Page 1

3
TensCare Ltd, 9 Blenheim Road, Longmead Business Park,
Epsom, Surrey KT19 9BE, UK Tel +44(0) 1372 723434
Email: painaway@tenscare.co.uk www.tenscare.com
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Pub Ref I-SPT2-UK Rev 1.0 10.12
Distributed by:
Sports TENS 2
0473
WWW.TENSMACHINES.CO.UK
TENS MED
WWW.TENSMACHINES.CO.UK
Page 2
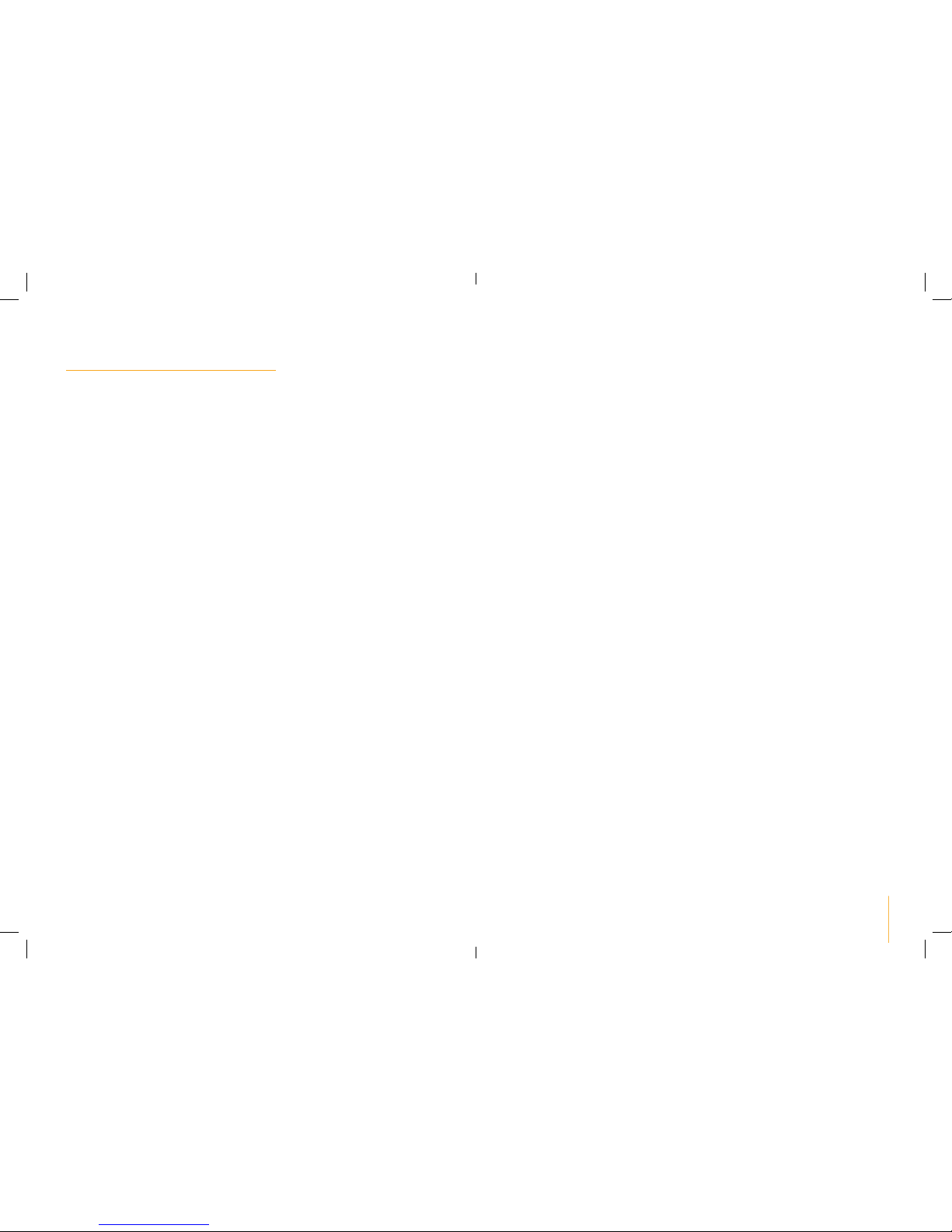
1
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Page No
1 Introduction 1
2 Contents 2
3 How TENS works 2
4 How EMS works 3
4.1 EMS successfully rebuilds and tones muscles 4
4.2 Relaxing applications 4
4.3 Mode of operation 4
4.4 Treatment time and treatment interval 5
4.5 Choosing the right strength 5
5 Stimulation parameters 6
6 Controls and Displays 9
7 The Programmes 13
7.1 TENS Programmes 13
7.2 EMS Programmes 14
7.3 Massage Programmes 17
8 Positioning of Electrode Pads 18
8.1 Electrode placement for TENS 18
8.2 Electrode placement for EMS 20
8.3 Electrode placement for Massage 24
9 General Pad Advice 25
10 The Belt Clip 25
11 Troubleshooting 25
12 Caution and Warnings 26
13 Cleaning 26
14 Charging the battery 27
15 Guarantee 27
16 Consumables and servicing 28
17 WEEE 28
18 Technical Specifications 29
19 EMC Precautions 30
20 TENS Dermatomes 32
21 EMS Electrode placement chart 34
Sports TENS 2
1. INTRODUCTION
The Sports TENS 2 is a multi-purpose combination unit that offers the latest in
electro muscle stimulation and TENS.
It has three basic functions, which can be used in combination:
1 . Stimulation of sensory nerves for Pain Relief (TENS).
2. Stimulation of motor nerves and muscle tissue (EMS) to build and
alter muscle function
3. A massage effect.
To achieve this, the device has two independent stimulation channels and four self
adhesive electrodes. It offers a choice from a large number of settings designed to
increase general wellbeing, alleviate pain, maintain physical fitness, aid relaxation,
revitalize muscles and combat fatigue. You can either select these settings from
preset programmes or determine them yourself according to your requirements.
• Powerful
Sports TENS is a powerful fitness and performance muscle stimulator for
body toning, shaping, beauty and relaxation. It has TENS settings to relieve
pain due to injury and over-training. Gentle massage is provided for relaxation
and de-stressing.
• Multiple Functions
Sports TENS is flexible enough to help with all stages of training and recovery.
It has 27 EMS programmes, 10 TENS programmes, 10 massage programmes
and 8 user defined programmes enabling you to experiment and save your
favourite settings – unrivalled performance for a product of this size and price.
• Memory
Sufficient memory for a 30 day exercise programme comprising of 3 uses a
day. The memory records usage time and average intensity used. For training,
this enables you to keep an exercise diary, for rehabilitation and pain relief it
offers an objective treatment record.
Special Features
•
Li-Ion mobile phone style battery making it lightweight and compact, and is
supplied complete with external charger.
• Unique locking lead connection and built-in cable tidy
• Backlit LCD screen
Whenever a button is pressed the screen will light up making the screen easy
to read and very clear.
• Comfortable strength Control
Each step in strength is small, thereby maximising the comfort level.
Page 3
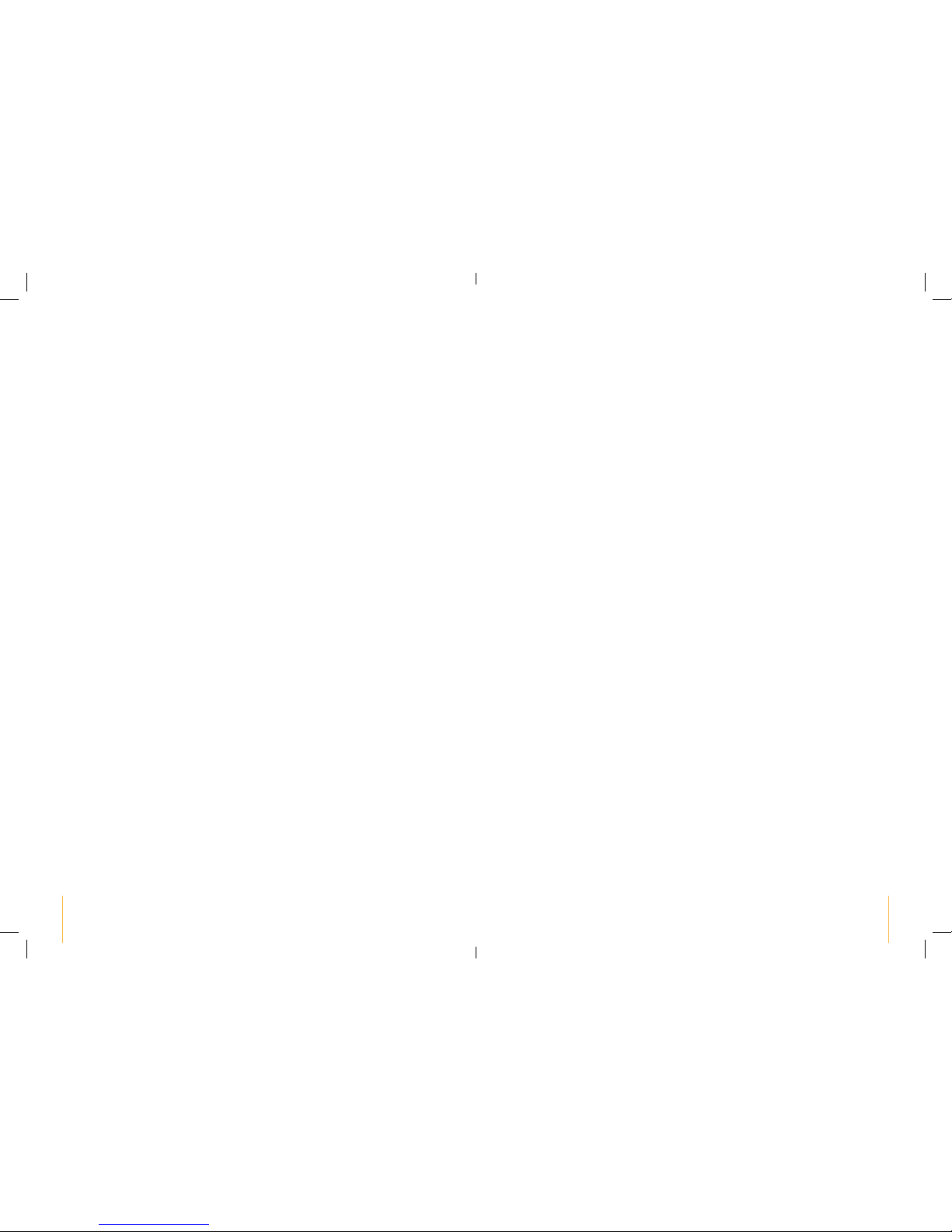
2 3
2. CONTENTS
• Sports TENS 2 unit with belt clip
• CM5050 pack of 4 self adhesive electrodes
• 2 x L-ST2 Connecting Lead wire
• B-BL6F Li-ion battery type BL-6F
• Charging cradle
• Power adaptor
• Instruction booklet
• Transit pouch
3. HOW TENS WORKS
TENS stands for Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation. TENS stimulates
your body’s own natural defences against pain. It is totally safe, and has been used
successfully by thousands of pain sufferers.
TENS sends a gentle stimulation through the skin which works in TWO ways:-
Pain Gate
Stimulating the sensory nerves, which carry touch and temperature signals. These
