Datasheet TC7136RCPL, TC7136RCLW, TC7136RCKW, TC7136CPL, TC7136ARCPL Datasheet (TelCom Semiconductor)
...
3-247
TELCOM SEMICONDUCTOR, INC.
7
6
5
4
3
1
2
8
TC7136
TC7136A
A or blank*
R (reversed pins) or blank (CPL pkg only)
* "A" parts have an improved reference TC
Package Code (see below):
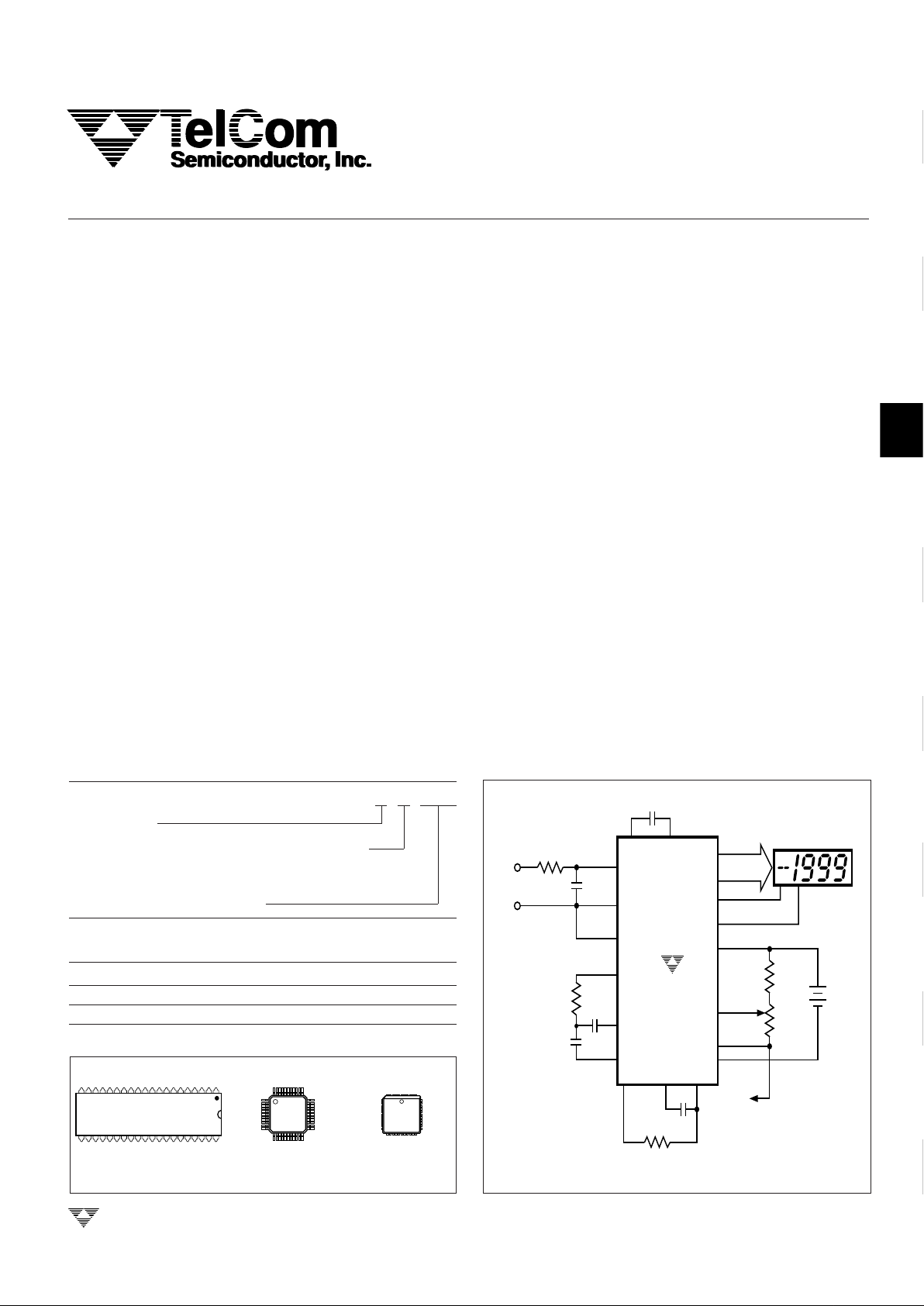
TYPICAL APPLICATIONS
■ Thermometry
■ Bridge Readouts: Strain Gauges, Load Cells, Null
Detectors
■ Digital Meters: Voltage/Current/Ohms/Power, pH
■ Digital Scales, Process Monitors
■ Portable Instrumentation
ORDERING INFORMATION
PART CODE TC7136X X XXX
Package Temperature
Code Package Pin Layout Range
CKW 44-Pin PQFP Formed Leads 0°C to +70°C
CLW 44-Pin PLCC — 0°C to +70°C
CPL 40-Pin PDIP Normal 0°C to +70°C
40-Pin Plastic DIP
44-Pin Plastic Quad Flat
Package Formed Leads
44-Pin Plastic Chip
Carrier PLCC
V
REF
+
TC7136
TC7136A
33
34
240 kΩ
10 kΩ
31
29
39 38 40
V
REF
–
0.47
µF
0.1 µF
V
–
1
OSC
3
OSC
2
OSC
TO ANALOG COMMON
(PIN 32)
1 CONVERSION/SEC
C
OSC
560 kΩ
180 kΩ
0.15 µF
0.01 µF
ANALOG
INPUT
+
–
C
REF
–
C
REF
+
V
IN
+
V
IN
–
ANALOG
COMMON
V
INT
V
BUFF
C
AZ
20
21
1
SEGMENT
DRIVE
9–19
22–25
POL
BP
V
+
MINUS SIGN
BACKPLANE
28
50 pF
LCD
1 MΩ
27
30
32
35
36
9V
+
R
OSC
26
TYPICAL OPERATING CIRCUIT
AVAILABLE PACKAGES
LOW POWER, 3-1/2 DIGIT ANALOG-T O-DIGITAL CONVERTERS
FEATURES
■ Fast Overrange Recovery, Guaranteed First
Reading Accuracy
■ Low Temperature Drift Internal Reference
TC7136 ....................................... 70 ppm/°C Typ
TC7136A.....................................35 ppm/°C Typ
■ Guaranteed Zero Reading With Zero Input
■ Low Noise....................................................15 µV
P-P
■ High Resolution .............................................. 0.05%
■ Low Input Leakage Current ......................1 pA Typ
10 pA Max
■ Precision Null Detectors With True Polarity at
Zero
■ High-Impedance Differential Input
■ Convenient 9V Battery Operation With
Low Power Dissipation ........................500 µW Typ
900 µW Max
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The TC7136 and TC7136A are low-power, 3-1/2 digit
with liquid crystal display (LCD) drivers with analog-todigital converters. These devices incorporate an "integrator output zero" phase which guarantees overrange
recovery. The performance of existing TC7126, TC7126A
and ICL7126-based systems may be upgraded with minor
changes to external, passive components.
The TC7136A has an improved internal zener reference voltage circuit which maintains the analog common
temperature drift to 35 ppm/°C (typical) and 75 ppm/°C
(maximum). This represents an improvement of two to four
times over similar 3-1/2 digit converters. The costly, spaceconsuming external reference source may be removed.
The TC7136/A limits linearity error to less than 1 count
on 200 mV or 2V full-scale ranges. Roll-over error — the
difference in readings for equal magnitude but opposite
polarity input signals — is below ±1 count. High-impedance
differential inputs offer 1 pA leakage currents and a 1012Ω
input impedance. The differential reference input allows
ratiometric measurements for ohms or bridge transducer
