Page 1

xx
MTS4EA
ZZZ
Elementary Stream Analyzer
Tutorials
This document applies to software version 6.0.
www.tektronix.com
001-1414-01
Page 2

Copyright © Tektronix. All rights reserved. Licensed software products are owned by Tektronix or its subsidiaries
or suppliers, and are protected by national copyright laws and international treaty provisions.
Tektronix products are covered by U.S. and foreign patents, issued and pending. Information in this publication
supersedes that in all previously published material. Specifications and pric e change privileges reserved.
TEKTRONIX and TEK are registered trademarks of Tektronix, Inc.
Contacting Tektronix
Tektronix, Inc.
14200 SW Karl Braun Drive
P.O . B o x 5 00
Beaverton, O
USA
For product information, sales, service, and technical support:
In North America, call 1-800-833-9200.
World w i de, visit www.tektronix.com to find contacts in your area.
R 97077
Page 3

Table of Contents
Getting Started ........... . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ..................... . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ..................... . ........... . . . . . . . . 1
Basic Functions ................................................................................................ 2
How to Begin a Tutorial ............. ................................ ................................ ......... 2
Tutorial 1: H.
Procedure ....................................................................................................... 3
Conclusion...................................................................................................... 9
Tutorial 2: H.263 Compliance and Motion Vectors ........................................................... 10
Procedure ...................................................................................................... 10
Conclusion..................................................................................................... 15
Tutorial 3: M
Procedure ...................................................................................................... 16
Conclusion..................................................................................................... 22
Tutorial 4: MPEG-4 Optimization............. ................................ ................................ .. 23
Procedure ...................................................................................................... 23
Conclusion..................................................................................................... 30
Tutorial 5: M
Procedure ...................................................................................................... 31
Conclusion..................................................................................................... 36
Tutorial 6: MP4 Optimization.................................................................................... 37
Procedure ...................................................................................................... 37
Conclusion..................................................................................................... 41
Tutorial 7:
Procedure ...................................................................................................... 42
Conclusion..................................................................................................... 46
Tutorial 8: H.264/AVC Syntax Error............................................................................ 47
Procedure ...................................................................................................... 47
Conclusion..................................................................................................... 50
Tutorial 9:
Procedure ...................................................................................................... 52
Conclusion..................................................................................................... 63
Tutorial 10: MPEG-2 Compliance..................... .................................. ........................ 64
Procedure ...................................................................................................... 64
Conclusion..................................................................................................... 73
Tutorial 1
Procedure ...................................................................................................... 74
Conclusion..................................................................................................... 83
261 ................................................................................................... 3
PEG-4 Compliance................................................................................ 16
P4 Compliance Basics. .................................. ................................ .......... 31
3GPP/MPEG-4 Compliance ........................................................................ 42
MPEG-4 and H.264/AVC Buffer Analysis ...................... .................................. 51
1: Fidelity Analysis.. ................................ ................................ .................. 74
MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials i
Page 4

Table of Contents
ii MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials
Page 5

Getting Started
This set of eleven tutorials helps you learn more about operating the Tektronix
MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer. Perform tutorials 1 through 11 in the
order they ar
e presented, regardless of the video standard of interest. Tutorial 10
relatesonlytoMPEG-2andinterlacedvideo.
The tutorial
s will help you answer the following questions:
How do you know that your video compression complies with the standards
If your codec doesn’t work well with other vendors’ codecs, where is the
problem — is it with your codec or theirs
Are you optimizing your Codec
Are you making the best use of available b andwidth
Which frames and movement types use the most bits and why
What changes to your codec software give the best reductions in bits used for
the least reduction in visual quality
What types of video content does your codec work poorly with and why
A descript
ion for each tutorial follows. (See Table 1.)
Table 1: Tutorial descriptions
Tutorial Name Standard Areas Covered
1 H.261 H.261
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
H.263 C ompliance and Motion
Vectors
MPEG-4 Compliance MPEG-4 Simple Profile Common errors; searching for areas
MPEG-4 Optimization MPEG-4 Adv. Simple Profile Common errors; HexView
MP4 Compliance Basics MP4/ Simple Profile/ L1(2) Extract and examine container files;
MP4 Optimization MP4/ Simple Profile/ L1(2)
3GPP/MPEG-4 Compliance 3GPP/MPEG-4 Simple Profile/ L1 Common errors; searching for areas
H.264/AVC Syntax Error H.264/AVC Extended Profile/ L3 Syntax error in PPS; trace analysis
MPEG-4 and H.264/AVC Buffer
Analysis
H.263 Baseline Errors and error log; motion vectors.
MPEG-4 ASP and H.264/AVC Buffer analysis in MPEG-4 and
Syntax error; compression
optimization; graph analysis
of codec optimization.
bitstream analysis; video navigator;
synchronize views; project files
level conformance error.
Using MB type overlays and
searching for areas of optimization.
for optimization
of syntax
H.264/AVC; fixing problems.
MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials 1
Page 6

Getting Started
Table 1: Tutorial descriptions (cont.)
Tutorial Name Standard Areas Covered
10
11 Fidelity Analysis
MPEG-2 Compliance MPEG-2 Main Profile / Main Level Syntax errors; MPEG structure
analysis; interlace.
MPEG-4, MPEG-2, and H.264 Fidelity analysis; visual difference.
Basic Functions
To complete the tutorial procedures, you must be familiar with the following basic
functions. To perform the desired function, click the associated icon or type the
appropriate keyboard shortcut. (See Table 2.)
Table 2: B
Function Forward Backward
Play video
Stop video
Pause/step one frame Ctrl + A Ctrl + Shift + A
Fast forward/backward Ctrl + F Ctrl + Shift + F
Pause on frame
Skip to next frame
type/number/time
asic functions
Icon Keyboard shortcut Icon Keyboard shortcut
Ctrl + P Ctrl + Shift + P
Ctrl + S Ctrl + S
Ctrl + K Ctrl + Shift + K
How to Begin a Tutorial
1. After starting MTS4EA, click anywhere to remove the splash screen. If you
do noth
2. Load the desired tutorial stream. Note that the demo version of the MTS4EA
will on
ing, the splash screen will disappear after 4 seconds.
ly play the provided example video fi les.
2 MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials
Page 7
Tutorial 1: H.261
Procedure
This tutorial shows non-compliance issues with the H.261 standard using temporal
references and graphical analysis.
1. To load the H.261 tutorial, click File > Example files > H.261 stream >
Conference Room. The window title changes to MTS4EA-H.261 Example
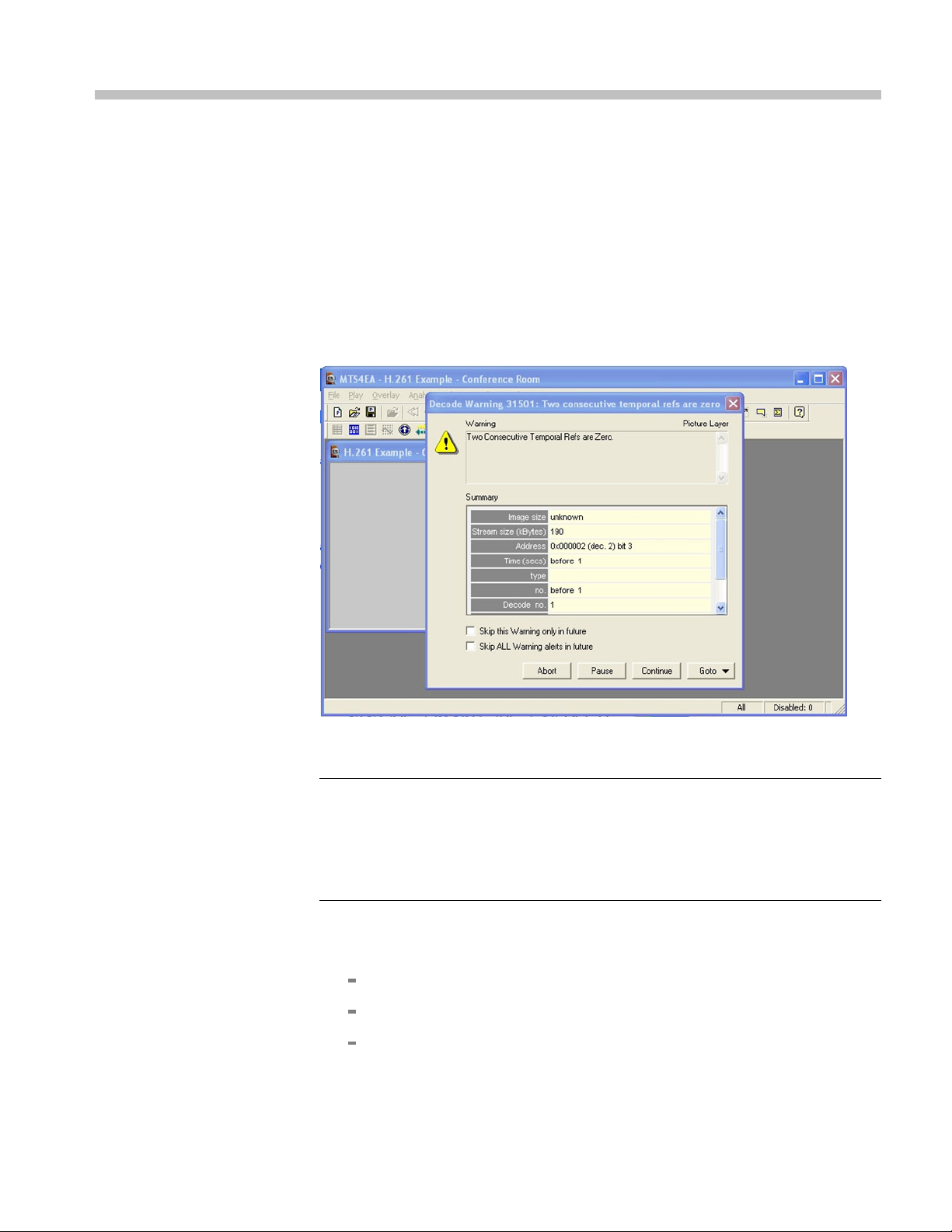
- Conference Room, and a warning message appears. (See Figure 1.)
Figure 1: Initial warning message
NOTE. The H .261 standard states that the temporal reference (TR) value is the
previous TR value + 1 + the number of skipped or non-reference pictures at the
picture clock frequency (PCF). TR is 8 bits only, 0–255, at the standard PCF of
29.97 frames per second. However, if a custom PCF is used, then TR is 10 bits: 8
LSBs are denoted as TR and 2 MSBs are ETR, but they are taken together as a
single 10-bit number.
2. View the warning message elements:
Warning - Indicates that two consecutive temporal references are zero.
Summary - Gives summary informat
Skip this Warning only in the future -electstoskipthisparticular
warning in the future (recommended).
MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials 3
ion about the stream.
Page 8
Tutorial 1: H.261
Skip ALL Warnin
all other alerts in the future.
3. Select Skip th
4. Click the
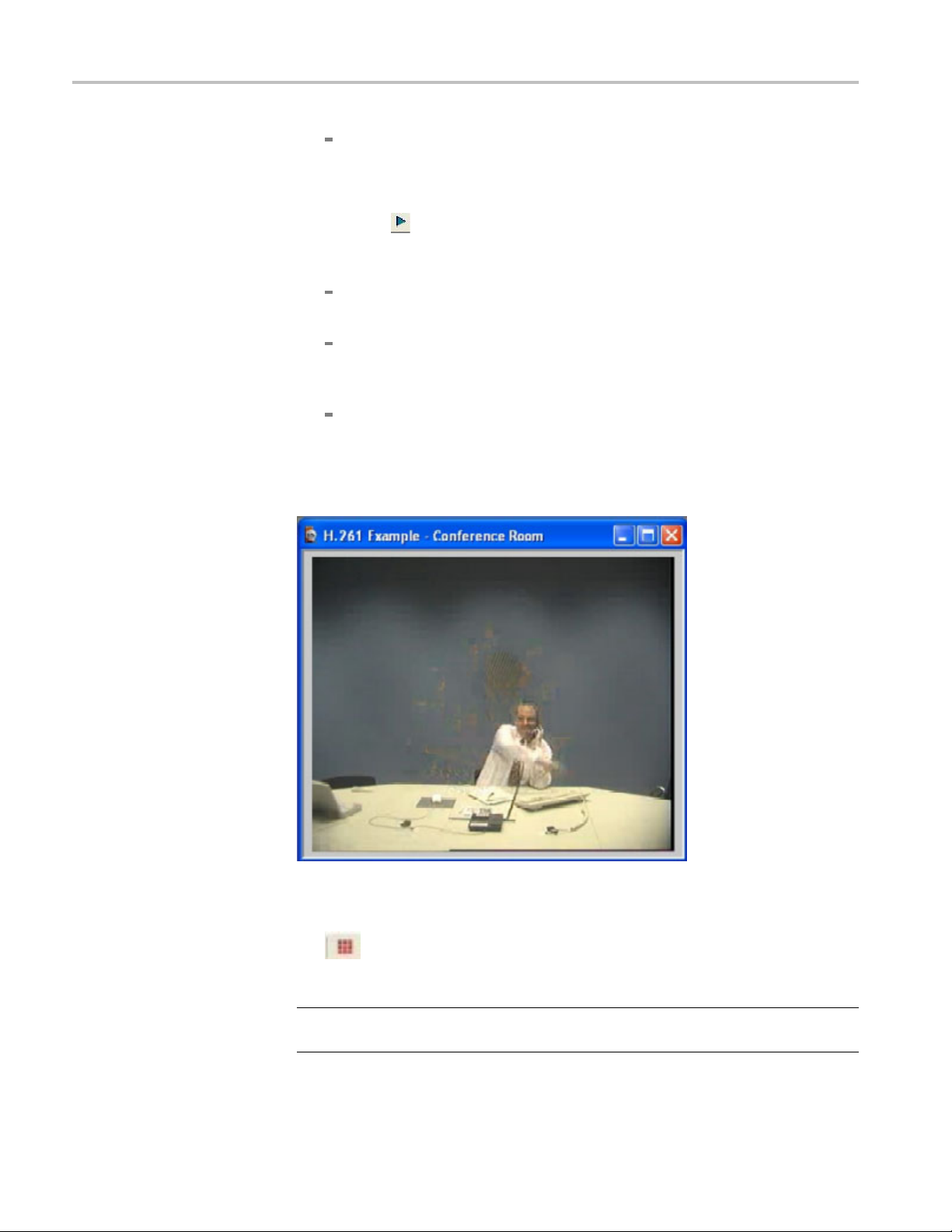
5. As you view the video, notice the following: (See Figure 2.)
Movement in the video is too quick (requires PC with processing speed
of greater than or equal to 1 GHz)
Unwanted noise (visual artifacts) is visible when the man waves his arm
(starting around frame 128, continuing into frame 161, with some artifacts
remaining until frame 203)
Status bar notes that one alert is disabled
Although the video stream will play and will probably be decoded by other
H.261 decoders, the H.261 sequence was incorrectly e ncoded, showing
temporal issues.
is Warning only in the future, and then click Continue.
toolbar icon or type CTRL + P to resume playing the video.
g alerts in the future -electstoskipthisalertand
Figure 2: Visual artifacts
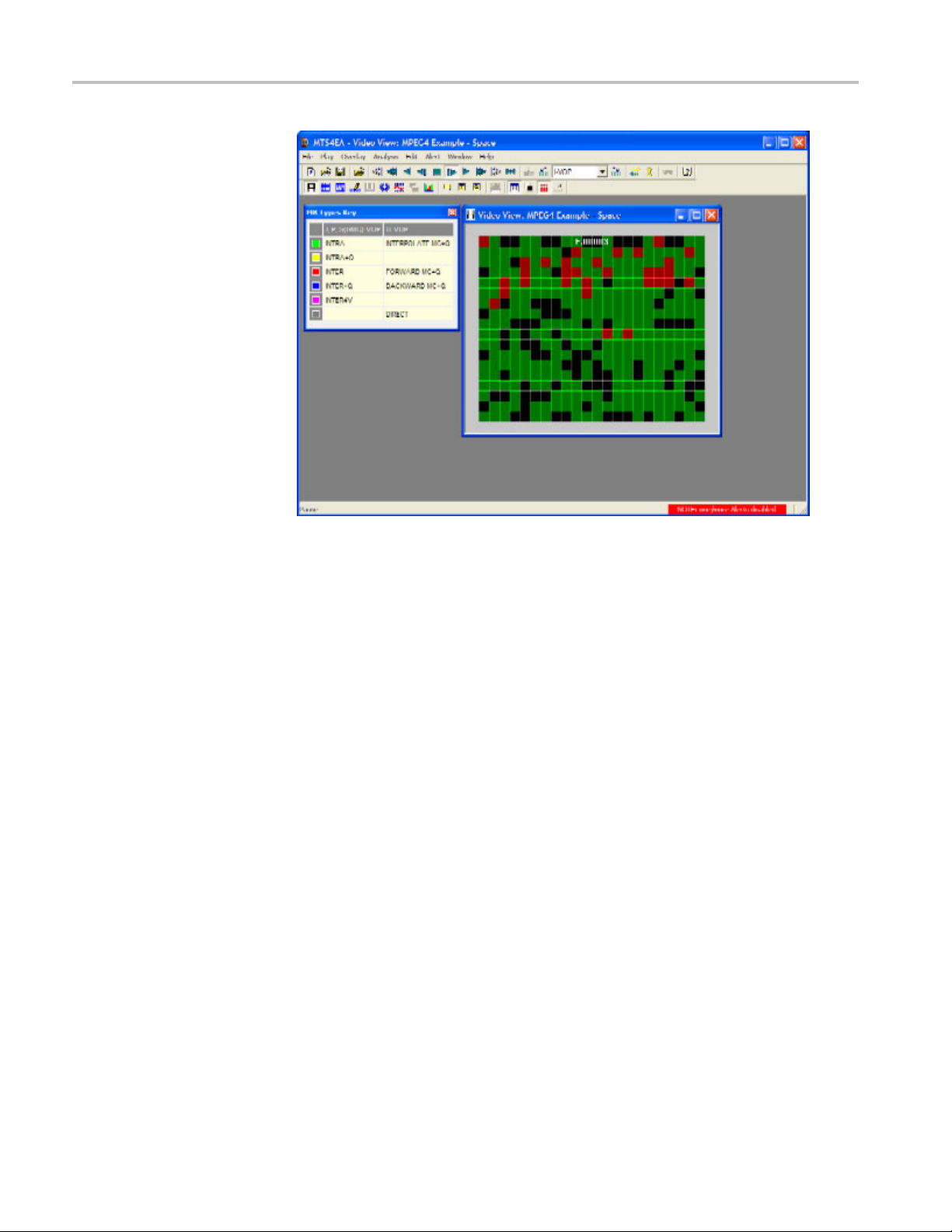
6. Click Overlay on the menu and select MB Types, or click the Overlay icon
on the toolbar. MB (macroblock) Types are color coded and can be
cked, resized, or switched off. (See Figure 3.)
undo
NOTE. The H.261 standard has 10 MB types. For more information on using
these, see the user manual.
4 MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials
Page 9

