Terrasat IBUC 2s, IBUC 2 User Manual

IBUC 2
Intelligent Block Upconverter
User Guide
24-Hour Technical Support: +1 408.782.2166

This document is provided to customers who have purchased Terrasat Communications, Inc.
equipment. This document is copyright protected and no part of this manual may be reproduced,
transcribed, or translated into any language or transmitted in any form whatsoever without the
prior written consent of Terrasat Communications, Inc.
Technical information contained in this publication is for reference purposes only and is subject
to change without notice. Every effort has been made to supply complete and accurate
information; however, Terrasat Communications, Inc. assumes no responsibility and will not be
liable for any errors, omissions, damage, or loss that might result from any use of this manual or
the information contained therein (even if this information is properly followed and problems still
arise).
© February 2013 Terrasat Communications, Inc.
Part Number: O&M-22062-0001
Revision: B
235 Vineyard Court Phone: +1 408.782.5911
Morgan Hill, CA 95037 FAX: +1 408.782.5912
www.terrasatinc.com

i
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Preface
Conventions and References .................................................................................................... P-1
Cautions and Warnings ..................................................................................................... P-2
Trademarks........................................................................................................................ P-2
Electrical Safety Notice ....................................................................................................P-2
Chapter 1, Introduction
Block Upconverters.................................................................................................................. 1-1
Reference Documents ..............................................................................................................1-2
Warranty Information............................................................................................................... 1-4
Export Regulations................................................................................................................... 1-5
Chapter 2, Functional Description
Introduction .............................................................................................................................. 2-1
System Components................................................................................................................. 2-1
DC Supply............................................................................................................................ 2-4
AC Supply............................................................................................................................ 2-5
Fuses..................................................................................................................................... 2-6
Monitor and Control............................................................................................................. 2-7
RF Signal Flow .................................................................................................................... 2-8
Software ............................................................................................................................... 2-12
System Configurations......................................................................................................... 2-13
Storage Information ............................................................................................................. 2-18
Chapter 3, Monitor and Control Features
Introduction .............................................................................................................................. 3-1
M&C Interfaces........................................................................................................................ 3-1
RS232................................................................................................................................... 3-1
Hand-held Terminal ............................................................................................................. 3-2
Multifunction LED............................................................................................................... 3-4
Frequency Shift Keying (FSK) Modem Interface................................................................ 3-5
RS485................................................................................................................................... 3-6
ASCII Mode...................................................................................................................... 3-6
Legacy Binary Mode......................................................................................................... 3-8
Ethernet ................................................................................................................................ 3-9
Determining the IP Address of Your IBUC 2................................................................... 3-9
Telnet ................................................................................................................................3-14
Web Server........................................................................................................................ 3-14
SNMP................................................................................................................................ 3-14
Power Measurement................................................................................................................. 3-16

ii
Chapter 4, Installation
Introduction .............................................................................................................................. 4-1
General Requirements .............................................................................................................. 4-1
Unpacking ......................................................................................................................... 4-1
Furnished Items................................................................................................................. 4-2
Accessories........................................................................................................................ 4-3
Installing the ODU ............................................................................................................... 4-4
Tools and Test Equipment ................................................................................................4-4
Site Considerations............................................................................................................ 4-4
Mounting Considerations.................................................................................................. 4-4
Power Requirements ......................................................................................................... 4-5
Grounding .........................................................................................................................4-6
Antenna Recommendations ..............................................................................................4-7
Antenna Mounting ............................................................................................................4-8
System Pressurization ....................................................................................................... 4-12
System Cabling Requirements .......................................................................................... 4-13
Cable and Waveguide Connections ..................................................................................4-16
Basic System Alignment...................................................................................................... 4-21
Test Equipment ................................................................................................................. 4-21
Setting the Tx and Rx Frequencies ................................................................................... 4-21
Transmit Power Alignment............................................................................................... 4-22
Final Checks............................................................................................................................. 4-24
Chapter 5, Operations
Introduction .............................................................................................................................. 5-1
Start-up Checklist..................................................................................................................... 5-1
Turning On the IBUC 2........................................................................................................ 5-2
Setting Operating Parameters............................................................................................... 5-2
Setting the Tx Frequency (L-band)................................................................................... 5-4
Setting Alarm Thresholds .................................................................................................5-4
Configuring Alarm States .................................................................................................5-5
Configuring ALC/AGC..................................................................................................... 5-5
Configuring the External Mute ......................................................................................... 5-6
Common Errors ........................................................................................................................ 5-7
LED is Red........................................................................................................................ 5-7
No Power to the IBUC 2 ................................................................................................... 5-7
Time Stamp Data is Incorrect ...........................................................................................5-8
Satellite Network Operations Center Doesn’t Recognize Signal...................................... 5-8
Transmit Power in Saturation............................................................................................5-9
Tx Input/Output Level Verification .................................................................................. 5-9
Chapter 6, Troubleshooting
Maintenance ............................................................................................................................. 6-1
Transceiver Fault Isolation................................................................................................... 6-1
AC Power Problems/Conditioning.................................................................................... 6-1

iii
Site-Related Problems .......................................................................................................6-2
M&C Checks .....................................................................................................................6-2
Power Supply Checks........................................................................................................6-3
Transmit Power Setting .....................................................................................................6-3
Common Problems ...............................................................................................................6-5
Tx Output is Disabled........................................................................................................6-5
Incorrect Frequency Settings .............................................................................................6-5
Damaged Cables ................................................................................................................6-5
10 MHz Reference Signal at the IBUC 2 is at the Wrong Level or Missing ....................6-5
Antenna is Pointed Toward Wrong Satellite or is Misaligned ..........................................6-6
Moisture Migrated Into the IBUC 2 ..................................................................................6-6
Bad Orthogonal Mode Transducer and/or Antenna ..........................................................6-7
LED is Red ........................................................................................................................6-7
Repair Policy.............................................................................................................................6-8
Returned Material Authorization (RMA) .............................................................................6-8
Appendix A, Part Numbering Schema
Identifying the Part and Serial Numbers...................................................................................A-1
Appendix B, Using HyperTerminal
Establishing a HyperTerminal Session .....................................................................................B-1
Using a Saved Connection........................................................................................................B-7
Ending a HyperTerminal Session .............................................................................................B-8
Appendix C, IBUC 2 Web Pages
Introduction...............................................................................................................................C-1
Screen Shots..............................................................................................................................C-5
Login..................................................................................................................................C-5
Information Tab.................................................................................................................C-6
Alarm Tab..........................................................................................................................C-8
Sensor Tab .........................................................................................................................C-11
Transmit Configuration Tab ..............................................................................................C-13
Interface Configuration Tab ..............................................................................................C-18
System Configuration Tab.................................................................................................C-21
Alarm Configuration Tab ..................................................................................................C-23
Redundancy Configuration Tab.........................................................................................C-26
Alarm Log Tab ..................................................................................................................C-28
Appendix D, IBUC 2 Hand-held Terminal Menu Tree
Menu Options ...........................................................................................................................D-1
Info & Sensors ...................................................................................................................D-4
Tx.......................................................................................................................................D-4
Alarm .................................................................................................................................D-5
Tx Thresholds ....................................................................................................................D-5
Interface .............................................................................................................................D-5

