Page 1

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
1
Page 2

Page 3

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
Table of Contents
COPYRIGHT STATEMENT .......................................................................................2
CHAPTER 1 PRODUCT OVERVIEW .....................................................................4
1.1 WHAT IT DOES .....................................................................................................4
1.2 FEATURES ............................................................................................................4
1.3 PACKAGE CONTENTS ...........................................................................................5
CHAPTER 2 HARDWARE ........................................................................................6
2.1 PANEL OVERVIEW ................................................................................................6
2.2 MINIMUM SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS ....................................................................7
2.3 HARDWARE INSTALLATION ..................................................................................7
CHAPTER 3 LOGIN TO WEB UTILITY ..................................................................9
CHAPTER 4 CONFIGURATIONS .......................................................................... 11
4.1 DEVICE INFO ..................................................................................................... 1 1
4.2 NETWORK .........................................................................................................14
4.3 SECURITY SETTINGS ..........................................................................................24
4.4 ADVANCED SETTINGS ........................................................................................34
4.5 WIRELESS SETTINGS .........................................................................................41
4.6 IPTV SETTINGS .................................................................................................52
4.7 TOOLS ...............................................................................................................53
A PPENDIX 1 CONFIG TCP/IP SETTINGS ON PC ...........................................58
3
Page 4

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
Chapter 1 Product Overview
1.1 What it does
The Tenda N6 Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router accommodates users
looking for extreme wireless performance. Delivering up to
speed, it uses dual band technology to deliver 2.4GHz and 5GHz wireless signals
simultaneously, allowing you to check email and browse the Internet using the 2.4GHz
while streaming High-Definition movies and other bandwidth-intensive applications on
the 5GHz band. Also, it reduces the possibility of interference from appliances and
cordless phones that use the 2.4GHz band.
1.2 Features
2.4GHz:IEEE802.11n, IEEE802.11g,IEEE 802.11b;5GHz:IEEE
802.11n,IEEE 802.11a;IEEE802.3,IEEE802.3u;
Deliver 2.4GHz and 5GHz wireless signals simultaneously
2 external dual-band 5dBi omni-directional antennas
1 10/100M WAN port for Internet connection
3 10/100M LAN ports for LAN connection
1 IPTV port
Up to 300+300Mbps wireless rate
Combines the function of a wireless AP, router, switch and firewall
Provides Internet connection types: Dynamic/ static IP,L2TP,PPTP,
PPPOE/ PPPOE dual access
Supports IPTV service
Built-in firewall supports domain name/MAC/IP address filter
WEP, WPA-PSK, WPA2-PSK and WPA&WPA2-PSK secure your
wireless network against unauthorized access
Supports guest network
WPS one-touch encryption
Hidden/invisible SSID; MAC-based access control
WMM streams your video and audio
Bandwidth control
SNTP, WDS, UPnP, DDNS and DMZ
Syslog records router's usage status
300+300Mbps wireless
4
Page 5

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
1.3 Package Contents
Please unpack the box and check the following items:
N6 Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
Power Adapter
Quick Installation Guide
CD-ROM
1-meter Ethernet cable
If any of the above items are incorrect, missing, or damaged, please contact your
Tenda reseller for immediate replacement.
5
Page 6
300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
Chapter 2 Hardware
2.1 Panel Overview
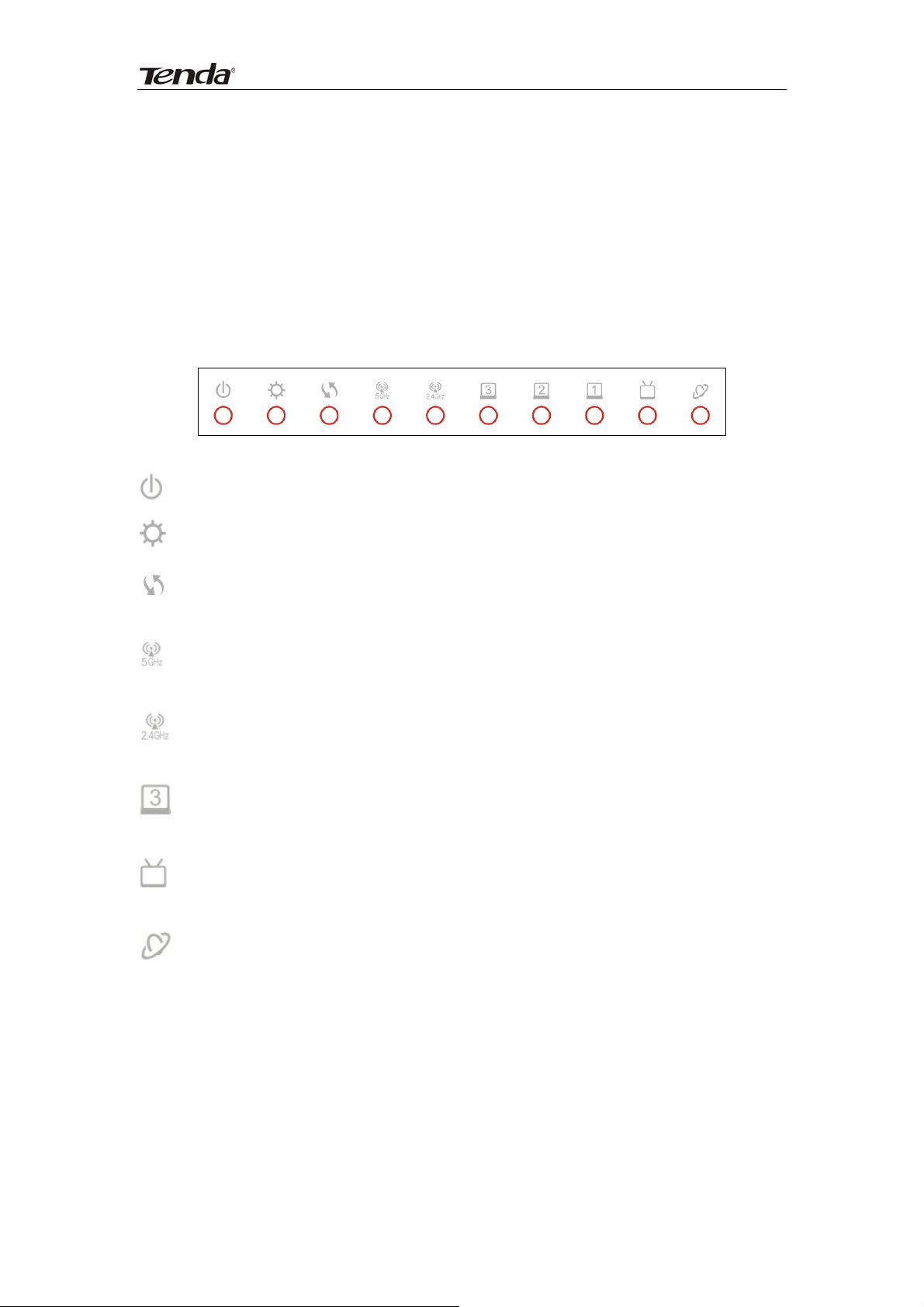
Front Panel
Power LED: A solid light indicates a proper connection to the power supply.
System LED: A blinking light indicates system is functioning correctly.
WPS LED: A blinking light indicates router is performing a WPS
authentication on a client device.
5G LED: A solid light indicates wireless is active while a blinking light
indicates router is transmitting data wirelessly over 5GHz.
2.4G LED: A solid light indicates wireless is active while a blinking light
indicates router is transmitting data wirelessly over 2.4 GHz.
LAN/1/2/3 LED: A solid light indicates corresponding LAN port is correctly
connected while a blinking light indicates such port is transmitting data.
IPTV LED: A solid light indicates corresponding IPTV port is correctly
connected while a blinking light indicates it is transmitting data.
WAN LED: A solid light indicates the WAN port is correctly connected
while a blinking light indicates it is transmitting data.
6
Page 7

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
Back Panel
WAN: Internet port(RJ-45 )for connection to an Internet-enabled xDSL
Modem/Cable Modem or existing Ethernet.
IPTV:IPTV port for connection to a network set-top box. However such port
can function as a LAN port if the IPTV STB port is not enabled.
LAN/1/2/3: 3 LAN ports (RJ-45) for connection to PC’s NIC or uplink to a hub,
switch or wireless AP.
WPS/Reset: WPS button/Reset button: Pressing it for about 1 second enables
WPS encryption with a blinking WPS LED while Pressing it for about 7
seconds restores the device to factory defaults.
2.2 Minimum System Requirements
Installed Network Adapter
Internet Explorer 5.0 or higher
Broadband Internet Service (through xDSL/Cable Modem/Ethernet)
2.3 Hardware Installation
1. Connect one end of the included power adapter to the router and then plug
the other end into a wall outlet nearby. (Using a power adapter with a different
voltage rating than the one included with the router will cause damage to the
product.)
7
Page 8

