Page 1

www.keithley.com
A GREATER MEASURE OF CONFIDENCE
Model KPCI-488LPA GPIB Controller Interface Card and Model KUSB-488B USB to GPIB Converter
Reference Manual
KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010
Page 2

Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B
Reference Manual
©2010, Keithley Instruments, Inc.
All rights reserved.
Cleveland, Ohio, U.S.A.
Any unauthorized reproduction, photocopy, or use the information herein, in whole or in part, without the
prior written approval of Keithley Instruments, Inc. is strictly prohibited.
All Keithley Instruments product names are trademarks or registered trademarks of Keithley Instruments, Inc.
Other brand names are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders.
National Instruments
Document number:
™ and NI™ are trademarks of the National Instruments Corporation.
KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010
Page 3

Table of Contents
Section T opic Page
1 Keithley Command-Compatible Functions .................................... 1-1
Introduction ................................................................................................. 1-2
Using Keithley command-compatible functions.......................................... 1-2
Microsoft
Microsoft Visual C/C++......................................................................... 1-4
Microsoft Visual C# .............................................................................. 1-4
Keithley command-compatible function reference...................................... 1-2
GPIBBOARDPRESENT....................................................................... 1-5
BOARDSELECT .................................................................................. 1-5
ENTER ................................................................................................. 1-5
FEATURE............................................................................................. 1-6
INITIALIZE ........................................................................................... 1-6
LISTENERPRESENT........................................................................... 1-7
PPOLL.................................................................................................. 1-7
RARRAY............................................................................................... 1-7
RECEIVE ............................................................................................. 1-7
SEND ................................................................................................... 1-8
SETINPUTEOS.................................................................................... 1-8
SETOUTPUTEOS................................................................................ 1-8
SETTIMEOUT ...................................................................................... 1-9
SPOLL.................................................................................................. 1-9
SRQ ..................................................................................................... 1-9
TARR AY ............................................................................................... 1-9
TRANSMIT......................................................................................... 1-10
WAITSRQDEVICE ............................................................................. 1-12
2 NI Command-Compatible Functions........................................................... 2-1
Introduction ................................................................................................. 2-3
Using NI command-compatible functions ................................................... 2-3
Microsoft Visual Basic version 6.0 and .NET ....................................... 2-3
Microsoft Visual C/C++......................................................................... 2-5
Microsoft Visual C# .............................................................................. 2-5
Overview of NI command-compatible functions ......................................... 2-6
IEEE-488 device-level functions .......................................................... 2-6
IEEE-488 board-level functions............................................................ 2-7
IEEE-488.2 functions ........................................................................... 2-8
Data types ............................................................................................ 2-9
NI command-compatible function reference............................................... 2-9
ibask..................................................................................................... 2-9
ibbna .................................................................................................. 2-12
ibcac................................................................................................... 2-12
ibclr..................................................................................................... 2-13
ibcmd.................................................................................................. 2-13
ibcmda................................................................................................ 2-13
ibconfig............................................................................................... 2-14
ibdev................................................................................................... 2-16
ibdma ................................................................................................. 2-17
ibeot ................................................................................................... 2-18
ibeos................................................................................................... 2-18
ibfind................................................................................................... 2-19
ibgts.................................................................................................... 2-20
®
Visual Basic® version 6.0 and .NET ................................... 1-2
Page 4

Table of Contents Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual
ibist..................................................................................................... 2-20
iblines ................................................................................................. 2-21
ibln...................................................................................................... 2-21
ibloc.................................................................................................... 2-22
ibonl.................................................................................................... 2-23
ibnotify................................................................................................ 2-23
ibpad .................................................................................................. 2-24
ibsad................................................................................................... 2-25
ibpct.................................................................................................... 2-25
ibppc................................................................................................... 2-26
ibrd ..................................................................................................... 2-26
ibrda ................................................................................................... 2-27
ibrdf .................................................................................................... 2-28
ibrpp ................................................................................................... 2-29
ibrsc.................................................................................................... 2-29
ibrsp ................................................................................................... 2-30
ibrsv.................................................................................................... 2-30
ibsic .................................................................................................... 2-31
ibsre ................................................................................................... 2-29
ibstop.................................................................................................. 2-31
ibtmo .................................................................................................. 2-32
ibtrg .................................................................................................... 2-33
ibwait .................................................................................................. 2-33
ibwrt.................................................................................................... 2-34
ibwrta.................................................................................................. 2-35
ibwrtf................................................................................................... 2-36
Multi-device functions ............................................................................... 2-37
AllSpoll ............................................................................................... 2-37
DevClear ............................................................................................ 2-37
DevClearList....................................................................................... 2-37
EnableLocal ....................................................................................... 2-38
EnableRemote ................................................................................... 2-38
FindLstn ............................................................................................. 2-38
FindRQS ............................................................................................
PassControl..
...................................................................................... 2-39
2-39
PPoll................................................................................................... 2-40
PPollConfig ........................................................................................ 2-40
PPollUnConfig.................................................................................... 2-41
RcvRespMsg...................................................................................... 2-41
ReadStatusByte ................................................................................. 2-42
Receive .............................................................................................. 2-42
ReceiveSetup..................................................................................... 2-43
ResetSys............................................................................................ 2-43
Send................................................................................................... 2-44
SendCmds ......................................................................................... 2-44
SendDataBytes .................................................................................. 2-45
SendList ............................................................................................. 2-45
SendIFC ............................................................................................. 2-46
SendLLO ............................................................................................ 2-46
SendSetup ......................................................................................... 2-46
SetRWLS ........................................................................................... 2-47
TestSRQ............................................................................................. 2-47
TestSys............................................................................................... 2-48
Trigger ................................................................................................ 2-48
TriggerList .......................................................................................... 2-49
WaitSRQ ............................................................................................ 2-49
ii KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010
Page 5

Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual Table of Contents
Appendix T opic Page
A Status/Error Codes ............................................................................... A-1
NI command-compatible status codes........................................................ A-2
NI command-compatible function error codes............................................ A-3
Index ............................................................... ............................................. Index-1
KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010 iii
Page 6

In this section:
Topic Page
Introduction..................................................................................... 1-2
Using Keithley command-compatible functions.......................... 1-2
Keithley command-compatible function reference...................... 1-5
Section 1
Keithley Command-Compatible Functions
Microsoft® Visual Basic® version 6.0 and .NET.......................... 1-2
Microsoft Visual C/C++............................................................... 1-4
Microsoft Visual C#..................................................................... 1-4
GPIBBOARDPRESENT ............................................................. 1-5
BOARDSELECT......................................................................... 1-5
ENTER ....................................................................................... 1-5
FEATURE................................................................................... 1-6
INITIALIZE .................................................................................. 1-6
LISTENERPRESENT ................................................................. 1-7
PPOLL ........................................................................................ 1-7
RARRAY..................................................................................... 1-7
RECEIVE.................................................................................... 1-7
SEND.......................................................................................... 1-8
SETINPUTEOS .......................................................................... 1-8
SETOUTPUTEOS ...................................................................... 1-8
SETTIMEOUT ............................................................................ 1-9
SPOLL ........................................................................................ 1-9
SRQ............................................................................................ 1-9
TARR AY...................................................................................... 1-9
TRANSMIT ................................................................................. 1-10
WAITSRQDEVICE...................................................................... 1-12
Page 7
Section 1: Keithley Command-Compatible Functions Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual
Introduction
This section contains information about Keithley Instruments command-compatible functions.
Refer to Section 2 for information about the National Instruments (NI™)
functions.
NOTE Refer to Section 2 for NI Command-Compatible Functions.
If you have any questions, please contact your local Keithley Instruments representative or call
Keithley Instruments corporate headquarters (toll-free inside the U.S. and Canada only) at
1-888-KEITHLEY (1-888-534-8453), or from outside the U.S. at +1-440-248-0400. For worldwide
contact numbers, visit our website at www.keithley.com.
Using Keithley command-compatible functions
Microsoft® Visual Basic® version 6.0 and .NET
To create a Keithley command-compatible application on Microsoft® Windows® XP/2000/Vista™
operating systems, use the the API and Microsoft
Step 1: Enter Visual Basic and open or create a project
To create a new project:
®
Visual Basic® to perform the following steps:
1
command-compatible
After opening Visual Basic, select File > New Project.
To use an existing project:
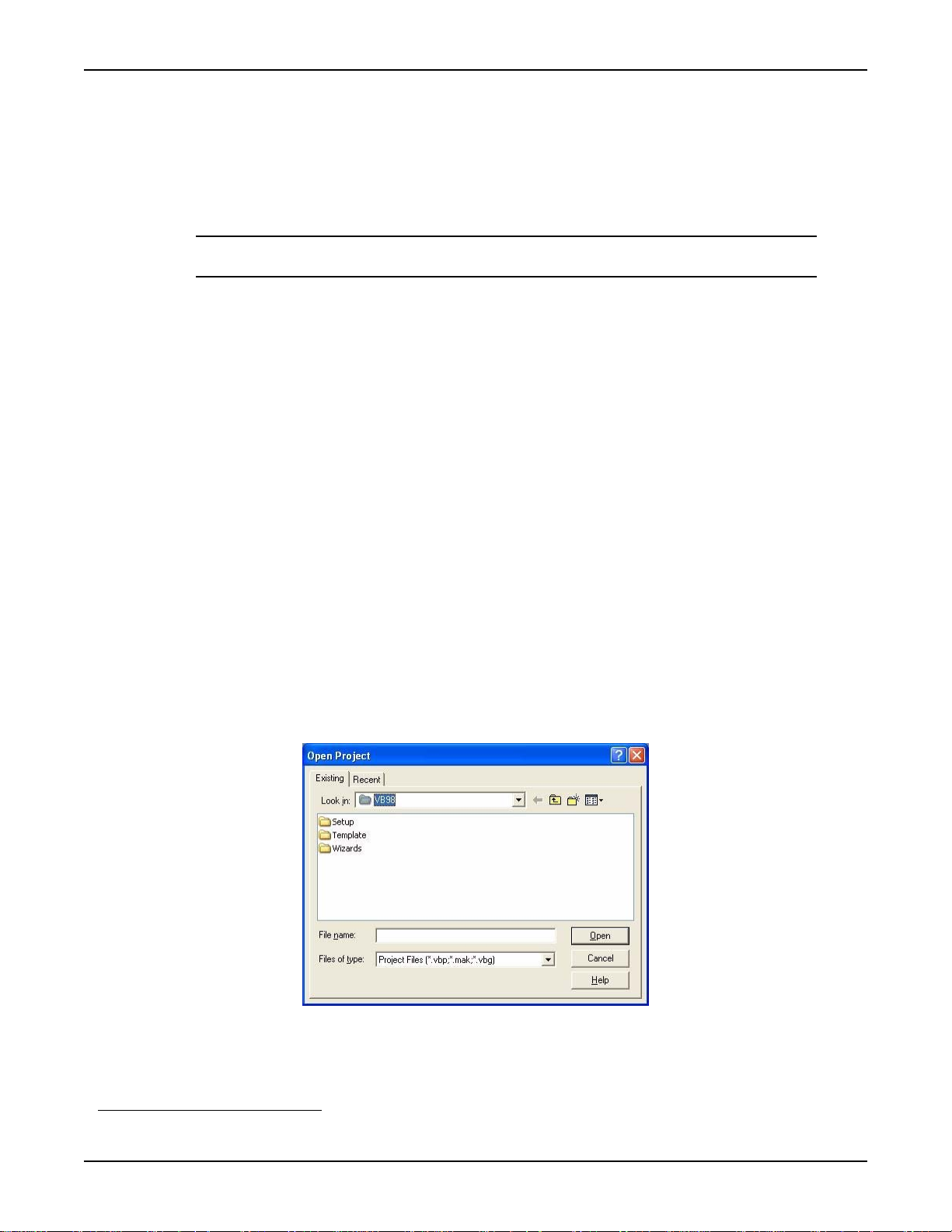
1. After opening Visual Basic, select File > Open Project. The Open Project dialog box
displays (Figure 1-1).
Figure 1-1: Open Project dialog box
2. Load the project by finding and double-clicking the project file name in the applicable
directory.
1. National Instruments™ and NI™ are trademarks of the National Instruments Corporation.
1-2 Return to Section Topics KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010
Page 8

Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual Section 1: Keithley Command-Compatible Functions
Step 2: Include function declarations and constants file
If it is not already included in the project, add the IEEEVB.BAS file (for Visual Basic version 6.0) or
the GPIB_vb.vb file (for Visual Basic .NET) file as a module to your project. All Keithley
command-compatible function declarations and constants are contained in this file, which is used
to develop user self-measurement applications.
Step 3: Design the application interface
Add elements (for example, a command button, list box, or text box) on the Visual Basic form used
to design the interface. These elements are standard controls from the Visual Basic Toolbox.
To place a needed control on the form:
1. Select the needed control from the Toolbox.
2. Draw the control on the form. Alternatively, to place the default-sized control on the form,
click the form, then use the Select Objects tool to reposition or resize controls.
Step 4: Set control properties
Set control properties from the properties list. To view the properties list, select the desired control
and do one of the following:
• Press F4
•Select View > Properties
or
• Click the Properties button on the toolbar
Step 5: Write the event codes
The event codes define the action desired when an event occurs.
To write the event codes:
1. Double-click the control or form needing an event code; the code module will display.
2. Add new codes as needed. All functions that are declared in IEEEVB.BAS or GPIB_vb.vb
(depending upon the Visual Basic version used) can be called to perform data acquisition
operations (for details, refer to Keithley command-compatible function reference).
Step 6: Run your application
To run the application, perform one of the following actions:
• Press F5
•Select Run > Start
or
• Click the Start icon on the toolbar
KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010 Return to Section Topics 1-3
Page 9

Section 1: Keithley Command-Compatible Functions Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual
Microsoft Visual C/C++
To create a Keithley command-compatible library application using the Keithley
command-compatible function library (which is CEC command-compatible) and Microsoft Visual
C/C++ on a Windows XP/2000 operating system, follow these steps:
Step 1: Enter Visual C/C++ and open an existing project or create a new project
NOTE The project can be a new project, or you can use an existing project.
Step 2: Include function declarations and constants file (IEEE-C.H)
Include the IEEE-C.H file in the Visual C/C++ source files that call Keithley command-compatible
functions by adding the following statement in the source file:
#include "IEEE-C.H"
NOTE Keithley command-compatible function declarations and constants are contained in the
IEEE-C.H file. Use the functions and constants to develop user self data-acquisition
applications.
Step 3: Build your application
1. Set suitable compile and link options.
2. Select Build from the Build menu (Visual C/C++ version 4.0 and later).
3. Remember to link the Keithley command-compatible library ieee_32m.lib.
Microsoft Visual C#
Step 1: Enter Visual C# and open an existing project or create a new project
Step 2: Include the function declarations and constants file (GPIB_CS.cs)
Add the GPIB_CS.cs file to your Visual C# project. All Keithley command-compatible functions
are contained in the file.
Step 3: Write the event codes
The event codes define the action desired when an event occurs.
To write the event codes:
1. Double-click the control or form needing an event code; the code module displays.
2. Add the new code, as needed. All functions that are declared in the GPIB_CS.cs file can
be called to perform data acquisition operations (refer to the Keithley command-compatible
function reference for details).
Step 4: Run your application
To run the application, perform one of the following actions:
• Press F5
1-4 Return to Section Topics KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010
Page 10

Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual Section 1: Keithley Command-Compatible Functions
• Select Run > Start
or
• Click the Start icon on the toolbar.
Keithley command-compatible function reference
This section contains a detailed description of Keithley Instruments command-compatible library
functions, including the compatible library data types and function reference.
GPIBBOARDPRESENT
Description Verifies whether a GPIB board is present in the GPIB system.
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
char gpib_board_present(void)
Visual Basic
GpibBoardPresent( ) As Long
Return value 0: GPIB board is not installed
BOARDSELECT
Description Designates which board is the active board.
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
Parameters board: The board number; valid values are 0 to 3
ENTER
Description Reads data from a specified device.
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
1: GPIB board is installed
void boardselect (long int bd)
Visual Basic
call boardselect (ByVal board As Long)
long int enter (char *buf, unsigned long maxlen,
unsigned long *len, long int addr,
long int *status)
Visual Basic
call enter(buf As String, maxlen As Integer,
len As Integer, addr As Integer, status As Integer)
KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010 Return to Section Topics 1-5
Page 11

