Page 1

Protocol Solutions Group
3385 Scott Blvd., Santa Clara, CA 950 54
Tel: +1/408.727.6600
Fax: +1/408.727.6622
PETrainer™
Scripting Language
Reference Manual
For PETrainer™ Software Version 7.xx
January 2014
Page 2

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Document Disclaim er
The information contained in this document has been carefully checked and is believed to be
reliable. However, no responsibility can be assumed for inaccuracies that may not have been
detected.
Teledyne LeCroy reserves the right to revise the information presented in this document without
notice or penalty.
Trademarks and Servicemarks
CATC Trace, PETrainer EML, PETra iner ML, P ETr ac er EML, PETrac er ML, PET rac er ,
PETracer Summit, Summit Z2-16, Summit Z3-16, and BusEngine are trademarks of Teledyne
LeCroy.
Microsoft and Windows are registered trademarks of Microsoft Inc.
All other trademarks are property of their respective companies.
Copyright
© 2012 Teledyne LeCroy, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
This document may be printed and reproduced without additional permission, but all copies
should contain this copyright notice.
ii
Page 3

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Contents
1 Introduction................................................................... 1
1.1 Support Resources ............................................................ 1
2 Command List............................................................... 2
3 Packet Command ......................................................... 3
3.1 Packet = TLP ..................................................................... 3
3.1.1 TLPType = MRd32, MRdlk32, MWr32 .....................................9
3.1.2 TLPType = MRd64, MRdLk64, MWr64 ................................. 10
3.1.3 TLPType = IoRd, IoWr ........................................................... 11
3.1.4 TLPType = Cfgrd0, Cfgwr0, Cfgrd1, Cfgwr1 ....................... 12
3.1.5 TLPType = Msg, Msgd .......................................................... 13
3.1.6 TLPType = Cpl, CplLk, CplD, CplDLk .................................. 15
3.1.7 TLP Field or Payload Substitution ....................................... 17
3.2 Packet = DLLP ................................................................. 19
3.2.1 DLLPType = Ack, Nak ........................................................... 21
3.2.2 DLLPType = InitFC1_P, InitFC1_NP, InitFC1_Cpl,
InitFC2_P, InitFC2_NP, InitFC2_Cpl, UpdateFC_P,
UpdateFC_NP, UpdateFC_Cpl .................................... 22
3.2.3 DLLPType = Vendor .............................................................. 23
3.3 Packet = OrderedSet ....................................................... 24
3.3.1 SetType = TS1, TS2 ............................................................... 25
3.3.2 SetType = Skip ...................................................................... 28
3.4 Packet = Raw................................................................... 29
3.5 Packet = <TemplateName> ............................................. 30
4 Idle Command ............................................................. 31
5 Link Command............................................................ 32
5.1 Link = L0 32
5.2 Link = L0s ........................................................................ 32
5.3 Link = L1 32
5.4 Link = L23 ........................................................................ 32
5.5 Link = Disabled ................................................................ 32
5.6 Link = HotReset ............................................................... 32
5.7 Link = Recovery ............................................................... 32
5.8 Link = Detect .................................................................... 33
5.9 Link = LTSSMOff ............................................................. 33
5.10 Link = InitFC .................................................................... 33
5.11 Link = PERST .................................................................. 33
5.12 Link = PERST_Asser t ...................................................... 33
5.13 Link = PERST_Deassert .................................................. 33
5.14 Link = 2_5 ........................................................................ 33
iii
Page 4

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
5.15 Link = 5_0 ........................................................................ 34
5.16 Link = 8_0 ........................................................................ 34
5.17 Link = Xn 34
6 Config Command........................................................ 35
6.1 Config = General .............................................................. 35
6.2 Config = FCTx .................................................................. 37
6.3 Config = FCRx ................................................................. 38
6.4 Config = TLP .................................................................... 39
6.5 Config = AckNak .............................................................. 40
6.6 Config = Transactions ...................................................... 42
6.7 Config = Link .................................................................... 43
6.8 Config = Definitions .......................................................... 44
6.9 Config = SendInterrupt ..................................................... 46
6.10 Config = NVMe ................................................................ 47
6.11 Config = NVMeDriveErrorInjection ................................... 48
7 Wait Command ........................................................... 50
7.1 Wait = TLP ....................................................................... 50
7.2 Wait = LinkCondition ........................................................ 53
7.3 Wait = Payload ................................................................. 54
7.4 Wait = User ...................................................................... 56
7.5 Wait = FastTransmitIdle ................................................... 57
7.6 Additional “Wait” Modifiers ............................................... 58
8 Branch Command....................................................... 59
8.1 Branch = <condition> ....................................................... 59
8.2 Branch = Disable ............................................................. 61
9 Proc Command ........................................................... 62
9.1 Proc = Begin .................................................................... 62
9.2 Proc = End ....................................................................... 62
10 Loop Command .......................................................... 63
10.1 Loop = Begin ................................................................... 63
10.2 Loop = End ...................................................................... 63
11 Repeat Command ....................................................... 64
11.1 Repeat = Begin ................................................................ 65
11.1.1 Counter Parameter ...................................................... 65
12 Template Com mand ................................................... 68
13 Include Command ...................................................... 70
14 AddressSpace Command .......................................... 71
14.1 AddressSpace = Read ..................................................... 72
14.2 AddressSpace = Write ..................................................... 73
iv
Page 5

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
15 Structure Command ................................................... 75
15.1 Command Parameters ..................................................... 75
15.2 Creating Errors in Structures ............................................ 78
16 FastTransmit Engine Commands ............................. 79
16.1 FastTrans mi t Command ................................................... 79
16.1.1 FastTransmit = Setup .................................................. 80
16.1.2 FastTransmit = Start .................................................... 80
16.1.3 FastTransmit = Pause ................................................. 80
16.1.4 FastTransmit = Continue ............................................ 80
16.1.5 FastTransmit = Stop .................................................... 80
16.2 Send Command ............................................................... 81
16.2.1 Send = MRd32/MWr32 ................................................. 83
16.2.2 Send = MRd64/MWr64 ................................................. 83
How to Contact Teledyne LeCroy .................................... 84
v
Page 6

