TECO L510-201-H1F-P, L510-2P2-H1F-P, L510-202-H1F-P, L510-2P2-H1-N, L510-203-H1F-P Operating Manual
...Page 1

L510 Series 100V
200V
400V
0.2~0.75KW
(0.25~1HP)
0.2~2.2KW
(0.25~3HP)
0.75~2.2KW
(1~3HP)
Microprocessor Controlled
IGBT Drive
Inverter Motor Speed Regulator
Operating Manual
Page 2

I
L510 Table of Contents
Chapter 0 Preface
0-1
0.1 Preface
0-1
Chapter 1 Safety Precautions
1-1
1.1 Before Power UP
1-1
1.2 During Power UP
1-2
1.3 Before Operation
1-2
1.4 During Operation
1-3
1.5 Inverter Disposal
1-3
Chapter 2 Part Number Definition
2-1
2.1 Model part number
2-1
2.2 Standard Product Specification
2-2
Chapter 3 Environment & Installation
3-1
3.1 Environment
3-1
3.2 Installation
3-2
3.2.1 Installation methods
3-2
3.2.2 Installation space
3-4
3.2.3 De-rating curve
3-5
3.3 Wiring guidelines
3-6
3.3.1 Power cables
3-6
3.3.2 Control cable selection and wiring
3-7
3.3.3 Wiring and EMC guidelines
3-8
3.3.4 Failure liability
3-9
3.3.5 Considerations for peripheral equipment
3-10
3.3.6 Ground connection
3-11
3.3.7 Inverter exterior
3-11
3.4 Specifications
3-12
3.4.1 Product Specifications
3-12
3.4.2 General Specifications
3-13
3.5 Standard wiring
3-15
3.5.1 Single phase(NPN input)
3-15
3.5.2 Single phase(PNP input)
3-16
3.5.3 Three phase(NPN input)
3-17
3.5.4 Three phase(PNP input)
3-18
3.6 Terminal Description
3-19
3.6.1 Description of main circuit terminals
3-19
3.6.2 Control circuit terminal description
3-20
3.7 Outline Dimensions
3-21
3.8 EMC filter Disconnection
3-23
Chapter 4 Software Index
4-1
4.1 Keypad Description
4-1
4.1.1 Operator Panel Functions
4-1
4.1.2 Digital Display Description
4-2
4.1.3 Digital Display Setup
4-4
Page 3

II
4.1.4 Example of Keypad Operation
4-6
4.1.5 Operation Control
4-8
4.2 Programmable Parameter Groups
4-9
4.3 Parameter Function Description
4-22
Chapter 5 Troubleshooting and Maintenance
5-1
5.1 Error Display and Corrective Action
5-1
5.1.1 Manual Reset and Auto-Reset
5-1
5.1.2 Keypad Operation Error Instruction
5-2
5.1.3 Special conditions
5-3
5.2 General troubleshooting
5-4
5.3 Troubleshooting of the inverter
5-5
5.3.1 Quick troubleshooting of the inverter
5-5
5.3.2 Troubleshooting for OC, OL error displays
5-7
5.3.3 Troubleshooting for OV, LV error
5-8
5.3.4 The Motor can not run
5-9
5.3.5 Motor Overheating
5-10
5.3.6 Motor runs unbalanced
5-11
5.4 Routine and periodic inspection
5-12
5.5 Maintenance
5-13
Chapter 6 Peripheral Components
6-1
6.1 Reactor Specifications
6-1
6.2 Electromagnetic Contactor and No fuse circuit breaker
6-1
6.3 Fuse Specification
6-1
6.4 Fuse Specification(UL Model Recommended)
6-1
6.5 Barking Resistor
6-2
Appendix I L510 Parameters Setting List
App1-1
Page 4
0-1
Chapter 0 Preface
0.1 Preface
To extend the performance of the product and ensure personnel safety, please read
this manual thoroughly before using the inverter. Should there be any problem in
using the product that cannot be solved with the information provided in the manual,
contact our technical or sales representative who will be willing to help you.
※Precautions
The inverter is an electrical product. For your safety, there are symbols such as
“Danger”, “Caution” in this manual as a reminder to pay attention to safety
instructions on handling, installing, operating, and checking the inverter. Be sure to
follow the instructions for highest safety.
Danger
Indicates a potential hazard that could cause death or serious
personal injury if misused.
Caution
Indicates that the inverter or the mechanical system might be damaged
if misused.
Danger
¾ Risk of electric shock. The DC link capacitors remain charged for five
minutes after power has been removed. It is not permissible to open the
equipment until 5 minutes after the power has been removed.
¾ Do not make any connections when the inverter is powered on. Do not check
parts and signals on circuit boards during the inverter operation.
¾ Do not disassemble the inverter or modify any internal wires, circuits, or
parts.
¾ Ensure that the Inveter Ground terminal is connected correctly.
Caution
¾ Do not perform a voltage test on parts inside the inverter. High voltage can
destroy the semiconductor components.
¾ Do not connect T1, T2, and T3 terminals of the inverter to any AC input
power supply.
¾
CMOS ICs on the inverter’s main board are susceptible to static electricity. Do
not touch the main circuit board.
Page 5
1-1
Chapter 1 Safety Precautions
1.1 Before Power Up
Danger
¾
Make sure the main circuit connections are correct. Single phase L1(L),L3(N), and
Three phase 200V L1(L),L2,L3(N); 400V : L1,L2,L3 are power-input terminals and
must not be mistaken for T1,T2 and T3. Otherwise, inverter damage can result.
Caution
¾ The line voltage applied must comply with the inverter’s specified input
voltage.(See the nameplate)
¾ To avoid the front cover from disengaging, or other damge do not carry the
inverter by its covers. Support the drive by the heat sink when transporting.
Improper handling can damage the inverter or injure personnel and should be
avoided.
¾ To avoid the risk of fire, do not install the inverter on a flammable object.Install on
nonflammable objects such as metal.
¾ If several inverters are placed in the same control panel, provide heat removal
means to maintain the temperature below 50 degree C to avoid overheat or fire.
¾ When disconnecting the remote keypad, turn the power off first to avoid any
damage to the keypad or the inverter.
Warning
¾ This product is sold subject to EN 61800-3 and EN 61800-5-1.
In a domestic environment this product may cause radio interference in which
case the user may be required to apply corrective measures.
Caution
¾ Work on the device/system by unqualified personnel or failure to comply with
warnings can result in severe personal injury or serious damage to material. Only
suitably qualified personnel trained in the setup, installation, commissioning and
operation of the product should carry out work on the device/system.
¾ Only permanently-wired input power connections are allowed.
Page 6

1-2
1.2 During Power Up
Danger
¾ When the momentary power los s is longer than 2 seconds, the inverter will not
have sufficient stored power for its control circuit. Therefore, when the power is
re-applied, the run operation of the inverter will be based on the setup of
following parameters:
• Run parameters. 00-02 or 00-03.
• Direct run on power up. Parameter. 07-04 and the status of external run
switch,
Note-: the start operation will be regardless of the settings for parameters
07-00/07-01/07-02.
Danger. Direct run on power up.
If direct run on power up is enabled and inverter is set to external run
with the run FWD/REV switch closed then the inverter will restart.
Danger
Prior to use, ensure that all risks and safety implications are considered.
¾ When the momentary power loss ride through is selected and the power loss is
short, the inverter will have sufficient stored power for its control circuits to
function, therefore,when the power is resumed the inverter will automatically
restart depending on the setup of parameters 07-00 & 07-01.
1.3 Before Operation
Caution
¾ Make sure the model and inverter capacity are the same as that set in
parameter 13-00.
Note : On power up the supply voltage set in parameter 01-01 will flash on display
for 2 seconds.
Page 7
1-3
1.4 During Operation
Danger
¾ Do not connect or disconnect the motor during operation. Otherwise, It may
cause the inverter to trip or damage the unit.
Caution
¾ Do not touch heat radiating components such as heat sinks and brake resistors.
¾ The inverter can drive the motor from low speed to high speed. Verify the allowable
speed ranges of the motor and the associated machinery.
¾ Note the settings related to the braking unit.
¾ Risk of electric shock. The DC link capacitors remain charged for five minutes after
power has been removed. It is not permissible to open the equipment until 5
minutes after the power has been removed.
Caution
¾ The Inverter should be used in environments with temperature range from
(14-104℉) or (-10 to 40℃) and relative humidity of 95%.
Danger
¾ Make sure that the power is switched off before disassembling or checking
any components.
1.5 Inverter Disposal
Caution
Please dispose of this unit with care as an industrial waste and according to your
required local regulations.
¾ The capacitors of inverter main circuit and printed circuit board are considered as
hazardous waste and must not be burnt.
¾ The Plastic enclosure and parts of the inverter such as the cover board will release
harmful gases if burnt.
Danger
¾ To avoid electric shock, do not take the front cover off while power is on.
¾ The motor will restart automatically after stop when auto-restart function is enabled.
In this case, care must be taken while working around the drive and associated
equipment .
¾ The operation of the stop switch is different than that of the emergency stop switch.
The stop switch has to be activated to be effective. Emergency stop has to be
de-activated to become effective.
Page 8

