Page 1

xx
P7500 Series
ZZZ
TriMode™ Probes
Technical Reference
*P077216102*
077-2161-02
Page 2

Page 3

xx
P7500 Series
ZZZ
TriMode™ Probes
Technical Reference
Revision A
www.tektronix.com
077-2161-02
Page 4

Copyright © Tektronix. All rights reserved. Licensed software products are owned by Tektronix or its subsidiaries
or suppliers, and are protected by national copyright laws and international treaty provisions.
Tektronix products are covered by U.S. and foreign patents, issued and pending. Information in this publication
supersedes that in all previously published material. Specifications and price change privileges reserved.
TEKTRONIX and TEK are registered trademarks of Tektronix, Inc.
TriMode is a trademark of Tektronix, Inc.
Velcro is a registered trademark of Velcro Industries B.V.
G3PO is a trademark of Corning Gilbert Inc.
Contacting Tektronix
Tektroni
14200 SW Karl Braun Drive
P.O . Bo x 50 0
Beaverton, OR 97077
USA
For pro
x, Inc.
duct information, sales, service, and t echnical support:
In North America, call 1-800-833-9200.
Worl d wide , vi sit www.tektronix.com to find contacts in your area.
Page 5

Warranty
Tektronix warrants that this product will be free from defects in materials and workmanship for a period of one (1)
year from the date of shipment. If any such product proves defective during this warranty period, Tektronix, at its
option, either will repair the defective product without charge for parts and labor, or will provide a replacement
in exchange for the defective product. Parts, modules and replacement products used by Tektronix for warranty
work may be n
the property of Tektronix.
ew or reconditioned to like new performance. All replaced parts, modules and products become
In order to o
the warranty period and make suitable arrangements for the performance of service. Customer shall be responsible
for packaging and shipping the defective product to the service center designated by Tektronix, with shipping
charges prepaid. Tektronix shall pay for the return of the product to Customer if the shipment is to a location within
the country in which the Tektronix service center is located. Customer shall be responsible for paying all shipping
charges, duties, taxes, and any other charges for products returned to any other locations.
This warranty shall not apply to any defect, failure or damage caused by improper use or improper or inadequate
maintenance and care. Tektronix shall not be obligated to furnish service under this warranty a) to repair damage
result
b) to repair damage resulting from improper use or connection to incompatible equipment; c) to repair any damage
or malfunction caused by the use of non-Tektronix supplies; or d) to service a product that has been modified or
integrated with other products when the effect of such modification or integration increases the time or difficulty
of servicing the product.
THIS WARRANTY IS GIVEN BY TEKTRONIX WITH RESPECT TO THE PRODUCT IN LIEU OF ANY
OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. TEKTRONIX AND ITS VENDORS DISCLAIM ANY
IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
TRONIX’ RESPONSIBILITY TO REPAIR OR REPLACE DEFECTIVE PRODUCTS IS THE SOLE
TEK
AND EXCLUSIVE REMEDY PROVIDED TO THE CUSTOMER FOR BREACH OF THIS WARRANTY.
TEKTRONIX AND ITS VENDORS WILL NOT BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL,
OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES IRRESPECTIVE OF WHETHER TEKTRONIX OR THE VENDOR HAS
ADVANCE NOTICE OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
[W2 – 15AUG04]
btain service under this warranty, Customer must notify Tektronix of the d efect before the expiration of
ing from attempts by personnel other than Tektronix representatives to install, repair or service the product;
Page 6

Page 7

Table of Contents
General Safety Summary .......................................................................................... v
Preface............................................................................................................. vii
Products Covered ..................... ................................ ................................ ....... vii
Theory of Op
Input Voltage Limits................................ ................................ ........................... 1
TriMode Operation ........................... ................................ ................................. 5
Probing Techniques to Maximize Signal Fidelity ......... ................................ ................. 7
Input Impedance and Probe Loading ........... .................................. .......................... 15
Reference ......... ................................ ................................ .................................. 17
Single-
Differential Measurements................................................................................... 19
Serial Bus Standards............................ ................................ .............................. 21
Specifications ............ ................................ ................................ .......................... 22
Warranted Characteristics.................................................................................... 22
Typical Characteristics ................. ................................ ................................ ...... 23
Nomi
Tip Specifications ............................................................................................. 27
User Service........................................................................................................ 35
Error Condition .. ... ... . .. . ... ... ... . ... ... ... ... . ... ... ... ... . ... ... ... . . .. . ... ... ... .. .. . ... ... ... .. .. . ... .. 35
Replaceable Parts ............................................................................................. 36
Preparation for Shipment .......... .................................. ................................ ........ 48
eration... ................................ ................................ ............................. 1
Ended Measurements Using A and B Modes ............................... ...................... 17
nal Characteristics...................................................................................... 26
P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference i
Page 8

Table of Contents
List of Figure
Figure 1: Operating voltage window ................ ................................ ............................. 2
Figure 2: Dynamic range versus linearity, 5X range (P7513 & P7516) ...................................... 3
Figure 3: Dynamic range versus linearity, 12.5X range (P7513 & P7516) .................................. 3
Figure 4: Dynamic range versus linearity, 5X range (P7520) ...... .................................. ......... 4
Figure 5: Dynamic range versus linearity, 12.5X range (P7520).............................................. 4
Figure 6: TriMode input structure ................................................................................ 6
Figure 7: Typical TriMode Probe Setup screen ................... .................................. ........... 6
Figure 8: P75TLRST TriMode Long Reach
Figure 9: TriMode Resistor solder tips........................................................................... 8
Figure 10: Typical wire length from probe tip to circuit....................................................... 9
Figure 11: P75TLRST solder tip with 0.010 in. of tip wire .. ................................ ................ 10
Figure 12: P75TLRST solder tip with 0.050 in. of tip wire .................................................. 10
Figure 13: P75TLRST solder tip with 0.100 in. of tip wire .................................................. 11
Figure 14: P75TLRST solder tip with 0.200 in. of tip wire .................................................. 11
Figure 15: P75PDPM Precision Differential Probing Module ............................................... 12
Figure 16: P75PDPM with short ground spring, 0.030 in. spacing.......................................... 13
Figure 17: P75PDPM with short ground spring, 0.050 in. spacing.......................................... 13
Figure 18: P75PDPM with short ground spring, 0.090 in. spacing.......................................... 14
Figure 19: P75PDPM with short ground spring, 0.180 in. spacing.......................................... 14
Figure 20: TriMode probe input model ......................................................................... 15
Figure 21: TriMode probe high frequency input impedance model ......................... ................ 15
Figure 22: Embedded probe fixture ......... ................................ ................................ .... 16
Figure 23: Typical channel isolation for P7500 Series TriMode probes .................................... 18
Figure 24: Simplified model of a differential amplifier ....................................................... 19
Figure 25: Typical CMRR for P7500 Series TriMode probes................................................ 20
Figure 26: Probe body and control box dimensions........................................................... 25
Figure 27: P75TLRS
Figure 28: TriMode probe with the P75TLRST solder tip.. .................................. ................ 28
Figure 29: P75TLRST differential impedance ................................................................. 28
Figure 30: TriMode Resistor solder tip dimensions ........................................................... 29
Figure 31: Step response with the TriMode Resistor solder tip .............. ................................ 30
Figure 32: TriMode Resistor solder tip differential impedance .......... ................................ .... 30
Figure 33: TriMode Extended Resistor solder tip dimensions ............................................... 31
Figure 34: Step response with the TriMode Extended Resistor solder tip .................... .............. 32
Figure 35: TriMode Extended Resistor solder tip differential impedance .................... .............. 32
Figure 36: P75PDPM Precision Differential Probing Module dimensions ................................. 33
Figure 37: TriMode probe with the P75PDPM probing module. .................................. .......... 34
Figure 38: P75PDPM differential impedance ...................... .................................. .......... 34
s
Solder Tip................................... ..................... 7
T TriMode Long Reach Solder Tip dimensions....................................... 27
ii P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference
Page 9

