Page 1

LE910Cx
HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev.8 – 2018-12-12
Page 2
LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 2 of 121 2018-12-12
SPECIFICATIONS ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE
NOTICE
While reasonable efforts have been made to assure the accuracy of this document, Telit
assumes no liability resulting from any inaccuracies or omissions in this document, or from
use of the information obtained herein. The information in this document has been
carefully checked and is believed to be reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed for
inaccuracies or omissions. Telit reserves the right to make changes to any products
described herein and reserves the right to revise this document and to make changes
from time to time in content hereof with no obligation to notify any person of revisions or
changes. Telit does not assume any liability arising out of the application or use of any
product, software, or circuit described herein; neither does it convey license under its
patent rights or the rights of others.
It is possible that this publication may contain references to, or information about Telit
products (machines and programs), programming, or services that are not announced in
your country. Such references or information must not be construed to mean that Telit
intends to announce such Telit products, programming, or services in your country.
COPYRIGHTS
This instruction manual and the Telit products described in this instruction manual may be,
include or describe copyrighted Telit material, such as computer programs stored in
semiconductor memories or other media. Laws in the Italy and other countries preserve
for Telit and its licensors certain exclusive rights for copyrighted material, including the
exclusive right to copy, reproduce in any form, distribute and make derivative works of the
copyrighted material. Accordingly, any copyrighted material of Telit and its licensors
contained herein or in the Telit products described in this instruction manual may not be
copied, reproduced, distributed, merged or modified in any manner without the express
written permission of Telit. Furthermore, the purchase of Telit products shall not be
deemed to grant either directly or by implication, estoppel, or otherwise, any license under
the copyrights, patents or patent applications of Telit, as arises by operation of law in the
sale of a product.
COMPUTER SOFTWARE COPYRIGHTS
The Telit and 3rd Party supplied Software (SW) products described in this instruction
manual may include copyrighted Telit and other 3rd Party supplied computer programs
stored in semiconductor memories or other media. Laws in the Italy and other countries
preserve for Telit and other 3rd Party supplied SW certain exclusive rights for copyrighted
computer programs, including the exclusive right to copy or reproduce in any form the
copyrighted computer program. Accordingly, any copyrighted Telit or other 3rd Party
supplied SW computer programs contained in the Telit products described in this
instruction manual may not be copied (reverse engineered) or reproduced in any manner
without the express written permission of Telit or the 3rd Party SW supplier. Furthermore,
the purchase of Telit products shall not be deemed to grant either directly or by
implication, estoppel, or otherwise, any license under the copyrights, patents or patent
applications of Telit or other 3rd Party supplied SW, except for the normal non-exclusive,
royalty free license to use that arises by operation of law in the sale of a product.
Page 3
LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 3 of 121 2018-12-12
USAGE AND DISCLOSURE RESTRICTIONS
I. License Agreements
The software described in this document is the property of Telit and its licensors. It is
furnished by express license agreement only and may be used only in accordance with
the terms of such an agreement.
II. Copyrighted Materials
Software and documentation are copyrighted materials. Making unauthorized copies is
prohibited by law. No part of the software or documentation may be reproduced,
transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or translated into any language or
computer language, in any form or by any means, without prior written permission of Telit
III. High Risk Materials
Components, units, or third-party products used in the product described herein are NOT
fault-tolerant and are NOT designed, manufactured, or intended for use as on-line control
equipment in the following hazardous environments requiring fail-safe controls: the
operation of Nuclear Facilities, Aircraft Navigation or Aircraft Communication Systems, Air
Traffic Control, Life Support, or Weapons Systems (High Risk Activities"). Telit and its
supplier(s) specifically disclaim any expressed or implied warranty of fitness for such
High-Risk Activities.
IV. Trademarks
TELIT and the Stylized T Logo are registered in Trademark Office. All other product or
service names are the property of their respective owners.
V. Third Party Rights
The software may include Third Party Right software. In this case you agree to comply
with all terms and conditions imposed on you in respect of such separate software. In
addition to Third Party Terms, the disclaimer of warranty and limitation of liability
provisions in this License shall apply to the Third-Party Right software.
TELIT HEREBY DISCLAIMS ANY AND ALL WARRANTIES EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
FROM ANY THIRD PARTIES REGARDING ANY SEPARATE FILES, ANY THIRD
PARTY MATERIALS INCLUDED IN THE SOFTWARE, ANY THIRD PARTY MATERIALS
FROM WHICH THE SOFTWARE IS DERIVED (COLLECTIVELY “OTHER CODE”), AND
THE USE OF ANY OR ALL THE OTHER CODE IN CONNECTION WITH THE
SOFTWARE, INCLUDING (WITHOUT LIMITATION) ANY WARRANTIES OF
SATISFACTORY QUALITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
NO THIRD PARTY LICENSORS OF OTHER CODE SHALL HAVE ANY LIABILITY FOR
ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR
CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION LOST PROFITS),
HOWEVER CAUSED AND WHETHER MADE UNDER CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHER
LEGAL THEORY, ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OR DISTRIBUTION OF
THE OTHER CODE OR THE EXERCISE OF ANY RIGHTS GRANTED UNDER EITHER
OR BOTH THIS LICENSE AND THE LEGAL TERMS APPLICABLE TO ANY SEPARATE
FILES, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
Page 4

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 4 of 121 2018-12-12
APPLICABILITY TABLE
This documentation applies to the following products:
Table 1: Applicability Table
Module Name
Description
LE910C1-NA
North America – AT&T with global roaming
LE910C1-NS
North America - Sprint variant
LE910C1-AP
APAC variant
LE910C4-EU
Europe CAT4 variant
LE910C1-EU
Europe CAT1 variant
LE910C4-NF
North America CAT4 variant
LE910C1-NF
North America CAT1 variant
LE910C1-SA
North America CAT1 variant – AT&T
LE910C1-ST
North America CAT1 variant – T Mobile
LE910C1-SV
North America CAT1 variant – Verizon
LE910C1-LA
Latin America CAT1 variant
Page 5

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 5 of 121 2018-12-12
CONTENTS
1. INTRODUCTION .............................................................................................9
Scope ............................................................................................................. 9
Audience......................................................................................................... 9
Contact Information, Support .......................................................................... 9
Text Conventions ...........................................................................................10
Related Documents .......................................................................................11
2. PRODUCT DESCRIPTION ............................................................................ 12
Overview........................................................................................................12
Applications ...................................................................................................13
General Functionality and Main Features.......................................................13
Block Diagram ...............................................................................................16
Environmental Requirements .........................................................................17
2.5.1. Temperature Range .......................................................................................17
2.5.2. RoHS Compliance .........................................................................................17
Operating Frequency Bands ..........................................................................18
2.6.1. RF Bands per Regional Variant .....................................................................18
2.6.2. Reference Table of RF Bands Characteristics ...............................................19
RF Parameters ..............................................................................................22
2.7.1. Sensitivity ......................................................................................................22
2.7.2. Output power .................................................................................................22
Mechanical Specifications ..............................................................................23
2.8.1. Dimensions ....................................................................................................23
2.8.2. Weight ...........................................................................................................23
3. MODULE CONNECTIONS ............................................................................ 24
Pin-out ...........................................................................................................24
Signals That Must Be Connected ...................................................................33
LGA Pads Layout ...........................................................................................35
Backward Compatibility to xE910 Family .......................................................36
4. ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS ................................................................. 37
Absolute Maximum Ratings – Not Operational ...............................................37
Recommended Operating Conditions ............................................................37
Logic Level Specifications ..............................................................................38
4.3.1. 1.8V Pads - Absolute Maximum Ratings ........................................................38
4.3.2. 1.8V Standard GPIOs ....................................................................................38
4.3.3. 1.8V SD Card Pads .......................................................................................39
Page 6

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 6 of 121 2018-12-12
4.3.4. 1.8V SIM Card Pads ......................................................................................40
4.3.5. Dual Voltage Pads - Absolute Maximum Ratings ...........................................40
4.3.6. SD Card Pads @ 2.95V .................................................................................41
4.3.7. SIM Card Pads @2.95V.................................................................................41
5. HARDWARE COMMANDS ........................................................................... 42
Turning on the LE910Cx Module ...................................................................42
Initialization and Activation State ...................................................................43
Turning off the LE910Cx Module ...................................................................45
5.3.1. Shutdown by Software Command ..................................................................46
5.3.2. Hardware Shutdown ......................................................................................47
5.3.3. Unconditional Hardware Shutdown ................................................................48
Powering OFF the Module .............................................................................49
6. POWER SUPPLY .......................................................................................... 50
Power Supply Requirements ..........................................................................50
Power Consumption ......................................................................................51
General Design Rules ....................................................................................53
6.3.1. Electrical Design Guidelines ..........................................................................53
6.3.1.1. + 5V Input Source Power Supply – Design Guidelines ...................................53
6.3.1.2. + 12V Input Source Power Supply – Design Guidelines .................................54
6.3.1.3. Battery Source Power Supply – Design Guidelines ........................................55
6.3.2. Thermal Design Guidelines ............................................................................55
6.3.3. Power Supply PCB Layout Guidelines ...........................................................56
7. ANTENNA(S) ................................ ................................................................ 58
GSM/WCDMA/TD-SCDMA/LTE Antenna Requirements ...............................58
GSM/WCDMA/TD-SCDMA/LTE Antenna – PCB Line Guidelines ..................59
GSM/WCDMA/LTE Antenna – Installation Guidelines....................................60
Antenna Diversity Requirements ....................................................................60
GNSS Antenna Requirements .......................................................................61
7.5.1. Combined GNSS Antenna .............................................................................61
7.5.2. Linear and Patch GNSS Antenna ..................................................................61
7.5.3. Front End Design Considerations ..................................................................62
7.5.4. GNSS Antenna – PCB Line Guidelines ..........................................................62
7.5.5. GNSS Antenna – Installation Guidelines ........................................................63
8. HARDWARE INTERFACES .......................................................................... 64
USB Port........................................................................................................65
HSIC Interface (Optional) ...............................................................................66
SGMII Interface..............................................................................................66
Page 7

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 7 of 121 2018-12-12
8.3.1. Ethernet Control interface ..............................................................................66
Serial Ports ....................................................................................................68
8.4.1. Modem Serial Port 1 Signals..........................................................................68
8.4.2. Modem Serial Port 2 ......................................................................................71
8.4.3. RS232 Level Translation ................................................................................71
Peripheral Ports .............................................................................................73
8.5.1. SPI – Serial Peripheral Interface ....................................................................73
8.5.2. I2C - Inter-integrated Circuit ...........................................................................74
8.5.3. SD/MMC Card Interface .................................................................................75
8.5.4. WiFi SDIO Interface .......................................................................................77
Audio Interface ..............................................................................................78
8.6.1. Digital Audio ..................................................................................................78
8.6.1.1. Short Frame Timing Diagrams .......................................................................79
8.6.1.2. Long Frame Timing Diagrams ........................................................................80
General Purpose I/O ......................................................................................82
8.7.1. Using a GPIO Pad as Input ............................................................................84
8.7.2. Using a GPIO Pad as an interrupt / Wakeup source ......................................84
8.7.3. Using a GPIO Pad as Output .........................................................................85
9. MISCELLANEOUS FUNCTIONS .................................................................. 86
Indication of Network Service Availability .......................................................86
Indication of Software Ready .........................................................................87
RTC – Real Time Clock .................................................................................87
VAUX Power Output ......................................................................................87
ADC Converter ..............................................................................................88
9.5.1. Description .....................................................................................................88
9.5.2. Using the ADC Converter ..............................................................................88
Using the Temperature Monitor Function .......................................................88
GNSS Characteristics ....................................................................................89
10. MOUNTING THE MODULE ON YOUR BOARD ........................................... 90
General ..........................................................................................................90
Finishing & Dimensions .................................................................................90
Recommended Footprint for the Application ..................................................93
Stencil ............................................................................................................94
PCB Pad Design ............................................................................................94
Recommendations for PCB Pad Dimensions (mm) ........................................95
Solder Paste ..................................................................................................95
10.7.1. Solder Reflow ................................................................ ................................96
10.7.2. Cleaning ........................................................................................................98
Page 8

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 8 of 121 2018-12-12
11. APPLICATION GUIDE .................................................................................. 99
Debug of the LE910Cx Module in Production ................................................99
Bypass Capacitor on Power Supplies .......................................................... 100
SIM Interface ............................................................................................... 101
11.3.1. SIM Schematic Example .............................................................................. 101
EMC Recommendations .............................................................................. 102
Download and Debug Port ........................................................................... 102
11.5.1. Fast Boot mode ........................................................................................... 103
11.5.2. Recovery Boot Mode ................................ ................................................... 103
12. PACKING SYSTEM .................................................................................... 104
Packing System – Tray ................................................................................ 104
Tape & Reel ................................................................................................. 106
Moisture Sensitivity ...................................................................................... 108
13. SAFETY RECOMMENDATIONS................................................................. 109
14. CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT ISSUES ..................................................... 110
FCC/ISED Regulatory Notices ..................................................................... 110
15. ACRONYMS ................................................................................................ 114
16. DOCUMENT HISTORY ............................................................................... 117
Page 9

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 9 of 121 2018-12-12
1. Introduction
Scope
This document introduces the Telit LE910Cx module and presents possible and
recommended hardware solutions for developing a product based on the LE910Cx
module. All the features and solutions detailed in this document are applicable to all
LE910Cx variants, where “LE910Cx” refers to the variants listed in the applicability table.
If a specific feature is applicable to a specific product only, it will be clearly marked.
NOTE:
LE910Cx refers to all modules listed in the Applicability Table.
This document takes into account all the basic functions of a wireless module; suggests a
valid hardware solution for each function and points out incorrect solutions and common
errors to be avoided.
Obviously, this document cannot embrace every hardware solution or every product that
can be designed. Obviously, avoiding invalid solutions must be considered mandatory.
Where the suggested hardware configurations need not be considered mandatory, the
information given should be used as a guide and a starting point for properly developing
your product with the Telit LE910Cx module.
NOTE:
The integration of the GSM/GPRS/EGPRS/WCDMA/HSPA+/LTE LE910Cx
cellular module within a user application must be done according to the
design rules described in this manual.
Audience
This document is intended for Telit customers, especially system integrators, about to
implement their applications using the Telit LE910Cx module.
Contact Information, Support
For general contact, technical support services, technical questions and report
documentation errors, contact Telit Technical Support at:
• TS-EMEA@telit.com
• TS-AMERICAS@telit.com
• TS-APAC@telit.com
Page 10
LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 10 of 121 2018-12-12
Alternatively, use:
http://www.telit.com/support
For detailed information about where you can buy the Telit modules or for
recommendations on accessories and components visit:
http://www.telit.com
To register for product news and announcements or for product questions contact Telit’s
Technical Support Center (TTSC).
Our aim is to make this guide as helpful as possible. Keep us informed of your comments
and suggestions for improvements.
Telit appreciates feedback from the users of our information.
Text Conventions
The following conventions are used to emphasize specific types of information:
DANGER:
Danger – This information MUST be followed, or catastrophic equipment
failure or bodily injury may occur.
WARNING:
Caution or Warning – Alerts the user to important points about integrating the
module, if these points are not followed, the module and end user equipment
may fail or malfunction.
NOTE:
Tip or Information – Provides advice and suggestions that may be useful
when integrating the module.
All dates are in ISO 8601 format, i.e. YYYY-MM-DD.
Page 11

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 11 of 121 2018-12-12
Related Documents
Table 2: Related Documents
Document Title
Document Number
Ref 1: LE920x4/LE910Cx AT Command User Guide
80490ST10778A
Ref 2: Telit EVB HW User Guide
1VV0301249
Ref 3: LE910Cx Interface Board HW User Guide
1VV0301323
Ref 4: LE910/LE920 Digital Voice Interface Application
Note
80000NT11246A
Ref 5: Telit_LE920A4_LE910Cx_WiFi_Interface_Application_Note_r1
80490NT11511A
Ref 6: Antenna Detection Application Note
80000NT10002A
Ref 7: High-Speed Inter-Chip USB Electrical Specification,
version 1.0
(a supplement to the USB 2.0 specification, Section 3.8.2)
Ref 8: ETH_Expansion_board_Application Note
80490NT11622A
Page 12

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 12 of 121 2018-12-12
2. Product Description
Overview
LE910Cx is Telit’s new LTE series for IoT applications.
In its most basic use case, LE910Cx can be applied as a wireless communication front-
end for telematics products, offering GNSS and mobile communication features to an
external host CPU through its rich interfaces.
LE910Cx is available in hardware variants as listed in Table 1: Applicability Table. For
differences in the designated RF band sets – refer to Section 2.6.1, RF Bands per
Regional Variant.
The information presented in this document is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no
responsibility is assumed by Telit Communications S.p.A. for its use, nor any infringement of patents
or other rights of third parties which may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or
otherwise under any patent rights of Telit Communications S.p.A. other than for circuitry embodied
in Telit products. This document is subject to change without notice.
NOTE:
(EN) The integration of the LE910Cx cellular module within user application
shall be done according to the design rules described in this manual.
(IT) L’integrazione del modulo cellulare LE910Cx all’interno dell’applicazione
dell’utente dovrà rispettare le indicazioni progettuali descritte in questo
manuale.
(DE) Die Integration des LE910Cx Mobilfunk-Moduls in ein Gerät muß gemäß
der in diesem Dokument beschriebenen Kunstruktionsregeln erfolgen.
(SL) Integracija LE910Cx modula v uporabniški aplikaciji bo morala upoštevati
projektna navodila, opisana v tem priročniku.
(SP) La utilización del modulo LE910Cx debe ser conforme a los usos para
los cuales ha sido deseñado descritos en este manual del usuario.
(FR) L’intégration du module cellulaire LE910Cx dans l’application de
l’utilisateur sera faite selon les règles de conception décrites dans ce manuel.
(HE)
Page 13