iv
SNMP................................................................................................................................ D-6
System............................................................................................................................... D-6
Redundancy....................................................................................................................... D-6
Appendix E, Legacy Binary Command Message Structure
Command Set ........................................................................................................................... E-1
Legacy Response Message Structure ....................................................................................... E-3
Data Field Definitions.......................................................................................................... E-5
Appendix F, ASCII Command/Response Structure
Command Set ........................................................................................................................... F-1
Common Commands............................................................................................................ F-4
Receive-only Commands ..................................................................................................... F-19
Transmit-only Commands.................................................................................................... F-26
Redundancy Commands....................................................................................................... F-42
Appendix G, Component Specifications and Reference Drawings
Reference Drawings ................................................................................................................. G-1
Data Sheets............................................................................................................................... G-10
Appendix H, Glossary
Glossary of Terms .................................................................................................................... H-1
Index

v
LIST OF TABLES
Table P.1 Typographical Conventions ........................................................................................ P-1
Table 1.1 Satellite Operation Standards...................................................................................... 1-2
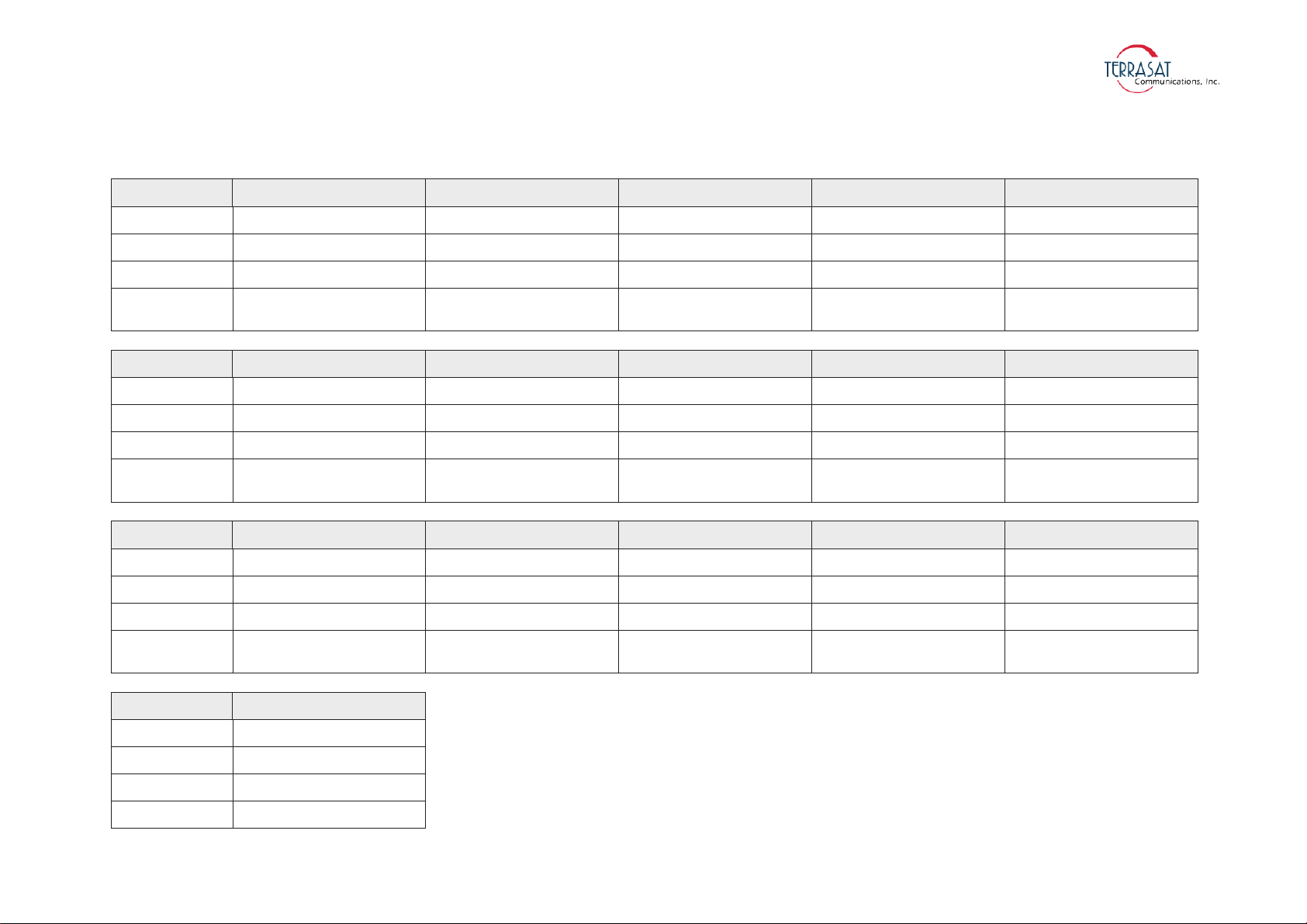
Table 2.1 IBUC 2 Transmit Frequency Plans ............................................................................. 2-3
Table 2.2 AC Supply Operating Voltage Ranges ....................................................................... 2-5
Table 2.3 Fuse Markings............................................................................................................. 2-6
Table 2.4 Fuse Markings Explained ........................................................................................... 2-7
Table 2.5 Internal 10 MHz Reference Signal Parameters........................................................... 2-8
Table 2.6 Basic System Requirements........................................................................................ 2-13
Table 3.1 Default Alarm Configuration...................................................................................... 3-4
Table 3.2 Transmitter Link Specifications.................................................................................. 3-5
Table 3.3 Receiver Link Specifications ......................................................................................3-5
Table 3.4 ASCII Mode Command Format.................................................................................. 3-7
Table 3.5 Packet Format ............................................................................................................. 3-8
Table 3.6 IBUC 2 Data Packet Byte Configuration .................................................................... 3-8
Table 4.1 IBUC 2 Interface Connector Schedule........................................................................4-13
Table 4.2 Pin Assignments for IBUC 2 M&C Connector J2 ...................................................... 4-14
Table 4.3 Pin Assignments for IBUC 2 DC Power Connector J3 .............................................. 4-15
Table 4.4 Pin Assignments for IBUC 2 AC Power Connector J3 .............................................. 4-16
Table 4.5 Pin Assigments for IBUC 2 Ethernet Connector J4.................................................... 4-16
Table 4.6 Recommended Test Equipment ..................................................................................4-21
Table 6.1 Possible Scenarios for IBUC 2s with an External 10 MHz Reference Signal ............ 6-6
Table C.1 Default Values for Power Monitor Frequency............................................................ C-14
Table C.2 Default Values for the Burst Threshold ...................................................................... C-15
Table E.1 IBUC 2 Commands..................................................................................................... E-1
Table E.2 Response to IBUC 2 Commands 0x01, 0x02, 0x03, 0x04, 0x08, and 0xFF ..............E-3
Table E.3 Response to IBUC 2 Commands 0x05 and 0x06 !
(When Data Byte 1 of Command Message = 0x00) ................................................... E-3
Table E.4 Response to IBUC 2 Command 0x06 !
(When Data Byte 1 of Command Message = 0x01) ................................................... E-4
Table E.5 Response to IBUC 2 Command 0x07 ......................................................................... E-4
Table E.6 Response to IBUC 2 Command 0x09 ......................................................................... E-5
Table E.7 Data Field Definitions ................................................................................................. E-5
Table F.1 Alarm Mask ................................................................................................................F-1
Table F.2 Alarm Flags................................................................................................................. F-2
Table F.3 Error Response Table.................................................................................................. F-3
Table F.4 Default Values for the TAH, TAL, and TBT Commands ..........................................F-32
Table F.5 Default Values for the TFR Command....................................................................... F-36