measurements. The 15 µV
P-P
noise performance guarantees a "rock solid" reading. The auto-zero cycle guarantees
a zero display readout for a 0V input.
TC7136-6 10/18/96
3-248
TELCOM SEMICONDUCTOR, INC.
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS*
Supply Voltage (V+ to V–)............................................15V
Analog Input Voltage (Either Input) (Note 1) ........ V+ to V
–
Reference Input Voltage (Either Input).................V+ to V
–
Clock Input ......................................................TEST to V
+
Package Power Dissipation (TA ≤ 70°C) (Note 2)
Plastic DIP ........................................................1.23W
Plastic Quad Flat Package ...............................1.00W
PLCC ................................................................1.23W
Operating Temperature Range
C Devices ..............................................0°C to +70°C
I Devices............................................–25°C to +85°C
Storage Temperature Range .................–65°C to +150°C
Lead Temperature (Soldering, 10 sec) .................+300°C
*Static-sensitive device. Unused devices must be stored in conductive
material. Protect devices from static discharge and static fields. Stresses
above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and functional
operation of the device at these or any other conditions above those
indicated in the operational sections of the specifications is not implied.
Exposure to Absolute Maximum Rating Conditions for extended periods
may affect device reliability.
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS: V
S
= 9V, f
CLK
= 16 kHz, and TA = +25°C, unless otherwise noted.
Symbol Parameter Test Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
Input
Zero Input Reading VIN = 0V – 000.0 ±000.0 +000.0 Digital
Full Scale = 200 mV Reading
Zero Reading Drift VIN = 0V, 0°C ≤ TA ≤ +70°C — 0.2 1 µV/°C
Ratiometric Reading VIN = V
REF
, V
REF
= 100 mV 999 999/1000 1000 Digital
Reading
NL Nonlinearity Error Full Scale = 200 mV or 2V – 1 ±0.2 1 Count
Max Deviation From Best
Straight Line
Roll-Over Error –VIN = +VIN ≈ 200 mV – 1 ±0.2 1 Count
e
N
Noise VIN = 0V, Full Scale = 200 mV — 15 — µV
P-P
I
L
Input Leakage Current VIN = 0V — 1 10 pA
CMRR Common-Mode Rejection VCM = ±1V, VIN = 0V, — 50 — µV/V
Ratio Full Scale = 200 mV
Scale Factor Temperature VIN = 199 mV, 0°C ≤ TA ≤ +70°C — 1 5 ppm/°C
Coefficient Ext Ref Temp Coeff = 0 ppm/°C
Analog Common
V
CTC
Analog Common 250 kΩ Between Common and V
+
Temperature Coefficient 0°C ≤ TA ≤ +70°C TC7136A — 35 75 ppm/°C
"C" Commercial Temp TC7136 — 70 150 ppm/°C
Range Devices
– 25°C ≤ T
A
≤ +85°C TC7136A — 35 100 ppm/°C
"I" Industrial Temp TC7136 — 70 150 ppm/°C
Range Devices
V
C
Analog Common Voltage 250 kW Between Common and V
+
2.7 3.05 3.35 V
LCD Drive
V
SD
LCD Segment Drive Voltage V+ to V– = 9V 4 5 6 V
P-P
V
BD
LCD Backplane Drive Voltage V+ to V– = 9V 4 5 6 V
P-P
Power Supply
I
S
Power Supply Current VIN = 0V, V+ to V– = 9V (Note 6) — 70 100 µA
NOTES: 1. Input voltages may exceed supply voltages when input current is limited to 100 µA.