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
1 Introduction
This manual describes the scripting language used to create traffic generation files for
PETrainer™, including the Summit Z2-16™ and Summit Z3-16™ Trainers.
1.1 Support Resources
As new functionalities are added, not all of them are supported by older versions of the PETracer
software. For newer releases of the analyzer's software, please refer to Teledyne LeCroy's web
site:
teledynelecroy.com/
Syntax
PETrainer™ Script files consist of the statements with the following format:
COMMAND = MODIFIER {
PARAM1 = VALUE1
...
PARAMn = VALUEn
}
See the list of all commands with all applicable modifiers on page 2. For some commands the list of the
parameters is optional.
All literals are not case sensitive.
All default values are zeros unless otherwise noted.
Integer literals represent numeric values with no fractions or decimal points.
Hexadecimal, decimal, and binary notations are supported:
• Hexadecimal numbers must be preceded by 0x: 0x2A, 0x54, 0xFFFFFF01
• Decimal numbers are written as usual: 24, 1256, 2
• Binary numbers are denoted with 0b: 0b01101100, 0b01, 0b100000
It is possible to use expressions, for example, (i - 239). See Page 65 for more examples.
String literals are surrounded by double quotes.
Array data types are represented by integer or string literals surrounded by “(“ and “)” characters, and
separated by a comma “,”. For example, (2,23,4).
Single-line comments are supported and should be preceded by a semicolon “;”.
Multi-line comments are also supported. Multi-line comments begin with a “/*” combination, and end with
the reverse “*/” combination.
1
Page 7
Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Defines and controls high-
16 Trainers.
MRd32, MWr32
Defines a sequence of packets to
Trainers.
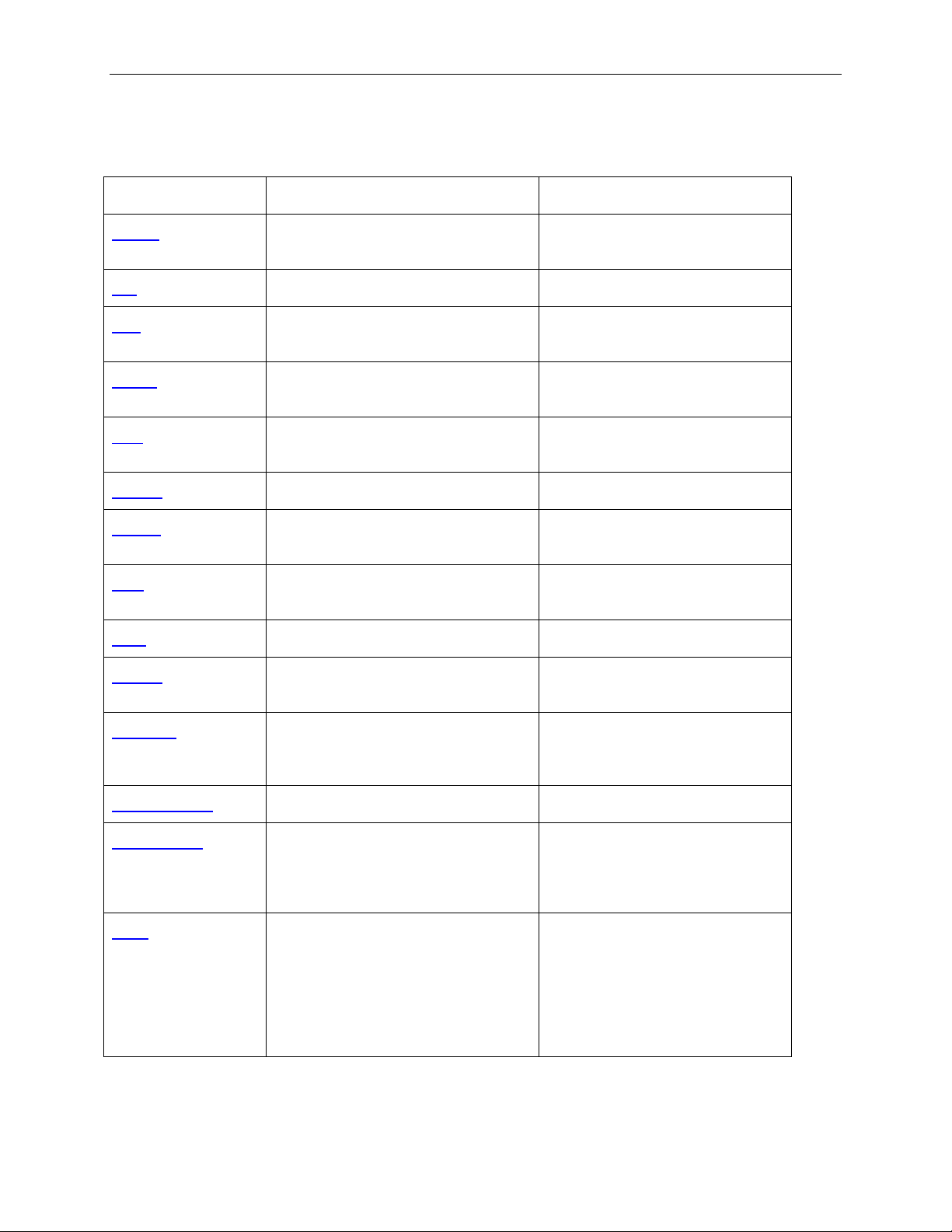
2 Command List
COMMAND MODIFIERS Comment
Packet TLP, DLLP, OrderedSet, Raw,
<TemplateName>
Idle <# of ns> Sends idle symbols (D0.0).
Link L0, L1, L0s, HotReset, Disabled,
Recovery, Detect, LTSSMOff, InitFC
Config General, FCTx, FCRx, TLP, AckNak,
Transactions, Link, Definitions
Wait TLP, DLLP, Error, LinkCondition,
BOB, Payload, User
Include <Include file path>
Branch TLP, DLLP, Error, Link, BOB,
Payload, User
Proc Begin, End Declares the procedure to be
Loop Begin, End
Repeat Begin, End Repeats traffic some number of
Sends a packet.
Sets a link condition.
Configures the PETrainer™
Waits for the condition specified.
Includes a PETrainer script file.
Enables/disables an interru pt for
the specified condition.
used in a branch statement.
Creates a PETrainer loop.
times.
Template TLP, DLLP, OrderedSet, Raw,
AddressSpace Read, Write Reads/Writes address space.
FastTransmit Setup, Start, Pause, Continue, Stop
Send
<TemplateName>
MRd64, MWr64
Creates a template for a packet
that can be used in the Packet
command.
performance generation.
Note: Available only for the
Summit Z2-16™ and Summit Z3-
send once, a number of times, or
repeatedly. Available only in a
Setup command section of a
FastTransmit block.
Note: Available only for the
Summit Z2-16 and Summit Z3-16
2
Page 8
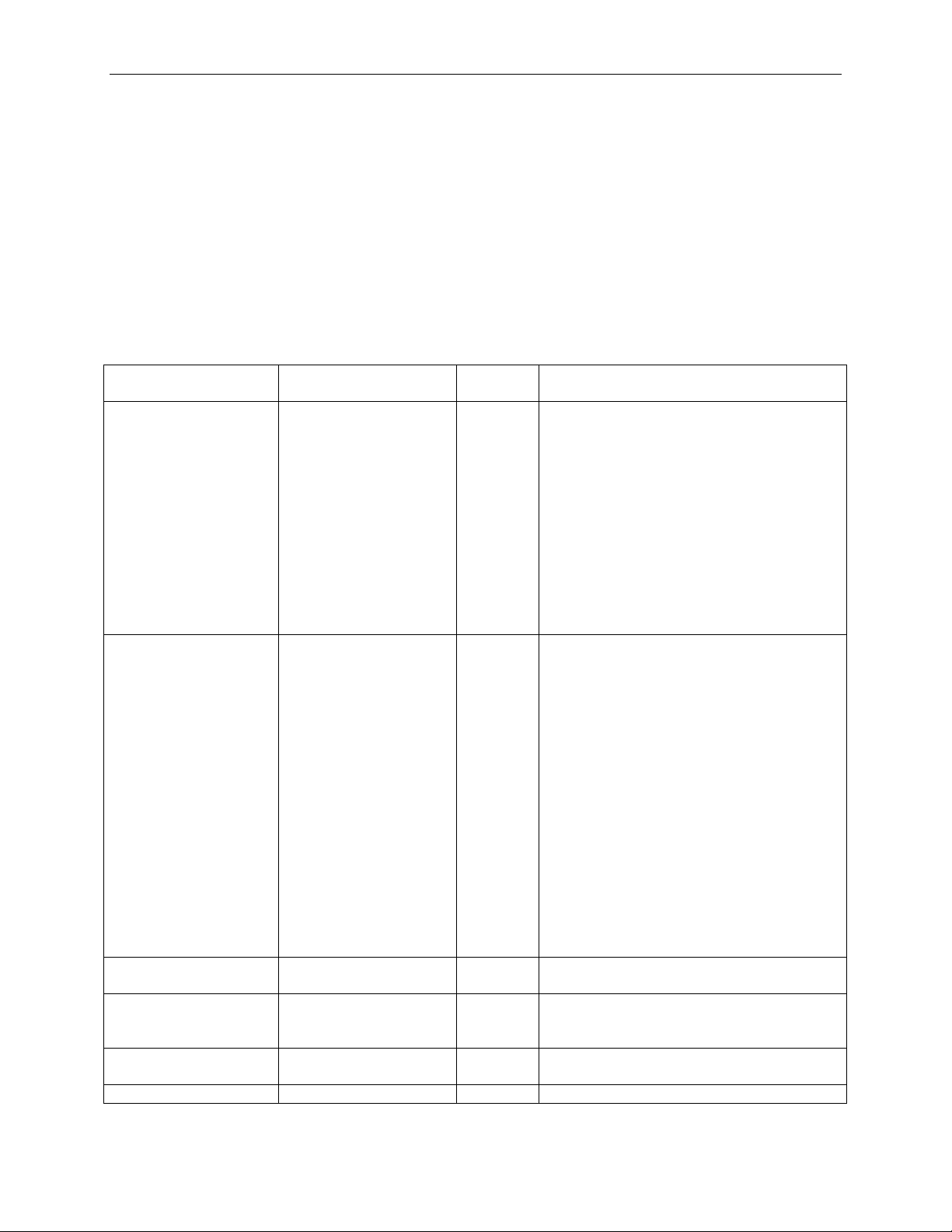
Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Parameter
Values
Default
Value
Comment
PSN
0:4095, Incr
0
When Incr is specified, the PSN for the
packets will have the same PSN.
TLPType
MRd32
CplDLk
0
Sets the Fmt (bits 6:5 of byte 0 in the TLP
TC
0:7
0
Traffic Class: bits 6:4 of byte 1 in the
TLP header
TD
0:1 0 Bit 7 of byte 2 in the TLP header:
form of a single DW at the end of the TLP.
EP
0:1 0 Bit 6 of byte 2 in the TLP header:
1 indicates the TLP is poisoned.
0:1 0 Bit 4 of byte 2 in the TLP header:
3 Packet Command
This command initiates transmission of a specified packet on the bus.
3.1 Packet = TLP
This command initiates transmission of TLP packet on the bus. The parameters of the Packet = TLP
command cover all the fields in the TLP header: TLP Payload, PSN (Packet Sequence Number), ECRC,
and LCRC. Reserved fields can be set with the RawData parameter.
current TLP is assigned as the PSN of the
previously sent TLP incremented by 1.
When the PSN is generated automatically
(see the AutoSeqNumber parameter,
Page 38), this parameter has no effect.
Note: When automatic PSN is turned off
PSN=Incr will work properly only for TLP
transmissions with Count=1. Count
instructs the exerciser to repeat the same
packet and when automatic PSN
generation is turned off, all repeated
MRdLk32
MWr32
MRd64
MRdLk64
MWr64
IoRd
IoWr
CfgRd0
CfgWr0
CfgRd1
CfgWr1
Msg
MsgD
Cpl
CplLk
CplD
header) and Type (bits 4:0 of byte 0 in the
TLP header) fields in the TLP header.
Also, this field can be specified as a direct
numeric value that specifies bits 6:0 of
byte 0 in the TLP header.
1 indicates presence of TLP digest in the
3
Page 9
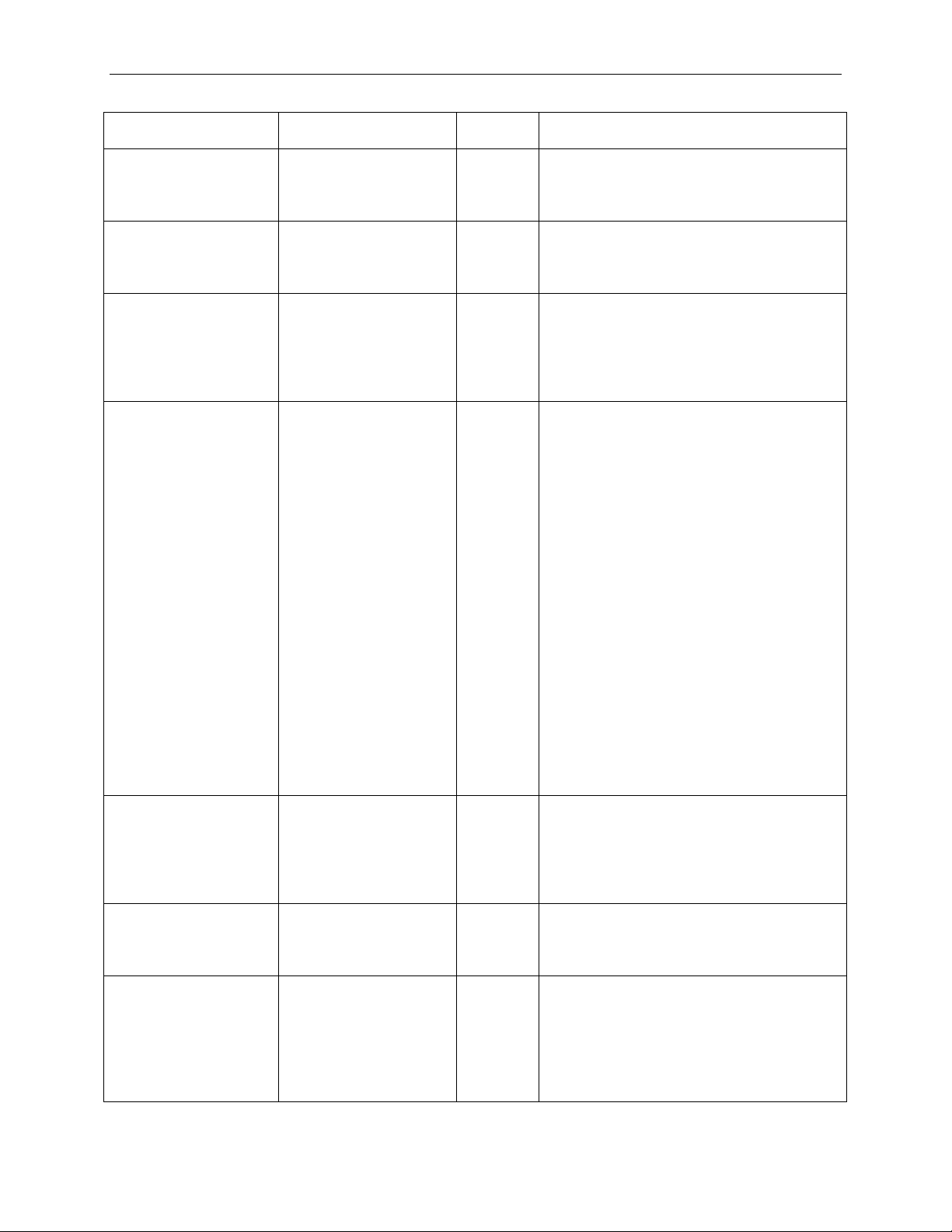
Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Parameter
Values
Default
Value
Comment
Snoop
0 indicates that hardware enforced cache
coherency is not expected.
Ordering
0:1 0 Bit 5 of byte 2 of TLP header:
Model.
Length
0:1023
1
Length of data payload in DWORDs.
(because 0 means 1024).
Tag
0:255
0
Byte 6 of the TLP Header for Memory, IO,
16 and Summit Z3-16 trainers.
RequesterID
(XX:XX:X) or direct
0
Bytes 4-5 of the TLP Header for Memory,
DeviceNumber : FunctionNumber)
ECRC
0x00000000:
Calculate
cally
When not specified, the PETracer™
LCRC
0x00000000:
Calculate
When not specified, the PETracer
parameter has no eff ec t.
coherency is expected.
1 indicates that hardware enforced cache
0 indicates PCI Strongly Ordered Model.
1 indicates PCI-X Relaxed Ordering
If not specified, this field is 1 for all read
requests and calculated according to the
actual payload for write requests.
For a length of 1024, set Length to 0
LAST_CFG_TAG
LAST_IO_TAG
LAST_MEM_TAG
value
and Configuration TLP packets.
Byte 10 for Completion TLP packets.
When Tags are generated automatically
(see the TagGeneration parameter, Page
38), this parameter has no effect for
Memory, IO, and Configuration TLP
packets.
The LAST_CFG_TAG,
LAST_IO_TAG, and
LAST_MEM_TAG modifiers are only valid
for the Summit Z2-16 and Summit Z3-16
Trainers and are only applicable to
Completion TLPs.
When a LAST_CFG_TAG,
LAST_IO_TAG, or
LAST_MEM_TAG modifier is used for a
completion TLP, the Tag field value is set
to the value of the Tag in the latestreceived Configuration, IO, or Memory
request, respectively, as seen by the Z2-
IO, and Configuration TLP packets.
Bytes 8-9 for Completion TLP packets.
This parameter can be set in the following
format: (BusNumber :
0xFFFFFFFF
0xFFFFFFFF
d
automati
d
automati
cally
4
software automatically calculates the
ECRC. (TD field has to be specified.)
software automatically calculates the
LCRC.
When LCRC is generated automatically
by the PETrainer™ hardware (see the
AutoLCRC parameter, Page 38
), this
Page 10
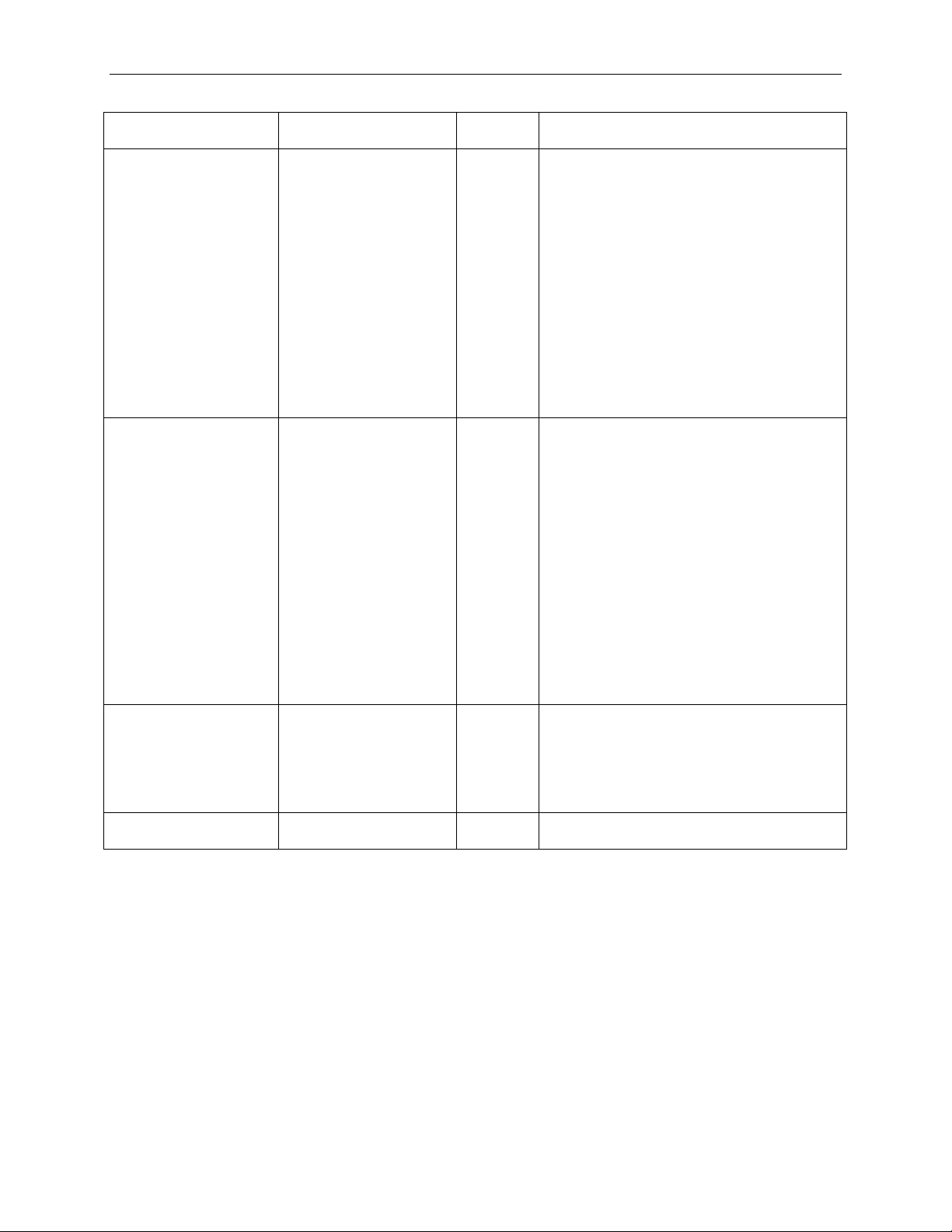
Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Parameter
Values
Default
Value
Comment
Payload
(XXXX,XXXX,…)
Specified as the array of DWORDs in
Data TLP packets.
Field[<start>:<end>]
The arbitrary TLP Header field could be
field.
RawData@<start>
Inserts raw data symbols at <start> byte
ML and EML Trainers.
Count
1:65535
1
Repeats this packet the number of times
specified.
Field[<pos>]
Incr
Random
Zeros
Ones
hexadecimal format (Big Endian).
The Payload parameter applies only to
TLP packets with data.
Incr: Specifies a payload as the sequence
(0, 1, …’Length’).
Random: Specifies a random payload.
Zeros: Specifies a payload of all zeros.
Ones: Specifies a payload of all ones.
Note: When Incr, Random, Zeros, and
Ones are used, the Length parameter
must be specified before the payload.
Payload can be specified for Memory, IO,
Configuration writes, and Completion with
specified by using Field parameter.
Start, end, and pos are bit positions from
the beginning of TLP Header.
Position 0 corresponds to the
Most Significant Bit of the first byte of TLP
Header.
Position 95 for 3 DWORD header (and
position 127 for 4 DWORD header)
correspond to the Least Significant Bit of
the last byte of TLP Header.
Fields are limited by 32 bit values.
Use Field[<start>:<end>] syntax to
specify multi bit field.
Use Field[<pos>] to specify single bit
position from the beginning of the TLP.
See the Packet = Raw des cr iption, Page
29, for possible raw data formats.
Note: This parameter is available only on
5
Page 11
Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Parameter
Values
Default
Value
Comment
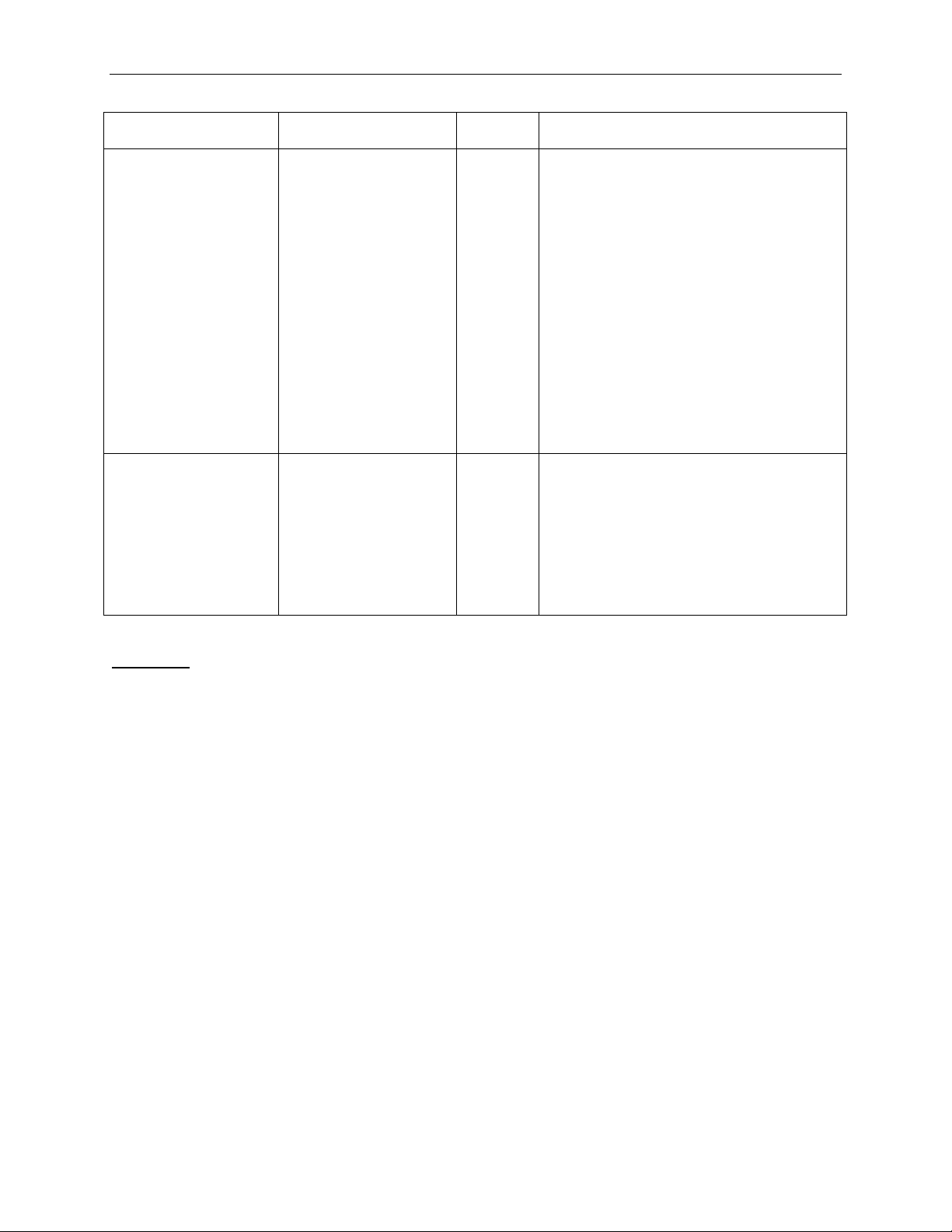
AutoIncrementAddress
Yes
No
This parameter is supported only for the
specified.
StoreData
( FROM_MEMxx_x,
N/A
This parameter is supported only for the
Substitution (see 3.1.7)
No
Summit Z2-16 and Summit Z3-16
Trainers.
It applies to Memory Write and Memory
Read Request TLPs.
If the parameter is set to the "Yes"
modifier, and the "Count" modifier is set to
a value greater than 1, the Summit Z2-16
and Summit Z3-16 Trainers perform a
"burst" of Memory Writes or Reads, with
the Address value for each subseque nt
address automatically incremented
according to the Length value for the write
or read.
The manual or automatic Tag policy is
applied to the transmitted TLPs as
offset )
Summit Z3-16 Trainer.
It can be used for any Memory Read TLP.
When used it instructs the Trainer to
collect all the data returned as a response
to this Memory Read and copy it to the
specified Address Space locat ion.
Values have the same notation as in Field
Example 1:
Read one DWORD of data from address 0x1000.
Length parameter is not specified, so the default value of 1 is used.
TC, TD, EP, Ordering, Snoop, and Tag parameters are not specified, so the default value of 0 is used.
LCRC is not specified, so the LCRC is calculated by software.
Packet = TLP {
PSN = 0
TLPType = MRd32
Address = 0x1000
}
6
Page 12

