Teledyne ISCO RediSep Rf Gold User Manual
Use of RediSep Gold® Amine
Columns in the Weak Ion
Exchange Mode
Abstract
The RediSep Rf Gold® Amine columns are useful for
normal phase purifications, but can also be converted
for use as a weak anion exchange (WAX) column. This
application note describes the conversion of the amine
column to a WAX column and an example run with
the converted column. Washing and conditioning the
column for another run is also described.
Background
Why Use Ion Exchange Resins?
Ion exchange resins are useful to purify ionic
compounds from non-ionic materials. Ionic compounds
may be resolved from each other based on their
ionization at a given pH or buffer concentration.
Compounds that contain strongly ionizable groups
such as sulfonates or phosphates can be captured
and released on a WAX column. These compounds are
generally very soluble in water and often difficult to
purify with other techniques.
RediSep Rf Gold Amine columns contain an aminopropyl bonded phase which becomes a weak ion
exchange (WAX) phase which can be used to isolate
and purify compounds with strongly anionic groups
after treatment with an acid or salt. Compounds
with phenolic, carboxylic, and other weakly anionic
groups can be purified on RediSep Rf SAX (strong ion
exchange) columns.
Once the RediSep Rf Gold Amine column is converted
for use as an ion exchange column, it is difficult to
convert it back to an un-ionized amine column. The
column should be labeled as a WAX column to avoid
confusion with an unmodified column.
CAUTION
This procedure uses non-volatile salts. Use of nonvolatile salts and buffers may reduce pump seal life. The
chromatography system must be flushed with water after
the runs are complete to prevent salts from precipitating
in the pumps and lines. See Application Note #28 on the
Teledyne ISCO web site
the entire system.
The compounds will be eluted with a large quantity
of salt that generally needs to be removed. Many
1
for a method to efficiently clean
Chromatography Application Note
AN99, August 2020
compounds can be desalted with a RediSep Rf Gold
C18Aq column. Test the procedure on a small scale
before purifying your entire compound mixture.
Experiment and Results
Column Capacity
Part # Column size Maximum sample
(grams) Load (mMol)
69-2203-504 5.5 6.4
69-2203-505 15.5 18.1
69-2203-506 30 35.1
69-2203-507 50 58.5
69-2203-508 100 117
69-2203-509 150 175.5
69-2203-510 275 321.7
Table 1: RediSep Rf Gold Amine loading capacities when used
as WAX columns
The maximum capacity of the RediSep Rf Gold Amine
columns, when used as WAX columns, is shown in
Table 1.
Column Preparation and Use
A new column should be conditioned with methanol
or 2-propanol, followed by a wash with at least 10
column volumes (CV) of 5% acetic acid. The acetic
acid converts the column from the free base to the
ionic form with acetate as the counter-ion. Compound
retention is improved with the use of buffers with
lower selectivity than the functional groups on your
compound. The selectivity order is:
•OH¯ < acetate < formate < HCO3¯< Cl¯ < HSO3¯<
citrate (ions on right displace those on left)
The compound mixture should be dissolved in water
and liquid-loaded on the column. If the compound is
dissolved in a buffer, the buffer concentration should
be kept below 0.05M to reduce competition on the
column between the buffer and the desired compound.
The column can be washed with water to elute neutral
and un-retained compounds.
Elute the compound with the buffer. The example
uses gradients that increases the ionic strength (salt
1. http://www.isco.com/WebProductFiles/Applications/101/Application_Notes/AN28_Solvent_Changing_on_CombiFlash_Systems.pdf retrieved 16 Aug 2012
Chromatography Technical Note TN99
0.5
Time (CV)
Absorbance (214 nm)
100
1M NaH2PO4 (%)
–
O
H
concentration) until the compounds elute. The gradient
can be a continuous or step-wise gradient.
Column Washing/Storage
After use, wash the column with 10 CV of 5% acetic
acid in water. The acetate regenerates the column by
displacing the counter-ion that was used last on the
column. Follow the acetic acid wash with a 5 CV water
wash. Store the column in 100% 2-propanol.