2. Dissipation rating assumes device is mounted with all leads soldered to PC board.
3. Refer to "Differential Input" discussion.
4. Backplane drive is in-phase with segment drive for "OFF" segment and 180° out-of-phase for "ON" segment. Frequency is 20 times
conversion rate. Average DC component is less than 50 mV.
5. See "Typical Operating Circuit".
6. A 48 kHz oscillator increases current by 20 µA (typical). Common current not included.
TC7136
TC7136A
LOW POWER, 3-1/2 DIGIT
ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTERS

3-249
TELCOM SEMICONDUCTOR, INC.
7
6
5
4
3
1
2
8
PIN CONFIGURATIONS
TC7136CPL
TC7136ACPL
(PDIP)
1
2
3
4
OSC
1
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
TEST
V
ANALOG
COMMON
C
AZ
V
+
D
NORMAL PIN
CONFIGURATION
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
2
C
2
B
2
A
2
F
2
E
2
D
3
B
3
F
3
E
3
AB
4
10's
100's
1000's
100's
OSC
2
OSC
3
+
REF
V
–
REF
C
+
REF
C
–
REF
V
+
IN
V
–
IN
V
BUFF
V
INT
V
–
G
C
A
G
BP
(BACKPLANE)
POL
(MINUS SIGN)
3
3
3
2
TC7136RCPL
TC7136ARCPL
(Reversed)
PDIP
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
100's
1000's
100's
REVERSE PIN
CONFIGURATION
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
D
1
C
1
B
1
A
1
F
1
G
1
E
1
1's
V
+
D
2
C
2
B
2
A
2
F
2
E
2
D
3
B
3
F
3
E
3
AB
4
POL
(MINUS SIGN)
D
1
C
1
B
1
A
1
F
1
G
1
E
1
1's
10's
OSC
TEST
V
ANALOG
COMMON
C
AZ
OSC
2
OSC
+
REF
V
–
REF
C
+
REF
C
–
REF
V
+
IN
V
–
IN
V
BUFF
V
INT
V
–
G
C
A
G
BP
(BACKPLANE)
3
3
3
2
3
1
NC = NO INTERNAL CONNECTION
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
7
4
3
2
1
NC
TC7136CKW
TC7136ACKW
(PQFP)
12 13 14 15 17 18
G
44 43 42 41 39 3840
REF HI
COM
16
37AZ36
BUFF35INT34V
19 20 21 22
D
26
8
+
25
9
24
10
23
11
IN HI
5
6
C
OSC
TEST
NC
NC
V
3
3
D2C2B2A
2F2E2
NC
OSC
2
OSC
1
REF LO
REFCREF
C
IN LO
–
2
3
A
3
G
3
BP
POL
AB
4
E
3
F
3
B
3
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
13
10
9
8
7
COMMON
REF LO
18 19 20 21 23 24
3
AB
4
POL
NC
BP
IN HI
NC
IN LO
B
6543 1442
A
OSC
22
43
OSC42OSC41TEST40REF HI
25 26 27 28
F
E
G
A
C
G
3214
AZ
2
3115
BUFF
2
3016
INT
E
2917
D
NC
11
12
NC
C
D
3
2
F
A
2
2
2
B
3
3
3
3
3
2
TC7136CLW
TC7136ACLW
(PLCC)
1
2
3
V
–
1B1C1D1V+
F
1
G
1
E
1
D
1
C
1
B
1
A
1F1G1E1
+
–
REF
C
REF
C
+
–
LOW POWER, 3-1/2 DIGIT
ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTERS
TC7136
TC7136A

3-250
TELCOM SEMICONDUCTOR, INC.
TC7136
TC7136A
LOW POWER, 3-1/2 DIGIT
ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTERS
COMMON
TC7136/A PIN DESCRIPTION
Pin No.
40-Pin PDIP
Normal (Reverse) Name Description
1 (40) V
+
Positive supply voltage.
2 (39) D
1
Activates the D section of the units display.
3 (38) C
1
Activates the C section of the units display.
4 (37) B
1
Activates the B section of the units display.
5 (36) A
1
Activates the A section of the units display.
6 (35) F
1
Activates the F section of the units display.
7 (34) G
1
Activates the G section of the units display.
8 (33) E
1
Activates the E section of the units display.
9 (32) D
2
Activates the D section of the tens display.
10 (31) C
2
Activates the C section of the tens display.
11 (30) B
2
Activates the B section of the tens display.
12 (29) A
2
Activates the A section of the tens display
13 (28) F
2
Activates the F section of the tens display.
14 (27) E
2
Activates the E section of the tens display.
15 (26) D
3
Activates the D section of the hundreds display.
16 (25) B
3
Activates the B section of the hundreds display.
17 (24) F
3
Activates the F section of the hundreds display.
18 (23) E
3
Activates the E section of the hundreds display.
19 (22) AB
4
Activates both halves of the 1 in the thousands display.
