Page 1

Instructions For Use
Flexistim
READ INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY BEFORE USE
flexistim instructions final.indd 1 27/11/2014 12:06
Page 2
FOREWORD
Read this User Manual carefully before you start using your Flexistim unit.
The manufacturer strongly recommends carefully reading of the “Warnings and Cautions” and
Chapters of this User Manual.
1 INTRODUCTION 1
2 WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS 2
3 HOW TENS WORKS 5
4 EMS: WHAT IT IS AND HOW IT WORKS 6
4.1 Mode of operation 7
4.2 Treatment time and treatment interval 7
4.3 Choosing the right strength 8
5 TENS and EMS STIMULATION PARAMETERS: 8
5.1 Pulse Waveform 8
5.2 Pulse Frequency 9
5.3 Pulse Width 9
5.4 Pulse Intensity 10
5.5 WORK 10
5.6 REST 10
5.7 RAMP 10
6 IFT: WHAT IT IS AND HOW IT WORKS 11
7 MICROCURRENT 12
8 KEYPAD AND DISPLAY 13
9 CONTENTS OF THE PACK 18
10 HOW TO ASSEMBLE YOUR UNIT 19
11 OPERATION 22
11.1 Turn on the Device 22
11.2 Select Mode 22
11.3 Select a Programme 22
11.4 Set Treatment Timer 23
11.5 Attach the Electrode Pads 23
11.6 Adjust the Intensity 24
11.7 Skip Function 24
12 ADJUSTING MANUAL PROGRAMMES 25
12.1 TENS 25
12.2 EMS 26
12.3 IFT 27
12.4 MICROCURRENT 27
13 LOCK AND UNLOCK YOUR OWN PROGRAMME 28
14 MEMORY MODE 28
15 PROGRAMMES 29
15.1 TENS PROGRAMMES 29
15.2 EMS PROGRAMMES 31
15.3 IFT PROGRAMMES 34
15.3.1 CHOOSING SETTINGS 34
15.4 MICROCURRENT PROGRAMMES 35
15.4.1 CHOOSING SETTINGS 35
15.4.2 HOW LONG SHOULD EACH SESSION LAST? 36
15.4.3 FOLLOW-UP 36
15.4.4 PROBLEMS 36
16 ELECTRODE PAD PLACEMENT 37
16.1 Electrode Pad Placement for TENS 37
16.2 Electrode Pad Placement for EMS 39
16.3 Electrode Pad Placement for IFT 44
16.4 Electrode Pad Placement for Microcurrent 46
17 FURTHER CLINICAL INFORMATION AND TREATMENT PROTOCOLS 47
18 CARE OF ELECTRODES 47
19 CHARGING THE BATTERY 48
20 TROUBLESHOOTING 50
21 CLEANING 51
22 CONSUMABLES AND SERVICING 51
23 WARRANTY 52
24 DISPOSAL OF WASTE ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC PRODUCTS (WEEE) 52
25 SPECIFICATIONS 53
26 STANDARD SYMBOLS 55
27 EMC PRECAUTIONS 55
flexistim instructions final.indd 2-3 27/11/2014 12:06
Page 3
1. INTRODUCTION
INTENDED USE
The Flexistim combines the treatment capabilities of a TENS device, an EMS or NMES
device, a MIC stimulator, and an IFT stimulator all in one unit.
TENS stands for Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation. The TENS settings are
used to provide symptomatic pain relief for chronic, acute or post-operative pain.
EMS stands for Electrical Muscular Stimulation. The EMS settings are used to provide a
muscular training for localised regeneration and muscular hypertrophy.
MIC stands for MicroCurrent Stimulation. The MIC settings are used to provide
symptomatic pain relief for chronic, acute or post-operative pain, and the DC setting is
used for wound healing.
IFT stands for Interferential Stimulation. The IFT settings are indicated for symptomatic
relief of chronic intractable pain.
The Flexistim is intended for use in both the Hospital and Home Healthcare Environments.
FLEXISTIM FEATURES
Flexistim includes many of the features of a professional desk-top unit in a compact,
portable, battery operated device.
1. Multiple Functions
10 TENS programmes, 27 EMS programmes, 4 IFT Programmes, 4 Microcurrent
Programmes and 6 user dened programmes enabling you to experiment and save your
favourite settings - unrivalled performance for a product of this size and price.
2. Output
99mA TENS and EMS
60mA Peak to Peak pure sinusoidal carrier wave with constant energy (modied constant
current) control and 40mA safety override for home use.
700μA Microcurrent with DC option.
3. Memory
Flexistim allows you to save and recall a particular programme setting and has a Usage
Timer to record the time it has been used.
1 2
4. Power Supply
Removeable, rechargeable Li-ion battery, with option of operation through external mains
power adaptor.
2. WARNING AND CAUTIONS
Contraindications:
1. Do not use this device on patients who have a cardiac pacemaker, implanted
debrillator, or other implanted electronic devices, because this may cause electric
shock, burns, electrical interference, or death.
2. Do not use this device on patients whose pain syndromes are undiagnosed.
Warnings:
1. Do not apply stimulation over the neck or mouth because this could cause severe
muscle spasms resulting in closure of the airway, difculty in breathing, or adverse
effects on heart rhythm or blood pressure.
2. Do not apply stimulation across the chest, because IFT currents penetrate deep into
the tissue and the introduction of electrical current into the chest may cause rhythm
disturbances to the patient’s heart, which could be lethal.
3. Do not apply stimulation over the pregnant uterus.
4. Do not apply stimulation, other than microcurrent, over open wounds or rashes,
or over swollen, red, infected, or inamed areas or skin eruptions (e.g. phlebitis,
thrombophlebitis, varicose veins).
5. Do not apply stimulation over, or in proximity to, cancerous lesions.
6. Do not apply stimulation in the presence of electronic monitoring equipment (e.g.
cardiac monitors, ECG alarms), which may not operate properly when the electrical
stimulation device is in use.
7. Do not apply stimulation when in the bath or shower.
8. Do not apply stimulation while driving, operating machinery, or during any activity in
which electrical stimulation can put the patient at risk of injury.
9. Consult with your physician before using this device, because the device may cause
lethal rhythm disturbances to the heart in susceptible individuals.
flexistim instructions final.indd 4-5 27/11/2014 12:06
Page 4
General Warnings:
1. Do not immerse any part of the unit in water
2. Do not place the unit close to excessive heat.
3. Do not use any electrodes which are less than 50mm X 50mm.
4. Use only the specied battery: 1x 3.7volt rechargeable lithium battery. The use of any
other battery could damage the unit.
5. Remove battery if unit is not used for a long period of time.
6. Do not use the unit while asleep.
7. Do not put the lead wire on, or wrapped around the neck.
8. Use this device only with the leads, electrodes and accessories recommended by the
manufacturer. Use of other parts materials supplied by the manufacturer can degrade
minimum safety and invalidate the warranty.
9. After inserting plugs into both CH1 and CH2 sockets, please do not remove the
plugs when the unit is working. Ensure that the unit is switched OFF before removing
the plugs.
10. Keep the unit away from sources of high magnetic elds such as TV’S, microwave
ovens and hi- speakers, as these may affect the LCD screen.
11. Keep the device away from a replace or radiant heater, as the heat may affect
the device.
12. Keep the device away from nebulizer or steam kettle, as the moisture may affect
the device.
13. Keep the device away from sunlight, as long-term exposure to sunlight may affect the
rubber causing it to become less elastic and crack.
14. Keep the device away from lint and dust, as long-term exposure to lint or dust may
affect the sockets or cause the battery connector to develop a bad contact.
15. Temperature & Relative Humidity of storage: -20°C–+40°C, 8%--70% R.H.
16. Temperature & Relative Humidity of transportation: -20°C–+40°C, 8%--70% R.H.
3
4
10. Apply stimulation only to normal, intact, clean, healthy skin.
11. Using the device directly over metallic implants could cause the currents to focus
over a small area, causing tissue burns. If you have metal implants, do not place the
pads near, or across the implant, and adjust the intensity with care.
Precautions:
1. Since the effects of stimulation of the brain are unknown, stimulation should not be
applied across the head and electrodes should not be placed on opposite sides of the
head, unless you are in Microcurrent mode.
2. The safety of electrical stimulation during pregnancy has not been established.
3. Some patients may experience skin irritation or hypersensitivity due to the electrical
stimulation or electrical conductive medium (gel).
4. Patients with suspected or diagnosed heart disease should follow precautions
recommended by their physicians.
5. Patients with suspected or diagnosed epilepsy should follow precautions recommended
by their physicians.
6. Use caution when the patient has a tendency to bleed internally, such as following an
injury or fracture.
7. Use caution following recent surgical procedures when stimulation may disrupt the
patient’s healing process.
8. Use caution if stimulation is applied over areas of skin with less than normal sensitivity.
9. Keep this device out of the reach of children.
Adverse Reactions:
• Patients may experience skin irritation and burns beneath the stimulation electrodes
applied to the skin.
• Patients may experience headache and other painful sensations during or following the
application of electrical stimulation near the eyes and to the head and face.
• Patients should stop using the device and should consult with their physicians if they
experience adverse reactions from the device.
flexistim instructions final.indd 6-7 27/11/2014 12:06
Page 5
5 6
3. HOW TENS WORKS
TENS stands for Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation. TENS stimulates your
body’s own natural defences against pain. It is totally safe and has been used successfully
by thousands of pain sufferers.
TENS sends a gentle stimulation through the skin which works in TWO ways:
Pain Gate
Stimulating the sensory nerves, which carry touch and temperature signals. These
nerves go to the same connections in the spine as the nerves carrying pain. A strong
sensory signal will block the pain signal travelling up the spine to the brain. This is known
as closing the “Pain Gate” and takes effect quite quickly after the unit is switched on. You
can use TENS several times a day, for as long as you like.
Endorphin Release
At low frequency settings, and slightly stronger output, TENS drives the motor nerves
to produce a small repetitive muscle contraction. This is seen by the brain as exercise
and this promotes release of Endorphins – your body’s own natural pain killer. The relief
builds up and normally takes about 40 minutes to reach a maximum level which can last
for hours after the machine is switched off.
By using TENS you can expect to achieve a signicant reduction in pain if not complete
pain relief.
Side Effects
There are no known side effects to TENS use and long-term TENS use is not harmful.
Positioning the electrodes for TENS
The TENS effect is conned to the nerves entering a single vertebra in the spine. To be
effective, you therefore need to stimulate a sensory nerve entering the spine at the same
level as the nerve carrying the pain. For this reason electrodes are usually rst placed
where the greatest pain is felt. Nerves follow the curve of the ribs and spiral around the
limbs, so you will need to try different positions until you nd the best for you. Try moving
the electrodes short distances to establish the positions that are most effective for you.
TENS is clinically tested and approved for many applications including:
• Back pain and lumbar and cervical spine problems
• Joint pain (e.g. knee joint, hip joint, shoulder)
• Neuralgia • Headaches • Women’s period pains
• Pain after injuries to musculoskeletal system
• Pain with circulatory problems
• Chronic pain through various causes
4. EMS: WHAT IT IS AND HOW IT WORKS
EMS stands for Electrical Muscle Stimulation and is a widespread and generally
recognised method which has been used for years in sports and rehabilitation medicine.
In the sports and tness eld, one of the uses of EMS is as a supplement to conventional
muscle training, in order to increase the efciency of muscle groups and adapt physical
proportions to the desired aesthetic results.
EMS has two main applications. Firstly, a targeted strengthening of musculature can
be produced (Activating application) and secondly a relaxing, resting effect can also be
achieved (Relaxing application).
EMS successfully rebuilds and tones muscles.
Different levels of muscle contraction are achieved by sending electrical impulses of
various types, depending on the programme selected, into the body. These muscle
contractions retrain the muscles, increase their effectiveness and improve their condition.
This is benecial where muscles - for whatever reason - have not been in regular use and
have lost condition (muscle atrophy). For sports, the benet is to increase the effect of
training and enhance performance.
Typical uses are:
• Muscle training to improve endurance performance
• Muscle training to support the strengthening of certain muscles or muscle groups in
order to achieve desired changes to body proportions
• Sports training, covering - warm-up, strength, speed, power, resistance, endurance
and recovery
• Rehabilitation in relation to sports injury
The effect on muscle tone of electrical stimulation (EMS) is generally only noticeable after
regularly repeated application. Electrical stimulation does not replace regular exercising
of the muscle, but is able to reasonably supplement it.
flexistim instructions final.indd 8-9 27/11/2014 12:06
Page 6
MONOPHASE PULSES
PULSE
INTENSITY
BIPHASIC PULSES
