Page 1

Teldat-3Ge Quick Guide
Teldat-Dm 406-I
Copyright© Version 10.1 Teldat S.A.
Teldat S.A.
Manual
Teldat-3Ge Quick Guide 1
Page 2

Legal Notice
Warranty
This publication is subject to change.
Teldat S.A. offers no warranty whatsoever for information contained in this manual.
Teldat S.A. is not liable for any direct, indirect, collateral, consequential or any other damage connected to the delivery, supply or use of this manual.
Manual Teldat S.A.
2 Teldat-3Ge Quick Guide
Page 3

Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
1.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Chapter 2 Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
2.1 Operating documentation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
2.1.1 Data Backup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
2.1.2 DHCP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
2.1.3 Voice Backup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
2.2 Teldat Router: Commands Console . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
2.3 Creating 3G Virtual Interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
2.4 3G Access Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
2.5 IP Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.6 L2TP Tunnel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.7 DHCP Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.8 Configuring Voice Backup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
2.8.1 Backup with analog telephones. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
2.8.2 Backup with SIP-IP telephones . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
2.9 WAN Reroute Backup Facility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
2.10 Updating the Firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
2.10.1 Using the router as a TFTP Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
2.11 Final Result . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Chapter 3 Monitoring. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
3.1 Monitoring Communications with the Teldat-3Ge device . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
3.2 Wireless WAN Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Chapter 4 Appendix . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
4.1 Several Teldat-3Ge in the same corporate LAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
4.1.1 Two Teldat-3Ge devices serving a router . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
4.1.2 Two routers, each with a Teldat-3Ge . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
4.2 LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Teldat S.A.
Table of Contents
Teldat-3Ge Quick Guide i
Page 4

Table of Contents Teldat S.A.
ii Teldat-3Ge Quick Guide
Page 5

Chapter 1 Introduction
1.1 Introduction
The Teldat-3Ge is a backup device for 3G communication routers that face one of the following issues:
• Poor coverage at the router’s location.
• Inability to run 3G communications due to not having the necessary hardware module.
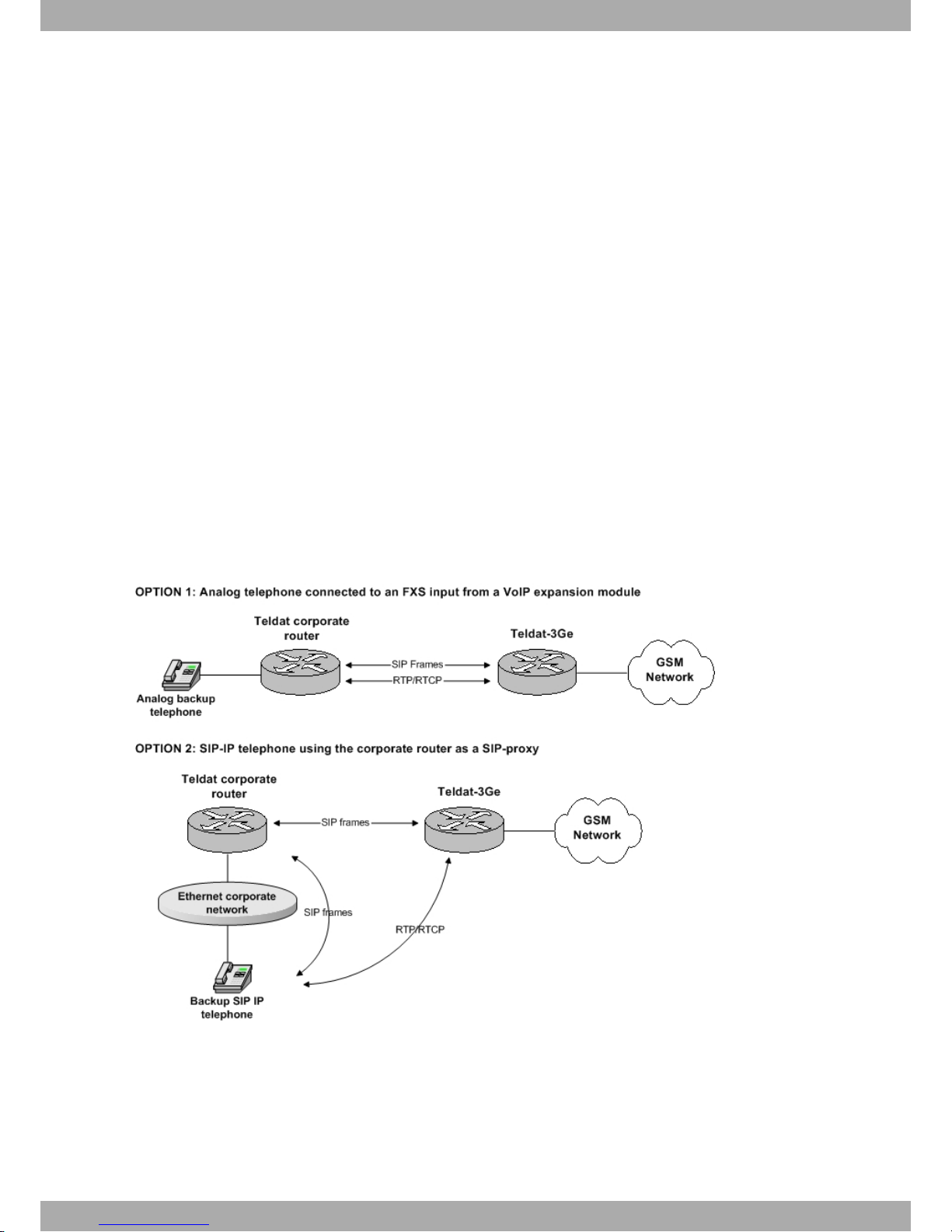
• In addition to data backup, the Teldat-3Ge is capable of acting as a SIP-gateway for one or various client tele-
phones. In cases where the telephone communications are interrupted, calls to the outside can be made from
these telephones. Similarly, external calls can be received on the same phones or on one single phone.
Fig. 1: Teldat-3Ge device.
The Teldat-3Ge device has two communication interfaces; one being a Wireless WAN interface and the other an
Ethernet interface (providing 3G communications to the office router).
Fig. 2: Teldat-3Ge : Application scenario.
Since it operates as an external 3G interface for the company's communications router, the management and opera-
Teldat S.A.
1 Introduction
Teldat-3Ge Quick Guide 1
Page 6