20 (21) POL Activates the negative polarity display.
21 (20) BP Backplane drive output.
22 (19) G
3
Activates the G section of the hundreds display.
23 (18) A
3
Activates the A section of the hundreds display.
24 (17) C
3
Activates the C section of the hundreds display.
25 (16) G
2
Activates the G section of the tens display.
26 (15) V
–
Negative power supply voltage.
27 (14) V
INT
The integrating capacitor should be selected to give the maximum voltage
swing that ensures component tolerance build-up will not allow the integrator
output to saturate. When analog common is used as a reference and the
conversion rate is 3 readings per second, a 0.047 µF capacitor may be used.
The capacitor must have a low dielectric constant to prevent roll-over errors.
See Integrating Capacitor section for additional details.
28 (13) V
BUFF
Integration resistor connection. Use a 180 kΩ for a 200 mV full-scale range
and a 1.8 MΩ for 2V full-scale range.
29 (12) C
AZ
The size of the auto-zero capacitor influences the system noise. Use a 0.47 µF
capacitor for a 200 mV full scale, and a 0.1 µF capacitor for a 2V full scale. See
paragraph on Auto-Zero Capacitor for more details.
30 (11) V
IN
–
The low input signal is connected to this pin.
31 (10) V
IN
+
The high input signal is connected to this pin.
32 (9) ANALOG This pin is primarily used to set the analog common-mode voltage for battery
operation or in systems where the input signal is referenced to the power
supply. See paragraph on Analog Common for more details. It also acts as a
reference voltage source.

3-251
TELCOM SEMICONDUCTOR, INC.
7
6
5
4
3
1
2
8
GENERAL THEORY OF OPERATION
(All Pin designations refer to 40-Pin Dip)
Dual-Slope Conversion Principles
The TC7136/A is a dual-slope, integrating analog-todigital converter. An understanding of the dual-slope conversion technique will aid in following detailed TC7136/A
operational theory.
The conventional dual-slope converter measurement
cycle has two distinct phases:
(1) Input signal integration
(2) Reference voltage integration (deintegration)
The input signal being converted is integrated for a fixed
time period (tSI), measured by counting clock pulses. An
opposite polarity constant reference voltage is then integrated until the integrator output voltage returns to zero. The
reference integration time is directly proportional to the input
signal (tRI).
In a simple dual-slope converter, a complete conversion
requires the integrator output to "ramp-up" and "rampdown."
A simple mathematical equation relates the input signal,
reference voltage, and integration time:
TC7136/A PIN DESCRIPTION (Cont.)
Pin No.
40-Pin PDIP
Normal (Reverse) Name Description
33 (8) C
–
REF
See pin 34.
34 (7) C
+
REF
A 0.1 µF capacitor is used in most applications. If a large common-mode
voltage exists (for example, the V
IN
–
pin is not at analog common), and a 200
mV scale is used, a 1 µF capacitor is recommended and will hold the roll-over
error to 0.5 count.
35 (6) V
–
REF
See pin 36.
(5) V
–
REF
The analog input required to generate a full-scale output (1999 counts). Place
100 mV between pins 35 and 36 for 199.9 mV full scale. Place 1V between
pins 35 and 36 for 2V full scale. See paragraph on Reference Voltage.
36 (4) TEST Lamp test. When pulled HIGH (to V+) all segments will be turned ON and the
display should read –1888. It may also be used as a negative supply for externally-generated decimal points. See paragraph under Test for additional information.
37 (3) OSC
3
See pin 40.
38 (2) OSC
2
See pin 40.
39 (1) OSC
1
Pins 40, 39 and 38 make up the oscillator section. For a 48 kHz clock (3 readings per
second) connect pin 40 to the junction of a 180 kΩ resistor and a 50 pF capacitor. The
180 kΩ resistor is tied to pin 39 and the 50 pF capacitor is tied to pin 38.
For a constant VIN:
VIN = V
R
.
1V
R
t
RI
RC RC
VIN(t) dt = ,
t
SI
where:
VR= Reference voltage
tSI= Signal integration time (fixed)
tRI= Reference voltage integration time (variable).
Figure 1. Basic Dual-Slope Converter
+
–
REF
VOLTAGE
ANALOG
INPUT
SIGNAL
+
–
DISPLAY
SWITCH
DRIVER
CONTROL
LOGIC
INTEGRATOR
OUTPUT
CLOCK
COUNTER
POLARITY CONTROL
PHASE
CONTROL
V
IN
V
IN
V
FULL SCALE
1.2 V
FULL SCALE
VARIABLE
REFERENCE
INTEGRATE
TIME
FIXED
SIGNAL
INTEGRATE
TIME
INTEGRATOR
C
INT
COMPARATOR
'
'
t
RI
t
SI[
]
0
∫
LOW POWER, 3-1/2 DIGIT
ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTERS
TC7136
TC7136A

3-252
TELCOM SEMICONDUCTOR, INC.
TC7136
TC7136A
LOW POWER, 3-1/2 DIGIT
ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTERS
Figure 2. Normal-Mode Rejection of Dual-Slope Converter
The dual-slope converter accuracy is unrelated to the
integrating resistor and capacitor values, as long as they are
stable during a measurement cycle. Noise immunity is an
inherent benefit. Noise spikes are integrated, or averaged,
to zero during integration periods. Integrating ADCs are
immune to the large conversion errors that plague successive approximation converters in high-noise environments.
