Page 1
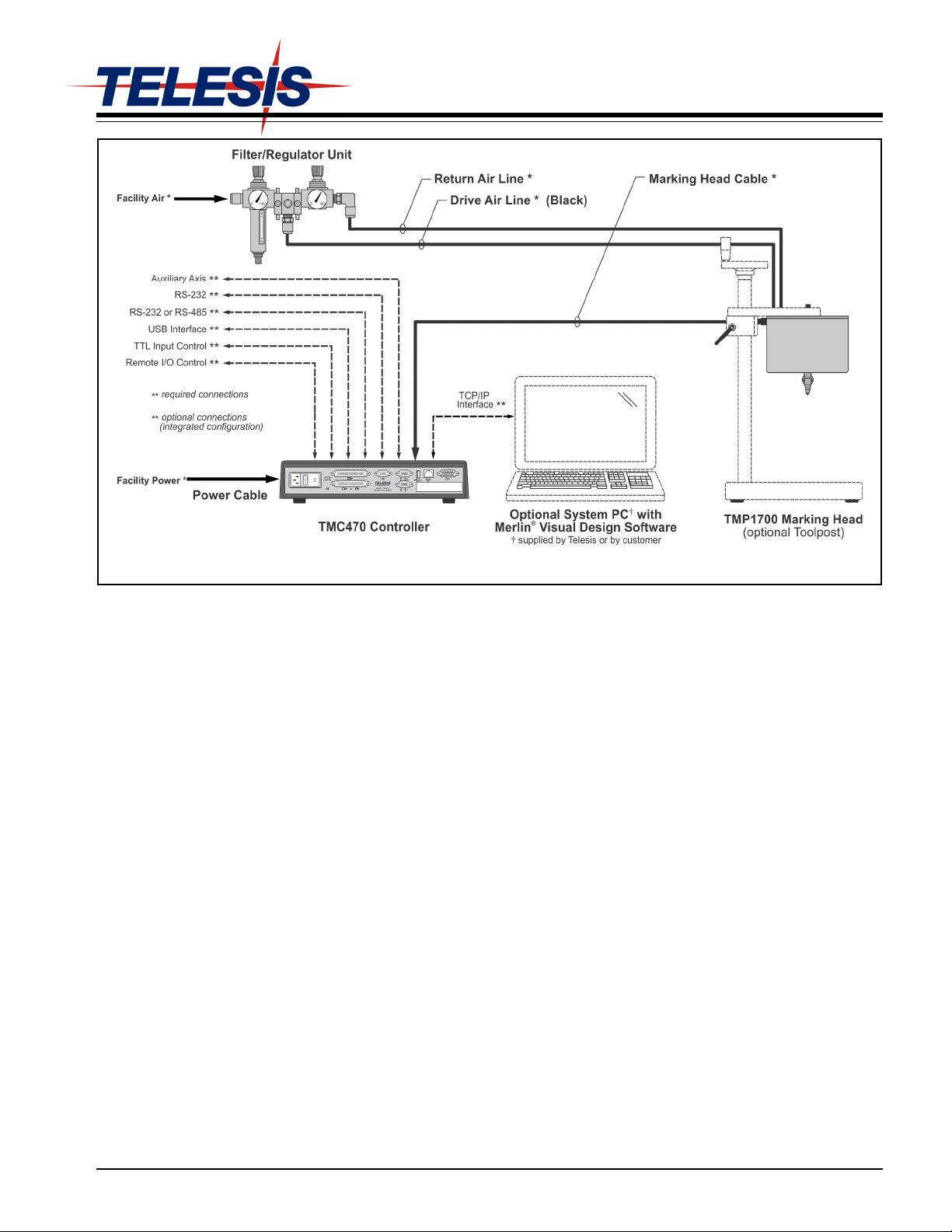
TMP1700/470 Marking System
TMP1700/470 Marking System – General Arrangement
SYSTEM OVERVIEW
The Telesis® TMP1700/470 PINSTAMP® marking system
permanently prints messages into a variety of materials such as
steel, aluminum, and plastic. A hardened pin is pneumatically
accelerated to indent dot matrix characters into the item being
marked. The shape, size, density, and location of characters are
determined by the user through the system software. The marking
head moves the pin cartridge through X- and Y-axis motions to
reach the correct position for each dot of the characters to be
marked. The system software automatically controls pin
extension and retraction to mark the message.
The system is compliant with UL, CSA, CE, and RoHS specifications.