vi
This page intentionally left blank
for double-sided printing.

vii
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 2.1 Front Panel of a DC-powered IBUC 2....................................................................... 2-4
Figure 2.2 Front Panel of an AC-powered IBUC 2..................................................................... 2-5
Figure 2.3 IBUC 2 Block Diagram (for DC-powered systems).................................................. 2-10
Figure 2.4 IBUC 2 Block Diagram (for AC-powered systems).................................................. 2-11
Figure 2.5 DC Power System Configuration............................................................................... 2-15
Figure 2.6 DC Power System Configuration with IFU ............................................................... 2-16
Figure 2.7 AC Power System Configuration............................................................................... 2-17
Figure 3.1 IBUC 2 Hand-held Terminal...................................................................................... 3-3
Figure 3.2 Location of Downloads on Terrasat Website............................................................. 3-10
Figure 3.3 Download Instructions for .zip File ........................................................................... 3-11
Figure 3.4 Contents of the IBUCUpgrade_v122 .zip File........................................................... 3-11
Figure 3.5 Extracting the .zip Files ............................................................................................. 3-12
Figure 3.6 Security Warning Dialog Box.................................................................................... 3-12
Figure 3.7 Results Window ......................................................................................................... 3-13
Figure 3.8 Blank Results Window .............................................................................................. 3-13
Figure 4.1 Contents of IBUC 2 Shipping Carton ........................................................................ 4-3
Figure 4.2 IBUC 2 Field Installation........................................................................................... 4-9
Figure 4.3 IBUC 2 Installation .................................................................................................... 4-10
Figure 4.4 Location of Mounting Holes...................................................................................... 4-11
Figure 4.5 Location of Adjustment Slots on Optional Mounting Bracket .................................. 4-12
Figure 4.6 Applying the Anti-Seize Lubricant............................................................................ 4-18
Figure 4.7 Waveguide Label and Channel for Gasket ................................................................ 4-19
Figure A.1 Identifying the Part and Serial Numbers.................................................................... A-1
Figure A.2 Part Numbering Schema for IBUC 2s and IBRs ....................................................... A-2
Figure A.3 Part Numbering Schema for IBUCs .......................................................................... A-3
Figure A.4 Part Numbering Schema for Transmit Redundant (Tx 1+1) Systems....................... A-4
Figure A.5 Part Numbering Schema for Receive Redundant (Rx 1+1) Systems ........................ A-5
Figure A.6 Part Numbering Schema for IBUC with PSUI Systems............................................ A-6
Figure A.7 Part Numbering Schema for IFU Systems................................................................. A-7
Figure A.8 Part Numbering Schema for LNBs............................................................................ A-8
Figure A.9 Part Numbering Schema for SSPAs .......................................................................... A-9
Figure A.10 Part Numbering Schema for Redundant SSPA 1+1 Systems.................................... A-10
Figure B.1 New Connection Description Window ...................................................................... B-2
Figure B.2 Connect To Window .................................................................................................. B-3
Figure B.3 COM1 Properties Window ........................................................................................ B-4
Figure B.4 Invalid Password Error Message................................................................................ B-5
Figure B.5 ASCII Setup Window ................................................................................................ B-5
Figure B.6 Invalid Value Error Message ..................................................................................... B-6
Figure B.7 Active HyperTerminal Window................................................................................. B-7
Figure C.1 Choosing Network Connections ................................................................................ C-2

viii
Figure C.2 Choosing the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties.................................................. C-2
Figure C.3 Typing the IP Address................................................................................................ C-3
Figure C.4 Invalid Subnet Mask Error Message.......................................................................... C-4
Figure C.5 Login.......................................................................................................................... C-5
Figure C.6 Information Tab ......................................................................................................... C-6
Figure C.7 Alarm Status Tab ....................................................................................................... C-8
Figure C.8 Sensor Tab ................................................................................................................. C-11
Figure C.9 Tx Configuration Tab ................................................................................................ C-13
Figure C.10 Interface Configuration Tab....................................................................................... C-18
Figure C.11 System Configuration Tab ......................................................................................... C-21
Figure C.12 Alarm Configuration Tab........................................................................................... C-23
Figure C.13 Redundancy Configuration Tab................................................................................. C-26
Figure C.14 Alarm Log Tab........................................................................................................... C-28
Figure D.1 Sample IBUC 2 HHT Display.................................................................................... D-2
Figure D.2 Sample IBUC 2 Info & Sensors Window .................................................................. D-2
Figure D.3 IBUC 2 Hand-held Terminal Menu Tree................................................................... D-3
Figure G.1 Fabrication Drawing, FBD-21012-XXXX, Rev A.................................................... G-2
Figure G.2 Fabrication Drawing, FBD-21984-XXXX, Rev B, page 1 of 2 ................................ G-3
Figure G.3 Fabrication Drawing, FBD-21984-XXXX, Rev B, page 2 of 2 ................................ G-4
Figure G.4 Fabrication Drawing, FBD-20351-0001, Rev A ....................................................... G-5
Figure G.5 Fabrication Drawing, FBD-20606-XXXX, Rev A.................................................... G-6
Figure G.6 Example Installation Drawing for Antenna Mounting, 339-44001-XXXX, !
Rev A, page 1 of 2 ..................................................................................................... G-7
Figure G.7 Example Installation Drawing for Antenna Mounting, 339-44001-XXXX, !
Rev A, page 2 of 2 ..................................................................................................... G-8
Figure G.8 Example Installation Drawing, IND-10521-0011, Rev A ......................................... G-9

ix
REVISION HISTORY
Revision Date Description
A February 2013 Initial Release
B February 2013
• Corrected values for the TFB command in
Appendix F
• Updated information about transmit frequency plans in Table 2.1

x
This page intentionally left blank
for double-sided printing.

