Features
➤
Provides accurate measure
ment of available charge in
NiCd, NiMH, and Li-Ion re
chargeable batteries
➤
Supports SBData charge con
trol commands for Li-Ion,
NiMH, and NiCd chemistries
➤
Designed for battery pack inte
-
gration
-
120µA typical operating
current
-
Small size enables
implementations in as little as
3
4
square inch of PCB
➤ Two-wire SMBus-like interface
➤ Measurements compensated for
current and temperature
➤ Programmable self-discharge
and charge compensation
➤ 16-pin narrow SOIC
General Description
The bq2092 Gas Gauge IC With
SMBus-Like Interface is intended
for battery-pack or in-system instal
lation to maintain an accurate
record of available battery charge.
The bq2092 directly supports capac
ity monitoring for NiCd, NiMH, and
Li-Ion battery chemistries.
The bq2092 uses the SMBus proto
col that supports many of the Smart
Battery Data (SBData) commands.
The bq2092 also supports SBData
charge control. Battery state-ofcharge, capacity remaining, remain
ing time and chemistry are available
over the serial link. Battery-charge
state can be directly indicated using
a four-segment LED display to
graphically depict battery full-toempty in 25% increments.
The bq2092 estimates battery selfdischarge based on an internal
timer and temperature sensor and
user-programmable rate informa
tion stored in external EEPROM.
The bq2092 also automatically
recalibrates or “learns” battery
capacity in the full course of a
discharge cycle from full to empty.
The bq2092 may operate directly
from three nickel chemistry cells.
With the REF output and an exter
nal transistor, a simple, inexpensive
regulator can be built to provide V
CC
for other battery cell configurations.
An external EEPROM is used to
program initial values into the
bq2092 and is necessary for proper
operation.
1
bq2092
Gas Gauge IC with SMBus-Like Interface
V
CC
3.0–5.5V
SCL Serial memory
clock
SDA Serial memory
data
SEG
1
LED segment 1
SEG
2
LED segment 2
SEG
3
LED segment 3
SEG
4
LED segment 4
V
SS
System ground
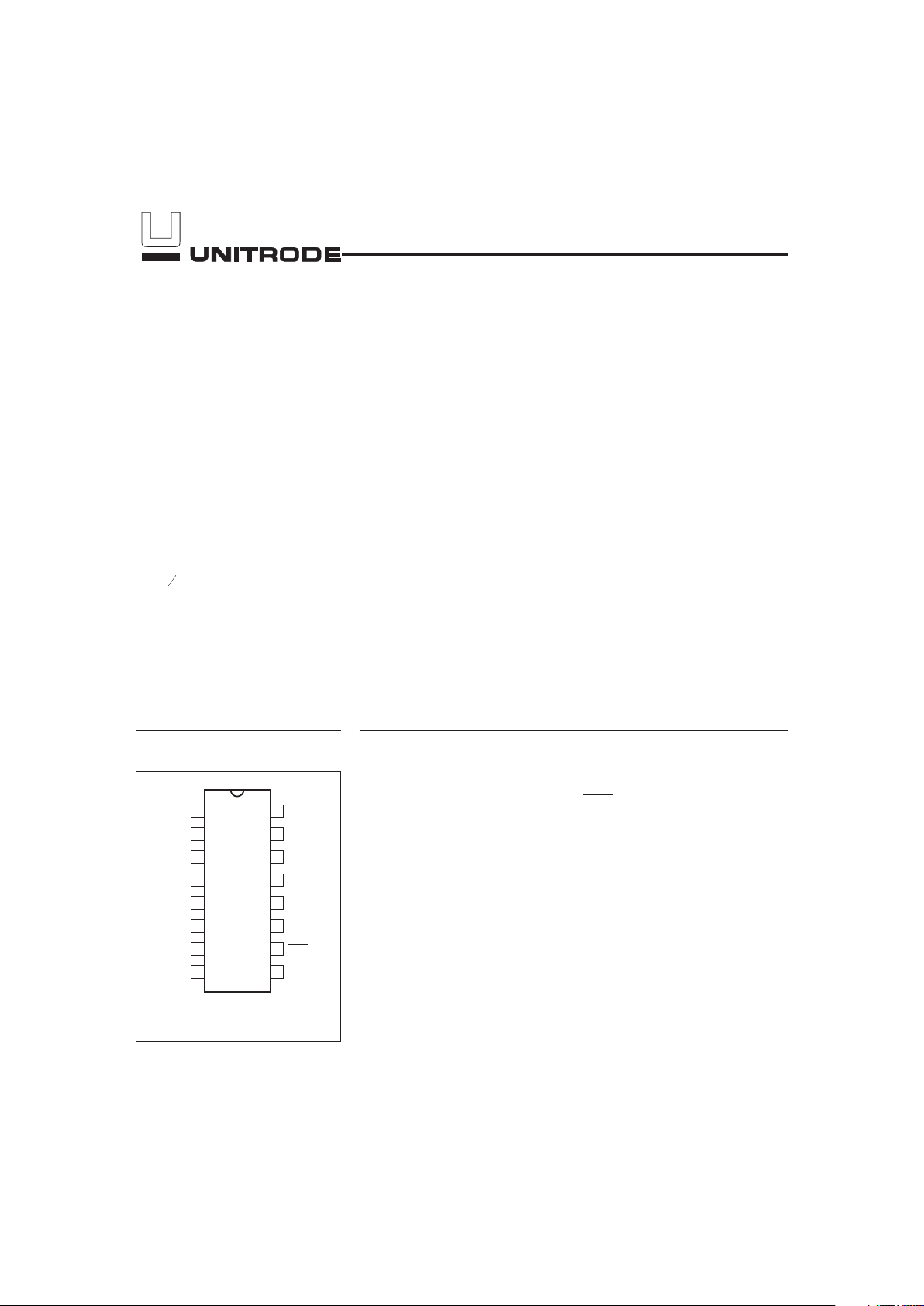
1
PN209101.eps
16-Pin Narrow SOIC
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
V
OUT
REF
SCC
SCD
NC
SB
DISP
SR
V
CC
SCL
SDA
SEG
1
SEG
2
SEG
3
SEG
4
V
SS
SR Sense resistor input
DISP
Display control input
SB Battery sense input
SCD Serial communication
data input/output
SCC Serial communication
clock
REF Voltage reference
output
V
OUT
EEPROM supply
output
6/99 C
Pin Connections Pin Names

Pin Descriptions
V
CC
Supply voltage input
SCL
Serial memory clock
This output is used to clock the data
transfer between the bq2092 and the ex
-
ternal nonvolatile configuration memory.