TMP1700 Marking Head includes the mechanical motion
components to position the marking pin at precise X/Y positions
and the pneumatic components to drive the marking pin from, and
return the pin to, the pin cartridge.
The floating pin design permits high quality, consistent marks on
irregular, slightly curved surfaces. It also accommodates
applications where marking surfaces cannot be positioned at a
consistent distance from the marker.
The TMP1700 marking head is an X/Y-traversing mechanism.
Using two stepper motor drives, it accurately and rapidly positions
the pin at coordinate-defined locations in marking window within
.001" (.025 mm). The TMP1700 accommodates the rigorous
dynamics of impacting, rebounding, and rapid positioning of the
marking pin through a system of rigid rails and ball bearing
saddles, timing belts, and direct-drive, toothed pulleys.
The internal mechanism is protected from debris by an integral
shield. Three stainless steel panels slide against one another,
constrained by the cartridge and the high-impact ABS cover, to
prevent debris from entering the marking head. A flexible, oilresistant fabric boot is also available for applications requiring
additional protection, especially against liquid sprays and mists.
Marker Cable, pre-wired to the marking head, connects the
marker to the controller. The highly flexible cable is 4m (13 ft.)
long. Optional extension cables are available for greater distances.
Pin Cartridges, machined from engineered plastic materials, offer
long life with little maintenance. Clasps are used to attach the pin
cartridge to the marking head for easy cleaning and pin replacement.
Marking Pins for the TMP1700 include the 25L-, 25XL-, 150S,
150SA-series and the 10MP MicroPin™. Refer to the TMP1700
Marking Head Dimensions drawing for pin stroke (pin extension)
dimensions. Refer to the marking depth tables for pin cone angles
and depths.
Filter/Regulator Unit includes two regulators with pressure
gauges to control the drive air and return air. The first regulator
contains a filter to help remove contaminants from the supply air.
Two air lines connect the regulated air to the marking head. Drive
air fires the impact pin; return air pushes it back into the cartridge.
The standard air lines are 12 ft. (3.6 m) long made of 1/4" tubing.
TMC470 Controller contains an integrated keyboard with an LCD
display. It provides a text-only operator interface and allows full
operational control of the TMP1700 marking head. The back panel
provides the electrical interface for connecting to optional, remote
I/O sources. Refer to TMC470 Controller Specifications for details.
Optional System Computer. The TMC470 Controller may be
connected to a PC that runs the Merlin
®
