Page 1
User Manual
Version V1.0-20171103
User Manual
For MatrixRTK
©2017 Tersus GNSS Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 2

Table of Content
Preface............................................................................................................................................... 1
1. Introduction .............................................................................................................................. 2
1.1 Introduction ................................................................................................................ 2
1.2 Features ...................................................................................................................... 2
1.3 Use and Precautions ................................................................................................... 4
2. MatrixRTK Receiver Introduction ............................................................................................ 7
2.1 Front Panel ................................................................................................................. 7
2.2 Back Panel .................................................................................................................. 8
2.3 Mainframe .................................................................................................................. 8
2.4 Button Function .......................................................................................................... 9
2.5 Indicator lights ........................................................................................................... 9
2.6 LCD .......................................................................................................................... 10
2.7 External port ............................................................................................................. 13
3. WEB Administration ............................................................................................................... 15
3.1 User login ................................................................................................................. 15
3.2 WEB page for administration ................................................................................... 17
3.3 Basic information ..................................................................................................... 18
3.4 Home page ............................................................................................................... 19
3.5 System info............................................................................................................... 20
3.6 Receiver config ........................................................................................................ 22
3.7 File management ...................................................................................................... 29
3.8 Advanced setting ...................................................................................................... 31
3.9 User management ..................................................................................................... 37
4. Basic operations ...................................................................................................................... 39
4.1 Architecture model ................................................................................................... 39
4.2 Basic composition and connection ........................................................................... 39
4.3 Connector installation .............................................................................................. 40
4.4 Network connection ................................................................................................. 41
4.5 LCD and button operation ........................................................................................ 46
4.6 Set the base station ................................................................................................... 47
Page 3

4.7 Add data record ........................................................................................................ 48
4.8 Add network transmission ........................................................................................ 49
4.9 Data download ......................................................................................................... 50
4.10 Firmware upgrade .................................................................................................... 53
4.11 Register the receiver ................................................................................................. 54
Appendix ......................................................................................................................................... 55
Reset .................................................................................................................................... 55
MatrixRTK technical performance parameters table ........................................................... 56
Standard configuration table ................................................................................................ 57
Page 4

Figure 1 network remote access ................................................................................................ 3
Figure 2 Antenna location ......................................................................................................... 5
Figure 3 Overall appearance of the receiver ............................................................................. 7
Figure 4 Front panel .................................................................................................................. 7
Figure 5 back panel ................................................................................................................... 8
Figure 6 Mainframe .................................................................................................................. 8
Figure 7 Main parameter information ..................................................................................... 10
Figure 8 Data transfer status ................................................................................................... 11
Figure 9 Position information ................................................................................................. 11
Figure 10 Satellite information ............................................................................................... 11
Figure 11 Receiver status information .................................................................................... 12
Figure 12 Status information ................................................................................................... 12
Figure 13 Setup menu ............................................................................................................. 12
Figure 14 System settings ....................................................................................................... 13
Figure 15 Login page .............................................................................................................. 16
Figure 16 WEB page ............................................................................................................... 17
Figure 17 Basic information.................................................................................................... 18
Figure 18 Status bar ................................................................................................................ 19
Figure 19Main page ................................................................................................................ 19
Figure 20 Equipment info ....................................................................................................... 20
Figure 21 Satellite info ............................................................................................................ 21
Figure 22 Navigation info ....................................................................................................... 22
Figure 23 Satellite setting ....................................................................................................... 22
Figure 24 Receiver setting ...................................................................................................... 23
Figure 25 base station setting .................................................................................................. 24
Figure 26 Rover setting ........................................................................................................... 25
Figure 27 Serial port setting .................................................................................................... 25
Figure 28 Comms transmission ............................................................................................... 26
Figure 29 Ntrip Client and Ntrip Server setting ...................................................................... 27
Figure 30 TCP/IP Client and UDP Client setting .................................................................... 27
Figure 31 TCP/IP Server and UDP Server setting................................................................... 28
Figure 32 Data logging ........................................................................................................... 28
Figure 33 File list .................................................................................................................... 29
Figure 34 FTP push ................................................................................................................. 30
Figure 35 System settings ....................................................................................................... 31
Figure 36 System settings ....................................................................................................... 32
Figure 37 Data download password ........................................................................................ 32
Figure 38 Upgrading the firmware .......................................................................................... 33
Figure 39 Remote control ....................................................................................................... 33
Figure 40 Event settings .......................................................................................................... 34
Figure 41 PPS setting .............................................................................................................. 34
Figure 42 Event Marker Setting .............................................................................................. 35
Figure 43 Network status and settings .................................................................................... 35
Figure 44 Wired settings ......................................................................................................... 36
Page 5

Figure 45 Wi-Fi Hotspot Setting ............................................................................................. 36
Figure 46 2G/3G Setting ......................................................................................................... 36
Figure 47 Log files .................................................................................................................. 37
Figure 48 Users ....................................................................................................................... 38
Figure 49 A typical architecture .............................................................................................. 39
Figure 50 Receiver connection................................................................................................ 40
Figure 51 Connector installation ............................................................................................. 40
Figure 52 Install/uninstall the SIM/TF card ............................................................................ 41
Figure 53 Line connection method ......................................................................................... 42
Figure 54 Mapping the external network connection method ................................................. 42
Figure 55 Set the IP address settings manually ....................................................................... 43
Figure 56 Automatically obtain the IP address settings .......................................................... 43
Figure 57 LCD button operation Wi-Fi network on/off .......................................................... 44
Figure 58 Web management system Wi-Fi settings ................................................................ 44
Figure 59 Mobile device home page ....................................................................................... 45
Figure 60 2G/3G network settings .......................................................................................... 45
Figure 61 Antenna settings ...................................................................................................... 47
Figure 62 Rover setting ........................................................................................................... 47
Figure 63 Base setting ............................................................................................................. 48
Figure 64 Daily Data Logging Settings .................................................................................. 48
Figure 65 Manual data logging setting .................................................................................... 49
Figure 66 Disposable plans data logging settings ................................................................... 49
Figure 67 Add network transmission ...................................................................................... 50
Figure 68 Normal data download ............................................................................................ 51
Figure 69 FTP download directory ......................................................................................... 51
Figure 70 FTP push ................................................................................................................. 52
Figure 71 FTP push time selection .......................................................................................... 52
Figure 72 Firmware upgrade ................................................................................................... 53
Figure 73 U disk installation diagram ..................................................................................... 54
Figure 74 Receiver registration ............................................................................................... 54
Page 6

Table 1 Button Description ....................................................................................................... 9
Table 2 Button Function Description ........................................................................................ 9
Table 3 Indicator light definition ............................................................................................... 9
Table 4 External port descriptions ........................................................................................... 13
Table 5 Authority class with different user groups .................................................................. 15
Table 6 reference station setting and data output .................................................................... 23
Table 7 LCD and button operation .......................................................................................... 46
Page 7

1
Preface
Introduction
Welcome to use Tersus’ MatrixRTK.
This manual provides detail about how to power on, install and configure MatrixRTK.
Experience Requirement
To help you make better use of Tersus’ products, it’s recommended that you read this instruction
carefully. If you are unfamiliar with the products, please go to www.tersus-gnss.com or mail to
support@tersus-gnss.com for more support.
Tips for Safe Use
Note: The contents here need your special attention. Please read the contents carefully.
Warning:
The contents here are very important. Any wrong operation may damage the machine, lost
the data, break down the system, or even make safety issue.
Page 8