BIPHASIC PULSES
7 8
Muscle wastage: EMS is used in the treatment of medical conditions involving muscle
wastage including: Neuromuscular facilitation - Muscle re-education - Muscle training Prevention/slowing of atrophy/hypotrophy - Preventing postoperative muscle weakness
- Reduction of spasticity - Maintaining or increasing range of motion - Training of partial
peripheral nerve damage with signs of re-innervation - Treatment of scoliosis.
4.1 Mode of operation
EMS uses external electrical impulses that act through the skin to stimulate the nerves
supplying a specic muscle group.
The muscle reacts in different ways depending on the strength of current and duration
and frequency of the electrical impulse.
Muscles are made up of two different types of bre:
- Red bre is slower contracting and aerobic working.
- White bre is faster acting and capable of anaerobic working.
The proportions of red and white bres depend on the way the muscle is used.
Fibre can be converted from one type to the other, depending on the signals it receives.
This is known as the Trophic effect.
Different frequencies have different effects: Low (1-10 Hz) frequencies coupled with
long impulse times have a purifying and relaxing effect through individual contractions,
whereby the circulation in the treated muscle is simultaneously improved and removal
of metabolic end products is supported (lymphatic drainage). The oxygen supply to the
muscle is improved.
In contrast, medium (20-50 Hz) frequencies can put a high level of strain on the muscle,
thus promoting the muscular structure.
Very high frequencies (60-90 Hz) can be used to promote muscle denition and bulk.
The body maps at the back of this guide show pad positioning in order to stimulate
specic muscle groups.
4.2 Treatment time and treatment interval
Treatment by EMS can vary between 15–60 minutes stimulation twice a week to treatment
several times per day.
4.3 Choosing the right strength
The object of EMS treatment is to produce powerful muscle contractions.
The strength of the current should be increased to about three times the level at which
you can rst feel the tingling, or to as high as you can stand without causing pain. You
will probably feel that electrical contraction is being more powerful than a voluntary
contraction, because the current also stimulates your sensory nerves. The signals have
a pain-relieving effect.
You may nd the sensation uncomfortable to start with, therefore you may not get up
to therapeutic strength at the start of treatment. The strength can be increased during
the course of the treatment, as you become accustomed to the sensation. Voluntary
muscular activity is more effective than stimulation, and it may improve progress if you
combine voluntary contraction with stimulation.
The powerful muscle contractions caused by electrical stimulation give rise to training
aches, which usually disappear within a week.
After treatment tingling sensations may continue or your skin may feel numb, this
is normal.
5. TENS and EMS STIMULATION PARAMETERS:
The effect of electrical stimulation on the body depends on the following current settings:
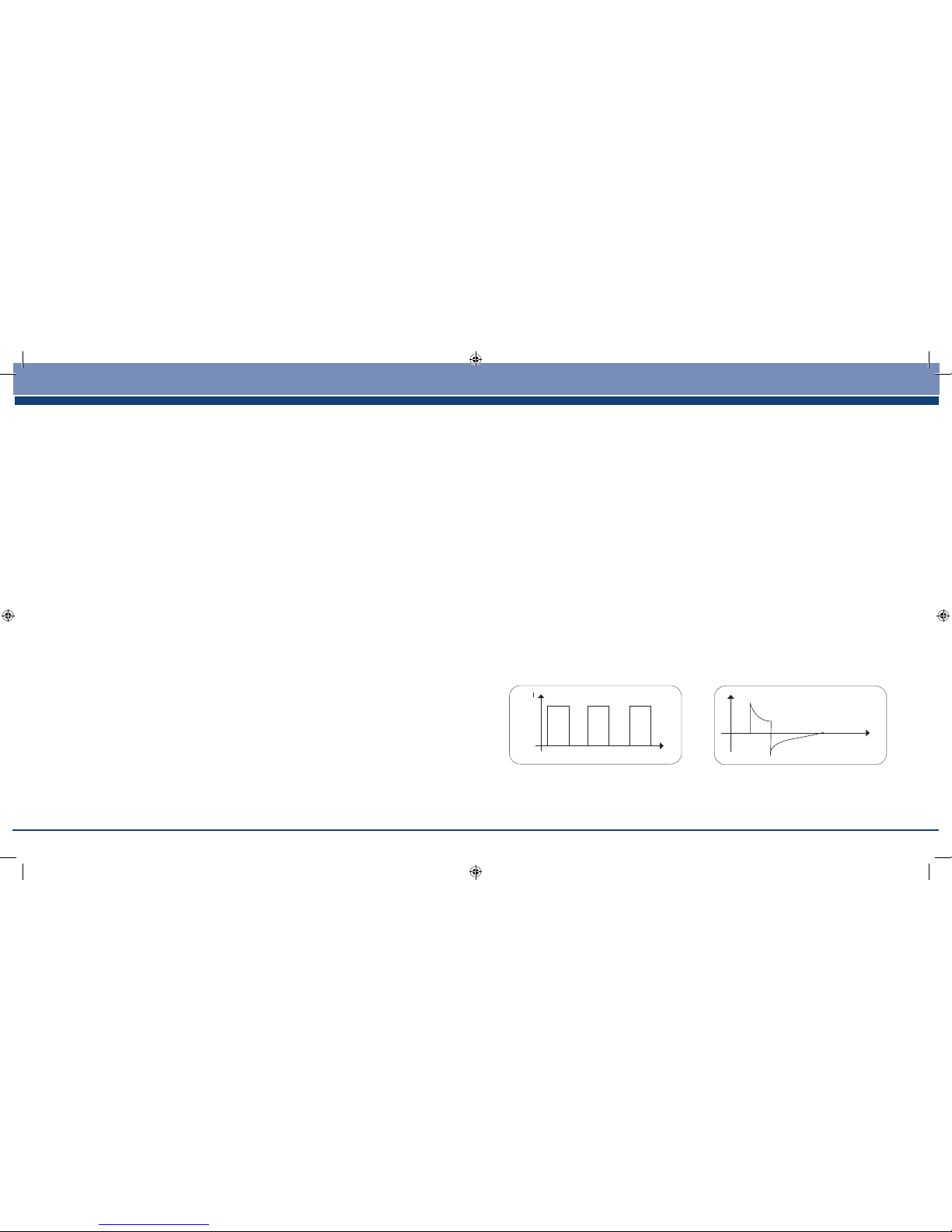
5.1 Pulse Waveform
This describes the time function of the excitation current which may be either monophasic
or biphasic.
With monophasic pulse trains, the current ows in one direction. With biphasic pulses,
the excitation current alternates its direction.
flexistim instructions final.indd 10-11 27/11/2014 12:06
Page 7
PULSE WIDE
BIPHASIC PULSES
9
10
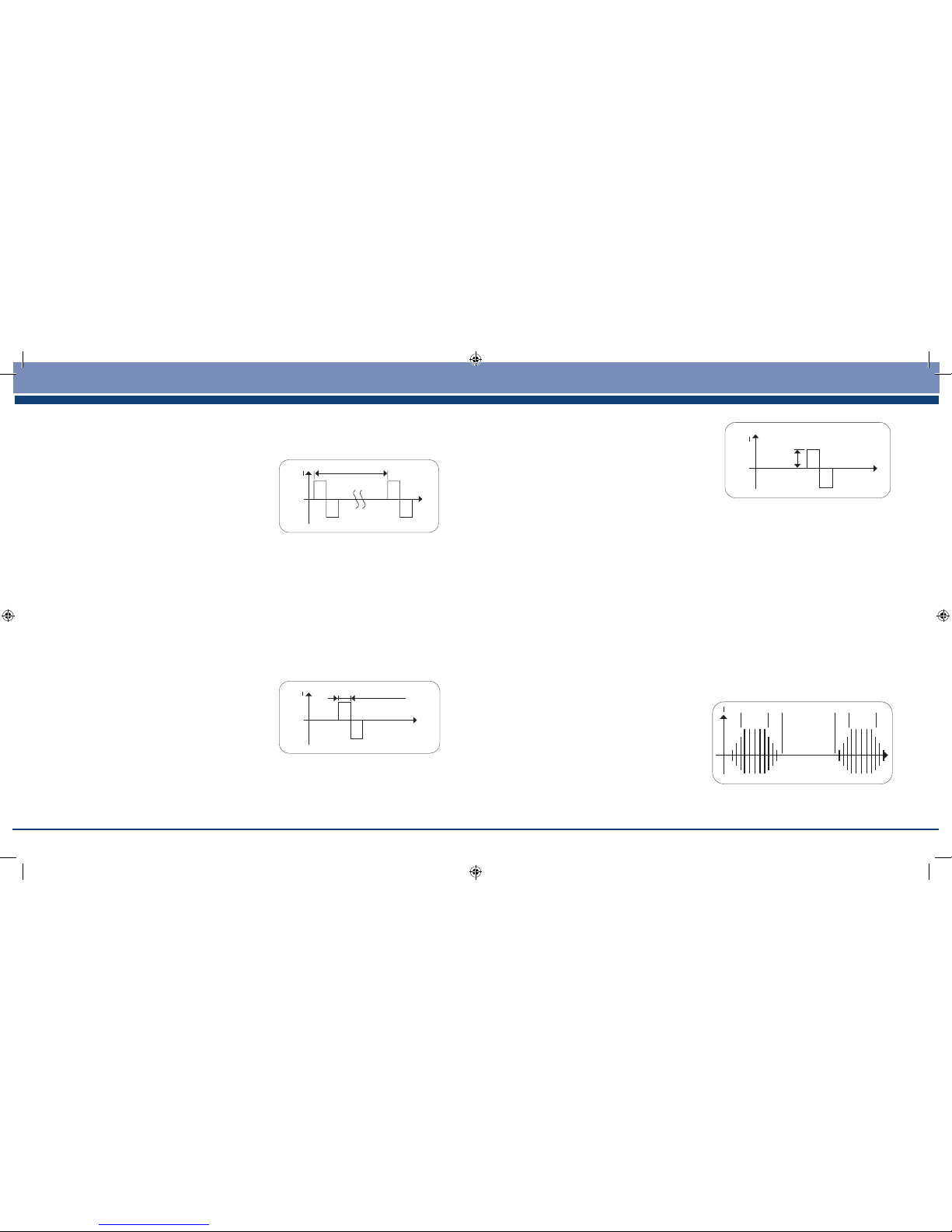
Frequency indicates the number of individual
pulses per second, and is indicated in
Hz (Hertz = pulses per second). It can be
calculated by working out the inverse value
of the periodic time.
Different types of muscle bres react preferentially to different frequencies:
Slow-response bres tend to react to lower pulse frequencies up to 15Hz, while fastresponse bres only respond to frequencies over approx. 35Hz.
With pulses of approx.45~70Hz, there is permanent tension in the muscle (tetany)
combined with premature muscle fatigue. Higher pulse frequencies can therefore
preferably be used for elasticity and maximum strength training.
For TENS:
A frequency of 110 Hz is good at blocking pain signals.
A low frequency of 4 or 10 Hz allows for the release of endorphins, the body’s natural
morphine-like substances.
5.3 Pulse Width
Pulse width is used to indicate the duration
of an individual pulse in microseconds
(millionths of a second). Pulse width also
determines the penetration depth of the
current. In general a greater muscle mass
requires a greater pulse width. A higher
pulse width is also more likely to activate pain nerves, so there is a ne balance between
maximum muscle stimulation and tolerable sensation.
EMS 50-400 depending on frequency
TENS 50 to 250 μS.
The Flexistim uses only biphasic pulse trains, as they reduce the strain on the muscle,
leading to less muscle fatigue as well as safer application and reduce the risk of skin
irritation under the electrode.
5.2 Pulse Frequency
PERIODIC TIME
PULSE WIDE
MONOPHASE PULSES
PULSE
INTENSITY
BIPHASIC PULSES
PULSE WIDE
INTENSITY
BIPHASIC PULSES
5.4 Pulse Intensity
Setting the degree of intensity is dependent
on the subjective feeling of each individual
user and is determined by a number of
parameters such as application site, skin
circulation, skin thickness as well as quality
of electrode contact. The actual setting
should be effective but should never produce any unpleasant sensation such as pain at
the site of application.
In TENS programmes, while a slight tingling sensation indicates sufcient stimulation
energy, any setting which leads to pain must be avoided.
In EMS programmes, the intensity needs to be as high as possible for maximum benet
– so set just below the pain threshold.
With prolonged application, you may need to increase intensity as nerves get used to the
stimulation and become less sensitive (known as accommodation).
5.5 WORK is the time in seconds that muscle is stimulated (not including Ramp time).
The Flexistim offers a range of work periods from 1-40 sec.
5.6 REST is the time in seconds at zero strength in between stimulation.
The Flexistim offers a range of rest periods from 1-40 sec. The EMS programmes use
an active rest - low frequency pulses help to clear metabolites in-between work periods.
WORK WORKREST
PERIODIC TIME
PULSE WIDE
MONOPHASE PULSES
INTENSITY
PULSE
INTENSITY
RA
MP
RA
MP
BIPHASIC PULSES
5.7 RAMP is the time in seconds taken to
move up and down between zero and the
set stimulation strength. The Flexistim has
a xed ramp time of 1.5 up and 0.75 down.
flexistim instructions final.indd 12-13 27/11/2014 12:06
Page 8
6. IFT: WHAT IT IS AND HOW IT WORKS
Many users will be familiar with TENS, which delivers intermittent pulses to stimulate
surface nerves and block the pain signal. Unlike TENS, Interferential Therapy delivers a
continuous stimulation deep into the affected tissue.
IFT achieves this deep penetration by using a 4000Hz carrier wave to overcome the
skin impedance. TENS signals travel around the top 1cm of the skin surface. IFT signals
travel almost directly between the electrodes.
Interferential Therapy uses two medium frequency 4000Hz currents that ‘interfere’ with
each other to produce a beat frequency that the body recognises as a low frequency
energy source.
Unlike TENS, which delivers intermittent pulses to stimulate surface nerves and block the
pain signal, IFT delivers continuous stimulation deep into the affected tissue. In addition
to providing pain relief by the same mechanism that TENS uses, most physiotherapists
consider that IFT’s major role is to accelerate the inammatory or healing rate.
IFT is believed to work by stimulating parasympathetic nerve bres to give increased
blood ow and oedema reduction and by passing currents across cell membranes; these
currents vary depending upon the tissue involved. By using particular frequencies in the
range, different systems within the body can be stimulated or used to increase the blood
supply, which in turn hastens the healing rate. IFT is used to treat almost any condition
where inammation is a problem. For example, sports injuries; arthritic conditions;
bruising and swellings, back pain, osteo-arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, muscular pain.
Many practitioners use a “Sweep” treatment which uses constantly changing interference
pulse frequency. Practical clinical experience suggests therapeutic benets for these
sweeps in addition to those of conventional nerve stimulation.
11 12
7. MICROCURRENT
MicroCurrent Stimulation (MIC) is a type of therapy where very low current is sent
into the cells of the body. MIC is a very faint current that is so small it is measured in
millionths of an amp (microamps). Human cells generate a current that is in the micro
amp range which is why some can’t feel it - the current is so low it doesn’t stimulate the
sensory nerves.
MIC is a physiological electric modality that increases ATP (energy) production in the
cells of your body. This dramatically increases the tissue’s healing rate. The immediate
response to the correct MIC frequency suggests that other mechanisms are involved as
well. The exact effects or changes in the tissue can be noticeable; scars can suddenly
soften; trigger points often become less painful when the “correct” frequency is applied.
In many situations the changes can be long lasting and even permanent in some cases.
Microcurrent has been shown to give very effective pain relief. In patient surveys over
90% of patients reported signicant improvement.
The results of MIC can be seen after only a minute or so of treatment in most people.
The range of this beat frequency in the Flexistim is 1 to 160Hz
10Hz
12Hz
flexistim instructions final.indd 14-15 27/11/2014 12:06
Page 9
13 14
8. KEYPAD AND DISPLAY
Mode Selection Key
Press this key to select the therapy Mode:
TENS
EMS I, II and III (small, medium and large muscles)
IFT
Microcurrent
When a programme is running, this key also acts a PAUSE button. The PAUSE
symbol
II will be displayed and the programme timer will stop. Pressing again
resumes the programme and the intensity gradually returns to the set value.
Programme Selection
Press the “Prog” key to select the programme you require (see section 15)
Parameter Menu Selection
Press these keys to select the following parameters one by one:
TENS Preset Mode (P1-P10) :
Treatment Timer (min)
TENS Manual Mode (P11-P12) :
FREQUENCY (Hz)
PULSE WIDTH (μs)
Treatment Timer (min)
EMS Preset Mode (P1-P09) :
Treatment Timer (min)
EMS Manual Mode (P10-P11) :
FREQUENCY (Hz)
PULSE WIDTH (μs)
SYNCHRONOUS/ALTERNATING - SYNCH/ALT in display
WORK TIME (sec)
REST TIME (sec)
RAMP UP/DOWN TIME (sec)
Treatment Timer (min)
ON/OFF
Channel 1
Intensity mA
Lock
Work/Rest/
Ramp Setting
Channel 2
Intensity mA
Lead Fault
Pause
Frequency
Mode
Pulse Width
Programme
Battery State
Warning
Timer
Keys:
ON/OFF Key (On top of unit)
This key switches the unit on or off.
Press once for 2 sec and the unit is on, the LCD display located at the front of
the unit will light up.
There will be no feeling from either lead at this point as the intensity always
starts at zero. Press this key again and the unit will switch off.
flexistim instructions final.indd 16-17 27/11/2014 12:07
Page 10
Check electrode pad position. If you are certain that the pads are positioned
safely, press the SKIP key to override.
The triangle will stop ashing and intensity can be increased to 60mA.
SKIP key
The EMS programmes have three phases: Warm/ Train/ Cool.
You can jump to the next phase by pressing the Skip key.
In IF MODE, use this key to override limit and set intensity at > 40mA.
15 16
IFT Mode
IFT Preset (P1-P3)
Treatment Timer (min)
IFT Manual (P4)
FREQUENCY (Hz) (P1-P3)
Treatment Timer (min)
Microcurrent Mode:
Preset (P1, P2 and P4)
Manual (P3)
WAVEFORM - Const /Square/Ramp
FREQUENCY (Hz)
PULSE WIDTH mS
Treatment Timer (min)
Parameter Adjustment Controls
Press these keys to increase or decrease the value of the parameter which
you have selected with the MENU keys.
Intensity Controls
Press the keys on the left to adjust the intensity in Ch1 and on the right to
adjust the intensity in Ch2
IF MODE:
I.F. signals penetrate deep into the tissue. Positioning pads across the chest
or head could be dangerous - see section 16.3.
For your safety, when intensity reaches 40mA, the warning triangle ashes
and intensity cannot be increased.
Manual Programme Lock
When “Manual” is showing, you can protect the manual settings by pressing
and holding this key for 3 seconds.
The key symbol will ash and you will be unable to change the manual settings.
Press and hold for 3 seconds to unlock programme.
Lead Fault Detector
In TENS and EMS modes, when one or both of the electrodes are not placed rmly
on the skin, or the leads are not properly connected and the intensity is >10, the
output level goes immediately to zero and a lead fault icon ashes.
Automatic keypad lock
There is an automatic keypad lock if no button is used for 10 seconds.
Key symbol appears.
Press the Intensity Down button for either channel to unlock.
flexistim instructions final.indd 18-19 27/11/2014 12:07
Page 11

