

Index
1 Document history..............................................................................................................................5
2 Package..............................................................................................................................................6
2.1 Box...............................................................................................................................................6
2.2 Package contents........................................................................................................................6
2.3 Router versions...........................................................................................................................7
3 General presentation.........................................................................................................................8
3.1 Front panel..................................................................................................................................8
3.2 Back panel...................................................................................................................................8
3.3 External connections...................................................................................................................9
3.3.1 GSM/UMTS/LTE antenna connector....................................................................................9
3.3.2 Modem serial port, either full RS232/RS485.......................................................................9
3.3.3 LAN connector......................................................................................................................9
3.3.4 Power supply connector.....................................................................................................10
3.3.5 SIM card holders.................................................................................................................10
3.4 Product sticker..........................................................................................................................10
4 Basic features and services..............................................................................................................11
5 Using the modem............................................................................................................................12
5.1 Setting up the modem..............................................................................................................12
5.1.1 Inserting SIM card(s)..........................................................................................................12
5.1.2 Connecting antenna...........................................................................................................13
5.1.3 Connecting power supply cable.........................................................................................14
5.1.4 Connecting LAN cable with RJ-45.......................................................................................14
5.2 Router configuration.................................................................................................................15
5.2.1 Setting up the connection..................................................................................................15
5.2.2 Modem status page............................................................................................................15
5.2.3 Local network.....................................................................................................................17
5.2.4 GSM network.....................................................................................................................18
5.2.5 WiFi network......................................................................................................................19
5.2.6 Connection control.............................................................................................................20
5.2.7 Ports configuration.............................................................................................................21
5.2.8 TCP/IP forwarding...............................................................................................................22

5.2.9 VLAN...................................................................................................................................23
5.2.10 Static routes.....................................................................................................................24
5.2.11 Dynamic DNS....................................................................................................................25
5.2.12 Access control..................................................................................................................26
5.2.13 Open VPN.........................................................................................................................27
5.2.14 Ipsec static/Ipsec mobile..................................................................................................29
5.2.15 Generating SSL certificates...............................................................................................32
5.2.16 NTRIP configuration page.................................................................................................34
5.2.17 SMS Actions......................................................................................................................35
5.2.18 Time..................................................................................................................................36
5.2.19 Syslog................................................................................................................................37
5.2.20 User files...........................................................................................................................38
5.2.21 Backup and restore..........................................................................................................39
5.2.22 Discard changes................................................................................................................39
5.2.23 Save settings ...................................................................................................................39
5.3 System logs description............................................................................................................40
5.4 Elproma Device Manager..........................................................................................................41
6 Troubleshooting...............................................................................................................................43
6.1 No communication with the modem........................................................................................43
6.2 Modem answers but there is no internet connection..............................................................43
7 Technical characteristics..................................................................................................................44
7.1 Mechanical characteristic.........................................................................................................44
7.2 Housing (dimension diagram)...................................................................................................44
7.3 Electrical characteristic.............................................................................................................44
7.3.1 Power supply......................................................................................................................44
7.3.2 RF characteristics................................................................................................................44
7.3.2.1 Frequency ranges – UMTS/HSPA variant.....................................................................44
7.3.2.2 Frequency ranges - LTE variant....................................................................................44
7.3.2.3 WiFi characteristics......................................................................................................45
7.3.2.4 External antenna.........................................................................................................45
7.4 Environmental characteristic....................................................................................................45
8 Router architecture..........................................................................................................................46
9 Safety recommendations.................................................................................................................47

9.1 General Safety...........................................................................................................................47
9.2 Care and Maintenance .............................................................................................................47
9.3 Responsibility ...........................................................................................................................47
10 Accessories....................................................................................................................................48
Power cable – open end.................................................................................................................48
RS232/485 cable............................................................................................................................48
DIN rail holder:...............................................................................................................................49
Velctro:...........................................................................................................................................49
11 Safety Recommendations..............................................................................................................50
12 Certifications..................................................................................................................................52
12.1 Conformity Assessment Issues...............................................................................................52
12.2 Declatarions of conformity.....................................................................................................52
12.3 National restrictions................................................................................................................52
13 List of Acronyms............................................................................................................................53
14 On-line support.............................................................................................................................55
1 Document history
Revision Date Changes
#0.6 8.03.2018 - Preliminary version
#0.8 21.05.2018 - New screenshots
#0.9 13.09.2018 - LED description

2 Package
2.1 Box
User can find product sticker on the box which matches sticker placed on the device - it
proves that your modem is an original product. More information about stickers are in chapter
Product sticker
2.2 Package contents
Complete package contains:
1. RBMTX-Lite router
2. Antenna GSM (SMA connector)
3. Power adapter
4. Wall holder
2.3 Router versions
There are many ways to upgrade your RBMTX-Lite router. List below shows typical
configuration and different combinations (variants) of this terminal.
Option Typical Option
Power supply 9-30V -
Memory
256MB RAM, 512MB MicroSD card
(part used for Linux system, the size of
SD card can be changed in the future)
-
Processor Cortex A7, max. 528MHz, I.MX6UL(L) -
RS232 System console RS485 1 -
Connection UMTS/HSPA LTE
Dual SIM - available
LAN Ethernet 10/100Mbps -
WiFi - available
Bluetooth - available