2
1. Introduction
1.1 Introduction
MatrixRTK is a GNSS receiver with powerful microprocessors, high-capacity high-speed flash
memory and battery, multi-communication ports, military grade standard design, firewall inside,
data encryption transmission. All the features make it more accurate, easy to operate and have better
availability. The MatrixRTK receiver is an ideal solution for CORS/VRS.
Note:
1.1 The specific configuration is provided in this manual.
1.2 Please open the box package carefully. If you find any loss of this product and
accessories, or damage, please contact your local dealer or Tersus immediately.
1.3 Please read the manual carefully before operating the MatrixRTK.
1.2 Features
Based on the Linux operating system
Based on the embedded Linux operating system kernel. Linux is a real multi-user, multi-tasking,
multi-platform operating system. This stable system has management and powerful network
functions. The embedded microprocessors, small size and low power consumption make it suitable
for long time work.
Support all GNSS signals
Adequate parallel receive channels supporting GPS, GLONASS, BDS, GALILEO and other global
satellite navigation and positioning system. Thereby it improves the measurement accuracy and
real-time RTK measurement performance.
20Hz data update rate
Supports up to 20Hz solution and raw measurements update.
Multi-task running simultaneously
The GNSS receiver can support multiple task operations simultaneously. It can download/output
different types of RTK or RTD corrections while continuously tracking and recording satellite data,
without causing data interrupted or lost.
Versatile communication ports supported.
Page 9
3
Six kinds of data transmission ports are provided, including: UHF radio, data line Modem,
broadband port, Fax Modem, TCP/IP, built-in 3G/2G wireless communication function. It can use
the Internet, wireless network and other means of communication for data transmission and
broadcast differential data.
Massive data storage, data download, data streaming transmission
Built-in 64GB high-performance storage and can support the maximum of 1TB industrial-grade U
disk storage or external USB storage devices; support U disk download, FTP download and remote
download; and the receiver also has a loop storage function.
High-precision measurement technology
The use of high-performance high-precision GNSS measurement technology to measure the engine,
the accuracy reaches millimeter, the measurement data with the highest level of quality assurance.
Excellent compatibility
With excellent compatibility, real-time output CMR, RTCM, RTCMV3, RTCM3.2, Rinex and other
formats of correction data to compatible with other GNSS receivers seamlessly. It can output
high-precision real-time GNSS raw data, too.
Network remote access
Figure 1 network remote access
Military grade standard design
Supports several data interfaces, including three RS-232 ports, two USB ports, a Wi-Fi, a 4G
communication port, an Ethernet port, an RS485 port, an external clock port, a PPS output port,
can meet the reference Station or peripheral data input and output requirements fully;
Page 10
4
Wide voltage multi-mode power supply
Built-in large capacity lithium battery, can work for 24 hours (related to configuration); external two
wide voltage power supply: 7VDC ~ 36VDC; support battery, solar and wind power. And if there is
failure supply of power, the receiver can recover to the final settings, and continue to work after
power on.
1.3 Use and Precautions
Although MatrixRTK GNSS receiver is based on military standard design and it is anodized with an
aluminum alloy, the precision instrument requires careful use and maintenance.
WARNING: The receiver must be used and stored within the specified
environment. Please refer to the
Page 11
5
MatrixRTK technical performance parameters table in the Appendix.
The MatrixRTK GNSS receiver uses anodized aluminum alloy for the box, but it should also be
kept as dry as possible. And in order to improve the stability of the receiver and extend the service
life, please avoid the receiver exposed to extreme environments, such as:
1. Damp
2. The temperature is higher than 75C
3. The temperature is less than -40C
4. Corrosive liquid or gas
Do not install the GNSS antenna nearby to the following sources of electricity or strong noise
signals:
1. Oil (spark plug)
2. TV and computer monitors
3. Generator
4. Electric motorcycle
5. DC - AC power conversion equipment
6. Fluorescent light
7. Power switch
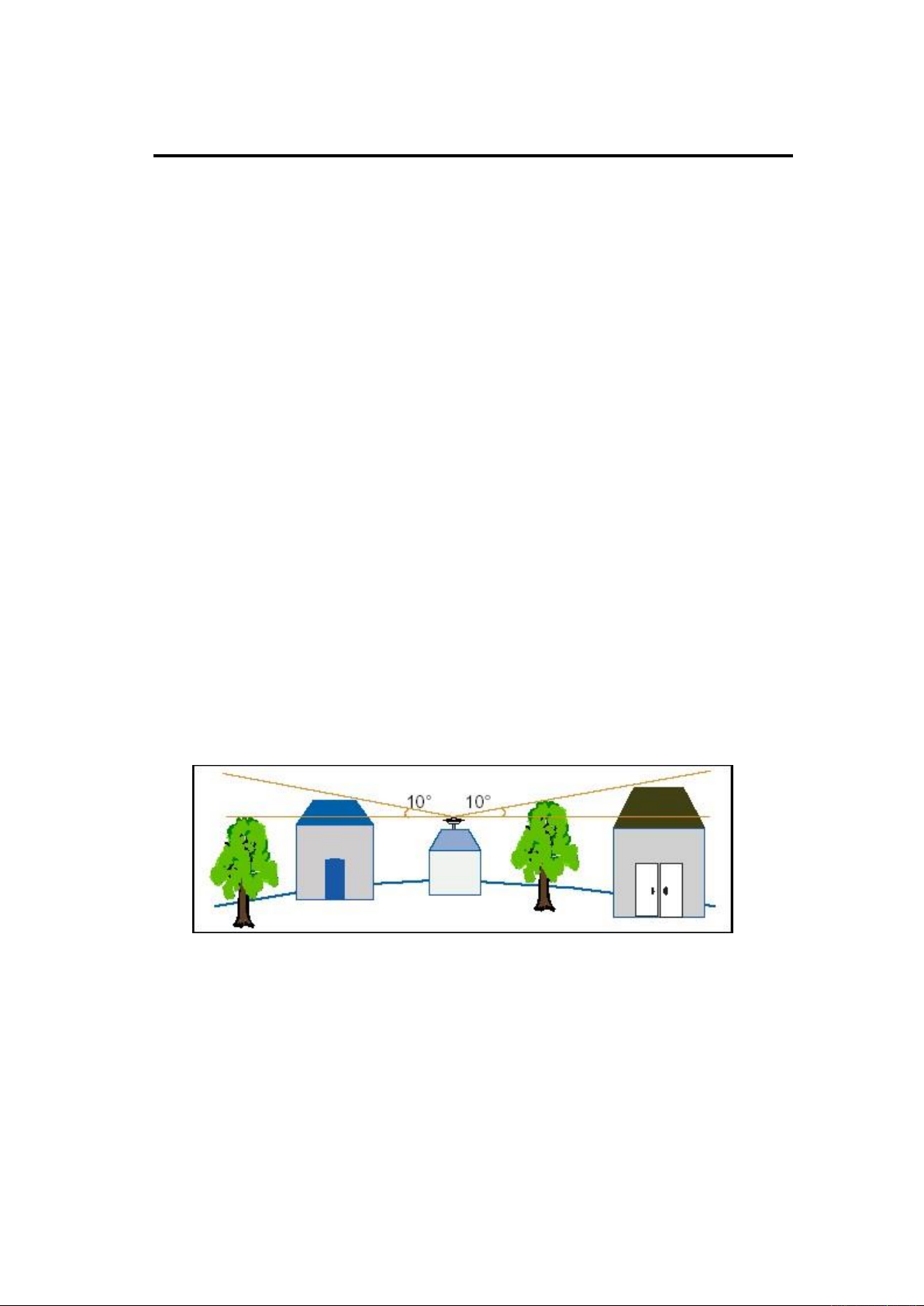
When selecting the position of the GNSS reference station for continuous operation, pay attention to
the following condition:
The site should be easy to install the receiving device and have a good view of sky. There is no
GNSS signals blockage above 10 degrees, as shown in Figure 2:
Figure 2 Antenna location
1. The location should be far away from a large area of water or possible noise source to the satellite
signals.
2. The site should be away from high-power radio transmission sources (such as television stations,
microwave stations, etc.). It's better to keep a distance greater than 200m; away from high-voltage
power lines, the distance should be greater than 50m to avoid electromagnetic interference on the
GNSS signals.
3. Can provide a stable device to fix the antenna.
Page 12

6
4. Can provide reliable and stable power supply and communication network.
5. Can provide protection of GNSS reference station equipment.
6. A place easy to arrive for inspection and maintenance.
Page 13
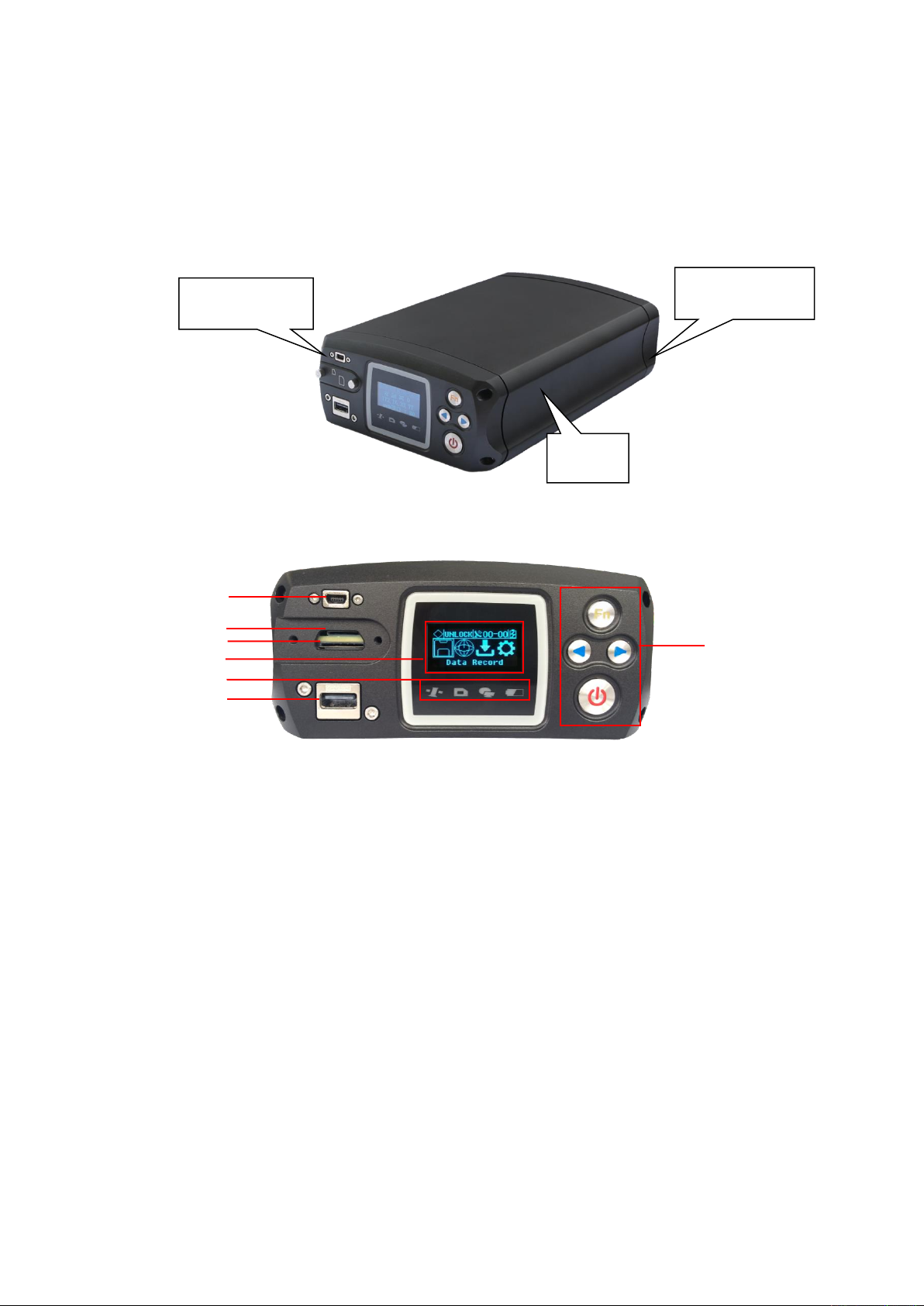
7
2. MatrixRTK Receiver Introduction
2.1 Front Panel
Figure 3 Overall appearance of the receiver
Figure 4 Front panel
1. Mini-USB port: Reserved
2. TF card slot: Install TF (micro SD) card to expand storage capacity;
3. SIM card slot: Install standard SIM card for 4G wireless network communication
4. LCD: Display receiver status information and boot button operation
5. Indicator light: Indicates tracking status, network status, recording and power status;
6. USB port: Connect a USB flash drive or USB storage device for storing/downloading data and
upgrading the firmware;
7. Button panel: Used to get status and configure the receiver.
Front Panel
Body
Back Panel
1 2 3
4
5
6
7
Page 14

