Page 1

Page 2

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
1 www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Chapter 1 Overview ....................................................................................................................... 3
1.1 The Package Contents ................................................................................................................................ 4
1.2 HAN Pilot Platform System CD ................................................................................................................. 4
1.3 Getting Help ............................................................................................................................................... 4
Chapter 2 Board Components ........................................................................................................ 6
2.1 Components and Layout ............................................................................................................................. 6
2.2 Block Diagram ............................................................................................................................................ 9
Chapter 3 Board Settings and Status Component ........................................................................ 11
3.1 Board Setting Switches ............................................................................................................................. 11
3.2 Board Setting Headers .............................................................................................................................. 12
3.3 Status LED ................................................................................................................................................ 15
3.4 JTAG Interface ......................................................................................................................................... 17
Chapter 4 FPGA Fabric Components ........................................................................................... 19
4.1 User Interface (LED/7-SEG/Button/Switch) ............................................................................................ 19
4.2 USB Type-C Port ...................................................................................................................................... 21
4.3 SFP+ Connector........................................................................................................................................ 26
4.4 SATA ........................................................................................................................................................ 29
4.5 PCIe .......................................................................................................................................................... 32
4.6 DDR4 ........................................................................................................................................................ 34
4.7 HDMI Transmitter and Receiver .............................................................................................................. 43
4.8 Gigabit Ethernet ........................................................................................................................................ 45
4.9 FMC Connector ........................................................................................................................................ 46
4.10 Temperature Sensor, Fan Control and Power Monitor ........................................................................... 54
4.11 Gyroscope, Accelerometer and Magnetometer ....................................................................................... 55
Chapter 5 HPS Fabric Components ............................................................................................. 57
5.1 User Push-buttons and LEDs .................................................................................................................... 57
Page 3

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
2 www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
5.2 Gigabit Ethernet ........................................................................................................................................ 57
5.3 UART to USB ........................................................................................................................................... 59
5.4 Micro SD Card Socket .............................................................................................................................. 60
5.5 USB OTG ................................................................................................................................................. 60
5.6 GPIO Header ............................................................................................................................................ 61
5.7 DDR4 (HPS) ............................................................................................................................................. 62
Chapter 6 System Clocks ............................................................................................................. 67
Chapter 7 Power .......................................................................................................................... 69
Chapter 8 HAN Pilot Platform System Builder .............................................................................. 70
8.1 Introduction .............................................................................................................................................. 70
8.2 General Design Flow ................................................................................................................................ 70
8.3 Using HAN Pilot Platform System Builder .............................................................................................. 71
Chapter 9 Appendix ..................................................................................................................... 79
Page 4

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
3 www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
Chapter 1
Overview
The HAN Pilot Platform provides users a combination of ARM software and FPGA hardware
development platforms. It has a vast memory device and peripherals on the hardware. This kit also
includes resourceful reference designs to help users to accomplish their design needs. The hardware
offers in the HAN Pilot Platform has the maximum capacity with 660K LEs in Arria 10 SoC FPGA
and featuring various types of high-speed image interface such as: HDMI, Display Port, and
12G-SDI and a large capacity of DDR4 memory. The board’s high speed network interface, Gigabit
Ethernet and SFP+10GbE, provides hardware resources for network communications related
applications.
The HPS can be reboot with any of these three removable daughter cards: MicroSD Card, Nand
Flash, and QSPI Flash. The FPGA on the main board can be connected to DDR4-SODIMM Socket
in addition to the DDR4 memory module. The FPGA on the main board can also be connected to
the Terasic QDR Memory Module as well. Beside the DDR4 memory module, you can also directly
connect to the FPGA on the main board via the High Pin Count FMC expansion port to expand
variety of functions.
The PCIe Gen3 x4 Connector interface comes with the Terasic PCA PCIe and PCIe Cable, which
can be used to connect the Host PC to allow data between the FPGA and the Host PC. The USB
Type-C interface on the motherboard allows the motherboard to obtain power for the host PC. The
Host PC displays information and images through the high-speed transmission USB 3.0 or the
Display Port.
Page 5

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
4 www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
11..1
1
TThhee PPaacckkaaggee CCoonntteennttss
Figure 1-1 Package Contents
1. HAN Pilot Platform Kit
2. MicroSD Card (Installed) and Card Reader
3. Fan (Installed)
4. Two Type A to Mini-B USB Cables
5. 12V DC Power Supply (Installed)
6. AC Power Cord (USA)
7. One 4GB DDR4 ECC SO-DIMM Module (Installed)
8. Screws, Copper Stands, and Silicon Footstands
11..2
2
HHAANN PPiilloott PPllaattffoorrmm SSyysstteemm CCDD
The HAN Pilot Platform System CD contains all the documents and supporting materials associated
with HAN Pilot Platform, including the user manual, system builder, reference designs and device
datasheets.
Users can download this system CD from the link: http://HAN Pilot Platform.terasic.com/cd.
11..3
3
GGeettttiinngg HHeellpp
Here are the addresses where you can get help if you encounter any problems:
▪ Terasic Technologies
▪ 9F., No.176, Sec.2, Gongdao 5th Rd, East Dist, Hsinchu City, 30070. Taiwan
▪ Email: support@terasic.com
Page 6

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
5 www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
▪ Tel.: +886-3-575-0880
▪ Website: HAN Pilot Platform.terasic.com
Page 7
HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
6 www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
Chapter 2
Board Components
This chapter provides an introduction to the features and design characteristics of the board.
22..1
1
CCoommppoonneennttss aanndd LLaayyoouutt
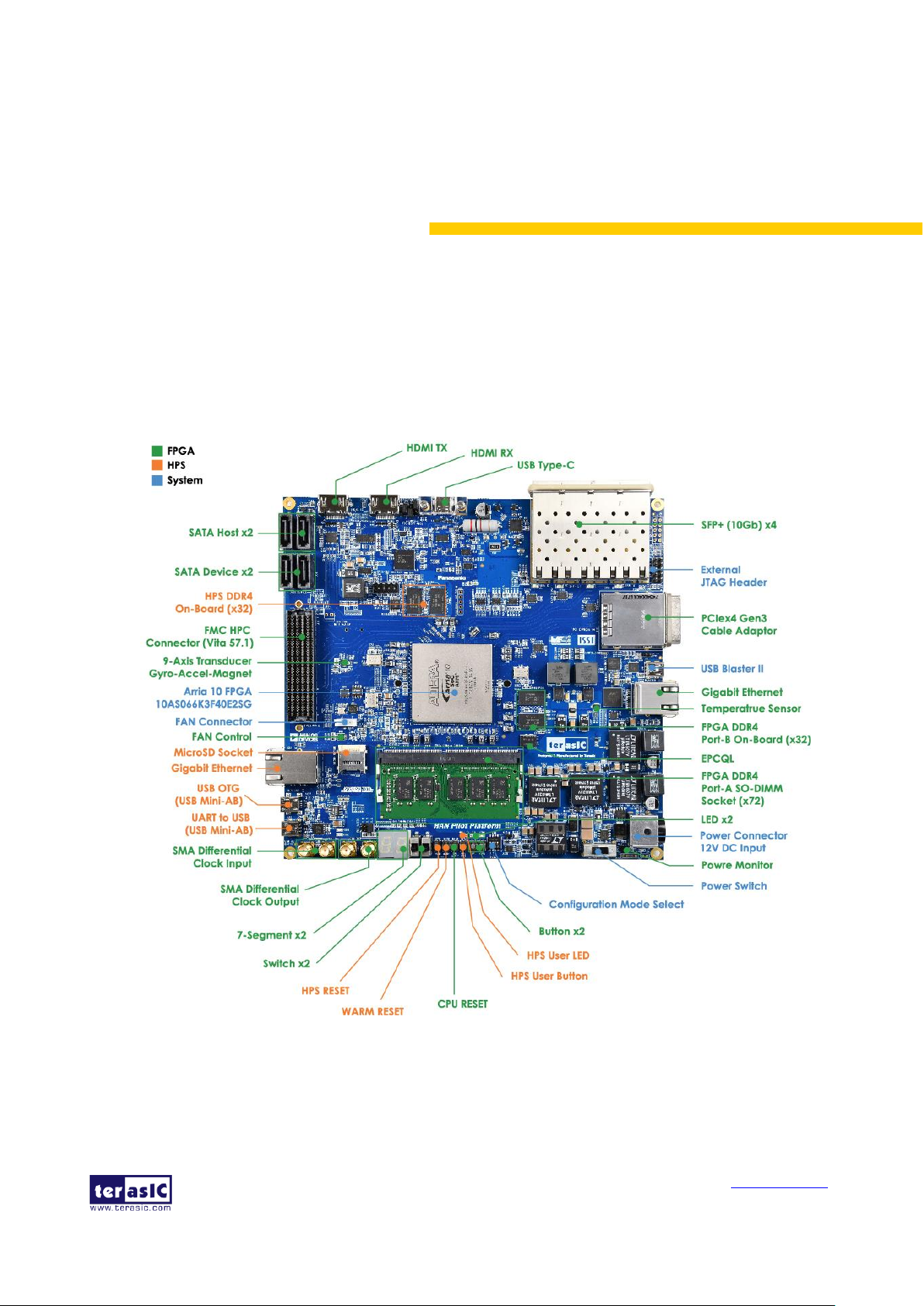
Figure 2-1 and Figure 2-2 shows a photograph of the board. It depicts the layout of the board and
indicates the location of the connectors and key components.
Figure 2-1 HAN Pilot Platform (top view)
Page 8
HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
7 www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
Figure 2-2 HAN Pilot Platform (bottom view)
The HAN Pilot Platform has many features that allow users to implement a wide range of designed
circuits, from simple circuits to various multimedia projects.
The following hardware are provided on the board:
◼ FPGA Device
• Intel ® Arria10® SoC 10AS066K3F40E2SG device (660K LEs)
• USB-Blaster II onboard for programming; JTAG Mode
• Serial configuration device – EPCQL1024
• One DDR4 SO-DIMM Socket, support ECC
• On-board 1GB DDR4-2400, 32-bit data width
• USB Type-C Interface
• Power Delivery
• DisplayPort TX/RX with 4 lanes
• USB 3.0/2.0
• HDMI TX/RX 2.0 for 4K2K@60- FPGA Transceiver
• PCIe Cabling Socket at Gen3 x4
Page 9

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
8 www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
• SFP+ Socket x4, 40Gbps
• SATA 3.0 Host and SATA Device x2 (SATA Connector x4)
• One Gigabit Ethernet Port
• SMA Clock-In and Clock-Out
• High Pin Count FMC Connector. Support VADJ 1.2V/1.5V/1.8V.
• Accelerometer, Gyroscope and Magnetometer
• Temperature Sensor
• Fan Control
• LED x2, KEY x2, Switch x2, 7-Segment x2
◼ HPS (Hard Processor System)
• 1.5GHz Dual-core ARM Cortex-A9 processor
• Boost Flash Slot:
• 1024 Mb QSPI Flash
• Nand Flash
• MicroSD Socket
• On-board 1GB DDR4-2400, 32-bit data width
• 1 Gigabit Ethernet PHY with RJ45 connector
• USB OTG Port, USB mini-AB connector
• UART to USB, USB Mini-B connector
• RTC
• One user button and one user LED
• Warm reset button and cold reset button
Page 10

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
9 www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
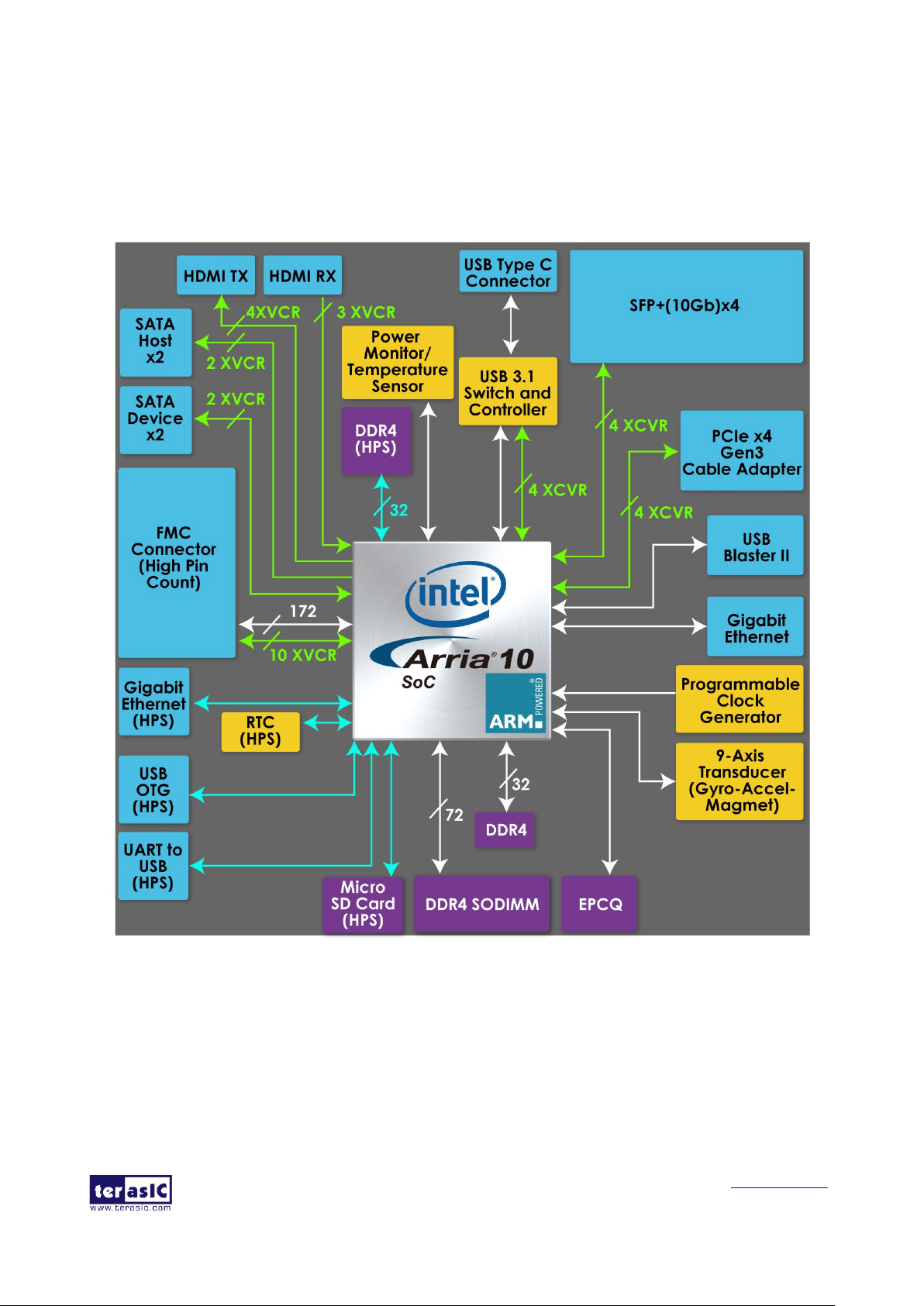
2.2 Block Diagram
Figure 2-3 is the block diagram of the board. All the connections are established through the Arria
10 SoC FPGA device to provide maximum flexibility for users. Users can configure the FPGA to
implement any system design.
Detailed information about Figure 2-3 are listed below.
▪ Arria 10 SoC 10AS066K3F40E2SG/10AS057K3F40E2SG FPGA
▪ Dual-core ARM Cortex-A9 (HPS)
▪ 660K programmable logic elements
▪ 42,660 Kbits embedded memory
▪ Hard memory controllers x5
▪ Transceivers x48(17.4 Gbps)
▪ 18-bit x 19-bit multipliers x3,356
▪ Accelerometer & Gyroscope Device MPU9250
▪ Configuration
▪ EPCQ1024L Serial Configuration Device
▪ Onboard USB-Blaster II (Mini-B USB connector)
▪ Memory Device
▪ On-board 1GB DDR4-2400, 32-bit data width
▪ Two DDR4 SO-DIMM SDRAM socket
▪ Micro SD card socket
▪ Communication
▪ USB OTG (Mini-AB USB connector)
▪ UART-to-USB (Mini-B USB Connector)
▪ Giga Ethernet x2
▪ PCIe Gen3 x4 Cabling Socket
▪ Expansion Ports
▪ FMC connector
▪ one HPC (high-pin count) FMC connector with xcvr
▪ Adjustable VADJ:1.2V/1.5V/1.8V
▪ Multimedia Interface
▪ HDMI TX and RX ports
▪ Clock
▪ Two SMA connectors for SMA Clock-In and Clock-Out
▪ On-board PLLs
▪ General user input/output
▪ Buttons x3 (FPGA x2, HPS x1)
▪ Switches x2 on FPGA
▪ LEDs x3 (FPGA x2, HPS x1)
▪ 7-segment displays x2
▪ System Monitor and Control
▪ Temperature Sensor on FPGA
▪ 12V Power Monitor
Page 11
HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
10
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
▪ Power Controller
▪ I2C Fan Control
▪ Power
▪ 12V DC input
Figure 2-3 Block diagram of HAN Pilot Platform
Page 12

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
11
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
Chapter 3
Board Settings and Status
Component
This chapter describes all the setting devices on HAN Pilot Platform board and their functions, such
as Switches and Headers. We also will describe the function of some status LEDs. The JTAG
interface will be described at the end of this chapter.
33..1
1
BBooaarrdd SSeettttiinngg SSwwiittcchheess
◼ Mode Select Switches
Mode Select Switch (SW5) is used to set the HAN Pilot Platform FPGA MSEL pin value. These
MSEL pins determined the Configuration Mode of the FPGA. Table 3-1 list the MSEL setting for
configuration scheme of FPGA, when MSEL is set to AS mode (Factory default setting), FPGA will
be booted from EPCQ device (See Figure 3-1). When MSEL is set to FPP mode (See Figure 3-2),
FPGA can be configured by HPS Fabric (From Micro SD Card).
Table 3-1 MSEL setting for configuration scheme of FPGA
Configuration Scheme
SW5 MSEL[2..0] Setting
Description
AS Mode (Factory Default)
010
FPGA boot from EPCQ
FPP Mode
000
FPGA boot from Micro SD Card
Page 13