17
Treatment Timer
When the Treatment Timer has been set, it begins to count down in minutes and the
time remaining is displayed on the LCD. When it reaches zero, the device automatically
shuts off.
Memory
There is a usage memory for each Mode.
Pressing the MODE and CH1▼ button together for 3 seconds enters Memory.
The Usage time will be accumulatively recorded when the output level is above zero. The
accumulative treatment time in minutes is displayed.
Press the same keys again to return back to the previous normal display.
Pressing CH2▼ key and MODE key together for 3 seconds will clear the treatment
time to zero.
Power Supply
The Flexistim may be operated from the re-chargeable battery, or
directly from the power adaptor. When the adaptor is plugged in to
the Flexistim, the internal battery is automatically disconnected.
The battery cannot be charged while in the unit, only in the charging
cradle supplied.
The rechargeable battery will give about 1 hours use at 50% intensity in
IFT Mode, and much longer in other Modes.
If you need to make more than one treatment you may either:
a) Purchase and recharge additional batteries
b) Connect to mains power using the mains adaptor
18
9. CONTENTS OF THE PACK
Your Flexistim pack should contain the following:
1 × Flexistim Unit
2 × Leads
4 × Self-Adhesive Electrodes with Connectors (Size: 50mm×50mm)
1 × 3.7V Rechargeable Lithium Battery (BL-6F)
1 × AC Power Cord
1 × Battery Charging Cradle
OTHER FEATURES
1. The LCD is backlit. To save energy the back light will switch off if the keypad is not
used for 30 secs. Pressing any key will re-activate it.
2. When the unit is turned on, if you do not press any of the keys, or intensity is set to
zero, for > 5 mins it will automatically shut off.
3. When you turn the unit on, it will automatically enter the mode that you used last.
4. When you change Programme, the output level will reset to zero immediately.
5. When the battery is low, the battery icon will ash indicating that the batteries should
be recharged.
WARNING: The power adaptor supplied has special medical grade isolation.
Use of any mains adaptor other than the one supplied with the device could
compromise electrical safety.
flexistim instructions final.indd 20-21 27/11/2014 12:07
Page 12