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
2. Connect one of the LAN ports on the Router to the NIC port on your PC
using an Ethernet cable.
3. Connect the Ethernet cable from Internet side to the WAN port on the
Router.
8
Page 9
300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
Chapter 3 Login to Web Utility
The device’s default IP is 192.168.0.1. You can change it to accommodate
your own needs. Here in this manual, we use the default IP.
Connect you PC to the router and config your PC’s TCP/IP settings
following instructions in appendix 1 hereto. And then do as follows to run a
Ping command to test connectivity between your PC and the router.
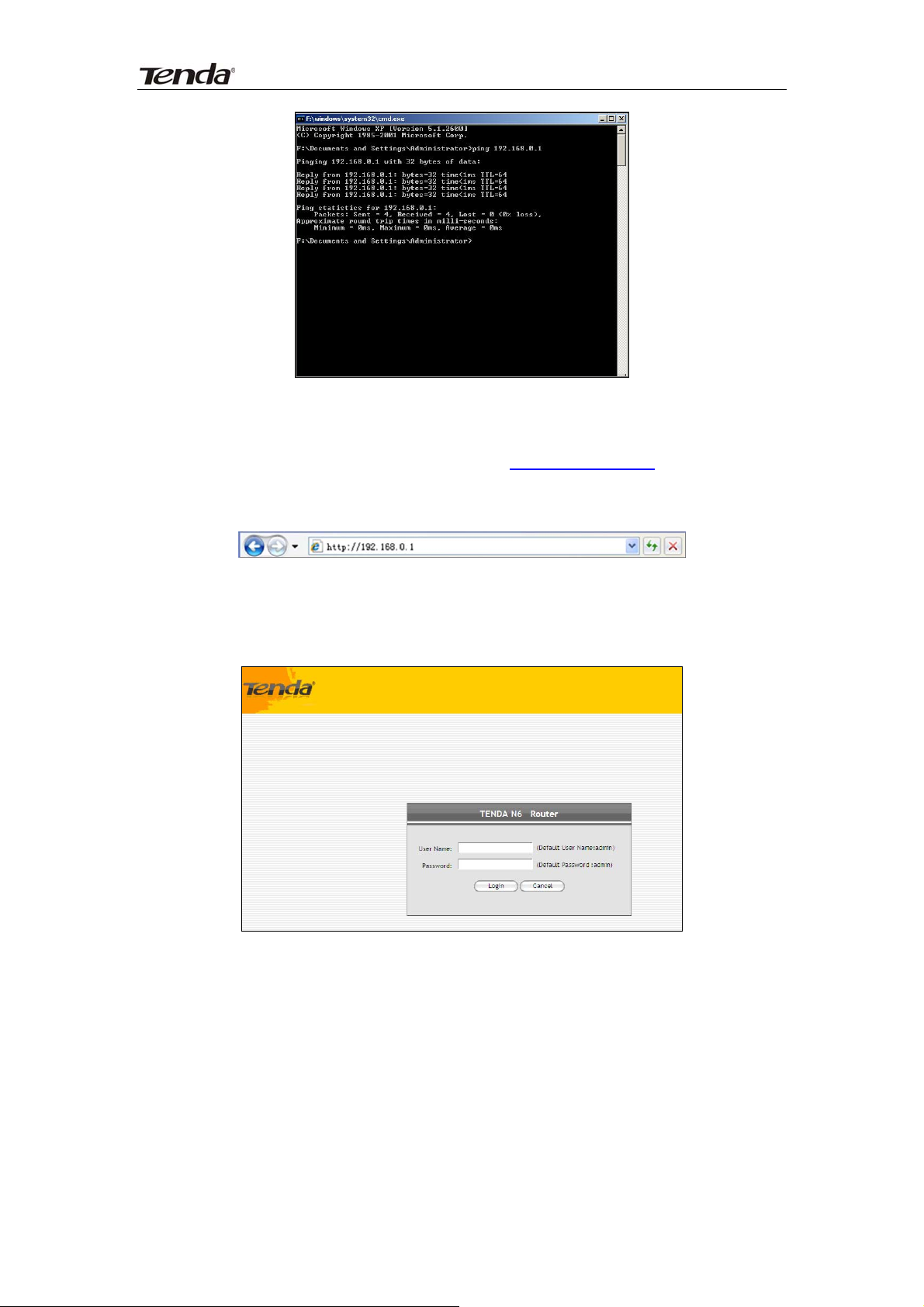
1. Select “Start”—“Run” and enter “cmd”. Then press “Enter”.
Enter “ping 192.168.0.1” and press “Enter”. If you see the following screen,
it means the router is reachable on your PC. If you don’t get the following
screen, verify router’s power supply, Ethernet cable connections and your
PC’s TCP/IP settings.
9
Page 10
300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
Login to web utility
Launch a web browser on your PC and enter http://192.168.0.1 as below. Then
press “Enter”.
Enter user name and password in corresponding fields on window below
(Default user name and password are respectively set to admin).
Note:
For security purpose, please change the default user name and password after
you logged in to web utility.
You will see the following interface if you entered a correct user name and a
correct password.
10
Page 11
300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
Chapter 4 Configurations
This chapter delivers a detailed presentation of router’s functionalities and
features under 7 main menus below, allowing you to manage the router with
ease.
During operation, if you are not clear about a certain feature, you can
simply click the “Help” button to read all related helpful info.
4.1 Device Info
WAN
11
Page 12
300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
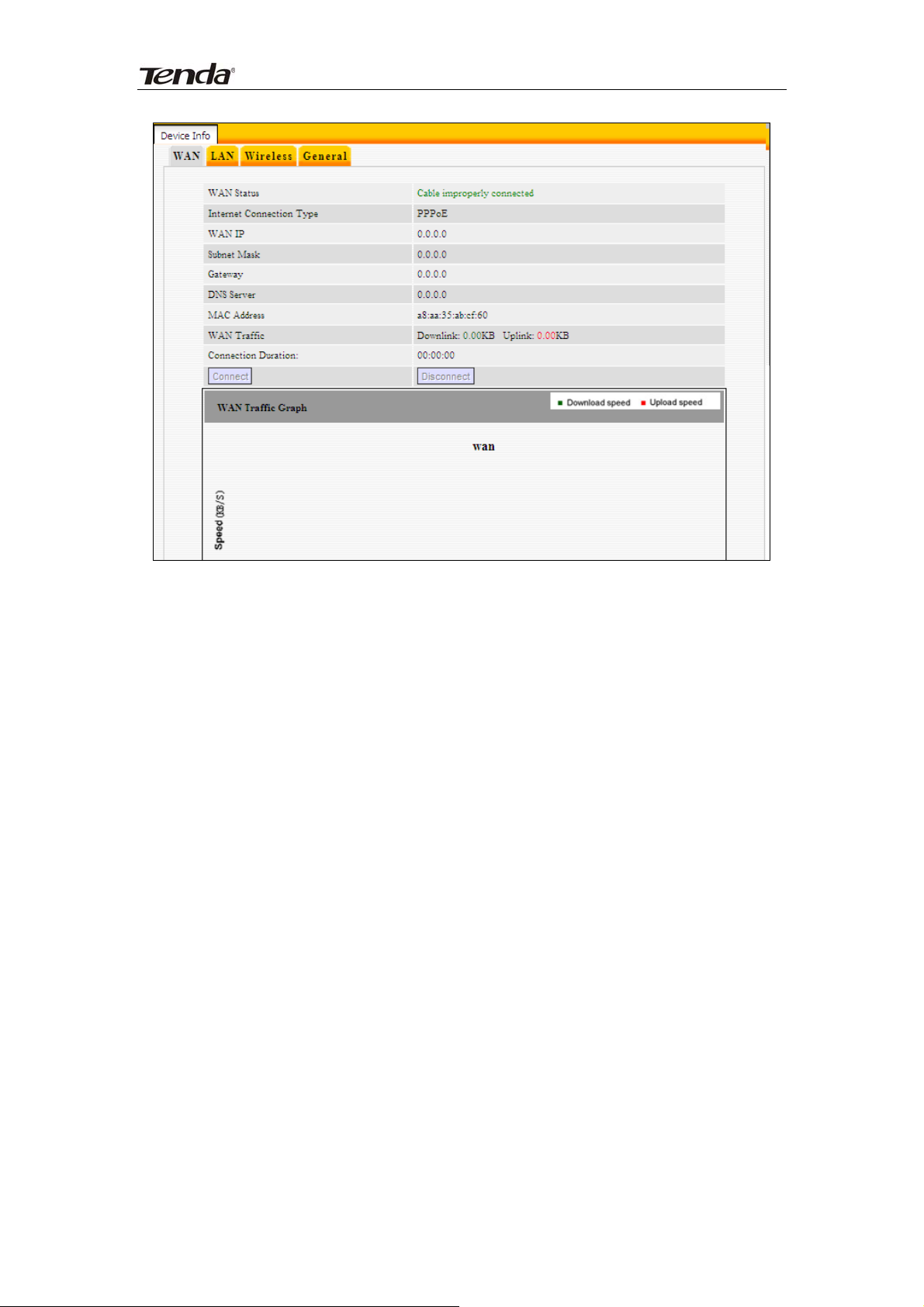
This section allows you to view the router’s WAN info listed below:
WAN Status: Displays WAN connection status: Disconnected, Connecting or
Connected.
Disconnected: Indicates that the Ethernet cable from your ISP side is / is not
correctly connected to the WAN port on the router or the router is not logically
connected to your ISP.
Connecting: Indicates that the WAN port is correctly connected and is
requesting an IP address from your ISP.
Connected: Indicates that the router has been connected to your ISP.
Internet Connection Type: Displays current Internet connection type.
WAN IP: Displays WAN IP address.
Subnet Mask: Displays WAN subnet mask.
Gateway: Displays WAN gateway address.
DNS Server: Displays WAN DNS address.
WAN MAC Address: Displays router’s WAN MAC address.
WAN Traffic: Displays bandwidth currently used by router in KB/s.
Connection Duration: Displays time duration indicating how long the router
has been connected to ISP.
WAN Traffic Graph: Displays a graphic presentation of the traffic flow.
LAN
This section allows you to view the router’s LAN info listed below:
12
Page 13
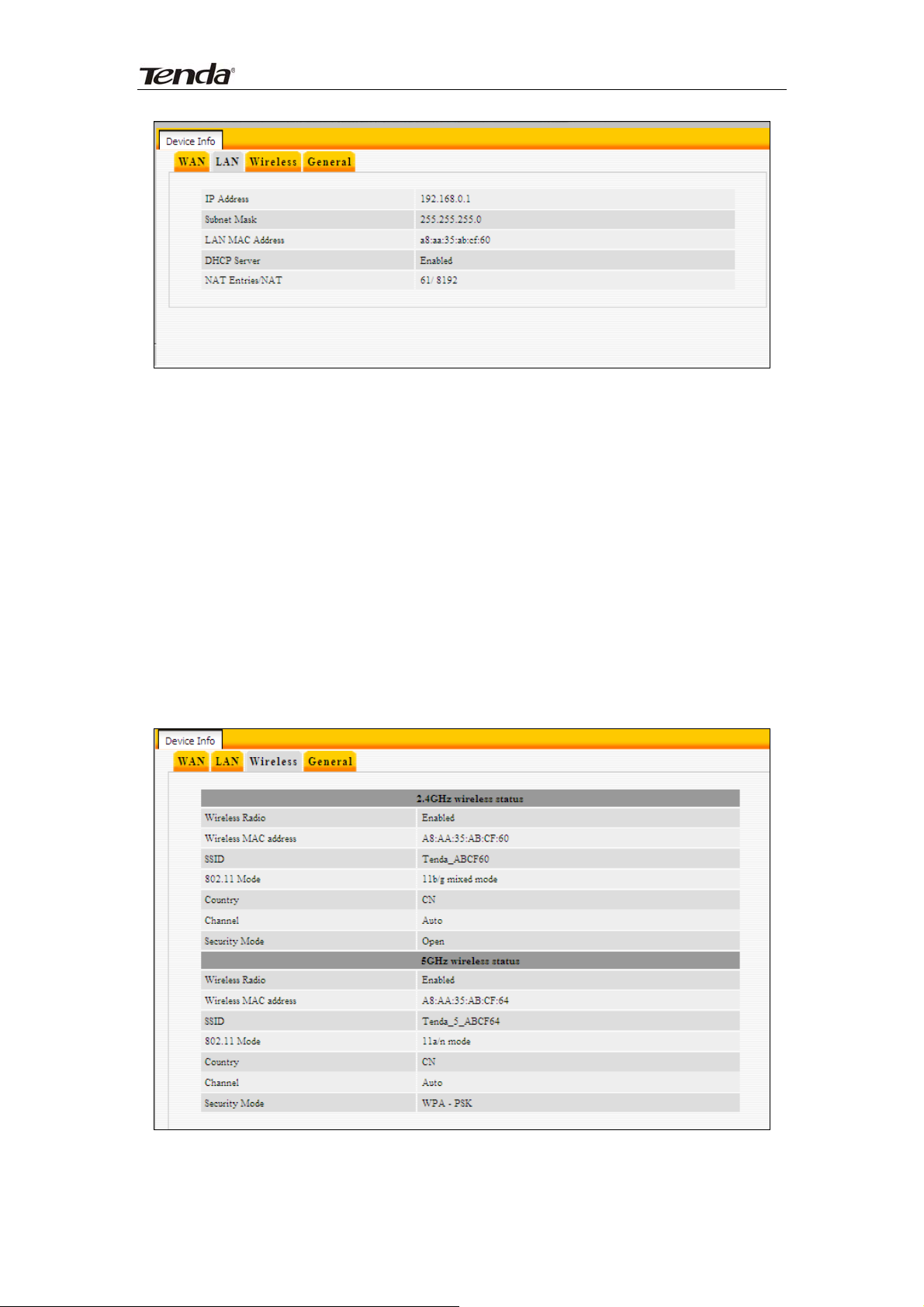
300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
IP Address:Displays LAN IP address.
Subnet Mask: Displays LAN subnet mask.
LAN MAC Address: Displays router’s LAN MAC address.
DHCP Server: Displays whether DHCP server is enabled or not.
NAT Entries/NAT: Displays number of used NAT entries and MAX NAT
entries.
Wireless
This section allows you to view the wireless info listed below:
Wireless Radio: Displays whether wireless is enabled or not.
13
Page 14
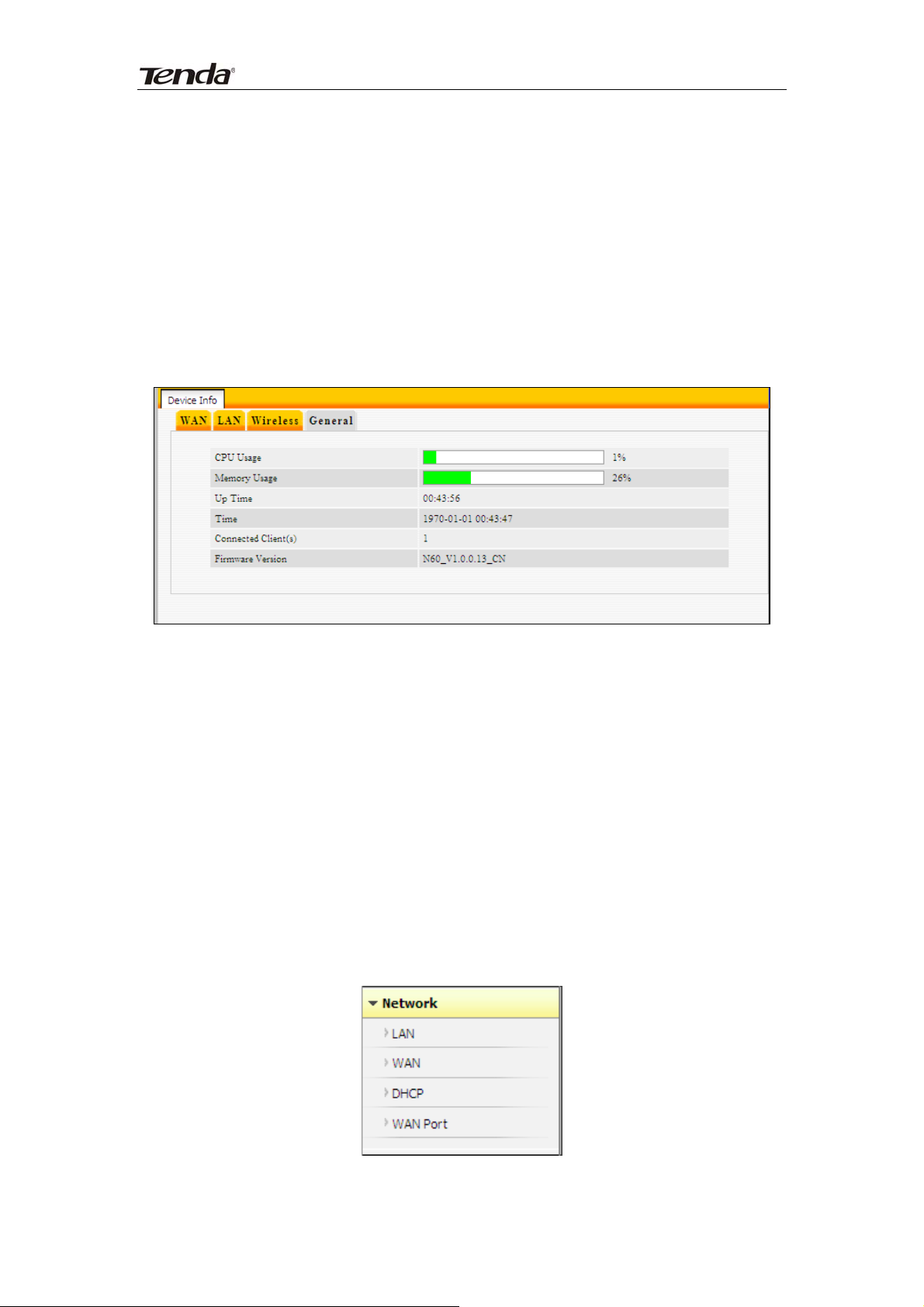
300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
Wireless MAC address: Displays MAC address of the router’s wireless
interface.
SSID: Displays current SSID.
802.11 Mode: Displays currently active network mode.
