Page 1
bq2002E/G
NiCd/NiMH Fast-Charge Management ICs
Features
Fast charge of nickel cadmium
➤
or nickel-metal hydride batter
ies
Direct LED output displays
➤
chargestatus
Fast-charge terminationby -∆V,
➤
maximum voltage, maximum
temperature, and maximum
time
Internal band-gap voltage ref
➤
erence
Optional top-off charge
➤
Selectable pulse trickle charge
➤
rates
➤
Low-power mode
➤
8-pin 300-mil DIP or 150-mil
SOIC
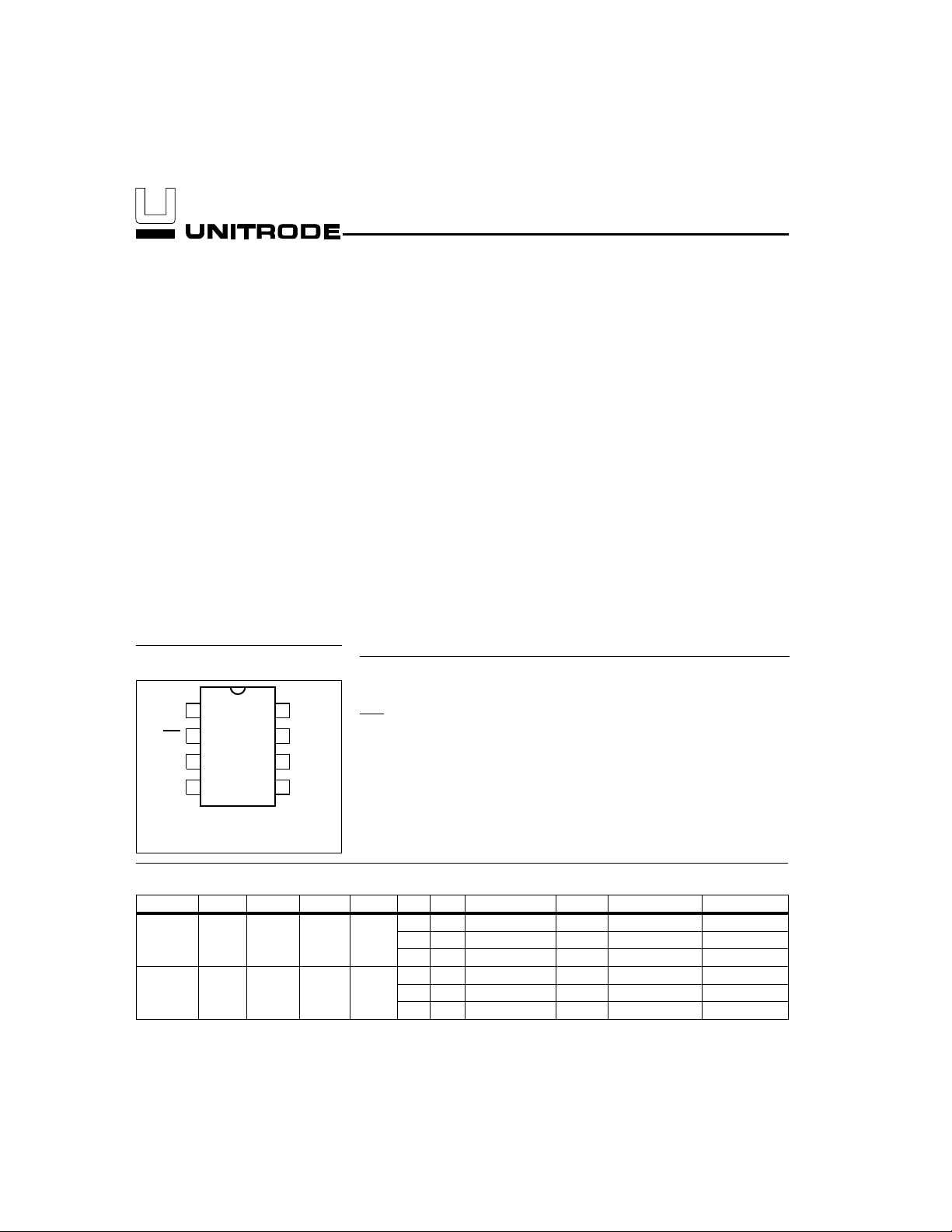
Pin Connections
TM
LED
BAT
V
SS
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
CC
INH
V
TS
CC
General Description
The bq2002E a n d bq2002G FastCharge ICs are low-cost CMOS bat
tery-charge controllers providing reli
able charge termination for both NiCd
and NiMH battery applications. Co n
trolling a current-limited or con
stant-current supply allows th e
bq2002E/G to be the basis for a costeffective stand-alone or system-inte
grated charger. The bq2002E/G inte
grates fast charge with optional top-off
and pulsed- trickle control in a single
IC for charging one or more NiCd or
NiMH battery cells.
Fast charge is initiated on application
of the charging supply or battery re
placement. Fo r safety, fast charge is
inhibited if the battery temperature
and voltage are outside configured
limits.
Pin Names
TM Timer mode select input
LED
BAT Battery voltage input
V
SS
Charging status output
System ground
Fast charge is terminated by any of
the following:
Peak voltage detection(PVD)
n
-
Negative delta voltage(-∆V)
n
-
Maximum voltage
n
Maximum temperature
n
Maximum time
n
-
-
After fast charge, the bq2002E/G op
tionally tops-off and pulse-trickles the
battery per the pre-configured limits.