2-1
Chapter 2 Part Number Definition
2.1 Model part number
L510 - 1P2 - H1 - N
Power supply
1:Single phase
3:Three phase
Specification
H:Standard Type
Supply voltage
1:100V Class
2:200V Class
4 : 400V Class
Horsepower
100V Class P2: 0.25 HP 400V Class 01: 1HP
P5: 0.5 HP 02 : 2HP
01: 0.75 HP 03: 3HP
200V Class P2: 0.25 HP
P5: 0.5 HP
01: 1 HP
02: 2 HP
03: 3 HP
Filter
F :Built-in
Blank:None
P:PNP
N:NPN
Internal Voltage
Blank : +12V Series
A:+24V Series
Page 9

2-2
2.2 Standard Product Specification
100V/200V (If the model is marked A, it means that it is built in the power supply of 24V; if not, then it
is built in the power supply of 12V.)
Model Filter
Model
Supply
Voltage
(Vac)
Frequency
(Hz)
(HP)
(KW)
NPN PNP
Built-in
None
L510-1P2-H1-N
0.25 0.2
◎ ◎
L510-1P5-H1-N
0.5 0.4
◎ ◎
L510-101-H1-N
1ph,
100~120V
+10%/-15%
1 0.75
◎ ◎
L510-2P2-H1F-P
0.25 0.2
◎ ◎
L510-2P5-H1F-P
0.5 0.4
◎ ◎
L510-201-H1F-P
1 0.75
◎ ◎
L510-202-H1F-P
2 1.5
◎ ◎
L510-203-H1F-P
3 2.2
◎ ◎
L510-2P2-H1-N
0.25 0.2
◎ ◎
L510-2P5-H1-N
0.5 0.4
◎ ◎
L510-201-H1-N
1 0.75
◎ ◎
L510-202-H1-N
2 1.5
◎ ◎
L510-203-H1-N
1ph,
200~240V
+10%/-15%
3 2.2
◎ ◎
L510-2P2-H3-N
0.25 0.2
◎
◎
L510-2P5-H3-N
0.5 0.4
◎ ◎
L510-201-H3-N
1 0.75
◎ ◎
L510-202-H3-N
2 1.5
◎ ◎
L510-203-H3-N
3ph,
200~240V
+10%/-15%
50/60Hz
3 2.2
◎ ◎
400V (Models of 400V machines are all marked A, built in the power supply of 24V.)
Model Filter
Model
Supply
Voltage
(Vac)
Frequency
(Hz)
(HP) (KW)
NPN PNP
Built-in
None
L510-401-H3-N A 1 0.75
◎ ◎
L510-402-H3-N A 2 1.5
◎ ◎
L510-403-H3-N A 3 2.2
◎ ◎
L510-401-H3F-P A 1 0.75
◎ ◎
L510-402-H3F-P A 2 1.5
◎ ◎
L510-403-H3F-P A
3ph,
380~480V
+10%/-15%
50/60Hz
3 2.2
◎ ◎
Suitable for use on a circuit capable of delivering not more than 5,000 rms symmetrical amperes,
120/240 volts maximum. The voltage shall be 120 for 100-120 V, 240 for 200-240 V, 480 for
380-480V rated units.
Page 10

3-1
Chapter 3 Environment & Installation
3.1 Environment
Installation environment has a direct affect on the correct operation and the life expectancy of the
inverter, Install the inverter in an environment complying with the following conditions:
Protection
Protection
class
IP20, NEMA/UL Open Type
Suitable environment
Operating
temperature
-10~40°C (-10~50°C with fan)
If several inverters are installed in the same control panel, ensure
adequate spacing and provide the necessary cooling and ventilation for
successful operation.
Storage
temperature
-20~60°C
Relative
Humidity
Max 95% (without condensation)
Notice prevention of inverter freezing up.
Shock
1G. (9.8m/s²) for 20Hz and below.
0.6G (5.88m/s²) from 20Hz to 50Hz
Installation site
Install in an environment that will not have an adverse effect on the operation of the unit
and ensure that there is no exposure to areas such as that listed below:-
¾ Direct sunlight, Rain or moisture
¾ Oil mist and salt
¾ Dust, lint fibbers, small metal filings and corrosive liquid and gas
¾ Electromagnetic interference from sources such as welding equipment
¾ Radioactive and flammable materials
¾ Excessive vibration from machines such as stamping, punching machines
¾ Add a vibration-proof pads if necessary
Tightening torque for terminals
Chart 3-1
TM1 TM2
Cable Size Cable Size
Tightening torque Tightening torque Model
AWG mm²
kgf.cm Ibf.in Nm
AWG mm²
kgf.cm Ibf.in Nm
Frame1
14 12.15 1.37
Frame2
22~10 0.34~6
12.24 10.62 1.2
24~12 0.25~4 4.08 3.54 0.4
Page 11

3-2
3.2 Installation
3.2.1 Installation methods
Frame1. Mounting on a flat surface.
Din rail type installation:
Din rail kit includes a plastic and a metal adaptor plates.
Assembly Steps:-
1) Attach the metal adaptor plate to the inverter base with the screws provided.
2) Attach the plastic Din rail adaptor to the metal adaptor plate.
3) Push the plastic adaptor forward to lock into position.
Disassembly Steps:-
1) Unlock by pushing the snap hooks
2) Retract and remove the plastic Din rail adaptor.
3) Unscrew the metal plate &Remove
Note:
JN5-DIN-L01 (Frame 1 Din rail kit part number), including the following parts
1. Metal plate adaptor
2. Plastic adaptor
3. Chamfer head screw: M3×6
Screw: M4
1. Metal plate adapto
r
2. Plastic adaptor
Snap hooks
1. Metal plate adaptor
2. Plastic adapto
r
Snap hooks
3. screws
3. screws
Assembly:-
Disassembly:-
Page 12