tion of the Teldat-3Ge is fully carried out from said router. For it to work properly, you need to add the necessary
configuration.
In cases where a Teldat-3Ge is going to be used as a SIP-gateway, the telephones receiving telephonic backup can
be:
• Analog (Option 1). In this case, the corporate communications router must have a VoIP expansion module installed
and the telephones must be connected to an FXS input.
• SIP IP Telephone (Option 2). In this case, the corporate communications router acts as a SIP-proxy between the
IP telephones and the Teldat-3Ge .
This document describes the text commands that need to be added to the router's Command Line Interface (CLI) for
it to manage the Teldat-3Ge serving as backup. The following sections offer a brief description on the communication between the Teldat-3Ge and the router. They go on to describe how to access the commands console and add
the configuration and monitoring commands for the available radio link. Finally, the Appendix shows how to combine
several Teldat-3Ge devices in a single private network and gives a description of the Teldat-3Ge status LEDs.
The device uses High Speed Uplink Packet Access technology (HSUPA).
Voice backup functionality is available in devices that are equipped with the Sierra Wireless MC8775V, MC8790V.
MC8791V, MC8792V, MC8795V, Option GTM382, Qisda H20 or Qisda H20D modems. To be able to use it, the
voice backup feature must be enabled by means of a license.
The Teldat-3Ge works with two types of electric power supply:
• An external power source handed together with the device.
• Through POE (Power over Ethernet).
If both are available, the external power source option is preferred.
Note
Before reading this document, Teldat recommends that you read the Teldat-3Ge Installation manual
(Dm398-I)
1 Introduction Teldat S.A.
2 Teldat-3Ge Quick Guide
Page 7

Chapter 2 Configuration
2.1 Operating documentation
2.1.1 Data Backup
The Teldat router manages the Teldat-3Ge through three virtual rcellular interfaces. This approach lets the router
provide the same configuration and monitoring features for the Teldat-3Ge as those offered over physical 3G interfaces (internal interfaces). Each rcellular interface has a different operational task:
• The first virtual interface (recellular1) monitors the radio link
• The second one (recellular2) is responsible for transmitting traffic the Teldat router sends over the 3G link.
• The third (recellular3) updates the Teldat-3Ge image (firmware).
Communications between the router and the Teldat-3Ge are achieved through a pseudowire L2TP tunnel where
three independent L2TP sessions are established; one for each rcellular interface registered in the router. Consequently, a monitoring session, a data session and a firmware updating session are transported through this L2TP
tunnel.
Fig. 3: L2TP tunnels between the corporate Router and the Teldat-3Ge .
RF monitoring consists of a series of parameters on the Teldat-3Ge RF connection level of quality with the GSM and
HSDPA/HSUPA network. This information enables you to appropriately select the location for the device. Monitoring
can be carried out in various ways:
(1) Through the rcellular1 interface sending an AT monitoring command (see manual Dm781-I Cellular Interface).
(2) Opening a Telnet session with the device and executing the monitoring line command.
(3) Accessing the device’s web page.
As already indicated, the backup traffic is sent through the rcellular2 interface L2TP tunnel. A PPP session between
the corporate router and the Teldat-3Ge is established over this tunnel with the aim of initiating the connection with
the HSDPA/HSUPA network (authentication and to obtain an IP address from the network).
Teldat S.A.
2 Configuration
Teldat-3Ge Quick Guide 3
Page 8
2.1.2 DHCP
The Teldat-3Ge starts up without a configuration (as this is defined in the router). The Teldat-3Ge gets its configuration through DHCP.
On startup, the Teldat-3Ge requests an IP address for its Ethernet interface through a DHCP_DISCOVER packet.
The device waits for a response from, among other DHCP servers, the TELDAT corporate router. For this to happen,
the router must have a DHCP server activated. Through the DHCP protocol options, both devices identify and the
Teldat-3Ge only accepts the IP address offered by the TELDAT corporate router. Once the IP address has been received, the Teldat-3Ge obtains the necessary operating information via the DHCP options.
2.1.3 Voice Backup
Voice backup uses SIP for signaling and RTP/RTCP to send the voice samples. Through these standard protocols,
the Teldat-3Ge can operate with routers that are not TELDAT.
As already mentioned, the Teldat-3Ge is a SIP-gateway.
Calls generated by the corporate telephone or telephones that are meant to exit through the device SIP-gateway are
routed through the GSM network. The person receiving the call takes it as if it were a call from a mobile phone. In the
same way, external calls to the corporate network telephones have to be made to the telephone number corresponding to the SIM card incorporated in the Teldat-3Ge . The device’s SIP-gateway routes the external GSM call to the
corporate router using SIP and RTP/RTCP. The latter transfers it to the telephone (or telephones) the router has configured to receive calls that arrive through the Teldat-3Ge .
Both in the analog and in the SIP IP telephone options, the corporate router acts as the SIP-proxy. That is, SIP traffic
is always produced between the corporate router and the Teldat-3Ge .
Fig. 4: Voice backup scenarios.
2.2 Teldat Router: Commands Console
Teldat-3Ge management is fully carried out through the Teldat router commands console. The console can be accessed both locally (through the device's configuration interface) and remotely (through a telnet connection to the
device's access IP address).
2 Configuration Teldat S.A.
4 Teldat-3Ge Quick Guide
Page 9
Explanations on how to access and operate the commands console are given in chapter 1 of manual Dm704-I Configuration and Monitoring. The Teldat console opening message looks like this:
User: Root
Password:****
Teldat (c)2001-2002
Router model XXXXX CPU MPC860 S/N: YYYY/YYYYY
1 LAN, 2 WAN Line , 2 ISDN Line
CIT software version: ZZZZZ
*
The configuration commands shown in this chapter are executed in the commands console configuration process.
The user can access this by executing the config command, as shown below:
*config 4
User Configuration
Config>
2.3 Creating 3G Virtual Interfaces
First we add the virtual interfaces recellular1, recellular2 and rcellular3, running the following commands:
add device rcellular 1
add device rcellular 2
add device rcellular 3
Then we define the function of each interface and configure the startup parameters for the Teldat-3Ge 3G module in
the monitoring interface (rcellular1).
network rcellular1
; -- Interface AT. Configuration --
description ETH-ANT-MON
coverage-timer 15
pin plain 5710
monitor-ifc 1
network mode automatic
network domain cs+ps
exit
;
network rcellular2
; -- Interface AT. Configuration --
description ETH-ANT-PPP
ppp-ifc 1
exit
;
network rcellular3
; -- Interface AT. Configuration --
description ETH-ANT-UPG
upgrade-ifc 1
exit
The pin plain 5710 command sets the PIN for the SIM card inserted in the Teldat-3Ge to 5710. If you want to set a
different PIN code, simply edit it using this command.
The "cs+ps" command network domain configures the device so that it can access the GSM and the HSDPA/HSUPA
networks at the same time.
Note
If the Teldat-3Ge is equipped with a module that doesn’t support voice backup, you should only configure the "ps" network domain.
On device startup, the sequence of events is as follows:
• The L2TP tunnels try and open on detecting the presence of an rcellular interface.
Teldat S.A.
2 Configuration
Teldat-3Ge Quick Guide 5
Page 10

