Page 1

SBAU090E–November 2003–Revised November 2018
ADS1256EVM and ADS1256EVM-PDK
User's Guide
This user's guide describes the characteristics, operation, and use of the ADS1256EVM, both by itself and
as part of the ADS1256EVM-PDK. This EVM is an evaluation fixture for the ADS1256 24-bit delta-sigma
(ΔΣ) analog-to-digital converter (ADC). It also serves as an evaluation platform for the ADS1255, which is
a proper subset of the ADS1256. It allows evaluation of all aspects of the ADS1256 device. A complete
circuit description, schematic diagram, and bill of materials are included.
The following related documents are available through the Texas Instruments web site at www.ti.com.
Device Literature Number
ADS1256 SBAS288
REF5025 SBOS410
OPA350 SBOS099
SBAU090E–November 2003–Revised November 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2003–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
ADS1256EVM and ADS1256EVM-PDK
1
Page 2

www.ti.com
Contents
1 EVM Overview ............................................................................................................... 3
2 Analog Interface.............................................................................................................. 6
3 Digital Interface .............................................................................................................. 7
4 Power Supplies .............................................................................................................. 8
5 Voltage Reference ......................................................................................................... 10
6 Clock Source................................................................................................................ 11
7 EVM Operation ............................................................................................................. 12
8 ADS1256EVM-PDK Kit Operation ....................................................................................... 15
9 Evaluating Performance with the ADCPro Software................................................................... 30
10 Schematics and Layout.................................................................................................... 38
List of Figures
1 ADS1256EVM................................................................................................................ 5
2 GPIO Pins .................................................................................................................... 8
3 Jumper Block................................................................................................................. 9
4 Switch S3.................................................................................................................... 10
5 Switch S4.................................................................................................................... 11
6 Switches S1 and S2 ....................................................................................................... 12
7 ADS1256EVM Default Jumper and Switch Locations................................................................. 14
8 ADS1256EVM-PDK Setup Wizard....................................................................................... 16
9 ADS1256EVM-PDK License Agreement................................................................................ 16
10 ADS1256EVM-PDK Installation in Progress............................................................................ 17
11 ADS1256EVM-PDK Installation Complete.............................................................................. 17
12 MMB0 Initial Configuration ................................................................................................ 18
13 Connecting the ADS1256EVM to the MMB0 ........................................................................... 19
14 MMB0 Powered From AC Adapter....................................................................................... 20
15 MMB0 Configured for Lab Power Supply ............................................................................... 21
16 NI-VISA Driver Installation Wizard, Screen 1........................................................................... 22
17 NI-VISA Driver Installation Wizard, Screen 2........................................................................... 23
18 NI-VISA Driver Installation Wizard, Screen 3........................................................................... 23
19 NI-VISA Driver Installation Wizard, Screen 4........................................................................... 24
20 NI-VISA Driver Verification Using Device Manager.................................................................... 25
21 ADCPro Software Start-up Display Window............................................................................ 25
22 ADS1256EVM-PDK Plug-In Display Window .......................................................................... 26
23 Install New Driver Wizard Screen 1...................................................................................... 27
24 Install New Driver Wizard Screen 2...................................................................................... 27
25 Install New Driver Wizard Screen 3...................................................................................... 28
26 Install New Driver Wizard Screen 4...................................................................................... 28
27 Install New Driver Wizard Screen 5...................................................................................... 29
28 USBStyx Driver Verification Using Device Manager................................................................... 29
29 ADS1256EVM-PDK Plug-In Averages, PGA Gain, and Effective Data Rate Controls ........................... 30
30 MUX Tab .................................................................................................................... 31
31 Clocks Tab .................................................................................................................. 32
32 GPIO Tab ................................................................................................................... 33
33 Power & Ref Tab........................................................................................................... 34
34 Cal Tab ...................................................................................................................... 35
35 EVM Software About Tab ................................................................................................. 36
36 Software Progress Indicator .............................................................................................. 37
2
ADS1256EVM and ADS1256EVM-PDK
Copyright © 2003–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
SBAU090E–November 2003–Revised November 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 3

www.ti.com
37 ADS1256EVM PCB: Top-Side Image ................................................................................... 39
38 ADS1256EVM PCB: Layer 1 ............................................................................................. 39
39 ADS1256EVM PCB: Layer 2 ............................................................................................. 39
40 ADS1256EVM PCB: Bottom-Side Image ............................................................................... 39
41 Schematic ................................................................................................................... 40
1 J1: Analog Interface Pinout................................................................................................. 6
2 J2: Serial Interface Pins..................................................................................................... 7
3 J5: GPIO Header Pins ...................................................................................................... 8
4 J5 Configuration: Power-Supply Input .................................................................................... 8
5 J4, J9, and J10 Configuration: Power Options ......................................................................... 10
6 Reference Input Select Switch ........................................................................................... 11
7 System Clock Select Switch .............................................................................................. 11
8 AIN0-1 Input Select Switch (S1).......................................................................................... 12
9 AIN2-3 Input Select Switch (S2).......................................................................................... 13
10 Default Jumper Positions.................................................................................................. 14
11 Default Switch Positions................................................................................................... 15
12 ADS1256EVM Bill of Materials .......................................................................................... 38
Trademarks
ADCPro is a trademark of Texas Instruments.
Microsoft, Windows are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
I2C is a trademark of NXP Semiconductors.
NI-VISA is a trademark of National Instruments.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
EVM Overview
List of Tables
1 EVM Overview
The ADS1256EVM is an evaluation fixture for the ADS1256 24-bit delta-sigma ADC.
1.1 Features
ADS1256EVM Features:
• Contains all support circuitry needed for the ADS1256
• Voltage reference options: off-board reference, or buffered REF5025 with high or low common-mode
voltage
• Compatible with the TI Modular EVM System
ADS1256EVM-PDK Features:
• Easy-to-use evaluation software for Microsoft®Windows
• Data collection to ASCII text files
• Built-in analysis tools including scope, FFT, and histogram displays
• Complete control of board settings
• Easily expandable with new analysis plug-in tools from Texas Instruments
For use with a computer, the ADS1256EVM-PDK is available. This kit combines the ADS1256EVM board
with the DSP-based MMB0 motherboard, and includes ADCPro™ software for evaluation.
The MMB0 motherboard allows the ADS1256EVM to be connected to the computer via an available USB
port. This manual shows how to use the MMB0 as part of the ADS1256EVM-PDK, but does not provide
technical details on the MMB0 itself.
®
SBAU090E–November 2003–Revised November 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2003–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
ADS1256EVM and ADS1256EVM-PDK
3
Page 4

EVM Overview
ADCPro is a program for collecting, recording, and analyzing data from ADC evaluation boards. It is based
on a number of plug-in programs, so it can be expanded easily with new test and data collection plug-ins.
The ADS1256EVM-PDK is controlled by a plug-in that runs in ADCPro. For more information about
ADCPro, see the ADCPro™ Analog-to-Digital Converter Evalutation Software User's Guide (literature
number SBAU128), available for download from the TI website.
This manual covers the operation of both the ADS1256EVM and the ADS1256EVM-PDK. Throughout this
document, the abbreviation EVM and the term evaluation module are synonymous with the
ADS1256EVM.
www.ti.com
4
ADS1256EVM and ADS1256EVM-PDK
Copyright © 2003–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
SBAU090E–November 2003–Revised November 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 5

www.ti.com
1.2 Introduction
The ADS1256EVM, shown in Figure 1, is an evaluation module built to the TI Modular EVM System
specification. It can be connected to any Modular EVM System interface card.
The ADS1256EVM is available as a stand-alone printed circuit board (PCB) or as part of the
ADS1256EVM-PDK, which includes an MMB0 motherboard and software. As a stand-alone PCB, the
ADS1256EVM is useful for prototyping designs and firmware.
Note that the ADS1256EVM has no microprocessor and cannot run software. To connect it to a computer,
some type of interface is required.
If you intend to use the ADS1255 in your application, use the ADS1256EVM for evaluation and test
purposes. The ADS1255 is in a smaller package, and lacks inputs AIN2 through AIN7; otherwise, it is
identical to the ADS1256.
EVM Overview
1.3 Built-In Accessories
The ADS1256EVM includes a system clock crystal and a low-noise voltage reference. Both are optional;
you can select an external system clock and an external reference using slide switches.
The +2.5V reference circuit is based on a REF5025 buffered by an OPA350 and filtered by a large
tantalum electrolytic capacitor. While its noise performance is not sufficiently low to allow the ADS1256 to
perform at its lowest noise level at all data rates, the circuit can closely approach this limit, and is
representative of the kind of reference circuit used in many applications.
1.4 Connectors
The ADS1256 device on the ADS1256EVM is connected through four headers: the analog connector, the
serial connector, the power connector, and the GPIO header. This section describes the respective
pinouts and locations for the connectors and header.
The analog connector (J1) carries analog I/O. The ADS1256 has a nine-input multiplexer connected
through pins 1 through 8 and 10. An optional external differential reference can be connected to pins 18
and 20.
The serial connector (J2) carries the ADS1256 serial digital interface, an optional external system clock
signal, and an I2C™ connection to the onboard serial EEPROM.
Figure 1. ADS1256EVM
SBAU090E–November 2003–Revised November 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2003–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
ADS1256EVM and ADS1256EVM-PDK
5
Page 6