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 13 of 121 2018-12-12
Applications
LE910Cx can be used for telematics applications where tamper-resistance, confidentiality,
integrity, and authenticity of end-user information are required, for example:
• Emergency call
• Telematics services
• Road pricing
• Pay-as-you-drive insurance
• Stolen vehicles tracking
• Internet connectivity
General Functionality and Main Features
The LE910Cx series of cellular modules features an LTE and multi-RAT modem together
with a powerful on-chip application processor and a rich set of interfaces.
The major functions and features are listed below:
Table 3: Features Table
Function
Features
Modem
• Multi-RAT cellular modem for voice and data communication
o LTE FDD Cat1 (Other variants) (10/5Mbps DL/UL).
o Carrier aggregation is not supported
o GSM/GPRS/EDGE
o WCDMA up to DC HSPA+, Rel.9
• Support for SIM profile switching
• Regional variants with optimal choice of RF bands for
worldwide coverage of countries and MNOs
• State-of-the-art GNSS solution with
GPS/GLONASS/BeiDou/Galileo/QZSS receiver
Digital audio
subsystem
• PCM/I2S digital audio interface
• Up to 48 kHz sample rate, 16-bit words
Two USIM ports
– dual voltage
• Class B and Class C support
• Hot swap support
• Clock rates up to 5 MHz
Application
processor
Application processor to run customer application code
• 32-bit ARM Cortex-A7 up to 1.3 GHz running the Linux
operating system
• Flash + DDR are large enough to allow for customer’s own
software applications
Page 14

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 14 of 121 2018-12-12
Function
Features
Interfaces
Rich set of interfaces, including:
• SD/MMC Card Interface supporting SD3.0 standard
• SDIO for external WiFi transceiver supporting SDIO3.0
standard
• SGMII for external Ethernet transceiver
o Compliant with IEEE802.3
o Full duplex operation at 1 Gbps
o Half/full duplex operation at 10/100 Mbps
o Support for VLAN tagging
o Support for IEEE1588, PTP (Precision Time Protocol)
• USB2.0 – USB port is typically used for:
o Flashing of firmware and module configuration
o Production testing
o Accessing the Application Processor’s file system
o AT command access
o High-speed WWAN access to external host
o Diagnostic monitoring and debugging
o NMEA data to an external host CPU
• HSIC (Optional)
o High-speed 480 Mbps (240 MHz DDR) USB transfers are
100% host driver compatible with traditional USB cable
connected topologies
o Bidirectional data strobe signal (STROBE)
o Bidirectional data signal (DATA)
o No power consumption unless a transfer is in progress
o Maximum trace length 10 cm
o Signals driven at 1.2V standard LVCMOS levels
• Peripheral Ports – SPI, I2C, UART
• GPIOs
• Antenna ports
Form factor
Form factor (28x28mm), accommodating the multiple RF bands in
each region variant
Environment
and quality
requirements
The entire module is designed and qualified by Telit for satisfying the
environment and quality requirements.
Single supply
module
The module generates all its internal supply voltages.
RTC
No dedicated RTC supply, RTC is supplied by VBATT
Page 15
LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 15 of 121 2018-12-12
Function
Features
Operating
temperature
Range -40 °C to +85 °C (conditions as defined in Section 2.5.1,
Temperature Range).
NOTE:
The following interfaces are unique for the LE910Cx and may not be
supported on other (former or future) xE910 family. Special care must be
taken when designing the application board if future compatibility is required:
- SGMII for Ethernet connectivity
- SDIO for WIFI connectivity
- SD/MMC for SD Card connectivity
Page 16
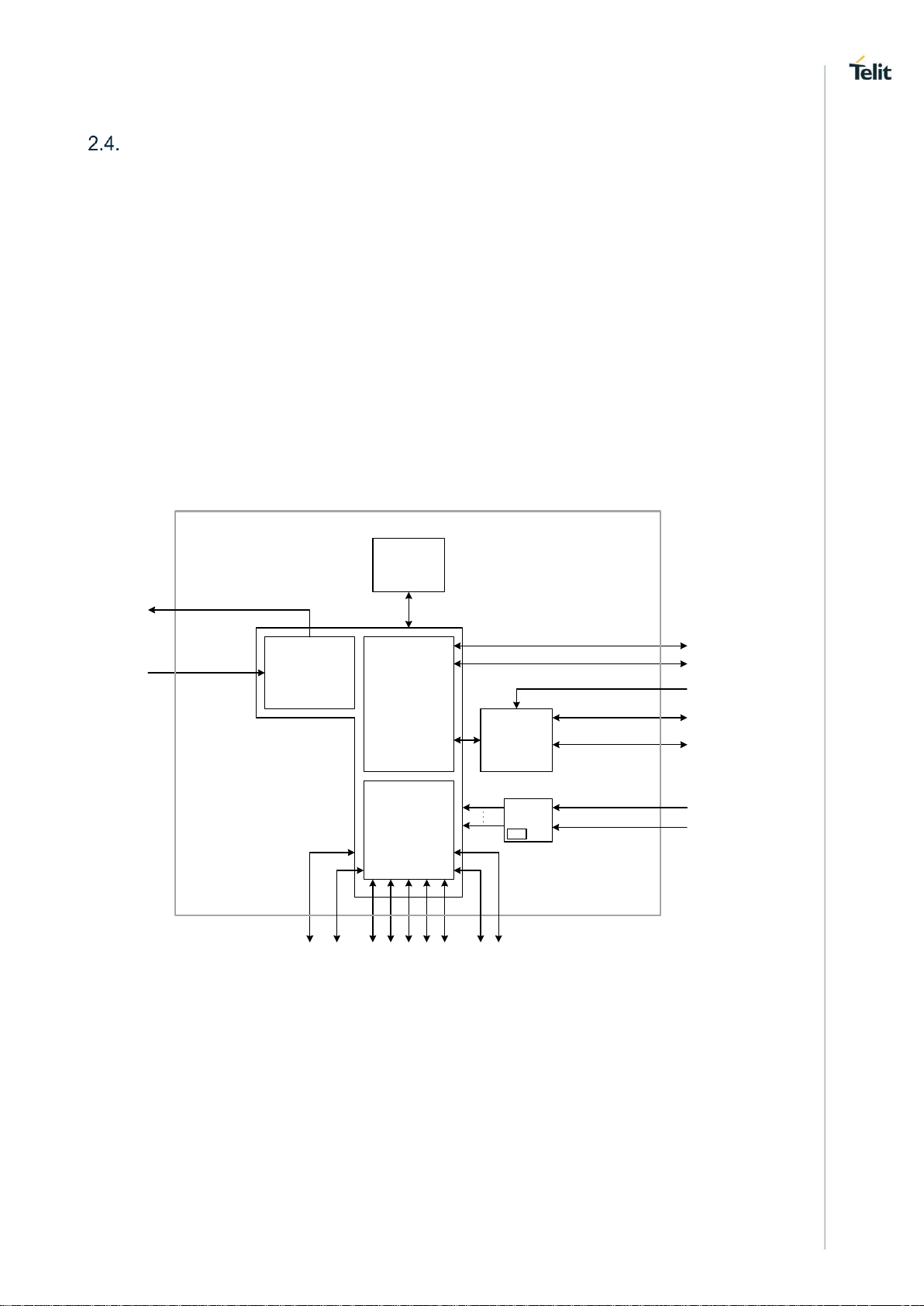
LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 16 of 121 2018-12-12
Block Diagram
Figure 1 shows an overview of the internal architecture of the LE910Cx module.
It includes the following sub-functions:
• Application processor, Modem subsystem and Location processing with their
external interfaces. These three functions are contained in a single SOC.
• RF front end and antenna ports.
• Digital Audio interface for external codec.
• Rich IO interfaces. Depending on which LE910Cx software features are enabled,
some of its interfaces that are exported due to multiplexing may be used internally
and thus may not be usable by the application.
• PMIC with the RTC function inside
Figure 1: LE910Cx Block Diagram
MEMORIES
RF
FRONTEND
GNSS Antennna
GPIO
Cellular antenna 1
Cellular antenna 2
PCM In/out
SIM
GNSS_Sync
APPLICATION
PROCESSOR
MODEM
LOCATION
HSICI2C USB2.0SGMIISPI
UART
JTAG
2xSDIO
PMIC
VBATT
ADC
VBATT_PA
RTC
Page 17
LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 17 of 121 2018-12-12
Environmental Requirements
2.5.1. Temperature Range
Operating
temperature
range
-40 ~ +85°C Ambient.
Temperatures outside of the range –20°C ÷ +55°C might slightly
deviate from ETSI specifications. The module is fully functional,
able to make and receive voice calls, data calls, SMS and GPRS
traffic.
Storage and nonoperating
temperature
range
–40°C ~ +90°C
2.5.2. RoHS Compliance
As a part of the Telit corporate policy of environmental protection, the LE910Cx complies
with the RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) directive of the European Union
(EU directive 2011/65/EU).
Page 18
LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 18 of 121 2018-12-12
Operating Frequency Bands
The operating frequencies in GSM850, EGSM900, DCS1800, PCS1900, WCDMA & LTE
modes conform to the 3GPP specifications.
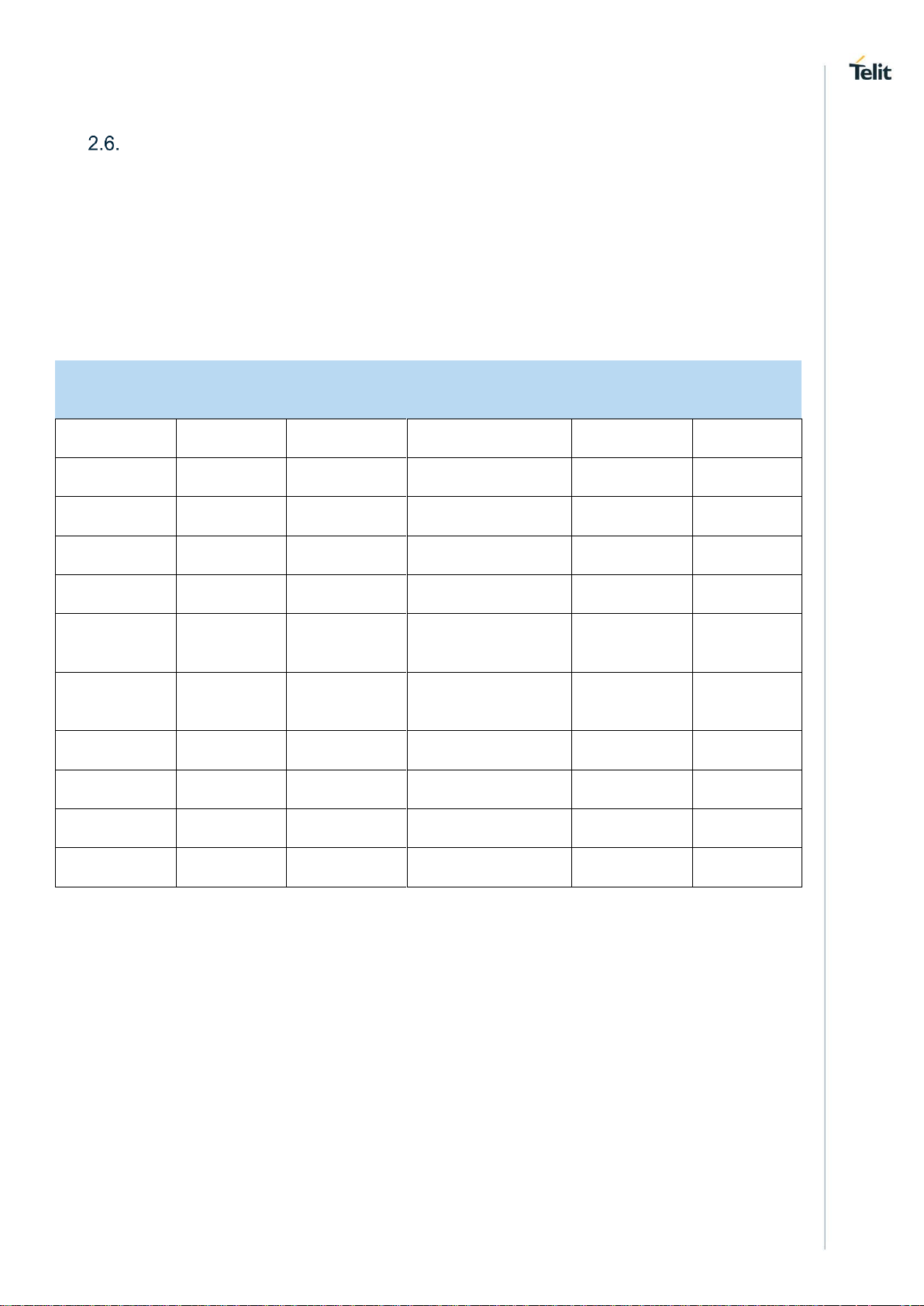
2.6.1. RF Bands per Regional Variant
Table 4 summarizes all region variants within the LE910Cx family, showing the supported
band sets in each variant and the supported band pairs for 2x carrier aggregation.
Table 4: RF Bands per Regional Variant
Region
Variant
2G
HSPA+
LTE FDD
LTE TDD
TD-SCDMA
LE910C1-NA
2, 3, 5, 8
1, 2, 4, 5, 8
2, 4, 12
-
-
LE910C1-NS
- - 2, 4, 5, 12, 25, 26
-
-
LE910C1-AP
-
1, 5, 6, 8, 19
1, 3, 5, 8, 9, 19, 28
-
-
LE910C4-EU
3, 8
1, 3, 8
1, 3, 7, 8, 20, 28A
-
-
LE910C1-EU
3, 8
1, 3, 8
1, 3, 7, 8, 20, 28A
-
-
LE910C4-NF
-
2, 4, 5
2, 4, 5, 12, 13, 14,
66, 71
- - LE910C1-NF
-
2, 4, 5
2, 4, 5, 12, 13, 14,
66, 71
-
-
LE910C1-SA
- - 2, 4, 12, 14, 66
-
-
LE910C1-ST
- - 2, 4, 12, 66, 71
- - LE910C1-SV
- - 4, 13
-
-
LE910C1-LA
2, 3, 5, 8
1, 2, 4, 5
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 28
-
-
Page 19
LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 19 of 121 2018-12-12
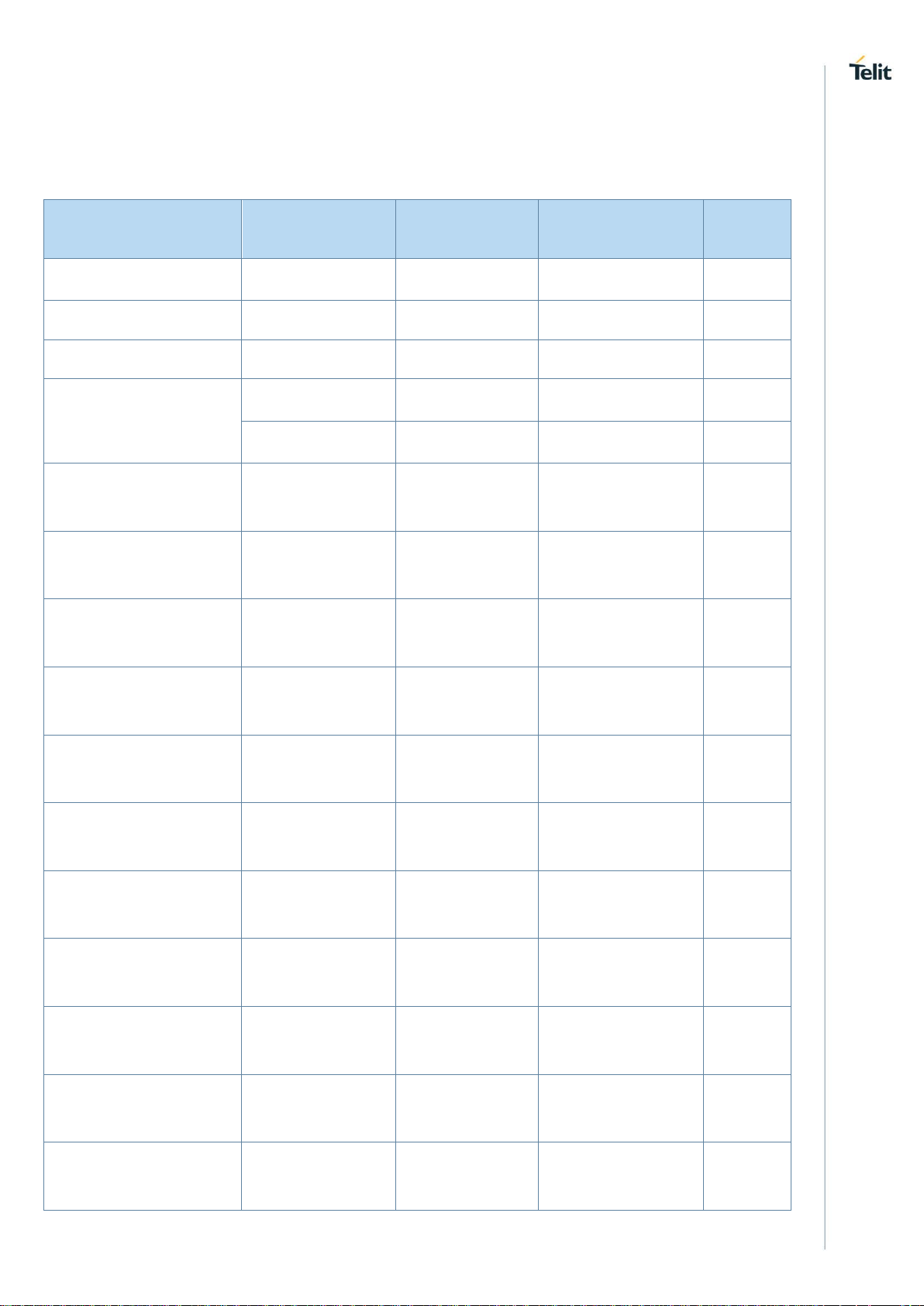
2.6.2. Reference Table of RF Bands Characteristics
Table 5: RF Bands Characteristics
Mode
Freq. Tx (MHz)
Freq. Rx (MHz)
Channels
Tx-Rx
Offset
PCS 1900
1850.2 ~ 1909.8
1930.2 ~ 1989.8
512 ~ 810
80 MHz
DCS 1800
1710 ~ 1785
1805 ~ 1880
512 ~ 885
95 MHz
GSM 850
824.2 ~ 848.8
869.2 ~ 893.8
128 ~ 251
45 MHz
EGSM 900
890 ~ 915
935 ~ 960
0 ~ 124
45 MHz
880 ~ 890
925 ~ 935
975 ~ 1023
45 MHz
WCDMA 2100 – B1
1920 ~ 1980
2110 ~ 2170
Tx: 9612 ~ 9888
Rx: 10562 ~ 10838
190 MHz
WCDMA 1900 – B2
1850 ~ 1910
1930 ~ 1990
Tx: 9262 ~ 9538
Rx: 9662 ~ 9938
80 MHz
WCDMA 1800 – B3
1710 ~ 1785
1805 ~ 1880
Tx: 937 ~ 1288
Rx: 1162 ~ 1513
95 MHz
WCDMA AWS – B4
1710 ~ 1755
2110 ~ 2155
Tx: 1312 ~ 1513
Rx: 1537 ~ 1738
400 MHz
WCDMA 850 – B5
824 ~ 849
869 ~ 894
Tx: 4132 ~ 4233
Rx: 4357 ~ 4458
45 MHz
WCDMA 900 – B8
880 ~ 915
925 ~ 960
Tx: 2712 ~ 2863
Rx: 2937 ~ 3088
45 MHz
WCDMA 1800 – B9
1750 ~ 1784.8
1845 ~ 1879.8
Tx: 8762 ~ 8912
Rx: 9237 ~ 9387
95 MHz
WCDMA 800 – B19
830 ~ 845
875 ~ 890
Tx: 312 ~ 363
Rx: 712 ~ 763
45 MHz
TDS CDMA 2000 – B34
2010 ~ 2025
2010 ~ 2025
Tx: 10054 ~ 10121
Rx: 10054 ~ 10121
0 MHz
TDS CDMA 1900 – B39
1880 ~ 1920
1880 ~ 1920
Tx: 9404 ~ 9596
Rx: 9404 ~ 9596
0 MHz
LTE 2100 – B1
1920 ~ 1980
2110 ~ 2170
Tx: 18000 ~ 18599
Rx: 0 ~ 599
190 MHz
Page 20

