
28 JULY 2016
TBS2000 Oscilloscope
Demo Guide

28 JULY 2016 2
Table of Contents
TBS2000 Series Oscilloscopes
About This Guide & Required Equipment
Setting up the Equipment
Front Panel Tour
Understanding the Display
1. Activating HelpEverywhere Tips
2. Using the Scope Intro Built-in Handbook
3. Using Autoset to Acquire a Waveform
4. Triggering the Scope
5. Using Pan and Zoom to Navigate through Long Records
6: Using Cursors to Measure Time and Amplitude
7. Making Automated Measurments
8. Using an FFT to Analyze Signal’s Frequency Spectrum
9. Saving Screen Images
10. Setting up a Wireless Connection
11. Using LXI for Remote Control
12. Updated Courseware function with step reference
13. Configure lab with TBS2000 and TekSmartlab software
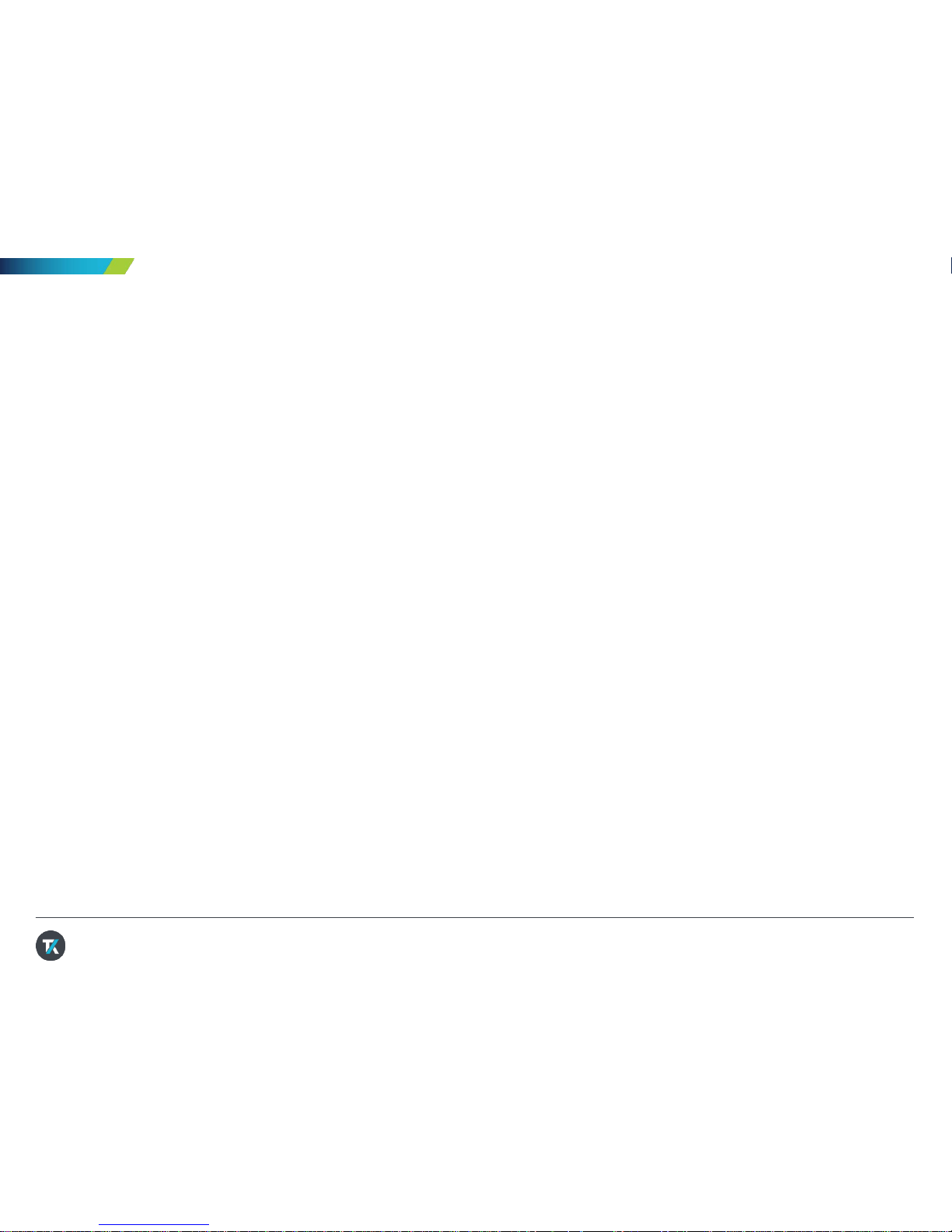
28 JULY 2016 3
TBS2000 Series Oscilloscopes
The TBS2000 offers the biggest display and longest record length in its class, so you can see
more of your signals. It offers a powerful set of measurement and analysis tools with built-in
tips make them easy to use.
◦ 100, 70 MHz bandwidth models
◦ 2 and 4 analog channel models
◦ U p to 1 GS/s sampling rate
◦ 9-inch WVGA color display
◦ 15 horizontal grids for 50% more signal
◦ TekVPI™ probe interface supports active
differential, and current probes with
automatic scaling and units
◦ Wi-Fi dongle supports wireless connectivity
◦ 32 automated measurements, and FFT
function for thorough waveform analysis
Key performance specifications
Key features
◦ Configurable HelpEverywhere provides on-
screen tips for specified settings
◦ 2-channel models are highly-portable at
2.62 kg
◦ Built-in Scope Intro handbook provides
operating instructions and oscilloscope
fundamentals
◦ Courseware education feature with step
assistant
◦ TekSmartlab collaboration working flow
assistant
◦ 20 megapoint record length on all channels
◦ 5-y ear w arranty