EVM Overview
The power connector (J3) carries the power supplies. The ADS1256EVM requires a +5V analog supply
and a +1.8V to +3.3V digital supply. The board is designed using a single ground net connected to DGND.
An AGND pin is also provided. Power options are routed through J4, J9, and J10.
The GPIO header (J5) provides a connection to the four GPIO pins on the EVM.
The ADS1256 uses separate supplies for its analog and digital sections. A jumper is inserted in each
supply line. These jumpers allow the current of each supply to be measured independently.
1.5 Controls
The ADS1256EVM is configured using four slide switches and a jumper.
Switches S1 and S2 select the input signal provided to the first four multiplexer inputs on the ADS1256.
Normally you will use the external input, but you can also use the switches to short the inputs together and
to connect the reference voltage to the inputs. Additionally, the latter two positions are useful for
conducting noise and functional tests.
Switch S3 selects the reference input. One position selects the external reference input pins on the analog
connector (J1). The other two positions connect the onboard +2.5V reference in one of two ways: between
ground and the reference, or between the reference and the analog supply.
Switch S4 selects the system clock source for the ADS1256. You can select between the onboard
7.68MHz crystal or an external clock.
All switches and their settings are additionally described in later sections of this user guide.
2 Analog Interface
For maximum flexibility, the ADS1256EVM is designed for easy interfacing to multiple analog sources.
Samtec part numbers SSW-110-22-F-D-VS-K and TSM-110-01-T-DV-P provide a convenient 10-pin, dualrow, header/socket combination at J1. This header/socket provides access to the analog input pins of the
ADS1256. Consult Samtec at www.samtec.com or call 1-800-SAMTEC-9 for a variety of mating connector
options.
Most of the pins on J1 are directly connected, with minimal filtering or protection. Use appropriate caution
when handling these pins. Table 1 summarizes the pinout for analog interface J1.
www.ti.com
Table 1. J1: Analog Interface Pinout
Pin Number Pin Name
J1.1 AIN0 AN0– Input Analog input 1 (switched by S1)
J1.2 AIN1 AN0+ Input Analog input 0 (switched by S1)
J1.3 AIN2 AN1– Input Analog input 3 (switched by S1)
J1.4 AIN3 AN1+ Input Analog input 2 (switched by S1)
J1.5 AIN4 AN2– Input Analog input 4
J1.6 AIN5 AN2+ Input Analog input 5
J1.7 AIN6 AN3– Input Analog input 6
J1.8 AIN7 AN3+ Input Analog input 7
J1.10 AINCOM AN4+ Input Analog input common
J1.18 SYSREFN REF– Input Inverting external reference input
J1.20 SYSREFP REF+ Input Noninverting external reference
J1.9-J1.19 odd GND AGND Input Signal ground
Standard
Name Direction Function
input
6
ADS1256EVM and ADS1256EVM-PDK
Copyright © 2003–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
SBAU090E–November 2003–Revised November 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 7

www.ti.com
3 Digital Interface
3.1 Serial Data Interface
The ADS1256EVM is designed to easily interface with multiple control platforms. Samtec part numbers
SSW-110-22-F-D-VS-K and TSM-110-01-T-DV-P provide a convenient 10-pin, dual-row, header/socket
combination at J2. This header/socket provides access to the digital control and serial data pins of the
TSC. Consult Samtec at www.samtec.com or call 1-800-SAMTEC-9 for a variety of mating connector
options.
All logic levels on J2 are 3.3V CMOS, except for the I2C pins, which conform to 3.3V I2C rules.
Some pins on J2 have weak pullup resistors. These resistors provide default settings for many of the
control pins. Most pins on J2 correspond directly to ADS1256 pins. See the ADS1256 product data sheet
for complete details on these pins. Table 2 describes the J2 serial interface pins.
Digital Interface
Table 2. J2: Serial Interface Pins
Pin Number Pin Name
J2.1 — CNTL — None Unused
J2.2 — GPIO0 — None Unused
J2.3 SCLK CLKX Input None Serial clock input
J2.4 DGND DGND I/O Power Digital ground
J2.5 — CLKR — None Unused
J2.6 — GPIO1 — None Unused
J2.7 CS FSX Input None Chip select (via J8)
J2.8 — GPIO2 — None Unused
J2.9 — FSR — None Unused
J2.10 DGND DGND I/O Power Digital ground
J2.11 DIN DX Input None Serial data input
J2.12 — GPIO3 — None Unused
J2.13 DOUT DR Input None Serial data output
J2.14 RESET GPIO4 Input Yes Reset input (via J7)
J2.15 DRDY INT Output None Data ready signal
J2.16 SCL SCL I/O None I2C clock line
J2.17 EXTCLK TOUT Input None External system clock input
J2.18 DGND DGND I/O Power Digital lround
J2.19 SYNC/PDW
N
J2.20 SDA SDA I/O None I2C data line
Standard
Name Direction Pulldown Function
GPIO5 Input Yes Synchronization and power
down control pin (via J6)
3.2 GPIO
The ADS1256 has four general-purpose I/O (GPIO) pins. One of these pins can also be configured as a
buffered system clock output. This output is typically used to clock additional ADS1255/ADS1256 devices,
but can be used for other purposes as well. The GPIO pins for the ADS1256 are shown in Figure 2. These
pins (from left to right) are D3 to D0.
SBAU090E–November 2003–Revised November 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2003–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
ADS1256EVM and ADS1256EVM-PDK
7
Page 8

Power Supplies
Each pin is connected to the GPIO header through a 100Ω resistor. 100kΩ pull-downs on each pin protect
the GPIOs when they are configured as inputs, which is the default setting. The GPIO header, J5, carries
the GPIO pins for the ADS1256.
The GPIO header pinout is described in Table 3.
www.ti.com
Figure 2. GPIO Pins
Table 3. J5: GPIO Header Pins
Pin Number Pin Name Function
1 D0 GPIO or buffered system clock
output
2 D1 GPIO
3 D2 GPIO
4 D3 GPIO
4 Power Supplies
J5 is the power-supply input connector. It is used as the primary supply source for the entire EVM. Table 4
lists the configuration details for J2.
Pin No. Pin Name Function Required
J5.1 +VA Positive analog supply, +5V to
J5.2 –VA Negative analog supply, -5V to
J5.3 +5VA Positive analog supply, +5V Always
J5.4 –5VA Negative analog supply, -5V No
J5.5 DGND Digital ground Optional connection to
J5.6 AGND Analog ground Ground
J5.7 +1.8VD Positive digital supply, +1.8V Digital supply; select
J5.8 VD1 Positive digital supply No
J5.9 +3.3VD Positive digital supply, +3.3V Digital supply; select
J5.10 +5VD Positive digital supply, +5V No
Table 4. J5 Configuration: Power-Supply Input
No
+18V
No
-18V
AGND through J10
using J9
using J10
8
ADS1256EVM and ADS1256EVM-PDK
Copyright © 2003–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
SBAU090E–November 2003–Revised November 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 9

www.ti.com
4.1 Power Options
There are six jumpers on the ADS1256EVM, arranged in a single jumper block of seven rows, each of
which can be shorted. (In the schematic, J4, J9, and J10 are all combined to make this single block). The
pinout of this jumper block is shown in Figure 3.
Power Supplies
Figure 3. Jumper Block
J4 connects AVDD from the +5V from the power-supply header, J3. J4 also connects the DVDD supply to
the ADS1256 device. DVDD can be set to 1.8V with J9, or to 3.3V with pins 1 and 2 of J10. Pins 3 and 4,
5 and 6, are used to set the ground of the EVM.
Pinouts and connections can all viewed in the schematic and the layout plots at the end of this user guide.
4.1.1 J4 Pins 1-2: ADS1256 Analog Power Supply
This jumper is used to measure the current of the ADS1256 analog power supply. For normal operation,
this jumper should be shorted.
4.1.2 J4 Pins 3-4: ADS1256 Digital Power Supply
Use this jumper to measure the current of the ADS1256 digital power supply. For normal operation, this
jumper should be shorted. The voltage of the digital supply is chosen by the jumper on pins 5-6 (1.8V) or
7-8 (3.3V).
4.1.3 J9 Pins 1-2: Select 1.8V Digital Supply Voltage
These pins select 1.8V for the digital supply voltage. If this selection is used, do not populate pins 7-8.
4.1.4 J10 Pins 1-2: Select 3.3V Digital Supply Voltage
These pins select 3.3V for the digital supply voltage. If this selection is used, do not populate pins 5-6.
4.1.5 J10 Pins 3-4: DGND Select
Shorting this jumper connects the ADS1256EVM ground net to DGND.
SBAU090E–November 2003–Revised November 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2003–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
ADS1256EVM and ADS1256EVM-PDK
9
Page 10

Voltage Reference
4.1.6 J10 Pins 5-6: AGND Select
Shorting this jumper connects the ADS1256EVM ground net to AGND. For normal operation, J4.1-2, J4.34, and J4.9-10 must be connected (either directly or through an ammeter); either J4.5-6 or J4.7-8 must be
connected, and either (or both) of J4.11-12 and J4.13-14 must be connected, as well. Otherwise, the
board will not function. Refer to Table 5 for details.
Table 5. J4, J9, and J10 Configuration: Power Options
Row Name Function
1-2 ADC AVDD AVDD supply current measurement point for the
3-4 ADC AVSS AVSS supply current measurement point for the
5-6 1.8V select When shorted, DVDD is sourced from the 1.8V
7-8 3.3V select When shorted, DVDD is sourced from the 3.3V
9-10 ADCDVDD DVDD supply current measurement point for the
11-12 DGND Connects DGND to board ground.
13-14 AGND Connects AGND to board ground.
www.ti.com
ADC. Must be connected for operation.
ADC. Must be connected for operation.
power-supply input pin. Should not be connected at
the same time as 7-8.
power-supply input pin. Should not be connected at
the same time as 5-6.
ADC. Must be connected for operation.
5 Voltage Reference
The ADS1256EVM has several reference options that can be selected by switch S3. First, there are
connections to apply an external reference voltage to the analog input header. The user can apply a
reference voltage to J1.18 and J1.20 in order to set the reference.
The ADS1256 also has a buffered REF5025 on board. This 2.5V reference can also be selected by switch
S3. VRN to VRP can be set from AGND to 2.5V or from 2.5V to AVDD. Figure 4 illustrates how switch S3
appears on the board. A description of switch S3 is provided in Table 6.
10
ADS1256EVM and ADS1256EVM-PDK
Figure 4. Switch S3
SBAU090E–November 2003–Revised November 2018
Copyright © 2003–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 11