P R E F A C E
This manual provides information about the Terrasat Communications, Inc. line of
intelligent block upconverters (IBUC 2s) and transmit redundant systems.
Conventions and References
Before you start using this manual, it is important to understand the typographical
conventions and terms used in the documentation.
Table P.1 describes typographical conventions used in Terrasat Communications, Inc.
documentation. For definitions of specialized terms used in the documentation, see
Appendix H, Glossary.
Table P.1
Typographical Conventions
Convention Description/Example
Emphasis
Used to emphasize the importance of a point.
The IP Address must be
a unique number.
Internal cross-references
References to a section in the same document are marked in blue and
are hype
rlinked.
See
Warranty Information on page 1-4.
Product and feature
na
mes
Named Terrasat products and features are identified on first use.
...line of intelligent block upconverters (IBUCs).
Technical Publication
Re
ferences
References to other Terrasat publications. If the reference is hyperlinked,
it is also underscored.
For detailed information, see the Terrasat Communications, Inc. IBUC
Operations Manual.
User-entered values
A special font marks text that you type.
At the password prompt, type
MyPassword.

P-2 | Preface
Cautions and Warnings
Trademarks
Other product names mentioned in this manual may be trademarks or registered
trademarks of their respective companies and are hereby acknowledged.
Electrical Safety Notice
This equipment has been designed to minimize exposure of personnel to hazards. All
operators and technicians must
• Know how to work around, with, and on high-voltage equipment.
• Exercise every precaution to ensure safety of personnel.
• Exercise extreme care when working near high voltages.
• Be familiar with the warnings in this manual.
CAUTION
CAUTION indicates a hazardous situation
that, if not avoided, could result in minor or
moderate injury. CAUTION might also be
used to indicate other unsafe practices or
risks of property damage.
HIGH VOLTAGE
HIGH VOLTAGE indicates the presence of a
high-voltage hazard.
WARNING
WARNING indicates a potentially
hazardous situation that, if not avoided,
could result in death or serious injury.

Block Upconverters | 1-1
C H A P T E R
C
HAPTER
1
I
NTRODUCTION
This manual is intended for users of Terrasat Communications, Inc. IBUC 2 systems.
It contains information about
• Installation, operation, and maintenance of IBUC 2 systems
• User of user interface protocols for remote monitor and control capabilities
Block Upconverters
The term “intelligent” block upconverter refers to the advanced features and monitor
and control capabilities of the IBUC 2 product. The IBUC 2 includes automatic gain
control (AGC) and automatic level control (ALC) features as well as internal
diagnostics. It also provides extensive monitoring and control through a menu of
software commands and alarms providing access to the numerous operating
parameters and features available in the unit. Access to features and monitor and
control (M&C) functions is provided via several methods including a hand-held
terminal, RS232, RS485, TCP/IP (Telnet, HTTP), UDP (SNMP) and FSK (frequency
shift keying) link via the IFL cable. The IBUC 2 is also fitted with a multifunction
LED for visual status indications.
1-2 | Introduction
Reference Documents
Use the satellite operation standards listed in Table 1.1 as reference documents.
Table 1.1
Satellite Operation Standards
Earth Station Standards
Intelsat IESS 308/309
Performance Characteristics for Intermediate Data Rate Digital
Carriers Usin
g Convolutional Encoding and QPSK Modulation
Eutelsat EESS 502
Minimum Technical and Operational Requirements for Earth Stations
Tran
smitting to a Eutelsat Transponder for Non-Standard Structured
Types of SMS Transmissions. Standard M.
ETS 300-332
Satellite Earth Stations (SES); Tran
smit-only or transmit-and-receive
very small aperture terminals (VSATs) used for communications
operating in the fixed satellite service (FSS) 6 GHz and 4 GHz
frequency bands.
ETS 300-159
Satellite Earth Stations (SES); Transmit/receive very small aperture
terminals (VSATs) used for data communications operating in the
fixed satellite service (FFS) 11/12/14 GHz frequency bands.
ETS 300-160
Satellite Earth Stations (SES); Control and monitoring functions for
very small aperture terminals (VSAT)
networks.
ETSI EN 301 427
Satellite Earth Stations
and Systems (SES); Harmonized EN for Low
Data Rate Mobile Satellite Earth Stations (MESs) except aeronautical
mobile satellite earth stations, operating in the 11/12/14 GHz
frequency bands covering essential requirements under article 3.2 of
the Radio & Telecommunications Terminal Equipment (R&TTE)
directive
ETSI EN 301 428
Satellite Earth Stations and Systems (SE
S); Harmonized EN for Very
Small Aperture Terminal (VSAT); Transmit-only, transmit/receive or
receive-only satellite earth stations operating in the 11/12/14 GHz
frequency bands covering essential requirements under article 3.2 of
the Radio & Telecommunications Terminal Equipment (R&TTE)
Directive.
ETSI EN 301 430
Satellite Earth Stations and
Systems (SES); Harmonized EN for
Satellite News Gathering Transportable Earth Stations (SNG TES)
operating in the 11-12/13-14 GHz frequency bands covering essential
requirements under article 3.2 of the R&TTE directive
ETSI EN 301 443
Satellite Earth Stations and Systems (SES); Harmonized EN for Very
Small Aperture Terminal (VSAT); Transmit-only, transmit/receive, or
receive-only satellite earth stations operating in the 4 GHz and 6 GHz
frequency bands covering essential requirements under article 3.2 of
the R&TTE Directive.
MIL-STD-188-164A!
with Change 3
Interoperability of SHF Satellite Communications Terminals for
ta
ctical and long-haul communications.
MIL-STD 810F
Materiel acquisition program planning and engineering direction for
consid
ering the influences that environmental stresses have on
materiel throughout all phases of its service life.
ANSI/TIA/EIA 568 Commercial Building Telecommunications Cabling Standard
Reference Documents | 1-3
ETS 300 019-1-1
Equipment Engineering (EE): Environmental Conditions and
Environmental Tests for Telecommunications Equipment. Part 1-1:
Classification of environmental conditions. Storage.
Environmental Standards
ETS 300 019-1-2
Equipment Engineering (EE): Environmental Conditions and
Environmental Tests for Telecommunications Equipment. Part 1-2:
Classification of environmental conditions. Transportation.
ETS 300 019-1-4
Equipment Engineering (EE): Environmen
tal Conditions and
Environmental Tests for Telecommunications Equipment. Part 1-4:
Classification of environmental conditions. Stationary use at nonweather protected locations.
ETS 300 019-2-1
Equipment Engineering (EE): Environmental Conditions and
Environmental Tests for Telecommunications Equipment. Part 2-1:
Specification of environmental tests; Storage
ETS 300 019-2-2
Equipment Engineering (EE): Environmental Conditions and
Environmental Tests for Telecommunications Equipment. Part 2.2:
Specification of environmental tests; Transportation
ETS 300 019-2-4
Equipment Engineering (EE): Environmental Conditions and
Environmental Tests for Telecommunications Equipment. Part 2-4:
Specification of environmental tests; Stationary use at non-weather
protected locations
EMC/EMI Standards
99/5/EEC
The Radio and Telecommunications Terminal Equipment Directive
(R&TTE)
ETSI EN 301 489-1 v1.8.1
Electromagnetic Compatibility and Radio Spectrum Ma
tters (ERM);
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) standard for radio equipment
and services; Part 1: Common technical requirements
ETSI EN 301 489-12 v2.2.2
Electromagnetic Compatibility and Radio Spectrum Ma
tters (ERM);
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) standard for radio equipment
and services; Part 12: Specific conditions for Very Small Aperture
Terminal, Satellite Interactive Earth Stations operated in the
frequency ranges from 4 GHz through 30 GHz in the Fixed Satellite
Services (FSS)
EN 55022A
Information Technology Equipment – Radio Disturbance
Ch
aracteristics – Limits and methods of measurement
EN 61000-3-2
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) – Part 3.2: Limits
for harmonic
current emissions (equipment input current < 16 A per phase)
EN 61000-3-3
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) – Part 3.3: Limitation
of voltage
changes, voltage fluctuations, and flicker in public low-voltage supply
systems for equipment with rated current ! 16 A per phase and not
subject to conditional connection
EN 61000-4-2
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) – Part 4-2: Testing and
measurement techniques – Electrostatic discharge immunity test
EN 61000-4-3
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) – Part 4-3
: Testing and
measurement techniques – Radiated, radio-frequency,
electromagnetic field immunity test
Table 1.1
Satellite Operation Standards (Continued)
1-4 | Introduction
Warranty Information
Determination of warranty status of equipment shall be in accordance with the
following Terrasat Communications, Inc. Warranty Policy.
(A) This warranty is for equipment of Terrasat Communications, Inc. The term
“Terrasat” as used throughout this warranty shall mean Terrasat Communications,
Inc., if the equipment was manufactured by Terrasat Communications, Inc.
(B) Terrasat warrants that its equipment shall be free from defects in material or
workmanship at the time of shipment and that it will conform to applicable
specifications.
For all Satcom products, the buyer shall exercise any and all warranty claims within a
period of twenty-four (24) months.
(1) The warranty does not apply to any part of a product if it has been altered,
repaired, or misused in any way that, in the opinion of Terrasat, affects the
reliability of, or detracts from the performance of any part of the product, or it is
damaged as a result of the use of such part in or in connection with equipment not
previously approved by Terrasat.
(2) The warranty does not apply to any product or parts thereof if its serial number
or the serial number of any of its parts has been altered, defaced, or removed.
(3) The warranty does not cover damages or losses incurred in transport.
EN 61000-4-4
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) – Part 4-4: Testing and
measurement techniques – Electrical fast transient/burst immunity
test
EMC/EMI Standards
EN 61000-4-5
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) –
Part 4-5: Testing and
measurement techniques – Surge immunity test
EN 61000-4-6
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) – Part 4-6: Testing and
measurement techniques – Immunity to conducted disturbances,
induced by radio-frequency fields
EN 61000-4-11
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) – Part 4-11: Testing and
measurement techniques – Voltage dips, short interruptions, and
voltage variations immunity tests
Safety Standards
2006/95/EC The Low Voltage Directive (supersedes 73/23/EEC)
EN 60950-1
Information technology equipment – Safety as applied to
mains-po
wered or battery-powered information technology
equipment, including electrical business equipment and associated
equipment, with a rated voltage not exceeding 600 V.
Table 1.1
Satellite Operation Standards (Continued)