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
12
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
Figure 3-1 The AS mode setting of SW5
Figure 3-2 The FPP mode setting of SW5
33..2
2
BBooaarrdd SSeettttiinngg HHeeaaddeerrss
◼ JTAG Interface Header
J17 is the header used to set the JTAG bus of FMC connector connect to JTAG interface of HAN
Pilot Platform system. The FMC connector will not be included in the JTAG chain if the headers are
set to open (See Figure 3-3). Table 3-2 list the setting of the J17 header.
Page 14

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
13
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
Table 3-2 JTAG Interface Headers Setting
Header
Setting
Descriptions
J17
Open (Default Setting)
Disable the JTAG interface of the FMC connector into the JTAG
chain
Figure 3-3 The FMC JTAG Header
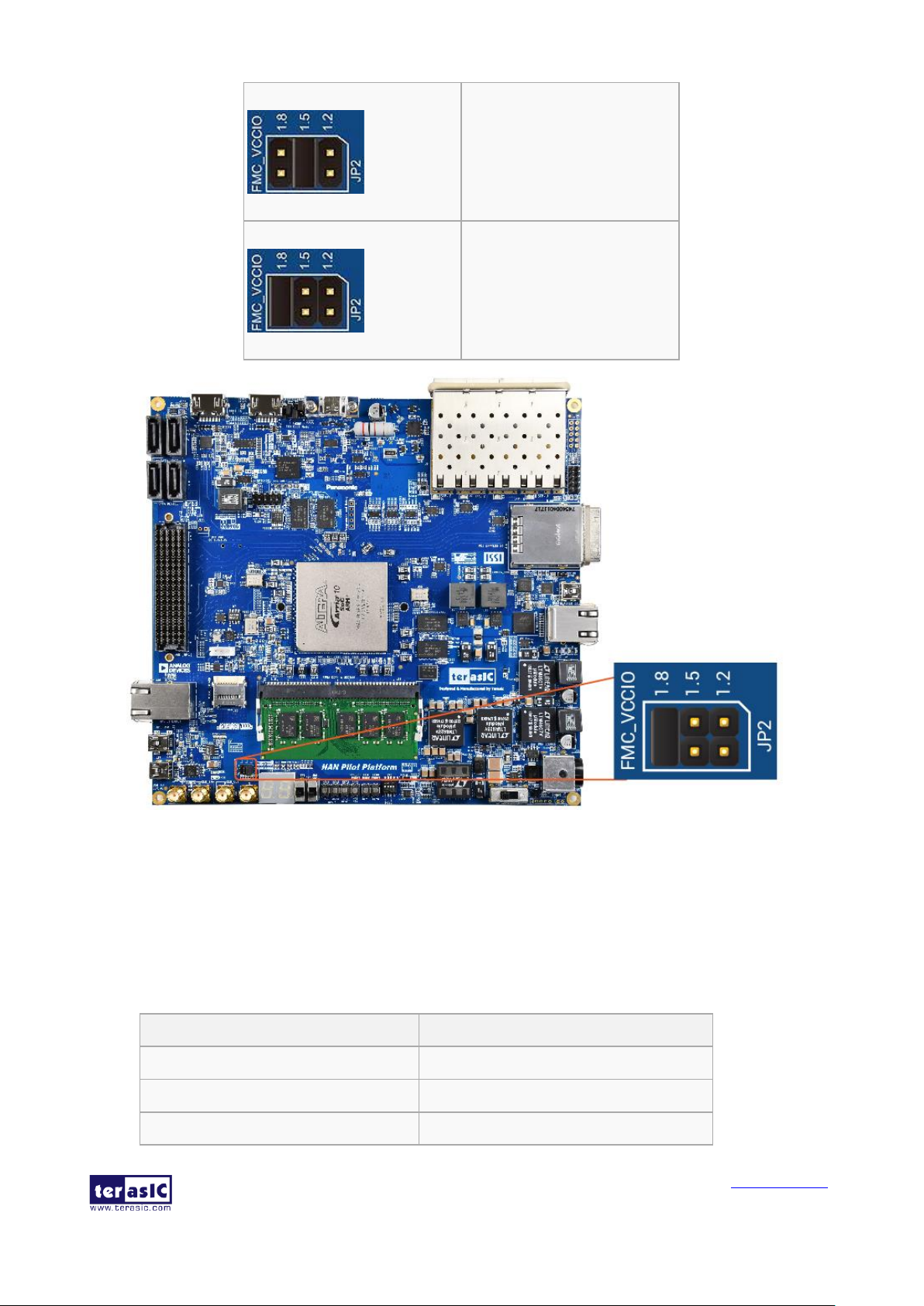
◼ FMC_VCCIO Select Header
JP2 is used to set the VCCIO voltage of FPGA I/O on FMC connector, as 1.2V/1.5V/1.8V are
supported, the FMC connector can support various I/0 standard FMC daughtercards. Table 3-3 list
the FMC_VCCIO Headers Setting.
Table 3-3 FMC_VCCIO Headers Setting
JP2 Setting
FMC VCCIO Voltage
1.2V
Page 15
HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
14
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
1.5V
1.8V (Default Setting)
Figure 3-4 The FMC VCCIO select header
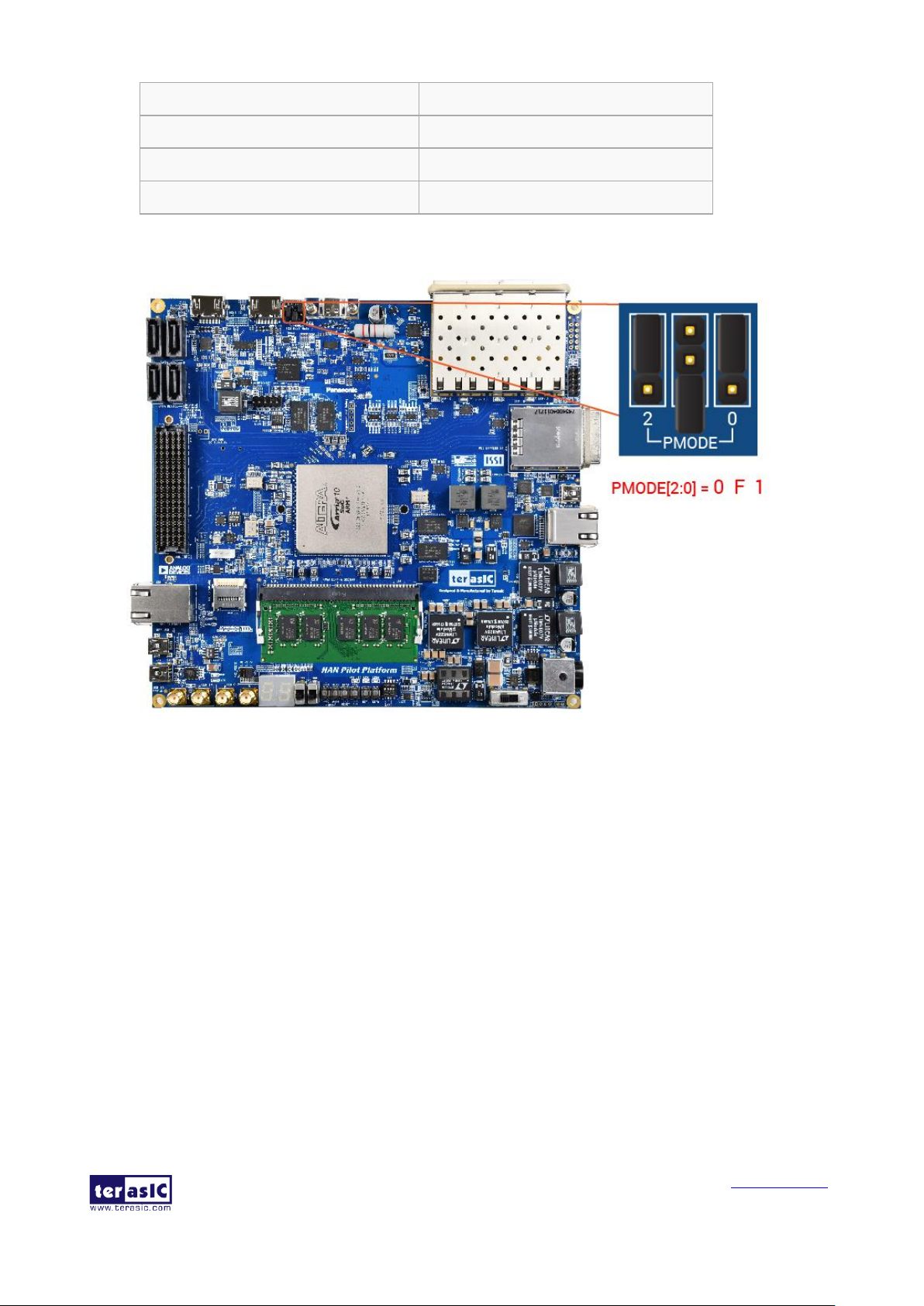
◼ PMODE Select Header
The USB 3.0 Controller (Cypress FX3) on the HAN Pilot Platform can be booted from the
different sources, selected by the configuration of the PMODE header (JP4/JP5/JP6) on HAN
Pilot Platform. Table 3-4 shows the boot options and associated settings. The default boot device
is the from a serial flash via SPI interface.
Table 3-4 PMODE Headers Setting
PMODE [2:0] (JP6/JP5/JP4) Setting
Boot Source
F00
Sync ADMux (16-bit)
F01
Async ADMux (16-bit)
F11
USB boot
Page 16
HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
15
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
F0F
Async SRAM (16-bit)
F1F
I2C, On Failure, USB Boot is Enabled
1FF
I2C only
0F1(Default)
SPI, On Failure, USB Boot is Enabled
◼ Note: F indicates Floating
Figure 3-5 The PMODE select header
33..3
3
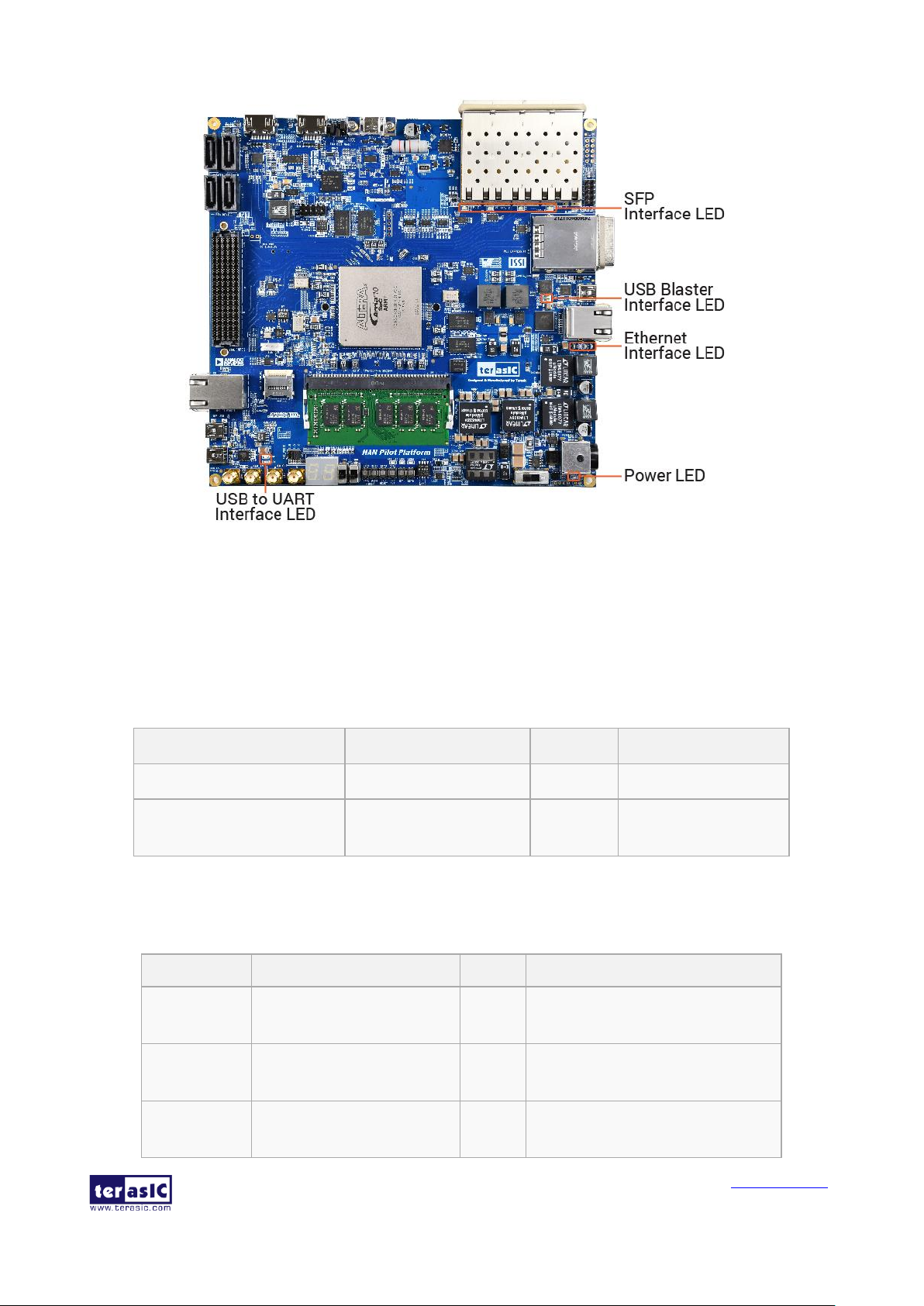
SSttaattuuss LLEEDD
This section describes the all status LED for the interfaces on HAN Pilot Platform board. Figure
3-6 shows all the status LED on the HAN Pilot Platform. Following are the detailed descriptions of
these interface LED.
Page 17
HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
16
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
Figure 3-6 The status LED on the HAN Pilot Platform board
◼ UART Interface
Table 3-5 list the two status LEDs for UART interface.
Table 3-5 Status LED for UART Interface
Component
Reference
Status
Descriptions
TXD1
UART_TXD
ON
Transmitting
RXD1
UART_RXD
ON
Receiving
◼ SFP Interface
Table 3-6 list the four status LEDs for SFP interface.
Table 3-6 Indicator LED for SFP Interface
Component
Reference
Status
Descriptions
D4
SFPA_MOD0_PRSNT_n
ON
Indicate that the SFP module is
present on the SFPA
D3
SFPB_MOD0_PRSNT_n
ON
Indicate that the SFP module is
present on the SFPB
D2
SFPC_MOD0_PRSNT_n
ON
Indicate that the SFP module is
present on the SFPC
Page 18
HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
17
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
D1
SFPD_MOD0_PRSNT_n
ON
Indicate that the SFP module is
present on the SFPD
◼ Ethernet Interface
Table 3-7 list the four status LEDs for Ethernet interface.
Table 3-7 Status LED for Ethernet Interface
Component
Reference
Status
Descriptions
D8
ETH_LED_TX
ON
Transmitting
D9
ETH_LED_RX
ON
Receiving
D10
ETH_LINK1000
ON
1000Mbps Link UP
D11
ETH_LINK100
ON
100Mbps Link UP
◼ Power
Table 3-8 list the two status LEDs for power.
Table 3-8 Status LED for Power
Component
Reference
Status
Descriptions
D31
12V~20V Power Indicator
ON
Illuminates when 12V~20V Power Supply is active
◼ USB Blaster
Table 3-9 list the two status LEDs for USB Blaster interface.
Table 3-9 Status LED for USB Blaster Interface
Component
Reference
Status
Descriptions
D5
JTAG_TX
ON
Illuminates when JTAG interface is transmitting data
D6
JTAG_RX
ON
Illuminates when JTAG interface is receiving data
33..4
4
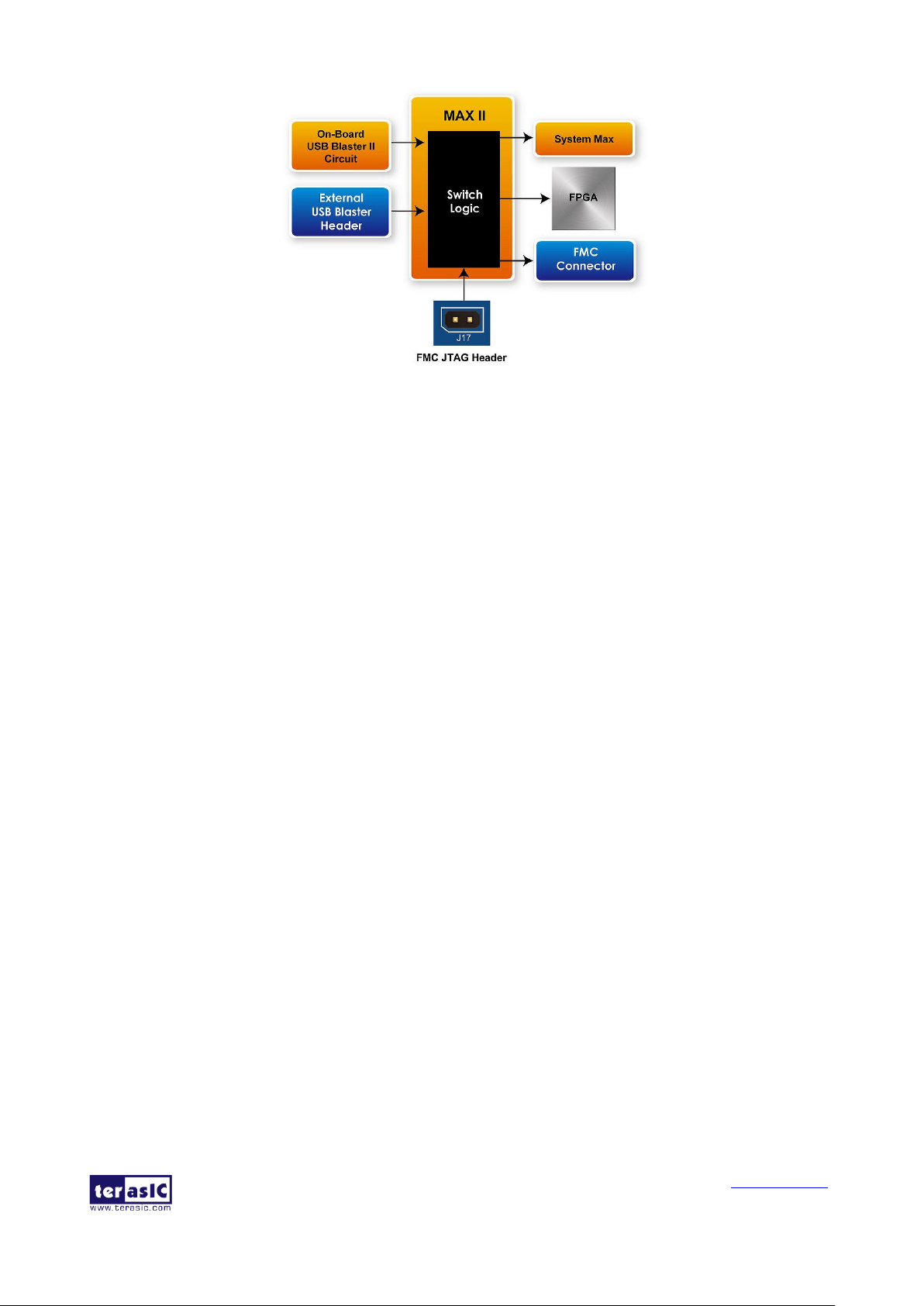
JJTTAAGG IInntteerrffaaccee
Figure 3-7 shows the JTAG interface of HAN Pilot Platform. Users can access to the JTAG
interface through the USB Blaster II circuit or connect external blaster to external blaster header. All
the devices which implement JTAG are connect to MAX II device, and switch via MAX II internal
switch logic. By using headers J17, users can include FMC connector JTAG interface in the HAN
Pilot Platform JTAG Chain, or exclude them from the JTAG Chain. The default JTAG path for
HAN Pilot Platform is: USB Blaster II ==> HPS ==> FPGA ==> (Bypass FMC connector) ==>
USB Blaster II. When the External JTAG connector is connected to the external blaster, the On
board's USB blaster II function will be replaced by the external blaster.
Page 19
HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
18
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
Figure 3-7 JTAG interface of HAN Pilot Platform
Page 20
HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
19
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
Chapter 4
FPGA Fabric Components
44..1
1
UUsseerr IInntteerrffaaccee ((LLEEDD//77--SSEEGG//BBuuttttoonn//SSwwiittcchh))
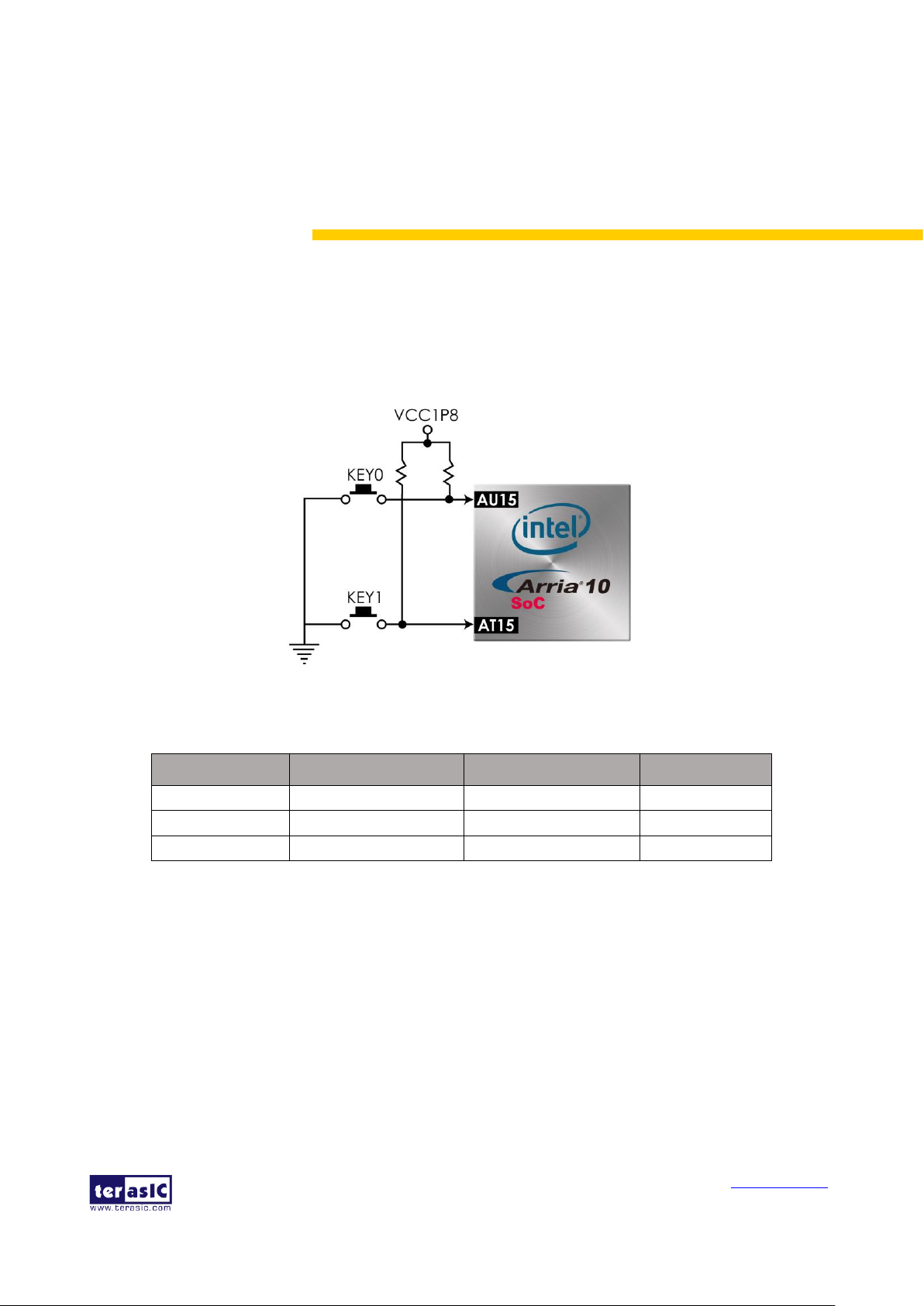
The board has two push-buttons connected to the FPGA, as shown in Figure 4-1. The two
push-buttons named KEY0 and KEY1 are connected directly to the Arria 10 SoC FPGA. Table 4-1
list the pin assignment of user push-buttons.
Figure 4-1 Connections between the push-buttons and the Arria 10 SoC FPGA
Table 4-1 Pin Assignment of Push-buttons
Signal Name
FPGA Pin Number
Description
I/O Standard
KEY[0]
PIN_AU15
Push-button[0]
1.8V
KEY[1]
PIN_AT15
Push-button[1]
1.8V
CPU_RESET_n
PIN_AN18
CPU_RESET button
1.8V
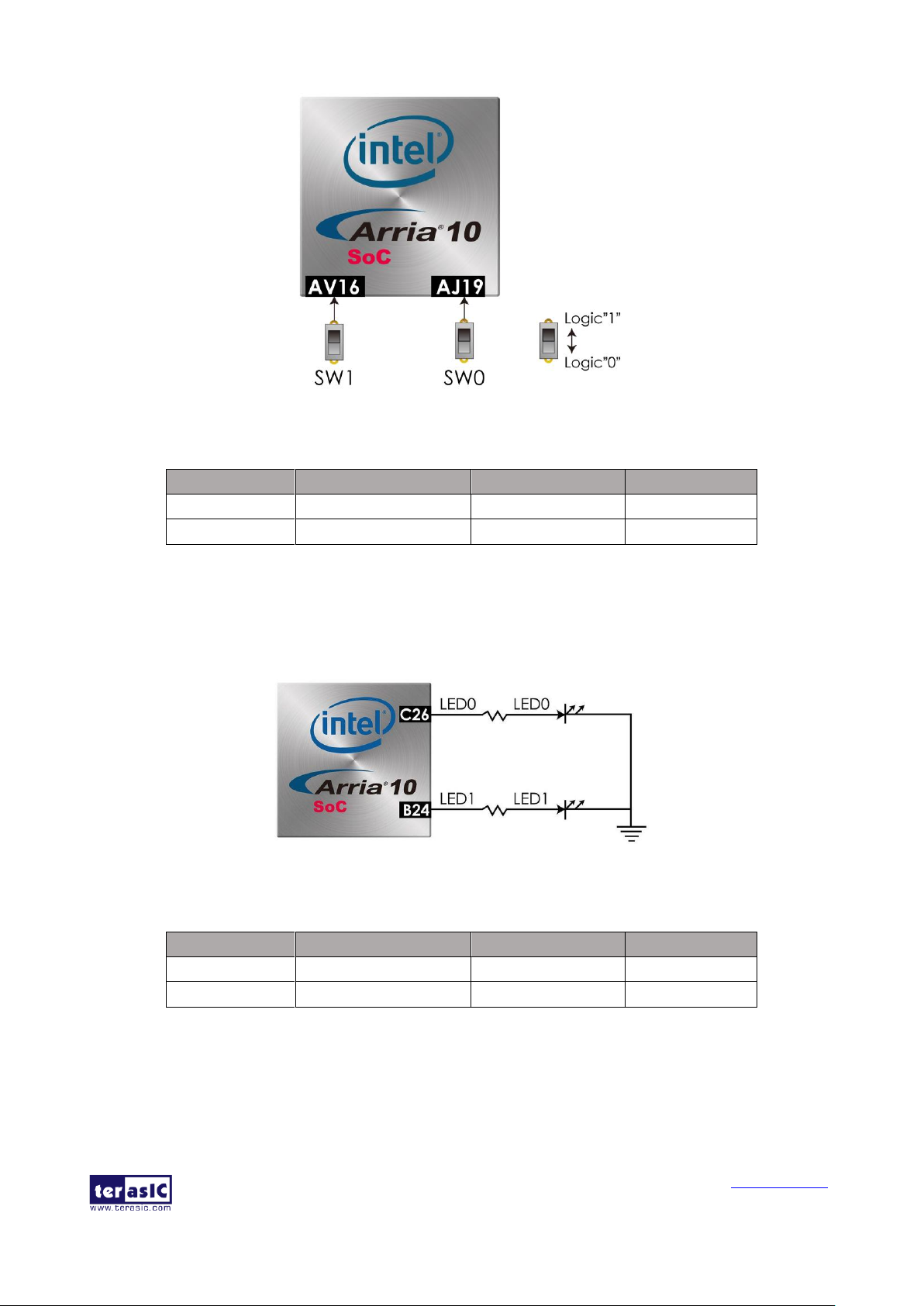
There are two slide switches connected to the FPGA, as shown in Figure 4-2. These switches are
not debounced and to be used as level-sensitive data inputs to a circuit. Each switch is connected
directly and individually to the FPGA. When the switch is set to the DOWN position (towards the
edge of the board), it generates a low logic level to the FPGA. When the switch is set to the UP
position, a high logic level is generated to the FPGA. Table 4-2 list the pin assignment of switches.
Page 21
HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
20
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
Figure 4-2 Connections between the switches and the Arria 10 SoC FPGA
Table 4-2 Pin Assignment of Switches
Signal Name
FPGA Pin Number
Description
I/O Standard
SW[0]
PIN_AJ19
Slide Switch[0]
1.8 V
SW[1]
PIN_AV16
Slide Switch[1]
1.8 V
There are also two user-controllable LEDs connected to the FPGA. Each LED is driven directly and
individually by the Arria 10 SoC FPGA; driving its associated pin to a high logic level or low level
to turn the LED on or off, respectively. Figure 4-3 shows the connections between LEDs and Arria
10 SoC FPGA. Table 4-3 list the pin assignment of LEDs.
Figure 4-3 Connections between the LEDs and the Arria 10 SoC FPGA
Table 4-3 Pin Assignment of LEDs
Signal Name
FPGA Pin Number
Description
I/O Standard
LEDG[0]
PIN_C26
LED [0]
1.8 V
LEDG[1]
PIN_B24
LED [1]
1.8 V
The DE10-Advanced board has two 7-segment displays. These displays are paired to display
numbers in various sizes. Figure 4-4 shows the connection of seven segments (common anode) to
pins on Arria 10 SoC FPGA. The segment can be turned on or off by applying a low logic level or
high logic level from the FPGA, respectively. Each segment in a display is indexed from 0 to 6,
Page 22