nerves go to the same connections in the spine as the nerves carrying pain. A strong
sensory signal will block the pain signal travelling up the spine to the brain. This
is known as closing the “Pain Gate” and takes effect quite quickly after the unit is
switched on. You can use TENS several times a day, for as long as you like.
Endorphin Release
At low frequency settings, and slightly stronger output, TENS drives the motor
nerves to produce a small repetitive muscle contraction. This is seen by the brain as
exercise, and this promotes release of Endorphins – your body’s own natural pain
killer. The relief builds up and normally takes about 40 minutes to reach a maximum
level which can last for hours after the machine is switched off.
By using TENS you can expect to achieve a significant reduction in pain if not
complete pain relief.
Side Effects
There are no known side effects to TENS use and long-term TENS use is not harmful.
Positioning the electrodes for TENS
The TENS effect is confined to the nerves entering a single vertebra in the spine. To
be effective, you therefore need to stimulate a sensory nerve entering the spine at
the same level as the nerve carrying the pain. For this reason electrodes are usually
first placed where the greatest pain is felt. Nerves follow the curve of the ribs, and
spiral around the limbs, so you will need to try different positions until you find the
best for you. Try moving the electrodes short distances to establish the positions
that are most effective for you.
TENS is clinically tested and approved for many applications including:
• Back pain, and lumbar and cervical spine problems
• Joint pain (e.g. knee joint, hip joint, shoulder)
• Neuralgia
• Headaches • Women’s period pains
• Pain after injuries to musculoskeletal system
• Pain with circulatory problems
• Chronic pain through various causes
4. E.M.S.: WHAT IT IS AND HOW IT WORKS
EMS stands for Electrical Muscle Stimulation and is a widespread and generally
recognized method that has been used for years in sports and rehabilitation
medicine. In the sports and fitness field, one of the uses of EMS is as a
supplement to conventional muscle training, in order to increase the efficiency of
muscle groups and adapt physical proportions to the desired aesthetic results.
EMS has two main applications. Firstly, a targeted strengthening of musculature
can be produced (Activating application) and secondly a relaxing, resting effect
can also be achieved (Relaxing application).
4.1 EMS successfully rebuilds and tones muscles.
Different levels of muscle contraction are achieved by sending electrical impulses
of various types, depending on the programme selected, into the body. These
muscle contractions retrain the muscles, increase their effectiveness and improve
their condition. This is beneficial where muscles - for whatever reason - have
not been in regular use and have lost condition (muscle atrophy). For sports, the
benefit is to increase the effect of training and enhance performance.
Typical uses are: -
• Muscle training to improve endurance performance
• Muscle training to support the strengthening of certain muscles or muscle
groups in order to achieve desired changes to body proportions.
• Sports training, covering - warm-up, strength, speed, power, resistance,
endurance and recovery
• Rehabilitation in relation to sports injury.
The effect on muscle tone of electrical stimulation (EMS) is generally only
noticeable after regularly repeated application. Electrical stimulation does not
replace regular exercising of the muscle, but is able to reasonably supplement it.
Muscle wastage: EMS is used in the treatment of medical conditions involving
muscle wastage including: Neuromuscular facilitation - Muscle reeducation
- Muscle training - Prevention/slowing of atrophy/hypotrophy - Preventing
postoperative muscle weakness - Reduction of spasticity - Maintaining or
increasing range of motion - Training of partial peripheral nerve damage with
signs of reinnervation - Treatment of scoliosis .
Page 4