SDA
Serial memory data and address
This bi-directional pin is used to trans
fer address and data to and from the
bq2092 and the external configuration
memory.
SEG
1
–
SEG
4
LED display segment outputs
Each output may activate an external LED
to sink the current sourced from V
CC
.
V
SS
Ground
SR
Sense resistor input
The voltage drop (V
SR
) across pins SR and
V
SS
is monitored and integrated over time
to interpret charge and discharge activity.
The SR input is connected to the sense resistor and the negative terminal of the
battery. V
SR<VSS
indicates discharge, and
V
SR>VSS
indicates charge. The effective
voltage drop, V
SRO
, as seen by the bq2092
is V
SR+VOS
(see Table 3).
DISP
Display control input
DISP
high disables the LED display. DISP
floating allows the LED display to be active
during charge if the rate is greater than
100mA. DISP
low activates the display for 4
seconds.
SB
Secondary battery input
This input monitors the cell pack voltage as
a single-cell potential through a highimpedance resistor divider network. The
cell pack voltage is reported in the SBD
register function Voltage (0x09) and is com
pared to end-of-discharge voltage and
charging voltage parameters.
NC
No connect
SCD
Serial communication data
This open-drain bidirectional pin is used to
transfer address and data to and from the
bq2092.
SCC
Serial communication clock
This open-drain bidirectional pin is used to
clock the data transfer to and from the
bq2092.
REF
Reference output for regulator
REF provides a reference output for an optional micro-regulator.
V
OUT
Supply output
This output supplies power to the external EEPROM configuration memory.
2
bq2092

Functional Description
General Operation
The bq2092 determines battery capacity by monitoring
the amount of charge input to or removed from a
rechargeable battery. The bq2092 measures discharge
and charge currents, estimates self-discharge, and
monitors the battery for low-battery voltage thresh
olds. The charge measurement is made by monitoring
the voltage across a small-value series sense resistor
between the battery's negative terminal and ground.
The available battery charge is determined by moni
