TEL DI158, DI158, DI156, DI156, DI154 Datasheet
...
DI100/150 THRU DI1010/1510
DUAL-IN-LINE GLASS PASSIVATED SINGLE-PHASE BRIDGE RECTIFIER
VOLTAGE - 50 to 1000 Volts CURRENT - 1.0~1.5 Amperes
FEATURES
l Plastic material used carries Underwriters
Laboratory recognition 94V-O
l Low leakage
l Surge overload rating— 30~50 amperes peak
l Ideal for printed circuit board
l Exceeds environmental standards of
MIL-S-19500/228
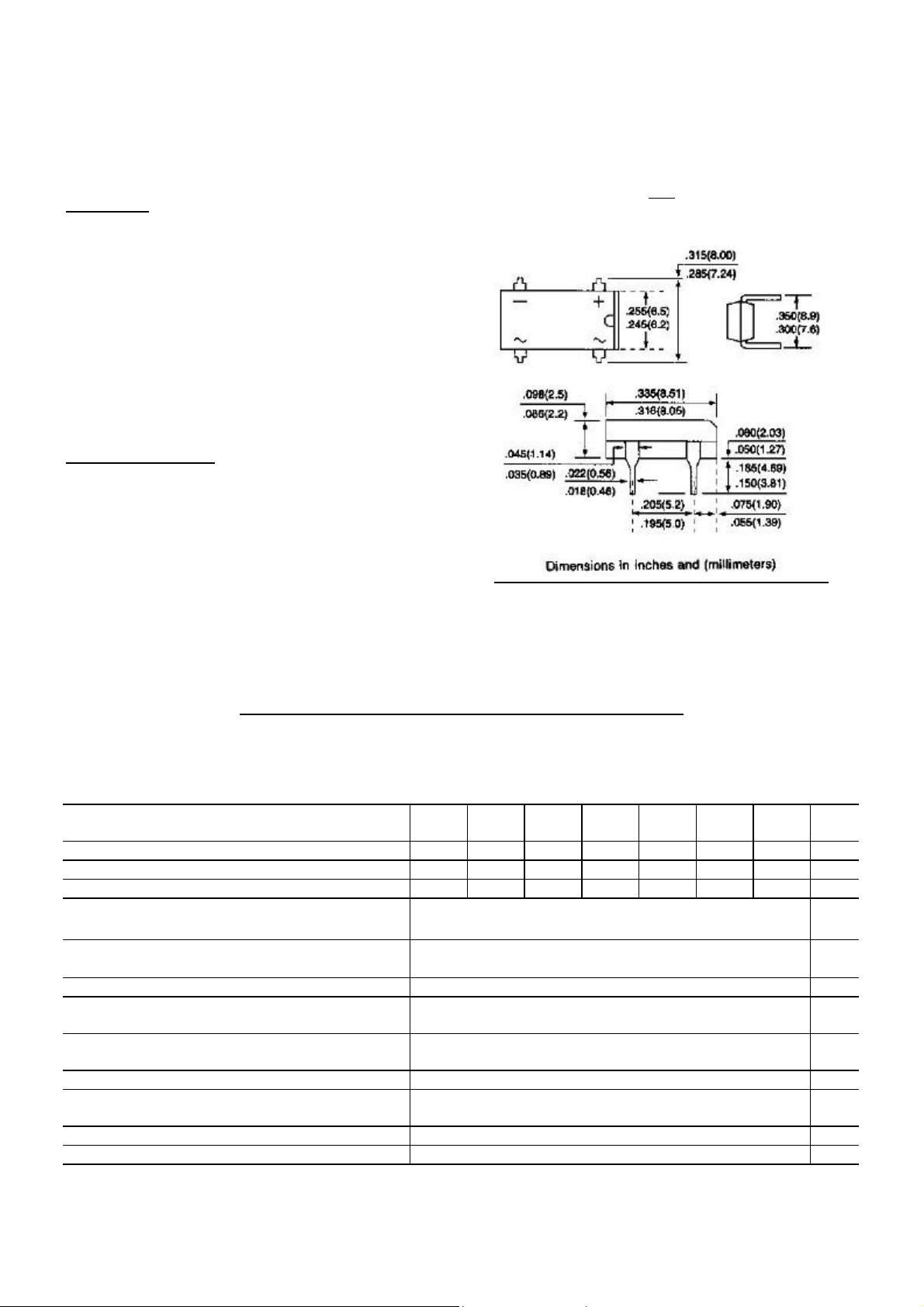
MECHANICAL DATA
Case: Reliable low cost construction utilizing molded
plastic technique results in inexpensive product
Terminals: Lead solderable per MIL-STD-202,
Method 208
Polarity: Polarity symbols molded or marking on body
Mounting Position: Any
DIP
Weight: 0.02 ounce, 0.4 gram
MAXIMUM RATINGS AND ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Ratings at 25 ambient temperature unless otherwise specified.
Single phase, half wave, 60Hz, Resistive or inductive load.
For capacitive load, derate current by 20%.