4 5
4.2 Relaxing applications includes the following:
• Muscle relaxation in order to loosen up muscular tension
• Improving muscular fatigue symptoms
• Accelerating muscle regeneration after high muscular performance
(e.g. after a marathon). Through integrated massage technology, the Sports
TENS Digital TENS/EMS also offers the possibility of reducing muscular
tension and combating fatigue symptoms using a programme based on
manual massage in terms of sensation and effect.
4.3 Mode of operation
EMS uses external electrical impulses that act through the skin to stimulate the
nerves supplying a specific muscle group.
The muscle reacts in different ways depending on the strength of current and
duration and frequency of the electrical impulse.
Muscles are made up of two different types of fibre:
- Red fibre is slower contracting and aerobic working.
- White fibre is faster acting and capable of anaerobic working.
The proportions of red and white fibres depend on the way the muscle is used.
Fibre can be converted from one type to the other, depending on the signals it
receives. This is known as the Trophic effect.
Different frequencies have different effects: Low (1-10 Hz) frequencies coupled
with long impulse times have a purifying and relaxing effect through individual
contractions, whereby the circulation in the treated muscle is simultaneously
improved and removal of metabolic end products is supported (lymphatic drainage).
The oxygen supply to the muscle is improved.
In contrast, medium (20-50 Hz) frequencies can put a high level of strain on the
muscle, thus promoting the muscular structure.
Very high frequencies (60-90 Hz) can be used to promote muscle definition and bulk.
The body maps at the back of this guide show pad positioning in order to stimulate
specific muscle groups.
4.4 Treatment time and treatment interval
Treatment by EMS can vary between 15–60 minutes stimulation twice a week to
treatment several times per day.
4.5 Choosing the right strength
The object of EMS treatment is to produce powerful muscle contractions.
The strength of the current should be increased to about three times the level
at which you can first feel the tingling, or to as high as you can stand without
causing pain. You will probably feel that electrical contraction is being more
powerful than a voluntary contraction, because the current also stimulates
your sensory nerves. The signals have a pain-relieving effect.
You may find the sensation uncomfortable to start with, so that you may
not get up to therapeutic strength at the start of treatment. The strength can
be increased during the course of the treatment, as you become accustomed
to the sensation. Voluntary muscular activity is more effective than
stimulation, and it may improve progress if you combine voluntary contraction
with stimulation.
The powerful muscle contractions caused by electrical stimulation give rise to
training aches, which usually disappear within a week.
After treatment tingling sensations may continue or your skin may feel numb,
this is normal.
5. STIMULATION PARAMETERS:
The effect of Electrical stimulation on the body depends on the following
current settings:
5.1 Pulse Waveform
This describes the time function of the excitation current which may be either
monophasic or biphasic. With monophasic pulse trains, the current flows in one
direction. With biphasic pulses, the excitation current alternates its direction
The Sports TENS uses only biphasic pulse trains, as they reduce the strain on the
muscle, leading to less muscle fatigue as well as safer application, and reduce
the risk of skin irritation under the electrode.
MONOPHASE PULSES
PULSE
INTENSITY
Page 5
6 7
5.2 Pulse frequency
Frequency indicates the number of individual pulses per second, and is indicated in
Hz (Hertz= pulses per second). It can be calculated by working out the inverse value
of the periodic time.
Different types of muscle fibres react preferentially to different frequencies:-
Slow-response fibres tend to react to lower pulse frequencies up to 15Hz, while
fast-response fibres only respond to frequencies over approx. 35Hz.
With pulses of approx.45~70Hz, there is permanent tension in the muscle (tetany)
combined with premature muscle fatigue. Higher pulse frequencies can therefore
preferably be used for elasticity and maximum strength training.
For TENS:
A frequency of 110 Hz is good at blocking pain signals.
A low frequency of 4 or 10 Hz allows for the release of endorphins, the body’s
natural morphine-like substances.
5.3.Pulse width
Pulse width is used to indicate the duration of an individual pulse in microseconds
(millionths of a second). Pulse width also determines the penetration depth of the
current. In general a greater muscle mass requires a greater pulse width. A higher
Pulse Width is more also more likely to activate pain nerves, so there is a fine
balance between maximum muscle stimulation and tolerable sensation.
EMS 50-400 depending on Frequency*
TENS 50 to 250 µS.
5.4 Pulse Intensity
Setting the degree of intensity is dependent on the subjective feeling of each
individual user and is determined by a number of parameters such as application
site, skin circulation, skin thickness as well as quality of electrode contact. The
actual setting should be effective but should never produce any unpleasant
sensation such as pain at the site of application.
In TENS programmes, while a slight tingling sensation indicates sufficient
stimulation energy, any setting which leads to pain must be avoided.
In EMS programmes, the intensity needs to be as high as possible for maximum
benefit – so set just below the pain threshold.
With prolonged application, you may need to increase intensity as nerves get
used to the stimulation and become less sensitive (known as accommodation).
5.5 WORK is the time in seconds that muscle is stimulated (not including Ramp
time). The Sports TENS 2 offers a range of work periods from 1-40 sec.
5.6 REST is the time in seconds at zero strength in between stimulation.
The Sports TENS 2 offers a range of rest periods from 1-40 sec. The EMS
programmes use an Active Rest –low frequency pulses help to clear metabolites
in between Work periods.
5.7 RAMP is the time in seconds taken to move up and down between zero and
the set stimulation strength .The Sports TENS 2 has a fixed ramp time of 1.5 up
and 0.75 down
PERIODIC TIME
PULSE WIDE
MONOPHASE PULSES
PULSE
INTENSITY
PULSE WIDE
PULSE WIDE
INTENSITY
WORK WORKREST
PERIODIC TIME
PULSE WIDE
MONOPHASE PULSES
INTENSITY
PULSE
INTENSITY
RA
MP
RA
MP
Page 6

8 9
TENS PROGRAMMES
5.8 Constant and Burst Modes
Constant mode is when the sensation is continuous as against Burst mode when the
sensation, is as its name implies, is one of on and off.
5.9 Modulation Modes
Modulation is when the Frequency (FM) or Intensity (IM) sweeps across a range of
settings. This enables the body to receive many different signals and can be very
beneficial and lessen any effect of accommodation.
WARNING
Consult your healthcare professional before altering these settings. Correct settings
depend on your muscle tone and exercise goals. Inappropriate settings could cause
discomfort, undesired muscle balance, or even muscle injury.
5.10 WARM, TRAIN & COOL Phases
Each EMS programme has three phases:
• A WARM up phase to prepare the muscle for work/training
• A TRAIN phase, which works the muscles
• A COOL down phase to minimise fatigue effects
6. CONTROLS AND DISPLAYS
MODE Programme
Preset/Manual
Pulse Width
Pulse Rate
Time setting
Menu
Parameter
Pause
Intensity Ch1 Intensity Ch 2
Warning
ON/OFF
Intensity Ch1
Intensity Ch 2
Programme
Select
Menu
Parameter
Confirm
Menu
Parameter
Adjust
Menu
Parameter
Select
MODE
Select
Cable Tidy
Page 7