28 JULY 2016 4
About This Guide
Begin by exploring the control s and di splay of the
TBS2000 Series. Then move on to a series of hands-on
exercises. Ac qui re w av eforms, learn about trig ger ing ,
take measurements, and learn how to save data. Get an
introduction to the TBS2000’s connec tivi ty and remote
control capabiliti es, and tools for education .
◦ T BS2000 Series Oscilloscope
◦ Power Cord for your region (included with
instrument)
◦ Two TPP0100 passive probes with hook tips
attached (included with instrument)
◦ A USB flash drive (to demonstrate screen image
capture)
◦ TEKUSBWIFI USB Wi-Fi dongle (to demonstrate
wireless communications)
◦ PC with Ethernet connection (to demonstrate LXI)
◦ Ethernet cable (to demonstrate LXI)
Required Equipment

28 JULY 2016 5
Setting up the Equipment
Power on the instrument
1. Plug in the power cord for your region
2. Press the power button to turn on the instrument. Allow the instrument’s power-up
sequence to finish.
3. Connect TPP0100 passive probes to Channel 1 and Channel 2
To see the firmware version
1. Press the Utility button
2. Press the Configuration bezel button
3. Scroll the Multipurpose knob to highlight System Status, and press the
Multipurpose knob to enter the System Status menu
4. Review the firmware version at the bottom. Visit
www.tek.com for the latest firmware.

6
Front Panel Tour, Two-Channel Models
Courseware
Student Lab
Support
HelpEverywhere
and Scope Intro
Multipurpose knob for
Waveform Navigation &
Quick Oscilloscope Setup
Probe
Compensation
Output
TekVPI™ Probe
interface
One-Button Save
USB Flash Drive (Host)
Port
9-inch WVGA Display
Menu On/Off
Power On/Off

7
Front Panel Tour, Four-Channel Models
Courseware
Student Lab
Support
HelpEverywhere
and Scope Intro
Multipurpose knob for
Waveform Navigation &
Quick Oscilloscope Setup
Probe Compensation
Output
TekVPI™ Probe interface
One-Button Save
USB Flash Drive (Host) Port
9-inch WVGA Display
Menu On/Off
Power On/Off

28 JULY 2016 8
Understanding the Display
Waveform
Record View
Wireless
Connectivity
Indicator
LAN Connectivity
Indicator
Data Transfer
in process
Time/Date
Hardware based Counter
Sample Rate and Record Length
Horizontal Scale
Trigger Delay
Vertical Scale
Channel Indicator
Active Channel
Acquisition Status
Trigger Status
HelpEverywhere
Enabled