Export Regulations | 1-5
(4) The warranty does not cover replacement or repair necessitated by loss or
damage resulting from cases beyond the control of Terrasat.
(5) The warranty does not include the furnishing of any labor involved or
connected with the removal and/or reinstallation of warranted equipment or parts
on site, or any labor required to diagnose the necessity for replacement or repair.
(6) In no event shall Terrasat be liable to buyer for any indirect, special, or
consequential damages or lost profits arising from the use of the equipment or
products, even if Terrasat has been advised of the possibility thereof, or for any
inability to use them either separated from or in combination with any other
equipment or products.
(C) Terrasat’s warranty, as stated herein, is in lieu of all other warranties, expressed,
implied or statutory, including those of merchantability and fitness for a particular
purpose, and Terrasat neither assumes nor authorizes any person to assume for it any
other obligation or liability to any person in connection with the sale or use of
Terrasat’s products. The buyer shall pass on to any purchaser, lessee, or other user of
Terrasat’s products, the aforementioned warranty and shall indemnify and hold upon
allegations that the buyer, its agents, or employees have made additional warranties or
representations as to product preference or use.
(D) A fixed charge established for each product will be imposed for all equipment
returned for warranty repair and where the cause of failure cannot be identified by
Terrasat.
Note:
Warranty seals are designed to break upon internal access. Access to the internal
electronic components without prior written approval will void the warranty.
For more information about returning a product for repair, see
Repair Policy on
page 6-8.
Export Regulations
Under the Arms Export Control Act (AECA), 22 U.S.C. § 2778 (1994), the United
States Department of State, Directorate of Defense Trade Controls (DDTC),
implements the International Traffic In Arm Regulations (ITAR), 22 C.F.R.
§§ 120-130, which control the export of defense articles and services from the United
States to foreign destinations and persons.
Terrasat X-band IBUC products are subject to ITAR regulations administered by the
U.S. State Department. Section 121.1 of the ITAR is the United States Munitions List
(USML) and includes the commodities, related technical data, and defense services
controlled for export purposes. The X-band IBUC is classified as USML Category
XI(a)(5) “Command, control and communications systems to include radios
(transceivers), navigation, and identification equipment.” As indicated in the ITAR,

1-6 | Introduction
items in this category are also designated “Significant Military Equipment (SME).”
These products are not considered dual use as defined by the U.S. Commerce
Department.
As ITAR-controlled items that are designated SME, each license application must be
accompanied by Form DSP-83 identifying the end user and intermediate consignees.
In addition, Exporters must ascertain the specific end user and end use prior to
submitting a license application to the Directorate of Defense Trade Controls. Terrasat
normally requests a separate letter to accompany the DSP-83 stating the type of
terminal in which the IBUC will be used and the satellite system over which it will
transmit.
Further, it is required that we inform the end user of the requirements of ITAR section
123.9, as follows:
The written approval of the Directorate of Defense Trade Controls must
be obtained before reselling, transferring, transshipping, or disposing of a
defense article to any end user, end use, or destination other than as stated
on the export license.
Details of ITAR requirements can be found at the U.S. State Department Web site at !
http://www.pmddtc.state.gov.

