Page 1

Service Manual
MTS300
MPEG Test System
071-0668-00
Warning
The servicing instructions are for use by qualified
personnel only. To avoid personal injury, do not
perform any servicing unless you are qualified to
do so. Refer to all safety summaries prior to
performing service.
www.tektronix.com
Page 2

Copyright © Tektronix, Inc. All rights reserved. Licensed software products are owned by Tektronix or its suppliers and
are protected by United States copyright laws and international treaty provisions.
Use, duplication, or disclosure by the Government is subject to restrictions as set forth in subparagraph (c)(1)(i i) of the
Rights in Technical Data and Computer Software clause at DFARS 252.227-7013, or subparagraphs (c)(1) and (2) of the
Commercial Computer Software -- Restricted Rights clause at FAR 52.227-19, as applicable.
Tektronix products are covered by U.S. and foreign patents, issued and pending. Information in this publication supercedes
that in all previously published material. Specifications and price change privileges reserved.
Tektronix, Inc., P.O. Box 500, Beaverton, OR 97077
TEKTRONIX and TEK are registered tradem arks of Tektronix, Inc.
Page 3

Hardware Warranty
Tektronix warrants that the products that it manufactures and sells will be free from defects in materials and
workmanship for a period of one (1) year from the date of shipment. If a product proves defective during this
warranty period, Tektronix, at its option, either will repair the defective product without charge for parts and labor,
or will provide a replacement in exchange for the defective product.
In order to obtain service under this warranty, Customer must notify Tektronix of the defect before the expiration
of the warranty period and make suitable arrangements for the performance of service. Customer shall be
responsible for packaging and shipping the defective product to the service center designated by Tektronix, with
shipping charges prepaid. Tektronix shall pay for the return of the product to Customer if the shipment is to a
location within the country in which the Tektronix service center is located. Customer shall be responsible for
paying all shipping charges, duties, taxes, and any other charges for products returned to any other locations.
This warranty shall not apply to any defect, failure or damage caused by improper use or improper or inadequate
maintenance and care. Tektronix shall not be obligated to furnish service under this warranty a) to repair damage
resulting from attempts by personnel other than Tektronix representatives to install, repair or service the product;
b) to repair damage resulting from improper use or connection to incompatible equipment; c) to repair any
damage or malfunction caused by the use of non-Tektronix supplies; or d) to service a product that has been
modified or integrated with other products when the effect of such modification or integration increases the time
or difficulty of servicing the product.
THIS W ARRANTY IS GIVEN BY TEKTRONIX IN LIEU OF ANY OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESS
OR IMPLIED. TEKTRONIX AND ITS VENDORS DISCLAIM ANY IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. TEKTRONIX’
RESPONSIBILITY TO REPAIR OR REPLACE DEFECTIVE PRODUCTS IS THE SOLE AND
EXCLUSIVE REMEDY PROVIDED TO THE CUSTOMER FOR BREACH OF THIS WARRANTY.
TEKTRONIX AND ITS VENDORS WILL NOT BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL,
INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES IRRESPECTIVE OF WHETHER TEKTRONIX OR
THE VENDOR HAS ADVANCE NOTICE OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
Page 4

Software Warranty
Tektronix warrants that the media on which thi s software product is furnished and the e ncoding of the programs on
the media will be free from defects in materials and workmanship for a period of three (3) months from the date of
shipment. If a medium or encoding proves defective during the warranty period, Tektronix will provide a
replacement in exchange for the defective medium. Except as to the media on which this software product is
furnished, this software product is provided “as is” without warranty of any kind, either express or impl ied.
Tektronix does not warrant that the functions contained in this software product will meet Customer’s
requirements or that the operation of the programs will be uninte rrupted or error-free.
In order to obtain service under this warranty, Customer must notify Tektronix of the defect before the expiration
of the warranty period. If Tektronix is unable to provide a replacement that is free from defects in materials and
workmanship within a reasonable time thereafter, Customer may terminate the license for this software product
and return this software product and any associated materials for credit or refund.
THIS W ARRANTY IS GIVEN BY TEKTRONIX IN LIEU OF ANY OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESS
OR IMPLIED. TEKTRONIX AND ITS VENDORS DISCLAIM ANY IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. TEKTRONIX’
RESPONSIBILITY TO REPLACE DEFECTIVE MEDIA OR REFUND CUSTOMER’SPAYMENTIS
THE SOLE AND EXCLUSIVE REMEDY PROVIDED TO THE CUSTOMER FOR BREACH OF THIS
WARRANTY. TEKTRONIX AND ITS VENDORS WILL NOT BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT,
SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES IRRESPECTIVE OF WHETHER
TEKTRONIX OR THE VENDOR HAS ADVANCE NOTICE OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGES.
Page 5

Table of Contents
Specifications
General Safety Summary ix...................................
Service Safety Summary xi....................................
Preface xiii...................................................
Manual Structure xiii................................................
Manual Conventions xiv..............................................
Related Documents xvi...............................................
MPEG Test System Applications xvi....................................
Contacting Tektronix xxi.............................................
Product Description 1--1........................................
Characteristic Tables 1--11.......................................
Monitoring Characteristics 1--11.........................................
Interface Platform Characteristics 1--12...................................
I/O Port Electrical Characteristics 1--12...................................
Power Characteristics 1--21.............................................
Environmental Characteristics 1--21......................................
Mechanical (Physical) Characteristics 1--22................................
Certifications and Compliances 1--22.....................................
Operating Information
Theory of Operation
Installation
Hardware Installation 2--1.............................................
Connecting MTS300 System I/O Ports 2--7...............................
Networking 2--12.....................................................
Operating Information 2--19.....................................
Starting the MTS300 System 2--20.......................................
Shutting Down the MTS300 System 2--25.................................
Application Overviews 2--28............................................
Front Panel Controls 2--39..............................................
Tutorial 2--43..................................................
Preliminary Setup 2--43................................................
Starting and Configuring the Master Client 2--44............................
Assigning Servers and Generating a Transport Stream 2--47...................
Monitoring a Transport Stream Input 2--48.................................
Configuring the Analysis Server 2--51....................................
Configuring the Data Logging Function 2--54..............................
Analyzing a Transport Stream 2--55......................................
Recording a Transport Stream Input 2--58.................................
Mainframe Operation 3--1.............................................
MTS300 System Modules Operation 3--5.................................
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
i
Page 6

Table of Contents
Performance Verification
10 MHz Reference Clock 4--1..........................................
I/O System 4--10.....................................................
MPEG-2 Software Components 4--17.....................................
TMCC Software Components 4--29......................................
Adjustment Procedures
Maintenance
Maintenance 6--1..............................................
Servicing Preparation 6--1.............................................
Cleaning and Preventive Maintenance 6--3................................
Repackaging for Shipment 6--6.........................................
Power-on Diagnostics and Troubleshooting 6--10............................
Network Troubleshooting 6--14..........................................
Troubleshooting the SCSI Drives 6--22....................................
Software Repair and Recovery 6--23...............................
Software Repair Strategy 6--23..........................................
Restoring System Settings 6--25.........................................
Restoring Device Drivers 6--39..........................................
Restoring the Operating System and Application Software 6--45...............
Removal and Replacement Procedures 6--53........................
Replaceable Modules 6--53.............................................
Recommended Tools 6--54.............................................
Accessing Replaceable Modules 6--54....................................
Replacing MTS300 Test System Modules 6--58.............................
Replacing Mainframe Modules 6--70.....................................
Options
Replaceable Electrical Parts
Diagrams
Replaceable Mechanical Parts
Parts Ordering Information 10--1.........................................
Module Servicing 10--2................................................
Using the Replaceable Parts List 10--2....................................
ii
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
Page 7

List of Figures
Table of Contents
Figure 1--1: MTS300 MPEG Test System 1--2......................
Figure 1--2: Parallel data timing, 188-byte packets 1--15..............
Figure 2--1: Typical MTS300 test system rear panel connectors 2--2....
Figure 2--2: Keyboard and mouse alternative connections 2--3........
Figure 2--3: Software Key 2--4...................................
Figure 2--4: Rear-panel configuration with one ASI/M2S (Option AS)
interface installed 2--8......................................
Figure 2--5: Rear-panel configuration with two ASI/M2S (Option AS)
interfaces installed 2--8......................................
Figure 2--6: Rear-panel configuration with ASI/M2S (Option AS)
and SSI (Option SS) interfaces installed 2--9....................
Figure 2--7: Rear-panel configuration with ASI/M2S (Option AS)
and DHEI (Option DE) interfaces installed 2--9.................
Figure 2--8: Rear-panel configuration with ASI/M2S (Option AS)
and SPI (Option LV) interfaces installed 2--10...................
Figure 2--9: Rear-panel configuration with one SSI (Option SS)
interface installed 2--10......................................
Figure 2--10: Rear-panel configuration with two SSI (Option SS)
interfaces installed 2--11......................................
Figure 2--11: Rear-panel configuration with SSI (Option SS)
and ASI/M2S (MTS3FAS) interfaces installed 2--11...............
Figure 2--12: Network dialog box showing TCP/IP Protocol item 2--14..
Figure 2--13: IP tab parameters 2--15..............................
Figure 2--14: DNS tab parameters 2--16............................
Figure 2--15: On/Stby switch 2--20................................
Figure 2--16: The Master client application window 2--29.............
Figure 2--17: The Expert client application window 2--30.............
Figure 2--18: The Configuration client application window 2--32.......
Figure 2--19: The Stream Player client application window 2--33.......
Figure 2--20: Stream Recorder client application window 2--34.........
Figure 2--21: TMCC Expert Client display 2--37.....................
Figure 2--22: TMCC Configuration Client display 2--38..............
Figure 2--23: Front-panel elements 2--39............................
Figure 2--24: Initial setup for the tutorial 2--44......................
Figure 2--25: Initial Master Client application window 2--45...........
Figure 2--26: Master Client connected to the local Server Manager 2--45.
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
iii
Page 8

Table of Contents
Figure 2--27: Changing the analysis display options 2--46.............
Figure 2--28: Assigning servers to I/O ports 2--47....................
Figure 2--29: Stream Player client 2--48............................
Figure 2--30: Monitoring a transport stream 2--49...................
Figure 2--31: Services panel details view 2--50.......................
Figure 2--32: Configuration Client display 2--51.....................
Figure 2--33: Setting ETR290 probes 2--52..........................
Figure 2--34: Changing the message level 2--53......................
Figure 2--35: Data Logging configuration panel 2--54.................
Figure 2--36: Launching the Expert Client 2--55.....................
Figure 2--37: Expert Client display showing errors 2--56..............
Figure 2--38: ETR290 view panel in the Expert Client 2--57...........
Figure 2--39: Stream Recorder client application window 2--58.........
Figure 3--1: Mainframe simplified block diagram 3--2...............
Figure 4--1: Removing the right-side handle screws 4--3..............
Figure 4--2: Removing the rear-panel feet 4--3......................
Figure 4--3: Removing the circuit board retaining plate 4--4..........
Figure 4--4: Location of 10 MHz clock test point 4--5................
Figure 4--5: Removing the PIA+ module 4--7.......................
Figure 4--6: Adjusting the 10 MHz reference clock 4--8..............
Figure 4--7: Typical initial equipment setup 4--11....................
Figure 4--8: Tektronix MPEG Test System program window 4--12......
Figure 4--9: Connect to local Server Manager 4--12..................
Figure 4--10: Start the testing routine 4--13.........................
Figure 4--11: Begin the self test routine 4--13........................
Figure 4--12: Window showing sample test results summary 4--14......
Figure 4--13: Message box with connection requirements 4--15.........
Figure 4--14: Connections for trigger test 4--16......................
Figure 4--15: Connections for clock test 4--16........................
Figure 4--16: ASI cabling 4--17....................................
Figure 4--17: Initial Master Client application window 4--18...........
Figure 4--18: Connecting to the local Server Manager 4--18............
Figure 4--19: Master Client window showing no assigned ports 4--19....
Figure 4--20: Port Manager panel showing Analysis Server
selected 4--20...............................................
Figure 4--21: Selecting Launch Stream Player Client 4--20............
Figure 4--22: Stream Player Application window 4--21...............
iv
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
Page 9

Table of Contents
Figure 4--23: C:\MTS300\Cfg-Trp directory 4--22....................
Figure 4--24: Starting transport stream analysis 4--23................
Figure 4--25: Master Client in Analysis mode 4--23...................
Figure 4--26: Expert Client application window 4--24................
Figure 4--27: Setup for testing second input 4--25....................
Figure 4--28: Exit Expert Client application 4--25....................
Figure 4--29: Expert Client application window 4--27................
Figure 4--30: Rear panel connections for I/O #3 test procedure 4--28....
Figure 4--31: Probes added in the TMCC Configuration Client 4-- 29....
Figure 4--32: TMCC Expert Client 4--30...........................
Figure 6--1: Repackaging the program monitor 6--7.................
Figure 6--2: Placement of bottom spacer pad in inner shipping box 6--8
Figure 6--3: Incorrect IP address 6--15.............................
Figure 6--4: Incorrect subnet mask 6--16...........................
Figure 6--5: Incorrect default gateway IP address 6--17...............
Figure 6--6: Ping.exe command window 6--19.......................
Figure 6--7: Tracert.exe command window 6--20.....................
Figure 6--8: Command prompt with nslookup results 6--21............
Figure 6--9: Deleting partitions using the Disk Administrator
utility 6--28.................................................
Figure 6--10: Software Protection key 6--47.........................
Figure 6--11: Checking the free disk space 6--48.....................
Figure 6--12: Removing the cabinet handle 6--55.....................
Figure 6--13: Removing the cabinet feet 6--55.......................
Figure 6--14: Circuit board retaining plate 6--58.....................
Figure 6--15: Easily damaged capacitor on the PIA+ module 6--59......
Figure 6--16: Clock and trigger cable connections for the ASI or
SSI board on the PIA+ module 6--61...........................
Figure 6--17: Attaching the SSI or ASI trigger and clock cables to
the rear-panel bracket 6--61...................................
Figure 6--18: Installing an optional SSI or ASI board on the
PIA+ module 6-- 62..........................................
Figure 6--19: Clock and trigger cable connections on an additional
SSI or ASI board 6--63.......................................
Figure 6--20: Additional ASI or SSI interface installation 6--63.........
Figure 6--21: Installing the DHEI board on the PIA+ module 6--64.....
Figure 6--22: Installing the ribbon cable on the DHEI board 6--65......
Figure 6--23: Optional DHEI interface installation 6--65..............
Figure 6--24: Installing the SPI board on the PIA+ module 6--66.......
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
v
Page 10

Table of Contents
Figure 6--25: Assembling the SPI rear-panel brackets and cables 6--67..
Figure 6--26: Connecting the ribbon cables on the SPI board 6--68.....
Figure 6--27: Optional SPI interface installation 6--69................
Figure 6--28: LCD Display assembly removal 6--70...................
Figure 6--29: Keypad assembly removal 6--72.......................
Figure 6--30: Floppy disk drive and CD audio connector
installation 6--73............................................
Figure 6--31: Chassis screw locations for CD drive 6--74..............
Figure 6--32: Chassis screw locations for the floppy disk drive 6--75....
Figure 6--33: Speaker installation 6--77............................
Figure 6--34: Front panel interface circuit board connectors 6--79......
Figure 6--35: Screw locations for the Front Panel Interface board 6--80..
Figure 6--36: Routing of fan and speaker wires to Front Panel
Interface board 6--81........................................
Figure 6--37: Removing the IDE hard drive 6--83....................
Figure 6--38: Power supply long and short screw locations 6--85........
Figure 6--39: Controller board orientation and screw locations 6--87....
Figure 6--40: Installing the Processor I/O board into slot 10 6--89.......
Figure 6--41: Installing the Processor I/O board into the backplane 6--90
Figure 6--42: Processor I/O board to Controller board
interconnections -- top connectors 6--90.........................
Figure 6--43: Processor I/O board to Controller board
interconnections -- bottom connectors 6--91......................
Figure 6--44: Top connection to Controller board 6--92...............
Figure 6--45: Location of J220 connections and wiring orientation 6--92.
Figure 6--46: Backplane orientation and screw locations 6--94.........
Figure 6--47: SCSI hard drive removal 6--96........................
Figure 6--48: Configuring the SCSI drive jumpers 6--97..............
Figure 6--49: Installing the mounting brackets on the SCSI drive 6--98..
Figure 10--1: Modules 10--6......................................
Figure 10--2: Front panel and associated parts, Backplane board,
anddiskdrives 10--9.........................................
Figure 10--3: Cables and hard drives 10--12..........................
Figure 10--4: Cabinet parts and accessories 10--14....................
vi
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
Page 11