Tutorial 1: H.261
Figure 3: MB overlay
7. Check that the video is in either Play or Pause mode.
8. Click the MB Tooltip icon
the left edge of the window, but you can undock it by pressing <CTRL> on
your keyboard while dragging the Tooltip with your mouse.
9. Move the mouse over the video. A white box will display around the MB
from which data is being read. The Tooltip shows information about that
MB. (Se
eFigure4.)
on the toolbar. The Tooltip typically docks at
Figure 4: MB types and data
MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials 5
Page 10
Tutorial 1: H.261
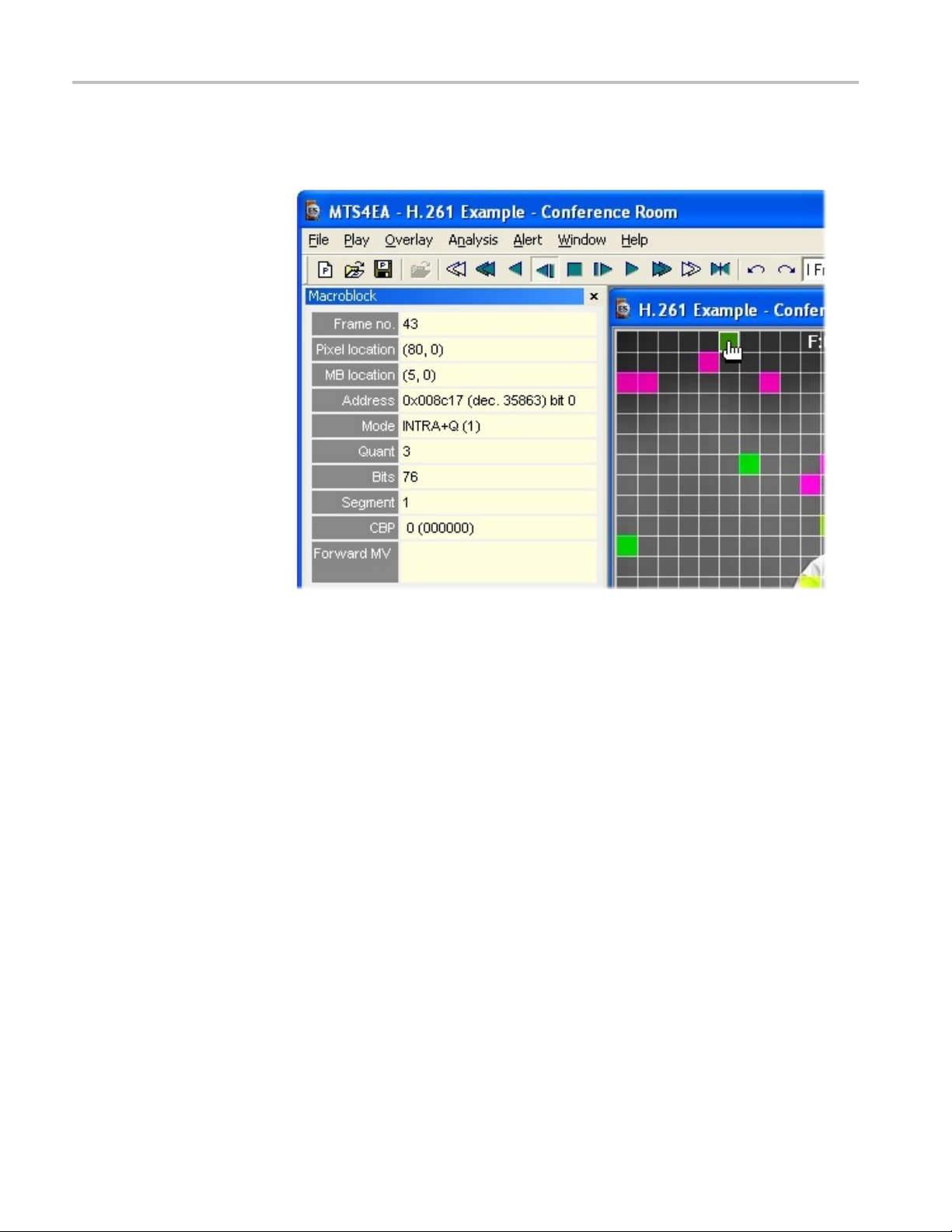
10. Advance throug
the background wall. These block types use the most bits. (See Figure 5.)
h the video frame by frame, noting many green Intra MBs in
Figure 5: Intra MBs in the background wall and MB data
11. Stop the video sequence.
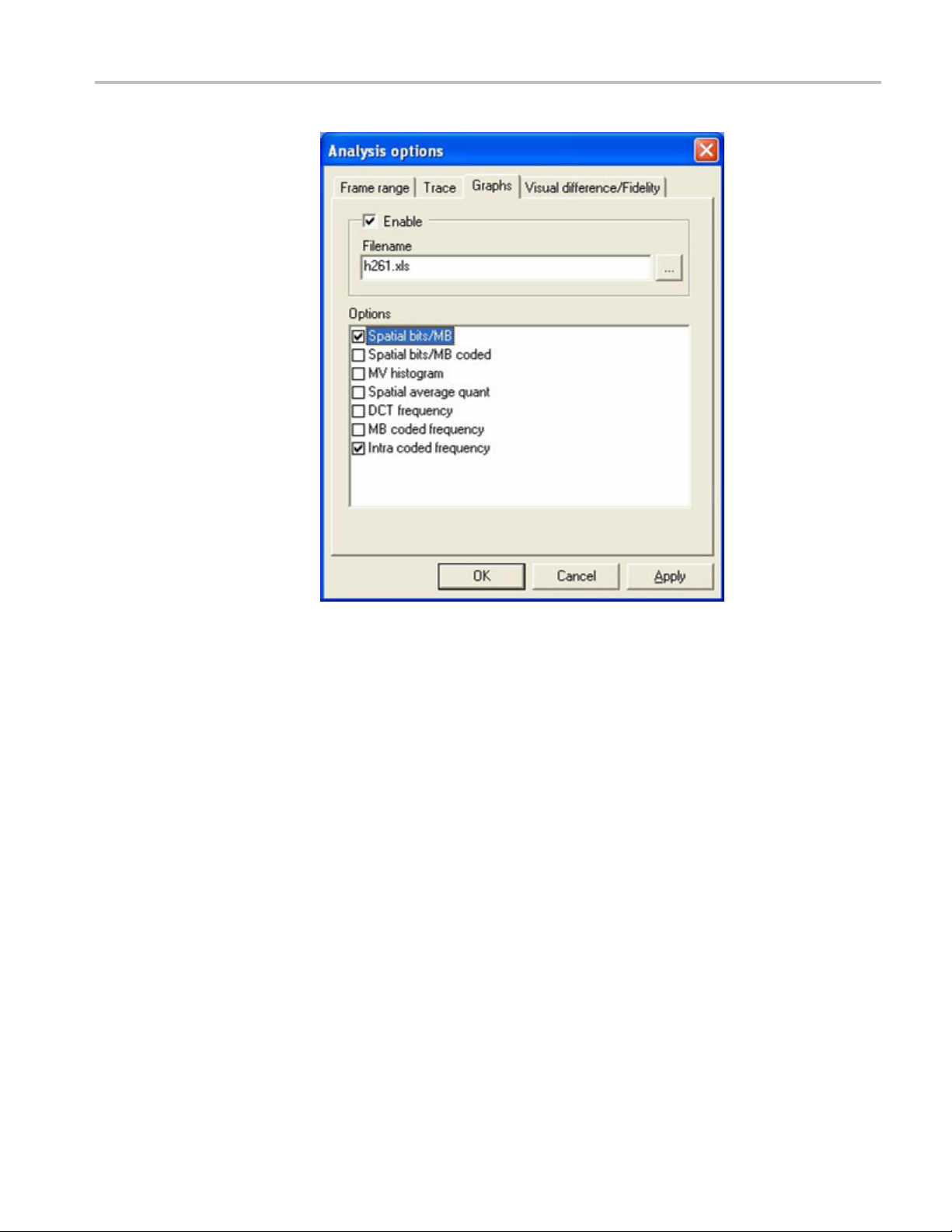
12. To analyze the MB data, select Analysis from the menu and select Video
graph enable. A dialog box will appear. (See Figure 6.)
6 MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials
Page 11
Tutorial 1: H.261
Figure 6: Analysis dialog box
13. Check the Enable, Spatial bits/MB,andIntra coded frequency boxes in the
Analysis dialog box.
14. Select the output filename: h261.xls.
15. Click O
16. When play ends, the data is exported to the .xls file and MS Excel will open.
Click E
17. Click Spatial Bits per MB to view a graph of the spatial bits per MB. (See
Figur
K andthenplaythevideo.
nable macros. The screen will flash as the macros run.
e7.)
MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials 7
Page 12