28 JULY 2016 9
1. Activating HelpEverywhere
Tips
While you’re learning your way around the scope,
HelpEverywher e pr ovides helpful tips . Once you
become proficient, you can turn the tips off if you
wish.
1. Press Function button on the front panel
2. Press HelpEverywhere bezel button (Figure
1).
3. Select Set A ll to On by pressing the
Multipurpose Knob (MPK)
4. When you use the Trigger, Measure, and
Cursor function lat er on, y ou’ l l see
HelpEverywher e tips that expl ain tr igg er
modes, measurements, and cur sor ty pes
(Figure 2).
Figure 1. Turning on HelpEverywhere
Figure 2. A HelpEverwhere tip helps with FFT setup. You’ll
see more tips as you work through the rest of this booklet.

28 JULY 2016 10
2. Using the Scope Intro Builtin Handbook
If you get stuck, or want to know more about a
particular control, Scope Intro provides a built-in,
handy reference.
1. Press Function button on the front panel
2. Press Scope Intro bezel button (Figure 3)
3. Select Oscilloscope Basic with the
Multipurpose Knob (MPK)
4. Select Why use an oscilloscope
5. Use the MPK to scroll through the c ontent
(Figure 4)
6. Press Scope Intro again back to the top
menu, and explore the other topics.
TBS2000 Overview giv es good expl anatio n
of the instrument’s controls and menus .
7. Press Menu On/Off to exit Scope Intro when
you are finished exploring.
Figure 3. Selecting Oscilloscope Basics
Figure 4. Using the Multipurpose Knob to scroll through
the handbook