List of Tables
Table of Contents
Table i: Tektronix MPEG Test System version 6.1 applications xiii...
Table 1--1: Platform characteristics 1--12...........................
T a b l e 1 -- 2 : A S I 1 -- 1 2...........................................
Table 1--3: SPI-LVDS parallel (Option MTS3FLV) 1-- 13.............
Table 1--4: LVDS parallel data pin connections 1--15.................
Table 1--5: SSI (Option SS) 1--16.................................
Table 1--6: DHEI-Digicipher II 1--17..............................
Table 1--7: DHEI Expansion In pin connections 1--19................
Table 1--8: DHEI Expansion Out pin connections 1--20..............
T able 1--9: AC power source characteristics 1--21....................
T able 1--10: Environmental characteristics 1--21....................
T able 1--11: Mechanical characteristics 1--22.......................
Table 1--12: Certifications and compliances 1--22....................
Table 1--13: Environmental limits and use classification for safety
certification compliance 1--23.................................
Table 2--1: Rear-panel connectors 2--1............................
T able 2--2: Electrical operating requirements 2--5..................
Table 2--3: Power cord identification 2--6.........................
Table 2--4: Default user names and passwords 2--21.................
Table 2--5: Front panel-key controls 2--40..........................
Table 2--6: Touch screen techniques 2 --41..........................
T able 4--1: Adjustment table for 10 MHz reference clock 4--9.........
Table 6--1: Static susceptibility 6--2..............................
Table 6--2: Packaging material 6--7..............................
Table 6--3: Troubleshooting power-on failures 6--10..................
Table 6--4: Power-up error messages 6--11..........................
Table 6--5: MTS300 system COM port settings 6--30.................
Table 6--6: Touchscreen driver hardware settings 6--44...............
Table 7--1: MTS300 test system options 7--1.......................
Table 7--2: Possible interface configurations 7--2...................
Table 7--3: MTS300 test system upgrades 7--3.....................
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
vii
Page 12

Table of Contents
viii
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
Page 13

General Safety Summary
Review the following safety precautions to avoid injury and prevent damage to
this product or any products connected to it. To avoid potential hazards, use this
product only as specified.
Only qualified personnel should perform service procedures.
ToAvoidFireor
Personal Injury
Use Proper Power Cord. Use only the power cord specified for this product and
certified for the country of use.
Ground the Product. This product is grounded through the grounding conductor
of the power cord. To avoid electric shock, the grounding conductor must be
connected to earth ground. Before making connections to the input or output
terminals of the product, ensure that the product is properly grounded.
Observe All Terminal Ratings. To avoid fire or shock hazard, observe all ratings
and markings on the product. Consult the product manual for further ratings
information before making connections to the product.
Do not apply a potential to any terminal, including the common terminal, that
exceeds the maximum rating of that terminal.
Use Proper Fuse. Use only the fuse type and rating specified for this product.
Avoid Exposed Circuitry. Do not touch exposed connections and components
when power is present.
Do Not Operate With Suspected Failures. If you suspect there is damage to this
product, have it inspected by qualified service personnel.
Do Not Operate in Wet/Damp Conditions.
Do Not Operate in an Explosive Atmosphere.
Keep Product Surfaces Clean and Dry.
Provide Proper Ventilation. Refer to the manual’s installation instructions for
details on installing the product so it has proper ventilation.
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
ix
Page 14

General Safety Summary
Symbols and Terms
Terms in this Manual. These terms may appear in this manual:
WARNING. Warning statements identify conditions or practices that could result
in injury or loss of life.
CAUTION. Caution statements identify conditions or practices that could result in
damage to this product or other property.
Terms on the Product. These terms may appear on the product:
DANGER indicates an injury hazard immediately accessible as you read the
marking.
WARNING indicates an injury hazard not immediately accessible as you read the
marking.
CAUTION indicates a hazard to property including the product.
Symbols on the Product. The following symbols may appear on the product:
CAUTION
Refer to Manual
Protective Ground
(Earth) Terminal
x
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
Page 15

Service Safety Summary
Only qualified personnel should perform service procedures. Read this Service
Safety Summary and the General Safety Summary before performing any service
procedures.
Do Not Service Alone. Do not perform internal service or adjustments of this
product unless another person capable of rendering first aid and resuscitation is
present.
Disconnect Power. To avoid electric shock, switch off the instrument power, then
disconnect the power cord from the mains power.
Use Care When Servicing With Power On. Dangerous voltages or currents may
exist in this product. Disconnect power, remove battery (if applicable), and
disconnect test leads before removing protective panels, soldering, or replacing
components.
To avoid electric shock, do not touch exposed connections.
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
xi
Page 16

Service Safety Summary
xii
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
Page 17

Preface
Manual Structure
This document describes how to service the Tektronix MTS300 MPEG Test
System. Basic operating information is included to aid you in the servicing of
the instrument.
If you purchased a Tektronix MTS300 MPEG Test System and are looking for
detailed installation instructions or first-time operation procedures, refer to the
MTS300 MPEG Test System Hardware and Software Installation Technical
Reference, Tektronix part number, 071-0667-XX.
This service manual is organized into the following sections:
Specifications. This section contains a brief product description and lists the
specification tables describing the performance characteristics of the MTS300
MPEG Test System.
Operating Information. This section contains installation and operating information related to the servicing of the instrument.
Theory of Operation. This section contains a description of how the MTS300
MPEG Test System operates to the level needed to perform module-level
servicing of the instrument.
Performance Verification. This section contains procedures to verify that the
instrument is performing according to the specifications.
Adjustment Procedures. This section contains procedures to adjust the instrument
so that the instrument can perform according to the specifications.
Maintenance. This section contains procedures for inspecting and cleaning the
instrument, instructions for removing and replacing internal modules and
components, procedures for troubleshooting the instrument, and other information useful for maintaining or repairing the instrument.
Options. This section lists the options that may be installed in the instrument.
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
xiii
Page 18

Preface
Manual Conventions
Replaceable Electrical Parts. This section lists the replaceable electrical assemblies and components of the instrument.
Diagrams. This section contains interconnect diagrams for the instrument.
Replaceable Mechanical Parts. This section lists the replaceable mechanical
assemblies and components of the instrument.
Glossary. The Glossary contains definitions of new, uncommon, and/or unique
terms used in this manual.
Throughout this manual the following typographic, symbolic, and terminology
conventions apply:
Typographic Conventions
In this manual the following typographic conventions apply:
H Bold terms are found in procedures and denote interface items that you need
to select in order to cause an event to occur. For instance, to configure
default directories the procedure would read as follows:
Select Directories from the Options menu.
In this example, even though the Options menu is an interface element, the
Directories selection is the element that displays the needed dialog box
(causes an event to occur) and is the only bold term in the step. When
interface items are referred to outside of procedures, the terms are not
boldface.
H Manual names, manual section names, and words that are defined in the text
are italicized.
H Specific input that you need to make is indicated in the text using
mono-spaced font. Unless otherwise stated, do not enter punctuation at the
end of a mono-spaced font entry.
xiv
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
Page 19

Preface
Symbols and Terminology
Conventions
This manual uses symbols and terminology consistent with the following
publications:
H For PSI elements, ISO/IEC Standard 11172 and 13818 (parts 1, 2, and 3)
H For DVB elements, ETSI Publication prETS 300 468
H For DVB-T elements, ETSI Publication TS 101 191 V1.2.1
H For ATSC elements, ATSC Document A/65
H For Windows elements, The Microsoft Manual of Style for Technical
Publications, 2nd ed.
The following ARIB (Association of Radio Industries and Business) and ITU-R
(International Telecommunications Union) standards were used to develop the
added ARIB and TMCC enhancements to the stream creation applications:
H ARIB STD-B10 (1.2), 1999, Service Information for Digital Broadcasting
System
H ARIB STD-B16 (1.1), 1999, Digital Receiver Commonly Used for Digital
Satellite Broadcasting Services Using Communication Satellites
H ARIB STD--B20 (1.1), 1999, Digital Broadcasting System and Related
Operational Guidelines for Broadcasting Satellites
H ITU-R BO. 1408, Transmission System for Advanced Multimedia Services
Provided by Integrated Services Digital Broadcasting in A Broadcasting
Satellite Channel
In cases where terms, symbols, or references are or may be ambiguous, check the
Glossary located at the back of this manual for definitions. Also, refer to the
Glossary for definitions unique to the MTS300 test system and applications.
Refer to the your Windows documentation for definitions and explanations of
Windows specific terminology.
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
xv
Page 20