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
21
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
with corresponding positions given in Figure 4-4. Table 4-4 shows the pin assignment of FPGA to
the 7-segment displays.
Figure 4-4 Connections between the 7-segment and the Arria 10 SoC FPGA
Table 4-4 Pin Assignment of 7-segment
Signal Name
FPGA Pin Number
Description
I/O Standard
HEX0[0]
PIN_AT32
Seven Segment Digit 0[0]
1.8V
HEX0[1]
PIN_AR32
Seven Segment Digit 0[1]
1.8V
HEX0[2]
PIN_AU32
Seven Segment Digit 0[2]
1.8V
HEX0[3]
PIN_AU30
Seven Segment Digit 0[3]
1.8V
HEX0[4]
PIN_AT30
Seven Segment Digit 0[4]
1.8V
HEX0[5]
PIN_AU29
Seven Segment Digit 0[5]
1.8V
HEX0[6]
PIN_AV29
Seven Segment Digit 0[6]
1.8V
HEX0_DP
PIN_AU31
Seven Segment Digit 0_DP
1.8V
HEX1[0]
PIN_AT28
Seven Segment Digit 1[0]
1.8V
HEX1[1]
PIN_AT29
Seven Segment Digit 1[1]
1.8V
HEX1[2]
PIN_AR30
Seven Segment Digit 1[2]
1.8V
HEX1[3]
PIN_AM27
Seven Segment Digit 1[3]
1.8V
HEX1[4]
PIN_AL27
Seven Segment Digit 1[4]
1.8V
HEX1[5]
PIN_AK27
Seven Segment Digit 1[5]
1.8V
HEX1[6]
PIN_AM26
Seven Segment Digit 1[6]
1.8V
HEX1_DP
PIN_AR31
Seven Segment Digit 1_DP
1.8V
44..2
2
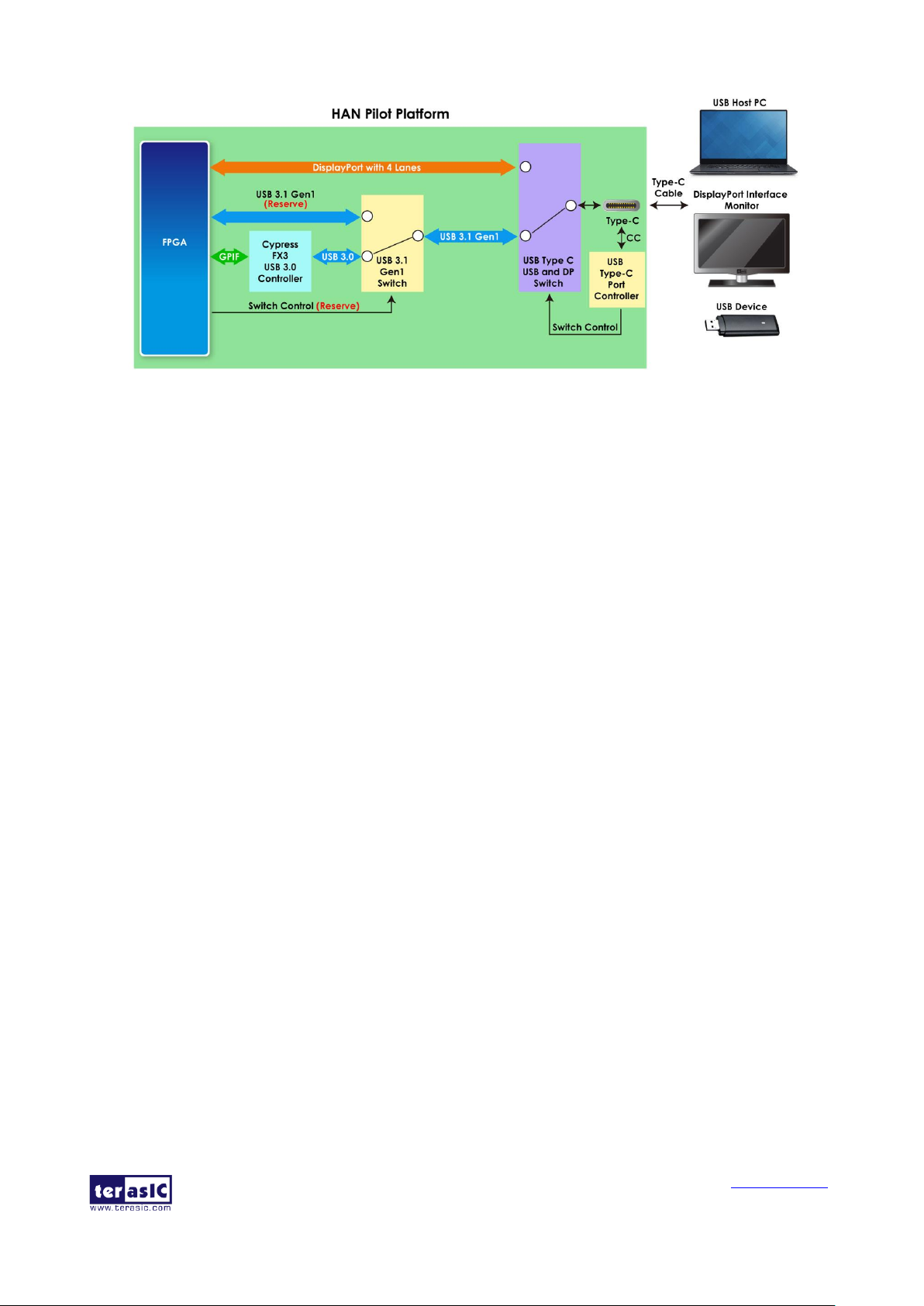
UUSSBB TTyyppee--CC PPoorrtt
The HAN Pilot Platform board features one USB Type-C connector. It is designed for high-speed
data transmission with computers and image output applications. Figure 4-5 shows the block
diagram of the connection between USB Type-C port and FPGA.
Page 23
HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
22
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
Figure 4-5 Block diagram of the connection between USB Type-C port and FPGA
As shown in Figure 4-5, it connects to FPGA through several switch circuits and USB controllers,
users can switch USB Type-C connector to a variety of applications as below:
▪ USB 3.0 Device to USB Host PC
▪ USB 2.0 OTG
▪ DisplayPort Source Application (Need DP Source IP)
The USB Type-C Port Controller will detect the type of USB device connected to the Type-C
connector, automatically switches the "USB and DP" switch (U11), and connects the USB Type-C
connector to the appropriate application in the HAN Pilot kit. If user connects a Display port
monitor to the USB type-C connector of the Han Pilot kit, the "USB and DP" switch will be
switched to the transceiver path of the FPGA by the USB type-C Port Controller, which is useful for
the Display port output application. Similarly, when a USB 3.0 host device is connected to the USB
Type-C connector, the "USB and DP" switch will be switched to the path of the cypress FX3.0 USB
controller for USB 3.0 applications.
We will describe the circuits diagram and these functions in detail below.
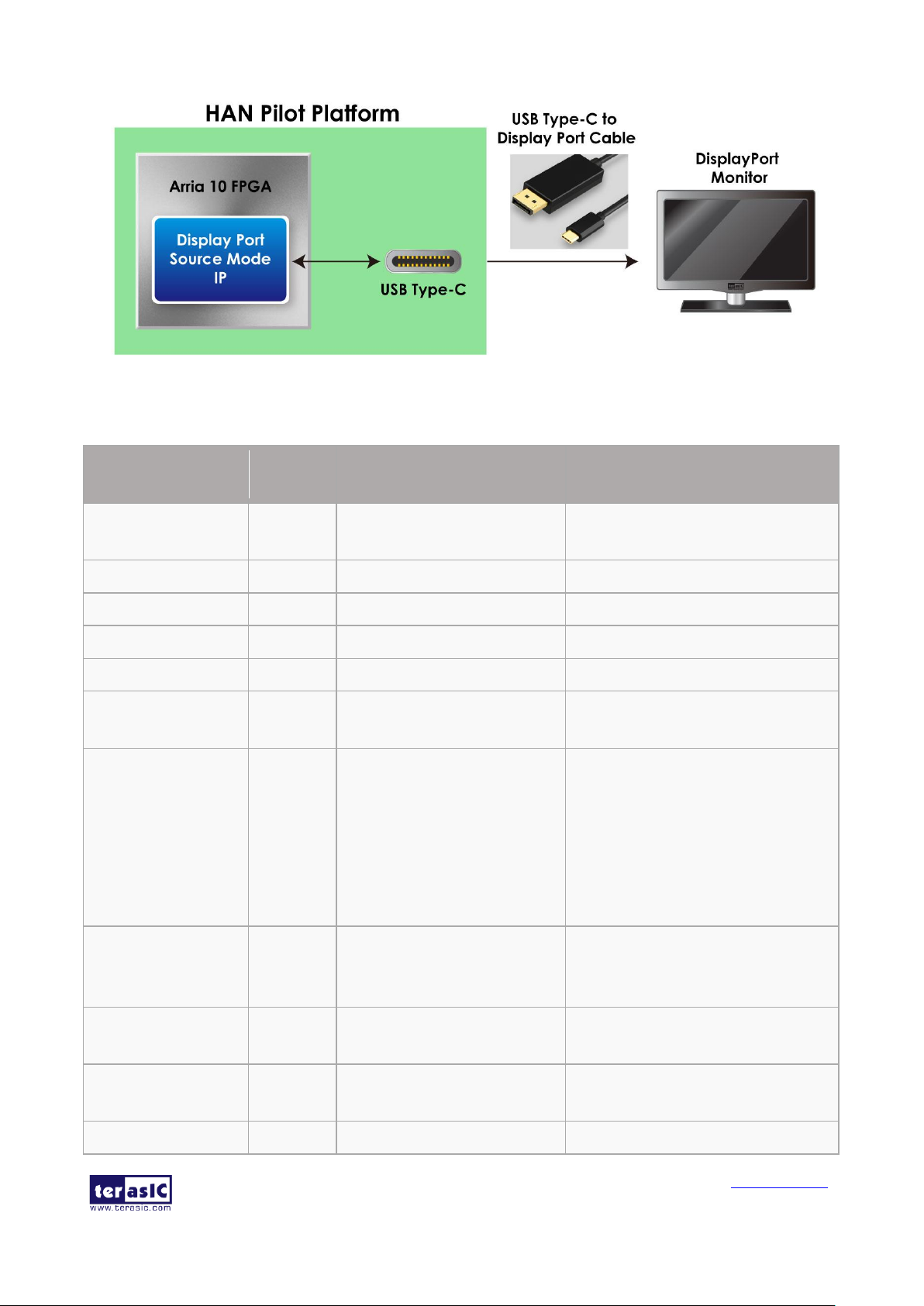
◼ Display Port
As shown in Figure 4-6, USB Type-C port can connect to FPGA transceiver. Users can implement
a Display port source mode IP in the FPGA, the HAN Pilot Platform board will implement the
features of display port source. Through the USB Type-C cable, users can connect HAN Pilot
Platform board to the monitor which supports Display port interface. Then the image processed by
FPGA can be displayed on the monitor. The display port provides data rate up to 5.4Gbps per lane
and 4 lanes in total, it supports DisplayPort 1.2a Spec. Table 4-5 list the pin assignment of
DisplayPorts.
Page 24
HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
23
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
Figure 4-6 USB Type-C Application: DisplayPort TX Source
Table 4-5 DisplayPort Signal Names and Functions
Signal Name
FPGA Pin
Number
Description
I/O Standard
DP_REFCLK_p
AM31
Display reference clock form
PLL
LVDS
DP_TX_p[0]
AW37
TX Lane 1
HSSI Differential I/O
DP_TX_p[1]
AV39
TX Lane 2
HSSI Differential I/O
DP_TX_p[2]
AU37
TX Lane 3
HSSI Differential I/O
DP_TX_p[3]
AT39
TX Lane 4
HSSI Differential I/O
DP_AUX_p
AM22
Display port AUX port
DIFFERENTIAL 1.8-V SSTL
CLASS I
DP_DX_SEL
AB27
Display Port channel TX or
RX(Reserve) select.
DP_DX_SEL = 0 : USB
TypeC in Display TX mode .
DP_DX_SEL = 1(Reserve):
USB TypeC in Display RX
mode
1.8 V
DP_AUX_SEL
AC28
AUX/DDC Selection Control
Pin in Conjunction with
Dx_SEL Pin
1.8 V
USBDP_SW_CNF0
AA27
Display port Switch
Configure 0
1.8 V
USBDP_SW_CNF1
AB26
Display port Switch
Configure 1
1.8 V
USBDP_SW_CNF2
AB25
Display port Switch
1.8 V
Page 25

