Page 1

Automatic Call Distribution (ACD)
SYSTEM MANUAL
76-110-0430/E Release 5 Issue 2
Page 2

76-110-0430/E
Release 5
Issue 2
Automatic Call Distribution (ACD)
SYSTEM MANUAL
Telrad Telecommunications Inc.
Farmingdale, N.Y.
Page 3

76-110-0430/E
Release 5
Issue 2
Telrad Telecommunications Inc.
Farmingdale, N.Y.
Page 4

NOTICE
This publication refers to Telrad Connegy’s Automatic Call Distribution (ACD) package
running on Telrad Connegy’s UNITe IP systems, Releases SB-3 and up, as of May, 1997.
Additional copies of this manual may be obtained from Telrad Connegy, Inc. Reproduction of
this manual or parts thereof, without written permission from Telrad Connegy, Inc., is strictly
prohibited.
Telrad Connegy reserves the right to modify the equipment and the software described herein
without prior notice. However, changes made to the equipment or to the software described
herein do not necessarily render this publication invalid.
Telrad Connegy IMAGEN is a registered trademark of Telrad Connegy, Inc.
ACD I.Q. is a proprietary trademark of Telrad Connegy, Inc.
1997, 2005 Telrad Connegy, Inc.
Farmingdale, New York
ב
Page 5

CONTENTS
CONTENTS
Section 1 INTRODUCTION.......................................................................................................1-1
1.1 CONTENTS OF THIS MANUAL ........................................................................................1-1
1.2 PRODUCT DEFINITION..................................................................................................... 1-1
1.2.1 General.....................................................................................................................................1-1
1.2.2 ACD integration with Telrad Connegy's UNITe IP systems ......................................................1-2
1.2.3 ACD I.Q. ...................................................................................................................................1-2
1.2.4 ACD integration with Telrad Connegy IMAGEN......................................................................1-2
1.3 SCOPE OF THE MANUAL................................................................................................. 1-3
1.4 STRUCTURE OF THE MANUAL ....................................................................................... 1-3
1.5 FOR WHOM IS THIS MANUAL INTENDED?.................................................................... 1-4
1.6 RELATED DOCUMENTATION .......................................................................................... 1-4
1.7 TYPOGRAPHIC CONVENTIONS ...................................................................................... 1-4
1.8 ACD FOR UNITe IP AND FOR UNITe IP 400.................................................................... 1-4
1.9 SYSTEM DEFINITION........................................................................................................ 1-5
1.9.1 General.....................................................................................................................................1-5
1.9.2 ACD environment.....................................................................................................................1-5
1.9.3 Basic ACD principles .................................................................................................................1-5
1.9.4 Path of an ACD call (example)..................................................................................................1-6
1.10HOW THE ACD DEALS WITH TRAFFIC LOADS.............................................................. 1-9
1.10.1 General.....................................................................................................................................1-9
1.10.2 Overflow...................................................................................................................................1-9
1.10.3 Interflow ...................................................................................................................................1-9
1.10.4 Thresholds ..............................................................................................................................1-10
1.11 THE ROLE OF THE AGENT............................................................................................ 1-11
1.12 THE ROLE OF THE SUPERVISOR ................................................................................. 1-11
1.12.1 Agent supervision...................................................................................................................1-12
1.1.2 ACD queue supervision..........................................................................................................1-14
1.1.3 Diagnosing extremes in call traffic..........................................................................................1-15
ג
Page 6

76-110-0430/E
1.13 ACD I.Q............................................................................................................................ 1-15
1.14 Telrad Connegy's IMAGEN ............................................................................................ 1-16
Section 2 ACD FEATURES........................................................................................................ 2-1
2.1 GENERAL.......................................................................................................................... 2-1
2.2 LIST OF ACD FEATURES................................................................................................. 2-1
Section 3 ACD SYSTEM FEATURES .......................................................................................... 3-1
3.1 GENERAL.......................................................................................................................... 3-1
3.2 LIST OF SYSTEM FEATURES.......................................................................................... 3-1
3.3 SYSTEM FEATURE EXPLANATIONS.............................................................................. 3-1
3.3.1 ACD groups..............................................................................................................................3-1
3.3.2 ACD routing plans....................................................................................................................3-2
3.3.3 ACD queues .............................................................................................................................3-2
3.3.4 Announcer plan........................................................................................................................3-3
3.3.5 Call routing ...............................................................................................................................3-4
3.3.6 Interflow ...................................................................................................................................3-4
3.3.7 Level Of Service (LOS) time .......................................................................................................3-4
3.3.8 Overflow program ....................................................................................................................3-5
3.3.9 Priority queueing.......................................................................................................................3-6
3.3.10 Ringback delay to answer time ................................................................................................3-6
3.3.11 SLT announcer..........................................................................................................................3-6
3.3.12 Statistics time............................................................................................................................3-6
3.3.13 Thresholds ................................................................................................................................3-7
Section 4 ACD AGENT FEATURES............................................................................................ 4-1
4.1 GENERAL.......................................................................................................................... 4-1
4.2 LIST OF AGENT FEATURES............................................................................................ 4-1
4.3 AGENT FEATURE EXPLANATIONS................................................................................ 4-1
4.3.1 [ACD QUEUE] button ..............................................................................................................4-1
4.3.2 Busy wrap up ...........................................................................................................................4-2
4.3.3 Forced busy state .....................................................................................................................4-2
4.3.4 Headset ....................................................................................................................................4-2
4.3.5 Help request and Help conference ..........................................................................................4-3
4.3.6 Login status LED ......................................................................................................................4-3
4.3.7 Not available.............................................................................................................................4-3
4.3.8 Programmable buttons ............................................................................................................4-4
4.3.9 Record calls (Telrad Connegy IMAGEN application).................................................................4-4
ד
Page 7

CONTENTS
Section 5 ACD SUPERVISOR FEATURES....................................................................................5-1
5.1 GENERAL .......................................................................................................................... 5-1
5.2 LIST OF SUPERVISOR FEATURES ................................................................................. 5-1
5.3 SUPERVISOR FEATURE EXPLANATIONS ..................................................................... 5-1
5.3.1 [ACD QUEUE] button ..............................................................................................................5-1
5.3.2 Agent status display.................................................................................................................5-2
5.3.3 Display mode toggle ................................................................................................................5-2
5.3.4 Monitoring and advising agents ..............................................................................................5-2
5.3.5 Monitoring the status of queues .............................................................................................5-3
5.3.6 Programmable buttons ............................................................................................................5-3
5.3.7 Softkey operation .....................................................................................................................5-3
Section 6 INSTALLATION, CONFIGURATION AND UPGRADING OF THE ACD...........................6-1
6.1 GENERAL .......................................................................................................................... 6-1
6.2 INSTALLING AND CONFIGURING A NEW UNITe IP SYSTEM WITH ACD.................... 6-1
6.3 UPGRADING AND CONFIGURING AN EXISTING UNITe IP SYSTEM WITH ACD ........ 6-2
6.3.1 General.....................................................................................................................................6-2
6.3.2 Upgrade steps (hardware and software)..................................................................................6-2
Section 7 ACD PROGRAMMING PARAMETERS .........................................................................7-1
7.1 GENERAL .......................................................................................................................... 7-1
7.2 WORKING WITH THE ADMINISTRATION PROGRAM................................................... 7-1
7.3 STEPS FOR PLANNING THE ACD CONFIGURATION ................................................... 7-1
7.4 PROGRAMMING THE PARAMETERS .............................................................................7-2
7.5 THE AUTOMATIC CALL DISTRIBUTION MENU .............................................................7-2
7.5.1 General ACD parameters CD→AP ...........................................................................................7-3
7.5.2 ACD groups CD→GR ...............................................................................................................7-3
7.5.3 Supervisor and ACD Groups CD→SV.......................................................................................7-6
7.5.4 ACD Routing plans CD→PL .....................................................................................................7-7
7.5.5 Announcer plans CD→NP .......................................................................................................7-9
7.6 RELATED SYSTEM CONFIGURATION PARAMETERS................................................ 7-11
ה
Page 8

76-110-0430/E
7.7 RECORDING THE ANNOUNCER MESSAGES.............................................................. 7-13
7.7.1 General...................................................................................................................................7-13
7.7.2 Programming announcer messages via Telrad Connegy IMAGEN........................................7-13
7.7.3 Programming announcer messages using SLT announcers...................................................7-13
7.8 CONFIGURING THE ACD I.Q. ........................................................................................ 7-14
Appendix A ACD PROGRAMMING FORMS .............................................................................. A-1
A.1 GENERAL..........................................................................................................................A-1
FIGURES
Figure 1-1 Sample ACD system .............................................................................................. 1-6
Figure 1-2 ACD call progress .................................................................................................. 1-7
Figure 1-3 ACD overflow, interflow and threshold programming...................................... 1-11
Figure 1-4 AGENTS STATUS Screen .................................................................................... 1-13
Figure 1-5 AGENT DATA Screen........................................................................................... 1-13
Figure 1-6 QUEUE STATISTICS Screen................................................................................ 1-14
Figure 1-7 Telrad Connegy IMAGEN recorded announcement program .......................... 1-17
Figure 4-1 Recommended agent button arrangement - Speakerphone set....................... 4-4
Figure 5-1 Supervisor station recommended programmable button layout ...................... 5-4
TABLES
Table 1-1 Comparison of UNITe IP and UNITe IP 400 specifications................................... 1-5
Table 1-2 Threshold flash rates ............................................................................................ 1-10
Table 4-1 Agent programmable buttons ................................................................................ 4-4
Table 5-1 Supervisor programmable buttons........................................................................ 5-3
ו
Page 9
INTRODUCTION
1.1 CONTENTS OF THIS MANUAL
This manual describes the Automatic Call Distribution (ACD)
package for the Telrad Connegy UNITe IP family of systems. It
applies both to the UNITe IP system, and to the UNITe IP 400
system.
The manual describes the installation, upgrading, programming
and maintenance of the ACD hardware and software. It lists and
explains the main agent, supervisor and system ACD features. It
also describes the environment in which ACD is used, and the
tasks of the agents and supervisor operating the ACD.
The appendix to this manual contains programming forms for
planning and updating the software configuration of the ACD.
Section 1
1.2 PRODUCT DEFINITION
1.2.1 General
Automatic Call Distribution (ACD) optimizes the distribution of
incoming calls so that incoming callers receive prompt service, and
so that the burden of answering calls is distributed evenly among
ACD agents.
ACD routes incoming calls to separate call queues, normally
reflecting different company departments, e.g. sales, billing,
customer inquiries etc. Each call queue is serviced by a group of
agents whose task is to answer the calls reaching the department.
In the event of a call queue being overloaded, calls can be
overflowed to less busy or idle queues and agents.
ACD supervisors oversee the operation of the ACD system and
agents. The supervisors can view online statistical information
concerning the status of the call queues and agents.
1-1
Page 10