10 11
6.1 Switch ON
Press
Unit will display the last programme used. Backlight will turn off 5 seconds after the
last button press. Press again to turn off.
6.6 Set Intensity
Use the buttons for each channel to adjust intensity.
Intensity in mA is displayed at the bottom of the screen.
6.7 Automatic Keypad Lock
There is an automatic keypad lock if no button is used
for 10 seconds.
Key symbol appears.
Press the Intensity Down button for either channel to unlock.
6.8 Manual Programme Lock
When “Manual” is showing, you can protect the manual settings
by pressing and holding for 5 seconds.
If you try to adjust the parameters, the key symbol will flash.
Press and hold for 5 seconds to unlock programme.
To unlock the buttons, simply press and hold button for 5 seconds again.
6.9 Pause
Pressing the MODE button while a programme is in use stops the stimulation
and the timer. Pause symbol is displayed.
Press again to resume the programme.
6.10 Low Battery
When the battery voltage is low the Low Battery warning symbol will display.
6.11 Warning
In EMS Manual programmes a Warning triangle will be displayed if the Rest
period is less than *Rest Time=Work Time*(WorkHz-16.66)/16.66 seconds.
If the warning triangle appears at any other time, see “Troubleshooting”.
6.12 Automatic switch off
If the electrodes become detached and the intensity is set to greater than 10,
the Sports TENS will automatically reset intensity to zero.
To preserve battery life, the Sports TENS automatically switches off if left at
zero intensity for more than 2 minutes.
The backlight turns off 5 secs after the last press of the keypad.
6.2 Select MODE
Press the M button.
Display will cycle through TENS/EMS I,II,III /MASS
(5 choices).
Modes EMS I, II, and III are for use on body areas with
Small, Medium and Large muscles. (See Programmes).
Each EMS programme has a WARM, TRAIN, and COOL
phase. Note: Intensity must be zero before MODE can be
changed, otherwise PAUSE is activated.
6.3 Select Programme
Press the P Programme to cycle through the available
programmes. The Hz and µS settings for each programme
are displayed
TENS 1-12
EMS 1-11
MASSAGE 1-10
6.4 Set Treatment Timer
The default setting for preset programmes is shown.
To alter the Treatment Timer setting, press Menu+/-
The Timer display will flash.
Use +/- buttons to adjust the treatment time.
Choices are: Continuous, 1-90 mins
6.5 Manual Settings
When a programme has manual settings available,
MANUAL will be displayed.
Press Menu + Menu - buttons to cycle through parameters
Selected Parameter flashes
Press +/- buttons to adjust setting.
Press return button to accept change
Flashing stops
Parameters cycle through
Hz, uS, Work, Rest, Ramp, Timer, “DATE”, “HOUR”, “MEM
D” and “MEM H” .
Page 8

12 13
7. PROGRAMMES
7.1 Tens Programmes
Using the TENS Programmes
Your nervous system is different to everyone else’s. Only you know how the
stimulation feels for you. The best way to use TENS is to try the programmes,
and see which ones work best for you. There are some general guidelines:
Programmes with High frequency (Pain Gate)
Programmes 1,2,8,9,10,11
These programmes use the Pain Gate to block the signals travelling along the
pain nerves.
The sensation will fade after 5 or 10 minutes. Keep increasing the intensity so
that you can always feel the stimulation clearly.
You can use these programmes as long as you like. The pain relief may wear
off after a few hours. In which case, you can take a break and try again later.
Programmes 8 and 9 keep changing the sensation, which some users find will
extend the effective pain relief.
Programmes with Low frequency (Endorphin release) elements
Programmmes 3,4,5,6,7,12
These programmes encourage production of your natural endorphins by
inducing very small, repetitive muscle twitches. All but Prog 3 combine this
with a higher frequency to combine the pain relief mechanisms, but may be a
little less comfortable.
To be effective, you need to keep the intensity high enough to induce small
muscle movements. This limts the time you can use these programmes – if you
use them for more than about 40 minutes, you may have aching muscles later.
6.13 Date and Time Setting
The Date (Day of month) and Time (Hour of day) can be set. This enables
the memory to give an exact history of daily usage.
To set date and time, press M+ and cycle through parameters to DATE.
Centre left shows Day of month and centre right shows Hour
Day is flashing
Adjust with +/- buttons and set with button
To set Hour, press Menu + and cycle through parameters to TIME.
Adjust with +/- buttons and set with button
6.14 Memory Mode
To view the memory, press M+ and cycle through
parameters to “MEM D” (for view the records on
that date).
If no programme has been used for more than 19
minutes, a NULL message is displayed and the unit
returns to waiting mode.
Then use the and buttons to select Day – shown
in Left centre window.
Having selected the required date, press M+ to cycle
to “MEM H ( to display hour of individual recordings
on that date).
Then use the and buttons to move between
Recordings (Up to 3 per day)
For each recording the hour is shown is centre right, and
values displayed for MODE, PROGRAM, Time in minutes
(0-99) in timer window, and average intensity (0-99) for
each channel in the mA window for that channel.
To clear the memory, press and hold the [M+] and [M-]
buttons together for approx. 5 seconds while in memory
mode MEM D or MEM H.
TENS PROGRAMMES
Prog Hz Pulse width Mode Time
1 80 150 Const C PRESET
2 100 200 Const C PRESET
3 2 250 Const 30 PRESET
4 100 150 Burst 30 PRESET
5 150 200 Burst 30 PRESET
6 2/80 200/100 Han 30 PRESET
7 2/100 200/150 Han 30 PRESET
8 10/100 250 PFM C PRESET
9 2/120 200/100 FM C PRESET
10 100 75 DTENS C PRESET
11 2-150 50-300 Const 5-90/C MANUAL
12 2-150 50-300 Burst 2Hz 5-90/C MANUAL
Page 9