3 General presentation
3.1 Front panel
3.2 Back panel
3.3 External connections
3.3.1 GSM/UMTS/LTE antenna connector
SMA antenna connector placed on front panel is used to connect external
GSM/UMTS/LTE. It must be connected to establish a connection with GSM/UMTS/LTE
network. In good circumstances (good coverage, level of received signal is high) use antenna
which is included in package. When signal strength is poor please use outdoor
directional/omnidirectional or indoor antenna.
Note: If antenna is not connected, connection with GSM/UMTS/LTE network will be
impossible.
3.3.2 Modem serial port, either full RS232/RS485
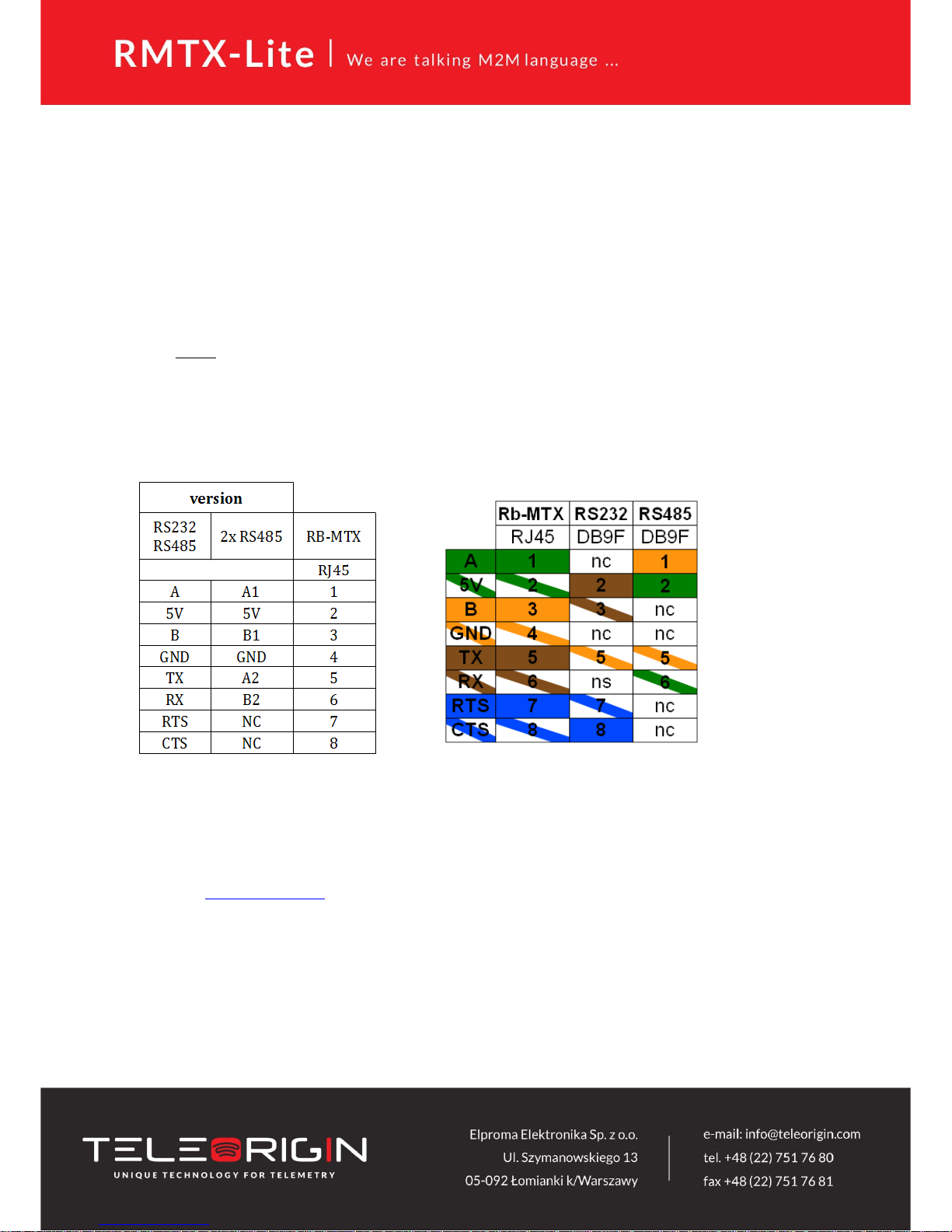
Serial RS232/RS485 (RJ-45 connector marked as “RS232/485”) is placed on front
panel of router. Serial connector pinout is described in a tables below.
3.3.3 LAN connector
Second RJ-45 connector (marked as “LAN”) is placed next to serial connector and is
used for communication with PC or laptop through Ethernet interface. WWW configuration is
available in the web browser (default IP address is 192.168.1.234). You can change the default
address in “Local network” tab.
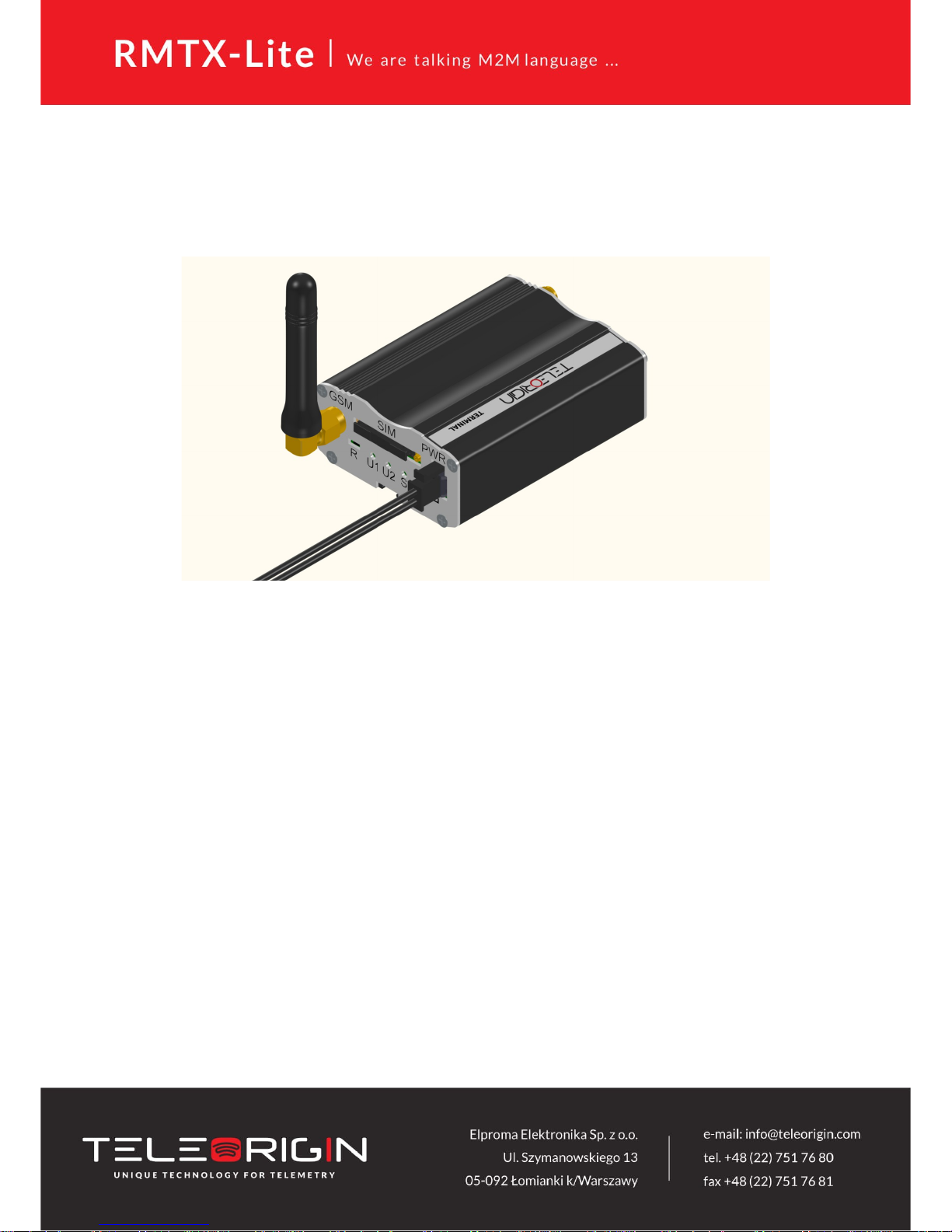
3.3.4 Power supply connector
Please use power adapter which is included in package. It ensures “clean” power
supply input and avoids short transients on power supply lines originating from inductive
load switching. Power supply range of RBMTX-Lite router is 9-30V.