76-110-0430/E
1.2.2 ACD integration with Telrad Connegy's UNITe IP
systems
ACD configuration is performed via the UNITe IP system
configuration programming. Agents and supervisors use regular
UNITe IP telephones. The ACD package requires a special
software cartridge on the Main Control card of the system. The
ACD I.Q. computer (see below) connects to a UNITe IP telephone
via a data adapter card.
1.2.3 ACD I.Q.
ACD I.Q. is an optional, Personal computer-based reports software
program which provides, online, detailed graphic and numeric call
traffic information concerning the ACD. The information is based on
up to two months of call traffic data which the ACD I.Q. computer
stores. The reports can be displayed on screen, or sent to a printer.
Reports can be generated on a per hour or per day cross-section.
ACD I.Q. enables the ACD supervisor to detect online peaks and
troughs in call traffic, and to plan the most cost-efficient agent and
supervisor manning levels.
For more information on ACD I.Q. refer to the UNITe IP system
ACD I.Q. System manual.
1.2.4 ACD integration with Telrad Connegy IMAGEN
ACD can make use of two Telrad Connegy IMAGEN facilities.
First, calls handled by agents or supervisors can be recorded into
an IVM mailbox, by pressing a programmed
telephone set. The call is recorded in the mailbox assigned to the
telephone extension.
Secondly, the Telrad Connegy IMAGEN can be used to record up
to nine announcements. These announcements are played to
callers waiting in queue. The announcements can be chained and
repeated any number of times as part of an Announcer plan.
For more details of these facilities, refer to the Telrad Connegy
IMAGEN System manual.
Announcer plans can also be constructed using analog SLT
announcers.
[RECORD] button on the
1.3 SCOPE OF THE MANUAL
This manual contains all information concerning the ACD, except
for agent and supervisor operating instructions.
Topics covered in this manual include:
1-2
Page 11

• Descriptions of ACD system, agent and supervisor features;
• Installation instructions for installing ACD on a new UNITe IP
system;
• Upgrading instructions, for installing ACD into an existing
UNITe IP system;
• Programming instructions for new and upgraded systems;
• Instructions for incorporating recorded announcements using
Telrad Connegy IMAGEN and SLT announcers.
1.4 STRUCTURE OF THE MANUAL
This manual is divided into the following sections:
Section 1: Introduction This section introduces the ACD and
describes the contents of the manual.
Section 2: ACD Features This section lists the system, agent and
supervisor features.
Section 3: ACD System Features This section lists and describes
the ACD system features.
Section 1: INTRODUCTION
Section 4: ACD Agent Features This section lists and describes
the ACD agent features.
Section 5: ACD Supervisor Features This section lists and
describes the ACD supervisor features.
Section 6: Installation, Configuration and Upgrading of the ACD
This section includes instructions for installing ACD on a new
UNITe IP system, and for enhancing an existing UNITe IP system
with ACD.
Section 7: ACD Programming Parameters This section provides a
field by field description of the parameters to be programmed in the
UNITe IP system configuration program, when configuring ACD.
Appendix A: ACD Programming Forms Appendix A contains the
programming forms required for planning and updating the ACD
configuration.
1-3
Page 12