Interfering signals with frequency components at multiples
of the averaging period will be attenuated. Integrating ADCs
commonly operate with the signal integration period set to a
multiple of the 50 Hz/60 Hz power line period.
ANALOG SECTION
In addition to the basic integrate and deintegrate dualslope cycles discussed above, the TC7136/A designs incorporate an "integrator output-zero cycle" and an "auto-zero
cycle." These additional cycles ensure the integrator starts
at 0V (even after a severe overrange conversion) and that all
offset voltage errors (buffer amplifier, integrator and comparator) are removed from the conversion. A true digital zero
reading is assured without any external adjustments.
A complete conversion consists of four distinct phases:
(1) Integrator output-zero phase
(2) Auto-zero phase
(3) Signal integrate phase
(4) Reference deintegrate phase
Integrator Output-Zero Phase
This phase guarantees the integrator output is at 0V
before the system-zero phase is entered. This ensures that
true system offset voltages will be compensated for even
after an overrange conversion. The count for this phase is a
function of the number of counts required by the deintegrate
phase.
The count lasts from 11 to 140 counts for non-overrange
conversions and from 31 to 640 counts for overrange
conversions.
Auto-Zero Phase
During the auto-zero phase, the differential input signal
is disconnected from the circuit by opening internal analog
gates. The internal nodes are shorted to analog common
(ground) to establish a zero input condition. Additional
analog gates close a feedback loop around the integrator
and comparator. This loop permits comparator offset voltage error compensation. The voltage level established on
CAZ compensates for device offset voltages. The auto-zero
phase residual is typically 10 µV to 15 µV.
The auto-zero duration is from 910 to 2900 counts for
non-overrange conversions and from 300 to 910 counts for
overrange conversions.
Signal Integration Phase
The auto-zero loop is entered and the internal differential inputs connect to V
IN
+
and V
–
IN
. The differential input signal
is integrated for a fixed time period. The TC7136/A signal
integration period is 1000 clock periods or counts. The
externally-set clock frequency is divided by four before
clocking the internal counters. The integration time period is:
tSI = 3 1000,
where f
OSC
= external clock frequency.
The differential input voltage must be within the device
common-mode range when the converter and measured
system share the same power supply common (ground). If
the converter and measured system do not share the same
power supply common, V
–
IN
should be tied to analog com-
mon.
Polarity is determined at the end of signal integrate
phase. The sign bit is a true polarity indication, in that signals
less than 1 LSB are correctly determined. This allows
precision null detection limited only by device noise and
auto-zero residual offsets.
Reference Integrate Phase
The third phase is reference integrate or deintegrate. V
IN
–
is internally connected to analog common and V
IN
+
is connected across the previously-charged reference capacitor.
Circuitry within the chip ensures that the capacitor will be
connected with the correct polarity to cause the integrator
output to return to zero. The time required for the output to
return to zero is proportional to the input signal and is
between 0 and 2000 internal clock periods. The digital
reading displayed is:
1000
30
20
10
0
NORMAL MODE REJECTION (dB)
0.1/t 1/t 10/t
INPUT FREQUENCY
t = MEASUREMENT PERIOD
4
f
OSC
V
IN
V
REF

3-253
TELCOM SEMICONDUCTOR, INC.
7
6
5
4
3
1
2
8
TC7136/A
THOUSANDS
HUNDREDS
TENS UNITS
4
39
OSC
V
TES
T
1
TO SWITCH DRIVERS
FROM COMPARATOR OUTPUT
CLOCK
7 SEGMENT
DECODE
40 38
2
OSC
3
OSC
1
÷
CONTROL LOGIC
26
500
W
DATA LATCH
+
BUFF
C
REF
–
R
INT
V
+
C
AZ
V
INT
28
29
27333634
10
µA
31
ZI & AZ
INT
AZ & DE (±)
32
INT
26
INTEGRATOR
TO
DIGITAL
SECTION
DE (+)
DE
(–)
DE
(+)
DE (–)
ANALOG
COMMON
C
REF
+
V
IN
+
V
IN
–
V
C
INT
V
REF
+
V
REF
–
ZI &
AZ
C
REF
+
35
+
–
LCD SEGMENT DRIVERS
÷ 200
BP
f
OSC
V
–
V
TH
= 1V
V
–
+
–
INTERNAL DIGITAL GOUND
LOW
TEMPCO
V
REF
COMPARATOR
–
AZ
ZI
V
+
– 2.8V
1
R
OSC
C
OSC
7 SEGMENT
DECODE
7 SEGMENT
DECODE
21
TYPICAL SEGMENT OUTPUT
INTERNAL DIGITAL GROUND
SEGMENT
OUTPUT
V
+
0.5 mA
2 mA
6.2V
LCD
+
–
37
Figure 3. TC7136A Block Diagram
LOW POWER, 3-1/2 DIGIT
ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTERS
TC7136
TC7136A

3-254
TELCOM SEMICONDUCTOR, INC.
TC7136
TC7136A
LOW POWER, 3-1/2 DIGIT
ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTERS
Figure 4. Conversion Timing During Normal Operation
System Timing
The oscillator frequency is divided by 4 prior to clocking
the internal decade counters. The four-phase measurement cycle takes a total of 4000 counts, or 16,000 clock
Figure 5. Conversion Timing During Overrange Operation
DIGITAL SECTION
The TC7136/A contains all the segment drivers necessary to directly drive a 3-1/2 digit LCD. An LCD backplane
driver is included. The backplane frequency is the external
clock frequency divided by 800. For three conversions per
second the backplane frequency is 60 Hz with a 5V nominal
amplitude. When a segment driver is in-phase with the
backplane signal, the segment is OFF. An out-of-phase
segment drive signal causes the segment to be ON, or
visible. This AC drive configuration results in negligible DC
voltage across each LCD segment, ensuring long LCD life.