Table of Contents
Figure 39: Remo
Figure 40: Installing the bullets. ... . ... ... ... .. .. . ... ... ... . ... ... ... . . .. . ... ... ... . ... ... ... . . .. . ... ... ... . ... .. 38
Figure 41: Large and small springs installed ..... ................................ .............................. 40
Figure 42: Set the gap....... ................................ .................................. .................... 41
Figure 43: Insert tool beneath spring............................................................................ 41
Figure 44: Transfer spring from tip to tool ..................................................................... 42
Figure 45: P
Figure 46: Set spring in front seat ............................................................................... 43
Figure 47: Set the spring in the rear seats....................................................................... 44
Figure 48: Properly seated spring................................................................................ 44
Figure 49: Disconnecting the tip cable...... ................................ .................................. .. 45
Figure 50: Probing module tips .................................................................................. 45
Figure 5
Figure 52: Separating the tip board pair ........................................................................ 46
Figure 53: Seating the tip in the top tabs...................................... .................................. 47
Figure 54: Snapping the tip into the bottom tabs .............................................................. 47
1: Removing the tip ..................................................................................... 46
ving the bullets................................................................................. 37
lace spring on tool .............. .................................. ................................ .. 43
P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference iii
Page 10

Table of Contents
List of Tables
Table i: TriMode probes ......................................................................................... vii
Table 1: Off
Table 2: Serial bus standards with dynamic range requirements............................................. 21
Table 3: Warranted electrical characteristics ......... ................................ .......................... 22
Table 4: Typical electrical characteristics................. .................................. .................... 23
Table 5: Typical mechanical characteristics .................................................................... 25
Table 6: Nominal electrical characteristics ............. .................................. ...................... 26
Table 7: T
Table 8: Required equipment............................... ................................ ...................... 36
set ranges......................................... ................................ .................... 17
riMode probes replaceable parts..................................................................... 36
iv P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference
Page 11

General Safety Summary
General Safet
To Avoid Fire or Personal
Injury
ySummary
Review the fo
this product or any products connected to it.
To avoid pot
Only qualified personnel should perform service procedures.
While using this product, you may need to access other parts of a larger system.
Read the safety sections of the other component manuals for warnings and
cautions r
Connect and Disconnect Properly. Connect the probe output to the measurement
instrument before connecting the probe to the circuit under test. Connect the
probe reference lead to the circuit under test before connecting the probe input.
Disconnect the probe input and the probe reference lead from the circuit under test
before
Observe All Terminal Ratings. To avoid fire or shock hazard, observe all ratings
and ma
information before making connections to the product.
Do no
exceeds the maximum rating of that terminal.
disconnecting the probe from the measurement instrument.
t apply a potential to any terminal, including the common terminal, that
llowing safety precautions to avoid injury and prevent damage to
ential hazards, use this product only as specified.
elated to operating the system.
rkings on the product. Consult the product manual for further ratings
ot Operate Without Covers. Do not operate this product with covers or panels
Do N
removed.
ot Operate With Suspected Failures. If you suspect that there is damage to this
Do N
product, have it inspected by qualified service personnel.
oid Exposed Circuitry. Do not touch exposed connections and components
Av
when power is present.
o Not Operate in Wet/Damp Conditions.
D
Do Not Operate in an Explosive Atmosphere.
Keep Product Surfaces Clean and Dry.
P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference v
Page 12

General Safety Summary
TermsinthisManual
Symbols and Terms on the
Product
These terms may
WARNING. Warning statements identify conditions or practices that could result
in injury or loss of life.
CAUTION. Caution statements identify conditions or practices that could result in
damage to this product or other property.
These terms may appear on the product:
DANGER in
the marking.
WAR NI NG
read the marking.
CAUTIO
The following symbol(s) may appear on the product:
appear in this manual:
dicates an injury hazard immediately accessible as you read
indicates an injury hazard not immediately a ccessible as you
N indicates a hazard to property including the product.
vi P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference
Page 13

Preface
Products Covered
This manual discusses topics that are not covered in depth in the P7500 Series
TriMode Probes Quick Start User Manual.
The main sections are:
Theory of Operation — Contains probe details not covered in the user manual.
Reference — Contains information about differential measurements and how
to increase measurement accuracy.
Specifications — Contains warranted, typical, and nominal characteristics for
the probe and probe tip accessories.
User Service — Describes troubleshooting and probe maintenance.
The table below lists the TriMode probes covered by this manual.
Table i: TriMode probes
Probe model Serial number
P7513 B020000 and above
P7516 B020000 and above
P7520 All
1
For information on probes with serial numbers below B020000, refer to the P7500 Series TriMode Probes
Technical Reference in the previous edition of the Product Documentation (Tektronix part number 020-2790-00).
You can also access the manual at w ww.tektronix.com/manuals.
1
1
P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference vii
Page 14

Preface
viii P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference
Page 15

Theory of Operation
This section discusses operating considerations and probing techniques. For more
detailed information about differential measurements and TriMode operation,
refer to Refe
The P7500 Series TriMode probes are optimized for high bandwidth; t hey
are not gene
characteristics and access to dense circuitry, and must be handled carefully.
CAUTION. To prevent damage to the probe, use care when handling the probe.
Rough or careless use can damage the probe.
Input Voltage Limits
The P7500 Series TriMode probes are designed to probe low-voltage circuits.
Before
the operating voltage window, and the differential-mode signal range. (See
Table 4 on page 23.)
rence. (Seepage17.)
ral-purpose probes. The probe tips are miniaturized for electrical
probing a circuit, take into account the limits for maximum input voltage,
Maximum Input Voltage
The ma
withstand without damaging the probe input circuitry.
CAUTION. To avoid damaging the inputs of the probes, do not apply more than
±15 V (DC + peak AC) between each input or between either probe input and
ground.
CAUTION. To avoid ESD damage to the probe, always use an antistatic wrist
strap (provided with your probe), and work at a static-approved workstation when
you handle the probe.
ximum input voltage is the maximum voltage to ground that the inputs can
P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference 1
Page 16

Theory of Operation
Operating Voltage Window
The operating v
to each input, with respect to earth ground, without saturating the probe input
circuitry. (See Figure 1.) A common-mode voltage that exceeds the operating
voltage window may produce an erroneous output waveform even when the
differential-mode specification is met.
Figure 1: Operating voltage window
oltage window defines the maximum voltage that you can apply
ential-Mode Signal
Differ
fset Voltage Range
Of
Range
The differential-mode signal range is the maximum voltage difference between
the A and B inputs that the probe can accept without distorting the signal. The
distortion from a voltage that exceeds this m aximum can result in a clipped or
wise inaccurate measurement. The P7500 Series probes have two attenuation
other
settings, 5X and 12.5X, that allow dynamic range to be traded off against signal
noise. The 12.5X attenuator setting has the largest dynamic range; the 5X
attenuator setting has the lowest noise. The graphs on the following pages
illustrate the linearity error over the dynamic voltage range of the probes in both
attenuation settings.
The Offset Voltage Control, accessible from the attached oscilloscope user
interface, allows the probe dynamic range to be effectively moved up and down
within the limits of the offset voltage range and the operating voltage window.
hen the offset voltage is set to zero volts and the input signal is zero volts
W
(inputs shorted to ground, not open), the displayed signal should be zero volts.
If a noticeable zero volt offset is present under the above conditions, a Probe
Cal operation should be performed. (See the P7500 Series Probes Quick Start
User Manual).
2 P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference
Page 17

Theory of Operation
Figure 2: Dynamic range versus linearity, 5X range (P7513 & P7516)
Figure 3: Dynamic range versus linearity, 12.5X range (P7513 & P7516)
P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference 3
Page 18

Theory of Operation
Figure 4: Dynamic range versus linearity, 5X range (P7520)
Figure 5: Dynamic range versus linearity, 12.5X range (P7520)
4 P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference
Page 19

Theory of Operation
TriMode Opera
tion
The TriMode feature of the new P7500 Series probe family is designed for
improved convenience and enhanced capability in measuring differential
signal quali
single-ended signals, full characterization of differential signal quality requires
more than a simple differential measurement. A TriMode probe features three
Input Modes that allow a differential signal to be fully characterized with four
measurements: differential, positive polarity and negative polarity single-ended,
and common mode.
A TriMode probe provides improved efficiency and convenience by enabling full
differential signal characterization from a single soldered connection. Using one
of the so
probe tip), probe connections are soldered to the two complementary signals (the
A signal and the B signal) and a ground reference. From this single DUT (device
under test) connection, the internal electronic switching control of the TriMode
probe allows any one of the three probe Input Modes (four measurements) to
be selected at a time. The TriMode probe inputs are routed on the p robe ASIC
(appl
that perform the following signal calculations:
A–B(
A – GND (for positive polarity single-ended measurement)
ty. Since a differential signal is composed of two complementary
lder tips available for the TriMode probes, (for example, the P75TLRST
ication-specific integated circuit) to a set of four independent input amplifiers
for differential signal measurement)
B – GND (for negative polarity single-ended measurement)
[A+B]/2 - GND (for common mode measurement)
NOTE. In the B – GND Mode, the negative polarity B input is not inverted.
The four input amplifiers are multiplexed together and only the selected Input
Mode function is output to the connected oscilloscope. (See Figure 6 on page 6.)
The figure shows a conceptual view of the TriMode probe input structure, where
the C input provides the probe ground reference and is connected to the probe tip
ground interconnect using the probe tip cable coaxial shields.
P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference 5
Page 20