8
2.2 Back Panel
1. DB9 port: Data output and connect to external devices;
2. GNSS antenna: Used to connect a GNSS antenna;
3. Power port: Power input;
4. External clock: TNC port for connecting an external atomic clock;
5. Ventilation holes: Water-proof ventilation holes;
6. External extension: 12V DC power output, RS-232 debugging port, RS-485/RS-422
communication port, hardware restart port;
7. LAN port: Cable connection port;
8. 4G antenna: The 4G cellular antenna port;
9. Five-core socket: Differential data output, host and external data link connection; auxiliary power
supply input;
10. PPS output: a SMA connector for PPS signal output;
11. Lighting-proof grounding port
2.3 Mainframe
The mainframe uses an all-aluminum alloy metal housing and uses an anodizing process, as shown
in Figure 6:
Figure 6 Mainframe
Figure 5 back panel
Page 15
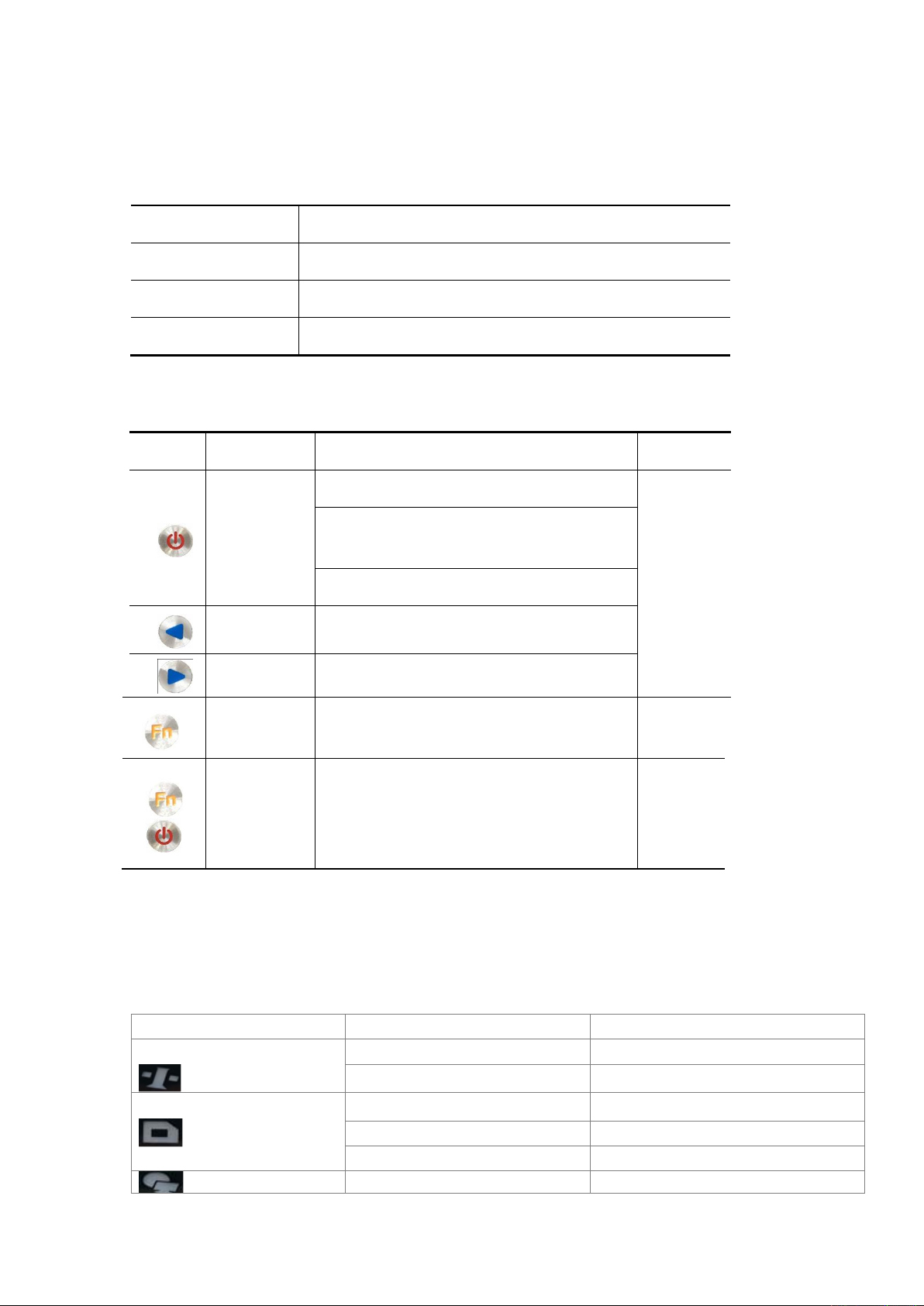
9
2.4 Button Function
Table 1 Button Description
Operation
Description
Click
button operation< 0.5s
Double Click
button operation interval <1s
Press
button operation>6s
Table 2 Button Function Description
Button
Name
Function
status
Power button
turns off/on the LCD when double-click;
See on the
LCD
Boots, verify or modify the parameters when
clicked;
Turns off MatrixRTK when held for 6s;
Left button
Moves left or up when clicked;
Right button
Moves right or down when clicked;
Function
Button
Cancels or page switch when clicked
see on the
LCD
Combination
Button
Press the Fn button and click the power button
to upgrade the kernel;
The
satellite
lights are
flashing
2.5 Indicator lights
Table 3 Indicator light definition
IF the
is
Then
Satellite lights
Always ON
Satellite locked
Always off
Satellite unlocked
Record lights
Blinks for 0.5 s
Record interval <1 second
Blinks for 1s
Recording interval≥1s
Always off
Recording stops
Network lights
Always ON
Connect the network
Page 16
10
Always off
No network connection
Power/Alarm Light
Red and Blinks for 0.5s
Alarm
Always Yellow
External power supply is connected.
Always Green
Battery is used.
Note: double-click the power button to open the LCD display, the lights will turn
off except for the network lights;
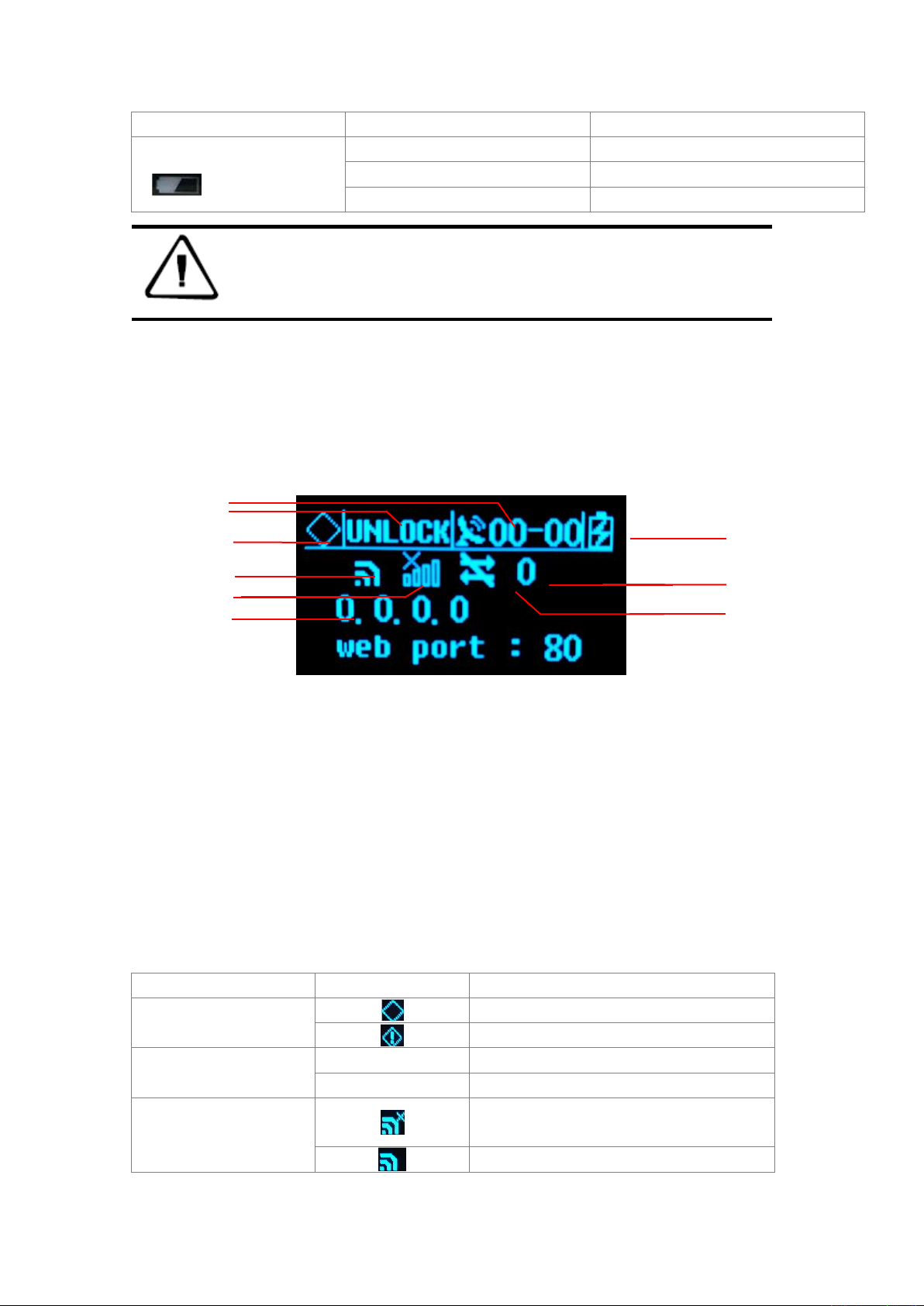
2.6 LCD
Status Display
Figure 7 Main parameter information
1 -Satellite number of board 1;
2 -Satellite lock status;
3 -Alarm status;
4 -Wi-Fi status;
5 -4G network status;
6 -IP address;
7 -Power supply/battery power;