Insert the battery Replace the
battery cover
19
10. HOW TO ASSEMBLE YOUR UNIT
Your Flexistim has been designed to be simple and easy to use. Assembly of the
Flexistim unit is very simple and requires only ve steps.
STEP 1: BATTERY
Slide belt clip down to access battery cover.
Remove the battery cover and insert the
battery (as shown on the diagram) inside
the battery compartment. Replace the
battery cover.
NOTE: Fully charge battery before initial use.
See “Charging the Battery” on page 48.
CAUTION:
There is a risk of explosion if the battery is tted incorrectly. Replace only with the
correct 3.7 volt lithium battery. Do not dispose of the battery in a re and keep it out of
reach of children. The battery must be removed from the unit if unit is not used for a
long period of time.
STEP 2: LEADS
If only using one lead, insert into one socket.
If using two leads, insert into both sockets.
A: Insert the lead wires
B: Turn the plug on the lead wire 90° to lock it
between the main body and handle of the unit.
This prevents accidental disconnection
during treatment.
STEP 4: PLACEMENT OF ELECTRODES
Ensure wherever you intend to place the electrodes, the skin is clean and thoroughly
dry. Remove the electrodes from the clear plastic shield and position on your body
as required.
20
STEP 3: ELECTRODES
Remove electrodes from the bag and connect to the leads.
flexistim instructions final.indd 22-23 27/11/2014 12:07
Page 13

Life of the Electrodes:
The electrodes are water based and can dry out if left outside of the PVC storage bag.
If the electrodes lose their adhesive quality in this way, it is possible to reactivate their
adhesiveness by applying a ne spray of water.
Replace the electrodes when they stop sticking well. This can affect the efciency of
the unit and may lead to skin irritation.
21
STEP 5: READING
Read sections 11 to 16 and decide how to use the unit for the treatment.
NOTE: AFTER USE
Always ensure that the unit is switched OFF before removing the electrodes. After use,
return the electrodes to the clear plastic shields and seal them in the PVC bag. There is
no need to separate the lead wires from the electrodes.
11. OPERATION
After assembling and connecting the device:
11.1 Turn on the device
Press ON/OFF KEY.
LCD displays when the device is on. The LCD is backlit. To save energy the back light
will switch off if the keypad is not used for 30 seconds. Pressing any key will re-activate it.
Always switch the device off before removing electrodes from the skin.
11.2 Select Mode
Use MODE key to select:
TENS
EMS I, II, and III (small, medium and large muscles)
IFT
Microcurrent
When a programme is running the MODE key acts as a PAUSE button.
The PAUSE symbol
II is displayed and the Timer stops. When you press again to resume
the programme, the intensity slowly increases to the set level.
11.3 Select a Programme
Use Programme Selection Key to choose a desirable program
(See section 15 Programmes)
The output intensity resets to zero when you change a treatment program.
22
flexistim instructions final.indd 24-25 27/11/2014 12:07
Page 14