3-3
Frame 2. Mounting on a flat surface.
Din rail type installation:
Din rail kit includes a plastic adaptor plate as an attachment for the inverter base.
Refere to Diagram below:-
Din Rail Mounting & Dismounting as shown in the diagram below:-Use a 35mm Din Rail.
Plastic adaptor plate.
JN5-DIN-L02 (Frame 2 Din rail kit part number)
Mounting
Dismounting
Assembly:-
Disassembly:-
Plastic Adaptor plate
Snap hook
Middle Snap hook
Screw: M4
Page 13
3-4
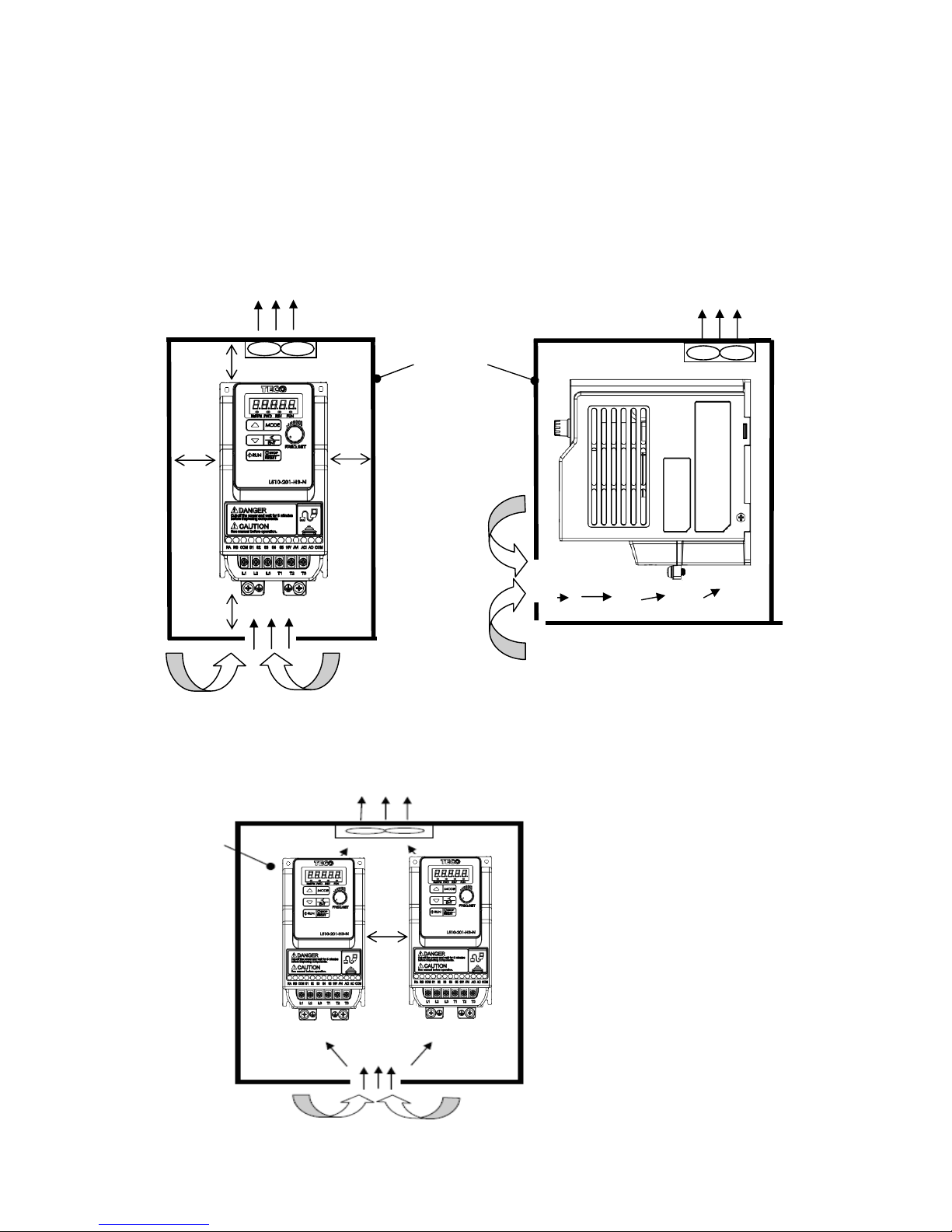
3.2.2 Installation space
Provide sufficient air circulation space for cooling as shown in examples below.
Install the Inverter on surfaces that provide good heat dissipation.
Single unit Installation
Install the inverter verticality to obtain effective cooling.
Frames1 & 2.
Side by side Installation
5cm 5cm
12cm
12cm
Front view
CONTROL
PANEL
Fan Fan
Side view
Provide the necessary
physical space and cooling
based on the ambient
temperature and the heat
loss in the panel
CONTROL
PANEL
5cm
Page 14
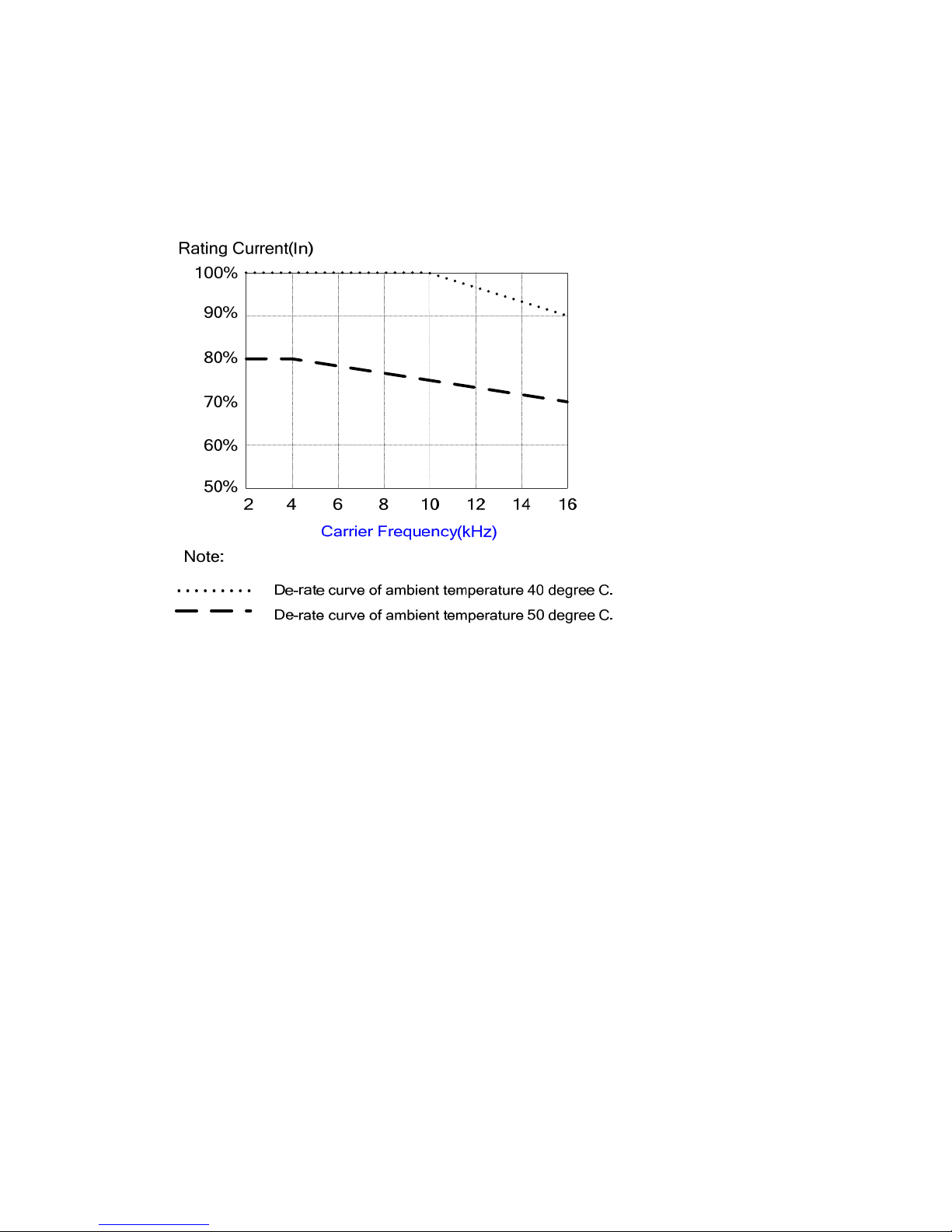
3-5
3.2.3 De-rating curve
Curves below show the applicable output current de-rate due to setting of carrier
frequency and the ambient operating temperatures of 40 and 50 degree C.
Page 15

3-6
3.3 Wiring Guidelines
3.3.1 Power Cables.
Supply power cable must be connected to TM1 terminal block, terminals L1(L) and L3(N) for
single phase 200V supply, L1(L), L2, L3(N) for three phase 200V supply and L1, L2, L3 for
three phase 400V supply.
Motor cable must be connected to TM1 terminals. T1, T2, T3.
Warning:- Connection of Supply line cable to terminals T1,T2& T3 will result in serious
damage to the drive components.
Example power connections:- Inverter with dedicated power line.
Inverter IM
Power
MCCB
¾
Install a Supply RFI filter or Isolation transformer when the power source is shared
with other high power electrical equipment as shown below.
Inverter IM
Machine
Insulation transformer
Power
MCCB
¾ The maximum rms symmetrical amperes and voltage are listed as follows:
Device Rating
voltage HP
Short circuit Rating Maximum Voltage
110V 0.2~1 5000A 120V
220V 0.2~3 5000A 240V
440V 1~3 5000A 480V
¾ Electrical ratings of terminals:
Horsepower Power Specification Voltage (Volt) Current(A)
0.25/0.5/1 220V 30
1 110V 20
2/3 220V
300
30
1/2/3 440V 600 28
Inverter IM
Machine
RFI
Filter
Power
MCCB
Page 16

3-7
3.3.2 Control Cable selection and Wiring.
Control cables should be connected to terminal block TM2.
Choose power & Control cables according to the following criteria:-
¾ Use copper wires with correct diameter and temperature rating of 60/75°C.
¾ Minimum cable voltage rating for 200V type inverters should be 300VAC.
¾ Route all cables away from other high voltage or high current power lines
to reduce interference effects.
Use a twisted pair shielded cable and connect the shield (screen) wire to the ground
terminal at the inverter end only. Cable length should not exceed 50 meters.
Shielding sheath
Protective covering
Connect the shield to inverter
ground terminal
Do not connect this end
Page 17
3-8
3.3.3 Wiring and EMC guidelines.
For effective interference suppression, do not route power and control cables in the same
conduit or trucking.
To prevent radiated noise, motor cable should be put in a metal conduit. Alternatively an
armored or shielded type motor cable should be used.
For effective suppression of noise emissions the cable armor or shield must be grounded at
both ends to the motor and the inverter ground. These connections should be as short as
possible.
Motor cable and signal lines of other control equipment should be at the least 30 cm apart.
L510 has a built in Class “A” EMC filter to first Environment Restricted. (Category C2).
For some installations such as residential,(Category C1) an optional external Class “B” type
filter will be necessary. Please consult your local supplier.
Typical Wiring.
5 6
7
8
Drive
2
3
1
4
1.Protective Earth Conductor.
Conductor size for enclosure &
Back plate must comply with the local electrical
standards. Min 10mm².
2.Back plate. Galvanised steel (Unpainted).
3.Ferrite core / Output reactor
ferrite cores can be used to reduce
radiated noise due to long motor cables.
If ferrite core is used loop motor wires, 3 times
round the core. Install core as close to the
inverter as possible
Output reactors provide additional
benefit of reducing dv/dt for protection of motor
windings.
4.Metal Cable clamp. no more than 150mm from
the inverter.
Note: If no enclosure & back plate is used then
connect the cable shield by a good 360 º
termination to the Inverter output terminal E.
5.Screened (Shielded four core cable).
6.Separate Protective Earth wire, routed outside
motor cable separated be at least 100mm.
Note:- this is the preferred method specially
for large output cables and long length.
Multi-core screened (3 core & protective
earth) can be used for small power and short
length.
7.Connect the cable shield by a good
360º termination and connect to the motor
protective earth terminal.
This link must be as short as possible.
8.Motor Earth terminal(Protective Earth).
L1(L)
L3(N)
E
L1(L)
L3(N)
E
E
T1 T2
T3
PE
M
Page 18