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 20 of 121 2018-12-12
Mode
Freq. Tx (MHz)
Freq. Rx (MHz)
Channels
Tx-Rx
Offset
LTE 1900 – B2
1850 ~ 1910
1930 ~ 1990
Tx: 18600 ~ 19199
Rx: 600 ~ 1199
80 MHz
LTE 1800 – B3
1710 ~ 1785
1805 ~ 1880
Tx: 19200 ~ 19949
Rx: 1200 ~ 1949
95 MHz
LTE AWS – B4
1710 ~ 1755
2110 ~ 2155
Tx: 19950 ~ 20399
Rx: 1950 ~ 2399
400 MHz
LTE 850 – B5
824 ~ 849
869 ~ 894
Tx: 20400 ~ 20649
Rx: 2400 ~ 2649
45 MHz
LTE 2600 – B7
2500 ~ 2570
2620 ~ 2690
Tx: 20750 ~ 21449
Rx: 2750 ~ 3449
120 MHz
LTE 900 – B8
880 ~ 915
925 ~ 960
Tx: 21450 ~ 21799
Rx: 3450 ~ 3799
45 MHz
LTE 1800 – B9
1749.9 ~ 1784.9
1844.9 ~ 1879.9
Tx: 21800 ~ 2149
Rx: 3800 ~ 4149
95 MHz
LTE AWS+ – B10
1710 ~ 1770
2110 ~ 2170
Tx: 22150 ~ 22749
Rx: 4150 ~ 4749
400 MHz
LTE 700a – B12
699 ~ 716
729 ~ 746
Tx: 23010 ~ 23179
Rx: 5010 ~ 5179
30 MHz
LTE 700c – B13
777 ~ 787
746 ~ 756
Tx: 23180 ~ 23279
Rx: 5180 ~ 5279
-31 MHz
LTE 700PS – B14
788 ~ 798
758 ~ 768
Tx: 23280 ~ 23379
Rx: 5280 ~ 5379
-30 MHz
LTE 700b – B17
704 ~ 716
734 ~ 746
Tx: 23730 ~ 23849
Rx: 5730 ~ 5849
30 MHz
LTE 800 – B19
830 ~ 845
875 ~ 890
Tx: 24000 ~ 24149
Rx: 6000 ~ 6149
45 MHz
LTE 800 – B20
832 ~ 862
791 ~ 821
Tx: 24150 ~ 24449
Rx: 6150 ~ 6449
-41 MHz
LTE 1500 – B21
1447.9 ~ 1462.9
1495.9 ~ 1510.9
Tx: 24450 ~ 24599
Rx: 6450 ~ 6599
48 MHz
Page 21
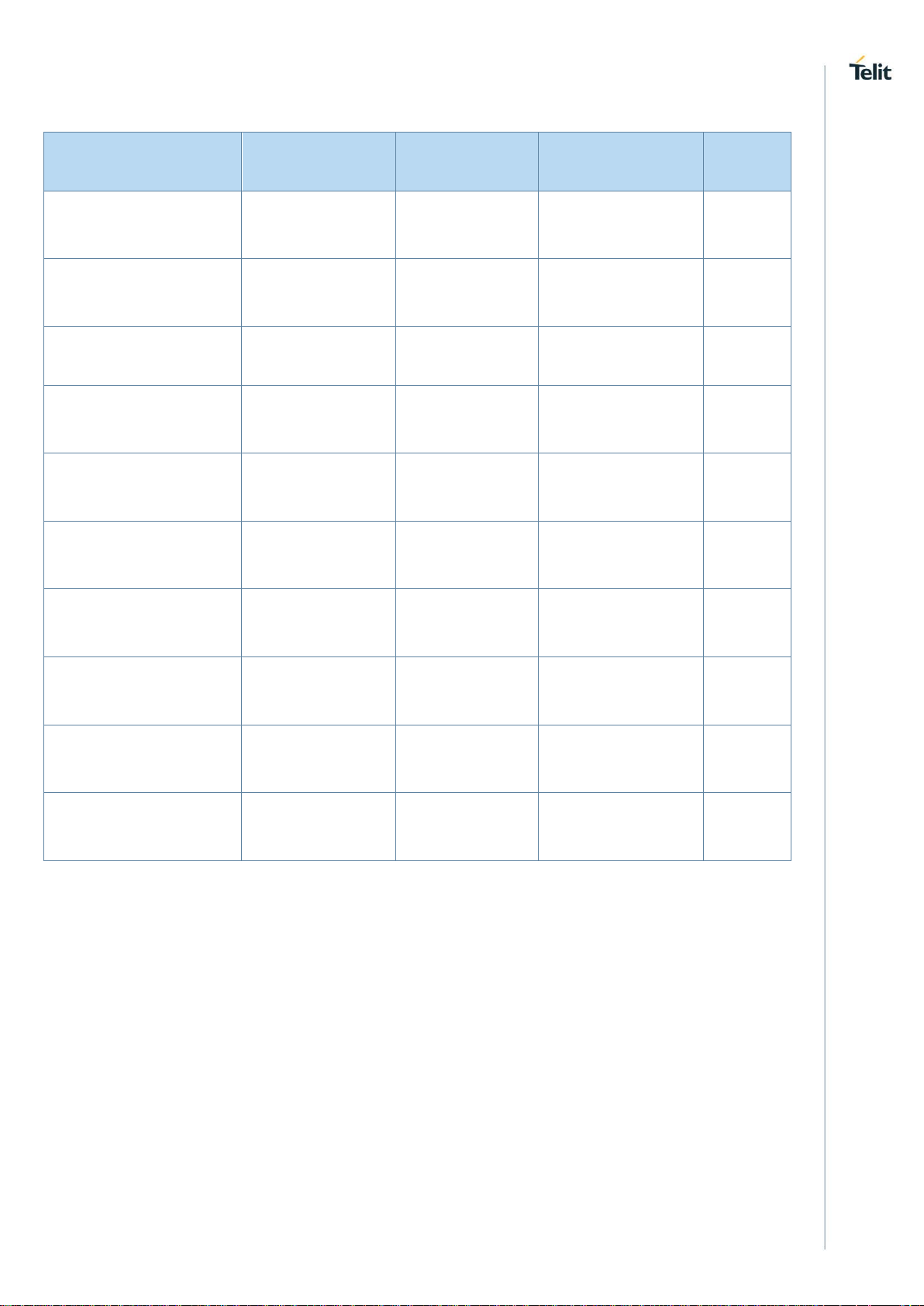
LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 21 of 121 2018-12-12
Mode
Freq. Tx (MHz)
Freq. Rx (MHz)
Channels
Tx-Rx
Offset
LTE 1900+ – B25
1930 ~ 1995
1850 ~ 1915
Tx: 26040 ~ 26689
Rx: 8040 ~ 8689
80 MHz
LTE 850+ – B26
814 ~ 849
859 ~ 894
Tx: 26690 ~ 27039
Rx: 8690 ~ 9039
45 MHz
LTE 700 – B28A
703 ~ 733
758 ~ 788
Tx: 27210 ~ 27510
Rx: 9210 ~ 9510
55 MHz
LTE 700 – B28
703 ~ 748
758 ~ 803
Tx: 27210 ~ 27659
Rx: 9210 ~ 9659
55 MHz
LTE AWS-3 – B66
1710 ~ 1780
2210 ~ 2200
Tx: 131972-132671
Rx: 66436-67335
400 MHz
LTE600 – B71
663 ~ 698
617 ~ 652
Tx: 133122-133471
Rx: 68568-68935
46 MHz
LTE TDD 2600 – B38
2570 ~ 2620
2570 ~ 2620
Tx: 37750 ~ 38250
Rx: 37750 ~ 38250
0 MHz
LTE TDD 1900 – B39
1880 ~ 1920
1880 ~ 1920
Tx: 38250 ~ 38650
Rx: 38250 ~ 38650
0 MHz
LTE TDD 2300 – B40
2300 ~ 2400
2300 ~ 2400
Tx: 38650 ~ 39650
Rx: 38650 ~ 39650
0 MHz
LTE TDD 2500 – B41M
2555 ~ 2655
2555 ~ 2655
Tx: 40265 ~ 41215
Rx: 40265 ~ 41215
0 MHz
Page 22

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 22 of 121 2018-12-12
RF Parameters
2.7.1. Sensitivity
Typical sensitivity levels are as follows:
• -108 dBm @ 2G
• -113.5 dBm @ 3G
• -103 dBm @ 4G FDD (BW=5 MHz)
2.7.2. Output power
Typical values for Max output level are as follow:
• 2G:
- LB: 33dBm
- HB: 30dBm
• 3G/TD-SCDMA: 24dBm
• 4G (FDD & TDD): 23dBm @1RB.
Page 23