Fast charge may be inhibited using
the INH pin. The bq2002E/G may
also be placed in low-standby-power
mode to reduce system power con-
-
sumption.
The bq2002E differs from the
bq2002G only in that a slightly different se t of fast-charge and top-off
time limits is available. All differences between the two ICs are illustrated in Table 1.
TS Temperature senseinput
V
CC
Supply voltage input
INH Charge inhibit input
CC Charge control output
-
8-Pin DIP or
Narrow SOIC
PN-200201.eps
bq2002E/G Selection Guide
Part No. LBAT TCO HTF LTF
bq2002E
bq2002G
SLUS132 - FEBRUARY 1999
0.175
V
0.175
V
∗
0.5
∗
0.6
V
CC
CC
CC
∗
0.5
∗
V
CC
V
0.6
V
∗
CC
∗
CC
None
None
PVD Fast Charge t
-∆V
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
1
MTO
Top-Off Maintenance
C/2 200 None C/32
1C 80 C/16 C/32
2C 40 None C/32
C/2 160 None C/32
1C 80 C/16 C/32
2C 40 None C/32
Page 2
bq2002E/G
Pin Descriptions
TM
LED
BAT
V
SS
TS
V
CC
INH
T ime rmodeinput
A three-level input that controls the settings
for the fast charge safety timer, voltage ter
mination mode, top-off, pulse-trickle, and
voltage hold-off time.
Charging output status
Open-drain output that indicates the charging
status.
Battery input voltage
Thebattery voltage sense input. The input to
this pin is created by a high-impedance re
sistor divider network connected between
the positive and negative terminals of the
battery.
System ground
Temperature sense input
Input for an external battery temperature
monitoring thermistor.
Supply voltage input
5.0V±20%power input.
Charge inhibit input
When high, INH suspends the fast charge in
progress. When returned low, the IC re-
sumes operation at the point where initially
suspended.
CC
-
Charge control output
An open-drain output used to control the
charging current to the battery. CC switch
ing to high impedance (Z) enables charging
current to flow, and low to inhibit charging
current. CC is modulated to provide top-off,
ifenabled,and pulse trickle.
Functional Description
Figure 2 shows a state diagram and Figure 3 shows a
block diagram ofth e bq2002E/G.
-
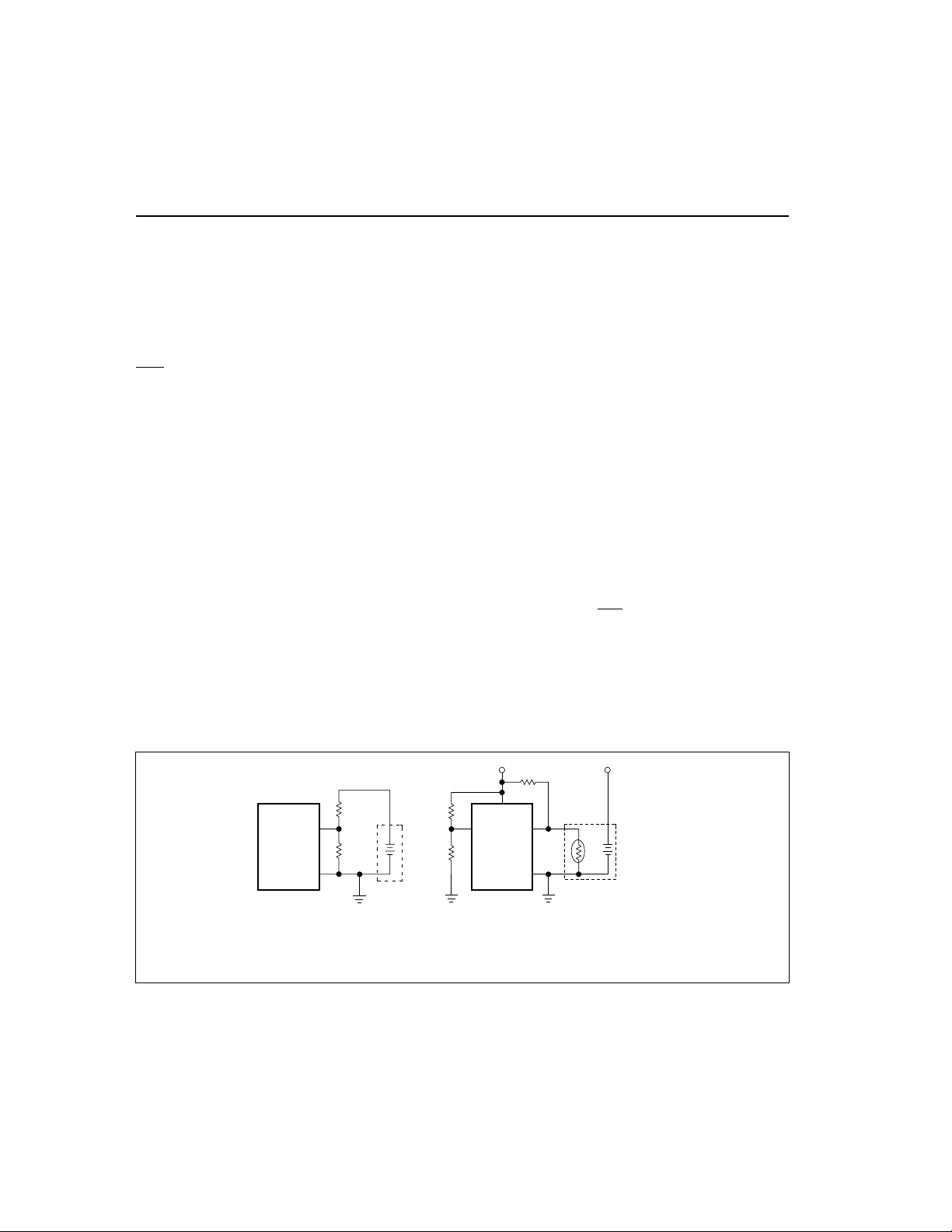
Battery Voltageand Temperature
Measurements
Battery voltage and temperature are monitored for
maximum allowable values. The voltage presented on
the battery sense input, BAT, should represent a
single-cell potential for the battery under charge. A
resistor-dividerratio of
RB1
= N - 1
RB2
is recommended to maintain the battery voltage within
the valid range, where N is th e number of cells, RB1 is
the resistor connected to the positive battery terminal,
and RB2 is the resistor connected to the negative battery terminal. SeeFigure 1.