III Visual Design Software.
The PC may be supplied by Telesis or by the customer. Refer to
PC-based Merlin III Software and TCP/IP Interface for details.
28575G © 2009 – 2011 Telesis Technologies, Inc. – All Rights Reserved 1 of 10
Page 2
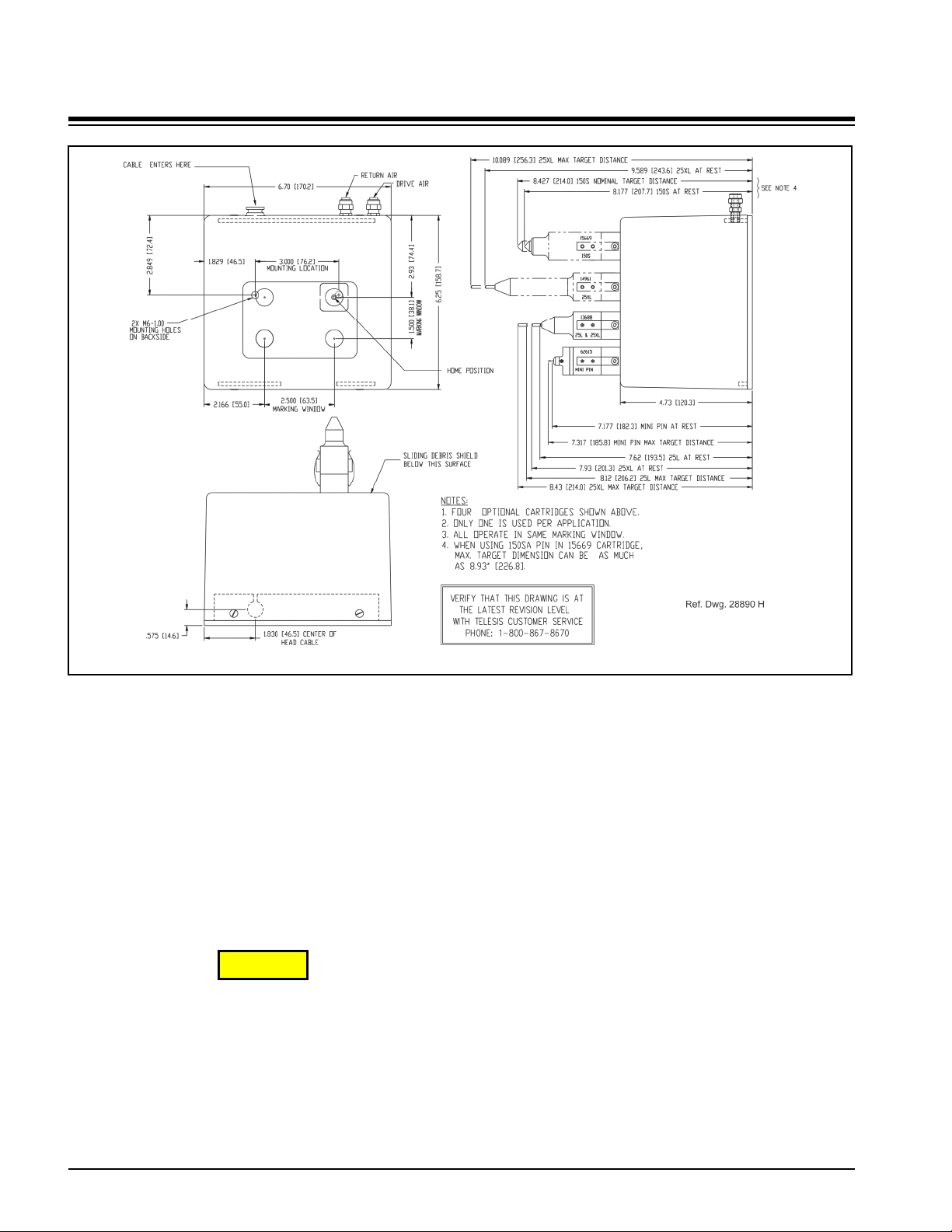
TMP1700/470 Marking System
TMP1700 Marking Head Dimensions
SYSTEM SETUP
When designing a fixture, allow for 3-axis adjustment to aid in
horizontal, vertical, and lateral alignment of the marking head.
1. Mount marking head to optional tool post assembly (or
other suitable fixture) using two M6 bolts. Mounting bolts
must not extend into marking head more than more
5/8" (15 mm).
2. Mount filter/regulator assembly within 12 ft. (3.6m) of
marker.
3. Connect drive air and return air lines to the marking head.
4. Connect supply air to input port on filter/regulator
assembly.
CAUTION
The TMC470 is not a sealed unit. Protect it from
potentially damaging conditions and contaminants. Do not
block vents in bottom of case. Ensure the marking system
is electrically isolated from any devices that may generate
extreme electromagnetic interference (EMI).
5. Locate controller as close as practical to marking head.
Standard marker cable length is 4 m (13 ft.).
6. Install the controller as a table-top, wall-mounted, panelmounted, or enclosure-mounted unit, as applicable.
7. Ensure controller power switch is OFF.
8. Connect marker cable to controller.
9. Connect power cable to controller.
10. (optional) For systems that connect to a PC running the
Merlin III Visual Design Software:
a. Ensure PC power switch is OFF.
b. Connect cable to controller Ethernet Port and to PC.
c. Connect power cable to PC.
d. Position PC power switch to ON.
e. (customer-supplied PC) Install marking system
software.
11. Position controller power switch to ON.
12. Start marking system software.
13. Adjust pin stroke, drive air, and return air for impact
depth.
2 of 10 28575G
Page 3
TMP1700/470 Marking System
SYSTEM OPTIONS
• Oil Resistant Fabric Boot
• Marking Head Extension Cables
• Tool Post Assembly
• Auxiliary Axis Driver Board Kit
• Motorized Z-axis Tool Post with Programmable Travel
• Motorized Theta-axis with Programmable Rotary Drive Unit
• TMC470 Controller Wall-mounting Bracket Kit
• TMC470 Controller Panel-mounting Bezel/Bracket Kit
• TMC470N NEMA
®
Enclosure
• Bar Code Scanner or Bar Code Wand with Cable
• Foot Switch (Start Print) or Pushbutton Station (Start/Abort)
• Backup Utility Software
• Upgrade Utility Software
• Logo/Font Generator Software
• Merlin III Visual Design Software
• System Computer (to run the Merlin III software)
TMP1700 MARKING HEAD
Specifications
The TMP1700 marking head specifications are subject to change
without prior notice.
