TEL S1A, S1B, S1D, S1K, S1J Datasheet
...
S1A THRU S1M
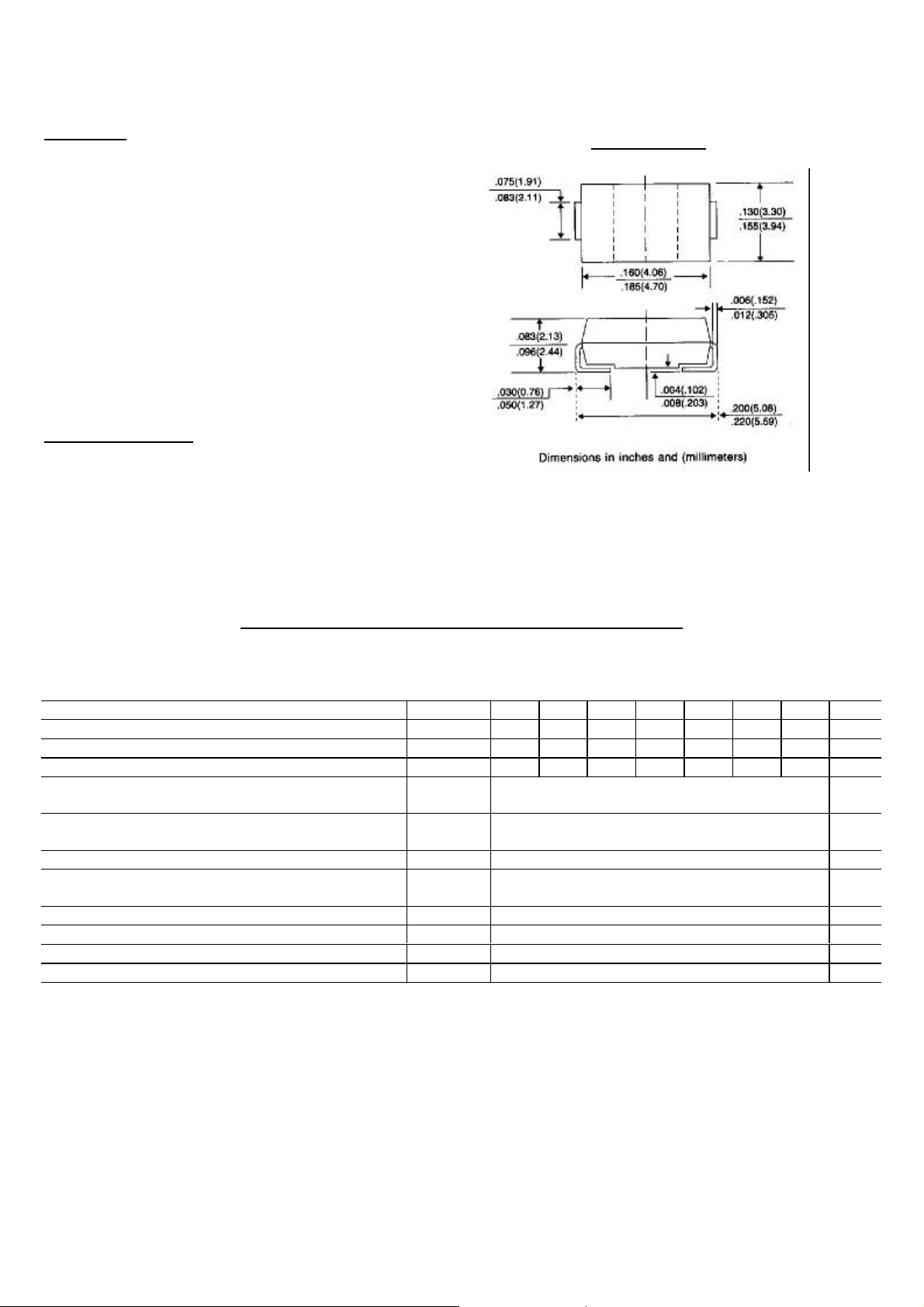
SURFACE MOUNT RECTIFIER
SMA/DO-214AA
VOLTAGE - 50 to 1000 Volts CURRENT - 1.0 Ampere
FEATURES
l For surface mounted applications
l High temperature metallurgically bonded-no
compression contacts as found in other
diode-constructed rectifiers
l Glass passivated junction
l Built-in strain relief
l Easy pick and place
l Plastic package has Underwriters Laboratory
Flammability Classification 94V-O
l Complete device submersible temperature of
260for 10 seconds in solder bath
MECHANICAL DATA
Case: JEDEC DO-214AA molded plastic
Terminals: Solder plated, solderable per MIL-STD-750,
Method 2026
Polarity: Indicated by cathode band
Standard packaging: 12mm tape (EIA-481)
Weight: 0.003 ounce, 0.093 gram
MAXIMUM RATINGS AND ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Ratings at 25 ambient temperature unless otherwise specified.
Single phase, half wave, 60 Hz, resistive or inductive load.
For capacitive load, derate current by 20%.