Note:
This resistor-divider network input impedance to
end-to-end should be at least 200k
Ω
and less than 1MΩ.
-
V
CC
RT
BAT
bq2002E/G
V
BAT pin connection Thermistor connection
RB1
RB2
SS
NTC = negative temperature coefficient thermistor.
R3
R4
Mid-level
setting for TM
V
CC
TM
bq2002E/G
V
T
S
SS
PACK +
N
T
C
Fg2002E/G01.eps
Figure 1. Voltage and Temperature Monitoring and TM Pin Configuration
2
Page 3
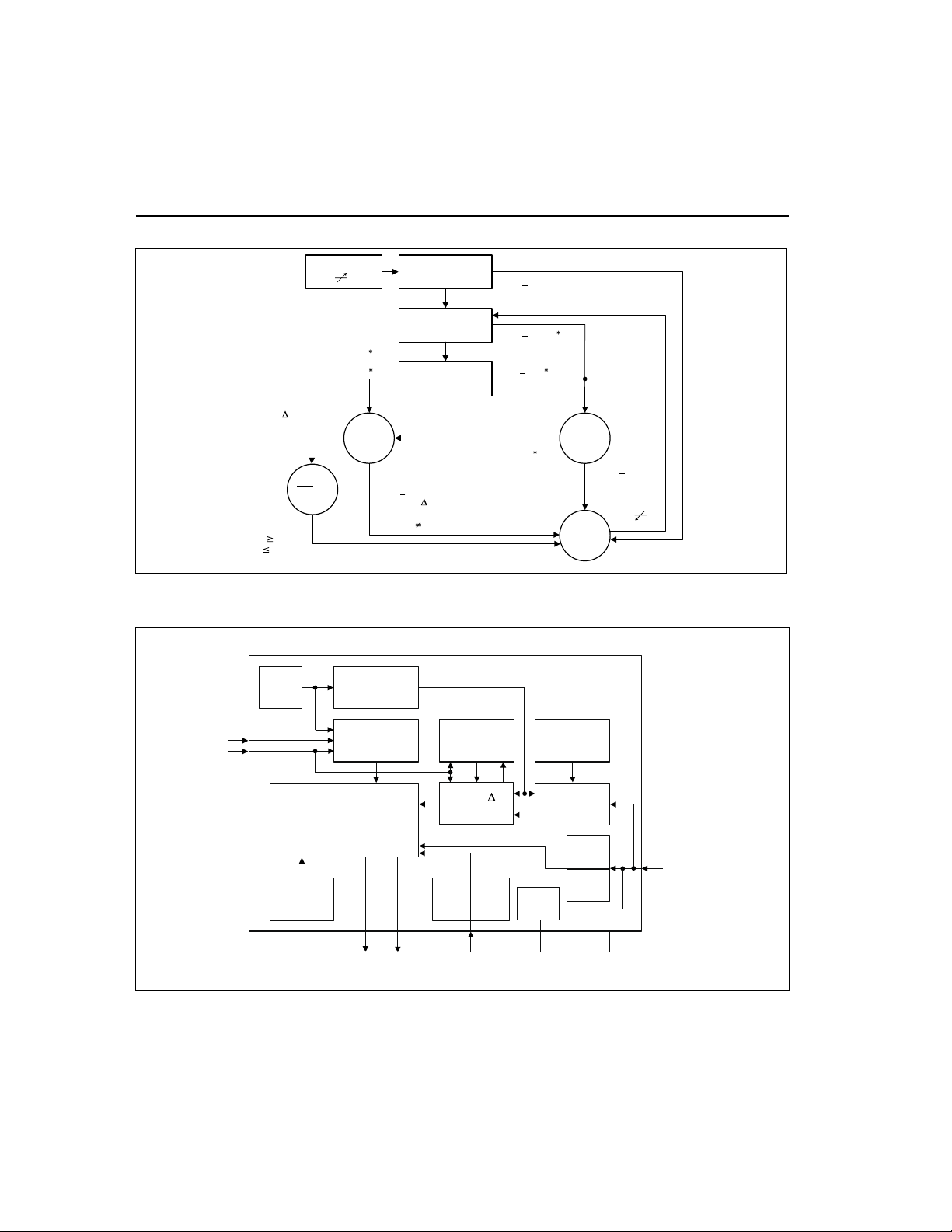
bq2002E/G
V or
(PVD or Maximum Time Out)
and TM = Low
Top-off
LED = Z
V
2V or
BAT
V
VCC/2 or
TS
Maximum Time Out
OSC
V
CC
Chip on
4.0V
V
TS
Battery Voltage
too High?
