Page 1
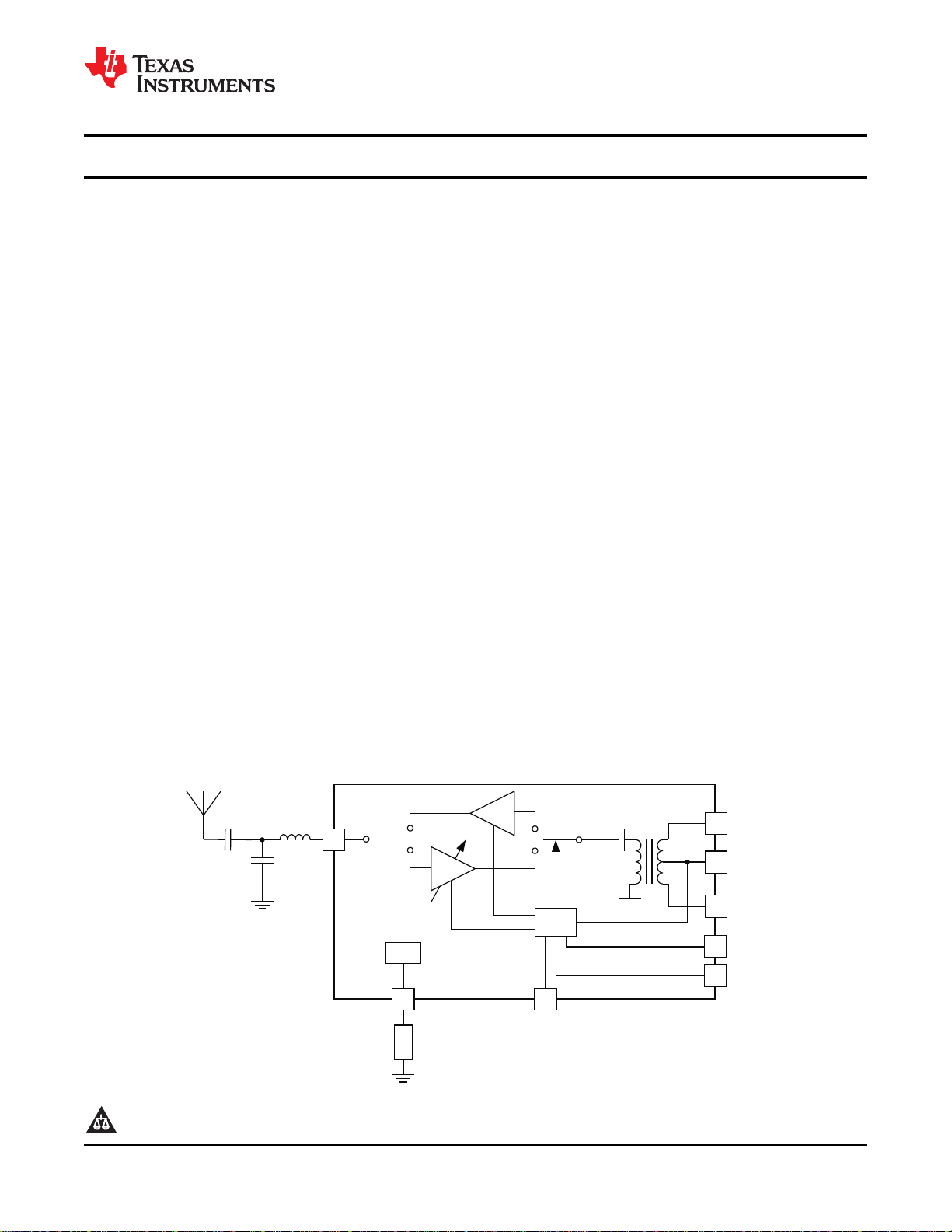
PA
Logic
Bias
15 7
2
3
4
11
LNA
5
6
BIAS
HGM
RF_P
RXTX
RF_N
PAEN
EN
BALUN
ANT
CC2590
www.ti.com
........................................................................................................................................................................................ SWRS080 – SEPTEMBER 2008
2.4-GHz RF Front End, 14-dBm output power
1
FEATURES APPLICATIONS
• Seamless Interface to 2.4-GHz Low Power RF
Devices from Texas Instruments
• Up to +14-dBm (25mW) Output Power
• 6-dB Typical Improved Sensitivity on CC24xx
and CC2500, CC2510, and CC2511
• Few External Components
– Integrated Switches
– Integrated Matching Network
– Integrated Balun
– Integrated Inductors
– Integrated PA
– Integrated LNA
• Digital Control of LNA Gain by HGM Pin System-on-Chip products from Texas Instruments.