Introduction | 2-1
C H A P T E R
C
HAPTER
2
F
UNCTIONAL
D
ESCRIPTION
The Terrasat outdoor unit (ODU) consists of an intelligent block upconverter
(IBUC 2), power supply unit (PSUI), and low-noise block converter (LNB) for use in
satellite earth stations. The outdoor equipment is designed to interface directly with an
L-band satellite modem.
Introduction
This chapter contains detailed information about the various components of the
IBUC 2 system.
System Components
The interfacility link (IFL) between the ODUs and the L-band modem uses
950 MHz to 2.0 GHz (L-band) as the interface frequency. This approach enables
transmission and reception over the entire satellite band as opposed to a single
transponder. The L-band IFL can also carry associated signals such as 10 MHz, DC
voltage, or FSK which simplify installation and reduce costs. Terrasat IBUC 2 systems
can be used for single channel per carrier/multiple channels per carrier (SCPC/
MCPC), point-to-point, or point-to-multiple point network applications (such as voice,
data, video, or IP services). The integrated RJ-45 J4 connector enables TelNet, SNMP,
and the embedded Web pages for monitor and control purposes. Its smaller form factor
and lighter weight make the IBUC 2 ideal for situations where mobility is key. The
IBUC 2 can be carried in a backpack or case or it can be mounted on antennas that can
be quickly assembled and disassembled. See
Figure 2.5 to Figure 2.7 on the following
pages for typical equipment configurations.
The IBUC 2 is available in a variety of frequency bands as shown in
Table 2.1 on
page 2-3. The IBUC 2 houses the IF interface (de-mux), the upconverter, the monitor
and control (M&C) card, a DC-to-DC converter (if DC powered) and associated
circuitry, an AC-to-DC converter (if AC powered), and a solid state power amplifier

2-2 | Functional Description
(SSPA) assembly. The IBUC 2 can also house an optional internal 10 MHz reference
signal module. Higher-power IBUC 2s also have an external cooling fan assembly.
The input interface to the IBUC 2 connects to a 50 " or an optional 75 " coaxial cable
that carries the L-band transmit signal, and can carry the external 10 MHz reference
oscillator signal, DC power, and bidirectional M&C FSK signals.
System Components | 2-3
Table 2.1
IBUC 2 Transmit Frequency Plans
Signal Standard C-band Palapa C-band Insat C-band Extended C-band Full C-band
L-band
950 MHz to 1525 MHz 975 MHz to 1275 MHz 1150 MHz to 1450 MHz 950 MHz to 1750 MHz 975 MHz to 1850 MHz
LO frequency
7.375 GHz 7.700 GHz 8.175 GHz 7.600 GHz 7.700 GHz
RF frequency
5.850 GHz to 6.425 GHz 6.425 GHz to 6.725 GHz 6.725 GHz to 7.025 GHz 5.850 GHz to 6.650 GHz 5.850 GHz to 6.725 GHz
Output Power
5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 40,
50 watts
5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 40,
50 watts
5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 40,
50 watts
5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 40,
50 watts
5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 40,
50 watts
Signal Low C-band (Band 6) X-band Standard Ku-band Full Ku-band Low Ku-band (Band 3)
L-band
950 MHz to 1650 MHz 950 MHz to 1450 MHz 950 MHz to 1450 MHz 950 MHz to 1700 MHz 950 MHz to 1450 MHz
LO frequency
7.375 GHz 6.950 GHz 13.050 GHz 12.800 GHz 11.800 GHz
RF frequency
5.725 GHz to 6.425 GHz 7.900 GHz to 8.400 GHz 14.000 GHz to 14.500 GHz 13.750 GHz to 14.500 GHz 12.750 GHz to 13.250 GHz
Output Power
5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 40,
50 watts
5, 10, 20, 25, 40, 50 watts
4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 25, 30,
40 watts
4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 25, 30,
40 watts
4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 25, 30,
40 watts
Signal Low Ku-band (Band 4) DBS-band (Band 1) DBS-band (Band 2) Ka-band (Band 1) Ka-band (Band 2)
L-band
1000 MHz to 1500 MHz 950 MHz to 1750 MHz 1150 MHz to 1450 MHz 1000 MHz to 1500 MHz 1000 MHz to 2000 MHz
LO frequency
11.800 GHz 16.350 GHz 16.950 GHz 28.500 GHz 29.000 GHz
RF frequency
12.800 GHz to 13.300 GHz 17.300 GHz to 18.100 GHz 18.100 GHz to 18.400 GHz 29.500 GHz to 30.000 GHz 30.000 GHz to 31.000 GHz
Output Power
4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 25, 30,
40 watts
5, 8, 10, 20, 25 watts 5, 8, 10, 20, 25 watts 5, 10, 16 watts 5, 10, 16 watts
Signal Ka-band (Band 3)
L-band
1000 MHz to 2000 MHz
LO frequency
28.000 GHz
RF frequency
29.000 GHz to 30.000 GHz
Output Power
5, 10, 16 watts

2-4 | Functional Description
DC Supply
DC power can be supplied through the N-connector or F-connector (labeled J1) of the
L-band input or through the external power connector (labeled J3). DC power for the
high-power units is supplied through the six-pin circular connector (labeled J3) of the
DC input. Higher-power units (such as Ku-band 20 watt and higher, C-band 40 watt
and higher, X-band 25 watt and higher, or DBS-band 10 watt and higher) cannot
accept DC input through the L-band input connector due to the higher current draw.
Terrasat IBUC 2s have several supply voltage options. The standard configuration is
48 VDC. However, a 24 VDC option is available for for lower power units. Refer to
the datasheets in
Appendix G for more information. This choice of 24 VDC or
48 VDC is available only when the IBUC 2 is ordered and configured at the factory.
The operating voltage range for the 24 VDC option is 20 VDC to 28 VDC. The
operating voltage range for lower-power units with 48 VDC is 37 VDC to 60 VDC.
DC-powered units are configured at the factory to have floating input.
Figure 2.1 depicts the front panel of a DC-powered IBUC 2.
Note:
The IBUC 2 pictured in Figure 2.1 has an F-type connector at J1.
Figure 2.1
Front Panel of a DC-powered IBUC 2
Mounting
Hole
Breather
Valve