• Once the L2TP tunnel is open, the link layer is considered to be established in this interface.
• Subsequently, the connection is tried through AT commands for the rcellular1 interface.
• Lastly the PPP connection is established through the rcellular2 interface.
Note
Configuring an incorrect PIN in the Teldat-3Ge can block your SIM card.
2.4 3G Access Parameters
The Name of the Access Point to the 3G network (APN) is configured as a call profile. Below, you can see an example showing how to access a fictitious carrier APN:
global-profiles dial
; -- Dial Profiles Configuration --
profile WWAN default
profile WWAN dialout
profile WWAN 3gpp-accessibility-control traffic 20 all
profile WWAN 3gpp-apn internet.es
profile WWAN idle-time 300
;
exit
If you want to access a different APN, the user must substitute internet.es in the profile WWAN 3gpp-apn internet.es command for the APN given by the cellular provider.
For further information on call profiles, please see manual Dm732-I Call Profiles.
Next, we define and configure a PPP interface. This is responsible for providing registration information to the 3G
network. The PPP interface must be mounted over the rcellular2 interface. The commands for accessing the 3G service are:
add device ppp 1
;
network ppp1
; -- Generic PPP User Configuration --
ip address unnumbered
;
ppp
; -- PPP Configuration --
authentication sent-user internet password internet
ipcp local address assigned
no ipcp peer-route
lcp echo-req off
exit
;
network rcellular2
; -- Interface AT. Configuration --
lcp-options acfc
lcp-options pfc
lcp-options accm 0
exit
;
base-interface
; -- Base Interface Configuration --
base-interface rcellular2 link
base-interface rcellular2 profile WWAN
;
exit
;
exit
;
2 Configuration Teldat S.A.
6 Teldat-3Ge Quick Guide
Page 11

The authentication sent-user internet password internet command configures the access credentials
(login/password). The user must replace internet with the corresponding login and password supplied by the carrier.
2.5 IP Configuration
The router Ethernet interface IP address and the static route to transmit traffic over the 3G network are configured.
Optionally, the router firewall is enabled. The following example shows how to configure the IP address
172.24.78.29/16 on the Ethernet interface and declare the default route over the PPP1 interface, which is the inter-
face that inherits the IP address that the WWAN network assigned to the Teldat-3Ge .
network ethernet0/0
; -- Ethernet Interface User Configuration --
ip address 172.24.78.29 255.255.0.0
;
exit
;
protocol ip
; -- Internet protocol user configuration --
route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 ppp1
;
rule 1 local-ip ppp1 remote-ip any
rule 1 napt translation
rule 1 napt firewall
;
classless
;
exit
;
2.6 L2TP Tunnel
The router initiates (LAC) the L2TP session with the Teldat-3Ge , which acts as the L2TP server (LNS). An L2TP
Pseudowire type tunnel is established between both devices through which the three sessions needed to ensure this
functions correctly are established.
It is important that you do not change the name of each session in the router’s configuration, ETH-ANT-MON , ETH-
ANT-PPP and ETH-ANT-UPG, as these are the ones configured in the Teldat-3Ge.
protocol l2tp
; -- Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol user configuration --
enable
;
group 1
; -- L2TP group configuration --
pseudowire ETH-ANT-MON
initiate-to 172.24.78.28
request-dialin
interface rcellular1
hello 9
exit
;
group 2
; -- L2TP group configuration --
pseudowire ETH-ANT-PPP
initiate-to 172.24.78.28
request-dialin
interface rcellular2
hello 9
exit
;
group 3
; -- L2TP group configuration --
pseudowire ETH-ANT-UPG
initiate-to 172.24.78.28
Teldat S.A.
2 Configuration
Teldat-3Ge Quick Guide 7
Page 12

request-dialin
interface rcellular3
hello 9
exit
;
exit
2.7 DHCP Server
A DHCP server is configured on the router to respond to requests for IP parameters from the Teldat-3Ge .
To avoid conflicts with other DHCP servers on the company network, we must restrict the Teldat router DHCP service to only accept requests from the registered Teldat-3Ge so that, in turn, the Teldat router is always selected.
To achieve this, the DHCP configuration is as follows:
protocol dhcp
; -- DHCP Configuration --
server
; -- DHCP Server Configuration -;
subnet teldatsubnet 0 network 172.24.0.0 255.255.0.0
subnet teldatsubnet 0 bootfile fwethant.img
subnet teldatsubnet 0 next-server 172.24.78.29
subnet teldatsubnet 0 router 172.24.78.29
;
enable
;
host eth-ant 0 client-id asc teldat
host eth-ant 0 fixed-ip 172.24.78.28
host eth-ant 0 option 43 asc antenna&sipport=5060&localphone=607081119&
ntpserver=80.26.59.78
;
exit
;
exit
;
The host eth-ant 0 option 43 asc antenna command specifies the option the Teldat-3Ge expects to receive from
the server in order to accept the received address (“antenna” in ASCII). The “client-id” command gives the
“client-id” the router expects to receive (“teldat” in ASCII).
Other important parameters that can be configured through option 43 are as follows:
• “sipport=”, SIP agent UDP port in the device.
• “localphone=”, telephone number the GSM external call is transferred to.
• “sipserver=”, SIP-proxy IP address, if you want this to be a different device from the Teldat router. If you don’t set
this IP address, the SIP-proxy is the default route IP address assigned to the Teldat-3Ge by default.
• “ntpserver=”, NTP server IP address the device uses to synchronize the time.
• “ntpinterval=”, time between synchronization requests. Default is 3600.
• “ntpoffset=”, offset time corresponding to the time zone where the device is installed. Default is 2 (GMT +2). From
software version 1.09 for the Teldat-3Ge, this parameter is ignored and is substituted for the “ timezone” parameter.
• “timezone=”, this specifies the time zone the device is in. The default value is the Paris/Madrid zone specified as
“timezone=CET-1CEST,M3.5.0/2,M10.5.0/3”.
You can also see that the subnet teldatsubnet 0 bootfile fwethant.img command and the subnet teldatsubnet 0
next-server 172.24.78.29 command specify, respectively, the Teldat-3Ge firmware file name and the access IP address for the TFTP server the Teldat-3Ge must go to in order to download the firmware.
2 Configuration Teldat S.A.
8 Teldat-3Ge Quick Guide
Page 13