toring this voltage over time and correcting the meas
urement for the environmental and operating condi
tions.
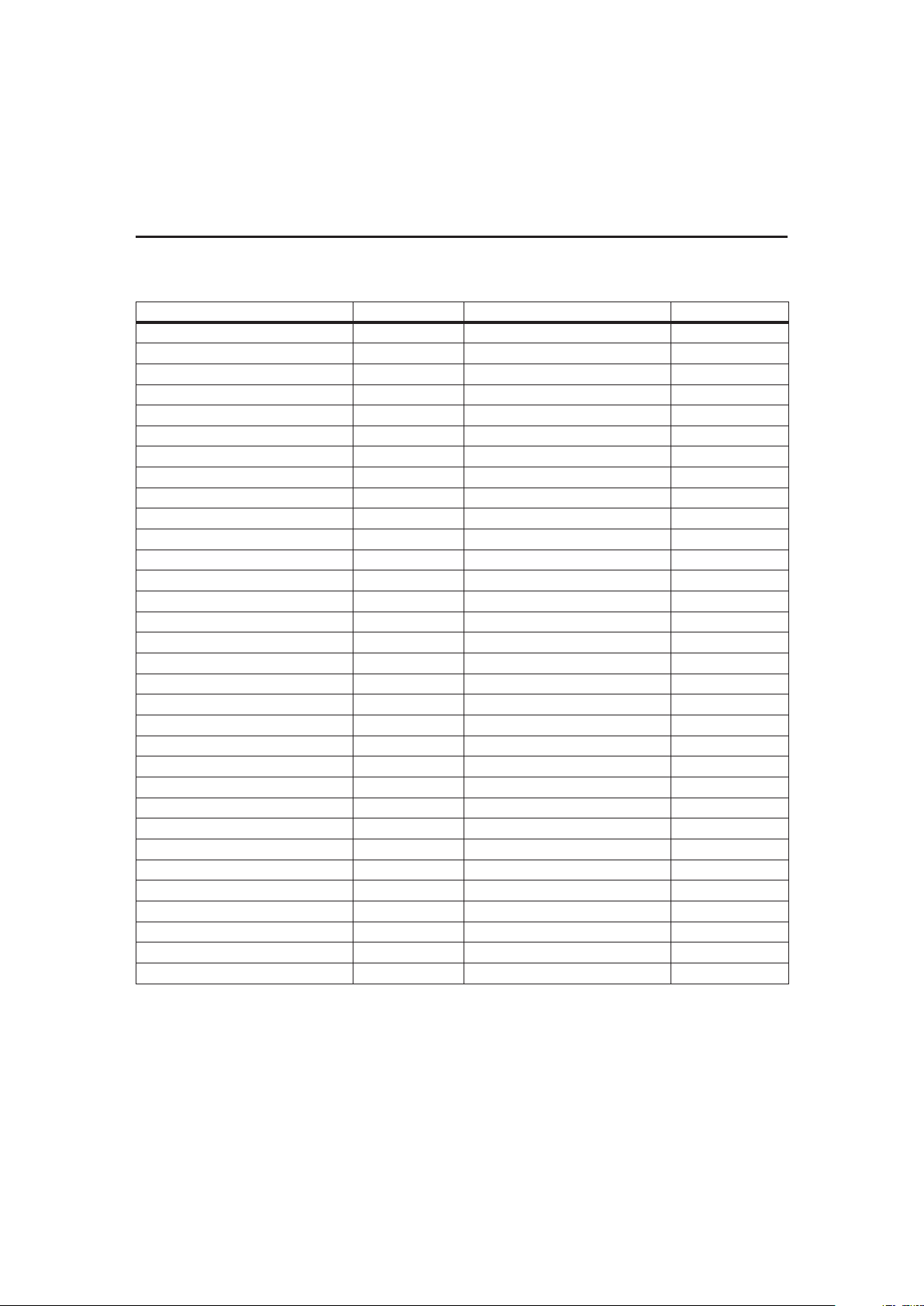
Figure 1 shows a typical battery pack application of the
bq2092 using the LED capacity display, the serial port,
and an external EEPROM for battery pack program
ming information. The bq2092 must be configured and
calibrated for the battery-specific information to ensure
proper operation. Table 1 outlines the externally
programmable functions available in the bq2092. Refer
to the Programming the bq2092 section for further
details.
An internal temperature sensor eliminates the need
for an external thermistor—reducing cost and compo
nents. An internal, temperature-compensated timebase eliminates the need for an external resonator,
further reducing cost and components. The entire
circuit in Figure 1 can occupy less than
3
4
square inch
of board space.
3
bq2092
V
CC
SCL
SDA
SEG1
SEG2
SEG3
SEG4
V
OUT
REF
SCC
SCD
NC
SB
DISP
SR
BZX84C5V6
BZX84C5V6
2192L.eps
Figure 1. Battery Pack Application Diagram—LED Display
4
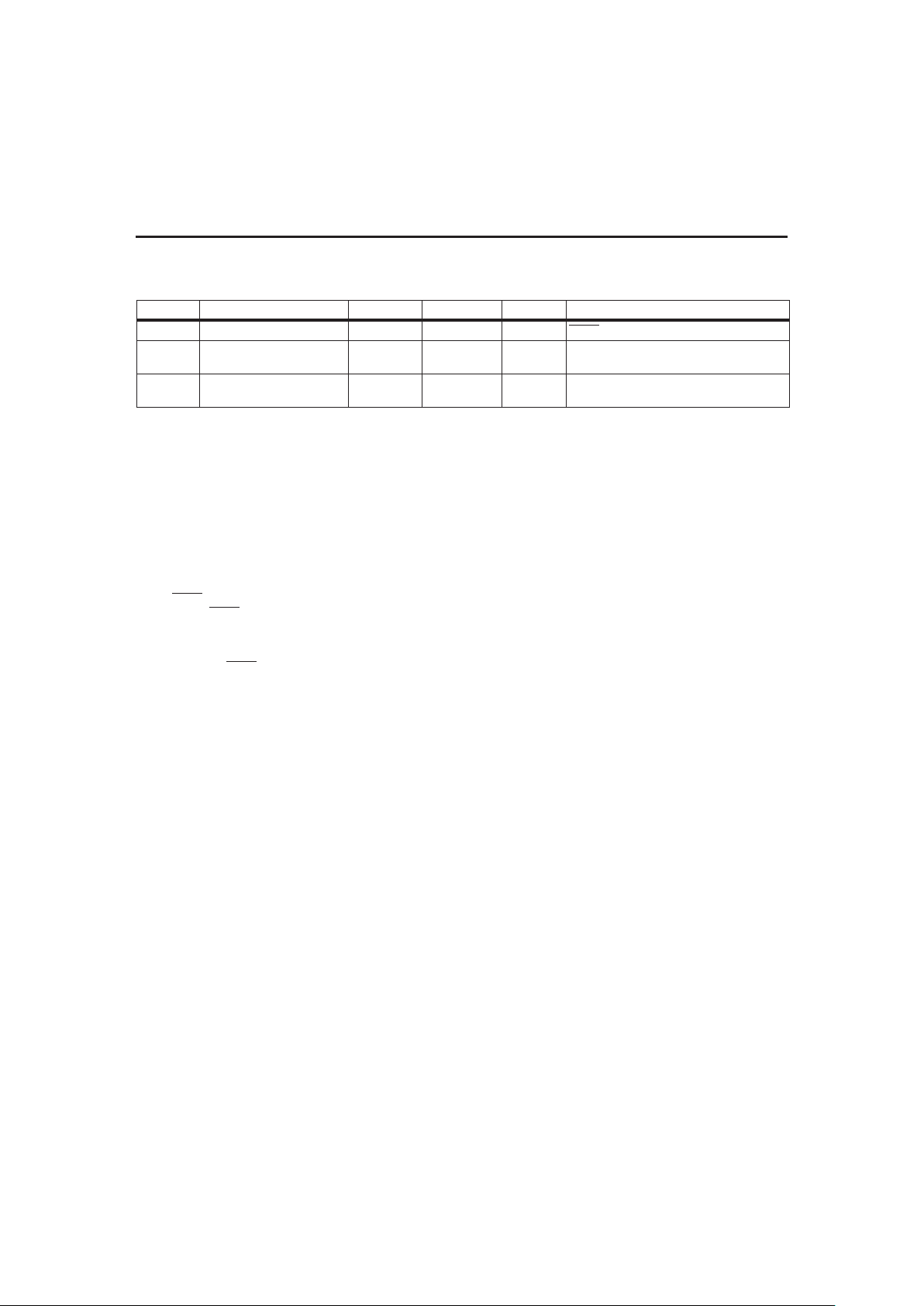
Parameter Name Address Length Units
Design capacity 0x00/0x01 16 bits: low byte, high byte mAh
Initial battery voltage 0x02/0x03 16 bits: low byte, high byte mV
Fast charging current 0x04/0x05 16 bits: low byte, high byte mA
Charging voltage 0x06/0x07 16 bit: low byte, high byte mV
Remaining capacity alarm 0x08/0x09 16 bits: low byte, high byte mAh
FLAGS1 0x0a 8 bits N/A
FLAGS2 0x0b 8 bits N/A
Current measurement gain 0x0c/0x0d 16 bits: low byte, high byte N/A
EDV
1
0x0e/0x0f 16 bits: low byte, high byte mV
EDV
F
0x10/0x11 16 bits: low byte, high byte mV
Temperature offset 0x12 8 bits 0.1°K
Maximum charge temperature/∆T/∆t 0x13 8 bits N/A
Self-discharge rate 0x14 8 bits N/A
Digital filter 0x15 8 bits N/A
Current integration gain 0x16/0x17 16 bits: low byte, high byte N/A
Full charge percentage 0x18 8 bits N/A
Charge compensation 0x19 8 bits N/A
Battery voltage offset 0x1a 8 bits mV
Battery voltage gain 0x1b/0x1c 16 bits: high byte, low byte N/A
Serial number 0x1d/0x1e 16 bits: low byte, high byte N/A
Hold-off timer 0x1f 8 bits N/A