System Components | 2-5
AC Supply
IBUC 2s are available with optional AC power. Table 2.2 lists the voltage ranges for
different bands and power levels.
Figure 2.1 depicts the front panel of an AC-powered IBUC 2.
Note:
The IBUC 2 pictured in Figure 2.1 has an N-type connector at J1.
Figure 2.2
Front Panel of an AC-powered IBUC 2
Table 2.2
AC Supply Operating Voltage Ranges
Voltage Band Watts
100 VAC to 240 VAC C-band 5 watt to 50 watt
100 VAC to 240 VAC X-band 5 watt to 50 watt
100 VAC to 240 VAC Ku-band 4 watt to 40 watt
100 VAC to 240 VAC DBS-band 5 watt to 25 watt
100 VAC to 240 VAC Ka-band 5 watt to 10 watt
Mounting
Hole
Breather
Valve

2-6 | Functional Description
Fuses
Table 2.3 lists the the fuse markings of the fuses required by different AC-powered
IBUC 2 models.
Table 2.4 on page 2-7 defines the international marking schema.
Table 2.3
Fuse Markings
Signal
Power
Level
Fuse Markings
115 VAC 230 VAC
C-band
5 W T1.6AL250V T1.6AL250V
10 W T2AL250V T1.6AL250V
15 W T2.5AL250V T1.6AL250V
20 W T3.15AL250V T1.6AL250V
25 W T4AL250V T2AL250V
30 W T4AL250V T2AL250V
40 W T5AL250V T2.5AL250V
50 W T5AL250V T2.5AL250V
60 W T6.3AL250V T3.15AL250V
X-band
5 W T1.6AL250V T1.6AL250V
10 W T2AL250V T1.6AL250V
20 W T3.15AL250V T1.6AL250V
25 W T4AL250V T2AL250V
40 W T5AL250V T2.5AL250V
50 W T6.3AL250V T3.15AL250V
60 W T6.3AL250V T3.15AL250V
Ku-band
4 W T1.6AL250V T1.6AL250V
8 W T2.5AL250V T1.6AL250V
12 W T2.5AL250V T1.6AL250V
16 W T3.15AL250V T1.6AL250V
20 W T4AL250V T2AL250V
25 W T5AL250V T2.5AL250V
30 W T8AL250V T4AL250V
40 W T8AL250V T4AL250V
DBS-band
5 W T2.5AL250V T1.6AL250V
8
W T3.15AL250V T1.6AL250V
10 W T4AL250V T2AL250V
16 W T4AL250V T2AL250V
20 W T5AL250V T2.5AL250V
25 W T5AL250V T2.5AL250V
Ka-band
5 W T2AL250V T1.6AL250V
10 W T3.15AL250V T1.6AL250V

System Components | 2-7
For IBUC 2s that require fuses up to 6.3 A, Terrasat recommends time lag fuses with a
high I2t value.
For IBUC 2s that require fuses greater than 6.3 A, Terrasat recommends time lag
fuses.
For reference, the IBUC 2s are delivered with Littelfuse 213 Series fuses (surge
withstand, time lag for up to 6.3 A) or 218 Series fuses (time lag for greater than
6.3 A).
Table 2.4 explains the fuse marking schema.
Monitor and Control
The IBUC 2 is equipped with extensive monitor and control (M&C) capabilities. Use
any of the following methods to access those capabilities:
• Via the M&C 19-pin circular connector (J2) utilizing two-wire RS485. This
method requires that a separate cable must be run and connected to J2.
• Via the J2 connector using RS232. This method requires that a separate cable must
be run and connected to J2.
Figure G.1 on page G-2 contains a drawing for fabricating your own cable.
• Via the J4 connector using TCP/IP. This method requires a separate Ethernet
cable.
Figure G.2 on page G-3 contains a drawing for fabricating your own cable.
• Via the J2 connector using an optional hand-held terminal. The hand-held terminal
has its own cable.
• Via the L-band input N-connector or F-connector (J1) utilizing frequency shift
keying (FSK). Using this method requires no additional cable(s) but does require
that the FSK be multiplexed onto the L-band cable.
Note:
Some modem manufacturers offer built-in FSK capabilities for communicating with
the IBUC 2 through the L-band IFL. Refer to the modem manufacturer’s
documentation for more information.
Table 2.4
Fuse Markings Explained
T 3,15A L 250V
250V = 250 Volts
L = Low Breaking Capacity (glass body)
3,15A = 3,15 Amp
T = Träge (Slow Blow)

2-8 | Functional Description
RF Signal Flow
L-band input to the IBUC 2 is through the input N-connector or the F-connector
(labeled J1). Required inputs include an L-band signal at -20 dBm or less and a
10 MHz sine wave reference signal between +5 dBm and -12 dBm (for those units that
do not have the optional internal 10 MHz reference signal). The internal 10 MHz
reference signal meets the minimum phase noise requirements listed in
Table 2.5.
Note:
If an external 10 MHz reference signal is applied to a unit with the optional internal
10 MHz reference signal, the external signal has priority. When the external signal is
removed from such units, the system automatically reverts to the internal 10 MHz
signal, requiring no additional user input.
Input to the IBUC 2 also includes AC or DC voltage (via the J3 connector) and DC
voltage for low-power units and an FSK signal via the J1 connector. The input
(L-band, FSK, 10 MHz, and DC via coaxial cable) is routed to the demultiplexer
circuitry where the various signals are split off and routed to the appropriate circuits
within the IBUC 2 . (Only IBUC 2s with direct DC or AC via the J3 connector feed
the power supply directly.) The input voltage from the demultiplexer circuitry is
routed to the power supply and the FSK signal is routed to the M&C card.
The external 10 MHz reference signal is routed to the multiplier circuitry where its
level is first detected and an alarm issued if the signal is low. However, if the signal
level is low and the system is equipped with the optional internal 10 MHz signal, the
system will automatically switch to the internal 10 MHz signal. The 10 MHz signal is
then multiplied to the frequency used for phase-locking purposes. The output of the
multiplier is routed to the phase detector circuitry where it is compared with the phase
of the DRO (dielectric resonator oscillator) signal sample and consequently generates
a voltage that is applied as a control voltage to the DRO to adjust its frequency. The
DRO has been optimized for phase noise at a single frequency based on the frequency
band of that particular IBUC 2 . The output of the DRO is amplified and routed to the
mixer.
Table 2.5
Internal 10 MHz Reference Signal Parameters
Minimum Maximum Condition
Phase Noise
-100 dBc/Hz 10 Hz
-130 dBc/Hz 100 Hz
-140 dBc/Hz 1 kHz
-145 dBc/Hz 10 kHz
Frequency Stability vs. Operating
T
emperature Range!
(referenced to frequency at +25 °C)
-100 ppb +100 ppb -40 °C to +85 °C
Tuning Range!
(referenced to nominal frequency)
±3 ppm ±10 ppm
Tuning Slope Positive