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 23 of 121 2018-12-12
Mechanical Specifications
2.8.1. Dimensions
The module’s overall dimensions are:
• Length: 28.2 mm, +/- 0.15 mm tolerance
• Width: 28.2 mm, +/- 0.15 mm tolerance
• Thickness: 2.2 mm, +/- 0.15 mm tolerance
NOTE:
Consider a typical label thickness of 0.1 mm in addition to the module
thickness.
2.8.2. Weight
The nominal weight of the LE910Cx module is 9.0 gram.
Page 24
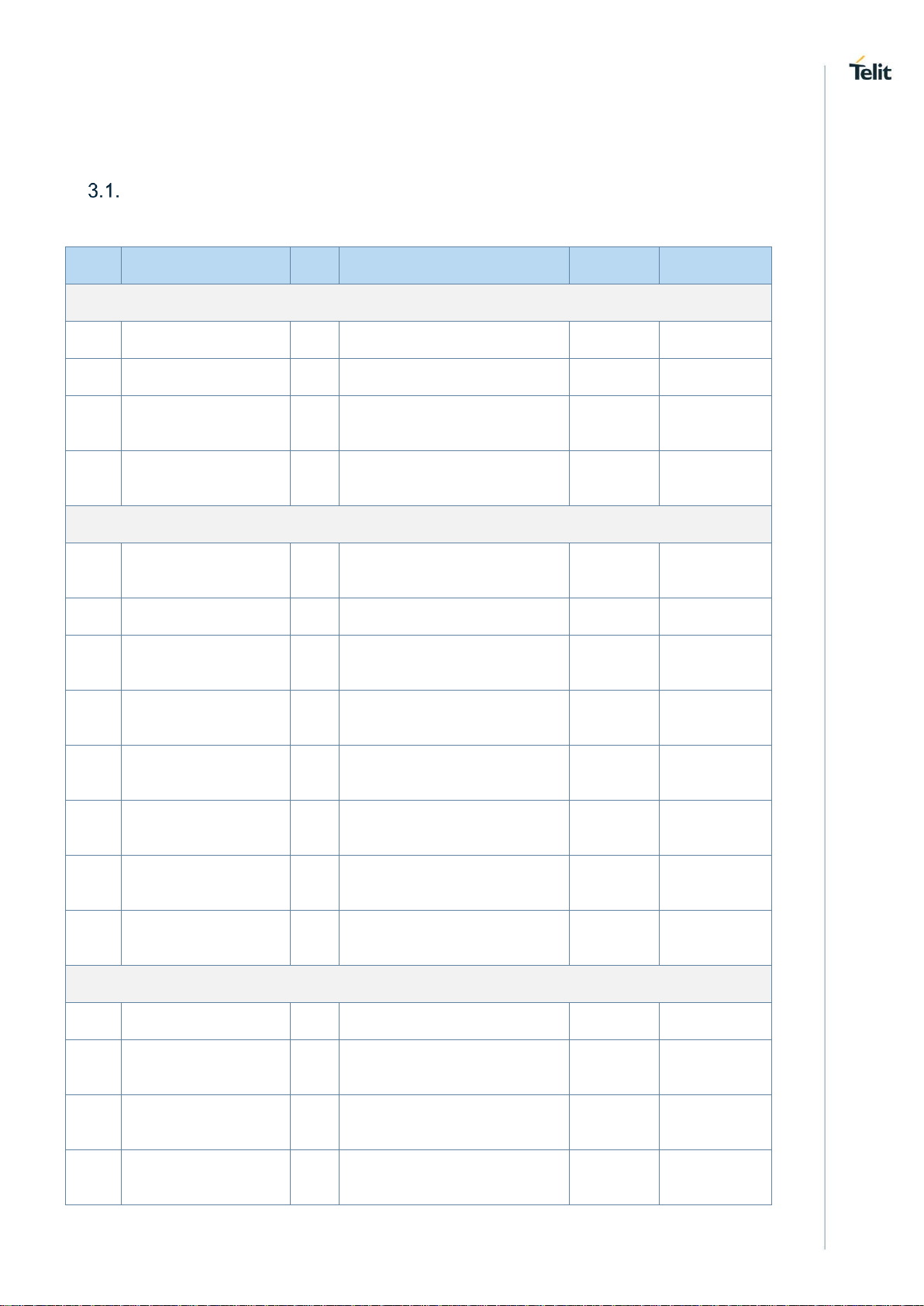
LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 24 of 121 2018-12-12
3. Module Connections
Pin-out
Table 6: Pin-out
PAD
Signal
I/O
Function
Type
Comment
USB HS 2.0 Communication Port
B15
USB_D+
I/O
USB differential Data (+)
C15
USB_D-
I/O
USB differential Data (-)
A13
USB_VBUS
AI
Power sense for the internal
USB transceiver
Power
A14
USB_ID
AI
USB ID
See note
below
Asynchronous UART
N15
C103/TXD
I
Serial data input (TXD) from
DTE
1.8V
M15
C104/RXD
O
Serial data output to DTE
1.8V
L14
C105/RTS
I
Input for Request to send
signal (RTS) from DTE
1.8V
P15
C106/CTS
O
Output for Clear to send signal
(CTS) to DTE
1.8V
P14
C107/DSR
O
Output for Data Set Ready
(DSR) to DTE
1.8V
Alternate Fn
GPIO_32
M14
C108/DTR
I
Input for Data Terminal Ready
(DTR) from DTE
1.8V
Alternate Fn
GPIO_34
N14
C109/DCD
O
Output for Data Carrier Detect
(DCD) to DTE
1.8V
Alternate Fn
GPIO_33
R14
C125/RING
O
Output for Ring Indication (RI)
to DTE
1.8V
Alternate Fn
GPIO_31
SPI – Serial Peripheral Interface / AUX UART
F15
SPI_CLK
O
SPI Clock output
1.8V
E15
SPI_MISO/ RX_AUX
I
SPI data Master Input Slave
output / RX_AUX
1.8V
D15
SPI_MOSI/TX_AUX
O
SPI data Master Output Slave
input/ TX_AUX
1.8V
H14
SPI_CS/GPIO11
O
SPI Chip select output /
GPIO11
1.8V
See note
below
Page 25
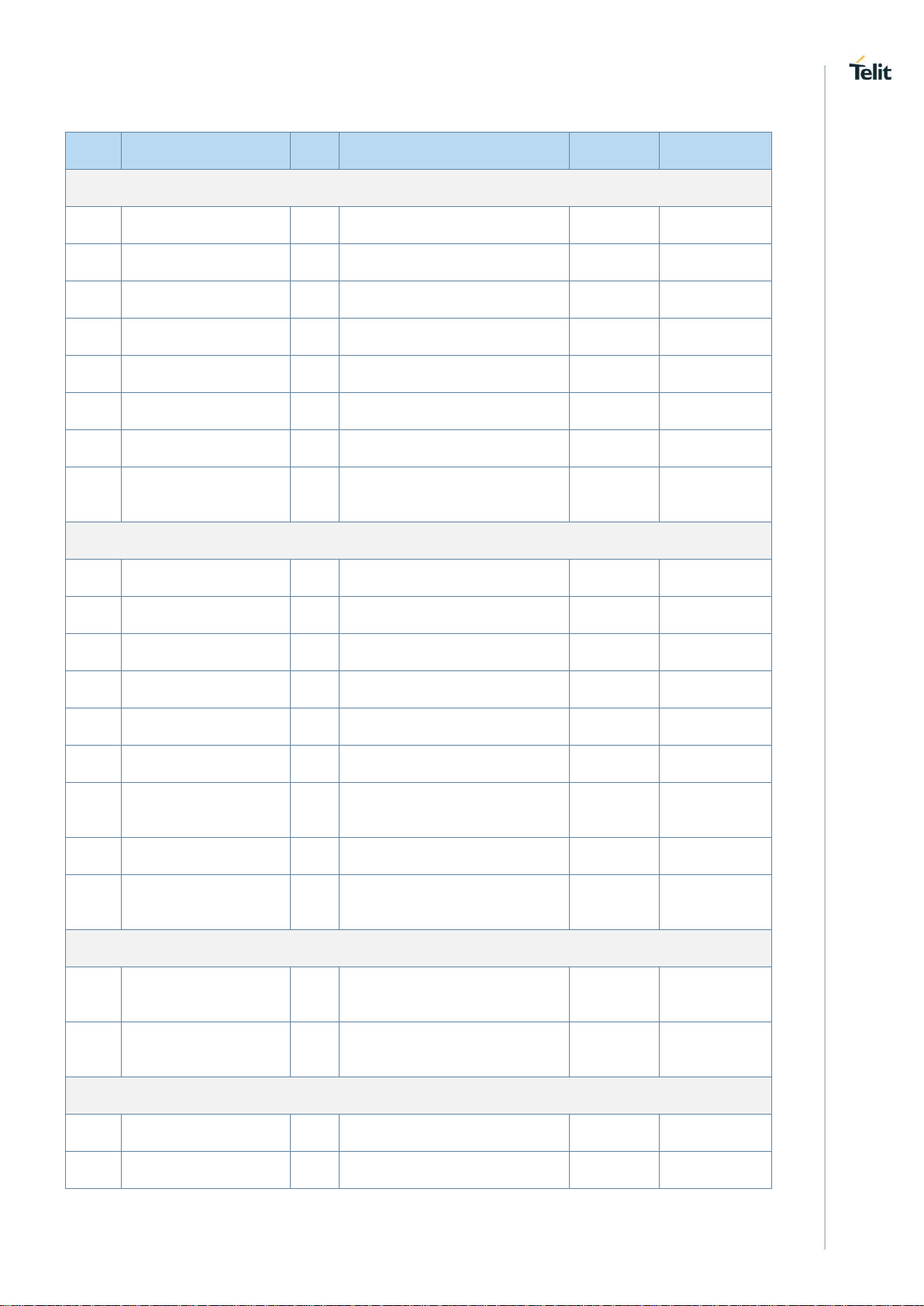
LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 25 of 121 2018-12-12
PAD
Signal
I/O
Function
Type
Comment
SD/MMC Card Digital I/O
J12
SD/MMC_CMD
O
SD Command
1.8/2.95V
F12
SD/MMC_CLK
O
SD Card Clock
1.8/2.95V
E12
SD/MMC_DATA0
I/O
SD Serial Data 0
1.8/2.95V
G12
SD/MMC_DATA1
I/O
SD Serial Data 1
1.8/2.95V
K12
SD/MMC_DATA2
I/O
SD Serial Data 2
1.8/2.95V
H12
SD/MMC_DATA3
I/O
SD Serial Data 3
1.8/2.95V
G13
SD/MMC_CD
I
SD card detect input
1.8V
Active Low
F13
VMMC
-
Power supply for MMC card
pull-up resistors
1.8/2.95V
WiFi (SDIO) Interface
N13
WiFi_SD_CMD
O
Wi-Fi SD Command
1.8V
L13
WiFi_SD_CLK
O
Wi-Fi SD Clock
1.8V
J13
WiFi_SD_DATA0
I/O
Wi-Fi SD Serial Data 0
1.8V
M13
WiFi_SD_DATA1
I/O
Wi-Fi SD Serial Data 1
1.8V
K13
WiFi_SD_DATA2
I/O
Wi-Fi SD Serial Data 2
1.8V
H13
WiFi_SD_DATA3
I/O
Wi-Fi SD Serial Data 3
1.8V
L12
WiFi_SDRST
O
Wi-Fi Reset / Power enable
control
1.8V
Active Low
M11
WLAN_SLEEP_CLK
O
Wi-Fi Sleep clock output
1.8V
M10
RFCLK2_QCA
O
Wi-Fi low noise RF clock
output
1.8V
LTE-WiFi Coexistence
M8
WCI_TX
O
Wireless coexistence interface
TXD
1.8V
M9
WCI_RX
I
Wireless coexistence interface
RXD
1.8V
SIM Card Interface 1
A6
SIMCLK1
O
External SIM 1 signal – Clock
1.8/2.85V
A7
SIMRST1
O
External SIM 1 signal – Reset
1.8/2.85V
Page 26
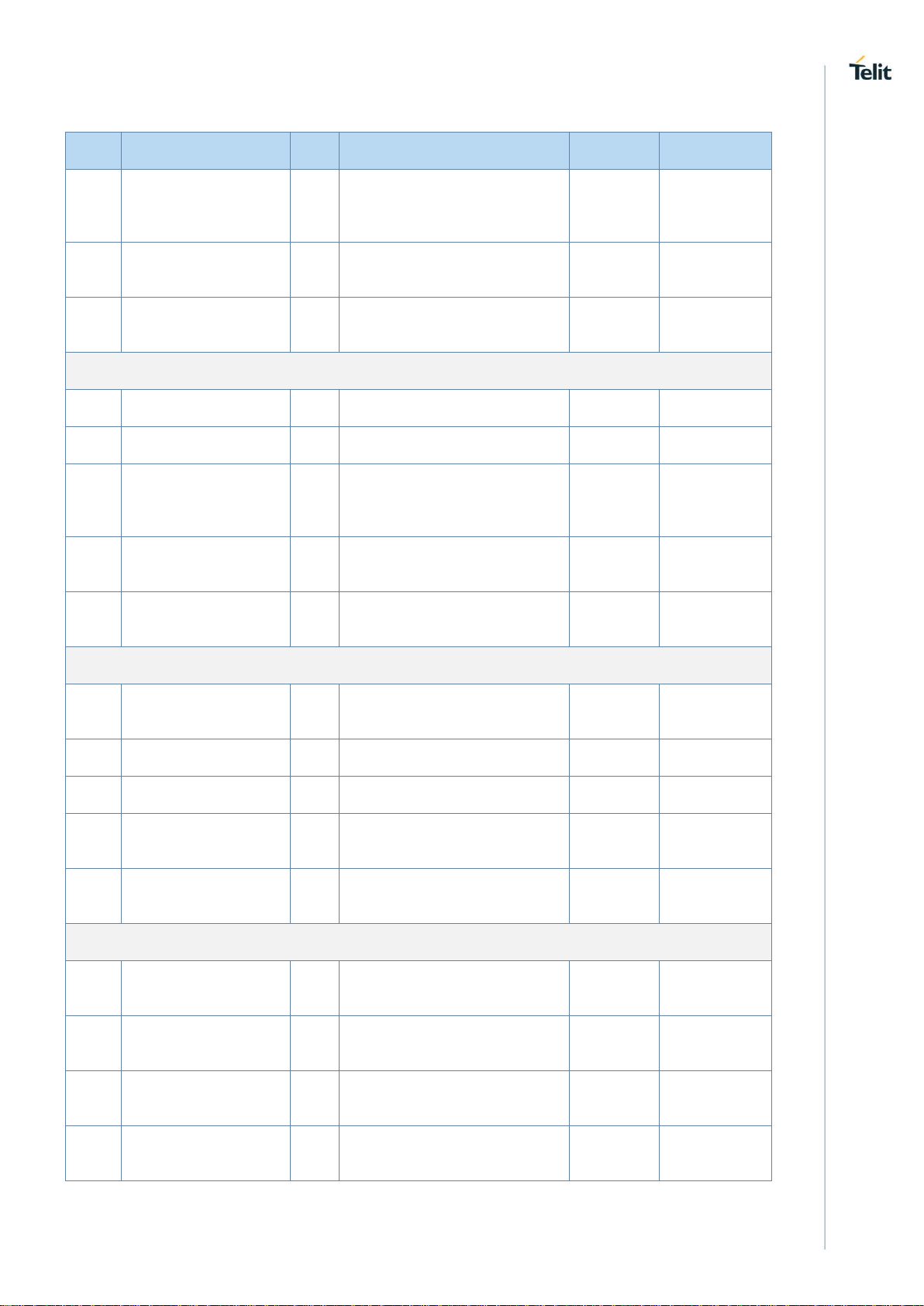
LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 26 of 121 2018-12-12
PAD
Signal
I/O
Function
Type
Comment
A5
SIMIO1
I/O
External SIM 1 signal - Data
I/O
1.8/2.85V
Internally PU
10 kΩ to
SIMVCC1
A4
SIMIN1
I
External SIM 1 signal Presence
1.8V
Active low
A3
SIMVCC1
-
External SIM 1 signal – Power
supply for SIM 1
1.8/2.85V
SIM Card Interface 2
C1
SIMCLK2
O
External SIM 2 signal – Clock
1.8/2.85V
D1
SIMRST2
O
External SIM 2 signal – Reset
1.8/2.85V
C2
SIMIO2
I/O
External SIM 2 signal – Data
I/O
1.8/2.85V
Internally PU
10kΩ to
SIMVCC2
G4
SIMIN2
I
External SIM 2 signal –
Presence
1.8V
Active low
D2
SIMVCC2
-
External SIM 2 signal – Power
supply for SIM 2
1.8/2.85V
Digital Voice Interface (DVI)
B9
DVI_WAO
O
Digital Voice interface (WAO
master output)
1.8V
B6
DVI_RX
I
Digital Voice interface (Rx)
1.8V
B7
DVI_TX
O
Digital Voice interface (Tx)
1.8V
B8
DVI_CLK
O
Digital Voice interface (CLK
master output)
1.8V
B12
REF_CLK
O
Reference clock for external
Codec
1.8V
See Note
below
General Purpose Digital I/O
C8
GPIO_01
I/O
GPIO_01 / STAT_LED
1.8V
Alternate Fn
I2C
C9
GPIO_02
I/O
GPIO_02
1.8V
Alternate Fn
I2C
C10
GPIO_03
I/O
GPIO_03
1.8V
Alternate Fn
I2C
C11
GPIO_04
I/O
GPIO_04
1.8V
Alternate Fn
I2C
Page 27
LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 27 of 121 2018-12-12
PAD
Signal
I/O
Function
Type
Comment
B14
GPIO_05
I/O
GPIO_05
1.8V
Alternate Fn
I2C
C12
GPIO_06
I/O
GPIO_06
1.8V
Alternate Fn
I2C
C13
GPIO_07
I/O
GPIO_07
1.8V
Alternate Fn
I2C
K15
GPIO_08
I/O
GPIO_08 / SW_RDY
1.8V
Alternate Fn
I2C
L15
GPIO_09
I/O
GPIO_09
1.8V
Alternate Fn
I2C
G15
GPIO_10
I/O
GPIO_10
1.8V
Alternate Fn
I2C
RF Section
K1
Antenna
I/O
GSM/EDGE/UMTS/LTE Main
antenna (50 Ohm)
RF F1
ANT_DIV
I
UMTS/LTE antenna diversity
input (50 Ohm)
RF
GPS Section
R9
ANT_GPS
I
GPS antenna (50 Ohm)
RF
R7
GPS_LNA_EN
O
Enables the external regulator
for GPS LNA
1.8V
N9
GPS_SYNC
O
GPS sync signal for Dead
Reckoning
1.8V
Miscellaneous Functions
R12
ON_OFF_N
I
Power ON / Power OFF input
Active low
R13
HW_SHUTDOWN_N
I
Unconditional Shutdown input
Active low
R11
VAUX/PWRMON
O
Supply output for external
accessories /
Power ON monitor
1.8V
B1
ADC_IN1
AI
Analog/Digital Converter Input
1
Analog
H4
ADC_IN2
AI
Analog/Digital Converter Input
2
Analog
D7
ADC_IN3
AI
Analog/Digital Converter Input
3
Analog
Page 28
LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 28 of 121 2018-12-12
PAD
Signal
I/O
Function
Type
Comment
SGMII Interface
E4
SGMII_RX_P
AI
SGMII receive – plus
PHY
F4
SGMII_RX_M
AI
SGMII receive – minus
PHY
D5
SGMII_TX_P
AO
SGMII transmit – plus
PHY
D6
SGMII_TX_M
AO
SGMII transmit - minus
PHY
HSIC Interface
A12
HSIC_DATA
I/O
High-speed inter-chip interface
- data
1.2V
Optional
A11
HSIC_STB
I/O
High-speed inter-chip interface
- strobe
1.2V
Optional
I2C Interface
B11
I2C_SCL
I/O
I2C clock
1.8V
Internally PU
2.2kΩ to 1.8V
B10
I2C_SDA
I/O
I2C Data
1.8V
Internally PU
2.2kΩ to 1.8V
Power Supply
M1
VBATT
-
Main Power Supply (Digital
Section)
Power
M2
VBATT
-
Main Power Supply (Digital
Section)
Power
N1
VBATT_PA
-
Main Power Supply (RF
Section)
Power
N2
VBATT_PA
-
Main Power Supply (RF
Section)
Power
P1
VBATT_PA
-
Main Power Supply (RF
Section)
Power
P2
VBATT_PA
-
Main Power Supply (RF
Section)
Power
A2
GND
-
Ground
B13
GND
Ground
D4
GND
-
Ground
E1
GND
-
Ground
E2
GND
-
Ground
Page 29

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 29 of 121 2018-12-12
PAD
Signal
I/O
Function
Type
Comment
E14
GND
-
Ground
F2
GND
-
Ground
G1
GND
-
Ground
G2
GND
-
Ground
G7
GND
-
Ground
G8
GND
-
Ground
G9
GND
-
Ground
H1
GND
-
Ground
H2
GND
-
Ground
H7
GND
-
Ground
H8
GND
-
Ground
H9
GND
-
Ground
J1
GND
-
Ground
J2
GND
-
Ground
J7
GND
-
Ground
J8
GND
-
Ground
J9
GND
-
Ground
K2
GND
-
Ground
L1
GND
-
Ground
L2
GND
-
Ground
M3
GND
-
Ground
M4
GND
-
Ground
M12
GND
-
Ground
N3
GND
-
Ground
N4
GND
-
Ground
N5
GND
-
Ground
N6
GND
-
Ground
P3
GND
-
Ground
Page 30
LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 30 of 121 2018-12-12
PAD
Signal
I/O
Function
Type
Comment
P4
GND
-
Ground
P5
GND
-
Ground
P6
GND
-
Ground
P8
GND
-
Ground
P9
GND
-
Ground
P10
GND
-
Ground
P13
GND
-
Ground
R2
GND
-
Ground
R3
GND
-
Ground
R5
GND
-
Ground
R6
GND
-
Ground
R8
GND
-
Ground
R10
GND
-
Ground
Reserved
A8
Reserved
-
Reserved
A9
Reserved
-
Reserved
A10
Reserved
-
Reserved
B2
Reserved
-
Reserved
B3
Reserved
-
Reserved
B4
Reserved
-
Reserved
B5
Reserved
-
Reserved
C3
Reserved
-
Reserved
C4
Reserved
-
Reserved
C5
Reserved
-
Reserved
C6
Reserved
-
Reserved
C7
Reserved
-
Reserved
C14
Reserved
-
Reserved
D3
Reserved
-
Reserved
Page 31

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 31 of 121 2018-12-12
PAD
Signal
I/O
Function
Type
Comment
D8
Reserved
-
Reserved
D9
Reserved
-
Reserved
D10
Reserved
-
Reserved
D11
Reserved
-
Reserved
D12
Reserved
-
Reserved
D13
Reserved
-
Reserved
D14
Reserved
-
Reserved
E3
Reserved
-
Reserved
E13
Reserved
-
Reserved
F3
Reserved
-
Reserved
F14
Reserved
-
Reserved
G3
Reserved
-
Reserved
G14
Reserved
-
Reserved
H3
Reserved
-
Reserved
H15
Reserved
-
Reserved
J3
Reserved
-
Reserved
J4
Reserved
-
Reserved
J14
Reserved
-
Reserved
J15
Reserved
-
Reserved
K3
Reserved
-
Reserved
K4
Reserved
-
Reserved
K14
Reserved
-
Reserved
L3
Reserved
-
Reserved
L4
Reserved
-
Reserved
M5
Reserved
-
Reserved
M6
Reserved
-
Reserved
M7
Reserved
-
Reserved
N7
Reserved
-
Reserved
Page 32

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 32 of 121 2018-12-12
PAD
Signal
I/O
Function
Type
Comment
N8
Reserved
-
Reserved
N10
Reserved
-
Reserved
N11
Reserved
-
Reserved
N12
Reserved
-
Reserved
P7
Reserved
-
Reserved
P11
Reserved
-
Reserved
P12
Reserved
-
Reserved
Reserved for future use
R4
RFU
-
Reserved for future use. Not
connected internally
Can be tied
to GND
WARNING:
GPIO_09 and WCI_RX are used as special HW flags during boot.
If they are used as GPIOs, they must be connected via a 3-state buffer to
avoid any undesirable effect during the boot.
NOTE:
When the UART signals are used as the communication port between the
host and the modem, the RTS must be connected to GND (on the module
side) if flow control is not used.
If the UART port is not used, all UART signals can be left disconnected.
NOTE:
Unless otherwise specified, RESERVED pins must be left unconnected
(floating).
Page 33