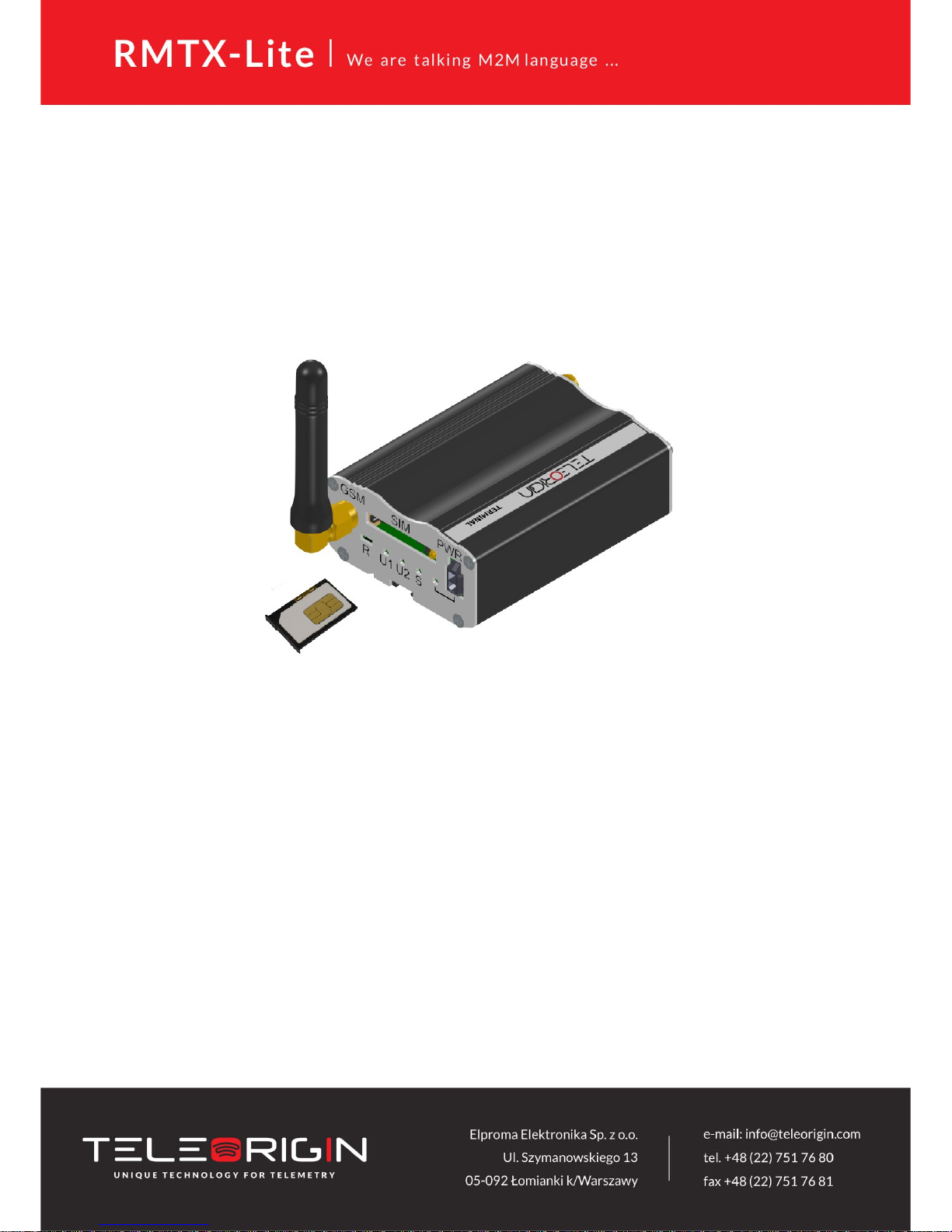
3.3.5 SIM card holders
One SIM card holder is placed in front panel of RBMTX-Lite and the second one is
located inside the device. To insert SIM card into the extractable holder push yellow button
and take SIM drawer out as show in the picture and place SIM card. To operate the module in
a GSM network, it is necessary to insert at least one active SIM card.
3.4 Product sticker
A production sticker includes the following information:
● Product serial number
● CE marking
● 15-digit bar code
● model signature (RBMTX-Lite)
3.5 LED operation
Router has four LED indicating its operation. The diode description is presented in the
table below.
Diode Color Description
U1 Green User controlled
U2 Yellow Network indicator:
RBMTX-Lite 3G:
• Flicker slowly (200ms ON, 1800ms OFF) – Network searching
• Flicker slowly (1800ms ON, 200ms OFF) – Idle/Data transfer
• Always ON – Voice/CSD calling
RBMTX-Lite 4G:
• Flicker slowly (200ms ON, 1800ms OFF) – Network searching
• Flicker slowly (1800ms ON, 200ms OFF) – Idle
• Flicker quickly (125ms ON, 125ms OFF) – Data transfer
• Always ON – Voice calling
S Blue Router activity
PWR Green Power supply
4 Basic features and services
Basic features and available services are contained in table below.
Feature /
service
Description
Supported
bands
UMTS/HSPA variant:
• GSM 900/1800 MHz
• UMTS 900/2100 MHz
LTE variant:
• GSM 900/1800 MHz
• WCDMA FDD B1, B8 Class 3
• LTE FDD B1, B3, B7, B8, B20 Cat. 1
Data
features
LTE Cat. 1 (downlink 10 Mbit/s, uplink 5 Mbit/s)
DC-HSPA+ (downlink 7.2 Mbit/s)
GPRS (Multi-slot class 10, max BR downlink 85,6 Kb/s)
Embedded protocols: PPP, TCP/IP, UDP/IP, MMS, HTTP, HTTPS, SSL, FTP, FTPS, SMTP,
SMTPS, NTP, NITZ, PING
Ports forwarding, Ipsec, OpenVPN
Class B GSM 07.10 multiplexing protocol
WiFi*
Standard:
• 802.11b/g/n
Date rate:
• up to 150 Mbps
Bluetooth*
V4.1+EDR
Power
supply
Nominal voltage range: 9V-30V
Maximum continuous (average) supply power: 5W
Peak (momentary) supply current: 1 A
Interfaces
(typical
version)
GSM/UMTS/LTE antenna connector: SMA
1x SIM Card: 1.8V, 3V standards
RS232 and RS485 via RJ-45
RJ-45 connector (x2)
microUSB (OTG)
Power supply connector
Factory default reset button
4 x LED
Options*
Dual SIM (second SIM is internal)
WiFi antenna connector: SMA male
Bluetooth antenna connector: SMA
Other
Physical size:
Max. Dimensions: 83 x 53.5 x 26 mm (w/ connectors)
Operating temperature range:
Min. -20°C Max. 60°C
*option
5 Using the modem
5.1 Setting up the modem
To set the modem, do the following steps:
5.1.1 Inserting SIM card(s)
Push yellow button placed on front panel and take SIM drawer out.
Place SIM card in the holder as shown in the picture:
Router is available with one or two SIM card slots. To insert the second SIM card please
unscrew one of the routers panel, eject PCB board and put the SIM into internal SIM holder.