Tutorial 1: H.261
Figure 7: Spatial bits per MB
NOTE. Notice that many bits are used in the center (by the man), top left (too
many), and along the bottom edge (too many). These last two are errors.
18. Click the Intra Coded Frequency tabtoviewagraphoftheIntraCoded
Frequency. (See Figure 8.)
8 MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials
Page 13
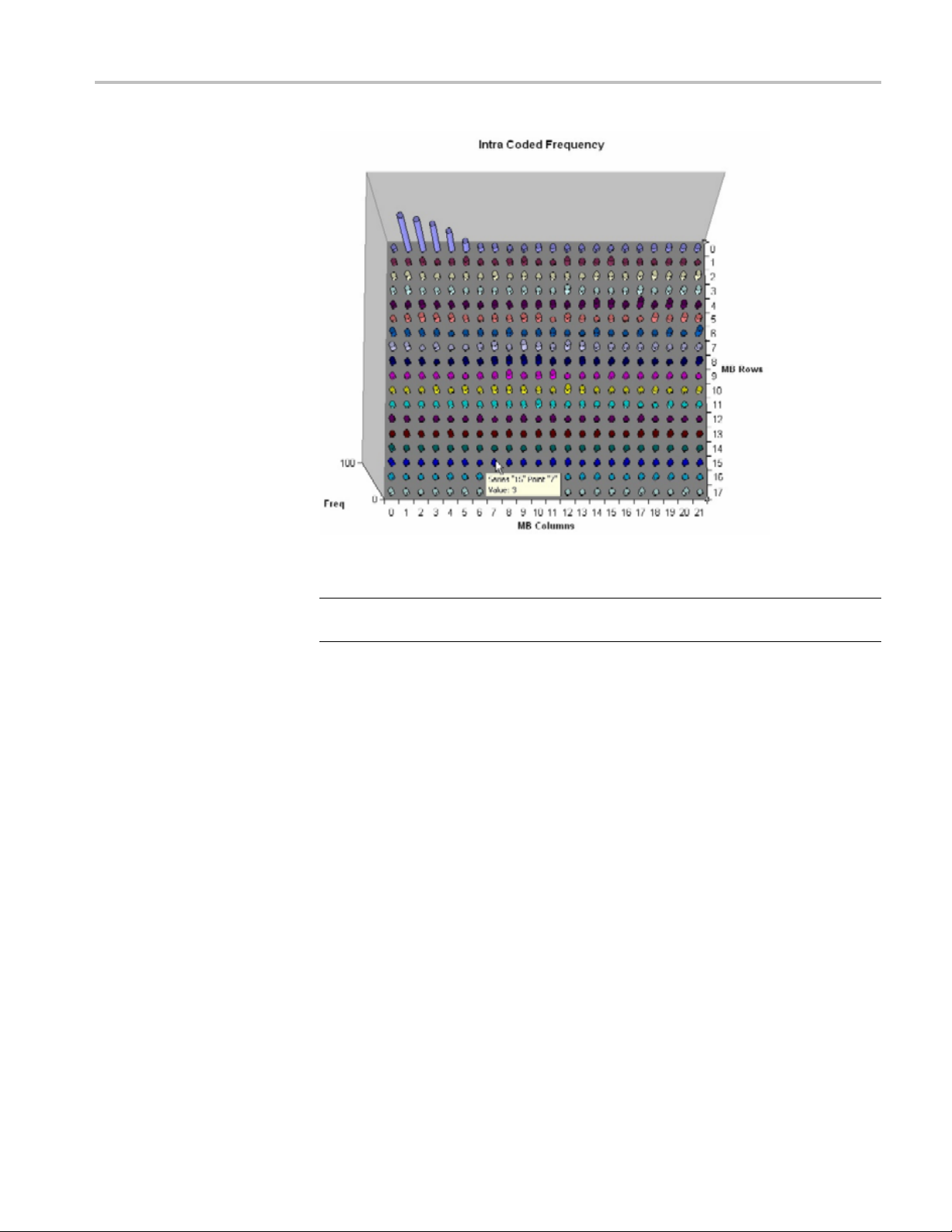
Tutorial 1: H.261
Conclusion
Figure 8
NOTE. Notice that there are many Intra-coded MBs at the top left of the graph.
This indicates that there is an error with Intra-coding in the encoder.
This tutorial demonstrated that the H .261 bitstream is not standard compliant and
that th
TR errors and frequency of playing. Coding inefficiencies were discovered
through graphical analysis.
: Intra coded frequency
ere were coding inefficiencies. These problems were discovered through
MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials 9
Page 14
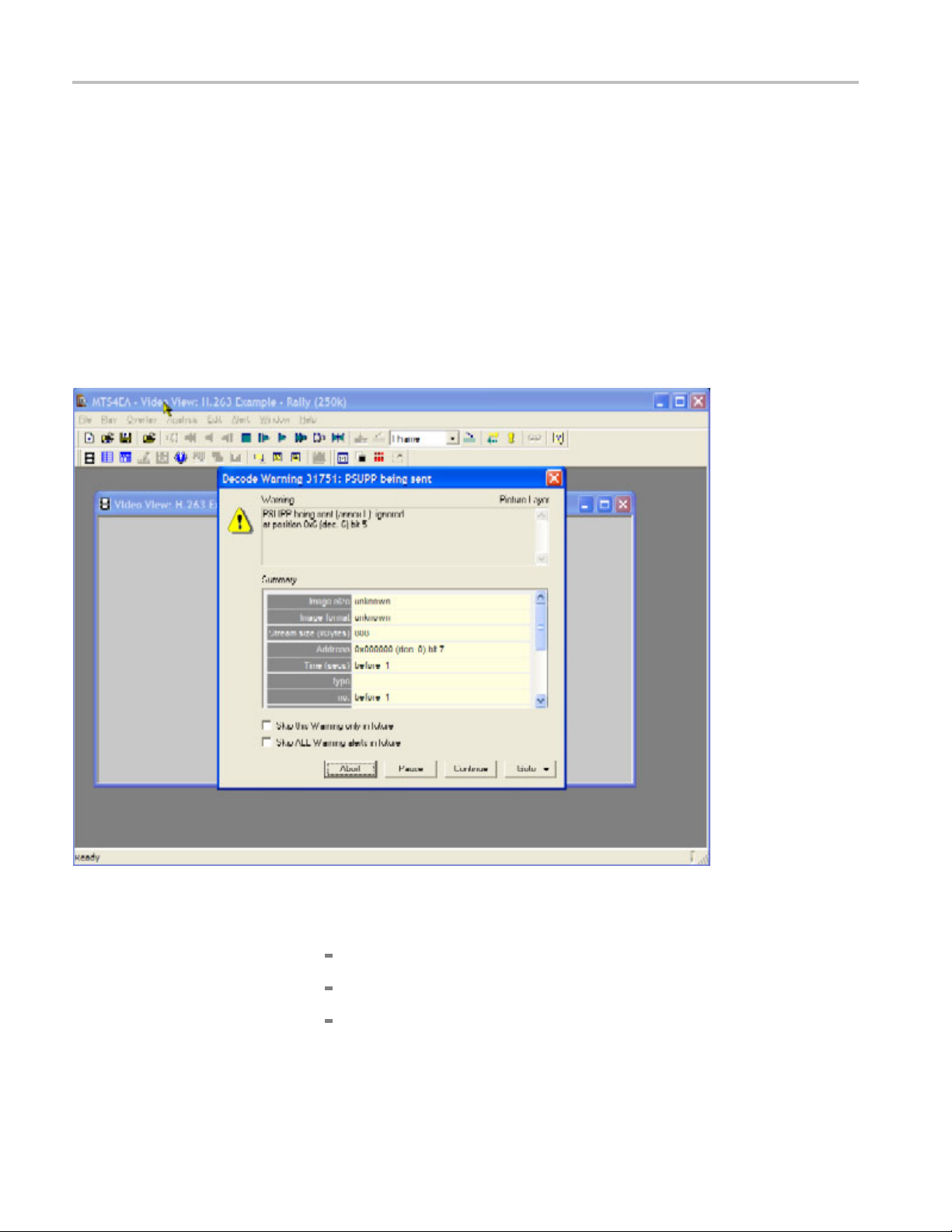
Tutorial 2: H.263 Compliance and Motion Vectors
Tutorial 2: H.
Procedure
263 Compliance and Motion Vectors
This tutorial
demonstrates the proper functioning of the motion vectors.
1. To load the H.263 tutorial, c lick File > Example files > H.263 stream >
Rally (250K). The window title changes to MTS4EA-H.263 Example Rally (250k), and a warning message appears. (See Figure 9.)
covers the standards and compliance issues in H.263 and also
Figure 9: Initial warning message
2. View the warning message elements:
Warning - Indicates that the PSUPP field is being sent and ignored.
Summary - Gives summary information about the stream.
Skip this Warning only in the future - elects to skip this particular
warning in the future (recommended).
10 MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials
Page 15
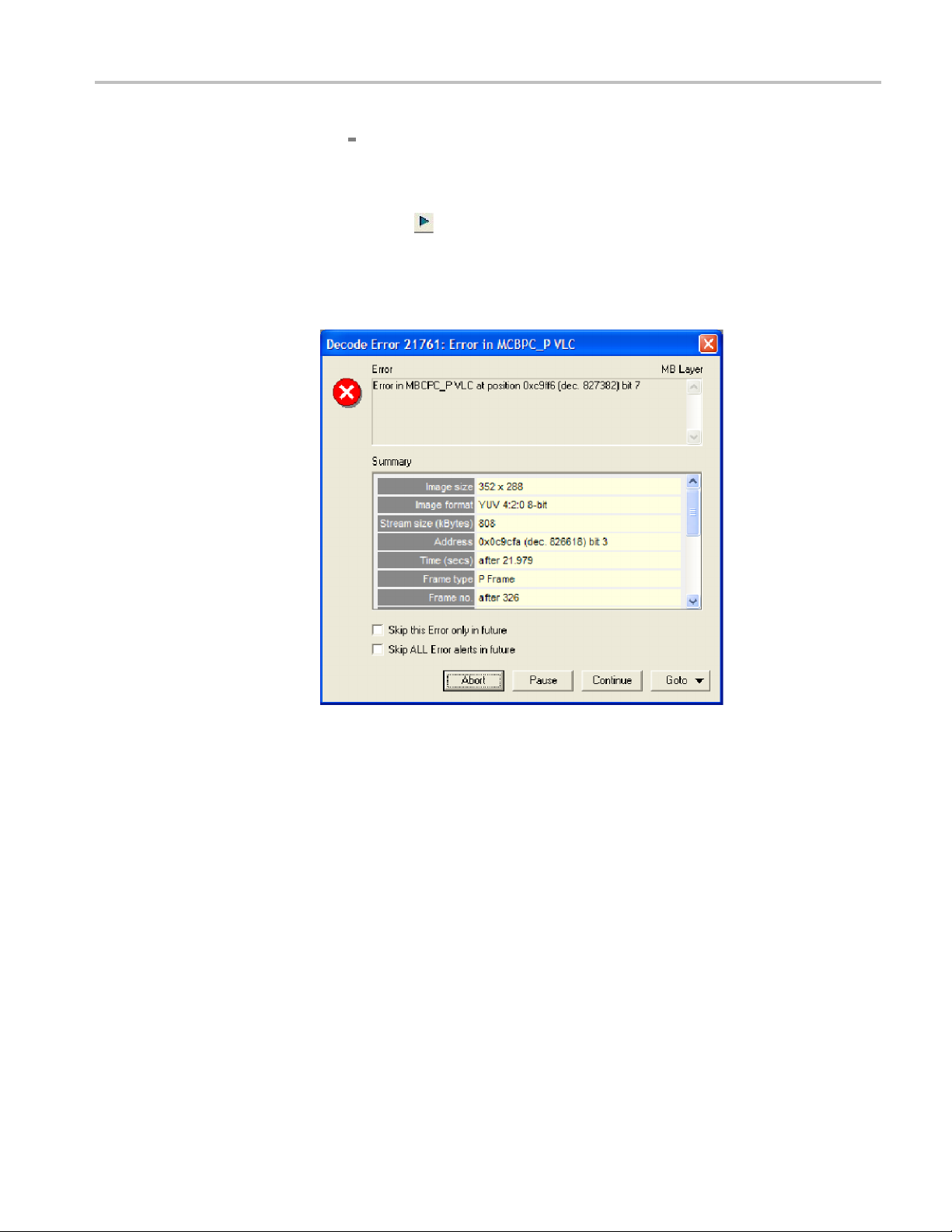
Tutorial 2: H.263 Compliance and Motion Vectors
Skip ALL Warnin
all other alerts in the future.
3. Select Skip th
4. Click the
Another error message appears. (See Figure 10.)
5. View the error information provided, which indicates a more serious error that
occurs at bitstream byte address 0x0c9cfa, bit 3, after frame 326.
is Warning only in the future, and then click Continue.
toolbariconortypeCTRL + P to resume playing the video.
g alerts in the future -electstoskipthisalertand
Figure
6. Click Co
7. Note that it was an MBCPC error that resulted in the Out of Sync alert
MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials 11