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 33 of 121 2018-12-12
NOTE:
The following pins are unique for the LE910Cx and may not be supported on
other (former or future) xE910 family modules. Special care must be taken
when designing the application board if future compatibility is required.
REF_CLK
SPI_CS
USB_ID
I2C_SCL
I2C_SDA
ADC_IN2
ADC_IN3
Signals That Must Be Connected
Table 7 lists the LE910Cx signals that must be connected even if not used by the end
application:
Table 7: Mandatory Signals
PAD
Signal
Notes
M1, M2, N1, N2, P1, P2
VBATT &
VBATT_PA
A2, B13, D4, E1, E2, E14, F2, G1,
G2, G7, G8, G9, H1, H2, H7, H8,
H9, J1, J2, J7, J8, J9, K2, L1, L2,
M3, M4, M12, N3, N4, N5, N6, P3,
P4, P5, P6, P8, P9, P10, P13, R2,
R3, R5, R6, R8, R10
GND
R12
ON/OFF
Main power on off signal
R13
HW_SHUTDOWN_N
Emergency power off
B15
USB_D+
If not used, connect to a
Test Point or an USB
connector
C15
USB_D-
If not used, connect to a
Test Point or an USB
connector
A13
USB_VBUS
If not used, connect to a
Test Point or an USB
connector
Page 34

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 34 of 121 2018-12-12
PAD
Signal
Notes
N15
C103/TXD
If not used, connect to a
Test Point
M15
C104/RXD
If not used, connect to a
Test Point
L14
C105/RTS
If flow control is not used,
connect to GND
P15
C106/CTS
If not used, connect to a
Test Point
D15
TX_AUX
If not used, connect to a
Test Point
E15
RX_AUX
If not used, connect to a
Test Point
K1
Antenna
MAIN antenna
F1
ANT_DIV
DIV antenna
R9
ANT_GPS
GPS antenna
C4, C5, C6, C7, D3, E3, G3, K4,
L4, P11
Reserved
Connect to a Test Point for
Telit internal use
L15
GPIO_09
If not used, connect to a
Test Point
M9
WCI_RX
If not used, connect to a
Test Point
Page 35

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 35 of 121 2018-12-12
LGA Pads Layout
Figure 2: LGA Pads Layout
A B C D E F G H J K L M N P R
1 ADC_IN1 SIMCLK2 SIMRST2 GND ANT_DIV GND GND GND ANT_MAIN GND VBATT VBATT_PA VBATT_PA
2 GND RES SIMIO2 SIMVCC2 GND GND GND GND GND GND GND VBATT VBATT_PA VBATT_PA GND
3 SIMVCC RES RES RES RES RES RES RES RES RES RES GND GND GND GND
4 SIMIN RES RES GND SGMII_RX_P SGMII_RX_M SIMIN2 ADC_IN2 RES RES RES GND GND GND RFU
5 SIMIO RES RES SGMII_TX_P RES GND GND GND
6 SIMCLK DVI_RX RES SGMII_TX_M RES GND GND GND
7 SIMRST DVI_TX RES ADC_IN3 GND GND GND RES R ES RES GPS_LNA_EN
8 RES DVI_CLK GPIO_01 RES GND GND GND WCI_TXD_TGPIO24 RES GND GND
9 RES DVI_WA0 GPIO_02 RES GND GND GND WCI_RXD_TGPIO25 GPS_SYNC GND ANT_GPS
10 RES I2C_SDA GPIO_03 RES RFCLK2_QCA RES GND GND
11 HSIC_STB I2C_SCL GPIO_04 RES WLAN_SLEEP_CLK RES RES VAUX/PWRMON
12 HSIC_DATA REF_CLK GPIO_06 RES MMC_DAT0 MMC_CLK MMC_DAT1 MMC_DAT3 MMC_CMD MMC_DAT2 WIFI_SDRST GND RES RES ON_OFF*
13 VUSB GND GPIO_07 RES RES VMMC MMC_CD WIFI_SD3 WIFI_SD0 WIFI_SD2 WIFI_SDCLK WIFI_SD1 WIFI_SDCMD GND HW_SHUTDOWN*
14 USB_ID GPIO_05 RES RES GND RES RES SPI_CS / GPIO_11 RES RES C105/RTS C108/DTR C109/DCD C107/DSR C125/RING
15 USB_D+ USB_D-
SPI_MOSI
/ TX_AUX
SPI_MISO
/RX_AUX
SPI_CLK GPIO_10 RES RES GPIO_8 GPIO_9 C104/RXD C103/TXD C106/CTS
Page 36

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 36 of 121 2018-12-12
Backward Compatibility to xE910 Family
The LE910Cx is a new series in the xE910 form factor
The LE910Cx is fully backward compatible to the previous xE910 in terms of:
• Mechanical dimensions
• Package and pin-map
To support the extra features and additional interfaces, the LE910Cx introduces more pins
compared to the xE910.
The extra pins of the LE910Cx can be considered as optional if not needed and can be left
unconnected (floating) if not used.
In this case, the new LE910Cx can be safely mounted on existing carrier boards designed
for the previous xE910.
The additional pins of the LE910Cx are shown in Figure 3 (marked as Green)
Figure 3: LE910Cx vs. LE910 Pin-out Comparison (top view)
Page 37

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 37 of 121 2018-12-12
4. Electrical Specifications
Absolute Maximum Ratings – Not Operational
WARNING:
A deviation from the value ranges listed below may harm the LE910Cx
module.
Table 8: Absolute Maximum Ratings – Not Operational
Symbol
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
VBATT
Battery supply voltage on pin VBATT
-0.5
+6.0
[V]
VBATT
TRANSIENT
Transient voltage on pin VBATT (< 10
ms)
-0.5
+7.0
[V]
VBATT_PA
Battery supply voltage on pin
VBATT_PA
-0.3
+6.0
[V]
Recommended Operating Conditions
Table 9: Recommended Operating Conditions
Symbol
Parameter
Min
Typ
Max
Unit
T
amb
Ambient temperature
-40
+25
+85
[°C]
VBATT
Battery supply voltage on
pin VBATT
3.4
3.8
4.2
[V]
VBATT_PA
Battery supply voltage on
pin VBATT_PA
3.4
3.8
4.2
[V]
I
BATT_PA
+ I
BATT
Peak current to be used to
dimension decoupling
capacitors on pin
VBATT_PA
-
80
2000
[mA]
Page 38

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 38 of 121 2018-12-12
Logic Level Specifications
Unless otherwise specified, all the interface circuits of the LE910Cx are 1.8V CMOS logic.
Only few specific interfaces (such as MAC, USIM and SD Card) are capable of dual
voltage I/O.
The following tables show the logic level specifications used in the LE910Cx interface
circuits. The data specified in the tables below is valid throughout all drive strengths and
the entire temperature ranges.
NOTE:
Do not connect LE910Cx digital logic signals directly to OEM digital logic
signals with a level higher than 2.7V for 1.8V CMOS signals.
4.3.1. 1.8V Pads - Absolute Maximum Ratings
Table 10: Absolute Maximum Ratings - Not Functional
Parameter
Min
Max
Input level on any digital
pin when on
-0.3V
+2.16V
Input voltage on analog
pins when on
-0.3V
+2.16 V
4.3.2. 1.8V Standard GPIOs
Table 11: Operating Range – Interface Levels (1.8V CMOS)
Pad
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Comment
VIH
Input high level
1.25V
--
[V]
VIL
Input low level
--
0.6V
[V]
VOH
Output high level
1.4V
--
[V] VOL
Output low level
--
0.45V
[V]
IIL
Low-level input leakage
current
-1
--
[uA]
No pull-up
IIH
High-level input leakage
current
--
+1
[uA]
No pull-down
RPU
Pull-up resistance
30
390
[kΩ]
Page 39

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 39 of 121 2018-12-12
Pad
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Comment
RPD
Pull-down resistance
30
390
[kΩ]
Ci
Input capacitance
-- 5 [pF]
NOTE:
Pull-Up and Pull-Down resistance of GPIO3, GPIO7 and GPIO8 is different
than above mentioned
GPIO3 pull resistance is specified as 10KΩ to 50KΩ
4.3.3. 1.8V SD Card Pads
Table 12: Operating Range – SD Card Pads Working at 1.8V
Pad
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Comment
VIH
Input high level
1.27V
2V
[V]
VIL
Input low level
-0.3V
0.58V
[V]
VOH
Output high level
1.4V
--
[V]
VOL
Output low level
0
0.45V
[V]
IIL
Low-level input leakage
current
-2 - [uA]
No pull-up
IIH
High-level input leakage
current
- 2 [uA]
No pull-down
RPU
Pull-up resistance
10
100
[kΩ]
RPD
Pull-down resistance
10
100
[kΩ]
Ci
Input capacitance
5 [pF]
Page 40

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 40 of 121 2018-12-12
4.3.4. 1.8V SIM Card Pads
Table 13: Operating Range – SIM Pads Working at 1.8V
Pad
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Comment
VIH
Input high level
1.35V
2V
[V] VIL
Input low level
-0.3V
0.43V
[V]
VOH
Output high level
1.35V
1.875V
[V]
VOL
Output low level
0V
0.4V
[V]
IIL
Low-level input leakage
current
-2 - [uA]
No pull-up
IIH
High-level input leakage
current
- 2 [uA]
No pull-down
RPU
Pull-up resistance
10
100
[kΩ]
RPD
Pull-down resistance
10
100
[kΩ]
Ci
Input capacitance
5 [pF]
4.3.5. Dual Voltage Pads - Absolute Maximum Ratings
Table 14: Absolute Maximum Ratings - Not Functional
Parameter
Min
Max
Input level on any
digital pin when on
-0.3V
+3.6V
Input voltage on analog
pins when on
-0.3V
+3.6 V
Page 41

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 41 of 121 2018-12-12
4.3.6. SD Card Pads @ 2.95V
Table 15: Operating Range – For SD Card Pads Operating at 2.95V
Pad
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Comments
VIH
Input high level
1.9V
3.1V
[V]
VIL
Input low level
-0.3V
0.7V
[V]
VOH
Output high level
2.1V
3.05V
[V]
VOL
Output low level
0V
0.4V
[V]
IIL
Low-level input leakage
current
-10 [uA]
No pull-up
IIH
High-level input leakage
current
10
[uA]
No pull-down
RPU
Pull-up resistance
10
100
[kΩ]
RPD
Pull-down resistance
10
100
[kΩ]
Ci
Input capacitance
5 [pF]
4.3.7. SIM Card Pads @2.95V
Table 16: Operating Range – For SIM Pads Operating at 2.95V
Pad
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Comment
VIH
Input high level
2.1V
3.1V
[V]
VIL
Input low level
-0.3V
0.55V
[V]
VOH
Output high level
2.25V
3.1V
[V]
VOL
Output low level
0V
0.4V
[V]
IIL
Low-level input leakage
current
-10 [uA]
No pull-up
IIH
High-level input leakage
current
10
[uA]
No pull-down
RPU
Pull-up resistance
10
100
[kΩ]
RPD
Pull-down resistance
10
100
[kΩ]
Ci
Input capacitance
5 [pF]
Page 42

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 42 of 121 2018-12-12
5. Hardware Commands
Turning on the LE910Cx Module
To turn on the LE910Cx module, the ON_OFF_N pad must be asserted low for at least 1
second and then released.
The maximum current that can be drained from the ON/OFF # pad is 0.1 mA. This pin is
internally pulled up; customers should expect to see ~ 800 mV on the output.
Figure 4 illustrates a simple circuit to power on the module using an inverted buffer output.
Figure 4: Power-on Circuit
NOTE:
Recommended values R2 = 47 kΩ, R1 = 10 kΩ.
Page 43

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 43 of 121 2018-12-12
Initialization and Activation State
After turning on the LE910Cx module, a predefined internal boot sequence performs the
HW and SW initialization of the module, which takes some time to complete fully. During
this process, the LE910Cx is not accessible.
As shown in Figure 5, the LE910Cx becomes operational at least 20 seconds after the
assertion of ON_OFF.
NOTE:
During the Initialization state, AT commands are not available. The DTE host
must wait for the Activation state prior to communicating with the LE910Cx.
Figure 5: LE910Cx Initialization and Activation
NOTE:
SW_RDY signal is available on GPIO_08 (by default GPIO_08 functions as
SW_RDY)
NOTE:
To check whether the LE910Cx has completely powered on, monitor the
SW_RDY hardware line. When SW_RDY goes high, the module has
completely powered on and is ready to accept AT commands.
1 Sec < T_Hold < 2 Sec
VBATT
ON_OFF
SW_RDY
T_RDY < 20 Sec
V_AUX
PWRMON
18 Sec < T_PWRMON < 20 Sec
OFF State Initialization State Active State
OK to Send AT
commands
All interfaces and pins
configured
Page 44

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 44 of 121 2018-12-12
NOTE:
During SW initialization of the LE910Cx, the SW configures all pads and
interfaces to their desired mode. When PWRMON goes high, this indicates
that the initialization of all I/O pads is completed.
NOTE:
Do not use any pull-up resistor on the ON_OFF_N line as it is internally
pulled up. Using a pull-up resistor may cause latch-up problems on the
LE910Cx power regulator and improper powering on/off of the module. The
ON_OFF_N line must be connected only in an open-collector configuration.
NOTE:
For systems not requiring controlled power ON/OFF, automatic power on can
be supported by shorting the ON_OFF signal directly GND
In this case, the module will start power on sequence immediately after
VBATT supply is applied
NOTE:
Active low signals are labeled with a name that ends with "#" or with “_N”
NOTE:
To avoid a back-powering effect, it is recommended to avoid having any
HIGH logic level signal applied to the digital pins of the module when it is
powered OFF or during an ON/OFF transition.
Page 45

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 45 of 121 2018-12-12
Turning off the LE910Cx Module
Turning off the device can be done in the following different ways:
• Shutdown by software using AT#SHDN software command
• Hardware shutdown using ON_OFF_N pad
• Hardware Unconditional Shutdown using the SHDN_N pad
When the device is shut down by a software command or a hardware shutdown, it issues
a detach request to the network, informing the network that the device will not be
reachable any more.
NOTE:
To check if the device has powered off, monitor the PWRMON hardware
line. When PWRMON goes low, this indicates that the device has powered
off.
NOTE:
To avoid a back-powering effect, it is recommended to avoid having any
HIGH logic level signal applied to the digital pins of the module when it is
powered OFF or during an ON/OFF transition.
Page 46

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 46 of 121 2018-12-12
5.3.1. Shutdown by Software Command
The LE910Cx module can be shut down by a software command.
When a shutdown command is sent, LE910Cx goes into the Finalization state and at the
end of the finalization process shuts down PWRMON.
The duration of the Finalization state can differ according to the current situation of the
module, so a value cannot be defined.
Usually, it will take more than 10 seconds from sending a shutdown command until
reaching a complete shutdown. The DTE host should monitor the status of PWRMON to
observe the actual power-off.
Figure 6: Shutdown by Software Command
NOTE:
To check whether the device has powered off, monitor the PWRMON
hardware line. When PWRMON goes low, the device has powered off.
Page 47

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 47 of 121 2018-12-12
5.3.2. Hardware Shutdown
To turn off the LE910Cx module, the ON_OFF_N pad must be asserted low for at least
2.5 seconds and then released. Use the same circuitry and timing for power-on.
When the hold time of ON/OFF# is above 2.5 seconds, LE910Cx goes into the
Finalization state and eventually shuts down PWRMON.
The duration of the Finalization state can differ according to the current situation of the
module, so a value cannot be defined.
Usually, it will take more than 15 seconds from sending a shutdown command until
reaching a complete shutdown. The DTE host should monitor the status of PWRMON to
observe the actual power-off.
Figure 7: Hardware Shutdown
NOTE:
To check whether the device has powered off, monitor the PWRMON
hardware line. When PWRMON goes low, the device has powered off.
Page 48

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 48 of 121 2018-12-12
5.3.3. Unconditional Hardware Shutdown
To unconditionally shut down the LE910Cx module, the HW_SHUTDOWN_N pad must be
tied low for at least 200 milliseconds and then released.
Figure 8 shows a simple circuit for applying an unconditional shutdown.
Figure 8: Circuit for Unconditional Hardware Shutdown
Figure 9 shows the system power-down timing when using HW_SHUTDOWN_N.
Figure 9: Power down timing using HW_SHUTDOWN_N
NOTE:
Recommended values are as follows: R2 = 47kΩ, R1 = 10kΩ.
200mS Sec < T_Hold
VBATT
SHDN_N
SW_RDY
T_RDY ~0 Sec
V_AUX
PWRMON
T_PWRMON ~0 Sec
OFF StateActive State
Page 49

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 49 of 121 2018-12-12
NOTE:
Do not use any pull-up resistor on the HW_SHUTDOWN_N line or any totem
pole digital output. Using a pull-up resistor may cause latch-up problems on
the LE910Cx power regulator and improper functioning of the module. The
HW_SHUTDOWN_N line must be connected only in an open-collector
configuration.
NOTE:
The Unconditional Hardware Shutdown must always be implemented on the
boards, but the software must use it only as an emergency exit procedure,
and not as a normal power-off operation.
Powering OFF the Module
Powering OFF the module should be done gracefully allowing the module to complete all
ongoing and pending tasks while properly handling all memory buffers.
In the case where a complete power supply shut down is needed, the following procedure
should be followed:
1. Perform a HW shutdown as described in Section 5.3.1
2. Wait for the HW Shutdown procedure to complete (monitor the PWRMON pin).
3. Turn OFF power supply to the module
WARNING:
Follow the recommended procedure for shut down and power off carefully.
Not following the recommended shut-down and power off procedures might
damage the device and consequently void the warranty.
Page 50

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 50 of 121 2018-12-12
6. Power Supply
The power supply circuitry and board layout are very important parts of the full product
design, with critical impact on the overall product performance. Read the following
requirements and guidelines carefully to ensure a good and proper design.
Power Supply Requirements
The LE910Cx power requirements are as follows:
Table 17: Power Supply Requirements
Nominal supply voltage
3.8V
Supply voltage range
3.4V – 4.2V
Max ripple on module input supply
30 mV
NOTE:
For PTCRB approval on the final products, the power supply is required to
be within the range of “Normal Supply voltage ranger”.
Page 51