Preface
Related Documents
For additional information about using MTS300 software to monitor, analyze,
and generate MPEG-2, DVB, and ATSC data streams, refer to the following
manuals:
H The MTS300 MPEG Test System Real-Time Analysis User Manual,
Tektronix part number 071-0658-XX, contains information about using the
real-time MPEG-2 System Analyzer application.
H The MTS300 MPEG Test System MPEG-2 DVB/ATSC System Analyzer User
Manual, Tektronix part number 071-0659-XX, contains information about
using the deferred-time MPEG-2 System Analyzer.
H The MTS300 MPEG Test System Program Stream Analyzer User Manual,
Tektronix part number 071-0662-XX, contains information about using the
deferred-time Program Stream Analyzer application.
H The MTS300 MPEG Test System Dolby Digital Audio Stream Analyzer User
Manual, Tektronix part number 071-0661-XX, contains information about
using the deferred-time AC-3 Audio Stream Analyzer application.
H The MTS300 MPEG Test System MPEG Audio Stream Analyzer User
Manual, Tektronix part number 071-0663-XX, contains information about
using the deferred-time MPEG Audio Stream Analyzer application.
H The MTS300 MPEG Test System Video Stream Analyzer User Manual,
Tektronix part number 071-0664-XX, contains information about using the
deferred-time MPEG Video Stream Analyzer application.
MPEG Test System Applications
The applications that appear in your MTS300 MPEG test System depend on the
software version and the options installed in the instrument. Table i summarizes
all of the test system applications available in software version 6.1.
xvi
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
Page 21
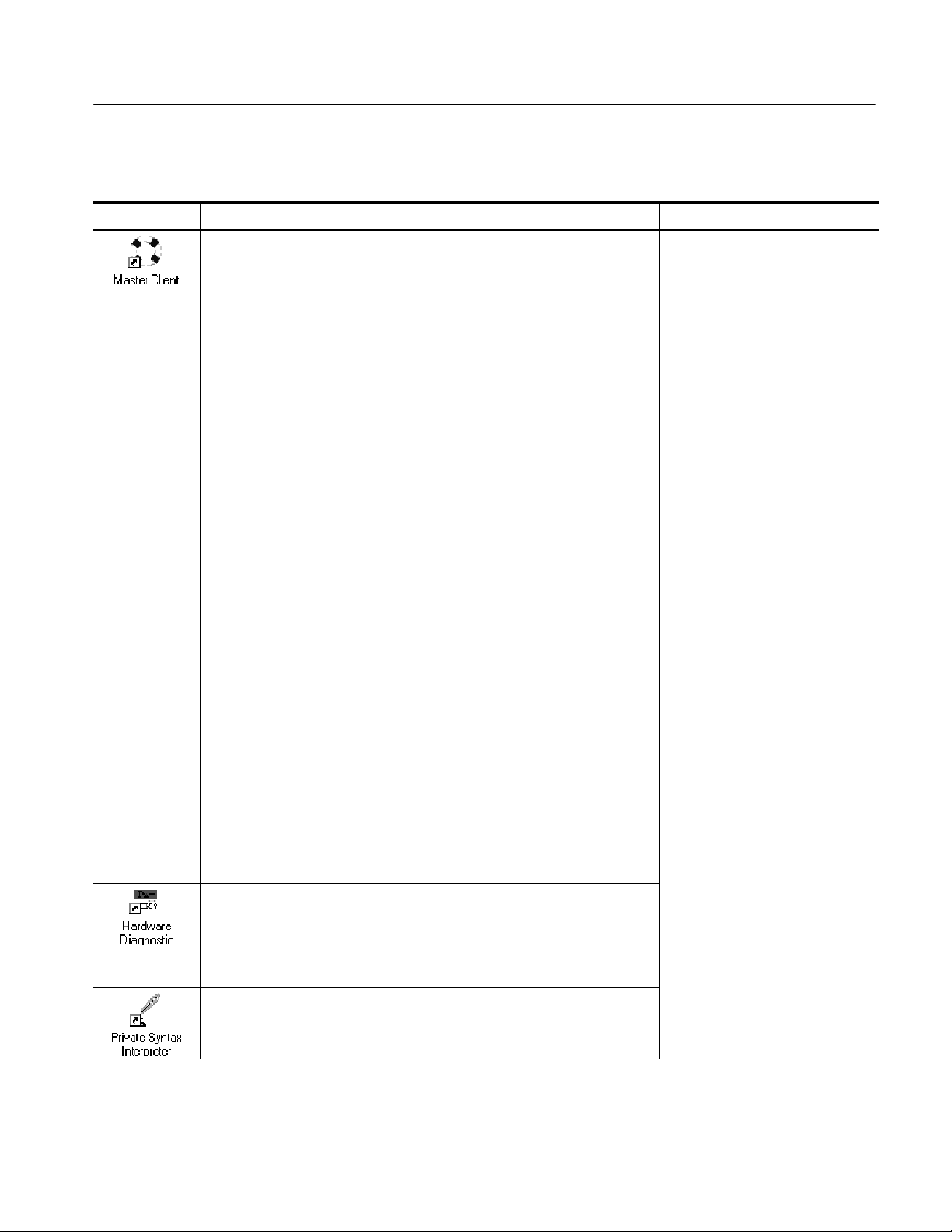
Table i: Tektronix MPEG Test System version 6.1 applications
Icon Application title Function User document
Master Client Continuously monitor an input bitstream for
compliance with the MPEG-2, DVB-SI,
ATSC PSIP, and ISDB/ARIB digital television
standards. Use this client to start or assign to an
input/output the following real-time applications
and servers:
Analysis Server, used to perform real-time
analysis on a transport stream input
TMCC Analysis Server,usedtoperform
real-time analysis on a TMCC transport stream
input
Expert Client, used display the results of
real-time transport stream analysis performed by
an analysis server.
MTS300 MPEG Test System
Real-Time Analysis User Manual
071-0658-XX
Preface
TMCC Expert Client, used to display t he results
of real-time transport stream analysis performed
by a TMCC analysis server.
Configuration Client, used to configure
analysis servers for specific errors.
TMCC Configuration Client, used to configure
TMCC analysis servers for specific errors.
Stream Player, used to generate transport
streams from a local file.
Stream Recorder, used to capture transport
stream input.
OpenMux, used to configure and generate
transport streams from local transport stream
and elementary stream files
Hardware Diagnostic Perform onboard self-tests for the MPEG Test
System.
Private Syntax Interpreter Create table definitions used by the Real-Time
Analyzer to interpret private syntax sections.
MTS300 MPEG Test System
Hardware and Software Installation
Technical Reference 071-0667-XX
(Information repeated in both
manuals)
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
xvii
Page 22
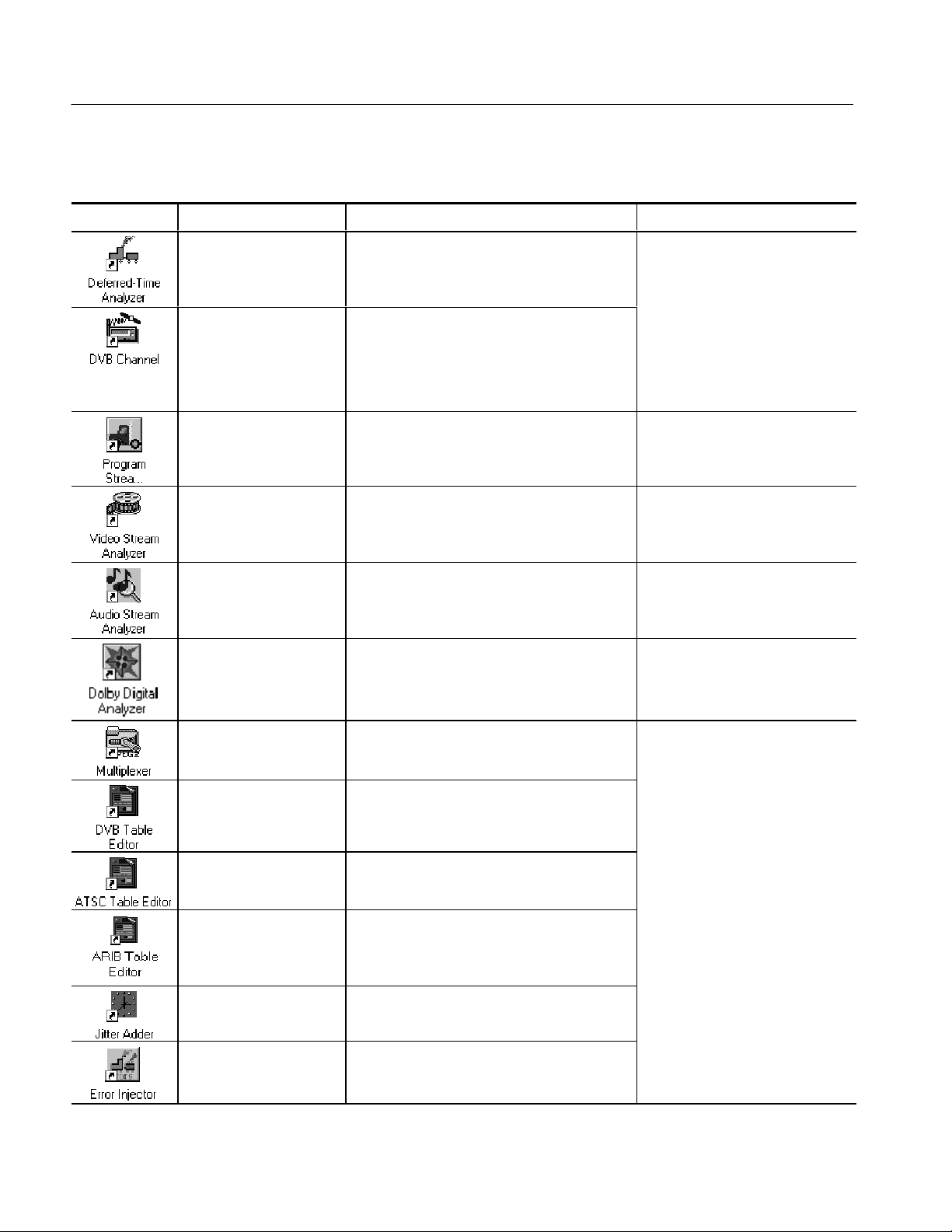
Preface
Table i: Tektronix MPEG Test System version 6.1 applications (Cont.)
Icon User documentFunctionApplication title
MPEG-2 DVB/ATSC
System Analyzer
Analyze transport streams and packetized
elementary streams saved to the system disks.
MTS300 MPEG Test System
MPEG-2 DVB/ATSC System
Analyzer User Manual 071-0659-XX
DVB Channel Coding
and Decoding
Program Stream Analyzer Analyze MPEG program stream files. MTS300 MPEG Test System
MPEG Video Stream
Analyzer
MPEG Audio Stream
Analyzer
Dolby Digital Audio Stream
Analyzer
MPEG-2 Transport Stream
Multiplexer
DVB Table Editor Create and edit PSI and DVB SI table files for
Code and decode transport stream files to DVB
specifications.
Analyze MPEG-1 and MPEG-2 video elementary
streams files or streams extracted from the
MPEG-2 System Analyzer or Program Stream
Analyzer.
Analyze MPEG-1 and MPEG-2 audio elementary
streams files or streams extracted from the
MPEG-2 System Analyzer or Program Stream
Analyzer.
Analyze Dolby Digital (AC-3) audio elementary
stream files or streams extracted from the
MPEG-2 System Analyzer.
Create transport stream files from PSI/SI/PSIP
table files, elementary stream files, and data
files.
use with the transport stream multiplexer.
MTS300 MPEG Test System
Stream Creation Applications User
Manual 071-0778-XX
(Information repeated in both
manuals)
Program Stream Analyzer User
Manual 071-0662-XX
MTS300 MPEG Test System Video
Stream Analyzer User Manual
071-0664-XX
MTS300 MPEG Test System Audio
Stream Analyzer User Manual
071-0663-XX
MTS300 MPEG Test System Dolby
Digital Audio Stream Analyzer User
Manual 071-0661-XX
MTS300 MPEG Test System
Stream Creation Applications User
Manual 071-0778-XX
xviii
ATSC Table Editor Create and edit PSI and ATSC PSIP table files
for use with the transport stream multiplexer.
ARIB Table Editor Create and edit PSI and ISDB ARIB table files
for use with the transport stream multiplexer. You
also use this editor to create and modify the SIT
and DIT.
Jitter Adder Add jitter to PCR data in MPEG-2 transport
stream files.
Error Injector Insert or correct errors in transport stream
packets.
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
Page 23
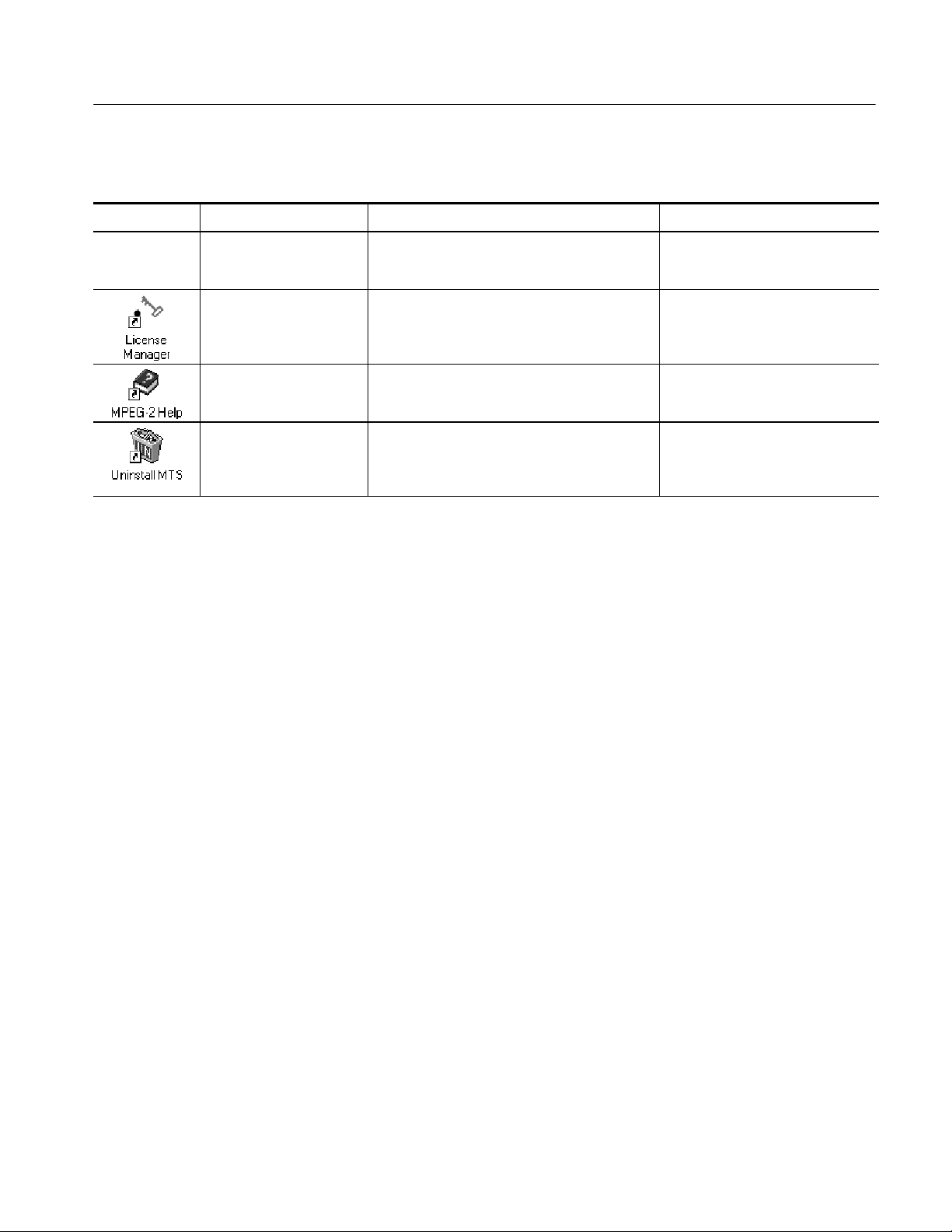
Table i: Tektronix MPEG Test System version 6.1 applications (Cont.)
Icon User documentFunctionApplication title
TMCC Combiner Adds TMCC information to a multiplex to
generate a valid ISDB-S transport stream fi le.
Tektronix Software
Protection
Enter or reenter the general password to enable
licensed applications.
Preface
MTS300 MPEG Test System
Stream Creation Applications User
Manual 071-0778-XX
Read This First, MTS300 MPEG
Test System Software V6.1
071-0666-XX
MPEG2_Part1
(ISO/IEC 13818-1)
Uninstall MTS Remove MPEG Test System software from the
Other Information Sources
For information about the Windows NT operating system, refer to the Microsoft
documentation that accompanied your system.
For the latest information about MTS300 Series Real-Time Analyzer features
and bugs, refer to the MTS300 Series Software Version 6.1 Read This First
document that accompanied your Tektronix MPEG Test System product.
Two sources of online information are provided with the MTS300 MPEG Test
System Stream Creation Applications: the application online help files and an
online help file of the MPEG-2, Part 1 (Systems) document. You can access
these sources of information using the following techniques:
H Access help topics by selecting Contents from the Help menu.
The international MPEG-2 system standard in
Windows Help format.
system disk.
none
MTS300 MPEG Test System User
Manuals
H To display the help, double click the MPEG-2 icon in the Tektronix MPEG
Test System program group window.
Included on the software application CD-ROM is a Read Me file for the
software. This file lists the application files included with the software installation types and other important information.
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
xix
Page 24

Preface
The following URLs access the websites for the standards organizations listed
(the URLs listed were valid as of January, 2001):
H MPEG-2 standards (International Organization for Standards)
http://www.iso.ch/
H DVB standards (European Technical Standards Institute)
http://www.etsi.org/
H ATSC standards (Advanced Television Systems Committee)
http://www.atsc.org/
xx
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
Page 25

Contacting Tektronix
Preface
Phone 1-800-833-9200*
Address Tektronix, Inc.
Department or name (if known)
14200 SW Karl Braun Drive
P.O. Box 500
Beaverton, OR 97077
USA
Web site www.tektronix.com
Sales support 1-800-833-9200, select option 1*
Service support 1-800-833-9200, select option 2*
Technical support Email: techsupport@tektronix.com
1-800-833-9200, select option 3*
6:00 a.m. -- 5:00 p.m. Pacific time
* This phone number is toll free in North America. After office hours, please leave a
voice mail message.
Outside North America, contact a Tektronix sales office or distributor; see the
Tektronix web site for a list of offices.
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
xxi
Page 26

Preface
xxii
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
Page 27

Product Description
This Specifications section contains a product description and lists the characteristic tables for the MTS300 MPEG Test system.
Refer to Options on page 7--1 for a list of the options you may find installed in
the instrument. Refer to Replaceable Mechanical Parts on page 10--1 for a list of
the standard and optional accessories available with the instrument.
Product Overview
The MTS300 MPEG Test System is a component of the Video Quality of
Service (VQoS) products offered by Tektronix. The MTS300 system (see
Figure 1--1) is a high-performance MPEG protocol diagnostic and analysis tool
that provides you with innovative solutions to meet the challenges of designing,
verifying, and characterizing products and systems using MPEG-2 technology.
The MTS300 system offers powerful acquisition and computational capabilities
for analyzing designs based on MPEG, DVB, ATSC, and ISDB standards. These
flexible and expandable capabilities include real-time monitoring, data rate
analysis, and Tektronix-exclusive timing analysis to help diagnose the most
challenging problems and characterize real-time performance.
NOTE. Refer to the MPEG-2, DVB, ATSC, and ISDB-S/ARIB standards for
detailed information about the syntax and semantics of each system.
The deferred-time (off-line) analysis provided by the MTS300 system helps you
fully verify compliance to standards and diagnose problems in complex transport
streams. Easy-to-use transport stream capture, playout, and on-line storage lets
you build extensive suites of test streams, and then use these streams to exercise
your designs. Additional stream editing capability, with error and jitter injection
and real--time multiplexing, gives you the ability to create and playout test
sequences that fully stress and characterize design parameters.
Each test system can monitor up to two transport stream inputs simultaneously
and accepts inputs in the following electrical formats:
H ASI/M2S (the test system automatically detects the format)
H SPI (LVDS parallel); available when you order the MTS3FLV upgrade
H DHEI (GI Digicipher II): available when you order the MTS3FDE upgrade
H SSI (SMPTE 310M); available when you order the MTS3FSS upgrade
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
1- 1
Page 28

Product Description
MPEG Test System
Figure 1- 1: MTS300 MPEG Test System
Primary Applications
Key Features
The MTS300 system was designed for the following applications:
H Evaluation and verification of MPEG, DVB, ATSC and ISDB designs
Design and verification of digital-video set-top boxes (STBs)
H
H Stress and characterization of electrical circuits and ICs developed for
products using MPEG-2 compressed digital-video technology
The MTS300 system provides the following key features:
H Real-time monitoring and compliance testing of MPEG, DVB, ATSC and
ISDB transport streams for complete application flexibility
H Dolby Digital AC--3 compliance testing and AAC stream monitoring for
testing advanced audio capabilities
H Tektronix-exclusive PCR overall jitter, drift and offset measurements allow
you to diagnose the most challenging real--time performance problems
H Real-time analysis of transport streams used in data broadcasting applica-
tions based on ISO/IEC 13818-6 (DSM-CC) and EN 301 192 standards
H Analysis of Mega-frame Initialization Packets (MIPs), specified in the DVB
TS 101 191 standard
1- 2
H Detailed off-line analysis of transport streams, program streams and
elementary streams available to fully verify design performance
H Logging of user-selected analysis events to tab-delimited text files for record
keeping and further analysis
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
Page 29