Dimensions ............................... refer to TMP1700 Marking Head
Weight ...................................... 6.4 lb. (2.9 kg)
Operating Temperature. .......... 32° to 122° F (0° to 50° C),
Air Supply ................................. Clean and dry, 60 to 120 psig
Air Consumption ...................... .04 SCFM (idle) 0.6 SCFM (marking)
Marking Area ............................ 2.5 x 1.5" (63 x 38 mm)
Pin Types .................................. 10MP-, 25L-, 25XL-, 150S, or
Pin Material............................... Carbide (10MP-series MicroPin™)
Powdered metal or stainless steel
Powdered metal or tool steel with
Dimensions drawing
non-condensing
(4.2 to 8.3 bars)
150SA-series
with diamond tip or carbide
(25L-, 25XL-series)
carbide tip (150S-, 150SA-series)
TMP1700 MARKING HEAD (continued)
Marking Characteristics
The TMP1700 can produce characters as small as .030" (.76mm),
printed at any angle within the marking window. Printing
resolutions range from 10 dots per inch to 200 dots per inch for an
engraved look. The depth of mark can be adjusted over a
significant range by adjusting the pin stroke and, to a lesser extent,
by adjusting the drive air pressure.
Marking Speeds
Generally, the system will mark four characters per second (using
5x7 font, .125" [3 mm] high characters). Speeds will vary slightly
depending on the selected character size, style, and dot density.
Specific times can be verified by a Telesis
Pin Life
representative.
Pin life depends largely on the type of material being marked, how
hard or abrasive it is, and the required marking depth. On typical
metals with a hardness of Rockwell Rb47, marking at a depth of
.005" (.127 mm), powdered steel pins average about 3 million
impressions before needing sharpened; carbide pins average
approximately 9 million impressions. If carbide pins are used,
marking times will increase by approximately 25% due to the
increased weight of the pins.
Marking Noise
When marking cold-rolled steel strips at 50% duty cycle, the noise
level of the TMP1700 Marking System has been measured at 74.6
dB, using the "time weighted average" approach (average sound
exposure over an 8 hour period). It is expected that as the duty
cycle rises, the time weighted average will rise also. Typical
applications average around 20%-30% duty cycle where the sound
pressure level would not exceed 70 dB (A).
Noise-level Tests have been carried out under controlled
conditions imitating as closely as possible predicted normal
operation. Conditions such as rigidity of the work piece, material,
setting of the machine, ambient noise, etc. may vary when in
operational use and would alter the actual noise level.
Despite detailed guidance notes provided with each machine,
these conditions would be out of the control of Telesis and must
remain the responsibility of the end user to conduct their own tests
to establish safe working levels of use.
28575G 3 of 10
Page 4

TMP1700/470 Marking System
TMP1700 MARKING HEAD (continued)
Marking Depth
The following tables provide sample marking depths. Drive air
was set at 80 psi (5.5 bars); return air was set at 20 psi (1.4 bars);
pin stroke was set to the maximum allowable distance for each pin
type to achieve the maximum depth of mark.
Depth – Type 25L & 25XL Powdered-Metal Pins
MATERIAL
(HARDNESS)
Aluminum
(Rb3)
Brass
(Rb18)
Cold Rolled Steel
(Rc18)
22°
CONE
.005 in.
.127 mm
.003 in.
.076 mm
.003 in.
.076 mm
30°
CONE
.007 in.
.178 mm
.005 in.
.127 mm
.005 in.
.127 mm
45°
CONE
.011 in.
.279 mm
.009 in.
.229 mm
.008 in.
.203 mm
60°
CONE
.016 in.
.406 mm
.012 in.
.305 mm
.012 in.
.305 mm
Depth – Type 25L & 25XL Carbide Pins
MATERIAL
(HARDNESS)
Aluminum
(Rb3)
Brass
(Rb18)
Cold Rolled Steel
(Rc18)
22°
CONE
.006 in.
.152 mm
.005 in.
.127 mm
.004 in.
.010 mm
30°
CONE
.007 in.
.178 mm
.007 in.
.178 mm
.005 in.
.127 mm
45°
CONE
.010 in.
.254 mm
.008 in.
.203 mm
.007 in.
.178 mm
60°
CONE
.011 in.
.279 mm
.009 in.
.229 mm
.009 in.
.229 mm
Depth – Type 150S Pins
MATERIAL
(HARDNESS)
Aluminum
(Rb3)
Brass
(Rb18)
Cold Rolled Steel
(Rc18)
22°
CONE
N/A
N/A
N/A
30°
CONE
.008 in.