5.1.2 Connecting antenna
Connect GSM/UMTS/LTE antenna to SMA connector
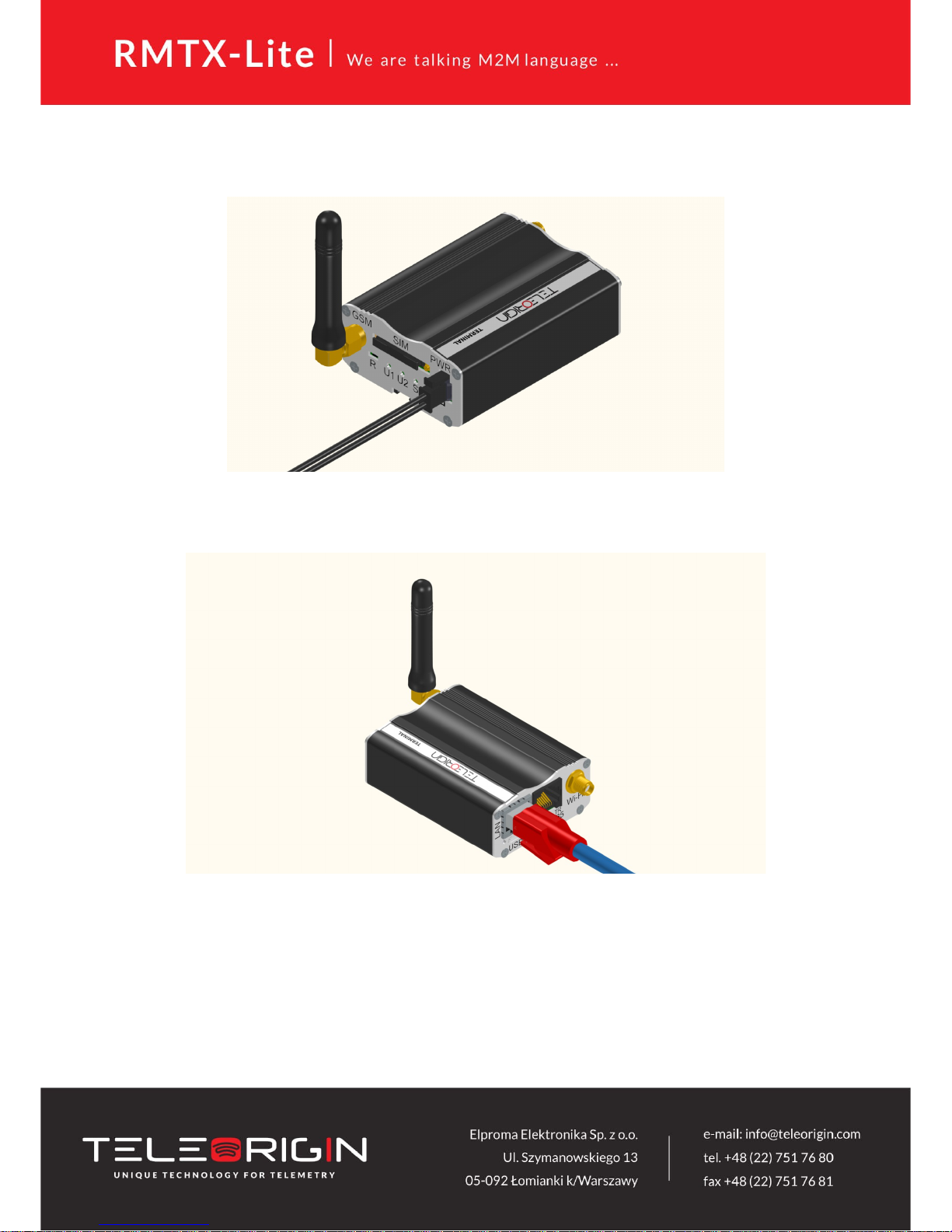
5.1.3 Connecting power supply cable
Connect power supply cable into power supply connector
5.1.4 Connecting LAN cable with RJ-45
Plug LAN cable into RJ-45 plug.
5.2 Router configuration
Router is configured via web browser. Modem settings are divided into sections which
allows user to easily find needed option. If you need to save new settings please apply them
using “Save settings”. You can also discard changes by choosing appropriate option from
menu.
WARNING: Cache of router is cleared on device reset.
NOTE: Not all tabs are available on every modem version.
5.2.1 Setting up the connection
When you connect all necessary cables (see Setting up the modem) you can setup
connection. Connect LAN cable to your computer and go to Internet protocol TCP/IP
properties (Network connections -> Local Area Connection ->Internet protocol TCP/IP->
Properties) and set your IP address as 192.168.1.x. Please read how to change TCP/IP
settings of your network card in this thread (example for Windows 7):
http://windows.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/change-tcp-ip-settings#1TC=windows-7
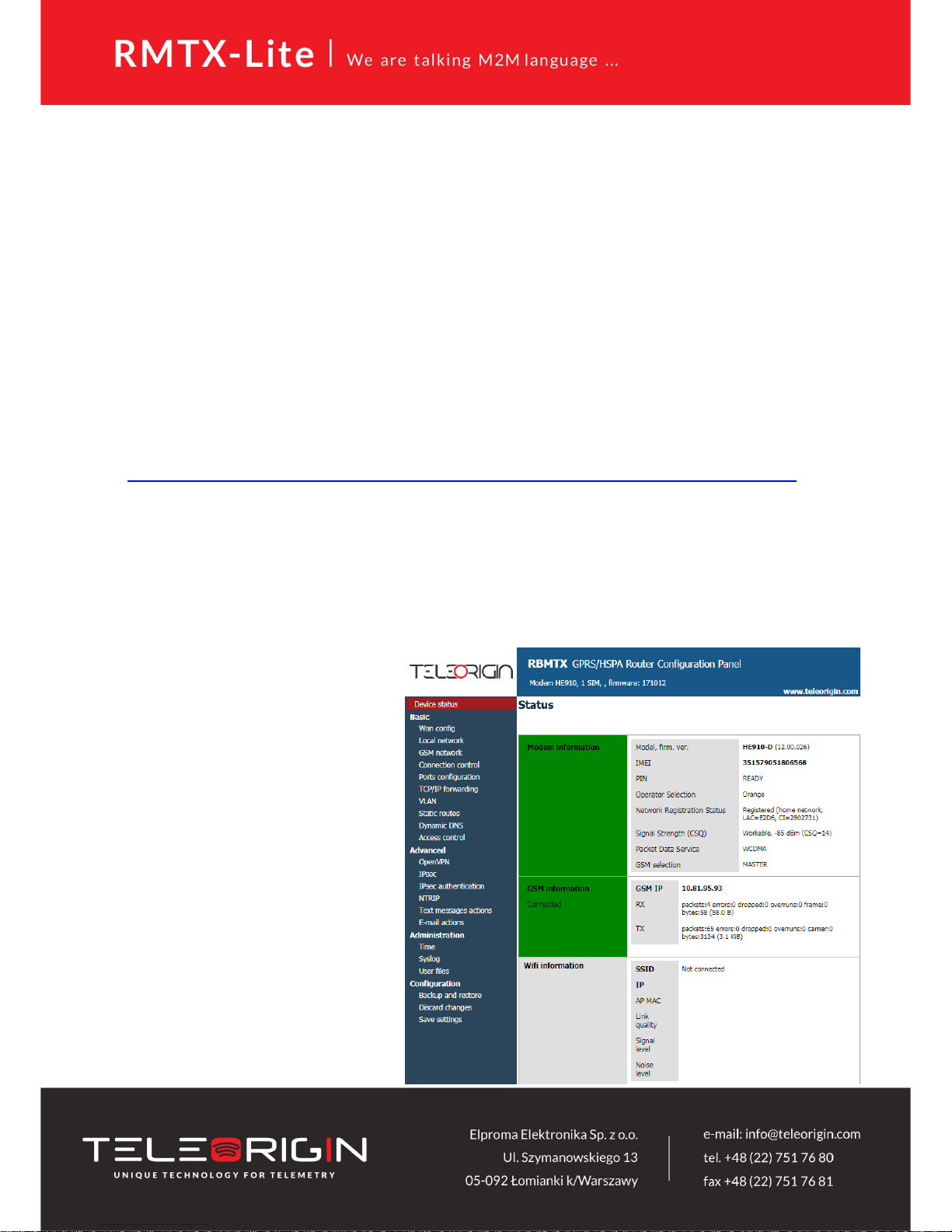
5.2.2 Modem status page
Go to your web browser and put IP address 192.168.1.234. You will be asked for
username and password. By default it is:
Username: admin
Password: 12345
If everything is configured correctly you should see following screen:
This is status page of RBMTXLite router. Here you can check if
modem is connected to network,
its parameters and information
about PPP connection. Device
status page is refreshing
automatically.
In table below you can find the description of each field in “Device status” tab:
Field Example Description
Model, firm. ver. GMM: LE910-C1 (19.01.522) GSM module info
IMEI 359852050093104 device serial number
PIN READY SIM card status:
SIM PIN - PIN lock (please set
right PIN number in “GSM
network” tab)
READY - SIM unlocked
SIM PUK - PUK lock
Operator Selection 0,0,Orange,2 name (3rd parameter), access
technology (4th parameter):
for UMTS/HSPA variant:
0 - GSM
2 - UTRAN
3 - GSM w/EGPRS
4 - UTRAN w/HSDPA
5 - UTRAN w/HSUPA
6 - UTRAN w/HSDPA and
HSUPA
for LTE variant:
0 - GSM
2 - UTRAN
3 - GSM w/EGPRS
4 - UTRAN w/HSDPA
5 - UTRAN w/HSUPA
6 - UTRAN w/HSDPA and
HSUPA
7 - E-UTRAN
Network Registration
Status
2,1,E2D6,280BAD1,2 registration status (2nd
parameter), location area code
(3rd parameter), cell ID (4th
parameter). Possible statuses:
0 - not registered, terminal is not
currently searching a new
operator to register to
1 - registered, home network
2 - not registered, but terminal is
currently searching a new
operator to register to
3 - registration denied
4 - unknown
5 - registered, roaming
Signal Strength (CSQ) 7 ( Marginal, -99 dBm ) -
Packet Data Service LTE type of packet data service
GSM selection MASTER SIM card selection
GSM IP 10.228.211.212 -
RX packets:12 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
-
TX
packets:20 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
-
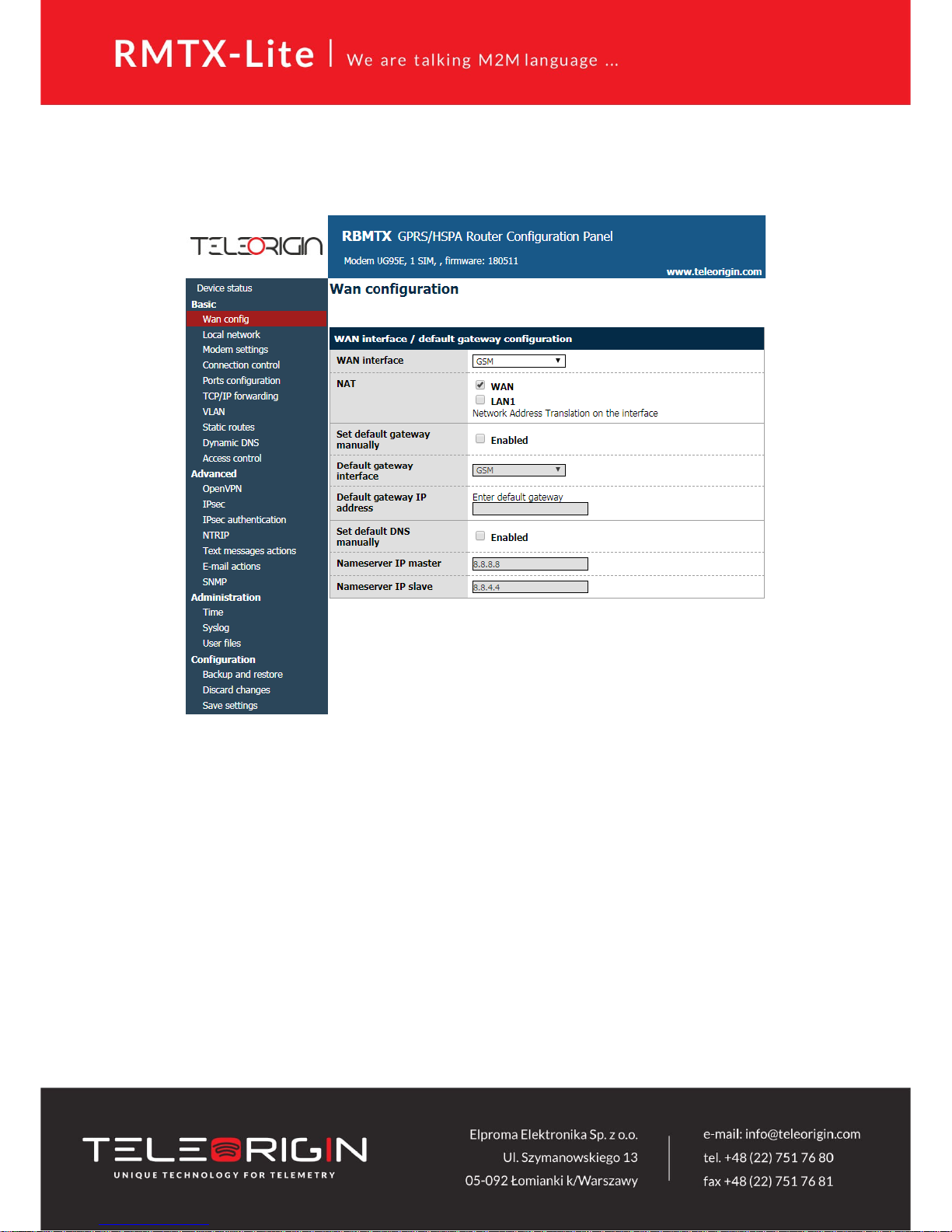
5.2.3 WAN config
WAN config page is shown in the illustration below.