76-110-0430/E
1.5 FOR WHOM IS THIS MANUAL INTENDED?
This manual serves two groups of personnel:
• Marketing personnel, system administrators and ACD
supervisors concerned with fully exploiting ACD features to
configure a system of maximum efficiency (see Sections 1
through 5).
• Technicians installing, programming and upgrading the ACD
system (see Sections 6 and onwards).
1.6 RELATED DOCUMENTATION
The following UNITe IP systems documentation publications
contain information relevant to ACD:
• ACD Agent Guide (Cat. No. 76-110-0425/E);
• ACD Supervisor's User Guide (Cat. No. 76-110-0440/E);
• ACD I.Q. System manual (Cat. No. 76-110-0675/E);
• Installation manual (Cat. No. 76-110-0410/E);
• Administration manual (Cat. No. 76-110-0175/E);
• Telrad Connegy IMAGEN System manual (Cat. No. 83-130-
8050/H);
• Software cartridge Installation Instructions
(Cat. No. 76-110-0115/E).
1.7 TYPOGRAPHIC CONVENTIONS
The following typographic conventions are used in this manual.
• Buttons on the telephone appear like this:
• Softkeys on the supervisor's telephone appear like this:
{<MONITOR>}.
1.8 ACD FOR UNITe IP AND FOR UNITe IP 400
The ACD packages for UNITe IP and UNITe IP 400 systems are
virtually identical.
They differ only in the following specifications (see Table 1-1,
below).
[HELP REQUEST].
1-4
Page 13
1.9 SYSTEM DEFINITION
1.9.1 General
Section 1: INTRODUCTION
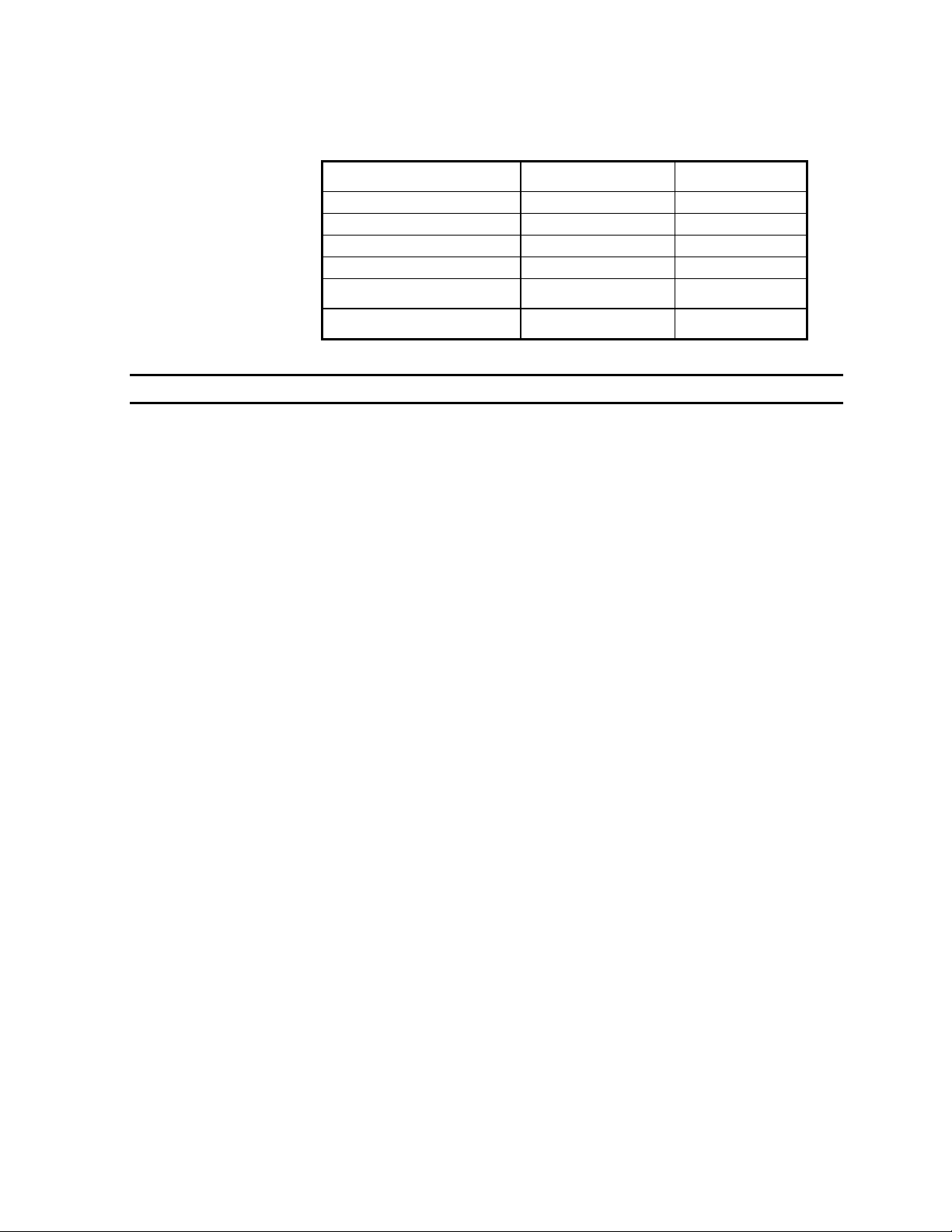
Table 1-1 Comparison of UNITe IP and UNITe IP 400
specifications
Parameter UNITe IP UNITe IP 400
ACD groups 16 24
Agents in system 160 300
ACD routing plans 32 48
Supervisors 8 16
Groups per supervisor 16 24
Supervisors per group 8 16
The rest of this section describes the ACD in detail. It explains and
gives examples of how the ACD works, and describes the roles of
the agent and supervisor.
Many of the terms used in this section are explained in more detail
in Sections 3, 4 and 5.
1.9.2 ACD
environment
ACD increases the efficiency of businesses which handle large
amounts of incoming call traffic. It enables businesses to provide
better and faster service, while saving resources.
The ACD package is especially effective for companies which
expend significant resources on manning telephone answering
positions e.g. for accepting orders (such as travel agents and
warehouses), and for offices which provide information (such as
train or bus time-tables).
1.9.3 Basic ACD principles
This section describes the basic stages a call routed via ACD goes
through.
1. A call arrives at the UNITe IP system.
2. The call is routed via ACD to the requested department,
3. The incoming call enters the department call queue and is
according to the number dialed.
queued according to the queue priority, programmed in system
programming.
4. The call is answered by the first agent servicing the department
queue, who becomes available.
1-5
Page 14
76-110-0430/E
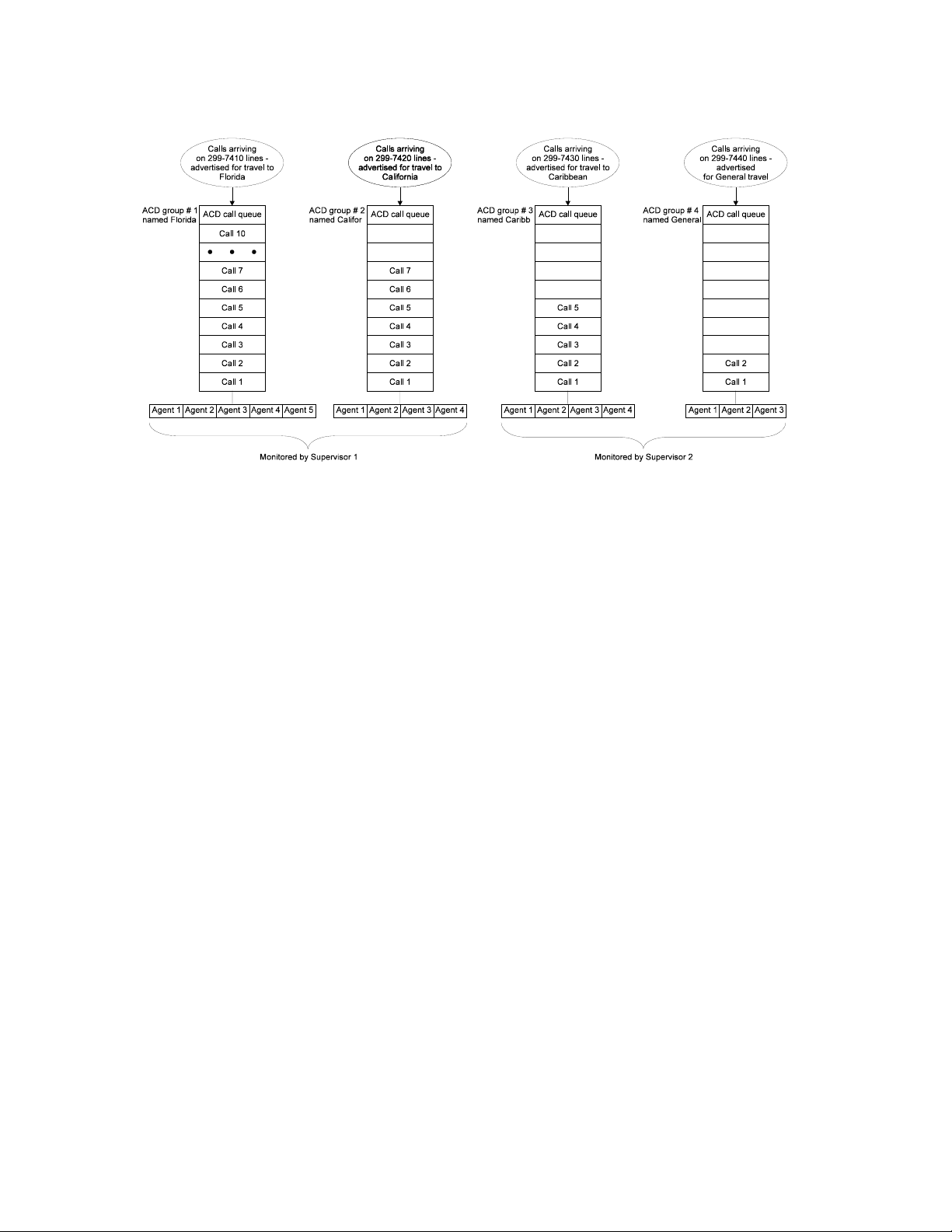
Figure 1-1 illustrates a sample ACD system.
Figure 1-1 Sample ACD system
1.9.4 Path of an ACD call (example)
The following sections describe the route an ACD call takes, from
the time it arrives at a fictitious travel agent's ACD system, until
answered by the agents. This description should help illustrate the
various elements in the ACD system:
• from the point of view of the caller;
• from the point of view of the ACD agent.
Figure 1-2, below, illustrates the progress of an ACD call in the
system.
Incoming ACD call path (caller's viewpoint)
1. The
2. The call may either be routed directly to the ACD group (the
caller dials the telephone number of the company with the
ACD system; the caller hears ringback tone.
caller hears ring tone), or, after a brief ringing period, it may be
answered by an announcer or Voice mail system.
The recorded announcement will say something like “Hello, you
have reached the Fly-with-us travel agency. Please hold.
Someone will be right with you”.
1-6
3. Next the caller hears either Music on Hold or a ring tone; the
call may be answered by an ACD agent at any time.
Page 15
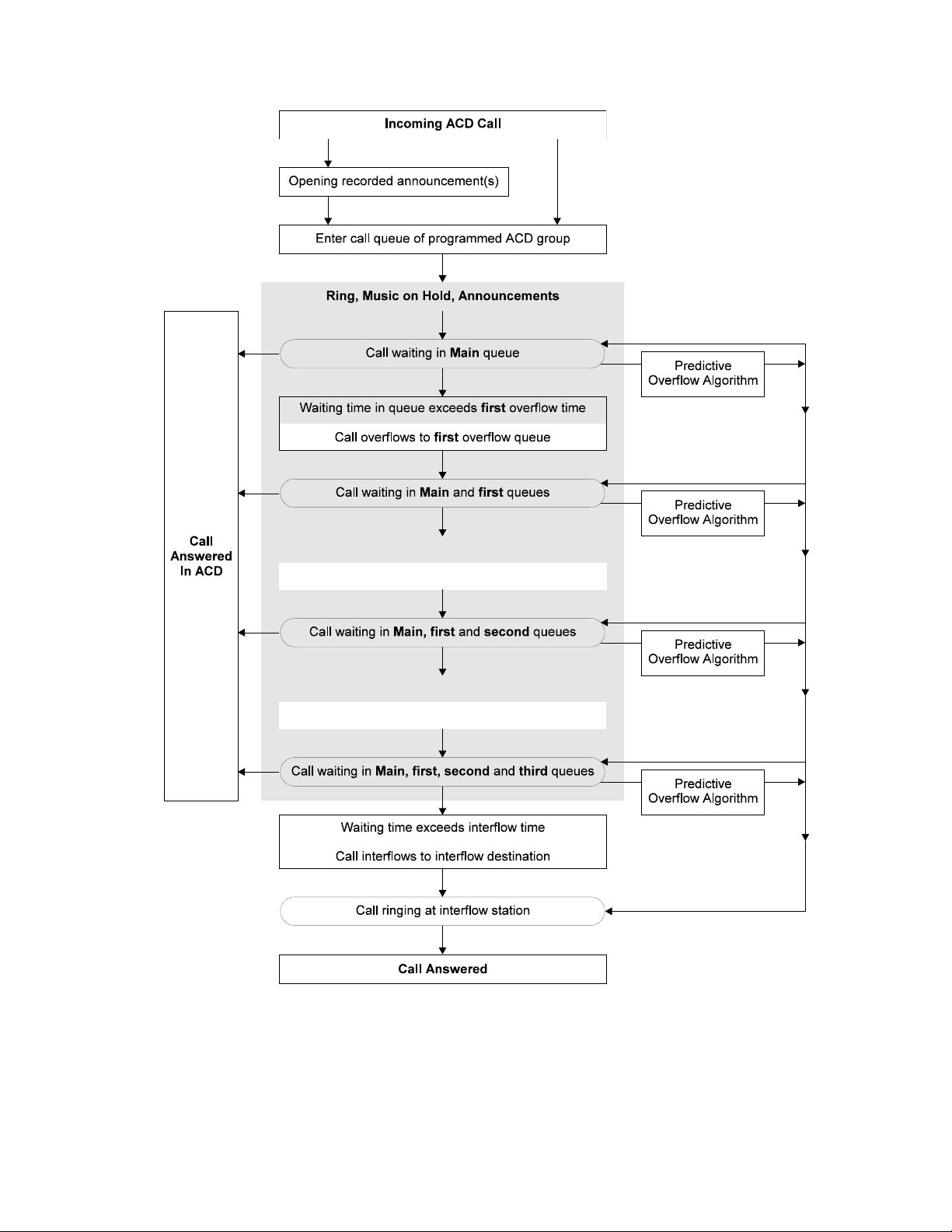
Section 1: INTRODUCTION
Figure 1-2 ACD call progress
1-7
Page 16

76-110-0430/E
4. If, after a timeout elapses, the call has not been answered, the
caller may hear a new recorded announcement saying
something like, “Fly-with-us Travel Agency is still busy. Please
hold on for a little longer”.
The
caller then hears either Music on Hold or ring tone, as in
Step 3, above.
5. The caller may hear the above announcement repeated, or
other announcements in its place, as time elapses.
6. Without the caller being aware of it, the call may be overflowed
to additional ACD queues.
If the call is not answered by any of the agents in the original
and overflow ACD queues, the call may be forwarded to an
interflow destination.
7. The call is answered.
The call may be answered during any of the above steps.
Incoming call path (system viewpoint)
1. An incoming call is received; the call is routed, according to the
ACD Route plan, to the ACD group where it is to be answered.
This group is called the Main group.
• The call will either ring, or be answered by an announcer.
The announcement is followed by ring tone or Music on
hold, and optionally, by further recorded announcements.
• When an agent becomes available, the call will ring the
agent's station.
2. If the call is not answered at the ACD Main queue within a
certain timeout (if, for example, all the agents are busy), ACD
can use two call routing mechanisms to increase the likelihood
of the call being answered. These two mechanisms are:
• overflow (see Section 1.10.2, below)
• interflow (see Section 1.10.3, below)
3. If the call is overflowed to one or more ACD groups, the first
agent to become available in either the Main group or any of
the overflow groups, will receive a ring and can answer the call.
If the call is not answered within the interflow time, the call exits
the ACD and is sent to the interflow destination.
1-8
Page 17