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 51 of 121 2018-12-12
Power Consumption
Table 18 provides typical current consumption values of LE910Cx for the various available
modes.
Table 18: LE910Cx Current Consumption
Mode
Average
(Typ.)
Mode Description
Switched Off
Switched off
25µA
Module supplied but switched Off (RTC On)
Idle Mode (Standby Mode; No Call in Progress)
AT+CFUN=4
1.0 mA
Tx and Rx disabled; module is not registered on
the network (Flight mode)
DRX
AT+CFUN=5
GSM
2.0 mA
DRx2
1.4 mA
DRx5
WCDMA
1.4 mA
DRx7
1.2 mA
DRx8
LTE
1.8mA
Paging cycle #128 frames (1.28 sec DRx cycle)
1.4mA
Paging cycle #256 frames (2.56 sec DRx cycle)
Operative Mode (LTE)
LTE (0dBm)
180mA
LTE CAT 1 channel BW 5 MHz, RB=1, Tx =
0 dBm
(Test case: BAND 1, Channel 300)
190mA
LTE CAT 1 channel BW 10 MHz, RB=1, Tx =
0 dBm
(Test case: BAND 1, Channel 300)
210mA
LTE CAT 1 channel BW 5 MHz, RB=1, Tx =
0 dBm
With FTP TpT session LTE to USB
10Mbps DL/5Mbps UL
(Test case: BAND 1, Channel 300)
Operative Mode (WCDMA)
WCDMA Voice
200mA
WCDMA voice call (Tx = 10 dBm)
WCDMA HSDPA
(0 dBm)
150mA
WCDMA data call (Cat 14, Tx = 0 dBm, Max
throughput)
Page 52

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 52 of 121 2018-12-12
Mode
Average
(Typ.)
Mode Description
WCDMA HSDPA
(22 dBm)
310mA
WCDMA data call (Cat 14, Tx = 22 dBm, Max
throughput)
Operative Mode (GSM)
GSM Tx and Rx mode
GSM900 PL5
250 mA
GSM voice call
DCS1800 PL0
170mA
GPRS 4 Tx + 1 Rx
GSM 900 PL5
430mA
GPRS Sending Data mode (CS-4)
DCS 1800 PL0
340mA
Operative Mode (GPS)
GPS tracking
40mA
LTE connection is idle
* Worst/best case current values depend on network configuration, not under module
control.
NOTE:
The electrical design for the power supply must ensure a peak current output
of at least 2.0A.
NOTE:
In GSM/GPRS mode, RF transmission is not continuous, but is packed into
bursts at a base frequency of about 216 Hz with relative current peaks as
high as about 2.0A. Therefore, the power supply must be designed to
withstand these current peaks without big voltage drops. This means that
both the electrical design and the board layout must be designed for this
current flow.
If the layout of the PCB is not well designed, a strong noise floor is
generated on the ground. This will reflect on all the audio paths producing an
audible annoying noise at 216 Hz.
If the voltage drops during the peaks, current absorption is too high. The
device may even shut down as a consequence of the supply voltage drop.
Page 53

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 53 of 121 2018-12-12
General Design Rules
The principal guidelines for the Power Supply Design embrace three different design
steps:
• Electrical design
• Thermal design
• PCB layout
6.3.1. Electrical Design Guidelines
The electrical design of the power supply depends strongly on the power source where
this power is drained. Power sources can be distinguished by three categories:
• +5V input (typically PC internal regulator output)
• +12V input (typically automotive)
• Battery
6.3.1.1. + 5V Input Source Power Supply – Design Guidelines
• The desired output for the power supply is 3.8V. So, the difference between the
input source and the desired output is not big, and therefore a linear regulator can
be used. A switching power supply is preferred to reduce power consumption.
• When using a linear regulator, a proper heat sink must be provided to dissipate the
power generated.
• A bypass low ESR capacitor of adequate capacity must be provided to cut the
current absorption peaks close to the LE910Cx module. A 100 μF tantalum
capacitor is usually suitable on both VBATT and VBATT_PA power lines.
• Make sure that the low ESR capacitor on the power supply output (usually a
tantalum one) is rated at least 10V.
• A protection diode must be inserted close to the power input to protect the
LE910Cx module from power polarity inversion.
Figure 10 shows an example of a linear regulator with 5V input.
Figure 10: Example of Linear Regulator with 5V Input
Page 54

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 54 of 121 2018-12-12
6.3.1.2. + 12V Input Source Power Supply – Design Guidelines
• The desired output for the power supply is 3.8V. Due to the big difference between
the input source and the desired output, a linear regulator is unsuitable and must
not be used. A switching power supply is preferable because of its better
efficiency, especially with the 2A peak current load expected during GSM Tx.
• When using a switching regulator, a 500-kHz or higher switching frequency
regulator is preferable because of its smaller inductor size and its faster transient
response. This allows the regulator to respond quickly to the current peaks
absorption.
• In any case, the selection of the frequency and switching design is related to the
application to be developed due to the fact that the switching frequency can also
generate EMC interference.
• For car batteries (lead-acid accumulators) the input voltage can rise up to 15.8V.
This must be kept in mind when choosing components: all components in the
power supply must withstand this voltage.
• A bypass low ESR capacitor of adequate capacity must be provided to cut the
current absorption peaks. A 100μF tantalum capacitor is usually suitable on
VBATT & VBATT_PA power lines.
• Make sure that the low ESR capacitor on the power supply output (usually a
tantalum one) is rated at least 10V.
• For automotive applications, a spike protection diode must be inserted close to the
power input to clean the supply of spikes.
• A protection diode must be inserted close to the power input to protect the
LE910Cx module from power polarity inversion. This can be the same diode as for
spike protection.
Figure 13 and Figure 14 show an example of switching regulator with 12V input.
Figure 11: Example of Switching Regulator with 12V Input – Part 1
Figure 12: Example of Switching Regulator with 12V Input – Part 2
Page 55

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 55 of 121 2018-12-12
6.3.1.3. Battery Source Power Supply – Design Guidelines
• The desired nominal output for the power supply is 3.8V, and the maximum
allowed voltage is 4.2V. Hence, a single 3.7V Li-Ion cell battery type is suitable for
supplying the power to the LE910Cx module.
NOTE:
Do not use any Ni-Cd, Ni-MH, and Pb battery types directly connected to the
LE910Cx module. Their use can lead to overvoltage on the LE910Cx and
damage it. Use only Li-Ion battery types.
• A bypass low ESR capacitor of adequate capacity must be provided to cut the
current absorption peaks; a 100μF tantalum capacitor is usually suitable.
• Make sure that the low ESR capacitor (usually a tantalum one) is rated at least
10V.
• A protection diode must be inserted close to the power input to protect the
LE910Cx module from power polarity inversion. Otherwise, the battery connector
must be done in a way to avoid polarity inversions when connecting the battery.
• The battery capacity must be at least 500 mAh to withstand the current peaks of
2A.
6.3.2. Thermal Design Guidelines
The thermal design for the power supply heat sink must be done with the following
specifications:
• Average current consumption during RF transmission @PWR level max in
LE910Cx as shown in Table 18: LE910Cx Current Consumption
• Average current consumption during Class10 GPRS transmission @PWR level
max as shown in Table 18: LE910Cx Current Consumption
• Average GPS current consumption during GPS tracking (LTE @ idle): mA (40mA)
NOTE:
The average consumption during transmission depends on the power level
at which the device is requested to transmit via the network. Therefore, the
average current consumption varies significantly.
Page 56

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 56 of 121 2018-12-12
NOTE:
The thermal design for the power supply must be made keeping an average
consumption at the max transmitting level during calls of (LTE/HSPA)/GPRS
plus average consumption in GPS Tracking mode.
Considering the very low current during Idle, especially if the Power Saving function is
enabled, it is possible to consider from the thermal point of view that the device absorbs
significant current only during an Active Call or Data session.
For the heat generated by the LE910Cx module, consider it to be 2W max during
transmission at Class10 GPRS upload.
In LTE/WCDMA/HSPA mode, the LE910Cx emits RF signals continuously during
transmission. Therefore, you must pay special attention how to dissipate the heat
generated.
The LE910Cx is designed to conduct the heat flow from the module IC’s towards the
bottom of the PCB across GND metal layers
The generated heat is mostly conducted to the ground plane under the LE910Cx module.
The application board should be properly designed to dissipate this heat.
Application board design needs to make sure the area under the LE910Cx module is as
large as possible. Make sure that the LE910Cx is mounted on the large ground area of
application board and provide many ground vias to dissipate the heat.
Even though peak current consumption in GSM mode is higher than in
LTE/WCDMA/HSPA, considerations for the heat sink are more important in the case of
WCDMA due to the continuous transmission conditions.
6.3.3. Power Supply PCB Layout Guidelines
As seen in the electrical design guidelines, the power supply must have a low ESR
capacitor on the output to cut the current peaks and a protection diode on the input to
protect the supply from spikes and polarity inversion. The placement of these components
is crucial for the correct operation of the circuitry. A misplaced component can be useless
or can even decrease the power supply performances.
• The bypass low ESR capacitor must be placed close to the LE910Cx power input
pads, or if the power supply is of a switching type, it can be placed close to the
inductor to cut the ripple, as long as the PCB trace from the capacitor to LE910Cx
is wide enough to ensure a drop-less connection even during the 2A current
peaks.
• The protection diode must be placed close to the input connector where the power
source is drained.
• The PCB traces from the input connector to the power regulator IC must be wide
enough to ensure that no voltage drops occur during the 2A current peaks.
Page 57

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 57 of 121 2018-12-12
Note that this is not done in order to avoid RF power loss but to avoid the voltage
drops on the power line at the current peaks frequency of 216 Hz that will reflect
on all the components connected to that supply (also introducing the noise floor at
the burst base frequency)
For this reason, while a voltage drop of 300-400 mV may be acceptable from the
RF power loss point of view, the same voltage drop may not be acceptable from
the noise point of view. If your application does not have an audio interface but
only uses the data feature of the LE910Cx, this noise is not so disturbing, and the
power supply layout design can be more forgiving.
• The PCB traces to LE910Cx and the bypass capacitor must be wide enough to
ensure that no significant voltage drops occur when the 2A current peaks are
absorbed. This is needed for the same above-mentioned reasons. Try to keep
these traces as short as possible.
• The PCB traces connecting the switching output to the inductor and the switching
diode must be kept as short as possible by placing the inductor and the diode very
close to the power switching IC (only for the switching power supply). This is done
to reduce the radiated field (noise) at the switching frequency (usually 100500 kHz).
• Use a good common ground plane.
• Place the power supply on the board in a way to guarantee that the high current
return paths in the ground plane do not overlap any noise sensitive circuitry, such
as the microphone amplifier/buffer or earphone amplifier.
• The power supply input cables must be kept separate from noise sensitive lines,
such as microphone/earphone cables.
Page 58

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 58 of 121 2018-12-12
7. Antenna(s)
Antenna connection and board layout design are the most important parts in the full
product design, and they have a strong influence on the product’s overall performance.
Read carefully and follow the requirements and guidelines for a good and proper design.
GSM/WCDMA/TD-SCDMA/LTE Antenna Requirements
The antenna for the LE910Cx device must meet the following requirements:
Table 19: Primary Antenna Requirements
Frequency range
The customer must use the most suitable antenna bandwidth
for covering the frequency bands provided by the network
operator and supported by the OEM while using the Telit
module.
The bands supported by each variant of the LE910Cx module
family are provided in Section 2.6.1, RF Bands per Regional
Variant.
Gain
Gain < 3 dBi
Impedance
50 Ohm
Input power
> 33 dBm(2 W) peak power in GSM
> 24 dBm average power in WCDMA & LTE
VSWR absolute max
<= 10:1
VSWR
recommended
<= 2:1
Since there is no antenna connector on the LE910Cx module, the antenna must be
connected to the LE910Cx antenna pad (AD1) by a transmission line implemented on the
PCB.
If the antenna is not directly connected to the antenna pad of the LE910Cx, a PCB line is
required to connect to it or to its connector.
This transmission line must meet the following requirements:
Table 20: Antenna Line on PCB Requirements
Characteristic impedance
50 Ohm
Max attenuation
0.3 dB
Avoid coupling with other signals.
Cold End (Ground Plane) of the antenna must be equipotential to the LE910Cx ground
pads.
Page 59

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 59 of 121 2018-12-12
Furthermore, if the device is developed for the US and/or Canada market, it must comply
with the FCC and/or IC approval requirements:
This device is to be used only for mobile and fixed application. The antenna(s) used for this
transmitter must be installed to provide a separation distance of at least 20 cm from all persons and
must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other antenna or transmitter. End-Users
must be provided with transmitter operation conditions for satisfying RF exposure compliance. OEM
integrators must ensure that the end user has no manual instructions to remove or install the
LE910Cx module. Antennas used for this OEM module must not exceed 3dBi gain for mobile and
fixed operating configurations.
GSM/WCDMA/TD-SCDMA/LTE Antenna – PCB Line Guidelines
• Make sure that the transmission line’s characteristic impedance is 50 Ohm.
• Keep the line on the PCB as short as possible since the antenna line loss should
be less than around 0.3 dB.
• Line geometry should have uniform characteristics, constant cross sections, and
avoid meanders and abrupt curves.
• Any suitable geometry/structure can be used for implementing the printed
transmission line affecting the antenna.
• If a ground plane is required in the line geometry, this plane must be continuous
and sufficiently extended so the geometry can be as similar as possible to the
related canonical model.
• Keep, if possible, at least one layer of the PCB used only for the ground plane. If
possible, use this layer as reference ground plane for the transmission line.
• Surround the PCB transmission line with ground (on both sides). Avoid having
other signal tracks facing the antenna line track directly.
• Avoid crossing any un-shielded transmission line footprint with other tracks on
different layers.
• The ground surrounding the antenna line on the PCB must be strictly connected to
the main Ground plane by means of via-holes (once per 2 mm at least) placed
close to the ground edges facing the line track.
• Place EM-noisy devices as far as possible from LE910Cx antenna line.
• Keep the antenna line far away from the LE910Cx power supply lines.
• If EM-noisy devices are present on the PCB hosting the LE910Cx, such as fast
switching ICs, take care to shield them with a metal frame cover.
• If EM-noisy devices are not present around the line, geometries like Micro strip or
Grounded Coplanar Waveguide are preferred because they typically ensure less
attenuation compared to a Strip line having the same length.
Page 60

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 60 of 121 2018-12-12
GSM/WCDMA/LTE Antenna – Installation Guidelines
• Install the antenna in a location with access to the network radio signal.
• The antenna must be installed such that it provides a separation distance of at
least 20 cm from all persons and must not be co-located or operating in
conjunction with any other antenna or transmitter.
• The antenna must not be installed inside metal cases.
• The antenna must be installed according to the antenna manufacturer’s
instructions.
Antenna Diversity Requirements
This product includes an input for a second Rx antenna to improve radio sensitivity. The
function is called Antenna Diversity.
Table 21: Antenna Diversity Requirements
Frequency range
The customer must use the most suitable antenna bandwidth
for covering the frequency bands provided by the network
operator and supported by the OEM while using the Telit
module.
The bands supported by each variant of the LE910Cx
module family are provided in Section 2.6.1, RF Bands per
Regional Variant
Impedance
50Ω
VSWR recommended
≤ 2:1
Since there is no antenna connector on the LE910Cx module, the antenna must be
connected to the LE910Cx antenna pad by means of a transmission line implemented on
the PCB.
If the antenna is not directly connected at the antenna pad of the LE910Cx (AU9), a PCB
line is required to connect to it or to its connector.
The second Rx antenna must not be located in close vicinity of the main antenna. To
improve diversity gain and isolation and to reduce mutual interaction, the two antennas
should be located at the maximum reciprocal distance possible, taking into consideration
the available space within the application.
NOTE:
If Rx Diversity is not used/connected, disable the Diversity functionality using
the AT+XRXDIV command (refer to Ref 1: LE920x4/LE910Cx AT Command
User Guide) and connect the Diversity pad AU9 to a 50 Ohm termination.
Page 61

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 61 of 121 2018-12-12
GNSS Antenna Requirements
LE910Cx supports an active antenna.
It is recommended to use antennas as follow:
• An external active antenna (17dB typ. Gain, GPS only)
• An external active antenna plus GNSS pre-filter (17dB typ. Gain)
NOTE:
The external GNSS pre-filter is required for the GLONASS application.
The GNSS pre-filter must meet the following requirements:
Source and load impedance = 50 Ohm
Insertion loss (1575.42–1576.42 MHz) = 1.4 dB (Max)
Insertion loss (1565.42–1585.42 MHz) = 2.0 dB (Max)
Insertion loss (1597.5515–1605.886 MHz) = 2.0 dB (Max)
NOTE:
It is recommended to add a DC block to the customer’s GPS application to
prevent damage to the LE910Cx module due to unwanted DC voltage.
NOTE:
It is recommended to add PI matching network near the GPS connector on
the application board in case that RF matching is needed.
7.5.1. Combined GNSS Antenna
The use of a combined RF/GNSS antenna is NOT recommended. This solution can
generate an extremely poor GNSS reception. In addition, the combination of antennas
requires an additional diplexer, which adds significant power loss in the RF path.
7.5.2. Linear and Patch GNSS Antenna
Using this type of antenna introduces at least 3 dB of loss compared to a circularly
polarized (CP) antenna. Having a spherical gain response instead of a hemispherical gain
response can aggravate the multipath behaviour and create poor position accuracy.
Page 62

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 62 of 121 2018-12-12
7.5.3. Front End Design Considerations
Since there is no antenna connector on the LE910Cx module, the antenna must be
connected to the LE910Cx through the PCB to the antenna pad.
If the antenna is not directly connected at the antenna pad of the LE910Cx, a PCB line is
required.
This line of transmission must meet the following requirements:
Table 22: Antenna Line on PCB Requirements
Characteristic impedance
50 Ohm
Max attenuation
0.3 dB
Avoid coupling with other signals.
Cold End (Ground Plane) of the antenna must be equipotential to the LE910Cx ground
pads.
Furthermore, if the device is developed for the US and/or Canada market, it must comply
with the FCC and/or IC requirements.
This device is to be used only for mobile and fixed application.
7.5.4. GNSS Antenna – PCB Line Guidelines
• Ensure that the antenna line impedance is 50 Ohm.
• Keep the line on the PCB as short as possible to reduce the loss.
• The antenna line must have uniform characteristics, constant cross section,
avoiding meanders and abrupt curves.
• Keep one layer of the PCB used only for the Ground plane; if possible.
• Surround (on the sides, over and under) the antenna line on the PCB with Ground.
Avoid having other signal tracks directly facing the antenna line track.
• The Ground around the antenna line on the PCB must be strictly connected to the
main Ground plane by placing vias at least once per 2mm.
• Place EM-noisy devices as far as possible from LE910Cx antenna line.
• Keep the antenna line far away from the LE910Cx power supply lines.
• If EM-noisy devices are around the PCB hosting the LE910Cx, such as fast
switching ICs, ensure shielding the antenna line by burying it inside the layers of
PCB and surrounding it with Ground planes; or shield it with a metal frame cover.
• If you do not have EM-noisy devices around the PCB of LE910Cx, use a Micro
strip line on the surface copper layer for the antenna line. The line attenuation will
be lower than a buried one.
Page 63

