Page 1
查询BZT55C10供应商
TELEFUNKEN Semiconductors
Silicon Epitaxial Planar Z–Diodes
Features
Very sharp reverse characteristic
Low reverse current level
Very high stability
Low noise
Available with tighter tolerances
BZT55C...
Applications
Voltage stabilization
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Tj = 25C
Parameter Test Conditions Type Symbol Value Unit
Power dissipation R
Z–current I
Junction temperature T
Storage temperature range T
300K/W P
thJA
Maximum Thermal Resistance
Tj = 25C
Parameter Test Conditions Symbol Value Unit
Junction ambient on PC board 50mmx50mmx1.6mm R
V
Z
j
stg
thJA
94 9373
500 mW
PV/V
Z
175 C
–65...+175 C
500 K/W
mA
Characteristics
Tj = 25C
Parameter Test Conditions Type Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
Forward voltage IF=200mA V
Rev . A1: 12.12.1994
F
1.5 V
1
Page 2
BZT55C...
TELEFUNKEN Semiconductors
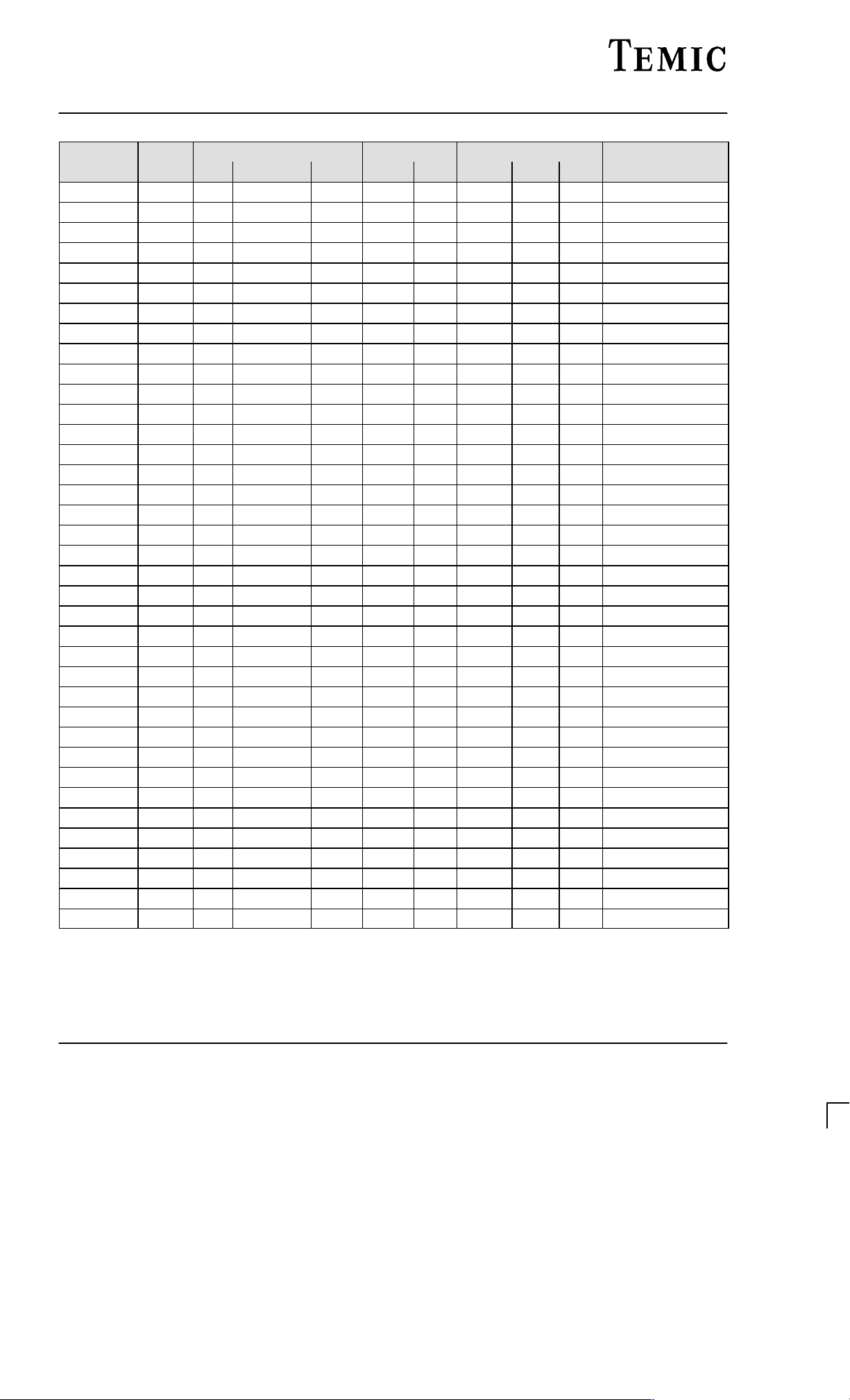
Type V
ZnormIZT
for VZT
1)
and r
zjT
r
zjk
at I
ZK
I
R
and I
2)
at V
R
R
TK
BZT55C... V mA V mA A A V %/K
2 V 4 2.4 5 2.28 to 2.56 < 85 < 600 1 < 100 < 50 1 –0.09 to –0.06
2 V 7 2.7 5 2.5 to 2.9 < 85 < 600 1 < 10 < 50 1 –0.09 to –0.06
3 V 0 3.0 5 2.8 to 3.2 < 90 < 600 1 < 4 < 40 1 –0.08 to –0.05