• 100-nA in Power Down (EN = PAEN = 0)
• Low Transmit Current Consumption
– 22-mA at 3-V for +12-dBm, PAE = 23%
• Low Receive Current Consumption
– 3.4-mA for High Gain Mode
– 1.8-mA for Low Gain Mode
• 4.6-dB LNA Noise Figure, including T/R Switch
and external antenna match
• RoHS Compliant 4 × 4-mm QFN-16 Package
• 2.0-V to 3.6-V Operation
• All 2.4-GHz ISM Band Systems
• Wireless Sensor Networks
• Wireless Industrial Systems
• IEEE 802.15.4 and ZigBee Systems
• Wireless Consumer Systems
• Wireless Audio Systems
DESCRIPTION
CC2590 is a cost-effective and high performance RF
Front End for low-power and low-voltage 2.4-GHz
wireless applications.
CC2590 is a range extender for all existing and future
2.4-GHz low-power RF transceivers, transmitters and
CC2590 increases the link budget by providing a
power amplifier for increased output power, and an
LNA with low noise figure for improved receiver
sensitivity.
CC2590 provides a small size, high output power RF
design with its 4x4-mm QFN-16 package.
CC2590 contains PA, LNA, switches, RF-matching,
and balun for simple design of high performance
wireless applications.
CC2590 BLOCK DIAGRAM
1
Please be aware that an important notice concerning availability, standard warranty, and use in critical applications of Texas Instruments semiconductor products and disclaimers thereto appears at the end of this data sheet.
PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date.
Products conform to specifications per the terms of the Texas
Instruments standard warranty. Production processing does not
necessarily include testing of all parameters.
Copyright © 2008, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 2
CC2590
SWRS080 – SEPTEMBER 2008 ........................................................................................................................................................................................
These devices have limited built-in ESD protection. The leads should be shorted together or the device placed in conductive foam
during storage or handling to prevent electrostatic damage to the MOS gates.
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Under no circumstances must the absolute maximum ratings be violated. Stress exceeding one or more of the limiting values
may cause permanent damage to the device.
PARAMETER VALUE UNIT
Supply voltage All supply pins must have the same voltage – 0.3 to 3.6 V
Voltage on any digital pin – 0.3 to V
Input RF level +10 dBm
Storage temperature range – 50 to 150 ° C
Reflow soldering temperature According to IPC/JEDEC J-STD-020 260 ° C
Human Body Model, all pins except pin 10 2000 V
ESD Human Body Model, pin 10 1900 V
Charged Device Model 1000 V
+ 0.3, max 3.6 V
DD
RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIONS
The operating conditions for CC2590 are listed below.
PARAMETER MIN MAX UNIT
Ambient temperature range – 40 85 ° C
Operating supply voltage 2.0 3.6 V
Operating frequency range 2400 2483.5 MHz
www.ti.com
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
TC= 25 ° C, V
external matching components.
Receive current, High Gain Mode HGM = 1 3.4 4.0 mA
Receive current, Low Gain Mode HGM = 0 1.8 2.0 mA
Transmit current
Transmit current No input signal 8.0 10.0 mA
Power down current EN = PAEN = 0 0.1 0.3 µ A
High input level (control pins) EN, PAEN, HGM, RXTX 1.3 V
Low input level (control pins) EN, PAEN, HGM, RXTX 0.3 V
Power down - Receive mode switching
time
Power down - Transmit mode switching
time
RF Receive
Gain, High Gain Mode HGM = 1 11.4 dB
Gain, Low Gain Mode HGM = 0 0 dB
Gain variation, 2400 – 2483.5 MHz, High
Gain Mode
Gain variation, 2.0V – 3.6V, High Gain
Mode
Noise figure, High Gain Mode 4.6 dB
Input 1 dB compression, High Gain Mode HGM = 1 – 21 dBm
= 3.0V , fRF= 2440MHz (unless otherwise noted). Measured on CC2590EM reference design including
DD
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
PIN= 0.5 dBm, P
PIN= – 3.5 dBm, P
HGM = 1 1.2 dB
HGM = 1 1.7 dB
HGM = 1, including internal T/R switch and external
antenna match
= 12.2 dBm 22.1 mA
OUT
= 10.0 dBm 16.8 mA
OUT
1.4 µ s
0.8 µ s
DD
V
2 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2008, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Link(s): CC2590
Page 3
CC2590
www.ti.com
........................................................................................................................................................................................ SWRS080 – SEPTEMBER 2008
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
TC= 25 ° C, V
external matching components.
Input IP3, High Gain Mode HGM = 1 – 9 dBm
Input reflection coefficient, S11 HGM = 1, measured at antenna port – 19 dB
RF Transmit
Gain 14.1 dB
Output power, P
Power Added Efficiency, PAE PIN= 0.5 dBm 23.5 %
Output 1 dB compression 10.4 dBm
Output IP3 23 dBm
Output power variation over frequency 2400 – 2483.5 MHz, PIN= 0.5 dBm 0.3 dB
Output power variation over power supply 2.0V – 3.6V , PIN= 0.5 dBm 3.2 dB
Output power variation over temperature -40 ° C – 85 ° C, PIN= 0.5 dBm 1.1 dB
2nd harmonic power limits by using an external LC filter and antenna. See – 14 dBm
3rd harmonic power limits by using an external LC filter and antenna. See – 28 dBm
= 3.0V , fRF= 2440MHz (unless otherwise noted). Measured on CC2590EM reference design including
DD
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
PIN= 4.5 dBm 13.8 dBm
OUT
PIN= 0.5 dBm 12.2 dBm
PIN= -3.5 dBm 10.0 dBm
The 2nd harmonic can be reduced to below regulatory
application note AN032 for regulatory requirements.