The polarity segment driver is ON for negative analog inputs.
If V
IN
+
and V
IN
–
are reversed, this indicator would reverse.
On the TC7136/A, when the TEST pin is pulled to V+, all
segments are turned ON. The display reads –1888. During
this mode the LCD segments have a constant DC voltage
impressed. DO NOT LEAVE THE DISPLAY IN THIS MODE
FOR MORE THAN SEVERAL MINUTES. LCDS MAY BE
DESTROYED IF OPERATED WITH DC LEVELS FOR
EXTENDED PERIODS.
The display font and segment drive assignment are
shown in Figure 6.
pulses. The 4000-count cycle is independent of input signal
magnitude.
Each phase of the measurement cycle has the following
length:
(1) Auto-zero phase: 3000 to 2900 counts
(1200 to 11,600 clock pulses)
(2) Signal integrate: 1000 counts
(4000 clock pulses)
This time period is fixed. The integration period is:
tSI = 4000 ,
where f
OSC
is the externally-set clock frequency.
(3) Reference integrate: 0 to 2000 counts
(4) Zero integrator: 11 to 640 counts
The TC7136 is a drop-in replacement for the TC7126
and ICL7126. The TC7136A offers a greatly-improved internal reference temperature coefficient. Minor component
value changes are required to upgrade existing designs and
improve the noise performance.
COMPONENT VALUE SELECTION
Auto-Zero Capacitor (CAZ)
The CAZ capacitor size has some influence on system
noise. A 0.47 µF capacitor is recommended for 200 mV fullscale applications where 1 LSB is 100 µV. A 0.1 µF capacitor
is adequate for 2V full-scale applications. A Mylar-type
dielectric capacitor is adequate.
Reference Voltage Capacitor (C
REF
)
The reference voltage, used to ramp the integrator
Figure 6. Display FONT and Segment Assignment
1
f
OSC
INT
DENT
ZI
AZ
4000
910–2900
1–2000
1000
11–140
AZ
4000
ZI
DEINT
INT
1000
2001–2090
31–640
300–910
DISPLAY FONT
1000's 100's 10's 1's

3-255
TELCOM SEMICONDUCTOR, INC.
7
6
5
4
3
1
2
8
Component
Value Nominal Full-Scale Voltage
200mV 2V
C
AZ
0.47 µF 0.1 µF
R
INT
180 kΩ 1.8 MΩ
C
INT
0.047 µF 0.047 µF
NOTE:f
OSC
= 48 kHz (3 readings per sec). R
OSC
= 180kΩ, C
OSC
= 50
output voltage back to zero during the reference integrate
phase, is stored on C
REF
. A 0.1 µF capacitor is acceptable
when V
–
REF
is tied to analog common. If a large common-
mode voltage exists (V
–
REF
≠ analog common) and the
application requires a 200 mV full scale, increase C
REF
to
1 µF. Roll-over error will be held to less than 0.5 count. A
Mylar-type dielectric capacitor is adequate.
Integrating Capacitor (C
INT
)
C
INT
should be selected to maximize integrator output
voltage swing without causing output saturation. Analog
common will normally supply the differential voltage reference this case, a ±2V full-scale integrator output swing is
satisfactory. For 3 readings per second (f
OSC
= 48 kHz) a
0.047 µF value is suggested. For one reading per second,
0.15 µF is recommended. If a different oscillator frequency
is used, C
INT
must be changed in inverse proportion to
maintain the nominal ±2V integrator swing.
An exact expression for C
INT
is:
Oscillator Components
C
OSC
should be 50 pF. R
OSC
is selected from the
equation:
f
OSC
= .
Note that f
OSC
is 44 to generate the TC7136A's internal
clock. The backplane drive signal is derived by dividing f
OSC
by 800.
To achieve maximum rejection of 60Hz noise pickup,
the signal integrate period should be a multiple of 60Hz.
Oscillator frequencies of 240kHz, 120kHz, 80kHz, 60kHz,
40kHz, etc. should be selected. For 50 Hz rejection, oscillator frequencies of 200kHz, 100kHz, 66-2/3 kHz, 50kHz,
40kHz, etc. would be suitable. Note that 40kHz (2.5 readings per second) will reject both 50Hz and 60Hz.
Reference Voltage Selection
A full-scale reading (2000 counts) requires the input
signal be twice the reference voltage.
0.45
RC
In some applications, a scale factor other than unity may
exist between a transducer output voltage and the required
digital reading. Assume, for example, a pressure transducer
output for 2000 lb/in.2 is 400 mV. Rather than dividing the
input voltage by two, the reference voltage should be set to
200 mV. This permits the transducer input to be used
directly.
The differential reference can also be used when a
digital zero reading is required when VIN is not equal to zero.
This is common in temperature measuring instrumentation.
A compensating offset voltage can be applied between
analog common and V
–
IN
The transducer output is connected
between V
+
IN
and analog common.