8 -Cellular signal strength;
9 -Cellular network transmission status;
IF the LCD
Shows
Which mean
Alarm status
Normal status
Alarm
Satellite lock status
UNLOCK
Satellite unlock
LOCK
Satellite lock
Wi-Fi status
Wi-Fi is disable
Wi-Fi is enable
1
2
3
4
5
6
7 8 9
Page 17
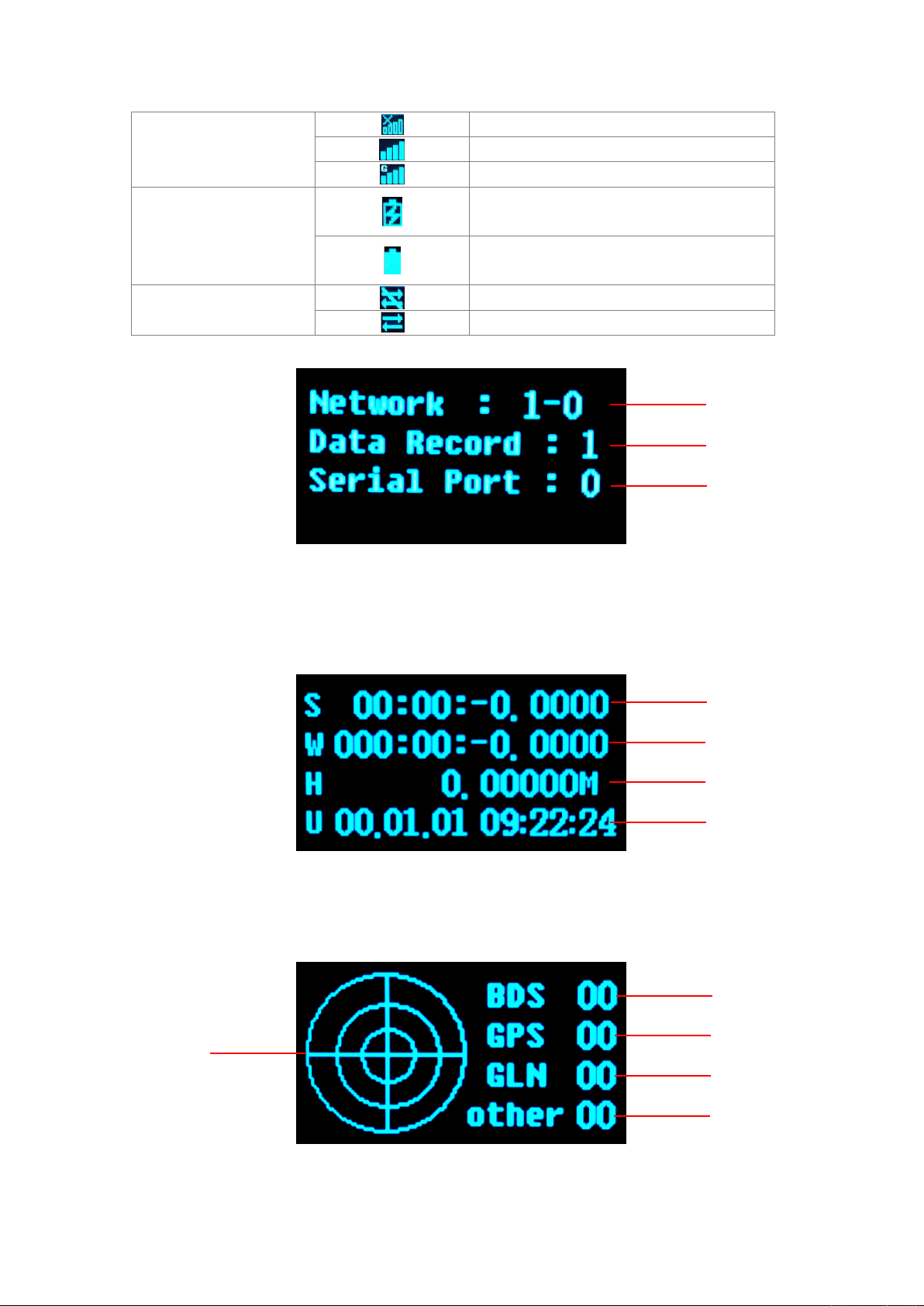
11
Cellular network status
The cellular module is off
The cellular module is on
Connected to a public network
Power supply
External power supply
Battery powered
Cellular network
transmission status
No data transmission
Data transmission is ON
Figure 8 Data transfer status
1- Total Network number - Enable Network number; 2- Data records number; 3Serial port number
Figure 9 Position information
1-Longitude; 2-Latitude; 3-Height; 4-UTC time
Figure 10 Satellite information
1
3
2
1 2 3
4
1 2 3
4
5
Page 18
12
1 -Satellite number of BDS; 2-Satellite number of GPS; 3-Satellite number of GLONASS;
4 -Satellite number of other constellations; 5-Satellite map in the sky
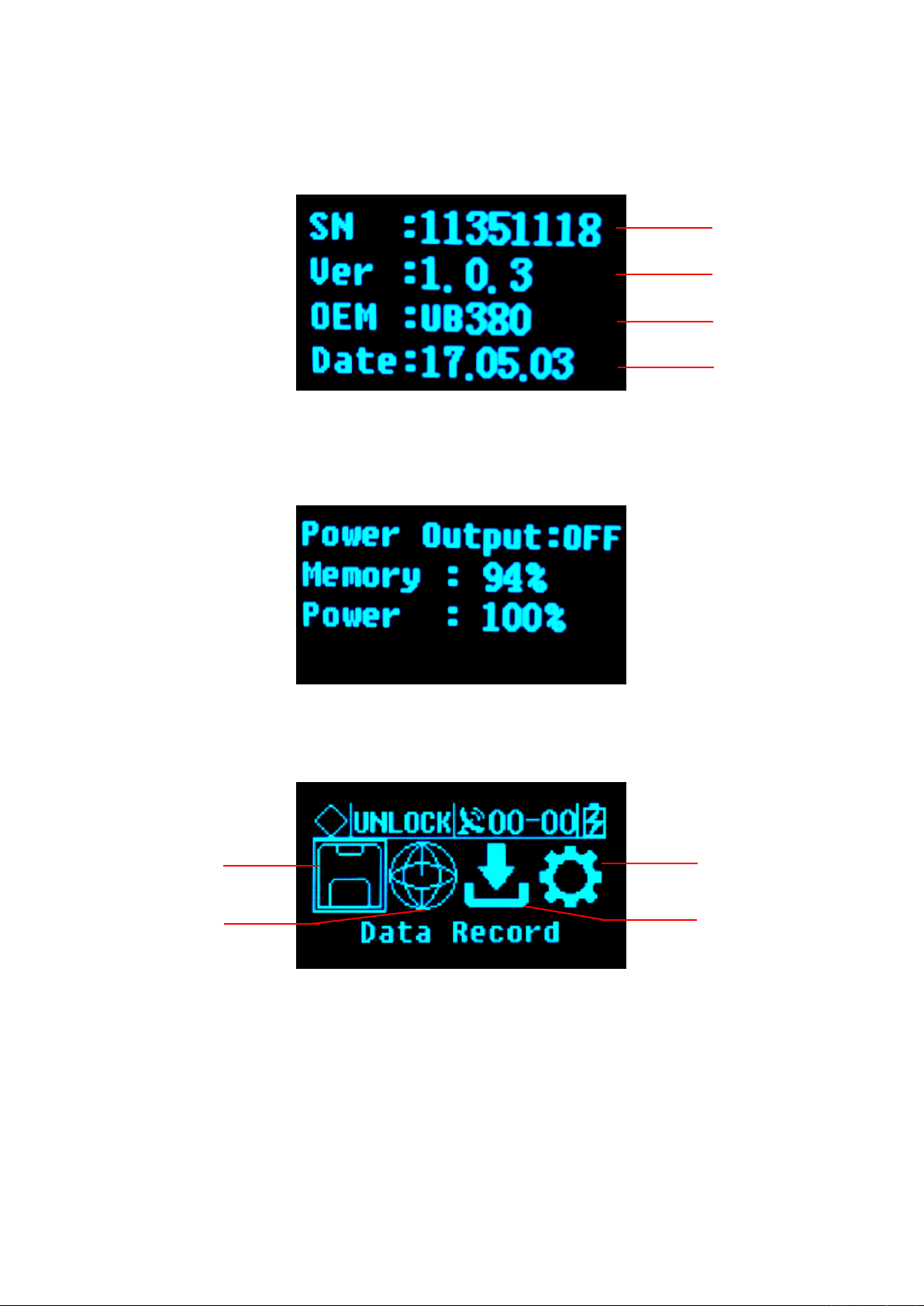
Figure 11 Receiver status information
1-Receiver SN number; 2-Version; 3 -Motherboard version; 4-Expire data;
Figure 12 Status information
3. Display setting
Figure 13 Setup menu
1-Data record; 2-Network settings; 3-Data download; 4-System settings;
4
1 2 3 4 3 1 2
Page 19
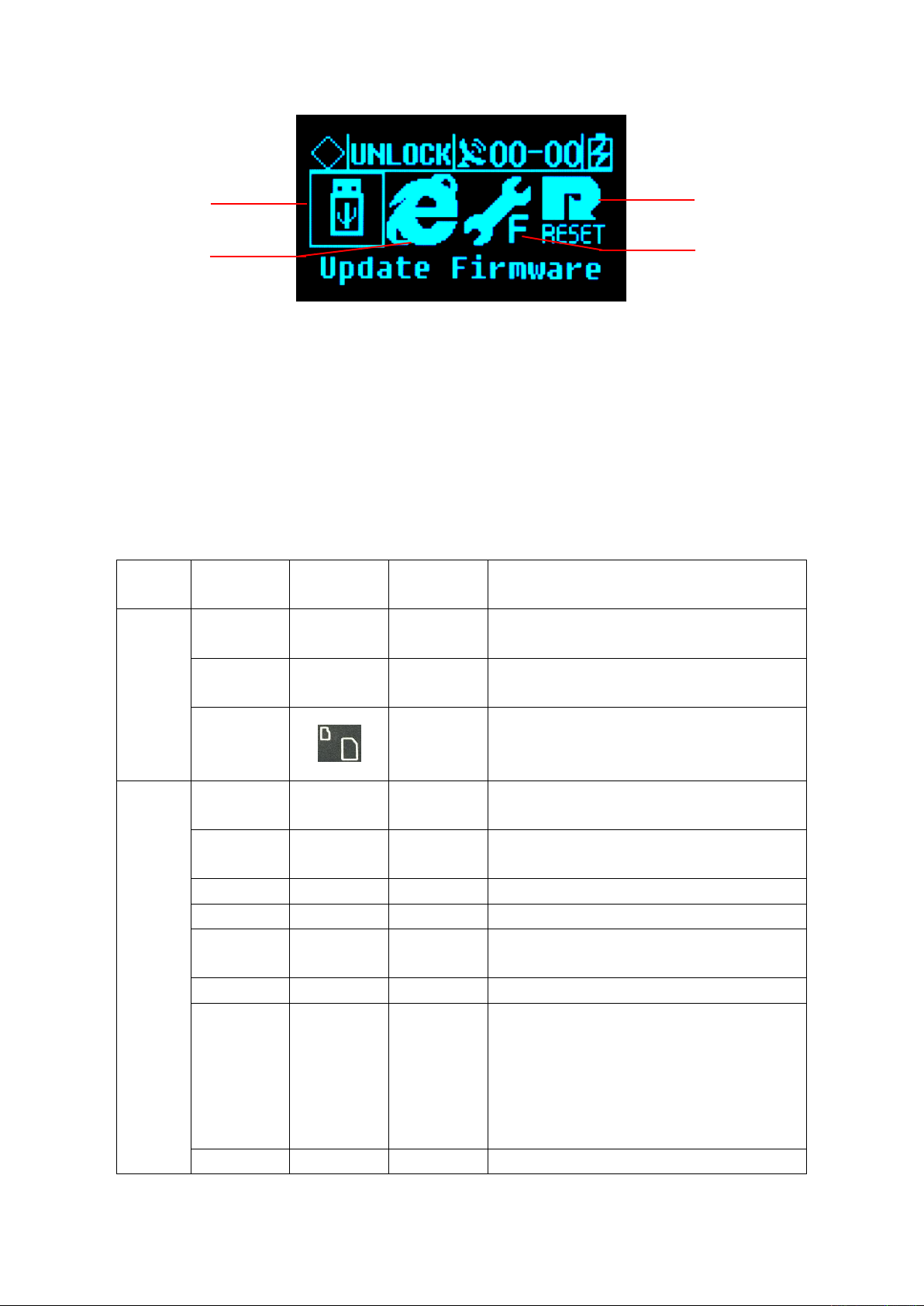
13
Figure 14 System settings
1 -Firmware Upgrade; 2 -Restore the default IP; 3-Reset; 4 -Reset the motherboard;
2.7 External port
Table 4 External port descriptions
Panel
Panel Name
Panel
instructions
Physical
port
Function
Front
Panel
Mini-USB
port
/
Mini-USB
/
USB port
/
USB-A
Data storage/download, upgrade firmware
available U disk and USB removable storage
TF/
SIM Card
slot
TF/SIM
Card slot
TF card: storage data and ROM;
SIM card: 4G wireless network
communication;
Back
Panel
GNSS
antenna
GNSS ANT
TNC
Connect to a GNSS antenna
External
clock input
OSC
TNC
Connect to an external atomic clock
4G antenna
4G ANT
SMA
Connect to a 4G cellular antenna
PPS output
PPS
SMA
PPS signal output
DB9 Serial
port
COM1
DB9
GNSS data output and external sensor
interface
LAN port
LAN
RJ45
Wired access to local area networks
External
extension
EXT Port
Fourteen
core port
(LEMO)
RS-485: GNSS data output and external sensor
interface;
RS-232: debug serial port;
EX12: 12VDC output;
PW_RST: hardware reboot;
EVT: external event input (reserved);
power input
PW1
Two core
Main power supply input;
1
2
4
3
Page 20