Country: Displays current country.
Channel: Displays current channel.
Security Mode: Displays current security Mode.
System Info
This section displays CPU/memory usage, uptime, system time, number of
connected client(s) and system version info.
CPU Usage: Displays current CPU usage status.
Memory Usage: Displays current memory usage status.
Up Time: Displays uptime.
Time: Displays device’s time synchronized with Internet or manually set by
user.
Connected Client(s):Displays the number of connected computers.
Firmware Version:Displays router’s firmware version.
4.2 Network
“Network” includes the following four submenus. Clicking any of them enters
corresponding interface for configuration. Below explains, in details, each such
feature.
14
Page 15
300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
4.2.1 LAN Settings
IP Address: Router’s LAN IP. The default is 192.168.0.1. You can change it
according to your need.
Subnet Mask: Router’s LAN subnet mask.
Note:
1. If you change the device’s LAN IP address, you must enter the new one in
your browser to get back to the web-based configuration utility. And LAN PCs’
gateway must be set to this new IP for successful Internet connection.
2. WAN IP, whether obtained automatically or specified manually, should NOT
be on the same IP net segment as the LAN IP, otherwise, the router will not
work properly. In case of emergency, press the hardware "Reset" button.
4.2.2 WAN Settings
The screen below displays WAN connection status and interface info.
Click the “Config” button to enter WAN configuration interface. The router
supports six Internet connection types, include Dynamic IP, Static IP, L2TP,
PPTP, PPPoE, and PPPoE dual access.
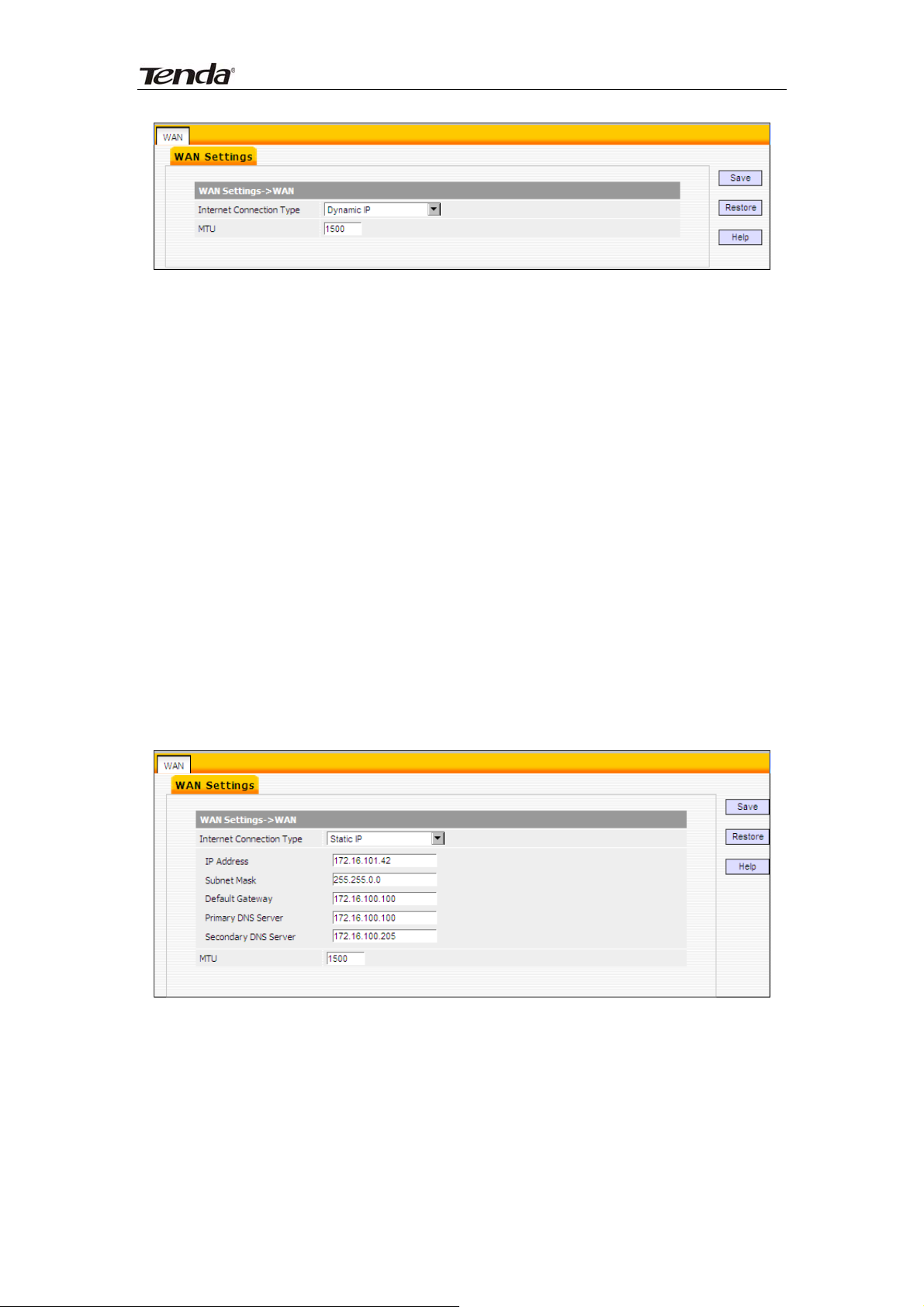
1) Dynamic IP (DHCP): Select this option to let router obtain IP settings
automatically from your ISP, if your ISP does not give you any IP information or
account information. You don’t need to configure any settings for this
connection.
15
Page 16
300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
Internet connection Type: Displays a list of available Internet connection
types.
MTU: Maximum Transmission Unit. The default value is1500.
Note:
DO NOT change the factory default MTU value unless necessary as an
improper MTU value may degrade your network performance or even lead to
network malfunction.
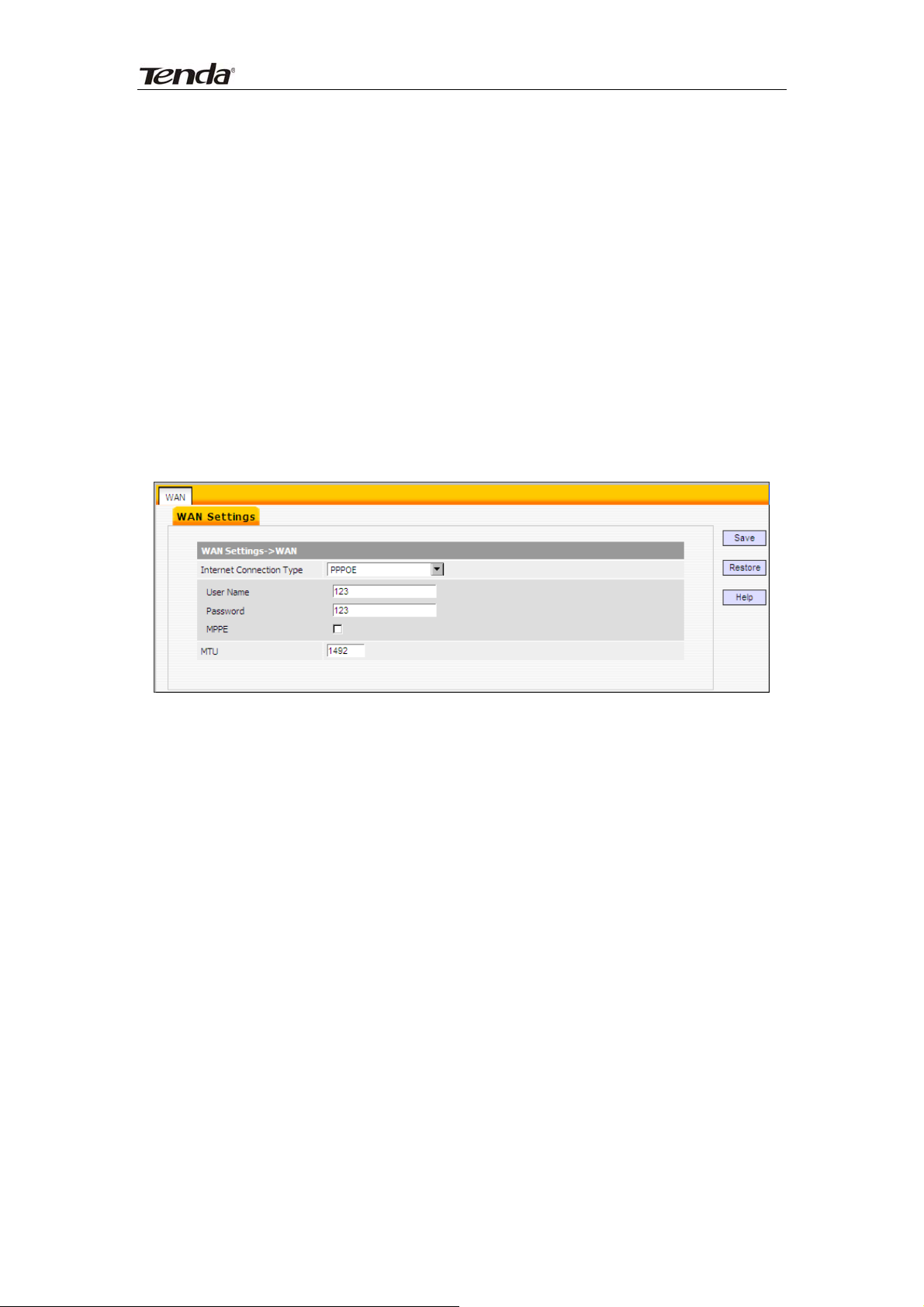
2) Static IP: If your ISP offers you static IP Internet connection type, select
“Static IP" from corresponding drop-down menu and then enter IP address,
subnet mask, Primary DNS and secondary DNS information provided by your
ISP in corresponding fields.
Internet connection Type: Displays a list of available Internet connection
types.
IP Address: Enter the WAN IP address provided by your ISP. Inquire your
ISP if you are not clear.
Subnet Mask: Enter WAN Subnet Mask provided by your ISP.
Default Gateway: Enter the WAN Gateway address provided by your ISP.
16
Page 17
300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
Primary DNS Server: Enter the necessary DNS address provided by your
ISP.
Secondary DNS Server: Enter the other DNS address if your ISP provides
you with 2 such addresses, and it is optional.
MTU: Maximum Transmission Unit. The default value is1500.
Note:
DO NOT change the factory default MTU value unless necessary as an
improper MTU value may degrade your network performance or even lead to
network malfunction.
3) PPPoE: Select PPPoE, if your ISP is using a PPPoE connection and
provide you with PPPoE user name and password info.
Internet connection Type: Displays a list of available Internet connection
types.
User Name: Enter the User Name provided by your ISP.
Password: Enter the password provided by your ISP.
MTU: Maximum Transmission Unit. The default value is 1492.
Note:
DO NOT change the factory default MTU value unless necessary as an