10: Initial error message
ntinue. Another error message will appear. (See Figure 11.)
messag
e. This often occurs when one syntax error triggers a series of alerts.
Page 16
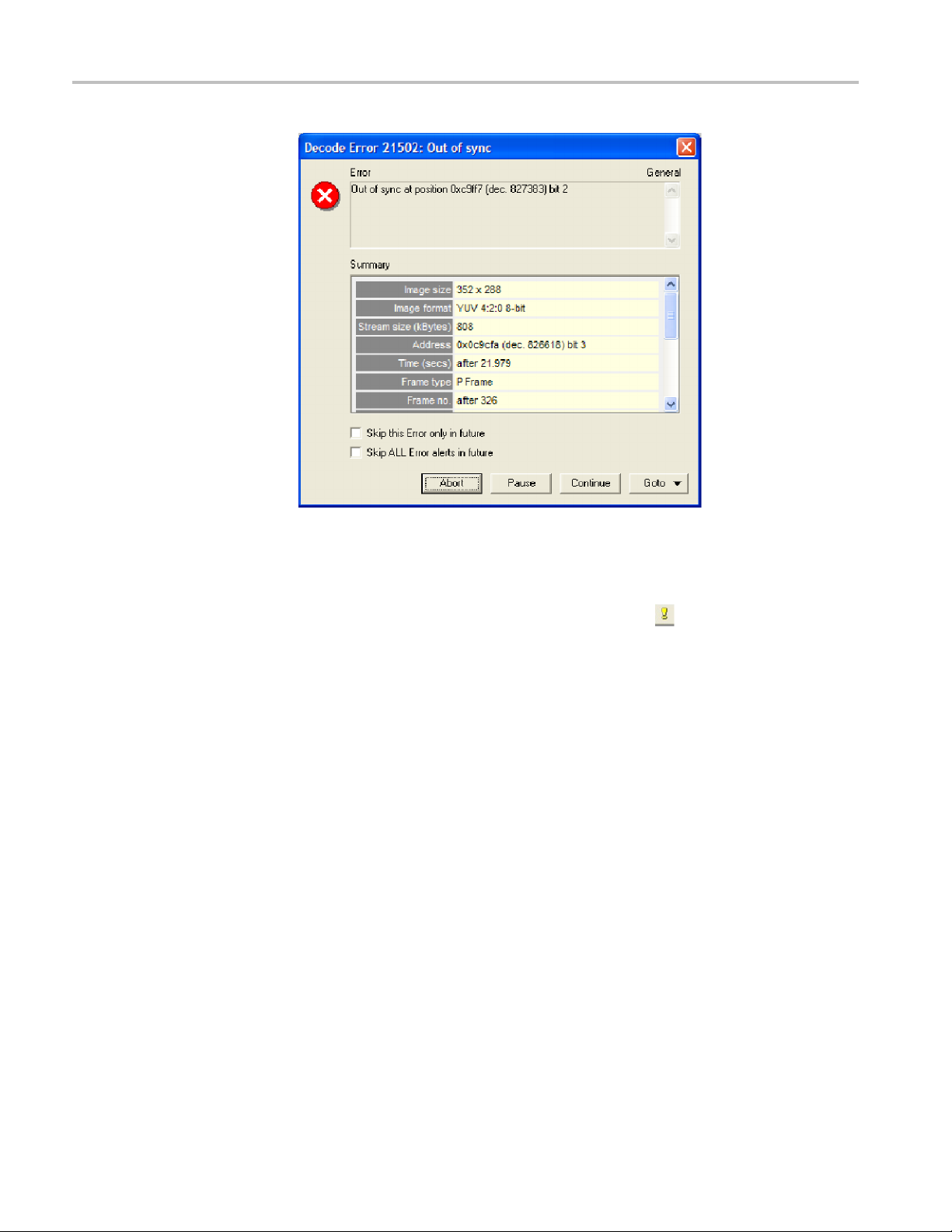
Tutorial 2: H.263 Compliance and Motion Vectors
Figure 11: Out of sync error message
8. Select the Skip ALL Error alerts in the future check box, and then click
Continue.
9. To open the Alert Log, click the Alert Log icon
will appear. (See Figure 12.)
10. Note the active filter button in the toolbar. Because Skip ALL error alerts in
the future was selected, the alert log view is filtered and the filter button is
active. The status bar indicates that 2 3 of 24 alerts are hidden.
11. Click the Filter icon to deactivate the filter and view all alerts. (See Figure 13.)
. The Alert log window
12 MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials
Page 17
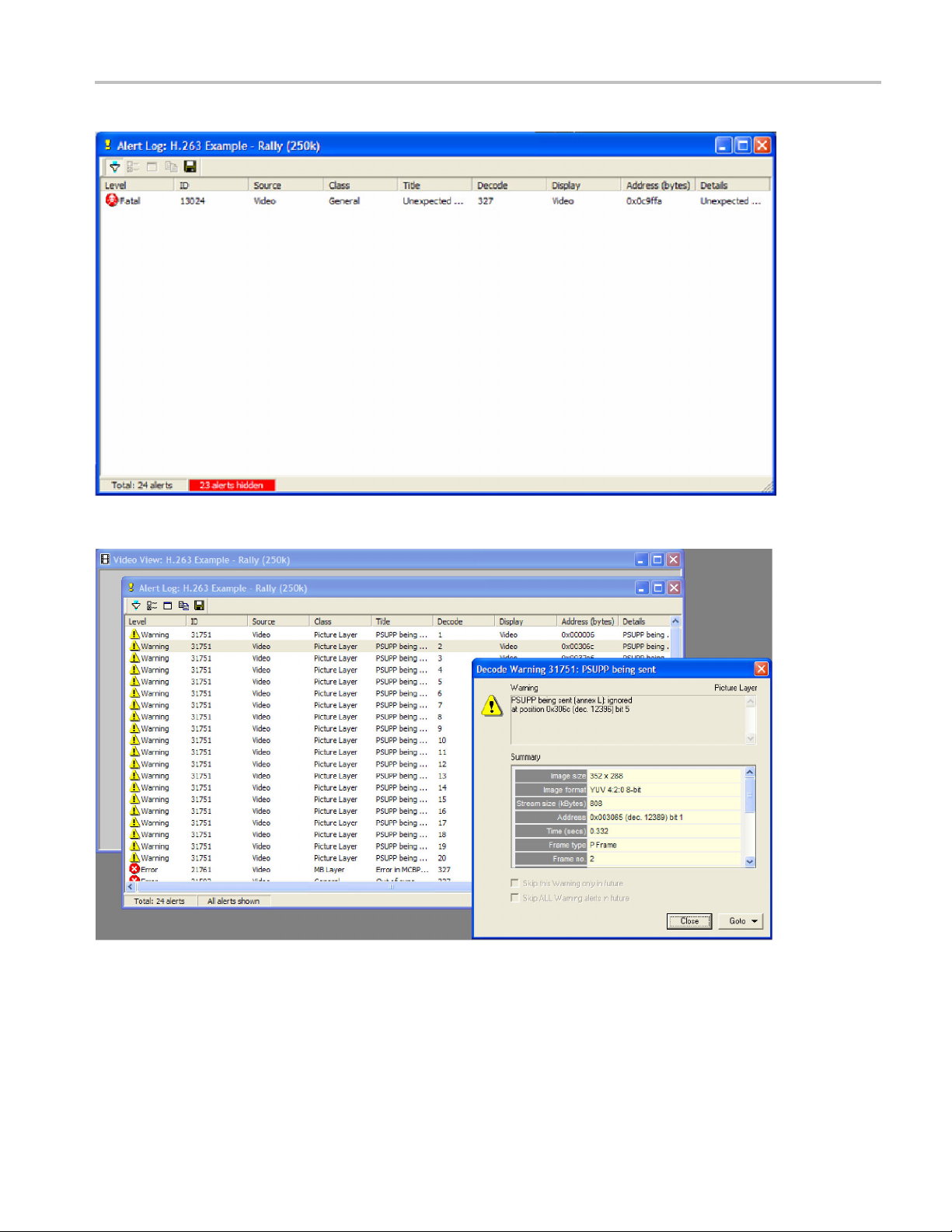
Figure 12: Alert Log window, filtered
Tutorial 2: H.263 Compliance and Motion Vectors
Figure 13: Alert Log and Alert Details
12. Double-click an alert to view the alert details and then click Close.View
the columns that appear in the alert log and note the column descriptions
that follow. (See Figure 14.)
MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials 13
Page 18
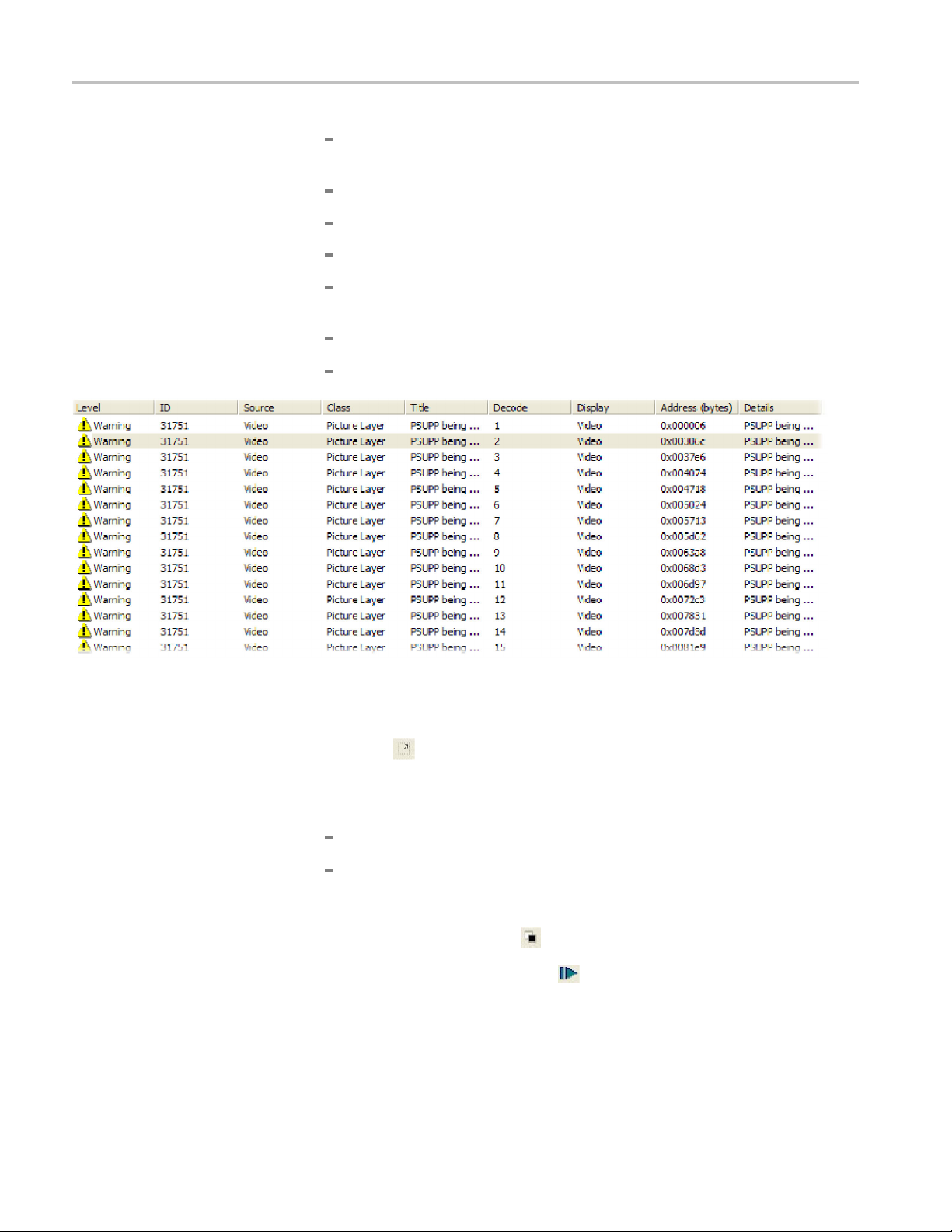
Tutorial 2: H.263 Compliance and Motion Vectors
Level -theseve
Error,andFatal.
ID - MTS4EA uni
Class - Syntax area where the alert occurs.
Title - Alert title.
Decode and Display - Frame numbers where the alert is decoded and
displayed (can vary).
Address - The address of the alert in the bitstream.
Details - Alert details.
rity level for the alert. Levels include Info, War ning,
que alert ID number.
Figure 14: Alert Log, unfiltered
13. Close the Alert log and return to the main page of the application.
14. Click the
visible. (See Figure 15.)
15. Note the following about the image:
The white dots are at the center of each MacroBlock.
The whit
the position in the previous frame that contains the data for the current
MacroBlock.
16. Click the color transfer icon
17. To play
motion vectors are clear and accurate.
icon to play the video again with the Motion Vectors (MVs)
e lines indicate motion vectors. The arrows for each MV point to
to change the overlay from white to black.
the video again, click the
icon or type CTRL + A. Note that the
14 MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials
Page 19