Note
In order for the voice backup feature to work, you must either give the Teldat-3Ge device a default
route from the DHCP server, or configure a SIP-proxy address through the “sipserver” parameter in option 43 of the DHCP protocol.
2.8 Configuring Voice Backup
The backup telephone configuration depends on the selected option (be this analog telephones, SIP telephones, or a
mixture of both).
The Teldat-3Ge device can operate with a SIP-proxy which is different from the router to which it is connected. You
only need to configure the SIP-proxy IP address through the “ sipserver” parameter (DHCP option 43). In this case,
the router connected to the Teldat-3Ge device does not need voice features.
Note
In order for the voice backup feature to work, you must either give the Teldat-3Ge device a default
route from the DHCP server, or configure a SIP-proxy address through the “sipserver” parameter in option 43 of the DHCP protocol.
2.8.1 Backup with analog telephones
Operating with one or several analog telephones means you have to install a VoIP expansion card in the TELDAT
router. The card has 4 lines that can be configured as FXS or FXO, depending on whether you are going to connect
telephone terminals or telephone lines. In this case, since the analog telephone is connected, you have to indicate
which line is going to be connected in the configuration. The following configuration defines the telephone connection
to line 1:
network voip1/0
; -- VoIP interface Configuration --
line 1 interface-type fxs
exit
;
The following point in the configuration is the definition of the dial-peers (for further information, please see manual
Dm722-I Telephony over IP). The following configuration defines two dial-peers, one for calls generated by the analog telephone and the other for calls to the analog telephone:
telephony
; -- Telephony configuration --
dial-peer 1 voice-port
no vad
destination-pattern 607081119
target voice-port voip1/0 1
exit
;
dial-peer 2 sip
no vad
codec g711alaw
destination-pattern T
target ipv4 192.24.78.28
exit
;
exit
;
Dial-peer 1 defines the mechanism to be followed when executing a call from the Teldat-3Ge . The destination-pattern parameter indicates that if the called number is the number that appears in the configuration, the call is routed
over the expansion module’s line 1.
Teldat S.A.
2 Configuration
Teldat-3Ge Quick Guide 9
Page 14

Dial-peer 2 establishes the Teldat-3Ge IP address of any calls detected by the SIP session to the IP address defined
in the target ipv4 parameter. Additionally, if RTP traffic is generated during the moments of silence and the audio codification is G711, the Teldat-3Ge must accept it.
The final step is to configure the router’s SIP agent (for more information, see manual Dm 766-I SIP):
protocol sip
; -- SIP protocol configuration --
application address 172.24.78.29
application gateway
exit
;
The IP address that appears in the application address parameter is the router’s address. This is the address where
the router receives the SIP traffic.
The application gateway parameter activates the router so it can establish calls between VoIP interfaces (analog
telephones) and SIP dial-peers.
The UDP/TCP port where the SIP server listens is, by default, 5060. In cases where you wish to change the port
value (e.g. to 5000), use the application port command as follows:
protocol sip
; -- SIP protocol configuration --
application address 172.24.78.29
application port 5000
application gateway
exit
;
A change in the value of this port affects the DHCP configuration. Option 43 must be modified to reconfigure the
Teldat-3Ge SIP agent listening port.
By default, the SIP traffic transport protocol in the corporate router is UDP. The transport protocol cannot be changed
to either TCP or TLS. The Teldat-3Ge SIP agent only uses the UDP protocol as in a corporate Ethernet environment. It doesn’t make sense to use protocols that further complicate SIP transport.
Note
The Teldat-3Ge SIP agent always uses the UDP protocol to transport SIP traffic. It never uses TCP.
The UDP port value is configurable through the DHCP protocol option 43 (configured in the router).
2.8.2 Backup with SIP-IP telephones
A VoIP expansion module is not necessary in this schema, meaning the configuration is limited to the part involving
the dial-peer and the SIP protocol.
The dial-peer configuration is as follows:
telephony
; -- Telephony configuration --
dial-peer 1 sip
no vad
destination-pattern T
target ipv4 192.24.78.28
exit
;
dial-peer 2 sip
destination-pattern 607081119
target dynamic
exit
;
exit
;
2 Configuration Teldat S.A.
10 Teldat-3Ge Quick Guide
Page 15

Dial-peer 1 defines how to route the call made from a SIP telephone, to the address defined in the target ipv4 parameter, which should be the one corresponding to the Teldat-3Ge .
Dial-peer 2 defines how to route the call coming from the Teldat-3Ge device. The telephone number that appears in
the destination-pattern parameter corresponds to that defined in the DHCP configuration with the localphone parameter, which is that corresponding to the Teldat-3Ge SIM card. If the number assigned to the SIP telephone is the
same one as that defined for the backup telephone, the configuration is reduced to the previous one. If, however, you
want to use a configuration where various SIP telephones can make and receive external calls over the Teldat-3Ge
GSM line, the following configuration is recommended:
telephony
; -- Telephony configuration --
dial-peer 1 sip
description “Outgoing external calls through the Teldat-3Ge ”
no vad
destination-pattern T
target ipv4 192.24.78.28
exit
;
dial-peer 2 sip
description “Extension receiving external calls from the Teldat-3Ge ”
destination-pattern 4560.
target dynamic
exit
;
dial-peer 3 group
description “Incoming external calls through the Teldat-3Ge ”
destination-pattern 607081119
target group 1
exit
;
peer-group 1
dial-peer 2 45600
dial-peer 2 45601
dial-peer 2 45602
dial-peer 2 45603
exit
;
exit
;
In this case, any call destined to a telephone number that does not match any defined dial-peer (different from extension 4560x or number 607081119) is routed to the Teldat-3Ge . If the Teldat-3Ge line is busy due to an incoming or
outgoing call, a signal indicating that the number trying to be reached is temporally unavailable will be heard. Incoming calls ring on all extensions defined by the peer-group 1.
The SIP protocol is configured as follows:
protocol sip
; -- SIP protocol configuration --
application address 172.24.78.29
application server default
exit
;
The IP address that appears in the application address parameter is the router’s address. This is the address where
the router receives SIP traffic.
The application gateway parameter activates the router so calls can be established between VoIP interfaces (analog
telephones) and SIP dial-peers.
The UDP/TCP port where the SIP server listens is, by default, 5060. If you want to change the port value (e.g. to
5000), use the application port command as follows:
protocol sip
; -- SIP protocol configuration --
application address 172.24.78.29
Teldat S.A.
2 Configuration
Teldat-3Ge Quick Guide 11
Page 16