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Example 2:
Read 32 DWORDs of data starting from address 0x1000.
PSN would accept values 0 for first TLP and 1 for second TLP.
TC, EP, Ordering, and Snoop parameters are not specified, so the default value of 0 is used.
LCRC is not specified, so the LCRC is calculated by software.
ECRC is not specified, so the ECRC is calculated by software.
Packet = TLP {
PSN = Incr
TLPType = MRd32
Tag = 0
Address = 0x1000
TD = 1
FirstDwBe = 0xF
Length = 16
}
Packet = TLP {
PSN = Incr
TLPType = MRd32
Tag = 1
Address = 0x1010
TD = 1
FirstDwBe = 0xF
Length = 16
}
Example 3:
This example does not specify PSN, Tag, and LCRC. Those values are calculated automatically by the
PETrainer hardware (see more on Config = TLP command, Page 39).
Config = TLP {
AutoSeqNumber = Yes
AutoLCRC = Yes
TagGeneration = Default
}
Packet = TLP {
TLPType = MRd32
Address = 0x1010
TD = 1
Length = 1
}
Example 4:
This example shows how to specify a reserved field in the TLP header using the RawData parameter
(see more on the RawData parameter, Page 29).
Packet = TLP {
TLPType = MRd32
Address = 0x1010
RawData@4 = ( D1 )
}
7
Page 13
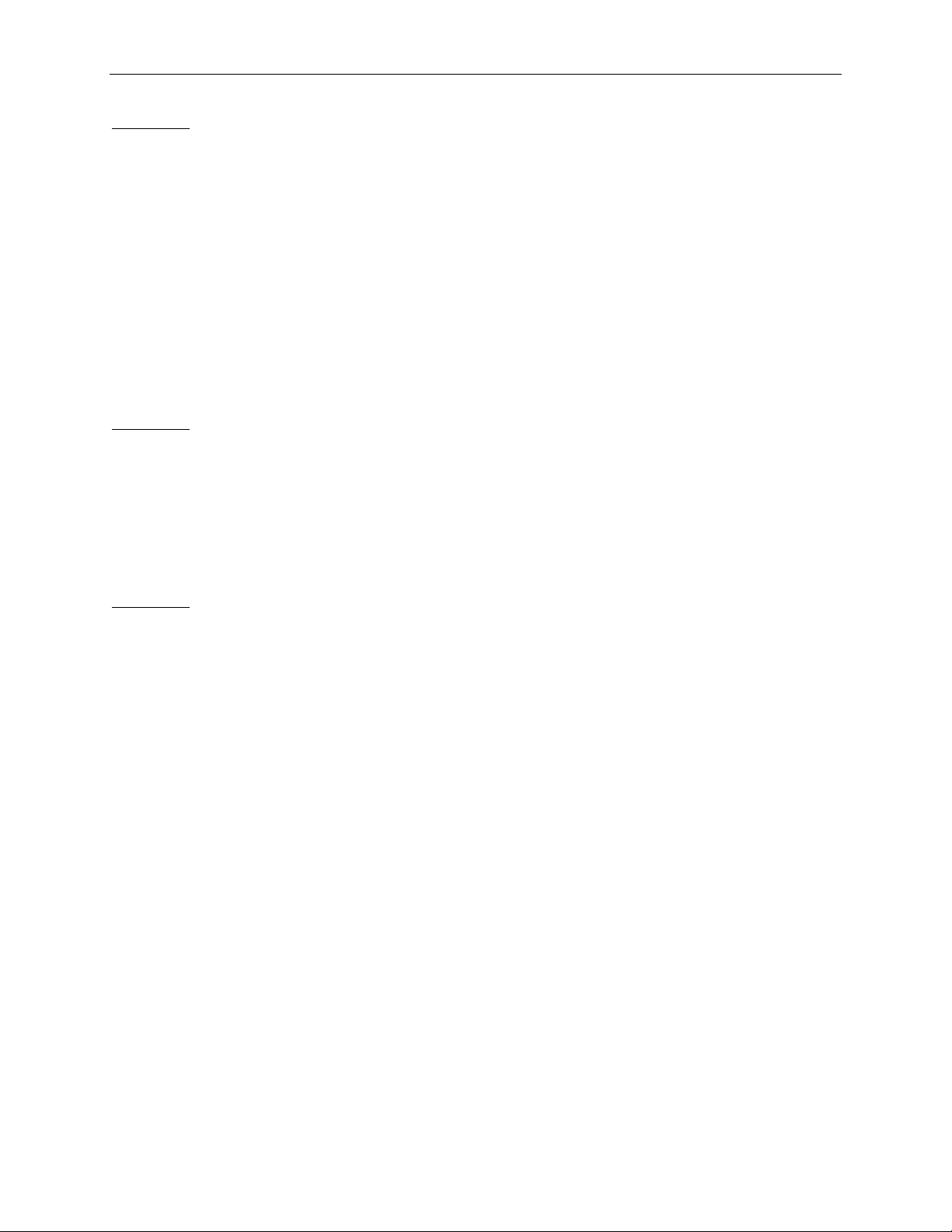
Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Example 5:
This example shows how to specify reserved fields in the TLP header using the Field parameter:
Packet=TLP {
TLPType=CfgRd0
Register = 0x34
Length = 1
FirstDwBe = 0xF
Field[0] = 0x1
Field[8] = 0x1
Field[12:15] = 0xF
Field[20:21] = 0x3
Field[80:83] = 0xF
}
Example 6:
This example shows how to specify the TLP type directly. Any invalid TLP type can be generated with this
method.
Packet = TLP {
TLPType = 0x4F
}
Example 7:
Repeat this TLP packet 64 times.
Packet = TLP {
TLPType = MRd32
Address = 0x1000
Count = 64
}
8
Page 14
Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
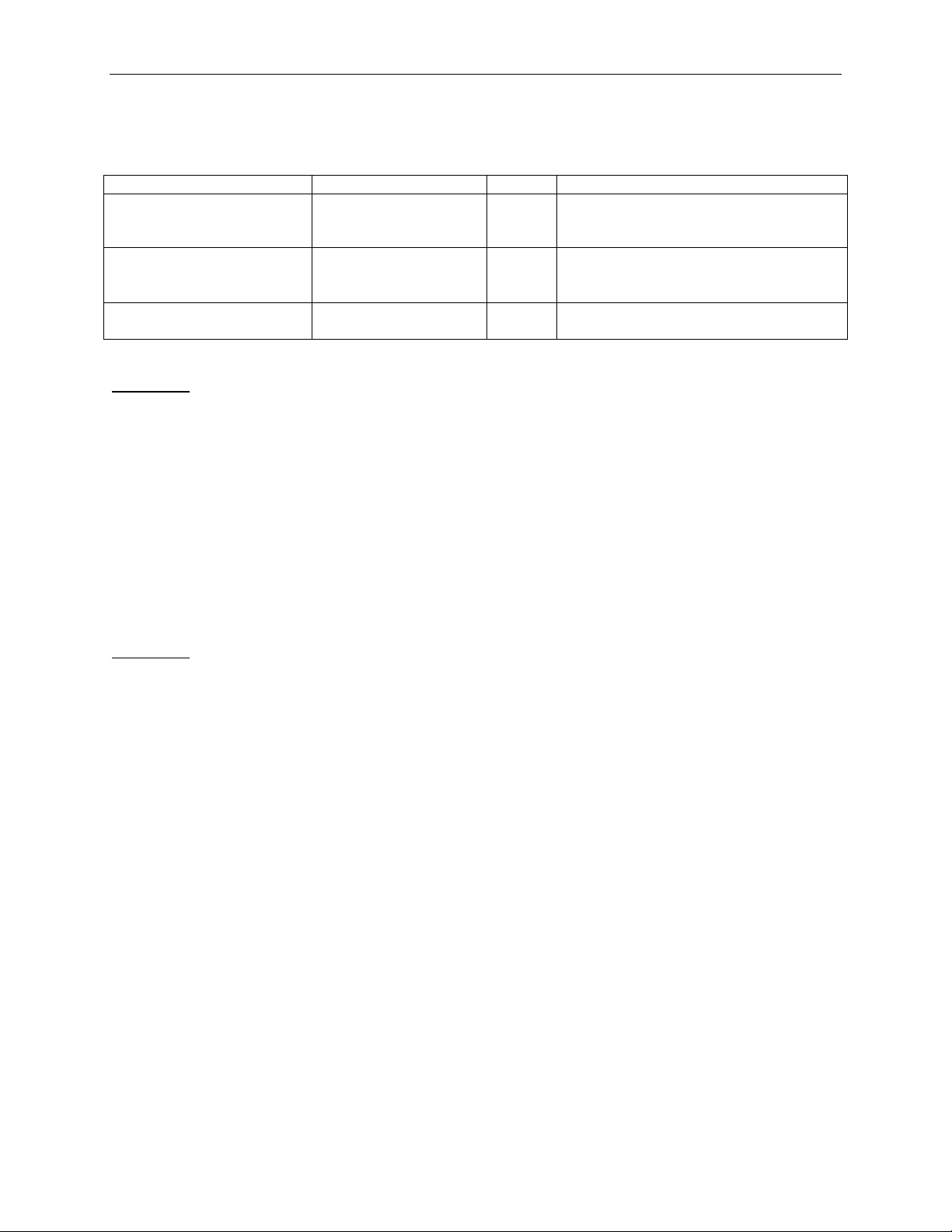
Parameter
Value
Default
Comment
LastDwBe
0:15
0
Byte 7 in the TLP header. See rules for
Specification.
FirstDwBe
0:15
0
Byte 7 in the TLP header. See rules for
Specification.
Address
0x00000000:
0xFFFFFFFF
0
Bytes 8-11 in the TLP header.
3.1.1 TLPType = MRd32, MRdlk32, MWr32
Last DW BE in the PCI Expres s
1st DW BE in the PCI Express
Example 1:
This example shows how to send a 32-bit Memory Write TLP.
The Length field is not specified, so it would be calculated by software. (Length = 4 would be used.)
TC, TD, EP, Ordering, Snoop, and Tag parameters are not specified, so the default value of 0 is used.
LCRC is not specified, so the LCRC is calculated by software.
Packet = TLP {
TLPType = MWr32
LastDwBe = 0xF
FirstDwBe = 0xF
Address = 0x1000
Payload = ( 0x2, 0x4, 0x6, 0x8 )
}
Example 2:
This example shows how to send a 32-bit Memory Write TLP. This command would generate a random
payload of 1024 DWORDs.
Packet = TLP {
TLPType = MWr32
LastDwBe = 0xF
FirstDwBe = 0xF
Address = 0x1000
Length = 0 ; 0 means 1024 DWORDs of payload
Payload = Random
}
9
Page 15
Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
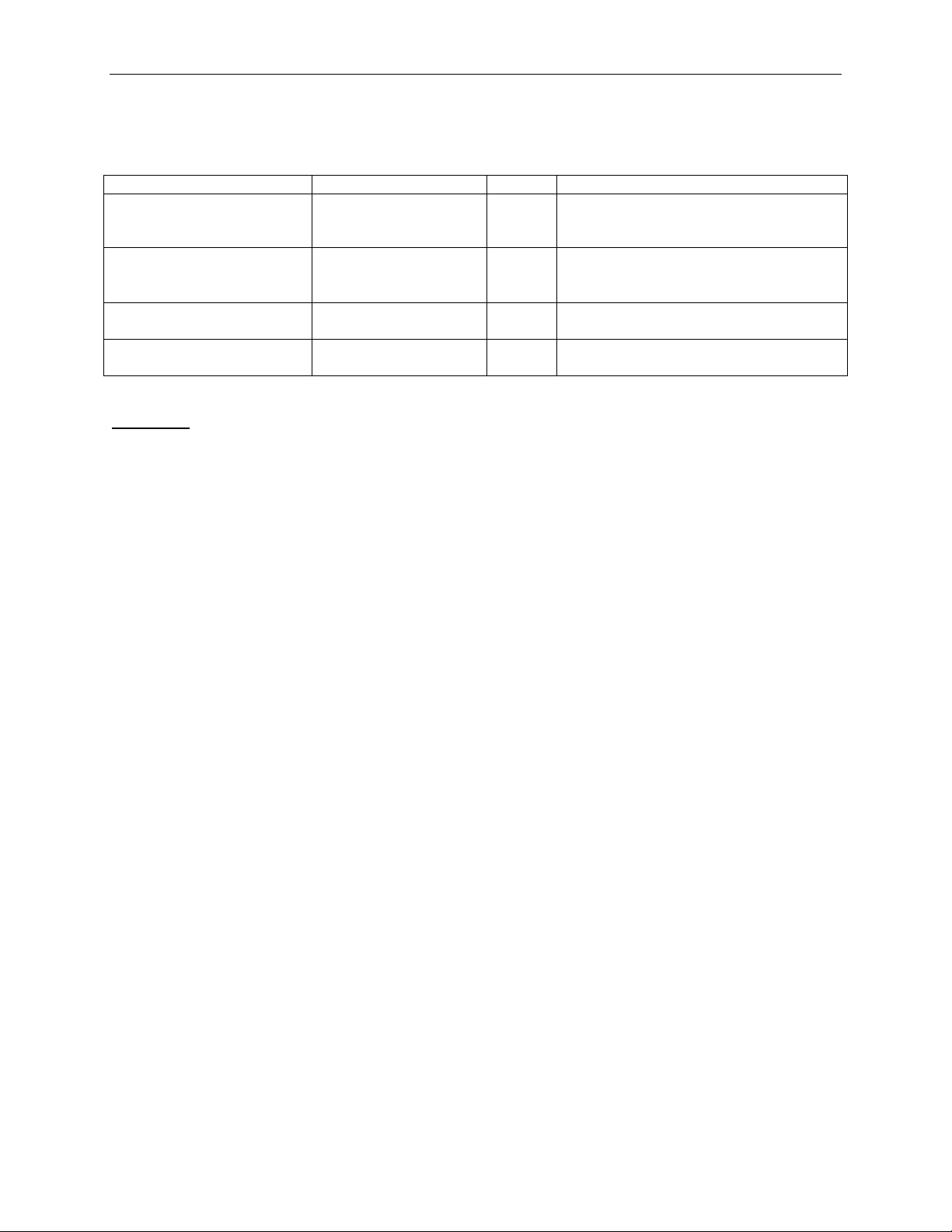
Parameter
Value
Default
Comment
LastDwBe
0:15
0
Byte 7 in the TLP header. See rules for
Specification.
FirstDwBe
0:15
0
Byte 7 in the TLP header. See rules for
Specification.
AddressLo
0x00000000:
0xFFFFFFFF
0
Bytes 8-11 in the TLP header.
AddressHi
0x00000000:
0xFFFFFFFF
0
Bytes 12-15 in the TLP header.
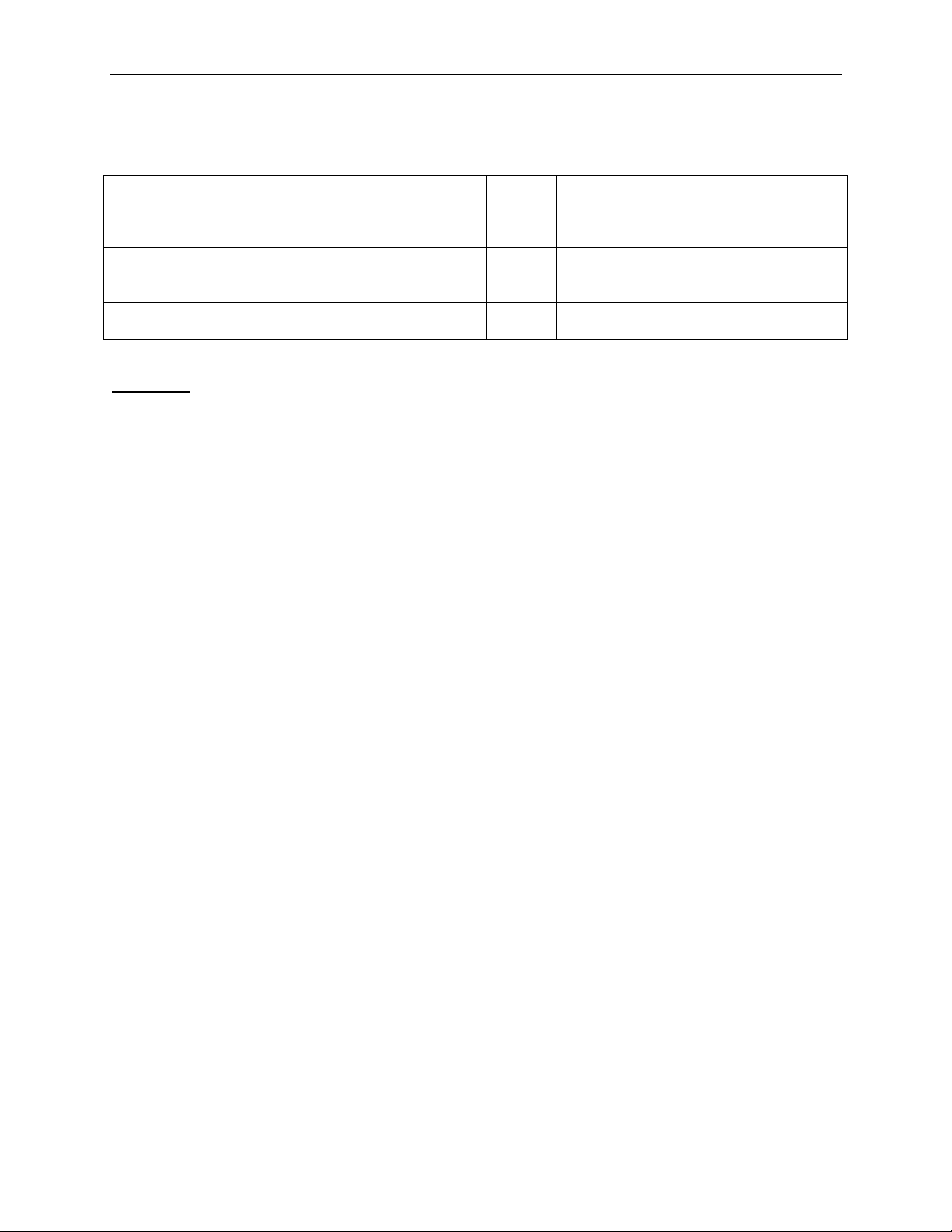
3.1.2 TLPType = MRd64, MRdLk64, MWr64
Last DW BE in the PCI Expres s
1st DW BE in the PCI Express
Example 1:
This example shows how to send a 64-bit Memory Write TLP.
Length parameter is set to 3 intentionally in order to generate a TLP with incorrect length.
TC, TD, EP, Ordering, Snoop, and Tag parameters are not specified, so the default value of 0 is used.
LCRC is not specified, so the LCRC is calculated by software.
Packet = TLP {
TLPType = MWr64
LastDwBe = 0xF
FirstDwBe = 0xF
AddressLo = 0x1000
AddressHi = 0x60000000
Payload = ( 0x2, 0x4, 0x6, 0x8, 0x2, 0x4, 0x6, 0x8 )
Length = 3
}
10
Page 16
Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Parameter
Value
Default
Comment
LastDwBe
0:15
0
Byte 7 in the TLP header. See rules for
Specification.
FirstDwBe
0:15
0
Byte 7 in the TLP header. See rules for
Specification.
Address
0x00000000:
0xFFFFFFFF
0
Bytes 8-11 in the TLP header.
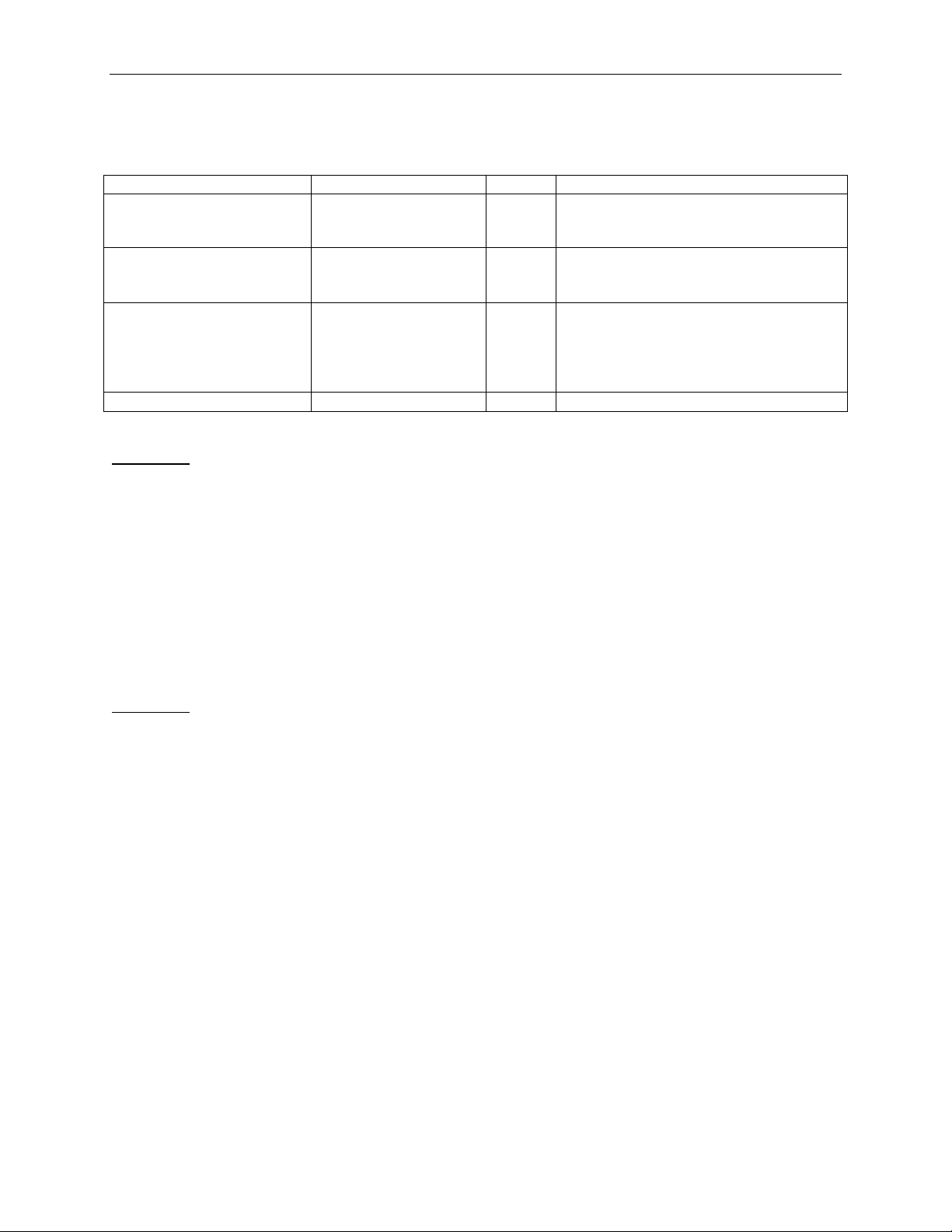
3.1.3 TLPType = IoRd, IoWr
Last DW BE in the PCI Expres s
1st DW BE in the PCI Express
Example 1:
Read one DWORD of data from address 0x1000 of the IO address space.
Length parameter is not specified, so the default value of 1 is used.
TC, TD, EP, Ordering, Snoop, and Tag parameters are not specified, so the default value of 0 is used.
LCRC is not specified, so the LCRC is calculated by software
Packet = TLP {
TLPType = IoRd
Address = 0x1000
}
11
Page 17
Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Parameter
Value
Default
Comment
LastDwBe
0:15
0
Byte 7 in the TLP header. See rules for
Specification.
FirstDwBe
0:15
0
Byte 7 in the TLP header. See rules for
Specification.
DeviceID
(XX:XX:X) or direct
0
Bytes 8-9 in the TLP header. This
FunctionNumber)
Register
0 Bytes 10-11 in the TLP header.
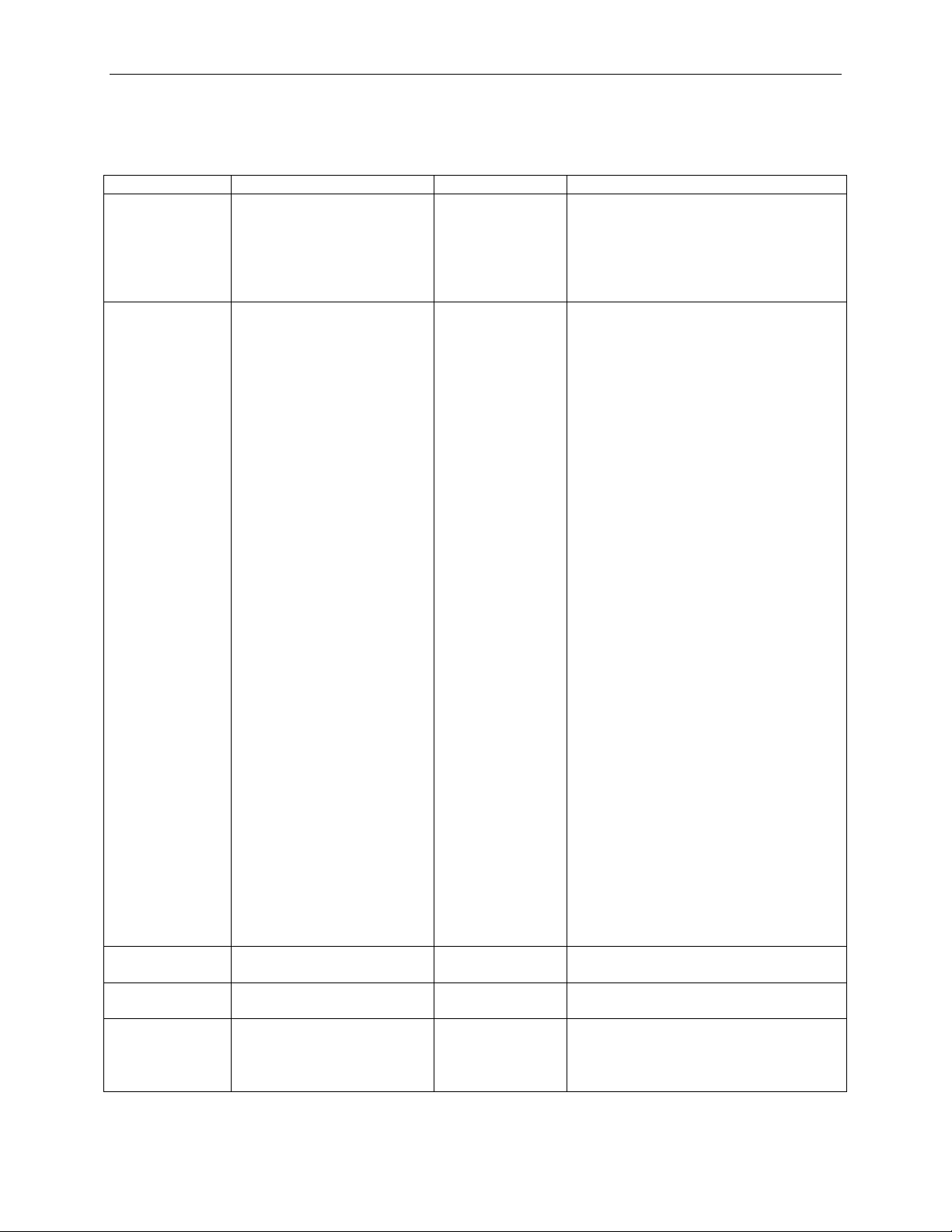
3.1.4 TLPType = Cfgrd0, Cfgwr0, Cfgrd1, Cfgwr1
Last DW BE in the PCI Express
1st DW BE in the PCI Express
value
Example 1:
This example reads the Capability Pointer from the device’s configuration space
(Bus Number 0, Device Number 2, Function Number 4).
Packet = TLP {
TLPType = CfgRd0
DeviceId = (0:2:4)
Register = 0x34
Length = 1
FirstDwBe = 0x1
}
Example 2:
This example writes to the Command Register of the device’s configuration space
(Bus Number 0, Device Number 0, Function Number 1).
Packet = TLP {
TLPType = CfgWr0
DeviceId = 1
Register = 0x04
Length = 1
FirstDwBe = 0x3
Payload = ( 0x03000000 )
}
parameter can be set in the following
format:
(BusNumber : DeviceNumber :
12
Page 18
Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Parameter
Value
Default
Comment
MessageRoute
ToRootComplex
Gather
ToRootComplex
MessageRoute affects the Type field
MessageCode
Assert_INTA
also be used.
0
Byte 7 in the TLP Header
AddressHi
0x00000000:
0xFFFFFFFF
0
Used only if
MessageRoute=ByAddress
AddressLo
0x00000000:
0xFFFFFFFF
0
Used only if
MessageRoute=ByAddress
DeviceID
(XX:XX:X) or direct value
0
Used only if MessageRoute=ById.
DeviceNumber : FunctionNumber)
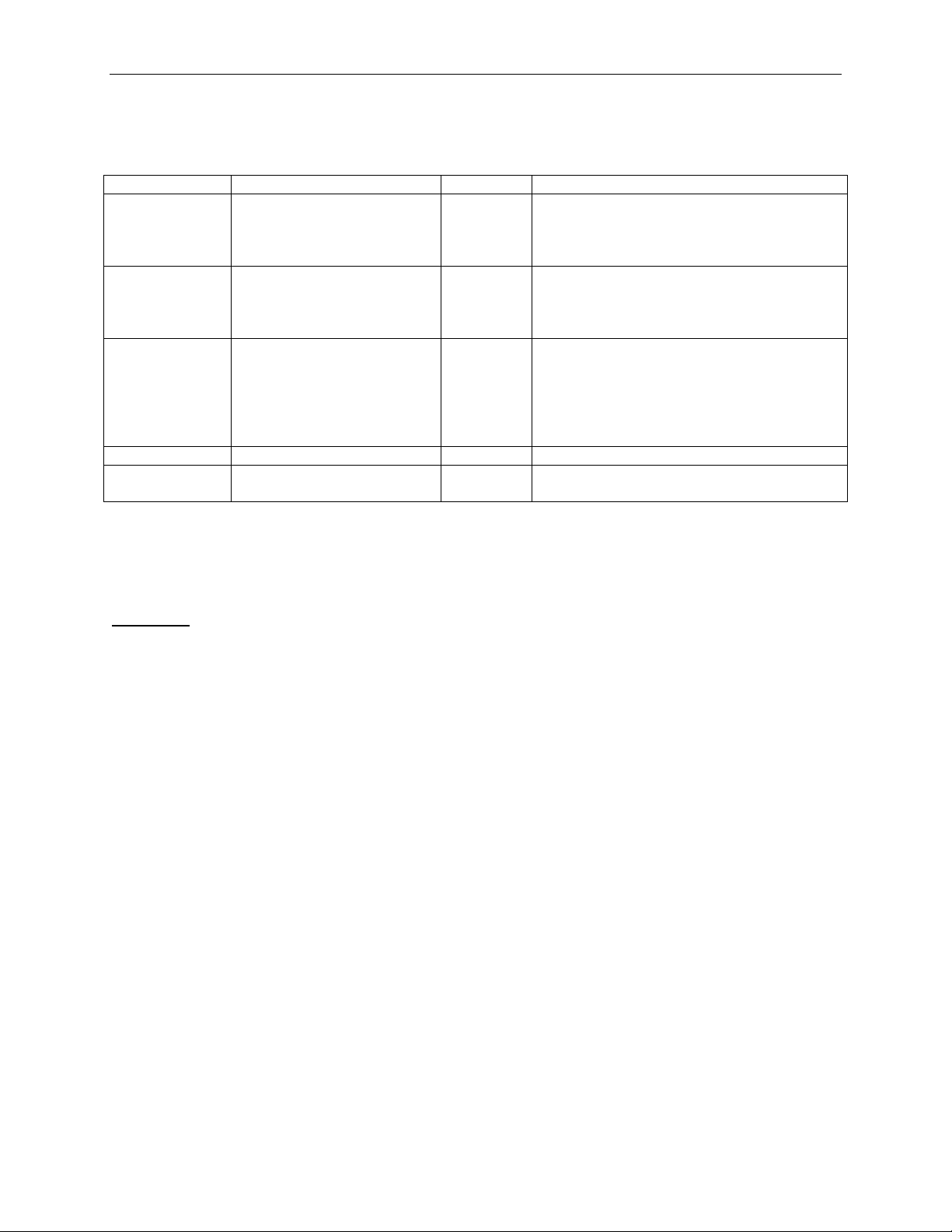
3.1.5 TLPType = Msg, Msgd
ByAddress
ByID
FromRootComplex
Local
Assert_INTB
Assert_INTC
Assert_INTD
Deassert_INTA
Deassert_INTB
Deassert_INTC
Deassert_INTD
PM_Active_State_Nak
PM_PME
PME_Turn_Off
PME_TO_Ack
ERR_COR
ERR_NONFATAL
ERR_FATAL
Unlock
Set_Slot_Power_Limit
Vendor_Defined_Type0
Vendor_Defined_Type1
Attention_Indicator_On
Attention_Indicator_Blink
Attention_Indicator_Off
Power_Indicator_On
Power_Indicator_Blink
Power_Indicator_Off
Attention_Button_Pressed
Direct numeric values can
of TLP header. (Bits 2:0).
This parameter can be set in the
following format: (BusNumber :
13
Page 19