The 3rd harmonic can be reduced to below regulatory
application note AN032 for regulatory requirements.
Copyright © 2008, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 3
Product Folder Link(s): CC2590
Page 4
1
2
3
4
5 6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
1516
GND
ANT
AVDD_PA2
GND
GND
HGM
EN
NC
RF_N
RXTX
RF_P
AVDD_BIAS
PABIAS
GND
AVDD_LNA
QFN-164x4mm
CC2590
SWRS080 – SEPTEMBER 2008 ........................................................................................................................................................................................
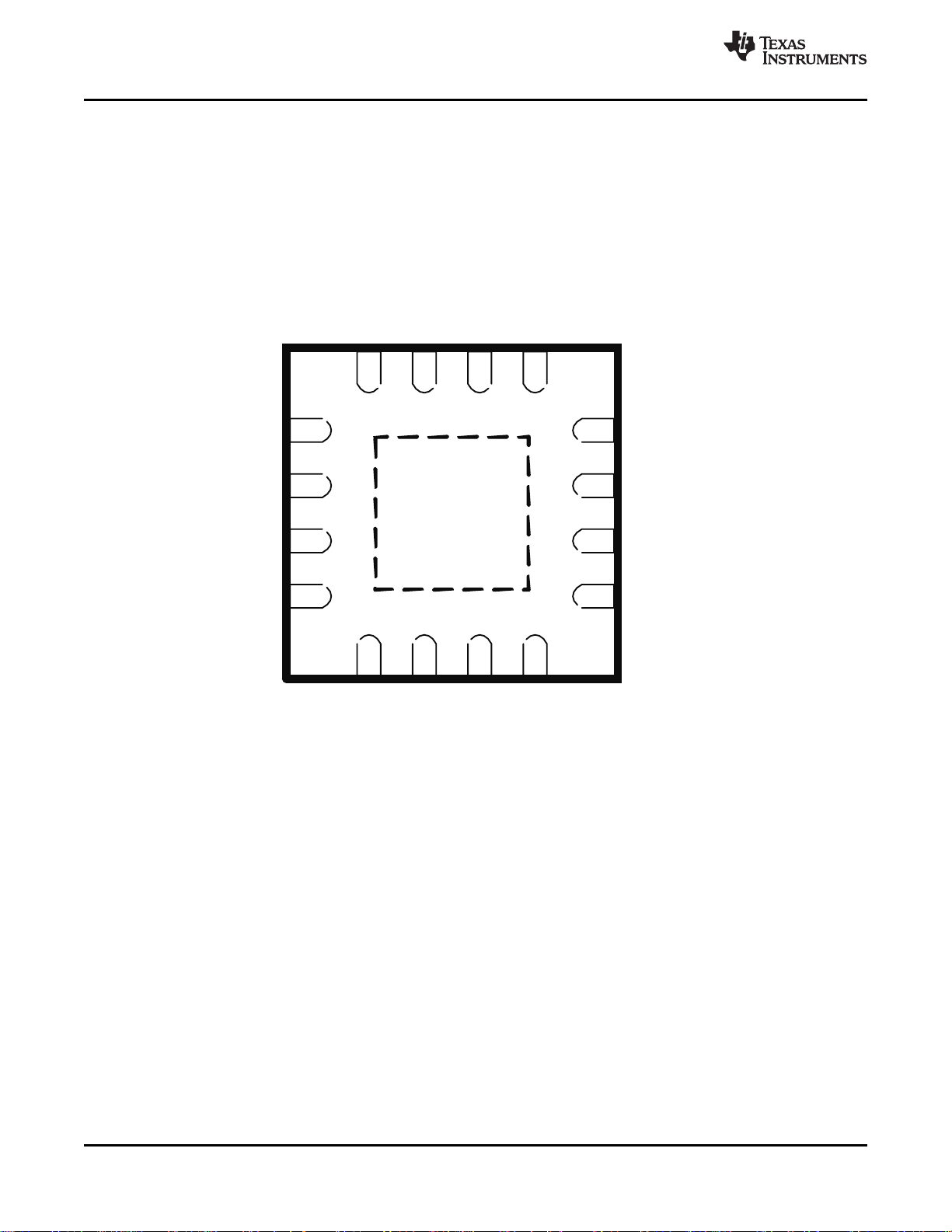
DEVICE INFORMATION
The CC2590 pinout and description are shown in Figure 1 and Table 1 , respectively.