< 2V
V
BAT
Battery Voltage
too Low?
V
0.175
> 0.6
< V
CC
V
CC
Fast
LED =
Low
V
> 2V or
BAT
VTS < VCC/2 or
((PVD or - V or
Maximum Time Out)
and TM
BAT
Battery
Temperature?
Low)
Figure 2. State Diagram
Clock
Phase
Generator
V
V
V
BAT
BAT
TS
V
BAT
V
BAT
V
TS
> 0.175
< 2V, and
> V
CC
2V
>
< 0.175
< 0.6
/2
VCC,
V
V
CC
CC
Trickle
LED =
Flash
Trickle
LED = Z
Charge
Pending
V
BAT
V
> 2V
BAT
2V
2
SD
s
p
.e
2C
00
TM
INH
Charge-Control
State Machine
Power-On
Reset
Timing
Control
Sample
History
PVD, - V
ALU
HTF
Check
CC
LED
Figure 3. Block Diagram
3
TCO
Check
TS
Power
Down
Voltage
Reference
A to D
Converter
LBAT
Check
MCV
Check
V
CC
V
SS
Bd2002CEG.eps
BAT
Page 4
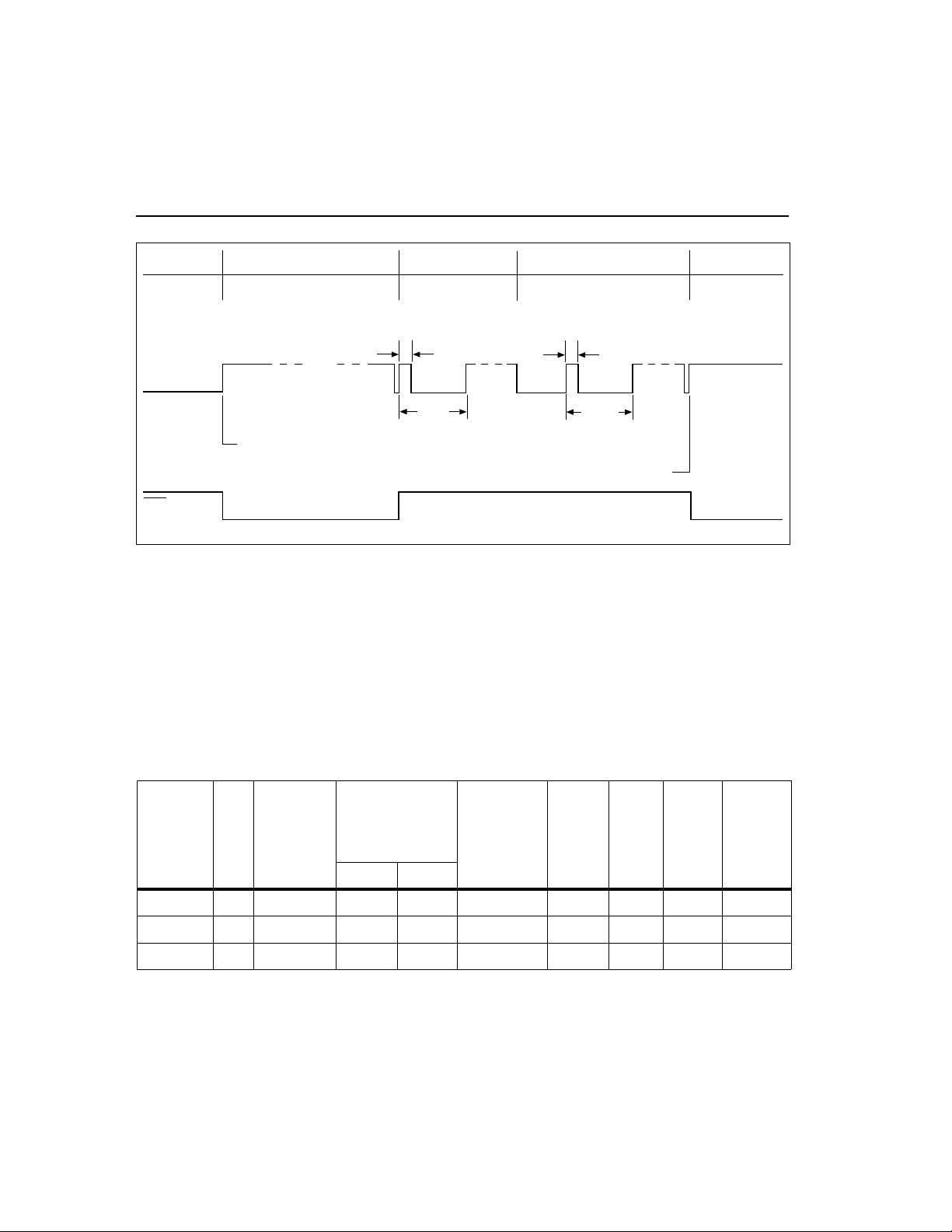
bq2002E/G
Fast ChargingVCC = 0 Fast Charging
(optional)
CC Output
73ms
1.17s 1.17s
Charge initiated by application of power
LED
Figure 4. Charge Cycle Phases
Aground-referenced negative temperature coefficient thermistor placed near the battery may be used as a low-cost
temperature-to-voltage transducer. The temperature
sense voltage input at TS is developed using a resistorthermistor network between V
and VSS. See Figure 1.