28 JULY 2016 11
3. Using Autoset to Acquire a
Waveform
Autoset can often provide a stable signal display,
automatically.
1. Attach a TPP0100 passive probe to the
Channel 1 BNC connector . Clip the probe tip
to the Probe Comp output. Cli p the g r ound
clip to the Probe Comp ground terminal.
2. Press Default Setup in Resources section of
the front panel. This will set the scope into
it’s default state.
3. Press Autoset at the top of the front panel to
automatically acq uir e and display the 5 Vpp,
1 kHz waveform from the probe
compensation output
Figure 5. Autoset button and display after pressing
autoset
28 JULY 2016 12
4. T riggering the Scope
Although the squar e wave signal of the probe
compensation does not require pulse wi dth triggering ,
we will set it up for demonstration purposes.
1. Keep Channel 1 connected to the Probe Comp
output, as in the last demonstrati o n .
2. Press Default Setup in Resources section of the
front panel
3. Adjust the Verti cal Scal e on Channe l 1 to 2.00V
4. The default trigger type is Edge with a rising
slope. The default level is 0V. This i s show n i n
yellow in the lower right of the display.
5. Adjust the Trigger Level toward the c enter of
the waveform. The tri gg er level indicator
appears during the adjustment.
6. Press Menu in the Trigg er secti on. Pr es s t he
Type side-bezel button (Figur e 6). Note that the
LED under the multipurpose knob (MPK) is
lighted, prompting for a selection.
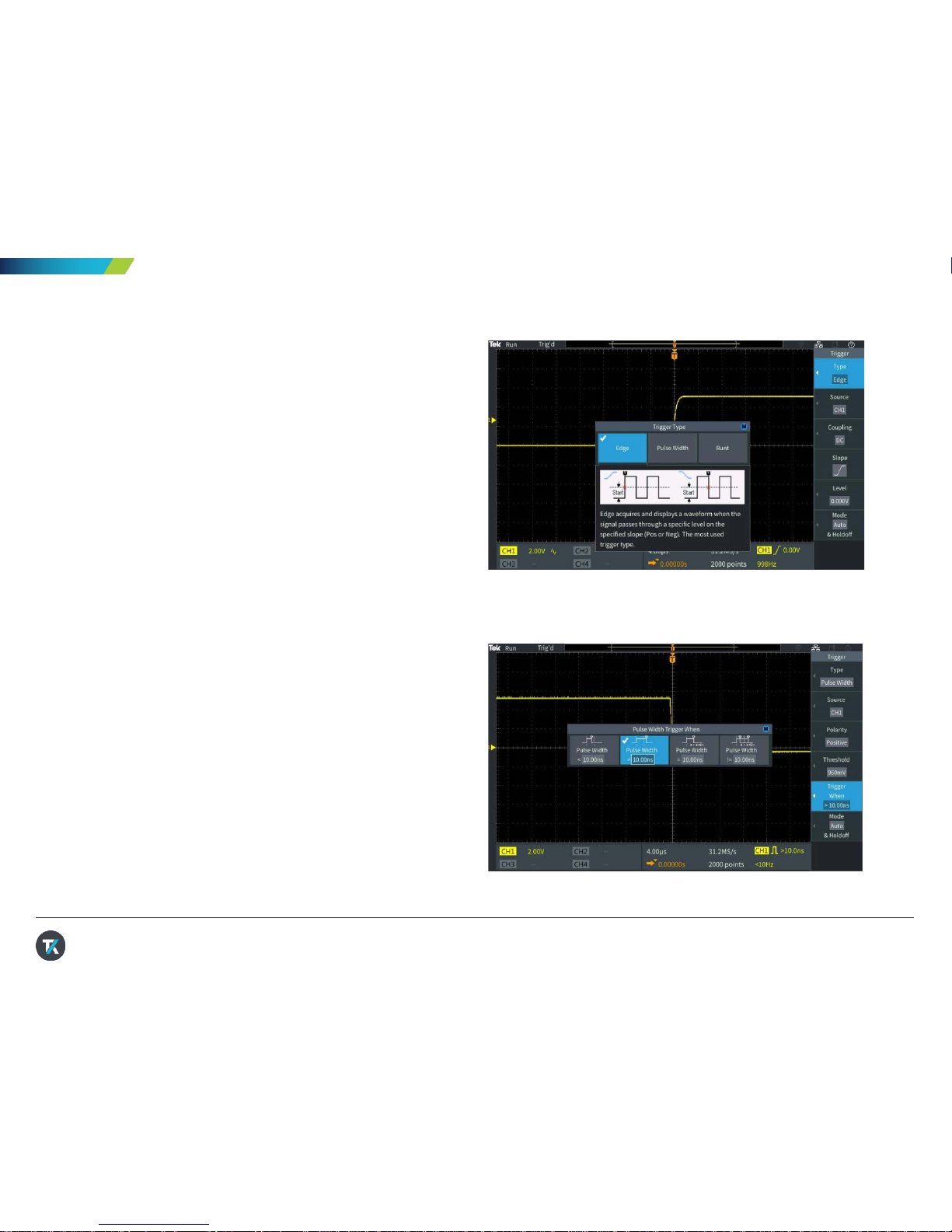
7. Scroll the MPK to highlight the Pulse Width
trigger type, and press the MPK to select it
8. Note that the Source is CH1 and the Polarity is
Positive
9. Press Trigger When, and use the MPK to select
Pulse Width >. Change the pulse duration to >
10ns. Since the pulse width is much greater
than 10 ns, the waveform triggers (Figur e 7).
10. Press Menu On/Off button below the display to
exit the menu
Figure 6. The M logo in the Trigger Type menu indicates
that the Multipurpose Knob (MPK) should be used for
selection
Figure 7. Setting pulse width trigger parameters

28 JULY 2016 13
5. Using Pan and Zoom to
Navigate through Long
Records
Especially for acquisiti ons of 20M points, it is
important to be able to navigate through the record.
Pan and zoom enable this.
1. Press the Acquire button on the front panel.
Notice that the Multipurpose Knob LED is on,
which means it can be used t o make a
selection.
2. Set Record Length to 20M by turning the
Multipurpose Knob (MPK) and press the
knob to make the selection.
3. Change the horizont al scale to 10ms/div w i th
the Horizontal Scale knob
4. Press the Zoom button. The button lights to
show that Zoom is active.
5. Turn the MPK to change the zoom scale
factor from 1X to 100000X. See the details
of the trigger edge (Figure 8).
6. Set the zoom factor back to 100X. Press the
Position bezel button. T ur n the MPK to
position a falling edge in the center of the
zoom area.
7. Press the Scale bezel button, and use the
MPK to zoom in on the falling edge detai l.
Adjust position if needed (Figure 9).
Figure 8. Zooming in on a rising edge
Figure 9. Zooming in on a falling edge