PIN AND I/O CONFIGURATION
(TOP VIEW)
www.ti.com
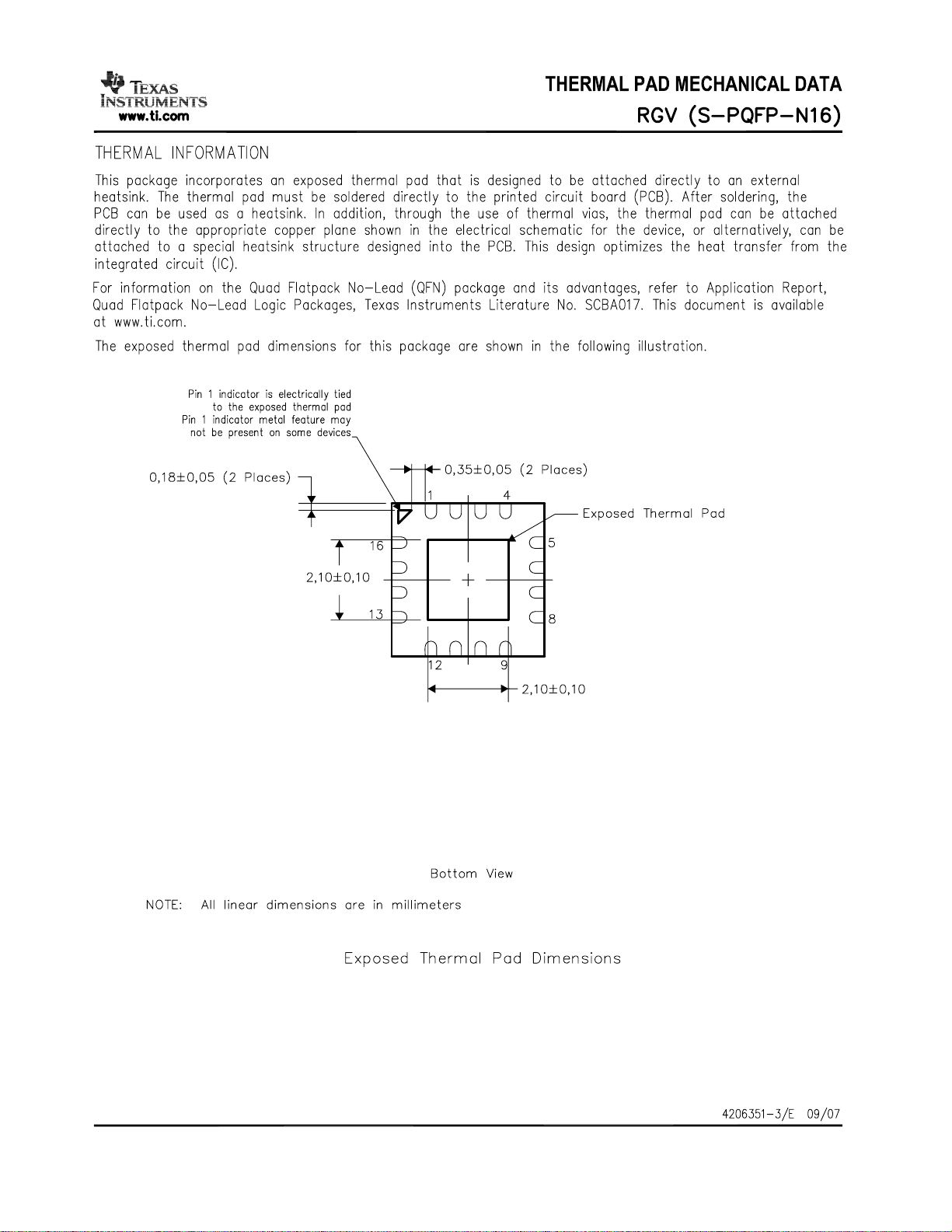
Figure 1.
The exposed die attach pad must be connected to a solid ground plane as this is the
primary ground connection for the chip. Inductance in vias to the pad should be
minimized. It is highly recommended to follow the reference layout. Changes will alter
the performance. Also see the PCB landpattern information in this data sheet.
For best performance, minimize the length of the ground vias, by using a 4-layer PCB
with ground plane as layer 2 when CC2590 is mounted onto layer 1.
NOTE:
4 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2008, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Link(s): CC2590
Page 5
CC2590
www.ti.com
........................................................................................................................................................................................ SWRS080 – SEPTEMBER 2008
Table 1. PIN FUNCTIONS
PIN
NO. NAME
— GND Ground
1 NC Not Connected
2 RF_N RF RF interface towards CC24xx or CC25xx device.
3 RXTX Analog/Control
4 RF_P RF RF interface towards CC24xx or CC25xx device
5 PAEN Digital Input Digital control pin. See Table 3 , Table 4 , and Table 5 for details.
6 EN Digital Input Digital control pin. See Table 3 , Table 4 , and Table 5 for details.
7 HGM Digital Input HGM=1 → Device in High Gain Mode
8, 9, 12, 14 GND Ground
10 AVDD_PA2 Power
11 ANT RF Antenna interface.
13 AVDD_LNA Power
15 BIAS Analog Biasing input. Resistor between this node and ground sets bias current to PAs.
16 AVDD_BIAS Power 2.0-V – 3.6-V Power.
TYPE DESCRIPTION
The exposed die attach pad must be connected to a solid ground plane. See
CC2590EM reference design for recommended layout.