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 63 of 121 2018-12-12
7.5.5. GNSS Antenna – Installation Guidelines
• The LE910Cx, due to its sensitivity characteristics, is capable of performing a fix
inside buildings. (In any case, the sensitivity could be affected by the building
characteristics i.e. shielding.)
• The antenna must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other
antenna or transmitter.
• The antenna must not be installed inside metal cases.
• The antenna must be installed according to the antenna manufacturer’s
instructions.
Page 64

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 64 of 121 2018-12-12
8. Hardware Interfaces
Table 23 summarizes all the hardware interfaces of the LE910Cx module.
Table 23: LE910Cx Hardware Interfaces
Interface
LE910Cx
SGMII
For Ethernet support
HSIC
x1 (Optional)
SD/MMC
x1 dual voltage interface for supporting SD/MMC card
SDIO
For WIFI support (1.8V only)
USB
USB2.0, Optional OTG support
SPI
Master only, up to 50 MHz
I2C
For sensors, audio control
UART
2 HS-UART (up to 4 Mbps)
Audio I/F
I2S/PCM, Analog I/O
GPIO
10 ~ 27 (10 dedicated + 17 multiplexed with other signals)
USIM
x2, dual voltage each (1.8V/2.85V)
ADC
Up to x3
Antenna
ports
2 for Cellular, 1 for GNSS
Page 65

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 65 of 121 2018-12-12
USB Port
The LE910Cx module includes a Universal Serial Bus (USB) transceiver, which operates
at USB high-speed (480Mbits/sec). It can also operate with USB full-speed hosts
(12Mbits/sec).
It is compliant with the USB 2.0 specification and can be used for control and data
transfers as well as for diagnostic monitoring and firmware update.
The USB port is typically the main interface between the LE910Cx module and OEM
hardware.
NOTE:
The USB_D+ and USB_D- signals have a clock rate of 480 MHz. The signal
traces must be routed carefully. Minimize trace lengths, number of vias, and
capacitive loading. The impedance value should be as close as possible to
90 Ohms differential.
Table 24 lists the USB interface signals.
Table 24: USB Interface Signals
Signal
Pad
No.
Usage
USB_VBUS
A13
Power and cable detection for the internal USB transceiver.
Acceptable input voltage range 2.5V – 5.5V @ max 5 mA
consumption
USB_D-
C15
Minus (-) line of the differential, bi-directional USB signal to/from
the peripheral device
USB_D+
B15
Plus (+) line of the differential, bi-directional USB signal to/from
the peripheral device
USB_ID
A14
Used for USB OTG to determine host or client mode
NOTE:
USB_VBUS input power is internally used to detect the USB port and start
the enumeration process.
It is a power supply pin with a maximum consumption of 5 mA.
Do not use pull up or a voltage divider for sourcing this supply
Page 66

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 66 of 121 2018-12-12
NOTE:
Even if USB communication is not used, it is still highly recommended to
place an optional USB connector on the application board.
At least test points of the USB signals are required since the USB physical
communication is needed in the case of SW update.
NOTE:
USB OTG support is optional and is not supported by default. An external
5V power supply is required on the application board for supporting USB
OTGץ
HSIC Interface (Optional)
The application processor exposes a High-Speed Inter-Chip (HSIC). HSIC eliminates the
analog transceiver from a USB interface for lower voltage operation and reduced power
dissipation.
• High-speed 480 Mbps (240 MHz DDR) USB transfers are 100% host driver
compatible with traditional USB cable connected topologies
• Bidirectional data strobe signal (STROBE)
• Bidirectional data signal (DATA)
• No power consumption unless a transfer is in progress
Further details will be provided in a future release of this document.
SGMII Interface
The SOC includes an integrated Ethernet MAC with an SGMII interface, having the
following key features:
• The SGMII interface can be used connect to an external Ethernet PHY, or an
external switch.
• When enabled, an additional network interface will be available to the Linux kernel.
• Further details can be found at Ref 8: ETH_Expansion_board_Application Note
8.3.1. Ethernet Control interface
When using an external PHY for Ethernet connectivity, the LE910Cx also includes the
control interface for managing the external PHY
Table 25 lists the signals for controlling the external PHY
Page 67

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 67 of 121 2018-12-12
Table 25: Ethernet Control Interface Signals
PAD
Signal
I/O
Function
Type
Comment
C2
MAC_MDC
O
MAC to PHY Clock
2.85V
Logic Level
Specifications are shown
in Section 4.3.7, SIM
Card Pads @2.95V,
Table 16
C1
MAC_MDIO
I/O
MAC to PHY Data
2.85V
D1
ETH_RST_N
O
Reset to Ethernet PHY
2.85V
G4
ETH_INT_N
I
Interrupt from Ethernet
PHY
1.8V
Logic Level
Specifications are shown
in Table 11
NOTE:
The Ethernet control interface is shared with USIM2 port!
When Ethernet PHY is used, USIM2 port cannot be used (and vice versa).
NOTE:
ETH_INT_N is a 1.8V input. It has an internal pull up to 1.8V inside the
module thus it should be connected to an open drain interrupt pin of the
Ethernet PHY. In case the PHY does not support 1.8V I/O, proper level
shifter needs to be used.
Page 68

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 68 of 121 2018-12-12
Serial Ports
The serial port is typically a secondary interface between the LE910Cx module and OEM
hardware. The following serial ports are available on the module:
• Modem Serial Port 1 (Main)
• Modem Serial Port 2 (Auxiliary)
Several serial port configurations can be designed for the OEM hardware. The most
common are:
• RS232 PC com port
• Microcontroller UART @ 1.8V (Universal Asynchronous Receive Transmit)
• Microcontroller UART @ 3.3V/5V or other voltages different from 1.8V
Depending on the type of serial port on OEM hardware, level translator circuits may be
needed to make the system operate. The only configuration that does not need level
translation is the 1.8V UART.
The LE910Cx UART has CMOS levels as described in Section 4.3, Logic Level
Specifications.
8.4.1. Modem Serial Port 1 Signals
On the LE910Cx, Serial Port 1 is a +1.8V UART with 7 RS232 signals. It differs from the
PC-RS232 in the signal polarity (RS232 is reversed) and levels. Table 26 lists the signals
of LE910Cx Serial Port 1.
Table 26: Modem Serial Port 1 Signals
RS232
Pin#
Signal
Pad No.
Name
Usage
1
DCD DCD_UART
N14
Data Carrier
Detect
Output from LE910Cx that
indicates carrier presence
2
RXD TX_UART
M15
Transmit line
*see Note
Output transmit line of LE910Cx
UART
3
TXD RX_UART
N15
Receive line
*see Note
Input receive line of LE910Cx
UART
4
DTR DTR_UART
M14
Data
Terminal
Ready
Input to LE910Cx that controls
the DTE READY condition
5
GND
A2, B13,
D4…
Ground
Ground
6
DSR DSR_UART
P14
Data Set
Ready
Output from LE910Cx that
indicates that the module is
ready
Page 69

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 69 of 121 2018-12-12
RS232
Pin#
Signal
Pad No.
Name
Usage
7
RTS RTS_UART
L14
Request to
Send
Input to LE910Cx controlling the
Hardware flow control
8
CTS CTS_UART
P15
Clear to Send
Output from LE910Cx
controlling the Hardware flow
control
9
RI RI_UART
R14
Ring
Indicator
Output from LE910Cx indicating
the Incoming call condition
NOTE:
DCD, DTR, DSR, RI signals that are not used for UART functions can be
configured as GPIO using AT commands.
NOTE:
To avoid a back-powering effect, it is recommended to avoid having any
HIGH logic level signal applied to the digital pins of the module when it is
powered OFF or during an ON/OFF transition.
NOTE:
For minimum implementations, only the TXD and RXD lines need be
connected. The other lines can be left open provided a software flow control
is implemented.
NOTE:
According to V.24, Rx/Tx signal names refer to the application side;
therefore, on the LE910Cx side, these signal are in the opposite direction:
TXD on the application side will be connected to the receive line (here
named TXD/ RX_UART) of the LE910Cx serial port and vice versa for Rx.
NOTE:
The DTR pin is used to control the UART and system sleep
Pulling the DTR pin low prevents the UART and the entire module from
entering low power mode.
DTR can be left floating if not used (DTR is internally pulled high).
Page 70

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 70 of 121 2018-12-12
Page 71

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 71 of 121 2018-12-12
8.4.2. Modem Serial Port 2
On the LE910Cx, Serial Port 2 is a +1.8V UART with Rx and Tx signals only.
The UART functionality is shared with SPI, thus simultaneous use of SPI and UART is not
supported.
Table 27 lists the signals of the LE910Cx Serial Port 2.
Table 27: Modem Serial Port 2 Signals
PAD
Signal
I/O
Function
Type
Comment
D15
TXD_AUX
O
Auxiliary UART (Tx Data to DTE)
1.8V
Shared with
SPI_MOSI
E15
RXD_AUX
I
Auxiliary UART (Rx Data to DTE)
1.8V
Shared with
SPI_MISO
NOTE:
To avoid a back-powering effect, it is recommended to avoid having any
HIGH logic level signal applied to the digital pins of the module when it is
powered OFF or during an ON/OFF transition.
NOTE:
The Auxiliary UART is used as the SW main debug console. It is required to
place test points on this interface even if not used.
8.4.3. RS232 Level Translation
To interface the LE910Cx with a PC COM port or an RS232 (EIA/TIA-232) application, a
level translator is required. This level translator must perform the following actions:
• Invert the electrical signal in both directions
• Change the level from 0/1.8V to +15/-15V
The RS232 UART 16450, 16550, 16650 & 16750 chipsets accept signals with lower levels
on the RS232 side (EIA/TIA-562), allowing a lower voltage-multiplying ratio on the level
translator. Note that the negative signal voltage must be less than 0V and hence some
sort of level translation is always required.
The simplest way to translate the levels and invert the signal is by using a single chip-level
translator. There are a multitude of them, differing in the number of drivers and receivers
and in the levels (be sure to get a true RS232 level translator, not a RS485 or other
standards).
Page 72

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 72 of 121 2018-12-12
By convention, the driver is the level translator from the 0-1.8V UART to the RS232 level.
The receiver is the translator from the RS232 level to 0-1.8V UART. To translate the
whole set of control lines of the UART, the following is required:
• 2 drivers
• 2 receivers
WARNING:
The digital input lines, operating at 1.8V CMOS levels, have absolute
maximum input voltage of 2.0V. The level translator IC outputs on the
module side (i.e. LE910Cx inputs) will cause damage to the module inputs if
the level translator is powered with +3.8V power.
So, the level translator IC must be powered from a dedicated +1.8V power
supply.
As an example, RS232 level adaption circuitry could use a MAXIM transceiver (MAX218).
In this case, the chipset is capable of translating directly from 1.8V to the RS232 levels
(example on 4 signals only).
Figure 13: RS232 Level Adaption Circuitry Example
NOTE:
In this case, the length of the lines on the application must be taken into
account to avoid problems in the case of high-speed rates on RS232.
The RS232 serial port lines are usually connected to a DB9 connector as shown in Figure
14. Signal names and directions are named and defined from the DTE point of view.
Figure 14: RS232 Serial Port Lines Connection Layout
Page 73

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 73 of 121 2018-12-12
Peripheral Ports
In addition to the LE910Cx serial ports, the LE910Cx supports the following peripheral
ports:
• SPI – Serial Peripheral Interface
• I2C - Inter-integrated circuit
• SD/MMC Card Interface
• SDIO Interface
8.5.1. SPI – Serial Peripheral Interface
The LE910Cx SPI supports the following:
• Master Mode only
• 1.8V CMOS level
• Up to 50 MHz clock rate
NOTE:
SPI is supported only on the Linux side.
The LE910Cx module supports Master mode only and cannot be configured
as Slave mode.
Table 28: SPI Signals
PAD
Signal
I/O
Function
Type
Comment
F15
SPI_CLK
O
SPI clock output
1.8V
E15
SPI_MISO
I
SPI data Master input Slave
output
1.8V
Shared with
RX_AUX
D15
SPI_MOSI
O
SPI data Master output Slave
input
1.8V
Shared with
TX_AUX
H14
SPI_CS
O
SPI chip-select output
1.8V
Figure 15: SPI Signal Connectivity
LE910Cx (Master)
SPI_CS
SPI_CLK
SPI_MOSI
SPI_MISO
Host (Slave)
SPI_CS
SPI_CLK
SPI_MOSI
SPI_MISO
Page 74

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 74 of 121 2018-12-12
8.5.2. I2C - Inter-integrated Circuit
The LE910Cx supports an I2C interface on the following pins:
• B11 - I2C_SCL
• B10 - I2C_SDA
The I2C can also be used externally by the end customer application.
In addition, SW emulated I2C functionality can be used on GPIO pins 1-10. Any GPIO
(among GPIO 1-10) can be configured as SCL or SDA.
LE910Cx supports I2C Master Mode only.
NOTE:
SW emulated I2C on GPIO lines is supported only from the modem side. For
more information, refer to Ref 1: LE920x4/LE910Cx AT Command User
Guide for command settings.
NOTE:
To keep backward compatibility with previous LE910 products, it is
recommended to keep using the SW emulated I2C available on GPIO’s 1-10.
Page 75

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 75 of 121 2018-12-12
8.5.3. SD/MMC Card Interface
The LE910Cx provides an SD port supporting the SD3.0 specification, which can be used
to support standard SD/MMC memory cards with the following features:
• Interface with SD/MMC memory cards up to 2 TB
• Max clock @ 2.95V - 50 MHz SDR
• Max Data: 25 MB/s
• SD standard: HS-SDR25 at 2.95V
• Max clock @ 1.8V - 200 MHz SDR
• Max Data: 100 MB/s
• SD standard: UHS-SDR104 at 1.8 V
• Max clock @ 1.8V - 50 MHz DDR
• Max Data: 50 MB/s
• SD standard: UHS-DDR50 at 1.8 V
Table 29 lists the LE910Cx SD card signals.
Table 29: SD Card Signals
PAD
Signal
I/O
Function
Type
Comments
J12
SD/MMC_CMD
O
SD command
1.8/2.95V
F12
SD/MMC_CLK
O
SD card clock
1.8/2.95V
E12
SD/MMC_DATA0
I/O
SD Serial Data 0
1.8/2.95V
G12
SD/MMC_DATA1
I/O
SD Serial Data 1
1.8/2.95V
K12
SD/MMC_DATA2
I/O
SD Serial Data 2
1.8/2.95V
H12
SD/MMC_DATA3
I/O
SD Serial Data 3
1.8/2.95V
G13
SD/MMC_CD
I
SD card detect input
1.8V
Active Low
F13
VMMC
-
Power supply for MMC
card pull-up resistors
1.8/2.95V
Max Current
is 50mA
Page 76

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 76 of 121 2018-12-12
Figure 16 shows the recommended connection diagram of the SD interface.
Figure 16: SD/MMC Interface Connectivity
NOTE:
SD/MMC is supported only on the Linux side.
The power supply to the SD/MMC card is to be provided by the Host
application board. The LE910Cx does not provide a dedicated power supply
for the SD/MMC card.
VMMC Supply is limited to 50mA thus can only supply the MMC card
external pull-up resistors.
Pull-up resistors must be placed on the host application board.
The card detection input has an internal pull-up resistor.
VMMC can be used for enabling of the external power supply (LDO Enable
signal)
SD/MMC_DATA2
SD/MMC_DATA3
SD/MMC_CMD
SD/MMC_CLK
SD/MMC_DATA0
SD/MMC_DATA1
LE910Cx
SD/MMC Interface
SD/MMC_CD
DATA2
DATA3
CMD
VDD
VSS
DATA0
DATA1
MicroSD
MMC_CD
GND
GND
10
101010
10
C=100nF
GND
External PS 3V
VMMC
Page 77

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 77 of 121 2018-12-12
8.5.4. WiFi SDIO Interface
The LE910Cx provides an SDIO port supporting the SDIO3.0 specification, which can be
used to interface with a WiFi chipset (Qualcomm QCA65x4 chipset or other WiFi
solutions). The LE910Cx module includes an integrated SW driver to support the
Qualcomm QCA6574 chipset.
NOTE:
Qualcomm QCA9377 WiFi chipset may be supported on some of the
LE910Cx variants.
Please contact your Telit representative for more details.
The LE910Cx SDIO port supports the SDIO 3.0 specification at 1.8V CMOS only, thus
cannot be used as an external SD/MMC card connection.
The LE910Cx module supports an LTE/WiFi coexistence mechanism via the WCI
(Wireless Coexistence Interface) port, which connects between the module and the
external WiFi IC.
For a detailed explanation, refer to Ref 5: Telit_LE920A4_LE910Cx_WiFi_Interface_Application_Note_r1.
Table 30: WiFi SDIO Interface Signals
PAD
Signal
I/O
Function
Type
Comments
N13
WIFI_SD_CMD
O
WiFi SD Command
1.8V
L13
WIFI_SD_CLK
O
WiFi SD Clock
1.8V
200 MHz
max.
J13
WIFI_SD_DATA0
I/O
WiFi SD Serial Data 0
1.8V
M13
WIFI_SD_DATA1
I/O
WiFi SD Serial Data 1
1.8V
K13
WIFI_SD_DATA2
I/O
WiFi SD Serial Data 2
1.8V
H13
WIFI_SD_DATA3
I/O
WiFi SD Serial Data 3
1.8V
L12
WIFI_SDRST
O
WiFi Reset / Power enable
control
1.8V
Active Low
M8
WCI_TX
O
Wireless coexistence
interface TXD
1.8V
M9
WCI_RX
I
Wireless coexistence
interface RXD
1.8V
Page 78