Section 1: Keithley Command-Compatible Functions Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual
Parameters buf: The buffer storing the received data
maxlen: The maximum bytes of data to receive; valid value is from 0 to 65535
len: Returns the actual number of received data bytes
addr: The GPIB address of the talker
status: 0: Read data successfully
8: Timeout error
FEA TURE
Description Returns the GPIB board settings or hardware features.
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
long int feature (long int f)
Visual Basic
GPIBFeature (ByVal f As Long) As Long
Parameters f: The feature or setting information desired. Valid FEATURE values are
contained in Table 1-1.
Table 1-1: FEATURE parameters
Feature
(constants)
IEEEListener 0 Verifies that ListenerPresent function is supported by
IEEEIOBASE 100 The board’s I/O base address
IEEETIMEOUT 200 The board’s I/O timeout setting
IEEEINPUTEOS 201 The current input EOS character setting
IEEEOUTPUTEOS1 202 The current output EOS character 1 setting
IEEEOUTPUTEOS2 203 The current output EOS character 2 setting
IEEEBOARDSELECT 204 The current active board number
Return value The value of the feature or setting
INITIALIZE
Description Opens and initializes a GPIB board.
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
Features
(values) Returned information
the GPIB board; this information value is always 1
void initialize (long int addr,
long int level)
Visual Basic
call initialize (ByVal addr As Long,
ByVal level As Long)
Parameters addr : GPIB address assigned to the board
level: 0: Specifies the board as a system controller
1: Specifies the board as a device
1-6 Return to Section Topics KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010
Page 12

Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual Section 1: Keithley Command-Compatible Functions
LISTENERPRESENT
Description Checks for a specified listener on the GPIB system.
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
char listener_present(long int addr)
Visual Basic
ListenerPresent (ByVal addr As Long) As Long
Parameters addr: The listener address to check
Return value 0: The specified listener is not present
1: The specified listener is present
PPOLL
Description Performs a parallel poll and reads the status of devices.
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
int ppoll (char *poll)
Visual Basic
Parameters poll: Returned parallel polling status
RARRA Y
Description Receives a block of binary data (up to 64K) from a device defined as the talker.
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
Parameters buf: The buffer storing the received binary data
Return value 0: Read data successfully
call ppoll(poll As Integer)
The GPIB addressing must be performed using the TRANSMIT function.
long int rarray (void *buf,
unsigned long count, unsigned long *len,
long int *status)
Visual Basic
call rarray(buf As Variant, ByVal count As Long,
l As Integer, status As Integer)
count: The maximum data bytes; valid value is 0 to 65535
len: Returns the actual number of received data bytes
8: Timeout error
32: Data transfer terminated with EOI
RECEIVE
Description Reads data from a specified device, but does not address a talker. The GPIB
addressing must be performed using the TRANSMIT function.
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010 Return to Section Topics 1-7
Page 13

Section 1: Keithley Command-Compatible Functions Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual
long int receive (char *buf, unsigned long maxlen,
unsigned long *len, long int *status)
Visual Basic
call receive (buf As String, maxlen As Integer,
len As Integer, status As Integer)
Parameters buf: The buffer storing the received data
maxlen: Sets maximum bytes of data to receive
len: Returns the actual number of received data bytes
Return value 0: Read data successfully
8: Timeout error
SEND
Description Sends commands to a specified GPIB device.
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
long int send (long int addr, char *buf,
unsigned long maxlen, long int *status)
Parameters addr: The listener address
Return value 0: Data sent successfully
SETINPUTEOS
Description Sets the terminating character for input data transfer.
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
Parameters eos_c: The terminating character for input data transfer
Visual Basic
call send(addr As Integer, buf As String,
status As Integer)
buf: The buffer storing the data to send
maxlen: Sets the maximum number of data bytes to send
8: Timeout error
void setinputEOS (long int eos_c)
Visual Basic
call setinputEOS (ByVal eos_c As Long)
SETOUTPUTEOS
Description Sets the terminating characters for output data transfer.
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
void setoutputEOS (long int e1, long int e2)
1-8 Return to Section Topics KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010
Page 14

Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual Section 1: Keithley Command-Compatible Functions
Visual Basic
call setoutputEOS (ByVal e1 As Long, ByVal e2 As Long)
Parameters e1: The first terminating character for output data transfer
e2: The second terminating character for output data transfer
SETTIMEOUT
Description Sets the maximum duration allowed for a read/write operation (timeout period).
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
void settimeout (unsigned long int timeout)
Visual Basic
call settimeout (ByVal timeout As Long)
Parameters timeout: The timeout value in milliseconds (ms)
SPOLL
Description Performs serial polling and reads the specified device’s status.
SRQ
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
long int spoll (long int addr, char *poll,
long int *status)
Visual Basic
call spoll(ByVal addr As Integer, poll As Integer,
status As Integer)
Parameters addr: The address of the device to poll
poll: Returns the result of serial polling
Return value 0: Data sent successfully
8: Timeout error
Description Checks for device service requests.
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
char srq(void)
Visual Basic
srq ( ) As Long
Return value 0: The device is not requesting service
1: The device is requesting service
T ARRAY
Description Sends a block of binary data from memory to the devices defined as listeners;
GPIB addressing must be performed using the TRANSMIT function.
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010 Return to Section Topics 1-9
Page 15

Section 1: Keithley Command-Compatible Functions Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual
long int tarray (void *buf,
unsigned long count, long int eoi,
long int *status)
Visual Basic
call tarray (buf as variant, ByVal count As Long,
ByVal eoi As Integer, status As Integer)
Parameters buf: The buffer storing the data to send
count: The maximum number of data bytes to transmit
eoi: Enable or disable EOI device mode; 0 = disable EOI;
1 = enable EOI
Return value 0: Read data successfully
8: Timeout error
32: Data transfer terminated with EOI
TRANSMIT
Description Sends GPIB commands and data according to a series of GPIB commands and
data in a specified string.
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
long int transmit (char * cmd,
unsigned maxlen, long int * status);
Visual Basic
call transmit(cmd As String, status As Integer)
Parameters cmd: The buffer containing the command string and data to send; valid cmd
string values are contained in Table 1-2.
maxlen: The maximum number of command string bytes to send
Return value status:
0: Sent command and data successfully
1: Illegal command syntax
8: Timeout error
16: Unknown command
32: Data transfer terminated with EOI
1-10 Return to Section Topics KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010
Page 16
Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual Section 1: Keithley Command-Compatible Functions
Table 1-2: TRANSMIT command string parameters
Commands Description Example
LISTEN
TALK
SEC
UNT
UNL
MTA
MLA
DATA
END
REN
EOI
GTL
SPE
SPD
PPC
PPD
PPU
DCL
LLO
CMD
GET
SDC
TCT
IFC
Sets the addresses of the listeners. The
values following LISTEN are the GPIB
addresses of the listeners.
Sets the address of the talker. The
values following
addresses of the talker. There is only
one talker at a time.
Sets the second address of the talker or
listener. This command should follow
TALK are the GPIB
TALK or LISTEN.
Untalk. "UNT"
Unlisten. "UNL"
“My Talk Address,” assigns the active
GPIB board as the talker.
“My Listen Address,” assigns the active
GPIB board as the listener.
Starts the data part. Before the DATA
command, the GPIB board must be set
as the talker. Strings are enclosed by
quotes(') and sent as characters.
Sends terminator characters. The DATA
command should be called before this
command.
Remote Enable "REN"
End-or-Identify. The data bytes following
EOI are the last bytes to transmit. The
last byte is sent with the EOI signal.
Go to local "GTL"
Serial poll enable "SPE"
Serial poll disable "SPD"
Parallel poll configure "PPC"
Parallel poll disable "PPD"
Parallel poll unconfigure "PPU"
Device clear "DCL"
Local lockout "LLO"
Starts GPIB command. The values
followed by
command messages and sent as binary
values.
Group execute trigger "GET"
Selected device clear "SDC"
Take control "TCT"
Interface clear "IFC"
CMD are treated as GPIB
"LISTEN 1 2 3"
Meaning: Configure devices whose GPIB
addresses are 1, 2, and 3, as listeners.
TALK 0"
"
Meaning: Configure device whose GPIB
address is 0, as talker.
"TALK 0 SEC 1"
Meaning: Configure device with primary
GPIB address of 0 and secondary address
of 1, as talker.
"MTA"
"MLA"
"DATA 'hello' 13 10"
"DATA '*IDN?' END"
Meaning: Send data message "*IDN?" and
then send terminator bytes
"DATA '*IDN?' EOI 10"
Meaning: Send data message "*IDN?" and
then send line feed with EOI signal.
CMD 20"
"
Meaning: Send GPIB command message,
device clear (DCL).
KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010 Return to Section Topics 1-11
Page 17

Section 1: Keithley Command-Compatible Functions Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual
W AITSRQDEVICE
Description This function waits until a device is requesting service or a timeout error occurs.
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
long int waitSRQDevice (long int addr,
char *poll, long int *status)
Parameters addr: The device address
poll: The returned poll status
status: Indicates whether or not a serial poll was performed
1-12 Return to Section Topics KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010
Page 18

In this section:
Topic Page
Introduction..................................................................................... 2-3
Using NI command-compatible functions .................................... 2-3
Overview of NI command-compatible functions.......................... 2-6
Section 2
NI Command-Compatible Functions
Microsoft Visual Basic version 6.0 and .NET.............................. 2-3
Microsoft Visual C/C++............................................................... 2-5
Microsoft Visual C#..................................................................... 2-5
IEEE-488 device-level functions................................................. 2-6
IEEE-488 board-level functions .................................................. 2-7
IEEE-488.2 functions.................................................................. 2-8
Data types................................................................................... 2-9
NI command-compatible function reference................................ 2-9
ibask ........................................................................................... 2-9
ibbna........................................................................................... 2-12
ibcac ........................................................................................... 2-12
ibclr ............................................................................................. 2-13
ibcmd .......................................................................................... 2-13
ibcmda ........................................................................................ 2-13
ibconfig ....................................................................................... 2-14
ibdev ........................................................................................... 2-16
ibdma.......................................................................................... 2-17
ibeot............................................................................................ 2-18
ibeos ........................................................................................... 2-18
ibfind ........................................................................................... 2-19
ibgts ............................................................................................ 2-20
ibist ............................................................................................. 2-20
iblines ......................................................................................... 2-21
ibln .............................................................................................. 2-21
ibloc ............................................................................................ 2-22
ibonl ............................................................................................ 2-23
ibnotify ........................................................................................ 2-23
ibpad........................................................................................... 2-24
ibsad ........................................................................................... 2-25
ibpct ............................................................................................ 2-25
ibppc ........................................................................................... 2-26
ibrd.............................................................................................. 2-26
ibrda............................................................................................ 2-27
ibrdf............................................................................................. 2-28
ibrpp............................................................................................ 2-29
ibrsc ............................................................................................ 2-29
Page 19

Section 2: NI Command-Compatible Functions Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual
Topic (continued) Page
ibrsp ........................................................................................... 2-30
ibrsv ........................................................................................... 2-30
ibsic............................................................................................ 2-31
ibsre ........................................................................................... 2-31
ibstop ......................................................................................... 2-31
ibtmo .......................................................................................... 2-32
ibtrg ............................................................................................ 2-33
ibwait.......................................................................................... 2-33
ibwrt ........................................................................................... 2-34
ibwrta.......................................................................................... 2-35
ibwrtf........................................................................................... 2-36
Multi-device functions....................................................................... 2-37
AllSpoll ....................................................................................... 2-37
DevClear .................................................................................... 2-37
DevClearList .............................................................................. 2-37
EnableLocal ............................................................................... 2-38
EnableRemote ........................................................................... 2-38
FindLstn ..................................................................................... 2-38
FindRQS .................................................................................... 2-39
PassControl ............................................................................... 2-39
PPoll........................................................................................... 2-40
PPollConfig ................................................................................ 2-40
PPollUnConfig............................................................................ 2-41
RcvRespMsg.............................................................................. 2-41
ReadStatusByte ......................................................................... 2-42
Receive ...................................................................................... 2-42
ReceiveSetup............................................................................. 2-43
ResetSys.................................................................................... 2-43
Send........................................................................................... 2-44
SendCmds ................................................................................. 2-44
SendDataBytes .......................................................................... 2-45
SendList ..................................................................................... 2-45
SendIFC..................................................................................... 2-46
SendLLO.................................................................................... 2-46
SendSetup ................................................................................. 2-46
SetRWLS ................................................................................... 2-47
TTestSRQ .................................................................................. 2-47
TestSys ...................................................................................... 2-48
Trigger........................................................................................ 2-48
TriggerList .................................................................................. 2-49
WaitSRQ .................................................................................... 2-49
2-2 Return to Section Topics KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010
Page 20

Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual Section 2: NI Command-Compatible Functions
Introduction
This section contains information about the National Instruments (NI™)1 command-compatible
functions and how to use them, as well as a reference section containing syntax examples
(Microsoft
command-compatible status codes and NI command-compatible function error codes.
NOTE Refer to Section 1 for Keithley Command-Compatible Functions.
If you have any questions, please contact your local Keithley Instruments representative or call
Keithley Instruments corporate headquarters (toll-free inside the U.S. and Canada only) at
1-888-KEITHLEY (1-888-534-8453), or from outside the U.S. at +1-440-248-0400. For worldwide
contact numbers, visit our website at www.keithley.com.
®
Visual C/C++, Visual Basic
®
, and so on). Appendix A contains information about NI
Using NI command-compatible functions
This section provides the fundamentals of building applications on Microsoft® Windows® XP/2000/
™
operating systems using NI command-compatible functions and either Microsoft® Visual
Vista
®
or Microsoft® Visual C/C++.
Basic
Microsoft Visual Basic version 6.0 and .NET
To create an application with NI command-compatible functions and Visual Basic, follow these
steps:
Step 1: Enter Visual Basic and open or create a project
To create a new project:
After opening Visual Basic, select File > New Project.
To use an existing project:
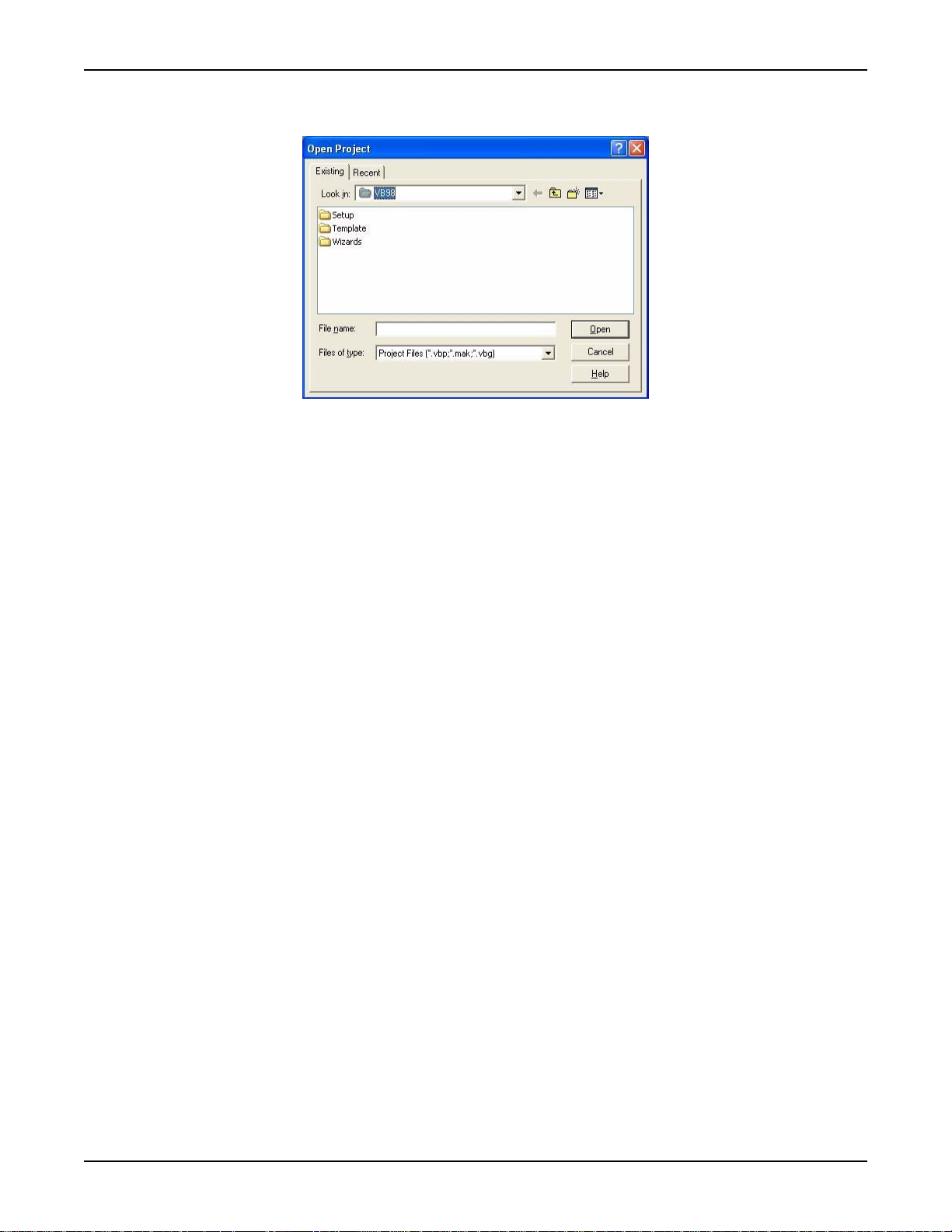
1. After opening Visual Basic, select File > Open Project. The Open Project dialog box
displays (see Figure 2-1).
1. National Instruments™ and NI™ are trademarks of the National Instruments Corporation.
KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010 Return to Section Topics 2-3
Page 21
Section 2: NI Command-Compatible Functions Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual
Figure 2-1: Open Project dialog box
2. Load the project by finding and double-clicking the project file name in the applicable
directory.
Step 2: Include function declarations and constants file
If it is not already included in the project, add the GPIB.BAS file (for Visual Basic 6.0) or GPIB.vb
file (for Visual Basic.NET) file. All NI command-compatible function declarations and constants
that you will use to develop applications are contained in this file.
Step 3: Design the application interface
Add elements (for example, a command button, list box, or text box) on the Visual Basic form used
to design the interface. These elements are standard controls from the Visual Basic Toolbox.
To place a needed control on the form:
1. Select the needed control from the Toolbox.
2. Draw the control on the form. Alternatively, to place the default-sized control on the form,
click the form, then use the Select Objects tool to reposition or resize controls.
Step 4: Set control properties
Set control properties from the properties list. To view the properties list, select the desired control
and do one of the following:
• Press F4
•Select View > Properties
or
Click the Properties button on the toolbar
Step 5: Write the event codes
The event codes define the action desired when an event occurs.
To write the event codes:
1. Double-click the control or form needing event code; the code module will display.
2. Add new code as needed. All functions that are declared in the GPIB.BAS or GPIB.vb files
(depending upon the Visual Basic version used) can be called to perform operations (for
details, refer to IEEE-488 device-level functions, Table 2-1 through Table 2-4).
2-4 Return to Section Topics KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010
Page 22
Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual Section 2: NI Command-Compatible Functions
Step 6: Run your application
To run the application, perform one of the following actions:
• Press F5
•Select Run > Start
or
• Click the Start icon on the toolbar
Microsoft Visual C/C++
To create an application with NI command-compatible functions and Microsoft Visual C/C++, follow
these steps:
Step 1: Enter Visual C/C++ and open an existing project or create a new project
NOTE The project can be a new project, or you can use an existing project.
Step 2: Include the function declarations and constants file (GPIB.H)
Include GPIB.H in the Visual C/C++ source files that call NI command-compatible functions by
adding the following statement in the source file:
#include "GPIB.H"
NOTE NI command-compatible function declarations and constants are contained in the
GPIB.H file. Use the functions and constants to develop user self data-acquisition
applications.
Step 3: Build your application as follows:
1. Set suitable compile and link options.
2. Select Build from the Build menu (Visual C/C++ 4.0 and later).
3. Remember to link the NI command-compatible import library GPIB-32.lib.
Microsoft Visual C#
Step 1: Enter Visual C# and open an existing project or create a new project
Step 2: Include the function declarations and constants file (GPIB.cs)
Add the GPIB.cs file to your Visual C# project. All NI command-compatible functions are
contained in the file.
Step 3: Write the event codes
The event codes define the action desired when an event occurs.
To write the event codes:
1. Double-click the control or form needing an event code; the code module displays.
KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010 Return to Section Topics 2-5
Page 23

Section 2: NI Command-Compatible Functions Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual
2. Add the new code, as needed. All functions that are declared in GPIB.cs can be called to
perform data acquisition operations (see NI command-compatible function reference for
details).
Step 4: Run your application
To run the application, perform one of the following actions:
• Press F5
• Select Run > Start
or
• Click the Start icon on the toolbar.
Overview of NI command-compatible functions
The NI command-compatible functions are grouped into three classes:
• IEEE-488 device-level functions
• IEEE-488 board-level functions
• IEEE-488.2 functions
IEEE-488 device-level functions
Table 2-1 contains IEEE-488 device-level functions.
Table 2-1: IEEE-488 device-level functions
Function Description
ibask
ibbna
ibclr
ibconfig
ibdev
ibeos
ibeot
ibln
ibloc
ibonl
ibpad
ibpct
ibppc
ibrd
ibrda
ibrdf
ibrdi
ibrdia
ibrpp
ibrsp
ibsad
ibstop
Returns the current value of the selected configuration item.
Assigns the access board of the designated device.
Sends the GPIB selected device clear (SDC) message to the designated
device.
Sets the value of the selected configuration item.
Opens and initializes a device descriptor.
Configures the EOS termination mode or character.
Enables or disables the action that sets the GPIB EOI line to enable while
the I/O operation completes.
Checks if there is an available device on the bus.
Sets the device to local control mode.
Sets the device online or offline.
Sets a device primary GPIB address.
Passes controller-in-charge (CIC) status to another GPIB device that has
controller capability.
Configures parallel polling.
Reads data from a device to the indicated buffer.
Reads data from a device to the indicated buffer asynchronously.
Reads data from a device to a file.
Reads data from a device to the indicated buffer.
Reads data from a device to the indicated buffer asynchronously.
Performs parallel polling.
Performs sequential polling.
Sets or disables a device secondary GPIB address.
Stops the asynchronous I/O operation.
2-6 Return to Section Topics KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010
Page 24

Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual Section 2: NI Command-Compatible Functions
Table 2-1: (continued) IEEE-488 device-level functions
Function Description
ibtmo
ibtrg
ibwait
ibwrt
ibwrta
ibwrtf
Sets the board or device timeout period.
Sends the group execute trigger (GET) message to a device.
Monitors events until one or more events occur that are described by mask
or that delay operating.
Writes data from a buffer to a device.
Writes data from a buffer to a device asynchronously.
Writes data from a file to a device.
IEEE-488 board-level functions
Table 2-2 contains IEEE-488 board-level functions.
Table 2-2: IEEE-488 board-level functions
Function Description
ibask Returns the current value of the selected configuration item.
ibcac Sets the assigned GPIB board to be the active controller by setting the
ATN line to enable.
ibcmd Sends GPIB commands.
ibcmda Sends GPIB commands asynchronously.
ibconfig Sets the value of the selected configuration item.
ibdma Enables or disables DMA.
ibeos Configures the EOS termination mode or character.
ibeot Enables or disables the action that sets the GPIB EOI line to enable while
the I/O operation completes.
ibfind Opens and initializes the GPIB board descriptor.
ibgts Sets the board from active control status to standby control status.
ibist Sets or clears the board individual status (ist) bit for parallel polling.
iblines Returns the GPIB control lines status.
ibln Checks for an available device on the bus.
ibloc Sets the device to local control mode.
ibonl Sets the device online or offline.
ibpad Sets the device’s primary GPIB address.
ibppc Configures parallel polling.
ibrd Reads data from a device to the indicated buffer.
ibrda Reads data from a device to the indicated buffer asynchronously.
ibrdf Reads data from a device to a file.
ibrdi Reads data from a device to the indicated buffer.
ibrdia Reads data from a device to the indicated buffer asynchronously.
ibrpp Performs parallel polling.
ibrsc Sends an interface clear (IFC) message or remote enable (REN) message
to request or release the system control.
ibrsv Requests service and changes the sequential polling status byte.
ibsad Sets or disables a board secondary GPIB address.
ibsic Sets the GPIB interface clear (IFC) line to enable at least 100 ns if the
GPIB interface is the system controller.
ibsre Sets or clears the remote enable (REN) line.
ibstop Stops the asynchronous I/O operation.
ibtmo Sets the board timeout period.
ibwait Monitors events until one or more events occur that are described by mask
or that delay operating.
ibwrt Writes data from a buffer to a device.
KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010 Return to Section Topics 2-7
Page 25

Section 2: NI Command-Compatible Functions Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual
Table 2-2: (continued) IEEE-488 board-level functions
Function Description
ibwrta Writes data from a buffer to a device asynchronously.
ibwrtf Writes data from a file to a device.
IEEE-488.2 functions
Table 2-3 contains IEEE-488.2 functions.
Table 2-3: IEEE-488.2 functions
Function Description
AllSpoll
DevClear
DevClearList
EnableLocal
EnableRemote
FindLstn
FindRQS
PassControl
PPoll
PPollConfig
PPollUnconfig
RcvRespMsg
ReadStatusByte
Receive
ReceiveSetup
ResetSys
Send
SendCmds
SendDataBytes
SendIFC
SendList
SendLLO
SendSetup
SetRWLS
TestSRQ
TestSys
Trigger
TriggerList
WaitSRQ
Polls one or more devices sequentially.
Sends the selected device clear (SDC) GPIB message to clear
the selected device.
Clears multiple devices.
Sends go to local (GTL) GPIB message to multiple devices to
allow local operation of the devices.
Sets remote enable (REN) line to allow remote programming of
devices.
Finds listening devices on the GPIB bus.
Sequentially polls devices to determine which device is requesting
service.
Sends take-control (TCT) GPIB message, allowing control to pass
to another GPIB device with control capability.
Performs parallel polling once.
Controls or releases GPIB data line to configure the device to
respond to parallel polling.
Removes configuration that allows device to respond to parallel
polling.
Reads data from a device.
Sequentially polls a device.
Reads data bytes from a device and then stores them in the
assigned buffer.
Configures device and interface to a talker and a receiver.
Resets and initializes the devices.
Writes data bytes from the buffer to the device.
Sends GPIB commands.
Sends data from the buffer to the device.
Sends the interface clear command to reset GPIB.
Sends data bytes to multiple GPIB devices.
Sends the local lockout (LLO) message to all devices.
Configures device to receive data.
Configures device to lockout status of remote-control mode.
Detects current status of the GPIB service request (SRQ) line.
Causes devices to process self tests; sends the "TST?" message
to the devices.
Sends group execute trigger (GET) GPIB message to a device.
Sends group execute trigger (GET) GPIB message to multiple
devices.
Waits until the device controls the GPIB SRQ line.
2-8 Return to Section Topics KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010
Page 26

Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual Section 2: NI Command-Compatible Functions
Data types
The GPIB.BAS file defines some data types. The defined data types are used by the NI
command-compatible function library and are suggested for your applications. Table 2-4 shows
the names, ranges, and the corresponding data types in Visual C/C++, Visual Basic, and Delphi.
These data types are not defined in either the GPIB.BAS or GPIB.PAS files (they are listed for
reference).
Table 2-4: Data types
Type
Visual C/C++
(32-bit
Type name Description Range (approximate)
U8 8-bit ASCII
character
I16 16-bit signed integer -32768 to 32767 Short Integer Word
U16
Addr4882_t
I32 ssize_t 32-bit signed integer -2147483648 to
U32 size_t 32-bit unsigned
F32 32-bit single-
F64 64-bit double-
16-bit unsigned
integer
integer
precision floating-
point
precision floating-
point
0 to 255 Unsigned
0 to 65535 Unsigned short Not
2147483647
0 to 4294967295 Unsigned long Not
-3.402823E38 to
3.402823E38
-1.797683134862315E308
to 1.797683134862315E309
compiler) Visual Basic Byte
Byte Small
character
supported;
placed by I16
Long Long Cardinal
supported;
placed by I32
Float Single Double
Double Double Double
integer
Long
integer
Single
NI command-compatible function reference
Use this section as a function reference for NI command-compatible functions. Refer to Section 1
for information about Keithley Command-Compatible Functions.
ibask
Description This command returns the current value of the selected configuration item.
Support Level Board / device level
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
int ibask (int ud, int option, int *value)
Visual Basic
ibask (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal opt As Integer,
rval As Integer) As Integer
-or-
call ibask (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal opt As
Integer, rval As Integer)
KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010 Return to Section Topics 2-9
Page 27

Section 2: NI Command-Compatible Functions Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual
Parameters ud: board or device unit descriptor
option: the configuration item value will be returned (refer to valid options as
shown in Table 2-5 and Table 2-6)
value: the current value of the selected configuration item returned
Return value The value of the ibsta
Error Codes EARG, ECAP, EDVR
Table 2-5: ibask board configuration parameter options
Options
(constants)
ibaPAD 0x0001 The board current primary address.
ibaSAD 0x0002 The board current secondary address.
ibaTMO 0x0003 The board current I/O timeout.
ibaEOT 0x0004 0: After termination of the writing operation, the GPIB EOI line is not
ibaPPC 0x0005 The current parallel polling configuration board setting.
ibaAUTOPOLL 0x0007 0: Disable the automatic sequential polling.
ibaCICPROT 0x0008 0: Disable the CIC protocol.
ibaIRQ 0x0009 0: Disable the interrupts.
ibaSC 0x000A 0: The board is not the GPIB system controller.
ibaSRE 0x000B 0: While the board becomes the system controller, the GPIB REN line
ibaEOSrd 0x000C 0: Ignore the EOS character during reading.
ibaEOSwrt 0x000D 0: The EOI line is not set to enable while the EOS character is sent
ibaEOScmp 0x000E 0: Compare all EOS with 7 bits.
ibaEOSchar 0x000F The board current EOS character.
ibaPP2 0x0010 0: The board in the PP1 mode (remote parallel polling configuration).
ibaTIMING 0x0011 The current board bus timing.
ibaDMA 0x0012 0: DMA is not used for GPIB transfer.
ibaSpollBit 0x0016 0: Disable the SPOLL bit of the ibsta.
Options
(Value) Returned information
set to enable.
1: After termination of the writing operation, the GPIB EOI line is set to
enable.
1: Enable the automatic sequential polling.
1: Enable the CIC protocol.
1: Enable the interrupts.
1: The board is the GPIB System Controller.
is not set to enable automatically.
1: While the board becomes the system controller, the GPIB REN line
is set to enable automatically.
1: The reading is stopped while the EOS character is read.
during writing.
1: The EOI line is set to enable while the EOS character is sent during
writing.
1: Compare all EOS with 8 bits.
1: The board in the PP2 mode (local parallel polling configuration).
1: Normal timing (2 μs T1 delay).
2: High speed timing (500 ns T1 delay).
3: Very high-speed timing (350 ns T1 delay).
1: DMA is used for GPIB transfer.
1: Enable the SPOLL bit of the ibsta.
2-10 Return to Section Topics KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010
Page 28

Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual Section 2: NI Command-Compatible Functions
Table 2-5: (continued) ibask board configuration parameter options
Options
(constants)
ibaSendLLO 0x0017 0: The GPIB LLO command is not sent while the device is
ibaPPollTime 0x0019 0: Use standard continue time (2 μs) during parallel polling.
ibaEndBitIsNormal al0x001A 0: The END bit of the
ibaist 0x0020 The individual status (ist) bit of the board.
ibaRsv 0x0021 The current status word of the sequential polling of the board.
Options
(Value) Returned information
connected by ibfind or ibdev.
1: The
GPIB LLO command is sent while the device is connected
ibfind or ibdev.
by
1 to 17 (approximate): Use different continue time during parallel
polling; time corresponds to the
and EOS are received; if the EOS is received without EOI, the END bit
is not set.
1: When EOI, EOS, or both EOI and EOS is received, the END bit is
set.
ibtmo timing value.
ibsta is set only when the EOI or both EOI
Table 2-6: ibask device configuration p arameter options
Options
(constants)
ibaPAD 0x0001 The current device primary address.
ibaSAD 0x0002 The current device secondary address.
ibaTMO 0x0003 The current device I/O timeout.
ibaEOT 0x0004 0: After termination of the writing operation, the GPIB EOI line is not
ibaREADDR 0x0006 0: The unnecessary addressing is not operated during the device-level
ibaEOSrd 0x000C 0: Ignore the EOS character during reading.
ibaEOSwrt 0x000D 0: The EOI line is not set to enable when the EOS character is sent
ibaEOScmp 0x000E 0: Compare all EOS with 7 bits.
ibaEOSchar 0x000F The board current EOS character.
ibaSPollTime 0x0018 The waiting time of the driver for the sequential polling response. The
ibaEndBitIsNormal al0x001A 0: The END bit of the ibsta is set only when the EOI or both EOI and
ibaBNA 0x0200 The index of the GPIB access board for the assigned device
Options
(values) Returned information
set to enable.
1: After termination of the writing operation, the GPIB EOI line is set to
enable.
writing or reading.
1: The addressing is operated continuously during the device-level
writing or reading.
1: The reading is stopped while the EOS character is read.
during writing.
1: The EOI line is set to enable when the EOS character is sent during
writing.
1: Compare all EOS with 8 bits.
time is represented by ibtmo timing value.
EOS are received; if the EOS is received without EOI, the END bit is
not set.
1: When the EOI, EOS, or both EOI and EOS is received, the END bit
is set.
descriptor.
KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010 Return to Section Topics 2-11
Page 29

Section 2: NI Command-Compatible Functions Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual
ibbna
Description This command assigns the device unit descriptor to the board name.
Support Level Device level
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
int ibbna (int ud, char *board_name)
Syntax Visual Basic
ibbna (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal udname As String)
As Integer
- or -
call ibbna (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal udname As String)
Parameters ud: Device unit descriptor
board_name: The access board name; gpib0 for example
Return value The value of the ibsta
Error Codes EARG, ECAP, EDVR, EOIP, ENEB
ibcac
Description Sets the assigned GPIB board to be the active controller by setting the ATN line to
enable. The GPIB board must be the controller-in-charge (CIC) before calling
ibcac. Use ibsic to set the board as the CIC. The board can take control
synchronously (1), asynchronously (2), or either (v). If either, the GPIB board tries
to create the ATN signal but does not terminate the data transfer (synchronous
control is tried first). If this fails, the board takes asynchronous control by
immediately creating the ATN signal without considering any current data transfer
for asynchronous control.
Support Level Board level
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
int ibcac(int ud, int synchronous)
Visual Basic
idcac (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal v As Integer) As
Integer
- or -
call ibcac (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal v As Integer)
Parameters ud: Board unit descriptor
v: Either synchronous or asynchronous control
0: Asynchronously
1: Synchronously
Return value The value of the ibsta
Error Codes EARG, ECIC, EDVR, EOIP, ENEB
2-12 Return to Section Topics KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010
Page 30

Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual Section 2: NI Command-Compatible Functions
ibclr
Description This command sends the GPIB selected device clear (SDC) message to the
assigned device.
Support Level Device level
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
int ibclr (int ud)
Visual Basic
idclr (ByVal ud As Integer) As Integer
- or -
call ibclr (ByVal ud As Integer)
Parameters ud: Device unit descriptor
Return value The value of the ibsta
Error Codes EARG, EBUS, ECIC, EDVR, EOIP, ENEB
ibcmd
Description Sends GPIB commands. Command words are used to configure the GPIB status;
ibwrt is used to send the device self-control command. To return the number of
transferred command bytes in the global variable, use ibcntl.
Support Level Board level
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
int ibcmd (int ud, const void *cmd, long cnt)
Visual Basic
idcmd (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal buf As String,
ByVal cnt As Long) As Integer
- or -
call ibcmd (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal buf As
String)
Parameters ud: Device unit descriptor
buf: The buffer contains the sent command string
cnt: The number of the command bytes; the command bytes that are to
be sent
Return value The value of the ibsta
Error Codes EARG, ECIC, EDVR, EOIP, ENEB, EABO, ENOL
ibcmda
Description This command sends GPIB commands asynchronously. Command words are
used to configure the GPIB status and control GPIB devices; ibwrt is used to
send the device self-control command. To return the number of transferred
command bytes in the global variable, use ibcntl.
KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010 Return to Section Topics 2-13
Page 31

Section 2: NI Command-Compatible Functions Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual
The asynchronous I/O commands (ibcmda, ibrda, ibwrta) are designed so
that applications can perform other non-GPIB operations while the I/O is in
progress. If asynchronous I/O has begun, later GPIB commands are strictly
limited; any commands that would interfere with the I/O that is in progress are not
allowed. If the I/O has completed, the application and the driver must be
resynchronized.
Use one of the following functions to resynchronize:
ibwait: If the CMPL bit of the returned ibsta is set, the driver and application are
resynchronized.
ibnotify: If the ibsta value sent to the ibnotify callback contains CMPL, the driver
and application are resynchronized.
ibstop: The I/O is stopped, and the driver and application are resynchronized.
ibonl: The I/O is stopped and the interface is reset; the driver and application
are resynchronized.
Support Level Board level
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
int ibcmda (int ud, const void *cmd, long cnt)
Syntax Visual Basic
Parameters ud: Device unit descriptor
Return value The value of the ibsta
Error Codes EARG, ECIC, EDVR, EOIP, ENEB, EABO, ENOL
ibconfig
Description This command sets the value of the selected configuration item.
Support Level Board / device level
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
idcmda (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal buf As String,
ByVal cnt As Long) As Integer
- or -
call ibcmda (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal buf As
String)
buf: The buffer contains the sent command string
cnt: The number of the command bytes; the command bytes to be sent
int ibconfig (int ud, int option, int value)
Syntax Visual Basic
idconfig (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal opt As Integer,
ByVal v As Integer) As Integer
- or -
call ibconfig (ByVal ud As Integer,
ByVal opt As Integer, ByVal v As Integer)
2-14 Return to Section Topics KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010
Page 32

Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual Section 2: NI Command-Compatible Functions
Parameters ud: Board or device unit descriptor
opt: The configuration item that needs to be changed (valid options are
shown in Table 2-7 and Table 2-8)
v: The value of the configuration item that needs to be changed
Return value The value of the ibsta
Error Codes EARG, ECAP, EDVR, EOIP
Table 2-7: Board configuration parameter options
Options
(constants)
ibcPAD
ibcSAD
ibcTMO
ibcEOT
ibcPPC
ibcAUTOPOLL
ibcSC
ibcSRE
ibcEOSrd
ibcEOSwrt
ibcEOScmp
ibcEOSchar
ibcPP2
ibcTIMING
ibcReadAdjust
ibcWriteAdjust
ibcSpollBit
Options
(value) Valid values
0x0001 Set the board current primary address.
0x0002 Set the board current secondary address.
0x0003 Set the board current I/O timeout.
0x0004 Set the data termination mode for writing.
0x0005 Configure the board for parallel polling.
Default: 0.
0x0007 0: Disable the automatic sequential polling.
1: Enable the automatic sequential polling.
0x000A Request or release system control. The same as ibrsc.
0x000B Control the remote enable (REN) line. The same as ibsre.
Default: 0.
0x000C 0: Ignore the EOS character during reading.
1: The reading is stopped while the EOS character is read.
0x000D 0: The EOI line is not set to enable while the EOS character is sent
during writing.
1: The EOI line is set to enable while the EOS character is sent
during writing.
0x000E 0: Compare all EOS with 7 bits.
1: Compare all EOS with 8 bits.
0x000F Any 8-bit value. This byte becomes the new EOS character.
0x0010 0: The board in the PP1 mode (remote parallel-polling
configuration).
1: The board in the PP2 mode (local parallel-polling configuration).
Default: 0.
0x0011 0: Disable.
1: Normal timing (2 μs T1 delay).
2: High-speed timing (500 ns T1 delay).
3: Very high-speed timing (350 ns T1 delay).
Default: 0.
The T1 delay is the GPIB source handshake timing.
0x0013 0: No byte swapping.
1: Swap pairs of bytes during reading.
Default: 0.
0x0014 0: No byte swapping.
1: Swap pairs of bytes during writing.
Default: 0.
0x0016 0: Disable the SPOLL bit of the ibsta.
1: Enable the SPOLL bit of the ibsta.
Default: 0.
KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010 Return to Section Topics 2-15
Page 33

Section 2: NI Command-Compatible Functions Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual
Table 2-7: (continued) Board configuration parameter options
Options
(constants)
ibcSendLLO
ibcPPollTime
ibcEndBitIsNormal
ibcist
ibcRsv
Options
(value) Valid values
0x0017 0: The GPIB LLO command is not sent while the device is
connected by ibfind or ibdev.
1: The GPIB LLO command is sent while the device is connected
by ibfind or ibdev.
Default: 0.
0x0019 0: Use standard continue time (2 μs) during parallel polling.
1 to 17 (approximate): Select a different continue time during
parallel polling; the time selected corresponds with the ibtmo timing
value.
Default: 0.
al0x001A 0: While the EOS is received, the END bit of the ibsta is not set.
1: While the EOS is received, the END bit of the ibsta is set.
Default: 1.
0x0020 Set the individual status (ist) bit of the board.
0x0021 Set the status byte of the board sequential polling.
Default: 0.
Table 2-8: Device configuration parameter options
Options
(constants)
ibcPAD 0x0001
ibcSAD 0x0002
ibcTMO 0x0003
ibcEOT 0x0004
ibcREADDR 0x0006
ibcEOSrd 0x000C
ibcEOSwrt 0x000D
ibcEOScmp 0x000E
ibcEOSchar 0x000F
ibcSPollTime 0x0018
ibcEndBitIsNormal al0x001A
Options
(values) Returned information
Set the current device primary address.
Set the current device secondary address.
Set the current device I/O timeout.
Set the data termination mode for writing.
0: Unnecessary addressing is not operated during device-level
writing or reading.
1: Addressing is operated continuously during the device-level
writing or reading.
0: Ignore the EOS character during reading.
1: The reading is stopped while the EOS character is read.
0: The EOI line is not set to enable while the EOS character is sent
during writing.
1: The EOI line is set to enable while the EOS character is sent
during writing.
0: Compare all EOS with 7 bits.
1: Compare all EOS with 8 bits.
Any 8-bit value. This byte becomes the new EOS character.
0 to 17 (approximate): Set the waiting time of the driver for the
sequential polling response. The time is represented by ibtmo
timing value.
Default: 11.
0: When the EOS is received, the END bit of the ibsta is not set.
1: When the EOS is received, the END bit of the ibsta is set.
Default: 1.
ibdev
Description Opens and initializes a device descriptor. If ibdev cannot get a valid device
descriptor, -1 is returned; the ERR bit of the ibsta and the EDVR bit of the iberr are
set.
2-16 Return to Section Topics KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010
Page 34

Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual Section 2: NI Command-Compatible Functions
Support Level Device level
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
int ibdev (int board_index, int pad, int sad,
int tmo, int send_eoi, int eosmode)
Visual Basic
ildev (ByVal bdid As Integer, ByVal pad As Integer,
ByVal sad As Integer, ByVal tmo As Integer,
ByVal eot As Integer, ByVal eos As Integer)
As Integer
- or -
call ibdev (ByVal bdid As Integer, ByVal pad As
Integer, ByVal sad As Integer, ByVal tmo As Integer,
ByVal eot As Integer, ByVal eos As Integer,
ud As Integer)
Parameters board_index: The index of the device access board
pad: The device primary GPIB address
ibdma
sad: The device secondary GPIB address
tmo: The I/O timeout value
eot: Enable or disable the device EOI mode
eos: Configure the device EOS character and device EOS modes
Return value The device descriptor or -1
Error Codes EARG, EDVR, ENEB
Description This function, which is not supported for the Model KPCI-488LP, enables or
disables DMA.
Support Level Board level
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
int ibdma (int ud, int v)
Visual Basic
ibdma (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal v As Integer)
As Integer
- or -
call ibdma (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal v As Integer)
Parameters ud: Board descriptor
dma: Enable or disable DMA mode
Return value The value of the ibsta
Error Codes EARG, ECAP, EDVR, ENEB, EOIP
KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010 Return to Section Topics 2-17
Page 35

Section 2: NI Command-Compatible Functions Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual
ibeot
Description Enables or disables the action that is setting GPIB EOI line to enable while the I/O
operation is completed. If the EOT mode is enabled, the EOI line is set to enable
while the last GPIB is written to bytes. Otherwise, there is no operation to be
performed while the last byte is sent.
Support Level Board / device level
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
int ibeot (int ud, int v)
Visual Basic
ileot (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal v As Integer)
As Integer
- or -
call ibeot (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal v As Integer)
Parameters ud: Board or device descriptor
v: Enable or disable eot mode
ibeos
Return value The value of the ibsta
Error Codes EDVR, ENEB, EOIP
Description Configures the EOS termination mode or character.
NOTE Defining an EOS byte does not automatically send it when I/O writing is terminated; you
must set the EOS byte after the data strings have been defined by the application.
Support Level Board / device level
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
int ibeot (int ud, int v)
Visual Basic
ibeos (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal v As Integer)
As Integer
- or -
call ibeos (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal v As Integer)
Parameters ud: Board or device descriptor
v: EOS mode and character information.
If v = zero: The EOS configuration is disabled.
If v is not = 0: Lower byte is the EOS character; upper byte
contains flags that define the EOS mode. Table 2-9
2-18 Return to Section Topics KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010
Page 36

Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual Section 2: NI Command-Compatible Functions
shows the different EOS configurations and the
corresponding values of v.
Configure Bits A and C to set I/O reading termination:
If Bit A = set, Bit C = clear: The I/O reading terminates when a byte
matching the low seven bits of the EOS character is received.
If Bit A = set, Bit C = set: The I/O reading terminates when a byte
matching all eight bits of the EOS character is received.
Configure Bits B and C to set GPIB EOI line control during I/O writing:
If Bit B = set, Bit C = clear: The EOI line is enabled when a byte
matching the low seven bits of the EOS character is written.
If Bit B = set, Bit C = set: The EOI line is enabled when a byte
matching all eight bits of the EOS character is written.
Table 2-9: EOS mode v value
v value
ibfind
EOS mode
Terminate reading when the
EOS is detected.
Through the write function,
set EOI with EOS.
Compare the entire eight bits
of the EOS byte rather than
the low seven bits.
Bit Upper byte Low byte
A 00000100 EOS character
B 00001000 EOS character
C 00010000 EOS character
Return value The value of the ibsta
Error Codes EARG, EDVR, ENEB, EOIP
Description Opens and initializes the GPIB board descriptor, which can be used in later
commands. Similar to the ibonl 1 command, the ibfind command performs a
board description initialization. Before the board is put offline by using the ibonl
0 command, the descriptor that is returned by ibfind is valid; -1 is returned if
ibfind is unable to get a valid descriptor. At the same time, the ERR bit of the
ibsta and the EDVR bit of the iberr are set.
Support Level Board level
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
int ibfind (const char *boardname)
Visual Basic
ibfind (ByVal boardname As String) As Integer
- or -
call ibfind (ByVal boardname As String, ud As
Integer)
KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010 Return to Section Topics 2-19
Page 37

Section 2: NI Command-Compatible Functions Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual
Parameters boardname: Board name, for example, gpib0
Return value The board descriptor or -1
Error Codes EBUS, ECIC, EDVR, ENEB
ibgts
Description Sets the board from active control status to standby control status. The ibgts
command sets the GPIB board as the standby control unit and releases the
control of the GPIB ATN line.
Support Level Board level
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
int ibgts (int ud, int shadow_handshake)
Visual Basic
ibgts (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal v As Integer)
As Integer
- or -
call ibgts (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal v As Integer)
ibist
Parameters ud: Board descriptor
v: Determines whether to handshake with receiver
Return value The value of the ibsta
Error Codes EADR, EARG, ECIC, EDVR, ENEB, EOIP
Description Sets or clears the board individual status (ist) bit for parallel polling.
Support Level Board level
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
int ibist (int ud, int ist)
Visual Basic
ibist (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal v As Integer)
As Integer
- or -
call ibist (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal v As Integer)
Parameters ud: Board descriptor
v: Shows whether to set or clear the ist bit
Return value The value of the ibsta
Error Codes EARG, EDVR, ENEB, EOIP
2-20 Return to Section Topics KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010
Page 38

Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual Section 2: NI Command-Compatible Functions
iblines
Description Returns the GPIB control lines status. The low-order lines byte (Bits 0 to 7) shows
that the GPIB interface has the capability to automatically detect the status of
each GPIB control line. The upper byte (Bits 8 to 15) shows the status of the GPIB
control line. A description of each byte is listed in Table 2-10.
To determine whether a GPIB line is controlled:
1. Check the appropriate bit of the low byte to ensure the line can be monitored.
2. Check whether the corresponding bit of the upper byte can be monitored (the
appropriate bit of the low byte is 1).
If the checked bit of the upper byte is set (1), the corresponding line is in
controlled status; if the checked bit of the upper byte is clear (0), the
corresponding line is not in controlled status.
Table 2-10: iblines
765432 1 0
EOI ATN SRQ REN INF NRFD NDAC DAV
ibln
Support Level Board level
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
int iblines (int ud, short *line_status)
Visual Basic
iblines (ByVal ud As Integer, lines As Integer)
As Integer
- or -
call iblines (ByVal ud As Integer, lines As Integer)
Parameters ud: Board descriptor
line_status: The status information of the returned GPIB control line
Return value The value of the ibsta
Error Codes EARG, EDVR, ENEB, EOIP
Description Determines if there is an available device on the bus.
Support Level Board / device level
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
int ibln (int ud, int pad, int sad,
short *found_listener)
Visual Basic
ibln (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal pad As Integer,
ByVal sad As Integer, found_listener As Integer)
As Integer
KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010 Return to Section Topics 2-21
Page 39

Section 2: NI Command-Compatible Functions Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual
- or -
call ibln (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal pad As Integer,
ByVal sad As Integer, found_listener As Integer)
Parameters ud: Board or device descriptor. The board tests for listeners if ud is a
board descriptor; ibln tests for listeners with the interface related to the device if
ud is a device descriptor. If a listener is detected, a nonzero value is returned in
the found_listener.
pad: Device primary address (addressing value between 0 and 30)
sad: The device secondary address (addressing value is between 96 and
126), NO_SAD or ALL_SAD.
NO_SAD: No secondary addressing; primary addressing only
ALL_SAD: Tests all secondary addresses
found_listener: Shows if there is a device available
Return value The value of the ibsta
Error Codes EARG, ECIC, EDVR, ENEB, EOIP
ibloc
Description If a board is not in lockout status, the ibloc command sets the board in local
control mode. If LOK does not exist in the status word, ibsta, the board is in a
lockout state. If a board is in lockout, calling ibloc has no effect.
If the computer is used as an apparatus, the ibloc command is used to simulate
a panel RTL (return to local) switch.
All device-level commands automatically set the device to remote mode (except
the Remote Enable (REN) line is not controlled by ibsre; ibloc is used to
temporarily set the device from remote mode to local mode before the next
device-level command is executed).
Support Level Board / device level
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
int ibloc (int ud)
Visual Basic
ibloc (ByVal ud As Integer) As Integer
- or -
call ibloc (ByVal ud As Integer)
Parameters ud: Board or device descriptor
Return value The value of the ibsta
Error Codes EBUS, ECIC, EDVR, ENEB, EOIP
2-22 Return to Section Topics KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010
Page 40

Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual Section 2: NI Command-Compatible Functions
ibonl
Description Resets the board or device parameters to default settings and sets the device
online or offline. If the device or interface is set to offline, the board or device
descriptor has no effect. Once called, use the ibdev or ibfind commands to
access the board or device.
Support Level Board / device level
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
int ibonl (int ud, int onl)
Visual Basic
ibonl (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal onl As Integer)
As Integer
- or -
call ibonl (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal onl As
Integer)
Parameters ud: Board or device descriptor
onl: Online (1) or offline (0)
Return value The value of the ibsta
Error Codes EARG, ENEB
ibnotify
Description Uses the selected callback function to notify you of one or more GPIB events. The
Support Level Board / device level
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
Parameters ud: Board or device descriptor
resynchronization handler is needed after the completion of the asynchronous I/O
operation; the global variable is passed to the callback function while the
operation of the I/O status is completed.
int ibnotify (int ud, int mask,
GpibNotifyCallback_t Callback, void *RefData)
mask: GPIB event code. Table 2-11 contains the valid event codes.
If GPIB mask is a non-zero value, the events specified by mask are
monitored by ibnotify; if one or more of the events appears, the
callback function is called. For board-level ibnotify call, all mask
bits are valid except for ERR and RQS. For device-level ibnotify
call, CMPL, TIMO, END, and RQS are the only valid mask bits. If
TIMO is set in the notify mask, ibnotify calls the callback function
even if no events have occurred during the time limit. If TIMO is not
KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010 Return to Section Topics 2-23
Page 41

Section 2: NI Command-Compatible Functions Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual
set in the notify mask, the callback function is not called until one or
more specified events occur.
Table 2-11: GPIB event codes for mask
Event
code Description
- 0 No mask
- TIMO The notify period is limited by the timeout period (see ibtmo)
- END END or EOS is detected
- SRQI SRQ signal is sent (only board level)
- RQS Device requested service (only device level)
- CMP I/O completion
- LOK GPIB interface is in lockout status (only board level)
- REM GPIB interface is in remote status (only board level)
- CIC GPIB interface is CIC (only board level)
- ATN Attention signal is sent (only board level)
- TACS GPIB interface is a talker (only board level)
- LACS GPIB interface is a listener (only board level)
- DTAS GPIB interface is in device trigger status (only board level)
- DCAS GPIB interface is in device clear status (only board level)
ibpad
Callback: The address callback function (Table 2-12 contains a description of
the function’s properties)
Table 2-12: Callback description (for ibnotify)
Property Description
Prototype int_std call Callback (int LocalUd,
int Localibsta, int LocalIberr,
long LocalIbcntl, void *RefData)
Parameters LocalUd: Board or device descriptor
ibsta: The ibsta value
Local
LocalIberr: The iberr value
LocalIbcntl: The ibcntl value
RefData: The user-defined reference data for the
callback function
Return value The next mask of the notified GPIB event
Error code EDVR
RefData: The user-defined reference data for the callback function
Return value The value of the ibsta
Error Codes EARG, ECAP, EDVR, ENEB, EOIP
.
Description Sets a board or device primary GPIB address.
Support Level Board / device level
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
int ibpad (int ud, int v)
2-24 Return to Section Topics KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010
Page 42

Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual Section 2: NI Command-Compatible Functions
Visual Basic
ibpad (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal v As Integer)
As Integer
- or -
call ibpad (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal v As Integer)
Parameters ud: Board or device descriptor
v: The GPIB primary address (the valid range is 0 to 30)
Return value The value of the ibsta
Error Codes EARG, EDVR, ENEB, EOIP
ibsad
Description Sets or disables a board or device secondary GPIB address.
Support Level Board / device level
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
int ibsad (int ud, int v)
ibpct
Visual Basic
ibsad (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal v As Integer)
As Integer
- or -
call ibsad (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal v As Integer)
Parameters ud: Board or device descriptor
v: Set or disable the GPIB secondary address
If v = 0: The secondary address is disabled
If v is not = 0: The secondary address is enabled with a secondary
address valid range of 96 to 126 (0x60 to 0x7E)
Return value The value of the ibsta
Error Codes EARG, EDVR, ENEB, EOIP
Description Passes controller-in-charge (CIC) status to another GPIB device that has
controller capability. The interface automatically releases the ATN line and goes to
controller idle status (CIDS).
Support Level Device level
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
int ibpct (int ud)
Visual Basic
ibpct (ByVal ud As Integer) As Integer
KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010 Return to Section Topics 2-25
Page 43

Section 2: NI Command-Compatible Functions Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual
- or -
call ibpct (ByVal ud As Integer)
Parameters ud: Device descriptor
Return value The value of the ibsta
Error Codes EARG, EBUS, ECIC, EDVR, ENEB, EOIP
ibppc
Description Configures parallel polling.
If ud is a device descriptor: The ibppc command enables or disables the
device response to parallel polling. The addressed device sends the parallel poll
enable (PPE) or parallel poll disable (PPD) message. Valid parallel poll messages
are 96 to 126 (hex 60 to hex 7E) or zero corresponding to sent PPD.
If ud is a board descriptor: The ibppc command uses the parallel poll
configuration value v to perform a local parallel poll configuration. Valid parallel
poll messages are 96 to 126 (hex 60 to hex 7E) or zero corresponding to send
PPD. If there are no errors within the calling period, iberr maintains the previous
value of the local parallel poll configuration.
ibrd
Support Level Board / device level
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
int ibppc (int ud, int v)
Visual Basic
ibppc (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal v As Integer)
As Integer
- or -
call ibppc (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal v As Integer)
Parameters ud: Device descriptor
v: Enable/disable parallel polling
Return value The value of the ibsta
Error Codes EARG, EBUS, ECAP, ECIC, EDVR, ENEB, EOIP
Description Reads data from a device to the indicated buffer.
The GPIB is addressed by ibrd, which reads count data bytes (count is the
counting value in the counter)
When ud is the device descriptor: The count data bytes are placed in the user
buffer. The operation ends when the count data bytes have been read or when
END is read. If the count bytes reading does not finish before the timeout period
ends, the operation stops with an error. The actual number of transferred bytes is
returned in the global variable, ibcntl.
When ud is the board descriptor: Count data bytes are read by ibrd and placed
in the user buffer. The GPIB has already been addressed by the board-level ibrd;
the operation ends when the count data bytes or END are read. If the count bytes
2-26 Return to Section Topics KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010
Page 44

Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual Section 2: NI Command-Compatible Functions
reading is not complete within the timeout period (or the board is not CIC, and CIC
sends the device clear message on the GPIB bus), the operation stops with an
error. The actual number of transferred bytes is returned in the global variable,
ibcntl.
Support Level Board / device level
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
int ibrd (int ud, void *buf, long cnt)
Visual Basic
ibrd (ByVal ud As Integer, buf As String,
ByVal cnt As Long) As Integer
- or -
call ibrd (ByVal ud As Integer, buf As String)
Parameters ud: Device descriptor
buf: The buffer that stores the data read from the GPIB
cnt: The number of the bytes read from the GPIB
ibrda
Return value The value of the ibsta
Error Codes EABO, EADR, EBUS, ECIC, EDVR, ENEB, EOIP
Description Asynchronously reads data from a device to the designated buffer. The GPIB is
addressed by ibrda, which reads count data bytes (count is the counting value in
the counter).
When ud is the device descriptor: The count data bytes are placed in the user
buffer. The operation ends when the count data bytes or END are read. If the count
bytes reading does not finish before the timeout period ends, the operation stops
with an error. The actual number of transferred bytes is returned in the global
variable, ibcntl.
When ud is the board descriptor: Count data bytes are read by ibrda and
placed in the user buffer. The GPIB has already been addressed by the
board-level ibrda; the operation ends when the count data bytes or END are read.
If the count bytes reading is not complete within the timeout period (or the board is
not CIC, and CIC sends the device clear message on the GPIB bus), the
operation stops with an error. The actual number of transferred bytes is returned
in the global variable, ibcntl.
The asynchronous I/O commands (ibcmda, ibrda, ibwrta) are designed so
that applications can perform other non-GPIB operations while the I/O is in
progress. Once the asynchronous I/O has begun, later GPIB commands are
KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010 Return to Section Topics 2-27
Page 45

Section 2: NI Command-Compatible Functions Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual
strictly limited; any command that would interfere with the I/O in progress will not
be allowed. In this case, EOIP is returned by the driver.
When the I/O is complete, the application and the driver must be resynchronized.
Use one of the following functions to resynchronize:
ibwait: If the CMPL bit of the returned ibsta is set, the driver and application
are resynchronized.
ibnotify: If the ibsta value sent to the ibnotify callback contains CMPL, the driver
and application are resynchronized.
ibstop: The I/O is stopped, and the driver and application are
resynchronized.
ibonl: The I/O is stopped and the interface is reset; the driver and
application are resynchronized.
Support Level Board / device level
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
int ibrda (int ud, void *buf, long cnt)
Visual Basic
ibrdf
ibrda (ByVal ud As Integer, buf As String, ByVal cnt
As Long) As Integer
- or -
call ibrda (ByVal ud As Integer, buf As String)
Parameters ud: Device descriptor
buf: The buffer that stores the data read from the GPIB
cnt: The number of the bytes read from the GPIB
Return value The value of the ibsta
Error Codes EABO, EADR, EBUS, ECIC, EDVR, ENEB, EOIP
Description Reads data from a device and saves it to a file.
The GPIB is addressed by ibrdf, which reads the data bytes from the GPIB
device, then saves them to a file (when ud is a device descriptor). The operation
stops when END is read. If the data transfer does not finish before the timeout
period ends, the operation stops with an error. The actual number of transferred
bytes is returned in the global variable, ibcntl.
Data bytes are read from the GPIB device by ibrdf, then saved to a file when ud
is the board descriptor. The GPIB has already been addressed by the board-level
ibrdf; the operation stops when END is read. If the data transfer is not complete
within the timeout period (or the board is not CIC, and CIC sends the Device
Clear message on the GPIB bus), the operation stops with an error. The actual
number of transferred bytes is returned in the global variable, ibcntl.
Support Level Board / device level
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
2-28 Return to Section Topics KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010
Page 46

Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual Section 2: NI Command-Compatible Functions
int ibrdf (int ud, const char *filename)
Visual Basic
ibrdf (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal filename As
String ) As Integer
- or -
call ibrdf (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal filename
As String)
Parameters ud: Device descriptor
filename: The file name; the file stores the read data
Return value The value of the ibsta
Error Codes EABO, EADR, EBUS, ECIC, EDVR, EFSO, ENEB, EOIP
ibrpp
Description Performs parallel polling.
ibrsc
Support Level Board / device level
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
int ibrpp (int ud, char *ppr)
Visual Basic
ibrpp (ByVal ud As Integer, ppr As Integer)
As Integer
- or -
call ibrpp (ByVal ud As Integer, ppr As Integer)
Parameters ud: Device descriptor
ppr: The parallel polling result
Return value The value of the ibsta
Error Codes EBUS, ECIC, EDVR, ENEB, EOIP
Description Sends the interface clear (IFC) or remote enable (REN) message to request or
release the system control. The operations that request system controller
capability are not allowed if the board releases system control; when the board
requests system control, operations that request system controller capability are
allowed.
Support Level Board level
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
int ibrsc (int ud, int v)
Visual Basic
ibrsc (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal v As Integer)
As Integer
KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010 Return to Section Topics 2-29
Page 47

Section 2: NI Command-Compatible Functions Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual
- or -
call ibrsc (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal v As Integer)
Parameters ud: Device descriptor
v: 0: Release system control; 1: Request system control
Return value The value of the ibsta
Error Codes EARG, EDVR, ENEB, EOIP
ibrsp
Description Performs sequential polling. The device is requesting service if Bit 6 of the
response is set. If automatic sequential polling is enabled, the device has already
been polled and the previous status byte value is returned by ibrsp.
Support Level Device level
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
int ibrsp (int ud, char *spr)
Visual Basic
ibrsv
ibrsp (ByVal ud As Integer, spr As Integer)
As Integer
- or -
call ibrsp (ByVal ud As Integer, spr As Integer)
Parameters ud: Device descriptor
spr: The sequential polling result
Return value The value of the ibsta
Error Codes EABO, EARG, EBUS, ECIC, EDVR, ENEB, EOIP, ESTB
Description Requests service and changes the status byte of the sequential polling.
Support Level Board level
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
ibrsv (int ud, int v)
Visual Basic
ibrsv (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal v As Integer)
As Integer
- or -
call ibrsv (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal v As Integer)
Parameters ud: Device descriptor
v: The status byte of the sequential polling
Return value The value of the ibsta
Error Codes EARG, EDVR, ENEB, EOIP
2-30 Return to Section Topics KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010
Page 48

Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual Section 2: NI Command-Compatible Functions
ibsic
Description Enables the GPIB interface clear (IFC) line to allow at least 100 ns when the GPIB
interface is the system controller by initializing the GPIB interface, designating it
as CIC, and activating the controller by setting ATN line.
Support Level Board level
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
int ibsic (int ud)
Visual Basic
ibsic (ByVal ud As Integer) As Integer
- or -
call ibsic (ByVal ud As Integer)
Parameters ud: Device descriptor
Return value The value of the ibsta
Error Codes EARG, EDVR, ENEB, EOIP, ESAC
ibsre
Description Sets or clears the remote enable (REN) line. The remote enable (REN) line is
used by devices to choose local or remote modes of operation; ibsre sets or
clears the REN line. The GPIB REN line is enabled when the remote enable line is
set, and disabled when the remote enable line is cleared. A device cannot enter
remote mode before it receives its listen address and the REN is initiated.
Support Level Board level
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
int ibsre (int ud, int v)
Visual Basic
ibsre (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal v As Integer)
As Integer
- or -
call ibsre (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal v As Integer)
Parameters ud: Board descriptor
v: Sets or clears REN line. 0: clear; 1: set
Return value The value of the ibsta
Error Codes EARG, EDVR, ENEB, EOIP, ESAC
ibstop
Description Stops asynchronous I/O operation. If the ibsta command is used when
asynchronous I/O is operating, the error code EABO is returned to show the I/O
was successfully stopped.
Support Level Board / device level
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010 Return to Section Topics 2-31
Page 49

Section 2: NI Command-Compatible Functions Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual
int ibstop (int ud)
Visual Basic
ibstop (ByVal ud As Integer) As Integer
- or -
call ibstop (ByVal ud As Integer)
Parameters ud: Board or device descriptor
Return value The value of the ibsta
Error Codes EABO, EBUS, EDVR, ENEB
ibtmo
Description Sets the board or device timeout period. The timeout period is the maximum
continuous time allowed for synchronous I/O operation (ibrd and ibwrt for
example); or the maximum waiting time of ibwait or ibnotify that uses TIMO in the
mask. If the operation is not completed within the timeout period, the operation is
stopped and returns TIMO in ibsta.
Support Level Board / device level
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
int ibtmo(int ud, int v)
Visual Basic
ibtmo (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal v As Integer)
As Integer
- or -
call ibtmo (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal v As Integer)
Parameters ud: Board or device descriptor
v: Timeout period value. Valid timeout values are shown in Table 2-13.
Table 2-13: ibtmo timeout values
Constant v value Minimum timeout
TNONE 0 Disabled - no timeout period
T10 μs 1 10 μs
T30 μs 2 30 μs
T100 μs 3 100 μs
T300 μs 4 300 μs
T1 ms 5 1 ms
T3 ms 6 3 ms
T10 ms 7 10 ms
T30 ms 8 30 ms
T100 ms 9 100 ms
T300 ms 10 300 ms
T1 s 11 1 s
T3 s 12 3 s
T10 s 13 10 s
T30 s 14 30 s
T100 s 15 100 s
T300 s 16 300 s
2-32 Return to Section Topics KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010
Page 50

Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual Section 2: NI Command-Compatible Functions
Table 2-13: (continued) ibtmo timeout values
Constant v value Minimum timeout
T1000 s 17 1000 s
Return value The value of the ibsta
Error Codes EARG, EDVR, ENEB, EOIP
ibtrg
Description This command sends the group execute trigger (GET) message to a device.
Support Level Device level
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
int ibtrg (int ud)
Visual Basic
ibtrg (ByVal ud As Integer) As Integer
- or -
ibwait
call ibtrg (ByVal ud As Integer)
Parameters ud: Device descriptor
Return value The value of the ibsta
Error Codes EARG, EBUS, ECIC, EDVR, ENEB, EOIP
Description ibwait waits for one or more events described by mask (including TIMO) to
occur. If TIMO in the wait mask is set, ibwait returns when the timeout period has
expired even if no other GPIB events occur. Setting TIMO to zero returns the
newest ibsta immediately. If the TIMO in the wait mask is cleared, the function
waits indefinitely for a GPIB event (described by mask).
The present ibwait mask bits are the same as ibsta bits. Only the TIMO, END,
RQS, and CMPL are valid wait mask bits if ud is a device descriptor. Except for
RQS, if ud is a board descriptor, all wait mask bits are valid.
Support Level Board / device level
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
int ibwait (int ud, int mask)
Syntax Visual Basic
ibwait (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal mask As Integer)
As Integer
- or -
call ibwait (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal mask As
Integer)
KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010 Return to Section Topics 2-33
Page 51

Section 2: NI Command-Compatible Functions Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual
Parameters ud: Board or device descriptor
mask: GPIB events that can be monitored. Valid code values are shown in
Table 2-14.
Table 2-14: ibwait valid mask codes
Mask Bit position Hex value Description
ERR 15 8000 GPIB error
TIMO 14 4000 Mask timeout
END 13 2000 END or EOS is detected by GPIB board
SRQI 12 1000 Send SRQ signal (only board)
RQS (only device
level)
SPOLL 10 400 Controller sequentially polls the board
EVENT 9 200 A DTAS, DCAS, or IFC event occur
CMPL 8 100 I/O completed
LOC 7 80 GPIB board is in lockout status
REM 6 40 GPIB board is in remote status
CIC 5 20 GPIB board is in CIC status
ATN 4 10 Send attention signal
TACS 3 8 GPIB board as a talker
LACS 2 4 GPIB board as a listener
DTAS 1 2 GPIB board is in device trigger status
DCAS 0 1 GPIB board is in device clear status
11 800 Device requesting service
ibwrt
Return value The value of the ibsta
Error Codes EARG, EBUS, ECIC, EDVR, ENEB, ESRQ
Description Writes data from a buffer to a device.
When ud is a device descriptor: ibwrt addresses the GPIB and writes count
data bytes (cnt is the tallying value in the counter) from the board’s memory to
the GPIB device. The operation normally ends when cnt number of data bytes
have been written; if cnt number of bytes are not written completely during the
timeout period, the operation stops with an error. The number of bytes actually
transferred is returned in the global variable, ibcntl.
When ud is a board descriptor: The board-level ibwrt automatically writes
cnt data bytes from the buffer to the GPIB device. Normally, this operation ends
when the cnt number of data bytes are completely written; if cnt number of
bytes are not completely written during the timeout period (or, if the board is not
CIC and CIC sends the device clear message on the GPIB bus), the operation
stops with an error. The number of bytes actually transferred is returned in the
global variable ibcntl.
Support Level Board / device level
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
int ibwrt (int ud, const void *buf, long cnt)
Visual Basic
ibwrt (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal buf As String,
ByVal cnt As Long) As Integer
2-34 Return to Section Topics KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010
Page 52

Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual Section 2: NI Command-Compatible Functions
- or -
call ibwrt (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal buf As
String)
Parameters ud: Device unit descriptor
buf: The buffer that contains the sent data bytes
cnt: The number of sent data bytes
Return value The value of the ibsta
Error Codes EADR, EABO, EBUS, ECIC, EDVR, EOIP, ENEB, ENOL
ibwrta
Description Asynchronously writes data from a buffer to a device.
When ud is a device descriptor: ibwrta addresses the GPIB and writes count
data bytes (cnt is the tallying value in the counter) from the board’s memory to
the GPIB device. The operation normally ends when the count data bytes have
been written; if the count bytes are not written completely during the timeout
period, the operation stops with an error. The number of bytes actually transferred
is returned in the global variable ibcntl.
When ud is a board descriptor: The board-level ibwrt automatically writes cnt
data bytes from the buffer to the GPIB device. Normally, this operation ends when
the count data bytes are completely written; if cnt bytes are not written during the
timeout period (or, if the board is not CIC and CIC sends the device clear
message on the GPIB bus), the operation stops with an error. The number of
bytes actually transferred is returned in the global variable ibcntl.
The asynchronous I/O commands (ibcmda, ibrda, ibwrta) are designed so
that applications can perform other non-GPIB operations while the I/O is in
progress. If asynchronous I/O has begun, later GPIB commands are strictly
limited; any commands that would interfere with the I/O in progress are not
allowed. If the I/O has completed, the application and the driver must be
resynchronized.
Use one of the following functions to resynchronize:
ibwait: If the CMPL bit of the returned ibsta is set, the driver and application
are resynchronized.
ibnotify: If the ibsta value sent to the ibnotify callback contains CMPL, the
driver and application are resynchronized.
ibstop: The I/O is stopped, and the driver and application are
resynchronized.
ibonl: The I/O is stopped and the interface is reset; the driver and
application are resynchronized.
Support Level Board / device level
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
int ibwrta (int ud, const void *buf, long cnt)
KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010 Return to Section Topics 2-35
Page 53

Section 2: NI Command-Compatible Functions Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual
Visual Basic
ibwrta (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal buf As String,
ByVal cnt As Long) As Integer
- or -
call ibwrta (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal buf As
String)
Parameters ud: Device unit descriptor
buf: The buffer that contains the sent data bytes
cnt: The number of sent data bytes
Return value The value of the ibsta
Error Codes EADR, EABO, EBUS, ECIC, EDVR, EOIP, ENEB, ENOL
ibwrtf
Description This command writes data from a file to a device.
When ud is a device descriptor: ibwrtf addresses the GPIB and writes all
data bytes in filename to the GPIB device. The operation normally ends when
all the data bytes are written; if all the bytes are not written during the timeout
period, the operation stops with an error. The number of bytes actually transferred
is returned in the global variable ibcntl.
When ud is a board descriptor: The board-level ibwrtf automatically writes all
data bytes in filename to the GPIB device. Normally, this operation ends when
all the data bytes are completely written; if all data bytes are not written during the
timeout period (or, if the board is not CIC and CIC sends the device clear
message on the GPIB bus), the operation stops with an error. The number of
bytes actually transferred is returned in the global variable, ibcntl.
Support Level Board / device level
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
int ibwrtf (int ud, const char *filename)
Visual Basic
ibwrtf (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal filename As
String) As Integer
- or -
call ibwrtf (ByVal ud As Integer, ByVal filename
As String)
Parameters ud: Device descriptor
filename: The file name; the file contains the data written
Return value The value of the ibsta
Error Codes EABO, EADR, EBUS, ECIC, EDVR
2-36 Return to Section Topics KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010
Page 54

Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual Section 2: NI Command-Compatible Functions
Multi-device functions
This section contains an NI command-compatible multi-device IEEE-488 function reference. Refer
to Section 1 for information about Keithley Command-Compatible Functions.
AllSpoll
Description Sequentially polls one or more devices. The responses and number of responses
of the poll are individually stored in resultList and ibcntl.
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
void AllSpoll (int board_desc,
const Addr4882_t addressList[], short resultList[])
Visual Basic
call AllSpoll (ByVal board_desc As Integer,
addressList ( ) As Integer,
resultList ( ) As Integer)
Parameters board_desc:Board ID
addressList:The list of the device addresses ended by NOADDR
Error Codes EARG, EABO, EBUS, ECIC, EDVR, EOIP, ENEB
DevClear
Description Sends the selected device clear (SDC) GPIB message to clear the selected
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
Parameters board_desc: Board ID
Error Codes EARG, EBUS, ECIC, EDVR, EOIP, ENEB
DevClearList
resultList: The list of sequential poll responses of the devices; the devices
correspond to the device addresses in addrlist
device. If the address is constant NOADDR (the end point of the list), the universal
device clear (DCL) message is sent to all devices.
void DevClear (int board_desc, Addr4882_t address)
Visual Basic
call DevClear (ByVal board_desc As Integer,
ByVal address As Integer)
address: The device address; the device that needs to be cleared
Description Clears multiple devices. If the address is the constant NOADDR, the DCL
message is sent to all devices.
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
void DevClearList (int board_desc,
const Addr4882_t addressList[])
KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010 Return to Section Topics 2-37
Page 55

Section 2: NI Command-Compatible Functions Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual
Visual Basic
call DevClearList (ByVal ud As Integer,
addressList ( ) As Integer)
Parameters board_desc: Board ID
addressList: The list of the device addresses ended by NOADDR; the devices
that need to be cleared
Error Codes EARG, EBUS, ECIC, EDVR, EOIP, ENEB
EnableLocal
Description Sends a go to local (GTL) GPIB message to multiple devices, setting them in local
mode so they can operate locally. If only the constant in addrlist is NOADDR,
the remote enable (REN) GPIB line is set to disable.
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
void EnableLocal (int board_desc,
const Addr4882_t addressList[])
Visual Basic
Parameters Board_desc: board ID
Error Codes EARG, EBUS, ECIC, EDVR, EOIP, ENEB, ESAC
EnableRemote
Description This command sets the remote enable (REN) line to enable, which places
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
Parameters board_desc: Board ID
call EnableLocal (ByVal ud As Integer,
addressList ( ) As Integer)
addressList: The list of the device addresses ended by NOADDR; the devices
are waiting to return to local mode
addressList devices into a listen-active state, allowing them to be programmed
remotely (remote GPIB programmable).
void EnableRemote (int board_desc,
const Addr4882_t addressList[])
Visual Basic
call EnableRemote (ByVal ud As Integer,
addressList ( ) As Integer)
addressList: The list of the device addresses ended by NOADDR; the devices
are waiting to go to remote-control mode
Error Codes EARG, EBUS, ECIC, EDVR, EOIP, ENEB, ESAC
FindLstn
Description Finds listening devices on the GPIB bus testing all primary addresses in padlist
as follows:
2-38 Return to Section Topics KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010
Page 56

Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual Section 2: NI Command-Compatible Functions
If a device exists in a given padlist: The device primary address is stored in
resultlist.
If a device does not exist in the padlist: The function tests all the secondary
addresses of the primary ones and stores the addresses of any finding devices.
ibcntl includes the actual numbers of addresses stored in resultlist.
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
void FindLstn (int board_desc,
const Addr4882_t padList[], Addr4882_t resultList[],
int maxNumResults)
Visual Basic
call FindLstn (ByVal ud As Integer, padList ( )
As Integer, resultList ( ) As Integer,
ByVal maxNumResults As Integer)
Parameters board_desc: Board ID
padList: The list of the GPIB primary addresses ended by NOADDR
resultList: The list of all listening device addresses; the listening devices found
by the FindLstn function
Error Codes EARG, EBUS, ECIC, EDVR, EOIP, ENEB, ETAB
FindRQS
Description Sequentially polls devices to determine which device is requesting service; the
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
Parameters board_desc: Board ID
maxNumResults: The maximum number of the resultList
resulting byte is returned in ibcntl. ibcntl contains the index of the device
requesting service in addrList. If no device is requesting service, ETAB and the
index of NOADDR are individually returned in iberr and ibcntl.
void FindRQS (int board_desc, const Addr4882_t
addressList[], short *result)
Visual Basic
call FindRQS (ByVal ud As Integer, addressList ( )
As Integer, result As Integer)
addressList:The list of the GPIB primary addresses ended by NOADDR
result: The sequentially polled return byte of the device requesting service
Error Codes EARG, EBUS, ECIC, EDVR, EOIP, ENEB, ETAB
PassControl
Description Sends the take control (TCT) GPIB message to the device to pass control to
another GPIB device with control capability. The device changes to
controller-in-charge (CIC) status when the interface is no longer CIC status.
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010 Return to Section Topics 2-39
Page 57

Section 2: NI Command-Compatible Functions Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual
void PassControl (int board_desc, Addr4882_t address)
Visual Basic
call PassControl (ByVal board_desc As Integer,
ByVal address As Integer)
Parameters board_desc: Board ID
address: The list of the GPIB primary addresses ended by NOADDR
Error Codes EAGR, EBUS, ECIC, EDVR, EOIP, ENEB
PPoll
Description Performs parallel polling one time. The board sends a command to all devices
(see PPollConfig and PPollUnconfig). The controller can simultaneously
obtain one-bit status messages relayed from up to eight devices when parallel
polling is performed.
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
void PPoll (int board_desc, short *result)
Visual Basic
Parameters board_desc: Board ID
Error Codes EBUS, ECIC, EDVR, EOIP, ENEB
PPollConfig
Description Controls or releases the GPIB data line to configure the device to respond to
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
call PPoll (ByVal board_desc As Integer,
result As Integer)
result: The result of the parallel polling
parallel polling.
If lineSense is equal to the ist bit of the device: The assigned GPIB data line is
controlled in a parallel polling duration.
If lineSense is not equal to the ist bit of the device: The assigned data line is
not controlled in a parallel polling duration. The controller can simultaneously
obtain one-bit status messages related with it from up to eight devices by a
parallel polling.
void PPollConfig (int board_desc, Addr4882_t address,
int dataLine, int lineSense)
Visual Basic
call PPollConfig (ByVal ud As Integer,
ByVal address As Integer, ByVal dataLine As Integer,
ByVal lineSense As Integer)
2-40 Return to Section Topics KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010
Page 58

Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual Section 2: NI Command-Compatible Functions
Parameters board_desc: Board ID
address: The device address of the device is waiting to be configured.
dataLine: Data line on which the device responds to parallel polling; its range is
from 1 to 8.
lineSense: Senses the parallel polling response; its value is either 0 or 1.
Error Codes EARG, EBUS, ECIC, EDVR, EOIP, ENEB
PPollUnConfig
Description Unconfigures the devices to respond to parallel polling. If there is only the
constant NOADDR in the address list (addrlist), the parallel poll
unconfigure (PPU) GPIB message is sent to all GPIB devices. The devices
unconfigured by this function will not be included in the following parallel polling.
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
void PPollUnconfig (int board_desc,
const Addr4882_t addressList[])
Parameters board_desc: Board ID
Error Codes EAGR, EBUS, ECIC, EDVR, EOIP, ENEB
RcvRespMsg
Description Reads data from a device. The RcvRespMsg function assumes that the interface
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
Visual Basic
call PPollUnconfig (ByVal ud As Integer,
addressList ( ) As Integer)
addressList: The list of the device addresses ended by NOADDR
is in the listen-active status and addresses a device as a talker. The function
reads data continuously, until either "count" data have been read or the terminal
condition is detected. If the terminal condition is DTOPend, the reading action is
stopped and the EOI line is set to enable while the STOPend is received.
Otherwise, the reading action is stopped while the eight-bit EOS character is
detected. Returns the actual number of transferred bytes in the global variable,
ibcntl.
void RcvRespMsg (int board_desc, void *buffer,
long count, int termination)
Visual Basic
call RcvRespMsg (ByVal ud As Integer, buf As String,
ByVal termination As Integer)
KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010 Return to Section Topics 2-41
Page 59

Section 2: NI Command-Compatible Functions Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual
Parameters board_desc: Board ID
buffer: The buffer for storing the read data
count: The number of read bytes
termination: The description of the data termination mode
Error Codes EABO, EADR, EARG, ECIC, EDVR, EOIP, ENEB
ReadStatusByte
Description Sequentially polls a device. If the sixth bit (hex 40) of the response is set, the
device is requesting service.
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
void ReadStatusByte (int board_desc,
Addr4882_t address, short *result)
Visual Basic
call ReadStatusByte (ByVal us As Integer,
ByVal addr As Integer, result As Integer)
Parameters board_desc: Board ID
Error Codes EABO, EARG, EBUS, ECIC, EDVR, EOIP, ENEB
Receive
Description Reads data bytes from a device, and then stores them in the assigned buffer.
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
address: Device address
result: Response byte of the sequential polling
Receives the device address described by addressing to a talker, setting the
interface to a receiver, reading count data bytes from the device, and storing
these data bytes into the buffer. The operation is normally stopped when the count
data bytes are read or the terminal condition is detected. If the terminal condition
is STOPend, the EOI line is set to enable while the STOPend byte is received.
Otherwise, the reading operation is stopped while the 8-bit EOS character is
detected. Returns the actual number of transferred bytes in the global variable,
ibcntl.
void Receive (int board_desc, Addr4882_t address,
void *buffer, long count, int termination)
Visual Basic
call Receive (ByVal ud As Integer,
ByVal addr As Integer, buf As String,
ByVal termination As Integer)
2-42 Return to Section Topics KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010
Page 60

Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual Section 2: NI Command-Compatible Functions
Parameters board_desc: Board id
address: The device address; the device is read by the function for data
buffer: The buffer that stores the read data
termination: Device termination mode (STOPend or EOS character)
Error Codes EABO, EARG, EBUS, ECIC, EDVR, EOIP, ENEB
ReceiveSetup
Description Configures the device to be a talker and the interface to a receiver. After the
command ReceiveSetup is sent, the RcvRespMsg function is usually called to
transfer the data from the device to the interface. ReceiveSetup is helpful for
multiple RcvRespMsg calls. When ReceiveSetup is enabled, the re-addressing
is not necessary when each data block is received.
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
void ReceiveSetup (int board_desc,
Addr4882_t address)
Visual Basic
call ReceiveSetup (ByVal ud As Integer,
ByVal addr As Integer)
Parameters board_desc: Board ID
address: The device address; the device you want the talker to address
Error Codes EARG, EBUS, ECIC, EDVR, EOIP, ENEB
ResetSys
Description Resets and initializes devices. The function contains three steps:
1. Reset the GPIB by controlling the remote enable (REN) line, and then controlling the
interface clear (IFC) line.
2. Send the universal device clear (DCL) GPIB message to clear all devices.
3. Finally, send the *RST\n message to the address list (addrlist) to complete resetting
and initialization of the device.
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
void ResetSys (int board_desc,
const Addr4882_t addressList[])
Visual Basic
call ResetSys (ByVal ud As Integer,
addressList ( ) As Integer)
Parameters board_desc: Board ID
addressList: The list of the device addresses ended by NOADDR
Error Codes EABO, EARG, EBUS, ECIC, EDVR, ENOL, EOIP, ENEB, ESAC
KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010 Return to Section Topics 2-43
Page 61

Section 2: NI Command-Compatible Functions Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual
Send
Description Writes data bytes from the buffer to the device. The operation is normally stopped
until the count data bytes have been written.
If eotmode is set to DABend: The EOI line is set to enable while the final byte is
sent.
If eotmode is set to NULLend: The EOI line is set to disable while the final byte
is sent.
If eotmode is set to NLend: The EOI line is controlled while the final byte and the
following new character \n has been sent.
Returns the actual number of transferred bytes in the global variable, ibcntl.
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
void Send (int board_desc, Addr4882_t address,
const void *buffer, long count, int eot_mode)
Visual Basic
call Send (ByVal ud As Integer,
ByVal addr As Integer, ByVal buf As String,
ByVal eot_mode As Integer)
Parameters board_desc: Board ID
Error Codes EABO, EARG, EBUS, ECIC, EDVR, ENOL, EOIP, ENEB
SendCmds
Description Sends GPIB commands, and then returns the number of transferred command
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
address: The device address
buffer: The sent data bytes
count: Data count
eot_mode: Data termination mode (DABend, NULLend, or NLend)
bytes in the global variable, ibcntl.
void SendCmds (int board_desc, const void *cmdbuf,
long count)
Visual Basic
call SendCmds (ByVal ud As Integer,
ByVal cmdbuf As String)
Parameters board_desc: Board ID
cmdbuf: The sent command bytes
count: Data count
Error Codes EABO, ECIC, EDVR, ENOL, EOIP, ENEB
2-44 Return to Section Topics KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010
Page 62

Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual Section 2: NI Command-Compatible Functions
SendDataBytes
Description Sends data from the buffer to the device. The SendDataBytes function assumes
that the interface on the GPIB bus is in the talk-active status and already
addresses the devices as listeners.
If eotmode is set to DABend: The EOI line is controlled while the final byte is
sent.
If eotmode is set to NULLend: The EOI line is not controlled while the final byte
is sent.
If eotmode is set to NLend: The EOI line is set to enable when the final byte and
the following new character \n have been sent.
Returns the actual number of transferred bytes in the global variable, ibcntl.
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
void SendDataBytes (int board_desc,
const void *buffer, long count, int eotmode)
Visual Basic
call SendDataBytes (ByVal ud As Integer,
ByVal buf As String, ByVal term As Integer)
Parameters board_desc: Board ID
Error Codes EABO, EADR, EARG, EBUS, ECIC, EDVR, ENOL, EOIP, ENEB
SendList
Description Sends data bytes to multiple GPIB devices. The SendList function addresses all
buffer: The sent data bytes
count: Data count
eot_mode: Data terminal mode (DABend, NULLend, NLend)
devices listed in address list (addrlist) as listeners, addresses the interface to
talk, and then transfers the data from the buffer to the devices.
If eotmode is set to DABend: The EOI line is set to enable while the final byte is
sent.
If eotmode is set to NULLend: The EOI line is set to disable while the final byte
is sent.
If eotmode is set to NLend: The EOI line is set to enable when the final byte and
the following new character \n has been sent.
Returns the actual number of transferred bytes in the global variable, ibcntl.
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
void SendList (int board_desc,
const Addr4882_t addressList[], const void *buffer,
long count, int eotmode)
KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010 Return to Section Topics 2-45
Page 63

Section 2: NI Command-Compatible Functions Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual
Visual Basic
call SendList (ByVal ud As Integer,
addressList ( ) As Integer, ByVal buf As String,
ByVal term As Integer)
Parameters board_desc: Board ID
addressList: The list of the device addresses; the devices that send data bytes
buffer: The sent data bytes
count: Data count
eotmode: Data termination mode (DABend, NULLend, or NLend)
Error Codes EABO, EARG, EBUS, ECIC, EDVR, EOIP, ENEB
SendIFC
Description Sends the interface clear (IFC) command to reset GPIB. The SendIFC command,
which is a part of GPIB initialization, forces the interface to controller-in-charge of
GPIB. The function also ensures that the connected devices are not addressed
and the interface calls of the devices are in idle status.
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
Parameters board_desc: Board ID
Error Codes ENEB, ESAC, EDVR, EOIP
SendLLO
Description Sends the local lockout (LLO) message to all devices. When the LLO is in effect,
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
Parameters board_desc: Board ID
void SendIFC (int board_desc)
Visual Basic
call SendIFC (ByVal ud As Integer)
only the controller-in-charge can change device states by sending appropriate
GPIB messages. SendLLO is reserved for use in uncommon local and remote
situations. Under normal conditions, SetRWLS is used to place a device in remote
operation with lockout.
void SendLLO (int board_desc)
Visual Basic
call SendLLO (ByVal ud As Integer)
Error Codes EBUS, ECIC, ENEB, ESAC, EDVR, EOIP
SendSetup
Description Configures the device to receive data by setting the devices listed in
addressList as listeners and setting the interface talk-active. After the
SendSetup call, SendDataBytes sends data from the interface to the devices.
2-46 Return to Section Topics KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010
Page 64

Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual Section 2: NI Command-Compatible Functions
When multiple SendDataBytes calls are used for transferring data, the address
setting capability of SendSetup is especially useful because each device does
not need to be addressed while each data block is transferred.
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
void SendSetup (int board_desc,
const Addr4882_t addressList[])
Visual Basic
call SendSetup (ByVal ud As Integer,
addrs ( ) As Integer)
Parameters board_desc: Board ID
addressList: The list of the devices ended by NOADDR
Error Codes EABO, EARG, EBUS, ECIC, EDVR, EOIP, ENEB
SetRWLS
Description Configures the device to lockout status of remote-control mode. SetRWLS sets the
devices listed in addrlist to remote-control mode by controlling the remote
enable (REN) GPIB line. Then, the LLO GPIB message sets the devices to
lockout status. Before the controller-in-charge calls EnableLocal to release
local lockout, you cannot locally operate these devices.
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
Parameters board_desc: Board ID
Error Codes EARG, EBUS, ECIC, EDVR, EOIP, ENEB, ESAC
T estSRQ
Description Detects the current status of the GPIB service request (SRQ) line. If the SRQ is
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
void SetRWLS ((int board_desc,
const Addr4882_t addressList[])
Visual Basic
call SetRWLS (ByVal ud As Integer,
addressList ( ) As Integer)
addressList: The list of the device addresses ended by NOADDR
controlled, the result contains a non-zero value. If it is not controlled, the result
contains a zero value. The TestSRQ command gets the current status of GPIB
SRQ line. The WaitSRQ command waits until the device controls the GPIB SRQ
line.
void TestSRQ (int board_desc, short *result)
Visual Basic
call TestSRQ (ByVal ud As Integer, result As Integer)
Parameters board_desc: Board ID
result: The status of the SRQ line
KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010 Return to Section Topics 2-47
Page 65

Section 2: NI Command-Compatible Functions Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual
Error Codes EDVR, EOIP, ENEB
T estSys
Description Causes devices to process self tests by sending the TST? message to the
devices, which makes the devices test themselves individually. It then reads 16-bit
self-test results from the devices. The self-test result 0\n shows that the device
passed its self test (if the self test result is not 0\n, it means that the device did
not pass its self test). Refer to the documents that came with the device to
determine cause of the failed self test.
If TestSys does not return Error (for example, the ERR bit is not set in ibsta),
the failure number of the self tests is contained in ibcntl.
Alternatively, the meaning of the ibcntl depends on the returned failure. If the
device does not send a response in a limited time, then the test result (?) is
reported, and the error EABO is returned.
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
void TestSys (int board_desc, Addr4882_t *addrlist,
short resultList[])
Visual Basic
T rigger
call TestSys (ByVal ud As Integer,
addrlist ( ) As Integer, resultList ( ) As Integer)
Parameters board_desc: Board ID
addrlist: The list of the device addresses ended by NOADDR
resultList: The list of the self test results; each test item corresponds to each
address listed in addrlist
Error Codes EABO, EARG, EBUS, EDVR, ECIC, EOIP, ENEB, ENOL
Description Sends the group execute trigger (GET) GPIB message to a device. If the address
is constant NOADDR, the GET messages are sent to the devices that are
currently listen-active on the GPIB bus.
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
void Trigger (int board_desc, Addr4882_t address)
Visual Basic
call Trigger (ByVal ud As Integer,
ByVal address As Integer)
Parameters board_desc: Board ID
address: The device address; the device to be triggered
Error Codes EARG, EBUS, EDVR, ECIC, EOIP, ENEB
2-48 Return to Section Topics KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010
Page 66

Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual Section 2: NI Command-Compatible Functions
T riggerList
Description Sends the group execute trigger (GET) GPIB message to multiple devices. If
there is only constant NOADDR in the addrlist, no device is addressed and the
GET message is sent to the devices that are currently listen-active on the GPIB
bus.
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
void TriggerList (int board_desc,
const Addr4882_t addressList[])
Visual Basic
call TriggerList (ByVal ud As Integer,
addressList ( ) As Integer)
Parameters board_desc: Board ID
addressList: The list of the device addresses ended by NOADDR
Error Codes EARG, EBUS, EDVR, ECIC, EOIP, ENEB
WaitSRQ
Description Waits until the device controls the GPIB SRQ line. When WaitSRQ returns, the
result contains a non-zero value if the SRQ line is controlled. If it is not controlled,
the result contains a zero value. Get the current status of the GPIB SRQ line by
using the TestSRQ command. Use WaitSRQ to wait before the SRQ line can be
controlled.
Syntax Microsoft C/C++ and Borland C++
void WaitSRQ (int board_desc, short *result)
Visual Basic
call WaitSRQ (ByVal ud As Integer,
result As Integer)
Parameters board_desc: Board ID
result: The status of the SRQ line
Error Codes EDVR, EOIP, ENEB
KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010 Return to Section Topics 2-49
Page 67

In this appendix:
Topic Page
NI command-compatible status codes............................................... A-2
NI command-compatible function error codes .................................. A-3
Appendix A
Status/Error Codes
Page 68

Appendix A: Status/Error Codes Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual
NI command-compatible status codes
This section contains information about possible error codes produced when using the National
Instruments™ (NI)
1
command-compatible functions. All commands update global status word
ibsta which contains the GPIB status and the message from the user's GPIB hardware. After every
command, the user can use the ERR bit of the ibsta to detect errors. The ibsta is a 16-bit word. A
bit value equal to one (1) means the condition occurred; a bit value equal to zero (0) means the
condition did not occur.
Table A-1: NI command-compatible status codes
Mnemonic Position Hex Type Description
ERR 15 8000 device, board GPIB error
TIMO 14 4000 device, board Timeout
END 13 2000 device, board END or EOS has been detected
SRQI 12 1000 board SRQ interrupt occurred
RQS 11 800 device Device requesting service
SPOLL 10 400 board Board has been sequentially polled by
controller
EVENT 9 200 board DCAS, DTAS, or IFC event occurred
CMPL 8 100 device, board I/O completion
LOK 7 80 board Lockout status
REM 6 40 board Remote status
CIC 5 20 board Control-In-Charge
ATN 4 10 board Send attention message
TACS 3 8 board Talk status
LACS 2 4 board Listen status
DATS 1 2 board Device trigger status
DCAS 0 1 board Device clear status
1. National Instruments™ and NI™ are trademarks of the National Instruments Corporation.
A-2 Return to Section Topics KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010
Page 69

Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual Appendix A: Status/Error Codes
NI command-compatible function error codes
NI command-compatible function error codes are listed in the following table. Note that, the error
variable is meaningful only when the ERR bit of the status variable, ibsta, is placed. Click the error
mnemonic, and you can obtain a detailed description and the solution for each error.
Table A-2: NI command-compatible function error codes
Error
mnemonic iberr value Meaning description
EDVR 0 OS error
ECIC 1 Function requests GPIB board as CIC
ENOL 2 No listen device on the GPIB bus
EADR 3 GPIB board addressing error
EARG 4 Invalid argument
ESAC 5 GPIB board is not on the system controller requesting
status
EABO 6 I/O operation is aborted (timeout)
ENEB 7 GPIB board does not exit
EDMA 8 DMA error
EOIP 10 Asynchronous I/O in progress
ECAP 11 The operation is not performed
EFSO 12 File system error
EBUS 14 GPIB bus error
ESTB 15 The status byte queue of the sequential polling overflow
ESRQ 16 SRQ is stuck in ON state
ETAB 20 Table problem
KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010 Return to Section Topics A-3
Page 70

Index
A
AllSpoll.....................................................2-37
Application
ATN line
................................................ 1-3
.........................................1-4, 2-3
Build
Design interface
.......................... 1-3, 1-4, 2-5, 2-6
Run
....................... 1-3, 2-4
.................................................. 2-12
B
Board-level functions ................................ 2-6
BOARDSELECT
....................................... 1-5
C
Contact Keithley ....................................... 1-2
Control properties
............................. 1-3, 2-4
D
Data types ................................................ 2-9
DevClear
DevClearList
Device configuration parameters
Device-level functions
......................................2-37, 2-45
........................................... 2-37
............2-16
..............................2-6
E
EnableLocal ............................................ 2-38
EnableRemote
ENTER
Error codes
Event codes
Visual C#
Write
........................................ 2-38
..................................................... 1-5
.............................................. A-1
............................. 1-3, 1-4, 2-5
..........................................1-4
........................ 1-3, 1-4, 2-4, 2-5
F
FEATURE ................................................. 1-6
FEATURE parameters
FindLstn
FindRQS
Function declarations and constants
Functions
.................................................. 2-38
................................................. 2-39
GPIB.BAS file
GPIB.cs file
GPIB_CS.cs
IEEE-C.H file
Include file
GPIB.vb file
Board-level
IEEE-488 board-level functions
IEEE-488 device-level functions
IEEE-488.2
.............................1-6
...................................2-4
......................................2-5
..................................... 1-4
.................................... 1-4
................................1-4, 2-4
......................................2-4
....................................... 2-7
...............................2-6, 2-8
.1-3, 2-5
........ 2-6
......2-6
G
GPIB.BAS file .................................... 2-4, 2-9
.................................................... 2-5
GPIB.cs
..................................................... 2-5
GPIB.H
GPIB.PAS file
GPIB.vb
GPIB_vb.vb file
GPIBBOARDPRESENT
........................................... 2-9
................................................... 2-4
........................................ 1-3
........................... 1-5
I
ibask ........................................................ 2-9
Board configuration parameters
...................................................... 2-11
ibbna
...................................................... 2-12
ibcac
................................................... 2-13
ibcdma
........................................................ 2-13
ibclr
ibcmd
..................................................... 2-13
................................................... 2-13
ibcmda
........................................ 2-14, 2-16
ibconfig
Board configuration parameters
...................................................... 2-16
ibdev
..................................................... 2-17
ibdma
...................................................... 2-18
ibeos
EOS mode
....................................................... 2-18
ibeot
...................................................... 2-19
ibfind
....................................................... 2-20
ibgts
ibist
........................................................ 2-20
..................................................... 2-21
iblines
......................................................... 2-21
ibln
ibloc
....................................................... 2-22
................................................... 2-23
ibnotify
Callback description
GPIB event codes for mask
....................................................... 2-23
ibonl
ibpad
...................................................... 2-24
....................................................... 2-25
ibpct
...................................................... 2-26
ibppc
ibrd
......................................................... 2-26
....................................................... 2-27
ibrda
........................................................ 2-28
ibrdf
ibrpp
....................................................... 2-29
....................................................... 2-29
ibrsc
....................................................... 2-30
ibrsp
ibrsv
....................................................... 2-30
...................................................... 2-25
ibsad
........................................................ 2-31
ibsic
ibsre
....................................................... 2-31
..................................................... 2-31
ibstop
...................................................... 2-32
ibtmo
Timeout values
........................................................ 2-33
ibtrg
...................................................... 2-33
ibwait
..................................... 2-19
....................... 2-24
........... 2-24
.............................. 2-32
.... 2-10
.... 2-15
KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010 Index-1
Page 71

Index Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual
Valid Mask codes ........................... 2-34
........................................................2-34
ibwrt
ibwrta
......................................................2-35
.......................................................2-36
ibwrtf
ieee_32m.lib
IEEE-488
IEEE-488 board-level functions
IEEE-488 device-level functions
IEEE-488.2 functions
IEEEVB.BAS file
INITIALIZE
.............................................1-4
..................................................2-6
................2-6
ADL-GPIB functions
......................... 2-7
...............2-6
ADL-GPIB functions
......................... 2-6
........................2-6, 2-8
....................................... 1-3
................................................ 1-6
K
Keithley command-compatible functions
BOARDSELECT ...............................1-5
ENTER
............................................. 1-5
FEATURE
GPIBBOARDPRESENT
INITIALIZE
LISTENER_PRESENT
PPOLL
RARRAY
RECEIVE
SEND
SETINPUTEOS
SETOUTPUTEOS
SETTIMEOUT
SPOLL
SRQ
TARRAY
TRANSMIT
WAITSRQDEVICE
Keithley command-compatible library
Keithley website
.........................................1-6
...................1-5
........................................1-6
..................... 1-7
.............................................. 1-7
..........................................1-7
..........................................1-7
...............................................1-8
................................1-8
............................1-8
.................................. 1-9
.............................................. 1-9
..................................................1-9
........................................... 1-9
.....................................1-10
......................... 1-12
.......................................1-2
L
LISTENER_PRESENT ............................. 1-7
M
Multi-device functions
...........................................2-37
AllSpoll
DevClear
DevClearList
EnableLocal
EnableRemote
FindLstn
FindRQS
PassControl
PPoll
PPollConfig
PPollUnConfig
RcvResMsg
ReadStatusByte
Receive
ReceiveSetup
ResetSys
Send
SendCmds
SendDataBytes
SendIFC
........................................2-37
................................... 2-37
....................................2-38
................................2-38
..........................................2-38
.........................................2-39
.................................... 2-39
...............................................2-40
.....................................2-40
................................2-41
....................................2-41
.............................2-42
..........................................2-42
.................................2-43
........................................2-43
...............................................2-44
......................................2-44
..............................2-45
......................................... 2-46
......1-4
SendList
SendLLO
SendSetup
SetRWLS
TestSRQ
TestSys
Trigger
TriggerList
WaitSRQ
......................................... 2-45
........................................ 2-46
..................................... 2-46
....................................... 2-47
........................................ 2-47
.......................................... 2-48
............................................ 2-48
...................................... 2-49
........................................ 2-49
N
NI command-compatible function library
.......................................................... 2-9
NI command-compatible function reference
.......................................................... 2-9
NI command-compatible functions
.NET
................................................. 2-3
........................................... 2-37
AllSpoll
Board configuration parameters
............................................ 2-6
Classes
Control properties
Create project
Design application interface
DevClear
DevClearList
Device configuration parameters
Error codes
EnableLocal
EnableRemote
Event codes
FindLstn
FindRQS
ibask
ibbna
ibcac
ibcdma
ibclr
ibcmd
ibcmda
ibconfig
ibdev
ibdma
ibeos
ibeot
ibfind
ibgts
ibist
iblines
ibln
ibloc
ibnotify
ibonl
ibpad
ibpct
ibppc
ibrd
ibrda
ibrdf
ibrpp
ibrsc
ibrsp
ibrsv
......................................... 2-38
........................................ 2-39
....................................... 2-9, 2-10
.............................................. 2-11
.............................................. 2-12
........................................... 2-13
................................................ 2-13
............................................. 2-13
........................................... 2-13
.......................................... 2-14
.............................................. 2-16
............................................. 2-17
.............................................. 2-18
............................................... 2-18
.............................................. 2-19
............................................... 2-20
................................................ 2-20
............................................. 2-21
................................................. 2-21
............................................... 2-22
........................................... 2-23
............................................... 2-23
.............................................. 2-24
............................................... 2-25
.............................................. 2-26
................................................. 2-26
............................................... 2-27
................................................ 2-28
............................................... 2-29
............................................... 2-29
............................................... 2-30
............................................... 2-30
............................ 2-4
.................................. 2-5
........................................ 2-37
.................................. 2-37
......................................A-3
................................... 2-38
............................... 2-38
............................. 2-4, 2-5
... 2-1, 2-3
..... 2-15
............. 2-4
... 2-16
Index-2 KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010
Page 72

Models KPCI-488LPA and KUSB-488B Reference Manual Index
NI command-compatible functions (continued)
ibsad
............................................... 2-25
................................................ 2-31
ibsic
................................................2-31
ibsre
.............................................. 2-31
ibstop
...............................................2-32
ibtmo
................................................2-33
ibtrg
.............................................. 2-33
ibwait
................................................ 2-34
ibwrt
.............................................. 2-35
ibwrta
............................................... 2-36
ibwrtf
Introduction
Open project
Overview
PassControl
PPoll
PPollConfig
PPollUnConfig
RcvResMsg
ReadStatusByte
Receive
ReceiveSetup
ResetSys
Run application
Send
SendCmds
SendDataBytes
SendIFC
SendList
SendLLO
SendSetup
SetRWLS
TestSRQ
TestSys
Trigger
TriggerList
Visual Basic
Visual C#
Visual C/C++
WaitSRQ
Parallel polling
Parameters
Feature
PassControl
......................................................1-7
PPOLL
PPoll
.......................................................2-40
PPollConfig
PPollUnConfig
Project
Create
Existing
Load
New
Open
.......................................2-3
..................................... 2-5
..........................................2-6
.................................... 2-39
...............................................2-40
.....................................2-40
................................2-41
....................................2-41
.............................2-42
..........................................2-42
.................................2-43
........................................2-43
..........................2-5, 2-6
...............................................2-44
......................................2-44
..............................2-45
......................................... 2-46
.........................................2-45
........................................ 2-46
......................................2-46
........................................2-47
.........................................2-47
..........................................2-48
............................................2-48
......................................2-49
...................................... 2-3
..........................................2-5
............................2-3, 2-5
........................................2-49
.................................1-7, 2-29
.............................................1-6
............................................2-39
............................................. 2-40
........................................2-41
.............................. 1-4, 2-3, 2-5
............................................. 1-2
.........................................1-2, 2-4
.................................................. 1-2
................................ 1-4, 2-3, 2-5
R
RARRAY ..................................................1-7
RcvRespMsg
ReadStatusByte
RECEIVE
Receive
ReceiveSetup
ResetSys
..........................................2-41
.....................................2-42
.................................................. 1-7
..................................................2-42
.........................................2-43
................................................2-43
S
Selected device clear
ADL-GPIB functions
....................................................... 1-8
SEND
....................................................... 2-44
Send
SendCmds
SendDataBytes
SendIFC
SendList
SendLLO
SendSetup
Serial polling
Service request
SETINPUTEOS
SETOUTPUTEOS
SetRWLS
SETTIMEOUT
SPOLL
SRQ........................................................... 1-9
Status codes
............................................. 2-44
...................................... 2-45
................................................. 2-46
................................................. 2-45
................................................ 2-46
............................................. 2-46
............................................ 1-9
.............................. 1-9, 1-12
........................................ 1-8
............................................... 2-47
.......................................... 1-9
..................................................... 1-9
............................................A-1
....................... 2-13
.................................... 1-8
T
TARRAY.................................................... 1-9
TestSRQ
TestSys
Timeout period
Timeout values
TRANSMIT
Trigger
TriggerList
................................................ 2-47
.................................................. 2-48
......................................... 1-9
....................................... 2-32
............................. 1-7, 1-9, 1-10
Command string parameters
.................................................... 2-48
.............................................. 2-49
V
Valid mask codes ................................... 2-34
Visual Basic
Visual C#
Visual C/C++
..................................... 1-2, 2-3
Create project
Load project
Open project
..........................1-2, 2-3
..................................... 1-2
............................1-2, 2-3
.......................................... 1-4, 2-5
Create project
Event codes
Function declarations and constants
GPIB_CS.cs file
Open project
Visual C#
Run application
.................................. 1-4
............................. 1-4, 2-5
............................... 1-4
.................................... 1-4
Create project
2-5
........................ 1-4, 2-6
............................1-4, 2-3, 2-5
Create project
Open project
.................................. 2-5
.................................... 2-5
W
WaitSRQ ................................................ 2-49
WAITSRQDEVICE
Warranty
.................................................. 1-1
................................. 1-12
......... 1-11
2-5
KI488-901-01 Rev. A / March 2010 Index-3
Page 73

WARRANTY
Keithley Instruments, Inc. warrants this product to be free from defects in material and workmanship for a period of
one (1) year from date of shipment.
Keithley Instruments, Inc. warrants the following items for 90 days from the date of shipment: probes, cables,
software, rechargeable batteries, diskettes, and documentation.
During the warranty period, Keithley Instruments will, at its option, either repair or replace any product that proves
to be defective.
To exercise this warranty, write or call your local Keithley Instruments representative, or contact
Keithley Instruments headquarters in Cleveland, Ohio. You will be given prompt assistance and return instructions.
Send the product, transportation prepaid, to the indicated service facility. Repairs will be made and the product
returned, transportation prepaid. Repaired or replaced products are warranted for the balance of the original
warranty period, or at least 90 days.
LIMITATION OF WARRANTY
This warranty does not apply to defects resulting from product modification without Keithley Instruments’ express
written consent, or misuse of any product or part. This warranty also does not apply to fuses, software,
non-rechargeable batteries, damage from battery leakage, or problems arising from normal wear or failure to follow
instructions.
THIS WARRANTY IS IN LIEU OF ALL OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING ANY
IMPLIED WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR USE. THE REMEDIES
PROVIDED HEREIN ARE BUYER’S SOLE AND EXCLUSIVE REMEDIES.
NEITHER KEITHLEY INSTRUMENTS, INC. NOR ANY OF ITS EMPLOYEES SHALL BE LIABLE FOR ANY
DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES ARISING OUT OF THE USE
OF ITS INSTRUMENTS AND SOFTWARE, EVEN IF KEITHLEY INSTRUMENTS, INC. HAS BEEN ADVISED IN
ADVANCE OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. SUCH EXCLUDED DAMAGES SHALL INCLUDE, BUT
ARE NOT LIMITED TO: COST OF REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION, LOSSES SUSTAINED AS THE RESULT OF
INJURY TO ANY PERSON, OR DAMAGE TO PROPERTY.
A G R E A T E R M E A S U R E O F C O N F I D E N C E
Keithley Instruments, Inc.
Corporate Headquarters • 28775 Aurora Road • Cleveland, Ohio 44139
440-248-0400 • Fax: 440-248-6168 • 1-888-KEITHLEY (1-888-534-8453) • www.keithley.com
3/07
Page 74

12/06
Specifications are subject to change without notice.
All Keithley trademarks and trade names are the property of Keithley Instruments, Inc.
All other trademarks and trade names are the property of their respective companies.
A GREATER MEASURE OF CONFIDENCE
Keithley Instruments, Inc.
Corporate Headquarters • 28775 Aurora Road • Cleveland, Ohio 44139 • 440-248-0400 • Fax: 440-248-6168 • 1-888-KEITHLEY • www.keithley.com
 Loading...
Loading...