Tutorial 2: H.263 Compliance and Motion Vectors
Conclusion
Figure 15
This tutorial demonstrated where there is a standards-compliance issue in the
H.263 bitstream, but also showed that other aspects of the H.263 bitstream, such
as the motion vectors, are implemented properly.
:Videoimage
MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials 15
Page 20

Tutorial 3: MPEG-4 Compliance
Tutorial 3: MP
Procedure
EG-4 Compliance
This tutorial
Basic functions
Alerts for syntax errors
Video summary tooltip
MacroBlock overlay MB types
Optimization
Frequency of
1. To load the H
Streams > Space. An error message w ill appear. (See Figure 16.)
2. View the err
covers the following:
intra-coding
.263 tutorial, click File > Example files > MPEG-4 Elementary
or details:
The error occurs at bitstream byte address 0x11, bit 3, before VOP 1.
The error is present in the header, and MTS4EA does an initial check of
the file header when it loads the file.
The error indicates that method 1 quantization is in use, which is not
allowed b ecause the stream is Simple Profile.
3. Click Continue. MTS4EA loads the stream, and the window title changes to
MTS4EA-MPEG4 Example-Space.
4. Click the
error message will appear. (See Figure 16.)
5. Click Continue. A warning message will appear. (See Figure 17.)
icon or type CTRL + P to resume playing the stream. The same
16 MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials
Page 21
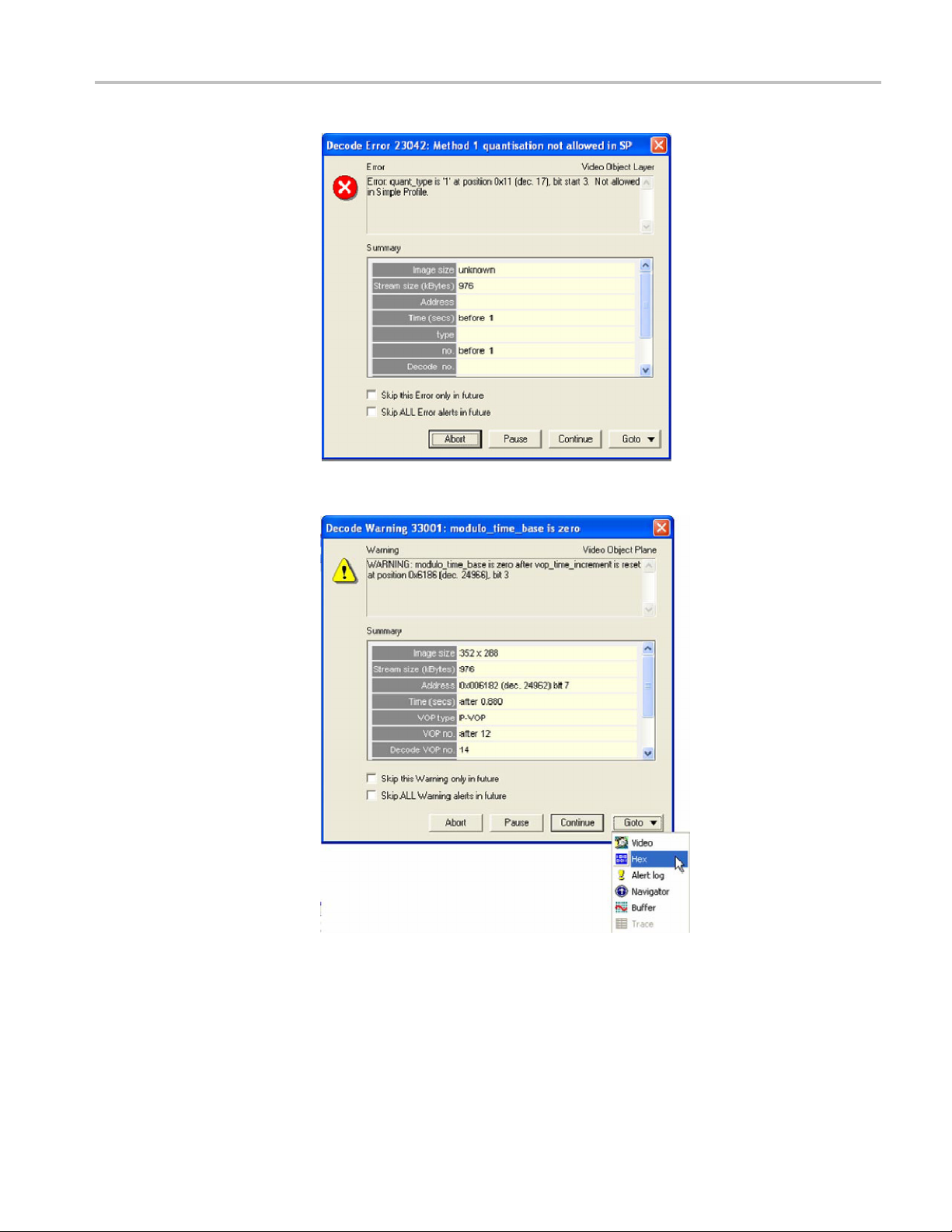
Figure 16: Initial error message
Tutorial 3: MPEG-4 Compliance
Figure 17: Initial warning message
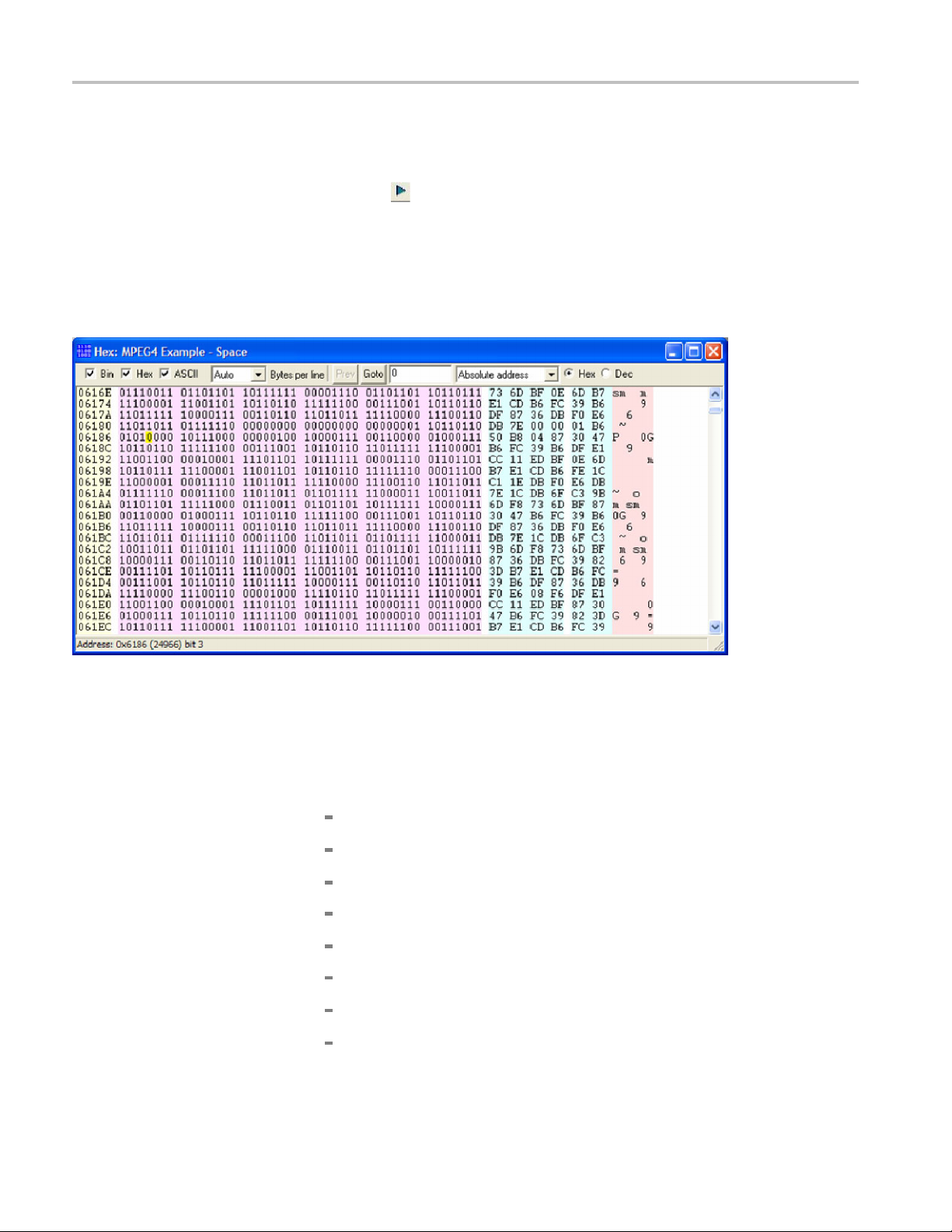
6. Click Goto, andthenclickHex. (See Figure 17.) The Hex view appears with
the error location highlighted. (See Figure 18.)
7. Close the Hex view and again view the initial error shown message. The error
occurs because modulo_time_base was set to 1 after a whole second elapsed
MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials 17
Page 22
Tutorial 3: MPEG-4 Compliance
since the modul
should be reset, although not necessarily to zero).
8. Click the
appears again. (See Figure 17.)
9. In the alert dialog box, select Skip this Warning only in the future,and
then click Continue.
10. Complete the video and observe whether it works properly.
o_time_base was last 1 (at which time vop_time_increment
icon or type CTRL + P to resume playing the stream. An alert
Figure 18: Hex view with error location
11. From the Overlay menu, click Video summary tooltip to enable the Video
12. View the Final Video Summary Tooltip and note these field descriptions.
Summary tooltip.
(See Figure 19.)
Image size: 352 pixels high x 288 pixels wide (CIF).
Stream size: 976 kBytes.
Total frames: 175.
Total play time of the sequence: 13.920 seconds.
Total bits: 7,998,576.
Bandwidth required to transmit this: 574 kbits/second.
Frame play rate: 12.50 frames per second (Hz).
Clip is MPEG-4 Simple Profile with Resync markers & Method 1
quantification.
18 MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials
Page 23

Tutorial 3: MPEG-4 Compliance
13. Observe how the
window.
sequence looks, and then close the Final Video Summary
Figure 19: Final video summary tooltip
14. To see if the codec makes the best use of the MPEG-4 standard, open the
Overlay menu, and then click MB Types (youcanalsotypeCTRL+ Y).
The MB Types key appears.
15. Move forward 3 frames. The MB types are color-coded. (See Figure 20.)
MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials 19
Page 24
Tutorial 3: MPEG-4 Compliance
Figure 20
16. Move forw
17. View frames 35, 36 and 37, and observe that the MacroBlocks disappear.
18. Go back to frame 34.
19. From th
20. View fr
21. Compa
: MB Types color key
ard to frame 34. Note that there are several green (intra) coded
MacroBlocks in the static black background (intra coded MBs generally use
the most bits). (See Figure 21.)
(See Figure 22.)
e Overlay menu, click MB Statistics, and then click Bits.Notethat
the black background uses a high number of bits. (See Figure 23.)
ames 35, 36 and 37, and observe that the background uses
progressively fewer bits. (See Figure 24.)
re frame 34 with frame 37. Observe that the black background in
frame 34 is coded and uses many bits, while the black background in frame
37 is not coded, and it uses no bits.
20 MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials
Page 25
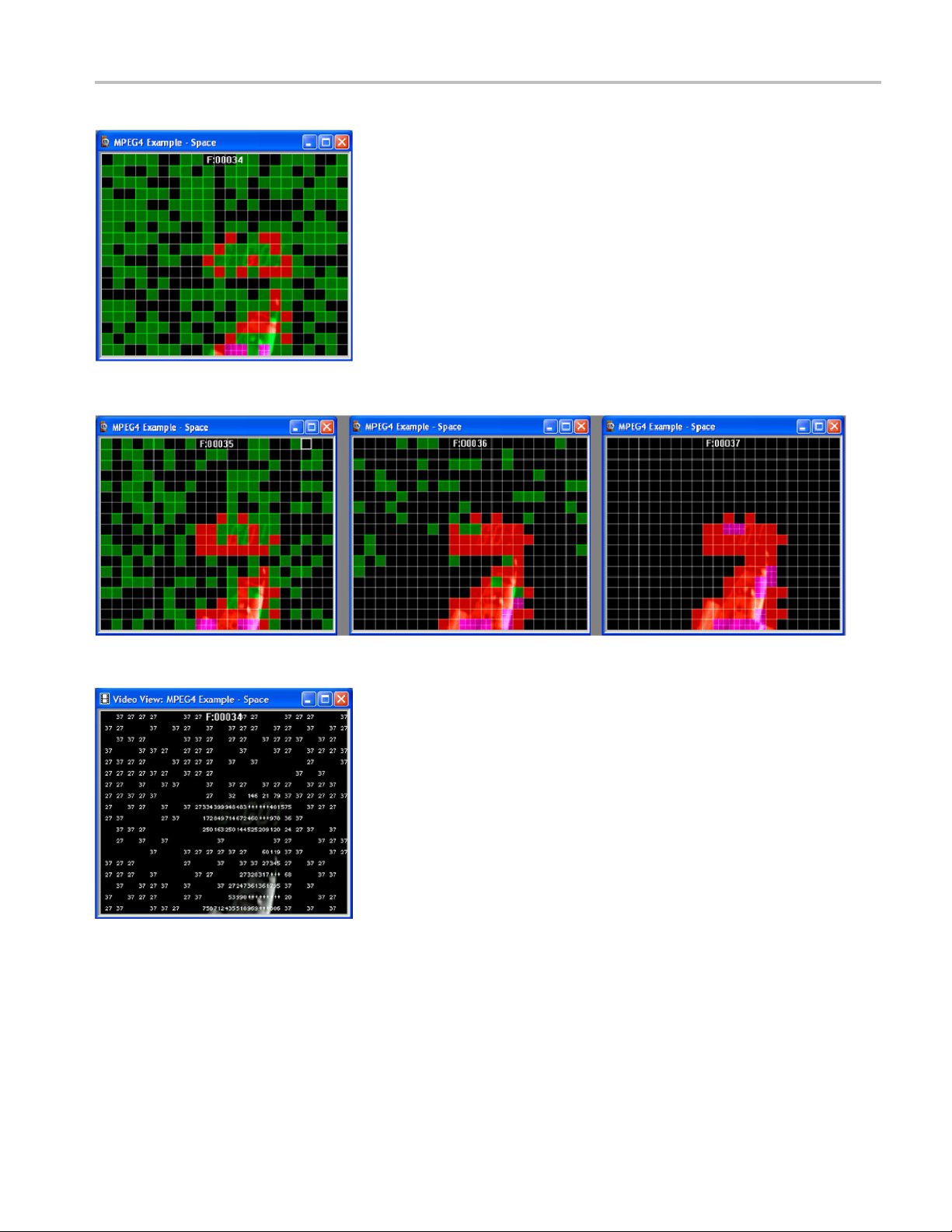
Figure 21: Frame 34, color key
Tutorial 3: MPEG-4 Compliance
Figure 22: Frames 35, 36, and 37, color key
Figure 23: Frame 34
MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials 21
Page 26