14
port
(LEMO)
Five-core
socket
PW2
COM2
Small five
core port
(LEMO)
Auxiliary power supply input;
Differential data output;
Ground
point
GND
/
Lightning protection grounding
Page 21

15
3. WEB Administration
3.1 User login
After network setting is successful, GNSS receiver can be accessed by LAN through the IP
Address.
For the convenience of management, all users are divided into three groups.
Guest: users can log in without entering an ID or a password. They are authorized to basic
status check only.
Normal users: Must provide an ID and a password to log in, being authorized to check system
status, change parameters, browse, download, and delete data file. Users are prioritized while
the amount of online users reach the maximum supported.
Administrator: Must log in with an ID and a password. Holding the highest level of authority
and being able to add/delete accounts and change password of other users. It is prioritized
while the amount of online users reach the maximum supported.
Table 5 Authority class with different user groups
Authority
Guest
Normal user
Administrator
Check status
Check navigation info and satellite
status
Check logging file
Check data transporting status
Modify configuration
Set coordinate system and
parameters for observation
Control and revise file logs
Download or delete observation
file
✓
Modify data output configuration
Change password
Page 22

16
Add or delete account
Disconnect other user
Restart the system
✓
Restart the device
Upgrading OS and Apps
When accessing the WEB administration page of MatrixRTK, a login page will show as the figure
3-1 below.
Figure 15 Login page
Note: WEB administration of MatrixRTK support PC, server, tablet, smart phone,
etc. Please use IE 9+/Firefox 11+/Chrome 20+ to access to the WEB
system.
Input ID and password and click [log in] to enter the WEB system. Or just click [Guest] to log in as
a guest with basic authority.
After initialization, the system creates an administrator account automatically with user name
Tersus_gnss and password Tersus_gnss. Normal user accounts can be created by administrator with
different authority level.
Note: only one administrator account is allowed and only password can be
changed. We advise the customer to change that after the instrument
installation. If you forget the password, please contact Tersus for
administrator account or contact the administrator to reset normal users’
passwords.
Page 23

17
3.2 WEB page for administration
Figure 16 WEB page
The following info is given in the WEB page:
1. Logo of Tersus
2. Navigation bar
3. Menu
4. Display & configuration
5. Operating time
6. Status bar
7. Basic information
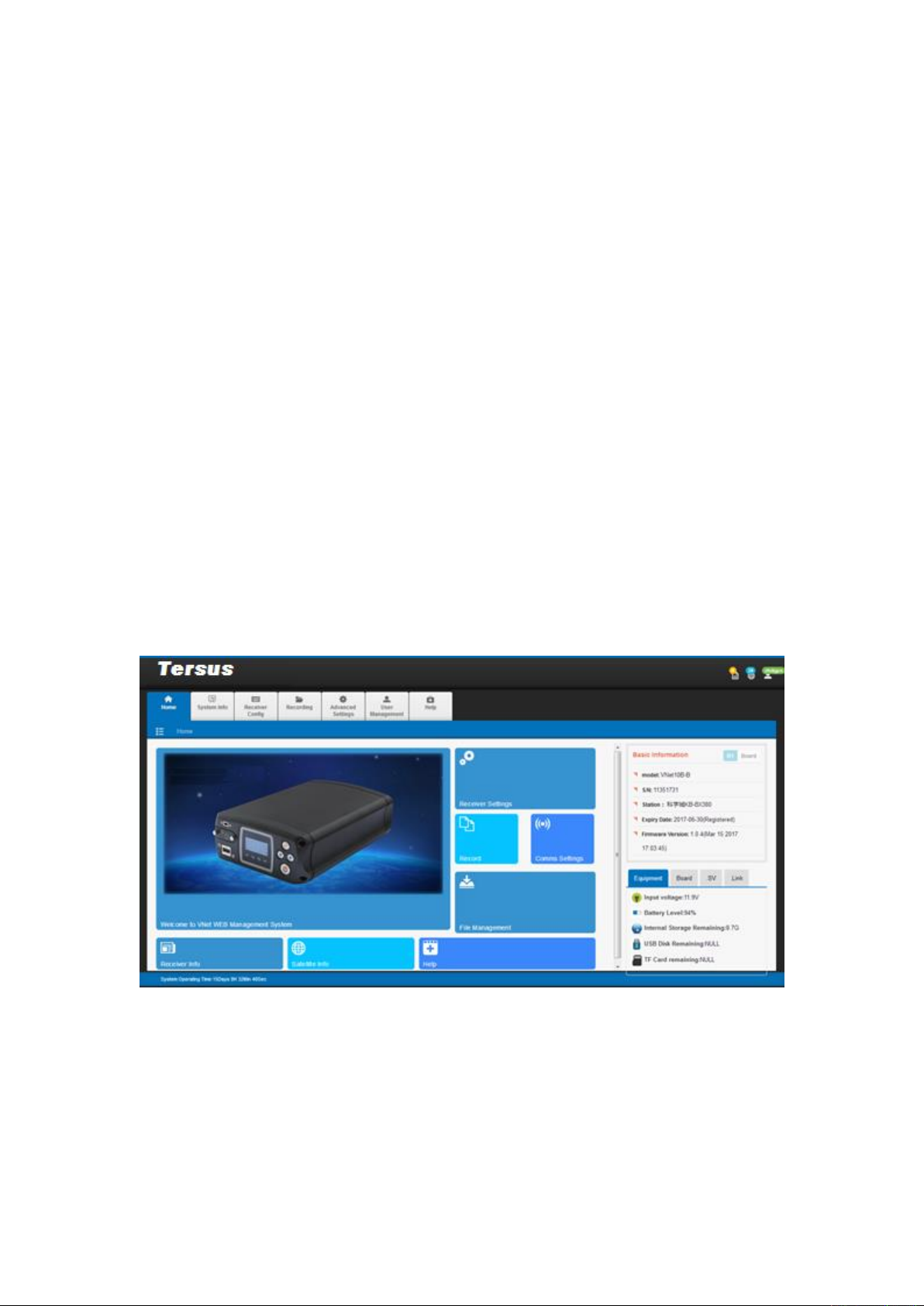
➢ Tersus logo: by clicking on it, page can directly go to main page.
➢ Navigation bar: the primary menu, consisting of status of the receiver and 7 menus.
➢ Menu: the secondary menu which makes more detailed categorizing.
➢ Display & configuration: receiver status displaying and parameters setting.
➢ Operating time: To display the time the receiver has continuously operating.
➢ Status bar: the displaying of satellite status, login account and language setting.
➢ Basic information: displaying the receiver’s model, serial number, firmware version,
registration, instrument status, motherboard info, amount of observing satellite, communication
Page 24

18
of receivers, etc.
3.3 Basic information
This sector is at the right side of the WEB page, showing the receiver’s model, S/N, firmware
version, input voltage, amount of observing satellite, communication of receivers, etc. This
information is always on the page for convenience.
Figure 17 Basic information
Page 25

19
Note: The display of satellite amount and data transmission will not be given for
an unregistered GNSS receiver or an expired registration code.
Please contact with Tersus for new code before it expires.
Status bar
At the up-right side of the WEB page, a status bar shows data recording items, number of tracking
satellites and login account. You can press the login account in the status bar to log out.
Figure 18 Status bar
3.4 Home page
This tab is comprised of welcome page, reference station configuration, data recording, online
transmission, files downloading, instrument info, satelliteview and hyperlink option. By clicking
the icon in hyperlink option sector, users can directly reach the corresponding page for further
operation.
Figure 19Main page
Page 26

20
3.5 System info
This tab contains three sub-menus: receiver info, satellite info and location map.
Receiver info
This sub-menu includes information about the equipment, the motherboard, the storage device, the
power supply and the network info, as shown in Figure 20.
Figure 20 Equipment info
In the storage device item, different storage address (internal storage, U-disk, TF card) can be
chosen by the pull-down menu. When the storage device is chosen, storage information will be
updated and displayed automatically.
Satellite info
This sub-menu shows the sky plot of satellites’ ID from all the constellation system, as well as the
Satellites’ elevation angle, azimuth, carrier-noise ratio (CNR), etc.
Page 27