3 V 3 3.3 5 3.1 to 3.5 < 90 < 600 1 < 2 < 40 1 –0.08 to –0.05
3 V 6 3.6 5 3.4 to 3.8 < 90 < 600 1 < 2 < 40 1 –0.08 to –0.05
3 V 9 3.9 5 3.7 to 4.1 < 90 < 600 1 < 2 < 40 1 –0.08 to –0.05
4 V 3 4.3 5 4.0 to 4.6 < 90 < 600 1 < 1 < 20 1 –0.06 to –0.03
4 V 7 4.7 5 4.4 to 5.0 < 80 < 600 1 < 0.5 < 10 1 –0.05 to +0.02
5 V 1 5.1 5 4.8 to 5.4 < 60 < 550 1 < 0.1 < 2 1 –0.02 to +0.02
5 V 6 5.6 5 5.2 to 6.0 < 40 < 450 1 < 0.1 < 2 1 –0.05 to +0,05
6 V 2 6.2 5 5.8 to 6.6 < 10 < 200 1 < 0.1 < 2 2 0.03 to 0.06
6 V 8 6.8 5 6.4 to 7.2 < 8 < 150 1 < 0.1 < 2 3 0.03 to 0.07
7 V 5 7.5 5 7.0 to 7.9 < 7 < 50 1 < 0.1 < 2 5 0.03 to 0.07
8 V 2 8.2 5 7.7 to 8.7 < 7 < 50 1 < 0.1 < 2 6.2 0.03 to 0.08
9 V 1 9.1 5 8.5 to 9.6 < 10 < 50 1 < 0.1 < 2 6.8 0.03 to 0.09
10 10 5 9.4 to 10.6 < 15 < 70 1 < 0.1 < 2 7.5 0.03 to 0.1
11 11 5 10.4 to 11.6 < 20 < 70 1 < 0.1 < 2 8.2 0.03 to 0.11
12 12 5 11.4 to 12.7 < 20 < 90 1 < 0.1 < 2 9.1 0.03 to 0.11
13 13 5 12.4 to 14.1 < 26 < 110 1 < 0.1 < 2 10 0.03 to 0.11
15 15 5 13.8 to 15.6 < 30 < 110 1 < 0.1 < 2 11 0.03 to 0.11
16 16 5 15.3 to 17.1 < 40 < 170 1 < 0.1 < 2 12 0.03 to 0.11
18 18 5 16.8 to 19.1 < 50 < 170 1 < 0.1 < 2 13 0.03 to 0.11