RXTX switching voltage when connected to CC24xx devices. See Table 3 , Table 4 ,
and Table 5 for details.
Digital control pin.
HGM=0 → Device in Low Gain Mode (RX only)
Secondary ground connections. Should be shorted to the die attach pad on the top
PCB layer.
2.0-V – 3.6-V Power. PCB trace to this pin serves as inductive load to PA. See
CC2590EM reference design for recommended layout.
2.0-V – 3.6-V Power. PCB trace to this pin serves as inductive load to LNA. See
CC2590EM reference design for recommended layout.
Copyright © 2008, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 5
Product Folder Link(s): CC2590
Page 6

c
RXTX
RF_N
RF_P
RXTX
RF_N
= PCBtraceinductor
CC2590
ANT
PAEN
EN
HGM
BIAS
VDD
A
VDD_PA2
AVDD_LNA
AVDD_BIAS
VDD
VDD
RF_P
RXTX
RF_N
R151
TL101
TL131
PAEN
EN
C111
L111
C161
C101/C102
C131/C132
HGM
RXTX
C2
LDB182G4520C-110
Balun
SMA
SMA
C112
CC2590
SWRS080 – SEPTEMBER 2008 ........................................................................................................................................................................................
CC2590EM Evaluation Module
www.ti.com
Figure 2. CC2590EM Evaluation Module
Table 2. List of Materials (See CC2590EM Reference Design)
DEVICE FUNCTION VALUE
L112 Part of antenna match. 1.5 nH: LQW15AN1N5B00 from Murata
C111 Part of antenna match. 0.5 pF, GRM1555C1HR50BZ01 from Murata
C112 DC block. 47 pF, GRM1555C1H470JZ01 from Murata
C161 Decoupling capacitor. 1 nF: GRM1555C1H102JA01 from Murata
C101/C102 27 pF: GRM1555C1H270JZ01 from Murata
C131/C132 18 pF: GRM1555C1H180JZ01 from Murata
Decoupling. Will affect PA resonance. See CC2590EM reference
design for placement.
Decoupling. Will affect LNA resonance. See CC2590EM reference
design for placement.
C2 Decoupling of external balun 1 nF: LWQ15AN1N5B00 from Murata
(1)
TL101
Transmission line. Will affect PA resonance. (simulated inductance: See CC2590EM reference design.
0.87nH) Transmission line: Length ≈ 40 mil, Width = 8 mil
TL131 Transmission line. Will affect LNA resonance. (simulated inductance: See CC2590EM reference design.
1.64nH) Transmission line: Length ≈ 100 mil, Width = 8 mil
R151 Bias resistor 4.3 k Ω : RK73H1ETTP4301F from Koa
(1) Transmission lines are measured from edge of pad of the CC2590 footprint to edge of pad of DC coupling capacitor. The length of the
transmission lines depend on the distance to the ground plane. If another PCB stack up is chosen the length of the transmission lines
needs to be adjusted.
PCB description: 4 layer PCB 1.6mm
Copper 1: 35 µ m
Dielectric 1-2: 0.35 mm (e.g. 2x Prepreg 7628 AT05 47% Resin)
Copper 2: 18 µ m
Dielectric 2-3: 0.76 mm (4 x 7628M 43% Resin)
6 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2008, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Copper 3: 18 µ m
Dielectric 3-4: 0.35 mm (e.g. 2x Prepreg 7628 AT05 47% Resin)
Copper 4: 35 µ m
DE104iML or equivalent substrate (Resin contents around 45%, which gives Er=4.42 at 2.4GHz, TanD=0.016)
Product Folder Link(s): CC2590
27 pF || 1 nF. The smallest cap closest to CC2590.
1 nF: GRM1555C1H102JA01 from Murata
18 pF || 1 nF. The smallest cap closest to CC2590.
1 nF: GRM1555C1H102JA01 from Murata
Page 7

Gain − dB
2400 2410 2420 2430 2440 2450 2460 2470 2480
f Frequency MHz
− −
NoiseFigure
− dB
-2
-1
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
3.9
4
4.1
4.2
4.3
4.4
4.5
4.6
4.7
4.8
4.9
5
5.1
5.2
5.3
5.4
GainHGM
NoiseFigureHGM
GainLGM
Gain − dB
T Temperature− − C
o
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80
-3
-2
-1
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
HGM
LGM
Gain − dB
PowerSupply − V
2 2.4 2.6 2.8 3 3.2 3.42.2 3.6
-3
-2
-1
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
HGM
LGM
freq(2.400GHzto2.485GHz)
S(1
,1)
m1
m1
freq=
S(1,1)=0.129/-31.279
impedance=61.723-j8.383
2.440GHz
CC2590
www.ti.com
........................................................................................................................................................................................ SWRS080 – SEPTEMBER 2008
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
LNA GAIN AND NOISE FIGURE LNA GAIN
vs vs
FREQUENCY TEMPERATURE
Figure 3. Figure 4.