Cycle count 0x20/0x21 16 bits: low byte, high byte N/A
Maintenance charge current 0x22/0x23 16 bits: low byte, high byte mA
Reserved 0x24/0x31 – –
Design voltage 0x32/0x33 16 bits: low byte, high byte mV
Specification information 0x34/0x35 16 bits: low byte, high byte N/A
Manufacturer date 0x36/0x37 16 bits: low byte, high byte N/A
Reserved 0x38/0x3f – –
Manufacturer name 0x40/0x4f 8 + 120 bits N/A
Device name 0x50/0x5f 8 + 120 bits N/A
Chemistry 0x60/0x6f 8 + 120 bits N/A
Manufacturer data 0x70/0x7f 8 +120 bits N/A
Table 1. Configuration Memory Programming Values
Note: N/A = Not applicable; data packed or coded. See “Programming the bq2092” for details.
bq2092

Voltage Thresholds
In conjunction with monitoring VSRfor charge/discharge
currents, the bq2092 monitors the battery potential
through the SB pin. The voltage potential is deter
mined through a resistor-divider network per the
following equation:
R
R
MBV
2.25
5
4
1=−
where MBV is the maximum battery voltage, R
5
is
connected to the positive battery terminal, and R
4
is
connected to the negative battery terminal. R
5/R4
should
be rounded to the next highest integer. The voltage at
the SB pin (V
SB
) should never exceed 2.4V.
The battery voltage is monitored for the end-ofdischarge voltage (EDV), for maximum pack voltage and
for alarm warning conditions. EDV threshold levels are
used to determine when the battery has reached an
“empty” state, and the charging voltage plus 5% thresh
old is used for fault detection during charging. The
battery voltage gain, two EDV thresholds, and charge
voltage limit are programmed via EEPROM. See the
Programming the bq2092 section for further details.
If V
SB
is below either of the two EDV thresholds, the associated flag is latched and remains latched, independent of
V
SB
, until the next valid charge.
EDV monitoring may be disabled under certain conditions. If the discharge current is greater than approximately 6A, EDV monitoring is disabled and resumes
after the current falls below 6A.
Reset
The bq2092 is reset when first connected to the battery
pack. The bq2092 can also be reset with a command
over the serial port, as described in the Software Reset
section.