1.10 HOW THE ACD DEALS WITH TRAFFIC LOADS
1.10.1 General
The ACD uses two mechanisms, overflow and interflow, for
ensuring that calls entering the ACD will be answered, and
employs various tools, such as the
indications, to warn the ACD agents and supervisors of extremes in
call traffic.
1.10.2 Overflow
An overflow timeout is defined per ACD routing plan for the Main
ACD group queue, and also for up to two other overflow queues.
Overflow is illustrated in, Figure 1-2 above, and Figure 1-3, below.
If the overflow timeout of the Main queue elapses before a call on
queue is answered, the call is placed in the first overflow queue
while still continuing to wait in the original Main queue. If the
second overflow timeout elapses, the call waits in the Main queue,
and in the first and second overflow queues. If the third overflow
timeout elapses, the call waits in the Main queue, and also in the
first, second and third overflow queues.
Section 1: INTRODUCTION
[ACD QUEUE] button LED
1.10.3 Interflow
As with the Main ACD queue, the system programmer can specify
the priority which a call will have in each of the overflow queues.
The first agent to become available to answer the call in either the
Main queue or any of the overflow queues, receives the call. When
the call is answered it stops waiting in all queues.
In system programming the overflow can be assigned a predictive
overflow mechanism, which estimates how long the call will wait
before being answered. Based on this calculation, the ACD may
send overflow ringing to the overflow queues before the overflow
timeouts elapse.
A second mechanism for ensuring that calls are answered is
Interflow. Interflow is illustrated in Figure 1-2, above, and
Figure 1-3, below.
Interflow is a sort of "no answer forward" destination for ACD calls.
If a call waits in queue until after the interflow timeout elapses, or if
no agents are ready in the Main ACD group and all overflow
groups, the call is disconnected from the ACD environment and
forwarded to a different destination (an attendant position,
Incoming Call Identifier (ICI) queue or Hunt group). The call will
then be answered outside the ACD.
1-9
Page 18
76-110-0430/E
1.10.4 Thresholds
[ACD QUEUE] button LED gives an indication of the status of the
The
ACD queue. The LED flash rate indicates whether calls are waiting
in queue (i.e. not ringing agent stations), and how long calls have
been waiting in queue - before a defined first threshold time,
between a first and second threshold time, or beyond a second
threshold time (see Figure 1-3, below). The threshold times are
programmed in the UNITe IP configuration program.
By watching the
[ACD QUEUE] button LED, agents and supervisors
can see at a glance the status of the ACD queue.
The LED color and statuses are as described in Table 1-2, below.
The threshold times are defined in system programming for each
ACD group.
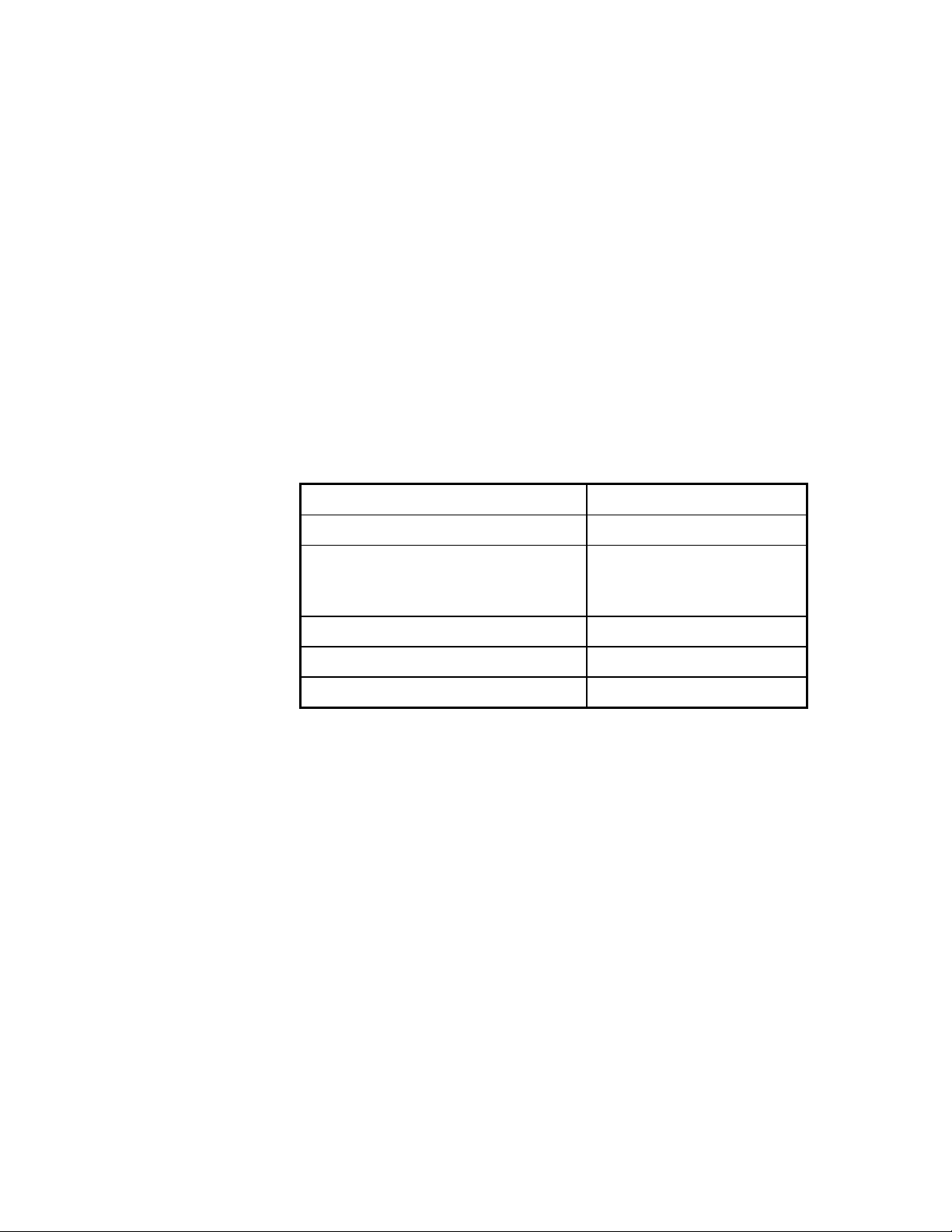
Table 1-2 Threshold flash rates
Queue status LED status
No calls in queue LED extinguished
Call ringing agent(s): No calls in queue
At ringing agent(s)
At idle agents
Before first threshold Green slow flash
Between first and second threshold Red slow flash
Past second threshold Red fast flash
Green slow flash
LED extinguished
Figure 1-3, below, shows the programmed overflow, interflow and
threshold parameters of a sample system, based on the following
programmed parameters:
1-10
• First Overflow Time: 20 seconds;
• Second Overflow Time: 20 seconds;
• Third Overflow Time: 20 seconds;
• Interflow Time: 90 seconds
• First Threshold Time: 30 seconds;
• Second Threshold Time: 70 seconds.
Note that the interflow time should be greater than the sum total of
the overflow times.
Page 19

Figure 1-3 ACD overflow, interflow and threshold programming
1.11 THE ROLE OF THE AGENT
Individual agents operate within groups of agents. Each group
services a single queue of calls and may be supervised by one or
more supervisors. The agents work together, to answer the calls
directed to their department queue.
Section 1: INTRODUCTION
To log in, the agent dials a Feature code or a Flexible Numbering
Plan (FNP) code, followed by an agent ID code (one to four digits).
Each agent also has a name (seven characters) for display
purposes. Note that an agent can log in to only one group at a time.
Any UNITe IP telephone may be used as an ACD agent station.
Telrad Connegy analog telephones and SLTs cannot serve as ACD
stations. The recommended agent station is the Display
Speakerphone set, with headset.
1.12 THE ROLE OF THE SUPERVISOR
The supervisor follows the call traffic and agent information which
is displayed on the supervisor's telephone display. The supervisor
can view a series of MAIN Screens which give an overall picture of
the state of the agents and queues, and can also select detailed
screens, which focus on a particular queue or agent.
1-11
Page 20

76-110-0430/E
1.12.1 Agent supervision
The supervisor's main tasks are:
• Supervising agents, monitoring agents calls and responding to
agents' requests for help;
• Supervising ACD queues and call traffic, and managing ACD
resources.
The supervisor uses an Executive station with expanded display.
The telephone display can be toggled between regular Display
mode and Supervisor Display mode. The screens described in this
manual are all from the Supervisor Display mode.
The supervisor uses the telephone's softkeys to move from screen
to screen.
The supervisor uses the information displayed on her telephone to
supervise the work of the agents. The supervisor can listen to any
agent calls, and can check the statistics provided by the ACD on
the agent's work performance.
The supervisor can monitor (i.e. listen to) agents' calls. When the
need arises, the supervisor can advise (i.e. provide guidance and
assistance to agents faced with unfamiliar situations), and even set
up three-way conference calls between the agent, the outside party
and the supervisor.
The supervisor is also available to respond to agents' requests for
help. For this reason, supervisors are often experienced agents.
In addition to general data appearing on the supervisor MAIN
Screen, the supervisor can view two detailed agent information
screens:
• AGENT STATUS Screen;
• AGENT DATA Screen.
AGENTS STATUS Screen The AGENT STATUS Screen (see,
Figure 1-4, below) displays the following information:
• Number of ACD calls processed by the agent since login;
• Number of ACD calls processed per hour;
• Current agent state.
Possible agent states are:
1-12
• Logged out;
• Available to receive ACD calls;
• ACD call;
• ACD ring;
• Non-ACD call;
• Not available;
Page 21

Section 1: INTRODUCTION
• Busy wrap up;
• Not ready;
• Forced busy.
Figure 1-4 AGENTS STATUS Screen
AGENT DATA Screen The AGENT DATA Screen (see
Figure 1-5, below) displays the following information:
• Agent name, code, DN;
• Current agent state;
• Login time and time period since login;
• Number of ACD calls since login and average call duration;
• Number of non-ACD calls since login and average call duration;
• Number of times agents station was in forced busy;
• Totals of busy wrap up time, Not available time and free time;
• Busy wrap up time, Not available time and free time, as
percentages of the login period.
Figure 1-5 AGENT DATA Screen
The supervisor refers to these screens to view the status of the
agents in the queue. By viewing the statistics displayed here, the
supervisor can draw many practical conclusions such as the agent
is underworked, overworked or spending too much time on private
calls.
1-13
Page 22

76-110-0430/E
Then the supervisor might recommend that:
• less busy agents help out temporarily with the call load in busy
queues;
• appropriate adjustments in the manning levels of queues be
implemented;
• changes be made to overflow and interflow timeouts and
programs.
1.12.2 ACD queue supervision
The supervisor can see, on the supervisor MAIN Screens and in a
detailed QUEUES STATISTICS Screen, a wide range of detailed
information concerning the operation of the ACD queue.
The information provided in the QUEUE STATISTICS Screen (see
Figure 1-6, below) includes, for each queue:
• Number of calls routed to the queue;
• Number of calls answered by agents in the group;
• Number of calls routed to the queue that were abandoned (i.e.
the caller hung up before being answered);
• Number of calls overflowed to other ACD groups;
• Number of routed calls which were interflowed;
• Number of calls overflowed to the ACD group;
• Average wait time of answered calls;
• Average time callers hang on before abandoning calls.
1-14
Figure 1-6 QUEUE STATISTICS Screen
The supervisor refers to this screen to view the status of the queue.
By viewing the statistics displayed here, the supervisor can draw
many practical conclusions.
Page 23