14 15
7.2 EMS PROGRAMMES
First select MODE I, II, or III
Use MODE I for small muscles like the face and hands
Use MODE II for medium sized muscles like arms and feet
Use MODE III for large muscles like thighs, buttocks, and abdomen
All EMS programmes include a WARM Up, TRAIN, and COOL Down phase.
During the TRAIN phase stimulation alternates between Work – when the muscles
are contracted - and Active Rest, with low frequency stimulation to promote
metabolite clearance and delay fatigue.
Each Work contraction starts and finishes with a gradual change in intensity –
called a Ramp
1. All preset TRAIN phases have Ramp up 1.5s, Ramp Down 0.75s.
2. All WARM phases are 6Hz at same PW as Work phase
3. All COOL phases are 3Hz at same PW as Work phase
4. All Active Rest phases have Ramp up 0.5s, Ramp down 0.5s.
5. All Active Rest phases are at 4 Hz, 200uS
Manual settings:
1. All WARM phases are 6Hz at same PW as set Work PW
2. All COOL phases are 3Hz at same PW as set Work PW
At first use of a Manual programme the default values are shown.
The Warning triangle is displayed if Rest period is less than
Rest Time=Work Time*(WorkHz-16.66)/16.66 seconds
This is because muscle fibres can only activate a limited number of times a minute
(about 1000) without becoming fatigued.
EMS PROGRAMMES
Prog Work Active Rest
Freq Hz Pulse width uS Sec Amp % Hz uS Time s Amp %
I II III
1 PRESET Warm 6 200 280 340 300 100 5
Train 10 200 280 340 9 80 4 200 2 50 41
Cool 3 200 280 340 600 70 10
2 PRESET Warm 6 200 280 340 120 100 2
Train 22 200 280 340 7 80 4 200 11 70 18
Cool 3 200 280 340 180 70 3
3 PRESET Warm 6 200 280 340 120 100 2
Train 25 200 280 340 7 80 4 200 11 50 21
Cool 3 200 280 340 180 70 3
4 PRESET Warm 6 200 280 340 120 100 2
Train 40 200 280 340 7 80 4 200 11 50 18
Cool 3 200 280 340 180 70 3
5 PRESET Warm 6 200 280 340 120 100 2
Train 55 200 280 340 5 80 4 200 11 50 27
Cool 3 200 280 340 180 70 3
6 PRESET Warm 6 200 280 340 300 100 5
Train 60 200 280 340 4 80 4 200 10 50 41
Cool 3 200 280 340 600 70 10
7 PRESET Warm 5 200 280 340 300 100 5
Train 65 200 280 340 4 80 4 200 11 25 20
Cool 3 200 280 340 600 70 10
8 PRESET Warm 6 200 280 340 120 100 2
Train 75 200 280 340 4 80 4 200 14 50 25
Cool 3 200 280 340 180 70 3
9 PRESET Warm 6 200 280 340 300 100 5
Train 100 200 280 340 6 80 4 200 36 25 28
Cool 3 200 280 340 600 70 10
10 MANUAL Warm 6 200 280 340 120 100 2
Train 10-120 100-350 1-30 80 1-60* 1-90
Cool 3 200 280 340 180 70 3
10 DEFAULT 35 280 5 9 20
11 MANUAL Warm 6 200 280 340 120 100 2
Train 10-120 100-350 1-30 80 1-60* 1-90
Cool 3 200 280 340 180 70 3
11 DEFAULT 50 300 5
Total
Time
Mins
Page 10

16 17
7.3 SPORTS TENS 2 MASSAGE PROGRAMMES
Mode Prog Work Phase Phase
1 2
Wave
No Time Min Time Min
Hz uS Hz uS
1 30 1 30 85 200 135 100 Burst
2 30 1 30 1 200 15 200 Burst 15s
3 30 1 30 25 200 80 200 Burst x2
1 4 1 250 4 250 FM
2 6 20 250 IM
3 6 4 250 IM
4 4 1 250 4 250 FM
5 6 30 250 IM
6 6 4 250 IM
4 44 7 4 1 250 8 250 FM
8 6 40 250 IM
9 6 4 250 IM
10 4 1 250 8 250 FM
11 6 50 250 IM
12 6 4 250 IM
13 4 1 250 8 250 FM
5 30 1 30 5 300 Con
2 30 8 300 Con
6 30 1 30 5 200 Con
2 30 8 200 Con
Massage 7 30 1 30 5 300 Con
Wave 2 30 8 300 Con
8 20 1 5 250 25 250 250 Burst 1Hz
2 5 Burst 1.25 Hz
3 5 Burst 1.42 Hz
4 5 Burst 1.66 Hz
9 30 1 25 200 2/2
2 30 200 2/2
3 40 200 1/1
4 50 200 1/1
5 70 200 0.5/1
6 80 200 0.5/1
10 30 1 1 200 15 pulses
2 2 200 11 pulses
3 3 200 18 pulses
4 4 200 11 pulses
5 5 200 15 pulses
6 6 200 20 pulses
7 9 200 26 pulses
8 11 200 33 pulses
9 15 200 30 pulses
10 25 200 1 pulses
11 15 200 30 pulses
12 11 200 33 pulses
13 9 200 26 pulses
14 6 200 20 pulses
15 5 200 15 pulses
16 4 200 11 pulses
17 3 200 18 pulses
18 2 200 11 pulses
Using the EMS Programmes
EMS can be used for a wide range of sports and medical applications, and
the application can get very complicated. The Sports TENS programmes have
been designed to simplify this as much as possible. You can use the manual
programmes if you want to modify the settings, or to experiment with completely
different ones. Here are some of the ways you can use the programmes:
Programme 1 Muscle Calming
Relaxing the muscles as much as possible and to promote the body’s natural
endorphins to promote pain relief and to improve the blood circulation and provide
oxygen into the muscle.
Programme 2 Resume Training 1
To promote the slow twitch fibres to build muscle strength to help reduce muscle
atrophy ready for resuming training activities. Used for all type of sports.
Programme 3 Resume Training 2
Progress from 2 as tolerance increases.
Programme 4 Resistance 1
Improving and increasing the capacity to develop very high level of muscle force
over a long period of time. Improving the efficacy of the oxygen consumption at the
muscle level and the capacity to withstand toxin build up, such as lactic acid. For
sports activities that require very high levels of prolonged muscle activity: Rowing,
Cycling, Middle distance running.
Programme 5 Resistance 2
Increasing the capacity to habitually develop a high level of muscle force.
Improving oxygen consumption at muscular level and to increase the capacity to
withstand toxin amassing. Used on sports activities requiring prolonged and high
levels of muscle force: Cycling, Rowing, Middle distance running
Alternative application Lipolysis
Increasing the flow of blood circulation, and modifying the metabolism of the
lipocytes. To help stimulate the subcutaneous deposits of fat. To assist reduce or
eliminate the –Orange Peel effect of the skin surface
Programme 6 Maximum Muscle Contraction
To increase muscle bulk and volume and to improve muscle force. Searching for
muscular hypertrophy
Programme 7 Muscle toning 1
Strengthening the muscles, improving blood circulation and capillary bed density.
Ideal for applying to the Thigh, Legs, Bottom and Abdomen.
Programme 8 Muscle toning 2
Similar to 7, but adding bulk in preference to endurance.
Programme 9 Force Output
Anaerobic activity- increasing the muscle capacity to a level of instantaneous
maximum muscle force, changing muscle force into explosive action. Used for all
activities requiring maximum muscle output in a very short space of time, such as
Judo, short distance sprinting, throwing the discus or shot-put.
(Cycle through
phases, then
start back at
Phase1)
(Cycle through
phases, then
start back at
Phase1)
Page 11