21
Figure 21 Satellite info
Location map
The position of the device is shown in this sector and displayed with base map (satellite image as
default, refer to Figure 22).
Page 28

22
Figure 22 Navigation info
Under the display with a map, press the arrow key in icon to move the map, press
for zoom in/out. And 2D digital map and satellite image can be chosen with sub-menu .
3.6 Receiver config
This tab is comprised of configuration of satellite, reference station, serial ports as well as online
transmission and data recording module.
Satellite setting
Satellite system switch on/off and cut-off angle setting: [OFF] means a system is disabled, and [ON]
means this system is being used. To drag icon will change the cut-off angle. Clicking [Confirm]
to enter the parameter setting and reset to default configure by pressing[reset]. The page will be
shown as the following figure.
Figure 23 Satellite setting
Receiver setting
Page 29

23
This menu displays the positioning status, antenna parameters and working mode. The local time,
latitude/longitude, elevation, HDOP, PDOP and VDOP are displayed in present positioning status
whereas reference station configuration is categorized into antenna setting and working mode
setting.
Figure 24 Receiver setting
Antenna type, height and antenna decrement can be configured in ‘Antenna setting’.
➢ Antenna decrement; the value can be set between 5dB and 20dB according to the motherboard
model and antenna type. Here is the calculating formula below:
Antenna decrement = antenna gain- motherboard gain- coax gain
➢ Antenna type: in base mode, the right antenna type can be used to calibrate the phase centre
position.
➢ Antenna height: in base mode, height is used to calibrate measured elevation value.
The receiver can be set as a base station or a rover in operating mode menu. Other settings about
data recording, GNSS data output via serial port, network transmitted data are given in the following
table.
Table 6 reference station setting and data output
Operating
mode
Second
correction
Time tag
Raw data option
Correction option
Page 30

24
Base
off
off
Output raw data
Output correction
on
off
Output correction
Output correction
off
on
Output raw data
Output time tab
on
on
Output correction
Output time tab
Rover
-
off
Output raw data
Output GGA data
-
on
Output raw data
Output time tag
a. Base station
Base station setting contains correction data format, correction interval, ephemeris output interval,
2nd correction output and station coordinates setting & auto-acquire.
Figure 25 base station setting
Ephemeris interval; interval can be 1min, 5mins, 15mins or 30mins.
Correction data format/2nd correction output; setting as OFF (no correction data output), CMR,
RTCM(RTCM2.3), RTCMV3(RTCM3.0), RTCM32(RTCM3.2) and Rinex;
If the coordinates is input manually, the format is DD:MM:SS and the decimal of the second value is
no more than 8.
If coordinates auto-acquire is chosen, please set operating mode as rover first and then change to
base (do not submit). Then click [click to acquire] button to smooth the measured coordinates and
automatically input to the correspondingly place. Press [submit] to finish the configure.
b. rover
In rover operating mode, correction data format, ephemeris interval and GGA output are set here.
Refer to the base station setting, correction data format, ephemeris interval are identical. GGA
messages outputs by correction message channel.
Page 31

25
Figure 26 Rover setting
Note: 1. In base mode, set correction format to RTCM if RTD correction is needed.
2. Raw data cannot be recorded and transmitted if the 2nd correction is
enabled. Refer to Table 6 for more details.
Serial port setting
RS-232 and RS485 ports have the same function that can be used for GNSS data output and sensor
data input. They have the same setting method e.g. serial port baud rate, data bits, stop bits, check
bits, etc.
Figure 27 Serial port setting
The introduction below is an example to set RS-232 as sensor data input and RS485 as GNSS data
output.
External sensor: set [serial port status] to [ON]. In [Connecting Device], choose [external sensor].
Then set baud rate, data bits, stop bits and check bits according to the equipment parameters and
confirm by clicking [submit].
GNSS data output: set [port status] to [ON], In [Connecting Device], choose [GNSS Data Output]
and choose corresponding [data type], set baud rate, data bits, stop bits and check bits and confirm
Page 32

26
by clicking [submit].
Comms transmission
This menu is used to check the online transmission status, add/delete, switch on/off transmission
and revising parameters, etc.
Network transmission consists of:
1. Serial number: the order code for online transmission.
2. Utilization: showing the status of chosen online transmission (on/off).
3. Status: connecting or connected.
4. Network type: the transmission means, can be wired, Wi-Fi or 2G/3G.
5. Protocol: the network protocol, including Ntrip Client, TCP/IP Client, UDP Client, Ntrip Server,
Ntrip caster, UDP server and TCP/IP Server.
6. IP address: this receiver’s IP address.
7. Operation: can be used to edit or delete a transmission.
Figure 28 Comms transmission
Click button to add a transmission. Click [edit] to edit the transmission. The transmission
configuration page will show when a transmission is added or edited.
Encryption status: when set to ON, the data is encrypted and can only be processed with Tersus’
Page 33

27
software.
Relevant definitions in [Comms transmission setting]
Network; cable, Wi-Fi, 2G/3G are available. Please make sure the corresponding network
configuration is available with right setting while choosing this method.
Data type: NMEA-0183, correction data, raw data, RS-232 data, RS485 data. Raw data output can
set [transmission interval] to (0.05s, 0.1s, 0.2s, 0.5s, 1s, 2s, 5s, 10s, 15s, 30s, 60s).
There are 7 protocols in network setting and data type. The setting steps are related to different
protocol, examples are given below:
Ntrip Client and Ntrip Server have the same setting items; refer to Figure 29 for detail about the
parameters.
Figure 29 Ntrip Client and Ntrip Server setting
TCP/IP Client and UDP Client have the same setting items, shown as Figure 30.
Figure 30 TCP/IP Client and UDP Client setting
TCP/IP Server, UDP Server transport protocol are applied with receivers as server. In this
configuration, IP address is the receiver’s address, only port is needed.
Page 34

28
Figure 31 TCP/IP Server and UDP Server setting
Note: 1. For network transmission, different protocol cannot be set connecting to the
same server IP and port.
2. Correction data output is related to receiver’s operating mode. In Base
mode, it outputs correction message while GGA data will be output for Rover
mode.
3. When outputting data with RS-232 or RS485 port, they have to be set to
ON and connecting External Sensor.
Data logging
In the Record menu, Click to add a new data record, it is similar to the network transmission
function, and each data record can be edited/deleted.
Figure 32 Data logging
Enable the data record and then set the flag name (the file name of data file header, the default
setting is the latter 3 digits of the SN), select the record data type, we provide the original data and
Rinex two formats.
Data records can be set to a different recording interval, recording methods are recorded every day,
manual recording and planning time records, etc. When the daily record mode is enabled, record file
can also choose a file every day, every hour, every two hours. The Select the data record format as
needed. After setting, click the [Submit] button.
[Start] and [Stop] are the status of existing records.
Page 35

29
Press [Delete] to erase the record.
3.7 File management
File management is used to manage the stored file, including File list and FTP push function. It is
capable of storing, checking, downloading, deleting all data files. This page is only accessible for
Normal users and Administrator.
File lists
In this sub-menu, users can check and manage the recording files stored in different device. Those
files can be auto deleted via setting ‘Auto clean time’.
File list: checking, downloading, deleting data categorized by stored directory and date. Stored
directory can choose internal (internal storage), U-disk and TF card. Once the record date is chosen,
the page will update correspondingly.
Items contained in File list:
1. File name: the name of recorded data files.
2. Type: the data type of files, normally they are RINEX file or Original data (raw data) file.
3. Size: Disk storage space.
Figure 33 File list
Page 36

30
4. Start recording time: the time when file was created.
5. End recording time: the time when this recording stop.
6. Operation: To download or delete this data record.
The downloading function of file list can be conducted by ordinary download or FTP download,
refer to chapter 4 basic operations.
Three ways for data deleting:
Simple delete: only to delete a single file, directly clicking [Delete] button on the recording item.
Selective delete: when delete more than one file, select the ones by ticking them on the row head
then click [Delete selected]. All items can be selected by tick the header tick box.
Format: deleting all data file existing in the current storage device.
FTP push
FTP push function can send the data file recorded between 00:00 and a fixed time to a server.
Detailed configuration displayed below:
Figure 34 FTP push
Click [Submit] to apply the setting and [Reset] button will reset the setting as factory default.
FTP Switch
Anonymity Switch
User name/ Pass word
Time setting
Page 37

31
3.8 Advanced setting
The Advanced page provides advanced commands/operations for the device, including host settings,
motherboard settings, network settings and log management viewing.
Advanced pages are available to administrators only.
System Settings
System settings is composed of system settings, data download password and system control.
Figure 35 System settings
1. System settings
a. Station name settings: set the station name, the default value is "Station A". To change it, just
directly input the name and then click [submit] button.
b. UTC time zone: from there are 25 zones in total from UTC -12 to UTC + 12, the default value is
UTC +8; to change it, select the right one and click [submit].
c. Five-pin serial Trend: this five-pin serial port has been connected with the motherboard directly,
which makes it possible to obtain data from the motherboard but limited from sending command or
message. To change it, select the port and click [submit].
Note: COM1 is for NMEA data output e.g. GGA, GSV, etc.
COM2 is for correction message/time tag.
COM3 is for raw data/second correction message output.
Page 38

32
d. Power output: This function can supply power (12VDC, 5W Max) to an external equipment, you
can click [submit] to switch between on/off.
Figure 36 System settings
2. Data download password
The password is for security of local data downloading. File downloading can be done with the
buttons on the front panel. This password is composed of four digits, the default is 1234. To change
it, enter the new password and click [submit]. Clicking [Reset] and [submit], the password will be
reset back to 1234.
Figure 37 Data download password
3. System control
You can access remotely to the receiver via this web page. This page includes: restore factory
settings, restart, and reset the motherboard, upgrading firmware, receiver registration and remote
control.
a. To restore the factory settings: Click [Restore Factory Settings], the dialog box will pop up.
Click [OK] to enter the factory default configure and the receiver will restart. After the restart,
all the data and settings are erased except the wired network IP address and registration code.
b. Reboot: Receiver restart, click [restart], select [OK] in the pop-up dialog box. The receiver will
restart within 10 seconds and restart for approximately 1 minute.
Restart operations include the end of the application and restart the device two links. During this
period, the receiver stops all data recording and data transmission, etc., after the completion of the
restart the receiver automatically restore the original settings and working status (restart the data
record to re-establish the log file).
c. Reset the motherboard: the GNSS board will restore to the factory settings, click [reset
motherboard], and select [OK] in the pop-up dialog box. After reset the application restarts, the
Page 39