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Example 1:
This example shows how to send a PME_Turn_Off Power Management Message while emulating the
Root Complex.
Packet = TLP {
TLPType = Msg
MessageCode = PME_Turn_Off
MessageRoute = FromRootComplex
}
Example 2:
This example shows how to send a Vendor_Defined_Type0 Vendor Defined Message to the function 1
of device 1 on bus 0.
Packet = TLP {
TLPType = Msg
MessageCode = Vendor_Defined_Type0
MessageRoute = ByID
DeviceID = (0:1:1)
}
14
Page 20
Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Parameter
Value
Default
Comment
CompleterId
(XX:XX:X) or direct value
0
Identifies the Completer.
FunctionNumber)
ComplStatus
SC
CA
SC
Indicates the completion status.
BCM
0:1
0
Byte Count Modified: Must not be set by
the entire remaining byte count.
ByteCount
0:4095
0
Remaining byte count for the request
LowerAddr
0:63
0
Lower byte address for the starting byte of
the completion
3.1.6 TLPType = Cpl, CplLk, CplD, CplDLk
This parameter can be set in the following
format: (BusNumber : DeviceNumber :
UR
CRS
PCI Express Completers and may only be
set by PCI-X completers.
Indicates that the Byte Count field reports
the size of just the first packet instead of
Note: For the Summit Z2-16 and Summit Z3-16 Trainers you can specify the automatic Tag value
modifiers to make the Completion automatically respond to incoming requests., See the modifier values
for the Tag parameter on page 5, in the Packets = TLP table, for reference.
Example 1:
This example shows how to send a Completion TLP. This Completion TLP returns Unsupported Request
(UR) status.
Requester is Function 0 of Device 0 on Bus 0.
Completer is Function 0 of Device 1 on Bus 0.
This completes the TLP request with Tag Number 4.
Packet = TLP {
TLPType = Cpl
RequesterId = (0:0:0)
CompleterId = (0:1:0)
Tag=4
ComplStatus = UR
}
15
Page 21

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Example 2:
This example shows how to send a Completion with Data TLP. This Completion TLP returns
Successful Completion (SC) status.
Requester is Function 0 of Device 0 on Bus 0.
Completer is Function 0 of Device 1 on Bus 0.
This completes the TLP request with Tag Number 4.
This is the last Completion of the Split Transaction, since ByteCount field is equal to the number of bytes
transferred and BCM is not set.
Packet = TLP {
TLPType = CplD
RequesterId = (0:0:0)
CompleterId = (0:1:0)
Tag=4
ComplStatus = SC
ByteCount = 32
Payload = ( 0x00000001, 0x00000002, 0x00000003, 0x00000004,
0x00000005, 0x00000006, 0x00000007, 0x00000008 )
}
16
Page 22