3-9
3.3.4 Failure liability
¾ Teco bears no responsibility for any failures or damaged caused to the inverter if the
recommendations in this instruction manual have not been followed specifically
points listed below,
¾ If a correctly rated Fuse or Circuit breaker has not been installed between the power
source and the inverter.
¾ If a magnetic contactor, a phase capacitor, burst absorber and LC or RC circuits have
been connected between the inverter and the motor.
¾ If an incorrectly rated three-phase squirrel cage induction motor has been used
Note:
When one inverter is driving several motors, the total current of all motors running
simultaneously must be less than the rated current of the inverter, and each motor
has to be equipped with a correctly rated thermal overload relay.
Page 19

3-10
3.3.5 Considerations for peripheral equipment
(
Power
Ensure that the supply voltage is correct.
A molded-case circuit breaker or fused disconnect
must be installed between the AC source and the
inverter
Circuit
Breaker
& RCD
Use a molded-case circuit breaker that conforms to
the rated voltage and current of the inverter.
Do not use the circuit breaker as the run/stop switch
for the inverter.
Residual Current Circuit Breaker(RCD)
Current setting should be 200mA or above and the
operating time at 0.1 second or longer to prevent
malfunctions.
Magnetic
contactor
Normally a magnetic contactor is not needed.
A contactor can be used to perform functions such
as external control and auto restart after power
failure.
Do not use the magnetic contactor as the run/stop
switch for the inverter.
AC reactor for
power quality
improvement
When a 200V/400V inverter with rating below 15KW
is connected to a high capacity power source
(600KVA or above) then an AC reactor can be
connected for power factor improvement and
reducing harmonics.
Input noise
filter
L510 inverter has a built-in filter to Class “A” first
Environment. (CategoryC2)
To satisfy the required EMC regulations for your
specific application you may require an additional
EMC filter.
Inverter
Connect the single phase power to Terminals, L1(L)
& L3(N) and three phase power to Terminals :
(200V : L1(L),L2,L3(N) or 400V : L1,L2,L3)
Warning! Connecting the input terminals T1, T2,
and T3 to AC input power will damage the inverter.
Output terminals T1, T2, and T3 are connected to U,
V, and W terminals of the motor.
To reverse the motor rotation direction just swap
any two wires at terminals T1, T2, and T3.
Ground the Inverter and motor correctly.
Ground Resistance for 200V power<100 Ohms.
Motor
Three-phase induction motor. Voltage drop on
motor due to long cable can be calculated.
Volts drop should be < 10%.
Phase-to-phase voltage drop (V) =
3 ×resistance of wire (Ω/km)×length of line
(m)×current×10
-3
Page 20

3-11
3.3.6 Ground connection
Inverter Ground terminal must be connected to installation ground correctly and
according to the required local wiring regulations.
¾ Ground cable size must be according to the required local wiring
regulations. Ground connection should be as short as possible.
¾ Do not share the ground of the inverter with other high current loads (Welding
machine, high power motors). Ground each unit separately.
¾ Ensure that all ground terminals and connections are secure
¾ Do not make ground loops when several inverters share a common ground point.
Note: Please leave at least 5cm while installing inverter side by side in order to provide
enough cooling space.
(a) Correct (b) Correct (c) Incorrect
3.3.7 Inverter exterior
RS485 Communication Port
Operator panel
TM2
TM1
Ground terminal
Page 21

3-12
3.4 Specifications
3.4.1 Product Specifications
100V Class : Single phase
Model : L510-□□□-H1-N □
1P2 1P5 101
Horse power (HP)
0.25 0.5 1
Suitable motor capacity (KW)
0.2 0.4 0.75
Rated output current (A)
1.8 2.6 4.3
Rated capacity (KVA)
0.68 1.00 1.65
Input voltage range(V)
Single Phase : 100~120V,50/60HZ
Allowable voltage fluctuation
+10%-15%
Output voltage range(V)
Three phase 0~24 0 V
Input current (A)*
9.5 13 19
Allowable momentary power loss time (S)
1.0 1.0 1.0
Enclosure
IP20
(If the model is marked A, it means that it is built in the power supply of 24V; if not, then it is built in
the power supply of 12V.)
200V Class : Single phase. F : Standards for built-in filter
Model : L510-
□□□-H1-N □
(L510-
□□□-H1F-P □)
2P2 2P5 201 202 203
Horse power (HP) 0.25 0.5 1 2 3
Suitable motor capacity (KW) 0.2 0.4 0.75 1.5 2.2
Rated output current (A) 1.8 2.6 4.3 7.5 10.5
Rated capacity (KVA) 0. 6 8 1 . 00 1.65 2.90 4.00
Input voltage range(V) Single Ph a s e : 200~240V,50/60HZ
Allowable voltage fluctuation
+10%-15%
Output voltage range(V) Three phase 0~240 V
Input current (A) 4.9 7.2 11 15.5 21
Allowable momentary power loss time (S) 1.0 1.0 1.0 2.0 2.0
Enclosure I P 2 0
(If the model is marked A, it means that it is built in the power supply of 24V; if not, then it is built in
the power supply of 12V.)
200V Class : Three phase
Model L510-
□□□-H3-N □
2P2 2P5 201 202 203
Horse power (HP) 0.25 0.5 1 2 3
Suitable motor capacity (KW) 0.2 0.4 0.75 1.5 2.2
Rated output current (A) 1.8 2.6 4.3 7.5 10.5
Rated capacity (KVA) 0.68 1.00 1.65 2.90 4.0 0
Input voltage range(V)* Three phase : 200 ~ 2 4 0 V , 5 0 / 60HZ
Allowable voltage fluctuation
+10%-15%
Output voltage range(V) Three phase 0~240 V
Input current (A) 3.0 4 . 0 6.4 9 . 4 1 2 . 2
Allowable momentary power loss time(S) 1.0 1.0 1.0 2.0 2.0
Enclosure I P 2 0
(If the model is marked A, it means that it is built in the power supply of 24V; if not, then it is built in
the power supply of 12V.)
Page 22

3-13
400V Class : Single phase. F : Standards for built-in filter
Model : L510-
□□□-H3-N A
(L510-
□□□-H3F-P A)
401 402 403
Horse power (HP) 1 2 3
Suitable motor capacity (KW) 0.75 1.5 2.2
Rated output current (A) 2.3 3.8 5.2
Rated capacity (KVA) 1 . 7 2 . 9 4 .0
Input voltage range(V) Three Pha s e : 380~480V,50/60HZ
Allowable voltage fluctuation
+10%-15%
Output voltage range(V) Three phase 0~480 V
Input current (A) 4 . 2 5 .6 7.3
Allowable momentary power loss time (S) 2 . 0 2.0 2. 0
Enclosure I P 2 0
(Models of 400V machines are all marked A, built in the power supply of 24V.)
*The input current is calculated value at full rated output current.
3.4.2 General Specifications
Item
L510
Control Mode
V/F Control + Auto-torque compensation function
Range 0.01~650.00Hz
Digital input : 0.01Hz
Setting resolution
Analog input : 0.06Hz/60Hz
Keypad : Set directly with▲▼ keys or the VR (Potentiometer)
on the keypad
External Input Terminals:
AVI(0/2~10V), ACI(0/4~20mA)input
Multifunction input up/down function(Group3)
Setting
Setting frequency by Communication method.
Frequency
Frequency limit
Lower and upper frequency limits
3 -skip frequency settings.
Keypad run, stop button
External terminals:
Multi- operation-mode 2 / 3 wire selection
Jog operation
Run
Operation set
Run signal by communication method.
V / F curve setting
6 fixed curve and one customized curve
Carrier frequency
1~16KHz(default 5KHz)
Acceleration and
deceleration control
2 off Acc / dec time parameters.
4 off S curve parameters.
Multifunction input
19 functions (refer to description on group3)
Multifunction output
14 functions (refer to description on group3)
Multifunction analog
output
5 functions (refer to description on group3)
Commonly
Control
Main features
Overload Detection, 8 preset speeds, Auto-run, Acc/Dec
Switch (2 Stages), Main/Alt run Command select, Main/Alt
Frequency Command select, PID control, torque boost, V/F
start Frequency ,Fault reset, Firemode.
Page 23

3-14
LED
Display: parameter/parameter value/frequency/line speed/DC
voltage/output voltage/output current/PID feedback/input and
output terminal status/Heat sink temperature/Program
Version/Fault Log.
Display
LED Status Indicator
For run/stop/forward and reverse.
Overload Protection
Integrated motor and Inverter overload protection.
Over voltage 100V/200V : Over 410V, 400V : Over 820V
Under voltage 100V/200V : Under 190V, 400V : Under 380V
Momentary Power Loss
Restart
Inverter auto-restart after a momentary power loss.
Stall Prevention
Stall prevention for Acceleration/ Deceleration/ and
continuous Run.
Short-circuit output
terminal
Electronic Circuit Protection
Protective
Functions
Grounding Fault Electronic Circuit Protection
Other protective
functions
Overheat protection, carrier frequency following as temperature
decreases, fault contact output, reverse limitation, unattended
start protection (USP) , times of automatic reset setting,
parameters locking and etc.
Protective
functions
International
authentication
CE/UL
communication control
Standard built in RS485 communication (Modbus), and it can
make control at one to one or one to more.
Operating temperature -10~50℃
Storage temperature -20~60℃
Humidity under 95%RH ( no condensation)
Shock
Under 20Hz, 1G(9.8m/s²)20~50Hz 0.6G(5.88m/s²)
Specifications of EMC complying with the first type of environment of EN61800-3
Specifications of LVD complying with the demand of EN50178
Security level UL508C
Environment
Protection level IP20
Page 24