improper MTU value may degrade your network performance or even lead to
network malfunction.
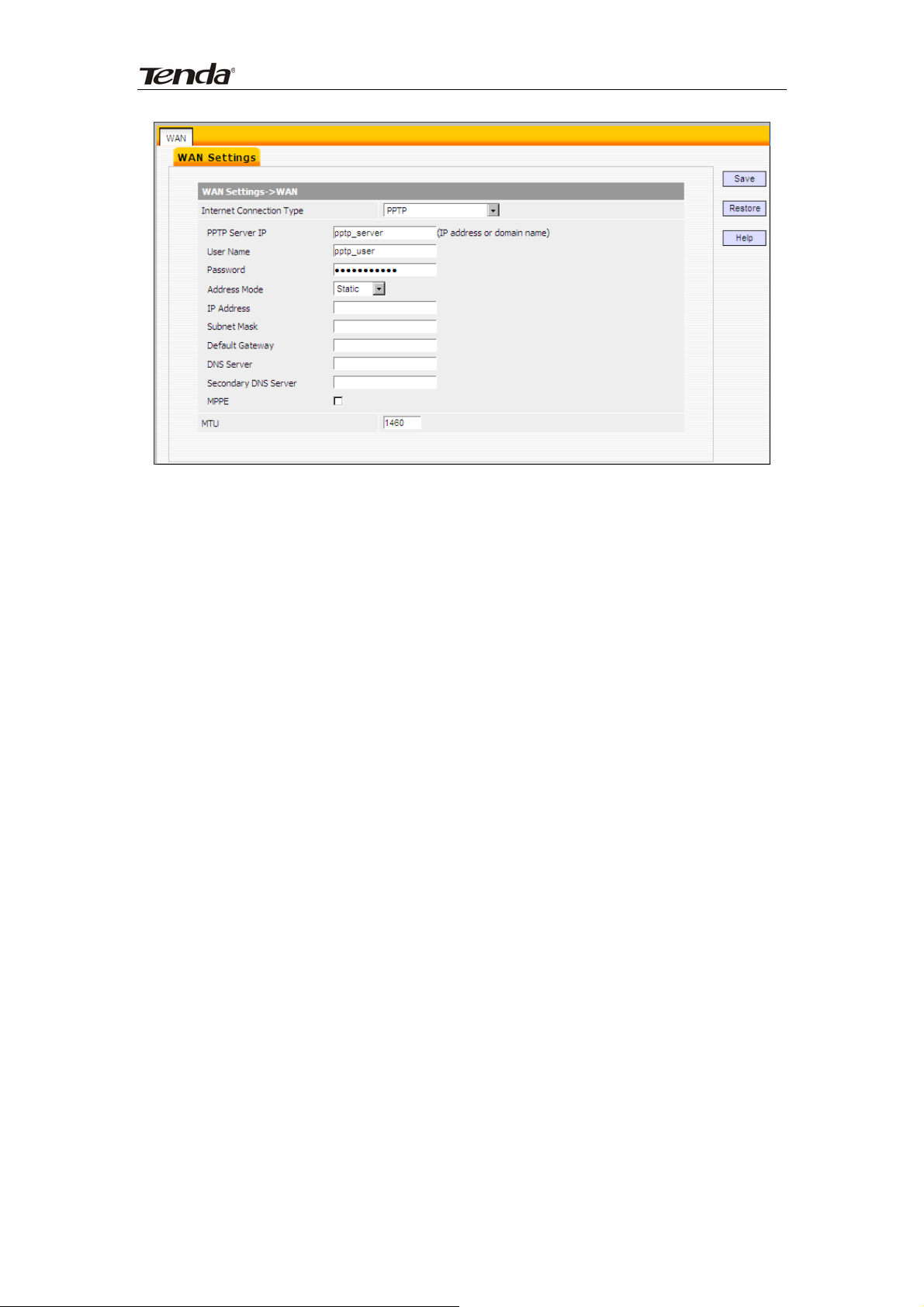
4)PPTP: Allows you to connect your router to a VPN server.
For example:A corporate branch and headquarter can use this connection
type to implement mutual and secure access to each other’s resources.
17
Page 18
300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
Internet connection Type: Displays a list of available Internet connection
types.
PPTP Server IP: Enter the IP address of a PPTP server.
Username/Password: Enter Username/Password defined by the PPTP
server.
Address mode: Select “Dynamic” if you don’t get any IP info from the PPTP
server side, otherwise select “Static”.
IP Address: Enter the IP address provided by your ISP. Inquire your local
ISP if you are not clear.
Subnet mask: Enter the subnet mask provided by your ISP.
Default Gateway: Enter the gateway provided by your ISP. Inquire your
local ISP if you are not clear.
DNS Server: Enter the necessary DNS address provided by your ISP.
Secondary DNS Server: Enter the other DNS address if your ISP provides
you with 2 such addresses, and it is optional.
MTU: Maximum Transmission Unit. The default value is 1460.
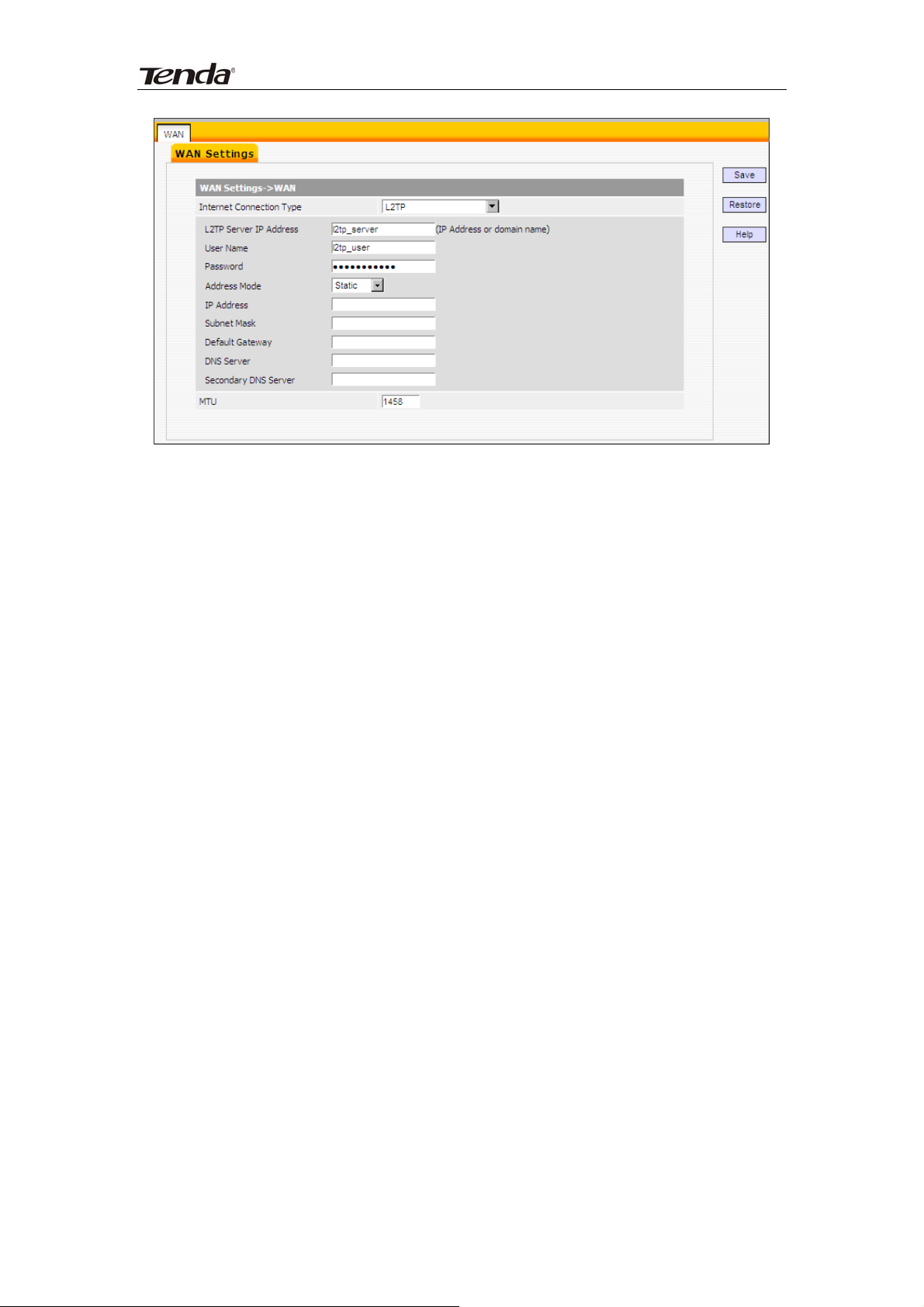
5)L2TP: Allows you to connect your router to a L2TP server.
For example:A corporate branch and headquarter can use this connection
type to implement mutual and secure access to each other’s resources.
18
Page 19
300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
Internet connection Type: Displays a list of available Internet connection
types.
L2TP Server IP Address: Enter the IP address of a L2TP server.
Username/Password: Enter Username/Password specified by the L2TP
server.
Address Mode: Select “Dynamic” if you don’t get any IP info from the L2TP
server, otherwise select “Static”.
IP address: Enter the IP address provided by your ISP. Inquire your local
ISP if you are not clear.
Subnet mask: Enter the subnet mask provided by your ISP.
Default Gateway: Enter the gateway provided by your ISP. Inquire your
local ISP if you are not clear.
DNS Server: Enter the necessary DNS address provided by your ISP.
Secondary DNS Server: Enter the other DNS address if your ISP provides
you with 2 such addresses, and it is optional.
MTU: Maximum Transmission Unit. The default value is 1458.
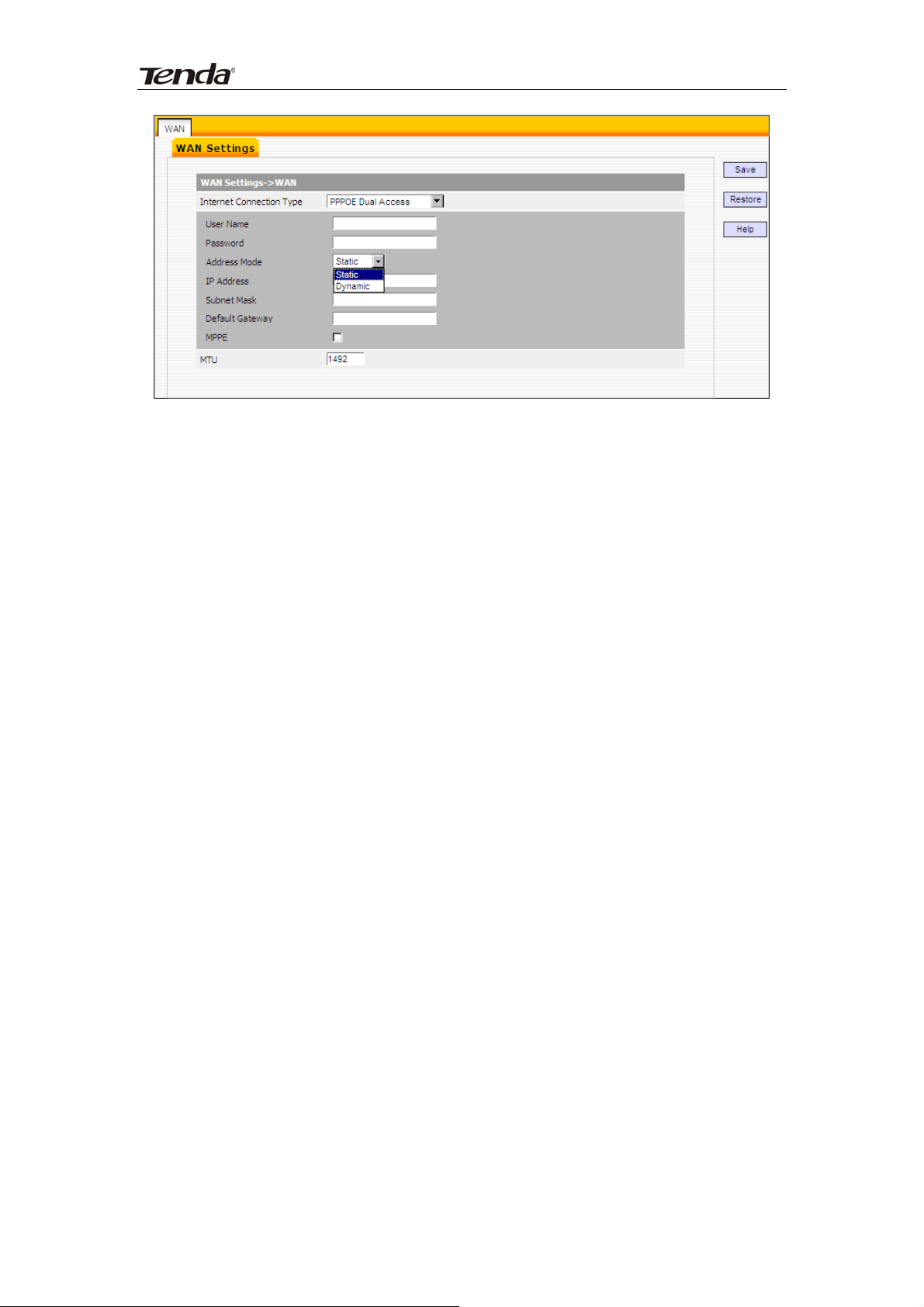
6) PPPOE Dual Access
19
Page 20
300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
Internet connection Type: Displays a list of available Internet connection
types.
Username: Enter the PPPOE account provided by your ISP.
Password: Enter the PPPOE password provided by your ISP.
Address mode: Select “Dynamic” if you don’t get any IP info from your ISP,
otherwise select “Static”.
IP address: The IP address provided by your ISP. Inquire your local ISP if
you are not clear.
Subnet mask: The subnet mask provided by your ISP.
Default Gateway: The gateway address provided by your ISP. Inquire your
local ISP if you are not clear.
MTU: Maximum Transmission Unit. The default value is 1492.
4.2.3 DHCP Settings
“DHCP” includes 3 submenus: DHCP Server, Client List and Static Assignment.
Clicking any of them enters corresponding interface for configuration. Below
explains, in details, each such feature.
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is an automatic
configuration protocol used on IP networks. If you enable the built-in DHCP
server on the device, it will automatically configure the TCP/IP settings for all
your LAN computers (including IP address, subnet mask, gateway and DNS
etc), eliminating the need for manual intervention. Just be sure to set such PCs
to DHCP clients by selecting “Obtain an IP Address Automatically” on each
such PC. When you turn these PCs on, they will automatically load the proper
TCP/IP settings provided by the device DHCP server.
20
Page 21