18 19
Low Back Pain Neck and Shoulder Tension Sciatica
Shoulder Pain Knee Pain Elbow Pain
Ankle Pain Wrist Pain Leg Pain
Where only two pads are shown on the arm, shoulder, and leg, use the other
two pads either on the opposite limb or place all four pads on the same limb in
a square pattern with each pad being about 4 inches apart.
Using the Massage Programmes
You can use the massage programmes to relieve stiffness caused by incorrect
posture caused by work (sitting for extended periods at a desk, work on the
computer, driving for long periods, constant standing, incorrect lifting and carrying
of heavy loads etc.) You can also use them after intensive exercise to prevent a
stiffening of the muscles or to help relieve stiffening more quickly.
Programme 8 has a special squeezing action designed to pump blood and fluid. It
is especially effective with swollen legs and veins.
8.0 POSITIONING OF ELECTRODE PADS
Ensure that intensity is zero before connecting electrodes
Insert connection lead(s) into the sockets below the handle.
Rotate the body of the plug to lock the lead in place. Plug the lead pins
into the sockets in the pad pigtails.
To avoid damage, remember to rotate the plug to unlock it before
removing the lead.
Only pull the lead by holding the body of the plug.
8.1 Electrode Placement for T.E.N.S.
The placement of electrodes is one of the most important parameters in achieving
effective pain relief using TENS. You may need to try various positions before you
find the most effective positioning. There are several positioning methods:
Across the painful area
This is the simplest method. Placing one pad over, or slightly further away from the
spine than, the source of the pain. Place the other pad closer to the spine so that
the stimulation travels through the area of pain.
Dermatomes
TENS only works at the level of one vertebra of the spine. The nerves carrying
pain and the TENS stimulation into each vertebra cover an area of the body called
a Dermatome. Each nerve root serves a known area of the skin. You can stimulate
the sensory nerves anywhere in this area to reduce the transmission in the pain
nerves. The nerves wrap around the trunk and limbs in a spiral, so the dermatomes
can give you a better idea of where to place the pads. See diagram at the back
of this book.
Trigger or Acupuncture points.
You can use low frequency TENS to stimulate therapy points. Accurately locating
these points can be difficult, so you may want to seek professional advice.
Example TENS Electrode Pad Positions
Page 12

20 21
8.2 Electrode Placement for E.M.S.
Electrode placement for electrical muscle stimulation is very important for obtaining
the best results. Place two electrodes over the bulk of the muscle, with one
electrode over the muscle’s motor point. The motor point is the area on the skin
that is located closest to the motor nerve’s entry into the muscle – about 1/3 of
the way down the muscle from the spine. Here it is easiest to trigger a contraction
by electrical stimulation. See the diagram at the back of this book. Experiment by
moving the electrode across the skin until you locate the point over the muscle that
gives the cleanest contraction. In the examples below the pads are colour-coded
to match the leads to be used but, because the waveform is bi-polar, this colour
coding is not critical.
Large muscle groups may require stimulation with two
channels, that is, four electrodes simultaneously.
The electrode pads must always be used in pairs,
so that the signal can flow in a circuit.
NOTE: Always check unit is OFF before
attaching or removing pads.
Use 50x50mm square electrode pads for all areas except the face, where smaller
25mm diameter electrodes may be necessary. When exercising smaller muscles,
take care to adjust the intensity slowly as the motor nerves may be more sensitive.
Example EMS Electrode Pad Positions
Eye care
We all are familiar with it. The ever-increasing set
of little wrinkles around the eyes. At first, they’re
accepted as laugh-lines and seen as a symbol of
maturity. But, when the eyes also start to swell up,
deep wrinkles plough their way through the skin
and puffy lids appear, the time has come to do
something about it.
You can use Programme7 stimulate the muscles
around the eyes. You will notice the muscles
working straight away from the slight twitching.
The activation of the muscles stimulates the
circulation. This relaxing skin care also contributes
to an increase in well-being, making you appear
more awake and content.
Use small 25mm round electrode. In order to
prevent triggering unpleasant sensations, you
should increase the current strength very carefully
Stomach / hips
Muscle training and fighting the fat
The stomach, that tiresome subject - you can’t magic it away.
Weight reduction is usually the magic word. Weight reduction is effectively aided
by training the stomach muscles. With Sports TENS 2 you can single out muscles
for direct stimulation. The stomach contains several different individual muscles.
The central stomach muscle is responsible for giving you a slim stomach and a
good upper body posture.
Bottom
The bottom is equipped with a very strong set of muscles.
Unfortunately, unwanted fat and cellulite zones are often to be found in this area
and are very difficult to combat. Muscular training is one way of improving shape.
The picture shows the possible electrode positions for building muscles.
Page 13

22 23
Upper Arms
Our upper arms often have little shape and flabby, coarse skin. The cause is usually
a lack of movement and muscular work. The Sports TENS 2 can be used to carry
out muscle training. In this case too, it is all about stimulation of the circulation
of blood. You have the option of treating the front side or the reverse side of both
upper arms depending on where the need is greatest.
Chest and shoulders
Building chest muscle affects posture and movement in the upper body as a whole.
Legs - thighs and calves
It is usually a lack of trained muscles in the legs which disturbs us most, particularly
in conjunction with areas of cellulite in the thigh area. Targeted muscle training for
the front and back of the thigh and calves is very simple to perform.
Page 14

24 25
8.3 Electrode Pads positions for Massage programmes
Neck/Tension headache Shoulders
Circulation/Swollen Legs – Program 8
Poor return of blood to the heart is a common problem leading to swollen legs and
varicose veins. This program supports what is known as the venous pump. Waste
products are discharged which in turn eases the flow of blood.
9. GENERAL PAD ADVICE
• The electrode pads supplied are reusable but are for single patient use.
• In order to obtain the best conductivity through the pads always ensure that
they are in good condition and tacky.
• Before use make sure your skin is clean and dry.
• Peel the electrode pads from their protective plastic shield by holding and lifting
one corner of the pad and pulling. Do not pull on the pigtail wire of the pad.
• After use always replace the pads on the plastic liner and replace in the re-
sealable plastic bag.
• If the pads dry out then it is best to buy a replacement pack of electrodes.
In an emergency it may be possible to restore some of the tackiness of the pad
by adding a tiny drop of water on each pad and spreading around. If too much
water is added the pads will become too soft then it is suggested in order to try
to re-establish some adhesiveness to place them sticky side up in a refrigerator
for a few hours.
• In very hot weather the gel on the pads may become soft. In such cases place
the pads, still on their plastic liners and in their bag into a fridge until they return
to their normal condition.
10. BELT CLIP
The Sports TENS 2 is supplied complete with a belt clip to allow you to
wear it at the waist.
Removing the belt clip
To remove the belt clip pull the central spine upwards, and slide the clip down.
Replacing the belt clip
To attach the belt clip, firmly slide it into the slot. Test to ensure that the lock
has engaged.
11. TROUBLESHOOTING
If your Sports TENS 2 is not working properly please check the following:
Problem: No display/ wont turn on:
BATTERY: i) Is it fitted? ii) Is it charged?
Problem: Intensity won’t go above 10 mA:
A circuit is not being made
i) Have you applied both electrode pads (per lead wire) to ensure a complete circuit?
ii) Are the lead wires properly connected at both ends?
iii) Is the lead damaged? (Try using the other lead – if this works, then the original
lead is faulty)
If the above review has failed to resolve your problem, call TensCare or your local
dealer (address on back cover) for advice.
Page 15