28 JULY 2016 14
6. Using Cursors to Measure
Time and Amplitude
Cursors enable quick visual measuremen ts on the
selected waveform. The TBS2000 features onwaveform readouts to make it easy to visualize
measurements.
1. Press Default Setup. Press Autoset.
2. Press the Cursors button beside the MPK
(Figure 10).
3. Press the Screen bezel button to select
independent control of both amplitude and time
cursors
4. Turn the MPK to move the left time cursor close
to the position you w oul d l i ke to measure
5. To position the cursor more precisely, press the
Fine button. Now turn the MPK to left cursor
exactly on a rising edge of the signal.
6. Press the MPK to change control to the right
time cursor. Turn the MPK and use Fine to
position the cursor on the next rising edge.
7. Note the delta time readout between the cursor s
and the time position for each bar
8. Press MPK again to change control to the upper
cursor for amplitude measurements. Mov e the
cursor to the top of the signal and note the delta
readout (Figure 11).
9. In the next section, you’ll us e automate d
measurements to get similar results.
Figure 10. Location of the Cursors and Fine
buttons (two-channel model shown)
Figure 11. Using the cursors to measure period and
amplitude of the Probe Comp signal

28 JULY 2016 15
7. Making Automated
Measurements
Automated measurements use the proces sing pow er of
the scope to provide a freq uency, time, amplitude, and
area measurements.
1. Connect passive probes to Channel 1 and
Channel 2. Connect both pr obe ti ps to Pr obe
Comp and both ground clips to Probe Comp
ground.
2. Press Autoset.
3. Press the Measure button in the res ource sec tion
of the front panel.
4. Notice, from top to bottom:
• Measurement selection indi cator bar
• Snapshot button
• Most Used measurement list
• Measurements grouped by Frequency, T ime,
Amplitude, Area
5. Press the CH1 bezel button. Scroll and press
MPK to select Frequency and +Duty for Channel
1.
6. Press the CH2 bezel button. Scroll and press
MPK to select Peak-Peak and Mean for Channel
2 (Figure 12).
7. Press Menu On/Off to return to the waveform
window.
8. Note the measurement readout (Fi gure 13).
9. Press Menu On/Off a couple of times to hide and
recall the measurement readout panel .
Figure 12. Peak-Peak and Mean measurements selected
for Channel 2. Note the two blue boxes in the
measurement selection indicator at the top of the display.
Figure 13. Transparent readouts let the signal show
through.

28 JULY 2016 16
8. Using an FFT to Analyze a
Signal’s Frequency Spectrum
The FFT function calculates the frequency i nput of the
source waveform. Cursor s make it easy to measure
frequency and ampli tud e in the spectrum.
1. Keep the TPP0100 passive probe c onnected to
Channel 1 and the Probe C omp output.
2. Press Default Setup. Press Autoset.
3. Press the F button for FFT function on t he front panel
(Figure 14).
4. By default, the source waveform is on. Turn it off by
pressing the Source wfm bezel button.
5. Source Channel, V ertic al Units, Window Type ,
Horizontal Center Posi tion and Scale may be adjusted
by selecting the correspondin g bezel button and
adjusting with the MPK .
6. The FFT readout panel in the top right corner of the
waveform display shows important setti ng s .
7. The default FFT window is Hanning. Use the Window
bezel button and MPK to switch to the Rectangular
window and note the result.
8. Press the Horizontal Scale bezel button and use the
MPK to adjust the horizontal scale to 1.56 kHz/div,
9. Press the Cursor button and position the cursors on
the third and fifth harmonic frequencies (Figure 15).
10. The delta between third harmonic and fifth harmonic
frequency should be 2 kHz, which is consistent with
the 1 kHz fundamental freq uency of the Probe Comp
output.
Figure 14. The FFT Menu
Figure 15. Cursors positioned on the 3 kHz and 5 kHz
harmonics of the 1 kHz probe comp output .