Temperature
The bq2092 monitors temperature using an internal
sensor. The temperature is used to adapt charge/dis
charge and self-discharge compensations as well as
maximum temperature and∆T/∆t during bq2092 con
trolled charge. Temperature may also be accessed over
the serial port. See the Programming the bq2092 section
for further details.
Layout Considerations
The bq2092 measures the voltage differential between
the SR and V
SS
pins. VOS(the offset voltage at the SR
pin) is greatly affected by PC board layout. For optimal
results, the PC board layout should follow the strict rule
of a single-point ground return. Sharing high-current
ground with small signal ground causes undesirable
noise on the small signal nodes. Additionally, in refer
-
ence to Figure 1:
n
The capacitors (C1, C2, and C4) should be placed as
close as possible to the SB and V
CC
pins, and their paths
to V
SS
should be as short as possible. A high-quality
ceramic capacitor of 0.1µf is recommended for V
CC
.
n
The sense resistor capacitor (C3) should be placed as
close as possible to the SR pin.
n
The sense resistor (R1) should be as close as possible
to the bq2092.
n
The IC should be close to the cells for the best
temperature measurement.
n
An optional zener may be necessary to ensure VCCis
not above the maximum rating during operation.
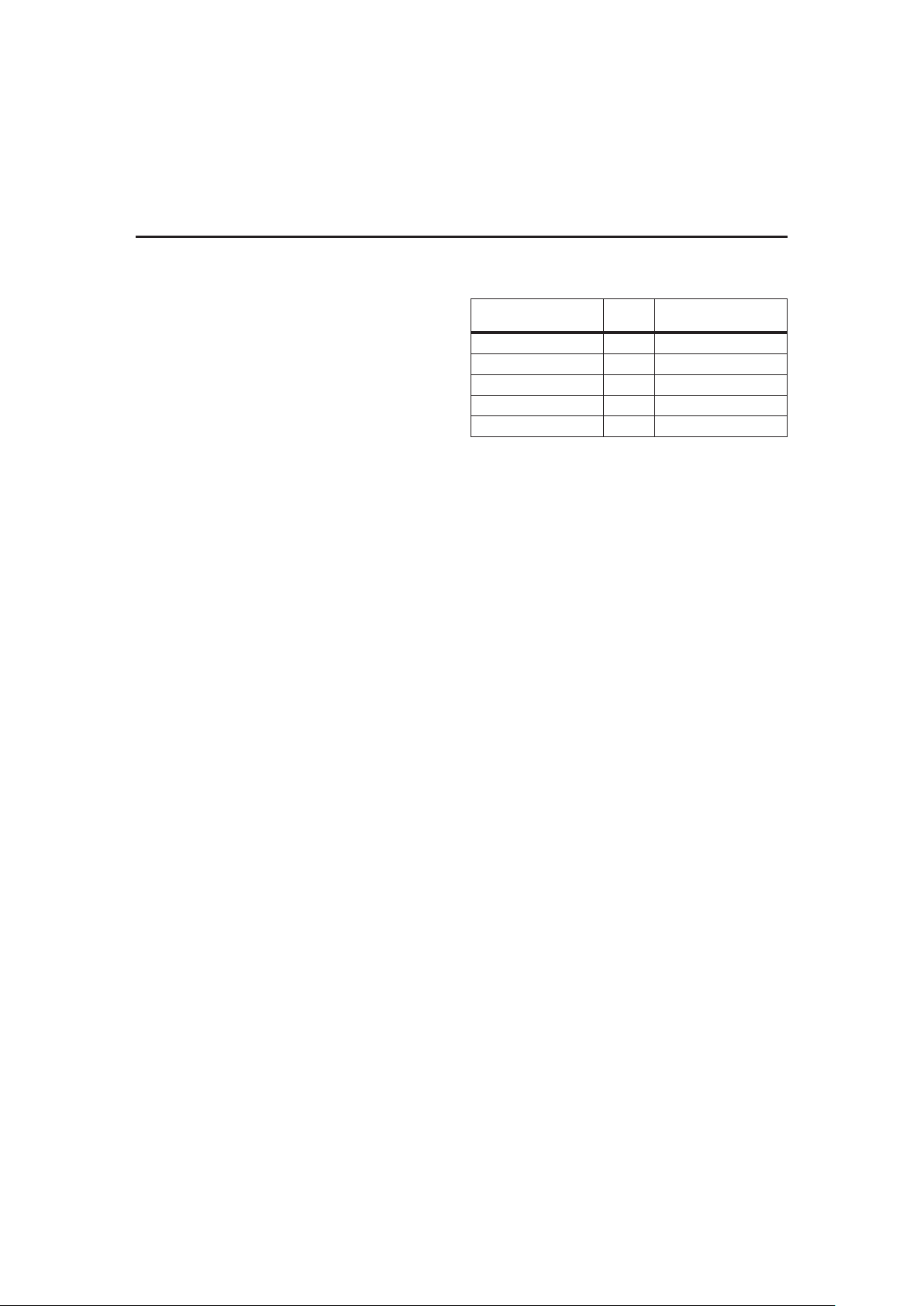
Gas Gauge Operation
The operational overview diagram in Figure 2 illustrates the operation of the bq2092. The bq2092 accumulates a measure of charge and discharge currents, as
well as an estimation of self-discharge. Charge currents
are compensated for temperature and state-of-charge.
Self-discharge is only temperature-compensated.