Product Description
H ASI/M2S, SPI (LVDS), SMPTE310M, and DHEI interfaces available to
support a variety of design configurations
H SNMP agent allows you to control the instrument from a remote location
H Private syntax table editor allows you to describe the syntax of a private
table
H Optional real-time multiplexing of elementary and transport streams
provides flexible real-time manipulation of stream content and parameters
H Optional TMCC data testing and transport stream creation for ISDB
environments
H Capture (manual and triggered), playback, and on-line storage of transport,
program and elementary streams
H Optional editing capability allows you to create custom transport streams and
inject errors or jitter to fully stress your design
H Modular architecture allows you to easily upgrade in the future
System Architecture
H Rackmount configuration kit included
H Microsoft NT operating system provides robust networking, performance
and functionality
The MTS300 system uses a client/server architecture consisting of a Server
Manager, two Analysis Server pairs (each pair consists of one MPEG analysis
server and one TMCC analysis server), and the following client applications:
Master Client, Expert Client, Configuration Client, Stream Recorder, Stream
Player, TMCC Expert Client, and TMCC Configuration Client
Combined, these client/server modules enable you to monitor multiple transport
stream inputs simultaneously, perform in-depth analyses on one transport stream
input, and to configure the monitoring and reporting parameters. The system is
tightly integrated, making it easy to use for experts and non-experts alike.
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
1- 3
Page 30

Product Description
Server Manager. The Server Manager is the process that makes the results of the
Analysis Servers and other real-time application servers available to Master
Clients. The Server Manager starts automatically when you start the transport
monitor. Only one Server Manager can run on a test system.
The Server Manager process interacts with the following entities:
H The Analysis Server sends analysis results (called traps)totheServer
Manager.
H The Stream Player, Stream Recorder, and optional OpenMux (MTS300,
Option OM) servers send state traps to the Server Manager. Unlike the
Analysis Server traps, the traps sent by these servers is limited to
H The Master Client displays the data collected by the Server Manager.
Analysis Servers. The Analysis Server is the process that actually analyzes
transport stream inputs. Each Analysis Server process consists of one MPEG
Analysis Server and one TMCC Analysis Server . Each MTS300 system can
support up to two Analysis Server processes of each type simultaneously.
The Analysis Server processes interact with the following entities:
H The Server Manager collects the Analysis Server results (called traps).
H The Expert Client displays the results of the MPEG Analysis Server directly.
Likewise, the TMCC Expert Client displays the results of the TMCC
Analysis Server .
H The Configuration Client sets the monitoring and analysis parameters for
each MPEG Analysis Server process operating on the inputs to the MTS300
system. Likewise, the TMCC Configuration Client sets the monitoring and
analysis parameters for each TMCC Analysis Server process.
1- 4
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
Page 31

Product Description
Master Client. The Master Client application provides an intuitive interface for
controlling and monitoring the status of the I/O ports on the MTS300 system.
You can run only one Master Client on each MTS300 system. In a network
environment, if a remote MTS300 system has a Master Client open, you must
shut down the remote Master Client before you can connect your local Master
Client to the Server Manager running on the system.
NOTE. Each MTS300 system is limited to operating two Analysis Server
processes of each type at a time, and can run only one Stream Player, one Stream
Recorder, and one OpenMux application at a time. In addition, the MTS300
system is limited to an aggregate data rate of 140 Mbs between all operating
applications.
From the Master Client, you can perform the following tasks:
H Monitor and analyze MPEG transport streams in real time using the Expert
Client and Configuration client applications.
H Monitor and analyze single- and multi-program TMCC transport streams in
real time using the TMCC Expert Client and TMCC Configuration Client
applications.
H Record and playback MPEG and TMCC transport streams using the Stream
Recorder and Stream Player applications.
H Generate multiplexed transport streams in real time using the OpenMux
application (MTS300, Option OM).
The Master Client uses three areas to display different type of information:
H The I/O Port Manager panel displays icons representing real-time application
servers and the input and output ports configured on your test system.
H The Services panel displays icons for the services (also called programs)
encoded in the transport stream you are monitoring.
H The Details panel displays icons indicating the type, status, and severity of
errors on a transport stream or service.
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
1- 5
Page 32

Product Description
Expert Client. The Expert Client application allows you to analyze a single
MPEG transport stream in greater detail. You will use the Expert Client as your
primary tool to help troubleshoot errors in your digital transmission system.
The Expert Client characteristics are shown in the following list:
H Graphical displays that show the structure (hierarchy) of the input transport
stream and display characteristics of each component of the input stream
(for example: PID and type allocation, section rate analyses, and timing
analyses).
H Report views that indicate the types of errors recorded by the Analysis
Server and the characteristics of the input stream.
H Error views that show specific errors recorded for the various components
of the transport stream; for instance, PMT section rate errors and ETR290
errors.
The Expert Client can display the results of only one MPEG Analysis Server
(input) at a time.
Configuration Client. The Configuration Client allows you to perform the
following tasks:
H Specify to which standard you are testing: MPEG-2, DVB, ATSC, or ISDB.
H Set, remove, or modify the probes that test transport streams for valid syntax
and semantics and rates.
H Specify the way in which errors are reported in both the Expert and Master
Clients. You can configure each probe to report an error as Critical, Major,
Minor, Warning, or as information only.
H Specify the types of transport stream events that are recorded using the Data
Logging function. You can also set the maximum file size and time period of
each log file.
H Stop and restart an MPEG Analysis Server running on a MTS300 system.
H Set passwords on specific inputs that prevent others from changing the
Analysis Server configuration for that input.
H Set parameters for capturing part of an input transport stream.
1- 6
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
Page 33

Product Description
Stream Recorder Client. The Stream Recorder application allows you to record a
transport stream onto the hard drive of the MTS300 system using a VTR-like
interface. You can specify the stream format, duration, file name, and location of
the recorded file.
The Stream Recorder is governed by the following MTS300 system limits:
H Only one Stream Recorder can be launched at a time on each MTS300
system.
H The Stream Recorder can only record transport stream files with data rates
between 1 Mbs and 140 Mbs onto the hard drive of the MTS300 system on
which the application was launched. You cannot record remote transport
stream files or use a remote Stream Recorder to record a local transport
stream file.
NOTE. It is recommended that you store transport stream files on the SCSI hard
drives (E: drive) of the MTS300 system. The response time of the C: drive on the
MTS300 system is limited and may affect the performance of the Stream
Recorder and Stream Player applications when you try to capture or play back
streams with bitrates greater than 30 Mbs.
H If the SCSI hard drives (E:) are 90% or more full, it is recommended that
you use a defrag utility to defragment the SCSI drives. You can use any
defrag utility that is compatible with the Microsoft Windows NT 4.0
operating system.
H The MTS300 system is limited to an aggregate data rate of 140 Mbs between
all operating applications. You may have to shut down other MTS300
applications if you need to record a transport stream with high data rates.
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
1- 7
Page 34

Product Description
Stream Player Client. The Stream Player application allows you to play back
transport streams saved on the hard disk of the MTS300 system using a
VTR-like interface. You can specify which portion of the transport stream to play
back, the rate of the transport stream (you can also apply an external clock to set
the rate), the format (ASI or M2S) of the transport stream, and the playback
mode (one time or loop).
The Stream Player is governed by the following MTS300 system limits:
H Only one Stream Player can be launched at a time on each MTS300 system.
H The Stream Player can only play back transport stream files with data rates
between 1 Mbs and 140 Mbs stored on the hard drive of the MTS300 system
on which the application was launched. You cannot play back remote
transport stream files or use a remote Stream Player to play back a local
transport stream file.
NOTE. It is recommended that you store transport stream files on the SCSI hard
drives (E: drive) of the MTS300 system. The response time of the C: drive on the
MTS300 system is limited and may affect the performance of the Stream
Recorder and Stream Player applications when you try to capture or play back
streams with bitrates greater than 30 Mbs.
H If the SCSI hard drives (E:) are 90% or more full, it is recommended that
you use a defrag utility to defragment the SCSI drives. You can use any
defrag utility that is compatible with the Microsoft Windows NT 4.0
operating system.
H The MTS300 system is limited to an aggregate data rate of 140 Mbs between
all operating applications. You may have to shut down other MTS300
applications if you need to play back a transport stream with high data rates.
1- 8
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
Page 35

Product Description
TMCC Expert Client. The TMCC (Transmission and Multiplexing Configuration
Control) Expert Client application allows you analyze the TMCC data of an
ISDB-S/ARIB-compliant transport stream input in real time. You can also
analyze an ISDB-S/ARIB-compliant transport stream file stored on your local
disk.
The TMCC Expert client has the following characteristics:
H Indicates the presence of sync bytes (0x47 for TMCC basic streams and W1,
W2, or W3 sync bytes for TMCC data streams)
H Displays the syntax of TMCC data
H Displays Slot, TSID, TS Name, and Modulation mode information
H Displays information, warning, and error messages
H Indicates the presence of TMCC alarm and update flags in the transport
stream
H Displays the overall stream rate
The TMCC Expert Client displays the results of only one TMCC Analysis
Server (input) at a time. You can connect more than one TMCC Expert Client to
the same TMCC Analysis Server input from your own instrument, or you can
connect to an Analysis Server from a remote MTS300 system.
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
1- 9
Page 36

Product Description
TMCC Configuration Client. The TMC C (Transmission and Multiplexing
Configuration Control) Configuration Client is used to configure the analyses
performed by the TMCC Analysis Server. The results of the analyses are
displayed in the TMCC Expert Client.
NOTE. Only one TMCC Configuration Client at a time can set parameters on a
TMCC Analysis Server. If a TMCC Configuration Client is already connected to
a TMCC Analysis Server, you can view the current settings, but you cannot
change them.
The settings in the TMCC Configuration Client only configure the measurements
made by the TMCC Analysis Server, which are displayed in the TMCC Expert
Client application. The TMCC Configuration Client settings do not affect the
configuration settings in the Configuration Client, which is used to configure the
measurements made by the MPEG Analysis Server.
The TMCC Configuration Client has the following characteristics:
SNMP Capabilities
H Uses multiple configuration panels to group related configuration functions.
H Uses a hierarchic navigation panel to select one of the multiple configuration
panels.
H Configures the TMCC Analysis Servers to operate in either TMCC basic or
TMCC data stream modes
H Enables you to specify a transport stream ID to analyze using the MPEG-2
Analysis Server (only in the TMCC data stream mode)
The MTS300 system includes SNMP management information bases (MIB)
installed at the following directory location: C:\Mib\. The Tektronix MIB is a
textual description of the Analysis Server objects (functions and parameters) that
can be monitored and controlled via SNMP. Refer to the user manual or the
online help for more information about the networking requirements of the
MTS300 system.
The MIB files are used by the real-time analysis applications and the Stream
Player, Stream Recorder, and OpenMux (MTS300, Option OM only)
applications.
The MIB file pairs for each application, for example, the RTAv1.mib and
RTAv2.mib files, are used for SNMPv1 and SNMPv2 systems respectively.
1- 10
The operations in SNMP are limited to retrieving the value of management
information, modifying the value of management information, and reporting an
event.
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
Page 37

Characteristic Tables
This section lists the electrical, environmental, and physical specifications of the
MTS300 system. All specifications are guaranteed unless labeled typical. Typical
specifications are provided for your convenience and are not guaranteed.
Electrical characteristics apply to test systems operating within the environmental conditions specified in Table 1--10.
To verify performance of the test system, use the procedures in the performance
verification section of the MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual,an
optional accessory. Contact your Tekronix representative for ordering information.
Monitoring Characteristics
MPEG Characteristics:
H Supports MPEG--2, DVB, and ATSC protocols.
Monitors transport and multiplex errors.
H Monitors PSI, SI, and PSIP table syntax and consistency errors.
Monitors transport signal for sync loss.
H Generates MPEG transport streams (including ATSC and DVB--SI).
Data Rate Characteristics:
H Up to 140 Mbps with one input or 240 Mbps total using 2 to 4 inputs.
For example, Port 1 can run at 100 Mbps while port 2 is running at
140 Mbps for a total of 240 Mbps.
Number of Inputs:
H Standard Inputs: Two ASI/M2S input/output pairs
H Optional inputs: Two SPI (LVDS parallel), two SMPTE310M (SSI), or two
DHEI (GI-Digicypher) input/output pairs.
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
1- 11
Page 38

Characteristic Tables
Interface Platform Characteristics
Table 1- 1: Platform characteristics
Characteristic Description Supplemental information
Operating system Windows NT 4.0 (Service pack 6)
Disk space System: 10 GB
MPEG Storage: 27 GB
COM Port RS-232
Ethernet 10/100-base T; RJ45
Mouse Mini DIN
Keyboard Mini DIN
SVGA 15-pin, High density, Sub-D
RAM 256MB
CD-ROM drive 8x
Display LCD, 800 x 600
Character input Touch screen and keyboard
Printer Port IEEE P1284
I/O Port Electrical Characteristics
Table 1- 2: ASI
Characteristic Description Supplemental information
Input Port (ASI/M2S)
Connector BNC
Bit Rate 270 Mbps ±100 ppm
Transport Stream Data rate Maximum: 140 Mbps
Minimum: 1 Mbps
Signal Amplitude Maximum: 800 mV
Minimum:: 200 mV
Termination 75 Ω nominal
p-p
p-p
Return Loss 17 dBm minimum from 27 MHz to 270 MHz
Output Port (ASI/M2S)
Connector BNC
Bit Rate 270 Mbps ±100 ppm
1- 12
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
Page 39

Table 1- 2: ASI (Cont.)
Transport Stream Data Rate Maximum: 140 Mbps
Minimum: 1 Mbps
Characteristic Tables
Supplemental informationDescriptionCharacteristic
Signal Amplitude Maximum: 880 mV
Minimum: 500 mV
Termination 75 Ω
Format Can be configured as ASI Burst, ASI Packet,
or M2S
Rise and Fall times 1.2 ns maximum, typical 20% to 80%
External Clock Input Port Clocks the stream player output byte rate
Voltage Levels TTL
Low: <0.8 V. typical
High: >2.0 V, typical
Termination 50 Ω resistive
nominal
Frequency Range 125 kHz to 17.5 MHz
External Trigger Input Port Initiates a capture of a transport stream input
Voltage Levels TTL
Low: <0.8 V
High: >2.0 V
Termination 50 Ω resistive
nominal
p-p,
p-p,
typical
typical
Table 1- 3: SPI-LVDS parallel (Option MTS3FLV)
Characteristic Description Supplemental information
Input Port See Table 1--4 on page 1--15 for pin descrip-
tions. See Figure 1--2 on page 1--15 for the
timing diagram.
Connector 25-pin sub D-type
Data Rate Maximum: 140 Mbps
Minimum: 1 Mbps
Signal Amplitude LVDS
Termination 100 Ω resistive
nominal, line-to-line
Timing reference Rising edge of clock
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
1- 13
Page 40

Characteristic Tables
Table 1- 3: SPI-LVDS parallel (Option MTS3FLV) (Cont.)
Supplemental informationDescriptionCharacteristic
Clock-to-Data Timing Data must be stable 5 ns of rising clock
edge
Output Port See Table 1--4 on page 1--15 for pin descrip-
tions. See Figure 1--2 on page 1--15 for the
timing diagram.
Connector 25-pin sub D-type
Data Rate Maximum: 140 Mbps
Minimum: 1 Mbps
Signal Amplitude (LVDS) Maximum: 454 mV
Minimum: 247 mV
,typical
p-p
p-p,
typical
Termination 100 Ω resistive
nominal, line-to-line
Signal Common-Mode Range
1.125 V to 1.375 V, typical
(LVDS)
External Clock Input Port Clocks the stream player output byte rate
Voltage Levels TTL
Low: <0.8 V
High: >2.0 V
Termination 50 Ω resistive
nominal
Frequency Range 125 KHz to 17.5 MHz
External Trigger Input Port Initiates a capture of a transport stream input
Voltage Levels TTL
Low: <0.8 V
High: >2.0 V
Termination 50 Ω resistive
nominal
1- 14
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
Page 41