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
DHCP Server-Enable: Check or uncheck the box to enable or disable the
device’s DHCP server feature.
Start IP Address: Enter the starting IP address for the DHCP server’s IP
assignment.
End IP Address: Enter the ending IP address for the DHCP server’s IP
assignment.
Lease Time: The length of time for the IP address lease. Configuring a
proper lease time improves the efficiency for the DHCP server to reclaim
disused IP addresses.
Primary DNS Server: Enter a DNS server address assigned to DHCP
clients.
Secondary DNS Server: Enter the other DNS address assigned to DHCP
clients (optional).
To benefit from the DHCP server feature, you must set all LAN PCs to DHCP
clients by selecting the “Obtain an IP Address Automatically” radio buttons
thereon.
DHCP Client List
This section displays a DHCP dynamic client list, which includes host name, IP
address, MAC address and lease time info.
IP Address: Displays IP address(es) that client(s) obtained from the DHCP
server.
MAC Address: Displays MAC address of a given host.
21
Page 22

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
Host name: Displays name of a given host (DHCP client).
Lease Time: Remaining time for a corresponding IP address lease.
Static Assignment
If you would like some devices on your network to always have fixed IP
addresses, you can use this feature and manually add a static DHCP
assignment entry for each such device.
For example: To have a PC at the MAC address of 00:15:58:c0:d4:3f always
receive the same IP address of 192.168.0.150, simply enter the IP and MAC
addresses in corresponding fields and click “Add” and then the “Save” button
as shown below.
IP Address: Enter the IP address for static DHCP assignment.
MAC Address: Enter the MAC address of a computer to always receive the
same IP address (the IP you just entered above).
Add: Click to add the current IP-MAC static assignment entry to the list.
Edit: Click to change a given static assignment entry.
Delete: Click to remove an existing entry.
4.2.4 WAN Port
“WAN Port” includes 2 submenus: MAC Clone, and Speed/Duplex. Clicking
either tab enters corresponding interface for configuration. Below explains, in
details, each such feature.
MAC Clone
This section allows you to set router’s WAN MAC address. You can either
manually enter a MAC or copy your PC’s MAC to the router.
22
Page 23