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
24
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
Configure 2
◼ USB 3.0 Device
The HAN Pilot Platform board has one Cypress FX3 USB Controller (CYUSB3014). The USB
controller is connected to FPGA through the programmable GPIF II interface, and connect to the
external USB Type-C connector, it provides USB 3.0 Device application for HAN Pilot Platform
board.
As shown in Figure 4-7, users can connect FX3 USB Controller to PC through USB Type-C cable,
and transfer USB 3.0 data between FPGA and USB Host PC with transfer rate 320MByte/s (Using
the demonstration provided by Cypress). Table 4-6 list the pin assignment of FX3 USB 3.0
Controller.
Figure 4-7 FX3 USB 3.0 Controller application
◼ USB 2.0 OTG
The Cypress FX3 USB controller also has a USB 2.0 OTG controller. It allows the HAN Pilot
Platform board function as an OTG Host to MSC as well as HID-class devices, as shown in Figure
4-8.
Figure 4-8 USB 2.0 OTG Controller application
Table 4-6 FX3 USB 3.0 Controller Signal Names and Functions
Signal Name
FPGA Pin Number
Description
I/O Standard
USBFX3_DQ[0]
AU21
GPIF II Data Bus 0
1.8 V
Page 26

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
25
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
USBFX3_DQ[1]
AW23
GPIF II Data Bus 1
1.8 V
USBFX3_DQ[2]
AW24
GPIF II Data Bus 2
1.8 V
USBFX3_DQ[3]
AW25
GPIF II Data Bus 3
1.8 V
USBFX3_DQ[4]
AW26
GPIF II Data Bus 4
1.8 V
USBFX3_DQ[5]
AV24
GPIF II Data Bus 5
1.8 V
USBFX3_DQ[6]
AW28
GPIF II Data Bus 6
1.8 V
USBFX3_DQ[7]
AW30
GPIF II Data Bus 7
1.8 V
USBFX3_DQ[8]
AW29
GPIF II Data Bus 8
1.8 V
USBFX3_DQ[9]
AV27
GPIF II Data Bus 9
1.8 V
USBFX3_DQ[10]
AV28
GPIF II Data Bus 10
1.8 V
USBFX3_DQ[11]
AU26
GPIF II Data Bus 11
1.8 V
USBFX3_DQ[12]
AV23
GPIF II Data Bus 12
1.8 V
USBFX3_DQ[13]
AU25
GPIF II Data Bus 13
1.8 V
USBFX3_DQ[14]
AR25
GPIF II Data Bus 14
1.8 V
USBFX3_DQ[15]
AP24
GPIF II Data Bus 15
1.8 V
USBFX3_DQ[16]
AL23
GPIF II Data Bus 16
1.8 V
USBFX3_DQ[17]
AM24
GPIF II Data Bus 17
1.8 V
USBFX3_DQ[18]
AK25
GPIF II Data Bus 18
1.8 V
USBFX3_DQ[19]
AM25
GPIF II Data Bus 19
1.8 V
USBFX3_DQ[20]
AT24
GPIF II Data Bus 20
1.8 V
USBFX3_DQ[21]
AR26
GPIF II Data Bus 21
1.8 V
USBFX3_DQ[22]
AP26
GPIF II Data Bus 22
1.8 V
USBFX3_DQ[23]
AP25
GPIF II Data Bus 23
1.8 V
USBFX3_DQ[24]
AN24
GPIF II Data Bus 24
1.8 V
USBFX3_DQ[25]
AN26
GPIF II Data Bus 25
1.8 V
USBFX3_DQ[26]
AK23
GPIF II Data Bus 26
1.8 V
USBFX3_DQ[27]
AJ25
GPIF II Data Bus 27
1.8 V
USBFX3_DQ[28]
AJ23
GPIF II Data Bus 28
1.8 V
USBFX3_DQ[29]
AH23
GPIF II Data Bus 29
1.8 V
USBFX3_DQ[30]
AR20
GPIF II Data Bus 30
1.8 V
USBFX3_DQ[31]
AP20
GPIF II Data Bus 31
1.8 V
USBFX3_CTL0_SLCS_n
AV26
GPIF II Control Bus 0
1.8 V
USBFX3_CTL1_SLWR_n
AT22
GPIF II Control Bus 1
1.8 V
Page 27

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
26
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
USBFX3_CTL2_SLOE_n
AT25
GPIF II Control Bus 2
1.8 V
USBFX3_CTL3_SLRD_n
AR27
GPIF II Control Bus 3
1.8 V
USBFX3_CTL4_FLAGA
AN22
GPIF II Control Bus 4
1.8 V
USBFX3_CTL5_FLAGB
AN23
GPIF II Control Bus 5
1.8 V
USBFX3_CTL6
AL24
GPIF II Control Bus 6
1.8 V
USBFX3_CTL7_PKTEND_n
AL25
GPIF II Control Bus 7
1.8 V
USBFX3_CTL8
AV21
GPIF II Control Bus 8
1.8 V
USBFX3_CTL9
AV22
GPIF II Control Bus 9
1.8 V
USBFX3_CTL10
AU24
GPIF II Control Bus
10
1.8 V
USBFX3_CTL11_A1
AU22
GPIF II Control Bus
11
1.8 V
USBFX3_CTL12_A0
AT23
GPIF II Control Bus
12
1.8 V
USBFX3_CTL15_INT_n
AW21
GPIF II Control Bus
15
1.8 V
USBFX3_RESET_n
AJ24
FX3 reset
1.8 V
USBFX3_PCLK
AT27
FX3 clok
1.8 V
USBFX3_UART_TX
AP23
USB to UART
transmitter
1.8 V
USBFX3_UART_RX
AU27
USB to UART
receiver
1.8 V
USBFX3_OTG_ID
AG26
OTG ID pin
1.8 V
44..3
3
SSFFPP++ CCoonnnneeccttoorr
The development board has four independent 10G SFP+ connectors that use one transceiver
channel each from the Arria 10 SoC FPGA device. These modules take in serial data from the Arria
10 SoC FPGA device and transform them to optical signals. The board includes cage assemblies for
the SFP+ connectors. Figure 4-9 shows the connections between the SFP+ and Arria 10 SoC
FPGA.
Page 28

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
27
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
Figure 4-9 Connection between the SFP+ and Arria 10 SoC FPGA
Table 4-7, Table 4-8, Table 4-9 and Table 4-10 list the four QSF+ connectors assignments and
signal names relative to the Arria 10 SoC FPGA.
Table 4-7 SFP+ A Pin Assignments, Signal Names and Functions
Signal Name
FPGA Pin
Number
Description
I/O Standard
SFPA_TXDISABLE
PIN_AV6
Turns off and disables the
transmitter output
1.2V
SFPA_TXFAULT
PIN_AP3
Transmitter fault
1.2V
SFPA_TX_p
PIN_AG37
Transmitter data
HSSI DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
SFPA_RX_p
PIN_AD35
Receiver data
HSSI DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
SFPA_LOS
PIN_AN6
Signal loss indicator
1.2V
SFPA_MOD0_PRSNT_n
PIN_AU4
Module present
1.2V
SFPA_RATESEL0
PIN_AM19
Rate select 0
1.8V
SFPA_RATESEL1
PIN_AN17
Rate select 1
1.8V
SFPA_MOD1_SCL
PIN_AW6
Transmitter data
1.2V
SFPA_MOD2_SDA
PIN_AW5
Receiver data
1.2V
Table 4-8 SFP+ B Pin Assignments, Signal Names and Functions
Signal Name
FPGA Pin
Number
Description
I/O Standard
SFPB_TXDISABLE
PIN_AU5
Turns off and disables the
transmitter output
1.2V
SFPB_TXFAULT
PIN_AE10
Transmitter fault
1.2V
Page 29

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
28
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
SFPB_TX_p
PIN_AF39
Transmiter data
HSSI DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
SFPB_RX_p
PIN_AC37
Receiver data
HSSI DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
SFPB_LOS
PIN_AN12
Signal loss indicator
1.2V
SFPB_MOD0_PRSNT_n
PIN_AT5
Module present
1.2V
SFPB_RATESEL0
PIN_AR18
Rate select 0
1.8V
SFPB_RATESEL1
PIN_AP18
Rate select 1
1.8V
SFPB_MOD1_SCL
PIN_AW4
Transmitter data
1.2V
SFPB_MOD2_SDA
PIN_AV4
Receiver data
1.2V
Table 4-9 SFP+ C Pin Assignments, Signal Names and Functions
Signal Name
FPGA Pin
Number
Description
I/O Standard
SFPC_TXDISABLE
PIN_AP30
Turns off and disables the
transmitter output
1.2V
SFPC_TXFAULT
PIN_AP28
Transmitter fault
1.2V
SFPC_TX_p
PIN_AE37
Transmiter data
HSSI DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
SFPC_RX_p
PIN_AC33
Receiver data
HSSI DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
SFPC_LOS
PIN_AN28
Signal loss indicator
1.2V
SFPC_MOD0_PRSNT_n
PIN_B27
Module present
1.2V
SFPC_RATESEL0
PIN_AK18
Rate select 0
1.8V
SFPC_RATESEL1
PIN_AR17
Rate select 1
1.8V
SFPC_MOD1_SCL
PIN_AV3
Transmitter data
1.2V
SFPC_MOD2_SDA
PIN_AW3
Receiver data
1.2V
Table 4-10 SFP+ D Pin Assignments, Signal Names and Functions
Signal Name
FPGA Pin
Number
Description
I/O Standard
SFPD_TXDISABLE
PIN_AR28
Turns off and disables the
transmitter output
1.2V
SFPD_TXFAULT
PIN_AP21
Transmitter fault
1.2V
SFPD_TX_p
PIN_AD39
Transmiter data
HSSI DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
Page 30

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
29
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
SFPD_RX_p
PIN_AB35
Receiver data
HSSI DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
SFPD_LOS
PIN_D26
Signal loss indicator
1.2V
SFPD_MOD0_PRSNT_n
PIN_AL28
Module present
1.2V
SFPD_RATESEL0
PIN_AH18
Rate select 0
1.8V
SFPD_RATESEL1
PIN_AW19
Rate select 1
1.8V
SFPD_MOD1_SCL
PIN_AV2
Transmitter data
1.2V
SFPD_MOD2_SDA
PIN_AV1
Receiver data
1.2V
SFP_REFCLK_p
PIN_AD31
SFP Reference clock
LVDS
44..4
4
SSAATTAA
Four Serial ATA (SATA) ports are available on the FPGA development board which are computer
bus standard with a primary function of transferring data between the motherboard and mass storage
devices (such as hard drives, optical drives, and solid-state disks). Supporting a storage interface is
just one of many different applications an FPGA can be used in storage appliances. The Arria 10
SoC device can bridge different protocols such as bridging simple bus I/Os like PCI Express (PCIe)
to SATA or network interfaces such as Gigabit Ethernet (GbE) to SATA. The SATA interface
supports SATA 3.0 standard with connection speed of 6 Gbps based on Arria 10 SoC device with
integrated transceivers compliant to SATA electrical standards.
The four Serial ATA (SATA) ports include two available ports for device and two available ports for
host capable of implementing SATA solution with a design that consists of both host and target
(device side) functions. Figure 4-10 depicts the host and device design examples.
Figure 4-10 PC and storage device connection to the Arria 10 SoC FPGA
Page 31