26 27
12. CAUTIONS AND WARNINGS
Do not use TENS or EMS :
• ifyouhaveaheartpacemakerorhaveaheartrhythmproblem.
• ifyouhaveepilepsy.
• duringtherstthreemonthsofpregnancy.
• whendrivingoroperatingmachineryordoinganyothertaskwheresudden
movement could be hazardous.
• ifyouaresufferingfromacute,feverishorinfectiousdiseases.
• tomaskorrelieveundiagnosedpain.
Do not place electrode pads :
• onbrokenskin,asthismayencourageinfection.
• toskinwhichdoesnothavenormalsensation.Iftheskinisnumb,toogreata
strength may be used, which could result in skin inflamation.
• onthecarotidsinusnerves,onthefrontoftheneck,asthesemayaffectheartrate.
• overtheeyes,oracrossthefrontofthehead.
• ontheabdomenatanytimewhenpregnant.
• nearmalignanttumours.
Do not:
• ignoreanyallergicreactiontotheelectrodepads:Ifaskinirritationdevelops,stop
use and allow the skin to heal. If the problem persists, try using a different make of
electrode or change the electrode, try moving the electrode position each day by
just the width of the electrode.
• startyourTENSorEMStreatmentuntilthecauseofpainhasbeendiagnosed.
If you are in any doubt about any of these warnings please consult your
medical adviser.
Also do not :
• immerseyourunitinwaterorplaceitclosetoexcessiveheat.
• attempttoopenuptheunit.Suchactionswillvoidtheguarantee.
• mixold,newordifferenttypesofbatteries.Besuretodisposeofoldbatteriessafely.
Caution:
• observecautionwhenusingelectrotherapyatthesametimeasbeing
connected to electro-monitoring equipment with body worn electrode pads as
interference may occur.
Do: Remove batteries from your machine if the unit is unlikely to be used for a long period.
13. CLEANING
The case and lead wires can be cleaned by wiping with a damp cloth and a
solution of mild soap and water. Wipe dry.
Do not immerse your TENS machine in water.
Do not use any other cleaning solution than soap and water.
14. CHARGING THE BATTERY
The Sports TENS 2 is powered by a type BL4B
rechargeable Li-ion battery.
A separate Charging Cradle and Power Adaptor are
included in the kit.
The battery should need charging about once a week.
When the battery is running low, a low battery indicator
will show on the screen (battery symbol).
Although the display fades as the batteries run down,
the strength of the output does not change until the
warning is shown.
NB: Remove the battery from your Sports TENS 2 if the
unit is unlikely to be used for a long period.
When the battery is charged, the indicator light on the
cradle will change from red to green.
For a replacement battery, contact Tenscare or your
local distributor.
Use only the power adaptor and charging cradle supplied.
USE OF OTHER CHARGERS COULD BE HAZARDOUS
AND WILL NEGATE THE GUARANTEE
Warning
There is a risk of smoke, fire, or rupture if the battery is not used according to the
following guidelines:-
•Donotdisassemblethebattery
•Donotshort-circuitthebattery
•Donotincinerateorheatthebattery
•Donotuseorleavebatterynearasourceofheat,stoveorheatedplace
(more than 80°C)
•Donotimmersethebatteryinwaterorseawater,orgetitwet
•Donotchargebatterynearbythereorinstrongsunlight
•Onlyusethechargerprovidedandobservecharginginstructions
Disposal
Always dispose of batteries responsibly according to local government guidelines.
15. GUARANTEE
Your TensCare device is guaranteed for two years from the date of purchase.
If a fault develops return the unit to TensCare at the address below, together with
a copy of your invoice and details of the problem. The guarantee does not cover
the batteries, electrode pads or mono lead wire.
Please note that the Guarantee is invalidated if
i) incorrect batteries have been fitted.
ii) the unit has been immersed in water, maltreated or tampered with.
Page 16

28 29
16. CONSUMABLES AND SERVICING
Replacement electrode pads, new batteries and lead wires are available from
your supplier or distributor (see back cover for contact details), by mail order from
TensCare, by telephone using a credit or debit card, or through our website.
PART NUMBER:
L-ST2 Replacement lead 1.25m
E-CM5050 Electrode pads 50x50mm for external use. Pack of 4
B-BL6F Li-Ion battery type BL-6F 3.7V 1100mAh
X-ST2CR Charger Cradle
X-STP Universal Power supply
X-STPP-UK Plug adaptor UK 3 pin
X-STPP-EU Plug adaptor EU 2 pin
X-STPP-US Plug adaptor US 2 pin
These consumables can be purchased either by contacting TensCare on
+44 (0)1372 72 34 34, by going online to www.tenscare.co.uk, or from
your local supplier.
Please ensure that you order the correct part number.
For servicing please call Tenscare on +44 (0)1372 72 34 34 to discuss
any problem.
If your unit needs to be returned please send it to: Service Department,
TensCare Ltd, 9 Blenheim Road, Epsom, Surrey KT19 9BE, UK
Please ensure that you enclose your name, address and contact telephone
number so that you can be contacted and informed about any problem and
any costs involved.
17. DISPOSAL OF WASTE ELECTRICAL AND
ELECTRONIC PRODUCTS (WEEE)
One of the provisions of the European Directive 2002/96/CE is that anything
electrical or electronic should not be treated as domestic waste and simply
thrown away. To remind you of this Directive all affected products are now being
marked with a crossed-out wheelie bin symbol, as depicted below.
To comply with the Directive you can return your old electro-therapy unit to us for
disposal. Simply print a postage-paid PACKETPOST RETURNS label from our
website www.tenscare.co.uk, attach this to an envelope or padded bag with the
unit enclosed, and post it back to us. Upon receipt we will send your old device
for components recovery and recycling to help to conserve the world’s resources
and minimise any adverse effects on the environment.
18. TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
Output: 99 mA zero to peak
Constant current 500-1500 Ohm, constant voltage > 1500 Ohm
Max Pulse energy: Total output limited to 25uC per pulse
Channels: Dual Channel
Output plugs: Fully shielded: touch proof
Waveform: Asymmetrical rectangular bi-phasic.
TENS: 2-150 Hz in steps of 1, 50-300 uS in steps of 5
EMS 10-120 Hz, 50-350 uS
Dimensions: 115x56x23mm
Weight: 110gm with battery
Power supply: BL-6F Li-Ion battery 3.7V 1100mAh
Mains adaptor with charging cradle.
Input 110-240V
Output 4.2V DC600mA
Safety Classification: Internal power source
Type BF Designed for continuous use.
No special moisture protection.
Environmental
Operating
Specifications: Humidity: 20 to 65% RH
Temperature range: 0 to 35C
Storage
Specifications: Humidity: 10 to 90% RH
Temperature range: 0 to 55C
STANDARD SYMBOLS
Follow operating instructions
CE medical device. Type BF
Caution
Do not dispose in normal dustbin – see para 17
Page 17