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
3.1.7 TLP Field or Payload Substitution
(For Summit Z2-16 and Summit Z3-16 Trainers only)
When the Summit Z2-16 and Summit Z3-16 Trainers Are Emulating a PCI Express™ Endpoint
Device
When you use the Summit Z2-16 and Sum mit Z3-16 Trainers to emulate a PCI Express Endpoint
Device, you must enable automatic handling of the device Configuration space.
You can also enable automatic handling of Memory and IO spaces. If you enable automatic handling of
Memory and IO spaces, and you perform BAR setup for the initial device Configuration Space image, you
can enable up to three memory spaces (Mem64, Mem32 A, and Mem32 B) and up to two IO spaces
(IO A and IO B). The enabled address spaces have a corresponding data image in the internal memory of
the -16 and Summit Z3-16 Trainers. Whatever the system writes into those spaces over PCI Express can
be read back over PCI Express.
For the Summit Z2-16 and Summit Z3-16 Trainers only, the PETrainer script language provides
extensions that allow data written into Configuration, Memory, or IO spaces to modify behavior of the
running script. If the script specifies values of specific fields and/or Payload in the TLPs for transmission,
you can define that the system use the value from a location in a Configuration, Memory, or IO space of
the device that the Summit Z2-16 and Summit Z3-16 Trainers are emulating.
Field payload substitution allows modifying the behavior of running scripts. When a script that has
substitution definitions is running, a test scenario can write new values to specific locations in
Configuration, Memory, or IO spaces. Subsequent TLPs transmitted by the script use the updated values
of the corresponding fields and/or Payload.
A substitution definition has the following format:
...
FieldName = ( address_space_designation, [address_space_offset], [SwapBytes])
...
The address_space_designation parameter specifies the address space from which to take the value
for the field. The defined address-space-ID keywords are:
o FROM_CFG
o FROM_MEM64
o FROM_MEM32_A
o FROM_MEM32_B
o FROM_IO_A
o FROM_IO_B
The address_space_offset parameter is optional. It defines the byte offset into the address space for the
location from which to take the substitution value. If you omit this parameter, the offset is zero and the
system takes the value from the beginning of the specified address space.
The SwapBytes parameter, when present, specifies that the PETrainer Z3 should swap the Endian order
of the bytes in a 2-byte or 4-byte field before copying it into the specified field of the TLP to transmit.
Some example field name substitution defin it ions are:
17
Page 23

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Address = ( FROM_MEM32_A, 32 )
The system takes the value of the Address field from the Mem32 A address space, starting with byte 32
from the beginning of the memory space image.
Tag = ( FROM_CFG, 256 )
The system takes the value of the Tag field from Configuration Space byte location 256 (which is register
location 64).
Payload = ( FROM_MEM64 )
The system copies the data Payload stream for this TLP from the beginning of the Memory Space 64
image.
Scripts can define substitution only for the following TLP fields:
o Payload
o Tag
o RequesterId
o CompleterId
o Address
o AddressLo
o AddressHi
o ComplStatus
Note: The Summit Z2-16 and Summit Z3-16 Trainers track all accesses and locations of address spaces.
The substitution address_space_offset parameter can be the string value LAST_WRITTEN. When
performing a substitution that uses LAST_WRITTEN for the address_space_offset parameter, the
Summit Z2-16 and Summit Z3-16 Trainers use the value from the beginning of the location where the
system performed the latest Write transaction. The LAST_WRITTEN option allows writing new values at
random locations or at locations that the script writer cannot determine beforehand and making such
values available for later field or Payload substitution.
An example Packet definition with field name substitution using the LAST_WRITTEN option is:
Packet=TLP
{
TLPType=MemWr32
Length = 16
...
Payload= ( FROM_MEM32_A, LAST_WRITTEN )
}
If the script transmits this TLP packet in a loop, initially the system sends a Payload f illed w ith zer oes (or
whatever value initialized memory space 32 A). Before the system writes into a memory space, the lastwritten address initializes to the beginning of the memory space, so the LAST_WRITTEN parameter
starts at 0. Now suppose that the system writes into memory space 32 A at offset 0x100. The next
transmitted TLP Payload specified by the above code includes 16 dwords of the data the system wrote
starting at offset 0x100 of memory space 32 A.
18
Page 24
Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Parameter
Values
Default
Comment
DLLPType
Ack
Vendor
First byte in the DLLP
CRC
0: 65535
Automatically
Bytes 4-5 in the DLLP.
calculated automatically.
Field[<start>:<end>]
The arbitrary DLLP field could
single bit field.
RawData@<start>
Inserts raw data symbols at
formats.
Count
1: 65535
1
Repeats this packet the
number of times specified.
3.2 Packet = DLLP
This command initiates transmission of DLLP packets on the bus.
Parameters for the Packet = DLP command cover all the fields in a DLLP.
Reserved fields can be set using the RawData parameter.
Nak
InitFC1_P
InitFC1_NP
InitFC1_Cpl
InitFC2_P
InitFC2_NP
InitFC2_Cpl
UpdateFC_P
UpdateFC_NP
UpdateFC_Cpl
PM_Enter_L1
PM_Enter_L23
PM_Active_State_Request_L1
PM_Request_Ack
Field[<pos>]
calculated
When not specified, it is
be specified by using Field
parameter.
Start, end, and pos are bit
positions from the beginning of
DLLP.
Position 0 corresponds to the
Most Significant Bit of the first
byte of DLLP.
Position 31 corresponds to the
Least Significant Bit of the last
byte of DLLP.
Use Field[<start>:<end>]
syntax to specify multi bit field.
Use Field[<pos>] to specify
<start> byte position from the
beginning of the DLLP.
See Packet = Raw description
(page 29
) for possible raw data
19
Page 25
Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Example 1:
This example shows how to send a PM_Active_State_Request_L1 power management DLLP. This
DLLP would be sent 132 times.
The DLLP’s CRC is calculated automatically since CRC is not specified.
Packet = DLLP {
DLLPType = PM_Active_State_Request_L1
Count = 132
}
Example 2:
This example shows how to send a DLLP with an incorrect CRC.
Packet = DLLP {
DLLPType = PM_Enter_L1
CRC = 0x1234
}
Example 3:
This example shows how to modify reserved fields in a DLLP using the RawData parameter. (See the
RawData parameter, Page 29.)
Packet = DLLP {
DLLPType = PM_Active_State_Request_L1
RawData@3 = ( D11.1, D11.2 )
}
Example 4:
This example shows how to specify reserved fields in a DLLP using the Field parameter.
Packet = DLLP {
DLLPType = Ack
Field[8:19] = 0b101001000111
}
20
Page 26

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Parameter
Values
Default
Comment
AckNak_SeqNum
0:4095
0
Bytes 2-3 in the DLLP
3.2.1 DLLPType = Ack, Nak
Example 1:
This example acknowledges all TLP packets with a sequence number less than or equal to 120 and
initiates retransmission of TLP packets with a sequence number more than 120. The DLLP’s CRC is
calculated automatically since CRC is not specified.
Packet = DLLP {
DLLPType = Ack
AckNak_SeqNum = 120
}
21
Page 27
Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Parameter
Values
Default
Comment
VC_ID
0:7 0 Virtual Channel, bits 2:0 in the first byte
of the DLLP
HdrFC
0:255
0
Contains the credit value for headers of
the indicated type (P, NP, or Cpl)
DataFC
0:4095
0
Contains the credit value for payload
(P, NP, or Cpl)
3.2.2 DLLPType = InitFC1_P, InitFC1_NP, InitFC1_Cpl, InitFC2_P, InitFC2_NP,
InitFC2_Cpl, UpdateFC_P, UpdateFC_NP, UpdateFC_Cpl
Data of the indicated type
Example 1:
The following example initializes credits for VC 0 for posted TLP requests.
Credit value for headers is 0. Credit value for data payload is infinite.
The DLLP’s CRC is calculated automatically since CRC is not specified.
Packet = DLLP {
DLLPType = InitFc1_P
VC_ID = 0
HdrFC = 2
DataFC = 0
}
22
Page 28

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Parameter
Values
Default
Comment
Data
0x000000:0xFFFFFF
0
Vendor specific data, bytes 1-3 in the DLLP
3.2.3 DLLPType = Vendor
Example 1:
Packet = DLLP {
DLLPType = Vendor
VendorSpecific = 0x010203
}
23
Page 29

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Parameter
Values
Default
Comment
SetType
TS1
Skip
RawData@<start>
Inserts raw data symbols at <start>
formats.
Count
1: 65535
1
Repeats this packet the number of
times specified.
3.3 Packet = OrderedS et
This command initiates transmission of ordered set on the bus.
TS2
FTS
Pattern
Idle
byte position from the beginning of the
ordered set.
See Packet = Raw (page 29)
description for possible raw data
Note: This command is supported by the PETrainer ML and EML Trainers.
Example:
The following example sends 255 Fast Training Sequences.
Packet = OrderedSet {
SetType = FTS
Count = 255
}
24
Page 30

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Parameter
Values
Default
Comment
LinkNumber
0:255, PAD
PAD
Link Number within component
LaneNumber
0:31, PAD
PAD
Lane Number within Port
N_FTS
0:255
0
The number of fast training ordered sets
bit and symbol lock.
TrainingControl
(X,X,X,X)
(0,0,0,0)
Training control bits.
DisableScrambling)
Identifier
(X,X,X…)
D10.2 for TS1 and
Use the same format as in Packet = Raw
codes.
3.3.1 SetType = TS1, TS2
required by the Receiver to obtain reliable
The order of the bits is as follows:
(HotReset, DisableLink, Loopback,
D5.2 for TS2
In x4, x8 or x16 configurations, the keys listed above apply to all lanes.
When you want to specify parameters for a particular lane, use the following format:
<key>@<lane_number> = <value>
(see page 29), with exception of 10-bit
25
Page 31

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Example 1:
The following example sends a TS1 ordered set.
N_FTS is equal to 255 for all lanes.
LinkNumber and LaneNumber are PADs (the default value) for all lanes.
TrainingControl bits are zeroes for all lanes.
Identifier symbols are (D10.2 D10.2 D10.2 D10.2 D10.2 D10.2 D10.2 D10.2 D10.2 D10.2) for all lanes.
Packet = OrderedSet {
SetType = TS1
N_FTS = 255
}
Example 2:
The following example sends a TS1 ordered set.
N_FTS is equal to 255 for all lanes.
LinkNumber is 0 for all lanes.
LaneNumber are 3, 2, 1, 0 for lanes 0, 1, 2, 3, and PADs for all other lanes.
TrainingControl bits are zeroes for all lanes.
Identifier symbols are (D10.2 D10.2 D10.2 D10.2 D10.2 D10.2 D10.2 D10.2 D10.2 D10.2) for all lanes.
Packet = OrderedSet {
SetType = TS1
LinkNumber = 0
LaneNumber@0 = 3
LaneNumber@1 = 2
LaneNumber@2 = 1
LaneNumber@3 = 0
N_FTS = 255
}
Example 3:
The following example sends a TS2 ordered set.
N_FTS is equal to 255 for all lanes.
LinkNumber and LaneNumber are PADs (the default value) for all lanes.
TrainingControl‘s Disable Scrambling bit is asserted on all lanes. All other TrainingControl bits are
de-asserted.
Identifier symbols are (D10.2 D10.2 D10.2 D10.2 D10.2 D10.2 D10.2 D10.2 D10.2 D10.2) for all lanes.
Packet = OrderedSet {
SetType = TS1
N_FTS = 255
TrainingControl = (0,0,0,1)
}
26
Page 32

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Example 4:
The following example sends a TS2 ordered set.
N_FTS is equal to 255 for all lanes.
LinkNumber and LaneNumber are PADs (the default value) for all lanes.
All TrainingControl bits are de-asserted.
Identifier symbols are ( D5.2, D5.2, D5.2, D5.2, D5.2, D5.2, D5.2, D5.2, D5.1, D5.2 ) for lane 2.
Identifier symbols are ( D5.2, D5.2, D5.2, D5.2, D5.2, D5.2, D5.2, D5.2, D5.2, D5.2 ) for all other lanes.
This would send a corrupted TS2 ordered set, since the Identifier is incorrect for lane 2.
Packet = OrderedSet {
SetType = TS2
N_FTS = 255
Identifier@2 = (D5.2,D5.2,D5.2,D5.2,D5.2,D5.2,D5.2,D5.2,D5.1, D5.2)
}
27
Page 33

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Parameter
Values
Default
Comment
SkipCount
0:5 3 Number of SKIP symbols to send after COMMA
3.3.2 SetType = Skip
Example 1:
This example sends a Skip ordered set. Comma followed by 3 SKIP symbols would be sent on each lane.
Packet = OrderedSet {
SetType = Skip
}
Example 2:
This example sends a Skip ordered set. Comma followed by 2 SKIP symbols would be sent on each lane.
Packet = OrderedSet {
SetType = Skip
SkipCount = 2
}
28
Page 34

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Parameter
Values
Default
Comment
RawData
(X,X,X…)
Specifies the array of bytes or 10-bit
symbols to send.
Count
1: 65535
1
Repeats packet specified number of
times.
3.4 Packet = Raw
This command initiates transmission of raw data on the bus.
Note: This command is supported by the PETrainers ML and EML.
The elements of data can be specified in the following formats:
1) Symbols:
Packet = Raw
{
RawData = ( K28.5, D21.5, K28.5, D10.2 )
}
2) Bytes in hexadecimal format with preceding K/D modifier:
Packet = Raw
{
RawData = ( KBC, DB5, KBC, D4A )
}
3) In addition, to generate fully qualified 10 bit symbols, you can specify running disparity sign for each
symbol:
Packet = Raw
{
RawData = ( K28.5+, D21.5-, K28.5-, D10.2- )
}
4) Specify 10 bit symbols in binary, hex, or decimal format:
Packet = Raw
{
RawData = ( 0b0011111010, 0b1100111001, 0b0011111010, 0b1110000110 )
}
29
Page 35

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
3.5 Packet = <Templat eName>
This command initiates transmission of the packet specified by the Template command (see page 68).
User can override packet fields according to the template.
Example 1:
This sequence issues three 32-bit Memory read requests. The address field of TLP header would accept
the values 0, 64, and 128. Every other field in the TLP header would accept the value from the packet
template.
Template = TLP {
Name = “TestPacket”
Type = MRd32
RequesterID = (1:0:0)
Length = 64
Address = 0
}
Packet = “TestPacket”
{
}
Packet = “TestPacket”
{
Address = 64
}
Packet = “TestPacket”
{
Address = 128
}
30
Page 36

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
4 Idle Command
This command sends idle symbols (D0.0) for the time specified.
Example:
The following example sends two TLP packets separated by D0.0 symbols. The idle time between those
TLP packets is 64 ns. Eight D0.0 symbols would be sent between TLP packets on each lane.
Packet = TLP {
TLPType = MRd32
Address = 0x1000
}
Idle = 64
Packet = TLP {
TLPType = MRd32
Address = 0x1000
}
31
Page 37

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
5 Link Command
All of these commands, with the exception of Link = InitFC, are controls to the Link Training and Status
State Machine (also known as the LTSSM). These commands are issued to the LTSSM to steer it to a
particular state. This is not a means to force the Link state to a particular value. For instance, if the Script
contains the Link = L0 command, it is a request to bring the link to the L0 state. The LTSSM is
responsible for managing all of the link training and all of the intermediate link states to accomplish this.
5.1 Link = L0
Transitions the link into the L0 state.
5.2 Link = L0s
Transitions the link into the L0s (low power) state. Applies only in L0 state.
5.3 Link = L1
Transitions the link into the L1 (low power) state. Applies only in L0 state.
The transition to L1 state will happen under the protocol selected (ASPM or PCIPM) in the generation
options file.
Note: Command supported only by Z3 Trainer.
5.4 Link = L23
Z3 initiates protocol to enter L2 (or L3 if Vaux is not present on the bus) low power state.
Note: Command supported only by Z3 Trainer.
5.5 Link = Disabled
Tells the LTSSM to move into the Disabled State. To get to this state, the LTSSM must either be in the
Configuration State or the Recovery State. If the link is currently in the Detect state, and the
Link=Disabled command is issued, it goes to Configuration first and then goes directly to Disabled. Once
in the Disabled state, the LTSSM sends 16 TS1's with the Disable Link modifier bit set, followed by an
electrical Idle ordered set, followed by electrical idle. To exit the Disabled state, simply set Link=Detect or
Link=L0.
Note: Command supported only by Z3 Trainer.
5.6 Link = HotReset
Tells the LTSSM to move into the HotReset State. To get to this state, the LTSSM must first be in the
Recovery state. Once in the HotReset State, the LTSSM sends TS1 ordered sets with the HotReset
modifier bit set. The LTSSM then goes to the Detect state automatically after 2 ms.
Note: Command supported only by Z3 Trainer.
5.7 Link = Recovery
Transitions the link into the Recovery state. Applies only in L0, L0S, or L1 States.
32
Page 38

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Parameter
Values
Default
Comment
Duration
In ns (rounded to nearest 8)
1000
Duration of the PERST# signal
Note: Command supported only by Z3 Trainer.
5.8 Link = Detect
Tells the PETrainer™ to immediately bring the Link down. In this state, the LTSSM drives all of the
PCI Express lanes to electrical idle. Before the lanes go to electrical idle, a single electrical idle ordered
set is transmitted. Applies while in any state.
Note: Command supported only by Z3 Trainer.
5.9 Link = LTSSMOff
Disables the LTSSM. This essentially means that the PETrainer is not responsible for managing the link
state. Instead, the user is free to transmit ordered sets, DLLP's, and RAW packets blindly.
Note: Command only supported by ML and EML Trainers.
5.10 Link = InitFC
Starts the flow control initialization state machine.
5.11 Link = PERST
Sends a PERST# signal for the period specified.
Note: This command is supported by the PETrainers ML and EML. These legacy products are no longer
supported by PETrace 7.00 and newer.
5.12 Link = PERST_Assert
In host mode, the Z3 trainer will drive a low in the bus for PERST#.
Note: Command supported only by Z3 Trainer.
5.13 Link = PERST_Deassert
In host mode, the Z3 Trainer will release PERST# and the bus will drive PERST# high.
Note: Command supported only by Z3 Trainer.
5.14 Link = 2_5
Initiates speed switch to 2.5 GT/s data rate. The system attempts to switch if the link is in the L0 state at
5.0 GT/s data rate.
Note: This command only applies to the Summit Z2-16 and Summit Z3-16 Trainers.
33
Page 39