20 20 5 18.8 to 21.2 < 55 < 220 1 < 0.1 < 2 15 0.03 to 0.11
22 22 5 20.8 to 23.3 < 55 < 220 1 < 0.1 < 2 16 0.04 to 0.12
24 24 5 22.8 to 25.6 < 80 < 220 1 < 0.1 < 2 18 0.04 to 0.12
27 27 5 25.1 to 28.9 < 80 < 220 1 < 0.1 < 2 20 0.04 to 0.12
30 30 5 28 to 32 < 80 < 220 1 < 0.1 < 2 22 0.04 to 0.12
33 33 5 31 to 35 < 80 < 220 1 < 0.1 < 2 24 0.04 to 0.12
36 36 5 34 to 38 < 80 < 220 1 < 0.1 < 2 27 0.04 to 0.12
39 39 2.5 37 to 41 < 90 < 500 1 < 0.1 < 5 30 0.04 to 0.12
43 43 2.5 40 to 46 < 90 < 600 0.5 < 0.1 < 5 33 0.04 to 0.12
47 47 2.5 44 to 50 < 110 < 700 0.5 < 0.1 < 5 36 0.04 to 0.12
51 51 2.5 48 to 54 < 125 < 700 0.5 < 0.1 < 10 39 0.04 to 0.12
56 56 2.5 52 to 60 < 135 < 1000 0.5 < 0.1 < 10 43 0.04 to 0.12
62 62 2.5 58 to 66 < 150 < 1000 0.5 < 0.1 < 10 47 0.04 to 0.12
68 68 2.5 64 to 72 < 200 < 1000 0.5 < 0.1 < 10 51 0.04 to 0.12
75 75 2.5 70 to 79 < 250 < 1500 0.5 < 0.1 < 10 56 0.04 to 0.12
1)
tp/T ≤ 100 ms, tighter tolerances available on request.
2)
at Tj = 150°C
VZ
2
Rev . A1: 12.12.1994
Page 3
TELEFUNKEN Semiconductors
)
)
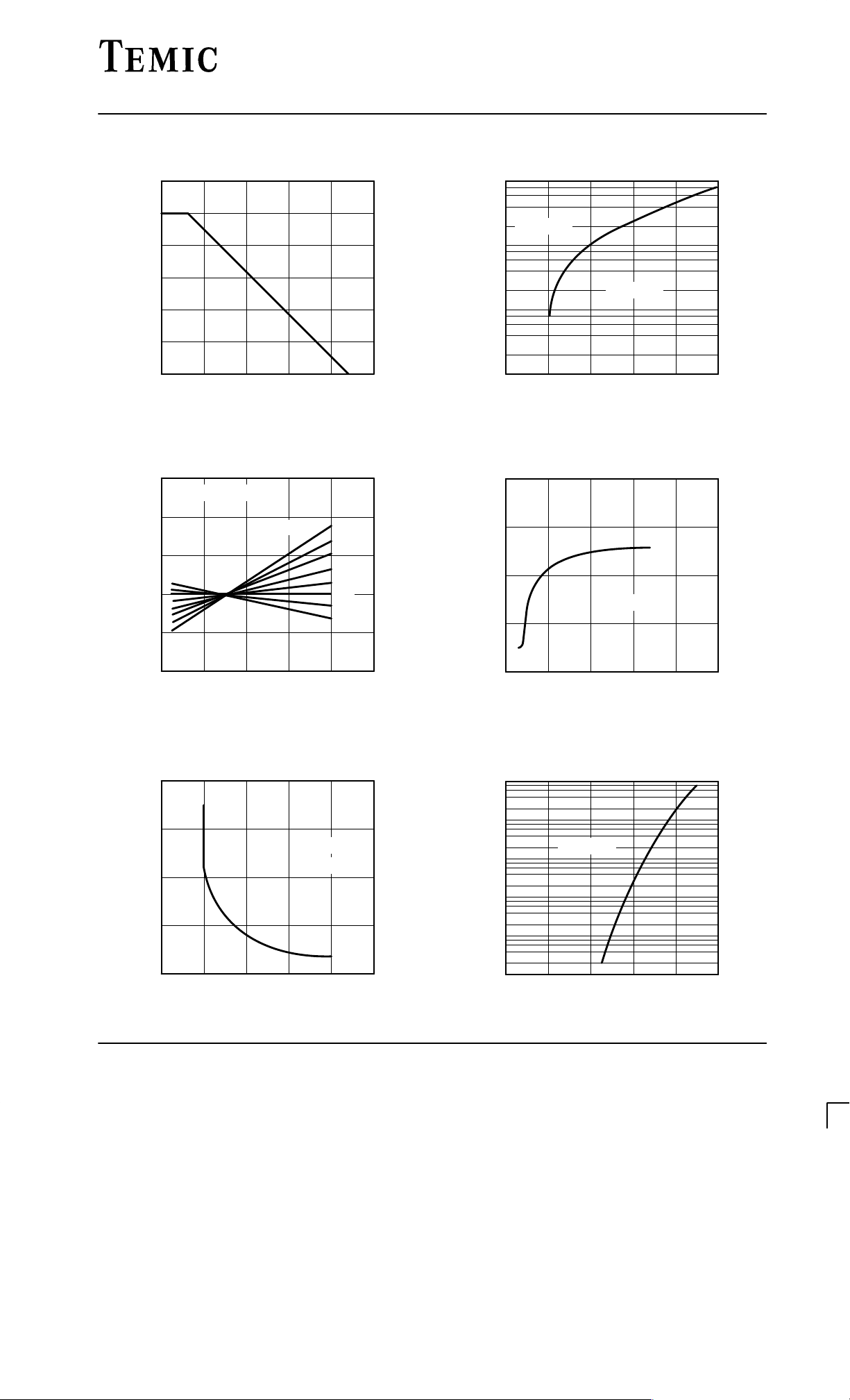
Typical Characteristics (Tj = 25C unless otherwise specified)
BZT55C...
600
500
400
300
200
100
tot