Tutorial 3: MPEG-4 Compliance
Figure 24: Frames 35, 36 and 37
Conclusion
This tutorial demonstrated how to:
Use and interpret the alert pop-up messages.
Additional Information
Covered
Use the Video summary tooltip and understand the information p rovided.
Use the MacroBlock overlays: MB types and motion vectors.
Use the hex
It appears that the encoder chooses MB types less than optimally by using intra
MBs for the background, which wastes many bits.
Consider whether there are software bugs, such that the encoder is too
sensitive to minor changes in the gray level.
Check the encoder part of the codec that decides when to use Intra MBs and
Inter MBs, and when to not code the MB.
Fixing this problem would save many wasted data bits.
NOTE. The MPEG-4 standard provides more data bits for intensity-gray level
than fo
level (this mimics the human visual system). However, it appears that the
sensitivity to gray in this example is too great.
r color information, so it is naturally more sensitive to changes in gray
view bitstream viewer.
22 MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials
Page 27

Tutorial 4: MPEG-4 Optimization
Tutorial 4: MP
EG-4 Optimization
This tutorial
Use of the video navigator view.
Use of trace.
Common error: stuffing bits; using HexView to examine bitstream data.
Synchronizing views.
Saving a setup in project files.
This tutoria
you can perform the following tasks:
Play, stop,
Use and interpret the alert messages.
Use the Video summary tooltip and understand the provided information.
Use the MacroBlock overlays: MB types and motion vectors.
Use the MacroBlock and Summary tooltips.
covers the following:
l requires that you have completed the previous tutorials and that
step forward, and fast forward a video.
Procedure
Use the hexview bitstream viewer.
View Trace
1. To load the
Elementary streams> Window Car.Astuffing_bits error occurs at stream
address 0x9, bit 1, when the file is loaded. (See Figure 25.)
2. Check the box next to Skip this, and then click Continue when the
stuffing_bits alert appears.
files: Parse bitstream and interpret.
MPEG-4 tutorial, click File > Example files > MPEG-4
MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials 23
Page 28

Tutorial 4: MPEG-4 Optimization
Figure 25: Stuffing_bits alert
3. Play the video to the end. Select Skip this and then click Continue when the
VCV overflow alert appears. (See Figure 26.)
Figure 26: VCV overflow alert
4. Click the Video Navigator icon
in either Detail (See Figure 27.) or Thumbnail view. (See Figure 28.)
Figure 27: Video Navigator window, detail view
. The Video Navigator window will appear
24 MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials
Page 29

Tutorial 4: MPEG-4 Optimization
Figure 28: Video Navigator window, thumbnail view
5. To synchronize the video window and the video navigator, start by selecting
Tile Hori
following views can also be synchronized:
zontally on the Window menu to view the tiles horizontally. The
Buffer an
HexView
Alert log
Fidelity analysis
Trace/Parse bitstream and Trace/Interpret
Figure 29: Horizontal view
6. Click the synchronize views icon. (See Figure 30.)
alysis
MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials 25
Page 30

Tutorial 4: MPEG-4 Optimization
Figure 30: Synchronizing views
7. Play through the entire sequence again. This time, the video navigator and the
video views are synchronized.
8. Click the icon at the top left corner of the video navigator window to see the
thumbnail view. Each thumbnail is labeled with the frame type, display frame
number, and the display time (in seconds). (See Figure 31.)
Figure 31: Video Navigator window, thumbnail view
26 MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials
Page 31

Tutorial 4: MPEG-4 Optimization
NOTE. The last f
9. Double-click on frame 57. Decoding restarts from the beginning and stops at
frame 57. (See
rame should now be displayed in the video window.
Figure 32.)
Figure 32: Synced navigator and video window views of frame 57 and frame 51
10. Double-click on frame 51 and note that the view immediately changes and
does not start from the beginning again. (See Figure 32.)
NOTE. MTS4EA has a cache of data, the size of which is selectable in the Play
menu under Decoder Options and then the General tab. However, if the video is
stopped (for example, played to the end), then the cache must be refilled.
11. Right-click on any view. Select Goto view, and then select Trace/Interpret
from the drop-down menu. View the Trace files, frames 1–3. An alert will
ar. (See Figure 33.)
appe
MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials 27
Page 32

Tutorial 4: MPEG-4 Optimization
Figure 33: T
NOTE. Warnings, errors, and fatals are always shown in the Trace/Parse
bitstream and Trace/Interpret files, whether or not the pop-up alerts are enabled.
12. In the Trace/Interpret window, select the address 0x00000009,1 and
right-click. Select Goto view and then Hex. The HexView will open with
the selected location highlighted. MTS4EA shows exactly where the problem
is: bits 1 and 0 of byte 9 are both 1, but for stuffing bits, they should be 01.
(See Figu
race files warning, frames 1–3
re 34.)
re 34: Selecting Hex from the Trace window
Figu
13. View
28 MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials
the HewView window and its information. You can search for items
using “.” as a wildcard character. For example, you can enter the start code
0001b. to find 0001b1, 0001b5, and 0001b6. (See Figure 35.)
Page 33

Tutorial 4: MPEG-4 Optimization
Figure 35: HexView window
14. Save your setup by clicking File andthenselectingSave project.Youcan
change the filename. (See Figure 36.)
Figure 36: Saving a project file
15. Close MTS4EA completely.
16. Restart MTS4EA.
17. Select the project file that you saved previously from the File drop-down
menu. An alert will pop up when the video file is loaded. D ismiss it by
selecting Skip this and Continue. (SeeFigure37.)
MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials 29
Page 34

Tutorial 4: MPEG-4 Optimization
Figure 37: Opening the project file
Conclusion
This tutor
ial demonstrated how to:
View different video data and navigate between different views.
Store setups.
Identify stuffed bit errors.
30 MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials
Page 35

Tutorial 5: MP4 Compliance Basics
Tutorial 5: MP
4 Compliance Basics
This tutorial
Opening an MP4 file and viewing the tracks.
Syntax error: not obeying Profile/Level restrictions.
Extracting a nd saving the video track.
Viewing MP4 file structure.
This tutorial requires that you have completed the previous tutorials and that
you can perform the following tasks:
Play, stop, step forward, and fast forward a video.
Use and inte
Use the Video summary tooltip and understand the provided information.
Use the MacroBlock overlays: MB types and motion vectors.
Use the hexview bitstream viewer.
covers the following:
rpret the alert messages.
Procedure
1. To load the MP4 tutorial, click File > Example files > MP4 Files> Packet
Woman. A list of tracks included in the MP4 appears in a dialog box. (See
Figure 38.)
2. View the track information included in the dialog box. The video track ID,
for example, is 001. Although there can be multiple tracks, the first video
track is
3. Click OK. The video track is analyzed, and an error message appears. (See
Figure 3
4. View the e rror message details: (See Figure 39.)
selected automatically.
9.)
The VOP has more MacroBlocks (396) than allowed in MPEG-4 / Simple
Profile / Level 1: the maximum number allowed is 99.
This is likely an error with the level. It is stated as Level 1 in the encoded
file, but it is actually the size of a Level 2.
MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials 31
Page 36

Tutorial 5: MP4 Compliance Basics
Figure 38: Track list
Figure 39: Initial error message
32 MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials
Page 37

Tutorial 5: MP4 Compliance Basics
5. Select Skip thi
MTS4EA will continue, by using the actual size. A buffer conformance
warning message appears. (See Figure 40.)
6. View the warning message details: (See Figure 40.)
Overflow by 29
This error is to be expected, because the Level is incorrectly given as
L1 (which has
a limit of 396 MBs).
s Error only in the future, and then click Continue.
7MB.
a limit of 99 MBs) whereas it should be L2 (which has
Figure 40: VCV overflow warning message
7. Select Skip this Warning only in the future, and then click Continue.
Another buffer conformance warning message appears. (See Figure 41.)
8. Select Skip this Warning only in the future, and then click Continue.
9. To ensure that the application window is active, click the Title bar.
10. From the analysis menu, select View video stream structure.TheStructure
window appears. (See Figure 42.)
11. View the top-level atoms in the MP4 file. Click the + next to each atom to
view the data for the atom.
MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials 33
Page 38

Tutorial 5: MP4 Compliance Basics
Figure 41: VBV underflow warning
Figure 42: Structure window
12. From the File menu, click Close stream, and then reopen the stream.
13. When the track list appears, click Extract. (See Figure 43.) The Save stream
file as dialog box appears. (See Figure 44.)
34 MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials
Page 39

Tutorial 5: MP4 Compliance Basics
Figure 43:
Figure 44: Save stream file as dialog box
14. In the Save stream file as dialog box, type a different file name if required.
Track list
The track ID and video file type has been automatically appended to the file
name.
NOTE.
extracted at the time the MP4 file was first opened, open the File menu and then
click Save stream file as.
MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials 35
To open this dialog box in the future for a video track that was not
Page 40

Tutorial 5: MP4 Compliance Basics
Conclusion
This tutorial demonstrated how to:
View the tracks in a n MP4 file.
Extract and play a video, while checking for errors.
Identify and locate the Level conformance error.
Identify two
analysis).
buffer conformance errors (see Tutorial 5 for details about buffer
36 MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials
Page 41

Tutorial 6: MP4 Optimization
Tutorial 6: MP
4 Optimization
This tutorial
Opening an MP4 file and viewing the video track.
Using the Video summary tooltip and the MB types overlay.
Performing optimization checks that could reduce bit usage by 45% in this
sequence.
This tutorial requires that you have completed the previous tutorials, and that
you know how to:
Play, stop, step forward, and fast forward the video.
Use and interpret the pop-up alerts.
Use the Video summary tooltip and understand the information provided.
Use the Mac
Use the hexview bitstream viewer.
Open MP4 files, view/extract the video, and view the MP4 file structure.
covers the following:
roBlock overlays: MB types and motion vectors.
Procedure
1. To load the MP4 tutorial, click File > Example files > MP4 Files > Picadilly
Circus. A list o f tracks included in the MP4 appears in a dialog box. (See
Figure 45
2. View the track information included in the dialog box. The video track ID,
for exam
track is selected automatically.
3. Click OK
4. To view t
5. To view the MB types overlay, click the
6. Click th
(See Figure 46.)
.)
ple, is 001. Although there can be multiple tracks, the first video
.
he Video Summary tooltip, click the
icon. A VCV buffer conformance warning message appears.
e
icon or type CTRL + U.
icon or type CTRL + M.
MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials 37
Page 42

Tutorial 6: MP4 Optimization
Figure 45: Track list
e 46: VCV buffer conformance warning message
Figur
7. Selec
t Skip this Warning only in the future, and then click Continue.
8. View the progression of frames, and note that the first frame is green, as is
y third frame (Intra MBs). (See Figure 47.) Another buffer conformance
ever
warning me ssage appears. (See Figure 48.)
38 MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials
Page 43

Figure 47: Progression of frames
Tutorial 6: MP4 Optimization
Figure 48: VBV underflow warning
9. Select Skip this Warning only in the future, and then click Continue.
10. To replay the video file, click Pause, step forward. Note that the first frame
takes 32,456 bits. (See Figure 49.)
MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials 39
Page 44