www.ti.com
Table 6. Reference Input Select Switch
Board Marking Switch Position Input Source VRP Connection VRN Connection
EST Down External J1.20 J1.18
OBH Middle Onboard, high common-
mode
OBL Up Onboard, low common-
mode
AVDD +2.5V
+2.5V AGND
In the EXT position, J1 pins 18 and 20 are connected to the ADS1256 reference input.
In the OBH position, the analog power supply is connected to the positive reference input, and the
negative reference input is connected to the output of the onboard reference.
In the OBL position, the onboard reference output is connected to the ADS1256 positive reference input
pin, and the negative reference input pin is grounded.
Both OBH and OBL provide a +2.5V reference to the ADS1256. The OBL position corresponds to the
standard method to connect a reference to the ADS1256, and should be used for most measurements.
The OBH position is useful for testing the reference input common-mode sensitivity, which can be
important for ratiometric connections.
6 Clock Source
As shown in Figure 5, switch S4 selects which of the two available clock sources on the ADS1256EVM
will be provided to the ADS1256. Table 7 summarizes the positions of the switch.
Clock Source
Table 7. System Clock Select Switch
Board Marking Switch Position Clock Source
XTAL Left Onboard 7.68MHz
EXT Right External (J2 pin 17)
SBAU090E–November 2003–Revised November 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2003–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Figure 5. Switch S4
crystal
ADS1256EVM and ADS1256EVM-PDK
11
Page 12

EVM Operation
7 EVM Operation
This section provides information on the analog input, digital control, and general operating conditions of
the ADS1256EVM.
7.1 Analog Input
The analog input sources can be applied directly to J1 (top or bottom side). Additionally, switches S1 and
S2 must be set to route the input signals from J1. Otherwise, the inputs are used to measure the
reference or inputs shorted to the reference. Switches S1 and S2 are shown in Figure 6.
www.ti.com
7.1.1 S1: AIN0-1 Input Select
These switches control which lines are routed to the ADS1256 AIN0-AIN1 inputs. Table 8 shows the
positions of these switches.
Board Marking Switch Position Input Source AIN0 Connection AIN1 Connection
EXT Left External J1.2 J1.1
REF Middle Reference voltage +2.5V AGND
ZERO Right Zero (shorted to
12
ADS1256EVM and ADS1256EVM-PDK
Figure 6. Switches S1 and S2
Table 8. AIN0-1 Input Select Switch (S1)
+2.5V +2.5V
reference)
SBAU090E–November 2003–Revised November 2018
Copyright © 2003–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 13

www.ti.com
In the EXT position, J1 pins 1 and 2 are connected to the ADS1256 AIN1 and AIN0 pins, respectively. In
the REF position, the reference is connected across the ADS1256 AIN0 and AIN1 pins. In the ZERO
position, both AIN0 and AIN1 are connected to the reference. This configuration gives a zero-scale
reading across AIN0 and AIN1.
The REF and ZERO positions are useful for noise tests.
7.1.2 S2: AIN2-3 Input Select
These switches control which lines are routed to the ADS1256 AIN2 through AIN3 inputs. The positions of
the switches are described in Table 9.
Board Marking Switch Position Input Source AIN0 Connection AIN1 Connection
EXT Left External J1.4 J1.3
REF Middle Reference voltage +2.5V AGND
ZERO Right Zero (shorted to
In the EXT position, J1 pins 3 and 4 are connected to the ADS1256 AIN3 and AIN2 pins, respectively. In
the REF position, the reference is connected across the ADS1256 AIN2 and AIN3 pins. In the ZERO
position, both AIN2 and AIN3 are connected to the reference. This configuration gives a zero-scale
reading across AIN2 and AIN3.
The REF and ZERO positions are useful for noise tests.
EVM Operation
Table 9. AIN2-3 Input Select Switch (S2)
+2.5V +2.5V
reference)
7.1.3 Input Filtering Capacitors
The ADS1256EVM has pads for filtering capacitors on every input pair and for the reference input. Each
input pair has pads for two common-mode capacitors and one differential capacitor.
The ADS1256 has a flexible input multiplexer, so these capacitors do not always function as commonmode and differential signal filters. For example, when measuring a single-ended input, the common-mode
capacitors act to filter the signal.
The ADS1256EVM is shipped with only some of the capacitor pads populated. This configuration allows
the board to be immediately used to measure both differential and single-ended inputs. As shipped, inputs
AIN0 through AIN7 have 10nF differential mode capacitors installed. A differential 1μF capacitor is
connected to the reference near the reference pins.
The input filtering capacitors are in relatively large 1210-size packages, in contrast to most of the other
passives on the board. These capacitors were designed to be large so that you can easily remove them or
replace them with other values. By exercising appropriate care, you can even solder leaded devices to
these large pads.
7.2 Digital Control
The digital control signals can be applied directly to J6 (top or bottom side). The modular ADS1256EVM
can also be connected directly to a DSP or microcontroller interface board, such as the 5-6K Interface or
HPA-MCU Interface boards available from Texas Instruments, or the MMB0 if purchased as part of the
ADS1256EVM-PDK. For a list of compatible interface and/or accessory boards for the EVM or the
ADS1256, see the relevant product folder on the TI web site.
7.3 ADS1256EVM-PDK Power Supply
The analog portion of the ADS1256EVM can either be powered by a 5V source generated via ac adapter,
or by applying the +5VA to the connector on the MMB0 board. The MMB0 board will provide the digital 5V
and 3.3V to the ADS1256EVM. To provide +5VA to the ADS1256EVM from the MMB0 board, make sure
the jumper at J13 (on the MMB0) is closed from +5V to +5VA.
SBAU090E–November 2003–Revised November 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2003–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
ADS1256EVM and ADS1256EVM-PDK
13
Page 14

EVM Operation
7.4 Default Jumper Settings and Switch Positions
Figure 7 shows the jumpers and switches found on the EVM and the respective factory default conditions
for each.
www.ti.com
Figure 7. ADS1256EVM Default Jumper and Switch Locations
The jumpers on J4 provide a convenient way to measure the current for any of the power-supply currents
AVDD (analog +V power), DVDD (digital power), AVSS (analog –V power), or the ground connections
VGND and DGND. Simply remove the jumper for the appropriate power supply and use a current meter
between the jumper pins. The supply voltage for the digital supply (DVDD) can also be selected to be
either 1.8V or 3.3V; refer to Table 5.
Table 10 and Table 11 provide a list of jumpers and switches found on the EVM and the respective factory
default conditions for each.
Table 10. Default Jumper Positions
Jumper
J4 1-2 and 3-4 AVDD and DVDD current
J6 2-3 SYNC/PDWN header connection
J7 1-2 RESET header connection
J8 1-2 CS header connection
J9 none +1.8VD connection
J10 1-2, 3-4, and 4-5 +3.3VD, AGND, and DGND
Default
Jumpers Jumper Description
measurement connection
Cconnection
14
ADS1256EVM and ADS1256EVM-PDK
SBAU090E–November 2003–Revised November 2018
Copyright © 2003–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 15

www.ti.com
Table 11. Default Switch Positions
Switch Default Position Switch Description
S1 Left AIN0-1 Input Select Switch
S2 Left AIN2-3 Input Select Switch
S3 Up Reference Input Select
S4 Left System Clock Select Switch
8 ADS1256EVM-PDK Kit Operation
This section provides information on using the ADS1256EVM-PDK, including setup, program installation,
and program usage. To prepare to evaluate the ADS1256 with the ADS1256EVM-PDK, complete the
following steps:
Step 1. Install the ADCPro software (if not already installed).
Step 2. Install the ADS1256EVM-PDK EVM plug-in software.
Step 3. Set up the ADS1256EVM-PDK.
Step 4. Connect a proper power supply or ac adapter.
Step 5. Complete the NI-VISA™ USB driver installation process.
Step 6. Run the ADCPro software.
Step 7. Complete the Microsoft Windows USB driver installation process.
Each task is described in the subsequent sections of this document.
ADS1256EVM-PDK Kit Operation
8.1 Installing the ADCPro Software
Do not connect the ADS1256EVM-PDK before installing the software. Failure to
observe this may cause Microsoft Windows to not recognize the ADS1256EVMPDK.
The latest software is available from Texas Instruments' website at http://www.ti.com/tool/ADS1256EVM-
PDK. Download the ADCPro Installer from the ADCPro product information page on the TI website. Refer
to the ADCPro User Guide for instructions on installing and using ADCPro.
To install the ADS1256EVM-PDK plug-in, download and run the file: ADS1256evm-pdk-plug-in-1.0.0.exe
from the ADS1256EVM-PDK product folder (1.0.0 is the version number, and increments with software
version releases). Double-click the file to run it; then follow the instructions shown.
Installation for the ADS1256EVM plug-in should be relatively straightforward. The plug-in comes as an
executable file. Once started, the program leads the user through the screens shown in Figure 8 through
Figure 11.
CAUTION
SBAU090E–November 2003–Revised November 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2003–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
ADS1256EVM and ADS1256EVM-PDK
15
Page 16

ADS1256EVM-PDK Kit Operation
www.ti.com
Figure 8. ADS1256EVM-PDK Setup Wizard
16
Figure 9. ADS1256EVM-PDK License Agreement
ADS1256EVM and ADS1256EVM-PDK
SBAU090E–November 2003–Revised November 2018
Copyright © 2003–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 17

www.ti.com
ADS1256EVM-PDK Kit Operation
Figure 10. ADS1256EVM-PDK Installation in Progress
Figure 11. ADS1256EVM-PDK Installation Complete
SBAU090E–November 2003–Revised November 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2003–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
ADS1256EVM and ADS1256EVM-PDK
17
Page 18