P – Total Power Dissipation ( mW )
0
200
95 9602
0 40 80 120 160
T
– Ambient Temperature ( °C
Figure 1 : Total Power Dissipation vs. Ambient Temperature
1.3
1.2
1.1
1.0
Ztn
0.9
V – Relative Voltage Change
V
Ztn=VZt/VZ
(25°C)
TKVZ=10 10–4/K
8 10–4/K
–4
6 10
4 10–4/K
–4
2 10
0
–2 10
–4 10
/K
/K
–4
/K
–4
/K
1000
Tj=25°C
100
IZ=5mA
10
Z
V – Voltage Change ( mV )
1
25
95 9598
0 5 10 15 20
V
– Z-Voltage ( V
Figure 2 : Typical Change of Working Voltage under Operating
Conditions at T
15
–4
Z
amb
=25C
10
5
IZ=5mA
0
0.8
–60 0 60 120 180
95 9599
Tj – Junction Temperature ( °C )
Figure 3 : Typical Change of Working Voltage vs. Junction
Temperature
200
150
VR=2V
Tj=25°C
100
50
D
C – Diode Capacitance ( pF )
0
95 9601
0 5 10 15
VZ – Z-Voltage ( V )
20
Figure 5 : Diode Capacitance vs. Z–Voltage
Rev . A1: 12.12.1994
240
25
VZ
–5
TK – Temperature Coefficient of V ( 10 /K )
95 9600
0102030
VZ – Z-Voltage ( V )
40
Figure 4 : Temperature Coefficient of Vz vs. Z–Voltage
100
10
Tj=25°C
1
0.1
F
I – Forward Current ( mA )
0.01
0.001
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8
95 9605
VF – Forward Voltage ( V )
Figure 6 : Forward Current vs. Forward Voltage
50
1.0
3
Page 4

BZT55C...