SYMBOLS S1A S1B S1D S1G S1J S1K S1M UNITS
Maximum Recurrent Peak Reverse Voltage V
Maximum RMS Voltage V
Maximum DC Blocking Voltage V
Maximum Average Forward Rectified Current,
RRM
RMS
I
(AV)
DC
50 100 200 400 600 800 1000
35 70 140 280 420 560 700
50 100 200 400 600 800 1000
1.0 Amps
Volts
Volts
Volts
at TL=100
Peak Forward Surge Current 8.3ms single half sine-
I
FSM
30.0 Amps
wave superimposed on rated load(JEDEC method)
Maximum Instantaneous Forward Voltage at 1.0A V
Maximum DC Reverse Current TA=25
At Rated DC Blocking Voltage TA=125
Maximum Reverse Recovery Time (Note 1) T
Typical Junction capacitance (Note 2) C
F
I
R
RR
J
1.10 Volts
5.0
A
50
2.5 S
12
P
Typical Thermal Resistance (Note 3) RJL 30.0 /W
Operating and Storage Temperature Range TJ,T
STG
-55 to +150
NOTES:
1. Reverse Recovery Test Conditions: I
=0.5A, IR=1.0A, Irr=0.25A
F
2. Measured at 1 MHz and Applied Vr=4.0 volts
3. 8.0mm
2
(.013mm thick) land areas
F
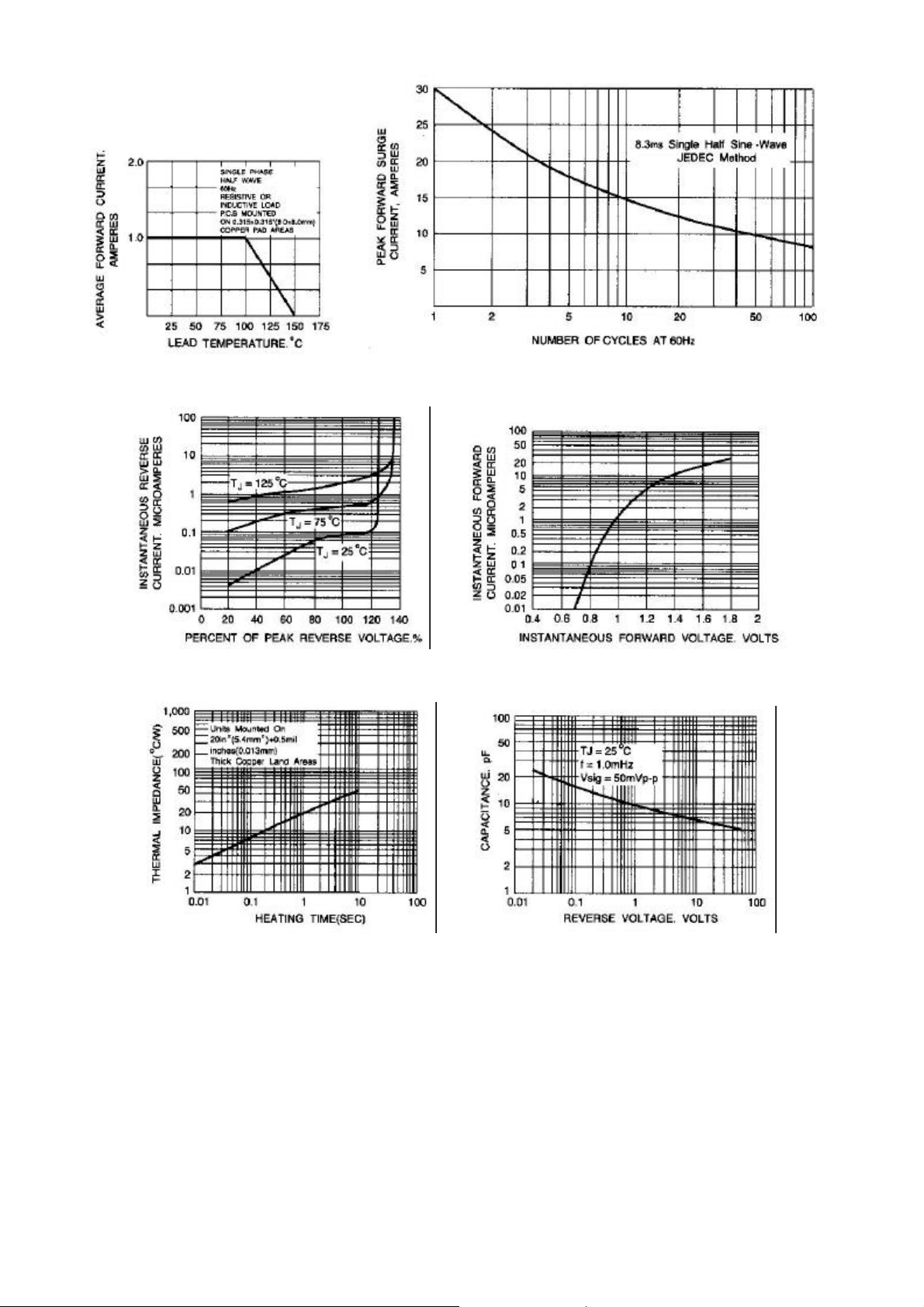
RATING AND CHARACTERISTIC CURVES
S1A THRU S1M
Fig. 1-FORWARD CURRENT DERATING CURVE Fig. 2-MAXIMUM NON-REPETITIVE PEAK
FORWARD SURGE CURRENT
Fig. 3-TYPICAL REVERSE CHARACTERISTICS Fig. 4-TYPICAL INSTANTANEOUS FORWARD
CHARACTERISTICS
Fig. 5-TRANSIENT THERMAL IMPEDANCE Fig. 6-TYPICAL JUNCTION CAPACITANCE
 Loading...
Loading...