5.2.4 Local network
On “Local network” configuration page you can find essential parameters needed for
LAN connection. Here you can set IP Address (or set it to be downloaded via DHCP), mask,
default gateway and DNS addresses. Last two options can be entered manually or downloaded
automatically via GSM or DHCP. Modem can also works as DHCP server - you can define its
range and set list of IP-MAC binds.
“Wireless configuration” field is available only in RBMTX-Lite with WiFi option. You can
set there a parameters of your WiFi connection. To scan all available networks please use
“Scanning” button. You will be redirected to page with list of networks in a view. You can set a
WiFi mode (Access point or Station), fill a name and password of selected network. You can
also enable DHCP server and AP clients.


5.2.5 Modem settings
On “Modem settings” page you can define internet connection parameters (APN,
username, password, CSD, ISP IP and Modem band) for one or two SIM cards (depending on
modem version). To use internet you should know those parameters - they are essential for
getting access to internet. The parameters should be ensured by your mobile network
provider.
To enter the PIN for SIM card you need to mark “Enabled” field and then fill the field
below with correct PIN. Please note that outgoing calls are made always on MASTER SIM card.

5.2.6 Connection control
Here you can set parameters of switching between two SIM cards. You can define time
for ping and ping counter for 4 IP addresses you choose. In example (picture) here after 3
pings that take 10 seconds each card will change from Master to Slave or opposite.

5.2.7 Ports configuration
User is able to set port settings under RS232/RS485 port configuration page. There are
3 configurable ports: /dev/ttyS0, /dev/ttyACM0 and /dev/ttyS1 or /dev/ttyUSB0 (depending
on modem version). Every port can be set to different mode. On /dev/ttyS0 you can set
terminal, ModBus gateway or NTRIP mode. Two other ports can work as modem port (modem
control and modem data) or SMS receiving port (see also: SMS Actions section).
Every port can also be set to forwarding mode that allows user to forward it to
TCP/UDP port (as server or client). Port /dev/ttyS0 can also be forwarded to modem control
or modem data port. In that case no other mode can be set on that port. Setting modes on
/dev/ttyS0 and /dev/ttyS1 (LTE modem variant only) enables setting port parameters: baud
rate, data bits, parity checking and protocol. If parameter is inactive, this means that user can't
control it in currently set mode.

5.2.8 TCP/IP forwarding
You can forward single port or port ranges onto certain IP address. To add new rule for
single port, enter TCP/IP Forwarding tab. In “Single port rules” section click button “New” and
enter all necessary informations: Identifier, check “Enabled” field, enter external and internal
port, choose protocol (TCP or UDP) and enter IP address. When adding new rule or switching
tab, currently edited rule is automatically saved. You can delete it (or any other rule) by
pressing “Delete” button. After changes click Save Settings to save whole configuration. You
can edit port range rules in the same way in Port range rules section. You can also set IP
address of demilitarized zone in DMZ section.



5.2.9 VLAN
VLAN tab enables user to create virtual IP addresses. You can define IP, netmask and
identifier from range 0-4095. If you enable IEEE 802.1Q tagging Virtual IP becomes part of
VLAN.

5.2.10 Static routes
Under static routes tab you can define your own routings. Please click Add new button
to add new routing. Enter identifier (used only to distinguish routings in www configuration),
choose interface, enter destination network, netmask and gateway.

5.2.11 Dynamic DNS
Dynamic DNS is a service which allows user to make your device available under
specific www address regardless of its IP changes. In order to do that you must create an
account on one of web pages that are supported by RBMTX-Lite modem (currently
DynDNS.org or No-IP.com). After creating account, please enter necessary information in
Dynamic DNS tab of www configuration: your service provider, in case of DynDNS its type,
username, password, host name and two intervals. Update interval is time between two
checks whether IP address had changed. Forced update interval is time between updating IP
data regardless of IP change. Please last two fields empty to use default value if you're not sure
what to input there.

5.2.12 Access control
First section of Access Control tab allows you to configure SSH protocol. You can turn it
on or off, set on which port and interfaces (also OpenVPN and IPsec tunnels) it should be
accessible. You can also toggle logging via SSH as root and change/delete passwords/keys for
root and service user. Remember to save whole configuration after changing password by
pressing Save Configuration button from main menu. Deleting password means that it won't
be needed to log on. When logging via SSH, key authentication has higher priority than
password. That means that user with authorized key won't be prompted for a password and
user without key will be able to login using password. You can paste multiple keys into SSH
root key and SSH service key fields.
ATTENTION: Service account is used to upgrade firmware. Turning SSH off will disable
firmware upgrades.


You can generate necessary keys directly on modem. Press the Generate button and
wait for a while-the process can take few minutes. You should not change settings or switch
tabs then. After the generation the message will be displayed. Public key will be automatically
pasted into the keys field (if the field wasn't empty before pressing the button, its contents will
be saved, the newly generated key will appear first on the list). From now you will be able to
download private and public keys by pressing Get private key and Get public key buttons. To
login using the key under Linux, you have to download private key, change its name to id_rsa
and put it in /home/user/.ssh folder.
In WWW config access section you can toggle HTTP/HTTPS access www configuration
and change ports and interfaces (OpenVPN and IPsec tunnels also) on which they will be
available. You can also change password for www configuration (the change will be
immediate, no saving configuration is needed). For security reasons disabling both HTTP and
HTTPS is not possible.
5.2.13 Open VPN
You can connect your modem to a VPN network or create your own one using OpenVPN
software. It is possible to create up to four VPN connections (tunnels). To view and change
settings of any of tunnels select it from Tunnel configuration list under OpenVPN tab. Then
choose if modem should be server or client and connection type: tun or tap. Tun connection
can be single- or multiclient. Depending on what you choose here, you will later need to enter
client/server IP addresses or network and netmask.
If the device should be server, please enter port on which it should listen for
connections (the default VPN port is 1194, remember to open the port you chose under the
firewall tab). Next, please select network device on which the connection should be held: eth
(external RJ45 port) or ppp (connection via mobile network). It is also necessary to choose
network protocol: TCP or UDP (use the second option if you are not sure what to choose). For
tun mode user should also enter server and client IPs
(we advise you to use addresses from 10.x.x.x pool). For tap mode please enter VPN sub
network address and net mask (for example 10.1.0.0 and 255.255.255.0). In most cases, your
device will reserve first IP address from the pool (that is 10.1.0.1 if you are using 10.1.0.0
network).
If the device is set into client mode, in addition to settings same as those for server, you
should input VPN server's IP in Remote Server IP field and its listening port in the Port field.
After filling in all necessary information user should fill in four certificate fields. The
certificates should be generated on any PC (see VPN online help for more information). The
contents of files should be pasted into appropriate fields of configuration. You can improve
security of your VPN connection by entering TLS key into the TLS key field on every device in
VPN network.
The last setting is toggling LZO compression (we advise you to enable it to improve
network communication) and adding extra configuration parameters in Additional
configuration field.