ADS1256EVM-PDK Kit Operation
The software should now be installed, but the USB drivers may not yet have been loaded by the PC
operating system. This step completes when the ADCPro software is executed; see Section 8.4, Running
the Software and Completing Driver Installation.
8.2 Setting Up the ADS1256EVM-PDK
The ADS1256EVM-PDK contains both the ADS1256EVM and the MMB0 motherboard; however, these
devices are shipped unconnected. Follow these steps to set up the ADS1256EVM-PDK:
Step 1. Unpack the ADS1256EVM-PDK kit.
Step 2. Set the jumpers and switches on the MMB0 as shown in Figure 12.
• Connect +5V and +5VA on jumper block J13 (if +5V is supplied from J14 +5VA).
• Leave +5V and +VA disconnected on jumper block J13.
• If the PDK will be powered from an ac adapter, and used in unipolar mode, connect J12.
If the PDK will be powered through the terminal block or will be used in bipolar mode,
disconnect J12. (See Section 8.3 for details on connecting the power supply.)
www.ti.com
18
ADS1256EVM and ADS1256EVM-PDK
Figure 12. MMB0 Initial Configuration
SBAU090E–November 2003–Revised November 2018
Copyright © 2003–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 19

www.ti.com
ADS1256EVM-PDK Kit Operation
space
Step 3. Plug the ADS1256EVM into the MMB0.
CAUTION
Do not misalign the pins when plugging the ADS1256EVM into the MMB0.
Check the pin alignment carefully before applying power to the PDK.
Step 4. Set the jumpers and switches on the ADS1256EVM as shown in Figure 13 (note that these
settings are the factory-configured settings for the EVM):
• Set jumper block J4 as shown in Figure 7.
• Set the reference source select switches S1 and S2 to the center position.
• Set up jumper block J3 as shown; refer to Figure 7.
Figure 13. Connecting the ADS1256EVM to the MMB0
SBAU090E–November 2003–Revised November 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2003–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
ADS1256EVM and ADS1256EVM-PDK
19
Page 20

ADS1256EVM-PDK Kit Operation
8.2.1 About the MMB0
The MMB0 is a Modular EVM System motherboard. It is designed around the TMS320VC5507, a DSP
from Texas Instruments that has an onboard USB interface. The MMB0 also has 16MB of SDRAM
installed.
The MMB0 is not sold as a DSP development board, and it is not available separately. TI cannot offer
support for the MMB0 except as part of an EVM kit. For schematics or other information about the MMB0,
contact Texas Instruments.
8.3 Connecting the Power Supply
The ADS1256EVM-PDK can be operated with a unipolar +5V supply or a bipolar ±5V supply.
If the ADS1256EVM-PDK is to be operated in unipolar mode only, either an ac adapter or a lab power
supply can be used. If the ADS1256EVM-PDK is to be operated in bipolar mode, a ±5V power supply
must be connected; an ac adapter cannot be used.
When the MMB0 DSP is powered properly, LED D2 glows green. The green light indicates that the 3.3V
supply for the MMB0 is operating properly. (It does not indicate that the EVM power supplies are
operating properly.)
8.3.1 Connecting an AC Adapter
An ac adapter can be connected to barrel jack J2 on the MMB0. J2 is located next to the USB connector.
Refer to the External Wall-Adapter Power-Supply Requirements section.
When an ac adapter is used, the ADS1256EVM cannot be used in bipolar mode.
Jumper J12 on the MMB0 connects a wall-mounted power supply to the board. To use the wall-mount
supply, J12 must be shorted, refer to Figure 14.
www.ti.com
20
Figure 14. MMB0 Powered From AC Adapter
ADS1256EVM and ADS1256EVM-PDK
SBAU090E–November 2003–Revised November 2018
Copyright © 2003–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 21

www.ti.com
8.3.1.1 External Wall-Adapter Power-Supply Requirements
The external wall-adapter power-supply requirements are as follows:
• Output voltage: 6 VDC to 9 VDC
• Maximum output current: ≥ 500 mA
• Output connector: barrel plug (positive center), 2.0-mm I.D. × 5.5-mm O.D. (9-mm insertion depth)
NOTE: Use an external power supply that complies with applicable regional safety standards; for
example, UL, CSA, VDE, CCC, PSE, and so forth.
8.3.2 Connecting a Laboratory Power Supply
A laboratory power supply can be connected through terminal block J14 on the MMB0, as shown in
Figure 15. Both unipolar and bipolar configurations are supported.
To use a unipolar lab power supply configuration:
• Disconnect J12 on the MMB0.
• Connect a +5V dc supply to the +5VD terminal on J14.
• Connect ground of the dc supply to the GND terminal on J14.
For bipolar mode, also connect a –5V dc supply to the –5VA terminal on J14. It is not necessary to
connect a +5V dc supply voltage to the +5VA terminal on J14 if the +5V/+5VA position on J13 is shorted.
ADS1256EVM-PDK Kit Operation
Figure 15. MMB0 Configured for Lab Power Supply
SBAU090E–November 2003–Revised November 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2003–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
ADS1256EVM and ADS1256EVM-PDK
21
Page 22

ADS1256EVM-PDK Kit Operation
8.4 Running the Software and Completing Driver Installation
NOTE: The software is continually under development. These instructions and screen images are
current at the time of this writing, but may not exactly match future releases.
The program for evaluating the ADS1256EVM-PDK is called ADCPro. This program uses plug-ins to
communicate with the EVM. The ADS1256EVM-PDK plug-in is included in the ADS1256EVM-PDK
package.
The program currently runs only on Microsoft Windows platforms of Windows XP; Windows Vista and
Windows 7 are NOT supported.
If this is the first time installing ADCPro and plug-ins, follow these procedures to run ADCPro and
complete the necessary driver installation. Make sure the ADCPro software and device plug-in software
are installed from the CD-ROM as described in Installing the ADCPro Software.
8.4.1 NI-VISA USB Device Driver Installation
1. After the ADCPro software is installed, apply power to the PDK and connect the board to an available
PC USB port.
2. The computer should recognize new hardware and begin installing the drivers for the hardware.
Figure 16 through Figure 19 are provided for reference to show the installation steps.
• For the first screen (Figure 16), it is not necessary to search for the software; it has already been
installed to your PC.
• For the remaining steps, accept the default settings.
www.ti.com
22
Figure 16. NI-VISA Driver Installation Wizard, Screen 1
ADS1256EVM and ADS1256EVM-PDK
SBAU090E–November 2003–Revised November 2018
Copyright © 2003–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 23

www.ti.com
ADS1256EVM-PDK Kit Operation
Figure 17. NI-VISA Driver Installation Wizard, Screen 2
Figure 18. NI-VISA Driver Installation Wizard, Screen 3
SBAU090E–November 2003–Revised November 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2003–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
ADS1256EVM and ADS1256EVM-PDK
23
Page 24

ADS1256EVM-PDK Kit Operation
Figure 19. NI-VISA Driver Installation Wizard, Screen 4
www.ti.com
24
ADS1256EVM and ADS1256EVM-PDK
SBAU090E–November 2003–Revised November 2018
Copyright © 2003–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 25

www.ti.com
This should complete the installation of the NI-VISA drivers. You can verify proper installation by opening
the Device Manager and locating the drivers as shown in Figure 20.
Figure 20. NI-VISA Driver Verification Using Device Manager
8.4.2 USBStyx Driver Installation
1. Start the software by selecting ADCPro from the Windows Start menu. The screen shown in Figure 21
appears.
ADS1256EVM-PDK Kit Operation
Figure 21. ADCPro Software Start-up Display Window
SBAU090E–November 2003–Revised November 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2003–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
ADS1256EVM and ADS1256EVM-PDK
25
Page 26