The main counter, RemainingCapacity (RM), represents
the available battery capacity at any given time. Battery
charging increments the RM register, whereas battery
discharging and self-discharge decrement the RM register
and increment the Discharge Count Register (DCR).
The Discharge Count Register (DCR) is used to update
the FullChargeCapacity (FCC) register only if a
complete battery discharge from full to empty occurs
without any partial battery charges. Therefore, the
bq2092 adapts its capacity determination based on the
actual conditions of discharge.
The battery's initial capacity is equal to the DesignCapacity
(DC). Until FCC is updated, RM counts up to, but not
beyond, this threshold during subsequent charges.
1. FullChargeCapacity or learned-battery
capacity:
FCC is the last measured discharge capacity of the
battery. On initialization (application of V
CC
or reset),
FCC = DC. During subsequent discharges, the FCC
is updated with the latest measured capacity in the
Discharge Count Register, representing a discharge
from full to below EDV1. A qualified discharge is
necessary for a capacity transfer from the DCR to the
FCC register. The FCC also serves as the 100% ref
erence threshold used by the relative state-of-charge
calculation and display.
5
bq2092
2. DesignCapacity (DC):
The DC is the user-specified battery capacity and is
programmed by using an external EEPROM. The
DC also provides the 100% reference for the absolute display mode.
3. Remaining Capacity (RM):
RM counts up during charge to a maximum value of
FCC and down during discharge and self-discharge to
0. RM is reset to 0000Ah when EDV1 = 1 and a valid
charge is detected. To prevent overstatement of
charge during periods of overcharge, RM stops incrementing when RM = FCC. RM may optionally
be written to a user-defined value when fully
charged when the battery pack is under bq2092
charge control. See the Charge Control section for
further details.
4. Discharge Count Register (DCR):
The DCR counts up during discharge independent
of RM and can continue increasing after RM has
decremented to 0. Before RM = 0 (empty battery),
both discharge and self-discharge increment the
DCR. After RM = 0, only discharge increments
the DCR. The DCR resets to 0 when RM = FCC.
The DCR does not roll over but stops counting
when it reaches FFFFh.
The DCR value becomes the new FCC value on the
first charge after a valid discharge to V
EDV1
if:
n
No valid charge initiations (charges greater than
10mAh, where V
SRO
>|V
SRD
|) occurred during
the period between RM = FCC and EDV1 de
-
tected.
n
The self-discharge count is not more than
256mAh.
n
The temperature is≥273°K (0°C) when the
EDV1 level is reached during discharge.
The valid discharge flag (VDQ) indicates whether
the present discharge is valid for FCC update. FCC
cannot be reduced by more than 256mAh during
any single cycle.
Charge Counting
Charge activity is detected based on a positive voltage
on the V
SR
input. If charge activity is detected, the
bq2092 increments RM at a rate proportional to V
SRO
and, if enabled, activates an LED display. Charge
actions increment the RM after compensation for charge
rate and temperature.
The bq2092 determines charge activity sustained at a
continuous rate equivalent to V
SRO
>|V
SRD
|. A valid
charge equates to sustained charge activity
greater than 10 mAh. Once a valid charge is detected,
charge counting continues until V
SRO
falls below
|V
SRD
|. V
SRD
is a programmable threshold as
described in the Digital Magnitude Filter section.
Discharge Counting
All discharge counts where V
SRO
<|V
SRD
| cause the
RM register to decrement and the DCR to increment.
V
SRD
is a programmable threshold as described in the
Digital Magnitude Filter section.
Self-Discharge Estimation
The bq2092 continuously decrements RM and incre
ments DCR for self-discharge based on time and
temperature. The self-discharge rate is dependent on
the battery chemistry. The bq2092 self-discharge esti
mation rate is externally programmed in EEPROM
6
bq2092
Rate and
Temperature
Compensation
Temperature
Compensation
Charge
Current
Discharge
Current
Self-Discharge
Timer
Remaining
Capacity
(RM)
Full
Charge
Capacity
(FCC)
Discharge
Count
Register
(DCR)
<
Qualified
Transfer
+
Temperature, Other Data
+
--
+
Inputs
Main Counters
and Capacity
Reference (FCC)
Outputs
Two-Wire
Serial Interface
Chip-Controlled
Available Charge
LED Display
Rate and
Temperature
Compensation
Figure 2. Operational Overview

and can be programmed from 0 to 25% per day at
20-30°C. This rate doubles every 10°C increase until T
>70°C or is halved every 10°decrease untilT<10°C.
The self-discharge estimate reduces RM by 0.39% of its
current value at time intervals spaced so that the aver
age reduction equals the programmed value adjusted for
temperature. The EEPROM program constant is the 2’s
complement of
52 73. X
, where
Xday= %
self-discharge
rate desired at 25°C.
Charge Control
The bq2092 supports SBD charge control by broadcast
ing ChargingCurrent() and ChargingVoltage() to the
Smart Charger address. Smart Charger broadcasts can
be disabled by writing bit 14 of Battery Mode() to 1. The
bq2092-based charge control can be enabled by setting
bit 4 in FLAGS2 (MSB of 0x2f) to 1. See Programming
the bq2092 for further details. If the Fully_Charged bit
is not set in BatteryStatus, the bq2092 broadcasts the
fast charge current and voltage to the Smart Charger.