LNA GAIN
POWER SUPPLY
Copyright © 2008, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 7
Figure 5. Figure 6. Input Impedance of LNA Measured from Antenna
vs
Product Folder Link(s): CC2590
Port on CC2590EM
Page 8

OutputPower(dBm)andPAE %
−
f Frequency− − MHz
CurrentConsumption mA
−
2400 2410 2420 2430 2440 2450 2460 2470 2480
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
18
18.5
19
19.5
20
20.5
21
21.5
22
22.5
23
23.5
24
24.5
25
I_VDD
PAE
Pout
OutputPower(dBm)andPAE %
−
InputPower − dBm
CurrentConsumption mA
−
-20 -18 -16 -14 -12 -10 -8 -6 -4 -2 0 2 4 6
-8
-4
-6
-2
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
20
22
24
26
28
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
20
22
24
26
28
30
32
34
36
38
40
I_VDD
PAE
Pout
OutputPower(dBm)andPAE %
−
T − Temperature − C
o
CurrentConsumption mA
−
8
21
-40 -30 -20 -10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80
10
12
14
16
18
20
22
24
26
28
21.2
21.4
21.6
21.8
22
22.2
22.4
22.6
22.8
23
PAE
Pout
I_VDD
OutputPower(dBm)andPAE %
−
PowerSupply − V
CurrentConsumption mA
−
8
18
20
22
24
26
17
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
16
14
12
10
18
2 2.2 2.4
2.6
2.8
3 3.2 3.4 3.6
PAE
I_VDD
P
OUT
CC2590
SWRS080 – SEPTEMBER 2008 ........................................................................................................................................................................................
www.ti.com
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
OUTPUT POWER, PAE AND OUTPUT POWER, PAE AND
CURRENT CONSUMPTION CURRENT CONSUMPTION
vs vs
INPUT POWER FREQUENCY
Figure 7. Figure 8.
OUTPUT POWER, PAE AND OUTPUT POWER, PAE AND
CURRENT CONSUMPTION CURRENT CONSUMPTION
TEMPERATURE POWER SUPPLY
8 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2008, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Figure 9. Figure 10.
vs vs
Product Folder Link(s): CC2590
Page 9

RF_P
RXTX
RF_N
RF_P
TXRX_SWITCH
RF_N
CC24xx
RREG_OUT (CC243x,CC2480),
VREGOUT (CC2420),GIO1(CC2400)
Alternatively
VDD/GNDto/MCU
(CC2420)
Alternatively
fromMCU
RF_P
RXTX
RF_N
= PCBtraceinductor
CC2590
ANT
PAEN
EN
HGM
BIAS
VDD
AVDD_PA2
AVDD_LNA
AVDD_BIAS
VDD
VDD
RF_P
RXTX
RF_N
L112
C113 C111
L111
C112
C161
C101/C102
C131/C132
R151
TL101
TL131
P1_1(CC243x),GPIO1(CC2480),
GIO6(CC2400)
L21
CC2590
www.ti.com
........................................................................................................................................................................................ SWRS080 – SEPTEMBER 2008
Controlling the Output Power from CC2590
The output power of CC2590 is controlled by controlling the input power. The CC2590 PA is designed to work in
compression (class AB), and the best efficiency is reached when a strong input signal is applied.
Input Levels on Control Pins
The four digital control pins (PAEN, EN, HGM, RXTX) have built-in level-shifting functionality, meaning that if the
CC2590 is operating from a 3.6-V supply voltage, the control pins will still sense 1.6-V - 1.8-V signals as logical
‘ 1 ’ .
An example of the above would be that RXTX is connected directly to the RXTX pin on CC24xx, but the global
supply voltage is 3.6-V. The RXTX pin on CC24xx will switch between 0-V (RX) and 1.8-V(TX), which is still a
high enough voltage to control the mode of CC2590.
The input voltages should however not have logical ‘ 1 ’ level that is higher than the supply.
Connecting CC2590 to a CC24xx Device
Table 3. Control Logic for Connecting CC2590 to a CC24xx Device
PAEN = EN RXTX HGM MODE OF OPERATION
0 X X Power Down
1 0 0 RX Low Gain Mode
1 0 1 RX High Gain Mode
1 1 X TX
Figure 11. CC2590 + CC24xx Application Circuit
Copyright © 2008, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 9
Product Folder Link(s): CC2590
Page 10

RF_P
RXTX
RF_N
RF_P
RF_N
CC25
CC2510
CC2511
00
Connectedto
VDD/GND/MCU
Alternatively
fromMCU
RF_P
RXTX
RF_N
= PCBtraceinductor
CC2590
ANT
PAEN
EN
HGM
BIAS
VDD
AVDD_PA2
AVDD_LNA
A
VDD_BIAS
VDD
VDD
RF_P
RXTX
RF_N
R151
TL101
TL131
NC
GDO0
GDO2
L112
C113 C111
L111
C112
C161
C101/C102
C131/C132
CC2590
SWRS080 – SEPTEMBER 2008 ........................................................................................................................................................................................