CC
Starting A Charge Cycle
Either of twoevents starts a chargecycle(see Figure 4):
Pulse-TrickleTop-Off
See Table 1
Charge initiated by battery replacement
1.Application ofpower to V
or
CC
2. Voltage at th e BAT pin falling through the maximum
cell voltage V
MCV
where
V
MCV
= 2V±5%.
If the battery is within th e configured temperature and
voltage limits, the IC begins fast charge. The valid battery voltage range is V
LBAT<VBAT<VMCV
,where
TD2002EG.eps
Table 1. Fast-Charge Safety Time/Hold-Off/Top-Off Table
Typical Fast-
Charge and
-
Corre
sponding
Fast-Charge
Rate TM Termination
Time Limits
(minutes)
bq2002E bq2002G
Typical PVD
and -∆V
Hold-Off Time
(seconds)
Top-Off
Rate
PulseTrickle
Rate
C/2 Mid PVD 200 160 300 Disabled C/32 73 18.7
1C Low PVD 80 80 150 C/16 C/32 37 18.7
Top-Off
2C High -
Notes:
Typical conditions = 25°C, VCC= 5.0V
Mid = 0.5*V
Tolerance on all timing is
V 40 40 75 Disabled C/32 18 9.4
∆
0.5V
±
CC
±
12%.
4
Pulse-
Trickle
Width
(ms)
Maximum
Synchro
nized
Sampling
Period
(seconds)
-
Page 5

bq2002E/G
V
= 0.175∗VCC±
LBAT
The valid temperature range isV
= 0.6∗VCC±
V
HTF
20%
TS>VHTF
5%.
where
If the battery voltage or temperature is outside of these
limits, th e IC pulse-trickle charges until the next new
chargecyclebegins.
If V
MCV<VBAT<VPD
newbattery is inserted, a delay of0.35 to 0.9s is imposed
(see “Low-Power Mode”) when a
before the new charge cyclebegins.
Fast charge continues until termination by one or more of
the five possible termination conditions:
Peak voltage detection (PVD)
n
Negative delta voltage (-∆V)
n
Maximum voltage
n
Maximum temperature
n
Maximum time
n
PVD and -∆V Termination
There are two modes for voltage termination, depending
on the state ofTM. For than any previously measured value by 12mV
∆
V (TM = high), if V
is lower
BAT
±
3mV, fast
charge is terminated. For PVD (TM = low or mid), a decrease of 2.5mV
and -
∆
Vtests are valid in the range 1V<V
±
2.5mV terminates fast charge. The PVD
BAT
<2V.
Synchronized Voltage Sampling
Voltage sampling at the BAT pin for PVD and -∆Vtermi
nation may be synchronized to an external stimulus using the INH input. Low-high-low input pulses between
100ns a nd 3.5ms in width must be applied at the INH
pin with a frequency greater than the “maximum syn
chronized sampling period” set by the state of the TM
pin as shown in Table 1. Voltage is sampled on the fal
ling edgeofsuch pulses.
If the time between pulses is greater than the synchro
nizing period, voltage sampling “free-runs” at once every
17 seconds. A sample is taken by averaging together
voltage measurements taken 57
32 measurements in PVD mode and 16 measurements
in -
∆
V mode. The resulting sample periods (9.17 and
18.18ms, respectively) filter out harmonics centered
around 55 and 109Hz. This technique minimizes the ef
fect of any AC line ripple that may feed through the
power supply from either 50or60Hz ACsources.
If the INH input remains high for more than 12ms, the
voltage sample history kept by the IC a nd used for PVD
and -
∆
V termination decisions is erased and a new his
tory is started. Such a reset is required when transition
ing from free-running to synchronized voltage sampling.
µ
s apart. The IC takes
The response of the IC to pulses less than 100ns i n
width or between 3.5ms and 12ms is indeterminate. Tol
±
erance on all timing is
12%.
Voltage TerminationHold-off
A hold-off period occurs at the start of fast charging.
During the hold-off time, the PVD a n d -
∆
Vterminations
are disabled. This avoids premature termination on the
voltage spikes sometimes produced by older batteries
when fast-charge current is first applied. Maximum
voltage and temperature terminations are not affected
by the hold-off period.
Maximum Voltage, Temperature,and Time
Any time the voltage on the BA T pin exceeds the maxi
mum cell voltage,V
chargeis terminated.
Maximum temperature termination occurs anytime t h e
voltage on the TS pin falls below the temperature cut-off
threshold V
TCO
Maximum charge time is configured using the TM pin.
Time settings a re available for corresponding charge
rates of C/2, 1C, and 2C. Maximum time-out termination is enforced on the fast-charge phase, then reset, and
enforced again on the top-off phase, if selected. There is
notime limit onthe trickle-charge phase.
, fast charge or optional top-off
MCV
where
V
TCO
= 0.5∗VCC±
5%.
Top-off Charge
An optional top-off charge phase may be selected to
follow fast charge termination for 1C and C/2 rates.
This phase may be necessary on NiMH or other ba t-
tery chemistries that have a tendency to terminate
charge before reaching full capacity. With top-off en
abled, charging continues at a r educed ra te after
fast-charge termination for a period of time selected
by t h e TM pin. (See Table 1.) During top-off, the CC
pin is modulated at a duty cycle of 73ms active for
every 1097ms inactive. This modulation results in a n
-
average rate 1/16th that ofthe fast charge rate. Maxi
mum voltage, time, an d temperature are the only ter
mination methods enabled during top-off.