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
30
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
The transmitter and receiver signals of the SATA ports are connected directly to the Arria 10 SoC
transceiver channels to provide SATA IO connectivity to both host and target devices. To verify the
functionality of the SATA host/device ports, a connection can be established between the two ports
by using a SATA cable as Figure 4-11 depicts the associated signals connected. Table 4-11 lists the
SATA pin assignments, signal names and functions.
Figure 4-11 Pin connection between SATA connectors
Table 4-11 SATA Pin Assignments, Signal Names and Functions
Signal Name
FPGA Pin
Number
Description
I/O Standard
Device
SATA_DEVICE_REFCLK_p
PIN_M31
SATA Device reference
clock
LVDS
SATA_DEVICE_REFCLK_n
PIN_M30
SATA Device reference
clock
LVDS
SATA_DEVICE_RX_n0
PIN_D34
Differential receive data
input after DC blocking
capacitor
HSSI
DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
SATA_DEVICE_RX_n1
PIN_B34
Differential receive data
input after DC blocking
capacitor
HSSI
DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
SATA_DEVICE_TX_n0
PIN_B38
Differential transmit data
output before DC
blocking capacitor
HSSI
DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
SATA_DEVICE_TX_n1
PIN_A36
Differential transmit data
output before DC
blocking capacitor
HSSI
DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
SATA_DEVICE_TX_p0
PIN_B39
Differential transmit data
output before DC
HSSI
DIFFERENTIAL
Page 32

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
31
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
blocking capacitor
I/O
SATA_DEVICE_TX_p1
PIN_A37
Differential transmit data
output before DC
blocking capacitor
HSSI
DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
SATA_DEVICE_RX_p0
PIN_D35
Differential receive data
input after DC blocking
capacitor
HSSI
DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
SATA_DEVICE_RX_p1
PIN_B35
Differential receive data
input after DC blocking
capacitor
HSSI
DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
Host
SATA_HOST_REFCLK_p
PIN_AF31
SATA Host reference
clock
LVDS
SATA_HOST_REFCLK_n
PIN_AF30
SATA Host reference
clock
LVDS
SATA_HOST_TX_p0
PIN_AJ37
Differential transmit data
output before DC
blocking capacitor
HSSI
DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
SATA_HOST_TX_p1
PIN_AH39
Differential transmit data
output before DC
blocking capacitor
HSSI
DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
SATA_HOST_RX_p0
PIN_AE33
Differential receive data
input after DC blocking
capacitor
HSSI
DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
SATA_HOST_RX_p1
PIN_AF35
Differential receive data
input after DC blocking
capacitor
HSSI
DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
SATA_HOST_TX_n0
PIN_AJ36
Differential transmit data
output before DC
blocking capacitor
HSSI
DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
SATA_HOST_TX_n1
PIN_AH38
Differential transmit data
output before DC
blocking capacitor
HSSI
DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
SATA_HOST_RX_n0
PIN_AE32
Differential receive data
input after DC blocking
capacitor
HSSI
DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
SATA_HOST_RX_n1
PIN_AF34
Differential receive data
input after DC blocking
capacitor
HSSI
DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
Page 33

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
32
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
44..5
5
PPCCIIee
The HAN Pilot Platform board features one PCIe Express downstream interfaces (x4 lane) which
are designed to interface with a PC motherboard x4 slot via PCIe cable and PCIe adapter card.
Utilizing built-in transceivers on an Arria 10 SoC device, it is able to provide a fully integrated PCI
Express-compliant solution for multi-lane (x4) applications. With the PCI Express hard IP block
incorporated in the Arria 10 SoC device, it will allow users to implement simple and fast protocols,
as well as saving logic resources for logic applications.
The PCI Express interface supports complete PCI Express Gen1 at 2.5Gbps/lane, Gen2 at
5.0Gbps/lane, and Gen3 at 8.0Gbps/lane protocol stack solution compliant to PCI Express base
specification 3.0 that includes PHY-MAC, Data Link, and transaction layer circuitry embedded in
PCI Express hard IP blocks.
To use PCIe interface, two external associated devices will be needed to establish a link with PC.
First, a PCIe half-height add-in host card with a PCIe x4 cable connector called PCA (PCIe Cabling
Adapter Card and See Figure 4-12) will be used to plug into the PCIe slot on a mother board. Then,
a PCIe x4 cable (See Figure 4-13) will be used to connect HAN Pilot Platform board and PCIe
add-in card as shown in Figure 4-14, the longest length is up to 3 meters. These two associated
devices are not included in HAN Pilot Platform kit. To purchase the PCA card as well as the
external cable, please refer to Terasic website pca.terasic.com and PCIe_Cable.terasic.com.
Figure 4-12 PCIe Cabling Adaptor(PCA) card
Page 34

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
33
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
Figure 4-13 PCIe External Cable
Figure 4-14 PCIe Link Setup between HAN Pilot Platform and PC
Table 4-12 summarizes the PCI Express pin assignments of the signal names relative to the Arria 10
FPGA.
Table 4-12 PCI Express pin assignments of the signal names
Schematic
Signal Name
Description
I/O Standard
Arria 10 Pin
Number
PCIE_REFCLK_p
PCIe reference clock
LVDS
PIN_AH31
PCIE_PREST_n
PCIe present, active low
1.8-V
PIN_AW20
PCIE_WAKE_n
PCIe wake
1.8-V
PIN_AL19
PCIE_TX_p[0]
PCIe Transmitter data p0
HSSI DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
PIN_AR37
PCIE_RX_p[0]
PCIe Receiver data p0
HSSI DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
PIN_AL33
PCIE_TX_p[1]
PCIe Transmitter data p1
HSSI DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
PIN_AP39
PCIE_RX_p[1]
PCIe Receiver data p1
HSSI DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
PIN_AM35
PCIE_TX_p[2]
PCIe Transmitter data p2
HSSI DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
PIN_AN37
PCIE_RX_p[2]
PCIe Receiver data p2
HSSI DIFFERENTIAL
PIN_AJ33
Page 35

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
34
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
I/O
PCIE_TX_p[3]
PCIe Transmitter data p3
HSSI DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
PIN_AM39
PCIE_RX_p[3]
PCIe Receiver data p3
HSSI DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
PIN_AK35
44..6
6
DDDDRR44
The board supports 1GB of DDR4 SDRAM comprising of two x16 bit DDR4 devices on FPGA
side. The DDR4 devices shipped with this board are running at 1067 MHz, for a total theoretical
bandwidth of over 66Gbps. Figure 4-15 shows the connections between the DDR4 and Arria 10
SoC FPGA. Table 4-13 lists the pin assignments of DDR4 and its description with I/O standard.
Figure 4-15 The connection between DDR4 and Arria 10 SoC FPGA
Table 4-13 The pin assignments of DDR4 component and its description with I/O standard
FPGA Pin Number
Signal Name
Description
I/O Standard
PIN_AU7
DDR4B_REFCLK_p
DDR4 A port Reference Clock
p
LVDS
PIN_AJ11
DDR4B_A[0]
Address [0]
SSTL-12
PIN_AH12
DDR4B_A[1]
Address [1]
SSTL-12
PIN_AP11
DDR4B_A[2]
Address [2]
SSTL-12
PIN_AN11
DDR4B_A[3]
Address [3]
SSTL-12
PIN_AM10
DDR4B_A[4]
Address [4]
SSTL-12
PIN_AM11
DDR4B_A[5]
Address [5]
SSTL-12
PIN_AP9
DDR4B_A[6]
Address [6]
SSTL-12
PIN_AN9
DDR4B_A[7]
Address [7]
SSTL-12
PIN_AR10
DDR4B_A[8]
Address [8]
SSTL-12
Page 36

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
35
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
PIN_AP10
DDR4B_A[9]
Address [9]
SSTL-12
PIN_AM9
DDR4B_A[10]
Address [10]
SSTL-12
PIN_AL10
DDR4B_A[11]
Address [11]
SSTL-12
PIN_AV8
DDR4B_A[12]
Address [12]
SSTL-12
PIN_AT8
DDR4B_A[13]
Address [13]
SSTL-12
PIN_AT9
DDR4B_A[14]
Address [14]/WE_n
SSTL-12
PIN_AR7
DDR4B_A[15]
Address [15]/CAS_n
SSTL-12
PIN_AR8
DDR4B_A[16]
Address [16]/RAS_n
SSTL-12
PIN_AU6
DDR4B_BA[0]
Bank Select [0]
SSTL-12
PIN_AP8
DDR4B_BA[1]
Bank Select [1]
SSTL-12
PIN_AN8
DDR4B_BG[0]
Bank Group Select[0]
SSTL-12
PIN_AJ14
DDR4B_BG[1]
Bank Group Select[1]
SSTL-12
PIN_AL13
DDR4B_CK
Clock p0
DIFFERENTIAL
1.2-V SSTL
PIN_AK13
DDR4B_CK_n
Clock n0
DIFFERENTIAL
1.2-V SSTL
PIN_AK10
DDR4B_CKE
Clock Enable pin
SSTL-12
PIN_AE12
DDR4B_DQS[0]
Data Strobe p[0]
DIFFERENTIAL
1.2-V POD
PIN_AL7
DDR4B_DQS[1]
Data Strobe p[1]
DIFFERENTIAL
1.2-V POD
PIN_AR6
DDR4B_DQS[2]
Data Strobe p[2]
DIFFERENTIAL
1.2-V POD
PIN_AT2
DDR4B_DQS[3]
Data Strobe p[3]
DIFFERENTIAL
1.2-V POD
PIN_AF13
DDR4B_DQS_n[0]
Data Strobe n[0]
DIFFERENTIAL
1.2-V POD
PIN_AK8
DDR4B_DQS_n[1]
Data Strobe n[1]
DIFFERENTIAL
1.2-V POD
PIN_AP6
DDR4B_DQS_n[2]
Data Strobe n[2]
DIFFERENTIAL
1.2-V POD
PIN_AT3
DDR4B_DQS_n[3]
Data Strobe n[3]
DIFFERENTIAL
1.2-V POD
PIN_AF10
DDR4B_DBI_n[0]
Data Bus Inversion [0]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AL8
DDR4B_DBI_n[1]
Data Bus Inversion [1]
1.2-V POD
Page 37

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
36
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
PIN_AN7
DDR4B_DBI_n[2]
Data Bus Inversion [2]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AN4
DDR4B_DBI_n[3]
Data Bus Inversion [3]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AF10
DDR4B_DBI_n[0]
Data Bus Inversion [0]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AJ9
DDR4B_DQ[0]
Data [0]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AG11
DDR4B_DQ[1]
Data [1]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AF9
DDR4B_DQ[2]
Data [2]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AG12
DDR4B_DQ[3]
Data [3]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AG9
DDR4B_DQ[4]
Data [4]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AF12
DDR4B_DQ[5]
Data [5]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AJ10
DDR4B_DQ[6]
Data [6]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AG10
DDR4B_DQ[7]
Data [7]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AL9
DDR4B_DQ[8]
Data [8]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AH9
DDR4B_DQ[9]
Data [9]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AK6
DDR4B_DQ[10]
Data [10]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AK7
DDR4B_DQ[11]
Data [11]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AH8
DDR4B_DQ[12]
Data [12]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AH7
DDR4B_DQ[13]
Data [13]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AJ8
DDR4B_DQ[14]
Data [14]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AE11
DDR4B_DQ[15]
Data [15]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AT4
DDR4B_DQ[16]
Data [16]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AM7
DDR4B_DQ[17]
Data [17]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AP5
DDR4B_DQ[18]
Data [18]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AL5
DDR4B_DQ[19]
Data [19]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AM5
DDR4B_DQ[20]
Data [20]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AM6
DDR4B_DQ[21]
Data [21]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AM4
DDR4B_DQ[22]
Data [22]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AR5
DDR4B_DQ[23]
Data [23]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AP1
DDR4B_DQ[24]
Data [24]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AR3
DDR4B_DQ[25]
Data [25]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AN3
DDR4B_DQ[26]
Data [26]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AR1
DDR4B_DQ[27]
Data [27]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AU2
DDR4B_DQ[28]
Data [28]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AP4
DDR4B_DQ[29]
Data [29]
1.2-V POD
Page 38

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
37
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
PIN_AR2
DDR4B_DQ[30]
Data [30]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AU1
DDR4B_DQ[31]
Data [31]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AF10
DDR4B_DM[0]
DDR3 Data Mask[0]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AL8
DDR4B_DM[1]
DDR3 Data Mask[1]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AN7
DDR4B_DM[2]
DDR3 Data Mask[2]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AN4
DDR4B_DM[3]
DDR3 Data Mask[3]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AJ13
DDR4B_CS_n[0]
Chip Select
SSTL-12
PIN_AH14
DDR4B_RESET_n
Chip Reset
1.2 V
PIN_AL12
DDR4B_ODT
On Die Termination
SSTL-12
PIN_AM12
DDR4B_PAR
Command and Address Parity
Input
SSTL-12
PIN_AH11
DDR4B_ALERT_n
Register ALERT_n output
SSTL-12
PIN_AH13
DDR4B_ACT_n
Activation Command Input
SSTL-12
PIN_AW8
DDR4B_RZQ
External reference ball for
output drive calibration
1.2 V
The development board also supports one bank of DDR4 SDRAM SO-DIMM on FPGA side. It is
wired to support a maximum capacity of 8GB with a 72-bit data bus. Using differential DQS
signaling for the DDR4 SDRAM interfaces, it is capable of running at up to 1067MHz memory
clock for a maximum theoretical bandwidth up to 132Gbps. Figure 4-16 shows the connections
between the DDR4 SDRAM SODIMM and Arria 10 SoC FPGA. The pin assignments for DDR4
SDRAM SO-DIMM are listed in Table 4-14.
Figure 4-16 The connection between the DDR4 SDRAM SO-DIMM and Arria 10 SoC FPGA
Page 39

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
38
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
Table 4-14 The pin assignments for DDR4 SDRAM SO-DIMM
FPGA Pin Number
Signal Name
Description
I/O Standard
PIN_AB12
DDR4A_REFCLK_p
DDR4 A port Reference Clock p
LVDS
PIN_AC1
DDR4A_A[0]
Address [0]
SSTL-12
PIN_AB1
DDR4A_A[1]
Address [1]
SSTL-12
PIN_AB4
DDR4A_A[2]
Address [2]
SSTL-12
PIN_AA5
DDR4A_A[3]
Address [3]
SSTL-12
PIN_AA3
DDR4A_A[4]
Address [4]
SSTL-12
PIN_AA4
DDR4A_A[5]
Address [5]
SSTL-12
PIN_Y2
DDR4A_A[6]
Address [6]
SSTL-12
PIN_AA2
DDR4A_A[7]
Address [7]
SSTL-12
PIN_AB5
DDR4A_A[8]
Address [8]
SSTL-12
PIN_AB6
DDR4A_A[9]
Address [9]
SSTL-12
PIN_W5
DDR4A_A[10]
Address [10]
SSTL-12
PIN_Y5
DDR4A_A[11]
Address [11]
SSTL-12
PIN_AA9
DDR4A_A[12]
Address [12]
SSTL-12
PIN_AB7
DDR4A_A[13]
Address [13]
SSTL-12
PIN_AA7
DDR4A_A[14]
Address [14]/WE_n
SSTL-12
PIN_AB10
DDR4A_A[15]
Address [15]/CAS_n
SSTL-12
PIN_AB11
DDR4A_A[16]
Address [16]/RAS_n
SSTL-12
PIN_Y7
DDR4A_BA[0]
Bank Select [0]
SSTL-12
PIN_AB9
DDR4A_BA[1]
Bank Select [1]
SSTL-12
PIN_AA10
DDR4A_BG[0]
Bank Group Select[0]
SSTL-12
PIN_AE2
DDR4A_BG[1]
Bank Group Select[1]
SSTL-12
PIN_AD3
DDR4A_CK
Clock p0
DIFFERENTIAL
1.2-V SSTL
PIN_AD4
DDR4A_CK_n
Clock n0
DIFFERENTIAL
1.2-V SSTL
PIN_AC2
DDR4A_CKE
Clock Enable pin
SSTL-12
PIN_AE8
DDR4A_DQS[0]
Data Strobe p[0]
DIFFERENTIAL
1.2-V POD
PIN_AF7
DDR4A_DQS[1]
Data Strobe p[1]
DIFFERENTIAL
1.2-V POD
PIN_AN1
DDR4A_DQS[2]
Data Strobe p[2]
DIFFERENTIAL
Page 40