3-15
3.5 Standard wiring
3.5.1 Single phase (NPN input)
AC Power
source
L1(L)
S2
S3
S4
+
T1
T2
T3
S5
COM
S1
-
Frequency
reference or PID
Multi-function input
Fuse
Inverter
output
Ground
E
Main
Switch
Power
input
RS485
Pin1 to Pin 8
AO
AGND
+
-
L3(N)
RB
RA
Multi-function output
0~10V
CON2
10V
AVI (0~10V)
ACI (0~20mA)
AGND
AO
Relay output
250VAC/1A
(30VDC/1A)
M
1:Data+
2:Data3:Data+
4:Reserved
5:Reserved
6:Data7:5V
8:GND
Model:
100V : L510-1P2-H1-N
□ / L510-1P5-H1-N □ / L510-101-H1-N □
200V : L510-2P2-H1-N
□ / L510-2P5-H1-N □ / L510-201-H1-N □
L510-202-H1-N
□ / L510-203-H1-N □
Page 25

3-16
3.5.2 Single phase (PNP input)
AC Power
source
L1(L)
S2
S3
S4
+
T1
T2
T3
S5
+12V
S1
-
Frequency
reference or PID
Multi-function input
Fuse
Inverter
output
Ground
E
Main
Switch
Power
input
RS485
Pin1 to Pin 8
AO
AGND
+
-
L3(N)
RB
RA
Multi-function output
0~10V
CON2
10V
AVI (0~10V)
ACI (0~20mA)
AGND
AO
Relay output
250VAC/1A
(30VDC/1A)
M
1:Data+
2:Data3:Data+
4:Reserved
5:Reserved
6:Data7:5V
8:GND
+24V (A)
Model:
200V : L510-2P2-H1F-P
□ / L510-2P5-H1F-P □ / L510-201-H1F-P □
L510-202-H1F-P
□ / L510-203-H1F-P □
Page 26

3-17
3.5.3 Three phase (NPN input)
AC Power
source
L1(L)
S2
S3
S4
+
T1
T2
T3
S5
COM
S1
-
Frequency
reference or PID
Multi-function input
Fuse
Inverter
output
Ground
E
Main
Switch
Power
input
RS485
Pin1 to Pin 8
AO
AGND
+
-
RB
RA
Multi-function output
0~10V
CON2
10V
AVI (0~10V)
ACI (0~20mA)
AGND
AO
Relay output
250VAC/1A
(30VDC/1A)
M
L3(N)
L2
1:Data+
2:Data3:Data+
4:Reserved
5:Reserved
6:Data7:5V
8:GND
P
BR
P
BR
P, BR for 400 series
Model:
200V : L510-2P2-H3-N
□ / L510-2P5-H3-N □ / L510-201-H3-N □
L510-202-H3-N
□ / L510-203-H3-N □
400V : L510-401-H3-N A / L510-402-H3-N A / L510-403-H3-N A
Page 27

3-18
3.5.4 Three phase (PNP input)
AC Power
source
L1(L)
S2
S3
S4
+
T1
T2
T3
S5
+24V (A)
S1
-
Frequency
reference or PID
Multi-function input
Fuse
Inverter
output
Ground
E
Main
Switch
Power
input
RS485
Pin1 to Pin 8
AO
AGND
+
-
RB
RA
Multi-function output
0~10V
CON2
10V
AVI (0~10V)
ACI (0~20mA)
AGND
AO
Relay output
250VAC/1A
(30VDC/1A)
M
L3(N)
L2
1:Data+
2:Data3:Data+
4:Reserved
5:Reserved
6:Data7:5V
8:GND
+12V
P
BR
P
BR
P, BR for 400 series
Model:
400V : L510-401-H3F-P A / L510-402-H3F-P A / L510-403-H3F-P A
Page 28

3-19
3.6 Terminal Description
3.6.1 Description of main circuit terminals
Terminal symbols TM1 Function Description
L1(L)
L2
L3(N)
Main power input, L1(L)/L2/L3(N)
P*
BR*
externally connected braking resistor
T1
T2
T3
Inverter output, connect to U, V, W terminals of motor
Ground terminal
*P,BR for 400V series
Single phase
Note: the screw on L2 terminal is removed for the single phase input supply models.
Three phase
Three phase (400V series)
L1(L) L2 L3(N) T1 T2 T3
L1(L) L2 L3(N) T1 T2 T3
L1 L2 L3 P BR T1 T2 T3
Page 29

3-20
3.6.2 Control circuit terminal description
Terminal symbols TM1 Function Description
RA
RB
Relay output terminal, Specification: 250VAC/1A(30VDC/1A)
COM
S1~S5 (COMMON) 【NPN】
+12V / +24V
S1~S5 (COMMON) 【PNP】(Model Name + A : 24V)
S1
S2
S3
S4
S5
Multi-function input terminals(refer to group3)
10V Built in Power for an external speed potentiometer
AVI Analog voltage input, Specification : 0~10VDC/ 2-10V
ACI Analog current input, Specification : 0/4~20mA
AO Multi function analog output terminal. Maximum output 10VDC/1mA
AGND Analog ground terminal
NPN:
PNP:
Page 30
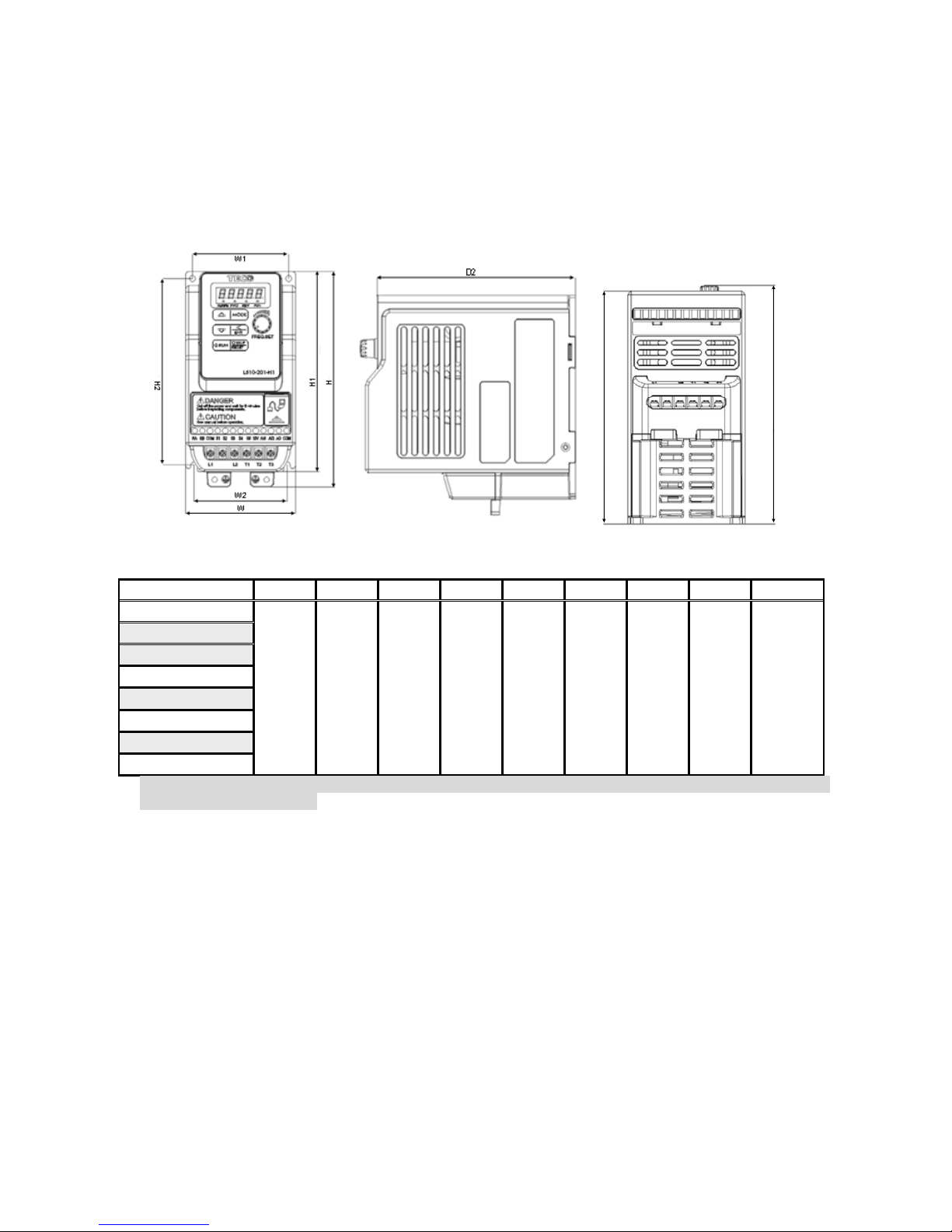
3-21
3.7 Outline Dimensions
(unit: mm)
Frame1
D1DD1
D
Unit : mm(inch)
Model W W1 W2 H H1 H2 D D1
Weight
L510-1P2-H1 □
L510-1P5-H1 □
L510-2P2-H1(F) □
L510-2P5-H1(F) □
L510-201-H1(F) □
L510-2P2-H3 □
L510-2P5-H3 □
L510-201-H3 □
72
(2.83)
63
(2.48)
61
(2.40)
141
(5.55)
131
(5.16)
122
(4.80)
139.2
(5.48)
136
(5.35)
0.9kg
(If the model is marked A, it means that it is built in the power supply of 24V; if not, then it is built in
the power supply of 12V.)
F : Built-in EMC filter
Page 31