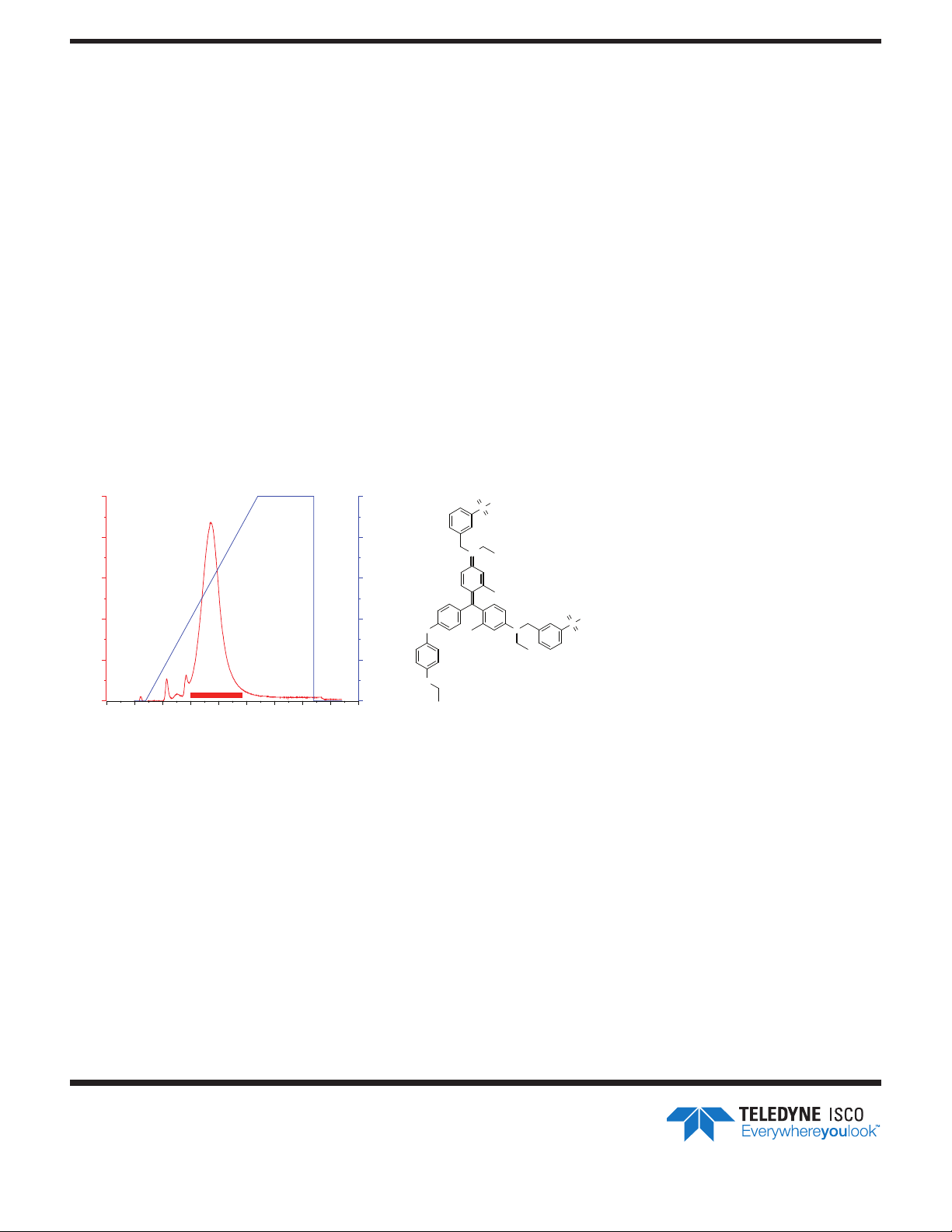
Purification of Brilliant Blue Dye
Brilliant blue (Figure 1) is a good example of both
capture/release and purification of a compound. This
compound possesses two sulfonate groups. A number
of minor impurities were resolved from the main
compound peak during the gradient elution.
0.4
0.3
80
60
Brilliant blue (50 g) was dissolved in 5 mL water and
injected on a 15.5 g RedSep Rf Gold Amine column (PN
69-2203-505) previously conditioned with 5% acetic
acid. The mixture was eluted with a gradient from 0 to
100% B solvent consisting of 1.0M NaH2PO4 in water;
the pH was not adjusted but measured to be pH 4.6.
Fractions from the main peak were combined and
desalted using a 5.5 g RedSep Rf Gold C18Aq column
(PN 69-2203-558).
Conclusion
The RedSep Rf Gold Amine column is versatile.
It can be run as a normal phase column or as an
ion exchanger. Once converted to ion exchange, it
can be reused for other ion exchange purifications.
The compounds are eluted using increasing buffer
concentration.
O
S
O
+
N
O
0.2
0.1
0.0
-5 0510 15 20 25 30 35 40
40
20
0
NH
O
N
O
S
O
Figure 1: Purification of brilliant blue dye with a RediSep Rf Gold Column in WAX mode
Teledyne ISCO
P.O. Box 82531, Lincoln, Nebraska, 68501 USA
Toll-free: (800) 228-4373 • Phone: (402) 464-0231 • Fax: (402) 465-3091
Teledyne ISCO is continually improving its products and reserves the right to change product
specifications, replacement parts, schematics, and instructions without notice.
 Loading...
Loading...