Theory of Operation
Figure 6: TriMode input structure
On oscilloscopes that do not provide full TriMode support, the TriMode features
are con
features like Probe Cal to be exercised only for the selected probe Input Mode.
On osc
probe GUI (graphical-user interface) can perform a Probe Cal operation on all
Input Modes and Attenuation Settings at once using the TriMode Probe Cal fixture
that is supplied with P7500 Series probes. (See the P7500 Series Quick Start
User Manual for instructions on running the Probe Cal routine.) Full TriMode
support will also allow storage and automatic recall of relevant settings like
Off
trolled by the probe Control Box switches, which allow oscilloscope
illoscopes that provide full TriMode support, the oscilloscope-controlled
set. (See Figure 7.)
Figure 7: Typical TriMode Probe Setup screen
6 P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference
Page 21

Theory of Operation
Probing Techn
iques to Maximize Signal Fidelity
P7500 TriMode Solder Tips
Signal fidelity is an indication of how accurately a probe represents the signal
being mea sured. The signal fidelity of the probe is best when the probe is
applied prop
connecting the P7500 probe tips are given in the following section.
There are several solder tips available for connecting the P7500 Series probes to
your circu
accessory. (See Figure 8.) Two resistor solder tips are available as optional
accessories. (See Figure 9 on page 8.)
P75TLRST TriMode Solder Tip. The P75TLRST probe tip is composed of a small
form factor interconnect circuit board with SMD0402 damping resistors and a set
of vias f
vias are designed for both 4 mil and 8 mil wire and a special high tensile strength
wire is supplied as part of the wire accessory kit. The expanded view of the probe
tip shows the location of the A and B signal inputs as well as the two ground
reference connections.
erly to the circuit with the P7500 probe tips. Recommendations for
it. The P75TLRST probe tip is shipped with the probes as a standard
or wire attachment to the DUT (Device Under Test). The circuit board
Figure 8: P75TLRST TriMode Long Reach Solder Tip
The recommended wire attachment method is to first solder the wires to the DUT,
ing careful to minimize the wire length of the signal and ground connections.
be
This is followed by threading the wires through the probe tip board vias, being
careful to achieve as symmetrical a wire pattern as possible between the two
signal inputs and a very short ground connection. Finally, the attachment is
completed by soldering the wires on top of the probe tip circuit board. Any excess
wire lead length extending through the probe tip board should be removed to
minimize possible signal reflection problems.
Because of the limited mechanical strength of the wire interconnect and probe
tip circuit board, the solder-down probe tip should be taped down at the DUT for
strain relief. Although the accessory kit includes adhesive strips that can be used
for the strain relief of the probe tip, the use o f mylar tape will generally provide
stronger attachment if room is available at the DUT.
P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference 7
Page 22

Theory of Operation
TriMode Resist
on-board damping resistors for each probe input (+ and –) into two components.
A surface mount, 75 Ω resistor is board-mounted in series w ith a 100 Ω leaded
resistor that extends off of the tip board. The other end of the resistor is soldered
to your circuit. The TriMode Extended Resistor solder tips allow a longer tip
reach to your circuit under test but reduce the measurement quality.
Figure 9
Since t
when reusing the tip, they limit the need to solder directly to the tip board,
extending the life of the tip. The tip resistors are replaceable and are available as a
kit. (See page 36, Replaceable Parts.)
he leads of the 100 Ω resistors take the repeated soldering cycles required
or Solder Tips. These solder tips separate the standard 175 Ω
: TriMode Resistor solder tips
Probe Tip Cables and Connectors. Attached to the probe tip circuit board is a pair
ry low skew (<1ps) coaxial cables and a polarized G3PO dual connector
of ve
block. The 3GPO connectors use a miniature, high frequency design that enables
quick and easy installation of the P75TLRST solder tip. The G3PO connector
block of the probe tip is inserted into the input nose piece on the end of the probe
body of the P7500 family probes. The probe body contains a mating, polarized
G3PO connector block with attached G3PO connector bullets.
The connector bullets are a part of the G3PO connector design, providing a
self-aligning interconnect mechanism between G3PO connectors. The G3PO
onnector in the probe body is designed to have higher detent force than the probe
c
tip connectors, which is intended to ensure that the G3PO bullets remain in the
probe body connector when disconnected. The probe body nose piece, with its
integral spring mechanism, helps to provide a self-aligning mechanism for hand
insertion of the probe tip. The probe body nose springs also give a secure capture
of the probe tip connector after insertion. Release of the probe tip is assisted by
using the wire-connected cable release holder on the probe tip connector. This
probe tip release holder should a lways be used rather than pulling on the probe tip
cables, which may cause tip cable damage.
8 P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference
Page 23
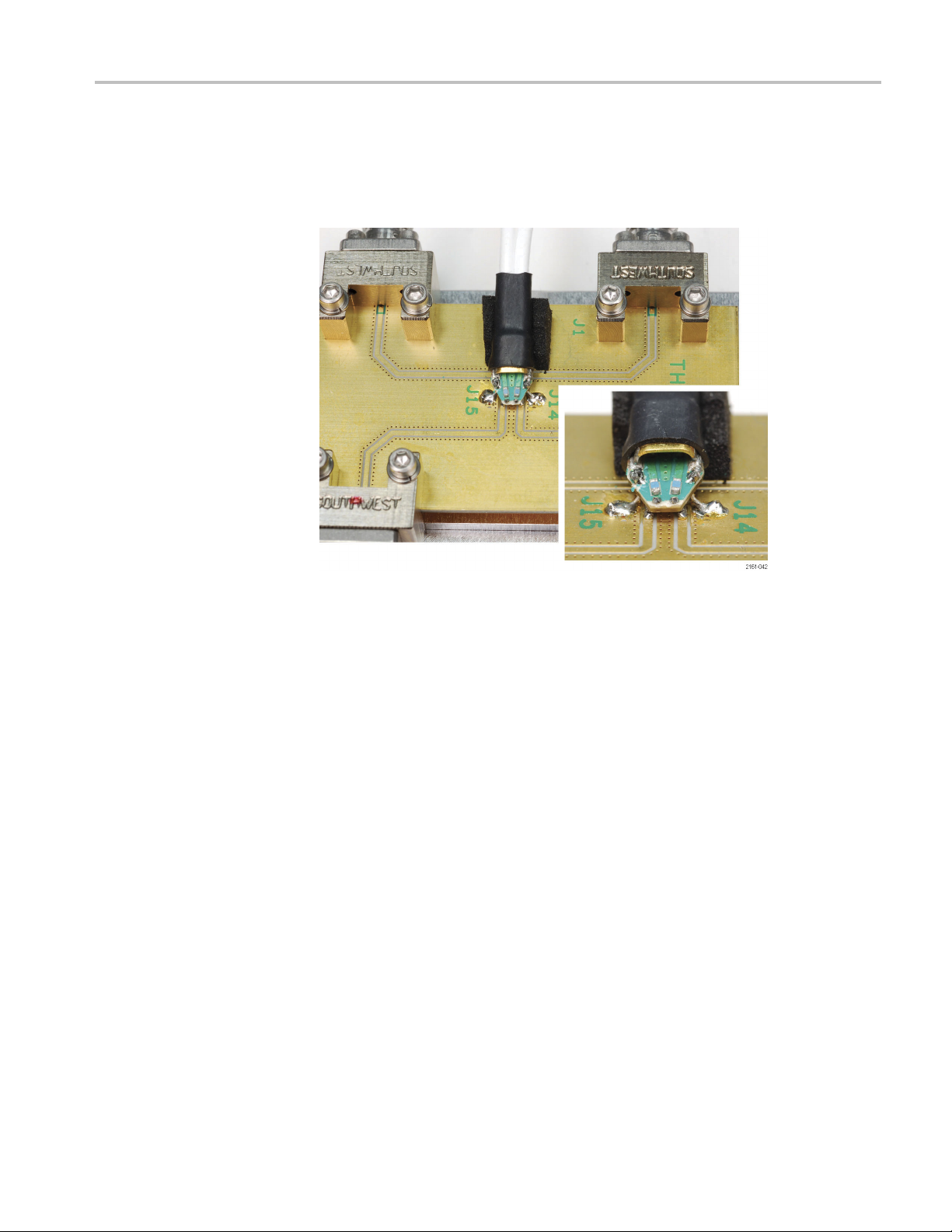
Theory of Operation
DUT Connection
between the probe tip board and the DUT must be kept as short as possible to
preserve the integrity of the measured signal. Typical wire lengths range from
0.010 in. to 0.100 in. (See Figure 10.)
s. The lead length of the resistor leads and connection wires
Figure 10: Typical wire length from probe tip to circuit
The following four figures illustrate the signal integrity effect on the P75TLRST
solder tip when used with different lengths of tip wire. Signal fidelity is best when
the wire length is kept as short as possible. The step generator that was used as a
signal source for these screenshots has a 30 ps 10-90% rise time. The table in each
figure contains data for two rise time measurements (10-90% and 20-80%). These
enshots can be used as a rough guide to gauge the effects of wire length, but
scre
actual results may vary depending on the other factors like characteristics of the
device under test (for example, rise time and impedance), precision of the solder
connection, and the model of oscilloscope.
P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference 9
Page 24