3-22
Frame2
Unit : mm(inch)
Model W W1 W2 H H1 H2 D D1
Weight
L510-101-H1 □
L510-202-H1(F) □
L510-203-H1(F) □
L510-202-H3 □
L510-203-H3 □
L510-401-H3(F) A
L510-402-H3(F) A
L510-403-H3(F) A
118
(4.65)
108
(4.25)
108
(4.25)
144
(5.67)
131
(5.16)
121
(4.76)
147.3
(5.80)
144.2
(5.68)
1.6kg
(If the model is marked A, it means that it is built in the power supply of 24V; if not, then it is built in
the power supply of 12V. Models of 400V machines are all marked A, built in the power supply of
24V)
F : Built-in EMC filter
Page 32

3-23
3.8 EMC Filter Disconnection
EMC filter may be disconnected:
Inverter drives with built-in EMC filter are not suitable for connection to certain type of
supply systems, such as listed below; in these cases the RFI filter can be disabled.
In all such cases consult your local electrical standards requirements.
IT type supply systems (ungrounded) & certain supply systems for medical
equipment.
For ungrounded supply systems If the filter is not disconnected the supply system
becomes connected to Earth through the Y capacitors on the filter circuit. This could
result in danger and damage to the Drive.
Disconnection steps:
1. Remove EMC filter protection cover by screwdriver.
2. Remove EMC line by pliers.
Note:- Disconnecting the EMC filter link will disable the filter function, please consult your local
EMC standards requirement..
① ②
Page 33

4-1
Chapter4 Software Index
4.1 Keypad Description
4.1.1 Operator Panel Functions
Type Item Function
Main digital displays
Frequency Display, Parameter, voltage, Current,
Temperature, Fault messages.
Digital
display &
LEDs
LED Status
Hz/RPM: ON when the frequency or line speed is displayed.
OFF when the parameters are displayed.
FWD: ON while the inverter is running forward. Flashes
while stopped.
REV: ON while the inverter is running reverse. Flashes
while stopped.
FUN: ON when the parameters are displayed. OFF when
the frequency is displayed.
Variable
Resistor
FREQ SET Used to set the frequency
RUN RUN: Run at the set frequency.
STOP/RESET
(Dual function keys)
STOP: Decelerate or Coast to Stop.
RESET: Use to Reset alarms or resettable faults.
▲
Increment parameter number and preset values.
▼
Decrement parameter number and preset values.
MODE Switch between available displays
Keys
On Keypad
</ENTER
(Dual function keys,
a short press for left
shift function, a long
press for ENTER
function)
“<” Left Shift:
Used while changing the parameters or parameter values
ENTER:
Used to display the preset value of parameters and for saving
the changed parameter values.
Page 34

4-2
4.1.2 Digital display Description
Alpha numerical display format
Digit
LED
Letter
LED
Letter
LED
Symbol
LED
0
A
n
-
1
b
o
°
2
C
P
_
3
d
q
.
4
E
r
5
F
S
6
G
t
7
H
u
8
J
V
9
L
Y
Digital display indication formats
Actual output frequency Set frequency
Digits are lit Continually Preset digits flashing Selected digit flashing
Page 35

4-3
LED display examples
Display
Description
In stop mode shows the set frequency
In run mode shows the actual output frequency
Selected Parameter
Parameter Value
Output Voltage
Output Current in Amps
DC Bus voltage
Temperature
PID feedback value
Error display
Analogue Current / Voltage ACID / AVI . Range ( 0~1000)
LED Status description
LED Indicator light Status
Frequency / line
speed Indicator
Hz/RPM
On
Menu mode indicator
FUN
On while not displaying frequency or line speed
FWD indicator
FWD
On while running
forward
FWD
Flashing while
stopped in
Forward mode.
REV indicator light
REV
On while running
reverse
REV
Flashing while
stopped in
Reverse mode
Hz/RPM
Fun
FWD
REV
FWD
REV
Page 36

4-4
4.1.3 Digital display set up
On power up digital display screens will be as shown below.
MODE
2sec later
Power supply
frequency
parameter
MODE
User selectable display formats:
12- 00 Display Mode
0 0 0 0 0
high
Low
Each of the above 5 digits can be set to any of the selections below from 0 to 7
【0】:Disable display 【1】:output Current
【2】:output Voltage 【3】:DC voltage
【4】:Temperature 【5】:PID feedback
Range
【6】:AVI 【7】:ACI
The highest bit of 12-00 sets the power on the display, other bits set the selected display from range
0-7.as Listed above.
Example1: Set parameter 12- 00=【10000】to obtain display format shown below.
MODE
MODE MODE
2sec later
display:Power supply
Output Current
Set frequency
parameter
Page 37

4-5
Example 2. Set parameter 2: 12- 00=【12345】 to obtain the display format shown below.
MODE
MODE
2sec later
MODE
MODE
MODE
MODE
MODE
Temperature
< 4 >
PIDfeedback
< 5 >
Output Current
< 1 >
Parameter
DC voltage
< 3 >
Output Voltage
< 2 >
Set Frequency
Display: Power supply
Increment/ Decrement key functions:
1.“
▲”/ “▼” :
Short time press
Long time press
T1
T2
Quick pressing of these keys will Increment or Decrement the selected digit by one.
Extended pressing will Increment or Decrement the selected digit continuously.
2.“</ENT” Key functions :
“</ENT”
short press for left shift
function
“</ENT”
long press for ENT
functi on
T1
T2
Quick pressing of this key will display the preset value of the parameter selected.
Extended pressing of this key will save the altered value of the selected parameter.
Page 38

4-6
4.1.4 Example of keypad operation
Example1: Modifying Parameters
Short time press
</ENT once
Short time press
</ENT twice
Short time
press
once
Long time press
</ENT once
Frequency
Short time
press
once
Long time press
</ENT once
Short time press
MODE once
▲
▲
Page 39

4-7
Example2: Modifying the frequency from keypad in run and stop modes.
Modify frequency in stopping
Modify frequency in operating
2sec later
2sec later
Short time press
</ENT once
Press RUN
5sec later
or long time press
</ENT once
Long time press
</ENT once
Without
pressing the
button
</ENT,
After 5
seconds to
return
Short time press
</ENT once
Power Supply
Power supply
Actual frequency
Actual frequency
Short time press
</ENT once
Short time press
</ENT once
Short time press
▲ once
Short time press
</ENT once
Short time press
</ENT once
Short time press
▲ once
Set frequency display Set frequency display
Modify bit<unit>
Modify bit<ten>
Modify bit<hundred>
Modify bit<hundred+1>
Modify bit<hundred+1>
Modify bit<hundred>
Modify bit<ten>
Modify bit<unit>
Note: frequency command setting will be limited to the range set by parameters for lower &
upper frequency.
Modify frequency is stopping
Modify frequency is stopping
Power supply Power supply
2sec later 2sec later
Set frequency display
Set frequency display
Press run
Short time press
</ENT once
Short time press
</ENT once
A
ctual frequency
Short time press
</ENT once
Short time press
</ENT once
Short time press
</ENT once
Short time press
</ENT once
Short time press
▲once
Short time press
▲once
5 sec later or long
time press </ENT
once
Long time press
</ENT once
Modify bit<unit>
Modify bit<unit>
Modify bit<ten>
Modify bit<ten>
Modify bit<hundred>
Modify bit<hundred>
Modify bit<hundred+1>
Modify bit<hundred+1>
A
ctual frequency
Without pressing
the button </ENT,
A
fter 5 seconds to
return
Page 40

4-8
4.1.5 Operation Control
Stop
Run
Stop
Actual
Output
frequency
Power
on
REV FWD
Run
REV
FWD
Stop
FWDFWD
FWD
FWD FWD
FWD
FWD
FWD
LED
REV
LED
REV
REV REV REV
REV
REV
REV
Page 41

4-9
4.2 Programmable Parameter Groups
Parameter Group No. Description
Group 00 Basic parameters
Group 01 V/F Pattern selections & setup
Group 02 Motor parameters
Group 03 Multi function digital Inputs/Outputs
Group 04 Analog signal inputs/ Analog output
Group 05 Preset Frequency Selections.
Group 06 Auto Run(Auto Sequencer) function
Group 07 Start/Stop command setup
Group 08 Drive and motor Protection
Group 09 Communication function setup
Group 10 PID function setup
Group 11 Performance control functions
Group 12 Digital Display & Monitor functions
Group 13 Inspection & Maintenance function
Parameter notes for Parameter Groups
*1
Parameter can be adjusted during running mode
*2
Cannot be modified in communication mode
*3
Does not change with factory reset
*4
Read only
Page 42