The bq2092 broadcasts the maintenance current values
(trickle rate) if the Fully_Charged bit is set or Voltage is
below EDVF.
The bq2092 internal charge control is compatible with
nickel-based and Li-Ion chemistries.
For Li-Ion, the bq2092 broadcasts the required ChargingCurrent and ChargingVoltage according to the values
programmed in the external EEPROM. During a valid
charge (VQ = 1), the bq2092 signals a valid charge
termination when the Terminate_Charge_Alarm and
Fully_Charged bits are set in BatteryStatus. These bits
are set when the battery is charged more than 256mAh
above FCC.
For nickel-based chemistries, the bq2092 broadcasts the
required charge current and voltage according to the
programmed values in the external EEPROM. Maxi
mum temperature and∆T/∆t are used as valid charge
termination methods. Note: Nickel-based chemistries
require a charge voltage higher than the maximum cell
voltage during charge to ensure constant-current charg
ing. During a valid charge (VQ = 1), if the bq2092 deter
mines a maximum temperature condition, a∆T/∆t rate
greater than the programmed value, or a charge state
greater than 256mAh above FCC, then the Termi
nate_Charge_Alarm, Over_Charge_Alarm, and
Fully_Charged bits are set in BatteryStatus.
Once the bq2092 detects a valid charge termination, the
Fully_Charged bit, Terminate_Charge_Alarm, and
Over_Charge_Alarm bits are set and the ChargingCurrent
is set to zero. Once the terminating condition ceases, the
Terminate_Charge_Alarm and OverCharge Alarm bits are
cleared and the ChargingCurrent is set to the maintenance
rate. The bq2092 requests the maintenance current and
charging voltage until RM falls below the full charge
percentage. Once this occurs, the Fully_Charged bit is
cleared, and the bq2092 requests the fast charging current
and charging voltage.
During fast charge, the bq2092 suspends charge by
requesting zero current and setting the Termi
nate_Charge_Alarm bit in BatteryStatus. Charge is
suspended if the actual charge current is 25% greater
than the programmed charged current. If the
programmed charge current is less than 1024mA, over
current suspend occurs if the actual charge current is
256mA greater than the programmed value. Charge is
also suspended if the actual battery voltage is 5%
greater than the programmed charge voltage. If the
battery temperature is greater than the programmed
maximum temperature before charge, then the bq2092
suspends charge requests until the temperature falls
below 50°C.
If the battery temperature is less than 0°C, the charging
current sets to maintenance (trickle) charge current.
The fast charging current is requested when the
temperature is above 5°C.
∆T/∆t
The ∆T/∆t used by the bq2092 is programmable in both
the temperature step (1.6°C–4.6°C) and time step (20
seconds–320seconds). Typical settings for 1°C/min
include 2°C over 120 seconds and 3°C over 180 seconds.
Longer times are required for increased slope resolution.
∆∆T
t
is set by the formula:
∆∆T
t
=
()
[]
lower nibble of 0 13 in E PROM
lower nibble
2
∗∗+216
2' s
()
[]
of 0 1f in E PROM
C
minute
2
∗∗
333.
o
In addition to the ∆T/∆t timer, there is a hold-off timer,
which starts when the battery is being charged at more
than 256mA and the temperature is above 25°C. (This is
valid only for NiMH chemistry, bit 5 in FLAGS2 set to
0.) Until this timer expires, ∆T/∆t is suspended. If the
temperature falls below 25°C, or if charging current
fallls below 255mA, the timer is reset and restarts only
if the above conditions are once again met.
Safety Termination
If charging continues for more than 256mAh beyond
RM = FCC, the Terminate_Charge_Alarm and
Fully_Charged bits are set, and the charging current is
modified to request maintenance current. If the battery
is discharged from full by less than 256mAh, then the
safety overcharge termination, for NiMH only, is allowed
to extend to 512 mAh.
Updating RM after a valid charge termination, RM may
optionally be set to a value from 0 to 100% of the Full
ChargeCapacity. If RM is below the value programmed
7
bq2092
in full charge percentage, RM is set to full charge
percentage of FCC on valid charge termination. If RM is
above the full charge percentage, RM is not modified.
Count Compensations
Charge activity is compensated for temperature and
state-of-charge before updating the RM and/or DCR. RM
is compensated for temperature before updating the RM
register. Self-discharge estimation is compensated for
temperature before updating RM or DCR.
Charge Compensation
Charge efficiency is compensated for state-of-charge,
temperature, and battery chemistry. For Li-Ion chemis
try cells, the charge efficiency is unity for all cases. The
charge efficiency for nickel chemistry cells, however, is
adjusted using the following equation:
RM RM Q Q
EFC ET
=∗ −()
where
RelativeStateofCharge FullChargePercentage≤
and
Q
EFC
is the programmed fast charge efficiency vary-
ing from .75 to .99.
RM RM Q Q
ETC ET
=∗ −()
where
RelativeStateofCharge FullChargePercentage≥
and
Q
ETC
is the programmed maintenance (trickle)
charge efficiency varying from 0.50 to 0.97.