Table 1- 4: LVDS parallel data pin connections
1
5
1
6
5
6
2
0
2
1
1
1
1
2
LVDS/ECL/RS422
parallel port
1
2
3
4
6
7
8
9
10
12
13
Asserted Low differential signal.
Pin Function Pin Function
1 DCLK 14 DCLK
2 Ground 15 Ground
14
3 DATA 7 16 DATA 7
4 DATA 6 17 DATA 6
16
17
5 DATA 5 18 DATA 5
18
6 DATA 4 19 DATA 4
19
7 DATA 3 20 DATA 3
8 DATA 2 21 DATA 2
21
9 DATA 1 22 DATA 1
22
23
10 DATA 0 23 DATA 0
24
11 DVALID 24 DVALID
25
12 PSYNC 25 PSYNC
13 Shield
Characteristic Tables
Active edge
DCLK
PSYNC
Data 0.....7
DVALID
Stuffing bytes
Figure 1- 2: Parallel data timing, 188-byte packets
Byte 1Byte 188Byte 187
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
1- 15
Page 42

Characteristic Tables
Table 1- 5: SSI (Option SS)
Characteristic Description Supplemental information
SSI input (SMPTE310M)
Connector BNC, Female
Input bit rate 19,392,658.5 bps 1000 bps
(typical)
38,785,316.9 bps 1000 bps
(typical)
Synchronization 0x47 Synchronization will occur when the
sync_byte is 0x47
Data format Compliant with SMPTE310M
Packet length 188 byte
Signal amplitude 880 mV
720 mV
Signal DC offset 0.5 VDC, maximum
Termination 75 Ω
Return loss –17 dB, 100 kHz to 77.6 MHz
SSI output (SMPTE310M)
Connector BNC, Female
Output bit rate 19,392,658.5 bps
(nominal) or
, maximum
p-p
, minimum
p-p
Same as the input when the output is a loop
through of the input
38,785,316.9 bps
(nominal)
Data format Compliant to SMPTE310M
Signal amplitude 880 mV
720 mV
maximum
p-p
minimum
p-p
Signal DC offset 0.5 VDC, maximum
Signal rise and fall times 0.4 ns minimum
5.0 ns maximum
Signal overshoot 10% of m aximum signal amplitude
Output impedance 75 Ω
Return loss –17 dB, 100 kHz to 77.6 MHz
Rise and fall times shall not diff er by more
than 1.6 ns, measured between 20% and
80%
1- 16
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
Page 43

Characteristic Tables
Table 1- 5: SSI (Option SS) (Cont.)
Characteristic Supplemental informationDescription
External Clock Input Port Clocks the stream player output bit rate
Voltage Levels TTL
Low: <0.8 V
High: >2.0 V
Termination 50 Ω resistive
nominal
Frequencies 19.393 MHz
38.785 MHz
External Trigger Input Port Initiates a capture of a transport stream input
Voltage Levels TTL
Low: <0.8 V
High: >2.0 V
Termination 50 Ω resistive
nominal
Table 1- 6: DHEI-Digicipher II
Characteristic Description Supplemental information
Expansion Input Port
Connector 26-pin D, HD-22 Series See Table 1--7 on page 1--19 for the pin
descriptions
Data Rate Maximum: 40 Mbps
Minimum: 1 Mbps
Signal Amplitude ECL
Termination 120 Ω resistive
nominal, line-to-line
Timing reference Falling Edge of clock
Clock-to-Data Timing Data must be stable 5 ns of falling clock
edge
Output Port See Table 1--8 on page 1--20 for the pin
descriptions
Connector 26-pin D, HD-22 Series
Data Rate Maximum: 40 Mbps
Minimum: 1 Mbps
Signal Amplitude ECL
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
1- 17
Page 44

Characteristic Tables
Table 1- 6: DHEI-Digicipher II (Cont.)
Supplemental informationDescriptionCharacteristic
Termination 120 Ω resistive
nominal, line-to-line
External Clock Input Port Clocks the stream player output bit rate
Voltage Levels TTL
Low: <0.8 V
High: >2.0 V
Termination 50 Ω resistive
nominal
Frequency range 1 MHz to 40 MHz
External Trigger Input Port Initiates a capture of a transport stream being
input to the real-time analyzer
Voltage Levels TTL
Low: <0.8 V
High: >2.0 V
Termination 50 Ω resistive
nominal
1- 18
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
Page 45

Table 1- 7: DHEI Expansion In pin connections
1
0
2
6
9
DHEI 26- pin connector Pin Function Description
1 PROTOGND Protective or shield ground
2 SENSEAIR Enable sense A input return
1
9
18
3 PSYNCAI-- Packet sync A input (--)
19
4 PDATAI-- Packet data A input (--)
5 PCLKAI+ Packet clock A input (+)
6 PCLKAI-- Packet clock A input (--)
7 REFCLKAI+ Ref_clock A input (+)
8 REFCLKAI-- Ref_clock A input (--)
9 SIGND Signal or circuit ground reference
10 RSVD DHEI reserved
11 SENSEAIL Enable sense A loop input
12 PSYNCAI+ Packet sync A input (+)
13 PDATAI+ Packet data A input (+)
14 RSVD DHEI reserved
15 PDATBO-- Packet data B output (--)
16 PSYNCBO-- Packet sync B output (--)
17 SENSEBOR Enable sense B output return
18 RSVD DHEI reserved
19 REFCLKBO+ Ref_clock B output (+)
20 REFCLKBO-- Ref_clock B output (--)
21 PCLKBO+ Packet clock B output (+)
22 PCLKBO-- Packet clock B output (--)
23 PDATBO+ Packet data B output (+)
24 PSYNCBO+ Packet sync B output (+)
25 SENSEBOL Enable sense B loop output
26 RSVD DHEI reserved
Characteristic Tables
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
1- 19
Page 46

Characteristic Tables
1
0
1
1
9
2
6
Table 1- 8: DHEI Expansion Out pin connections
DHEI 26- pin connector Pin Function Description
10
1 PROTOGND Protective or shield ground
2 SENSEAOR Enable sense A output return
3 PSYNCAO-- Packet sync A output (--)
4 PDATAO-- Packet data A output (--)
5 PCLKAO+ Packet clock A output (+)
6 PCLKAO-- Packet clock A output (--)
7 REFCLKAO+ Ref_clock A output (+)
8 REFCLKAO-- Ref_clock A output (--)
9 SIGND Signal or circuit ground reference
26
9
10 RSVD DHEI reserved
11 SENSEAOL Enable sense A loop output
18
12 PSYNCAO+ Packet sync A output (+)
13 PDATAO+ Packet data A output (+)
14 RSVD DHEI reserved
15 PDATBI-- Packet data B input (--)
16 PSYNCBI-- Packet sync B input (--)
17 SENSEBIR Enable sense B input return
18 RSVD DHEI reserved
19 REFCLKBI+ Ref_clock B input (+)
20 REFCLKBI-- Ref_clock B input (--)
21 PCLKBI+ Packet clock B input (+)
22 PCLKBI-- Packet clock B input (--)
23 PDATBI+ Packet data B input (+)
24 PSYNCBI+ Packet sync B input (+)
25 SENSEBIL Enable sense B loop input
26 RSVD DHEI reserved
1- 20
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
Page 47

Characteristic Tables
Power Characteristics
Table 1- 9: AC power source characteristics
Characteristic Description
Source Voltage 100 VAC to 240 VAC
47 Hz to 63 Hz, continuous range CAT II
Maximum Power Consumption 170 Watts, typical
Environmental Characteristics
Table 1- 10: Environmental characteristics
Characteristic Description
Cooling Airflow Intake is from the front and sides of the instrument. Exhaust is to t he bott om and rear of
the instrument.
Required Clearance 2 in (50 mm) air space adjacent to the bottom of the instrument is required.
Use Rating Rated for indoor use only.
Atmospherics
Temperature:
Operating +5° Cto+40° C, 30° C/hr max gradient, noncondensing (derated 1° C per 1,000 ft
above 5,000 ft altitude)
Nonoperating -- 2 0 ° Cto60° C, 30° C/hr max gradient (without disk m edia installed in disk drives)
Humidity
Operating 20% to 80% relative humidity, noncondensing. Max wet bulb temperature: 29° C
(derates relative humidity to ~22% at 50° C)
Nonoperating 8% to 80% relative humidity, noncondensing. Max wet bulb temperature: 40° C
(derates relative humidity to ~55% at 50° C)
Altitude
Operating Up to 10,000 ft (3,040 m), (derated 1°C per 1,000 ft above 5,000 ft altitude)
Nonoperating Up to 40,000 ft (12,190 m)
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
1- 21
Page 48

Characteristic Tables
Mechanical (Physical) Characteristics
Table 1- 11: Mechanical characteristics
Characteristic Description
Classification Transportable platform intended for either rackmount or bench applications
Overall Dimensions
Height 8.9 i n (w/o feet) (22.6 cm)
Width 17 in (43.2 cm)
Depth 22 in (56 cm)
Weight 38 lb (17.3 kg)
Rack Space 5 rack units, standard length
Certifications and Compliances
Table 1- 12: Certifications and compliances
Category Standard
EC Declaration of Conformity-EMC Meets the intent of Directive 89/336/EEC for El ectromagnetic Compatibility.
Compliances was demonstrated using EN 61326: 1997 EMC Product Family Standard for
Electrical Equipment for Measurement, Control, and Laboratory use.
Emissions
EN 61326 Class A Radiated and Conducted Emissions
IEC 61000-3-2 Conducted Power Line Harmonic Current
Immunity
IEC 61000-4-2 Electrostatic Discharge Immunity
IEC 61000-4-3 Radiated RF Electromagnetic Field Immunit y
IEC 61000-4-4 Electrical Fast Transient/Burst Immunity
IEC 61000-4-5 Power Line Surge Immunity
IEC 61000-4-6 Conducted RF Immunity
IEC 61000-4-11 Voltage Dips and Short Interruptions Immunity
Australia/New Zealand declaration of
conformity
FCC Compliance Emissions comply with FCC Code of Federal Regulations 47, Part 15, Subpart B, Class A
Complies with EMC Framework and demonstrated per Emission standard:
AS/NZS 2064 Industrial, Scientific, and Medical Equipment.
Limits
1
:
1
:
2
2
1
Compliance demonstrated using high quality, shielded interface cables.
2
Performance Criterion: Product continues to operate properly and display remains readable.
1- 22
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
Page 49

Characteristic Tables
Table 1- 13: Environmental limits and use classification for safety certification compliance
Category Standards or description
Safety Certification Compliance
Temperature, operating +5_ Cto+40_ C
Altitude (maximum operating) 2000 meters
Equipment Type Test and measuring
Safety Class Class 1 (as defined in IEC 61010-1, Annex H) -- grounded product
Installation (Overvoltage)
Category
Pollution Degree Pollution Degree 2 (as defined in IEC 61010-1). Note: Rated for indoor use only.
Supply Voltage Range 100 VAC to 240 VAC, 50/60 Hz, single phase
Fuse Rating Mains fuse is 10A, 250V, Fast; Not operator replaceable. Refer servicing to qualified service
Current Rating 6.0 Amps maximum
Relative Humidity
(maximum operating)
Pollution Degree Definition A measure of the contaminates that could occur in the environment around and within a
European Union Compliance
Overvoltage Category II (as defined in IEC 61010-1, Annex J)
personnel.
80 % for temperatures up to 31° C, decreasing linearly to 50 % at 40° C
product. Typically the internal environment inside a product is considered to be the same as the
external environment. Products should be used only in the environment for which they are
rated.
Pollution Degree 1 No pollution or only dry, nonconductive pollution occurs. Products
in this category are generally encapsulated, hermetically sealed, or
located in clean rooms.
Pollution Degree 2
Pollution Degree 3
Compliance was demonstrated to the fol lowing specification as listed in the Official Journal of
the European Union:
Normally only dry, nonconductive pollution occurs. Occasional ly a
temporary conductivity that is caused by condensation must be
expected. This location is a typical office/home environment.
Temporary condensation occurs only when the product is out of
service.
Conductive pollution, or dry, nonconductive pollution that becomes
conductive due to condensation. These are sheltered locations
where neither temperature nor humidity is controlled. The area is
protected from direct sunshine, rain, or direct wind.
Low Voltage Directive 73/23/EEC, amended by 93/68/EEC
EN 61010-1/A2 Safety Requirements for Electrical Equipment for Measurement
Listing by a U.S. Nationally
Recognized Testing Laboratory
Canadian Certification CAN/CSA C22.2 No.
ANSI/ISA S82.01 Safety Standard for Electrical and Electronic Test, Measuring,
1010.1
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
Control and Laboratory Use.
Controlling, and Related Equipment., 1994.
Safety Requirements for Electrical Equipment for Measurement,
Control, and Laboratory Use.
1- 23
Page 50

Characteristic Tables
Table 1- 13: Environmental limits and use classification for safety certification compliance (Cont.)
Category Standards or description
Additional Compliance UL3111-1 Standard for Electrical Measuring and Test Equipment.
IEC61010-1/A2 Safety Requirements for Electrical Equipment for Measurement,
Control, and Laboratory Use.
Installation (Overvoltage) Category
Laser Classification This product contains a CD ROM drive which utilizes a Class 1 laser and complies with
Terminals on this product may have different installation (overvoltage) category designations.
The installation categories are:
CAT III Distribution-level mains (usually permanently connected). Equipment at this level is
typically in a fixed industrial location.
CAT II Local-level mains (wall sockets). Equipment at this level includes appliances, portable
tools, and similar products. Equipment is usually cord-connected.
CAT I Secondary (signal level) or battery operated circuits of electronic equipment.
EN60825--1:94, as well as with the U.S. FDA regulations. The drive is marked with the laser’s
classification and the date of manufacture, as wel l as the followi ng inf ormation:
Complies with the DHHS rules 21 CFR Chapter 1, Subchapter J applicable at the date of
manufacture.
1- 24
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
Page 51

Installation
Hardware Installation
This Operating Information section contains installation and operating informa-
tion related to the servicing of the instrument.
This subsection provides instructions for installing the MTS300 system and
making the necessary electrical connections. Also provided are repackaging
instructions, including part numbers for replacement packaging.
The MTS300 system can be operated from a bench or installed in a rack using
the optional rack-mount kit. The rack-mount kit includes installation instructions
for the rackmounting hardware.
CAUTION. For proper cooling, provide at least two inches (5.1 cm) of clearance
at the rear and to the sides of the test system, and ensure that the air temperature
at all air intake vents (inside of the rack) does not exceed 40
Use the two collapsible front feet on the bottom of the MTS300 system to
change the height of the front panel.
° C.
Test System
Interconnections
The location of the connectors on a typical test system rear panel is shown in
Figure 2--1. Table 2--1 describes the transport stream, network, and peripheral
device connectors. Refer to Connecting the MTS300 System I/O Ports on
page 2--7 for illustrations of the various rear-panel connector configurations.
Table 2- 1: Rear-panel connectors
Connector Description
Transport stream input/output
ASI/M2S Input/Output
SPI (LVDS) Input/Output
DHEI (GI Digicypher)
Input/Output
SSI Input/Output
Monitor 15-pin female high density-D-sub connector for SVGA
Each format includes two input/output pairs
monitor
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
2- 1
Page 52

Installation
Power
Table 2- 1: Rear-panel connectors (Cont.)
Connector Description
Keyboard Mini-DIN connectors for PS2 compatible keyboard (on rear
and side panels)
Mouse Mini-DIN connectors for PS2 compatible mouse (on rear and
side panels)
Printer 25-pin sub-D connector for parallel communication
LAN (Ethernet) 10 Base-T/100 Base-T, RJ45 connector for Ethernet
communications
RS-232/422 9-pin D-sub type connector for serial communication
SCSI Standard, PC compatible Ultra-Wide SCSI port, 68 Pins
SPI (LVDS) I/O
ASI I/O
(Option LV or MTS3FLV)
Ethernet
Parallel Port
RS-232
COM Port 1
Figure 2- 1: Typical MTS300 test system rear panel connectors
2- 2
SCSI
MouseKeyboardSVGA
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
Page 53