11.7 Skip Function
The EMS programmes have three phases:
• Warm
• Train
• Cool
You can jump to the next phase by pressing the SKIP key.
11.6 Adjust the Intensity
Use the left hand keys to adjust the intensity in the left hand lead (Ch1) and the
right hand keys to adjust the intensity in the right hand lead (Ch2).
In IFT MODE both channels are linked and there is only one intensity adjustment.
You can adjust a desired intensity by pressing either of the intensity controls.
For your safety, when intensity reaches 40mA, the warning triangle ashes and
intensity cannot be increased.
Check electrode pad position. If you are certain that the pads are positioned safely - not
through the chest, head or neck - press the SKIP key to override.
The triangle will stop ashing and intensity can be increased to 60mA.
11.4 Set Treatment Timer
The Treatment Timer defaults to Continuous (C) for some TENS programmes and a
safe standard treatment time for others. If you wish to adjust the Treatment Timer proceed
as follows;
To set a Treatment Time, Press either of the Parameter Selection keys:
MENU +/-
The Timer symbol will ash
Use the Parameter Adjustment Controls +/- to select your desired treatment
period ranging from 1 to 90 minutes.
Press any intensity key or wait 10 seconds to return to the main screen
The Treatment Timer starts counting as soon as you increase the intensity above zero.
At this point, the display begins to count down from its preset value.
When the preset treatment period is elapsed, the device switches off its output.
11.5 Attach the Electrode Pads
Attach the leads as shown in section 10 and position the electrode pads as shown in
section 16.
23 24
Automatic keypad lock
There is an automatic keypad lock if no button is used for 10 seconds.
Key symbol appears.
Press the Intensity Down button for either channel to unlock.
flexistim instructions final.indd 26-27 27/11/2014 12:07
Page 15

12.2 EMS
Press MODE button until EMS I, II, or III selected.
I, II and III are for small, medium, and large muscles and use different Pulse Width settings
P1 appears
Press PROG to Select P10 or 11 MANUAL
Press MENU +: Hz ashes
Menu steps:
FREQUENCY (Hz)
PULSE WIDTH (μs)
SYNCHRONOUS/ALTERNATING
(SYNCH/ALT in display)
WORK TIME (sec)
REST TIME (sec)
RAMP UP/DOWN TIME (sec)
Treatment Timer (min)
Press +/- to adjust the setting
Press MENU +/- to save and advance to next Parameter.
A warning triangle
will be displayed
when the Rest period is less than Rest
Time = Work Time X (Work Hz-16.66)/16.66 seconds. You will not be able to increase the
intensity above zero. When setting the Rest time, you can over-ride this by pressing the
LOCK key , but be aware that using settings outside of this ratio may cause muscle
fatigue. The triangle will continue to ash while you are outside recommended settings.
When using ALTERNATING, ensure that the “Ramp Up Time”, “Work Time”, and “Ramp
Down Time” equals “Rest Time”. The will appear on your screen if this formula is not
followed in EMS manual mode.
If the warning triangle appears at any other time, see “Troubleshooting”.
Adjust intensity above zero to start an EMS programme.
The EMS programmes have three phases: Warm / Train / Cool. You can jump to the next
phase by pressing the SKIP key.
12. ADJUSTING MANUAL PROGRAMMES
Press PROG to select one of the manual programmes
Press MENU+ key to cycle through the available parameters (see list below)
Use the Parameter Adjustment controls to select the required value, then press MENU+
or MENU- to move to the next parameter.
12.1 TENS
Press MODE button until TENS is selected
P1 appears
Press PROG to Select P11 MANUAL
Press MENU+: Hz ashes
Menu steps:
FREQUENCY (Hz)
PULSE WIDTH (μs)
Treatment Timer (min)
Press +/- to adjust Parameter
Press MENU +/- to save and advance to next Parameter.
Press any intensity button or wait 10 sec to exit setting menu.
25 26
flexistim instructions final.indd 28-29 27/11/2014 12:07
Page 16

Menu steps:
FREQUENCY (Hz)
PULSE WIDTH mS (milliseconds)
WAVEFORM - SQUARE/SAW/DC
Treatment Timer (min)
Press +/- to adjust the setting.
13. LOCK AND UNLOCK YOUR OWN PROGRAMME
To lock a programme, rst adjust the intensity to zero, then press & hold the LOCK key for
3 seconds. When you turn on the device again, this programme will load automatically. 3
seconds is a long time, but you will want to avoid accidental activation of this key.
To unlock the programme, reduce the intensity to zero, then press and hold LOCK key
for 2 seconds.
14. MEMORY MODE
Once you set intensity >5 in TENS and EMS and >0 in IF and Micro, the Usage Timer
automatically and accumulatively counts your total usage up to 999 hours 59 minutes.
There is a memory for each MODE.
To enter MEMORY and view the Usage Timer, set intensity to zero, select the MODE,
then press & hold the PROG and CH1▼ keys for 3 seconds.
The number at bottom left shows the number HOURS,
and at bottom right the number of MINUTES.
The number at the top left shows
the numbers of uses.
Press the same keys to return back to the
previous normal display.
To reset the Usage Timer to zero, press the CH2▼ key and PROG key together for 3 seconds.
12.3 IFT
Press MODE button until IFT is selected.
P1 appears
Press PROG to Select P4 MANUAL
Press MENU +: Hz ashes,
Menu steps:
FREQUENCY (Hz)
Treatment Timer (min)
Press +/- to adjust the setting
Press MENU +/- to save and advance to next Parameter.
Adjust intensity above zero to start the programme.
In IFT MODE both channels are linked and there is only one intensity adjustment. You
can adjust a desired intensity by pressing either of the intensity controls.
For your safety, when intensity reaches 40mA, the warning triangle ashes and
intensity cannot be increased.
Check electrode pad position. If you are certain that the pads are positioned safely, press
the SKIP key to override. The triangle will stop ashing and intensity can be increased
to 60mA.
12.4 MICROCURRENT
Press MODE button until MICRO is selected.
P1 appears
Press PROG to Select P3 MANUAL
Press MENU +: Hz ashes
27 28
Uses
Hours
Minutes
flexistim instructions final.indd 30-31 27/11/2014 12:07
Page 17

15. PROGRAMMES
15.1 TENS PROGRAMMES
Using the TENS Programmes
Your nervous system is different to everyone else’s. Only you know how the stimulation
feels for you. The best way to use TENS is to try the programmes, and see which ones
work best for you. There are some general guidelines:
Programmes with high frequency (Pain Gate)
Programmes 1, 2, 3, 8, 9,10
These programmes use the Pain Gate to block the signals travelling along the
pain nerves.
Prog Hz Pulse width Mode Time EFFECT
Pain Gate
Endorphin
Release
1 110 50 Const C PRESET PG
2 80 150 Const C PRESET PG
3 110 200 Const C PRESET PG
4 2 250 Const 30 PRESET ER
5 4 200 Const 30 PRESET ER
6 100 150 Burst 30 PRESET PG+ER
7 150 200 Burst 30 PRESET PG+ER
8 10/100 250 PFM C PRESET PG+ER
9 2/120 200/100 FM C PRESET PG +ER
10 2/100 200/150 Han 30 PRESET PG+ER
11 2-150 50-300 Const 5-90/C MANUAL
12 2-150 50-300 Burst 2Hz 5-90/C MANUAL
29
The sensation will fade after 5 or 10 minutes. Keep increasing the intensity so that you
can always feel the stimulation clearly.
You can use these programmes as long as you like. The pain relief may wear off after a
few hours. In which case, you can take a break and try again later.
Programmes 8 and 9 keep changing the sensation, which some users nd will extend
the effective pain relief.
Programme 1 is the gentlest stimulation. If you have not used TENS before, start with this
until you are comfortable with the feeling.
Programmes 2 and 3 are similar to 1, but feel stronger and deeper.
Programmes with low frequency (Endorphin release) elements
Programmmes 4, 5, 6, 7, 12
These programmes encourage production of your natural endorphins by inducing very
small, repetitive muscle twitches. All but programmes 4 & 5 combine this with a higher
frequency to combine the pain relief mechanisms, but may be a little less comfortable.
To be effective, you need to keep the intensity high enough to induce small muscle
movements. This limits the time you can use these programmes - if you use them for
more than about 40 minutes, you may have aching muscles later.
30
flexistim instructions final.indd 32-33 27/11/2014 12:07
Page 18