TELEFUNKEN Semiconductors
Z
I – Z-Current ( mA )
95 9604
W
100
80
P
T
60
40
20
0
04 81216
VZ – Z-Voltage ( V )
Figure 7 : Z–Current vs. Z–Voltage
1000
IZ=1mA
100
=500mW
tot
=25°C
amb
50
P
=500mW
40
tot
T
=25°C
amb
30
20
Z
I – Z-Current ( mA )
10
0
20
95 9607
15 20 25 30
VZ – Z-Voltage ( V )
35
Figure 8 : Z–Current vs. Z–Voltage
5mA
10mA
10
Z
r – Differential Z-Resistance ( )
1
0 5 10 15 20
95 9606
VZ – Z-Voltage ( V )
Figure 9 : Differential Z–Resistance vs. Z–Voltage
1000
tp/T=0.5
100
tp/T=0.2
10
tp/T=0.1
tp/T=0.02
tp/T=0.05
1
thp
Z – Thermal Resistance for Pulse Cond. (K/W)
–1
10
0
10
Tj=25°C
tp/T=0.01
25
Single Pulse
1
10
iZM=(–VZ+(V
2
+4rzjDT/Z
Z
R
=300K/W
thJA
DT=T
jmax–Tamb
1/2
)
)/(2rzj)
thp
2
10
tp – Pulse Length ( ms )95 9603
Figure 10 : Thermal Response
4
Rev . A1: 12.12.1994
Page 5

TELEFUNKEN Semiconductors
Dimensions in mm
technical drawings
according to DIN
specifications
94 9372
BZT55C...
Cathode Identification
Quadro MELF
Glass Case similar to
JEDEC DO 213 AA
0.35
0.30
3.7
3.3
0.35
0.30
1.5
1.3
Rev . A1: 12.12.1994
5
Page 6

BZT55C...
TELEFUNKEN Semiconductors
OZONE DEPLETING SUBSTANCES POLICY STATEMENT
It is the policy of TEMIC TELEFUNKEN microelectronic GmbH to
1. Meet all present and future national and international statutory requirements and
2. Regularly and continuously improve the performance of our products, processes, distribution and operating systems
with respect to their impact on the health and safety of our employees and the public, as well as their impact on the
environment.
Of particular concern is the control or elimination of releases into the atmosphere of those substances which are known
as ozone depleting substances (ODSs).
The Montreal Protocol (1987) and its London Amendments (1990) will soon severely restrict the use of ODSs and forbid
their use within the next ten years. Various national and international initiatives are pressing for an earlier ban on these
substances.
TEMIC TELEFUNKEN microelectronic GmbH semiconductor division has been able to use its policy of continuous
improvements to eliminate the use of any ODSs listed in the following documents.
1. Annex A, B and list of transitional substances of the Montreal Protocol and the London Amendments respectively
2. Class I and II ozone depleting substances in the Clean Air Act Amendments of 1990 by the Environmental Protection
Agency (EPA) in the USA and
3. Council Decision 88/540/EEC and 91/690/EEC Annex A, B and C (transitional substances) respectively .
TEMIC can certify that our semiconductors are not manufactured with and do not contain ozone depleting substances.
We reserve the right to make changes to improve technical design without further notice.
Parameters can vary in different applications. All operating parameters must be validated for each customer
application by the customer. Should the buyer use TEMIC products for any unintended or unauthorized application,
the buyer shall indemnify TEMIC against all claims, costs, damages, and expenses, arising out of, directly or
indirectly , any claim of personal damage, injury or death associated with such unintended or unauthorized use.
TEMIC TELEFUNKEN microelectronic GmbH, P.O.B. 3535, D-74025 Heilbronn, Germany
Telephone: 49 (0)7131 67 2831, Fax Number: 49 (0)7131 67 2423
6
Rev . A1: 12.12.1994
Page 7

WWW.ALLDATASHEET.COM
Copyright © Each Manufacturing Company.
All Datasheets cannot be modified without permission.
This datasheet has been download from :
www.AllDataSheet.com
100% Free DataSheet Search Site.
Free Download.
No Register.
Fast Search System.
www.AllDataSheet.com
 Loading...
Loading...