DEVICE PIN FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
Differential Signal Inputs
V
+
IN
(Pin 31), V
–
IN
(Pin 30)
The TC7136/A is designed with true differential inputs
and accepts input signals within the input stage commonmode voltage range (VCM). The typical range is V+ –1V to V
–
+1V. Common-mode voltages are removed from the system
when the TC7136A operates from a battery or floating power
source (isolated from measured system), and V
IN
–
is con-
nected to analog common (V
COM
). (See Figure 7.)
Required Full-Scale Voltage* V
REF
200 mV 100 mV
2V 1V
*VFS = 2 V
REF
.
where: f
OSC
= Clock frequency at pin 38
VFS= Full-scale input voltage
R
INT
= Integrating resistor
V
INT
= Desired full-scale integrator output swing.
C
INT
must have low dielectric absorption to minimize
roll-over error. A polypropylene capacitor is recommended.
Integrating Resistor (R
INT
)
The input buffer amplifier and integrator are designed
with Class A output stages. The output stage idling current
is 6 µA. The integrator and buffer can supply 1 µA drive
currents with negligible linearity errors. R
INT
is chosen to
remain in the output stage linear drive region, but not so
large that PC board leakage currents induce errors. For a
200 mV full scale, R
INT
is 180 kΩ. A 2V full scale requires
1.8 MΩ.
C
INT
=,
1
f
OSC
(
V
FS
R
INT
()
)
(4000)
V
INT
LOW POWER, 3-1/2 DIGIT
ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTERS
TC7136
TC7136A

3-256
TELCOM SEMICONDUCTOR, INC.
Figure 7. Common-Mode Voltage Removed in Battery Operation With VIN = Analog Common
In systems where common-mode voltages exist, the
86 dB common-mode rejection ratio minimizes error. Common-mode voltages do, however, affect the integrator output level. A worst-case condition exists if a large positive
VCM exists in conjunction with a full-scale negative differential signal. The negative signal drives the integrator
output positive along with VCM (see Figure 8.) For such
applications, the integrator output swing can be reduced
below the recommended 2V full-scale swing. The integrator output will swing within 0.3V of V+ or V– without increased linearity error.
Differential Reference
V
+
REF
(Pin 36), V
–
REF
(Pin 35)
The reference voltage can be generated anywhere
within the V+ to V– power supply range.
To prevent roll-over type errors being induced by large
common-mode voltages, C
REF
should be large compared to
stray node capacitance.
The TC7136/A offers a significantly improved analog
common temperature coefficient. This potential provides a
very stable voltage, suitable for use as a voltage reference.
The temperature coefficient of analog common is typically
35 ppm/°C.
ANALOG COMMON (Pin 32)
The analog common pin is set at a voltage potential
approximately 3V below V+. The potential is guaranteed to
be between 2.7V and 3.35V below V+. Analog common is
tied internally to an N-channel FET capable of sinking
100µA. This FET will hold the common line at 3V below V
+
if an external load attempts to pull the common line toward
V+. Analog common source current is limited to 1 µA. Analog
common is therefore easily pulled to a more negative
voltage (i.e., below V+ – 3V).
The TC7136/A connects the internal V
IN
+
and V
IN
–
inputs to analog common during the auto-zero phase. During
the reference-integrate phase, V
IN
–
is connected to analog
common. If V
IN
–
is not externally connected to analog common, a common-mode voltage exists, but is rejected by the
converter's 86 dB common-mode rejection ratio. In battery
operation, analog common and V
IN
–
are usually connected,
removing common-mode voltage concerns. In systems where
V
IN
–
is connected to the power supply ground or to a given
voltage, analog common should be connected to V
–
IN
The analog common pin serves to set the analog section reference, or common point. The TC7136A is specifically designed to operate from a battery or in any measurement system where input signals are not referenced (float)
with respect to the TC7136A power source. The analog
common potential of V+ –3V gives a 7V end of battery life
voltage. The common potential has a 0.001%/% voltage
coefficient.
With sufficiently high total supply voltage (V+–V– >7V),
Figure 8. Common-Mode Voltage Reduces Available Integrator
Swing (V
COM
≠ VIN)
V
BUF
CAZV
INT
BPPOL
SEGMENT
DRIVE
OSC
1
OSC
3
OSC
2
V
–
V
+
V
REF
+
V
REF
–
ANALOG
COMMON
V
–
V
+
V
–
V
+
GND
GND
MEASURED
SYSTEM
POWER
SOURCE
9V
LCD
TC7136
TC7136A
+
V
–
V
+
R
I
+
–
V
IN
V
C
I
INTEGRATOR
V
I
=
[
[
V
CMVIN
–
INPUT
BUFFER
C
I
=
=
R
I
Integration capacitor
Integration resistor
4000
f
Integration timeT
I
==
Where:
V
I
CM
OSC
–
+
–
+
T
I
R
I CI
TC7136
TC7136A
LOW POWER, 3-1/2 DIGIT
ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTERS

3-257
TELCOM SEMICONDUCTOR, INC.
7
6
5
4
3
1
2
8
V
–
ANALOG
COMMON
TC7136
TC7136A
V
REF
+
32
35
36
26
240 kΩ
10 kΩ
V
REF
–
V
REF
1
+
9V
SET V
REF
= 1/2 V
FULL SCALE
V
+
analog common is a very stable potential with excellent
temperature stability (typically 35 ppm/°c). for TC7136A
This potential can be used to generate the TC7136A's
reference voltage. An external voltage reference will be
unnecessary in most cases because of the 35 ppm/°C
temperature coefficient. See TC7136A Internal Voltage
Reference discussion.