For example, in the Marketing department queue, if the number of
abandoned calls rises, the supervisor can recommend:
• Adding agents to the Marketing department queue;
• Adding agents to other queues which overflow to the Marketing
department;
• Changing the ACD routing plan so that other queues do not
overflow to the Marketing department queue;
• Modifying the system answering message, requesting callers to
wait patiently;
• Adding a series of recorded announcements to keep up the
caller's expectation of being quickly answered.
The information available to the supervisor is described in detail in
the Supervisor User Guide.
1.12.3 Diagnosing extremes in call traffic
The supervisor can check the parameters listed below for each
ACD group (viewed in the supervisor Display mode), to ensure that
they remain within reasonable upper and lower limits:
Section 1: INTRODUCTION
1.13 ACD I.Q.
• Number of waiting calls;
• Average wait time;
• Number of abandoned calls;
• Number of overflowed calls;
• Number of interflow calls;
• Level of Service.
Telrad Connegy has developed a PC-based Management
Information System (MIS) program called ACD I.Q. which displays
online, in both graphic and numeric form, the agents and queue
status. ACD I.Q. stores all the call traffic information two months
back and can print both graphic and numeric reports of call traffic,
agent information and queue information for any period during the
previous two months.
ACD I.Q. provides the supervisor with a simple and powerful tool
for monitoring system operation, over extended periods of time.
The ACD I.Q. will help the supervisor to plan precisely the most
cost-effective ACD configuration.
More information on ACD I.Q. can be found in the UNITe IP
Product Description, System Description, and in the ACD I.Q.
System manual.
1-15
Page 24

76-110-0430/E
1.14 Telrad Connegy IMAGEN
Telrad Connegy IMAGEN is Telrad Connegy's Integrated Voice
Mail system. ACD makes use of the IVM feature called Recorded
Announcements. The Telrad Connegy IMAGEN administrator
records up to nine recorded announcements. These can be played
to a caller waiting on hold in the ACD system until the call is
answered.
The system supports 50 allocations of announcements. The
announcements may come from the Telrad Connegy IMAGEN
Recorded Announcements, or from SLT announcers. Each
recorded announcement can be repeated any number of times and
can be incorporated in all Announcer plans.
Figure 1-7, below, depicts a Telrad Connegy IMAGEN-based
Announcer program of a fictitious travel agency.
The Telrad Connegy IMAGEN features and services are described
in detail in the Telrad Connegy IMAGEN System manual and User
guides.
For programming of recorded announcements in the ACD routing
plan, refer to Section 7.5.5, below.
1-16
Page 25

Section 1: INTRODUCTION
Figure 1-7 Telrad Connegy IMAGEN recorded announcement program
1-17
Page 26

76-110-0430/E
THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK
1-18
Page 27

2.1 GENERAL
This section provides an alphabetical list of ACD system, agent and
supervisor features. These features are described in detail in
Sections 3, 4 and 5, respectively.
2.2 LIST OF ACD FEATURES
System features
• ACD groups;
• ACD routing plans;
• ACD queues;
• Announcer plan;
• Call routing;
• Interflow;
• Level Of Service (LOS) time;
• MIS (Management Information System) - ACD I.Q.;
• Overflow program;
• Priority queueing;
• Ring delay to answer time;
• SLT announcer;
• Statistics time;
• Thresholds.
Section 2
ACD FEATURES
Agent features
•
[ACD QUEUE] button;
• Busy wrap up;
• Forced busy state;
• Headset;
• Help request and Help conference;
• Login status LED;
• Not available;
• Programmable buttons;
• Record calls.
2-1
Page 28

76-110-0430/E
Supervisor features
[ACD QUEUE] button;
•
• Agent status display;
• Display mode toggle;
• Monitoring and advising agents;
• Monitoring the status of queues;
• Programmable buttons;
• Softkey operation.
2-2
Page 29

ACD SYSTEM FEATURES
3.1 GENERAL
This section lists alphabetically, and describes, the ACD system
features.
3.2 LIST OF SYSTEM FEATURES
• ACD groups;
• ACD routing plans;
• ACD queues;
• Announcer plan;
• Call routing;
• Interflow;
• Level of Service (LOS) time;
• MIS (Management Information System) - ACD I.Q.;
• Overflow program;
• Priority queueing;
• Ringback delay to answer time;
• SLT announcer;
• Statistics time;
• Thresholds.
Section 3
3.3 SYSTEM FEATURE EXPLANATIONS
3.3.1 ACD groups
In the UNITe IP up to 16 ACD groups can be defined, and up to 24
groups for UNITe IP 400.
The ACD group consists of:
• a calls waiting queue;
• a set of agents which can log in to the group and receive calls
routed to the group.
3-1
Page 30

76-110-0430/E
Incoming calls which are routed to an ACD group, will ring at the
telephones of agents servicing that group. When no agents are
available to receive incoming calls, the calls wait in the group's call
waiting queue.
Each group is assigned a group name (up to seven characters),
and a group number. The group number is used when defining
ACD routing plans. Each group can have up to 64 agents, with a
total of 160 agents for the UNITe IP and 300 for the UNITe IP 400.
Each group can be supervised by any or all of the supervisors (8
for UNITe IP; 16 for UNITe IP 400).
3.3.2 ACD routing plans
The ACD routing plan is assigned a system Directory Number (DN)
which acts as an address or destination for routing ACD calls. Calls
intended for the ACD are routed, in the system configuration
program, to the ACD routing plan DN.
The UNITe IP system has up to 32 routing plans; UNITe IP 400 has
up to 48 routing plans. Each plan can be assigned a plan name
(16 ASCII characters). The plan name appears on the ACD station
display for the first ten seconds of the call, and indicates to the
agent which plan the incoming call was routed to.
3.3.3 ACD queues
For each ACD routing plan the following parameters are defined:
• Main group and insertion priority;
• Interflow time;
• Interflow port;
• Main overflow time;
• First, second and third overflow groups;
• First and second overflow times;
• Priority of calls in overflow groups.
An ACD call waiting queue holds the calls routed to an ACD group,
which have not yet been dealt with by agents. Each queue is
administered FIFO (First In-First Out), unless priorities have been
defined, in which case calls are queued according to priority. While
waiting to be attended by agents, the callers may be connected to
ring tone, Music On Hold, or to one or more recorded
announcements.
[ACD QUEUE] button on the supervisor and agent stations
The
indicates the status of the ACD queues.
3-2
Page 31

3.3.4 Announcer plan
Section 3: ACD SYSTEM FEATURES
A caller into an ACD system can be connected to an announcer or
series of recorded announcements, while waiting in queue to be
answered by an ACD agent. The announcements may be
messages such as We apologize for the delay in answering your
call. Our agent will be with you as soon as possible.
Each ACD routing plan is optionally assigned an Announcer plan.
The recorded announcements may be recorded using regular SLT
announcers, or using the Telrad Connegy IMAGEN Recorded
Announcements (RAN) feature. The Telrad Connegy IMAGEN
RAN feature can make up to nine recordings.
Several announcements can be combined into an Announcer plan,
which consists of several messages with defined intervals between
them. For example, after 30 seconds waiting, a call will hear RAN1;
after 90 seconds waiting, the caller is connected to RAN4 etc. SLT
announcers and Telrad Connegy IMAGEN recorded
announcements can be freely mixed in the Announcer plan. Also,
the same recorded announcement can be used in several different
Announcer plans.
Announcements can be played once or repeated many times. The
time delay between announcements is programmable.
In the gap between announcements you can define whether the
caller hears ringback tone or music on hold. You can also have
ringback tone played to the outside caller when his/her call finishes
waiting in queue and starts ringing an agent telephone.
The announcement may be defined as a forced announcement, in
which case, even if an ACD agent becomes available, the caller will
not be forwarded to ring an ACD station until the recorded
announcement has finished.
The UNITe IP supports 16 announcer plans.
The UNITe IP 400 supports 24 announcer plans.
A maximum of 50 announcement allocations to plans, are
permitted.
For more details of the Telrad Connegy IMAGEN recorded
announcements, refer to the Telrad Connegy IMAGEN System
manual.
3-3
Page 32

76-110-0430/E
3.3.5 Call routing
3.3.6 Interflow
Incoming
calls on outside lines are routed, via the regular ring routing
program, to the ACD routing plan DN. Calls may enter the ACD from
trunks, trunk groups, DID lines, TIE lines or extensions (i.e regular
internal calls). Calls either ring directly to the agents, or are answered
automatically after a preprogrammed number of delay rings (also
called delay to answer time) by an SLT announcer or by Telrad
Connegy IMAGEN.
If the call waits on queue beyond the first, second
or third overflow times, the call will be directed also to ring at one or
more overflow queues. If the call is not answered in the queues, it can
be disconnected from the ACD system and routed to an interflow DN.
When a call arrives, if one or more agents are available, the call is
directed to the longest idle station (Uniform Call Distribution).
Interflow
is a type of 'no answer forward" destination for ACD calls.
When the interflow timeout elapses, the call will stop waiting in the
queues and instead will ring the programmed interflow destination.
The interflow destination can be an Attendant position, an ICI queue
or a Hunt group. If the interflow destination is busy, the system checks
every few seconds, to see if it has become available. In the
meantime, the call continues to wait in the ACD queues.
Calls also reach the interflow port when the queue enters "Interflow
mode". Interflow mode is when all agents in the Main group and
overflow groups are either logged out or in the Not available or
forced busy state.
See also Figure 1-2 and Figure 1-3, above.
3.3.7 Level Of Service (LOS) time
The Level Of Service (LOS) is the percentage of calls that, during
the statistics time, are answered by agents within the period
defined as the LOS time.
Statistics time: 3 to 30 minutes (default: 15 minutes);
time: 2 seconds to 59 minutes and 59 seconds (default: 20
LOS
seconds).
These timers are defined in system programming, per ACD group.
For example, if the LOS time is 20 seconds, and 8 out of 10 calls
are answered by agents within 20 seconds of automatic answer or
ringing, then the Level Of Service is 80%.
3-4
Page 33

3.3.8 Overflow program
A call which is not answered within the Main overflow timeout can
overflow to one, and later, after the elapse of additional timeouts, at
up to two more overflow groups. See Figures 1-2 and 1-3, above.
Overflow times are defined per queue and per ACD routing plan.
Overflow calls wait in parallel at both the original and the overflow
queues. Calls will ring at the first station which becomes available
in the Main or any of the overflow groups.
The user can specify the priority with which the call will be inserted
in each of the overflow queues, ranging from 1 to 99 (1 is the
highest priority).
Overflow can be programmed as predictive. The ACD evaluates
the wait time (i.e. how long until an agent becomes available to
answer the call), and if the predicted wait time exceeds the
overflow time, the call overflows to the overflow queue. If the
predicted wait time exceeds the second and third overflow
timeouts, the call will overflow also to the second and third overflow
queues.
Section 3: ACD SYSTEM FEATURES
The predictive overflow mechanism works in three stages:
• It estimates, cyclically for each call, how long the call will wait in
the queue before being answered.
• It compares the estimated wait time with the programmed
overflow time.
• If the estimated overflow time is greater than the programmed
overflow time, it causes the call to overflow.
The estimated time until answer is calculated as follows:
(Average duration of last 20 ACD calls x Position of call in queue) ק Number of active agents
For example:
• Average duration of last 20 ACD calls: 60 seconds;
• Number of active agents in queue: 4;
• First overflow time: 35 seconds;
• Second overflow time: 35 (Total = 70 seconds);
• Third overflow time: 15 (Total = 85 seconds).
3-5
Page 34