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
5.15 Link = 5_0
Initiates speed switch to 5.0 GT/s data rate. The system attempts to switch if the link is in the L0 state at
2.5 GT/s data rate, and both Summit Z2-16 and Sum m it Z3-16 Trainers and the DUT advertise the 5.0
GT/s data rate.
Note: This command only applies to the Summit Z2-16 and Summit Z3-16 Trainers.
5.16 Link = 8_0
Initiates speed switch to 8.0 GT/s data rate. The system attempts to switch if the link is in the L0 state at
2.5 GT/s or 5.0 GT/s data rate, and the Summit Z3-16 Trainer and the DUT advertise the 8.0 GT/s data
rate. 8.0GT/s data rate is available only on the Summit Z3-16 Trainer.
Note: This command only applies to the Summit Z3-16 Trainer.
5.17 Link = Xn
Transitions the width of the link to the one specified by the command. Applies only in L0 state.
Note: Command supported only by Z3 Trainer.
34
Page 40

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Parameter
Values
Default
Comment
AutoDetect
Yes, No
No
Automatically detect link parameters.
LinkWidth
1,4,8,16
4
Ignored in PETrainer ML if AutoDetect
is set.
DirectionRx
Upstream, Downstream
U DisableScrambleTx
Yes, No
No
Ignored if AutoDetect is set.
DisableDescrambleRx
Yes, No
No
Ignored if AutoDetect is set.
ReverseLanesTx
Yes, No
No
Ignored if AutoDetect is set.
ReverseLanesRx
Yes, No
No
Ignored if AutoDetect is set.
InvertPolarityTx
(X,X,X,X,…)
The array of 1/0 elements.
link width.
InvertPolarityRx
(X,X,X,X,…)
The array of 1/0 elements.
Ignored if AutoDetect is set.
BaseSpec10
Yes, No
No
SkewTx
(X,X,X,X,…)
The array of integer elements.
from 0 to 7.
UseExtRefClock
Yes, No
No
Use external reference clock.
Applicable for PETrainer ML only.
TrainerReset
Yes, No
No
When set, resets PETrainer before
script execution.
6 Config Command
This command configures the PETrainer™.
6.1 Config = Genera l
This command should precede any statement in a PETrainer script file. There should be only one
Config = General command in a PETrainer script file. All Config = General commands from included
files (see page 70) are ignored.
The size of the array should match the
The size of the array should match the
link width.
The size of the array should match the
link width.
Measured in symbols, valid values are
35
Page 41

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Example 1:
The following example configures PETrainer to generate traffic on an x4 link (LinkWidth = 4) as a host
emulator (DirectionRx = Upstream) and invert polarit y on the firs t two lanes on i nc oming traffic
(InvertPolarityRx = (1,1,0,0)).
The PETrainer is reset before script execution (TrainerReset = Yes).
All options that are not specified (DisableScrambleTx, DisableDescrambleRx, ReverseLanesTx,
ReverseLanesRx, InvertPolarityTx, BaseSpec10, SkewTx, and UseExtRefClock) are taken from the
Generation Options dialog.
Config = General {
LinkWidth = 4
DirectionRx = Upstream
InvertPolarityRx = (1,1,0,0)
TrainerReset = Yes
}
Example 2:
The following example configures PETrainer to generate traffic on an x8 link (LinkWidth = 8) as a device
emulator (DirectionRx = Downstream).
Outgoing lanes are reversed (ReverseLanesTx = Yes).
Polarity on the last four outgoing lanes on outgoing traffic is inverted:
(InvertPolarityTx = ( 0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1 )).
Lanes 0 and 4 have a skew value of 1 symbol time.
PETrainer is reset before script execution (TrainerReset = Yes).
Config = General
{
LinkWidth = 8
DirectionRx = Downstream
SkewTx = (1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0)
InvertPolarityTx = ( 0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1 )
ReverseLanesTx = Yes
TrainerReset = Yes
}
36
Page 42

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Parameter
Values
Default
Comment
CareForFC
Yes, No
Yes
When not set, the TLP packets are sent
available.
6.2 Config = FCTx
This command allows you to specify the policy for TLP transmission for received Flow Control DLLP
packets.
without regard for how many credits are
Example:
In this example, Flow Control checking is turned off for outgoing TLP packets.
The TLP packets that are declared after this Config = FCTx command are sent without checking for
available FC credits.
Config = FCTx {
CareForFC = No
}
Packet = TLP {
TLPType = CfgRd0
Length = 1
Register = 0
Count = 10000
}
37
Page 43

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Parameter
Values
Default
Comment
Timer
In ns (rounded to nearest 8), Off
4200
Periodic timer that controls the sending
of UpdateFC DLLP packets
PH
0:255
1
Posted Request Headers
NPH
0:255
1
Non-Posted Request Headers
CplH
0:255
1
Completion Headers
PD
0:4095
1024
Posted Request Data Payload
NPD
0:4095
1
Non-Posted Request Data Payload
CplD
0:4095
1024
Completion Data Payload
6.3 Config = FCRx
This command configures automatic UpdateFC DLLP generation.
Example:
In this example, the timer for sending Update FC DLLP packets is specified.
Also, the initial number of FC credits for headers to advertise is specified.
The default value is used for data credits.
Config = FCRx {
Timer = 4000 ; Send UpdateFC DLLP packets every 4000 ns
PH = 1 ; 1 credit for Posted Request Headers
NPH = 2 ; 2 credits for Non-Posted Request Headers
CplH = 0 ; Infinite number of credits for Completion
Headers
}
38
Page 44

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Parameter
Values
Default
Comment
AutoSeqNumber
Yes, No
Yes
If set to 0, overrides automatic
command (see Page 3).
AutoLCRC
Yes, No
Yes
If set to 0, overrides automatic
Packet = TLP command (see Page 3).
ReplayTimer
In ns (rounded to nearest 8), Off
4200
Timeout in the TLP transmitter path that
timer expiration.
AutoRetrain
Yes, No
Yes
If set, enables automatic retraining of
is not turned off.
TagGeneration
Manual,
Manual
Tag generation policy for posted TLP
and 8-bits of Tag.
6.4 Config = TLP
This command facilitates data integrity control.
generation of the TLP sequence
number and uses the user-defined
value as set in the Packet = TLP
generation of the TLP LCRC and uses
the user-defined value as set in the
counts time since the latest Ack or Nak
DLLP was received.
If set, automatically retransmits TLP
packets that were Nak’ed or on replay
Default,
Extended,
Phantom1,
Phantom2,
Phantom3
Example:
This example shows how to turn off automatic PSN and LCRC generation for outgoing TLP packets.
The ReplayTimer, AutoRetrain, and TagGeneration parameters are omitted so the default values are
used.
Config = TLP {
AutoSeqNumber = No
AutoLCRC = No
}
the link in case the number of
retransmitted TLPs is 4.
Applicable only when the ReplayTimer
packets:
Manual: Tags are taken from the script.
Default: Use lower 5-bits of Tag field.
Zero out higher 3 bits.
Extended: Use 8-bits of Tag field.
Phantom1: Use 1 most significant bit of
the Function field and 8-bits of Tag.
Phantom2: Use 2 most significant bits
of the Function field and 8-bits of Tag.
Phantom3: Use 3 bits of Function field
39
Page 45

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Parameter
Values
Default
Comment
AckNak
Auto,
Auto
Auto: Automatic Ack/Nak
defined by the ActionCount parameter.
Delay
In ns (rounded to
0
Timer that controls how much delay is added to
Valid if AckNak is set to Auto, Ack, or Nak.
ActionCount
Number of times
0
For Summit Z2-16 and Summit Z3-16 only
settings.
SeqNumberForAction
Sequence number
0
For Summit Z2-16 and Summit Z3-16 only
settings.
6.5 Config = AckNak
Ack,
Nak,
Disable
For Summit Z2-16
and Summit Z3-16
only:
NakSeveral
TimeOutSeveral
NakSeqNumber
TimeOutSeqNumber
Ack: Alwa ys Ack
Nak: Always Nak
Disable: Disable automatic Ack/Nak DLLP
generation.
For Summit Z2-16 and Summit Z3-16 only:
The Summit Z2-16 and Summit Z3-16 Link
layer can execute an action a number of times
specified by the NakSeveral,
TimeOutSeveral, NakSeqNumber, and
TimeOutSeqNumber settings. After executing
the action the specified number of times, the
Summit Z2-16 and Summit Z3-16 Link layer
goes back to automatic Ack/Nak DLLP
generation.
NakSeveral: Sends Nak for a number of
incoming TLPs defined by the ActionCount
parameter.
TimeOutSeveral: Does not send Ack or Nak
for a number of incoming TLPs defined by the
ActionCount parameter.
NakSeqNumber: Sends Nak for the next
incoming TLP with a sequence number defined
by the SeqNumberForAction parameter. The
number of times to send the Nak is defined by
the ActionCount parameter.
TimeOutSeqNumber: Does not send Ack or
Nak for the next incoming TLP with a sequence
number defined by the SeqNumberForAction
parameter. The number of times not to send is
nearest 8)
Example:
This example shows how to configure the PETrainer so that it Naks each incoming TLP packet.
Config = AckNak {
AckNak = Nak
}
Ack/Nak DLLP response after TLP reception.
Specifies the number of times to perform the
action for the NakSev eral , TimeOutSeveral,
NakSeqNumber, and TimeOutSeqNumber
Specifies the sequence number for the
NakSeqNumber and TimeOutSeqNumber
40
Page 46

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
This example shows how to configure the PETrainer to NAK only one incoming TLP packet:
Config=AckNak
{
AckNak = NakSeveral
ActionCount = 1
}
Also note that encountering a Config=AckNak statement in the script overrides the setting for the
ACK/NAK policy in
the Generation Options. An empty Config=AckNak statement
Config=AckNak
{
}
is the same as an Automatic Ack/Nak policy.
Config=AckNak
{
AckNak = Auto
}
41
Page 47

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Parameter
Values
Default
Comment
AutoCfgCompletion
Yes, No
No
If set, automatically handles Configuration Read
Configuration Write Completion is returned.
AutoMemIoCompletion
Yes, No
No
If set, automatically handles Memory and IO
applicable to Host Memory Regions)
EnableUR
Yes, No
No
If set, enables Unsupported Request (UR) status
applicable to Host Memory Regions)
EnableCA
Yes, No
No
If set, enables Completer Abort (CA) status for
applicable to Host Memory Regions)
Poisoned
Yes, No
No
If set, all Memory/IO completions have the
applicable to Host Memory Regions)
FastMemCompleter
On, Off
Off
If On, enables the high performance Fast Memory
(Summit Z2-16 and Summit Z3-16 Trainers only)
6.6 Config = Transactions
This command determines the behavior of PETrainer as it responds to Memory, Configuration, and IO
TLP requests. So that it properly responds to Memory and IO TLP requests, Configuration Address
Space must be defined (see Page 71)
and Write TLP transactions.
For a Configuration Read transaction, Completion
TLP contains the data read from the internal
Configuration Space according to specified register
address.
For a Configuration Write transaction, internal
Configuration Space is updated at the address with
the data taken from Configuration Write TLP, and a
Read/Write TLP transactions.
For Memory and IO Read transactions, a
Completion TLP contains the data read from the
internal Memory/IO Address Space according to
specified address.
For Memory and IO Write transactions, internal
Memory/IO Address Space is updated at the
address with the data taken from the TLP.
(PETrainer EML, Z2 and Z3. For PETrainer Z3 also
Example:
This example enables automatic completion for Configuration TLP requests.
To automatically complete Configuration TLP requests, the Configuration Space must be configured first
(see Page 73).
for Memory/IO completions.
AutoMemIoCompletion must be set to enable UR
completions.
(PETrainer EML, Z2 and Z3. For PETrainer Z3 also
Memory/IO completions.
AutoMemIoCompletion must be set to enable CA
completions.
(PETrainer EML, Z2 and Z3. For PETrainer Z3 also
Poisoned bit set.
(PETrainer EML, Z2 and Z3. For PETrainer Z3 also
Completer.
42
Page 48

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Parameter
Values
Default
Comment
FTSCount
0:255
255
Number of FTS ordered sets required
(as sent in TS)
ExtendedSynch
Yes, No
Yes
When set, forces the transmission of
4096 FTS ordered sets.
SkipTimer
In ns (rounded to nearest 8), Off
4720
Periodic timer that controls sending of
Timer’s value is measured in 1-us units.
Config = Transactions {
AutoCfgCompletion = Yes
; Automatically complete Configuration TLP requests.
}
Note: After this command, automatic completion for Memory and I/O TLP requests are turned off, since
the default value (No) is used for the AutoMemIoCompletion parameter.
6.7 Config = Link
SKIP ordered sets at specific intervals.
Example:
This example configures the number of Fast Training Sequences to send when transitioning from L0s
state (see Page 32).
This number also is advertised during Link Training.
This command also configures the periodic timer for SKIP Ordered Sets – sent every 4700 ns.
Config = Link
{
SkipTimer = 4700
FTSCount = 255
}
43
Page 49

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Parameter
Values
Default
Comment
Any literal
Any integer, string,
The defined values can be used
Only payload field supports arrays.
6.8 Config = Definitions
payload array, or
predefined value
Example 1:
Config = Definitions {
my_register = 0x24
my_tlptype = CfgWr0
my_payload = ( 0x12345678 0xAABBCCDD 0x01020304 )
my_wait_message = “my wait”
}
Packet = TLP {
PSN = Incr
TlpType = my_tlptype
Register = my_register
Payload = my_payload
}
Config = Definitions {
my_register = 0x20
my_tlptype = CfgWr1
}
Packet = TLP {
PSN = Incr
TlpType = my_tlptype
Register = my_register
Payload = my_payload
}
wait = my_wait_message
anywhere in the script as a parameter
value.
44
Page 50

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Example 2:
This example shows how to use definitions in the expressions (see Page 65) and how to redefine the
values.
Config = Definitions {
READ_START = 0x10
}
; Repeat 10 times.
Repeat = Begin {
Count=10
Counter = i
}
; Send TLP using repeat counter (i) and
; READ_START to specify the address.
Packet = TLP {
TLPType = CfgRd0
Register = ( READ_START + ( 4 << i ) )
}
Repeat=End
; Redefine READ_START, now READ_START is 0x40.
Config = Definitions
{
READ_START = ( READ_START + 0x30 )
}
; Send TLP using READ_START to specify the address.
Packet = TLP {
TLPType = CfgRd0
Register = READ_START
}
45
Page 51

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Parameter
Values
Default
Comment
Vector
Zero to Maximum
0
If neither MSI nor MSI-X is enabled or
upon this command
6.9 Config = SendInter r u pt
This command is only valid for Device Emulation and allows initiating MSI or MSI-X interrupt to the
system. It is only supported on PETrainer Z3. In order to be able to use this feature, Z3 has to be booted
in the system with initial configuration space image loaded that contains MSI and/or MSI-X capability
structures. After the system has enabled MSI or MSI-X, this command can be used to send the interrupt
for the specified vector. The Z3 will figure out by itself which interrupt scheme is enabled and generate
the appropriate Memory Write TLP to the address containing data that was configured by the system for
this interrupt vector.
Example:
Config=SendInterrupt
{
Vector = 1 ; change to the desired vector number
}
allocated vector
vector doesn’t exist, Z3 will do nothing
46
Page 52

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Parameter
Values
Default
Comment
Enable
Yes/No
No
Turns on or off automatic handling of
NVMe drive emulation
IdentifyDataLocation
( FROM_MEMxx_x,
offset )
N/A
Same notation as in Field Substitution
(see 3.1.7)
6.10 Config = NVMe
This command is only valid for Device Emulation. It starts and configures NVMe Drive (Controller)
emulation. It is only supported on PETrainer Z3.
In order to use this feature, the Z3 has to be configured for Device Emulation, and inserted in a PCI
Express slot on the system under test while it is powered down. The Z3 has to have the initial
configuration space image loaded that contains:
- MSI and/or MSI-X capability structures;
- BAR 0 that is set up as defined by the NVMe specification;
- Class Code register as defined by the NVMe specification for NVMe controller.
Also, the binary Identify data for the Controller and Namespace(s) has to be written to a certain memory
location on the Z3 (which is referenced by this instruction).
After this is done, the script containing this instruction and then the Connect script can be executed and
system under test booted up. After an NVMe driver is loaded for the Drive Emulation device, it will come
up in the system as an unformatted drive. It can be initialized and formatted, after which it acts as a
normal disk drive. Drive capacity up to 320 Megabytes is supported.
Example:
Config=NVMe
{
Enable = Yes
IdentifyDataLocation = ( FROM_MEM32_B, 0 )
}
The SampleFiles\Z3-16TrainerScripts\NVMe_DriveEmulation folder of the PETracer software contains
files needed to set up NVMe drive emulation. The file "nvme_drive_config_space.dat" can be loaded as
the initial Configuration Space image. Also, the file "nvme_identify_data.dat" included in this sample folder
can be written to the Mem32B location, offset zero. The sample file start_nvme_drive.peg contains the
instruction described here.
After the Z3 configured for NVMe Drive Emilation has been booted in the PCI Express system, the
Windows7 64-bit driver can be loaded from the
Z3-16TrainerScripts\NVMe_DriveEmulation\Drivers\Windows7 folder.
For NVMe drive emulation in other Windows versions and Linux environments refer to the corresponding
folders under Z3-16TrainerScripts\NVMe_DriveEmulation\Drivers folder.
47
Page 53