ADS1256EVM-PDK Kit Operation
space
2. Select ADS1256EVM from the EVM drop-down menu. The ADS1256EVM-PDK plug-in appears in the
left pane, as Figure 22 shows.
www.ti.com
26
Figure 22. ADS1256EVM-PDK Plug-In Display Window
3. The ADS1256EVM-PDK plug-in window has a status area at the top of the screen. When the plug-in is
first loaded, the plug-in searches for the board. You will see a series of messages in the status area
indicating this action.
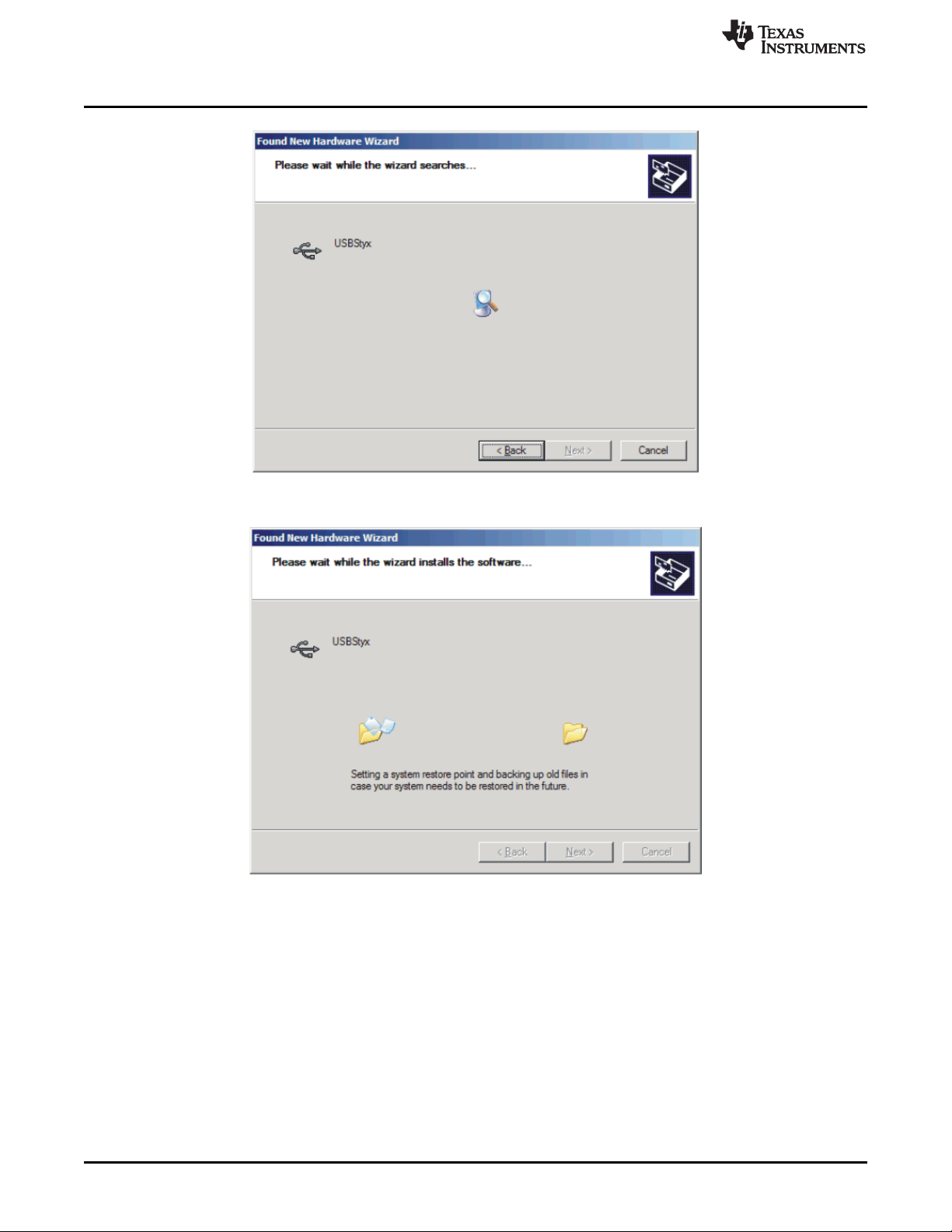
4. If you have not yet loaded the operating system drivers, Windows will display the Windows Install New
Driver Wizard sequence (illustrated in Figure 23 through Figure 27). Accept the default settings.
NOTE: During the driver installation, a message may appear indicating the firmware load has
TIMED OUT. Click OK and continue driver installation. The plug-in will attempt to download
the firmware again once the driver installation completes.
ADS1256EVM and ADS1256EVM-PDK
Copyright © 2003–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
SBAU090E–November 2003–Revised November 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 27

www.ti.com
ADS1256EVM-PDK Kit Operation
Figure 23. Install New Driver Wizard Screen 1
Figure 24. Install New Driver Wizard Screen 2
SBAU090E–November 2003–Revised November 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2003–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
ADS1256EVM and ADS1256EVM-PDK
27
Page 28
ADS1256EVM-PDK Kit Operation
www.ti.com
Figure 25. Install New Driver Wizard Screen 3
28
Figure 26. Install New Driver Wizard Screen 4
ADS1256EVM and ADS1256EVM-PDK
SBAU090E–November 2003–Revised November 2018
Copyright © 2003–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 29

www.ti.com
5. Once Windows finishes installing the software driver, the plug-in downloads the firmware to the MMB0.
Verify the proper installation of the USBStyx driver using the Device Manager. Note that the first driver
item, NI-VISA USB Devices, disappears and a new item, LibUSB-Win32 Devices appears, as Figure 28
shows.
ADS1256EVM-PDK Kit Operation
Figure 27. Install New Driver Wizard Screen 5
The status area will display Connected to EVM when the device is connected and ready to use. If the
firmware does not load properly, you can try resetting the MMB0 by pressing Reset and then reloading
the plug-in.
Figure 28. USBStyx Driver Verification Using Device Manager
The driver installation wizard sequence should not appear again, unless you connect the board to a
different USB port
SBAU090E–November 2003–Revised November 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2003–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
ADS1256EVM and ADS1256EVM-PDK
29
Page 30

Evaluating Performance with the ADCPro Software
9 Evaluating Performance with the ADCPro Software
The evaluation software is based on ADCPro, a program that operates using a variety of plug-ins. (The
ADS1256EVM plug-in is installed as described in the installation section, Section 8.)
To use ADCPro, load an EVM plug-in and a test plug-in. To load an EVM plug-in, select it from the EVM
menu. To load a test plug-in, select it from the Test menu. To unload a plug-in, select the Unload option
from the corresponding menu.
Only one of each kind of plug-in can be loaded at a time. If you select a different plug-in, the previous
plug-in is unloaded.
9.1 Using the ADS1256EVM-PDK Plug-in
The ADS1256EVM-PDK plug-in for ADCPro provides complete control over all settings of the ADS1256. It
consists of a tabbed interface (see Figure 22), with different functions available on different tabs. These
controls are described in this section.
You can adjust the ADS1256EVM settings when you are not acquiring data. During acquisition, all
controls are disabled and settings may not be changed. When you change a setting on the ADS1256EVM
plug-in, the setting is immediately updated on the board.
If you unload and reload the plug-in, the software attempts to load settings from the board.
Settings on the ADS1256EVM correspond to settings described in the ADS1256 product data sheet; see
the ADS1256 data sheet (available for download at www.ti.com) for details.
In the upper left corner, the Averages control sets the ADS1256 averaging mode. This control may be set
to 1, 4, 16, or 64. Note that this is a setting for the ADS1256 device itself; no software averaging is done in
the ADS1256EVM-PDK plug-in.
The PGA pull-down menu controls the PGA gain in the ADS1256.
Because the effective data rate of the ADS1256 depends upon the settings of the multiplexer mode,
clocks, switch time delay, chopping, and averages, the Effective Data Rate indicator in the upper right
corner of the plug-in interface is always visible and updates whenever a setting that affects the data rate
changes.
The previous controls are all found at the top of the ADS1256EVM plug-in and shown in Figure 29.
www.ti.com
30
Figure 29. ADS1256EVM-PDK Plug-In Averages, PGA Gain, and Effective Data Rate Controls
ADS1256EVM and ADS1256EVM-PDK
Copyright © 2003–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
SBAU090E–November 2003–Revised November 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 31

www.ti.com
9.1.1 MUX Tab
The first tab of the ADS1256EVM plug-in is the MUX tab. In the tab, two columns of push buttons are
used to select the positive and negative inputs for ADS1256. This selection, combined with switches S1
and S2, selects the measurement for the inputs applied to the analog interface J1. The MUX tab is shown
in Figure 30.
Evaluating Performance with the ADCPro Software
SBAU090E–November 2003–Revised November 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2003–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Figure 30. MUX Tab
ADS1256EVM and ADS1256EVM-PDK
31
Page 32

Evaluating Performance with the ADCPro Software
9.1.2 Clocks Tab
The next tab is the Clocks tab, as shown in Figure 31. This tab controls the master clock of the
ADS1256EVM. Enter the master clock frequency in the Clock In window. The clock source can be
selected from between the EVM onboard crystal and the MMB0. The DO/CLKOUT rate can be set by the
Clock Out Rate pull-down menu. There are options to set CLKOUT to f
CLKIN
, f
CLKIN
/2, f
www.ti.com
/4, or to turn it off.
CLKIN
32
ADS1256EVM and ADS1256EVM-PDK
Figure 31. Clocks Tab
SBAU090E–November 2003–Revised November 2018
Copyright © 2003–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 33

www.ti.com
9.1.3 GPIO Tab
The GPIO tab is used to control the GPIO pins (D0 through D3) on the ADS1256. Four switches are used
to select the GPIO mode (input or output). If the pin is selected as an output, a push button is used to set
the output to be either high or low. If the pin is selected as an input, the Read Inputs button read the
inputs and an indicator light shows if the input is high or low. Figure 32 illustrates the GPIO tab.
Evaluating Performance with the ADCPro Software
SBAU090E–November 2003–Revised November 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2003–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Figure 32. GPIO Tab
ADS1256EVM and ADS1256EVM-PDK
33
Page 34

Evaluating Performance with the ADCPro Software
9.1.4 Power and Reference Tab
The Power & Ref tab selects the reference input, the sensor detect magnitude, and the standby condition.
The VREF Source window has three pushbuttons that select the reference source and should correspond
with the reference setting for switch S3. OBL sets the reference input from AGND to VREF, while OBH
sets the reference input from VREF to AVDD. External sets the input from VREF– to VREF+ on the
analog input header. If the user applies an external reference, the Vref window can be set to calculate the
voltage when using the Multichannel Scope test plug-in.
The ADS1256 has sensor detect current sources that can be used to detect a burned out sensor. These
current sources are applied to the inputs internal to the ADC. The sensor detect current sources can be
set to 0.5mA, 2mA, 10mA, or turned off through using a series of pushbuttons.
To reduce the operating current when the device is not in use, the ADS1256 can be put into standby
mode with a pushbutton labeled Standby. Pressing the Wakeup button releases the ADS1256 from this
mode.
The Power & Ref tab is illustrated in Figure 33.
www.ti.com
34
ADS1256EVM and ADS1256EVM-PDK
Figure 33. Power & Ref Tab
SBAU090E–November 2003–Revised November 2018
Copyright © 2003–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 35

www.ti.com
9.1.5 Calibration Tab
The Cal tab (as Figure 34 illustrates) controls the calibration of the offset and gain error of the ADS1256.
Pressing a pushbutton at the top of the tab runs a self-calibration of the device. Four buttons allow four
other calibration options: Self Offset Calibration, System Offset Calibration, Self Gain Calibration, and
System Gain Calibration.
At the bottom of the tab, there are four windows that allow for manually entering and reading back
calibration values for the offset calibration register and the gain calibration register. The Set button enters
the value in the window into the calibration register, while the Read button reads the current calibration
register value.
Evaluating Performance with the ADCPro Software
SBAU090E–November 2003–Revised November 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2003–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Figure 34. Cal Tab
ADS1256EVM and ADS1256EVM-PDK
35
Page 36