application port 5000
application gateway
exit
;
A change in the value of this port affects the DHCP configuration. Option 43 must be modified to reconfigure the
Teldat-3Ge SIP agent listening port.
The SIP traffic transport protocol in the corporate router is UDP by default. The transport protocol cannot be changed
to either TCP or TLS. Since the Teldat-3Ge SIP agent only uses the UDP protocol as in a corporate Ethernet environment, it doesn’t make sense to use protocols that further complicate the SIP transport.
Note
The Teldat-3Ge SIP agent always uses the UDP protocol to transport SIP traffic. It never uses TCP.
The UDP port value is configurable through the DHCP protocol (option 43,configured in the router).
For the system to operate properly, the SIP-IP telephones configuration must have the following parameters configured:
The SIP server IP address, which is the same as that configured in the backup TELDAT router.
The SIP server port to which the telephone sends SIP traffic, which is the same as that configured in
the corporate router.
The SIP server transport protocol, which is UDP.
Audio codification: G711 A-law.
Time between RTP packets: 10ms, 20ms, 30ms and 40 ms. We recommend using 20ms.
Deactivate Voice Activation Detection.
DTMF SIP INFO signaling out of band.
2.9 WAN Reroute Backup Facility
To prevent the router from routing backup traffic if the connection between the device and the Teldat-3Ge drops, you
need to add an entry to the router’s WAN Reroute Backup feature (see manual Dm727-I Backup WAN Reroute ).
The configuration steps are as follows:
(1) Access the feature configuration menu:
feature wrr-backup-wan
; -- WAN Reroute Backup user configuration --
(2) Enable the feature:
enable
(3) Associate the Ethernet interface of the router connected to the Teldat-3Ge device and the PPP interface:
pair 1 primary interface ethernet0/0 secondary interface ppp1
(4) Configure it as an inverse backup (i.e. if the main interface drops, the secondary also drops and if the main in-
terface activates, the secondary does as well).
pair 1 inverse-wrr
Thus, the configuration part we need to add is:
feature wrr-backup-wan
; -- WAN Reroute Backup user configuration --
pair 1 primary interface ethernet0/0 secondary interface ppp1
pair 1 inverse-wrr
;
enable
exit
2 Configuration Teldat S.A.
12 Teldat-3Ge Quick Guide
Page 17

2.10 Updating the Firmware
The updating process initializes once the firmware file name (fwethant.img) and the TFTP server IP address have
been received during the DHCP negotiation, as explained in the previous section.
The Teldat-3Ge sends periodic requests (approximately every 30 seconds) to the TFTP server to check if the version stored in this is different to the one currently being executed. In cases where it is different, the new application is
downloaded and the device restarted.
The user can check the current firmware version by looking at the RemoteName field for the created L2TP tunnels,
which is the result of running the tunnel-info all monitoring command in the L2TP protocol monitoring menu:
RemoteIP:10.1.2.2 LocalIP:0.0.0.0 Port:1701
RemoteName:01.00-EthAnt-00 State:established
LocalID:9240 RemoteID:1589 Sessions:3
group 3
Pseudowire:ETH-ANT-MON Interface:rcellular1 Sequencing:off
(...)
You can also check the current firmware version by visiting the Teldat-3Ge Web page. To do this, start the Web
browser and ask for the HTTP page for the Teldat-3Ge access IP address (in the example given here, this is http://172.24.78.28).
The STATUS LED lights up in steady YELLOW while the application is being updated.
2.10.1 Using the router as a TFTP Server
You can configure the Teldat router TFTP server to teleload the Teldat-3Ge firmware.
Firstly, you must teleload the required file in the Teldat router by means of the usual FTP process.
You also have to enable the TFTP protocol in the server router, executing the configuration commands shown below.
feature tftp
-- TFTP user configuration -server file-system DSK
server enable
exit
2.11 Final Result
Once all the steps indicated in this chapter have been carried out, the Teldat router is configured. You can list the
new active configuration by using the show config command. The results for an analog telephone and a VoIP expansion module are as follows:
log-command-errors
no configuration
add device ppp 1
add device rcellular 1
add device rcellular 2
add device rcellular 3
global-profiles dial
; -- Dial Profiles Configuration --
profile WWAN default
profile WWAN dialout
profile WWAN 3gpp-accessibility-control traffic 20 all
profile WWAN 3gpp-apn internet.es
profile WWAN idle-time 300
;
exit
;
network ethernet0/0
; -- Ethernet Interface User Configuration --
ip address 172.24.78.29 255.255.0.0
Teldat S.A.
2 Configuration
Teldat-3Ge Quick Guide 13
Page 18

;
exit
;
network rcellular2
; -- Interface AT. Configuration --
lcp-options acfc
lcp-options pfc
lcp-options accm 0
exit
;
telephony
; -- Telephony configuration --
dial-peer 1 voice-port
no vad
destination-pattern 607081119
target voice-port voip1/0 1
exit
;
dial-peer 2 sip
no vad
codec g711alaw
destination-pattern T
target ipv4 192.24.78.28
exit
;
exit
;
network ethernet0/0
; -- Ethernet Interface User Configuration --
ip address 172.24.78.29 255.255.0.0
;
exit
;
;
network rcellular1
; -- Interface AT. Configuration --
description ETH-ANT-MON
coverage-timer 15
pin plain 5710
monitor-ifc 1
network mode automatic
network domain cs+ps
exit
;
network rcellular2
; -- Interface AT. Configuration --
description ETH-ANT-PPP
ppp-ifc 1
exit
;
network rcellular3
; -- Interface AT. Configuration --
description ETH-ANT-UPG
upgrade-ifc 1
exit
;
network voip1/0
; -- VoIP interface Configuration --
line 1 interface-type fxs
;
exit
;
network ppp1
; -- Generic PPP User Configuration --
ip address unnumbered
;
2 Configuration Teldat S.A.
14 Teldat-3Ge Quick Guide
Page 19

ppp
; -- PPP Configuration --
authentication sent-user internet password internet
ipcp local address assigned
no ipcp peer-route
lcp echo-req off
exit
;
base-interface
; -- Base Interface Configuration --
base-interface rcellular2 link
base-interface rcellular2 profile WWAN
;
exit
;
exit
;
protocol ip
; -- Internet protocol user configuration --
route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 ppp1
;
rule 1 local-ip ppp1 remote-ip any
rule 1 napt translation
rule 1 napt firewall
;
classless
;
exit
;
;
protocol dhcp
; -- DHCP Configuration --
server
; -- DHCP Server Configuration -;
subnet teldatsubnet 0 network 172.24.0.0 255.255.0.0
subnet teldatsubnet 0 bootfile fwethant.img
subnet teldatsubnet 0 next-server 172.24.78.29
subnet teldatsubnet 0 router 172.24.78.29
;
enable
;
host eth-ant 0 client-id asc teldat
host eth-ant 0 fixed-ip 172.24.78.28
host eth-ant 0 option 43 asc antenna&sipport=5060&localphone=607081119
;
exit
;
exit
;
protocol l2tp
; -- Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol user configuration --
enable
;
group 1
; -- L2TP group configuration --
pseudowire ETH-ANT-MON
initiate-to 172.24.78.28
request-dialin
interface rcellular1
hello 9
exit
;
group 2
; -- L2TP group configuration --
pseudowire ETH-ANT-PPP
initiate-to 172.24.78.28
Teldat S.A.
2 Configuration
Teldat-3Ge Quick Guide 15
Page 20