Installation
The following procedure identifies the electrical connections.
1. Plug in the keyboard and mouse to the proper rear panel connectors. Refer to
Figure 2--1. Figure 2--2 shows alternative connectors for a mouse and
keyboard. The optional connections are located on the instrument side panel.
Earphones
USB
Keyboard
Mouse
Figure 2- 2: Keyboard and mouse alternative connections
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
2- 3
Page 54

Installation
2. Install the Software Key on the rear panel Parallel port. MTS300 MPEG Test
System software applications will not run without the Software Key
installed; do not remove or misplace the Software Key.
To use the Parallel port with the Software Key installed, attach any parallel
port cables (such as a printer) directly to the Software Key. The Software
Key does not interfere with parallel communications.
NOTE. To run MTS300 MPEG Test System applications, the Software Key must
be on the computer Parallel port. If you return the test system to a Tektronix
Service Center for upgrade or repair, include the Software Key.
Supplying Power
Figure 2- 3: Software Key
The MTS300 MPEG Test System platform is designed to operate from a
single-phase power source having one of its current carrying conductors at or
near earth ground (the neutral conductor). Power sources that have both current
carrying conductors live with respect to ground, such as phase-to-phase or
multiphase systems, are not recommended. A protective ground connection, by
way of the grounding conductor in the power cord, is essential for safe operation.
The electrical operating requirements are listed in Table 2--2.
2- 4
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
Page 55

Installation
Table 2- 2: Electrical operating requirements
Requirement Specification
Source Voltage 100 VAC to 240 VAC
47 Hz to 63 Hz
Fuse Rating 10 A Fast / 250 V
Maximum Power Consumption 170 Watts typical
Inrush Surge Current 36 Amps maximum
Power Factor Correction Yes
After you have installed the MTS300 system and completed making the signal,
network, and peripheral connections, plug the power cord into the mains. See
Figure 2--1 for location of power connector.
CAUTION. Do not supply power to the instrument until all connections have been
made.
WARNING. The test system is designed for connection to an earth-grounded AC
outlet. To avoid risk of electrical shock or equipment damage, do not disable the
grounding plug.
Mains Voltage Range. You can power the test system computer and monitor from
mains that supply between 100 VAC and 240 VAC without setting a voltage
selection switch.
Mains Frequency. The test system computer and monitor operate on either 50 Hz
or 60 Hz line frequencies.
CAUTION. To prevent damage, protect the system computer from power fluctuations and temporary interruptions with a regulating noninterruptible power
supply. This device protects the hardware from damage caused by power surges
and voltage spikes. In addition, it allows the system to operate temporarily
during a power failure.
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
2- 5
Page 56

Installation
Power Cord Options. Unless a specific power cord option is ordered, the system
computer and monitor come standard with a power cord for North American
60 Hz, 115 VAC supplies. Table 2--3 lists the power cord options.
Table 2- 3: Power cord identification
Plug configuration Normal usage Option number
North America
125 V/15A Plug
NEMA 5-15P
Europe
230 V
United Kingdom
230 V
Australia
230 V
Switzerland
230 V
Standard
A1
A2
A3
A5
2- 6
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
Page 57

Connecting MTS300 System I/O Ports
Figure 2--4 through Figure 2--11 show the available input and output (I/O)
connector configurations on the MTS300 rear panel. For I/O port specifications,
refer to the Specifications section beginning on page 3-1. Use the I/O ports that
best suit your operating environment and signal sources. A description of each
connector type follows.
Installation
Input
Trigger Input
Clock Input
Output to Other
Equipment
You must provide input to the MTS300 system to monitor an MPEG-2, DVB, or
ATSC bit stream. The MTS300 system I/O ports can be ASI serial, SPI (LVDS),
DHEI (GI-Digicypher), or SSI (SMPTE310M). To change the configuration,
refer to Configuration Client Reference in the MTS300 MPEG Test System
Real-Time Analysis User Manual.
The trigger input accepts a TTL level (0 V to +5 V) signal you can use to control
capture of the MTS300 system input stream to the system disks. You can
configure the system to start/stop data capture on either the rising edge (low to
high transition) or the falling edge (high to low transition) of the trigger signal.
Refer to the MTS300 MPEG Test System Real-Time Analysis User Manual for
further information on capturing transport stream inputs.
Each output port has a corresponding clock input which can be used to clock the
transport stream output when using Stream Player. The clock rate is at the byte
rate of the transport stream for the ASI/M2S and SPI (LVDS) formats. The clock
rate is at the bit rate of the transport stream for the SMPTE310M (SSI) and
DHEI (GI Digicypher) formats.
Applications generating an output will do so on the I/O port to which the
application has been assigned. Applications requiring an input have an output
activation option that will loop-through the input signal to the output connector
on the assigned I/O port.
When an output port is used to generate signals using the Stream Player or
OpenMux applications, the corresponding input port cannot be used.
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
2- 7
Page 58

Installation
ASI/M2S I/O
Figure 2- 4: Rear-panel configuration with one ASI/M2S (Option AS) interface installed
ASI/M2S I/O ASI/M2S I/O
Figure 2- 5: Rear-panel configuration with two ASI/M2S (Option AS) interfaces installed
2- 8
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
Page 59

ASI/M2S I/O SSI (SMPTE310M) I/O
Installation
Figure 2- 6: Rear-panel configuration with ASI/M2S (Option AS) and SSI (Option SS) interfaces installed
ASI/M2S I/O
DHEI (GI-Digicypher) I/O
Figure 2- 7: Rear-panel configuration with ASI/M2S (Option AS) and DHEI (Option DE) interfaces installed
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
2- 9
Page 60

Installation
ASI I/O SPI (LVDS) I/O
Figure 2- 8: Rear-panel configuration with ASI/M2S (Option AS) and SPI (Option LV) interfaces installed
SSI (SMPTE310M) I/O
Figure 2- 9: Rear-panel configuration with one SSI (Option SS) interface installed
2- 10
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
Page 61

Installation
SSI (SMPTE310M) I/OSSI (SMPTE310M) I/O
Figure 2- 10: Rear-panel configuration with two SSI (Option SS) interfaces installed
SSI (SMPTE310M) I/O
ASI/M2S I/O
Figure 2- 11: Rear-panel configuration with SSI (Option SS) and ASI/M2S (MTS3FAS) interfaces installed
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
2- 11
Page 62

Installation
Networking
This subsection provides the following information:
H Network requirements for the Tektronix MTS300 MPEG Test System
H Network installation procedures for configuring the TCP/IP and SNMP
parameters of your test system
H Network troubleshooting techniques for solving basic networking issues
common to many network installations
Refer to Network Troubleshooting on page 6--14 for information to help you
solve problems with installing the MTS300 system on your network.
Network Requirements
The Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) protocol stack is
pre-loaded on Tektronix MTS300 MPEG Test Systems. The open nature of
TCP/IP allows you to create networks using various protocols and signaling
techniques. This section lists the physical and network requirements for using
test systems over a network.
Physical Requirements. The following list describes the physical requirements for
networking MTS300 systems:
H Ethernet network or subnetwork to the MTS300 system
H 10Base-T / 100Base-T network drop to your local MTS300 system
H Network interface card (NIC) and driver
NOTE. The Intel EtherExpress Pro/100B Adapter NIC and E100BT.sys adapter
driver are pre-loaded on all test systems; this combination of NIC and adapter
driver is the only one supported by the test system.
Network management stations do not have requirements beyond basic connectivity between two points; the network adapter at a network management station
can be of any type that allows it to communicate over a TCP/IP network. The
routers installed in the network convert data to the appropriate format for the
protocols used in your network.
2- 12
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
Page 63

Installation
Minimum Network Requirements. To use the test system over a network, you must
install it in a TCP/IP network. TCP/IP networks have specific addressing and
routing requirements that your network administrator will typically have already
configured. Use this section as a checklist for the TCP/IP parameters that your
network administrator assigns to your test system.
H Unique IP address
H Unique host name
H Subnet mask (if you are installing the test system in a network with multiple
subnets)
H Default gateway IP address (if your environment uses multiple networks or
subnets)
H DNS server IP address(es) (if you use the DNS service to resolve Internet
addresses; some networks use multiple DNS servers)
H WINS server IP address(es) (if your system uses WINS to resolve computer
names to IP addresses; some networks use multiple WINS servers)
Network Installation
NOTE. In order to use test systems over a network, your network administrator
needs to assign your host machine an IP address: you cannot use the test system
with Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP).
This section describes how to set the parameters listed in Minimum Network
Requirements, and how to configure test systems to be managed in an SNMP-
based network management environment. The information in this section will
not replace the value added by networking professionals and describes only basic
network installation procedures.
Setting TCP/IP Parameters. Each network uses specific values for such parameters
as IP addresses and default gateways, so the parameter values used in the
examples for this section are for illustrative purposes only unless otherwise
specified. You can configure test systems as stand-alone instruments which need
only minimal network parameters set, or you can configure them to be installed
into a LAN or WAN (local or wide area network, respectively).
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
2- 13
Page 64

Installation
Display the Microsoft TCP/IP Properties dialog box.
1. Click the Start button on the taskbar, point to Settings and then Control
Panel. (Alternatively, right-click the Network Neighborhood icon and
select Properties from the shortcut menu. Skip to step 3.)
2. Double-click the Network icon.
3. Select the Protocols tab from the Network dialog box as shown in
Figure 2--12.
2- 14
Figure 2- 12: Network dialog box showing TCP/IP Protocol item
4. Highlight TCP/IP Protocol from the Network Protocol selection box, and
then click Properties.
The TCP/IP Properties dialog box is displayed showing the IP Address tab. See
Figure 2--13 on page 2--15.
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
Page 65

Installation
Set IP Address tab parameters.
5. Set the following IP Address tab parameters as shown in Figure 2--13 and
described below:
a. Select the Intel EtherExpress Pro Adapter (it should be the only option
available for MTS300 systems).
b. Select Specify an IP Address.
c. Enter the IP address for your MTS300 system. If not already specified,
obtain the IP address from your network administrator. IP addresses
must be unique.
d. If necessary, enter the subnet mask value and default gateway, both of
which, you obtain from your network administrator.
Figure 2- 13: IP tab parameters
Incorrect values for any one of these parameters can make your MTS300
system behave unpredictably over a network. Refer to IP Parameters
beginning on page 6--15 for more information about these values.
6. Click Apply, and then click the DNS tab.
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
2- 15
Page 66

Installation
Set DNS tab parameters.
7. Set the following DNS values as indicated in Figure 2--14:
NOTE. Do not set DNS parameters unless your network uses the DNS service.
Setting these parameters when your network does not use this service will make
your host machine run very slowly when trying to resolve network addresses.
a. Enter your host machine name provided by your network administrator
into the Host name text box. Host/domain name pairs must be unique.
b. Enter the name of the domain of which your MTS300 system is a
member in the Domain text box as directed by your network administrator.
c. Click Add in the DNS Service Search Order group, and then enter the IP
address of the Domain Name System server in the TCP/IP DNS Server
dialog box.
d. Click Add to accept your changes and dismiss the TCP/IP DNS Server
dialog box.
2- 16
Figure 2- 14: DNS tab parameters
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
Page 67

Installation
It should not be necessary to configure the parameters on the WINS Address
or the Routing tabs.
8. Click OK when you are finished configuring the IP Address and DNS tab
parameters and are certain that all of the values correct.
9. Restart your MTS300 system or network management station for the TCP/IP
changes to take effect.
SNMP Network
Management
SNMP is a communication protocol built on the top of UDP/IP. It implements a
set of commands consisting of operations and variables. Equipment or applications (such as the MTS300 test system MTS300 system) that support SNMP
present a set of variables that you can modify or consult as well as a set of
notifications. All of these parameters are grouped into a Management Information Base (MIB).
MIBs are specifications containing definitions of management information so
that network systems can be remotely monitored, configured, and controlled.
Accessing the MIB files. The Tektronix MIB is a textual description of the
Analysis Server objects (functions and parameters) that can be monitored and
controlled via SNMP. The MIB text files are installed at the following location:
C:\Mib\
The MIB files are used by the real-time analysis applications and the Stream
Player, Stream Recorder, and OpenMux (MTS300, Option OM only)
applications.
The MIB file pairs for each application, for example, the RTAv1.mib and
RTAv2.mib files, are used for SNMPv1 and SNMPv2 systems respectively.
The operations in SNMP are limited to retrieving the value of management
information, modifying the value of management information, and reporting an
event.
Retrieval. The most common type of retrieval operation requires that the
identities are those that exactly match the identity of returned variables. This
retrieval operation is called GET.
For instance, from a DOS prompt window you can run the following command
to check that the Analysis Server is running on the first input:
getone -v2c <machineName> rta0 rtaStartStop.0
Where <machineName> is the network name of the test system for which you are
trying to determine the Analysis Server status.
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
2- 17
Page 68

Installation
Modification. There is one modification operation, which is called SET. The
operand for SET is a list of pairs. Each pair consists of the identity of a variable
and its desired value. Use this operation to configure and control a managed
system.
For instance, from a DOS prompt window you can run the following command
(all on one line) to stop analysis on the first input of a named MTS300 system:
setany -v2c <machineName> rta0 rtaStartStop.0
-i stop
Where <machineName> is the network name of the MTS300 system for which
you are trying to start the Analysis Server.
To restart the Analysis Server, use the same syntax, but change the -i switch
parameter to start.
setany -v2c <machineName> rta0 rtaStartStop.0
-i start
Event Reporting. The SNMP event reporting operation is called TRAP. It
specifies an event and a list of pairs. A pair consists of the identity of a variable
and its value or values. This operation reports the occurrence of events on a
managed system to a list of managers configured to receive events.
2- 18
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
Page 69

Operating Information
This subsection provides basic operating information so that you can perform
service on the instrument. The following information is provided:
H Starting the MTS300 System page 2--20
H Shutting Down the MTS300 System page 2--25
H Application Overviews page 2-- 28
H Front Panel Controls page 2--39
H Tutorial page 2--43
Refer to Installation starting on page 2--1 for information about the external
connectors and I/O ports on the MTS300 system.
Refer to Supplying Power on page 2--4 for instructions on how to power on the
MTS300 system.
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
2- 19
Page 70

Operating Information
Starting the MTS300 System
Perform the following procedure to power on the MTS300 system:
1. Connect the power cord to the rear-panel power connector.
2. Press the On/Stby switch to power on the instrument. Figure 2--15 shows
the switch location.
MPEG Test System
On/Stby switch
Figure 2- 15: On/Stby switch
3. The Windows NT initialization process takes up to two minutes. Under
normal circumstances, no action is required until the Begin Logon message
appears.
4. When the Begin Logon message appears, simultaneously press the
CTRL + ALT + Delete keys to open the Logon Information dialog box.
5. Perform the procedure in Logging On startingonpage2--21.
2- 20
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
Page 71

Operating Information
Logging On
The MTS300 system provides three user name/password combinations you can
use to logon to the instrument. Table 2--4 lists the default user name and
passwords supplied with the MTS300 system.
Table 2- 4: Default user names and passwords
User name Password Description
MTS300 No password Intended for the standard user and for normal instrument
operation. Users logging on as “MTS300” have full access to
files and applications.
Guest No password Intended for users with limited system knowledge. Users
logging on as “Guest” have limited access to files and
applications.
Administrator MPEG2 Intended for the master user responsible for software
upgrades or installations. Users logging on as “Administrator” have full administrative rights to all system files and
applications. You must use this user name and password to
perform any software upgrades or reinstallat ions.
CAUTION. To prevent potential network conflicts, it is strongly recommended that
you do not use the Administrator user name and password for normal instrument
operation. The administrator user logon includes all administrative privileges
and may allow administrative access within the network.
To log on to the test system the first time, use these steps:
1. Enter MTS300 in the User name box.
2. Leave the Password box blank, and press ENTER (these are the default
values set at the factory). Use this user name for most of your work.
Changing the Passwords. After you logon to the MTS300 system using a user
name and password combination, you can change the password for that user
name. Refer to the Windows NT online help for instructions.
Refer to Setting, Resetting, and Disabling Auto Logon on page 2--22 if you want
to enable automatic logon to Windows NT when you power-on the instrument.
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
2- 21
Page 72