Q
ET
is used to adjust the charge efficiency as the battery
temperature increases according to the following:
QifT
ET
=<030
°C
QCTC
ET
=°≤<°002 30 40.if
QTC
ET
=≥°005 40.if
Remaining Capacity Compensation
The bq2092 adjusts the RM as a function of tempera
ture. This adjustment accounts for the reduced capacity
of the battery at colder temperatures. The following
equation is used to adjust RM:
If T C≥°5
RemainingCapacity
Nominal Available Capacity (NAC)
=
If T < 5°C
RM() NAC() TCC T 5 C))=+∗−°((1
Where T = temperature °C
TCC = 0.004
RM adjusts upward to Nominal Available Capacity as
the temperature increases.
Digital Magnitude Filter
The bq2092 has a programmable digital filter to elimi
nate charge and discharge counting below a set
threshold. Table 2 shows typical digital filter settings.
The proper digital filter setting can be calculated
using the following equation.
|V
SRD
(mV)| = 45 / DMF
Error Summary
Capacity Inaccurate
The FCC is susceptible to error on initialization or if no
updates occur. On initialization, the FCC value includes
the error between the design capacity and the actual
capacity. This error is present until a valid discharge
occurs and FCC is updated (see the DCR description on
page 6). The other cause of FCC error is battery wearout. As the battery ages, the measured capacity must be
adjusted to account for changes in actual battery capac
ity. Periodic discharges from full to empty will mini
mize errors in FCC.
Current-Sensing Error
Table 3 illustrates the current-sensing error as a func
tion of V
SR
. A digital filter eliminates charge and
discharge counts to the RM register when V
SRO
is
between V
SRQ
and V
SRD
.
Display
The bq2092 can directly display capacity information
using low-power LEDs. The bq2092 displays the battery
charge state in either absolute or relative mode. In rela
tive mode, the battery charge is represented as a
percentage of the FCC. Each LED segment represents
25% of the FCC.
8
bq2092
DMF
DMF
Hex. |V
SRD
(mV)|
75 4B
±0.60
100 64 ±0.45
150 (default) 96 ±0.30
175 AF ±0.26
200 C8 ±0.23
Table 2. Typical Digital Filter Settings
In absolute mode, each segment represents a fixed
amount of charge, 25% of the design capacity. As the
battery wears out over time, it is possible for the FCC to
be below the design capacity. In this case, all of the
LEDs may not turn on in absolute mode, representing
the reduction in the actual battery capacity.
The displayed capacity is compensated for the present
battery temperature. The displayed capacity varies as
temperature varies, indicating the available charge at
the present conditions.
When DISP
is tied to VCC, the SEG
1–4
outputs are inac-
tive. When DISP
is left floating, the display becomes
active whenever the bq2092 detects a charge rate of
100mA or more. When pulled low, the segment outputs
become active immediately for a period of approximately
4 seconds. The DISP
pin must be returned to float or
V
CC
to reactivate the display.
The segment outputs are modulated as two banks of two,
with segments 1 and 3 alternating with segments 2 and 4.
The segment outputs are modulated at approximately
100Hz with each segment bank active for 30% of the period.
SEG
1
blinks at a 4Hz rate whenever VSBhas been
detected to be below V
EDV1
(EDV1= 1), indicating a low-
battery condition. V
SB
below V
EDVF
(EDVF= 1) disables
the display output.
Microregulator
The bq2092 can operate directly from three nickel chem
istry cells. To facilitate the power supply requirements
of the bq2092, an REF output is provided to regulate an
external low-threshold n-FET. A micropower source for
the bq2092 can be inexpensively built using the FET
and an external resistor; see Figure 1. Note that an
optional zener diode may be necessary to limit V
CC
during charge.
Communicating With the bq2092
The bq2092 includes a simple two-pin (SCC and SCD)
bidirectional serial data interface. A host processor uses
the interface to access various bq2092 registers; see
Table 4. This allows battery characteristics to be easily
monitored. The open-drain SCD and SCC pins on the
bq2092 are pulled up by the host system, or may be
connected to V
SS
, if the serial interface is not used.
The interface uses a command-based protocol, where the
host processor sends the battery address and an eightbit command byte to the bq2092. The command directs
the bq2092 to either store the next data received to a
register specified by the command byte or output the
data specified by the command byte.
bq2092 Data Protocols
The host system, acting in the role of a Bus master, uses
the read word and write word protocols to communicate
integer data with the bq2092. (See Figure 3.)
Host-to-bq2092 Message Protocol
The Bus Host communicates with the bq2092 using one
of three protocols:
n
Read word
n
Write word
n
Read block
The particular protocol used is a function of the
command. The protocols used are shown in Figure 3.
Host-to-bq2092 Messages
(see Table 4)
ManufacturerAccess() (0x00)
This optional function is not operational for the bq2092.
RemainingCapacityAlarm() (0x01)
This function sets or returns the low-capacity alarm
value. When RM falls below the RemainingCapac
ityAlarm value, the Remaining_Capacity_Alarm bit
is set in BatteryStatus (0x16). The system may alter
this alarm value during operation.
9
Symbol Parameter Typical Maximum Units Notes
V
OS
Offset referred to V
SR
±
50
±
150
µ
V DISP
= VCC.
INL
Integrated non-linearity
error
±
2
±
4
%
Add 0.1% per °C above or below 25°C
and 1% per volt above or below 4.25V.
INR
Integrated nonrepeatability error
±
1
±
2
%
Measurement repeatability given
similar operating conditions.
Table 3. bq2092 Current-Sensing Errors
bq2092
 Loading...
Loading...