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
39
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
1.2-V POD
PIN_AH2
DDR4A_DQS[3]
Data Strobe p[3]
DIFFERENTIAL
1.2-V POD
PIN_P1
DDR4A_DQS[4]
Data Strobe p[4]
DIFFERENTIAL
1.2-V POD
PIN_J3
DDR4A_DQS[5]
Data Strobe p[5]
DIFFERENTIAL
1.2-V POD
PIN_R5
DDR4A_DQS[6]
Data Strobe p[6]
DIFFERENTIAL
1.2-V POD
PIN_V9
DDR4A_DQS[7]
Data Strobe p[7]
DIFFERENTIAL
1.2-V POD
PIN_V2
DDR4A_DQS[8]
Data Strobe p[8]
DIFFERENTIAL
1.2-V POD
PIN_AD8
DDR4A_DQS_n[0]
Data Strobe n[0]
DIFFERENTIAL
1.2-V POD
PIN_AE7
DDR4A_DQS_n[1]
Data Strobe n[1]
DIFFERENTIAL
1.2-V POD
PIN_AN2
DDR4A_DQS_n[2]
Data Strobe n[2]
DIFFERENTIAL
1.2-V POD
PIN_AH3
DDR4A_DQS_n[3]
Data Strobe n[3]
DIFFERENTIAL
1.2-V POD
PIN_R1
DDR4A_DQS_n[4]
Data Strobe n[4]
DIFFERENTIAL
1.2-V POD
PIN_K3
DDR4A_DQS_n[5]
Data Strobe n[5]
DIFFERENTIAL
1.2-V POD
PIN_R6
DDR4A_DQS_n[6]
Data Strobe n[6]
DIFFERENTIAL
1.2-V POD
PIN_W9
DDR4A_DQS_n[7]
Data Strobe n[7]
DIFFERENTIAL
1.2-V POD
PIN_V3
DDR4A_DQS_n[8]
Data Strobe n[8]
DIFFERENTIAL
1.2-V POD
PIN_AC11
DDR4A_DQ[0]
Data [0]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AD10
DDR4A_DQ[1]
Data [1]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AC9
DDR4A_DQ[2]
Data [2]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AG7
DDR4A_DQ[3]
Data [3]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AD13
DDR4A_DQ[4]
Data [4]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AD11
DDR4A_DQ[5]
Data [5]
1.2-V POD
Page 41

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
40
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
PIN_AC8
DDR4A_DQ[6]
Data [6]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AF8
DDR4A_DQ[7]
Data [7]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AE6
DDR4A_DQ[8]
Data [8]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AJ6
DDR4A_DQ[9]
Data [9]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AG6
DDR4A_DQ[10]
Data [10]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AD6
DDR4A_DQ[11]
Data [11]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AG5
DDR4A_DQ[12]
Data [12]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AK5
DDR4A_DQ[13]
Data [13]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AC7
DDR4A_DQ[14]
Data [14]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AH6
DDR4A_DQ[15]
Data [15]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AK1
DDR4A_DQ[16]
Data [16]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AL4
DDR4A_DQ[17]
Data [17]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AJ4
DDR4A_DQ[18]
Data [18]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AM1
DDR4A_DQ[19]
Data [19]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AK3
DDR4A_DQ[20]
Data [20]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AL2
DDR4A_DQ[21]
Data [21]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AJ3
DDR4A_DQ[22]
Data [22]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AM2
DDR4A_DQ[23]
Data [23]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AF2
DDR4A_DQ[24]
Data [24]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AH1
DDR4A_DQ[25]
Data [25]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AG4
DDR4A_DQ[26]
Data [26]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AE5
DDR4A_DQ[27]
Data [27]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AF3
DDR4A_DQ[28]
Data [28]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AH4
DDR4A_DQ[29]
Data [29]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AG1
DDR4A_DQ[30]
Data [30]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AF4
DDR4A_DQ[31]
Data [31]
1.2-V POD
PIN_K1
DDR4A_DQ[32]
Data [32]
1.2-V POD
PIN_P4
DDR4A_DQ[33]
Data [33]
1.2-V POD
PIN_N2
DDR4A_DQ[34]
Data [34]
1.2-V POD
PIN_K2
DDR4A_DQ[35]
Data [35]
1.2-V POD
PIN_M2
DDR4A_DQ[36]
Data [36]
1.2-V POD
PIN_P3
DDR4A_DQ[37]
Data [37]
1.2-V POD
PIN_N1
DDR4A_DQ[38]
Data [38]
1.2-V POD
Page 42

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
41
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
PIN_J1
DDR4A_DQ[39]
Data [39]
1.2-V POD
PIN_N3
DDR4A_DQ[40]
Data [40]
1.2-V POD
PIN_P5
DDR4A_DQ[41]
Data [41]
1.2-V POD
PIN_M5
DDR4A_DQ[42]
Data [42]
1.2-V POD
PIN_R2
DDR4A_DQ[43]
Data [43]
1.2-V POD
PIN_N4
DDR4A_DQ[44]
Data [44]
1.2-V POD
PIN_P6
DDR4A_DQ[45]
Data [45]
1.2-V POD
PIN_L4
DDR4A_DQ[46]
Data [46]
1.2-V POD
PIN_R3
DDR4A_DQ[47]
Data [47]
1.2-V POD
PIN_V6
DDR4A_DQ[48]
Data [48]
1.2-V POD
PIN_T7
DDR4A_DQ[49]
Data [49]
1.2-V POD
PIN_U5
DDR4A_DQ[50]
Data [50]
1.2-V POD
PIN_U7
DDR4A_DQ[51]
Data [51]
1.2-V POD
PIN_T4
DDR4A_DQ[52]
Data [52]
1.2-V POD
PIN_W6
DDR4A_DQ[53]
Data [53]
1.2-V POD
PIN_T3
DDR4A_DQ[54]
Data [54]
1.2-V POD
PIN_U6
DDR4A_DQ[55]
Data [55]
1.2-V POD
PIN_W8
DDR4A_DQ[56]
Data [56]
1.2-V POD
PIN_Y12
DDR4A_DQ[57]
Data [57]
1.2-V POD
PIN_Y11
DDR4A_DQ[58]
Data [58]
1.2-V POD
PIN_W10
DDR4A_DQ[59]
Data [59]
1.2-V POD
PIN_Y13
DDR4A_DQ[60]
Data [60]
1.2-V POD
PIN_Y8
DDR4A_DQ[61]
Data [61]
1.2-V POD
PIN_Y10
DDR4A_DQ[62]
Data [62]
1.2-V POD
PIN_W11
DDR4A_DQ[63]
Data [63]
1.2-V POD
PIN_V1
DDR4A_DQ[64]
Data [64]
1.2-V POD
PIN_Y1
DDR4A_DQ[65]
Data [65]
1.2-V POD
PIN_W3
DDR4A_DQ[66]
Data [66]
1.2-V POD
PIN_W1
DDR4A_DQ[67]
Data [67]
1.2-V POD
PIN_Y3
DDR4A_DQ[68]
Data [68]
1.2-V POD
PIN_W4
DDR4A_DQ[69]
Data [69]
1.2-V POD
PIN_U1
DDR4A_DQ[70]
Data [70]
1.2-V POD
PIN_U2
DDR4A_DQ[71]
Data [71]
1.2-V POD
Page 43

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
42
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
PIN_AD9
DDR4A_DBI_n[0]
Data Bus Inversion [0]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AJ5
DDR4A_DBI_n[1]
Data Bus Inversion [1]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AK2
DDR4A_DBI_n[2]
Data Bus Inversion [2]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AG2
DDR4A_DBI_n[3]
Data Bus Inversion [3]
1.2-V POD
PIN_L2
DDR4A_DBI_n[4]
Data Bus Inversion [4]
1.2-V POD
PIN_L3
DDR4A_DBI_n[5]
Data Bus Inversion [5]
1.2-V POD
PIN_U4
DDR4A_DBI_n[6]
Data Bus Inversion [6]
1.2-V POD
PIN_V8
DDR4A_DBI_n[7]
Data Bus Inversion [7]
1.2-V POD
PIN_V4
DDR4A_DBI_n[8]
Data Bus Inversion [8]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AE1
DDR4A_CS_n
Chip Select
SSTL-12
PIN_AE3
DDR4A_RESET_n
Chip Reset
1.2 V
PIN_AC3
DDR4A_ODT
On Die Termination
SSTL-12
PIN_AC6
DDR4A_PAR
Command and Address Parity
Input
SSTL-12
PIN_AC12
DDR4A_ALERT_n
Register ALERT_n output
SSTL-12
PIN_AD1
DDR4A_ACT_n
Activation Command Input
SSTL-12
PIN_T5
DDR4A_EVENT_n
Chip Temperature Event
1.2 V
PIN_AD5
DDR4A_AC_R[0]
Reserved for
QDRII+/RLDRAM3
SSTL-12
PIN_Y6
DDR4A_AC_R[1]
Reserved for
QDRII+/RLDRAM3
SSTL-12
PIN_AC4
DDR4A_C[0]
Reserved for
QDRII+/RLDRAM3
SSTL-12
PIN_AB2
DDR4A_C[1]
Reserved for
QDRII+/RLDRAM3
SSTL-12
PIN_AA8
DDR4A_RZQ
External reference ball for
output drive calibration
1.2 V
The DDR4 SDRAM SO-DIMM socket can support many kinds of memory devices, such as
standard DDR4 SO-DIMM with ECC up to 8GB at 1067MHz, Terasic QDRII+ module, as shown
in Figure 4-17, Figure 4-18.
Page 44

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
43
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
Figure 4-17 Standard DDR4 SO-DIMM with ECC
Figure 4-18 Terasic QDRII+ module with DDR4 SO-DIMM interface
44..7
7
HHDDMMII TTrraannssmmiitttteerr aanndd RReecceeiivveerr
The HAN Pilot Platform board features HDMI transmitter and receiver.
For HDMI transmitter, as shown in Figure 4-19. The board features a Transition Minimized
Differential Signal (TMDS) retimer IC (TI:SN75DP159). Users can implement Intel or third-party
IP in FPGA; HDMI video or audio data is encoded to TMDS signal and output from FPGA
transceiver. The signals transmit to the retimer IC and display on HDMI monitor through HDMI
connector.
For HDMI Receiver, it features a Redriver IC (DIDOES: PI3HDX1204B1). It transmits the input
TMDS signal into FPGA, and decoded to image video data by Intel or third-party IP, then will be
processed next step. Table 4-15 lists the HDMI Transmitter and Receiver pin assignments, signal
names and functions.
Page 45

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
44
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
Figure 4-19 The HDMI transceiver interface of the HAN Pilot Platform
Table 4-15 HDMI TX and RX port Pin Assignments, Signal Names and Functions
Signal Name
FPGA Pin
Number
Description
I/O Standard
HDMI_REFCLK_p
V31
HDMI reference clock from
external PLL
LVDS
HDMI_TX_CLK_p
V39
TX TMDS clock channel
HSSI Differential I/O
HDMI_TX_D_p[0]
U37
TX TMDS data channel 0
HSSI Differential I/O
HDMI_TX_D_p[1]
T39
TX TMDS data channel 1
HSSI Differential I/O
HDMI_TX_D_p[2]
R37
TX TMDS data channel 2
HSSI Differential I/O
HDMI_TX_SCL
A25
I2C clock of the TX re-timer IC
and DCC
1.8V
HDMI_TX_SDA
AB25
I2C data of the TX re-timer IC
and DCC
1.8V
HDMI_HPD
AF28
TX Hot Plug Detect
1.8V
HDMI_TX_CEC
AK26
HDMI TX Consumer
Electronics Control
1.8V
HDMI_RX_CLK_p
Y31
RX TMDS clock channel
HSSI Differential I/O
HDMI_RX_D_p[0]
Y35
RX TMDS data channel 0
HSSI Differential I/O
Page 46

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
45
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
HDMI_RX_D_p[1]
W37
RX TMDS data channel 1
HSSI Differential I/O
HDMI_RX_D_p[2]
W33
RX TMDS data channel 2
HSSI Differential I/O
HDMI_RX_SCL
V7
I2C clock of the RX re-driver IC
1.2 V
HDMI_RX_SDA
T2
I2C clock of the RX re-driver IC
1.2 V
HDMI_HPD_RX
AG27
RX Hot Plug Detect
1.8V
HDMI_RX_5V_N
B26
Detect if the TX terminal has 5V
output
1.8V
HDMI_RX_CEC
AP29
HDMI RX Consumer
Electronics Control
1.8V
DDCSCL_RX
AN27
HDMI DDC(Display Data
Channel) I2C clock
1.8V
DDCSDA_RX
AJ26
HDMI DDC(Display Data
Channel) I2C data
1.8V
44..8
8
GGiiggaabbiitt EEtthheerrnneett
The development board supports one RJ45 10/100/1000 base-T Ethernet using Marvell 88E1111.
SGMII AC coupling interface is used between PHY and FPGA transceiver. The device is an
auto-negotiating Ethernet PHY with an SGMII interface to the FPGA. The Arria 10 SoC FPGA can
communicate with the LVDS interfaces at up to 1.6 Gbps, which is faster than 1.25 Gbps for SGMII.
The MAC function must be provided in the FPGA for typical networking applications. The Marvell
88E1111 PHY uses 2.5-V and 1.1-V power rails and requires a 25MHz reference clock driven from
a dedicated oscillator. It interfaces to an RJ-45 with internal magnetics for driving copper lines with
Ethernet traffic. Figure 4-20 shows the SGMII interface between the FPGA and Marvell 88E1111
PHY. Table 4-16 lists the Ethernet PHY interface pin assignments.
Figure 4-20 SGMII Interface between FPGA and Marvell 88E1111 PHY
Table 4-16 Ethernet PHY Pin Assignments, Signal Names and Functions
Signal Name
FPGA Pin Number
Description
I/O Standard
ETH_TX_p
PIN_AP19
SGMII TX data
LVDS
ETH_RX_p
PIN_AM20
SGMII RX data
LVDS
ETH_INT_n
PIN_AU19
Management bus interrupt
1.8V
Page 47

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
46
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
ETH_MDC
PIN_AT19
Management bus control
1.8V
ETH_MDIO
PIN_AJ20
Management bus data
1.8V
ETH_RST_n
PIN_AK20
Device reset
1.8V
44..9
9
FFMMCC CCoonnnneeccttoorr
The FPGA Mezzanine Card (FMC) interface provides a mechanism to extend the peripheral-set of
an FPGA host board by means of add-on daughter cards, which can address today’s high-speed
signaling requirements as well as low-speed device interface support. The FMC interfaces support
JTAG, clock outputs and inputs, high-speed serial I/O (transceivers), and single-ended or differential
signaling.
There is one FMC connector on the HAN Pilot Platform board, it is a High Pin Count (HPC) size of
connector, The HPC connector on HAN Pilot Platform board can provides 172 user-define,
single-ended signals (include clock signals) and 10 serial transceiver pairs. Figure 4-21 is the FMC
connector on HAN Pilot Platform board. Table 4-17 lists the FMC connector pin assignments,
signal names and functions
Figure 4-21 FMC connector on HAN Pilot Platform board
Table 4-17 FMC Connector Pin Assignments, Signal Names and Functions
Signal Name
FPGA Pin Number
Description
I/O Standard
FMC_CLK2_BIDIR_p
PIN_AW18
FMC bidirection Clock
signal
1.8 V
FMC_CLK2_BIDIR_n
PIN_AV17
FMC bidirection Clock
signal
1.8 V
FMC_CLK3_BIDIR_p
PIN_C1
FMC bidirection Clock
signal
1.8 V
FMC_CLK3_BIDIR_n
PIN_D1
FMC bidirection Clock
signal
1.8 V
FMC_CLK_M2C_p[0]
PIN_K5
Clock input 0
1.8 V
Page 48

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
47
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
FMC_CLK_M2C_p[1]
PIN_AW14
Clock input 1
1.8 V
FMC_CLK_M2C_n[0]
PIN_L5
Clock input 0
1.8 V
FMC_CLK_M2C_n[1]
PIN_AW15
Clock input 1
1.8 V
FMC_HA_p[0]
PIN_K12
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HA_p[1]
PIN_M12
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HA_p[2]
PIN_D10
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HA_p[3]
PIN_E12
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HA_p[4]
PIN_H13
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HA_p[5]
PIN_J11
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HA_p[6]
PIN_N13
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HA_p[7]
PIN_L13
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HA_p[8]
PIN_J14
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HA_p[9]
PIN_F13
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HA_p[10]
PIN_D13
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HA_p[11]
PIN_G14
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HA_p[12]
PIN_A10
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HA_p[13]
PIN_G12
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HA_p[14]
PIN_A12
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HA_p[15]
PIN_A7
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HA_p[16]
PIN_A9
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HA_p[17]
PIN_C12
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HA_p[18]
PIN_B11
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HA_p[19]
PIN_M7
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HA_p[20]
PIN_F10
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HA_p[21]
PIN_C9
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HA_p[22]
PIN_C8
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HA_p[23]
PIN_G11
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HA_n[0]
PIN_L12
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HA_n[1]
PIN_N12
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HA_n[2]
PIN_E10
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HA_n[3]
PIN_F12
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HA_n[4]
PIN_J13
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HA_n[5]
PIN_K11
FMC data bus
1.8 V
Page 49

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
48
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
FMC_HA_n[6]
PIN_P13
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HA_n[7]
PIN_L14
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HA_n[8]
PIN_K13
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HA_n[9]
PIN_F14
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HA_n[10]
PIN_E13
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HA_n[11]
PIN_H14
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HA_n[12]
PIN_B10
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HA_n[13]
PIN_H12
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HA_n[14]
PIN_B12
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HA_n[15]
PIN_A8
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HA_n[16]
PIN_B9
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HA_n[17]
PIN_C13
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HA_n[18]
PIN_C11
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HA_n[19]
PIN_N7
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HA_n[20]
PIN_G10
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HA_n[21]
PIN_D9
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HA_n[22]
PIN_D8
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HA_n[23]
PIN_H11
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HB_p[0]
PIN_E1
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HB_p[1]
PIN_G4
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HB_p[2]
PIN_N8
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HB_p[3]
PIN_J4
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HB_p[4]
PIN_H2
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HB_p[5]
PIN_G5
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HB_p[6]
PIN_D3
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HB_p[7]
PIN_A2
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HB_p[8]
PIN_B1
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HB_p[9]
PIN_AT13
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HB_p[10]
PIN_AM17
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HB_p[11]
PIN_AJ16
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HB_p[12]
PIN_AW13
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HB_p[13]
PIN_AV14
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HB_p[14]
PIN_AP14
FMC data bus
1.8 V
Page 50