Evaluating Performance with the ADCPro Software
9.1.6 About Tab
The About tab displays information about the EVM and software, as Figure 35 shows.
The Plugin Version and Firmware Version indicators show the version numbers of the plug-in and
firmware code, respectively. The Notes indicator may show relevant notes about the plug-in or firmware
code, if there are any.
www.ti.com
36
ADS1256EVM and ADS1256EVM-PDK
Figure 35. EVM Software About Tab
SBAU090E–November 2003–Revised November 2018
Copyright © 2003–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 37

www.ti.com
9.1.7 Collecting Data
Once you have configured the ADS1256 for your test scenario, pressing the ADCPro Acquire button
starts the collection of the number of datapoints specified in the Test plug-in Block Size control. The
ADS1256EVM-PDK plug-in disables all the front panel controls while acquiring, and displays a progress
bar as shown in Figure 36.
Evaluating Performance with the ADCPro Software
Figure 36. Software Progress Indicator
For more information on testing analog-to-digital converters in general and using ADCPro and Test plugins, refer to the ADCPro User Guide.
9.2 Troubleshooting
If ADCPro stops responding while the ADS1256EVM-PDK is connected, try unplugging the power supply
from the PDK. Unload and reload the plug-in before reapplying power to the PDK.
SBAU090E–November 2003–Revised November 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2003–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
ADS1256EVM and ADS1256EVM-PDK
37
Page 38
Schematics and Layout
10 Schematics and Layout
A schematic for the ADS1256EVM is appended to this user's guide. The bill of materials is provided in
Table 12. Figure 37 through Figure 40 illustrate the ADS1256EVM printed circuit board (PCB) layouts.
Table 12. ADS1256EVM Bill of Materials
Item No Qty Value Ref Des Description Vendor Part No
1 1 10kΩ R1 1/10W 5% chip resistor Panasonic ERJ-3GEYJ103V
2 2 47kΩ R2, R3 1/10W 5% chip resistor Panasonic ERJ-3GEYJ473V
3 3 100Ω RA1, RA2, RA3 Resistor array, eight terminal,
4 1 100kΩ RA4 Resistor array, eight terminal,
5 2 18pF C21. C22 50V ceramic chip capacitor, ±5%,
6 2 0.1μF C23, C24 16V ceramic chip capacitor,
7 2 1μF C3, C18 16V ceramic chip, ±10%, X7R TDK C2012X7R1C105KT
8 2 4.7μF C19, C20 6.3V ceramic chip ±20%, X5R TDK C2012X5R0J475KT
9 1 100μF C4 10V low ESR tantalum capacitor,
10 4 10nF C1, C2, C7, C10 16V PPS chip capacitor, ±2% Panasonic ECH-U1C103GX5
11 1 U1 Analog to digital converter Texas Instruments ADS1256IDB
12 1 U2 Operational amplifier Texas nstruments OPA350UA
13 1 U3 +2.5V voltage reference Texas Instruments REF5025ID
14 1 U4
15 2 J1A, J2A 20 pin SMT plug Samtec TSM-110-01-L-DV-P
16 2 J1B, J2B 20 pin SMT socket Samtec SSW-110-22-F-D-VS-K
17 1 J3A 10 pin SMT plug Samtec TSM-105-01-L-DV-P
18 1 J3B 10 pin SMT socket Samtec SSW-105-22-F-D-VS-K
19 3 J6, J7, J8 Three-position header, 0 .1
20 1 J5 Four-position header, 0 .1in
21 1 J4 2 x 2 position header, 0.1in
22 1 J10 2 x 3 position header, 0.1in
23 1 N/A ADS1256EVM PWB Texas Instruments 6450840
24 3 S1, S2, S3 DP3T Switch E-Switch EG2305A
25 1 S4 SPDT Switch NKK SS12SDP2
26 1 X1 Crystal, SMD Citizen HCM49-7.680MABJ-UT
27 8 N/A Jumper top Samtec SNT-100-BK-T
Not
Installed
Not
Installed
1 J9 1×2 Position header, 0.1”
C5, C6, C8, C9, C11,
C12,C13, C14, C15,
C16, C17
four resistor
four resistor
C0G
±10%, X7R
±20%
256K I2C EEPROM
spacing
spacing
spacing
spacing
spacing
CTS 744C083101JPTR
CTS 744C083104JPTR
TDK C1608C0G1H180JT
TDK C1608X7R1C104KT
Kemet T520D107M010ATE055
Microchip 24AA256-I/SN
Samtec TSW-103-07-L-S
Samtec TSW-104-07-L-S
Samtec TSW-102-07-L-D
Samtec TSW-103-07-L-D
Samtec TSW-102-07-L-S
www.ti.com
38
ADS1256EVM and ADS1256EVM-PDK
SBAU090E–November 2003–Revised November 2018
Copyright © 2003–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 39

www.ti.com
Schematics and Layout
Figure 37. ADS1256EVM PCB: Top-Side Image
Figure 38. ADS1256EVM PCB: Layer 1
Figure 39. ADS1256EVM PCB: Layer 2
Figure 40. ADS1256EVM PCB: Bottom-Side Image
SBAU090E–November 2003–Revised November 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2003–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
ADS1256EVM and ADS1256EVM-PDK
39
Page 40

AVDD
2
3
6
7
4
U2
OPA350
R1
10K
AVDD
AVDD
C4
100U TA
AVDD
DVDD
VOLTAGE REFERENCE FILTERCAPACITORS C3-C5
C3: 1UF MLCC, 0805 PKG
MURATA
KEMET C0805C105K4RACTU
INSTALL EITHER C4 OR C5
C4: 100UF LOW ESR TANTALUM
KEMET "KO-CAP" T520D107M010AS4350
C5: 22UF MLCC
MURATA
KEMET
PANASONIC
AVDD
1
AGND
2
VRN
3
VRP
4
AINCOM
5
AIN0
6
AIN1
7
AIN2
8
AIN3
9
AIN4
10
AIN5
11
AIN6
12
AIN7
13
SYNC/PDWN
14
RESET
15
DVDD
16
DGND
17
XTAL2
18
XTAL1/CLKIN
19
CS
20
DRDY
21
DOUT
22
DIN
23
SCLK
24
D0/CLKOUT
25
D1
26
D2
27
D3
28
U1
ADS1256
AN0+
2
AN1+
4
AN2+
6
AN3+
8
AN4+
10
AN5+
12
AN6+
14
AN7+
16
REF-
18
REF+
20
AGND
17
AGND
19
AN0-
1
AN1-
3
AN2-
5
AN3-
7
AGND
9
AGND
11
AGND
13
VCOM
15
J1
ANALOGHDR
1
2
3
4
J5
HEADER-4
RA3
100
CS
SCLK
DIN
DOUT
DRDY
SYNC/PDWN
RESET
D0
D1
D2
D3
CLKX
FSX
DX
DR
INT
TOUT
GPIO5
GPIO4
D0C
D1C
D2C
D3C
S3
ESW_EG2305A
S1
ESW_EG2305A
C18
1U
C13
DNP
C12
DNP
C1
10nF
C15
DNP
C14
DNP
S2
ESW_EG2305A
C2
10nF
C17
DNP
C16
DNP
AVDD
AIN0
AIN1
AIN2
AIN3
AIN4
AIN5
AIN6
AIN7
AINCOM
OBREF
AN1+
AN1-
AN0+
AN0-
REF-
REF+
VRP
VRN
ADCAVDD
ADCDVDD
A0
1
A1
2
GND
4
SDA
5
SCL
6
WP
7
VCC
8
A2
3
U4
MCP_24AA256-I/SN
AGNDIN
DGNDIN
X1
7.68MHZ
C21
18P
C22
18P
S4
NKK_SS12SDP2
C19
4U7
C20
4U7
DVDD
SDA
SCL
C10
10nF
C7
10nF
C8
DNP
C6
DNP
C11
DNP
C9
DNP
EXTCLK
CLKIN
XTAL2
RA1
100
RA2
100
RA4
100K
C5: OPTIONAL MLCC REF CAP
CNTL
1
CLKX
3
CLKR
5
FSX
7
FSR
9
DX
11
DR
13
INT
15
TOUT
17
GPIO5
19
GPIO0
2
DGND
4
GPIO1
6
GPIO2
8
DGND
10
GPIO3
12
GPIO4
14
SCL
16
DGND
18
SDA
20
J2
SERIALHDR
+3.3VIN
+1.8VIN
123
J6
SYNC/PDWN
123
J7
RESET
123
J8
CS
DVDD
DVDD
R2
47k
R3
47k
-VA
2
-5VA
4
AGND
6
VD1
8
+5VD
10
+VA
1
+5VA
3
DGND
5
+1.8VD
7
+3.3VD
9
J3
POWERHDR
VIN2VOUT
6
TRIM
5
GND
4
TEMP
3
U3
REF5025
C3
1U 16V X7R
C23
0.1uF
C24
0.1uF
C5
DNP
1 2
3 4
J4
JPR-2X2
1 2
3 4
5 6
J10
JPR-2X3
1 2
J9
JPR-2X1
Schematics and Layout
40
ADS1256EVM and ADS1256EVM-PDK
www.ti.com
Figure 41. Schematic
SBAU090E–November 2003–Revised November 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2003–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 41

www.ti.com
Revision History
Revision History
NOTE: Page numbers for previous revisions may differ from page numbers in the current version.
Changes from D Revision (May 2016) to E Revision ...................................................................................................... Page
• Added Schematic image................................................................................................................ 40
Changes from C Revision (July 2010) to D Revision ..................................................................................................... Page
• Updated software download links in the Installing the ADCPro Software section............................................... 15
• Added External Wall-Adapter Power-Supply Requirements section. ............................................................. 21
SBAU090E–November 2003–Revised November 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2003–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Revision History
41
Page 42