28 JULY 2016 17
9. Saving Screen Images
You can save screen i mag es, waveform data, and
setups to a USB flash drive. This demonstr a t ion
shows how to save a screen i mag e.
1. Press Default Setup. Press Autoset.
2. Plug a USB flash drive into the USB host port on
the oscilloscope’ s front panel
3. Press Save/Recall in the Res our ce section of the
front panel
4. Use the side bezel button to set the Action to
Save Image
5. Set the Format to JPG
6. Assign the button with the floppy disk icon to
“Assign to Image”. Now each time you press the
button above the side bezel buttons, a screen w ill
be saved.
7. Press File Utility, press New Folder, and use the
MPK to set up a new folder named “DEMO
GUIDE” (Figure 16).
8. Press Back
9. Highlight and sel ect the new DEMO GUIDE folder
with the MPK
10. Press the Floppy Disk button outside the right
top corner of the display t o save an image into the
DEMO GUIDE folder on the USB thumb. The hint
line should say that the image was successfully
saved.
11. Take the flash dri ve to a PC equipped with a USB
host port. You can now open the screenshot
image as you would any .jpg file.
Figure 16. Setting up a directory on a flash drive
Figure 17. The hint line, in the upper left of the display,
indicates a successful save.

28 JULY 2016 18
10. Setting up a Wireless
Connection
The TBS2000 Series supports wi rel ess
communication thr oug h a U SB to Wi-Fi adapter. To
remotely control the scope, a PC, tablet or cell
phone must be avai lable and on the same network
as the instrument.
1. Press Default Setup. Press Autoset.
2. Plug the TEK-USB-WIFI adapter into the rear
USB host port (Figure 18)
3. Press Utility, press Config, select Wi-Fi
Config and press Available Networks. Select
the wireless networ k that will be used for
control (Figure 19)
4. Enter the network key /pas sword if the network
is secured. This is usually an encryption
key/password set in the network router. (Note:
The TBS2000 does not support enteri ng a
username and password for a corporate
network)
5. Press Wi-Fi Settings menu to confirm
configuration informati on
6. The Wireless Icon in the top right corner of
the display should be on, i ndic ati ng that the
scope is connected to Wi-Fi
Figure 18. Insert the TEK-USB-WIFI adapter to enable
wireless communications
Figure 19. Configuring Wi-Fi communications via the Utility
Menus

28 JULY 2016 19
11. Using LXI for Remote Control
The built-in web server in the TBS2000 enables remote
control from any device with an Ethernet connectio n and w eb
browser. This demonstration requires a PC and an Ethernet
cable. Note: If you established a wireless connection in the
previous exercise, you can als o use that connection .
1. With the probe connected to the Probe Comp output,
press Default Setup in the Resource section of the
front panel
2. Connect an Ethernet c abl e from the PC to the LAN port
on the rear of the instrument.
3. Verify that the Ether net connection icon is on in the
upper right corner of the di s play
4. In a few seconds a window w i ll pop up on t he sc ope
display, saying “DHCP On Instrument IP Address:
XXX.XX.XXX.XXX.” (If not, go to Utility->Config>Ethernet Config-> DHCP to set DHCP on, and r epeat)
5. Open a web browser on the PC.
6. Type the IP address of the instrument into the address
box of the web browser . (Refer to the scope’ s LAN
settings menu if you missed the pop up dialog window.)
7. The Welcome Page displays important configura tion
information
8. Before you can control the scope, you will be asked for
a password. The default password is blank.
9. Click the Control Panel button on the top of the PC
screen, to access the control panel.
10. Press Menu Off on the scope
11. Click Autoset on the PC to get a stable waveform.
Figure 20. After connecting the cable, you should see the Ethernet
icon (upper right) and the scope’s IP address
Figure 21. On the PC, the IP has been entered into the address box of
the browser, and autoset has been performed remotely
3GW-60591-0 7/16
 Loading...
Loading...