEETS), DESIGN RESOURCES (INCLUDING REFERENCE
DESIGNS), APPLICATION OR OTHER DESIGN ADVICE, WEB TOOLS, SAFETY INFORMATION, AND OTHER RESOURCES “AS IS”
AND WITH ALL FAULTS, AND DISCLAIMS ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESS AND IMPLIED, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION ANY
IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE OR NON-INFRINGEMENT OF THIRD
PARTY INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS.
These resources are intended for skilled developers designing with TI products. You are solely responsible for (1) selecting the appropriate
TI products for your application, (2) designing, validating and testing your application, and (3) ensuring your application meets applicable
standards, and any other safety, security, or other requirements. These resources are subject to change without notice. TI grants you
permission to use these resources only for development of an application that uses the TI products described in the resource. Other
reproduction and display of these resources is prohibited. No license is granted to any other TI intellectual property right or to any third
party intellectual property right. TI disclaims responsibility for, and you will fully indemnify TI and its representatives against, any claims,
damages, costs, losses, and liabilities arising out of your use of these resources.
TI’s products are provided subject to TI’s Terms of Sale (www.ti.com/legal/termsofsale.html) or other applicable terms available either on
ti.com or provided in conjunction with such TI products. TI’s provision of these resources does not expand or otherwise alter TI’s applicable
warranties or warranty disclaimers for TI products.
Mailing Address: Texas Instruments, Post Office Box 655303, Dallas, Texas 75265
Copyright © 2020, Texas Instruments Incorporated
 Loading...
Loading...