15.2 EMS PROGRAMMES
Prog Work Active Rest Total
Freq Hz Pulse width uS Sec Amp % Hz uS Time s Amp %
time
I II III mins
31
All EMS programmes include a WARM Up, TRAIN, and COOL Down phase.
During the TRAIN phase stimulation alternates between Work - when the muscles are
contracted - and Active Rest, with low frequency stimulation to promote metabolite clearance
and delay fatigue.
Each Work contraction starts and nishes with a gradual change in intensity - called a Ramp
1. All preset TRAIN phases have Ramp up 1.5s, Ramp Down 0.75s
2. All WARM phases are 6Hz at same PW as Work phase
3. All COOL phases are 3Hz at same PW as Work phase
4. All Active Rest phases have Ramp up 0.5s, Ramp down 0.5s
5. All Active Rest phases are at 4 Hz, 200uS
6. Press SKIP key to move to next phase
Manual Settings:
1. All WARM phases are 6Hz at same PW as set Work PW
2. All COOL phases are 3Hz at same PW as set Work PW
At rst use of a Manual programme the default values are shown.
The Warning triangle is displayed if Rest period is less than Rest Time=Work Time X
(WorkHz-16.66)/16.66 seconds.
This is because muscle bres can only activate a limited number of times a minute (about
1000) without becoming fatigued.
Using the EMS Programmes
EMS can be used for a wide range of sports and medical applications, and the application
can get very complicated. The Flexistim programmes have been designed to simplify this
as much as possible. You can use the manual programmes if you want to modify the
settings, or to experiment with completely different ones. Here are some of the ways you
can use the programmes:
Programme 1 Muscle Calming
Aims to relax the muscles as much as possible. Encourages production of the body’s natural
endorphins to promote pain relief, and improves the blood circulation which supplies oxygen
to the muscle.
32
1 PRESET Warm 6 200 280 340 300 100 5
Train 10 200 280 340 9 80 4 200 2 50 41
Cool 3 200 280 340 600 70 10
2 PRESET Warm 6 200 280 340 120 100 2
Train 22 200 280 340 7 80 4 200 11 70 18
Cool 3 200 280 340 180 70 3
3 PRESET Warm 6 200 280 340 120 100 2
Train 25 200 280 340 7 80 4 200 11 50 21
Cool 3 200 280 340 180 70 3
4 PRESET Warm 6 200 280 340 120 100 2
Train 40 200 280 340 7 80 4 200 11 50 18
Cool 3 200 280 340 180 70 3
5 PRESET Warm 6 200 280 340 120 100 2
Train 55 200 280 340 5 80 4 235 11 50 27
Cool 3 200 280 340 180 70 3
6 PRESET Warm 5 200 280 340 300 100 5
Train 60 200 280 340 4 80 5 20 10 50 41
Cool 3 200 280 340 600 70 10
7 PRESET Warm 5 200 280 340 300 100 5
Train 65 200 280 340 4 80 4 200 11 25 20
Cool 3 200 280 340 600 70 10
8 PRESET Warm 6 200 280 340 120 100
Train 75 200 280 340 4 80 4 200 14 50 25
Cool 3 200 280 340 180 70
9 PRESET Warm 5 200 280 340 300 100
Train 100 200 280 340 6 80 4 200 36 25 28
Cool 3 200 280 340 600 70
10 MANUAL Warm 6 200 280 340 120 100
Train 10-120 100-350 1-30 80 1-60* 1-90
Cool 3 200 280 340 180 70
10 DEFAULT 35 280 5 9 20
11 MANUAL Warm 6 200 280 340 120 100
Train 10-120 100-350 1-30 80 1-60* 1-90
Cool 3 200 280 340 180 70
11 DEFAULT 50 300 5
flexistim instructions final.indd 34-35 27/11/2014 12:07
Page 19

Programme 2 Resume Training 1
To promote growth of the slow twitch bres. This builds muscle strength and helps reduce
muscle atrophy, keeping muscles ready for when you want to resume training. Used for
all type of sports.
Programme 3 Resume Training 2
Progress from 2 as tolerance increases.
Programme 4 Resistance 1
Improving and increasing the capacity to develop very high level of muscle force over a long
period of time. Improving the efcacy of the oxygen consumption at the muscle level and the
capacity to withstand toxin build up, such as lactic acid. Used for sports activities that require
very high levels of prolonged muscle activity: Rowing, Cycling, Middle distance running.
Programme 5 Resistance 2
Improving oxygen consumption at muscular level and increasing the capacity to withstand
build up of toxins. Used with sports activities requiring prolonged and high levels of
muscle force: Cycling, Rowing, Middle distance running.
Alternative application: Lipolysis. Increasing the circulation, and modifying the metabolism
of the lipocytes. Helps stimulate the subcutaneous deposits of fat. Helps to reduce or
eliminate the - Orange Peel effect of the skin surface.
Programme 6 Maximum Muscle Contraction
To increase muscle bulk and volume and to improve muscle force. Searching for muscular
hypertrophy.
Programme 7 Muscle Toning 1
Strengthening the muscles, improving blood circulation and capillary bed density. Ideal
for applying to the Thigh, Legs, Bottom and Abdomen.
Programme 8 Muscle Toning 2
Similar to 7, but adding bulk in preference to endurance.
Programme 9 Force Output
Anaerobic activity - increasing the muscle capacity to a level of instantaneous maximum
muscle force, changing muscle force into explosive action. Used for all activities requiring
maximum muscle output in a very short space of time, such as Judo, short distance
sprinting, throwing the discus or shot-put.
33
15.3 IFT PROGRAMMES
Programme table:
P1 2-10Hz Sweep over 6s
P2 2-100 Hz sweep over 6s
P3 80-150 Hz sweep over 6s
P4 The pulse frequency varies from -30% to +60% of the set pulse frequency
over 6 secs. The transition is ramping (triangular wave function).
In IFT MODE both channels are linked and there is only one intensity adjustment. You
can adjust a desired intensity by pressing either of the intensity controls.
For your safety, when intensity reaches 40mA, the warning triangle ashes and intensity
cannot be increased.
Check electrode pad position. If you are certain that the pads are positioned safely, press
the SKIP key to override. The triangle will stop ashing and intensity can be increased
to 60mA.
15.3.1 CHOOSING SETTINGS
IFT works in the same way a TENs, but penetrates much deeper into the body. So you
can use IFT with the same settings as the TENS programmes.
Many therapists believe, however, that IFT has additional effects, and can be used to
reduce swelling and muscle tension. One of the leading textbooks says:
2Hz Around this frequency the metencephalins are stimulated which will result in
short term pain relief.
10Hz This frequency has a benecial effect on the immune system and tends to
make patients wakeful yet relaxed.
130Hz This frequency stimulates the production of endorphins and results in longer
term pain relief and some local anaesthesia.
1-100Hz This frequency sweep will increase the inammatory rate.
45-90Hz This frequency sweep will depress the sympathetic nervous system so
allowing increased activity of the parasympathetic system and increase the
blood supply.
See the Flexistim page on www.tenscare.co.uk for some published clinical protocols for IFT.
34
flexistim instructions final.indd 36-37 27/11/2014 12:07
Page 20

15.4 MICROCURRENT PROGRAMMES
Prog Waveform Hz PW mS Treatment default mins
1 Square 0.5 998 20
2 Saw 30 10 20
3 Manual 0.5-50 10-998 20
4 DC / / 20
max 99uA Ch1 only
Frequency: 0.5Hz 1Hz 1.5Hz 2Hz 3Hz 4Hz 5Hz to 50Hz
Pulse Width: 0.01-1 SECOND = 10-999 mS
Manual settings:
- Frequency: 0.5Hz 1Hz 1.5Hz 2Hz 3Hz 4Hz 5Hz to 50Hz
- Pulse Width: 0.01-1 SECOND = 10-999 mS
In Programmes 1, 2 & 3: PW≤ 1/2xFrequency
Treatment Time: 20 mins default
Intensity: 0-700uA in 10uA steps (Chen: Less than 750uA promotes ATP)
15.4.1 CHOOSING SETTINGS
For most conditions, use a low frequency 1-10 Hz, starting at 0.5Hz in programme P1.
A higher frequency up to 100 Hz may give faster results when treating inammatory
problems (e.g. arthritis, tendonitis, etc.).
However, you should always follow this up with a short treatment at low frequency.
Set the current intensity level at the highest comfortable position. This is usually 500 to
600 μA, which most people can barely feel.
If you have a very sensitive condition like neuralgia, you can start with a very low current
- unlike TENS there is no lower threshold.
PREPARING FOR MICROCURRENT TREATMENT
To gain the best results make sure that you are in a relaxed position for the treatment.
Make sure you do not have tense muscles.
35
15.4.2 HOW LONG SHOULD EACH SESSION LAST?
Start with 10 minutes, then pause to re-evaluate your pain. Stop treatment when the pain
is completely gone or when there is no further improvement. This could take an hour or
more. However, continuing to treat after the pain has gone may cause it to return. More
is not necessarily better when using microcurrent to relieve pain.
15.4.3 FOLLOW-UP
Although results will usually be seen immediately, in some people the effects will be
delayed, continuing to improve from several hours to over a day or two after the treatment.
In others, it may take several treatments before you start to see noticeable improvement.
The effects of microcurrent therapy are cumulative.
Use daily for 1-2 weeks, then switch to every other day.
15.4.4 PROBLEMS
While microcurrent therapy can provide a noticeable improvement on more than 90% of
users, it will not work for everyone. Where there appear to be no effects, try the following:
1) Increase your uid intake. If you are dehydrated you may not respond well.
2) Some people who have had a signicant exposure to strong electrical current may
be poor candidates for microcurrent therapy. If you have had a severe electric
shock in the past, or have used TENS for a long time, microcurrent may not work
as quickly for you. You may need prolonged treatment to gain results.
3) Microcurrent electrical therapy works through very small electrical ows in the
body. These can be affected by earlier surgical scars and traumatic injuries
some distance from the present pain. It is possible to clear the body of these
“blocks”. Try covering the scar with the electrodes or, on larger scars, putting
one electrode at each end, and treating for 10 minutes four days in a row.
As this treatment “unblocks” your body’s electrical ow, you may feel increased
energy and the pain may also temporarily increase. After treating the scar, allow
time to treat the painful area as well.
4) Try using a lower current setting of 100 μA for longer - an hour or more.
See the Flexistim page on www.tenscare.co.uk for some published references
for Microcurrent.
36
flexistim instructions final.indd 38-39 27/11/2014 12:07
Page 21