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
WAN MAC Address: Displays router's current WAN MAC address, you can
manually change it.
Restore to Factory Default MAC: Click it to restore router’s WAN MAC to
factory default value.
Clone MAC: Click to copy your PC’s MAC to router’s WAN MAC Address
field.
NOTE:
1. Normally you don't need to change the default WAN MAC value. However,
some ISP may bind client PC’s MAC address for Internet connection
authentication. In this case, simply enter such MAC in the WAN MAC Address
field or click the “Clone MAC” button. Note that the WAN MAC address in
running status interface will be updated accordingly.
2. Do remember to reboot the router to activate the new WAN MAC. DO NOT
use the “Clone MAC” feature if your ISP does not bind your PC’s MAC.
Speed/Duplex
This section allows you to config the router’s WAN port speed/duplex settings.
You can select a WAN port speed/duplex mode that best suit your network
environment from the drop-down list, which includes auto, 10M half-duplex,
10M full-duplex, 100M half-duplex, 100M full-duplex.
Note:
The WAN port speed/duplex mode must match that of its link partner to
achieve successful communication; otherwise, the WAN port may not function
23
Page 24

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
properly. So, if you are not sure about the link partner’s speed/duplex mode,
please select “Auto”.
4.3 Security Settings
“Security Settings” includes the following 5 submenus. Clicking any of
them enters corresponding interface for configuration. Below explains, in
details, each such feature.
4.3.1 Group Settings
“Group Settings” includes 2 submenus: Group Settings, User Group and Time
Group. Clicking either tab enters corresponding interface for configuration.
Below explains, in details, each such feature.
User Group
To create a user group, you need to specify a group name/description and
an IP address/range. The user group feature works together with other related
features.
For example: If you want to add a user group for a R&D department within an
IP of 192.168.0.20-192.168.0.30, first click the “Add” button and then follow
steps below:
24
Page 25

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
1. Enter R_D in group name field.
2. Enter R_D IP Range in group description field.
3. Enter “192.168.0.20” and “192.168.0.30” in IP fields.
4. Click “Add “and then the “Save “button; you will find
such entry in User Group list below:
Time Group
To create a time group, you need to specify a group name/description and a
time / time range.
For example: If you want to set a period of time from 8:00 to 18:00 on working
days from Monday to Friday to a time group, first click the “Add” button and
then follow steps below:
25
Page 26

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
1. Enter “Working days” in group name field.
2. Enter “working days” in group description field.
3. Select the time and days.
4. Click “Save” and you will find such entry in Time Group list below:
4.3.2 Port Filter
To better manage PCs in LAN, you can allow or disallow such PCs to access
certain ports on Internet using the Port Filter functionality.
26
Page 27

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
Click “Add” to enter page below:
Filter Mode: Select Deny or Allow according to your own needs.
Deny Access to Internet: Disallow specified packets to pass through the
router; other packets are processed according to default rule.
Allow Access to Internet: Allow specified packets to pass through the
router; other packets are processed according to default rule.
Enable: Check to enable current filter entry.
Description: Enter a meaningful name to yourself for a new filter rule.
User Group: Select an added user group from the drop-down list.
Time Group: Select an added time group from the drop-down list.
WAN Port Range: Enter port IDs. You can specify a range of ports or a
single port. Allowed port ID ranges from 1 to 65535.
Protocol: Select a protocol or protocols for the traffic (“Both” includes TCP
and UDP).
For Example: If you want to disallow PCs within IP addresses ranging from
192.168.0.20 to 192.168.0.30(“R&D” user group) to access web sites from
8:00 to 18:00 on working days – from Monday to Friday (“Working days” time
group), do as follows:
1. Select “Deny” from the filter mode drop-down list.
2. Check the “Enable” box.
3. Enter “Forbid websites” in description field.
4. Select “R&D” from the user group drop-down list.
5. Select “Working days” from time group drop-down list.
6. Enter “80” in both boxes of “WAN Port Range”.
7. Select “Both” from “Protocol” drop-down list.
27
Page 28

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
8. Click “Save” and you will find such entry in the List below.
9. Select “Allow” from the “Default” drop-down list and check “Enable” Port
Filter feature.
28
Page 29

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
4.3.3 URL Filter
To better control LAN PCs, you can use the URL filter functionality to allow or
disallow such PC to access certain websites within a specified time range.
Click “Add” to display page below:
Filter Mode: Select Deny or Allow according to your own needs.
Deny Access to Internet: Disallow specified packets to pass through the router;
other packets are processed according to default rule.
¾
Allow Access to Internet: Allow specified packets to pass through the router;
other packets are processed according to default rule.
User Group: Select an added user group from drop-down list.
¾
Time Group: Select an added time group from drop-down list.
¾
Description: Enter a meaningful name to yourself for a new filter rule.
¾
URL character string: Enter domain name string to be filtered.
¾
For Example: If you want to disallow PCs within IP addresses ranging from
192.168.0.20 to 192.168.0.30(“R_D” user group) to access only web sites containing
“yahoo” from 8:00 to 18:00 on working days – from Monday to Friday (“Working days”
time group), without restricting other PCs, do as follows:
29
Page 30

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
1. Select “Deny” from the filter mode drop-down list.
2. Check the “Enable” box.
3. Enter “Disallow yahoo” in description field.
4. Select “R_D” from the user group drop-down list.
5. Select “Working days” from time group drop-down list.
6. Enter “yahoo” in URL String field.
7. Click “Save” to display page below:
30
Page 31

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
8. Select “Allow” from the “Default” drop-down list and check the “Enable” URL Filter
feature.
4.3.4 MAC Address Filter
To better manage PCs in LAN, you can use the MAC Address Filter function to
allow/disallow such PCs to access to Internet.
Click “Add” to display page below:
31
Page 32

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
Filter Mode: Select Deny or Allow according to your own needs.
Deny Access to Internet: Disallow specified packets to pass through the
router; other packets are processed according to default rule.
Allow Access to Internet: Allow specified packets to pass through the
router; other packets are processed according to default rule.
Description: Briefly describe a new filter rule
MAC: Enter the computer’s MAC address that you want to filter out in the
MAC address field or select one from the MAC address list.
Time: Select a time range for the new MAC address filter rule to take effect.
The default is 00:00-00:00, which means 24 hours.
Day: select a day or several days for the new MAC address filter rule to
take effect.
For Example: To only prevent a PC at the MAC address of 00:B0:0C:77:88:00
from accessing Internet from 8:00 to 18:00 everyday, without restricting other
PCs, config same settings on the screenshot below on your device:
Click “Save” to display the following page. Select “Allow” from the “Default”
drop-down list and check the “Enable MAC Filter” feature as below.
32
Page 33

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
4.3.5 WAN Access Control
The WAN Access Control feature allows users to configure your router from
Internet via a web browser.
Enable: Check or uncheck to enable or disable the WAN Access Control
feature.
Port: Enter a port ID for remote web-based management. The default is
8080.
IP Address: Enter the IP address of a PC on Internet authorized to access
and manage your router’s web-based utility remotely.
Note:
If you enter 0.0.0.0 in the IP address box, then all PCs on Internet can access
your router’s Web-based utility to view or change your settings remotely once
you enable the feature.
For example:
If you want to allow only a PC at the IP address of 58.60.111.221
to access your router’s web-based utility from Internet via port: 8080, you need
to configure same settings as shown on the interface below on your router.
And what this IP user needs to do is to simply launch a browser and enter
http://58.251.88.90:8080 (provided that your router’s WAN IP address is
58.251.88.90).
33
Page 34

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
4.4 Advanced Settings
“Advanced Settings” includes the following 6 submenus. Clicking any of them
enters corresponding interface for configuration. Below explains, in details,
each such feature.
4.4.1 Virtual Server
The Virtual Server feature grants Internet users access to services on your
LAN. It is useful for hosting online services such as FTP, Web, or game
servers. For each Virtual Server, you define a WAN port on your router for
redirection to an internal LAN IP Address and LAN port.
Click “Add” to display below page.
34
Page 35

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
WAN Port: Enter the WAN service port.
Well-Known Service Ports: The “Well-Known Service Port” lists commonly
used protocol ports such as DNS(53, FTP(21), GOPHER(70), HTTP(80),
NNTP(1190), POP3(110), PPTP(1723) , SMTP(25), SOCK(1080),
TELNET(23). In case that you don’t find the port ID you need, add it
manually.
LAN Port: Enter LAN service port.
LAN IP: The IP address of a computer used as a server in LAN.
Protocol: Includes TCP, UDP and Both. Select “Both” if you are not sure
about which protocol to use.
Enable: Check the “Enable” option to activate corresponding entry.
For example: If you create a web server using port 80 on a LAN PC at the IP
address of 192.168.0.10, and you want WAN users to access such server via
http://x.x.x.x:4000 (x.x.x.x represents router’s WAN IP address), then do as
follows:
1. Enter “4000” in WAN Port field, 80 in LAN port field and 192.168.0.10 in
Private IP field.
2. Select “Both” from protocol drop-down list.
3. Check the “Enable” box.
4. Click “Save” to save such settings.
35
Page 36

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
Note:
Setting WAN port hereon to the same value as that on WAN access control
section will deactivate the virtual server feature.
4.4.2 DMZ Settings
In some cases, we need to set a computer to be completely exposed to
extranet for implementation of a bidirectional communication. To do so, we set
it as a DMZ host.
DMZ Host IP Address: Enter the IP address of a LAN computer which you
want to set to a DMZ host.
Enable: Check/uncheck to enable/disable the DMZ host.
NOTE:
1. If you set a PC to a DMZ host, it will be completely exposed to extranet and
gains no more protection from the device firewall.
2. A WAN user accesses the DMZ host through a corresponding WAN IP
address.
4.4.3 UPnP Settings
UPnP (Universal Plug and Play) requires Windows ME/Windows XP or later or
application softwares that support such UPnP feature.
36
Page 37

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
ID: Entry ID.
Remote Host: Description of a remote host that receives/sends responses.
WAN Port: Port on router side.
LAN Host: Description of an internal host that receives/sends responses.
LAN Port: Port on host side.
Protocol: Indicates whether to perform TCP or UDP port forwarding.
Description: Software info of a mapped port.
4.4.4 DDNS Settings
Dynamic DNS or DDNS is a term used for the updating in real time of Internet
Domain Name System (DNS) name servers. We use a numeric IP address
allocated by Internet Service Provider (ISP) to connect to Internet; the address
may either be stable ("static"), or may change from one session on the Internet
to the next ("dynamic"). However, a numeric address is inconvenient to
remember; an address which changes unpredictably makes connection
impossible. The DDNS provider allocates a static hostname to the user;
whenever the user is allocated a new IP address this is communicated to the
DDNS provider by software running on a computer or network device at that
address; the provider distributes the association between the hostname and
the address to the Internet's DNS servers so that they may resolve DNS
queries. Thus, uninterrupted access to devices and services whose numeric IP
address may change is maintained.
37
Page 38