Connecting CC2590 to the CC2500, CC2510, or CC2511 Device
Table 4. Control Logic for Connecting CC2590 to a CC2500/10/11 Devices
PAEN EN RXTX HGM MODE OF OPERATION
0 0 NC X Power Down
0 1 NC 0 RX Low Gain Mode
0 1 NC 1 RX High Gain Mode
1 0 NC X TX
1 1 NC X Not allowed
www.ti.com
Figure 12. CC2590 + CC2500/10/11 Device Application Circuit
10 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2008, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Link(s): CC2590
Page 11

RF_P
RXTX
RF_N
RF_P
RF_N
CC2520
Alternativelyto
VDD/GND/MCU
Alternatively
fromMCU
RF_P
RXTX
RF_N
= PCBtraceinductor
CC2590
ANT
PAEN
EN
HGM
BIAS
VDD
AVDD_PA2
AVDD_LNA
AVDD_BIAS
VDD
VDD
RF_P
RXTX
RF_N
R151
TL101
TL131
NC
GPIO5
GPIO4
C1
L112
C113 C111
L111
C112
C161
C101/C102
C131/C132
GPIO3
CC2590
www.ti.com
........................................................................................................................................................................................ SWRS080 – SEPTEMBER 2008
Connecting CC2590 to a CC2520 Device
Table 5. Control Logic for Connecting CC2590 to a CC2520 Device
PAEN EN RXTX HGM MODE OF OPERATION
0 0 NC X Power Down
0 1 NC 0 RX Low Gain Mode
0 1 NC 1 RX High Gain Mode
1 0 NC X TX
1 1 NC X Not allowed
Figure 13. CC2590 + CC2520 Application Circuit
PCB Layout Guidelines
The exposed die attach pad must be connected to a solid ground plane as this is the primary ground connection
for the chip. Inductance in vias to the pad should be minimized. It is highly recommended to follow the reference
layout. Changes will alter the performance. Also see the PCB landpattern information in this data sheet. For best
performance, minimize the length of the ground vias, by using a 4-layer PCB with ground plane as layer 2 when
CC2590 is mounted onto layer 1.
PCB trace inductors are used to be able to optimize the inductance value, and they are too small to be replaced
by discrete inductors. The placement of the power supply decoupling capacitors C101/C102 and C131/C132 are
important to set the PCB trace inductance values accurately.
Copyright © 2008, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 11
Product Folder Link(s): CC2590
Page 12

PACKAGE OPTION ADDENDUM
www.ti.com
2-Oct-2008
PACKAGING INFORMATION
Orderable Device Status
(1)
Package
Type
Package
Drawing
Pins Package
Qty
Eco Plan
CC2590RGVR ACTIVE QFN RGV 16 2500 Green (RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
CC2590RGVT ACTIVE QFN RGV 16 250 Green (RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
(1)
The marketing status values are defined as follows:
ACTIVE: Product device recommended for new designs.
LIFEBUY: TI has announced that the device will be discontinued, and a lifetime-buy period is in effect.
NRND: Not recommended for new designs. Device is in production to support existing customers, but TI does not recommend using this part in
a new design.
PREVIEW: Device has been announced but is not in production. Samples may or may not be available.
OBSOLETE: TI has discontinued the production of the device.
(2)
Eco Plan - The planned eco-friendly classification: Pb-Free (RoHS), Pb-Free (RoHS Exempt), or Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br) - please check
http://www.ti.com/productcontent for the latest availability information and additional product content details.
TBD: The Pb-Free/Green conversion plan has not been defined.
Pb-Free (RoHS): TI's terms "Lead-Free" or "Pb-Free" mean semiconductor products that are compatible with the current RoHS requirements
for all 6 substances, including the requirement that lead not exceed 0.1% by weight in homogeneous materials. Where designed to be soldered
at high temperatures, TI Pb-Free products are suitable for use in specified lead-free processes.
Pb-Free (RoHS Exempt): This component has a RoHS exemption for either 1) lead-based flip-chip solder bumps used between the die and
package, or 2) lead-based die adhesive used between the die and leadframe. The component is otherwise considered Pb-Free (RoHS
compatible) as defined above.
Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br): TI defines "Green" to mean Pb-Free (RoHS compatible), and free of Bromine (Br) and Antimony (Sb) based flame
retardants (Br or Sb do not exceed 0.1% by weight in homogeneous material)
(2)
Lead/Ball Finish MSL Peak Temp
Call TI Level-2-260C-1 YEAR
Call TI Level-2-260C-1 YEAR
(3)
(3)
MSL, Peak Temp. -- The Moisture Sensitivity Level rating according to the JEDEC industry standard classifications, and peak solder
temperature.