16. ELECTRODE PAD PLACEMENT
Ensure that intensity is zero before connecting electrodes.
Insert connection lead(s) into the sockets below the handle.
Rotate the body of the plug to lock the lead in place. Plug the lead pins into the
sockets in the pad pigtails.
To avoid damage, remember to rotate the plug to unlock it before removing
the lead.
Only pull the lead by holding the body of the plug.
16.1 Electrode Pad Placement for TENS
The placement of electrodes is one of the most important parameters in achieving
effective pain relief using TENS. You may need to try various positions before you nd
the most effective positioning. There are several positioning methods:
Across the painful area
This is the simplest method. Placing one pad over, or slightly further away from the
spine than, the source of the pain. Place the other pad closer to the spine so that the
stimulation travels through the area of pain
Dermatomes
TENS only works at the level of one vertebra of the spine. The nerves carrying pain and
the TENS stimulation into each vertebra cover an area of the body called a Dermatome.
Each nerve root serves a known area of the skin. You can stimulate the sensory nerves
anywhere in this area to reduce the transmission in the pain nerves. The nerves wrap
around the trunk and limbs in a spiral, so the dermatomes can give you a better idea
of where to place the pads. You can download a dermatome diagram from our website
www.tenscare.co.uk.
Trigger or Acupuncture Points
You can use low frequency TENS to stimulate therapy points. Accurately locating these
points can be difcult, so you may want to seek professional advice.
37
Example TENS Electrode Pad Positions
Low Back Pain
Sciatica
Neck and
Shoulder Tension
Shoulder Pain
Elbow Pain
Knee Pain
Ankle Pain
Leg Pain
Wrist Pain
Where only two pads are shown on the arm, shoulder, and leg, use the other two pads
either on the opposite limb or place all four pads on the same limb in a square pattern
with each pad being about 4 inches apart.
38
flexistim instructions final.indd 40-41 27/11/2014 12:07
Page 22

16.2 Electrode Pad Placement for EMS
Electrode placement for electrical muscle stimulation is very important for obtaining the
best results. Place two electrodes over the bulk of the muscle, with one electrode over
the muscle’s motor point. The motor point is the area on the skin that is located closest
to the motor nerve’s entry into the muscle - about 1/3 of the way down the muscle from
the spine. Here it is easiest to trigger a contraction by electrical stimulation. Experiment
by moving the electrode across the skin until you locate the point over the muscle that
gives the cleanest contraction.
Large muscle groups may require stimulation with
two channels, that is, four electrodes simultaneously.
The electrode pads must always be used in pairs,
so that the signal can ow in a circuit.
NOTE: Always check unit is OFF before attaching or removing pads.
When exercising smaller muscles, take care to adjust the intensity slowly as the motor
nerves may be more sensitive.
Example EMS Electrode Pad Positions
Eye care
We all are familiar with it. The ever-increasing set of little wrinkles around the eyes. At
rst, they’re accepted as laugh-lines and seen as a symbol of maturity. But, when the
eyes also start to swell up, deep wrinkles plough their way through the skin and puffy
lids appear, the time has come to do something about it.
You can use Programme 7 to stimulate the muscles around the eyes. You will notice the
39
muscles working straight away from the slight twitching. The activation of the muscles
stimulates the circulation. This relaxing skin care also contributes to an increase in well-
being, making you appear more awake and content.
Use small 25mm round electrodes. In order to prevent triggering unpleasant sensations,
you should increase the current strength very carefully.
• Do not attach electrodes from one side of the head to the other
• Do not attach electrodes to the front of the neck
40
flexistim instructions final.indd 42-43 27/11/2014 12:07
Page 23

Stomach / Hips
Muscle training and ghting the fat
The stomach, that tiresome subject - you can’t wish it away.
Weight reduction is usually the magic word. Weight reduction is effectively aided by
training the stomach muscles. With Flexistim you can single out muscles for direct
stimulation.
The stomach contains several different individual muscles.
The central stomach muscle is responsible for giving you a slim stomach and a good
upper body posture.
Bottom
The bottom is equipped with a very strong set
of muscles.
Unfortunately, unwanted fat and cellulite zones are
often to be found in this area and are very difcult to
combat. Muscular training is one way of improving
shape. The picture shows the possible electrode
positions for building muscles.
41
Upper Arms
Our upper arms often have little shape and abby, coarse skin. The cause is usually
a lack of movement and muscular work. The Flexistim can be used to carry out
muscle training.
In this case too, it is all about stimulation of the circulation of blood. You have the option
of treating the front side or the reverse side of both upper arms depending on where the
need is greatest.
42
flexistim instructions final.indd 44-45 27/11/2014 12:07
Page 24

Legs - Thighs and Calves
It is usually a lack of trained muscles in the legs which disturbs us most, particularly in
conjunction with areas of cellulite in the thigh area. Targeted muscle training for the front
and back of the thigh and calves is very simple to perform.
43
16.3 Electrode Pad Placement for IFT
The diagrams on the following pages shows how pads can be placed in various
body areas.
They all follow the same principles.
The interferential electrical signal is created by the interaction of the signals from all four
pads (i.e. between the pads of each channel). So the pads need to applied in positions
so that the signals from each channel cross over the point to be treated.
The two channels add and subtract to create an interference pattern. In theory this looks
like the cross shaped diagram. In real tissue the pattern is difcult to predict and you may
need to adjust the pad positions until you can sense the stimulation in the correct area.
44
Chest and Shoulders
Building chest muscle affects posture and movement in the upper body as a whole.
flexistim instructions final.indd 46-47 27/11/2014 12:07
Page 25

Elbow Knee
Alternative knee
setting
Neck
Shoulder
Lower Back Constipation in Children
45
16.4 Electrode Pad Placement for Microcurrent
Pad positioning is NOT like TENS and is closer to Interferential.
The pads should be placed so that a straight line between them passes through the
problem area. This is different to TENS, where the aim is to stimulate the correct sensory
and motor nerves.
Since the body is three dimensional, this often means going from front to back, and side
to side. The four alternatives for headache below show how many possibilities there are:
There is no single correct placement, and the best position may vary from day to day.
WARNING: Positions 1 & 4 on the head must NOT be used in other MODES
One position for treatment of arm pain:
Microcurrent seems to work better if
you also treat the OPPOSITE side
of the body to where the pain is felt
(with the second pair of pads). Also try
connecting both sides of the body by
placing one pad at the site of the pain,
and the other on the opposite side (i.e.
left hand to right hand), for 10 mins.
46
L1
L1L2
L2
L1
L1
L2
L2
L1
L1
L2
L2
L1
L1
L2
L2
L1
L1
L2
L2
L1
L1
L2
L2
L1
L1
L2
L2
flexistim instructions final.indd 48-49 27/11/2014 12:07
Page 26

17. FURTHER CLINICAL INFORMATION AND
TREATMENT PROTOCOLS
For further information and clinical references go to www.tenscare.co.uk and look on
the Flexistim product page.
18. CARE OF ELECTRODES
The electrodes that are supplied with your Flexistim are self-adhesive and can be used
several times. Skin must be allowed to breathe, so the electrodes should be removed
periodically. When not in use, the electrodes should be placed onto the clear plastic shield.
The condition of the electrodes has a direct effect on conductivity, and therefore the
effectiveness of the treatment. When the electrodes start to lose their adhesive quality,
it is possible to reactivate their adhesiveness by applying a ne spray of water to the gel
side of the electrode. In time, this technique will not work, the gel will not reactivate and
new electrodes should be used.
GENERAL PAD ADVICE
• The electrode pads supplied are reusable but are for single patient use.
• In order to obtain the best conductivity through the pads always ensure that they are in
good condition and tacky.
• Before use make sure your skin is clean and dry.
• Peel the electrode pads from their protective plastic shield by holding and lifting one
corner of the pad and pulling. Do not pull on the pigtail wire of the pad.
• After use always replace the pads on the plastic liner and replace in the re-sealable
plastic bag.
• If the pads dry out then it is best to buy a replacement pack of electrodes. In an
emergency it may be possible to restore some of the tackiness of the pad by adding
a tiny drop of water on each pad and spreading around. If too much water is added
the pads will become too soft then it is suggested in order to try to re-establish some
adhesiveness to place them sticky side up in a refrigerator for a few hours.
47
• In very hot weather the gel on the pads may become soft. In such cases place the
pads, still on their plastic liners and in their bag, into a fridge until they return to their
normal condition.
WARNINGS
Do not use any electrodes less than 50mm X 50mm. However 25mm x 25mm electrodes
can be used for the microcurrent treatment
Allergic reactions to the self-adhesive electrodes can occur even though they
are hypoallergenic.
• Do not apply to broken skin.
• Do not apply electrodes to areas with less than normal sensitivity. This could lead to
setting intensities at higher levels than intended.
19. CHARGING THE BATTERY
The Flexistim is powered by a type BL-6F
rechargeable Li-ion battery.
The battery cannot be charged while it is in the
unit. A separate charging cradle and power
adaptor are included in the kit.
The battery should need charging about once
a week unless you are using IF, in which case
the battery may only last about one hour.
A battery state indicator on the screen shows how
much charge is in the battery. When it gets low,
this will start to ash.
NB: Remove the battery from your Flexistim if the unit is unlikely to be used for a
long period.
When the battery is charged, the indicator light on the cradle will change from red to green.
For a replacement battery, contact Tenscare or your local distributor.
Use only the power adaptor and charging cradle supplied.
48
flexistim instructions final.indd 50-51 27/11/2014 12:07
Page 27