Operating Information
Setting, Resetting, and
Disabling Auto Logon
The Auto Logon option allows you to select a user name and password that the
MTS300 system will use to automatically log on to Windows NT when you
power-on the instrument. This section contains two procedures. The first
procedure initializes the Auto Logon option and changes an existing Auto Logon
user name and password. The second procedure disables the Auto Logon option
(requiring the entry of a user name and password each time the instrument is
powered on).
Setting and Resetting Auto Logon. Perform the following procedure to set or reset
the automatic logon option:
1. Boot up the MTS300 system (without a recovery CD in the CD-ROM drive).
2. Select Run from the Windows NT Start menu, and then click Browse in the
Run dialog box.
3. The Auto Logon utility is located in two directory locations:
H D:\Tools\Autologn.exe of the MTS300 MPEG Test System Operating
System Recovery CD
H C:\Mts300\Bin\AutoLogon.exe on the MTS300 system
4. In the Browse dialog box, specify one of the directory paths shown above,
andthenclickOpen.
5. Click OK in the Run dialog box to run the selected Auto Logon utility. The
Auto Logon dialog box will open.
CAUTION. If the MTS300 system is already setup to Auto Logon, entering a new
user name and password will overwrite the existing user name and password
used by the MTS300 system to Auto Logon.
T o prevent potential network conflicts, it is strongly recommended that you do
not use the Administrator user name and password for Auto Logon.
6. Use the Auto Logon dialog box to enter the user name and password that the
MTS300 system will use to automatically logon to Windows NT when the
instrument boots.
7. Click OK to apply the Auto Logon setting. The next time the MTS300
system boots, the new Auto Logon settings will be used.
2- 22
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
Page 73

Operating Information
Disabling Auto Logon. Perform the following procedure to disable Auto Logon
(requiring the entry of a user name and password each time the instrument is
powered on):
1. Boot up the MTS300 system (without a recovery CD in the CD-ROM drive).
2. Select Run from the Windows NT Start menu.
3. Enter regedt32 in the Run dialog box, and then click Open. This opens the
Registry Editor window.
4. In the Registry Editor window, select the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE on
Local Machine panel.
5. In the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE on Local Machine panel, select
Winlogon in the following directory path:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion
6. After you select Winlogon, the right pane of the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE on Local Machine panel displays the contents of the file. Highlight
the line in the right pane that starts DefaultUserName:, and then select
Edit | Delete from the menu.
7. Click Yes in the Warning message box.
8. Highlight the line in the right pane that starts DefaultPassword:,andthen
select Edit | Delete from the menu.
9. Click Yes in the Warning message box.
10. Select Registry | Exit from the menu to close the Registry Editor window.
11. The next time the MTS300 system boots, Auto Logon will be disabled and
the user will be asked for user name and password to logon to Windows NT.
CAUTION. To prevent the loss of data, if you change the default user names and
passwords, secure the new names in a safe place. If you forget your user-defined
user names and passwords and cannot logon to the MTS300 system, you will
have to reinstall the operating system software which will result in the loss of all
data on the hard drives of the MTS300 system.
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
2- 23
Page 74

Operating Information
Starting MTS300 System
Applications
After you have logged on, the Tektronix MPEG Test System program group
window appears as shown below. Double-click the appropriate application icon
to launch the desired application.
NOTE. The example below shows an MTS300 system program group with most of
the available options installed. Depending on which options you ordered with
your MTS300 system, your program group may not contain all of the application
icons shown below.
2- 24
NOTE. You must open the Master Client application to access the Expert Client,
Configuration Client, Stream Recorder, and Stream Player applications.
Refer to Tutorial beginning on page 2--43 for procedures on connecting to a
Server Manager and configuring a workspace.
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
Page 75

Shutting Down the MTS300 System
This section contains information about how to exit MTS300 system applications and how to shutdown the MTS300 system.
Operating Information
Exiting MTS300 System
Applications
Shutting Down the
MTS300 System
To exit an program monitor application, select Exit/Quit from the File menu or
click the close button in the upper-right corner of the application window.
Close
button
There are three methods to shut down the MTS300 system: soft power down,
standard Windows NT power down, and hard power down. For the standard and
hard power-down methods, it is strongly recommended that you exit all MTS300
applications prior to initiating an instrument power down.
Soft Power Down. The MTS300 system is shipped from the factory with a soft
power-down capability enabled. The soft power-down capability allows you to
directly exit Windows NT without closing the MTS300 applications first. The
MTS300 system will automatically close all open applications and put the
instrument into standby mode.
To soft power-down the MTS300 system, perform the following steps:
1. Press and release the On/Stby switch to initiate the soft power-down
process. Some applications will prompt you to save unsaved data before
exiting.
2. After the MTS300 system goes into standby mode, you can restart the
instrument by pressing the On/Stby switch.
3. To completely remove power to the instrument, disconnect the power cord at
the rear panel.
NOTE. If the soft power-down feature does not work properly, you can restore the
Soft Power-Off Driver by performing the procedure located in the MTS 300
MPEG Test System Hardware and Software Installation Technical Reference
manual (Tektronix part number 071-0667-XX) supplied with the MTS300 system.
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
2- 25
Page 76

Operating Information
Standard Windows NT Power Down. To power down the MTS300 system during
normal instrument operations, perform the following standard Windows NT
power down procedure:
1. Exit all open MTS300 applications.
CAUTION. To prevent data loss, exit all open MTS300 applications before
powering down the instrument. Some applications will prompt you to save
unsaved data before exiting.
2. After the MTS300 applications are closed, shut down Windows NT by
selecting Shut Down from the Windows NT Start menu as shown below.
CAUTION. To prevent data loss and possible system problems during subsequent
Windows NT initializations, always exit Windows NT before you power down the
MTS300 system. Wait until the message “It is now safe to turn off your computer” appears before you press the On/Stby switch.
3. Select Shut down the computer? in the resulting Shut Down Windows
dialog box shown below, and then click Yes.
4. After the Shutdown Computer window appears with the message “It is now
safe to turn off your computer,” press the On/Stby switch to put the MTS 300
system into standby mode.
2- 26
5. After the MTS300 system goes into standby mode, you can restart the
instrument by pressing the On/Stby switch.
6. To completely remove power to the instrument, disconnect the power cord at
the rear panel.
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
Page 77

Operating Information
Hard Power Down. You can use the hard power-down capability to immediately
power-down the MTS300 system in an emergency situation such as fire.
CAUTION. To prevent data loss and the corruption or deletion of application and
system files, do not perform this procedure. Use the following procedure only if
all other attempts to shut down the MTS300 system have failed.
Using this hard power down procedure will likely cause file problems. When you
use this method to power down the MTS300 system, the next time the instrument
is powered on, the operating system will use the Scan Disk utility to perform a
check for missing or corrupt files. You may be prompted to reinstall the
operating system or application software.
To hard power-down the MTS300 system, perform the following steps:
1. Press and hold the On/Stby button for about 3 or 4 seconds.
2. After the MTS300 system goes into standby mode, you can restart the
instrument by pressing the On/Stby switch. Read the power-on messages for
information about possible missing or corrupted files.
3. To completely remove power to the instrument, disconnect the power cord at
the rear panel.
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
2- 27
Page 78

Operating Information
Application Overviews
NOTE. If you are not familiar with the Windows NT 4.0 operating system, review
the Windows NT online help.
This section provides a functional overview of the MTS300 MPEG Test System
client modules.
Application Overviews describes the following MTS300 applications:
H The Master Client application monitors transport page 2--29
stream inputs at various levels of detail.
H The Expert Client application analyzes in detail the page 2--30
characteristics of a transport stream input and the
errors occurring on that input.
H The Configuration Client application sets analysis page 2--32
probes on transport stream inputs.
Online Help
H The Stream Player Client application outputs a transport page 2--33
stream using the MTS300 rear-panel outputs.
H The Stream Recorder Client application captures part page 2--34
of a transport stream to the SCSI drives.
H The TMCC Expert Client application analyzes in detail the page 2--36
characteristics of a TMCC transport stream input and the
errors occurring on that input.
H The TMCC Configuration Client application sets analysis page 2--38
probes on TMCC transport stream inputs.
H Front Panel describes the front-panel controls. page 2--39
Each of the MTS300 system applications allow you to access detailed information about the application using online help. You can access the online help using
the following methods:
H For the Master Client, Expert Client, and Configuration Client, select the
appropriate command from the Help menu
H For the Stream Player Client and the Stream Recorder Client, right-click in
the Title bar and select Help Topics from the menu
2- 28
H For the TMCC Expert Client and the TMCC Configuration Client, click on
the Help icon
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
Page 79

Operating Information
Master Client
Selection
Indicator bar
Port Manager
panel
Services panel
The Master client views and elements enable you to monitor the results of the
analyses being performed by Analysis Servers one or two transport stream
inputs. See Figure 2--16.
Address bar
Error gauge
Details panel
Figure 2- 16: The Master client application window
Note the following characteristics of the Master client window in Figure 2--16:
H The Port Manager panel shows the inputs configured for the test system to
which you are connected. In Figure 2--16, an Analysis Server is on I/O#1 is
monitoring a transport stream being generated by the Stream Player on
I/O#2.
H The Address bar shows that the Master client is connected to the Server
Manager running on carnac.
H The Selection Indicator bar shows the currently selected items in the Port
Manager and Services panels.
H The Services panel shows the services encoded on the input selected in the
Multiplex panel.
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
2- 29
Page 80

Operating Information
H The Details panel shows the status, types, and severity of errors occurring on
the currently selected service or multiplex.
H The Error gauge displays the severity of the most recent error for the service
(or multiplex) displayed in the Details panel.
See the tutorial later in this section for an introduction to using the Master client.
Hierarchic
view
Client
area
Expert Client
The Expert client views and elements show the detailed results of analyses being
performed on one transport stream input. See Figure 2--17.
Address bar
Report view
toolbar
Hierarchic panel of
the Report view
Figure 2- 17: The Expert client application window
2- 30
Messages panel of
the Report view
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
Page 81

Operating Information
Note the following characteristics of the Expert Client window in Figure 2--17:
H The Hierarchic view shows the structure of the transport stream you are
monitoring. The hierarchy shown is based on the transport stream elements.
For instance, since the Program Map Table (PMT), and the program
elements the PMT references, are referenced by the Program Allocation
Table (PAT), the PMT icons are shown subordinate to the PAT icon.
H The Address bar shows that the Expert client is connected to the Analysis
Server analyzing the transport stream being input through I/O#1 on novo2.
H The Client area is displays the Program Allocation panel, which is one of the
panel in the Statistics view. The Statistics view panels display statistical
information about the input stream to which the Expert client is connected.
Other views can also be displayed in the Client area. These views are
accessed using shortcut menus displayed when you right-click an icon in the
Hierarchic view.
H The Messages panel of the Report view shows the errors occurring on the
input selected in the Hierarchic panel of the Report view. You can display
more detail about a specific error by double-clicking the line on which the
error is reported.
H The Hierarchic panel of the Report view allows you to select different ways,
or modes, of displaying errors or statistics about the transport stream being
analyzed. The mode of the Report view is determined using the toolbar to
the left. The current mode is Program and FUN TV is selected.
H The Report view toolbar allows you to change the mode of the Report view.
Using this toolbar you can display errors grouped in one of four logical
modes: by program, ETR290 priority, error type, or error severity.
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
2- 31
Page 82

Operating Information
Configuration Client
Navigation
panel
Configuration
panel
The Configuration client views and elements allow you to quickly and easily set,
modify, and remove probes for analyzing and monitoring transport stream inputs.
See Figure 2--18.
Address bar
Selection Indicator bar
Figure 2- 18: The Configuration client application window
Note the following characteristics of the Configuration client window in
Figure 2--18:
H The Navigation panel allows you to quickly choose the category of error for
which you want the Analysis Server to probe.
H The Address bar shows that the Configuration client is connected to the
Analysis Server that is analyzing the transport stream being input through
I/O#2 on oxford6.
H The Selection Indicator bar shows the item currently selected in the
Navigation panel.
H The Configuration panel allows you to specify probes or configure analyses
for the Analysis Server indicated in the address bar . This panel changes
depending on the item selected in the Navigation panel.
2- 32
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
Page 83

Operating Information
Stream Player Client
The Stream Player application allows you to play back transport streams saved
on the hard disk of the MTS300 system using a VTR-like interface. See
Figure 2--19. You can specify which portion of the transport stream to play back,
the rate of the transport stream (you can also apply an external clock to set the
rate), the format (ASI or M2S) of the transport stream, and the playback mode
(single play or loop play).
Figure 2- 19: The Stream Player client application window
Note the following characteristics of the Stream Player client window in
Figure 2--19:
H The Server address boxes contain the name or IP address of the server and
the I/O port number to which the Stream Player is connected. You can use
the text boxes to connect to a different MTS300 system or to a different I/O
port number.
H The Filename indicates the name and location of the transport stream file
currently being output.
H The Start Time and End Time are editable fields that you can use to limit the
part of the transport stream file that you will output. The default is to output
the complete file.
H The Duration indicates how long the specified section will play.
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
2- 33
Page 84

Operating Information
H The Rate, Packet Size, and the Format and Mode are extracted from the
transport stream file. If you change the Start or End time, you can edit the
Rate field.
When you select the External Clock option, the Rate box displays EXT
CLK. To reset the rate, browse to the transport stream file and reselect it.
H The Slide Bar and Selector Buttons allow you to control which portion of the
file will be played back.
H Playback Time. When a stream output is in progress, the Stream Player
displays the current position in time (hours, minutes, seconds, and
hundredths of a second) of the output in progress.
H Control Buttons. The three Control buttons (from left to right: Stop, Play,
and Loop Play) allow you to control the stream output. Click on a Control
button to perform the desired task.
Stream Recorder Client
The Stream Recorder application provides a VTR-like display that allows you to
control the recording of a transport stream input. The display includes the
following items:
The Stream Recorder application allows you to record an MPEG transport
stream onto the hard drive of the MTS300 system using a VTR-like interface.
You can specify the stream format, duration, file name, and location of the
recorded file. See Figure 2--20.
2- 34
Figure 2- 20: Stream Recorder client application window
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
Page 85

Operating Information
Note the following characteristics of the Stream Recorder client window:
H Server Address. If you launch the Stream Recorder from the Master Client,
the Server address boxes contain the name or IP address of the server and the
I/O port number to which the Stream Recorder is connected. You can use the
text boxes to connect to a different MTS300 system or to a different I/O port
number.
NOTE. Store transport stream files on the E: drive of the MTS300 system. The
response time of the MTS300 system C: drive is limited and may affect the
performance of the Stream Recorder and Stream Player when you try to capture
or playback streams with bitrates greater than 30 Mbps.
H Filename. The Filename box list the directory path and filename of the file
you will capture with the Stream Recorder.
H Stream Format. Select the format you will record the input in:
H Select TS to record MPEG--2, DVB, or ATSC transport streams.
H Select S_TMCC for single transport stream TMCC multiplexes.
H Select M_TMCC for multiple transport stream TMCC multiplexes.
When M_TMCC is selected, you can choose to acquire the whole stream
by selecting All in the list box to the right, or you can select only an
MPEG-2 stream of the multiplex. To record only a portion of the
multiple stream format, select the appropriate TS ID from the TS ID list
box.
H Duration and Free. Use the Duration box to set the size of the transport
stream file you are capturing. You can set the duration time (hours, minutes,
seconds, and hundredths of a second) to any value not exceeding the value
listed in the Free box.
The Free box displays the amount of memory available (hours, minutes,
seconds, and hundredths of a second) to record a transport stream file on the
hard drive you selected in the Filename box.
H Rate and Packet Size. The bitstream rate and the packet size of the input
transport stream are displayed in these boxes.
H Output Activation. When you select the Output Activation option, the
transport stream on the I/O port input to which the Stream Recorder is
connected is looped through to the output connector of that I/O port.
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
2- 35
Page 86

