TEL GBU8A, GBU8J, GBU8J, GBU8G, GBU8G Datasheet
...
GBU8A THRU GBU8K
GLASS PASSIVATED SINGLE-PHASE BRIDGE RECTIFIER
VOLTAGE - 50 to 800 Volts CURRENT - 8.0 Amperes
FEATURES
l Plastic package has Underwriters Laboratory
Flammability Classification 94V-O
l Ideal for printed circuit board
l Reliable low cost construction utilizing molded
plastic technique
l Surge overload rating: 200 Amperes peak
l High temperature soldering guaranteed:
260/10 seconds/.375”(9.5mm) lead length
at 5 lbs. (2.3kg) tension
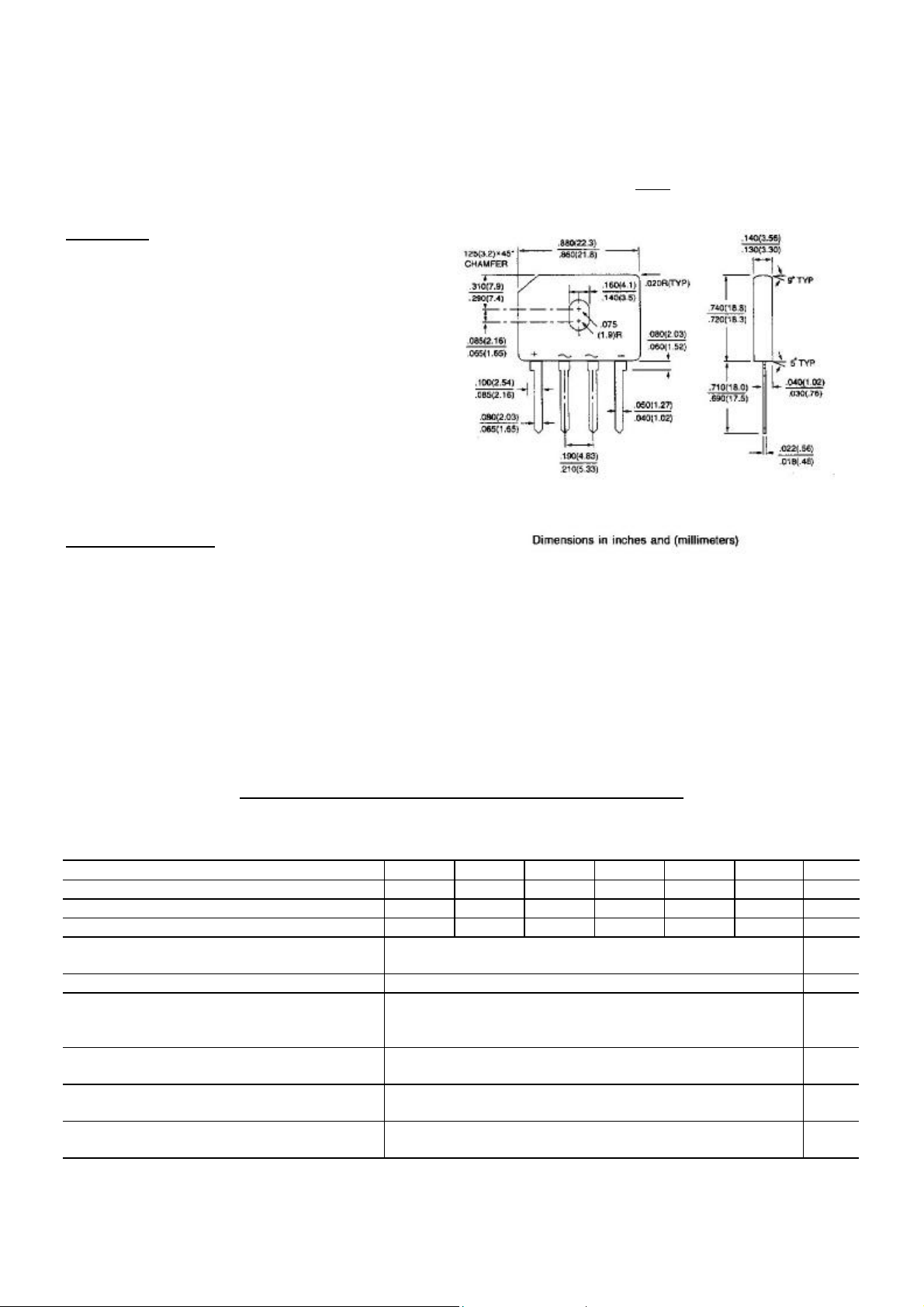
MECHANICAL DATA
Case: Reliable low cost construction utilizing
molded plastic technique
Terminals: Leads solderable per MIL-STD-202,
GBU
Method 208
Mounting position: Any
Mounting torque: 5 in. lb. Max.
Weight: 0.15 ounce, 4.0 grams
MAXIMUM RATINGS AND ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Rating at 25ambient temperature unless otherwise specified. Resistive or inductive load, 60Hz.
For Capacitive load derate current by 20%.