request-dialin
interface rcellular2
hello 9
exit
;
group 3
; -- L2TP group configuration --
pseudowire ETH-ANT-UPG
initiate-to 172.24.78.28
request-dialin
interface rcellular3
hello 9
exit
;
exit
;
protocol sip
; -- SIP protocol configuration --
application address 172.24.78.29
application gateway
exit
;
feature tftp
-- TFTP user configuration -server file-system DSK
server enable
exit
;
feature wrr-backup-wan
; -- WAN Reroute Backup user configuration --
pair 1 primary interface ethernet0/0 secondary interface ppp1
pair 1 inverse-wrr
;
enable
exit
;
dump-command-errors
end
Configuration for SIP-IP telephones is as follows:
log-command-errors
no configuration
add device ppp 1
add device rcellular 1
add device rcellular 2
add device rcellular 3
global-profiles dial
; -- Dial Profiles Configuration --
profile WWAN default
profile WWAN dialout
profile WWAN 3gpp-accessibility-control traffic 20 all
profile WWAN 3gpp-apn internet.es
profile WWAN idle-time 300
;
exit
network rcellular2
; -- Interface AT. Configuration --
lcp-options acfc
lcp-options pfc
lcp-options accm 0
exit
;
telephony
; -- Telephony configuration --
dial-peer 1 sip
description “Outgoing external calls through the Teldat-3Ge”
2 Configuration Teldat S.A.
16 Teldat-3Ge Quick Guide
Page 21

no vad
destination-pattern T
target ipv4 192.24.78.28
exit
;
dial-peer 2 sip
description “Extension receiving external calls from the Teldat-3Ge
destination-pattern 4560.
target dynamic
exit
;
dial-peer 3 group
description “Incoming external calls through the Teldat-3Ge”
destination-pattern 607081119
target group 1
exit
;
peer-group 1
dial-peer 2 45600
dial-peer 2 45601
dial-peer 2 45602
dial-peer 2 45603
exit
;
exit
;
;
network ethernet0/0
; -- Ethernet Interface User Configuration --
ip address 172.24.78.29 255.255.0.0
;
exit
;
;
;
network rcellular1
; -- Interface AT. Configuration --
description ETH-ANT-MON
coverage-timer 15
pin plain 5710
monitor-ifc 1
network mode automatic
network domain cs+ps
exit
;
network rcellular2
; -- Interface AT. Configuration --
description ETH-ANT-PPP
ppp-ifc 1
exit
;
network rcellular3
; -- Interface AT. Configuration --
description ETH-ANT-UPG
upgrade-ifc 1
exit
;
network ppp1
; -- Generic PPP User Configuration --
ip address unnumbered
;
ppp
; -- PPP Configuration --
authentication sent-user internet password internet
ipcp local address assigned
no ipcp peer-route
Teldat S.A.
2 Configuration
Teldat-3Ge Quick Guide 17
Page 22

lcp echo-req off
exit
;
base-interface
; -- Base Interface Configuration --
base-interface rcellular2 link
base-interface rcellular2 profile WWAN
;
exit
;
exit
;
protocol ip
; -- Internet protocol user configuration --
route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 ppp1
;
rule 1 local-ip ppp1 remote-ip any
rule 1 napt translation
rule 1 napt firewall
;
classless
;
exit
;
;
protocol dhcp
; -- DHCP Configuration --
server
; -- DHCP Server Configuration -;
subnet teldatsubnet 0 network 172.24.0.0 255.255.0.0
subnet teldatsubnet 0 bootfile fwethant.img
subnet teldatsubnet 0 next-server 172.24.78.29
subnet teldatsubnet 0 router 172.24.78.29
;
enable
;
host eth-ant 0 client-id asc teldat
host eth-ant 0 fixed-ip 172.24.78.28
host eth-ant 0 option 43 asc antenna&sipport=5060&localphone=607081119
;
exit
;
exit
;
protocol l2tp
; -- Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol user configuration --
enable
;
group 1
; -- L2TP group configuration --
pseudowire ETH-ANT-MON
initiate-to 172.24.78.28
request-dialin
interface rcellular1
hello 9
exit
;
group 2
; -- L2TP group configuration --
pseudowire ETH-ANT-PPP
initiate-to 172.24.78.28
request-dialin
interface rcellular2
hello 9
exit
2 Configuration Teldat S.A.
18 Teldat-3Ge Quick Guide
Page 23

;
group 3
; -- L2TP group configuration --
pseudowire ETH-ANT-UPG
initiate-to 172.24.78.28
request-dialin
interface rcellular3
hello 9
exit
;
exit
;
protocol sip
; -- SIP protocol configuration --
application address 172.24.78.29
application server default
exit
;
;
feature tftp
-- TFTP user configuration -server file-system DSK
server enable
exit
;
feature wrr-backup-wan
; -- WAN Reroute Backup user configuration --
pair 1 primary interface ethernet0/0 secondary interface ppp1
pair 1 inverse-wrr
;
enable
exit
;
dump-command-errors
end
Teldat S.A.
2 Configuration
Teldat-3Ge Quick Guide 19
Page 24

Chapter 3 Monitoring
3.1 Monitoring Communications with the Teldat-3Ge device
The L2TP tunnel monitoring commands can be accessed from the corresponding section in the monitoring process
(process 3), as shown below:
*process 3
+protocol l2tp
L2TP+
As already mentioned in chapter2 “Configuration” section 6) L2TP Tunnel, the tunnel-info all monitoring command
summarizes the L2TP general operations.
L2TP+tunnel-info all
Number of L2TP Tunnels: 1
Number of L2TP Sessions: 2
RemoteIP:172.24.78.28 LocalIP:0.0.0.0 Port:1701
RemoteName:ramfs-antennaeth State:established
LocalID:52623 RemoteID:13425 Sessions:3
group 3
Pseudowire:ETH-ANT-MON Interface:rcellular1 Sequencing:off
LAC LocalID:20774 RemoteID:43001 State:established
LastChange:4m35s Events:Show
encaps:20 decaps:32 missed:0 dropped:0
Pseudowire:ETH-ANT-PPP Interface:rcellular2 Sequencing:off
LAC LocalID:52943 RemoteID:58150 State:established
LastChange:4m35s Events:Show
encaps:1 decaps:1 missed:0 dropped:0
Pseudowire:ETH-ANT-UPG Interface:rcellular3 Sequencing:off
LAC LocalID:14495 RemoteID:49170 State:established
LastChange:4m35s Events:Show
encaps:0 decaps:0 missed:0 dropped:0
L2TP+
In cases where the tunnel is not established (unlike the above capture, where the state is shown as correct according
to the State:established field) the router won’t have access to the Teldat-3Ge . The reasons for this abnormal behavior can be one of two things:
• There is an element in the local network blocking the L2TP traffic.
• The DHCP negotiation between both devices has not completed correctly.
More detailed information on the DHCP negotiation can be obtained with the leases command (under the DHCP
server monitoring section):
L2TP+exit
+protocol dhcp
DHCP Protocol monitor
DHCP+server
DHCP-Server+leases
========================================
..:: Currently assigned DHCP Leases ::..
========================================
172.24.78.28 hardware ethernet 00:a0:26:fe:98:89
start Thu Sep 06 2007 11:25:55 end Thu Sep 06 2007 23:25:55
uid 'teldat'
The Teldat-3Ge responds to the ping application. Therefore, you need to be able to obtain the responses to the ping
command by sending this from the router to address 172.24.78.28, as in the example:
+ping 172.24.78.28
PING 172.24.78.28: 56 data bytes
64 bytes from 172.24.78.28: icmp_seq=0. time<1. ms
64 bytes from 172.24.78.28: icmp_seq=1. time<1. ms
3 Monitoring Teldat S.A.
20 Teldat-3Ge Quick Guide
Page 25