Pulse-Trickle Charge
Pulse-trickle is used to compensate for self-discharge
while the battery is idle in the charger. The battery is
pulse-trickle charged by driving the CC pin active once
every 1.17s for the period specified in Table 1. This re
sults in a trickle rate ofC/32.
TM Pin
The TM pin is a three-level pin used to select th e
chargetimer,top-off, voltage termination mode, trickle
-
-
-
-
-
-
5
Page 6

bq2002E/G
rate, and voltage hold-off period options. Table 1 d e
scribes the states selected by t he TM pin. The midlevel selection input is developed by a resistor di
vider between V
on TM at V
CC
and ground that fixes the voltage
CC
/2±0.5V. See Figure 4.
Charge Status Indication
Afast charge in progress is uniquely indicated when the
LED
pin goes low. The LED pin is driven to the high-Z
state for all conditions other than fast charge. Figure 2
outlines the state of the LED
pinduring charge.
Charge Inhibit
Fast charge and top-off may be inhibited by using th e
INH pin. When high, INH suspends all fast charge and
top-off activity a n d the internal charge timer. INH
freezes the current state of LED
Temperature monitoring is not affected by the INH pin.
During charge inhibit, the bq2002E/G continues to
pulse-trickle charge the battery per the TM selection.
When INH returns low, charge control and the charge
timer resume from the point where INHbecame active.
until inhibit is removed.
-
Low-Power Mode
The IC enters a low-power state when V
above the power-down threshold (V
V
= VCC- (1V±0.5V)
PD
Both the CC pin and the LED
pin are driven to t he
PD
)where
BAT
high-Z state. The operating current is reduced to less
than 1
µ
A in this mode. When V
below V
newchargecyclebegins.
, t he IC pulse-trickle charges until the next
PD
returns to a value
BAT
is driven
6
Page 7

bq2002E/G
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Symbol Parameter Minimum Maximum Unit Notes
V
CC
V
T
T
OPR
T
STG
T
SOLDER
T
BIAS
Note:
VCCrelative to V
SS
DC voltage applied on any pin
excluding V
relative to V
CC
SS
-0.3 +7.0 V
-0.3 +7.0 V
Operating ambient temperature 0 +70 °C Commercial
Storage temperature -40 +85 °C
Soldering temperature - +260 ° C 10 sec max.
Temperature under bias -40 +85 °C
Permanent device damage may occur if
Absolute Maximum Ratings
are exceeded. Functional opera
tion should be limited to the Recommended DC Operating Conditions detailed in this data sheet. Expo
sure to conditions beyond the operational limits for extended periods of time may affect device reliability.
-
-
DC Thresholds (T
= 0 to 70°C; V
A
CC
20%)
±
Symbol Parameter Rating Tolerance Unit Notes
V
TCO
V
HTF
V
MCV
V
LBAT
-
∆
V
PVD BAT input change for
Temperature cutoff 0.5*V
High temperature fault
0.6
∗
Maximum cell voltage 2
Minimum cell voltage
BAT input change for
-
∆
Vdetection
0.175
-12
-2.5
VCC
∗
5% V V
CC
V
CC
±
±
5%
5% V
±
±
20%
±
3
±
2.5
TS
fast charge and top-off
VV
TS<VHTF
start
V
BAT
fast charge and top-off
VV
BAT<VLBAT
start
mV
mV
inhibits/terminates
V
≤
TCO
inhibits fast charge
≥
V
inhibits/terminates
MCV
inhibits fast charge
PVDdetection
7
Page 8

bq2002E/G
Recommended DC Operating Conditions (T
= 0 to 70°C)
A
Symbol Condition Minimum Typical Maximum Unit Notes
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
Supply voltage 4.0 5.0 6.0 V
CC
-∆V, PVD detect voltage 1 - 2 V
DET
Battery input 0 - V
BAT
Thermistor input 0.5 - V
TS
Logic input high 0.5 - - V INH
IH
Logic input high V
Logic input mid
IM
Logic input low - - 0.1 V INH
IL
- 0.5 - - V TM
CC
V
CC
- 0.5
2
-
CC
CC
V
CC
+
05
2
V
VVTS< 0.5V prohibited
.
VTM
Logic input low - - 0.5 V TM
V
V
I
CC
I
SB
Logic output low - - 0.8 V LED,CC,IOL= 10mA
OL
Power down VCC- 1.5 - VCC- 0.5 V V
PD
Supply current - - 500
Standby current - - 1
BAT
down bq2002E/G;
V
BAT
normal operation.
A Outputs unloaded,
µ
V
CC
AVCC= 5.1V, V
µ
V
max. powers
≥
PD
< VPDmin. =
= 5.1V
BAT
= V
PD
I
OL
I
L
I
OZ
Note:
LED,CCsink 10 - - mA @VOL= VSS+ 0.8V
Input leakage - -
Output leakage in
-5 - -
1
±
A INH, CC,V = VSSto V
µ
A LED,CC
µ
high-Z state
All voltages relative to VSS.