Theory of Operation
Figure 11: P75TLRST solder tip with 0.010 in. of tip wire
Figure 12: P75TLRST solder tip with 0.050 in. of tip wire
10 P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference
Page 25

Figure 13: P75TLRST solder tip with 0.100 in. of tip wire
Theory of Operation
Figure 14: P75TLRST solder tip with 0.200 in. of tip wire
P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference 11
Page 26

Theory of Operation
P75PDPM Precision
Differential Probing
Module
The P75PDPM Pro
applications. The P75PDPM probe tip is composed of two replaceable probe tip
circuit boards with a pin on one end and a G3PO socket connector on the other.
Damping resistors on the tip bo ards near the input pins and a 50 Ω transmission
line on the board transmit the signal from the input pin to the G3PO socket
connector. The probe tip boards are connected to the P7500 probe body with a
very low ske
The left-side and right-side probe tip boards mount at an angle in the P75PDPM
adjustmen
(0.76 – 4.57 mm) using the thumb-operated screw. Because of the variable spacing
between the two probe tip boards, a gold-plated ground spring is connected
between the probe tip boards to ensure a good common mode ground return near
the probe tip pins.
t housing. The probe tip spacing is adjustable from 0.030 – 0 .180 in.
bing Module is designed for handheld and fixtured probing
w (<1 ps) cable assembly (P75TC).
Figure 15: P75PDPM Precision Differential Probing Module
The P75PDPM probe tip circuit boards mount in an articulating metal housing
that also supports the variable spacing control. The angle of the probe tip housing
can be adjusted and locked in place using an articulation screw in the probe holder
bar. The probe holder bar contains mechanical details for retaining the probe tip
cable assembly as well as a retaining clamp for the probe body. The probe holder
bar can be held manually or can be mounted for fixtured probing on an articulating
probe arm using mechanical features in the holder bar.
The P75PDPM design features improved mechanical compliance in probe
tip attachment to the DUT. Mechanical compliance is a significant issue for
differential probes because of the difficulty in making reliable contact with two
DUT connections at the same time. The reliability in making this dual point
connection can be improved by a tip structure with good mechanical compliance,
in which there is sufficient give in the probe tips to absorb interconnect surface
irregularity.
The P75PDPM does not have a local DUT ground connection because of the
great difficulty in making a good three-point interconnect without soldering. As a
result, the only low-noise TriMode Input Mode available with the P75PDPM is
the A-B (DIFF) mode, since for differential signals, there is an inherent virtual
ground present in the measurement circuit.
12 P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference
Page 27

Theory of Operation
The following f
spacing on the P75PDPM Probing Module. Signal fidelity is best with the tips at
the smallest spacing. The step generator that was used as a signal source for these
screenshots has a 30ps 10-90% rise time. The table in each figure contains data
for two rise time measurements (10-90% and 20-80%). These screenshots can be
used as a rough guide to gauge the effects of probe tip spacing, but actual results
mayvarydep
test (for example, rise time and impedance) and the model of oscilloscope.
our figures illustrate the signal integrity effect of changing the
ending on the other factors like characteristics of the device under
Figure 16: P75PDPM with short ground spring, 0.030 in. s pacing
Figure 17: P75PDPM with short ground spring, 0.050 in. s pacing
P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference 13
Page 28

Theory of Operation
Figure 18: P75PDPM with short ground spring, 0.090 in. spacing
Figure 19: P75PDPM with short ground spring, 0.180 in. spacing
14 P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference
Page 29

Input Impedance and Probe Loading
When you connect the probe inputs to a circuit, you are introducing a new
resistance, capacitance, and inductance into the circuit. Each input of the
differential probe has a DC input impedance of 50 kΩ to ground. (See Figure 20.)
Figure 20: TriMode probe input model
For signals with low source impedance and frequency, the 50 kΩ input impedance
on each input is large enough to prevent the inputs from loading the signal
sources. The more the signal source impedance on an input increases, the more
the probe loads the source and reduces the signal amplitude. The greater the
source
take these factors into account.
impedances and the higher the signal frequencies, the more you must
Theory of Operation
equency of the signal also affects signal measurement. As the frequency of
The fr
the signal increases, the input impedance of the probe decreases. The lower the
impedance of the probe relative to that of the source, the more the probe loads
the circuit under test and reduces the signal amplitude. A high frequency input
impedance model is shown below. (See Figure 21.)
gure 21: TriMode probe high frequency input impedance model
Fi
or plots an d representative R-L-C values of the individual TriMode solder tips,
F
refer to t he specifications.(Seepage27,Tip Specifications.)
P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference 15
Page 30

Theory of Operation
Embedded Probe
It is possible t
an embedded connection in your circuit. (See Figure 22.) Connectors that mate to
the P75TC Tip Cable can be incorporated in the circuit board design and carefully
placed to balance any reflections or other characteristics that may affect the
circuit or measurement. An embedded probe connection will generally provide
optimum probe performance because the signal interconnect lead length can be
minimized i
connections, contact Tektronix.
o acquire signals with the P7500 Series TriMode probes by including
f implemented correctly. For more information about embedded probe
Figure 22: Embedded probe fixture
16 P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference
Page 31

Reference
This section contains information about taking measurements with the TriMode
probes and increasing measurement accuracy.
Single-Ended Measurements Using A and B Modes
A differential probe such as the P7516 TriMode Probe can be used for single-ended
measureme
Single-ended probes such as the P7240 typically have a wider offset range than
differential probes, but with much lower bandwidth performance. (See Table 1.)
Table 1: Offset ranges
nts within the limits of its dynamic and offset voltage ranges.
Probe DC Offset, 5X
P7240
P7513 & P7516 (differential mode)
P7513 & P7516 (single-ended and common-mode)
P7520 (differential mode)
P7520 (single-ended and common-mode)
+/- 5 V
+2.5 V, -1.5 V 1.5 V
+3.4 V, -1.8 V 1.5 V
+2.5 V, -1.5 V 1.25 V
+3.4 V, -1.8 V 1.25 V
Differential probes are ideal for a class of single-ended measurements where the
reference voltage is not ground:
SSTL_1,2: VTT,V
PECL: V
measure single-ended signals in this class, connect the B input of the P7500
To
TriMode Probe to V
differential probe in these applications displays the true signal despite any AC
A
or DC variation in V
=VCC-1.3
REF
REF
REF
the signal plus the variation in V
Differential probes can also be used to make ground referenced single-ended
measurements on either single-ended signals or differential signals like PCI
Express or Serial ATA. To measure ground referenced single-ended signals with
the handheld module, connect the B input of the P7500 TriMode Probe to ground.
REF
Dynamic
Range, 5X
4V
=VDD/2
PP
PP
PP
PP
PP
DC Offset,
12.5X
–
Dynamic
Range, 12.5X
—
+2.5 V, -1.5 V 3.5 V
+3.4 V, -1.8 V 3.5 V
+2.5 V, -1.5 V 3.2 V
+3.4 V, -1.8 V 3.2 V
PP
PP
PP
PP
.
from its nominal value. A single-ended probe displays
.
REF
Single-ended measurements on differential signals are used to measure common
mode voltage and check for differential signal symmetry. By using the TriMode
solder tip, you can easily take these measurements with one connection. Cycle the
Input Mode switch to display the signal that you want to view.
P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference 17
Page 32