76-110-0430/E
Following the statistics in the example, the overflow pattern,
described below, emerges:
3.3.9 Priority queueing
Calls waiting in the Main queue and overflow queues can be
queued according to priorities defined in system programming. For
calls arriving in each ACD plan, a queue priority of 1 (highest
priority) to 99 (lowest priority) is defined.
Call No. Predicted answer (seconds) Overflows to queues
1 15 -
2 30 -
3 45 1
4 60 1
5 75 1 & 2
6 90 1, 2 & 3
7 105 1, 2 & 3
This feature can be used, for example, to provide calls which have
already overflowed to overflow queues with higher priority, to
ensure that the treatment of such calls not be delayed longer than
necessary.
3.3.10 Ringback delay to answer time
This parameter can be used to ensure that an outside caller always
hears ringing before being answered. During the ringback delay
time, programmed in system configuration, the ACD does not send
ring tone to agents or answering machines. The caller will always
hear ringing for a limited period, before being answered.
3.3.11 SLT announcer
Analog SLT announcers can be defined in the UNITe IP system, as
ports of the SLD card. These announcers can then be used in an
announcer plan. The chaining of the announcers, and the number
of times each announcer message is repeated, are programmed in
system configuration. For more details see Announcer plan, above.
The UNITe IP supports up to four SLT announcers; the UNITe IP
400 supports up to eight SLT announcers.
3.3.12 Statistics time
Statistics provided on the supervisor station are based on a system
programmable time period of from three to 30 minutes. This time is
used when calculating figures such as the Level Of Service (LOS).
The default statistics time is 15 minutes.
3-6
Page 35

3.3.13 Thresholds
Section 3: ACD SYSTEM FEATURES
When calls have been waiting in queue beyond the time periods
defined for these two thresholds, the
[ACD QUEUE] button flashes
with distinctive LED color and flash rates. Table 1-2, above, lists
[ACD QUEUE] button LED colors and flash rates.
the
The threshold times are defined individually for each ACD group.
Thresholds are illustrated in Figure 1-3, above.
3-7
Page 36

76-110-0430/E
THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK
3-8
Page 37

ACD AGENT FEATURES
4.1 GENERAL
This section lists alphabetically and describes the ACD agent
features.
4.2 LIST OF AGENT FEATURES
• [ACD QUEUE] button;
• Busy wrap up;
• Forced busy state;
• Headset;
• Help request and Help conference;
• Login status LED;
• Not available;
• Programmable buttons;
• Record calls.
Section 4
4.3 AGENT FEATURE EXPLANATIONS
4.3.1 [ACD QUEUE] button
The agent's
queue. Its LED color and flash rate indicates the status of the
queue which the agent is servicing (see Table 1-2, above).
Supervisors can have individual queue buttons for each queue that
they supervise.
[ACD QUEUE] button is used for answering calls in the
4-1
Page 38

76-110-0430/E
4.3.2 Busy wrap up
Depending on the programming of a Busy Wrap Up timer, after an
ACD call ends, the agent may:
• Immediately receive more calls;
• Not receive any calls until the
[WRAP UP] button is pressed;
• Be allowed a programmable period of time (during which calls
are not directed to the ACD agent), for wrapping up jobs and
notes related to the previous call.
The state described in points 2 and 3 above is called Busy Wrap
Up. When Busy Wrap Up is active, the agent is registered as "Not
ready".
The agent can activate Busy Wrap Up manually by pressing the
programmable
[WRAP UP] button on the telephone set.
Pressing the
button when Busy Wrap Up is active, cancels Busy Wrap Up. Calls
will again be routed to the agent's station.
If the
stops and the agent enters Busy Wrap Up state. The call is returned
to the ACD queue.
4.3.3 Forced busy state
When an agent does not answer a call which has been ringing
beyond a programmed period of time, the system automatically
puts the station into forced busy state. The assumption is that the
agent is not sitting at his/her station. Forced busy appears in the
display and the
The station will no longer receive ACD calls. Pressing any button or
going offhook will take the station out of the Forced Busy state.
4.3.4 Headset
The use of a headset is strongly recommended for the ACD agent.
Headset operation greatly simplifies the job of the agent and frees
both hands for other tasks, such as writing notes or working on a
computer. A headset button is used to perform onhook and
offhook.
[WRAP UP] button or the [N. AVAIL] (Not Available)
[WRAP UP] button is pressed while a call is ringing, the ringing
[WRAP UP] button will flash quickly, with a red LED.
4-2
Page 39

4.3.5 Help request and Help conference
An agent can dial the supervisor or request help from a supervisor
during a call, using the
REQUEST]
ANSWER]
button once to request help. The supervisor's [HELP
button will start to flash. Press [HELP REQUEST] a second
time to cancel the request.
If the agent is in an ACD conversation when the supervisor
responds, a three way connection is established in which the
supervisor listens only (i.e. monitors the call). If the supervisor
wishes, she can press
make it a full three way conference, or, press
conversation in which the supervisor can talk to the agent, and
listen to the outside party, but the outside party cannot hear the
supervisor.
4.3.6 Login status LED
This button, particularly useful for agent sets without a display,
indicates whether the agent is logged in (LED green) or logged out
(LED extinguished).
Section 4: ACD AGENT FEATURES
[HELP REQUEST] button. Press the [HELP
{<CONFERENCE>} to break into the call and
{<ADVISE>} to create a
4.3.7 Not available
Not available is activated by agents wishing to take a short break.
Pressing the
[N. AVAIL] (Not Available) button suspends the flow of
ACD calls to the station until the button is pressed again.
Alternatively, answering an ACD call from the station will also
cancel the Not available state.
When the
[N. AVAIL] button is pressed:
• During idle: it induces the Not available state;
• During ring: it stops the ringing and induces the Not available
state;
• During a call: it induces the Not available state, without
disconnecting the current call.
During Not available, the
[N. AVAIL] button will flash slowly with a
green LED.
4-3
Page 40

76-110-0430/E
4.3.8 Programmable buttons
Table 4-1 lists and describes the function of the programmable
buttons that can be defined at the agent's station. It is
recommended that the agent use a Display Speakerphone Set.
Figure 4-1 illustrates the recommended button layout on an agent's
Display Speakerphone Set telephone map.
Button Description
Login status Indicates if the station is logged in
ACD QUEUE Indicates queue status and answers calls from the queue
Not available Activates/deactivates Not available state
Wrap up Activates/deactivates Busy wrap up
Call record Records current ACD call (Telrad Connegy IMAGEN
Table 4-A Agent programmable buttons
application). Call record will not record a three-way
conversation.
Help request Places a request for help to the supervisor
Headset Used for headset operation
Figure 4-A Recommended agent button arrangement -
Speakerphone set
4.3.9 Record calls (Telrad Connegy IMAGEN
application)
ACD calls can be recorded in the same manner as regular calls are
recorded, using the Call record feature of Telrad Connegy
IMAGEN.
4-4
Page 41

Section 5
ACD SUPERVISOR FEATURES
5.1 GENERAL
This section lists alphabetically and describes the ACD supervisor
features.
5.2 LIST OF SUPERVISOR FEATURES
• [ACD QUEUE] button;
• Agent status display;
• Display mode toggle;
• Monitoring and advising agents;
• Monitoring the status of queues;
• Programmable buttons;
• Softkey operation.
5.3 SUPERVISOR FEATURE EXPLANATIONS
5.3.1 [ACD QUEUE] button
The agent's
the ACD queue. The button's LED color and flash rate indicate the
status of the queue which the agent is servicing (see Table 1-2,
above).
supervisor station. The supervisor can view the queue status LED
and can press the queue button to answer calls from the queue.
[ACD QUEUE] button is used for answering calls from
[ACD QUEUE] buttons are also programmed on the
5-1
Page 42

76-110-0430/E
5.3.2 Agent status display
The supervisor can view the status of each agent under
supervision using the agent status display screen. Possible agent
statuses are:
• Logged out;
• Available to receive ACD calls;
• ACD call;
• ACD ring;
• Non-ACD call;
• Not available;
• Busy wrap up;
• Not ready;
• Forced busy.
5.3.3 Display mode toggle
At the press of a button the supervisor can change from the
regular telephone display mode to the ACD display mode, and vice
versa. This feature is useful for supervisors who fill other tasks, in
addition to that of supervisor, and who regularly need to operate
the phone in the usual manner. However, even while in regular
display mode, the supervisor telephone continues to operate as a
supervisor, and receives Help requests from agents.
5.3.4 Monitoring and advising agents
in supervisor display mode, the supervisor can "monitor" (listen
When
to) agents' calls, by selecting an agent in a queue, and pressing the
{<MONITOR>} softkey.
In system programming it can be defined whether agents hear a
tone when the supervisor starts monitoring calls, and whether the
incoming caller also hears the tone. Thus agents may not be aware
that their calls are being monitored.
The supervisor offers advice to agents either:
• in response to an agent's request for help, or;
• on the supervisor's initiative.
agent requests help by pressing the [HELP REQUEST] button. This
An
causes the supervisor's [HELP ANSWER] button to light.
Pressing
the [HELP ANSWER] button sets up a call between the
supervisor and the agent.
When the supervisor is monitoring an agent's calls, the supervisor
may wish to offer advice to the agent, on his/her own initiative. To
do this the supervisor presses either the
which sets up a three-way conversation between the supervisor,
{<CONFERENCE>} button
5-2
Page 43

the agent and the outside party, or the {<ADVISE>} button, which
establishes a three party connection in which the supervisor can
hear the outside party, but the outside party cannot hear the
supervisor.
5.3.5 Monitoring the status of queues
The supervisor has individual queue buttons for each queue under
supervision. LED indications indicate the status of calls in queues
(see Table 1-2, above). A general rule states that the faster the
flash rate, the longer the call has been waiting, and therefore, the
more urgent it is to answer the call.
5.3.6 Programmable buttons
Table 5-1 lists and describes the function of the buttons that can be
defined at the supervisor station.
Table 5-A Supervisor programmable buttons
Button Description
Section 5: ACD SUPERVISOR FEATURES
Figure 5-1, below, illustrates the recommended button layout on
the supervisor's Executive station map.
5.3.7 Softkey operation
Since the supervisor station is an Executive station with expanded
display, the supervisor benefits from the ease of softkey operation.
The softkeys are used to travel from screen to screen when
analyzing agent and queue status (e.g.
{<PREV>}, {<MORE>}), and for performing the regular supervisor
duties (e.g.
ACD login status Optional. Shows ACD login status of supervisor.
Display mode Toggles between supervisor mode and regular
telephone operation.
ACD queue
status
Record Records the current two-way conversation (Record will
Help answer Answers agents' requests for help.
Headset Used for headset operation (optional).
{<CALL>}, {<MONITOR>}).
Answers calls in queue: LED flash rate indicates queue
status.
not record a three party call i.e. a monitor, advise or
conference call).
{<MOVE>}, {<SCROLL>},
5-3
Page 44