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Parameter
Values
Default
Comment
ErrorInjectionType
NVME_DRV_ERR_REGISTER
N/A
Specifies the type of NVMe
NVMe commands
Action
CPL_ACTION_DROP_CPL
N/A
Applies to command
completion
6.11 Config = NVMeDriveErrorInjection
This command is only valid for Device Emulation. It configures error injection for NVMe Drive (Controller)
emulation. It is only supported on PETrainer Z3.
In order to use this feature, the Z3 has to be configured for NVMe Drive Emulation, as described in the
Config = NVMe section, and brought up as a drive in the System Under Test.
The command adds a certain type of Error Injection to the Drive Emulation. The error injection is going to
be applied on the next matching NVMe command(s) the Drive Emulator receives from the system.
NVME_DRV_ERR_COMPLETION
NVME_DRV_ERR_COMMAND
CPL_ACTION_DROP_INT
CPL_ACTION_DROP_CPL_INT
CPL_ACTION_CORRUPT_DATA
CPL_ACTION_CORRUPT_RESERVED
CPL_ACTION_CORRUPT_STATUS
drive error injection:
- Error injection for
Controller Registers
- Error injection for
NVMe command
completions
- Error injection for
completions:
- Don’t update the
completion queue
with the completion,
but send interrupt
- Update the
completion queue
with the completion,
but don’t send
interrupt
- Don’t update the
completion queue
with the completion,
and don’t send
interrupt
- Corrupt the
completion data by
setting all the bytes to
0xFF
- Introduce non-zero
data in the reserved
fields of the
completion
- Substitute the status
(sf) field with data
supplied in the
RegisterData
parameter. Can be
use to insert any type
of status in the
48
Page 54

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
CMD_ACTION_DROP_CMD
N/A
Applies to NVMe commands:
doorbell write
PersistsThroughC
Yes/No
No
If set to “No”, a controller
error injection stays active
ErrorCount
Number
1
Number of times to assert this
error injection
ControllerReg
Address
0
Used for
to
QueueID
Number
0
Used for
injection on
RegisterData
Number or Timeout
0
Used for
status field
- Don’t read and
execute the
command upon the
ontrollerReset
reset to the NVMe Drive
emulator from the host clears
this error injection. If “Yes”,
NVME_DRV_ERR_REGISTE
R error injection only.
Specifies the address of the
register to apply the injection
NVME_DRV_ERR_COMPLE
TION and
NVME_DRV_ERR_COMMAN
D error injections. Specifies
the number of admin (0) or IO
queue to apply this error
NVME_DRV_ERR_REGISTE
R error injection. Specifies the
value to return upon a read
from the register instead of
the real value. A special value
of 0xFFFFFFFF specifies
Timeout error injection – a
completion with data will not
be returned upon a read from
the register.
Also used for the
CPL_ACTION_CORRUPT_S
TATUS error injection to
specify the value to be
returned in the command
49
Page 55

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Parameter
Values
Default
Comment
Timeout
0
Timeout in nanoseconds. 0 means infinite timeout.
Display
Any string literal
Message displayed during the wa it ing in status bar
Count
1: 65535
1
Repeats wait specified number of times.
7 Wait Command
This command yields script execution until condition specified is true or timeout expires.
Note: Setup of wait condition for Summit Z2 and Summit Z3 Trainers during script execution may take
tens of microseconds. The Summit Z2 and Summit Z3 trainers will miss events that are coming
during wait condition setup.
7.1 Wait = TLP
This command waits for a TLP that matches the defined condition. Only TLP Header fields can be
specified. All parameters from Packet = TLP command (see Page 3) are valid, except PSN, ECRC,
LCRC and Payload parameters.
TLP Header fields can be masked using the following format:
0x0XAXX For hexadecimal values
0b0001XX For binary values
Example:
This command waits infinitely for a Configuration Write request to registers from 0x1000 to 0x1FFF.
Wait = TLP {
TLPType = CfgWr
Register = “0x1XXX”
Timeout = 0
}
Note: When using wait commands in the Z3 script keep in mind that it takes time for the command to be
configured in the Bus Engine. Thus when running a script that starts with a wait on a packet command,
the DUT should not issue the packet within at least 100 microseconds. However, when the DUT issues
its TLP as a response to the TLP in the script, the Z2/Z3 takes care of properly setting up the wait
condition prior to issuing it's TLP, so the wait would always work properly for a construct like this:
packet=TLP
{
...
}
wait=TLP ; send as the response to the TLP from the script
{
...
}
50
Page 56

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Wait = DLLP
This command waits for a DLLP that matches the defined condition. All parameters from Packet = DLLP
command (see Page 19) are valid, except the CRC field.
DLLP fields can be masked using the following format:
0x0XAXX For hexadecimal values
0b0001XX For binary values
Example 1:
This command waits for Ack DLLP.
The execution continues when Ack DLLP is received or after the 256 ns timeout expires.
Wait = DLLP {
DLLPType = Ack
Timeout = 256
}
Example 2:
This command waits for a Vendor DLLP with the Least Significant Bit of the vendor specific data set.
The execution continues when such DLLP is received or after the 256 ns tim eout expir es.
Wait = DLLP {
DLLPType = Vendor
VendorSpecific = "0bXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX1"
Timeout = 256
}
51
Page 57

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Parameter
Values
Default
Comment
Errors
DLLPCRC
EndBadPacket
The list of errors for which to wait.
Wait = Error
TLPLCRC
If not specified, this waits for any error.
Delimiter
Disparity
Symbol
IdleData
SkipLate
OrdSetFormat
Note: This command is supported by the PETrainers ML and EML.
Example:
This command waits for a Delimiter, Disparity, or Symbol error to occur in incoming traffic.
The script continues running when any of the specified errors occurs or after the 1024 ns timeout expires.
Wait = Error {
Errors = (Delimiter, Disparity, Symbol)
Timeout = 1024
}
52
Page 58

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Parameter
Values
Default
Comment
Conditions
SKIP
LinkAlive
The list of conditions for which to wait.
TrainingControl
(X,X,X,X)
Training control bits. The order of the
PETrainer™ ML and EML
7.2 Wait = LinkConditi on
IDLE
TS1
TS2
FTS
PATN
DLLP
TLP
COMMA
ElectrIdle
Example 1:
This command waits for the COMMA symbol in incoming traffic.
The script execution continues when the COMMA symbol is received or after the 1024 ns timeout expires.
Wait = LinkCondition {
Conditions = ( COMMA )
Timeout = 1024
}
Example 2:
This command waits for a Training Sequence Ordered Set (TS1 or TS2) in incoming traffic with the
HotReset bit asserted in the TrainingControl bits.
The script execution also continues after the 1024 ns timeout expires.
Wait = LinkCondition {
Conditions = ( TS1, TS2 )
TrainingControl = ( 1, 0, 0, 0 )
Timeout = 1024
}
Note: Conditions IDLE, PATN,
ElectrIdle are only supported by ML
and EML Trainers.
Note: Condition LinkAlive waits for bus
to be at L0 state and it is supported
only by Z2 and Z3 Trainers
bits is as follows:
(HotReset, DisableLink, Loopback,
DisableScrambling)
Parameter supported only for
53
Page 59

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Parameter
Values
Default
Comment
Data
Mask and Match up to four DWORDs of TLP payload
PETrainer EML: Zero offset from the beginning of payload
Data@<offset>
Mask and Match up to four DWORDs of TLP payload
(PETrainer EML only)
7.3 Wait = Payload
This command waits for TLP payload match.
PETrainer ML: Any offset from the beginning of payload
starting from <offset> offset from the beginning of payload
Up to four DWORDs of the payload can be specified.
Note: This command is supported only by ML and EML Trainers.
Example 1:
This command waits for a TLP with data payload 0x12345678.
Note: When this command is executed on PETrainer EML, it matches only the first DWORD of the
TLP payload.
When this command is executed on PETrainer ML, it matches any DWORD from the TLP
payload.
Script execution continues when a TLP with the specified payload is received or after the 1024 ns timeout
expires.
Wait = Payload {
Data = ( 0x12345678 )
Timeout = 1024
}
Example 2:
This command waits for a TLP with a data payload that matches the following criteria:
1) The 1
2) The 4
3) The 2
Only the first four DWORDs of a TLP payload are checked when this command is executed on PETrainer
EML.
Any four subsequent DWORDs of a TLP payload are checked when this command is executed on
PETrainer ML.
Script execution continues w hen a TLP with specified payload is received or after the 1024 ns timeout
expires.
Wait = Payload {
}
st
DWORD’s upper-most word must have 0xABCD.
th
DWORD’s lowest word must have 0x1234.
nd
and 3rd DWORDs are insignificant.
Data = ( 0xABCDXXXX, 0xXXXXXXXX, 0xXXXXXXXX, 0xXXXX1234 )
Timeout = 1024
54
Page 60

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Example 3:
The following example can be executed only on PETrainer EML.
This command waits for a TLP with a data payload that matches the following criteria:
1) The 3
2) The 9
3) The 10
rd
DWORD’s upper-most word must have 0xABCD.
th
DWORD’s lowest word must have 0x1234.
th
DWORD’s upper-most byte must have 0x56.
Script execution continues when a TLP with specified payload is received or after the 1024 ns timeout
expires.
Wait = Payload {
Data@2 = ( 0xABCDXXXX )
Data@8 = ( 0xXXXX1234, 0x56XXXXXX )
Timeout = 1024
}
55
Page 61

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
7.4 Wait = User
This command waits for user input. The script execution would continue when user resumes the script
from PETracer™ software UI.
Example:
This example pauses the script execution and displays the message to the user.
Wait = User {
Display = “Now you can continue”
}
56
Page 62

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
7.5 Wait = FastTrans m i tI dle
Note: This command is available only for the Summit Z2-16 and Summit Z3-16 Trainers.
This command synchronizes execution of different FastTransmit blocks and synchronizes highperformance and regular generation.
During high-performance generation, the Wait=FastTransmitIdle command waits for the current
FastTransmit block to finish execution. If the system is not executing a FastTransmit block when the
script calls this command, the Wait condition is immediately satisfied.
57
Page 63

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
7.6 Additional “Wait” Modifiers
1. Wait = <number>
Unconditionally yields script execution for the specified number of nanoseconds.
Example:
Wait = 500
2. Wait = <Text>
Equivalent to
Wait = User {
Display = <Text>
}
Example:
Wait = “Press the button to continue script execution”
A count parameter can be applied to this command, which causes it to wait for that number clicks
on the user input button.
58
Page 64

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Parameter
Values
Default
Comment
BranchName
Any string literal
Name of the branch.
Must be specified if this branch is to be disabled later.
ProcName
Any string literal
Name of the procedure to execute when branch
conditions are met.
RunConcurrently
Yes
No
Applicable only to the Summit Z2-16 and Summit Z3-
and Summit Z3-16 Firmware.
8 Branch Command
This command enables/disables the branch procedure for the condition specified.
8.1 Branch = <condition>
This command enables the branch procedure for the condition specified. The conditions are the same as
in the Wait command (see Page 28), except User. The parameter list is the same as the Wait command,
except for the Timeout, Display, and Count parameters.
The following lists the additional parameters for the Branch = <Condition> command:
No
ProcName parameter is mandatory.
BranchName parameter could be omitted if you do not plan to disable the branch later in the script.
The procedure that handles the branch condition must be defined before the Branch = <Condition>
command (see Page 35).
Note: Branch=FastTransmitIdle is supported only for the Summit Z2-16 and Summit Z3-16 Trainers.
16 Trainers.
If the value is Yes, the Summit Z2-16 and Summit Z316 Firmware run the branch procedure concurrently
with the main script procedure and other concurrent
branches, as a separate task within the Summit Z2-16
59
Page 65

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Example:
...
Proc = Begin {
ProcName = “Procedure1”
}
...
Proc = End
; The following statement specifies that if Delimiter, Disparity
; or Symbol error occurs, then the code declared in “Procedure1”
; should be executed.
Branch = Error {
BranchName = “SomeErrorBranch”
ProcName = “Procedure1”
Errors = (Delimiter, Disparity, Symbol)
}
...
; Disable the branch “SomeErrorBranch” that is specified above.
Branch = Disable {
BranchName = “SomeErrorBranch”
}
...
60
Page 66

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Parameter
Values
Default
Comment
BranchName
Any string literal
Name of the branch
8.2 Branch = Disable
This command disables the branch procedure that was previously enabled.
Branch with the name specified in BranchName parameter must be defined.
61
Page 67

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Parameter
Values
Default
Comment
ProcName
Any string literal
Name of the procedure
9 Proc Command
This command declares the procedure to be executed for the Branch command. Procedure declaration
must precede its usage in the Branch statement.
9.1 Proc = Begin
This command declares the start point of the procedure.
9.2 Proc = End
This command declares the end point of the procedure.
62
Page 68

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Parameter
Values
Default
Comment
Count
0:65535
Infinite
Specifies how many times to repeat the loop.
Setting Count to 0 causes an infinite loop.
10 Loop Command
This command causes the PETrainer™ BusEngine™ to re-execute a block of commands a predefined
number of times.
Note: Loops require up to 1 us to branch to the beginning of the loop. During this time, script execution is
paused. Internally generated packets, such as SKIP ordered sets, Ack/Nak DLLP packets, and flow
control updates, still occur as programmed.
Loops can be nested up to 4 deep (up to 8 deep for the Summit Z2-16 and Summit Z3-16 Trainers).
10.1 Loop = Begin
This command marks the beginning of the loop.
10.2 Loop = End
This command marks the end of the loop.
Example:
Loop = Begin { count = 10 }
Packet = TLP { TLPType = CfgRd0 Length = 1 Register = 0 }
Loop = End
63
Page 69

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
11 Repeat Command
This command causes one or more commands to be repeated. This is not implemented as a branch
instruction in the BusEngine™, but is a replication of commands during script compilation in the software.
This allows back-to-back execution of these commands with as little as 0 symbol times of IDLE traffic
between them.
This command increases the size of the script object that is downloaded to the PETrainer™ and
increases download time accordingly.
64
Page 70

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Parameter
Values
Default
Comment
Count
1:65535
Values of Infinite and 0 are not
supported
Counter
11.1 Repeat = Begin
This command marks the beginning of the code being repeated.
11.1.1 Counter Parameter
Any string literal can be used for the Counter parameter.
The value of the Counter parameter can be used within the Repeat statement (i.e., between
Repeat=Begin and Repeat=End) in arithmetic expressions for any parameter, except the parameters
that require the array data type (such as Payload for TLP packet).
The value of the Counter parameter changes from 0 to the value of the Count parameter minus one.
Arithmetic expressions must be included in round brackets (parentheses).
The operators are: +, -, *, /, <<, >>, &, |, ~.
Example 1:
Within this repeat, ppp can be used in arithmetic expressions for any packet field. The value of ppp
changes from 0 to 3 in the example.
The Tag parameter accepts the values 0x10, 0x11, 0x12, and 0x13.
The AddressHi parameter accepts the values 0x00400000, 0x00400001, 0x00400001, and
0x00400002.
Repeat = Begin { Count = 4 Counter = ppp }
Packet = TLP {
TLPType = MRd64
Tag = ( ppp + 0x10 )
AddressHi = ( 0x400000 + 4 / ( 5 - ppp ) )
}
Repeat = End
65
Page 71

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Example 2:
The following example shows the usage of the counters in nested repeats.
The counter qqq is used for the outer repeat.
The counter www is used for the inner repeat.
Packet = TLP in the inner repeat uses both counters to construct the AddressHi parameter.
Repeat = Begin { Count = 3 Counter = qqq }
Packet = DLLP {
DLLPType = Ack
AckNak_SeqNum = ( qqq + 1 )
}
Packet = DLLP {
DLLPType = Ack
AckNak_SeqNum = ( 0xf & ~qqq )
}
Repeat = Begin { Count=4 Counter = www }
Packet = TLP {
TLPType = MRd64
AddressHi = ( 0x400000 + www * 4 + qqq ) )
}
Repeat = End
Repeat = End
Example 3:
The following example shows the usage of the counter in Payload. When arithmetic expressions with
counter are used inside the Payload field, square brackets [] are used to separate each DWORD of the
payload.
Config=Definitions
{
MY_CONSTANT = 10
}
repeat = Begin { Count = 10 Counter = i }
; one TLP with variable fields is sent
packet = TLP
{
TLPType = MWr32
LastDwBe = 0xF
FirstDwBe = 0xF
Address = ( i << 24 )
Length = 2
Payload = ( [ ( ( ( i + MY_CONSTANT ) * 2 ) << 16 ) | ( i*2 ) ] [ 0xAB <<
i ] ) ; Two DWORDs of the Payload are defined using arithmetic expressions
with counter and constant
Tag = ( i & 0xFF )
}
66
Page 72

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
repeat = End
This command marks the end of the code being repeated.
Example:
Repeat = Begin { count = 10 }
Packet = TLP { TLPType = CfgRd0 length = 1 register = 0 }
Repeat = End
67
Page 73

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
12 Template Command
This command creates a template for a packet that can be used in the Packet command. The fields
specified in the Template command may be overridden in the Packet command.
Example 1:
The following example issues three Memory Read requests.
Template = TLP {
Name = “TestPacket”
Type = MRd32
TC = 0
Tag = 0
RequesterID = (1:0:0)
Length = 64
Address = 0
}
Packet = “TestPacket” {
}
Packet = “TestPacket” {
Address = 64
}
Packet = “TestPacket” {
Address = 128
}
68
Page 74

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Example 2:
The following example shows nested templates (i.e. when one template is based on another template).
; First define the template "SomeTlp3" for TLP packet.
Template = TLP {
Name = "SomeTlp3"
TLPType = MRd32
RequesterID = (0:1:2)
Length = 0x40
LastDwBe = 0xF
FirstDwBe = 0xF
Address = 0x10000
}
; The template "SomeTlp4" is based on the template "SomeTlp3"
; with Address overridden.
Template = "SomeTlp3" {
Name = "SomeTlp4"
Address = 0x10040
}
; This TLP packet has Address parameter equal to 0x10000.
Packet = "SomeTlp3" {
Length = 0x80
}
; This TLP packet has Address parameter equal to 0x10040.
Packet = "SomeTlp4" {
Length = 0x80
}
69
Page 75