Important Information and Disclaimer:The information provided on this page represents TI's knowledge and belief as of the date that it is
provided. TI bases its knowledge and belief on information provided by third parties, and makes no representation or warranty as to the
accuracy of such information. Efforts are underway to better integrate information from third parties. TI has taken and continues to take
reasonable steps to provide representative and accurate information but may not have conducted destructive testing or chemical analysis on
incoming materials and chemicals. TI and TI suppliers consider certain information to be proprietary, and thus CAS numbers and other limited
information may not be available for release.
In no event shall TI's liability arising out of such information exceed the total purchase price of the TI part(s) at issue in this document sold by TI
to Customer on an annual basis.
Addendum-Page 1
Page 13

Page 14
Page 15

Page 16

IMPORTANT NOTICE
Texas Instruments Incorporated and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make corrections, modifications, enhancements, improvements,
and other changes to its products and services at any time and to discontinue any product or service without notice. Customers should
obtain the latest relevant information before placing orders and should verify that such information is current and complete. All products are
sold subject to TI’s terms and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgment.
TI warrants performance of its hardware products to the specifications applicable at the time of sale in accordance with TI’s standard
warranty. Testing and other quality control techniques are used to the extent TI deems necessary to support this warranty. Except where
mandated by government requirements, testing of all parameters of each product is not necessarily performed.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or customer product design. Customers are responsible for their products and
applications using TI components. To minimize the risks associated with customer products and applications, customers should provide
adequate design and operating safeguards.
TI does not warrant or represent that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any TI patent right, copyright, mask work right,
or other TI intellectual property right relating to any combination, machine, or process in which TI products or services are used. Information
published by TI regarding third-party products or services does not constitute a license from TI to use such products or services or a
warranty or endorsement thereof. Use of such information may require a license from a third party under the patents or other intellectual
property of the third party, or a license from TI under the patents or other intellectual property of TI.
Reproduction of TI information in TI data books or data sheets is permissible only if reproduction is without alteration and is accompanied
by all associated warranties, conditions, limitations, and notices. Reproduction of this information with alteration is an unfair and deceptive
business practice. TI is not responsible or liable for such altered documentation. Information of third parties may be subject to additional
restrictions.
Resale of TI products or services with statements different from or beyond the parameters stated by TI for that product or service voids all
express and any implied warranties for the associated TI product or service and is an unfair and deceptive business practice. TI is not
responsible or liable for any such statements.
TI products are not authorized for use in safety-critical applications (such as life support) where a failure of the TI product would reasonably
be expected to cause severe personal injury or death, unless officers of the parties have executed an agreement specifically governing
such use. Buyers represent that they have all necessary expertise in the safety and regulatory ramifications of their applications, and
acknowledge and agree that they are solely responsible for all legal, regulatory and safety-related requirements concerning their products
and any use of TI products in such safety-critical applications, notwithstanding any applications-related information or support that may be
provided by TI. Further, Buyers must fully indemnify TI and its representatives against any damages arising out of the use of TI products in
such safety-critical applications.
TI products are neither designed nor intended for use in military/aerospace applications or environments unless the TI products are
specifically designated by TI as military-grade or "enhanced plastic." Only products designated by TI as military-grade meet military
specifications. Buyers acknowledge and agree that any such use of TI products which TI has not designated as military-grade is solely at
the Buyer's risk, and that they are solely responsible for compliance with all legal and regulatory requirements in connection with such use.
TI products are neither designed nor intended for use in automotive applications or environments unless the specific TI products are
designated by TI as compliant with ISO/TS 16949 requirements. Buyers acknowledge and agree that, if they use any non-designated
products in automotive applications, TI will not be responsible for any failure to meet such requirements.
Following are URLs where you can obtain information on other Texas Instruments products and application solutions:
Products Applications
Amplifiers amplifier.ti.com Audio www.ti.com/audio
Data Converters dataconverter.ti.com Automotive www.ti.com/automotive
DSP dsp.ti.com Broadband www.ti.com/broadband
Clocks and Timers www.ti.com/clocks Digital Control www.ti.com/digitalcontrol
Interface interface.ti.com Medical www.ti.com/medical
Logic logic.ti.com Military www.ti.com/military
Power Mgmt power.ti.com Optical Networking www.ti.com/opticalnetwork
Microcontrollers microcontroller.ti.com Security www.ti.com/security
RFID www.ti-rfid.com Telephony www.ti.com/telephony
RF/IF and ZigBee® Solutions www.ti.com/lprf Video & Imaging www.ti.com/video
Mailing Address: Texas Instruments, Post Office Box 655303, Dallas, Texas 75265
Copyright © 2008, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Wireless www.ti.com/wireless
 Loading...
Loading...