5.2.14 Ipsec static/Ipsec mobile
IPsec is group of internet protocols that enables user to create safe connection between
devices. To configure such connection on RBMTX-Lite modem you need to go through three
tabs of configuration: Tunnels, Mobile Clients, Keys and Certificates. First of all, you need to
enable IPsec under Tunnels tab. Below this option there is a combo box that enables you to
switch between different tunnel configurations. If you want to enable specific tunnel, please
select Enable tunnel checkbox. Then specify network interface on which the connection will
be held. It is impossible to discuss all ways to create IPsec connection, so we have described
sample configuration below.
Let's say we want to connect two RBMTX-Lite modems with following IP numbers:
123.45.67.1, 123.45.67.2. First option, DPD interval is time after which the connection is
closed if the other device is not responding. You can put any value here, we will enter 3600
seconds. Then you have to choose local subnet that will be available on remote side of the
connection. It can be single host, network or LAN subnet. Let's say we will be connecting more
devices later so we choose network. On first modem we enter following settings:
IP=192.168.36.1, Network=192.168.36.0 and Netmask=255.255.255.0. The IP must be set
properly according to the network and netmask. Next step is entering remote subnet. The
local subnet on first device must match remote subnet on the second device and vice versa.
We have specified local subnet on second modem with following settings: IP=192.168.35.1,
Network=192.168.35.0, Netmask=255.255.255.0, so on the first modem we enter following
remote subnet: Address=192.168.35.0, Netmask=255.255.255.0. After specifying local and
remote subnets, you should enter remote gateway which should be other device's IP. In our
case we enter 123.45.67.2 on first modem and 123.45.67.1 on second one.
Afterwards we have to define first phase of the proposal. We choose negotiation modeaggressive is les secure, but faster than main. Next setting is device's identifier. The most
common setting is My IP address for PSK authentication and RSA Cert subject for RSA
certificates. Now, please choose encryption, hash algorithm and DH key group-they must be
the same on both sides of connection. Blowfish encryption is usually the fastest and AES is the
slowest but most secure. You can optionally set lifetime of phase 1 or leave the field blank to
use default value. The most important setting of phase 1 is choosing authentication method:
Pre-shared key is like password, you have to enter the same key on both sides. More
sophisticated authentication method is using RSA certificates, but you need to generate
certificate and key for every device. You have two options here: either input other device's
certificate in Peer certificate field or add CA certificate (we will cover that topic later).

In the second phase of proposal please specify the protocol (ESP is authentication with
encryption, AH is authentication only), encryption algorithm, hash algorithm and PFS key
group. Please note that you can choose multiple algorithms, but at least one should match on
both sides of the connection. The last setting is phase 2 lifetime (leave field empty for using
default value).
After configuring all settings remember to save configuration. The configuration of
IPsec connection is finished unless you chose to authenticate with RSA certificates and CA
certificate. In that case click on Keys and Certificates tab. Here you can add multiple Preshared keys and CA certificates. Adding both is similar, so we will explain only adding CA
certificates. To add new one, please click on Add new button. Specify Identifier (which is used
only for distinguish them in www configuration), paste CA certificate and certificate revoke
list. Last field is optional and lets you ban users that shouldn't be allowed to join your network
anymore.
IMPORTANT: After filling in fields click Save button and then save whole configuration
by clicking Save settings. If you want to delete certificate, choose it from the list, click Delete
button and then save whole configuration.
It is possible to create IPsec connection with non-static-IP-devices. In order to do this
please click Mobile clients tab. Configuration is similar to the tunnel configuration, but there
are less settings (for example there is no PSK field-you should add pre-shared keys for mobile
clients in Keys and Certificates tab).
IMPORTANT: When configuring IPsec connection you will sometimes want to add
custom routing. This topic is covered in next section.
5.2.15 Generating SSL certificates
In order to use SSL authentication creating few files and copying them into adequate
fields under OpenVPN or IPsec tabs of www configuration is needed. This can be done using
PC with Linux and openssl installed. There is also Windows version of software available at
http://gnuwin32.sourceforge.net/packages/openssl.htm.
At first we need to create folder, in which all our keys and certificates will be stored.
Let's say it will be ~/keys. We create two files in it: list of certificates and file enumerating
them:
touch index.txt
echo 00 > serial
and subdirectories, where the certificates and keys will be stored:
mkdir private certs newcerts crl
In order to create certificates, the certificate authority (CA) is needed . It is ,,main''
certificate used to create other certificates. After creating private CA key:
openssl genrsa -des3 -out private/cakey.pem 1024
Warning: please remember the CA password!


The CA certificate is generated:
openssl req -new -x509 -days 365 -key private/cakey.pem -out cacert.pem
When creating a certificate user has to provide some information like country,
state/province, city, company name, e-mail address and common name. The last field is most
important, it has to be unique for every device.
After creating CA certificate generation of certificate for every device used is needed.
At first the private key is generated:
openssl genrsa -des3 -out private/device1key.pem
Then we generate certificate request:
openssl req -new -key private/device1key.pem -out device1req.pem
Here user has to enter country, state etc. again. They can be the same as before except
the common name.
Certificate authority signs the certificate:
openssl ca -notext -in device1req.pem -out device1cert.pem
If certificate will be used on RBMTX-Lite modem, password on private key has to be disabled:
openssl rsa -in private/device1key.pem -out private/device1key.pem_nopass
The whole process is repeated for every device (unique common names and filenames
have to be unique for different devices!).
If IPsec protocol will be used, certain fields in www configuration under Ipsec/Tunnels
tab have to be filled in. Content of device1cert.pem file should be pasted into the Certificate
field and contents of device1key.pem_nopass into the Key field. Peer Certificate field can be
filled with another device's certificate file or left empty. In this case the CA certificate has to be
provided under Keys and Certificates tab. Contents of cacert.pem file should be inserted
there.
If the OpenVPN protocol will be used, under OpenVPN tab content of cacert.pem has to
be pasted into CA cert field, content of device1cert.pem into Server/Client cert field and
device1key.pem_nopass into Server/Client private key field. The Diffie- Hellman parameters
file has to be created for VPN connection:
openssl dhparam -out dh1024.pem 1024
And its content should be copied into DH PEM field. This file is common for all devices
in VPN network.


5.2.16 NTRIP configuration page
One of /dev/ttyS0 port modes is communication with external device using NTRIP
protocol. If you decide to use it, it is necessary to set the mode under RS232 Port configuration
page. Then, enter settings in NTRIP page. Server address, port and initial position fields are
necessary. Username and passwords are optional.
It is also possible to choose data request mode. After entering required data, please
click Get List button to download data streams list from the server – it may take a while,
please be patient. After downloading the list please select one of data streams.
Attention: Entering initial position is necessary to login to NTRIP server if no external
device sending NMEA frames is connected to the S0 port.

5.2.17 Text messages actions
Text messages (SMS) actions tab allows user to define shell scripts that will be executed
every time modem receives SMS with specified content.
To enable this option ensure that global SMS Actions checkbox is enabled and you have
set one of available ports into SMS receiving mode under Ports configuration tab. Then click
New button, enter any identifier and command-sms content that will trigger action. You can
write any shell script you want and/or set GPIO action to be executed.

5.2.18 E-mail actions
In the “E-mail Actions” section, the user can set up an e-mail account for sending
messages (set the parameters: recipient, sender, server address, port, user and password). It is
also possible to set up a script that will be launched automatically (messages can be sent with
attachments or not, it is possible to compress the file before sending).


5.2.19 SNMP

5.2.20 Time
Here you can manually set hardware clock or input IP of NTP server to synchronize
time automatically

5.2.21 Syslog
Here you can define how modem should save your logs. Modem has internal memory
that get overwritten when it reaches its end. You can also save logs on your computer by
clicking download (manually). It is also possible to get remote access to logs by enabling
Remote service and setting SYSLOG host.

5.2.22 User files
You can upload to the modem your own scripts and executable files and set them to be
used in certain situations (e.x. when the VPN connection is established or at modem startup).
Under User files tab there is a list of user files. It is refreshed automatically after selecting tab,
it can be also manually refreshed by pressing Refresh button. To delete file, select it from the
list and press Delete button. To upload file, click Upload new button. You will be redirected to
separate site. Choose file by pressing Browse... button and commit your choice by clicking
Upload. After upload you will be informed if the whole operation was successful or the error
message will be displayed. Use link to return to the main page of www configuration. All files
are stored with rights for file execution, so they can be used in scripts.
Below the file upload panel there are two fields, where you can write scripts. Startup
script will be executed after startup procedure of modem and Reconfiguration script every
time you click Save Configuration button in www configuration. You can write your scripts in
Bash or PHP, but remember to use special header for scripts ((#!/bin/bash lub
#!/usr/bin/php). You can execute uploaded user files, they are stored in /root/userfiles.
WARNING: Binary files uploaded to modem should be compiled for processor installed
in modem!