4-10
Group 00- The basic parameters group
No. Description Range
Factory
Setting
Unit Note
00-00
Reserved
00-01
Motor rotation
0:Forward
1:Reverse
0 - *1
0:Keypad
1:External Run/Stop Control
00-02
Main Run
Source Selection
2:Communication
0 -
0:Keypad
1:External Run/Stop Control
00-03
Alternative Run
Source Selection
2:Communication
0 -
0: Forward/Stop-Reverse/Stop
1: Run/Stop-Reverse/Forward
00-04
Operation modes for
external terminals
2: 3-Wire Control Mode-Run/Stop
0 -
0:Keypad
1:Potentiometer on Keypad
2:External AVI Analog Signal Input
3:External ACI Analog Signal Input
4:External Up/Down Frequency
Control
5:Communication setting Frequency
00-05
Main Frequency
Source Selection
6:PID output frequency
0 -
0:Keypad
1:Potentiometer on Keypad
2:External AVI Analog Signal Input
3:External ACI Analog Signal Input
4:External Up/Down Frequency
Control
5:Communication setting Frequency
00-06
Alternative Frequency
Source Selection
6:PID output frequency.
4 -
00-07
Main and Alternative
Frequency Command modes
0: Main Or Alternative Frequency
1: Main frequency+Alternative
Frequency
0 -
00-08
Communication
Frequency Command
0.00~650.00 Hz *4
00-09
Frequency command
Save mode
(Communication mode)
0:Save the frequency before power
down
1:Save the communication frequency
0 -
0:by Current Frequency Command
1:by 0 Frequency Command
00-10
Initial Frequency
Selection ( keypad mode)
2:by 00-11
0 -
00-11
Initial Frequency
Keypad mode
0.00~650.00 50.00/60.00 Hz
00-12
Frequency Upper Limit 0.01~650.00 50.00/60.00 Hz
00-13
Frequency Lower Limit 0.00~649.99 0.00 Hz
00-14
Acceleration Time 1 0.1~3600.0
10.0
s
*1
00-15
Deceleration Time 1 0.1~3600.0
10.0
s
*1
00-16
Acceleration Time 2 0.1~3600.0
10.0
s
*1
00-17
Deceleration Time 2 0.1~3600.0 10.0 s *1
00-18
Jog Frequency 1.00~25.00 2.00 Hz *1
00-19
Jog Acceleration Time 0.1~25.5
0.5
s
*1
00-20
Jog Deceleration Time 0.1~25.5
0.5
s
*1
Page 43

4-11
Group 01- V/F Pattern selection & Setup
No. Description Range
Factory
Setting
Unit Note
01-00
Volts/Hz Patterns 1~7 1/4 -
01-01
V/F Max voltage
200V:198.0~256.0
400V:323.0~528.0
220.0/440.0 Vac
01-02
Max Frequency 0.20 ~ 650.00 50.00/60.00 Hz
01-03
Max Frequency Voltage Ratio 0.0 ~ 100.0 100.0 %
01-04
Mid Frequency 2 0.10 ~ 650.00 25.00/30.00 Hz
01-05
Mid Frequency Voltage Ratio 2 0.0 ~ 100.0 50.0 %
01-06
Mid Frequency 1 0.10 ~ 650.00 10.00/12.00 Hz
01-07
Mid Frequency Voltage Ratio 1 0.0 ~ 100.0 20.0 %
01-08
Min Frequency 0.10 ~ 650.00 0.50/0.60 Hz
01-09
Min Frequency Voltage Ratio 0.0 ~ 100.0 1.0 %
01-10
Volts/Hz Curve Modification
(Torque Boost)
0 ~ 10.0 0.0 % *1
01-11
V/F start Frequency 0.00~10.00 0.00 Hz
Group 02- Motor parameters
No. Description Range
Factory
Setting
Unit Note
02-00
Motor No Load Current
----
A *3
02-01
Motor Rated Current
(OL1) ----
A
02-02
Motor rated Slip
Compensation
0.0 ~ 100.0 0.0 % *1
02-03
Motor Rated Speed
----
Rpm
02-04
Motor Rated Voltage
---- Vac *4
Page 44

4-12
Group 03- Multi function Digital Inputs/Outputs
No. Description Range
Factory
Setting
Unit Note
03-00
Multifunction Input Term. S1 0:Forward/Stop Command or Run /Stop
0 -
03-01
Multifunction Input Term. S2
1:Reverse/Stop Command Or
REV/FWD 1 -
03-02
Multifunction Input Term. S3
2:Preset Speed 1 (5-02) 8 -
03-03
Multifunction Input Term. S4
3:Preset Speed 2 (5-03) 9 -
4:Preset Speed 4 (5-05)
6:Jog Forward Command
7:Jog Reverse Command
8:Up Command
9:Down Command
10:Acc/Dec 2
11:Acc/Dec Disabled
12:Main/Alternative Run Command
select
13:Main/Alternative Frequency
Command select
14:Rapid Stop ( Decel to stop)
15:Base Block
16:Disable PID Function
17:Reset
03-04
Multifunction Input Term. S5
18:Auto Run Mode enable
17 -
03-05
Reserved
03-06
Up/Down frequency band 0.00~5.00 0.00 Hz
0:When Up/Down is used, the preset
frequency is held as the inverter stops,
and the UP/Down function is disabled.
1:When Up/Down is used, the preset
frequency is reset to 0 Hz as the
inverter stops.
03-07
Up/Down Frequency modes
2:When Up/Down is used, the preset
frequency is held as the inverter stops,
and the UP/Down is available.
0 -
03-08
S1~S5 scan confirmation 1~400. Number of Scan cycles 20 1ms
xxxx0:S1 NO xxxx1:S1 NC
xxx0x:S2 NO xxx1x:S2 NC
xx0xx:S3 NO xx1xx:S3 NC
x0xxx:S4 NO x1xxx:S4 NC
03-09
S1~ S5 switch type select
0xxxx:S5 NO 1xxxx:S5 NC
00000 -
03-10
Reserved
0:Run
1:Fault
2:Setting Frequency Agree
3:Frequency Agree (3-13±3-14)
4:Output Frequency Detection1(> 3-13)
5:Output Frequency Detection2(< 3-13)
6:Auto-Restart
7:Momentary AC Power Loss
8:Rapid Stop
9:Base Block
10:Motor Overload Protection(OL1)
11:Drive Overload Protection(OL2)
12:Reserved
03-11
Output Relay(RY1)
13:Output Current Agree
0 -
Page 45

4-13
14:Brake Control
03-12
Reserved
03-13
Output frequency detection
level (Hz)
0.00~650.00 0.00 Hz *1
03-14
Frequency Detection band
0.00~30.00 2.00 Hz *1
03-15
Output Current Agree
Setting
0.1~15.0 0.1 A
03-16
Current Agree Delay Time
0.1~10.0 0.1 s
03-17
External Brake Release
level
0.00~20.00 0.00 Hz
03-18
External Brake Engage
Level
0.00~20.00 0.00 Hz
03-19
Relay Output function type
0:A (Normally open)
1:B (Normally close)
0 -
※ “NO” indicates normally open, “NC” indicates normally closed.
Group 04- Analog signal inputs/ Analogue output functions
No. Description Range
Factory
Setting
Unit Note
AVI ACI
0:0~10V 0~20mA
1:0~10V 4~20mA
2:2~10V 0~20mA
04-00
AVI/ACI analog Input
signal type select
3:2~10V 4~20mA
0 -
04-01
AVI Signal Verification
Scan rate
1~400 100 1ms
04-02 AVI Gain
0 ~ 1000 100 % *1
04-03 AVI Bias
0 ~ 100 0 % *1
04-04 AVI Bias Selection
0: Positive 1: Negative 0 - *1
04-05 AVI Slope
0: Positive 1: Negative 0 - *1
04-06
ACI Signal Verification
Scan rate
1~400 100 1ms
04-07
ACI Gain 0 ~ 1000 100 % *1
04-08
ACIBias 0 ~ 100 0 % *1
04-09
ACI Bias Selection 0: Positive 1: Negative 0 - *1
04-10
ACI Slope 0: Positive 1: Negative 0 - *1
04-11
Analog Output
mode(AO)
0: Output Frequency
1: Frequency Command
2: Output Voltage
3: DC Bus Voltage
4: Motor Current
0 - *1
04-12
Analog Output AO Gain
(%)
0 ~ 1000 100 % *1
04-13
Analog Output AO Bias
(%)
0 ~ 1000 0 % *1
04-14
AO Bias Selection
0: Positive
1: Negative
0 - *1
04-15
AO Slope
0: Positive
1: Negative
0 - *1
Page 46