Operating Information
H Progress Bar. The Progress bar displays the progress of an active recording
process. The display elements in the Progress bar light up from left to right
to indicate how far the capture process of the Stream Recorder has
proceeded.
H Recording Time. When a stream capture is in progress, the Stream Recorder
displays the beginning time (0:00:00.00), the ending time (as set in the
Duration box), and the current duration of the recording in progress.
H Control Buttons. The three Control buttons (from left to right: Stop, Record,
and Loop Record) allow you to control the stream capture. Click a Control
button to perform the desired task.
H Minimize/Maximize Button. Click the Minimize/Maximize button to remove
or add the setup portion of the Stream Recorder display. When you minimize
the Stream Recorder setup display, the Stream Recorder appears as shown
below.
TMCC Expert Client
The TMCC (Transmission and Multiplexing Configuration Control) Expert
Client application allows you analyze the TMCC data of an ARIB-compliant
transport stream input real time. See Figure 2--21. You can also analyze an
ARIB-compliant transport stream file stored on your local disk.
Note the following characteristics of the TMCC Expert Client window:
H Address Bar. The Address bar shows that the TMCC Expert client is
connected to the Analysis Server analyzing the transport stream being input
through I/O#2A on oxford6.
H Slots View. The Slots view displays the properties of each slot using three
columns. The first column lists the slot numbers (1 through 48). The second
column shows the TSID (transport stream identifier) associated with each
slot. The third column lists the modulation mode for each slot and the
number of effective slots. Each modulation mode is represented by a
different color.
NOTE. When the modulation mode and the number of slots are not consistent, the
Modulation column information is displayed in red.
H Syntax View. The Syntax view displays the content of the TMCC data in a
hierarchic list, including the length, value, and description of the hierarchic
item. Each hierarchic item is represented by a colored icon. A green icon
indicates the field value is correct or that all fields of a group are correct. A
red icon indicates an error exists in the field value of the item or in one of the
subitems of a group.
2- 36
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
Page 87

Address bar
Slots view
Syntax view
Raw data view
Operating Information
Message view
Figure 2- 21: TMCC Expert Client display
Raw Data View
The Raw Data view displays the hexadecimal values of the TMCC data. You can
use standard Windows NT methods for selecting and copying the data to a text
file.
Message View
The Message view displays error, warning, and information messages for the
TMCC analysis in progress. The messages include the message type (error,
warning, and information), the message content, and the time of the message.
The maximum number of displayed messages is 1000. Additional messages are
handled on a first in first out basis.
You can right-click in the Message view to open a dialog box where you can sort
and clear messages, and set the number of lines allowed for each message. You
can set the Message view for 1, 2, or 3 lines per message.
NOTE. Some messages are too long to display within three lines; in this case,
double-click the message to display a window containing the complete message.
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
2- 37
Page 88

Operating Information
TMCC Configuration
Address bar
Navigation
panel
Configuration
panel
Client
The TMCC (Transmission and Multiplexing Configuration Control) Configuration Client is used to configure the analyses performed by the TMCC Analysis
Server. See Figure 2--22. The results of the analyses are displayed in the TMCC
Expert Client and the Master Client.
Figure 2- 22: TMCC Configuration Client display
Note the following characteristics of the TMCC Configuration client window:
H The Address bar shows that the TMCC Configuration client is connected to
the Analysis Server that is analyzing the transport stream being input
through I/O#2 on oxford6.
H The Navigation panel allows you to quickly choose the category of error for
which you want the Analysis Server to probe.
H The Configuration panel allows you to specify probes or configure analyses
for the Analysis Server indicated in the address bar . This panel changes
depending on the item selected in the Navigation panel.
2- 38
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
Page 89

Front Panel Controls
MPEG Test System
Operating Information
The MTS300 MPEG Test System front-panel controls allow you to control the
MTS300 applications using either the keypad or the touch screen when a
keyboard and mouse are not available. See Figure 2--23.
Keypad
Floppy disk drive
(standard)
CD-ROM drive
(standard)
Touch screen
Figure 2- 23: Front-panel elements
This section shows how to use the touch screen features. Table 2--5 describes the
keypad controls, Table 2--6 lists touch screen techniques for working with the
Master client. Use similar techniques for the other client applications.
CAUTION. Do not use sharp or abrasive objects to perform operations using the
touch screen. Using sharp or abrasive objects can damage the LCD display.
Included as a standard accessory with all test systems is a stylus that gives you
more precise control over the items you touch on the touch screen.
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
2- 39
Page 90

Operating Information
Table 2- 5: Front panel-key controls
Control name Mechanism Description
Up Arrow Button Use to navigate and change focus from
Left Arrow Button
Right Arrow Button
Down Arrow Button
Select Button Same as the space key.
Adjust Knob Knob (Rotary encoder) Not enabled.
Run/Stop Button Not enabled.
Esc Button Standard Escape key.
Tab Button Standard Tab key.
Print Button Prints the current display.
Touch Button (w/hand icon) Toggle function not enabled. The touch
onewindow function toanother.
screen is always on.
Menu (Application key) Button (w/pointer icon) Displays shortcut menus for selected
items.
Help Button Opens the Help contents. Standard F1 key.
Print Screen Button (w/printer icon) Copies the screen to the clipboard. Alt plus
Print Screen copies the active window.
START Key Button (w/Windows logo) Opens the Windows Start menu.
Numbers 0 to 9, . (period), and -- (minus)
Fctn ButtonwithLED Modifier for numeral keys to create keys
Del Button Deletes selected text or object.
Ctrl ButtonwithLED Control key. LED indicates when keypad is
Alt ButtonwithLED Alternate key. LED indicates when keypad
Space Button Use it like a keyboard space bar or use it
Buttons Standard number keys, most have second
(Shift) and third (Function) functions.
F1 through F12. LED indicates when
active.
Button Backspace key.
Button Enter key.
in control mode.
is in alternate m ode.
as mouse button 1.
2- 40
Shift ButtonwithLED Shift key. LED indicates when keypad is in
shift mode. Locked mode key feature.
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
Page 91

Operating Information
NOTE. Some of the functions of the Expert and Configuration clients require the
use of an external keyboard and mouse.
Table 2- 6: Touch screen techniques
Task Action
Highlighting an item Touch the item.
Selecting an item
Making a menu selection Touch the menu name, and then touch the menu item.
Moving a window Touch and drag t he ti tle bar of the window without lifting the
stylus from the touch screen.
Displaying shortcut menus Touch an icon that has a shortcut menu associated with it (for
instance, a multiplex or service icon) and press the Menu
button from the keypad.
Checking or clearing option
boxes
Entering values in text boxes Touch the text box until a cursor appears in the text box, and
Scrolling through a list Touch the scrolling list until a cursor appears in the list, and
Scrolling a window Touch and drag a scroll bar without lifting the stylus from the
Resizing windows Touch and drag the lower right corner of the window to the
Following links in the online
help
Expanding or collapsing a
hierarchy
Copying text or other values Touch and drag over the area you want to copy, and then press
Pasting text or other values Touch the area into which you want to paste the contents of the
Touch the option name or check box.
then enter values using the keypad. (Onl y numeric values and
the letters M, k, m, u, n, and p can be entered from the
keypad.)
then press the Down Arrow button from the keypad.
touch screen.
desired size without lifting the stylus from the touch screen.
Touch the link text.
Double-tap the touch screen item at the point you want to
expand or collapse a hierarchical display, or touch the
Expand/Collapse control next to the item nam e.
the Shift button followed by the Copy button on the keypad.
clipboard, and then press the Shift button followed by the
Paste button on the keypad.
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
2- 41
Page 92

Operating Information
2- 42
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
Page 93

Tutorial
This tutorial will introduce you to the capabilities and features of the MTS300
system client modules. Refer to the Reference section for detailed operating
information for each client module.
Perform this tutorial with your own input stream, and then spend some time
experimenting with the various monitoring, configuration, and analysis options.
The sections of the tutorial begin on the following pages:
H Preliminary Setup page 2--43
H Starting and Configuring the Master Client page 2--44
H Assigning Servers and Generating a Transport Stream page 2--47
H Monitoring a Transport Stream Input page 2--48
H Configuring the Analysis Server page 2--51
H Configuring the Data Logging Function page 2--54
H Analyzing a Transport Stream page 2--55
Preliminary Setup
H Recording a Transport Stream Input page 2--58
NOTE. If you are not familiar with the Windows NT 4.0 operating system, review
the Windows NT online help.
1. Connect the output of I/O port 2 to the input of I/O port 1 using a 75 Ω BNC
cable as shown in Figure 2--24.
2. Power up and log on to the MTS300 system as described in Starting the
MTS300 System on page 2--20.
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
2- 43
Page 94

Tutorial
Input on
I/O port 1
Figure 2- 24: Initial setup for the tutorial
75 ohm
BNC cable
Output on
I/O port 2
Starting and Configuring the Master Client
Use the following procedure to start and configure the Master Client:
1. From the Windows NT start menu, select Programs | Tektronix MPEG
Test System | Master Client. An empty Master Client window is displayed
as shown in Figure 2--25.
You can also start the Master Client by double-clicking the Master Client
icon in the Tektronix MPEG Test System program group.
Before you can start monitoring inputs, you must connect the Master Client to a
Server Manager. The Server Manager (represented by the life preserver icon in
the system tray) collects the information generated by the Analysis Servers about
the transport stream errors and statistics. There are several methods you can use
to connect to a local Server Manager, but for this tutorial, use the simplest
technique:
2. Click the Home button on the Master Client toolbar as shown in Figure
2--25. The toolbar changes and the Server Manager to which you are
connected is displayed in the Address bar (see Figure 2--26).
2- 44
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
Page 95

Tutorial
Address bar
Selection
Indicator bar
Port Manager
panel
Services panel
Details panel
Error gauge
Figure 2- 25: Initial Master Client application window
Figure 2- 26: Master Client connected to the local Server Manager
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
2- 45
Page 96

Tutorial
Using the Workspace dialog box, you can specify the manner in which the
Master Client reports errors and displays icons.
3. Select Edit from the Workspace menu to open the Workspace dialog box.
4. Select Graphics in the Navigation panel to open the Graphics panel.
5. Change the Analysis display options to show only Critical and Major errors
as shown in Figure 2--27.
6. Click OK to apply your changes and return to the Master Client. After
creating a workspace, the Master Client window should look similar to
Figure 2--26.
Experiment with the other options available in the Workspace dialog box.
Return to the Master Client when you are ready to continue with the tutorial.
Analysis display options
Figure 2- 27: Changing the analysis display options
2- 46
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
Page 97

Assigning Servers and Generating a Transport Stream
In this part of the tutorial, you will assign servers to specific I/O ports, and then
you will generate a transport stream that you will monitor and analyze later in
this tutorial. These steps assume you have performed the steps in the Starting
and Configuring the Master Client procedure starting on page 2--44.
1. Right click the Free icons in the Port Manager panel, and then assign an
Analysis Server to I/O#1 and the Stream Player to I/O#2 as shown in
Figure 2--28.
Tutorial
Figure 2- 28: Assigning servers to I/O ports
2. Click on the icons and white space in the Port Manager panel and notice how
the Details panel and Selection Indicator bar change.
3. Right-click the Stream Player icon and select Launch Stream Player Client
from the shortcut menu. The Stream Player client is displayed and will look
similar to Figure 2--29 on page 2--48.
4. Click the Browse button, and then navigate to and open a suitable MPEG-2,
DVB, or ATSC transport stream file. You can select any transport stream file
on your local MTS300 system to output using the Stream Player.
5. When you return to the Stream Player client, accept all of the default settings
and click the Loop Play button to begin generating the transport stream in
loop mode. In Figure 2--29, the file DVBT002a.trp is playing in loop mode
and is 9.11 seconds into a 28.55 second loop.
6. Minimize the Stream Player client and return to the Master Client. Notice the
change in the Stream Player client icon appearance.
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
2- 47
Page 98

Tutorial
Figure 2- 29: Stream Player client
Monitoring a Transport Stream Input
Browse button
Loop button
In this part of the tutorial you will learn how to interpret the icons used by the
Master Client, and you will learn how the different Master Client panels allow
you to see different levels of error details. These steps assume you have
performed the steps in the Assigning Servers and Generating a Transport Stream
procedure starting on page 2--47.
1. Right-click the Analysis Server icon (the train icon) and select Start
Analysis from the shortcut menu. The Services panel (to the right of the Port
Manager panel) should update showing the services that are part of the
transport stream you are now monitoring. The display should now look
similar to Figure 2--30.
2. Experiment with the icons by right-clicking each and familiarizing yourself
with the contents of the shortcut menus.
If your input is displaying any critical or major errors, you will see error icons
overlaying the icons in the Port Manager and Services panels. Refer to the online
help for descriptions of the error icons.
3. Select one of the icons in the Port Manager panel. Notice the changes to the
Details panel and the Selection Indicator bar. Notice also that when you
select an icon in the Port Manager panel that the Error gauge changes.
The Error gauge shows you the severity of errors being recorded on the
selected item. In step 5 on page 2--46, you set the Master Client workspace
to show only critical or major errors. Refer to the online help for descriptions
of the error icons.
2- 48
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
Page 99

Analysis
Server icon
Stream Player
server icon
Tutorial
Figure 2- 30: Monitoring a transport stream
4. Click one of the icons in the Services panel experiencing errors. As you roll
your cursor over an icon in the Services panel, a tool tip is displayed
showing you the transport stream ID and service ID pair for the service.
Notice the changes to the Details panel and the Selection Indicator bar. The
Details panel shows a different set of icons than those that were displayed
when an Multiplex icon was selected.
5. Right-click an icon in the service panel, and then select Associate Logo
from the shortcut menu as shown below.
6. Navigate to the Logos folder (C:\MTS300\Bin\Logos) and choose a *.jpg
or *.bmp file that you want to associate with the selected service.
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
2- 49
Page 100

Tutorial
7. Click OK. You are returned to the Master Client, and the logo is displayed in
place of the default service icon.
NOTE. Some service providers do not allow their logos to be used without
permission. Check with the service provider before you use their logo.
You can also go to the following URL to download logos for satellite
services: http://www.satlogo.com/. This link was valid as of June, 2000.
Refer to the online help for information about restoring the default service
icon to a service.
8. Right-click again in the service panel and choose Details from the shortcut
menu. The Services panel changes to show a tabular display that lists the
more information about each service. See Figure 2--31.
9. Click and drag the left border of the Services panel to display all of the
columns in the Details view. You can sort the inputs shown in this view by
clicking on the column headers.
2- 50
Figure 2- 31: Services panel details view
10. Experiment with some of the other Services panel shortcut menu items, and
then set the Services panel to display Large Icons when you are finished and
ready to proceed with the tutorial.
11. Select the Analysis Server icon and notice again the change to the Details
panel. The icons in this panel indicate the types, severity, and status of errors
occurring on the multiplex at the transport stream level. Refer to the online
help for a description of the icons displayed in the Details panel when a
Multiplex icon is selected.
12. Select a Services panel icon and note again the changes to the Details panel.
When a Services icon is selected the Details panel icons show the type,
severity, and status of the errors occurring on the multiplex at the service, or
program level. Refer to the online help for descriptions of the error icons.
MTS300 MPEG Test System Service Manual
 Loading...
Loading...