Reference
Channel Isolation
Under ideal con
probe, no part of a signal applied to one input of the probe would appear on the
other input. In reality some portion of the signal on one input does “bleed” over to
the other input, and this effect increases with frequency. Channel isolation is a
measure of how much crosstalk occurs between the two probe inputs. The channel
isolation is defined with S-parameter measurements below, where:
A input = S1, B input = S2, Output = S3
A ISOLATION = 20 log (S32 / S31) | A Mode
B ISOLATION = 20 log (S31 / S32) | B Mode
A typical isolation plot for the P7500 series TriMode probes using an embedded
probe with zero-ground lead length is shown. Channel isolation performance is
highly dependent on probe tip attachment lead length. Good channel isolation
requires keeping the interconnect lead length for both signal and ground
connections very short. (See Figure 23.)
ditions when taking single-ended measurements with a differential
Figure 23: Typical channel isolation for P7500 Series TriMode probes
18 P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference
Page 33

Reference
Differential
Measurements
A differential probe is optimized to measure high speed differential signals.
Differential signals are formed from two complementary signals with a common
reference vo
Devices designed for differential measurements avoid problems presented by
single-end
differential amplifiers, and isolators.
A differen
differential measurements that reject any voltage that is common to the inputs and
amplifies any difference between the inputs. Voltage that is common to both
inputs is often referred to as the Common-Mode Voltage (V
is different as the Differential-Mode Voltage (V
ltage. (See Figure 24.)
ed systems. These devices include a variety of differential probes,
tial probe is basically a differential amplifier, which is used to make
) and voltage that
CM
).
DM
mon-Mode Rejection
Com
Ratio
Figure 24: Simplified model of a differential amplifier
Differential amplifiers cannot reject all of the common-mode signal. The ability
of a differential amplifier to reject the common-mode signal is expressed as the
mon-Mode Rejection Ratio (CMRR). The CMRR is the differential-mode
Com
gain (A
) divided by the common-mode gain (ACM). It is expressed either as
DM
a ratio or in dB.
CMRR generally is highest (best) at DC and degrades with increasing frequency.
A typical CMRR plot for the P7500 Series TriMode probes is shown. (See
Figure 25 on page 20.)
P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference 19
Page 34

Reference
Figure 25: Typical CMRR for P7500 Series TriMode probes
Assessing CMRR Error
Input Impedance Effects
on CMRR
Differential-Mode
Rejection
The CMRR of the P7500 Series TriMode Probes is shown in graphs assuming a
sinusoidal common-mode signal.
A quick way to assess the magnitude of CMRR error when the common-mode
signal is not sinusoidal is to connect both leads to the same point in the circuit. The
oscilloscope displays only the common-mode component that is not fully rejected
by the probe. While this technique may not give you accurate measurements, it
does allow you to determine if the magnitude of the common-mode error signal
is significant. Make the probe tip wires the same length to maximize the probe
CMRR.
The lower the input impedance of the probe relative to the source impedance,
thelowertheCMRRforagivensourceimpedance imbalance. Differences
in the source impedance driving the two inputs lowers the CMRR. Note that
single-ended measurements generally result in asymmetric source impedances
which tend to reduce the differential mode CMRR.
When making common-mode signal measurements (A+B/2 -GND) with the
TriMode probe, it is desirable to reject the differential-mode signal present
between the two inputs. This rejection is expressed as the Differential-Mode
Rejection Ratio (DMRR), and is defined as the common-mode gain (A
by the differential-
mode gain (A
). It is expressed either as a ratio or in dB, and
DM
) divided
CM
degrades at higher frequencies.
20 P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference
Page 35

Reference
Serial Bus Sta
ndards
The table below lists some popular high-speed data communication standards that
can be measured with the P7500 Series TriMode Probes.
Tabl e 2: Ser
Standard Data Rate Vdm_max Vdm_min Vcm_max Vcm_min
HDMI/DVI 1.65 Gb/s
InfiniBand TX 2.5 Gb/s
InfiniBand RX 2.5 Gb/s
PCI Express TX 2.5 Gb/s
PCI Express RX 2.5 Gb/s
Serial ATA TX 1.5 Gb/s
Serial ATA RX 1.5 Gb/s
XAUI TX 3.125 Gb/s
XAUI RX 3.125 Gb/s
OIF-SxI-5 TX 3.125 Gb/s
OIF-SxI-5 RX 3.125 Gb/s
LV PECL (std ECL) >12 GHz
LV PECL (RSECL) >12 GHz
ial bus standards with dynamic range requirements
800 mV 150 mV 3.3 V 2.8 V
1.6 V 1.0 V 1.0 V 0.5 V
1.6 V 0.175 V 1.0 V 0.5 V
1.2 V 0.8 V
1.2 V 0.175 V
0.6 V 0.4 V 0.3 V 0.2 V
0.6 V 0.325 V 0.3 V 0.2 V
0.4 V
0.1 V
1.0 V 0.5 V 1.23
1.4
0.7
5V
8V
0V
1.0 V 0.17
6V
1.6
(typ)
5V
1.0
AC AC
AC AC
1.30
1.3 V (vt) 0.5 V (vt)
1.3 V (vt) 0.5 V (vt)
V
V
0.72
1.10
V
V
P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference 21
Page 36

Specifications
Specification
s
These specifi
cations apply to the P7500 Series TriMode Probes installed on an
oscilloscope with a TekConnect interface. When the probe is used with another
oscilloscope, the oscilloscope must have an input impedance of 50 Ω. The probe
must have a warm-up period of at least 20 minutes and be in an environment that
does not exceed the allowed limits. (See Table 3.)
Specifications for the P7500 Series TriMode Probes fall into three categories:
warranted, typical, and nominal characteristics.
Warrante
dCharacteristics
Warranted characteristics describe guaranteed performance within tolerance limits
or certain type-tested requirements.
Table 3
Characteristic Specification (applies to all models unless specified otherwise.)
Rise time
DC attenuation accuracy 0.200 ±2% (5X)
Out
Te
Humidity
Altitude
1
: Warranted electrical characteristics
P7513 P7516 P7520
1
put Offset Zero
mperature
Measurements taken using an embedded probe fixture and a 250 mV step (18 to 28 ºC +64 to +82 °F)
10–90
20–80%
<40 ps <32 ps
%
<28 ps <24 ps
800 ±2% (12.5X)
0.0
V (+20 to +30 °C, +68 to +86 °F) (5X) ±15 mV on oscilloscope
±3 m
±3 mV (+20 to +30 ° C, +68 to +86 °F) (12.5X) ±37.5 mV on oscilloscope
Operating: 0 to +40 °C (+32 to +104 °F),
Nonoperating: –20 to +71 °C (-4 to +160 °F)
Operating: 20–80% RH, at up to +40 °C (+104 °F)
onoperating: 5–90% RH
N
perating: 3000 meters (10,000 feet)
O
Nonoperating: 12,000 meters (40,000 feet)
<27 ps
<29 ps (A, B, CM)
<18 ps (differential)
<20 ps (A, B, CM)
(differential)
22 P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference
Page 37