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
Enable DDNS: Check the box to Enable or Disable the DDNS feature.
DDNS Service Provider: Select your DDNS service provider from the
drop-down menu (Dyndns or Noip).
Username: Enter the DDNS username registered on DDNS server.
Password: Enter the DDNS password registered on DDNS server.
Domain Name: Enter the DDNS domain name distributed by your DDNS
service provider.
Connection Status: Displays current status connection with the DDNS
server.
4.4.5 Routing
This section talks about Routing Table and Static Routing features.
Routing Table
This page displays the router’s core routing table which lists destination IP,
subnet mask, gateway, hop count and interface.
Static Routing
You can use this section to set up router’s static routing feature.
Click “Add” to add static routing entries.
38
Page 39

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
Destination Network: Enter a destination IP address.
Subnet Mask: Enter a Subnet Mask that corresponds to the destination IP
address you entered.
Gateway: Next-hop IP address.
4.4.6 Bandwidth Control
To better manage bandwidth allocation and optimize network performance,
use the Custom Bandwidth Allocation feature.
Custom Bandwidth Allocation: Select this option to customize a bandwidth
allocation policy that best fits your network. You can set specific limits on
uplink and downlink bandwidth of PCs within a specified IP range.
Click “Add” to display the page below:
39
Page 40

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
Enable: Check/uncheck to enable/disable current bandwidth entry.
IP Range: Enter a single IP or an IP range.
Upstream Bandwidth Limit: Max total upload bandwidth for a specified PC
or a range of PCs.
Downstream Bandwidth Limit: Max total download bandwidth for a
specified PC or a range of PCs.
P2P Download Control: Regulates P2P download rate to ensure each user
a guaranteed share of bandwidth.
Allocation Mode: Select either "Individual (Each member of the IP range
shall utilize the allocated bandwidth individually)" or "Collective (All
members of the IP range shall share the allocated bandwidth collectively)"
Allocation Policy: Select either "Utilize only the allocated bandwidth" or
"Utilize more bandwidth if available".
Description: Brief description of current entry.
Note:
1. Please note the bandwidth unit.
2. If you enable the P2P Download Control feature, it will limit P2P download
rate (smaller than the specified value) to ensure other applications such as
web browsing a reserved and guaranteed share of bandwidth.
3. If you select "Utilize more bandwidth if available", router will dynamically
adjust uplink/downlink bandwidth allocation to ensure defined and additional
bandwidth if available or only defined bandwidth.
For example:
If you want each PC within the IP range of 192.168.0.100-192.168.0.120 to
have up to 2M uplink and 2M downlink bandwidth, and want to control P2P
download bandwidth, then config same settings as shown on the screen below
on your router:
40
Page 41

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
4.5 Wireless Settings
Wireless Settings includes 8 submenus as shown in the screenshot below.
Clicking any tab enters corresponding interface for configuration.
4.5.1 Basic Settings
This section allows you to manage your wireless network (2.4G or 5G). You
can config country code, wireless network name (SSID), network mode and
channel settings, etc the way you want.
Basic Settings-- 2.4G
41
Page 42

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
Country: Select your country code from the drop-down list. There are 11
options available.
2.4GHz Wireless Network: Check/uncheck to enable/disable the 2.4GHz
wireless feature. If disabled, all 2.4GHz-based features will be disabled
accordingly.
SSID Broadcast: Select “Enable”/“Disable” to make your wireless network
visible/ invisible to any wireless clients within coverage when they perform
a scan they perform a scan to see what’s available. When disabled, such
wireless clients will have to first know this SSID and manually enter it on
their devices if they want to connect to the SSID. By default, it is enabled.
SSID :A SSID (Service Set Identifier) is the unique name of a wireless
network.
802.11 Mode: Select a right mode according to your wireless client. The
default mode is 11b/g/n mixed.
Channel: For an optimal wireless performance, you may select the least
interferential channel. It is advisable that you select an unused channel or
“Auto” to let device detect and select the best possible channel for your
wireless network to operate on from the drop-down list.
Channel Bandwidth: Select a proper channel bandwidth to enhance
wireless performance. When there are 11b/g and 11n wireless clients,
please select the 802.11n mode of 20/40M frequency band; when there
are only non-11n wireless clients, select 20M frequency band mode; when
the wireless network mode is 11n mode, please select 20/40 frequency
band to boost its throughput.
Extension Channel:Working network frequency range for 11n mode.
WMM-Capable:Enabling this option may boost transmission capacity of
wireless multimedia data (such as online video play).
ASPD Capable:Select to enable/disable the auto power saving mode.
Basic Settings-- 5G
42
Page 43

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
Country: Select your country code from the drop-down list. There are 10
options available.
5GHz Wireless Network: Check/uncheck to enable/disable the 5GHz
wireless feature. If disabled, all 5GHz-based features will be disabled
accordingly.
SSID Broadcast: Select “Disable” to hide your SSID. When disabled, no
wireless clients will be able to see your wireless network when they
perform a scan to see what’s available. If they want to connect to your
router, they will have to first know this SSID and then manually enter it on
their devices. By default, this option is enabled.
SSID: A SSID (Service Set Identifier) is the unique name of a wireless
network (changeable).
802.11 Mode: Select a right mode according to your wireless client. The
default mode is 11a/n.
Channel: The Channel can be changed to fit the channel setting for an
existing wireless network or to customize the wireless network. From the
drop-down list,you can select a most effective channel. You can also
select “Auto Select” to let system detect and choose one that best fits your
network.
WMM-Capable: Enabling this option may boost transmission capacity of
wireless multimedia data (such as online video play).
ASPD Capable: Select to enable/disable the auto power saving mode.
4.5.2 Wireless Security
This section allows you to encrypt both 2.4GHz wireless and 5GHz wireless
networks to block unauthorized accesses and malicious packet sniffing.
To config wireless security settings for 2.4GHz network, enter page below:
43
Page 44

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
Available options for security mode include “Open”, “Shared”, “WPA-PSK”,
“WPA2-PSK”, “Mixed WPA/WPA2-PSK”. See below for details.
1. OPEN/SHARED
WEP is intended to provide data confidentiality comparable to that of a
traditional wired network. Two methods of authentication can be used with
WEP: Open System authentication and Shared Key authentication.
Security Mode: Select a proper security mode from the drop-down menu.
Default Key: Select one key from the 4 preset keys to encrypt wireless
data on the network.
2. WPA-PSK
The WPA protocol implements the majority of the IEEE 802.11i standard. It
44
Page 45

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
enhances data encryption through the Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP)
which is a 128-bit per-packet key, meaning that it dynamically generates a new
key for each packet. WPA also includes a message integrity check feature to
prevent data packets from being hampered with. Only authorized network
users can access the wireless network.
Cipher Type: Select either AES (advanced encryption standard) or TKIP
(temporary key integrity protocol) type.
Security Key: Enter a security key,which must be between 8-63 ASCII
characters.
Key Renewal Interval: Enter a valid time period for the key.
3. WPA2-PSK
The later WPA2 protocol features compliance with the full IEEE 802.11i
standard and uses Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) in addition to TKIP
encryption protocol to guarantee better security than that provided by WEP or
WPA.
Cipher Type: Select one cipher type from AES (advanced encryption
standard), TKIP (temporary key integrity protocol) or TKIP&AES.
Security Key: Enter a security key,which must be between 8-63 ASCII
characters.
Key Renewal Interval: Enter a valid time period for the key.
4.5.3 WPS Settings
45
Page 46

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
Wi-Fi Protected Setup makes it easy for home users who know little of wireless
security to establish a secure wireless home network, as well as to add new
devices to an existing network without entering long passphrases or
configuring complicated settings. Simply enter a PIN code or press the
software PBC button or hardware WPS button (if any) and a secure wireless
connection is established.
Enable WPS: Select to enable/disable the WPS encryption.
WPS Mode: Select PBC (Push-Button Configuration) or PIN.
Reset OOB: When clicked, the WPS LED turns off; WPS function will be
disabled automatically; WPS server on the Router enters idle mode and
will not respond to client’s WPS connection request.
Operation Instructions
PBC: If you find the WPS LED blinking for 2 minutes after you press the
hardware WPS button on the device, it means that PBC encryption method is
successfully enabled. And an authentication will be performed between your
router and the WPS/PBC-enabled wireless client device during this time; if it
succeeds, the wireless client device connects to your device, and the WPS
LED turns off. Repeat steps mentioned above if you want to connect more
wireless client devices to the device.
PIN:To use this option, you must know the PIN code from the wireless client
and enter it in corresponding field on your device while using the same PIN
code on client side for such connection.
Note: The WPS encryption can be implemented only between your Router and
another WPS-capable device.
4.5.4 WDS Settings
WDS (Wireless Distribution System) feature can be used to extend your
existing 2.4G or 5G wireless network coverage. Here we present you how to
config such feature in 2.4GHz, which also apply to 5GHz.
46
Page 47

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
Select Repeater Mode to display below page:
AP MAC Address: Enter the MAC address of a wireless link partner or
populate this field using the Open Scan option.
WDS Mode: Select Disable or Repeater Mode.
For example: If you want to implement the WDS feature on 2 N6 routers
labeled N6-1 and N6-2 respectively, then first select “Repeater Mode” and
follow steps below:
1. If you already know N6-2’s MAC address, then you can manually enter it on
N6-1 and click “Save”.
2. Or you can use the Open Scan option.
1) Click the “Open Scan” button to select N6-2’s SSID and confirm on the
47
Page 48

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
appearing dialogue box and then click “Save”. N6-2’s MAC address will be
added automatically.
2) Save your settings.
3. Repeat steps 1-2 on N6-2. After the 2 devices have added each other’s
48
Page 49

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
MAC address the WDS feature can be implemented.
Note:
1. WDS feature can only be implemented between 2 wireless devices that both
support the WDS feature. Plus, SSID, channel, security settings and security
key must be the same on both such devices.
2. To encrypt your wireless network, see sections 4.5.2-4.5.3. Do remember to
reboot the device after you saved your wireless security settings, otherwise the
WDS feature may not function.
4.5.5 Guest Network
The Guest Network feature allows guests to access Internet and other users
on the guest network while disallowing them to access device web manager,
users on primary network and clients behind the LAN ports. You can find it
available in both 2.4G and 5G network. Here we present you how to config
such feature in 2.4GHz, which also apply to 5GHz.
Guest Network: Check/uncheck to enable/disable the guest network
feature.
SSID Broadcast: Select “Disable” to hide your SSID. When disabled, no
wireless clients will be able to see your wireless network when they
perform a scan to see what’s available. If they want to connect to your
router, they will have to first know this SSID and then manually enter it on
their devices. By default, it is enabled.
49
Page 50