.203 mm
.007 in.
.178 mm
.006 in.
.152 mm
45°
CONE
.012 in.
.305 mm
.010 in.
.254 mm
.008 in.
.203 mm
60°
CONE
.018
.457 mm
.017
.432 mm
.013 in.
.330 mm
Depth – Type 150SA Pins
MATERIAL
(HARDNESS)
Aluminum
(Rb3)
Brass
(Rb18)
Cold Rolled Steel
(Rc18)
22°
CONE
N/A
N/A
N/A
30°
CONE
.008 in.
.203 mm
.007 in.
.178 mm
.006 in.
.152 mm
45°
CONE
.012 in.
.305 mm
.010 in.
.254 mm
.008 in.
.203 mm
60°
CONE
N/A
N/A
N/A
Vibration Data
Vibration tests were performed under controlled conditions
imitating, as closely as possible, typical normal operation.
Conditions such as rigidity of the work piece, material, setting of
the machine, etc. may vary in actual operational use and would
alter the actual vibration level. Despite detailed guidance
instructions provided with each machine, such conditions are
beyond the control of Telesis and must remain the responsibility
of the end user. Accordingly, you should conduct your own tests
to establish safe working levels of use.
The vibration tests were conducted using the following
parameters:
Drive Air Pressure ................... 4.08 bars (60 psi)
Return Air Pressure ................ 1.36 bars (20 psi)
Pin Stroke ................................ 8 mm (.31 in)
Marking Base .......................... 20 mm (.79 in) thick steel
Marking Surfaces .................... 2 mm (.08 in) thick steel plate
4 mm (.16 in) thick aluminum plate
Marking Mode .......................... Dot
Text Marked ............................. TELESIS
(11x16 font, 5mm [.20 in] characters)
HHHEEE000888
(5x7 font, 3mm [.12 in] characters)
The following test results reflect the worst-case scenarios under
the given test conditions.
Steel Marking Surface
Pin VM T
25C 0.4 m/s2 more than 24 hr more than 24 hr
150SA 0.8 m/s2 more than 24 hr more than 24 hr
Aluminum Marking Surface
Pin VM T
25C 0.6 m/s2 more than 24 hr more than 24 hr
150SA 1.2 m/s2 more than 24 hr more than 24 hr
T
(EAV)
T
(EAV)
(ELV)
(ELV)
4 of 10 28575G
where:
VM = hand/arm vibration magnitude.
T
= time to reach the Exposure Action Value based
(EAV)
on continuous marking.
T
= time to reach the Exposure Limit Value based on
(ELV)
continuous marking.
Page 5

TMP1700/470 Marking System
TMC470 Controller Dimensions – Table-top and Wall-mounted Configurations
TMC470 CONTROLLER
The TMC470 controller may be installed as a table-top unit, a
wall-mounted unit, a panel-mounted unit, or an enclosuremounted unit. All configurations provide features and connectivity
for external communications. Differences occur only in the
mounting configuration.
TMC470 Specifications
The TMC470 Controller specifications are subject to change
without prior notice.
Compliance .............................. CE, RoHS
Configurations .......................... Table-top, Wall-mounted, Panel-
mounted, or Enclosure-mounted
Rating ....................................... NEMA 1 (I.P. 30) table-top or wall-
mounted
NEMA 12 (I.P. 65) panel-mounted
using appropriate customer-supplied
panel
NEMA 12 (I.P. 65) enclosure-
mounted using Telesis-supplied
TMC470N enclosure
Dimensions ............................... refer to the appropriate TMC470
Controller Dimensions drawing
Weight ...................................... 3.69 lb. (1.68 kg) controller only
3.90 lb. (1.77 kg) with wall-mount kit
5.52 lb. (2.51 kg) with panel-mount kit
28.1 lb. (12.77 kg) with TMC470N
enclosure
TMC470 Specifications
Operating Temperature ......... 32° to 122° F (0° to 50°C)
Operating Humidity ................. 10% to 80% non-condensing
Cooling ..................................... Internal, thermostatically-controlled fan
Power Requirements .............. 95 to 250 VAC, 2 amps, 50-60 Hz,
Communications...................... TTL, Discrete I/O, RS232, RS485,
Input Signals ............................ Twelve (12) total, optically isolated
10 VDC (minimum voltage)
30 VDC (maximum voltage)
12 to 24 VDC (nominal voltage)
2.3 mA @ 12VDC; 4.9 mA @ 24VDC
Output Signals ......................... Six (6) total, optically isolated
0.25 amps (maximum current)
0.50 ohms (maximum On resistance)
40 VDC (maximum line voltage)
12 to 24 VDC (nominal line voltage)
(continued)
single phase
TCP/IP, and USB (data backup &
transfer)
8 dedicated, 1 programmable,
3 available
(nominal current)
4 dedicated, 2 available
28575G 5 of 10
Page 6

TMP1700/470 Marking System
TMC470 Controller Dimensions – Panel-mounted Configuration
Environmental Considerations
The following environmental considerations must be taken into
account when installing the TMC470 Controller.