8
CC
Page 9

bq2002E/G
Impedance
Symbol Parameter Minimum Typical Maximum Unit
R
BAT
R
TS
Battery input impedance 50 - - M
TS input impedance 50 - - M
Ω
Ω
Timing (T
Symbol Parameter Minimum Typical Maximum Unit Notes
d
FCV
t
DLY
Note:
= 0 to +70°C; V
A
Time base variation -12 - 12 %
Start-up delay 0.35 - 0.9 s Starting from V
Typical is at TA= 25°C, VCC= 5.0V.
CC
±
10%)
MCV<VBAT<VPD
9
Page 10

bq2002E/G
8-Pin DIP(PN
E1
E
e
)
D
C
8-Pin SOIC Narrow (SN)
8-Pin PN(0.300" DIP
Dimension
A 0.160 0.180 4.06 4.57
A1 0.015 0.040 0.38 1.02
B 0.015 0.022 0.38 0.56
B1 0.055 0.065 1.40 1.65
A
A1
L
S
B1
B
G
C 0.008 0.013 0.20 0.33
D 0.350 0.380 8.89 9.65
E 0.300 0.325 7.62 8.26
E1 0.230 0.280 5.84 7.11
e 0.300 0.370 7.62 9.40
G 0.090 0.110 2.29 2.79
L 0.115 0.150 2.92 3.81
S 0.020 0.040 0.51 1.02
Min. Max. Min. Max.
)
Inches Millimeters
8-Pin SN(0.150" SOIC
Inches Millimeters
Dimension
A 0.060 0.070 1.52 1.78
A1 0.004 0.010 0.10 0.25
B 0.013 0.020 0.33 0.51
C 0.007 0.010 0.18 0.25
D 0.185 0.200 4.70 5.08
E 0.150 0.160 3.81 4.06
e 0.045 0.055 1.14 1.40
H 0.225 0.245 5.72 6.22
L 0.015 0.035 0.38 0.89
Min. Max. Min. Max.
)
10
Page 11

PACKAGE OPTION ADDENDUM
www.ti.com
7-May-2007
PACKAGING INFORMATION
Orderable Device Status
(1)
Package
Type
Package
Drawing
Pins Package
Qty
Eco Plan
BQ2002EPN ACTIVE PDIP P 8 50 Pb-Free
BQ2002EPNE4 ACTIVE PDIP P 8 50 Pb-Free
BQ2002ESN ACTIVE SOIC D 8 75 Green (RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
BQ2002ESNG4 ACTIVE SOIC D 8 75 Green (RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
BQ2002ESNTR ACTIVE SOIC D 8 2500 Green (RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
BQ2002ESNTRG4 ACTIVE SOIC D 8 2500 Green (RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
BQ2002GPN ACTIVE PDIP P 8 50 Pb-Free
BQ2002GPNE4 ACTIVE PDIP P 8 50 Pb-Free
BQ2002GSN ACTIVE SOIC D 8 75 Green(RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
BQ2002GSNG4 ACTIVE SOIC D 8 75 Green (RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
BQ2002GSNTR ACTIVE SOIC D 8 2500 Green (RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
BQ2002GSNTRG4 ACTIVE SOIC D 8 2500 Green (RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
(1)
The marketing status values are defined as follows:
ACTIVE: Product device recommended for new designs.
LIFEBUY: TI has announced that the device will be discontinued, and a lifetime-buy period is in effect.
NRND: Not recommended for new designs. Device is in production to support existing customers, but TI does not recommend using this part in
a new design.
PREVIEW: Device has been announced but is not in production. Samples may or may not be available.
OBSOLETE: TI has discontinued the production of the device.
(RoHS)
(RoHS)
(RoHS)
(RoHS)
(2)
Lead/Ball Finish MSL Peak Temp
CU NIPDAU N / A for Pkg Type
CU NIPDAU N / A for Pkg Type
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
CU NIPDAU N / A for Pkg Type
CU NIPDAU N / A for Pkg Type
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
(3)
(2)
Eco Plan - The planned eco-friendly classification: Pb-Free (RoHS), Pb-Free (RoHS Exempt), or Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br) - please check
http://www.ti.com/productcontent for the latest availability information and additional product content details.
TBD: The Pb-Free/Green conversion plan has not been defined.
Pb-Free (RoHS): TI's terms "Lead-Free" or "Pb-Free" mean semiconductor products that are compatible with the current RoHS requirements
for all 6 substances, including the requirement that lead not exceed 0.1% by weight in homogeneous materials. Where designed to be soldered
at high temperatures, TI Pb-Free products are suitable for use in specified lead-free processes.
Pb-Free (RoHS Exempt): This component has a RoHS exemption for either 1) lead-based flip-chip solder bumps used between the die and
package, or 2) lead-based die adhesive used between the die and leadframe. The component is otherwise considered Pb-Free (RoHS
compatible) as defined above.
Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br): TI defines "Green" to mean Pb-Free (RoHS compatible), and free of Bromine (Br) and Antimony (Sb) based flame
retardants (Br or Sb do not exceed 0.1% by weight in homogeneous material)
(3)
MSL, Peak Temp. -- The Moisture Sensitivity Level rating according to the JEDEC industry standard classifications, and peak solder
temperature.
Important Information and Disclaimer:The information provided on this page represents TI's knowledge and belief as of the date that it is
provided. TI bases its knowledge and belief on information provided by third parties, and makes no representation or warranty as to the
accuracy of such information. Efforts are underway to better integrate information from third parties. TI has taken and continues to take
reasonable steps to provide representative and accurate information but may not have conducted destructive testing or chemical analysis on
incoming materials and chemicals. TI and TI suppliers consider certain information to be proprietary, and thus CAS numbers and other limited
information may not be available for release.