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 78 of 121 2018-12-12
Audio Interface
The LE910Cx module supports a digital audio interface.
8.6.1. Digital Audio
The LE910Cx module can be connected to an external codec through the digital interface.
The product provides a single Digital Audio Interface (DVI) on the following pins:
Table 31: Digital Audio Interface (DVI) Signals
PAD
Signal
I/O
Function
Type
Comments
B9
DVI_WA0
O
Digital Audio Interface (WA0)
B-PD 1.8V
PCM_SYNC
B6
DVI_RX
I
Digital Audio Interface (RX)
B-PD 1.8V
PCM_DIN
B7
DVI_TX
O
Digital Audio Interface (TX)
B-PD 1.8V
PCM_DOUT
B8
DVI_CLK
O
Digital Audio Interface (CLK)
B-PD 1.8V
PCM_CLK
B12
REF_CLK
O
Audio Master Clock
B-PD 1.8V
I2S_MCLK
LE910Cx DVI has the following characteristics:
• PCM Master and slave modes using short or long frame sync modes
• 16-bit linear PCM format
• PCM clock rates of 256 kHz, 512 kHz, 1024 kHz and 2048 kHz (Default)
• Frame size of 8, 16, 32, 64, 128 & 256 bits per frame
• Sample rates of 8 kHz and 16 kHz
In addition to the DVI port, the LE910Cx module provides a master clock signal
(REF_CLK on Pin B12) which can either provide a reference clock to an external codec or
form an I2S interface together with the DVI port where the REF_CLK acts as the
I2S_MCLK.
The REF_CLK default frequency is 12.288 MHz.
When using the DVI with REF_CLK as an I2S interface, 12.288 MHz is 256 x fs (where fs
= 48 kHz)
Page 79

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 79 of 121 2018-12-12
8.6.1.1. Short Frame Timing Diagrams
Figure 17: Primary PCM Timing
Table 32: PCM_CODEC Timing Parameters
Page 80

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 80 of 121 2018-12-12
8.6.1.2. Long Frame Timing Diagrams
Figure 18: Auxiliary PCM Timing
Page 81

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 81 of 121 2018-12-12
Table 33: AUX_PCM_CODEC Timing Parameters
Page 82

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 82 of 121 2018-12-12
General Purpose I/O
The general-purpose I/O pads can be configured to act in three different ways:
• Input
• Output
• Alternative function (internally controlled)
Input pads can only be read, reporting digital values (high / low) present on the pad at the
reading time. Output pads can only be written or queried and set values on the pad
output. Alternative function pads can be internally controlled by LE910Cx firmware and act
according to the implementation.
The following GPIOs are always available as a primary function on the LE910Cx.
Table 34: Primary GPIOs
PAD
Signal
I/O
Function
Type
Drive
Strength
Note
C8
GPIO_01
I/O
Configurable
GPIO
CMOS
1.8V
2-16 mA
*
C9
GPIO_02
I/O
Configurable
GPIO
CMOS
1.8V
2-16 mA
C10
GPIO_03
I/O
Configurable
GPIO
CMOS
1.8V
2-16 mA
C11
GPIO_04
I/O
Configurable
GPIO
CMOS
1.8V
2-16 mA
B14
GPIO_05
I/O
Configurable
GPIO
CMOS
1.8V
2-16 mA
*
C12
GPIO_06
I/O
Configurable
GPIO
CMOS
1.8V
2-16 mA
*
C13
GPIO_07
I/O
Configurable
GPIO
CMOS
1.8V
2-16 mA
*
K15
GPIO_08
I/O
Configurable
GPIO
CMOS
1.8V
2-16 mA
L15
GPIO_09
I/O
Configurable
GPIO
CMOS
1.8V
2-16 mA
*
G15
GPIO_10
I/O
Configurable
GPIO
CMOS
1.8V
2-16 mA
Page 83

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 83 of 121 2018-12-12
WARNING:
GPIO’s marked with (*) should not be pulled high externally (by the carrier
board) during module power on procedure. Pulling those pads high during
module power up might lead to unwanted/non-operational boot mode.
The additional GPIOs below can be used in case their initial functionality is not used:
Table 35: Additional GPIOs
PAD
Signal
I/O
Initial Function
Alternate
Function
Type
Drive
Strength
Note
L12
GPIO_13
I/O
WIFI_SDRST
Configurable
GPIO
CMOS
1.8V
2-16 mA
*
N13
GPIO_14
I/O
WIFI_SDIO_CMD
Configurable
GPIO
CMOS
1.8V
2-16 mA
J13
GPIO_15
I/O
WIFI_SDIO_D0
Configurable
GPIO
CMOS
1.8V
2-16 mA
M13
GPIO_16
I/O
WIFI_SDIO_D1
Configurable
GPIO
CMOS
1.8V
2-16 mA
K13
GPIO_17
I/O
WIFI_SDIO_D2
Configurable
GPIO
CMOS
1.8V
2-16 mA
H13
GPIO_18
I/O
WIFI_SDIO_D3
Configurable
GPIO
CMOS
1.8V
2-16 mA
L13
GPIO_19
I/O
WIFI_SDIO_CLK
Configurable
GPIO
CMOS
1.8V
2-16 mA
M8
GPIO_24
I/O
WCI_TXD
Configurable
GPIO
CMOS
1.8V
2-16 mA
*
M9
GPIO_25
I/O
WCI_RXD
Configurable
GPIO
CMOS
1.8V
2-16 mA
*
R14
GPIO_31
I/O
UART_RI
Configurable
GPIO
CMOS
1.8V
2-16 mA
P14
GPIO_32
I/O
UART_DSR
Configurable
GPIO
CMOS
1.8V
2-16 mA
N14
GPIO_33
I/O
UART_DCD
Configurable
GPIO
CMOS
1.8V
2-16 mA
*
M14
GPIO_34
I/O
UART_DTR
Configurable
GPIO
CMOS
1.8V
2-16 mA
F15
GPIO_35
I/O
SPI_CLK
Configurable
GPIO
CMOS
1.8V
2-16 mA
Page 84

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 84 of 121 2018-12-12
PAD
Signal
I/O
Initial Function
Alternate
Function
Type
Drive
Strength
Note
E15
GPIO_36
I/O
SPI_MISO
Configurable
GPIO
CMOS
1.8V
2-16 mA
D15
GPIO_37
I/O
SPI_MOSI
Configurable
GPIO
CMOS
1.8V
2-16 mA
H14
GPIO_11
I/O
SPI_CS
Configurable
GPIO
CMOS
1.8V
2-16 mA
WARNING:
GPIO’s marked with (*) should not be pulled high externally (by the carrier
board) during module power on procedure. Pulling those pads high during
module power up might lead to unwanted/non-operational boot mode.
NOTE:
LE910Cx GPIOs 1~10 can also be used as alternate I2C function. Refer to
Section 8.5.2, I2C - Inter-integrated Circuit.
8.7.1. Using a GPIO Pad as Input
GPIO pads, when used as inputs, can be connected to a digital output of another device
and report its status, provided this device has interface levels compatible with the 1.8V
CMOS levels of the GPIO.
If the digital output of the device is connected with the GPIO input, the pad has interface
levels different from the 1.8V CMOS. It can be buffered with an open collector transistor
with a 10 kΩ pull-up resistor to 1.8V.
8.7.2. Using a GPIO Pad as an interrupt / Wakeup source
GPIO pads that are used as input can also be used as an interrupt source for the
software. In general, all GPIO pads can be also used as interrupts. However, not all
GPIO’s can be used as a wakeup source of the module (wakeup from sleep).
Only the following GPIO’s can be used for waking up the system from sleep:
• GPIO1
• GPIO4
• GPIO5
• GPIO8
Page 85

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 85 of 121 2018-12-12
8.7.3. Using a GPIO Pad as Output
GPIO pads, when used as outputs, can drive 1.8V CMOS digital devices or compatible
hardware. When set as outputs, the pads have a push-pull output, and therefore the pullup resistor can be omitted.
Figure 19: GPIO Output Pad Equivalent Circuit
Page 86

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 86 of 121 2018-12-12
9. Miscellaneous Functions
Indication of Network Service Availability
The STAT_LED pin status shows information on the network service availability and call
status. In the LE910Cx module, the STAT_LED usually needs an external transistor to
drive an external LED.
The STAT_LED does not have a dedicated pin. The STAT_LED functionality is available
on GPIO_01 pin (by default GPIO_01 functions as STAT_LED)
Table 36: Network Service Availability Indication
LED Status
Device Status
Permanently off
Device off
Fast blinking (Period 1s, Ton 0,5s)
Net search / Not registered /
Turning off
Slow blinking (Period 3s, Ton 0,3s)
Registered with full service
Permanently on
A call is active
Figure 20: Status LED Circuit Example
Page 87

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 87 of 121 2018-12-12
Indication of Software Ready
The SW_RDY signal provides indication about the ability of the module to receive
commands. As long as the SW_RDY is asserted low, it indicates that the LE910Cx has
not yet finished booting. Once the SW_RDY is asserted high, it indicates that the
LE910Cx is ready to receive commands.
The SW_RDY does not have a dedicated pin. The SW_RDY functionality is available on
GPIO_08 pin (by default GPIO_08 functions as SW_RDY).
RTC – Real Time Clock
The RTC within the LE910Cx module does not have a dedicated RTC supply pin. The
RTC block is supplied by the VBATT supply.
If the battery is removed, RTC is not maintained so if maintaining an internal RTC is
needed, VBATT must be supplied continuously.
In Power OFF mode, the average current consumption is ~25uA.
VAUX Power Output
A regulated power supply output is provided to supply small devices from the module.
This output is active when the module is ON and goes OFF when the module is shut
down. The operating range characteristics of the supply are as follows:
Table 37: Operating Range – VAUX Power Supply
Min
Typical
Max
Output voltage
1.75V
1.80V
1.85V
Output current
100 mA
Output bypass capacitor (within the
module)
1 μF
Page 88

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 88 of 121 2018-12-12
ADC Converter
9.5.1. Description
The LE910Cx module provides three on-board 8-bit Analog to Digital converters. Each
ADC reads the voltage level applied on the relevant pin, converts it and stores it into an 8bit word.
Table 38: ADC Parameters
Min
Max
Units
Input voltage range
0.1
1.7
Volt
AD conversion
- 8 bits
Resolution
-
< 6.6
mV
9.5.2. Using the ADC Converter
An AT command is available to use the ADC function.
The command is AT#ADC=1,2. The read value is expressed in mV.
Refer to Ref 1: LE920x4/LE910Cx AT Command User Guide for the full description of this
function.
Using the Temperature Monitor Function
The Temperature Monitor supports temperature monitoring by giving periodic temperature
indications, to execute some function at extreme state. If properly set (see the
#TEMPMON command in Ref 1: LE920x4/LE910Cx AT Command User Guide), it raises a
GPIO to High Logic level when the maximum temperature is reached.
Page 89

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 89 of 121 2018-12-12
GNSS Characteristics
Table 39 specifies the GNSS characteristics and expected performance. The values are
related to typical environment and conditions.
Table 39: GNSS Characteristics
Parameters
Typical
Measurement
Notes
Sensitivity
Standalone or MS Based
Tracking Sensitivity
-162.3 dBm
Acquisition
-157.5 dBm
Cold Start Sensitivity
-157.5 dBm
TTFF
Hot
1.1s
GPS+GLONASS
Simulator test
Warm
22.1s
GPS+GLONASS
Simulator test
Cold
29.94s
GPS+GLONASS
Simulator test
Accuracy
0.8 m
GPS+GLONASS
Simulator test
Min Navigation update rate
1Hz
Dynamics
2g
Operation limits
515 m/sec
A-GPS
Supported
Page 90

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 90 of 121 2018-12-12
10. Mounting the Module on your Board
General
The LE910Cx module is designed to be compliant with a standard lead-free soldering
process.
Finishing & Dimensions
The below figure shows the mechanical dimensions of the LE910Cx module.
Figure 21: LE910Cx Mechanical Dimensions (Bottom View)
4 x Route
Inhibit
Pin
B1
Lead-free Alloy:
Surface finishing Ni/Au for all solder pads
Page 91

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 91 of 121 2018-12-12
Figure 22: LE910Cx Mechanical Dimensions (Top view)
Page 92

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 92 of 121 2018-12-12
Figure 23: LE910Cx Mechanical Dimensions (Side view)
Page 93

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 93 of 121 2018-12-12
Recommended Footprint for the Application
Figure 24 shows the recommended footprint for the application board (dimensions are in
mm).
To facilitate replacing the LE910Cx module if necessary, it is suggested to design the
application board with a 1.5 mm placement inhibit area around the module.
It is also suggested, as a common rule for an SMT component, to avoid having a
mechanical part of the application board in direct contact with the module.
NOTE:
In the customer application, the region marked as INHIBIT WIRING in Figure
24 must be clear of signal wiring or ground polygons.
Figure 24: Recommended Footprint - Top View, 181 pads
4 x Route
Inhibit
Page 94

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 94 of 121 2018-12-12
Stencil
Stencil’s apertures layout can be the same as the recommended footprint (1:1). The
suggested thickness of stencil foil is greater than 120 µm.
PCB Pad Design
The solder pads on the PCB are recommended to be of the Non-Solder Mask Defined
(NSMD) type.
Figure 25: PCB Pad Design
Page 95

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 95 of 121 2018-12-12
Recommendations for PCB Pad Dimensions (mm)
Figure 26: PCB Pad Dimensions
It is not recommended to place around the pads a via or micro-via that is not covered by
solder resist in an area of 0.15 mm unless it carries the same signal as the pad itself. Micro
via inside the pads are allowed.
Holes in pad are allowed only for blind holes and not for through holes.
Table 40: Recommendations for PCB Pad Surfaces
Finish
Layer Thickness (um)
Properties
Electro-less Ni / Immersion
Au
3-7 / 0.05-0.15
Good solder ability protection,
high shear force values
The PCB must be able to resist the higher temperatures, which occur during the lead-free
process. This issue should be discussed with the PCB-supplier. Generally, the wettability
of tin-lead solder paste on the described surface plating is better compared to lead-free
solder paste.
Solder Paste
We recommend using only “no clean” solder paste to avoid the cleaning of the modules
after assembly.
Page 96

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 96 of 121 2018-12-12
10.7.1. Solder Reflow
Figure 27 shows the recommended solder reflow profile.
Figure 27: Solder Reflow Profile
Page 97

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 97 of 121 2018-12-12
Table 41: Solder Profile Characteristics
Profile Feature
Pb-Free Assembly
Average ramp-up rate (TL to TP)
3°C/second max
Preheat
– Temperature min (Tsmin)
– Temperature max (Tsmax)
– Time (min to max) (ts)
150°C
200°C
60-180 seconds
Tsmax to TL
– Ramp-up rate
3°C/second max
Time maintained above:
– Temperature (TL)
– Time (tL)
217°C
60-150 seconds
Peak temperature (Tp)
245 +0/-5°C
Time within 5°C of actual peak
Temperature (tp)
10-30 seconds
Ramp-down rate
6°C/second max
Time 25°C to peak temperature
8 minutes max
NOTE:
All temperatures refer to the top side of the package, measured on the
package body surface.
WARNING:
The LE910Cx module withstands one reflow process only.
Page 98

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 98 of 121 2018-12-12
10.7.2. Cleaning
In general, cleaning the module mounted on the carrier board is not recommended.
• Residues between module and host board cannot be easily removed with any
cleaning method.
• Cleaning with water or any organic solvent can lead to capillary effects where the
cleaning solvent is absorbed into the gap between the module and the host board
or even leak inside the module (due to the gap between the module shield and
PCB) . The combination of soldering flux residues and encapsulated solvent could
lead to short circuits between conductive parts. The solvent could also damage the
module label.
• Ultrasonic cleaning could damage the module permanently. Especially for crystal
oscillators where the risk of damaging is very high.
Page 99

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 99 of 121 2018-12-12
11. Application Guide
Debug of the LE910Cx Module in Production
To test and debug the mounting of the LE910Cx module, we strongly recommend adding
several test pads on the application board design for the following purposes:
• Checking the connection between the LE910Cx itself and the application
• Testing the performance of the module by connecting it with an external computer
Depending on the customer application, these test pads include, but are not limited to the
following signals:
• TXD
• RXD
• ON/OFF
• HW_SHUTDOWN_N
• GND
• VBATT
• TX_AUX
• RX_AUX
• USB_VBUS
• USB_D+
• USB_D-
• GPIO_09
• WCI_RX
In addition, the following signals are also recommended (but not mandatory):
• PWRMON
• GPIO_01 (STAT_LED)
• GPIO_08 (SW_RDY)
Page 100

LE910Cx HW User Guide
Doc#: 1VV0301298
Rev. 2.0 Page 100 of 121 2018-12-12
Bypass Capacitor on Power Supplies
When a sudden voltage step to or a cut from the power supplies is asserted, the steep
transition causes some reactions such as overshoot and undershoot. This abrupt voltage
transition can affect the device causing it to not operate or to malfunction.
Bypass capacitors are needed to alleviate this behaviour. The behaviour can appear
differently depending on the various applications. Customers must pay special attention to
this issue when they design their application board.
The length and width of the power lines must be considered carefully, and the capacitance
of the capacitors must be selected accordingly.
The capacitor will also prevent ripple of the power supplies and the switching noise
caused in TDMA systems, such as GSM.
Especially, a suitable bypass capacitor must be mounted on the following lines on the
application board:
• VBATT & VBATT_PA (M1, M2, N1, N2, P1, P2)
• USB_VBUS (Pad A13)
Recommended values are:
• 100uF for both VBATT and VBATT_PA together
• 4.7uF for USB_VBUS (including the 1uF capacitor inside the module)
Customers must still consider that the capacitance mainly depends on the conditions of
their application board.
Generally, more capacitance is required when the power line is longer.
 Loading...
Loading...