System Components | 2-9
The L-band signal that is split off in the demultiplexer circuitry is first filtered and a
sample of it detected for input power detection and control purposes. The signal is then
amplified, and goes through a variable attenuator. The attenuation is used to provide
an attenuation adjustment of 30 dB in 0.1 dB steps and to provide automatic level
control (ALC) or automatic gain control (AGC).
After additional amplification and filtering, the signal is routed to the mixer. The
L-band signal is then mixed with the DRO signal to “upconvert” to the appropriate RF
signal based on the frequency band of the IBUC 2 . The RF signal is filtered,
amplified, and then routed to the temperature compensation circuitry. The temperature
compensation circuitry has been calibrated so that the IBUC 2 gain does not vary more
than 3 dB at any given frequency.
Note:
Some units can vary up to 4 dB at any given frequency.
The signal is then routed through an isolator to the solid-state power amplifier (SSPA).
Some models have an additional mechanical filter between the isolator and the SSPA.
The SSPA amplifies the signal which is then routed to the output through an isolator
for reverse power protection. The RF output is detected for M&C purposes. The
IBUC 2 gain has been calibrated so that at minimum attenuation, a -30 dBm input
results in rated power of at least P1dB at the output at any frequency or temperature.
Note:
Ka-band BUC 2 rated power is measured at P
SAT
.
To operate at lower power levels, reduce the input to the IBUC 2 or reduce the IBUC 2
gain by using the variable attenuator, accessible using any of the M&C interfaces. The
output of a C-band IBUC 2 is a CPR137G waveguide or an N-type connector, the
output of an X-band is a CPR112G waveguide, the output of a Ku-band IBUC 2 is a
WR75 cover with groove waveguide, the output of a DBS-band IBUC 2 is a
WR62 UG cover with groove waveguide, and the output of a Ka-band IBUC 2 is a
WR28 UG cover with groove waveguide.
Figure 2.3 depicts the signal flow for units that are DC powered and Figure 2.4 depicts
the signal flow for units that are AC powered.
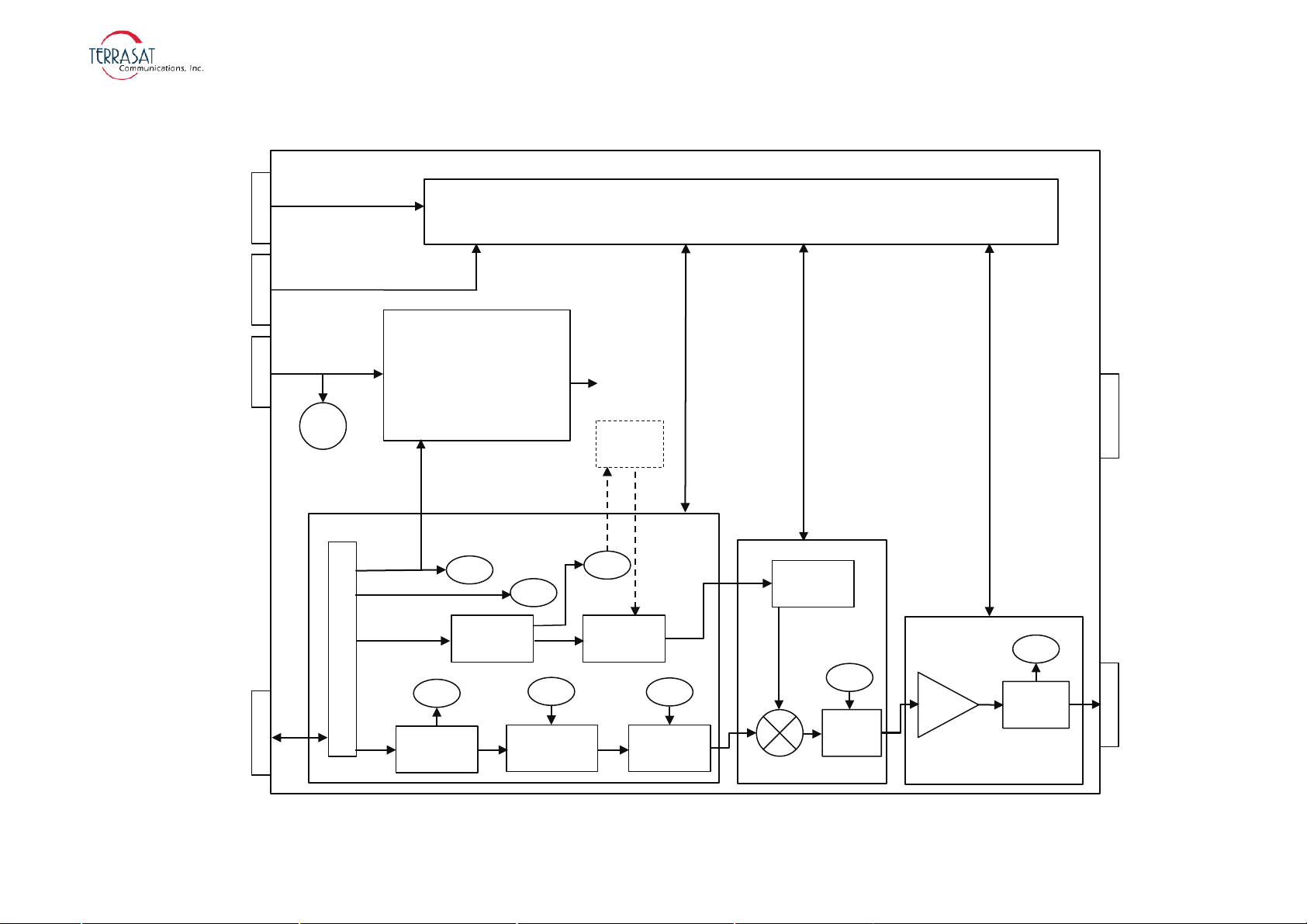
2-10 | Functional Description
Figure 2.3
IBUC 2 Block Diagram (for DC-powered systems)
J1
J2
RF OUT
FAN
Monitor and Control (M&C)
RS485
RS232
HHT
Alarm
Switch Control
VDC
VDC
FSK
External 10 MHz
L-band
DC/DC
Power Supply
De-Mux
Detector
Multiplier
Detector
Gain Adjust ALC/AGC
External
10 MHz
M&C
M&C
M&C
M&C
M&C
M&C
FSK
PL DRO
M&C
Temp
Comp
SSPA
M&C
Detector
Internal
10 MHz
All Circuits
VDC
M&C
J3
J4
TCP/IP
 Loading...
Loading...