STANDARD TERMS FOR EVALUATION MODULES
1. Delivery: TI delivers TI evaluation boards, kits, or modules, including any accompanying demonstration software, components, and/or
documentation which may be provided together or separately (collectively, an “EVM” or “EVMs”) to the User (“User”) in accordance
with the terms set forth herein. User's acceptance of the EVM is expressly subject to the following terms.
1.1 EVMs are intended solely for product or software developers for use in a research and development setting to facilitate feasibility
evaluation, experimentation, or scientific analysis of TI semiconductors products. EVMs have no direct function and are not
finished products. EVMs shall not be directly or indirectly assembled as a part or subassembly in any finished product. For
clarification, any software or software tools provided with the EVM (“Software”) shall not be subject to the terms and conditions
set forth herein but rather shall be subject to the applicable terms that accompany such Software
1.2 EVMs are not intended for consumer or household use. EVMs may not be sold, sublicensed, leased, rented, loaned, assigned,
or otherwise distributed for commercial purposes by Users, in whole or in part, or used in any finished product or production
system.
2 Limited Warranty and Related Remedies/Disclaimers:
2.1 These terms do not apply to Software. The warranty, if any, for Software is covered in the applicable Software License
Agreement.
2.2 TI warrants that the TI EVM will conform to TI's published specifications for ninety (90) days after the date TI delivers such EVM
to User. Notwithstanding the foregoing, TI shall not be liable for a nonconforming EVM if (a) the nonconformity was caused by
neglect, misuse or mistreatment by an entity other than TI, including improper installation or testing, or for any EVMs that have
been altered or modified in any way by an entity other than TI, (b) the nonconformity resulted from User's design, specifications
or instructions for such EVMs or improper system design, or (c) User has not paid on time. Testing and other quality control
techniques are used to the extent TI deems necessary. TI does not test all parameters of each EVM.
User's claims against TI under this Section 2 are void if User fails to notify TI of any apparent defects in the EVMs within ten (10)
business days after delivery, or of any hidden defects with ten (10) business days after the defect has been detected.
2.3 TI's sole liability shall be at its option to repair or replace EVMs that fail to conform to the warranty set forth above, or credit
User's account for such EVM. TI's liability under this warranty shall be limited to EVMs that are returned during the warranty
period to the address designated by TI and that are determined by TI not to conform to such warranty. If TI elects to repair or
replace such EVM, TI shall have a reasonable time to repair such EVM or provide replacements. Repaired EVMs shall be
warranted for the remainder of the original warranty period. Replaced EVMs shall be warranted for a new full ninety (90) day
warranty period.
3 Regulatory Notices:
3.1 United States
3.1.1 Notice applicable to EVMs not FCC-Approved:
FCC NOTICE: This kit is designed to allow product developers to evaluate electronic components, circuitry, or software
associated with the kit to determine whether to incorporate such items in a finished product and software developers to write
software applications for use with the end product. This kit is not a finished product and when assembled may not be resold or
otherwise marketed unless all required FCC equipment authorizations are first obtained. Operation is subject to the condition
that this product not cause harmful interference to licensed radio stations and that this product accept harmful interference.
Unless the assembled kit is designed to operate under part 15, part 18 or part 95 of this chapter, the operator of the kit must
operate under the authority of an FCC license holder or must secure an experimental authorization under part 5 of this chapter.
3.1.2 For EVMs annotated as FCC – FEDERAL COMMUNICATIONS COMMISSION Part 15 Compliant:
CAUTION
This device complies with part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) This device may not
cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause
undesired operation.
Changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance could void the user's authority to
operate the equipment.
FCC Interference Statement for Class A EVM devices
NOTE: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to part 15 of
the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is
operated in a commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not
installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio communications.
Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference in which case the user will be required to
correct the interference at his own expense.
Page 43

FCC Interference Statement for Class B EVM devices
NOTE: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to part 15 of
the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential
installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance
with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference
will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which
can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more
of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
3.2 Canada
3.2.1 For EVMs issued with an Industry Canada Certificate of Conformance to RSS-210 or RSS-247
Concerning EVMs Including Radio Transmitters:
This device complies with Industry Canada license-exempt RSSs. Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
(1) this device may not cause interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference, including interference that may
cause undesired operation of the device.
Concernant les EVMs avec appareils radio:
Le présent appareil est conforme aux CNR d'Industrie Canada applicables aux appareils radio exempts de licence. L'exploitation
est autorisée aux deux conditions suivantes: (1) l'appareil ne doit pas produire de brouillage, et (2) l'utilisateur de l'appareil doit
accepter tout brouillage radioélectrique subi, même si le brouillage est susceptible d'en compromettre le fonctionnement.
Concerning EVMs Including Detachable Antennas:
Under Industry Canada regulations, this radio transmitter may only operate using an antenna of a type and maximum (or lesser)
gain approved for the transmitter by Industry Canada. To reduce potential radio interference to other users, the antenna type
and its gain should be so chosen that the equivalent isotropically radiated power (e.i.r.p.) is not more than that necessary for
successful communication. This radio transmitter has been approved by Industry Canada to operate with the antenna types
listed in the user guide with the maximum permissible gain and required antenna impedance for each antenna type indicated.
Antenna types not included in this list, having a gain greater than the maximum gain indicated for that type, are strictly prohibited
for use with this device.
Concernant les EVMs avec antennes détachables
Conformément à la réglementation d'Industrie Canada, le présent émetteur radio peut fonctionner avec une antenne d'un type et
d'un gain maximal (ou inférieur) approuvé pour l'émetteur par Industrie Canada. Dans le but de réduire les risques de brouillage
radioélectrique à l'intention des autres utilisateurs, il faut choisir le type d'antenne et son gain de sorte que la puissance isotrope
rayonnée équivalente (p.i.r.e.) ne dépasse pas l'intensité nécessaire à l'établissement d'une communication satisfaisante. Le
présent émetteur radio a été approuvé par Industrie Canada pour fonctionner avec les types d'antenne énumérés dans le
manuel d’usage et ayant un gain admissible maximal et l'impédance requise pour chaque type d'antenne. Les types d'antenne
non inclus dans cette liste, ou dont le gain est supérieur au gain maximal indiqué, sont strictement interdits pour l'exploitation de
l'émetteur
3.3 Japan
3.3.1 Notice for EVMs delivered in Japan: Please see http://www.tij.co.jp/lsds/ti_ja/general/eStore/notice_01.page 日本国内に
輸入される評価用キット、ボードについては、次のところをご覧ください。
http://www.tij.co.jp/lsds/ti_ja/general/eStore/notice_01.page
3.3.2 Notice for Users of EVMs Considered “Radio Frequency Products” in Japan: EVMs entering Japan may not be certified
by TI as conforming to Technical Regulations of Radio Law of Japan.
If User uses EVMs in Japan, not certified to Technical Regulations of Radio Law of Japan, User is required to follow the
instructions set forth by Radio Law of Japan, which includes, but is not limited to, the instructions below with respect to EVMs
(which for the avoidance of doubt are stated strictly for convenience and should be verified by User):
1. Use EVMs in a shielded room or any other test facility as defined in the notification #173 issued by Ministry of Internal
Affairs and Communications on March 28, 2006, based on Sub-section 1.1 of Article 6 of the Ministry’s Rule for
Enforcement of Radio Law of Japan,
2. Use EVMs only after User obtains the license of Test Radio Station as provided in Radio Law of Japan with respect to
EVMs, or
3. Use of EVMs only after User obtains the Technical Regulations Conformity Certification as provided in Radio Law of Japan
with respect to EVMs. Also, do not transfer EVMs, unless User gives the same notice above to the transferee. Please note
that if User does not follow the instructions above, User will be subject to penalties of Radio Law of Japan.
Page 44