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
49
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
FMC_HB_p[15]
PIN_AK16
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HB_p[16]
PIN_AU16
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HB_p[17]
PIN_AT17
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HB_p[18]
PIN_AM15
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HB_p[19]
PIN_AR15
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HB_p[20]
PIN_AP16
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HB_p[21]
PIN_AV18
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HB_n[0]
PIN_E2
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HB_n[1]
PIN_H4
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HB_n[2]
PIN_P8
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HB_n[3]
PIN_J5
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HB_n[4]
PIN_H3
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HB_n[5]
PIN_H6
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HB_n[6]
PIN_E3
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HB_n[7]
PIN_B2
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HB_n[8]
PIN_C2
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HB_n[9]
PIN_AT14
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HB_n[10]
PIN_AL17
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HB_n[11]
PIN_AH16
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HB_n[12]
PIN_AV13
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HB_n[13]
PIN_AU14
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HB_n[14]
PIN_AP15
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HB_n[15]
PIN_AK17
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HB_n[16]
PIN_AU17
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HB_n[17]
PIN_AT18
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HB_n[18]
PIN_AM16
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HB_n[19]
PIN_AR16
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HB_n[20]
PIN_AN16
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_HB_n[21]
PIN_AV19
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_p[0]
PIN_A3
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_p[1]
PIN_B4
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_p[2]
PIN_T9
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_p[3]
PIN_M10
FMC data bus
1.8 V
Page 51

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
50
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
FMC_LA_p[4]
PIN_U9
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_p[5]
PIN_J10
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_p[6]
PIN_H8
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_p[7]
PIN_L9
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_p[8]
PIN_M9
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_p[9]
PIN_G6
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_p[10]
PIN_E8
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_p[11]
PIN_B6
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_p[12]
PIN_A5
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_p[13]
PIN_D5
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_p[14]
PIN_B7
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_p[15]
PIN_E6
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_p[16]
PIN_E5
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_p[17]
PIN_F9
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_p[18]
PIN_K8
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_p[19]
PIN_R8
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_p[20]
PIN_F7
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_p[21]
PIN_C4
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_p[22]
PIN_U11
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_p[23]
PIN_V11
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_p[24]
PIN_R11
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_p[25]
PIN_F2
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_p[26]
PIN_R7
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_p[27]
PIN_T12
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_p[28]
PIN_J6
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_p[29]
PIN_G1
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_p[30]
PIN_K7
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_p[31]
PIN_P10
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_p[32]
PIN_M6
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_p[33]
PIN_N11
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_n[0]
PIN_A4
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_n[1]
PIN_C3
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_n[2]
PIN_T10
FMC data bus
1.8 V
Page 52

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
51
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
FMC_LA_n[3]
PIN_M11
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_n[4]
PIN_U10
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_n[5]
PIN_K10
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_n[6]
PIN_J8
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_n[7]
PIN_L10
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_n[8]
PIN_N9
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_n[9]
PIN_H7
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_n[10]
PIN_F8
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_n[11]
PIN_C6
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_n[12]
PIN_B5
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_n[13]
PIN_D6
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_n[14]
PIN_C7
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_n[15]
PIN_E7
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_n[16]
PIN_F5
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_n[17]
PIN_G9
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_n[18]
PIN_L8
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_n[19]
PIN_P9
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_n[20]
PIN_G7
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_n[21]
PIN_D4
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_n[22]
PIN_U12
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_n[23]
PIN_V12
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_n[24]
PIN_R12
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_n[25]
PIN_G2
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_n[26]
PIN_T8
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_n[27]
PIN_T13
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_n[28]
PIN_K6
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_n[29]
PIN_H1
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_n[30]
PIN_L7
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_n[31]
PIN_R10
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_n[32]
PIN_N6
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_LA_n[33]
PIN_P11
FMC data bus
1.8 V
FMC_GBTCLK_M2C_p[0]
PIN_P31
LVDS input from the
installed FMC card to
LVDS
Page 53

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
52
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
dedicated reference clock
inputs
FMC_GBTCLK_M2C_p[1]
PIN_K31
LVDS input from the
installed FMC card to
dedicated reference clock
inputs
LVDS
FMC_REFCLK_p
PIN_T31
Reference Clock
LVDS
FMC_DP_C2M_p[0]
PIN_M39
Transmit channel
HSSI
DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
FMC_DP_C2M_p[1]
PIN_L37
Transmit channel
HSSI
DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
FMC_DP_C2M_p[2]
PIN_K39
Transmit channel
HSSI
DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
FMC_DP_C2M_p[3]
PIN_J37
Transmit channel
HSSI
DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
FMC_DP_C2M_p[4]
PIN_H39
Transmit channel
HSSI
DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
FMC_DP_C2M_p[5]
PIN_G37
Transmit channel
HSSI
DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
FMC_DP_C2M_p[6]
PIN_F39
Transmit channel
HSSI
DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
FMC_DP_C2M_p[7]
PIN_E37
Transmit channel
HSSI
DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
FMC_DP_C2M_p[8]
PIN_D39
Transmit channel
HSSI
DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
FMC_DP_C2M_p[9]
PIN_C37
Transmit channel
HSSI
DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
FMC_DP_M2C_p[0]
PIN_P35
Transmit channel
HSSI
DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
Page 54

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
53
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
FMC_DP_M2C_p[1]
PIN_R33
Transmit channel
HSSI
DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
FMC_DP_M2C_p[2]
PIN_M35
Transmit channel
HSSI
DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
FMC_DP_M2C_p[3]
PIN_N33
Transmit channel
HSSI
DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
FMC_DP_M2C_p[4]
PIN_K35
Transmit channel
HSSI
DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
FMC_DP_M2C_p[5]
PIN_L33
Transmit channel
HSSI
DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
FMC_DP_M2C_p[6]
PIN_H35
Transmit channel
HSSI
DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
FMC_DP_M2C_p[7]
PIN_J33
Transmit channel
HSSI
DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
FMC_DP_M2C_p[8]
PIN_F35
Transmit channel
HSSI
DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
FMC_DP_M2C_p[9]
PIN_G33
Transmit channel
HSSI
DIFFERENTIAL
I/O
FMC_GA[0]
PIN_E11
FMC geographical address
0
1.8 V
FMC_GA[1]
PIN_AL18
FMC geographical address
1
1.8 V
FMC_SCL
PIN_J9
Management serial clock
line
1.8 V
FMC_SDA
PIN_F4
Management serial data line
1.8 V
Page 55

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
54
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
44..110
0
TTeemmppeerraattuurree SSeennssoorr,, FFaann CCoonnttrrooll aanndd PPoowweerr MMoonniitto
o
rr
The FPGA board is equipped with a temperature sensor, TMP441AIDCNT, which provides
temperature sensing. This function is accomplished by connecting the temperature sensor to the
internal temperature sensing diode of the Arria 10 SoC device. The temperature status and alarm
threshold registers of the temperature sensor can be programmed by a two-wire SMBus, which is
connected to the Arria 10 SoC FPGA. In addition, the 7-bit POR slave address for this sensor is set
to ‘0011100b'.
A 3-pin +12V fan located on J22 of the FPGA board is intended to reduce the temperature of the
FPGA. The board is equipped with a Fan-Speed regulator and monitor MAX6650 with an
I2C/SMBus interfaces, Users regulate and monitor the speed of fan depending on the measured
system temperature.
The HAN Pilot Platform has implemented a power monitor chip to monitor the board input power
voltage and current. Figure 4-22 shows the connection between the power monitor chip and the
Arria 10 SoC FPGA. The power monitor chip monitors both shunt voltage drops and board input
power voltage allows user to monitor the total board power consumption. Programmable calibration
value, conversion times, and averaging, combined with an internal multiplier, enable direct readouts
of current in amperes and power in watts. Note that, the temperature sensor, fan control and power
monitor share the same I2C/SMBUS. Table 4-18 lists the pin assignments, signal names and
functions
Figure 4-22 Connections between the temperature sensor/fan control/power monitor and the
Arria 10 SoC FPGA
Table 4-18 Temperature Sensor and Fan Speed Control Pin Assignments, Schematic Signal
Names and Functions
Schematic Signal Name
Description
I/O
Standard
Arria 10 SoC Pin
Number
TEMPDIODEp
Positive pin of temperature diode in
Arria 10
--
--
TEMPDIODEn
Negative pin of temperature diode
in Arria 10
--
--
Page 56

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
55
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
FPGA_I2C_SCL
SMBus clock
1.8V
M1
FPGA_I2C_SDA
SMBus data
1.8V
M4
FAN_ALERT
Active-low ALERT input
1.8V
E25
44..111
1
GGyyrroossccooppee,, AAcccceelleerroommeetteerr aanndd MMaaggnneettoommeetteerr
The HAN Pilot Platform board is equipped with a Motion-Tracking device named MPU-9250. The
MPU-9250 is a 9-axis Motion-Tracking device that combines a 3-axis gyroscope, 3-axis
accelerometer and 3-axis magnetometer. Detail features of these sensors are listed below.
Figure 4-23 Connections between the MPU-9250 and the Arria 10 SoC FPGA
◼ Gyroscope
The MPU-9250 consists of three independent vibratory MEMS rate gyroscopes, which detect
rotation about the X-, Y-, and Z- Axes. When the gyros are rotated about any of the sense axes, the
Coriolis Effect causes a vibration that is detected by a capacitive pickoff. The resulting signal is
amplified, demodulated, and filtered to produce a voltage that is proportional to the angular rate.
This voltage is digitized using individual on-chip 16-bit Analog-to-Digital Converters (ADCs) to
sample each axis. The full-scale range of the gyro sensors may be digitally programmed to ±250,
±500, ±1000, or ±2000 degrees per second (dps). The ADC sample rate is programmable from
8,000 samples per second, down to 3.9 samples per second, and user-selectable low-pass filters
enable a wide range of cut-off frequencies.
◼ Accelerometer
The MPU-9250’s 3-Axis accelerometer uses separate proof masses for each axis. Acceleration
along a particular axis induces displacement on the corresponding proof mass, and capacitive
sensors detect the displacement differentially. The MPU-9250’s architecture reduces the
accelerometers’ susceptibility to fabrication variations as well as to thermal drift. When the device
is placed on a flat surface, it will measure 0g on the X- and Y-axes and +1g on the Z-axis. The
accelerometers’ scale factor is calibrated at the factory and is nominally independent of supply
voltage. Each sensor has a dedicated sigma-delta ADC for providing digital outputs. The full scale
range of the digital output can be adjusted to ±2g, ±4g, ±8g, or ±16g.
Page 57

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
56
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
◼ Magnetometer
The 3-axis magnetometer uses highly sensitive Hall sensor technology. The magnetometer portion
of the IC incorporates magnetic sensors for detecting terrestrial magnetism in the X-, Y-, and ZAxes, a sensor driving circuit, a signal amplifier chain, and an arithmetic circuit for processing the
signal from each sensor. Each ADC has a 16-bit resolution and a full scale range of ±4800 μT.
Communication with all registers of the device is performed using either I2C at 400kHz on the
HAN Pilot platform. or SPI at 1MHz. For applications requiring faster communications, the sensor
and interrupt registers may be read using SPI at 20MHz. The I2C address is 7’b1101001. For more
detailed information of better using this chip, please refer to its datasheet which is available on
manufacturer’s website or under the /datasheet folder of the system CD. Table 4-19 gives the pin
assignment information of the LCD touch panel. For more detailed information of better using this
chip, please refer to its datasheet which is available on manufacturer’s website or under the
/datasheet folder of the system CD.
Table 4-19 Pin names and descriptions of the MPU-9250
Signal Name
FPGA Pin Number
Description
I/O Standard
MPU_INT
PIN_E26
Interrupt digital output
1.8V
FPGA_I2C_SCL
PIN_M1
I2C serial clock
1.2V
FPGA_I2C_SDA
PIN_M4
I2C serial data
1.2V
Page 58

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
57
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
Chapter 5
HPS Fabric Components
This section intro duces the interfaces connected to the HPS section of the Arria 10 SoC FPGA.
Users can access these interfaces via the HPS processor.
55..1
1
UUsseerr PPuusshh--bbuuttttoonnss aanndd LLEEDDss
Similar to the FPGA, the HPS also has its set of switches, buttons, LEDs, and other interfaces
connected exclusively. Users can control these interfaces to monitor the status of HPS. Table 5-1
gives the pin assignment of all the LEDs, switches and push-buttons.
Table 5-1 Pin Assignment of LEDs, Switches and Push-buttons
Signal Name
HPS Pin Number
Function
I/O Standard
HPS_KEY
PIN_A29
I/O
1.8 V
HPS_LED
PIN_D29
I/O
1.8 V
55..2
2
GGiiggaabbiitt EEtthheerrnneett
The board supports Gigabit Ethernet transfer by an external Micrel KSZ9031RNX PHY chip and
HPS Ethernet MAC function. The KSZ9031RNX chip with integrated 10/100/1000 Mbps Gigabit
Ethernet transceiver also supports RGMII MAC interface. Figure 5-1 shows the connections
between the HPS, Gigabit Ethernet PHY, and RJ-45 connector. The pin assignment associated with
Gigabit Ethernet interface is listed in Table 5-2. More information about the KSZ9031RNX PHY
chip and its datasheet, as well as the application notes, is available on the manufacturer’s website.
Figure 5-1 Connections between the HPS and Gigabit Ethernet
Page 59

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
58
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
Table 5-2 Pin Assignment of Gigabit Ethernet PHY
Signal Name
FPGA Pin Number
Description
I/O Standard
HPS_ENET_GTX_CLK
PIN_F25
GMII Transmit Clock
1.8V
HPS_ENET_MDC
PIN_D24
Management Data Clock Reference
1.8V
HPS_ENET_MDIO
PIN_C24
Management Data
1.8V
HPS_ENET_RX_CLK
PIN_K22
GMII and MII receive clock
1.8V
HPS_ENET_RX_DATA[0]
PIN_H23
GMII and MII receive data[0]
1.8V
HPS_ENET_RX_DATA[1]
PIN_J23
GMII and MII receive data[1]
1.8V
HPS_ENET_RX_DATA[2]
PIN_F24
GMII and MII receive data[2]
1.8V
HPS_ENET_RX_DATA[3]
PIN_G24
GMII and MII receive data[3]
1.8V
HPS_ENET_RX_DV
PIN_L22
GMII and MII receive data valid
1.8V
HPS_ENET_TX_DATA[0]
PIN_H24
MII transmit data[0]
1.8V
HPS_ENET_TX_DATA[1]
PIN_J24
MII transmit data[1]
1.8V
HPS_ENET_TX_DATA[2]
PIN_M22
MII transmit data[2]
1.8V
HPS_ENET_TX_DATA[3]
PIN_M21
MII transmit data[3]
1.8V
HPS_ENET_TX_EN
PIN_G25
GMII and MII transmit enable
1.8V
There are four LEDs, two green LEDs(LEDG) and two yellow LEDs(LEDY), which represent the
status of Ethernet PHY (KSZ9031RNX). The LED control signals are connected to the LEDs on the
RJ45 connector. The state and definition of LEDG and LEDY are listed in Table 5-3. For instance,
the connection from board to Gigabit Ethernet is established once the LEDG lights on.
Table 5-3 State and Definition of LED Mode Pins
LED (State)
LED (Definition)
Link /Activity
LEDG
LEDY
LEDG
LEDY
H H OFF
OFF
Link off
L H ON
OFF
1000 Link / No Activity
Toggle
H
Blinking
OFF
1000 Link / Activity (RX, TX)
H L OFF
ON
100 Link / No Activity
H
Toggle
OFF
Blinking
100 Link / Activity (RX, TX)
L L ON
ON
10 Link/ No Activity
Toggle
Toggle
Blinking
Blinking
10 Link / Activity (RX, TX)
Page 60

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
59
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
55..3
3
UUAARRTT ttoo UUSSBB
An USB to Serial device (Cypress: CY7C65215) is used on the HAN Pilot Platform to connect to
other on-board devices through JTAG / UART / I2C interface. Let Host PC can communicate with
these devices through the USB interface (See Figure 5-2).
There are two serial communication blocks (SCB) in CY7C652152, in which SCB0 is used to
connect HPS UART channel or USB PD controller (CYPD3125) I2C bus. The default setting is
preset to HPS UART function, so HPS UART can communicates with Host PC vis this channel.
Another option is the USB Type-C controller's I2C bus. This is reserved for the user to configure
the firmware of the USB Type-C controller function from the Host PC. The channel is also
connected to the FPGA at the same time, so that the FPGA can read the registers in the USB Type-C
controller to monitor the state. If user wants to change the SCB0 to I2C, it needs to be modified
from the setting software on the host PC.
The other channel of the CY7C65215 SCB1 is used as the JTAG interface, which is connected to
the USB FX3 device, allowing the user to debug the FX3 chip via the JTAG interface through the
Host PC software. Table 5-4 lists the pin assignment of USB to serial device connected to the
FPGA.
Figure 5-2 Connections between the HPS and USB Mini-B connector
Table 5-4 Pin Assignment of UART Interface
Signal Name
FPGA Pin Number
Description
I/O Standard
USB_PD_SCL
PIN_AJ19
I2C Serial Clock
1.8V
USB_PD_SDA
PIN_AV16
I2C Serial Data
1.8V
I2C_INT
PIN_AH27
inter-integrated circuit
1.8V
HPS_RXD_M(HPS_DIO_13)
PIN_L20
HPS UART Receiver
1.8V
Page 61