3.2 Wireless WAN Service
The 3G service parameters are available from the rcellular1 interface monitoring section. We will now see how to access the said section as well as the available commands.
+network rcellular1
rcellular1 AT+?
at-mode Send AT commands directly to the module
buffer Display saved commands and answers
command Send AT command to the module
list List interface and module parameters
module Module related commands
network 3G Network related commands
reset Send reset command
voice-call Voice-call supervision commands
exit
rcellular1 AT+
A more detailed description on each of the above commands can be found in the Teldat router 3G interface manual,
chapter 3.1 (Dm781-I Cellular Interface).
Teldat S.A.
3 Monitoring
Teldat-3Ge Quick Guide 21
Page 26

Chapter 4 Appendix
4.1 Several Teldat-3Ge in the same corporate LAN
Particular care must be paid when installing several Teldat-3Ge devices on the same LAN network, especially when
it comes to configuring the DHCP protocol. The DHCP server must identify the Teldat-3Ge s and offer different IP
addresses to each. The Teldat-3Ge s are identified through the MAC address assigned to the device's Ethernet interface. The MAC address value is found on the label attached to the underside of the case containing the device.
4.1.1 Two Teldat-3Ge devices serving a router
DHCP server configuration in a Teldat router where two Teldat-3Ge devices serve a single router:
protocol dhcp
; -- DHCP Configuration --
server
; -- DHCP Server Configuration --
subnet subnetea 0 network 172.24.0.0 255.255.0.0
subnet subnetea 0 bootfile fwethant.img
subnet subnetea 0 next-server 172.24.78.29
subnet subnetea 0 router 172.24.78.29
;
enable
;
host eth-ant1 0 ethernet 00-a0-26-53-29-02
host eth-ant1 0 fixed-ip 172.24.78.31
host eth-ant1 0 option 43 asc antenna&sipport=5060&localphone=607081119
;
host eth-ant2 0 ethernet 00-a0-26-53-29-03
host eth-ant2 0 fixed-ip 172.24.78.32
host eth-ant2 0 option 43 asc antenna
In both configurations, the device with physical MAC address 00-a0-26-53-29-02 is given the SIP configuration and is
the equipment that acts as the SIP-gateway. The other device will only back up data.
Moreover, when compared to the basic scenario explained in this document, in this case the user needs to specify 2
PPP interfaces (each one with an rcellular base interface and each of these with their L2TP tunnel). Consequently,
and as you can see in the resulting configuration that follows, 6 rcellular interfaces and 6 L2TP tunnels are configured in the router.
log-command-errors
no configuration
set hostname ATLAS
add device ppp 1
add device ppp 2
4 Appendix Teldat S.A.
22 Teldat-3Ge Quick Guide
Page 27

add device rcellular 1
add device rcellular 2
add device rcellular 3
add device rcellular 4
add device rcellular 5
add device rcellular 6
global-profiles dial
; -- Dial Profiles Configuration --
profile WWAN default
profile WWAN dialout
profile WWAN 3gpp-accessibility-control traffic 20 all
profile WWAN 3gpp-apn internet.es
profile WWAN idle-time 300
;
exit
;
;
network ethernet0/0
; -- Ethernet Interface User Configuration --
ip address 172.24.78.29 255.255.0.0
;
exit
;
network rcellular1
; -- Interface AT. Configuration --
description ETH-ANT-MON
coverage-timer 15
pin plain 5710
monitor-ifc 1
network mode automatic
network domain cs+ps
exit
;
network rcellular2
; -- Interface AT. Configuration --
description ETH-ANT-PPP
ppp-ifc 1
lcp-options acfc
lcp-options pfc
lcp-options accm 0
exit
;
network rcellular3
; -- Interface AT. Configuration --
description ETH-ANT-UPG
upgrade-ifc 1
exit
network rcellular4
; -- Interface AT. Configuration --
description ETH-ANT-MON
coverage-timer 15
pin plain 6453
monitor-ifc 2
network mode automatic
network domain cs+ps
exit
;
network rcellular5
; -- Interface AT. Configuration --
description ETH-ANT-PPP
ppp-ifc 2
exit
;
network rcellular6
Teldat S.A.
4 Appendix
Teldat-3Ge Quick Guide 23
Page 28

; -- Interface AT. Configuration --
description ETH-ANT-UPG
upgrade-ifc 2
exit
;
network ppp1
; -- Generic PPP User Configuration --
ip address unnumbered
;
ppp
; -- PPP Configuration --
authentication sent-user internet password internet
ipcp local address assigned
no ipcp peer-route
lcp echo-req off
exit
;
base-interface
; -- Base Interface Configuration --
base-interface rcellular2 link
base-interface rcellular2 profile WWAN
;
exit
;
exit
;
;
network ppp2
; -- Generic PPP User Configuration --
ip address unnumbered
;
ppp
; -- PPP Configuration --
authentication sent-user internet password internet
ipcp local address assigned
no ipcp peer-route
lcp echo-req off
exit
;
base-interface
; -- Base Interface Configuration --
base-interface rcellular4 link
base-interface rcellular4 profile WWAN
;
exit
;
exit
;
telephony
; -- Telephony configuration --
dial-peer 1 sip
no vad
destination-pattern T
target ipv4 192.24.78.31
exit
;
dial-peer 2 sip
destination-pattern 607081119
target dynamic
exit
;
exit
;
protocol ip
; -- Internet protocol user configuration --
route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 ppp1
;
4 Appendix Teldat S.A.
24 Teldat-3Ge Quick Guide
Page 29

rule 1 local-ip ppp1 remote-ip any
rule 1 napt translation
rule 1 napt firewall
;
rule 2 local-ip ppp2 remote-ip any
rule 2 napt translation
rule 2 napt firewall
classless
;
exit
;
;
protocol dhcp
; -- DHCP Configuration --
server
; -- DHCP Server Configuration --
subnet subnetea 0 network 172.24.0.0 255.255.0.0
subnet subnetea 0 bootfile fwethant.img
subnet subnetea 0 next-server 172.24.78.29
subnet subnetea 0 router 172.24.78.29
;
enable
;
host eth-ant1 0 ethernet 00-a0-26-53-29-02
host eth-ant1 0 fixed-ip 172.24.78.31
host eth-ant1 0 option 43 asc antenna&sipport=5060&localphone=607081119
;
host eth-ant2 0 ethernet 00-a0-26-53-29-03
host eth-ant2 0 fixed-ip 172.24.78.32
host eth-ant2 0 option 43 asc antenna
;
;
exit
;
exit
;
protocol l2tp
; -- Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol user configuration --
enable
;
group 1
; -- L2TP group configuration --
pseudowire ETH-ANT-MON
initiate-to 172.24.78.31
request-dialin
interface rcellular1
hello 9
exit
;
group 2
; -- L2TP group configuration --
pseudowire ETH-ANT-PPP
initiate-to 172.24.78.31
request-dialin
interface rcellular2
hello 9
exit
;
group 3
; -- L2TP group configuration --
pseudowire ETH-ANT-UPG
initiate-to 172.24.78.31
request-dialin
interface rcellular3
hello 9
exit
Teldat S.A.
4 Appendix
Teldat-3Ge Quick Guide 25
Page 30