5.2.23 Backup and restore
Under backup and restore tab user can:
Save/load alternative configurations
Configure FTP client to periodically check FTP server for latest configuration
Download/Upload backup configuration

5.2.24 Discard changes
Discard current changes in configuration which were not saved yet.
5.2.25 Save settings
To save your settings click save setting and wait until message will show up to confirm
your configuration data was saved.

5.3 System logs description
This paragraph shows structure of typical System log with some basic errors:
01/01/0000:00:30 rbmtx-lite syslogd 1.4.1: restart.
01/01/0000:00:31 rbmtx Start: RBMTX-Lite - FIRM:171026 – modem and firmware info
01/01/0000:00:35 rbmtx supervisor[560]: SIM Holder open/closed – SIM holder open/closed by software
01/01/0000:00:36 rbmtx supervisor[560]: Modem init 1 – first initialization try
01/01/0000:01:09 rbmtx supervisor[560]: Init /dev/ttyS1 – port initialization
01/01/0000:01:10 rbmtx supervisor[560]: Init /dev/ttyACM0
01/01/0000:01:13 rbmtx supervisor[560]: Modem is not registered on the GSM network – modem is not able
to log into network
01/01/0000:01:13 rbmtx supervisor[560]: Entering Modem is ready
01/01/0000:01:13 rbmtx supervisor[560]: Entering PIN OK – modem is ready for connection
01/01/0000:01:13 rbmtx supervisor[560]: Entering PIN error code: - wrong PIN message
01/01/0000:01:14 rbmtx login[811]: unable to change tty `/dev/ttyS0' for user `root'
01/01/0000:01:14 rbmtx login[811]: ROOT LOGIN on `ttyS0'
01/01/0000:01:20 rbmtx pppd[901]: pppd 2.4.5 started by root, uid 0 – connection
01/01/0000:01:21 rbmtx chat[903]: timeout set to 2 seconds
01/01/0000:01:21 rb chat[903]: send (AT)
01/01/0000:01:21 rbmtx chat[903]: expect (OK)
01/01/0000:01:21 rbmtx chat[903]: AT
01/01/0000:01:21 rbmtx chat[903]: OK
01/01/0000:01:21 rbmtx chat[903]: send (ATZ0)
01/01/0000:01:21 rbmtx chat[903]: expect (OK)
01/01/0000:01:21 rbmtx chat[903]: ATZ0
01/01/0000:01:21 rbmtx chat[903]: OK
01/01/0000:01:21 rbmtx chat[903]: send (AT)
01/01/0000:01:21 rbmtx chat[903]: abort on (NO DIALTONE)
01/01/0000:01:21 rbmtx chat[903]: abort on (ERROR)
01/01/0000:01:21 rbmtx chat[903]: abort on (NO ANSWER)
01/01/0000:01:21 rbmtx chat[903]: abort on (BUSY)
01/01/0000:01:21 rbmtx chat[903]: expect (OK)
01/01/0000:01:21 rbmtx chat[903]: AT
01/01/0000:01:21 rbmtx chat[903]: OK
01/01/0000:01:21 rbmtx chat[903]: send (ATZ0)
01/01/0000:01:21 rbmtx chat[903]: abort on (NO CARRIER)
01/01/0000:01:21 rbmtx chat[903]: timeout set to 30 seconds
01/01/0000:01:21 rbmtx chat[903]: expect (OK)
01/01/0000:01:21 rbmtx chat[903]: ATZ0
01/01/0000:01:21 rbmtx chat[903]: OK
01/01/0000:01:21 rbmtx chat[903]: send (AT)
01/01/0000:01:21 rbmtx chat[903]: expect (OK)
01/01/0000:01:21 rbmtx chat[903]: AT
01/01/0000:01:21 rbmtx chat[903]: OK
01/01/0000:01:21 rbmtx chat[903]: send (AT+CGDCONT=1,"ip","example.apn")
01/01/0000:01:22 rbmtx chat[903]: clear abort on (ERROR)
01/01/0000:01:22 rbmtx chat[903]: send (dddATD*99#)
01/01/0000:01:23 rbmtx supervisor[560]: pppd check loop:1
01/01/0000:01:25 rbmtx chat[903]: expect (CONNECT)
01/01/0000:01:25 rbmtx chat[903]: AT+CGDCONT=1,"ip","example.apn"

5.4 Elproma Device Manager
Elproma Device Manager is an application which allows you to find RBMTX-Lite
modems in local area network (LAN) and then restore factory settings by entering their IMEI
number. It is particularly useful when you forgot IP number of device and you can't access it by
terminal on serial port.
The installation process is pretty simple-you launch .exe file and choose path where to
unpack the application. The main window of program consists of table-list of devices available
on your network and buttons: Scan, Clear List, Reset and About. First you need to scan the
network for devices. It takes few seconds to list all the devices. Please also keep in mind that it
takes a while to boot modem so it won't respond immediately after you turn it on.

When the scan is complete you can see list of available devices in the table. You can
review information like IP address, MAC address, device name, firmware version and uptime.
If you want to restore factory settings on any device on the list, click the Reset button and
enter IMEI. Program will send special packet to all devices, but only the one with IMEI you
have entered will be affected. If the IMEI is correct and the factory settings have been restored
you should see ,,IMEI OK'' in one of cells of last column. This device will now reset to load new
settings and after about 1-2 minutes it will confirm that whole operation was successful - you
should see then that ,,IMEI OK'' will change to ,,done''.

6 Troubleshooting
6.1 No communication with the modem
If there is no communication with the modem do the following steps:
Check all external connections of the modem
Verify if power supply is correct
Check if TCP/IP parameters are correct
Check if any firewall is not blocking connection with the modem
6.2 Modem answers but there is no internet connection
If there is no internet connection do following:
Check if antenna is connected properly
Check if you have reception of GPRS/UMTS/LTE signal in your area (on website of GSM provider
Check if you configured your modem with proper parameters provided by your network provider
(they should match in order to connect to internet)
In case you do not have internet access contact your provider in order to get internet access

7 Technical characteristics
7.1 Mechanical characteristic
Max. dimensions 72 x 53.5 x 26 mm (w/o connectors)
Weight ≈90 g (only modem w/o any external connection)
Volume ≈100 cm3 (w/o connectors)
7.2 Housing (dimension diagram)
7.3 Electrical characteristic
7.3.1 Power supply
Nominal voltage range: 9V-30V
Maximum continuous (average) supply power: 5W
Peak (momentary) supply current: 1A

7.3.2 RF characteristics
7.3.2.1 Frequency ranges – UMTS/HSPA variant

7.3.2.2 Frequency ranges - LTE variant

7.3.2.3 WiFi characteristics
Standards 802.11b/g/n
Frequency band 2.4 Ghz
Output power
13 dBm@11n
17 dBm@11b
15 dBm@11g
tolerance ±2 dBm.
Data rates: up to 150Mbps
7.3.2.4 External antenna
The external antenna is connected to the modem via SMA connector.
Antenna must have parameters as shown below in table.
Antenna frequency range Supporting GSM, UMTS or LTE frequencies for GSM
or ISM 2.4 GHz for WIFI
Impedance 50 Ω
DC impedance 0 Ω
Gain 0 dBi
VSWR (with cable) -10 dB
The antenna chosen for working with modem should best fit to circumstances of
environment it is used in. When the modem is placed in a room or somewhere where the
range of networks signal is too low, the outdoor or specific indoor antenna should be used
to increase it.