Contaminants. The vented TMC470 is rated NEMA 1 (IP30) and
contains a thermostatically-controlled, variable speed fan.
Accordingly, in environments where solid and/or liquid
contaminants are present, the possibility exists that these
contaminants can be drawn into the TMC470 controller and
possibly result in failure. For that reason, in these types of
environments, the controller must
be located in a sealed industrial
enclosure. To facilitate such installations, Telesis offers on
optional panel mounting kit for use with an appropriate customersupplied panel or enclosure. Telesis also offers an optional
TMC470N NEMA 12 (I.P. 65) enclosure in which the controller
can be mounted.
EMI Susceptibility. Although the system has been found to be in
compliance with pertinent susceptibility standards, care should be
taken when installing near welders and other extreme generators
of electromagnetic interference (EMI). Particular care should be
taken to ensure welder currents are not injected through the
marking head chassis. The marking head chassis is connected to
the electrical service earth ground through the marking head cable.
The marking head should be electrically isolated from all surfaces
which could become part of a welder current path.
TMC470-based System Software
The system software is permanently installed in the controller. It
provides the user interface for the operator to control the marker.
The software also provides a library for storing, loading, and
editing user-defined patterns. Patterns are files stored in the
controller’s memory. Depending on the size of the pattern files, the
controller can store up to 200 patterns. Each pattern contains one or
more fields; each field defines a single object. Printable objects
may be created to define text strings, arc-text strings, geometric
shapes , graphics, and machine-readable data matrix symbols. Nonprintable objects may be defined to specific commands to the
marker (e.g., Pause, Go to, Input, or Output). Printable text fields
may include alphanumeric characters, symbols, and special
message flags. Message flags automatically insert data into the text
string, such as serial numbers, times, dates and user-defined codes.
PC-based Merlin III Visual Design Software
Optionally, the TMC470 Controller may be connected to a PC that
runs the Telesis Merlin III Visual Design Software. The software is
a 32-bit Windows
®
based WYSIWYG application that provides a
graphical user interface to make pattern design quick and easy. Just
“click and drag” for immediate adjustment to field size, location, or
orientation. The Merlin III software includes tools to create and
edit text, arc text, rectangles, circles, ellipses, and lines. Existing
DXF files can also be imported for marking.
After downloading patterns to the controller, the PC can be
disconnected from the controller to allow the TMC470 to control
marking operations. Optionally, the PC may remain connected to
the controller and allow the Merlin III software to fully control the
marking system.
6 of 10 28575G
Page 7

TMP1700/470 Marking System
TMC470 Controller Dimensions – Enclosure-mounted Configuration
Interface Panel
The back panel of the controller provides various ports for
connecting the marker, host computers, logic controllers, optional
accessories, and remote I/O devices. See below.
Serial Interface. The Comm 1 and Comm 2 Ports allow
connection to remote serial devices such as a host computer or a
bar code scanner. See Host Communications for details.
Discrete I/O Interface. The optically-isolated I/O Port allows
you to connect a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) or other
DC I/O source for remotely controlling marker operations. See
Discrete I/O Controls for details.
TTL Interface. The TTL Port allows the system to connect with
a simple contact closure circuit such as a remote push button
station or foot pedal switch. These types of devices can remotely
control Start Print and Stop Print operations.
TCP/IP Interface. The Ethernet Port typically connects to a PC
over a local area network (LAN). It allows you to define the
controller as a client or a server socket using Telesis Extended
Protocol. See Host Communications for details.
USB Interface. The USB Port allows you to connect a memory
stick/flash drive for pattern storage/retrieval and for software
upgrades.
(optional) Auxiliary Axis Interface. The Auxiliary Axis Port
allows the system to connect with up to four optional motion
devices such as motorized tool posts, rotational drive units, and
linear slides or actuators.