Specifications
Typical Chara
cteristics
Typical characteristics describe typical but not guaranteed performance.
Table 4: Typical electrical characteristics
Characteristic Specification (applies to all models unless specified otherwise)
P7513 P7516 P7520
Bandwidth
Operating Voltage
Window
Differential signal
range (DC coupled)
Linearity
Offset voltage range
(referred to input)
DC offset drift
(referred to input)
DC voltage
measurement
accuracy
Maximum nondestructive input voltage ±15 V
Input impedance
Differential input resistance, DC coupled 100 kΩ ±6 kΩ
Input resistance matching
Common-mode input resistance,
DC coupled
Common-mode rejection ratio,
differential-mode
1
5X ±0.750 V ±0.750 V ±0.625 V
12.5X ±1.75 V ±1.75 V ±1.60 V
5X
12.5X
Differential
Single-ended and
common-mode
Differential 0.093 ±2%Offset scale accuracy
Single-ended and
common-mode
Differential –0.47 mV/ °C (5X)
Single-ended and
common-mode
5X
12.5X
1
>13 GHz >16 GHz >20 GHz (differential)
>18GHz(A,B,CM)
-2.0 V to +4.0 V -2.0 V to +4.0 V -2.0 V to +3.7 V
±1% over a dynamic range of –0.75 V to +0.75 V ±1% over a dynamic range
of –0.625 V to +0.625 V
±1% over a dynamic range of –1.75 V to +1.75 V ±1% over a dynamic range
of –1.60 V to +1.60 V
–1.5 V to +2.5 V
–1.8 V to +3.4 V
0.186 ±2%
–0.100 μV/ °C (5X)
–0.72 mV/ °C (12.5X)
+0.47 mV/ °C (5X)
+0.24 mV/ °C (12.5X)
±(2% of input + 2% of offset + 15 mV + 6.25 mV) ±(2% of input + 2% of
±(2% of input + 2% of offset + 37.5 mV + 16 mV) ± (2% of input + 2% of
(DC + peak AC)
(See page 27, Tip Specifications.)
±250 Ω side-to-side with respect to ground
50 kΩ ±3 kΩ
>60 dB at DC
>40dBto50MHz
>30 dB to 1 GHz
>20 dB to 7 GHz
>15dBto13GHz
between each input or between either probe inputs and ground
>60 dB at DC
>40dBto50MHz
>30dBto1GHz
>20dBto8GHz
>15dBto16GHz
–0.60 μV/ °C (12.5X)
+0.100 μV/ °C (5X)
+0.30 μV/ °C (12.5X)
offset + 15 mV + 6.25 mV)
offset + 37.5 mV + 16 mV)
>60 dB at DC
>40dBto50MHz
>30dBto1GHz
>20dBto10GHz
>12dBto20GHz
P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference 23
Page 38

Specifications
Characteristic Specification (applies to all models unless specified otherwise)
P7513 P7516 P7520
Differential
-mode rejection ratio,
common-mode
1
>40dBto50MHz
>30dBto1GHz
>20dBto7GHz
>15dBto13GHz
Channel isolation, single-ended mode
1
>40dBto50MHz
>30dBto1GHz
>20dBto7GH
z
>10dBto13GHz
Noise
Differential
Single-ended and
common-mode
<33 nV/ (5X)
<48 nV/
<38 nV/
<52 nV/
(12.5X)
(5X)
(12.5X)
Delay time 4.4 ns ±0.1 ns
1
Embedded probe only. Refer to Tip Specifications for specifications when using TriMode accessory tips. (See page 27, Tip Specifications.)
>40dBto50MHz
>30dBto1GHz
>20dBto8GHz
>15dBto16GHz
>40dBto50MHz
>30dBto1GHz
>15dBto8GH
z
>4 dB to 16 GHz
>40dBto50MHz
>30dBto1GHz
>20dBto9GHz
>12dBto18GHz
>40dBto50MHz
>30dBto1GHz
>15dBto9GH
>6 dB to 18 GHz
<33 nV/
<48 nV/
z
(5X)
(12.5X)
24 P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference
Page 39

Specifications
Tabl e 5: Typica
Characteristic Description
Dimensions, c
Dimensions,
Dimensions
Unit weight
l mechanical c haracteristics
ontrol box
probe body
, cable length
125.4 mm × 41 mm × 35 mm (4.9 in × 1.6 in × 1.4 in)
101.6 m m × 8.89 mm × 19 mm (4.0 in × 0.350 in × 0.750 in)
1.0 m (39.3 in) (from the probe body to the control box)
1.550 g (3.1 lbs) (probe, accessories and packaging)
Figure 26: Probe body and control box dimensions
P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference 25
Page 40

Specifications
Nominal Chara
cteristics
Nominal characteristics describe guaranteed traits, but the traits do not have
tolerance limits.
Table 6: Nom
Characteristic Description
Input configuration
Output c
Probe attenuation
s
setting
inal electrical characteristics
P75TLRST solder tip Differential (two signal inputs, A and B; shared with single-ended)
TriMode Resistor & Extended
Resistor
P75PDPM handheld module
oupling
solder tips
Single-ended (one each A and B signal input and two ground inputs)
Differential (two signal inputs, A and B; shared with single-ended)
Single-e
Differen
DC
5X and 12.5X
nded (one each A and B signal input and two ground inputs)
tial (two inputs, A and B)
26 P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference
Page 41

Specifications
Tip Specificat
ions
This section lists specifications that are applicable to the probe when used with
the accessory tips available for the TriMode probes.
P75TLRST Tri
Mode Long
Reach Solder Tip
Probe model
(bandwidth) Rise time CMRR DMRR Channel Isolation
P7513
(>13.0 GHz)
P7516
(>16.0 GHz)
P7520
(>20 GHz
mode)
(>18 GHz
A, B, CM
)
Diff
10%–90%: <40 ps
20%–80%: <32 ps
10%–90%: <28 ps
20%–80%:
10%–90
<27 ps (Diff mode)
<29 ps
(A, B, C
20%–80%:
<18 ps (Diff mode)
<20 ps
(A, B, CM modes)
<24 ps
%:
M modes)
Specifications are typical and apply to all ranges and input modes unless specified
otherwise.
>60 dB at D C
>40dBat50MHz
>30 dB at 1 G
>20 dB at 7 GHz
>15dBat13GHz
>60 dB at D C
>40 dB at 5
>30 dB at 1 GHz
>20 dB at 8 GHz
>15 dB at
>60 dB a
>40dBat50MHz
>30 dB at 1 GHz
>20 dB a
>15dBat20GHz
Hz
0MHz
16 GHz
tDC
t10GHz
>40 dB at 50
>30 dB at 1 GHz
>20 dB at 7 GHz
>15 dB at 13
>40dBat50MHz
>30 dB at 1 GHz
>20 dB at 8
>15dBat16GHz
>40dBat50MHz
>30 dB at
>20 dB at 9 GHz
>15dBat18GHz
MHz
GHz
GHz
1GHz
>40 dB at 50
>30 dB at 1 GHz
>20 dB at 7 GHz
>10 dB at 13
>40dBat50MHz
>30 dB at 1 GHz
>20 dB at 8
>6 dB at 16 GHz
>40dBat50MHz
>30 dB at
>15 dB at 9 GHz
>6 dB at 18 GHz
MHz
GHz
GHz
1GHz
Figure 27: P75TLRST TriMode Long Reach Solder Tip dimensions
P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference 27
Page 42

Specifications
The following fi
with the P75TLRST solder tip. A 50 ps rise time pulse source was used for this
measurement.
Figure 28: TriMode probe with the P75TLRST solder tip
gure shows the typical step response of the TriMode probes
The following figure shows a typical impedance plot of the TriMode probes with
the P75
Fi
TLRST solder tip.
gure 29: P75TLRST differential impedance
28 P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference
Page 43

Specifications
TriMode Resistor Solder
Tip
Probe model
(bandwidth) Rise time CMRR DMRR
P7513
(>13.0 GHz
Diff mode)
(>12.0 GHz
A, B modes)
(>5.0 GHz
CM mode)
P7516
(>16.0 GHz
Diff mode)
(>15.0 GHz
A, B modes)
(>12.0 GHz
CM mode)
P7520
(>18.0 GHz
Diff mode)
(>15.0 GHz
A, B modes)
(>12.0 GHz
CM mode)
10%–90%: <40 ps
20%–80%: <28 ps
10%–90%:
<32 ps Diff mode
<34 ps A, B modes
<36 ps CM mode
20%–80%:
<24 ps Diff mode
<24 ps A, B modes
<26 ps CM mode
10%–90%:
<29 ps Diff mode
<32 ps A, B modes
<34 ps CM mode
20%–80%:
<20 ps Diff mode
<22 ps A, B modes
<24 ps CM mode
Specifications
otherwise.
>60dBatDC
>40 dB at 50 MHz
>30 dB at 1 G Hz
>20 dB at 7 G Hz
>15 dB at 13 GHz
>60dBatDC
>40 dB at 50 MHz
>30 dB at 1 G Hz
>20 dB at 8 G Hz
>15 dB at 16 GHz
>60dBatDC
>40 dB at 50 MHz
>30 dB at 1 G Hz
>20 dB at 10 GHz
>15 dB at 20 GHz
are typical and apply to all ranges and input modes unless specified
>40dBat50MHz
>30 dB at 1 GHz
>20 dB at 7 GHz
>15dBat13GHz
>40dBat50MHz
>30 dB at 1 GHz
>20 dB at 8 GHz
>15dBat16GHz
>40dBat50MHz
>30 dB at 1 GHz
>20 dB at 9 GHz
>15dBat18GHz
Channel
Isolation
>40dBat50MHz
>30 dB at 1 GHz
>15 dB at 7 GHz
>10dBat13GHz
>40dBat50MHz
>30 dB at 1 GHz
>15 dB at 8 GHz
>10dBat16GHz
>40dBat50MHz
>30 dB at 1 GHz
>15 dB at 9 GHz
>10dBat18GHz
gure 30: TriMode Resistor solder tip dimensions
Fi
P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference 29
Page 44