76-110-0430/E
Figure 5-A Supervisor station recommended programmable
button layout
5-4
Page 45

INSTALLATION, CONFIGURATION AND
6.1 GENERAL
Section 6
UPGRADING OF THE ACD
This section describes the physical installation and software
configuration of the ACD system in a UNITe IP or UNITe IP 400
exchange.
It is necessary to distinguish between two distinct installation and
configuration processes:
• Installing and configuring a brand new UNITe IP system with
the ACD option (see Section 6.2);
• Updating an existing UNITe IP system with the ACD option
(see Section 6.3).
6.2 INSTALLING AND CONFIGURING A NEW UNITe IP SYSTEM WITH ACD
This procedure is fully described in the UNITe IP Installation
manual and UNITe IP Administration manual. Refer to the
following steps as a guideline only.
1. Follow the regular installation instructions. Take care to check
the label of the MPD software cartridge. It must be labeled
"ACD".
2. Program the ACD parameters in the system configuration
program. Refer to Section 7, below.
3. Refer to the Telrad Connegy IMAGEN System manual for
instructions on recording announcements, if these are included
in the ACD configuration.
4. Refer to the ACD I.Q. System manual for instructions on
connecting and programming ACD I.Q., if the ACD I.Q. MIS
program is to be used in conjunction with the ACD.
6-1
Page 46

76-110-0430/E
6.3 UPGRADING AND CONFIGURING AN EXISTING UNITe IP SYSTEM
WITH ACD
6.3.1 General
The following sections explain the steps performed for
hardware installation and software configuration of the ACD
in an existing UNITe IP system. Explanations of the system
configuration programming parameters are provided in
Section 7.
6.3.2 Upgrade steps (hardware and software)
1. Plan the ACD configuration and fill out the programming forms
(see Section 7, below).
2. Backup the existing system configuration to diskette (see the
UNITe IP Administration manual).
3. Install the new MPD Memory cartridge. Follow the instructions
packed together with the box of the MPD cartridge card, or the
instructions provided in the UNITe IP Installation manual.
4. Restore the configuration to the system (see the UNITe IP
Administration manual).
5. Program the ACD screens and related features, in accordance
with the configuration on the programming forms.
6. (Optional) If applicable, record the Telrad Connegy IMAGEN
recorded announcements (1 to 9). Refer to the Telrad Connegy
IMAGEN System manual;
or
If applicable, record the announcements on SLT announcers.
7. Label the buttons of the ACD agent and supervisor stations.
8. Connect ACD I.Q. (optional) (see the ACD I.Q. System
manual).
6-2
Page 47

ACD PROGRAMMING PARAMETERS
7.1 GENERAL
Section 7
This section contains the data for planning and programming the
ACD configuration. The information in this section also appears in
the DIGITAL family of systems Administration manual.
Administration forms for programming the ACD parameters are
appended to this manual as Appendix A. These are copies of the
administration forms found in the DIGITAL Administration manual,
and follow the same numbering scheme.
This also includes brief instructions for programming Recorded
announcements from the Telrad IMAGEN. For further details refer
to the Telrad IMAGEN System manual.
Parameters located elsewhere in the configuration program which
may have a bearing on the configuration of ACD are listed in
Section 7.6, below.
7.2 WORKING WITH THE ADMINISTRATION PROGRAM
When configuring the ACD, the same steps and procedures are
followed as with all system programming. These are described in
detail in the DIGITAL family of systems Administration manual.
7.3 STEPS FOR PLANNING THE ACD CONFIGURATION
First, the Customer Sales Representative discusses the ACD
configuration with the customer. Next the agreed configuration is
transferred onto the programming forms (see Appendix A, below).
After that, the ACD configuration is programmed into the DIGITAL
configuration program (either offline or online). Finally, the new
configuration is loaded into the system.
7-1
Page 48

76-110-0430/E
7.4 PROGRAMMING THE PARAMETERS
This section describes each screen, and each field of each screen,
of the configuration program that is related to ACD. It follows the
format of the comparable section of the DIGITAL Administration
manual.
For each screen, this section provides:
• Screen name, definition and path;
• Explanations of screen fields or ACD features;
• Field default values;
• Field legal range of values.
Most of the data relevant to ACD is contained in the AUTOMATIC
CALL DISTRIBUTION Menu and its five sub-screens described
below.
7.5 THE AUTOMATIC CALL DISTRIBUTION MENU
The AUTOMATIC CALL DISTRIBUTION Menu appears on the
MAIN Screen of the DIGITAL configuration program, and is
accessed with the letter C.
The AUTOMATIC CALL DISTRIBUTION Menu provides access to
the following screens:
• AP: General ACD parameters;
• GR: ACD groups;
• SV: Supervisor & ACD groups;
• PL: ACD routing plans;
• NP: Announcer plans.
Other screens accessed from various locations in the ACD submenu are:
• ACD ID LIST Screen (F3 from screens listed below);
• Agent List (F9 from ACD GROUPS Screen);
• Announcement program (F9 from ANNOUNCER PLAN
Screen);
• Interflow and overflow programming (F9 from the ACD
ROUTING PLANS Screen).
ACD ID LIST Screen The ACD ID LIST Screen can be accessed
from:
7-2
• General ACD parameters;
• ACD groups;
• Supervisor & ACD groups;
• ACD routing plans;
• Agent list.
Page 49

The ACD ID LIST Screen lists all the ACD agents and supervisors
according to their ACD ID and ACD name. For agents it also
specifies the Group number; for supervisors it specifies the
supervisor number in ACD group.
7.5.1 General ACD parameters CD→AP
This screen contains general ACD parameters.
To organize the data to be entered on this screen, use
Administration form number 68.
Forced busy time If an agent does not answer a ringing call
before this timeout elapses, the station is automatically put into a
forced busy state, and calls are no longer routed to the station.
Pressing any button on the station or lifting the handset cancels the
forced busy state.
Legal values: 0:02 - 59:59 (minutes:seconds),
UL (Unlimited - disables forced busy);
Section 7: ACD PROGRAMMING PARAMETERS
Default: 30 seconds.
Monitoring notification This parameter determines whether a
tone is heard when a supervisor starts monitoring the call of an
agent. Either no tone is heard, the tone is heard only by the agent
and supervisor, or the tone is heard by the agent, supervisor and
the outside caller.
Legal values: NO(ne);
Default: No(ne).
Predictive overflow This parameter defines if the ACD overflow
process uses the predictive overflow algorithm.
Legal values: Y, N (Yes, No);
Default: Y.
7.5.2 ACD groups CD→GR
This screen defines many of the ACD group parameter features. It
is also used to access the ACD agent list screen (F9).
AG(gent); AL(l);
To organize the data to be entered on this screen, use
Administration forms number 69 and 70.
7-3
Page 50

76-110-0430/E
Group Displays the ACD group number (up to 16 for DIGITAL
KEY BX; up to 24 for DIGITAL 400). This is a display only field.
Name An ACD group name is assigned for each ACD queue.
Agent stations display the name of the group to which the agent
belongs, on the second display line. The ACD group name is also
used to identify ACD groups on the display of the supervisor
telephone.
Legal values: Any seven characters.
Wrap up time This parameter defines the duration of the pause
granted to the agent after ending a call, before new calls are routed
to the agent's station.
Legal values:
0:02 - 59:59
(mm:ss)
UL The
do not ring until the timer elapses, unless
Calls
the [WRAP UP] button is pressed.
[WRAP UP] button must be pressed before
new calls will ring;
- Calls are presented immediately.
Queue first threshold This parameter defines the timeout after
which the
flash, to red, slow flash indicating calls are backing up in the
queue.
Legal values:
Default: 0:02 - 59:59 (minutes:seconds),
[ACD QUEUE] button flash rate changes from green, slow
UL.
Queue second threshold This parameter defines the timeout after
which the
flash, to red fast flash, indicating calls are backing up in the queue.
[ACD QUEUE] button flash rate changes from red, slow
7-4
Legal values: 0:02 - 59:59 (minutes:seconds),
UL.
Default: UL.
Page 51

Section 7: ACD PROGRAMMING PARAMETERS
Stat (Statistics) time This parameter sets the period of time over
which the ACD statistical calculations are made.
Legal values: 3 - 30 (minutes);
Default: 15 minutes.
LOS (Level Of Service) time This parameter determines the time
in which calls should be answered. Calls not answered within this
time will reduce the ACD Level Of Service, calculated for the
statistics period.
Legal values: 0:02 - 59:59 (mm:ss),
Default: 20 seconds.
To view the ACD ID list (CD→GR→<F3>) Pressing F3 from all
the screens listed in Section 7.5 opens the ACD ID LIST Screen.
This screen is used to display ACD IDs defined in the AGENT
Screen (CD→GR→<F9>) and in the supervisor screen (CD→SV).
The screen provides the following information:
• ID;
• Name;
• Type (supervisor (SV) or agent);
• Group number (to what group does the agent belong);
• Supervisor number (the supervisor serial number).
To define agents assigned to each ACD group (CD→GR→<F9>)
Pressing F9 from the ACD groups screen opens the AGENT LIST
Screen. This screen is used for defining new agents and editing
agent data.
Maximum number of agents in each group: 64;
Maximum agents in system:
• DIGITAL KEY BX: 160;
• DIGITAL 400: 300.
To organize the data to be entered on this screen, use
Administration form number 70.
7-5
Page 52

76-110-0430/E
ID Enter the agent ID. This agent ID code is used by the agent when
logging in the ACD. The code must be unique. The same number must
not be allocated to other agents or supervisors. The first digit of the
agent ID cannot be a zero.
Legal values: Up to four digits (0-9).
Name Enter the agent name. This name is used to identify the
agent on the supervisor's telephone display, and in the ACD
S.T.A.R computer.
Legal values: Any seven characters.
7.5.3 Supervisor and ACD Groups CD→SV
This screen is used to define supervisor details and the allocation
of supervisors to ACD groups.
To organize the data to be entered on this screen, use
Administration form number 71.
Supervisor This field displays the supervisor number.
For DIGITAL KEY BX: Up to eight supervisors;
For DIGITAL 400: Up to 16 supervisors.
ID This field defines the supervisor ID code. This code is used by
the supervisor when logging into the ACD. The code must be
unique. The same number must not be allocated to other agents or
supervisors. The first digit of the supervisor ID cannot be a zero.
Legal values: Any four digits - 0-9, -.
Name This field defines the supervisor name. This name appears
on the telephone display of the supervisor MAIN Screen.
Legal values: Any seven characters.
ACD group
Group 1 to 16 (DIGITAL KEY BX);
Group 1 to 24 (DIGITAL 400).
7-6
For each supervisor, enter Y(Yes) or N(No) opposite each group to
determine whether the supervisor supervises, and receives help
requests from that group. Each supervisor may supervise any
number of ACD groups.
Page 53