Discrete I/O Controls
The TMC470 is configured for 12 VDC to 24 VDC I/O only and
is provided to connect a PLC or other DC I/O source. The
optically-isolated I/O Port allows you to remotely select and load
patterns, start printing, stop printing, place the marker online, and
monitor the system output signals. Cable connectors and
connector pins are supplied with the controller for constructing
appropriate interface cables.
Input Signals. These input signals provide the following controls:
INPUT COMM ................... For all inputs (+ or – supply)
START PRINT .................. Begins print cycle
STOP ............................... Stops the print cycle
SEL_0 thru _6 * ................ Remotely selects & loads up to
SPARE_1, 2, 3 .................. Three (3) spares for custom
System software allows SEL_6 signal to be configured for remotely
*
selecting patterns or for remotely placing the marker online. If used for
marker online, pattern selection is reduced to 63 patterns (max).
127* pattern files
applications
Output Signals. These output signals indicate the following states:
OUTPUT COMM ............... For all outputs (+ or – supply)
DONE .............................. Print cycle is complete
READY ............................ System ready for message or for start
PAUSED .......................... System paused (waiting timeout or
NO FAULT ....................... System status (normal or fault
SPARE_1, 2 ...................... Two (2) spares for custom applications
print command
command)
detected)
28575G 7 of 10
Page 8

TMP1700/470 Marking System
Host Communications
The marking system software allows you to configure
communication parameters to transmit and receive data to and
from a host computer. To provide maximum integration
flexibility, the system software supports RS-232 and RS-485 serial
interfaces and Ethernet TCP/IP interfaces. The system software
also provides two protocol choices: Programmable Protocol and
Extended Protocol.
RS-232 Interface. The serial (RS-232) communications interface
is most often used with remote devices such as host computers,
terminals, or bar code scanners. The Comm 1 RS-232 interface
supports both Telesis Extended Protocol and Telesis
Programmable Protocol. The Comm 2 RS-232 interface supports
only Telesis Programmable Protocol.
RS-485 Interface. The RS-485 interface is normally used for
long transmission distances or multi-drop networks of up to 31
TMC470 controllers. You must use Telesis Extended Protocol
with the RS-485 interface.
The following describes the serial data character format on all
transmissions to and from the TMC470 Controller.
• Asynchronous
• 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400, or 115200 Baud
• 1 or 2 Stop Bits
• 7 or 8 Data Bits
• None, Even or Odd Parity
TCP/IP Interface. The Ethernet (TCP/IP) interface is most often
used with host computers communicating over a local area
network (LAN). You must use Telesis Extended Protocol with the
TCP/IP interface.
The Port parameter identifies the host computer socket that is
assigned to the marking system. If more than one marking system
is installed in a network configuration, each system must use a
separate and unique port number. The Address parameter
identifies the IP address of the host computer. The marking system
software supports both fixed addressing and dynamic addressing.
Optionally, the Ethernet Port may be connected to a PC running
the Merlin III Visual Design Software. Any computer that runs the
Merlin III software must
• Windows
Windows
• Pentium
®
®
®
4 Processor
satisfy the following requirements:
2000, XP, Vista
®
(Business Edition), or
7 (32-bit Professional Edition) operating system
• Sufficient RAM as per operating system requirements
• Video board
• 2GB hard drive
• CD-ROM disk drive
• One available Ethernet port
• SVGA color monitor, mouse, and keyboard
Host Communications
(continued)
Programmable Protocol. Use this protocol where very simple
one-way communications are required (such as with bar code
scanners). Programmable Protocol provides no error checking or
acknowledgment of the transmitted data. Note that XON/XOFF
Protocol applies even when Programmable Protocol is selected.
Starting Character specifies where the software begins to
count character positions. This number must be entered in
decimal format (e.g., "2" for ASCII Start of Text "STX").
Terminating Character identifies the end of transmitted string
(usually "13" for ASCII carriage return character).
Character Position counted from the starting character
ignoring all characters preceding it.
Character Length accepts variable length messages (if set
to 0) or messages of a pre-specified, fixed number of characters.
Ignore Character identifies the character to ignore when sent
from the host (usually "10" for ASCII line feed character)).
Message Type allows message-type recognition which defines
how the marking system will use data it receives from the host.
1 Message type 1 overwrites the first line of the first text
field with data extracted from the host
P Message type P loads a specific pattern identified by
data extracted from host
Q Message type Q updates the text in the first query
buffer with data extracted from the host
V Message type V updates the first variable text flag
found in the pattern with data extracted from the host
0 Message type 0 (zero) indicates that host will provide
message type, field number (if applicable), line number
(if applicable), and data; delegates message type
selection to the host on message-by-message basis.