TEST (Pin 37)
The TEST pin potential is 5V less than V+. TEST may be
used as the negative power supply connection for external
CMOS logic. The TEST pin is tied to the internally-generated
negative logic supply through a 500Ω resistor. The TEST pin
load should not be more than 1 mA. See the Applications
Section for additional information on using TEST as a
negative digital logic supply.
If TEST is pulled high (to V+), all segments plus the
minus sign will be activated. DO NOT OPERATE IN THIS
MODE FOR MORE THAN SEVERAL MINUTES. With TEST
= V+, the LCD segments are impressed with a DC voltage
which will destroy the LCD.
TC7136A Internal Voltage Reference
The TC7136 analog common voltage temperature stability has been significantly improved (Figure 9). The "A"
version of the industry-standard TC7136 device allows
users to upgrade old systems and design new systems
without external voltage references. External R and C values do not need to be changed; however, noise performance will be improved by increasing CAZ. (See Auto-Zero
Capacitor section.) Figure 10 shows analog common supplying the necessary voltage reference for the TC7136/A.
Figure 9. Analog Common Temperature Coefficient
Decimal Point and Annunciator Drive
The TEST pin is connected to the internally-generated
digital logic supply ground through a 500Ω resistor. The
TEST pin may be used as the negative supply for external
CMOS gate segment drivers. LCD annunciators for decimal
points, low battery indication, or function indication may be
added without adding an additional supply. No more than 1
mA should be supplied by the TEST pin: its potential is
approximately 5V below V+.
TYPICAL
GUARANTEED
MAXIMUM
TYPICAL
GUARANTEED
MAXIMUM
TYPICAL
NO MAXIMUM
SPECIFIED
200
180
160
140
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
ANALOG COMMON
TEMPERATURE COEFFICIENT (ppm/°C)
TC7136TC7136A
ICL7136
Figure 10. TC7136A Internal Voltage Reference Connection
APPLICATIONS INFORMATION
Liquid Crystal Display Sources
Several manufacturers supply standard LCDs to interface with the TC7136A 3-1/2 digit analog-to-digital converter.
Representative
Manufacturer Address/Phone Part Numbers
*
Crystaloid 5282 Hudson Dr. C5335, H5535,
Electronics Hudson, OH 44236 T5135, SX440
216-655-2429
AND 720 Palomar Ave. FE 0201, 0501
Sunnyvale, CA 94086 FE 0203, 0701
408-523-8200 FE 2201
VGI, Inc. 1800 Vernon St. Ste. 2 I1048, I1126
Roseville, CA 95678
916-783-7878
Hamlin, Inc. 612 E. Lake St. 3902, 3933, 3903
Lake Mills, WI 53551
414-648-2361
*
NOTE:
Contact LCD manufacturer for full product listing/specifications.
LOW POWER, 3-1/2 DIGIT
ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTERS
TC7136
TC7136A

3-258
TELCOM SEMICONDUCTOR, INC.
TC7136
TC7136A
LOW POWER, 3-1/2 DIGIT
ANALOG-TO-DIGIT AL CONVERTERS
Figure 11. Decimal Point and Annunciator Drives
Figure 13. Temperature Sensor
Figure 12. Low Parts Count Ratiometric Resistance
Measurement
TC7136
TC7136A
V
+
V
–
V
IN
–
V
IN
+
V
REF
+
V
REF
–
COMMON
5.6 kΩ 160 kΩ
R
2
20 kΩ
1N4148
9V
R
1
20 kΩ
+
R
3
0.7%/°C
PTC
TC7136
TC7136A
V
+
V
–
V
IN
–
V
IN
+
V
REF
+
V
REF
–
COMMON
50 kΩ
R
2
160 kΩ 300 kΩ 300 kΩ
R
1
50 kΩ
1N4148
SENSOR
9V
+
Ratiometric Resistance Measurements
The TC7136A's true differential input and differential
reference make ratiometric readings possible. In ratiometric
operation, an unknown resistance is measured with respect
to a known standard resistance. No accurately-defined
reference voltage is needed.
The unknown resistance is put in series with a known
standard and a current passed through the pair. The voltage
developed across the unknown is applied to the input and
the voltage across the known resistor applied to the reference input. If the unknown equals the standard, the display
will read 1000. The displayed reading can be determined
from the following expression:
Displayed reading = × 1000.
The display will overrange for R
UNKNOWN
≥
2×R
STANDARD
.
R
UNKNOWN
R
STANDARD
V
REF
+
V
REF
–
V
IN
+
V
IN
–
ANALOG
COMMON
TC7136
TC7136A
LCD
R
STANDARD
R
UNKNOWN
V
+
V
+
V
+
TC7136
TC7136A
V
+
V
+
TC7136
TC7136A
4049
4030
BP
TEST
BP
TEST
GND
GND
TO LCD
DECIMAL
POINT
TO LCD
BLACK
PLANE
TO LCD
DECIMAL
POINTS
DECIMAL
POINT
SELECT
21
37
Multiple Decimal Point or
Annunciator Driver
Simple Inverter for Fixed Decimal Point
or Display Annunciator
Figure 14. Positive Temperature Coefficient Resistor
Temperature Sensor
 Loading...
Loading...