7.5.4 ACD Routing plans CD→PL
This screen is used to define the ring routing plans of the ACD
calls.
For DIGITAL KEY BX:Up to 32 routing plans;
For DIGITAL 400: Up to 48 routing plans.
To organize the data to be entered on this screen, use
Administration form number 72.
DN Enter the ACD routing plan DN.
Legal values: Up to four digits (#, * included).
Name This field defines the ACD routing plan name e.g. Sales
Department. This name appears for 10 seconds on the agent's
telephone display after the call is answered and identifies the Main
group to which the call was directed.
Section 7: ACD PROGRAMMING PARAMETERS
Legal values: Any 16 characters.
Main group number This field defines the ACD group to which
calls directed to the ACD routing plan DN, will be routed.
Legal values: DIGITAL KEY BX: 1 - 16;
DIGITAL 400: 1 - 24.
Priority value This field defines the priority which calls arriving on
this ACD Routing plan DN receive in the Main queue.
Legal values: 1 (Highest) - 99 (Lowest);
Default: 1.
Announcer plan Enter the number of the Announcer plan
applying to the ACD routing plan (see the Announcer Plan CD→NP
of Section 7.5.5, below).
Legal values: DIGITAL KEY BX: 1 - 16;
DIGITAL 400: 1 - 24.
7-7
Page 54

76-110-0430/E
To design the Interflow and Overflow parameters
(CD→PL→<F9>) Pressing F9 from the ACD ROUTING PLANS
Screen (CD→PL) opens the Interflow and OVERFLOW
PROGRAMMING Screen. This screen is used to define the
interflow and overflow programs of the ACD plans.
To organize the data to be entered on this screen, use
Administration form number 73.
DN This field displays the ACD plan DNs.
Interflow time The interflow time is the timer after which calls are
taken out of the ACD system and routed to an interflow port.
Legal values: 0:02 - 59:59 (mm:ss), - (no interflow).
Interflow port This is an attendant position, Incoming Call
Identifier (ICI) queue or hunt group to which calls are routed, after
the interflow time has elapsed.
Legal values: ATT1 - ATT4, ICI11- ICI48, hunt group DN, -
First overflow time This field defines how long an ACD call waits
for the Main ACD group to which it was routed, before it is
overflowed to the first overflow group.
Legal values: 0:02 - 59:59 (mm:ss), -
First overflow group # This is the ACD group to which calls are
routed, after the first overflow time has elapsed.
First overflow priority This field defines the priority, in the first
overflow queue, of calls overflowing from the Main ACD group.
Calls are positioned in the overflow queue according to the priority
level.
Legal values: 1 (Highest) - 99 (Lowest);
Default: 1.
Second overflow time This field defines how long an ACD call
waits in the Main and first overflow group, before it is overflowed to
the second overflow ACD group.
7-8
Legal values: 0:02 - 59:59 (mm:ss), -
Second overflow group # This is the ACD group to which calls
are routed, after the second overflow time has elapsed.
Page 55

Section 7: ACD PROGRAMMING PARAMETERS
Second overflow priority This field defines the priority, in the
second overflow queue, of calls overflowing from the Main ACD
group. Calls are positioned in the overflow queue according to the
priority level.
Legal values: 1 (Highest) - 99 (Lowest);
Default: 1.
Third overflow group # This is the ACD group to which calls are
routed, after the third overflow time has elapsed.
Third overflow time This field defines how long an ACD call waits
in the Main and first overflow group, before it is overflowed to the
second overflow ACD group.
Legal values: 0:02 - 59:59 (mm:ss), -
Third overflow priority This field defines the priority, in the third
overflow queue, of calls overflowing from the Main ACD group.
Calls are positioned in the overflow queue according to the priority
level.
Legal values: 1 (Highest) - 99 (Lowest);
Default: 1.
7.5.5 Announcer plans CD→NP
This screen is used to define the parameters related to the ACD
Announcer Plan.
To organize the data to be entered on this screen, use
Administration form number 74.
Plan This field displays the Plan Number.
For DIGITAL KEY BX: 1 - 16;
For DIGITAL 400: 1 - 24.
7-9
Page 56

76-110-0430/E
Ringback delay During the ringback delay time, agents do not
receive ring tone. After the ringback delay time, agents and
announcer machines receive ringing. This parameter can be used,
for example, to ensure that an outside caller always hears ringing
before being answered.
Legal values: 2 - 59 seconds, - (no delay);
Default: 3 seconds.
Forced announcement If forced announcement is programmed Y
(Yes), then an incoming caller will always hear the complete
opening announcer message, even if agents are available to
answer the call. Calls cannot be seized by agents while the
announcement is running.
Legal values: Y, N (Yes, No);
Default: N.
Music source This parameter specifies whether a call on hold in
the ACD will be connected to ring tone or to Music On Hold.
Legal values: MOH (Music on Hold), RNG (Ring tone);
Default: MOH.
Tone on station ring When this parameter is programmed as Y
(Yes) then when the agent phone starts ringing, the caller hears
ring tone.
Legal values: Y, N (Yes, No);
Default: N.
To define the announcer plan specifications (CD→NP→<F9>)
This screen is used to define the Announcement program,
consisting of one or a chain of SLT announcers and Telrad
IMAGEN Recorded Announcements, for each Announcer plan (up
to 16 for DIGITAL KEY BX systems and up to 24 for DIGITAL 400
systems). A total of 50 entries may be made for the system.
7-10
To organize the data to be entered on this screen, use
Administration form number 75.
Page 57

Section 7: ACD PROGRAMMING PARAMETERS
The maximum number of announcer messages is:
• Nine Telrad IMAGEN messages (if installed).
• DIGITAL KEY BX: four SLT announcers;
DIGITAL 400: eight SLT announcers.
Announcer Enter the DN of the SLT announcer or the Telrad
IMAGEN recorded announcement to be played in the announcer
plan.
Legal values: Announcer DN, RAN1 - RAN9, -
Post announcing delay This parameter defines the interval
between the recorded announcements. During this time, the caller
hears either Music on Hold or ringback tone. Only the last
announcement in the chain can be programmed with an unlimited
post announcing delay.
Legal values: 0:02 - 59:59 (mm:ss), UL (unlimited);
Default: UL.
Times This parameter specifies the number of times that the
announcement is repeated. Only the last announcement in the
chain can be programmed with an unlimited number of times.
Legal values: 1, 99, UL (unlimited);
Default: UL.
7.6 RELATED SYSTEM CONFIGURATION PARAMETERS
This section lists the parameters in system programming which
you should be aware of when you program an ACD system. Some
of these may need reprogramming.
Below is a list of the screens where these parameters are
programmed, the relevant programming form number, and a brief
explanation of the meaning of the parameters and how they affect
the ACD.
SLT announcer ports
Path: OC→OL→<F9>
Administration form number: 12
This screen is used to define SLT ports on SLD and SHD cards for
the use of SLT announcers.
7-11
Page 58

76-110-0430/E
IVM/Serial applications
Path: OC→IS
Administration form number: 15
This screen is used to define the DN of the station containing the
Universal Data Interface card, to which the ACD I.Q. computer is
connected.
Music on Hold
Path: OC→BG
Administration form number: 21
On this screen define the Music On Hold source.
ACD login and logout code
Path: SP→FN
Administration form number: 25
Define here the codes used by agents and supervisors for logging
in and out of the ACD.
TIE/DID group features
Path: GR→TF
Administration form number: 38
For TIE/DID trunks directly routed to the ACD, in the Auto
completion field, assign the ACD Plan DN.
Trunk routing (for trunks and trunk groups)
Path: GR→DR; GR→NR; PT→DR; PT→NR;
Administration form numbers: 41, 42, 45, 46
On these screens, route trunks and trunk groups to the ACD
routing plan DN (defined on screen (CD - PL) for day and night
service.
7-12
Page 59

Section 7: ACD PROGRAMMING PARAMETERS
Programmable keys
Path: FE→PK
Administration form numbers: 52, etc.
Assign the programmable buttons required by the ACD agents and
supervisors to their telephone set button maps.
DID routing
Path: RD
Administration form number: 82
In the Day routing and Night routing fields, assign the ACD DN
Plan to route calls arriving on this DID trunk directly to the ACD.
7.7 RECORDING THE ANNOUNCER MESSAGES
7.7.1 General
Announcer messages can be recorded in one of two ways:
• Using Telrad IMAGEN;
• Using regular SLT announcers.
7.7.2 Programming announcer messages
via Telrad IMAGEN
The messages are recorded in the regular fashion under the
announcer messages option of the SYSTEM GREETING Menu.
The nine messages are automatically assigned the logical names
RAN1 through RAN9. On the ANNOUNCEMENT PROGRAM
Screen of the system programming (CD→NP→<F9>), the
announcer plan is defined using these messages RAN1 to RAN9.
A DIGITAL system, with both ACD and Telrad IMAGEN accesses
the RAN messages from the Telrad IMAGEN and plays them to the
callers waiting on hold.
The Telrad IMAGEN System manual provides details of how to
record and edit the recording of the announcer messages.
7.7.3 Programming announcer messages
using SLT announcers
Individual announcer machines must be acquired and defined for
each recorded announcement (i.e. for four announcements you
need four SLT announcers and four SLT ports).
The SLT announcers must be defined in the On Line Configuration
(each with its own DN).
7-13
Page 60

76-110-0430/E
7.8 CONFIGURING THE ACD I.Q.
If your ACD system is enhanced with ACD I.Q., there are various
configuration requirements that must be met, and various
recommended programming practices to be followed, which will
enable you to derive the maximum benefit from the ACD I.Q. and
ACD systems.
For instructions concerning installing and configuring the ACD I.Q.,
refer to the ACD I.Q. System manual.
7-14
Page 61

ACD PROGRAMMING FORMS
1st.1 GENERAL
Appendix A
This appendix contains the programming forms required for the
ACD.
Number Screen name Path
68 General ACD parameters CD→AP
69 ACD groups CD→GR
70 Agent list CD→GR→<F9>
71 Supervisor and ACD Groups CD→SV
72 ACD plans CD→PL
73 Interflow and overflow programming CD→PL→ <F9>
74 Announcer plans CD→NP
75 Announcement program CD→NP→<F9>
1-1
Page 62

76-110-0430/E
THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK
1-2
 Loading...
Loading...