Addendum-Page 1
Page 12

PACKAGE OPTION ADDENDUM
www.ti.com
In no event shall TI's liability arising out of such information exceed the total purchase price of the TI part(s) at issue in this document sold by TI
to Customer on an annual basis.
7-May-2007
Addendum-Page 2
Page 13

PACKAGE MATERIALS INFORMATION
www.ti.com
TAPE AND REEL INFORMATION
19-Mar-2008
*All dimensions are nominal
Device Package
BQ2002ESNTR SOIC D 8 2500 330.0 12.4 6.4 5.2 2.1 8.0 12.0 Q1
BQ2002GSNTR SOIC D 8 2500 330.0 12.4 6.4 5.2 2.1 8.0 12.0 Q1
Type
Package
Drawing
Pins SPQ Reel
Diameter
(mm)
Reel
Width
W1 (mm)
A0 (mm) B0 (mm) K0 (mm) P1
(mm)W(mm)
Pin1
Quadrant
Pack Materials-Page 1
Page 14

PACKAGE MATERIALS INFORMATION
www.ti.com
19-Mar-2008
*All dimensions are nominal
Device Package Type Package Drawing Pins SPQ Length (mm) Width (mm) Height (mm)
BQ2002ESNTR SOIC D 8 2500 340.5 338.1 20.6
BQ2002GSNTR SOIC D 8 2500 340.5 338.1 20.6
Pack Materials-Page 2
Page 15

IMPORTANT NOTICE
Texas Instruments Incorporated and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make corrections, modifications, enhancements, improvements,
and other changes to its products and services at any time and to discontinue any product or service without notice. Customers should
obtain the latest relevant information before placing orders and should verify that such information is current and complete. All products are
sold subject to TI’s terms and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgment.
TI warrants performance of its hardware products to the specifications applicable at the time of sale in accordance with TI’s standard
warranty. Testing and other quality control techniques are used to the extent TI deems necessary to support this warranty. Except where
mandated by government requirements, testing of all parameters of each product is not necessarily performed.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or customer product design. Customers are responsible for their products and
applications using TI components. To minimize the risks associated with customer products and applications, customers should provide
adequate design and operating safeguards.
TI does not warrant or represent that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any TI patent right, copyright, mask work right,
or other TI intellectual property right relating to any combination, machine, or process in which TI products or services are used. Information
published by TI regarding third-party products or services does not constitute a license from TI to use such products or services or a
warranty or endorsement thereof. Use of such information may require a license from a third party under the patents or other intellectual
property of the third party, or a license from TI under the patents or other intellectual property of TI.
Reproduction of TI information in TI data books or data sheets is permissible only if reproduction is without alteration and is accompanied
by all associated warranties, conditions, limitations, and notices. Reproduction of this information with alteration is an unfair and deceptive
business practice. TI is not responsible or liable for such altered documentation. Information of third parties may be subject to additional
restrictions.
Resale of TI products or services with statements different from or beyond the parameters stated by TI for that product or service voids all
express and any implied warranties for the associated TI product or service and is an unfair and deceptive business practice. TI is not
responsible or liable for any such statements.
TI products are not authorized for use in safety-critical applications (such as life support) where a failure of the TI product would reasonably
be expected to cause severe personal injury or death, unless officers of the parties have executed an agreement specifically governing
such use. Buyers represent that they have all necessary expertise in the safety and regulatory ramifications of their applications, and
acknowledge and agree that they are solely responsible for all legal, regulatory and safety-related requirements concerning their products
and any use of TI products in such safety-critical applications, notwithstanding any applications-related information or support that may be
provided by TI. Further, Buyers must fully indemnify TI and its representatives against any damages arising out of the use of TI products in
such safety-critical applications.
TI products are neither designed nor intended for use in military/aerospace applications or environments unless the TI products are
specifically designated by TI as military-grade or "enhanced plastic." Only products designated by TI as military-grade meet military
specifications. Buyers acknowledge and agree that any such use of TI products which TI has not designated as military-grade is solely at
the Buyer's risk, and that they are solely responsible for compliance with all legal and regulatory requirements in connection with such use.
TI products are neither designed nor intended for use in automotive applications or environments unless the specific TI products are
designated by TI as compliant with ISO/TS 16949 requirements. Buyers acknowledge and agree that, if they use any non-designated
products in automotive applications, TI will not be responsible for any failure to meet such requirements.
Following are URLs where you can obtain information on other Texas Instruments products and application solutions:
Products Applications
Amplifiers amplifier.ti.com Audio www.ti.com/audio
Data Converters dataconverter.ti.com Automotive www.ti.com/automotive
DSP dsp.ti.com Broadband www.ti.com/broadband
Clocks and Timers www.ti.com/clocks Digital Control www.ti.com/digitalcontrol
Interface interface.ti.com Medical www.ti.com/medical
Logic logic.ti.com Military www.ti.com/military
Power Mgmt power.ti.com Optical Networking www.ti.com/opticalnetwork
Microcontrollers microcontroller.ti.com Security www.ti.com/security
RFID www.ti-rfid.com Telephony www.ti.com/telephony
RF/IF and ZigBee® Solutions www.ti.com/lprf Video & Imaging www.ti.com/video
Mailing Address: Texas Instruments, Post Office Box 655303, Dallas, Texas 75265
Copyright © 2008, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Wireless www.ti.com/wireless
 Loading...
Loading...