Tutorial 6: MP4 Optimization
Figure 49: Frame 1
11. Click the red close button to remove the MB Types Key window.
12. Click the
13. To undock the MB Types Key window, hold the CTRL key, while dragging
it with the mouse pointer.
14. View the next six frames, including Frame 2. (See Figure 50.)
15. For each frame, view the details, which are outlined in Table 3.
icon twice to reopen the MB Types Key window.
40 MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials
Page 45

Tutorial 6: MP4 Optimization
Conclusion
Figure 50: Frame 2
Table 3: Frame details
Frame Frame type Bits used
2
3
4
5
6
7
P-VOP
P-VOP
I-VOP
P-VOP
P-VOP
I-VOP
7,208
7,792
33,152
7,216
8,776
34,344
This tutorial demonstrated the following:
The I-V
OPs require about 4.5 times as many bits as the P-VOPs.
There are I-VOPs every 3rd frame.
There is no need to have I-VOPs so often. If the frequency of I-VOPs were
reduced to 1 in 30, the bits used for the sequence would reduce by ~45%.
You can reduce the number of bits used.
MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials 41
Page 46

Tutorial 7: 3GPP/MPEG-4 Compliance
Tutorial 7: 3G
PP/MPEG-4 Compliance
This tutorial
Opening a 3GPP file and viewing the tracks.
Viewing syntax errors using r eserved Profile/Level indication.
Performing optimization checks that may or may not be applicable in a
wireless environment.
This tutorial requires that you have completed the previous tutorials, and that
you know how to:
Play, stop, step forward, and fast forward the video.
Use and interpret the pop-up alerts.
Use the Video summary tooltip and understand the information p rovided.
Use the Mac
Use the hexview bitstream viewer.
Open MP4 files, view/extract the video, and view the MP4 file structure.
covers the following:
roBlock overlays: MB types and motion vectors.
Procedure
1. To load the 3GPP tutorial, click File > Example files > 3GPP File > Mobile
Hands. A list of tracks included in the 3GPP appears in a dialog box. The
first vide
o track is automatically selected. (See Figure 51.)
42 MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials
Page 47

Tutorial 7: 3GPP/MPEG-4 Compliance
Figure 51: 3GPP track list
2. Click OK.
3. An alert will appear for a syntax error. This error shows as a reserved value
(0) for profile_and_level_indication. (See Figure 52.)
4. Click Continue anddonotenableSkip.
Figure 52: Syntax error alert
5. Run Trace/Interpret (frame 1) and look at the error at address 4, bit 7. (See
Figure 53.)
MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials 43
Page 48

Tutorial 7: 3GPP/MPEG-4 Compliance
Figure 53: Trace/Interpret error at address 4, bit 7
6. Play the video again and at the error, click Goto andthenselectHex from the
drop-down menu. (See Figure 54.)
Figure 54: Selecting Hex from the Goto drop down menu
7. The HexView window will appear with the location of the error bits
highlighted. (See Figure 55.)
44 MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials
Page 49

Tutorial 7: 3GPP/MPEG-4 Compliance
Figure 55: HexView window with error locations highlighted
8. To look at the VOP types, first stop the stream if it is playing.
9. Click the Summary tooltip icon
10. Click the MB Types Overlay icon
11. Play or Pause/Step forward through the sequence to the end. Notice that the
first frame and every second frame are Intra-MBs. (See Figure 56.)
Figure 56: Viewing VOP types
12. Now examine the error resilience by clicking the Summary tooltip icon
to turn the tooltip on again, if it is not already on.
to turn on the tooltip.
to turn on the overlay.
13. Click the Pause/Step Forward icon
14. Notice in the Summary window that resync markers and data partitioning
are both on. This is vital for good error resilience in a mobile environment.
(See Figure 57.)
MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials 45
to move to frame 1.
Page 50

Tutorial 7: 3GPP/MPEG-4 Compliance
Figure 57: Summary window data
Conclusion
This tutorial demonstrated the following:
Using the Summary tooltip allows you to look at VOP types.
Reducing the frequency of I-VOPs can allow for better quality video in the
same bit-rate.
With error resilience tools in use, the frequency of I-VOPs can be reduced,
reducing the bit-rate by approximately 15%.
46 MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials
Page 51

Tutorial 8: H.264/AVC Syntax Error
Tutorial 8: H.
Procedure
264/AVC Syntax Error
This tutorial
Opening an H.264/AVC byte stream.
Syntax error in PPS
Finding the frame number of the error.
Examining the byte stream syntax and finding the error using Trace/Parse
bitstream and Trace/Interpret.
1. To load the tutorial, click File > Example files > H.264/AVC Byte Streams>
Canary Wharf.
2. An incorrect direct_8x8_inference_flag error will occur at address 0x0, bit 7,
when the file is loaded. (See Figure 58.)
covers the following:
Figure 58: Direct_8x8_inference_flag error alert
3. Notice that the s yntax error occurs before frame 1. This is the displayed frame
number. Check the Skip this box and then click Continue.(SeeFigure58.)
MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials 47
Page 52

Tutorial 8: H.264/AVC Syntax Error
4. An invalid Pict
frame 1. Use the scroll bar to view all of the information in the error dialog
box. (See Figure 59.)
ure Parameter Set ID error will occur during the decode of
Figure 59: Invalid Picture Parameter Set ID error
5. Click on Analysis in the menu. Select Trace enable andthenselectFrame
range from the drop-down menu.
6. Set the frame range from 1 to 2. This will run the Trace/Interpret and
Trace/Parse bitstream o n frames 1 and 2.
7. View the Trace file and clear the Frame box. Click Find Next three times.
An error alert will appear. (See Figure 60.)
Figure 60: Trace/Parse bitstream error
48 MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials
Page 53

Tutorial 8: H.264/AVC Syntax Error
8. View the Trace/
Find Next twice. An error alert will appear. (See Figure 61.)
Figure 61: Trace/Interpret error alert
9. To determine if the pic_parameter_set_id number 1 has been set, search for
it in the Trace/Interpret file that is already open (frames 1 and 2).
10. Select the Te x t box in the Trace/Interpret window and type
pic_parameter_set_id= in the text box.
11. Click Find Prev to search for an occurrence of pic_parameter_set_id before
the error. Note that it does not occur before the location of the PPS ID error
(at 0x1c, 7). (See Figure 62.)
Interpret for the same range. Clear the Frame box and click
Figure 62: Pic_parameter_set_id error location search
MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials 49
Page 54

Tutorial 8: H.264/AVC Syntax Error
Conclusion
This tutorial demonstrated the following:
NOTE. This may not always be possible and could generate other consequential
errors.
The pic_parameter_set_id=1 did not occur before the slice header tried to use
this in frame 1, and therefore caused an error.
It is an error to set the PPS ID to 1 at stream address 0x1c, bit 7.
With this error, the MTS4EA decoder uses the data from the last known good
pic_parameter_Set_id (ID 0) and continues decoding.
THE MTS4EA showed what the error was and where it occurred.
50 MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials
Page 55

Tutorial 9: MPEG-4 and H.264/AVC Buffer Analysis
Tutorial 9: MP
EG-4 and H.264/AVC Buffer Analysis
This tutorial
Buffer analysis in real-time (VBV, VCV, VMV of MPEG-4 ES).
Buffer conformance errors/alerts.
Achieving conformance.
HRD buffer analysis in H.264/AVC.
This tutorial requires that you have completed the previous tutorials, and that
you know how to:
Play, stop, step forward, and fast forward a video.
covers the following:
Information provided - values, overflow/underflow indications.
Icon controls for navigation through the graphs.
Graphs.
Error dialog boxes.
Altering the buffer parameters and seeing the effect in the graph.
Adjusting values to prevent overflow.
Use and interpret the alert messages.
This tutorial also requires that you already understand the principles of buffer
analysis/conformance (VBV, VCV, VMV) in MPEG-4 and H.264/AVC (HRD).
The following table provides the functions of each Buffer Analysis toolbar icon.
(See Table 4.)
Table 4: Buffer analysis icons
Icon Function
Zoom in (+) and zoom out (-) centered on the window; affected by the
Lock X / Y icons.
Fit all data into window.
Go to origin (zero), which is the start of the video sequence.
Lock X/Y zoom in/out and scrolling/panning. When the Lock Y button is
pressed, zoom in and zoom out and scroll/pan only affect the X-direction.
This allows you to keep a useful vertical scale, while still viewing the length
of the video sequence.
Autoscroll; fill the analysis data in real time as the video is being decoded
and scroll the window to the right.
MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials 51
Page 56

Tutorial 9: MPEG-4 and H.264/AVC Buffer Analysis
Table 4: Buffer analysis icons (cont.)
Icon Function
Measure the data at the cursor. The data values are reported on the status
line at the bottom of the analysis window. Offsets and angles/slopes of
lines can also be measured by holding the mouse and dragging.
Scroll/pan (the cursor changes to show the scroll/pan direction); this is
affected by the Lock X-Y icons.
Zoom in/zoom out centered on the location of this cursor; this is affected by
the Lock X-Y icons. Press the < shift> key to zoom out.
Procedure
1. To load the t
utorial, click File > Example files > MPEG-4 Elementary
Streams> Man Walking. Ensure that the video is not playing.
2. From the An
alysis menu, click View buffer analysis.TheBuffer Analysis
window appears. (See Figure 63.)
3. View the b
uffer analysis graph example, as well as the descriptions in the
table. (See Table 5.)
Figure 63: Buffer analysis window, example graph
52 MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials
Page 57

Tutorial 9: MPEG-4 and H.264/AVC Buffer Analysis
Table 5: Buffer
Area Description
1
2 Frame type, number.
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
analysis descriptions
Graph window c
Graph window.
List of analyses for VBV, VCV, and VMV.
Location of overflows and underflows in stream.
Scroll bar for sequence.
Time through sequence.
Vertical blue line at time=0; vertical gray lines at each VOP decode time.
Status lines.
Custom values.
Switch on/off VBV, VCV, VMV graphs.
Source of buffer analysis values.
ontrol toolbar.
4. Observe the VBV, VCV and VMV values that appear beside the graph. (See
Figure 64.) These parameters are specified in the stream, or from the implied
values from the Profile/Level, as given in the standard, or the implied values
from the Ob
ject Type (Simple or Advanced Simple), at the highest level for
each. You can enter them manually by selecting Use custom parameters.
Figure 64: VBV, VCV and VMV values
5. Click the Pause/ Step Forward icon
three times. Nothing appears in
the window because the Man Walking sequence contains B-VOPs, and the
er analysis cannot start until there is sufficient data for the calculations
buff
(this will not occur until frame 4).
6. Click the Pause/ Step Forward icon
one more time. The graph appears.
MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials 53
Page 58

Tutorial 9: MPEG-4 and H.264/AVC Buffer Analysis
7. Click the Fit to Window icon for a more detailed view o f the graph.
(See Figure 65
.)
8. Click the Fast forward icon
9. Note that the VBV overflow occured while decoding frame 55 (the display
frame number is 54).
. A warning message occurs. (See Figure 66.)
Figure 65: Buffer analysis graph, detailed view
54 MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials
Page 59

Tutorial 9: MPEG-4 and H.264/AVC Buffer Analysis
Figure 66: VBV overflow warning
10. Select Skip this Warning only in the future, and then click Continue.
11. Observe that the red VBV line goes above the Buffer limit line. (See
Figure 67.)
12. Observe that when the decoding stops, the graph looks like the section that
appears between 75% and 105% buffer occupancy. Note also that the number
of frames with VBV overflow appears at the bottom of the screen. In this
case, th
e number of frames with VBV overflow is 106.
MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials 55
Page 60

Tutorial 9: MPEG-4 and H.264/AVC Buffer Analysis
Figure 6
13. To fittheg
7: Buffer limit graph
raph to the window, click the
toolbar. The red line displays the VBV overflow.(SeeFigure68.)
icon on the Buffer Analysis
56 MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials
Page 61

Tutorial 9: MPEG-4 and H.264/AVC Buffer Analysis
Figure 68: Comparative video verifier graph
14. Consider the information presented by the graph. The standard values used
for a frame result in a VBV overflow, which means that the decoding rate
cannot keep up with the input data rate, and frames will drop, beginning with
frame 54.
Solutions include:
Increase the vbv_buffer_size so that it does not overflow.
Decrease the bit-rate, w hich is the rate at which the encoder sends the
data to the decoder.
Increase the displayed frame rate, so that the decoder removes bits more
quickly.
Increase the number of bits per frame by changing the quantizer or
increasing the frame size.
Change the Profile/Level indication, so that it stays within the set limits
(for example, change to ASP at Level 2).
Use custom values in the vbv_parameters in the sequence header.
15. Clear the check boxes for VCV and VMV so that o nly the VBV check box
is selected. Note that the vertical scale is now measured in bits, not %. (See
Figure 69.)
MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials 57
Page 62

Tutorial 9: MPEG-4 and H.264/AVC Buffer Analysis
16. Observe that th
set for the VBV.
17. Click the
three times for a detailed view of the graph. (See Figure 70.)
eVBVlinehasdisappearedbecause it is beyond the scale
icon on the Buffer Analysis toolbar,andthenclickthe icon
Figure 69: Frame 2
58 MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials
Page 63

Tutorial 9: MPEG-4 and H.264/AVC Buffer Analysis
Figure 7
18. Note the
19. Click the
20. Select the Use custom parameters option button. (See Figure 71.) The word
0: Graph details
following details about the graph:
The Y scale o f the graph is locked, which keeps the graph at a useful
zoom lev
The VBV graph is higher at the end of every frame than at the start, which
shows t
BUF appears in a yellow box in the main MTS4EA status bar, indicating that
custom buffer parameters are in use. (See Figure 72.)
el.
hat the VBV buffer is filling faster than the decoder can empty it.
icon to zoom out.
MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials 59
Page 64