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
AP Isolation: If enabled, clients connecting to the guest network will be
mutually inaccessible.
SSID: A SSID (Service Set Identifier) is the unique name of a wireless
network.
Security Mode: Determine whether to require authentication on wireless
clients. Select a proper mode from the drop-down menu.
4.5.6 Wireless Access Control
The MAC-based Wireless Access Control feature can be used to allow or
disallow clients to connect to your 2.4G or 5G wireless network. Here we
present you how to config such feature in 2.4GHz, which also apply to 5GHz.
MAC Address Filter: Selecting “Disable” means to deactivate the MAC
address filter feature. “Allow” means to only allow PCs at specified MAC
addresses to connect to your wireless network while “Deny” means to only
block PCs at specified MAC addresses from connecting to your wireless
network.
MAC Address:Enter the MAC addresses of a wireless client.
Add: Click it to add a new MAC to the MAC address list.
50
Page 51

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
Delete: Click it to remove an existing entry.
To allow only a PC at the MAC address of 00:e8:c8:a4:56:75 to connect to your
wireless network, do as follows:
Step1. Select “Allow” from MAC Address Filter drop-down menu.
Step2. Enter 00:e8:c8:a4:56:75 in the MAC address box and click “Add”.
Step3. Click the “OK” button to save your settings and you can add more MAC
addresses, if you like, simply repeating the above steps.
4.5.7 Connection Status
This interface displays the information of currently connected 2.4G and 5G
wireless clients (if any).
4.5.8 Wireless –Advance Settings
This section allows you to config advanced settings, including Beacon interval,
Fragment threshold,RTS threshold and DTIM interval, etc, for both 2.4G and
5G wireless networks.
51
Page 52

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
AP Isolation: Isolates clients connecting to the private SSID.
Beacon Interval: A time interval between any 2 consecutive Beacon
packets sent by device. Do NOT change the default value of 100 unless
necessary.
Fragment Threshold: Enter a Fragment Threshold (256-2346). Any
wireless packet exceeding such set value will be divided into several
fragments. DO NOT change the default value of 2346 unless necessary.
RTS Threshold: If a packet exceeds such set value, RTS/CTS scheme will
be used to reduce collisions. Set it to a smaller value provided that there
are distant clients and interference. For normal SOHO, it is recommended
to keep the default value unchanged; otherwise, device performance may
be degraded.
DTIM Interval: A time interval between any two consecutive broadcast and
multicast packet messages sent by the device to clients. When such
packets arrive at device’s buffer, the device will send DTIM (delivery traffic
indication message) and DTIM interval to wake clients up for receiving
these packets.
4.6 IPTV Settings
The IPTV feature makes it possible to enjoy online videos on your TV set via a
set-top box while surfing Internet.
Enable IPTV: Check/uncheck to enable/disable the IPTV feature.
52
Page 53

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
Enable IPTV STB Port: Check/uncheck to enable/disable the IPTV-specific
port.
See below for the topology:
Note:
1. If you enabled both options mentioned above, then note below:
(a). Set IPTV connection type to DHCP/dynamic IP or static IP (IMPORTANT:
Note that the IP address should be on the same IP net segment as router’s
WAN IP.) if the set-top box is connected to any LAN port from 1-3.
(b). Select the dial mode provided by your ISP if the set-top box is connected
to the IPTV-specific port.
2. After the IPTV port is set for IPTV purpose, PC that connects to such port
will not be able to obtain an IP address or access Internet. So think twice
before you start. Plus, LAN ports1-3 can only be used to connect PCs instead
of an IPTV set-top box.
3. The IPTV feature does not support wireless access.
4.7 Tools
System tools include the following 8 submenus. Clicking any of them enters
corresponding interface for configuration. Below explains, in details, each such
feature.
53
Page 54

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
4.7.1 Time Settings
This section assists you in setting the device’s system time; you can either
select to set the time and date manually or automatically obtain the GMT time
from Internet.
Sync with Internet time servers: Time and date will be updated
automatically from Internet.
Sync Interval: Determines a time length when device periodically updates
its time and date info from Internet. The default is 2 hours.
Time Zone: Select your current time zone.
Copy Local Time: Click it to copy your PC’s time to the device.
4.7.2 Firmware Upgrade
Firmware upgrade is released periodically to improve the functionality of your
device and also to add new features. If you run into a problem with a specific
54
Page 55

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
feature of the device, log on to our website www.tendacn.com to download the
latest firmware to update your device.
To update firmware, do as follows:
1. Click "Browse” to locate the firmware and "Upgrade” to update.
2. Router will reboot automatically when upgrade completes.
NOTE: Do not disconnect the device from your management PC (the PC you
use to configure the device) or power off it during the upgrade process;
otherwise, it may be permanently damaged. The device will restart
automatically when the upgrade process, which takes several minutes,
completes.
4.7.3 Backup/Restore Settings
This section allows you to backup current settings or to restore the previous
settings configured on the device.
Backup Settings: Once you have configured the device the way you want it,
you can save these settings to a configuration file on your local hard drive
that can later be imported to your device in case that the device is restored
to factory default settings. To do this, click the “Backup” button and specify
a directory to save settings on your local hardware.
Restore Settings: Click the "Browse" button to locate and select a
configuration file that is saved previously to your local hard drive. And then
click the "Restore" button to reset your device to previous settings.
55
Page 56

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
4.7.4 Restore to Factory Default Settings
To restore all settings to the device's factory default values, click the "Restore
to Factory Default” button:
Factory Default Settings:
User Name: admin
Password: admin
IP Address: 192.168.0.1
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
Note: To activate your settings, you need to reboot the device after you reset it.
4.7.5 Change Password/User Name
This section allows you to change login password and user name for
accessing device’s Web-based interface.
¾ Old Password/User Name: Enter the old password/user name.
¾ New Password/User Name: Enter a new password/user name.
¾ Confirm New Password: Re-enter the new password for confirmation.
¾ Save: Click it to save new settings.
NOTE: For the sake of security, it is highly recommended that you change
default login password and user name.
56
Page 57

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
4.7.6 Reboot
This section allows you to reboot the device.
To restart your device, click the “Reboot” button.
4.7.7 Statistics
Statistics displays current traffic of PCs on your LAN.
Enable Traffic Statistics: Check/uncheck the box to enable/disable the
Traffic Statistics feature.
Refresh: Click to update statistic data.
Clear: Click to remove statistic data.
57
Page 58

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
Note: Enabling the Traffic Statistics feature may degrade router’s packet
processing capacity. So, do not enable it unless necessary.
4.7.8 logs
The Syslog option allows you to view all events that occur upon system
startup and check whether there is attack present in your network.
The logs are classified into 3 types: “All”, “System “and “WAN”.
A ppendix 1 Config TCP/IP Settings on PC
58
Page 59

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
This section presents you how to config your PC’s TCP/IP settings (in
Windows XP and Windows 7). Before you start, make sure your PC has an
installed NIC. If not, please install one first.
Windows XP
If you are using Windows XP operating system, do as follows:
1. Right click “My Network Places” and select “Properties”.
2. Right click “Local Area Connection” and select “Properties”
3. Select “Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)” on the appearing window and click
“Properties” button.
59
Page 60

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
4. Select “Use the following IP address” or “Obtain an IP address
automatically”.
a. To “Obtain an IP address automatically” simply click the corresponding
button.
60
Page 61

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
b. “Use the following IP address”
IP address: Enter 192.168.0.xxx (xxx can be any value from 2~254).
Subnet mask: Enter 255.255.255.0.
Default gateway: Enter 192.168.0.1.
Preferred DNS server: Enter 192.168.0.1 in case that you don’t know the local
DNS server address (Or contact your ISP for help).
At last, click OK to save your settings.
Windows7
If you are using Windows 7 operating system, do as follows:
1. Right click “Network” on your desktop and select “Properties”.
2. Click “Change adapter settings”.
3. Right click “Local Area Connection” and select “Properties”.
61
Page 62

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
4.Select “Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)” on the appearing window and click the
“Properties” button.
5. Select “Use the following IP address” or “Obtain an IP address
automatically”.
a. To “Obtain an IP address automatically” simply click the corresponding
button.
62
Page 63

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
b. “Use the following IP address”
IP address: Enter 192.168.0.xxx (xxx can be any value from 2~254).
Subnet mask: Enter 255.255.255.0.
Default gateway: Enter 192.168.0.1.
Preferred DNS server: Enter 192.168.0.1 in case that you don’t know the local
DNS server address (Or contact your ISP for help).
At last, click OK to save your settings.
63
Page 64

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
NCCNotice
經型式認證合格之低功率射頻電機,非經許可,公司、商號或使用者均不得擅自變更頻率、加大功率或變
更設計之特性及功能。
低功率射頻電機之作用不得影響飛航安全及幹擾合法通信;經發現有幹擾現象時,應立即停用,並改善至
無幹擾時方得繼續使用。前項合法通信,指依電信規定作業之無線電信。低功率射頻電機須忍受合法通信
或工業、科學及醫療用電波輻射性電機設備之幹擾。
5.25~5.35GHz 限室內使用 (802.11aused)
FCCStatement
Operations in the 5.15-5.25GHz band are restricted to indoor usage only.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the
following two conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference,
and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including
interference that may cause undesired operation.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class
B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are
designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a
residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio
frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the
instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications.
However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular
installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and
on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one of the
following measures:
- Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
- Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
- Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to
which the receiver is connected.
- Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
FCC Caution: Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the
party responsible for compliance could void the user's authority to operate this
equipment.
64
Page 65

300Mbps Concurrent Dual Band Wireless N Router
This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any
other antenna or transmitter.
Radiation Exposure Statement
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an
uncontrolled environment. This equipment should be installed and operated
with minimum distance 20cm between the radiator & your body.
NOTE: (1)The manufacturer is not responsible for any radio or TV interference
caused by unauthorized modifications to this equipment.(2) To avoid
unnecessary radiation interference, it is recommended to use a shielded RJ45
cable
CE Mark Warning
Operations in the 5.15-5.25GHz band are restricted to indoor usage only.
This is a Class B product in a domestic environment, this product may cause
radio interference, in which case the user may be required to take adequate
measures
NOTE: (1) The manufacturer is not responsible for any radio or TV
interference caused by unauthorized modifications to this equipment. (2) To
avoid unnecessary radiation interference, it is recommended to use a shielded
RJ45 cable
"The product can be used without restrictions in the following countries: all EU
member states except France and Norway.
The product can be used with limitations in the following countries: France (for
indoor use only) and Norway (20 km in the center of Ny-Ĺlesund)."
Safety Instructions
1.Operation temperature range :0-40℃
2.For applicable power supplies see user manual
Adapter information:
Model:TEA09X-09100 (X=A or E or U or D)
Input: 100-240V,50/60Hz,0.3A
Output:DC9V-1A
65
 Loading...
Loading...