33
data record re-creates the log file.
d. Upgrade the firmware: Upgrade the receiver firmware, please note the file name is
"MatrixRTK_Update.bin" and it cannot be modified. Click [Upgrade Firmware] to expand the
following page, click [Browse] to select the file and click [Upload]. For details, see [Basic
Operation] → [Firmware Upgrade].
Figure 38 Upgrading the firmware
e. Receiver registration: When the registration code expires, data transfer and data logging will
stop and the number of satellites will not be displayed. Detailed Operation about the Receiver
Registration, please refer to section [Registration Receiver] in chapter 4 Basic Operation.
f. Remote control: Click [Remote control] and the following page will show:
Figure 39 Remote control
Closing remote control by shift state to [OFF] and click [Submit]
Opening remote control by shift state to [ON], choose the way of connecting, IP and port and click
[Submit].
Event settings
This section is composed of Event marker setting and PPS setting.
Page 40

34
Figure 40 Event settings
Event Marker Setting: setting Event input and External clock input.
➢ Event input: switch it on/off and trigger (Rising Edge or Falling Edge).
➢ External Clock input: to input an external clock, please make sure you have an external clock
connected before switch on and click [Submit]. The switch has to be off before disconnecting
the external clock.
Note: Enable the external clock with cautions. All operation has to follow the
instruction, or it may damage the motherboard.
PPS setting: the output frequency is per second. This tab is capable of setting PPS switch on/off,
trigger mode (Rising Edge or Falling Edge), PPS Satellite System (GPS, BDS, GLONASS),
time-tag, pulse width.
Figure 41 PPS setting
When the time-tag is ON, this data is output as correction message. If you prefer get that info from
the five-pin serial port, the [Five-pin serial trend] should be set as COM2. Pulse width can be
1000us, 5000us or 10000us.
Page 41

35
Figure 42 Event Marker Setting
Network Status and Setting
Network setting consists of wired settings, Wi-Fi Hotspot settings, Bluetooth transmission switch,
2G/3G settings, server port settings and Firewall switch.
Figure 43 Network status and settings
Wired setting: there are two ways to obtain IP address via wired connection, DHCP (automatic
detecting) and static IP (set manually). The receiver will set all parameters automatically under
DHCP mode, and all parameters have to be input manually in Static IP, such as IP address, subnet
mask, Gateway, DNS, etc. The configuration page is shown as Figure 44.
Page 42

36
Figure 44 Wired settings
Wi-Fi Hotspot Setting: several parameters can be configured in this sub-menu, including channel,
password and IP address of the receiver. The default setting for SSID and Password are SN and
‘192.168.9.1’. Users are able to visit Web administration page after connecting Wi-Fi.
Figure 45 Wi-Fi Hotspot Setting
2G/3G setting: this tab is to set 2G/3G function and settings (APN or Auto mode). Access point,
Username and Password must be input manually in APN mode, and all the fields can be set
automatically under Auto mode.
Figure 46 2G/3G Setting
Page 43

37
Log Files
System log files records all user operation during the operating time and they’re listed according to
time sequence. The content mainly contains users logging in, page switching, setting changing, data
file downloading, transmitting, deleting. As well as the network setting, restart and FW upgrading,
etc.
On the log files page, setting time zone above the table to inspect all the log files generated during
this time zone. [Delete] button is used to delete all the files shown on the form.
Fields on the list:
1. Time: the time point of record under 24-hour system.
2. User: the logged user of corresponding operation.
3. IP: the IP address of recorded user.
4. Event: recorded event.
Figure 47 Log files
3.9 User management
This menu has two sub-menus, Users and Admin.
Users
Reset the current user’s password.
Page 44

38
Figure 48 Users
Admin
This tab is authorized to administrator (Tersus_gnss) only and being allowed to add/delete normal
users only.
Adding new user: define user name and password on the User Account Management tab (user name
is must composed of numbers, letters and underline, starts with letters with the length of 5~16 digits.
The password must be 6~12 digits long). Click [Submit] to finish the creation.
Deleting user: Deleting account by clicking [Delete] button.
Page 45

39
4. Basic operations
4.1 Architecture model
GNSS receiver products can be used for ground-based augmentation systems and CORS. A weather sensor
or other sensors can be input to a receiver, which is connected to the data service center through the network
cable or cellular network. Its typical architecture is shown in Figure 49:
Figure 49 A typical architecture
4.2 Basic composition and connection
The kit includes: a GNSS receiver, a data/power cable (VS-3P), a 4G cellular antenna, a GNSS antenna cable,
a power adapter (CL-1233), an Ethernet cable. The connection is shown in Figure 50.
Page 46

40
Figure 50 Receiver connection
4.3 Connector installation
The MatrixRTK receiver has three self-locking sockets, they’re a five core socket, an external expansion
socket and a power input socket. Please ensure the red dot on cable connector is aligned with the red dot on
the receiver socket, or it cause damage to the receiver and cable connector.
Figure 51 Connector installation
GNSS Antenna cable
Ethernet Cable
Power Adapter
VS-3P cable
2G/3G antenna
DB9 port
Red dot on connector
Socket
Page 47

41
Install/uninstall the SIM/TF card
1. In the front panel, the SIM/TF card slot is protected with a metal cover, remove it with a screw driver.
2. Install the SIM/TF card: the contact of the SIM card is up, the contact of the TF card is down. When a
sound is heard, installation is successful.
3. Uninstall the SIM/TF card: push the card inward, the card will be rejected.
Figure 52 Install/uninstall the SIM/TF card
4.4 Network connection
1. LAN network connection
You can use the cable to connect the GNSS receiver with the LAN, input GNSS receiver wired network IP
address (default: 192.168.0.200) in the browser, then enter the Web management system login page.
GNSS receiver and INTERNET can be directly accessed, you can also map through the LAN external
network IP to access.
Directly access: in the local connection under the Internet protocol, click [Advanced], in the pop-up page,
input the IP address and gateway into WAN IP and gateway, as shown in Figure 53 below.
Page 48

42
The GNSS receiver base station connects to the network by mapping the external network IP. As shown in
Figure 54:
1. Change the IP of the GNSS receiver
There are two ways to change the IP address of a GNSS receiver: Manual settings and match automatically
acquire settings;
A. Manual settings
Firstly, obtain GNSS receiver's local IP, such as the default value is 192.168.0.200 (if you do not know the
receiver's IP, double-press the “power button” to open the LCD, then see the receiver IP address). Use a
network cable to connect PC and GNSS receiver, set PC IP and GNSS receiver IP in the same network
WAN IP: 202.96.185.34
Fiber optic transponders or ADSL
MODEN
GNSS receiver IP
WAN IP:202.96.185.34
Fiber optic transponders or ADSL
Router IP:192.168.1.1
Switch
GNSS receiver
IPaddress:192.168.168.1.20
Other computer's IP address:
192.168.1.101
Other computer's IP address:
Figure 53 Line connection method
Figure 54 Mapping the external network connection method
Page 49

43
segment, but different IP; such as 192.168.0.148, then the PC login and access the GNSS receiver WEB
management system using IP 192.168.0.200.
Go to [Advanced Settings] - [Network Settings] - [Cable Settings], set the GNSS receiver's IP address, subnet
mask, gateway, DNS (DNS cannot set), and Click [submit], as shown in Figure 55:
B. Match automatically acquire settings
Double-press the “power button” to open the LCD, click the "Fn button" to enter the menu options, click
"right" select [network settings], press the “power button” to enter and select [wired network], press the
“power button” to set the Receiver wired network mode to [DHCP]. The system will automatically obtain the
IP and wired network-related parameters; then press the "Fn button" to return to the status display main page
to check the IP. The GNSS receiver web management system can be accessed with this IP address.
Go to [Advanced Settings] - [Network Settings] - [Cable Settings] - [IP Acquisition Mode] - [Static IP], and
set the receiver IP address, subnet mask, gateway, DNS (DNS does not set), and click [submit], see Figure 56:
2. Mapping the external network IP
Figure 55 Set the IP address settings manually
Figure 56 Automatically obtain the IP address settings
Page 50

44
Open the page and enter the address: http: //192.168.1.1 (default IP address) pop up following dialog box (if
cannot enter the login screen, please consult network administrator).
Enter the user name and password, the general TP-LINK initial default user name: admin, password: admin.
Set the local LAN LAN port, and set the IP address as the GNSS receiver IP address.
Wi-Fi network
Wi-Fi network can be operated by LCD with button operation and WEB management system, WEB
management system also can set the Wi-Fi network password, channel and login IP address;
A. LCD display and key operation: double-press the “power button” to open the LCD display, click the "Fn
button" to enter the menu options, click the "right button" to select [network settings], press the “power
button” to enter and select [WIFI], press the “power button” to control the Wi-Fi network switch, as shown in
Figure 57:
Figure 57 LCD button operation Wi-Fi network on/off
B. WEB management system: log in WEB management system, set the [Advanced Settings] - [Network
Status and Settings] - [Wi-Fi Hotspot Settings]; shown in Figure 58
After the MatrixRTK's Wi-Fi is enabled, use a device to search the Wi-Fi SSID, then enter the password
(default: SN number). Then input the IP address of the GNSS receiver (default: 192.168.9.1). The mobile will
show the page in Figure 59 after logging in. (Account and password same with the PC side)
Figure 58 Web management system Wi-Fi settings
Page 51

45
Figure 59 Mobile device home page
4G cellular network
To do FTP push, remote control and network transmission with 4G cellular network, you need to connect the
4G antenna, install the SIM card. Go to [Advanced Settings] - [Network Status and Settings], open 2G/3G
network.
If Non-APN (green line) card is used, please select [2G/3G settings] - [Auto] and [submit], the system will
automatically dial and connect.
If APN line card is used, the users need to obtain the access point, user name and password from the network
operator, and select [APN] mode to fill in the access point, user name and password (as shown below), click
[submit], system will automatically load the data and connect the data, shown in Figure 60:
Figure 60 2G/3G network settings
Page 52