Specifications
The following fi
the TriMode resistor solder tip. A 50 ps rise time pulse source was used for this
measurement.
Figure 31: Step response with the TriMode Resistor solder tip
gure shows the typical step response of the TriMode probes with
The following figure shows a typical impedance plot of the TriMode probes with
Mode resistor solder tip.
the Tri
Figure 32: TriMode Resistor solder tip differential impedance
30 P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference
Page 45

Specifications
TriMode Extended Resistor
Solder Tip
Probe model
(bandwidth) Rise time CMRR DMRR Channel Isolation
P7513
(>5.6 GHz
Diff mode)
(>3.4 GHz
A, B modes)
(>2.5 GHz
CM mode)
P7516
(>5.8 GHz
Diff mode)
(>3.6 GHz
A, B modes)
(>2.5 GHz
CM mode)
P7520
(>7 GHz
Diff mode)
(>4 GHz
A, B modes)
(>2.5 GHz
CM mode)
10%–90%:
<40 ps Diff mode
<110 ps A, B modes
<120 ps CM mode
20%–80%:
<28 ps Diff mode
<32 ps A, B modes
<40 ps CM mode
10%–90%:
<36 ps Diff mode
<100 ps A, B modes
<120 ps CM mode
20%–80%:
<24 ps Diff mode
<30 ps A, B modes
<40 ps CM mode
10%–90%:
<32 ps Diff mode
<50 ps A, B modes
<120 ps CM mode
20%–80%:
<24 ps Diff mode
<30 ps A, B modes
<40 ps CM mode
Specifications
otherwise.
>60 dB at D C
>40dBat50MHz
>30 dB at 1 GHz
>20 dB at 7 GHz
>15dBat13GHz
>60 dB at D C
>40dBat50MHz
>30 dB at 1 GHz
>20 dB at 8 GHz
>15dBat16GHz
>60 dB at D C
>40dBat50MHz
>30 dB at 1 GHz
>20dBat10GHz
>15dBat20GHz
are typical and apply to all ranges and input modes unless specified
>40 dB at 50 MHz
>30 dB at 1 GHz
>20 dB at 7 GHz
>15 dB at 13 GHz
>40 dB at 50 MHz
>30 dB at 1 GHz
>20 dB at 8 GHz
>15 dB at 16 GHz
>40 dB at 50 MHz
>30 dB at 1 GHz
>20 dB at 9 GHz
>15 dB at 18 GHz
>40dBat50MHz
>30 dB at 1 GHz
>15 dB at 7 GHz
>10dBat13GHz
>40dBat50MHz
>30 dB at 1 GHz
>15 dB at 8 GHz
>10dBat16GHz
>40dBat50MHz
>30 dB at 1 GHz
>15 dB at 9 GHz
>10dBat18GHz
Figure 33: TriMode Extended Resistor solder tip dimensions
P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference 31
Page 46

Specifications
The following fi
the TriMode extended resistor solder tip. A 50 ps rise time pulse source was used
for this measurement.
Figure 34: Step response with the TriMode Extended Resistor solder tip
gure shows the typical step response of the TriMode probes with
The following figure shows a typical impedance plot of the TriMode probes with
Mode extended resistor solder tip. The L=0 value gives a simplified model
the Tri
that follows the lower impedance limit envelope.
Figure 35: TriMode Extended Resistor solder tip differential impedance
32 P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference
Page 47

Specifications
P75PDPM Precision
Differential Probing
Module
Specifications
are typical and apply to all ranges and input modes unless specified
otherwise.
Probe model (bandwidth) Rise time CMRR
P7513
(>13.0 GHz )
P7516
(>16.0 GHz)
P7520
(>18.0 GHz)
10%–90%: <40 ps
20%–80%: <32 ps
10%–90%: <28 ps
20%–80%: <24 ps
10%–90%: <29 ps
20%–80%: <20 ps
>60 dB at DC
>40dBat50MHz
>30 dB at 1 GHz
>20 dB at 7 GHz
>15 dB at 13 GHz
>60 dB at DC
>40dBat50MHz
>30 dB at 1 GHz
>20 dB at 8 GHz
>15 dB at 16 GHz
>60 dB at DC
>40dBat50MHz
>30 dB at 1 GHz
>20 dB at 10 GHz
>15 dB at 20 GHz
gure 36: P75PDPM Precision Differential Probing Module dimensions
Fi
P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference 33
Page 48

Specifications
The following fi
the P75PDPM probing module. A 50 ps rise time pulse source was used for this
measurement.
Figure 37: TriMode probe with the P75PDPM probing module
gure shows the typical step response of the TriMode probes with
The following figure shows the typica l differential impedance of the TriMode
probes
Fi
with the P75PDPM probing module.
gure 38: P75PDPM differential impedance
34 P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference
Page 49

User Service
This section covers troubleshooting and probe maintenance.
If your probe does not meet the specifications listed in the Specifications,youcan
send the probe to Tektronix for repair. (See page 48, Preparation for Shipment.)
Error Condi
tion
The LEDs on the probe alert you to error or status conditions affecting the probe.
When the probe is functioning correctly, there is a quick flash of the LEDs on
the probe
otherwise appear to be malfunctioning, an error condition may exist. Disconnect
the probe and reconnect it to another channel to isolate the problem. If the
symptoms persist with the probe, call your Tektronix repres entative for service.
just after connecting to the oscilloscope. If the probe LEDs flash or
P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference 35
Page 50

User Service
Replaceable Parts
The following parts may need to be replaced due to normal wear and damage.
When you replace these components, secure the probe in a small vise or positioner
to simplify the procedure.
Table 7: TriMode probes replaceable parts
Description Replacement part number
Probe body bullet contacts
P75TLRST solder tip wires
TriMode Resistor (020-2936-xx)
& TriMode Extended Resistor
(020-2944-xx) solder tip resistors
P75PDPM Probing Module
springs
P75PMT Probing Module tips
(left and right)
P75TC Probing Module Tip Cable P75TC, qty. 1
013-0359-xx, kit of 4
020-2754-xx, Wire Replacement Kit, includes one
bobbin each: 4 mil wire, 8 mil wire, and SAC305 solder
020-2937-xx Replacement Resistor Kit, includes 50
each:
100 Ω leaded resistors, 75 Ω surface mount resistors,
nonconductive tubing
016-1998-xx, kit of 4 (large springs)
016-1999-xx, kit of 4 (small springs)
P75PMT, one pair
Refer t
o the user manual for a list of the accessories that are available for your
probe.
Table 8: Required equipment
Description Minimum requirement Recommended example
1897-xx
Connector separator tool Custom tool
Ground spring tool Custom tool
ezers
Twe
Magnifying glass or
microscope
Probe positioner or bench
vise
1
Nine-digit part numbers (xxx-xxxx-xx) are Tektronix part numbers.
General purpose
ee standing to allow
Fr
hands-free use
Able to hold probe PPM203B or PPM100
003-
003
-1900-xx
1
36 P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference
Page 51

User Service
Replacing probe body
bullet contacts
The bullet cont
cycles. Follow these steps to replace the bullets by using the removal tool:
Remove.
1. Squeeze the tool plunger to extend the holder tangs.
2. Insert the tool into the probe body so that the holder tangs surround one of the
bullets.
3. Release the plunger to secure the holder tangs on the bullet.
4. Gently pull the tool outward to remove the bullet.
5. Repeat for the other bullet.
CAUTION. If you cannot extract the bullets with the bullet removal tool, use fine
needle-nosed pliers and a magnifying glass or microscope. Be careful not to
damage the probe body with the pliers.
acts in the probe body should be replaced every 200 insertion
Figure 39: Removing the bullets
P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference 37
Page 52