【無線電波を送信する製品の開発キットをお使いになる際の注意事項】 開発キットの中には技術基準適合証明を受けて
いないものがあります。 技術適合証明を受けていないもののご使用に際しては、電波法遵守のため、以下のいずれかの
措置を取っていただく必要がありますのでご注意ください。
1. 電波法施行規則第6条第1項第1号に基づく平成18年3月28日総務省告示第173号で定められた電波暗室等の試験設備でご使用
いただく。
2. 実験局の免許を取得後ご使用いただく。
3. 技術基準適合証明を取得後ご使用いただく。
なお、本製品は、上記の「ご使用にあたっての注意」を譲渡先、移転先に通知しない限り、譲渡、移転できないものとします。
上記を遵守頂けない場合は、電波法の罰則が適用される可能性があることをご留意ください。 日本テキサス・イ
ンスツルメンツ株式会社
東京都新宿区西新宿6丁目24番1号
西新宿三井ビル
3.3.3 Notice for EVMs for Power Line Communication: Please see http://www.tij.co.jp/lsds/ti_ja/general/eStore/notice_02.page
電力線搬送波通信についての開発キットをお使いになる際の注意事項については、次のところをご覧ください。http:/
/www.tij.co.jp/lsds/ti_ja/general/eStore/notice_02.page
3.4 European Union
3.4.1 For EVMs subject to EU Directive 2014/30/EU (Electromagnetic Compatibility Directive):
This is a class A product intended for use in environments other than domestic environments that are connected to a
low-voltage power-supply network that supplies buildings used for domestic purposes. In a domestic environment this
product may cause radio interference in which case the user may be required to take adequate measures.
4 EVM Use Restrictions and Warnings:
4.1 EVMS ARE NOT FOR USE IN FUNCTIONAL SAFETY AND/OR SAFETY CRITICAL EVALUATIONS, INCLUDING BUT NOT
LIMITED TO EVALUATIONS OF LIFE SUPPORT APPLICATIONS.
4.2 User must read and apply the user guide and other available documentation provided by TI regarding the EVM prior to handling
or using the EVM, including without limitation any warning or restriction notices. The notices contain important safety information
related to, for example, temperatures and voltages.
4.3 Safety-Related Warnings and Restrictions:
4.3.1 User shall operate the EVM within TI’s recommended specifications and environmental considerations stated in the user
guide, other available documentation provided by TI, and any other applicable requirements and employ reasonable and
customary safeguards. Exceeding the specified performance ratings and specifications (including but not limited to input
and output voltage, current, power, and environmental ranges) for the EVM may cause personal injury or death, or
property damage. If there are questions concerning performance ratings and specifications, User should contact a TI
field representative prior to connecting interface electronics including input power and intended loads. Any loads applied
outside of the specified output range may also result in unintended and/or inaccurate operation and/or possible
permanent damage to the EVM and/or interface electronics. Please consult the EVM user guide prior to connecting any
load to the EVM output. If there is uncertainty as to the load specification, please contact a TI field representative.
During normal operation, even with the inputs and outputs kept within the specified allowable ranges, some circuit
components may have elevated case temperatures. These components include but are not limited to linear regulators,
switching transistors, pass transistors, current sense resistors, and heat sinks, which can be identified using the
information in the associated documentation. When working with the EVM, please be aware that the EVM may become
very warm.
4.3.2 EVMs are intended solely for use by technically qualified, professional electronics experts who are familiar with the
dangers and application risks associated with handling electrical mechanical components, systems, and subsystems.
User assumes all responsibility and liability for proper and safe handling and use of the EVM by User or its employees,
affiliates, contractors or designees. User assumes all responsibility and liability to ensure that any interfaces (electronic
and/or mechanical) between the EVM and any human body are designed with suitable isolation and means to safely
limit accessible leakage currents to minimize the risk of electrical shock hazard. User assumes all responsibility and
liability for any improper or unsafe handling or use of the EVM by User or its employees, affiliates, contractors or
designees.
4.4 User assumes all responsibility and liability to determine whether the EVM is subject to any applicable international, federal,
state, or local laws and regulations related to User’s handling and use of the EVM and, if applicable, User assumes all
responsibility and liability for compliance in all respects with such laws and regulations. User assumes all responsibility and
liability for proper disposal and recycling of the EVM consistent with all applicable international, federal, state, and local
requirements.
5. Accuracy of Information: To the extent TI provides information on the availability and function of EVMs, TI attempts to be as accurate
as possible. However, TI does not warrant the accuracy of EVM descriptions, EVM availability or other information on its websites as
accurate, complete, reliable, current, or error-free.
Page 45

6. Disclaimers:
6.1 EXCEPT AS SET FORTH ABOVE, EVMS AND ANY MATERIALS PROVIDED WITH THE EVM (INCLUDING, BUT NOT
LIMITED TO, REFERENCE DESIGNS AND THE DESIGN OF THE EVM ITSELF) ARE PROVIDED "AS IS" AND "WITH ALL
FAULTS." TI DISCLAIMS ALL OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, REGARDING SUCH ITEMS, INCLUDING BUT
NOT LIMITED TO ANY EPIDEMIC FAILURE WARRANTY OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS
FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE OR NON-INFRINGEMENT OF ANY THIRD PARTY PATENTS, COPYRIGHTS, TRADE
SECRETS OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS.
6.2 EXCEPT FOR THE LIMITED RIGHT TO USE THE EVM SET FORTH HEREIN, NOTHING IN THESE TERMS SHALL BE
CONSTRUED AS GRANTING OR CONFERRING ANY RIGHTS BY LICENSE, PATENT, OR ANY OTHER INDUSTRIAL OR
INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT OF TI, ITS SUPPLIERS/LICENSORS OR ANY OTHER THIRD PARTY, TO USE THE
EVM IN ANY FINISHED END-USER OR READY-TO-USE FINAL PRODUCT, OR FOR ANY INVENTION, DISCOVERY OR
IMPROVEMENT, REGARDLESS OF WHEN MADE, CONCEIVED OR ACQUIRED.
7. USER'S INDEMNITY OBLIGATIONS AND REPRESENTATIONS. USER WILL DEFEND, INDEMNIFY AND HOLD TI, ITS
LICENSORS AND THEIR REPRESENTATIVES HARMLESS FROM AND AGAINST ANY AND ALL CLAIMS, DAMAGES, LOSSES,
EXPENSES, COSTS AND LIABILITIES (COLLECTIVELY, "CLAIMS") ARISING OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH ANY
HANDLING OR USE OF THE EVM THAT IS NOT IN ACCORDANCE WITH THESE TERMS. THIS OBLIGATION SHALL APPLY
WHETHER CLAIMS ARISE UNDER STATUTE, REGULATION, OR THE LAW OF TORT, CONTRACT OR ANY OTHER LEGAL
THEORY, AND EVEN IF THE EVM FAILS TO PERFORM AS DESCRIBED OR EXPECTED.
8. Limitations on Damages and Liability:
8.1 General Limitations. IN NO EVENT SHALL TI BE LIABLE FOR ANY SPECIAL, COLLATERAL, INDIRECT, PUNITIVE,
INCIDENTAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR EXEMPLARY DAMAGES IN CONNECTION WITH OR ARISING OUT OF THESE
TERMS OR THE USE OF THE EVMS , REGARDLESS OF WHETHER TI HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF
SUCH DAMAGES. EXCLUDED DAMAGES INCLUDE, BUT ARE NOT LIMITED TO, COST OF REMOVAL OR
REINSTALLATION, ANCILLARY COSTS TO THE PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES, RETESTING,
OUTSIDE COMPUTER TIME, LABOR COSTS, LOSS OF GOODWILL, LOSS OF PROFITS, LOSS OF SAVINGS, LOSS OF
USE, LOSS OF DATA, OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION. NO CLAIM, SUIT OR ACTION SHALL BE BROUGHT AGAINST TI
MORE THAN TWELVE (12) MONTHS AFTER THE EVENT THAT GAVE RISE TO THE CAUSE OF ACTION HAS
OCCURRED.
8.2 Specific Limitations. IN NO EVENT SHALL TI'S AGGREGATE LIABILITY FROM ANY USE OF AN EVM PROVIDED
HEREUNDER, INCLUDING FROM ANY WARRANTY, INDEMITY OR OTHER OBLIGATION ARISING OUT OF OR IN
CONNECTION WITH THESE TERMS, , EXCEED THE TOTAL AMOUNT PAID TO TI BY USER FOR THE PARTICULAR
EVM(S) AT ISSUE DURING THE PRIOR TWELVE (12) MONTHS WITH RESPECT TO WHICH LOSSES OR DAMAGES ARE
CLAIMED. THE EXISTENCE OF MORE THAN ONE CLAIM SHALL NOT ENLARGE OR EXTEND THIS LIMIT.
9. Return Policy. Except as otherwise provided, TI does not offer any refunds, returns, or exchanges. Furthermore, no return of EVM(s)
will be accepted if the package has been opened and no return of the EVM(s) will be accepted if they are damaged or otherwise not in
a resalable condition. If User feels it has been incorrectly charged for the EVM(s) it ordered or that delivery violates the applicable
order, User should contact TI. All refunds will be made in full within thirty (30) working days from the return of the components(s),
excluding any postage or packaging costs.
10. Governing Law: These terms and conditions shall be governed by and interpreted in accordance with the laws of the State of Texas,
without reference to conflict-of-laws principles. User agrees that non-exclusive jurisdiction for any dispute arising out of or relating to
these terms and conditions lies within courts located in the State of Texas and consents to venue in Dallas County, Texas.
Notwithstanding the foregoing, any judgment may be enforced in any United States or foreign court, and TI may seek injunctive relief
in any United States or foreign court.
Mailing Address: Texas Instruments, Post Office Box 655303, Dallas, Texas 75265
Copyright © 2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 46

IMPORTANT NOTICE AND DISCLAIMER
TI PROVIDES TECHNICAL AND RELIABILITY DATA (INCLUDING DATASHEETS), DESIGN RESOURCES (INCLUDING REFERENCE
DESIGNS), APPLICATION OR OTHER DESIGN ADVICE, WEB TOOLS, SAFETY INFORMATION, AND OTHER RESOURCES “AS IS”
AND WITH ALL FAULTS, AND DISCLAIMS ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESS AND IMPLIED, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION ANY
IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE OR NON-INFRINGEMENT OF THIRD
PARTY INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS.
These resources are intended for skilled developers designing with TI products. You are solely responsible for (1) selecting the appropriate
TI products for your application, (2) designing, validating and testing your application, and (3) ensuring your application meets applicable
standards, and any other safety, security, or other requirements. These resources are subject to change without notice. TI grants you
permission to use these resources only for development of an application that uses the TI products described in the resource. Other
reproduction and display of these resources is prohibited. No license is granted to any other TI intellectual property right or to any third
party intellectual property right. TI disclaims responsibility for, and you will fully indemnify TI and its representatives against, any claims,
damages, costs, losses, and liabilities arising out of your use of these resources.
TI’s products are provided subject to TI’s Terms of Sale (www.ti.com/legal/termsofsale.html) or other applicable terms available either on
ti.com or provided in conjunction with such TI products. TI’s provision of these resources does not expand or otherwise alter TI’s applicable
warranties or warranty disclaimers for TI products.
Mailing Address: Texas Instruments, Post Office Box 655303, Dallas, Texas 75265
Copyright © 2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
 Loading...
Loading...