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
13 Include Command
This command includes the PETrainer™ script file inline. All commands in the included file are executed,
with the exception of the Config = General command.
The format of this command is following:
Include = <file_path>
where file_path is a path to the file to be included. If file_path is not a fully qualified path, then the
relative path to the current script file would be used.
Example 1:
In this example, all commands from the included1.peg file would be executed first, then all commands
from the included2.peg file would be executed, and then the 32-bit Memory Read TLP would be sent.
Include = "included1.peg" ; All packets from included1.peg file
; would be inserted here.
Include = "included2.peg" ; All packets from included2.peg file
; would be inserted here.
Packet = TLP ; Sending 32-bit Memory Read TLP request
{
TLPType = MRd32 ; Memory Read request (32 bit)
TC = 0x7 ; Traffic class is 7.
TD = 0x1 ; TLP digest is present.
EP = 0x0 ; TLP is not poisoned.
Address = 0x1000 ; Reading from address 1000h of memory space
Length = 0x40 ; Reading 40h DWORDs
}
Example 2:
The first command of this example includes all commands from the file c:/Testing/included1.peg.
If we assume that the current script is located in the folder c:/Testing/TLP, then the second command of
this example includes all commands from the file c:/Testing/TLP/included2.peg.
If we assume that the current script is located in the folder c:/Testing/TLP, then the third command of this
example includes all commands from the file c:/Testing/included3.peg.
Include = "c:/Testing/included1.peg"; All packets from included1.peg
; file would be inserted here.
Include = "included2.peg" ; All packets from included2.peg
; file would be inserted here.
Include = "../included3.peg" ; All packets from included3.peg
; file would be inserted here.
70
Page 76

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Address Space
Size
Configuration
4 KB
32-bit memory
128 MB
64-bit memory
512 MB
IO
256 MB
Memory Region
BAR
Mem64
First BAR that defines 64-bit Memory Address Space
Mem32A
First BAR that defines 32-bit Memory Address Space
Mem32B
Second BAR that defines 32-bit Memory Address Spa ce
IOA
First BAR that defines IO Address Space
IOB
Second BAR that defines IO Address Space
14 AddressSpace Command
This command reads/writes the PETrainer™ memory region.
PETrainer maps Memory and IO address spaces to its internal memory region according to
Base Address Registers (BAR) specified in the Configuration Address Space.
PETrainer uses its memory regions when processing Memory, IO, and Configuration TLP requests
(see Section 0).
PETrainer maps Configuration address space to its internal memory region (Cfg).
PETrainer supports one 64-bit Memory region, two 32-bit Memory regions, and two IO Memory regions.
Maximum address space sizes supported by PETrainer are as follows:
Mapping of BARs to PETrainer memory regions:
In order to properly respond to Memory and IO TLP requests, the Configuration space must be written to
the PETrainer first.
Mem64, Mem32A, Mem32B, IOA, and IOB memory regions are not implemented in PETrainer ML.
71
Page 77

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Parameter
Values
Default
Comment
Location
Cfg
Specifies the memory region from
PETrainer EML only.
Offset
Any number from 0 to
Location parameter
0
Specifies offset in bytes from the
Size
Any number from 0.
Location parameter.)
Maximum
Specifies number of bytes to read
SaveTo
Any file path
File path to store the memory read.
14.1 AddressSpace = Read
This command reads specified memory region from PETrainer and stores it in specified file.
Example 1:
This command reads the whole Mem32A memory region and stores it in the c:/mem.bin file.
The offset is 0. The read size is 128MB.
AddressSpace = Read {
Location = Mem32A
SaveTo = “c:/mem.bin”
}
Example 2:
This command reads 16 bytes from address 0x1000 of Mem64 memory region and stores it in the
c:/mem.bin file.
AddressSpace = Read {
Location = Mem64
Size = 0x10
Offset = 0x1000
SaveTo = “c:/mem.bin”
}
Mem64
Mem32A
Mem32B
IOA
IOB
the maximum allowed
address determined by
the memory region
specified in the
The combination of
Offset and Size
parameters is limited by
the maximum allowed
address.
(The maximum allowed
address is determined
by memory region
specified in the
allowed
size for
memory
region
specified
in the
Location
parameter
which to read.
The memory region is mapped to the
address space according to the rules
described above.
Mem64, Mem32A, Mem32B, IOA,
and IOB are applicable to
beginning of memory region specified
in the Location parameter.
starting from the address specified in
the Offset parameter.
72
Page 78

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Parameter
Values
Default
Comment
Location
Cfg
Specifies the memory region into
PETrainer EML only.
Offset
Any number from 0 to
Location parameter
0
Specifies offset in bytes from the
Size
Any number from 0.
If Zeros, Ones, Random,
parameter.
Specifies number of bytes to
LoadFrom
Any file path
Incr
Zeros
14.2 AddressSpace = Write
This command writes specified memory region into PETrainer from specified data source.
During write operations into Mem64, Mem32A, Mem32B, IOA, and IOB regions, the automatic
completions of Memory and IO TLP requests are disabled (see Section 0).
During write operations into Cfg region, the automatic completions of Configuration TLP requests are
disabled (see Section 0).
Mem64
Mem32A
Mem32B
IOA
IOB
the maximum allowed
address determined by
the memory region
specified in the
The combination of
Offset and Size
parameters is limited by
the maximum allowed
address.
(The maximum allowed
address is determined
by the memory region
specified in the
Location parameter.)
or Incr is specified for the
LoadFrom parameter,
then the default value is
the maximum allowed size
for the memory region
specified in the Location
parameter.
Otherwise, the default size
is the size of data
specified in the LoadFrom
which to write.
The memory region is mapped to
the address space according to
the rules described above.
Mem64, Mem32A, Mem32B,
IOA, and IOB are applicable to
beginning of the memory region
specified in the Location
parameter.
write starting from the address
specified in the Offset
parameter.
Any array of bytes
Zeros
Ones
Random
Example 1:
This command clears the whole Mem32A memory region.
AddressSpace = Write {
Location = Mem32B
LoadFrom = Zeros
}
73
Page 79

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Example 2:
This command writes 16 bytes, starting from address 0x1000, into the Mem64 memory region from file
c:/mem.bin.
AddressSpace = Write {
Location = Mem64
Offset = 0x1000
Size = 0x10
LoadFrom = “c:/mem.bin”
}
Example 3:
This command writes 7 bytes, starting from address 0x1000, into the Mem64 memory region from data
specified.
AddressSpace = Write {
Location = Mem64
Offset = 0x1000
LoadFrom = ( 0x02, 0x08, 0x01, 0x03, 0x06, 0x07, 0x07 )
}
Example 4:
This command writes 48 bytes of random data, starting from address 0x10, into the IOA memory region.
AddressSpace = Write {
Location = IOA
Offset = 0x10
Size = 0x30
LoadFrom = Random
}
74
Page 80

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Parameter
Values
Default
Comment
NVMeStructType
AdminCommand
Choosing one of the structure
structure.
Parameter
Values
Default
Comment
AhciStructType
Command
Choosing one of the structure
structure.
15 Structure Command
This command writes the PETrainer™ memory region, allowing you to specify various structures
to be placed in the previously defined Host Memory Region.
It is used for Host Emulation of a storage protocol using the Z3-16 Trainer.
The structure command is equivalent to the AddressSpace=Write command, but it allows
specifying the data to be written field by field and conforms to a specific PCIe-based storage
specification.
Currently, two types of structures are supported: AHCI and NVMe.
15.1 Command Parameters
The Location and Offset parameters are the same as for AddressSpace = Write command.
Additional parameters for NVMe structures:
Additional parameters for AHCI structures:
Examples of NVMe structures:
Structure=NVMe
{
Location=Mem64
Offset = 0
NVMeStructType=AdminCommand
OpcodeAdmin = ADMIN_IDENTIFY
PRP1_Low = 0x3F25B190
PRP1_High = 0x8
PRP2_Low = 0x3F25C000
PRP2_High = 0x8
CNS = Controller
}
NVMCommand
PRP
FIS
PRDT
types determines the total size
of the structure. Additional
parameters will display in the
list on the right allowing you to
further specify the opcodes and
fields of the corresponding
types determines the total size
of the structure. Additional
parameters will display in the list
on the right allowing you to
further specify the opcodes and
fields of the corresponding
75
Page 81

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Structure=NVMe
{
Location=Mem64
Offset = 0x1000
NVMeStructType = NVMCommand
OpcodeNvm = Write
CID = 5
NamespaceId = 1
PRP1_Low = 0xA0000000
PRP1_High = 0x4
StartLBALow = 12
NumLBlocks = 0
}
Structure=NVMe
{
Location=Mem64
Offset = 0x1040
NVMeStructT ype = PRP
PageBaseAddrLow = 0xCD000000
PageBaseAddrHigh = 0xA0B
}
Examples of AHCI structures:
Structure=AHCI
{
Location=Mem64
Offset = 0
AhciStructType=Command
PRDTL = 1
FISLength = 5
CTBA = 0xA0001000
CTBAU = 0x4
}
Structure=AHCI
{
Location=Mem64
Offset = 0x1000
AhciStructType=FIS
FISType = RegisterH2D
ATACommand = IDENTIFY_DEVICE
C = Yes
Device = 0xA0
}
Structure=AHCI
{
76
Page 82

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Location=Mem64
Offset = 0x1080
AhciStructType=PRDT
DBA = 0x3F3B2048
DBAU = 0x2
DBC = 511
}
77
Page 83

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
15.2 Creating Errors in Structures
There are several ways of inserting various errors in the NVMe and AHCI/ATA structures
- Using “Field” construct to set non-zero values to reserved fields.
The “Field” directive (described in 3.1) can be used to set non zero values in reserved fields within first 8
DWORDs of any structure:
Structure=NVMe
{
Location=Mem64
Offset = 0
NVMeStructType=AdminCommand
OpcodeAdmin = ADMIN_IDENTIFY
PRP1_Low = 0x3F25B190
PRP1_High = 0x8
PRP2_Low = 0x3F25C000
PRP2_High = 0x8
CNS = Controller
Field[63:71] = 0xA5 ; setting non-zero value of a reserved byte in Command DW 2
}
- Assigning undefined values to structure fields.
A numeric value can be assigned to any of the defined structure fields that is undefined or invalid:
Structure=AHCI
{
Location=Mem64
Offset = 0x1000
AhciStructType=FIS
FISType = 0x15 ; undefined FIS type instead of RegisterH2D
Features = 0x02
ATACommand = SET _F EAT U RE S
C = Yes
Device = 0xA0
}
- Using AddressSpace=Write to supply raw byte image of the structure with any contents desired.\
As before Structure command was implemented, AddressSpace=Write can be used to place the byte
stream of the desired structure in the Host Memory Region. This way any byte image of a structure can
be programmed, creating any type of error desired.
78
Page 84

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
16 FastTransmit Engine Commands
Note: The commands in this section are available only for the Summit Z2-16 and Summit Z3-16 Trainers.
16.1 FastTransmit Command
This command defines and controls high-performance generation, which ex ecutes using FastTransmit
blocks. A FastTransmit block has Setup comm ands followed b y the Start command:
FastTransmit = Setup
<Send commands>
FastTransmit = Start
FastTransmit block script commands can also Pause, Continue, and/or Stop execution of highperformance generation.
FastTransmitIdle between FastTransmit Blocks
Defining a FastTransmit block initializes the High-Performance Transmitter. Therefore, high-performance
generation requires that each FastTransmit block finish before executing the next FastTransmit block.
To ensure that the previously started high-performance generation FastTransmit block has finished
execution, use the Wait=FastTransmitIdle command before starting a new FastTransmit block.
Inserting this Wait command between FastTransmit blocks guarantees that the previous block
completes and the system goes to the FastTransmitIdle state before starting the next block. There is no
other way to guarantee previous-block execution completion.
High-Performance and Regular-Performance Generation Operate in Parallel
High-performance and regular-performance generation occur in parallel. Regular-performance commands
have priority. Even if a FastTransmit block contains infinite loops or commands, regular-performance
code still runs in parallel.
High-Performance Transmitter and Completer Are Independent
The High-Performance Completer is independent of the High-Performance Transmitter. FastTransmit
blocks initialize the High-Performance Transmitter but do not control the High-Performance Completer.
Scripts can use the Config command to enable or disable Fast Completion anywhere in the script,
except in a FastTransmit block.
Send Command
A Send command defines a sequence of high-performance packets to send once, a number of times, or
repeatedly. Send commands are in the Setup command section of a FastTransmit block. A
FastTransmit block can have up to 32 Send commands. (For more information about the Send
command, see the next section of this manual.)
Note: Currently, Send commands are the only commands allowed in the Setup section of FastTransmit
blocks.
79
Page 85

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
16.1.1 FastTransmit = Setup
Begins the definition section of a FastTransmit block.
16.1.2 FastTransmit = Start
Ends the definition section of a FastTransmit block and starts execution of the high-performance
generation defined by the block.
16.1.3 FastTransmit = Pause
Pauses high-performance generation of the currently running FastTransmit block.
If a FastTransmit block is not currently defined or running, this command does nothing.
16.1.4 FastTransmit = Continue
Continues high-performance generation of the paused FastTransmit block.
If a FastTransmit block is not currently defined or paused, this command does nothing.
16.1.5 FastTransmit = Stop
Stops high-performance generation of the currently running or paused FastTransmit block and goes to
the FastTransmitIdle state, which has no defined or running FastTransmit block.
If a FastTransmit block is not currently running or paused, this command does nothing.
80
Page 86

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Default
Value
Snoop
0:1
0
Bit 4 of byte 2 in the TLP header:
not expected.
Ordering
0:1
0
Bit 5 of byte 2 of TLP header:
1 = PCI-X Relaxed Ordering Model.
Length
0:1023
1
Length of data payload in DWORDs. If not
(because 0 means 1024).
RequesterID
(XX:XX:X) or
0
Bytes 4-5 of the TLP Header for
(BusNumber:DeviceNumber:FunctionNumber)
Count
0:255
1
Repeats the memory transaction the number of
executing loop of the FastTransmit block.
LoopCount
0:255
1
Repeats this command the number of times
}
16.2 Send Command
A Send command defines a sequence of high-performance packets to send once, a number of times, or
repeatedly. Send commands are allowed only in the Setup command section of a FastTransmit block. A
FastTransmit block can have up to 32 Send commands.
Note: Currently, Send commands are the only commands allowed in the Setup section of FastTransmit
blocks.
The Send command is similar to the Packet=TLP command. The difference is that the Send command
specifically sends memory transactions, which send MRd32/64 or MWr32/64 TLPs at the highest possible
rate. Also, the Send command omits definition of some low-level TLP fields, because they are set
automatically during transmission.
The Send command contains parameters to specify creation of a TLP set or sets:
Parameter Values
(Default: NoSnoop)
(Default: Relaxed)
direct value
Comment
0 = hardware enforced cache coherency is
expected.
1 = hardware enforced cache coherency is
0 = PCI Strongly Ordered Model.
specified, this field is 1 for all read/write requests.
For a length of 1024, set Length to 0
Memory TLP packets.
This parameter can be set in the following format:
times specified in a row within the currently
specified, within the entire FastTransmit block,
which loops through commands.
LoopCount indicates up to which loop increment
this command repeats. For example:
for(i = 0; i < 255; i++)
{
if(i < this LoopCount)
repeat this Send command
if(i < another LoopCount)
repeat another Send command
etc.
81
Page 87

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Default
Value
PayloadGrowth
FixedByte
FixedByte
Specifies how to generate the payload of size
all Send commands.
PayloadSeed
PayloadGrowth =
0
Specifies the fixed value from which to generate
growth type of FixedByte or FixedDWord.
IncrementAddress
No
No
Specifies if the Address value for each
looping (LoopCount > 1).
Parameter Values
FixedDWord
IncrementByte
IncrementDWord
FixedByte
0x00 : 0xFF
FixedDWord
0x000 : 0x3FF
Comment
Length:
FixedByte: Specifies the payload as a repeated
pattern of byte PayloadSeed.
FixedDWord: Specifies the payload as a
repeated pattern of dword PayloadSeed.
IncrementByte: Specifies the payload as an
incrementing pattern of bytes starting from
Payload Seed Value.
Note: If Payload Seed Value is not specified,
the pattern will start from value 0.
IncrementDWord: Specifies the payload as an
incrementing pattern of dwords starting from
Payload Seed Value.
Note: If Payload Seed Value is not specified,
the pattern will start from value 0.
Note: The PayloadGrowth parameter applies to
the payload:
PayloadGrowth = FixedByte: This parameter is
an 8-bit field.
PayloadGrowth = FixedDWord: This parameter
is a 10-bit field.
Note: The PayloadSeed parameter applies only
when PayloadGrowth applies and is set to a
OnCount
subsequent address of a repeated read or write
TLP packet (Count > 1) is incremented.
The Address value is incremented to point to the
next memory location, according to the Length
set for the memory transaction.
Note: This parameter only increments the original
Address value for repeating (Count > 1), not for
82
Page 88

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Parameter
Value
Default
Comment
Address
0x00000000:
0xFFFFFFFF
0
Bytes 8-11 in the TLP header.
Parameter
Value
Default
Comment
AddressLo
0x00000000:
0xFFFFFFFF
0
Bytes 8-11 in the TLP header.
AddressHi
0x00000000:
0xFFFFFFFF
0
Bytes 12-15 in the TLP header.
16.2.1 Send = MRd32/MWr32
16.2.2 Send = MRd64/MWr64
Note: The Send command supports field substitution (see section 4.1.7). The Send command supports
substitution for the following fields:
o RequesterId
o Address
o AddressLo
o AddressHi
o PayloadSeed
83
Page 89

Teledyne LeCroy PETrainer Scripting Language
Type of Service
Contact
Call for technical support
US and Canada: 1 (800) 909-7112
Worldwide: 1 (408) 653-1260
Fax your questions
Worldwide: 1 (408) 727-6622
Write a letter
Teledyne LeCroy Customer Sup por t
Santa Clara, CA 95054-3115
Send e-mail
psgsupport@teledynelecroy.com
Visit Teledyne LeCroy’s web site
teledynelecroy.com
How to Contact Teledyne LeCroy
3385 Scott Blvd.
84
 Loading...
Loading...