Maximum Recurrent Peak Reverse Voltage 50 100 200 400 600 800 V
Maximum RMS Input Voltage 35 70 140 280 420 560 V
GBU8A GBU8B GBU8D GBU8G GBU8J GBU8K UNITS
Maximum DC Blocking Voltage 50 100 200 400 600 800 VDC
Maximum Average Forward TC=100
Rectified Output Current at TA=45
8.0
6.0
I2t Rating for fusing ( t<8.3ms) 166 A2Sec
Peak Forward Surge Current single sine-
200 APK
wave superimposed on rated load
(JEDEC method)
Maximum Instantaneous Forward Voltage
Drop per element at 8.0A
Maximum Reverse Leakage at rated TA=25
Dc Blocking Voltage per element TC=100
Typical Thermal Resistance per leg (Note 2) RJA
Typical Thermal Resistance per leg (Note 3) RJL
1.0
5.0
500
18.0
3.0
RRM
RMS
A
(AV)
A
(AV)
VPK
A
A
/W
Operating and Storage Temperature Range,
TJ,T
-55 TO +150
STG
NOTES:
1. Recommended mounting position is to bolt down on heatsink with silicone thermal compound
for maximum heat transfer with #6 screw.
2. Units Mounted in free air, no heatsink, P.C.B at 0.375”(9.5mm) lead length with 0.5×0.5”
(12×12mm)copper pads.
3. Units Mounted on a 3.0×3.0” ×0.11” thick (7.5×7.5×0.3cm) AL plate heatsink.
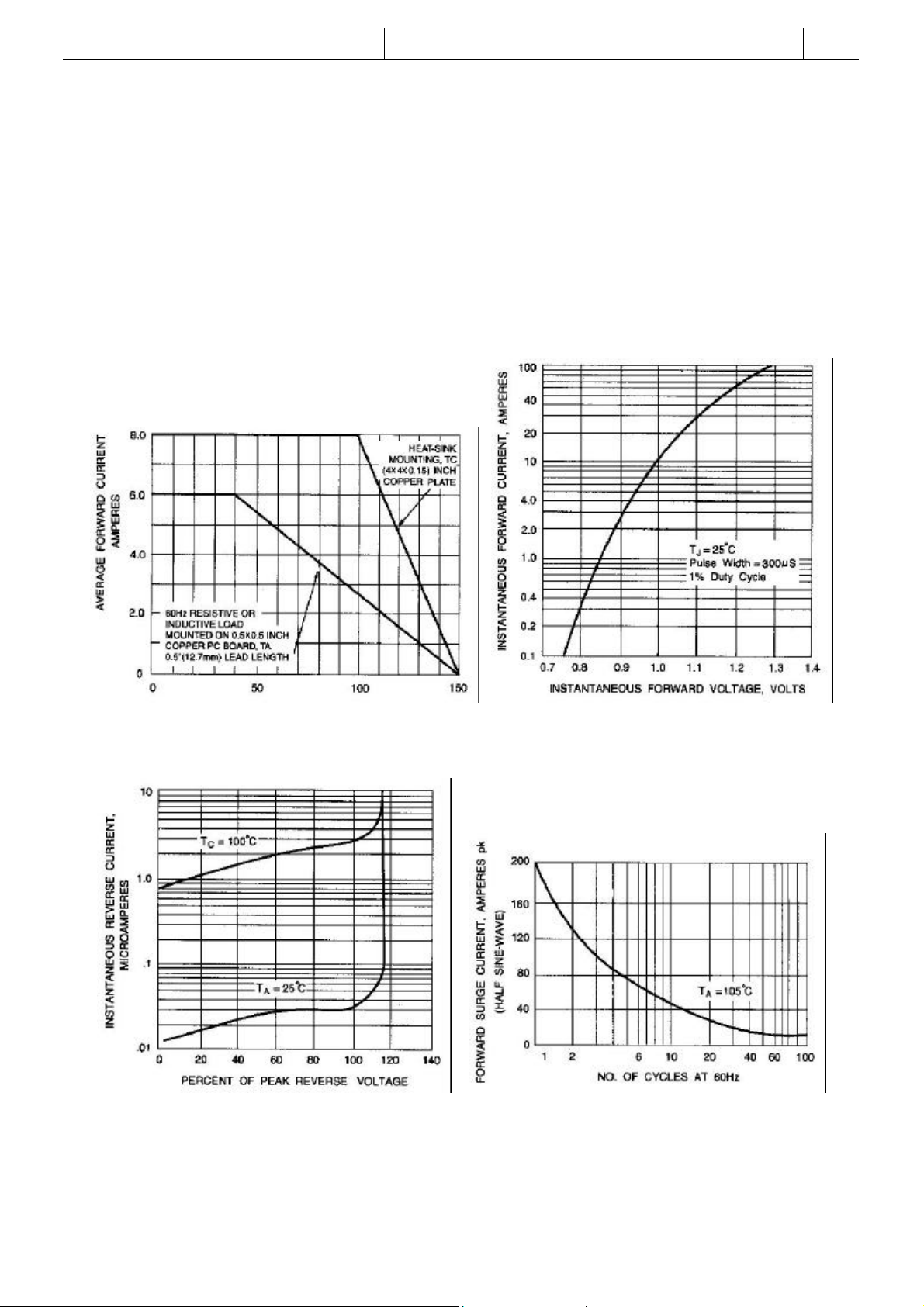
RATING AND CHARACTERISTIC CURVES
GBU8A THRU GBU8K
Fig. 1-DERATING CURVE FOR OUTPUT Fig. 2-TYPICAL INSTANTANEOUS FORWARD
RECTIFIED CURRENT CHARACTERISTICS PER ELEMENT
Fig. 3-TYPICAL REVERSE CHARACTERISTICS Fig. 4- MAXIMUM NON-REPETITIVE PEAK
FORWARD SURGE CURRENT
 Loading...
Loading...