Tutorial 9: MPEG-4 and H.264/AVC Buffer Analysis
Figure 71: Buffer analysis configurations
Figure 72: Buffer parameter indicator
21. View the video buffer verifier. (See Figure 73.) The default vbv_buffer_size
for ASP L0 is 163,840 bits = 20,480 bytes, which is not very large.
22. Enter 655,360 bits = 80 kbytes, click Apply, and then click the Fit to window
icon
overflows or underflows.
60 MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials
. Observe that the graph stays below the limit and there are no
Page 65

Tutorial 9: MPEG-4 and H.264/AVC Buffer Analysis
23. Consider the fo
What if your mobile device cannot spare 80 KBs of memory, and can only
spare 20 KBs, a
By how much does the input data rate need to be reduced?
Does this comply with the specifications of the network on which your
device will operate?
llowing:
sspecified by the standard?
Figure 73: Video buffer verifier graph
24. Reset the parameters by clicking Use parameters from stream header,and
then reselect the Use custom parameters check box. The VBV graph shows
he decoder is being supplied with data faster than it can decode.
that t
25. Reduce the bit rate to 121072 bits, and then click Apply. (See Figure 74.)
aph goes up slightly and there are fe wer frames with overflow. (See
The gr
Figure 75.)
MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials 61
Page 66

Tutorial 9: MPEG-4 and H.264/AVC Buffer Analysis
Figure 74: Bit rate configurations
Figure 75: Video buffer verifier graph
26. Reduce the bit rate to 111072 bits and then click Apply.(SeeFigure76.)
27. Observe that the graph line now stays below the buffer limit. (See Figure 77.)
28. Consid
specifications.
62 MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials
er whether the maximum rate of 111,072 bits meets your network’s
Page 67

Tutorial 9: MPEG-4 and H.264/AVC Buffer Analysis
Figure 76: Video buffer verifier configurations
Figure 77: Video buffer verifier graph
Conclusion
This tutorial demonstrated that the bufferanalysisoftheMPEG-4example,Man
Walking, showed that the stream does not comply with the buffer constraints. The
tutorial recommended ways to resolve this issue.
The tutorial also brought up the following considerations:
How much memory needs to be allocated? Can your hardware allow this
much memory usage?
Is the input data rate limit appropriate for your network?
MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials 63
Page 68

Tutorial 10: MPEG-2 Compliance
Tutorial 10: M
Procedure
PEG-2 Compliance
This tutorial
OpeninganMPEG-2programstream.
Interpreting syntax errors:
Using the HexView:
Looking at the MPEG-2 program stream structure.
Looking at MacroBlock types in an interlaced video.
covers the following:
Person track: invalid VLC for dct_differential.
Grenadier guards: frame_rate_extension denominator and numerator
equal but not zero.
Going from the alert pop-up to the H exView.
Examining t
he bitstream in the HexView.
1. To load this tutorial, click File > Example files > MPEG-2 Program
Streams> Person Track. A list of tracks included in the MPEG-2 program
stream ap
2. View the track information included in the dialog box. The video track ID,
for examp
track is selected automatically.
pears in a dialog box. (See Figure 78.)
le, is 0xe0. Although there can be multiple tracks, the fi rst video
64 MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials
Page 69

Tutorial 10: MPEG-2 Compliance
Figure 78: Track list
3. Click OK. The video track is analyzed and an error appears. (See Figure 79.)
4. View the
the point of the error.
5. Click Co
box is not selected. Another buffer conforma nc e error message appears.
(See Figure 80.)
error message details, which provide a summary of the stream up to
ntinue. Ensure that the Skip this Error only in the future check
MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials 65
Page 70

Tutorial 10: MPEG-2 Compliance
Figure 79: Initial error message
Figure 80: Invalid VLC error message
6. View the error message details. An invalid VLC has been used for the
dct_differential field at bitstream byte address 0x1000, bit 5.
7. Click Continue. Ensure that the Skip this Error only in the future check box
is not selected. Repeat this step for an additional error message that appears.
8. Resume playing the video. Observe that the error is visible in frame 1. (See
Figure 81.)
66 MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials
Page 71

Tutorial 10: MPEG-2 Compliance
Figure 81:
9. Click the P
10. Click Continue.AnInvalidVLCerrormessageappears.(SeeFigure82.)
11. From the Goto menu, click Hex.
12. Click Continue, a nd then view the HexView window. Note that the error is
13. Observe the bits surrounding the error and consider whether it is a start code
Error in image
ause, Step forward icon
highlighted automatically. (See Figure 83.)
emulation.
. An error message appears.
MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials 67
Page 72

Tutorial 10: MPEG-2 Compliance
Figure 83: HexView window
Figure 82: Invalid VLC error message
14. To open the Grenadier Guards program stream, Click File > Example files
> MPEG-2 Program Streams> Grenadier Guards. An error message
appears. (See Figure 84.)
68 MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials
Page 73

Tutorial 10: MPEG-2 Compliance
15. View the detail
frame_rate_extension is 1, but it must be 0 in Main Profile.
Figure 84: Error message
16. Select Skip this Error only in the future, and then click Continue.The
status ba
Figure 86.) and a warning message (See Figure 87.) appear.
r indicates one disabled alert. (See Figure 85.) An error mess age (See
s of the error message: the value of the denominator of
Figure 8
17. For both
MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials 69
5: Disabled alert indicator
error messages, select Skip this Error or Warning in the future,
and then click Continue. Do not resume playing the video.
Page 74

Tutorial 10: MPEG-2 Compliance
Figure 86: Error message
Figure 87: Warning message
18. From the Analysis menu, select View video stream structure.TheStructure
w appears. (See Figure 88.)
windo
19. View the top-level atoms in the MPEG-2 program stream. Click the + next to
atom to view the data for the atom.
each
70 MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials
Page 75

Tutorial 10: MPEG-2 Compliance
Figure 88: Structure window
20. Resume playing the video. The Interlace toolbar appears. (See Figure 89.)
Figure
21. Click t
22. On the Interlace toolbar, click the Split fields view icon
89: Interlace toolbar
he Pause, Step Forward icon
bottom fields are displayed separately. (See Figure 90.)
to view frame 2.
.Thetopand
MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials 71
Page 76

Tutorial 10: MPEG-2 Compliance
Figure 90
23. Maximize
24. Click the
:Frame2
(See Figure 91.)
the video window.
con. Different MB types appear in the top and bottom fields.
i
Figure 91: Varied MB types
72 MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials
Page 77

Conclusion
Tutorial 10: MPEG-2 Compliance
This tutorial demonstrated the following:
There is one error in the Person Track stream:
The error is in frame 1, at bitstream location 0x1000, bit start 5.
This error affects the visual quality.
There are two
stream:
The errors ar
bit start 6.
The warning
This does not appear to affect the visual quality.
You can see the different MacroBlock types in the top and bottom fields.
errors and one warning message in the Grenadier Guards
e in the header (before frame 1), at bitstream location 0x15,
message highlights the same error.
MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials 73
Page 78

Tutorial 11: Fidelity Analysis
Tutorial 11: Fidelity Analysis
This tutorial covers the following:
Fidelity analysis in real-time (PSNR).
Using a YUV source reference file.
Fidelity metrics.
Procedure
Graph naviga
Comparing the fidelity of the same bitstream compressed with either MPEG-2
or H.264/AVC
Viewing the visual difference between the compressed bitstream a nd the YUV
source refe
This tutorial requires that you have completed the previous tutorials and that
you can:
Open example streams.
Play, stop, step forward, and rewind a video.
Use and interpret alert pop-up messages.
Use the icons and controls on the buffer analysis graphical display.
This tutorial also requires that you already understand the principles of fidelity
analysis (this topic is not covered in this tutorial; however, the user manual
contains descriptions of the fidelity metrics).
tion.
.
rence video.
1. To load the tutorial, click File > Example files > MPEG-4 Elementary
Streams> Man Walking. Ensure that the video is not playing.
2. From the Analysis menu, click Enable fidelity analysis.TheVideo analysis
options dialog box appears for theYUV reference file. This file will later be
used for comparison with the compressed video file. The YUV reference
file is p
filename field. (See Figure 92.)
3. Set the
74 MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials
rovided as an example, as indicated by the text under the Reference
Frame rate to 30. (See Figure 92.)
Page 79

Tutorial 11: Fidelity Analysis
Figure 92: Video analysis options
4. From the Metric drop-down menu, select PSNR (full signal range),and
then clic
in the user manual).
5. From the
6. On the Trace tab, select the Enable check box, choose the filename
mp4asp_
Figure 93.)
7. On the F
OK. The video window appears with the fidelity analysis icon
the Vi
k OK. (A detailed description of each fidelity metric is available
Analysis menu, click Enable fidelity trace.
1_video and then, under Options,selectVOP Fidelity.(See
rame range tab, select the All frames check box and then click
enabled in
ews toolbar. (See Figure 94.)
MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials 75
Page 80

Tutorial 11: Fidelity Analysis
Figure 93: Video analysis options
Figure 94: Frame range tab
8. Click the Fidelity analysis icon
appears. Observe that the graph is empty b ecause a video has not been played.
(See Figure 95.)
9. Click the
10. Observe the following about the graph:
The graph area is not filled with each click because the bitstream includes
B-VOPS, and a certain number of frames must be decoded before each
frame can be displayed.
Some of the YUV PSNR values are not visible. This is because the graph
auto-scales with the first few values. You can click the
the graph.
icon four times. A graph appears. (See Figure 96.)
.TheFidelity analysis graph view
icon to rescale
76 MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials
Page 81

Tutorial 11: Fidelity Analysis
The thumbnail b
11. View the descriptions of the Fidelity analysis window in the figure and the
table. (See Fi
ar view shows that the fidelity data has been collected.
gure97.) (SeeTable6.)
Figure 95: Fidelity analysis graph
MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials 77
Page 82

Tutorial 11: Fidelity Analysis
Figure 96
: Fidelity a nalysis graph
78 MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials
Page 83

Tutorial 11: Fidelity Analysis
Figure 97: Fidelity analysis window descriptions
Table 6: Fidelity analysis window descriptions
Area Description
1
2YUVcolorkey
3
4 Time through sequence
5
6 Thumbnail bar line; displays overview
7
8 Frame type, number
9
Graph window
Scroll bar; appears and disappears according to zoom scale
Status line; display measurements
Vertical blue line at time=0; vertical gray lines at each VOP decode time
Graph window control toolbar
12. To open the Grenadier Guards program stream, Click File > Example files
> MPEG-2 Program Streams> Grenadier Guards. An error message
appears.
13. Select Skip this Error only in the future, and then click Continue.
14. From the Analysis menu, select View analysis options.
MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials 79
Page 84

Tutorial 11: Fidelity Analysis
15. On the Visual di
then click OK.
16. An error messa
Click OK, and then view the graph result. (See Figure 98.)
17. Load the MPEG
Figure 99.)
18. Compare the fi
example. (See Figure 99.) (See Figure 100.) Note that the PSNR is higher for
H.264/AVC in Y, U, and V.
fference/ Fidelity tab, set the YUV frame rate to 25, and
ge appears because there are only 10 frames of YUV data.
-2 program stream example, Grenadier Guards. (See
rst MPEG-2 program stream with the H.264/AVC PSNR
Figure 98: Graph result, YUV frame rate 25
80 MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials
Page 85

Tutorial 11: Fidelity Analysis
Figure 99: MPEG-2 program stream, Grenadier Guards
Figure 100: H.264/AVC stream, Grenadier Guards
19. Click the View trace icon. (See Figure 101.)
MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials 81
Page 86

Tutorial 11: Fidelity Analysis
Figure 101: View trace icon
20. The trace view gives the numerical values for the pictures’ PSNR. (See
Figure 102.)
21. Consider the following:
What encoder parameters, such as frame type, were used for H.264/AVC
and MPEG-2?
Could the H.264/AVC or the MPEG-2 encoding parameters be changed to
improve the areas of lower PSNR?
Compare other fidelity analyses; do the same kinds of differences occur?
Although the PSNR is better for the H.264/AVC sequence, it does not
necessarily look better. Consider the visual differences.
Figure 102: H.264/AVC sequence
22. Load the MPEG-2 stream, Grenadier Guards.
23. From the Overlay menu, click Visual difference, and then select the Enable
check box.
24. Set the Frame rate to 25, and then click OK.TheVisual difference toolbar
appears.
25. Use the following icons to view the visual difference.
82 MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials
Page 87

Tutorial 11: Fidelity Analysis
Conclusion
Table 7: Visual
Icon Function
difference icons
View encoded
View YUV reference
View difference
View luma only (not U or V)
26. Load the H.264/AVC stream, Grenadier Guards. Consider whether there is a
difference in visual quality between the two streams.
This tutorial demonstrated the following:
A method for assessing visual quality through:
The use of metrics such as PSNR.
Identifyin
g the visual difference between the encoded video and the
reference (source) video that is used for the e ncoding.
Visual qual
ity analysis and visual quality improvement require that you
consider encoding parameters (such as frame types and motion vectors) and
bit-rates of encoding.
This tutorial provided the tools to help you begin your visual analysis in a
quantifiable and logical fashion.
MTS4EA Elementary Stream Analyzer Tutorials 83
 Loading...
Loading...