User Service
Install. When b
following:
1. Squeeze the to
2. Insert a new bullet into the tool so that the holder tangs surround the bullet.
3. Release the plunger to secure the holder tangs on the bullet.
4. Insert the tool into the probe body and seat the bullet in the recess.
5. Squeeze the tool plunger to release the bullet.
6. Gently pull the tool out of the probe body.
7. Repeat fo
8. Test that the bullets are installed correctly by connecting and then removing
an acces
that the bullets remain seated in the probe head.
oth bullets have been removed, install new bullets by doing the
ol plunger to extend the holder tangs.
r the other bullet.
sory solder tip to the probe head. Inspect the probe head and verify
Figure 40: Installing the bullets
38 P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference
Page 53

User Service
P75TLRST Solder Tip
Wires
The solder vias
small (0.012 in.), and require small wires to attach to your circuit. (Use the 4-mil
and 8-mil wires included with the Wire Replacement kit to make the connections.)
Because of the small dimensions, the solder tips have a limited number of solder
cycles that the vias can withstand before the Solder Tips become unusable. If you
expect to make frequent soldering changes, consider using the optional TriMode
Resistor so
number of solder cycles and can be replaced when necessary.
NOTE. Axial-leaded tip resistors (included in the TriMode resistor replacement
kit, Tektronix part number 020-2937-XX), should not be used in place of wires
with the P75TLRST probe tip unless the surface-mount, SMD0402 resistors
are also changed. The total probe tip resistance for the P7500 Series probes is
designe
CAUTION. To prevent damage to the circuit board or circuit board connections
due to a
you secure the tip to the circuit board using the adhesive tip tape provided in your
accessory kit. You can also use other materials such as Kapton tape or hot glue.
To avoid damage to the tip or the circuit under test, avoid applying excessive heat
from the soldering iron. Use a low wattage, temperature-controlled soldering iron
and appropriately sized soldering iron tip.
dtobe175Ω.
ccidental movement of the probe and soldered leads, we recommend that
on the circuit board at the end of the P75TLRST Solder Tip are
lder tips. The resistors that extend off of these tips can accept a higher
To prolong the life of your solder tips, consider the following points before you
use the solder tips.
Consider the types of measurements that you plan to take. If you are going to take
a few measurements at one location and then move to another, you may be able to
use longer wires. Longer wires may degrade your measurement slightly (which
may not matter), but the wires can then be cut or desoldered at your circuit and
eused, rather than subjecting the solder tip to a desolder/solder cycle.
r
Perhaps the optional P75PDPM Precision Differential Probing Module is a better
choice for the test points that you do not m easure as often. The probing module
can take both single-ended and differential measurements, and when used with
a probe positioner, can provide hands-free access to tight spaces. Depending
on your measurement requirements and circuit geometries, the probing module
might be a preferable alternative.
At critical test points such as circuit outputs, you might need to keep the wires
as short as possible. If possible, use the solder tip dimensions shown in the
Specifications section to lay out a matching footprint o n your circuit board.
P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference 39
Page 54

User Service
P75PDPM Probing Module
Springs
Use the followi
For best soldering results, use a microscope to examine the quality of the
solder joints
Use a low-wattage, temperature-controlled soldering iron and a small mass
soldering i
possible, while still providing a reliable solder joint.
Use SAC305 s
wires to the circuit under test.
When repla
remove the excess solder from the probe tip circuit board via holes. Be careful
not to overheat the via and damage the board.
Theattachmentwiresshouldbebentsymmetrically to vary the interconnect
spacing. Use care when you solder a tip to a circuit under test to avoid
inadvertently desoldering either the attachment wires or the damping resistor.
For optimum performance and signal integrity, keep the lead length between
the DUT (Device Under Test) and the tip as short as possible, and the lead
lengths the same length.
Equipment Required: ground spring tool, magnifying glass or microscope,
tweezers, probe holder
ng precautions when you solder the tips:
.
ron tip. The soldering iron temperature should be set as low as
older (included with the wire replacement kit) to attach the tip
cing tip wires or axial-lead resistors, solder wick can be used to
Figure 41: Large and small springs installed
40 P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference
Page 55

User Service
Remove.
1. Adjust the tip gap using the gap measurement tab on the spring tool. Set the
tool between the tip circuit boards, not the tips.
Figure 4
2. Insert
Figure 43: Insert tool beneath spring
2: Set the gap
the ground spring tool under the top of the spring.
P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference 41
Page 56

User Service
3. Rock the tool aw
ay from the tips so that the spring clears the seat edge.
Figure 44: Transfer spring from tip to tool
4. Gently pull the tool away; the spring should come away with the tool.
5. Put the spring in the accessory container or a safe place to avoid losing the
spring.
42 P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference
Page 57

User Service
Install.
1. Two spring sizes are available: the small spring allows 0.030 – 0.090 in.
(0.76 – 2.28 mm) tip span, the large spring allows 0.050 – 0.180 in.
(1.27–4.57m
2. Check that the tip gap is .032 in. using the gap measurement tab on the spring
tool. Adjus
3. Using tweezers, install the spring on the tool. The tool has a large and small
side, one f
of the tool as shown.
m) tip span.
t if necessary.
or each size spring. Make sure the gap in the spring is on the top
Figure 45: Place spring on tool
4. Set the bottom of the spring in the front seats (those closest to the tip ends).
Maintain a slight pressure on the spring to keep it in the front seats.
Figure 46: Set spring in front seat
P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference 43
Page 58

User Service
5. Set the top of th
the rear seat with the top of the spring.
e spring in the rear seats by lifting the tool to clear the edge of
Figure 47: Set the spring in the rear seats
6. Gently retract the tool from the spring. Verify that the spring is seated as
shown.
Figure 48: Properly seated spring
44 P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference
Page 59

User Service
P75TC Probing Module Tip
Cable
Equipment Requ
1. Disconnect the Cable Tip by the inserting the tool between the connectors.
The tapered ed
tip connector.
Figure 49: Disconnecting the tip cable
ired: connector separator tool
ges of the tool gently separate the cable connector from the
P75PMT Probing Module
Tips (Left and Right)
2. Repeat for the other cable and then pull both cables away from the tip
connectors.
Equipment Required: connector separator tool, magnifying glass or microscope
(preferred), tweezers, and probe holder.
NOTE. The probing module tips are electrically matched pairs and should be
replaced together. Failure to do so may degrade the performance of your probe.
Figure 50: Probing module tips
P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference 45
Page 60

User Service
Remove.
1. DisconnecttheCableTips. (Seepage45,P75TC Probing Module Tip Cable.)
2. Remove the spring. (See page 40, P75PDPM Probing Module Springs.)
3. Adjust the tip gap to maximum width.
4. Use the connector separator tool or a small sc rewdriver to pry the board up
from the bottom. The bottom tabs are designed to flex; the top tabs are not.
Figure 51: Removing the tip
5. Repeat for the other tip.
Install.
6. Separate the new tip board pair by snapping the board against a sharp edge.
Figure 52: Separating the tip board pair
46 P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference
Page 61

User Service
7. Select the corr
board is notched to align it to the tip body.
Figure 53: Seating the tip in the top tabs
8. Press the bottom of the board to snap it past the bottom tabs.
ect board (left or right), and seat the board in the top tabs. The
Figure 54: Snapping the tip into the bottom tabs
9. Repeat steps 7 and 8 for the other tip.
10. Attach the spring. (See page 40, P75PDPM Probing Module Springs.)
11. Reattach the cable pair.
P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference 47
Page 62

User Service
Preparation f
or Shipment
If the original packaging is unfit for use or not available, use the following
packaging guidelines:
1. Use a corrugated cardboard shipping carton having inside dimensions at least
2. Put the probe into an antistatic bag or wrap to protect it from dampness.
3. Place the probe into the box and stabilize it with light-weight packing material.
4. Seal the carton with shipping tape.
5. Refer to Contacting Tektronix on the copyright page of this manual for the
one inch greater than the probe dimensions. The box should have a carton
test streng
shipping address.
th of at least 200 pounds.
48 P7500 Series TriMode Probes Technical Reference
 Loading...
Loading...