The
Flexistim
can also be operated directly from the charger. Just plug it directly into the
socket in the side of the unit. This automatically disconnects the battery.
USE OF OTHER CHARGERS COULD BE HAZARDOUS AND WILL NEGATE
THE GUARANTEE
Warning
There is a risk of smoke, re, or rupture if the battery is not used according to the following
guidelines:
• Do not disassemble the battery
• Do not short-circuit the battery
• Do not incinerate or heat the battery
• Do not use or leave battery near a re, stove or heated place (more than 80°C)
• Do not immerse the battery in water or sea water, or get it wet
• Do not charge battery nearby the re or in strong sunlight
• Only use the charger provided and observe charging instructions
Disposal
Always dispose of batteries responsibly according to local government guidelines.
49
20. TROUBLESHOOTING
If your Flexistim is not working properly please check the following:
Problem:
No display/won’t turn on: BATTERY:
i) Is it tted?
ii) Is it charged?
Controls don’t work i) Press Ch1 or Ch2 ▼button to unlock
the keypad
ii) No showing. Ensure battery is charged.
No impulse output from electrodes A circuit is not being made.
i) Have you applied both electrode pads (per
lead wire) to ensure a complete circuit?
ii) Are the lead wires properly connected at both
ends?
iii) Is the lead damaged? (Try using the other
lead - if this works, then the original lead is faulty)
Warning triangle ashing, You are in EMS Manual Programme 10 or 11. When
cannot increase intensity. using ALTERNATING, ensure that the “Ramp Up
Time”, “Work Time”, and “Ramp Down Time” equals
“Rest Time”. These will appear on your screen if this
formula is not followed in EMS manual mode.
In EMS Manual programmes10 or 11 a Warning triangle
will be displayed if the Rest period is less than Rest
Time=Work Time X (WorkHz-16.66)/16.66 seconds.
In IF MODE when intensity reaches 40mA, the
warning triangle ashes and intensity cannot
be increased.
Check electrode pad position. If you are certain that
the pads are positioned safely, press the SKIP key to
override. The triangle will stop ashing and intensity
can be increased to 60mA.
If the above review has failed to resolve your problem, call TensCare or your local dealer
for advice.
50
flexistim instructions final.indd 52-53 27/11/2014 12:07
Page 28

21. CLEANING
• Clean your device before use.
• Remove the battery from the device every time when you clean the device.
• The case and lead wires can be cleaned by wiping with a damp cloth and a solution of
mild soap and water. Wipe dry.
• Do not immerse your Flexistim in water.
• Do not use any other cleaning solution than soap and water.
22. CONSUMABLES AND SERVICING
Original Accessory
The unit must be used only with the original accessories, supplied by the manufacturer.
Replacement electrode pads, new batteries and lead wires are available from your
supplier or distributor (see back cover for contact details), by mail order from TensCare,
by telephone using a credit or debit card, or through our website.
PART NUMBER:
L-ST2 Replacement lead 1.25m
E-CM5050 Electrode pads 50x50mm for external use. Pack of 4
B-BL6F Li-Ion battery type BL-6F 3.7V 1100mAh
X-ST2CR Charging Cradle
X-FLEXIPA Power adaptor
Apart from these items, there are no user-serviceable parts or calibration.
• Maintenance and all repairs should only be carried out by an authorised agency. The
manufacturer will not be held responsible for the results of maintenance or repairs by
unauthorised persons.
• The user must not attempt any repairs to the device or accessories. Please contact the
retailer for repair.
• Opening of the equipment by unauthorised agencies is not allowed and will terminate
any claim to warranty.
• Check the unit before each use for signs of wear and/or damage. Replace worn items
as required.
51
23. WARRANTY
In addition to your statutory rights, the manufacturer agrees that if any defect in materials
or workmanship appears in this product within two years after the original date of
consumer purchase, it will repair or at its option, replace the product in question free of
charge. This applies only if the product has been used for domestic purposes and has
not been damaged through misuse, accident or neglect and has not been modied or
repaired by anyone other than the manufacturer or its authorised agents.
If a defect appears, please make sure that the unit is being used in accordance with the
instructions, if so, return it with this warranty and the proof of purchase to your nearest
Flexistim dealer. Note: only our authorised service agents should carry out repairs of the
Flexistim units.
Exclusions: The batteries, lead wires and electrode pads are not considered covered by
this warranty.
The supplier will make available on request circuit diagrams, component part lists,
descriptions, calibration instructions, or other information which will assist the user’s
appropriately qualied technical personnel to repair those parts of equipment which are
designated by the manufacturer as repairable.
24. DISPOSAL OF WASTE ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC
PRODUCTS (WEEE)
One of the provisions of the European Directive 2002 / 96 / CE is that anything electrical
or electronic should not be treated as domestic waste and simply thrown away. New
products are now being marked with the symbol to remind you. Your local council or
retailer will be able to tell you where your nearest facility is. The collection facilities will
send items for treatment, recovery and recycling, so by using them you’ll help to save
resources and minimise the effects on the environment.
52
flexistim instructions final.indd 54-55 27/11/2014 12:07
Page 29

25. SPECIFICATIONS
TENS & EMS:
Output: 99 mA zero to peak
Constant current 500-1500 Ohm,
Constant voltage > 1500 Ohm
Max Pulse Energy Total output limited to 25uC per pulse
Channels Dual Channel
Waveform Asymmetrical rectangular bi-phasic
TENS 2-150 Hz in steps of 1, 50-250 μS in steps of 10
Modes Burst/Continuous
EMS 10-120 Hz, 50-400μS in steps of 10
Ramp Up/Down Time 0-8s, in steps of 1s
Work Time 1-30s, in steps of 1s
Rest Time 1-60s, in steps of 1s
Modes: Synchronous (S) Alternating (A)
IFT:
Intensity 60 steps, 0-60mA peak to peak at 500 Ohm load
Carrier Frequency 4000Hz xed(CH1)
Modulating Frequency 4004-4160Hz, in steps of 4Hz(CH2)
Pulse Width 125μs
Mode 4 pole
Waveform Symmetrical balanced sine wave
Treatment Timer Continuous, 1-90 mins
MICROCURRENT:
Frequency 0.5Hz 1Hz 1.5Hz 2Hz 3Hz 4Hz 5Hz to 50Hz
Pulse Width 10-999 mS
Waveforms A continuous, B square unipolar, C sawtooth unipolar
Treatment Time 20 mins default
Intensity 0-700uA in 10uA steps
53
GENERAL
Output Plugs Fully shielded: touch proof
Dimensions 61×123×22mm (exclude belt clip)
Weight 160g (with battery)
Power Supply BL-6F Li-Ion battery 3.7V 1100mAh
Mains adaptor (Class II, IEC60601-1) with charging cradle
Input 100-240V
Output DC 5V 1000mA
Safety Classication Type BF Designed for continuous use
IP22
Environmental
Operating Specications Humidity: 20 to 93% RH
Temperature range: 0 to 40C
Atmospheric Pressure: 700hPa to 1060hPa
Storage and Humidity: 10 to 93% RH
Transport Specications Temperature range: -20 to 70C
Atmospheric Pressure: 700hPa to 1060hPa
Typical Operation Time No less than 1 week (@50%AMP, 4 hours per day, in
TENS/EMS/MIC Mode)
No less than 1 hour (@50%AMP, in IFC Mode)
Expected Service Life No less than 5 years
54
flexistim instructions final.indd 56-57 27/11/2014 12:07
Page 30

26. STANDARD SYMBOLS
Type BF Applied part
Attention, consult accompanying document
Complies with WEEE regulations
CE marking
Manufacturer
The rst number 2: Protected against access to hazardous parts with a nger, and
the jointed test nger of 12 mm Ф, 80 mm length, shall have adequate clearance
from hazardous parts, and protected against solid foreign objects of 12.5 mm Ф
and greater.
The second number: Protected against vertically falling water drops when
enclosure is tilted up to 15º. Vertically falling drops shall have no harmful effects
when the enclosure is tilted at any angle up to 15’’ on either side of the vertical.
27. EMC PRECAUTIONS
Wireless communications equipment such as wireless home network devices, mobile
phones, cordless telephones and their base stations, walkie-talkies can affect this
equipment and should be kept at least a distance d = 3,3 m away from the equipment.
(Note: As indicated in Table 6 of IEC 60601-1-2:2007 for ME EQUIPMENT, a typical cell
phone with a maximum output power of 2 W yields d = 3,3 m at an IMMUNITY LEVEL
of 3 V/m)
.
IP22
55
EC Declaration of Conformity
TensCare Ltd hereby declare that an examination
of the production quality assurance system has
been carried out following the requirements
of the UK national legislation according to
Annex V of the Directive 93/42/EEC on medical devices.
We certify that the production quality system conforms
with the relevant provisions of the aforementioned
legislation, and the result entitles the organisation to use
the CE 0473 marking on this product.
56
flexistim instructions final.indd 58-59 27/11/2014 12:07
Page 31

TensCare Ltd, 9 Blenheim Road,
Epsom, Surrey KT19 9BE, UK
Tel: +44(0) 1372 723434
www.tenscare.co.uk
Distributed by:
Pub No.: I-FLEX-UK Version 1.0 09/14
Manufactured by:
flexistim instructions final.indd 60 27/11/2014 12:07
 Loading...
Loading...