7.4 Environmental characteristic
Attention! Exceeding the values may result in permanent damage to the module.
Parameter Min Max Unit
Ambient Operating
Temperature
-20 60 °C

8 Router architecture
Diagram below shows simplified architecture of RBMTX-Lite. Features marked with
dotted lines are available as option

9 Safety recommendations
9.1 General Safety
Please follow safety regulations regarding the use of radio equipment due to the
possibility of radio frequency interference. Read given advices carefully.
Switch off GSM terminal when:
in an aircraft – using cellular telephones in aircraft may endanger the operation of the aircraft; it is
illegal
at a refuelling point
in any area with potentially explosive atmosphere which could cause an explosion or fire
in hospitals and any other places where medical equipment is in use
Respect restrictions on the use of radio equipment in any area or place where it is
signalized that using cellular telephony is forbidden or dangerous.
Using GSM modem close to other electronic equipment may also cause interference if
the equipment is inadequately protected. It may lead to damage or failure of GSM modem or
the other equipment.
9.2 Care and Maintenance
The RBMTX-Lite terminal is a electronic product that should be treated with care.
Please follow suggestions shown below due to using modem for many years.
Do not expose terminal to any extreme circumstances like high temperature or high humidity
Do not keep modem in dirty and dust places
Do not disassemble the modem
Do not expose the modem to any water, rain or steam
Do not drop, shake or knocking your modem
Do not place your modem close to magnetic devices – credit cards, etc
Use of third party equipment or accessories, not made or authorized by Elproma Electronika Sp. z o.o.
may invalid the warranty of modem and/or cause failure or permanent damage of modem
Do not expose the modem to children under 3 years
9.3 Responsibility
The modem is under your responsibility. Please treat it with care, and respect local
regulations. This is not a toy – keep it out of the reach of children.
Try to use security features (PIN etc.) to block unauthorized use or theft.

10Accessories
The tables below shows recommended accessories for RBMTX-Lite terminal.
Power cable – open end
RS232/485 cable
Part No.
RB-PS12VP2L15 12V power adaptor <1,5m> 2 PIN
RB-PSCP2L15 2PIN <1,5m> open end
RB-904G 2J011
RB-89MSH MOLEX 0912360001
RB-MDI DIN Holder
RB-MR2R4
Name Description
Supply cable
GSM/UMTS/LTE antenna
SIM drawer
RS232/RS485 2in1 cable

DIN rail holder:
Velctro:

11Safety Recommendations
READ CAREFULLY
Be sure the use of this product is allowed in the country and in the environment
required. The use of this product may be dangerous and has to be avoided in the following
areas:
• Where it can interfere with other electronic devices in environments such as hospitals,
airports, aircrafts, etc
• Where there is risk of explosion such as gasoline stations, oil refineries, etc
It is responsibility of the user to enforce the country regulation and the specific
environment regulation.
Do not disassemble the product; any mark of tampering will compromise the
warranty validity.
We recommend following the instructions of the hardware user guides for a correct
wiring of the product. The product has to be supplied with a stabilized voltage source and the
wiring has to be conforming to the security and fire prevention regulations.
The product has to be handled with care, avoiding any contact with the pins because
electrostatic discharges may damage the product itself. The same cautions have to be taken for
the SIM, checking carefully the instruction for its use. Do not insert or remove the SIM when
the product is in power saving mode.
The system integrator is responsible of the functioning of the final product;
therefore, care has to be taken to the external components of the module, as well as of any
project or installation issue, because the risk of disturbing the GSM network or external
devices or having impact on the security. Should there be any doubt, please refer to the
technical documentation and the regulations in force.
Every module has to be equipped with a proper antenna with specific
characteristics. The antenna has to be installed with care in order to avoid any interference
with other electronic devices and has to guarantee a minimum distance from the people
(20 cm). In case of this requirement cannot be satisfied, the system integrator has to assess
the final product against the SAR regulation.
1. The unit does not provide protection from lightning and surge. For outdoor
installation use outdoor nonmetallic case safety approved according UL 50. Additionally you
should provide protection from lightning and over voltage according National code.
2. Be sure the use of this product is allowed in the country and in the environment
required. The use of this product may be dangerous and has to be avoided in the following
areas: Where it can interfere with other electronic devices in environments such as hospitals,
airports, aircrafts, etc. Where there is risk of explosion such as gasoline stations, oil refineries,
etc. It is responsibility of the user to enforce the country regulation and the specific
environment regulation. Do not disassemble the product; any mark of tampering will
compromise the warranty validity. We recommend following the instructions of the hardware
user guides for a correct wiring of the product. The product has to be supplied with
a stabilized voltage source and the wiring has to be conforming to the security and fire
prevention regulations. The product has to be handled with care, avoiding any contact with

the pins because electrostatic discharges may damage the product itself. Same cautions have
to be taken for the SIM, checking carefully the instruction for its use. Do not insert or remove
the SIM when the product is in power saving mode. The system integrator is responsible of the
functioning of the final product; therefore, care has to be given to the external components of
the unit, as well as of any project or installation issue, because the risk of disturbing the GSM
network or external devices or having impact on the security. Should there be any doubt,
please refer to the technical documentation and the regulations in force. Every unit has to be
equipped with a proper antenna with specific characteristics. The antenna has to be installed
with care in order to avoid any interference with other electronic devices and has to guarantee
a minimum distance from the body (20 cm/8”). In case this requirement cannot be satisfied,
the system integrator should assess the final product against the SAR regulation. The
European Community provides some Directives for the electronic equipment introduced on
the market. All the relevant information and the text of the Directive 2014/53/EU (RED)
regarding telecommunication equipment are available at the European Commission website:
http://ec.europa.eu/growth/sectors/electrical-engineering/red-directive_en

12 Certifications
12.1 Conformity Assessment Issues
The RBMTX-Lite has been assessed in order to satisfy the essential requirements of the RED
Directive 2014/53/EU (Radio Equipment Directive) to demonstrate the conformity against the
harmonised standards with the final involvement of a Notified Body.
12.2 Declatarions of conformity
The RBMTX-Lite product is in conformity with the following standards or other normative
documents:
12.3 National restrictions
This device is intended for use in all EU countries (and other countries following the EU
directive 2014/53/EU) without any limitation except for the countries mentioned below:
Norway This subsection does not apply for the geographical area within a radius of 20 km
from the centre of Ny-Ålesund

13List of Acronyms
ACM Accumulated Call Meter
ASCII American Standard Code for Information Interchange
AT Attention commands
CB Cell Broadcast
CBS Cell Broadcasting Service
CCM Call Control Meter
CLIP Calling Line Identification Presentation
CLIR Calling Line Identification Restriction
CMOS Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor
CR Carriage Return
CSD Circuit Switched Data
CTS Clear To Send
DAI Digital Audio Interface
DCD Data Carrier Detected
DCE Data Communications Equipment
DRX Data Receive
DSR Data Set Ready
DTA Data Terminal Adaptor
DTE Data Terminal Equipment
DTMF Dual Tone Multi Frequency
DTR Data Terminal Ready
EMC Electromagnetic Compatibility
ETSI European Telecommunications Equipment Institute
FTA Full Type Approval (ETSI)
GPRS General Radio Packet Service
GSM Global System for Mobile communication
HF Hands Free
IMEI International Mobile Equipment Identity
IMSI International Mobile Subscriber Identity
IRA Internationale Reference Alphabet
ITU International Telecommunications Union
IWF Inter-Working Function
LCD Liquid Crystal Display

LED Light Emitting Diode
LF Linefeed
ME Mobile Equipment
MMI Man Machine Interface
MO Mobile Originated
MS Mobile Station
MT Mobile Terminated
OEM Other Equipment Manufacturer
PB Phone Book
PDU Protocol Data Unit
PH Packet Handler
PIN Personal Identity Number
PLMN Public Land Mobile Network
PUCT Price per Unit Currency Table
PUK PIN Unblocking Code
RACH Random Access Channel
RLP Radio Link Protocol
RMS Root Mean Square
RTS Ready To Send
RI Ring Indicator
SAR Specific Absorption Rate (e.g. of the body of a person in an electromagnetic field)
SCA Service Center Address
SIM Subscriber Identity Module
SMD Surface Mounted Device
SMS Short Message Service
SMSC Short Message Service Center
SPI Serial Protocol Interface
SS Supplementary Service
TIA Telecommunications Industry Association
UDUB User Determined User Busy
USSD Unstructured Supplementary Service Data

14 On-line support
Elproma provides a range on on-line support which includes:
• the latest version of this document
• the latest drivers for RBMTX-Lite
• technical support
This information can be found on our websites at:
www.elpromaelectronics.com or www.teleorigin.com
For further information You can contact us at:
email: info@teleorigin.com or info@elpromaelectronics.com
tel.: +48 (22) 751 76 80
fax.: +48 (22) 751 76 81

 Loading...
Loading...