30 31
19. EMC PRECAUTIONS
Use special precautions regarding EMC according to the information provided below.
• Other portable and mobile RF communications equipment can
affect performance.
• Do not use when adjacent to or stacked with other electrical equipment.
• Use of leads or electrodes other than those listed in section 16 may affect
EMC performance.
Guidance and manufacturer’s declaration - electromagnetic emissions
The Sports TENS 2 is intended for use in the electromagnetic environment specified below. The customer or the user of the Sports
TENS 2 should assure that it is used in such an environment.
Emissions test Compliance Electromagnatic environment - guidance
RF emissions Group 1 The Sports TENS 2 uses RF energy only for its
CISPR 11 internal function. Therefore, its RF emissions
are ver y low and are not likely to cause any
interference in nearby electronic equipment.
RF emissions Class B The Sports TENS 2 is suitable for used in
domestic establishment and in establishment
directly connected to a lo w voltage power
supply network which supplies buildings used
for domestic purposes.
Harmonic emissions
IEC61000-3-2 Not applicable
Voltage fluctuations/
flicker emissions
IEC 61000-3-3 Not applicable
The Sports TENS 2 is intended for use in the electromagnetic environment specified below. The customer or
the user of the Sports TENS 2 should assure that it is used in such an environment.
Immunity test IEC 60601 test level Compliance level Electromagnetic
environment guidance
Electrostatic ±6 kV contac ±6 kV contact Floors should be wood,
discharge (ESD) ±8 kV air ±8 kV air concrete or ceramic tile
IEC 61000-4-2
If floors are covered with synthetic material, the relative humidity should be at least 30%.
Electrical fast
transient/burst ±2 kV for power supply lines Not applicable Not applicable
IEC 61000-4-4 ±1 kV for Input/output lines
Surge
IEC 61000-4-5 ±1 kV differential mode Not applicable Not applicable
±2 kV common mode
Voltage dips, short <5 % UT (>95 % dip in UT) for 0,5 cycle
interruptions and 40 % UT(60 % dip in UT ) for 5 cycles
voltage variations 70 % UT (30 % dip in UT ) for 25 cycles
on power supply <5 % UT (>95 % dip in UT ) for 5s
input lines
IEC 61000-4-11
Power frequency (50/60 3 A/m Not applicable Not applicable
Hz) magnetic field
IEC 61000-4-8
NOTE UT is the a.c. mains voltage prior to application of the test level
The Sports TENS 2 is intended for use in the electromagnetic environment specified below. The customer or
the user of the Sports TENS 2 should assure that it is used in such an environment.
Immunity test IEC 60601 test level Compliance level Electromagnetic environment guidance
Conducted RF 3 Vrms 3 Vrms
IEC 61000-4-6 150 kHz to 80 MHz
Radiated RF 3 Vrms 3 Vrms
IEC 61000-4-3 80 MHz to 2,5 GHz
NOTE 1 At 80 MHz and 800 MHz, the higher frequency range applies. NOTE 2 These guidelines may not a pply in all situations.
Electromagnetic propagation is affected by absorption and reflection from structures, objects and people.
a. Field strengths from fixed transmitters, such as base stations for radio (cellular/cordless) telephones and land mobile radios,
amateur radio, AM and FM radio broadcast and TV broadcast cannot be predicted theoretically with accuracy. To assess the
electromagnetic environment due to fixed RF transmitters, an electromagnetic site survey should be considered. If the measured
field strength in the location in which the Sports TENS 2 is used exceeds the applicable RF compliance level above, the model
Sports TENS 2 should be observed to verify normal operation. If abnormal performance is observed, additional measures may be
necessary, such as re-orienting or relocating the model Sports TENS 2.
b.Over the frequency range 150 kHz to 80 MHz, field strengths should be less than 3 V/m.
Portable and mobile RF communications
equipment should be used no closer to any part
of the Sports TENS 2, including cables, than the
recommended separation distance calculated
from the equation applicable to the frequency of
the transmitter
Recommended separation distance 3V
d = 1.2√ P 80M Hz to 800MHz
d = 2.3√ P 800MHz to 2.5GHz
where P is the maximum output power rating
of the transmitter in watts (W) according to
the transmitter manufacturer and d is the
recommended separation distance in meters (m).
Field strengths from fixed RF transmitters, as
determined by an electromagnetic site survey,
should be less than the compliance level in each
frequency range.
Interference may occur in the vicinity of equipment
marked with the symbol on the left of this box
Recommended separation distances between portable and mobile RF communications equipment
and the Sports TENS 2
The Sports TENS 2 is intended for use in an electromagnetic environment in which radiated RF disturbances are controlled.
The customer or the user of the model Sports TENS 2 can help prevent electromagnetic interference by maintaining a
minimum distance between portable and mobile RF communications equipment (transmitters) and the model Sports TENS 2
as recommended below, according to the maximum output power of the communications equipment.
Rated maximum Separation distance according to frequency of transmitter M
output power of
transmitter W 150kHz to 80MHz 80 MHz to 800 MHz 800MHz to 2.5GHz
d=1.2√ P d=2.3√ P d=2.3√ P
0.01 0.12 0.12 0.23
0.1 0.38 .38 0.73
1 1.2 1.2 2.3
10 3.8 3.8 7.3
100 12 12 23
For transmitters rated at a maximum output power not listed above, the recommended separation distance d in meters (m) can be
estimated using the equation applicable to the frequency of the transmitter, where P is the maximum output power rating of the
transmitter in watts (W) according to the transmitter manufacturer.
NOTE 1 At 80 MHz and 800 MHz, the separation distance for the higher frequency range applies.
NOTE 2 These guidelines may not apply in all situations. Electromagnetic propagation is affected by absorption and reflection
from structures, objects and people.
Page 18

32 33
20. TENS DERMATOMES
Page 19

34 35
s.s.
i.s. i.s.
s.s.
dd
t t
e.x.e.x.
b.f.
b.f.
g.c. g.c.
s.s. M. supraspinatus
i.s. M. infraspinatus
t. M. triceps brachi
ex. Extensors on the underarm:
M. extensor carpi radialis
M. extensor carpi ulnaris
M. extensor digitorum
b.f.+st. M. biceps femoris
+ M. semitendinosus
g.c. M. gastrocnemius
(+ M. soleus)
21. EMS ELECTRODE PLACEMENT CHART
O.O
z.m
z.m
L.LL.L
o.f
s.s.
i.s. i.s.
s.s.
o.f
s.c.m
dd
dd
b
fl.
fl.
b
t t
e.x.e.x.
s.c.m
p.m.
r.a.
s
r.f. r.f.
v.l.
b.f.
p.l.p.l.
t.a. t.a.
v.m.v.m.v.l.
s
r.a.
p.m.
O.O
b.f.
g.c. g.c.
O.O M.orbicularis oculi
z.m M. zygomaticus major
o.f M.occipito frontalis, pars frontalis
L.L M. levator latii
s.c.m. M. sternocleido-mastoideus
d. M. deltoideus
b. M. biceps brachii
fl. Underarm flexors:
M. flexor carpi radialis et ulnaris
M. flexor digitorum superficialis
M. palmaris longus
p.m. M. pectoralis major
r.a. M. rectus abdominis
s. M. sartorius
r.f. M. rectus femoris
v.l. M. vastus lateralis
v.m. M. vastus medialis
p.l. M. peroneus
(fibularis) longus
t.a. M. tibialis anterior
Page 20

36 37
This product is manufactured by Tenscare Ltd.,
in compliance with the European Union Medical Device Directive
MDD93/42/EEC under the supervision of Intertek
Notified Body number 0473.
0473
NOTES:
WWW.TENSMACHINES.CO.UK
 Loading...
Loading...