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
60
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
HPS_TXD_M(HPS_DIO_12)
PIN_J19
HPS UART Transmitter
1.8V
55..4
4
MMiiccrroo SSDD CCaarrdd SSoocckkeett
The board supports Micro SD card interface with x4 data lines. It serves not only an external
storage for the HPS, but also an alternative boot option for DE10-Standard board. Figure 5-3 shows
signals connected between the HPS and Micro SD card socket to the HPS.
Figure 5-3 Connections between the FPGA and SD card socket
Table 5-5 Pin Assignment of Micro SD Card Socket
Signal Name
FPGA Pin Number
Description
I/O Standard
SD_CLK
PIN_K18
HPS SD Clock
1.8V
SD_CMD
PIN_F22
HPS SD Command Line
1.8V
SD_DATA0
PIN_J18
HPS SD Data[0]
1.8V
SD_DATA1
PIN_E23
HPS SD Data[1]
1.8V
SD_DATA2
PIN_G21
HPS SD Data[2]
1.8V
SD_DATA3
PIN_H21
HPS SD Data[3]
1.8V
55..5
5
UUSSBB OOTTGG
The board has one USB 2.0 type-A port with a SMSC USB3320 controller. The SMSC USB3320
device in 32-pin QFN RoHS Compliant package. This device supports UTMI+ Low Pin Interface
(ULPI), which communicates with the USB 2.0 controller in HPS. The PHY operates in Host mode
by connecting the ID pin of USB3320 to ground. When operating in Host mode, the device is
powered by the USB type-A port. Figure 5-4 shows the connections of USB PTG PHY to the HPS.
Table 5-6 lists the pin assignment of USB OTG PHY to the HPS.
Page 62

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
61
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
Figure 5-4 Connections between the HPS and USB OTG PHY
Table 5-6 Pin Assignment of USB OTG PHY
Signal Name
FPGA Pin Number
Description
I/O Standard
HPS_USB_CLKOUT
PIN_L25
60MHz Reference Clock Output
1.8V
HPS_USB_DATA[0]
PIN_K25
HPS USB_DATA[0]
1.8V
HPS_USB_DATA[1]
PIN_G26
HPS USB_DATA[1]
1.8V
HPS_USB_DATA[2]
PIN_E27
HPS USB_DATA[2]
1.8V
HPS_USB_DATA[3]
PIN_F27
HPS USB_DATA[3]
1.8V
HPS_USB_DATA[4]
PIN_L24
HPS USB_DATA[4]
1.8V
HPS_USB_DATA[5]
PIN_M24
HPS USB_DATA[5]
1.8V
HPS_USB_DATA[6]
PIN_K23
HPS USB_DATA[6]
1.8V
HPS_USB_DATA[7]
PIN_L23
HPS USB_DATA[7]
1.8V
HPS_USB_DIR
PIN_J25
Direction of the Data Bus
1.8V
HPS_USB_NXT
PIN_H26
Throttle the Data
1.8V
HPS_USB_STP
PIN_M25
Stop Data Stream on the Bus
1.8V
55..6
6
GGPPIIOO HHeeaaddeerr
There is a 2x5 pin header(2.54mm) on the HAN Pilot Platform which connected to six FPGA HPS
fabric GPIOs. These I/Os can be used as GPIO that are directly controlled by HPS. Or it can be
used as SPI interface (HPS_DIO[11:8]), using the SPI master controller in HPS to communicate
with other SPI devices. Table 5-7 shows the pin assignment of the HPS GPIO header.
Page 63

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
62
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
Figure 5-5 Connection between FPGA and HPS GPIO Header
Table 5-7 Pin Assignment of GPIO Header
Signal Name
FPGA Pin
Number
Description
I/O
Standard
HPS_DIO8
PIN_D23
HPS GPIO 8;
SPIM0_CLK
1.8V
HPS_DIO9
PIN_C23
HPS GPIO 9;
SPIM0_MISO
1.8V
HPS_DIO10
PIN_F23
HPS GPIO 10;
SPIM0_CLK
1.8V
HPS_DIO11
PIN_G22
HPS GPIO 11;
SPIM0_SS0
1.8V
HPS_DIO12
PIN_J19
HPS GPIO 12; Reserve
1.8V
HPS_DIO13
PIN_L20
HPS GPIO 13; Reserve
1.8V
55..7
7
DDDDRR44 ((HHPPSS))
The board supports 1GB of DDR4 SDRAM comprising of two x16 bit DDR4 devices on the HPS
shared I/O Banks (Bank 2J and 2K). The signals are connected to the dedicated HPS external
memory interface and the target speed is 1067 MHz. If users do not include any HPS external
memory interface in their system, users can use these DDR4 devices by FPGA fabric. Figure 3 26
shows the connections between the DDR4 and Arria 10 SoC FPGA. Table 3 18 lists the pin
assignment of DDR4 and its description with I/O standard.
Page 64

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
63
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
Figure 5-6 Connection between FPGA and HPS DDR4 devices
FPGA Pin Number
Signal Name
Description
I/O Standard
PIN_M27
DDR4H_REFCLK_p
DDR4 A port Reference Clock
p
LVDS
PIN_U27
DDR4H_A[0]
Address [0]
SSTL-12
PIN_V27
DDR4H_A[1]
Address [1]
SSTL-12
PIN_P28
DDR4H_A[2]
Address [2]
SSTL-12
PIN_N27
DDR4H_A[3]
Address [3]
SSTL-12
PIN_N26
DDR4H_A[4]
Address [4]
SSTL-12
PIN_P26
DDR4H_A[5]
Address [5]
SSTL-12
PIN_R26
DDR4H_A[6]
Address [6]
SSTL-12
PIN_R25
DDR4H_A[7]
Address [7]
SSTL-12
PIN_R28
DDR4H_A[8]
Address [8]
SSTL-12
PIN_R27
DDR4H_A[9]
Address [9]
SSTL-12
PIN_T25
DDR4H_A[10]
Address [10]
SSTL-12
PIN_U25
DDR4H_A[11]
Address [11]
SSTL-12
PIN_K26
DDR4H_A[12]
Address [12]
SSTL-12
PIN_G29
DDR4H_A[13]
Address [13]
SSTL-12
PIN_H28
DDR4H_A[14]
Address [14]/WE_n
SSTL-12
PIN_K28
DDR4H_A[15]
Address [15]/CAS_n
SSTL-12
PIN_L28
DDR4H_A[16]
Address [16]/RAS_n
SSTL-12
PIN_AU6
DDR4H_BA[0]
Bank Select [0]
SSTL-12
PIN_AP8
DDR4H_BA[1]
Bank Select [1]
SSTL-12
PIN_AN8
DDR4H_BG[0]
Bank Group Select[0]
SSTL-12
PIN_AJ14
DDR4H_BG[1]
Bank Group Select[1]
SSTL-12
Page 65

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
64
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
PIN_U26
DDR4H_CK
Clock p
DIFFERENTIAL
1.2-V SSTL
PIN_V26
DDR4H_CK_n
Clock n
DIFFERENTIAL
1.2-V SSTL
PIN_V28
DDR4H_CKE
Clock Enable pin
SSTL-12
PIN_A20
DDR4H_DQS[0]
Data Strobe p[0]
DIFFERENTIAL
1.2-V POD
PIN_B17
DDR4H_DQS[1]
Data Strobe p[1]
DIFFERENTIAL
1.2-V POD
PIN_L15
DDR4H_DQS[2]
Data Strobe p[2]
DIFFERENTIAL
1.2-V POD
PIN_F18
DDR4H_DQS[3]
Data Strobe p[3]
DIFFERENTIAL
1.2-V POD
PIN_B20
DDR4H_DQS_n[0]
Data Strobe n[0]
DIFFERENTIAL
1.2-V POD
PIN_C17
DDR4H_DQS_n[1]
Data Strobe n[1]
DIFFERENTIAL
1.2-V POD
PIN_M15
DDR4H_DQS_n[2]
Data Strobe n[2]
DIFFERENTIAL
1.2-V POD
PIN_F19
DDR4H_DQS_n[3]
Data Strobe n[3]
DIFFERENTIAL
1.2-V POD
PIN_H18
DDR4H_DBI_n[0]
Data Bus Inversion [0]
1.2-V POD
PIN_E18
DDR4H_DBI_n[1]
Data Bus Inversion [1]
1.2-V POD
PIN_D16
DDR4H_DBI_n[2]
Data Bus Inversion [2]
1.2-V POD
PIN_E20
DDR4H_DBI_n[3]
Data Bus Inversion [3]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AJ9
DDR4H_DQ[0]
Data [0]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AG11
DDR4H_DQ[1]
Data [1]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AF9
DDR4H_DQ[2]
Data [2]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AG12
DDR4H_DQ[3]
Data [3]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AG9
DDR4H_DQ[4]
Data [4]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AF12
DDR4H_DQ[5]
Data [5]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AJ10
DDR4H_DQ[6]
Data [6]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AG10
DDR4H_DQ[7]
Data [7]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AL9
DDR4H_DQ[8]
Data [8]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AH9
DDR4H_DQ[9]
Data [9]
1.2-V POD
Page 66

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
65
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
PIN_AK6
DDR4H_DQ[10]
Data [10]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AK7
DDR4H_DQ[11]
Data [11]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AH8
DDR4H_DQ[12]
Data [12]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AH7
DDR4H_DQ[13]
Data [13]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AJ8
DDR4H_DQ[14]
Data [14]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AE11
DDR4H_DQ[15]
Data [15]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AT4
DDR4H_DQ[16]
Data [16]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AM7
DDR4H_DQ[17]
Data [17]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AP5
DDR4H_DQ[18]
Data [18]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AL5
DDR4H_DQ[19]
Data [19]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AM5
DDR4H_DQ[20]
Data [20]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AM6
DDR4H_DQ[21]
Data [21]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AM4
DDR4H_DQ[22]
Data [22]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AR5
DDR4H_DQ[23]
Data [23]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AP1
DDR4H_DQ[24]
Data [24]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AR3
DDR4H_DQ[25]
Data [25]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AN3
DDR4H_DQ[26]
Data [26]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AR1
DDR4H_DQ[27]
Data [27]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AU2
DDR4H_DQ[28]
Data [28]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AP4
DDR4H_DQ[29]
Data [29]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AR2
DDR4H_DQ[30]
Data [30]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AU1
DDR4H_DQ[31]
Data [31]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AF10
DDR4H_DM[0]
DDR3 Data Mask[0]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AL8
DDR4H_DM[1]
DDR3 Data Mask[1]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AN7
DDR4H_DM[2]
DDR3 Data Mask[2]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AN4
DDR4H_DM[3]
DDR3 Data Mask[3]
1.2-V POD
PIN_AJ13
DDR4H_CS_n[0]
Chip Select
SSTL-12
PIN_Y26
DDR4H_RESET_n
Chip Reset
1.2 V
PIN_Y28
DDR4H_ODT
On Die Termination
SSTL-12
PIN_T27
DDR4H_PAR
Command and Address Parity
Input
SSTL-12
PIN_A23
DDR4H_ALERT_n
Register ALERT_n output
SSTL-12
PIN_Y25
DDR4H_ACT_n
Activation Command Input
SSTL-12
Page 67

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
66
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
PIN_J26
DDR4H_RZQ
External reference ball for
output drive calibration
1.2 V
Page 68

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
67
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
Chapter 6
System Clocks
Figure 6-1 shows the Clock Net connected to FPGA on HAN Pilot Platform.
The Si5350c provides the fixed system frequencies to FPGA, HPS and other important components.
There are four 50 MHz connected to the dedicated clock pins of the FPGA, which can be used by
PLL for clock multiplier or frequency division. In addition, there are Programmable PLL
(CDCM6280, BGA/FXXXXX) available for providing the clocks to the peripherals on the board,
such as HDMI and communication interfaces. There is a default clock when power on, it also
supports the users to change the frequency via I2C interface for special requirement.
Figure 6-1 System Clock in the HAN Pilot Platform
Page 69

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
68
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
Figure 6-2 The default settings for different PLLs
Page 70

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
69
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
Chapter 7
Power
Figure 7-1 is HAN Pilot Platform Power Tree. HAN Pilot Platform can be supplied by the 12V
power adapter in the package, or external connecting to USB Type-C as power supply. The
maximum load of the system supports is 60W (FPGA usage is 92 %) by our test.
However, please note that it is different FPGA efficient for different project. This result is only for a
reference.
Figure 7-1 The power tree of the HAN Pilot Platform
Page 71

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
70
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
Chapter 8
HAN Pilot Platform System
Builder
This chapter describes how users can create a custom design project with the tool named HAN Pilot
Platform System Builder.
88..1
1
IInnttrroodduuccttiioonn
The System Builder is a Windows based software utility. It is designed to help users create a
Quartus Prime project for the FPGA board within minutes. The Quartus Prime project files
generated include:
▪ Quartus Prime Project File (.qpf)
▪ Quartus Prime Setting File (.qsf)
▪ Top-Level Design File (.v)
▪ Synopsis Design Constraints file (.sdc)
▪ Pin Assignment Document (.htm)
The above files generated by the HAN Pilot Platform System Builder can also prevent occurrence
of situations that are prone to compilation error when users manually edit the top-level design file or
place pin assignment. The common mistakes users may encounter are:
▪ Board is damaged due to incorrect bank voltage setting or pin assignment
▪ Board is malfunctioned because of wrong device chosen, declaration of pin location or
direction is incorrect or forgotten
▪ Performance degradation due to improper pin assignment
88..2
2
GGeenneerraall DDeessiiggnn FFllooww
This section will introduce the general design flow to build a project for the FPGA board via the
System Builder. The general design flow is illustrated in the Figure 8-1.
Page 72

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
71
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
Figure 8-1 The general design flow of building a project
Users should launch System Builder and create a new project according to their design requirements.
When users complete the settings, the System Builder will generate two major files which include
top-level design file (.v) and the Quartus Prime setting file(.qsf).
The top-level design file contains top-level Verilog wrapper for users to add their own design/logic.
The Quartus Prime setting file contains information such as FPGA device type, top-level pin
assignment, and I/O standard for each user-defined I/O pin.
Finally, Quartus Prime programmer must be used to download SOF file to the FPGA board using
JTAG interface.
88..3
3
UUssiinngg HHAANN PPiilloott PPllaattffoorrmm SSyysstteemm BBuuiillddeerr
This section provides the detailed procedures on how to use the HAN Pilot Platform System
Builder.
◼ Install and Launch the HAN Pilot Platform System Builder
The HAN Pilot Platform System Builder is located in the directory: “Tools\SystemBuilder” of the
HAN Pilot Platform System CD. Users can copy the entire folder to a host computer without
installing the utility. A window will pop up, as shown in Figure 8-2, after executing the HAN Pilot
Platform SystemBuilder.exe on the host computer.
Page 73

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
72
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
Figure 8-2 The GUI of HAN Pilot Platform System Builder
◼ Enter Project Name
Enter the project name in the circled area, as shown in Figure 8-3. The project name typed in will
be assigned automatically as the name of your top-level design entity.
Page 74

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
73
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
Figure 8-3 Project Name in the System Builder window
◼ Select Top File Type
The system builder can generate Verilog or VHDL Quartus top file according to users’ requirement.
Users can select their desired file type in the Top File Type list-box shown in Figure 8-4.
Page 75

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
74
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
Figure 8-4 Top File Type in the System Builder window
◼ System Configuration
Users are given the flexibility of enabling their choices of components connected to the FPGA
under System Configuration, as shown in Figure 8-5. Each component of the FPGA board is listed
to be enabled or disabled according to users’ needs. If a component is enabled, the System Builder
will automatically generate the associated pin assignments including its pin name, pin location, pin
direction, and I/O standards. Note: The pin assignments for some components (e.g. DDR4 and
SFP+) require associated controller codes in the Quartus project or it would result in compilation
error. Hence please do not select them if they are not needed in the design.
Page 76

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
75
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
Figure 8-5 System Configuration group
◼ FMC Expansion
If users connect any compatible Terasic FMC-based daughter cards to the FMC connector on HAN
Pilot Platform, the HAN Pilot Platform System Builder can generate a project that include the
corresponding module, as shown in Figure 8-6. It will also generate the associated pin assignment
automatically, including pin name, pin location, pin direction, and I/O standard.
The “Prefix Name” is an optional feature that denotes the pin name of the daughter card assigned in
your design. Users may leave this field blank.
Page 77

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
76
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
Figure 8-6 FMC expansion group
◼ Programmable Clock Generator
There are some oscillators on-board (Si5350C,CDCM6208) that provide reference clocks for the
following signals:
▪ HDMI_REFCLK
▪ SFP_REFCLK
▪ FMC_REFCLK
▪ DP_REFCLK
▪ USB_REFCLK
To use these clocks, users can select the desired frequency on the Programmable Oscillator group,
as shown in Figure 8-7. DDR4, or SFP+ must be checked before users can start to specify the
desired frequency in the programmable oscillators. As the Quartus project is created, System
Builder automatically generates the associated controller according to users’ desired frequency in
Verilog which facilitates users’ implementation as no additional control code is required to
configure the programmable oscillator.
Note: If users need to dynamically change the frequency, they would need to modify the generated
control code themselves.
Page 78

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
77
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
Figure 8-7 External programmable oscillators
◼ Project Setting Management
The System Builder also provides functions to restore default setting, load a setting, and save board
configuration file, as shown in Figure 8-8. Users can save the current board configuration
information into a .cfg file and load it into the System Builder.
Page 79

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
78
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
Figure 8-8 Project Settings
◼ Project Generation
When users press the Generate button, the HAN Pilot Platform System Builder will generate the
corresponding Quartus Prime files and documents as listed in Table 8-1.
Table 8-1 The files generated by HAN Pilot Platform System Builder
No.
File Name
Descriptions
1
<Project name>.v
Top Verilog Quartus Prime File
2
<Project name>.qpf
Quartus Prime Project File
3
<Project name>.qsf
Quartus Prime Setting File
4
<Project name>.sdc
Quartus Prime Synopsis Design Constraints File
5
<Project name>.htm
Pin Assignment Document
Users can use Quartus Prime software to add custom logic into the project and compile the project
to generate the SRAM Object File. (.sof).
Page 80

HAN Pilot Platform
Hardware Manual
79
www.terasic.com
July 5, 2019
Chapter 9
Appendix
◼ Revision History
Version
Date
Change Log
V1.0
10/24, 2018
Initial Version (Preliminary)
V1.1
7/5, 2019
Modify FPP x32 mode MSEL setting to 000
◼ Copyright Statement
Copyright © 2018 Terasic Inc. All rights reserved.
 Loading...
Loading...