Maximum Recurrent Peak Reverse Voltage 50 100 200 400 600 800 1000
Maximum RMS Bridge input Voltage 35 70 140 280 420 560 700
DI100
DI150
DI101
DI151
DI102
DI152
DI104
DI154
DI106
DI156
DI108
DI158
DI1010
DI1510
Maximum DC Blocking Voltage 50 100 200 400 600 800 1000
DI100
TA=40
Peak Forward Surge Current, 8.3ms single
half sine-wave superimposed on rated load
I2t Rating for fusing ( t < 8.35 ms) 10.0 A2t
Maximum Forward Voltage Drop per Bridge
DI150
DI100
DI150
1.0 Maximum Average Forward Current
1.5
30.0
50.0
1.1 V
Element at 1.0A
Maximum Reverse Current at Rated TJ= 25
DC Blocking Voltage per element TJ=125
Typical Junction capacitance per leg (Note 1) CJ
Typical Thermal resistance per leg (Note 2) RJA
Typical Thermal resistance per leg (Note 2) RJL
Operating Temperature Range T
Storage Temperature Range T
J
A
5.0
0.5
25.0
40.0
15.0
-55 to +125
-55 to +150
UNITS
V
V
V
A
A
A
mA
F
P
/W
NOTES:
1. Measured at 1.0 MHz and applied reverse voltage of 4.0 Volts
2. Thermal resistance from junction to ambient and from junction to lead mounted on P.C.B. with
0.5×0.5”(13×13mm) copper pads
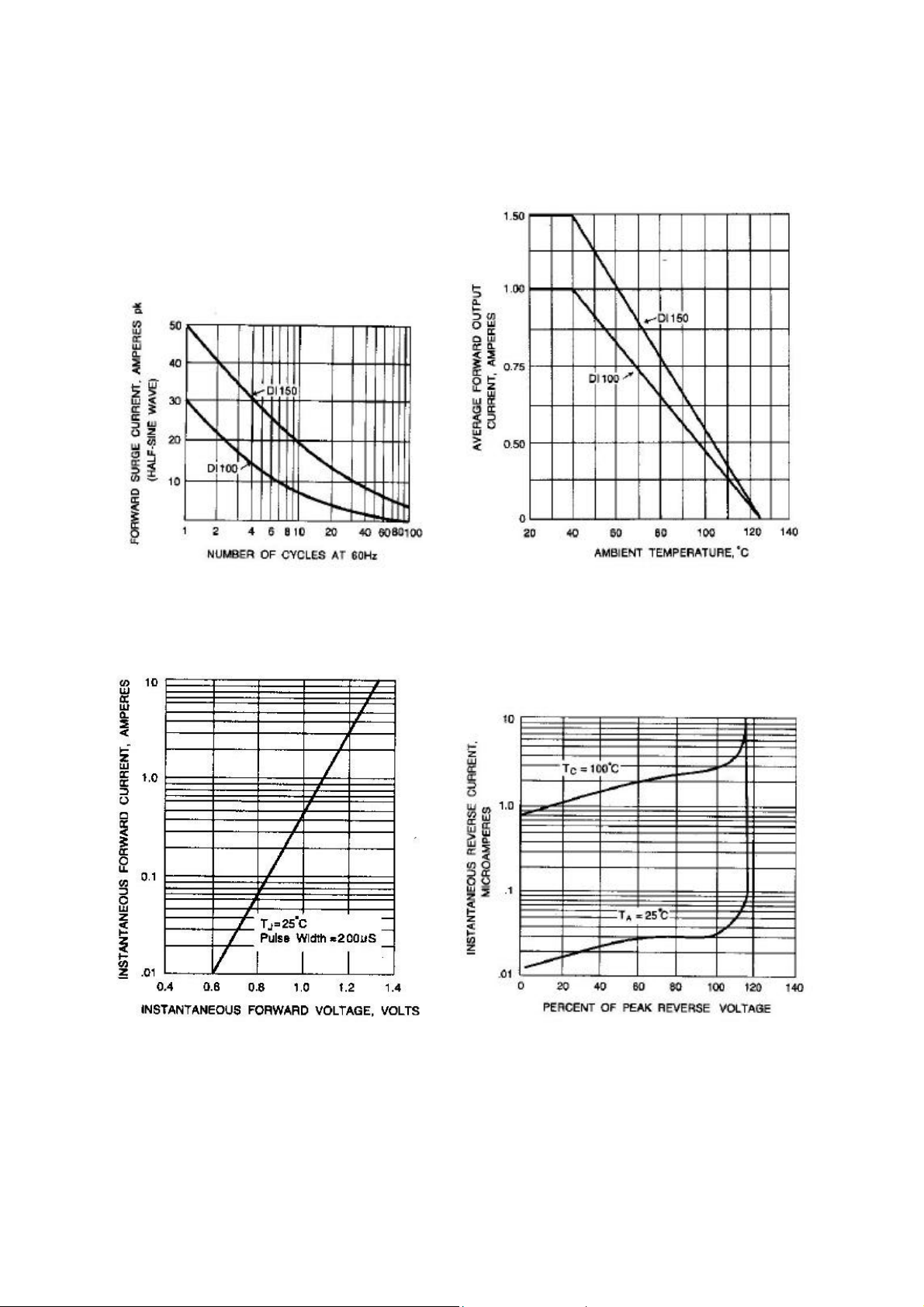
RATING AND CHARACTERISTIC CURVES
DI100/150 THRU DI1010/1510
Fig. 1-MAXIMUM NON-REPETITIVE SURGE CURRENT Fig. 2-DERATING CURVE FOR OUTPUT RECTIFIED
CURRENT
Fig. 3-TYPICAL FORWARD CHARACTERISTICS Fig. 4-TYPICAL REVERSE CHARACTERISTICS
 Loading...
Loading...