The host message must use the format:
Tnn<string>
where:
T = 1, P, Q, or V to indicate message type
nn = two-digit field number or query text buffer
<string> = For Message Type P, indicates the pattern
where data will be placed.
Note: Not used with Message Type P.
name to be loaded.
For Message Types 1, Q, or V, indicates
the data to be
query text buffer, as applicable.
inserted into the field or the
8 of 10 28575G
Page 9

TMP1700/470 Marking System
Host Communications (continued)
Extended Protocol. This protocol selection includes error checking and transmission acknowledgment. It should be used in applications
where serial communication is a vital part of the marking operation. All communications are carried out in a parent/child relationship with
the host being the parent. Only the host has the ability to initiate communications. If the host does not receive a response within three
seconds, it should re-transmit its original message. If no response is received after three tries, it should declare the link to be down.
The following describes the Extended Protocol message format as
sent from the host to the TMC470 controller.
SOH TYPE [##] STX [DATA] ETX BCC CR
where:
SOH ASCII Start of Header character (001H). The controller
ignores all characters received prior to the SOH.
TYPE A single, printable ASCII character that defines the
meaning (type) and content of the message downloaded
from the host, where:
1 Message Type 1 overwrites a specific field in
currently loaded pattern with data supplied in the
host message. See [DATA] for details.
P Message Type P specifies the pattern name to be
loaded for printing. See [DATA] for details.
Q Message Type Q updates a specific query buffer
with data supplied in the host message.
See [DATA] for details.
V Message Type V updates the variable text in a
specific text field of the currently loaded pattern with
data supplied in the host message.
See [DATA] for details.
O Message Type O resets marker and places it online
G Message Type G initiates a print cycle to mark the
currently loaded pattern
I Message Type I requests the marker return the
status of standard output and input signals. The
system will return a hexadecimal code for the 6
output signals and 12 input signals in the following
format:
OO;III
where:
bit 1 READY 0x01
bit 2 DONE 0x02
bit 3 PAUSED 0x04
bit 4 NO_FAULT 0x08
bit 5 SPARE_1 0x10
bit 6 SPARE_2 0x20
bit 1 START 0x001
bit 2 STOP 0x002
bit 3 SEL_0 0x004
bit 4 SEL_1 0x008
bit 5 SEL_2 0x010
bit 6 SEL_3 0x020
bit 7 SEL_6 * 0x040
bit 8 SEL_4 0x080
bit 9 SEL_5 0x100
bit 10 SPARE_1 0x200
bit 11 SPARE_2 0x400
bit 12 SPARE_3 0x800
Note: Input SEL_6 may be configured
to place machine online (default)
or for Remote Pattern Selection.
[##] Optional two-digit ASCII number that specifies the Station
ID of the controller when used in multi-drop network
applications. The Station ID may range from 00-31. Note
that “00” is reserved for applications where only one
controller is used. In such applications, this field may be
eliminated and “00” will be assumed.
STX ASCII Start of Text Character (002H).
[DATA] Optional character string that may be required for certain
message types (e.g., Type 1, P, Q, and V).
Typically, data is sent in the format:
nn<string>.
where:
nn = two-digit field number or query text buffer
where data will be placed.
Note: Not used with Message Type P.
<string> = For Message Type P, indicates the pattern
name to be loaded.
For Message Types 1, Q, or V, indicates
the data to be inserted into the field or the
query text buffer, as applicable.
ETX ASCII end of text character (003H).
BCC Optional Block Check Code that is generated and sent to
improve link reliability by providing fault detection. The
BCC is calculated by taking an eight bit addition of the
TYPE and DATA TEXT characters and transmitting them
as a three digit ASCII decimal number in the range from
000 to 255. If the sum is greater than 255, the most
significant bit overflows and is discarded.
CR ASCII Carriage Return Character (00DH).
28575G 9 of 10
Page 10

TMP1700/470 Marking System
TRADEMARKS
Telesis, PINSTAMP, and Merlin are registered trademarks of
Telesis Technologies, Inc. in the United States.
MicroPin is a trademark of Telesis Technologies, Inc. in the
United States.
NEMA is the registered trademark and service mark of the
National Electrical Manufacturers Association.
Pentium is a registered trademark of Intel Corporation in the
United States and other countries.
Windows and Vista are registered trademarks of Microsoft
Corporation in the United States and other countries.
10 of 10 28575G
 Loading...
Loading...