46
4.5 LCD and button operation
Table 7 LCD and button operation
Function
Operation
Content
Turn on/off the
LCD
Double-press the power
button
Displays the home page of the status information
Switch status
information
Press the left/right button
View the status information of the receiver
Switch status
and settings
display
Press the Fn button
Status and setting page loop switch
Return to the
upper
menu/Cancel
Press the Fn button
Switch the menu
Press the left/right button
Menu page: Data record, network setting, data download,
system setting;
System Settings menu page: Firmware upgrade, restore the
default IP, reset, restoring the motherboard, the language
selection; operating cycle through the menu;
Go to the menu
subordinate
Press the power button
The main menu: Data record, network setting, data
download, system setting
System Setup menu: Upgrade firmware, restore default IP,
restore factory settings, restore motherboard, language
selection;
Data record
Press the left/right button
Move options
Press the power button
Modify the record mode or confirm the settings
Network settings
Press the left/right button
Move options
Press the power button
Modify the parameter value
Data download
Press the power button
Set, move to the next step and confirm the settings
Press the left/right button
Password: left button plus 1, right minus 1; number of days:
switch the number of days options;
U disk upgrade
Press the power button
Upgrade firmware, firmware to be placed in the root
directory of U disk;
language
selection
Press the power button and
press the left/right button
Restore the
default IP;
Reset; Reset the
motherboard
Press the power button
Reset: Press the “power button” to enter the confirmation
reset prompt page, press the “power button”; Reset the
motherboard and restore the default IP the same.
Note:
1. If there is no operation for 60s, the LCD will be OFF and the indicator light will be ON.
2. Button set data record is temporary record, the record will be deleted after restart; but the data
Page 53

47
will not lost;
3. When a text or icon is surrounded by a box, it means that the text is selected, you can modify
or enter the subordinate settings;
4. If a menu has not a confirming option, it means the configure will take effect immediately
after modification, such as network settings.
4.6 Set the base station
Login WEB management page, click the Reference station settings link or Click [work mode] - [Settings] to
set;
1. Antenna settings
According to the actual parameters of the antenna information, set the antenna attenuation, antenna type, and
antenna height:
2. Base settings
Set the work mode of the reference station as [rover] and submit it; as shown in Figure 62:
Set the work mode of the reference station as [Base Station], choose [Correction Format] according to actual
needs (OFF, CMR, RTCM, RTCMV3, RTCM32, RINEX for selection), ephemeris interval is recommended
to select [every 30 minutes], enter the known latitude, longitude and elevation, and click [submit], see Figure
63:
Figure 61 Antenna settings
Figure 62 Rover setting
Page 54

48
4.7 Add data record
Log in WEB management system page, click on the data record quick link or click [work mode] - [data
record] to set.
Click the button in this page to pop up [Data Logging Settings] dialog box, enable the status dial to [ON],
set the file [Identification name] (the first four digits and the last four of the file is serial numbers added by the
system) [Data type] Select [raw data] or [Rinex] according your needs, [record interval [S]] is recommended
to 1, [record type] can be Per Day, manual and planned ways, then click[submit]. Record ways are shown
below:
Record every day (24 hours record without break up, or record a file every hour, or record a file every two
hours), as shown in Figure 64.
Figure 64 Daily Data Logging Settings
Figure 63 Base setting
Page 55

49
Configure for manual recording is shown in Figure 65.
Disposable plan records (need to input start/end time), shown in Figure 66:
4.8 Add network transmission
Log in WEB management system page, click the network transmission quick link or click [work mode] [network transmission] to set.
Click the button in this page, the [Network Transfer Settings] dialog box will pop up, put the state dial to
[ON], [Encryption state] sets according your need, [Network] Recommended [Wired] (wired, Wi- Fi,
2G/3G), [transmission protocol] sets according to your need, [data type] sets according to your needs (choose
from raw data, NMEA-0183, correction data, RS-232 serial data, RS485 serial port data), [Transmission
Figure 65 Manual data logging setting
Figure 66 Disposable plans data logging settings
Page 56

50
interval [S]] is recommend to 1, the server IP, Port, user name and other settings are related to transmission
protocol, see the specific[work mode] - [network transmission] of the [WEB management system
introduced], set as shown in Figure 67:
Note:
1. The three kinds of network modes can exist at the same time, but the IP address transmitted
to the server must be different.
2. When opening the second correction output, the [original data] turn into the second
correction.
4.9 Data download
Normal download
In the WEB management system [File Management] - [File List], select the location of the data storage and
the date of the record; pop up intraday data list, click the right side of data list [operation] - [download] then
download the corresponding data, shown in Figure 67:
Figure 67 Add network transmission
Page 57

51
FTP download
Before FTP download data, make sure the routing and LAN has opened the FTP port. In the WEB
management system [file management] - [file list], click [FTP download] button, automatically go to the FTP
download list; the home page download list shown in Figure 68:
Figure 69 FTP download directory
Click the catalog folder of the storage (select it according to the actual requirements), enter the date list, and
then click the corresponding date
FTP push
FTP push can periodically push the data file to the server. Set the parameters as shown in Figure 70:
Figure 68 Normal data download
Page 58

52
First, enable the FTP push function, set anonymous or non-anonymous user, server IP and port (data to be
pushed to FTP server IP and port), push mode (select cable, Wi-Fi or 4G) and push time, as shown above.
Push time page for quick selection of time and customization. When the first click, pop-up time check box;
you can click hour to modify hour, pop up hour selection box, select the desired hour; modify second is the
same, and finally click "OK"; finally, click [submit]. Shown in Figure 71:
U disk download
In order to protect the security of data, a password is needed (the default password is: 1234. This password
can be modified in [advanced settings] - [Data download password] )
In the LCD menu, select [Data Download], press the “power button” to enter the password input page; enter
the password, press the “power button”, then display the box into the first underlined, then the first figure of
the password can be modified, click the "right button" to plus 1, click the "left button" to minus 1. After that,
Figure 70 FTP push
Figure 71 FTP push time selection
Page 59

53
press the “power button” to modify the second password, until password input completely, press the “power
button” to enter the download page.
Press the “power button” to the download days selection, click the left/right button to change the number of
days, press the “power button” to comfirm, then press the “power button” to download (before U disk data
downloading, make sure an U disk has been properly installed, or "no U disk" will be prompted). After the
download is done, the LCD shows "Download Complete";
Note:
1.When downloading the Rinex file data, you need to download *.17p and *.17o files to
the same folder, or the solution will be abnormal;
2.In FTP server local (internal memory) folder, the folder named by date is for the
receiver to collect the raw data and Rinex data; log is the system log folder; mail folder is the
mailbox receive the corresponding file; lost + found Folder is the system folder;
3.Prohibit of use download tools to download.
4.Download time is related to the size of file and your network's connection speed,
please be patient. When downloading, you can close the page and browser, do not disconnect
the network or reboot the device.
4.10 Firmware upgrade
Web page upgrade firmware
In the WEB management system select [advanced settings] - [Host settings] - [System control] click
[Upgrade the firmware] Expand the dialog box, as shown in Figure 72.
Note:
1. Update the firmware with file MatrixRTK_Update.bin. Please don’t modify this file
name, or firmware upgrade will fail;
2. Upload firmware package, please do not close the browser, or firmware upgrade the
will fail.
3. The time of firmware upgrade is related to your computer, generally is about 10 seconds.
U disk upgrade firmware
Firstly, copy the firmware file MatrixRTK_Update.bin to the U disk root directory, and then insert the U disk
into the UAB-A port at the front panel of the receiver; as shown in:
Figure 72 Firmware upgrade
Page 60

54
Figure 73 U disk installation diagram
In the LCD menu, go to [System settings] - [Upgrade the firmware], press "Power button", Pop-up prompt
box". Please confirm the insertion of U disk" after confirmation, press the “power button” prompt sending
successfully (if U disk is not inserted identify as error, it will prompt "no U disk" and return to [upgrade
firmware] selection page) about 1 minute later, the receiver restart after the firmware upgrade is successful.
4.11 Register the receiver
In the WEB management system, select [advanced settings] - [Host settings] - [System control] - [Receiver
registration] to expand the dialog box as shown in Figure 74.
The receiver license format is 24 digits, divided into 8 groups, each group contains 3 digits. Enter the
registration code (the system will ignore blanks of the registration code while entering), confirm and click
[submit].
Figure 74 Receiver registration
Page 61

55
Appendix
Reset
Major items
Content
The parameters after recovery
Reference station
UTC Time zone
UTC+8
Antenna attenuation [dB]
5
Antenna type
AT -1200B
Antenna high [m]
0
Reference station work
mode
Rover
Ephemeris interval
Every 30min
Correction data format
RTCMV3
Satellite system
All open
Height cutoff angle
10°
Storage device
Internal storage
Receiver function
4G internet
OFF
RS-232/RS485 Serial port
OFF
Server port settings
80
Firewall
OFF
Time input
OFF
External clock input
OFF
PPS output
OFF
FTP Push
OFF
User
Only retain administrator privileges, and restore the
default password
Automatic cleaning time
after full
1 day
Small five-core serial port
pointing
Motherboard 1COM2
Power output
OFF
Network transmission
Delete all
Data management
Data record
Delete all
Internal data
Delete all
Log management
Delete all
Page 62

56
MatrixRTK technical performance parameters table
GNSS features
Constellations
GPS: L1, L2, L5
GLONASS: G1, G2
BDS: B1, B2, B3
Galileo: L1BOC, E5a, E5b, E5AltBOC
SBAS: L1 C/A, L5
Accuracy
RTK horizontal accuracy: (8mm + 1X10-6D)
RTK vertical accuracy: (15mm + 1X10-6D)
Static horizontal accuracy: (2.5mm + 1X10-6D)
Static vertical accuracy: (5mm + 1X10-6D)
Initialization
time
Typical <10S
Initialization
reliability
>99.9%
Ports
3 RS232 port
1 USB port
1 Wi-Fi, Bluetooth communication port
1 3G/2G Communication port
1 RS485/RS422 port
1 Ethernet interface
1 PPS Output Interface
Internal storage
64GB
External storage
Maximum support 1TB
Correction format
CMR,RTCM2.x, RTCM3.0 and RTCM3.2
Interaction
Web management system
LCD, indicator, button
Battery
External power: 7V – 36VDC
Build-in battery: 24h continuous work (depend to configure)
Power consumption: <5W
Environmental
Operating temperature
-40C – 75C
Storage temperature
-40C – 80C
Relative humidity
100%
Protection class
IP67
Anti-corrosion
GJB150.11
Vibration
GJB 1032
Shock
JB/T 9329 30g 3 times/axis
Bump
JB/T 9329 10g 1000 times
Drop
GB-T 2423.8 protect from 1
meter’s drop
Page 63

57
Standard configuration table
Item Name
Number
GNSS Receiver
1
Power Adapter
1
AC power cord
1
Data cable
1
Direct cable
1
Ground reinforcement system product manual
1
Aluminum lugs
3
Cross plate head machine wire [M3*6]
3
Warranty Card
1
Factory inspection certificate
1
 Loading...
Loading...