;
group 4
; -- L2TP group configuration --
pseudowire ETH-ANT-MON
initiate-to 172.24.78.32
request-dialin
interface rcellular4
hello 9
exit
;
group 5
; -- L2TP group configuration --
pseudowire ETH-ANT-PPP
initiate-to 172.24.78.32
request-dialin
interface rcellular5
hello 9
exit
;
group 6
; -- L2TP group configuration --
pseudowire ETH-ANT-UPG
initiate-to 172.24.78.32
request-dialin
interface rcellular6
hello 9
exit
exit
;
protocol sip
; -- SIP protocol configuration --
application address 172.24.78.31
application gateway
exit
;
feature tftp
; -- TFTP user configuration --
server file-system DSK
server enable
exit
;
feature wrr-backup-wan
; -- WAN Reroute Backup user configuration --
pair 1 primary interface ethernet0/0 secondary interface ppp1
pair 1 inverse-wrr
;
enable
exit
;
dump-command-errors
;
end
You can use the GSM telephone line in each Teldat-3Ge to execute voice calls using a suitable router configuration.
To do this, you only have to add a dial-peer with the IP address for each Teldat-3Ge . You also have to add the sip-
port parameters and the localphone to the DHCP configuration destined for each Teldat-3Ge . When this configura-
tion is active, if one of the Teldat-3Ge GSM lines defined in the first dial-peer is busy, the router sends the call to the
Teldat-3Ge defined in the next dial-peer and so on.
The following console shows an example of this type of voice backup configuration when three Teldat-3Ge devices
are being used:
telephony
; -- Telephony configuration --
dial-peer 1 sip
description “Outgoing external calls through the Teldat-3Ge 1”
no vad
4 Appendix Teldat S.A.
26 Teldat-3Ge Quick Guide
Page 31

destination-pattern T
target ipv4 192.24.78.28
exit
;
dial-peer 2 sip
description “Outgoing external calls through the Teldat-3Ge 2”
no vad
destination-pattern T
target ipv4 192.24.78.27
exit
;
dial-peer 3 sip
description “Outgoing external calls through the Teldat-3Ge 3”
no vad
destination-pattern T
target ipv4 192.24.78.26
exit
;
dial-peer 4 sip
description “Extension receiving calls from the Teldat-3Ge devices”
destination-pattern 4560.
target dynamic
exit
;
dial-peer 5 group
description “Incoming external calls through the Teldat-3Ge 1”
destination-pattern 607081119
target group 1
exit
;
dial-peer 6 group
description “Incoming external calls through the Teldat-3Ge 2”
destination-pattern 607081129
target group 2
exit
;
dial-peer 7 group
description “Incoming external calls through the Teldat-3Ge 3”
destination-pattern 607081139
target group 3
exit
;
peer-group 1
dial-peer 2 45601
exit
;
peer-group 2
dial-peer 2 45602
exit
;
peer-group 3
dial-peer 2 45603
exit
;
exit
;
4.1.2 Two routers, each with a Teldat-3Ge
Case involving two routers and two Teldat-3Ge s connected to the same LAN: each router acts as server for its respective Teldat-3Ge . The DHCP configuration is shown below:
Router1:
protocol dhcp
; -- DHCP Configuration --
server
Teldat S.A.
4 Appendix
Teldat-3Ge Quick Guide 27
Page 32

; -- DHCP Server Configuration --
subnet subnetea 0 network 172.24.0.0 255.255.0.0
subnet subnetea 0 bootfile fwethant.img
subnet subnetea 0 next-server 172.24.78.29
subnet subnetea 0 router 172.24.78.29
;
enable
;
host eth-ant 0 ethernet 00-a0-26-53-29-02
host eth-ant 0 fixed-ip 172.24.78.31
host eth-ant 0 option 43 asc antenna&sipport=5060&localphone=607081119
Router 2:
protocol dhcp
; -- DHCP Configuration --
server
; -- DHCP Server Configuration --
subnet subnetea 0 network 172.24.0.0 255.255.0.0
subnet subnetea 0 bootfile fwethant.img
subnet subnetea 0 next-server 172.24.78.30
subnet subnetea 0 router 172.24.78.30
;
enable
;
host eth-ant 0 ethernet 00-a0-26-53-29-03
host eth-ant 0 fixed-ip 172.24.78.32
host eth-ant 0 option 43 asc antenna&sipport=5060&localphone=607326598
4.2 LEDs
The device has several LEDs and their meaning is as follows:
LED STATUS DESCRIPTION
POWER ON/OFF When this is lit up, the device is receiving power.
WWAN OFF Error in the WWAN module. 3G communications are not possible.
Flashing Green (slow) The SIM card hasn’t been detected or the PIN is incorrect.
Flashing Green (fast) The module cannot register in the network.
Steady Green Communications at the PPP layer.
Ethernet Connector ON/OFF The left hand LED lights up in yellow when there is link level and the
right hand one flashes in green when there is data communication.
STATUS Steady Red Error in the WWAN module. 3G communications are not possible.
• Check that the module is correctly connected.
• Check that it has the appropriate software.
• Look to see if the WWAN LED is lit up.
Flashing Red The WWAN module is operating correctly but the device hasn’t got
an IP address yet.
• Check the status of the Ethernet connector LEDs.
• The device has access to the DHCP server.
• Follow the instructions given in the "Monitoring" section.
Flashing yellow The device has received the IP address but hasn’t managed to es-
4 Appendix Teldat S.A.
28 Teldat-3Ge Quick Guide
Page 33

tablish the L2TP tunnel.
• Check the router’s L2TP configuration.
• Follow the instructions given in the "Monitoring" section.
Steady Green The L2TP tunnel has established. The device is ready to operate
normally.
Flashing Green There is traffic through the WWAN interface.
Steady Yellow The device is updating the firmware.
The meaning of the STATUS LED after a startup or rebooting process once the firmware has been updated is as follows:
• On startup, it lights up for a moment in yellow.
• While the application starts up, it flashes in green.
• When the application is ready, it stays green.
If there is any problem during start-up, the LED lights up in red for a few seconds and then starts flashing in green.
Teldat S.A.
4 Appendix
Teldat-3Ge Quick Guide 29
 Loading...
Loading...