4-14
Group 05- Preset Frequency Selections.
No. Description Range
Factory
Setting
Unit Note
0: Common Accel/Decel
Accel/Decel 1 or 2 apply to all speeds
05-00
Preset Speed Control
mode Selection
1: Individual Accel/Decel Accel/ Decel
0-7 apply to the selected preset
speeds (Acc0/Dec0~ Acc7/Dec7)
0 -
05-01
Preset Speed 0
(Keypad Freq)
5.00 Hz
05-02
Preset Speed1 (Hz)
5.00 Hz *1
05-03
Preset Speed2 (Hz)
10.00 Hz *1
05-04
Preset Speed3 (Hz)
20.00 Hz *1
05-05
Preset Speed4 (Hz)
30.00 Hz *1
05-06
Preset Speed5 (Hz)
40.00 Hz *1
05-07
Preset Speed6 (Hz)
50.00 Hz *1
05-08
Preset Speed7 (Hz)
0.00 ~ 650.00
50.00 Hz *1
05-09
~
05-16
Reserved
05-17
Preset Speed0-Acctime
10.0 s *1
05-18
Preset Speed0-Dectime
10.0
s
*1
05-19
Preset Speed1-Acctime
10.0
s
*1
05-20
Preset Speed1-Dectime
10.0
s
*1
05-21
Preset Speed2-Acctime
10.0
s
*1
05-22
Preset Speed2-Dectime
10.0
s
*1
05-23
Preset Speed3-Acctime
10.0
s
*1
05-24
Preset Speed3-Dectime
10.0
s
*1
05-25
Preset Speed4-Acctime
10.0
s
*1
05-26
Preset Speed4-Dectime
10.0
s
*1
05-27
Preset Speed5-Acctime
10.0
s
*1
05-28
Preset Speed5-Dectime
10.0
s
*1
05-29
Preset Speed6-Acctime
10.0
s
*1
05-30
Preset Speed6-Dectime
10.0
s
*1
05-31
Preset Speed7-Acctime
10.0
s
*1
05-32
Preset Speed7-Dectime
0.1 ~ 3600.0
10.0
s
*1
Page 47

4-15
Group 06- Auto Run(Auto Sequencer) function
No. Description Range
Factory
Setting
Unit Note
06-00
Auto Run
(sequencer)
mode selection
0: Disabled.
1: Single cycle.
(Continues to run from the Unfinished
step if restarted).
2: Periodic cycle.
(Continues to run from the unfinished
step if restarted).
3: Single cycle, then holds the speed Of
final step to run.
(Continues to run from the unfinished
step if restarted).
4: Single cycle.
(Starts a new cycle if restarted).
5: Periodic cycle.
(Starts a new cycle if restarted).
6: Single cycle, then hold the speed of
final step to run
(Starts a new cycle if restarted).
0 -
06-01
Auto _ Run Mode
frequency command 1
0.00 Hz *1
06-02
Auto _ Run Mode
frequency command 2
0.00 Hz *1
06-03
Auto _ Run Mode
frequency command 3
0.00 Hz *1
06-04
Auto _ Run Mode
frequency command 4
0.00 Hz *1
06-05
Auto _ Run Mode
frequency command 5
0.00 Hz *1
06-06
Auto _ Run Mode
frequency command 6
0.00 Hz *1
06-07
Auto _ Run Mode
frequency command 7
0.00~650.00
0.00 Hz *1
06-08
~
06-15
Reserved
06-16
Auto_ Run Mode
running time setting 0
0.0 s
06-17
Auto_ Run Mode
running time setting 1
0.0 s
06-18
Auto_ Run Mode
running time setting 2
0.0 s
06-19
Auto_ Run Mode
running time setting 3
0.0 s
06-20
Auto_ Run Mode
running time setting 4
0.0 s
06-21
Auto_ Run Mode
running time setting 5
0.0 s
06-22
Auto_ Run Mode
running time setting 6
0.0 s
06-23
Auto_ Run Mode
running time setting 7
0.0 ~ 3600.0
0.0 s
06-24
~
06-31
Reserved
06-32
Auto_ Run Mode
running direction 0
0 -
06-33
Auto_ Run Mode
running direction 1
0: Stop
1: Forward
2: Reverse
0 -
Page 48

4-16
06-34
Auto_ Run Mode
running direction 2
0 -
06-35
Auto_ Run Mode
running direction 3
0 -
06-36
Auto_ Run Mode
running direction 4
0 -
06-37
Auto_ Run Mode
running direction 5
0 -
06-38
Auto_ Run Mode
running direction 6
0 -
06-39
Auto_ Run Mode
running direction 7
0 -
Group 07- Start/Stop command setup
No. Description Range
Factory
Setting
Unit Note
07-00
Momentary Power
Loss and Restart
0: Momentary Power Loss and Restart disable
1: Momentary power loss and restart enable
0 s
07-01
Auto Restart Delay
Time
0.0~800.0
0.0 s
07-02
Number of Auto
Restart Attempts
0~10
0 -
07-03
Reset Mode Setting
0: Enable Reset Only when Run Command is
Off
1: Enable Reset when Run Command is On or
Off
0 -
07-04
Direct Running After
Power Up
0: Enable Direct run on power up
1: Disable Direct run on power up
1 -
07-05 Delay-ON Timer 1.0~300.0
1.0 s
07-06
DC Injection Brake
Start Frequency
(Hz) In Stop mode
0.10 ~ 10.00
1.5 Hz
07-07
DC Injection Brake
Level (%) In stop
mode
0 ~20
5 %
07-08
DC Injection Brake
Time (Seconds)
In stop mode
0.0 ~ 25.5
0.5 s
07-09
Stopping Method
0: Deceleration to stop
1: Coast to stop
0
Page 49

4-17
Group 08- Drive & Motor Protection functions
No. Description Range
Factory
Setting
Unit Note
08-00
Trip Prevention Selection
xxxx0: Enable Trip Prevention During
Acceleration
xxxx1: Disable Trip Prevention During
Acceleration
xxx0x: Enable Trip Prevention During
Deceleration
xxx1x: Disable Trip Prevention During
Deceleration
xx0xx: Enable Trip Prevention in Run
Mode
xx1xx: Disable Trip Prevention in Run
Mode
x0xxx: Enable over voltage Prevention
in Run Mode
x1xxx: Disable over voltage Prevention
in Run Mode
00000 -
08-01
Trip Prevention Level
During Acceleration (%)
50 ~ 200 200
08-02
Trip Prevention Level
During Deceleration (%)
50 ~ 200 200
08-03
Trip Prevention Level In
Run Mode (%)
50 ~ 200 200
Inverter
Rated
Current
100%
08-04
over voltage Prevention
Level in Run Mode
350~390 380 VDC
08-05
Electronic Motor
Overload Protection
Operation Mode
0: Enable Electronic Motor Overload
Protection
1: Disable Electronic Motor Overload
Protection
1 -
08-06
Operation After
Overload Protection is
Activated
0: Coast-to-Stop After Overload
Protection is Activated
1: Drive Will Not Trip when Overload
Protection is Activated (OL1)
0 -
08-07
Over heat Protection
(cooling fan control)
0: Auto (Depends on temp.)
1: Operate while in RUN mode
2: Always Run
3: Disabled
1 -
0: AVR function enable
1: AVR function Disable
2: AVR function disable for stop
3: AVR function disable for deceleration
4: AVR function disable for stop and
deceleration.
08-08
AVR Function
(Auto Voltage
Regulation)
5: When VDC>(360V/740V), AVR
function disable for stop and
deceleration.
4 -
08-09
Input phase lost
protection
0: Disabled
1: Enabled
0 -
Page 50

4-18
Group 09- Communication function setup
No. Description Range
Factory
Setting
Unit Note
09-00
Assigned
Communication
Station Number
1 ~ 32 1 - *2*3
09-01
RTU code /ASCII
code select
0:RTU code
1:ASCII code
0 - *2*3
09-02
Baud Rate Setting
(bps)
0:4800
1:9600
2:19200
3:38400
2 bps *2*3
09-03
Stop Bit Selection
0:1 Stop Bit
1:2 Stop Bits
0 - *2*3
09-04
Parity Selection
0:Without Parity
1:With Even Parity
2:With Odd Parity
0 - *2*3
09-05
Data Format
Selection
0: 8-Bits Data
1: 7-Bits Data
0 - *2*3
09-06
Communication
time-out detection
time
0.0 ~ 25.5
0.0 s
09-07
Communication
time-out operation
selection
0:Deceleration to stop
(00-15: Deceleration time 1)
1:Coast to stop
2: Deceleration to stop
(00-17: Deceleration time 2)
3: continue operating
0 -
09-08
Error 6 verification
time.
1 ~ 20
3
09-09
Drive Transmit
delay Time(ms)
5 ~ 65
5 ms
Page 51

4-19
Group10- PID function Setup
No. Description Range
Factory
Setting
Unit Note
10-00
PID target value selection
(when 00-03\00-04=6
,this function is enabled)
0:Potentiometer on Keypad
1: Analog Signal Input. (AVI)
2: Analog Signal Input. (ACI)
3: Frequency set by communication
4: KeyPad Frequency parameter
10-02
1 - *1
10-01
PID feedback value selection
0:Potentiometer on Keypad
1: Analog Signal Input. (AVI)
2: Analog Signal Input. (ACI)
3: Frequency set by communication
2 - *1
10-02 PID Target (keypad input) 0.0~100.0
50.0 % *1
10-03
PID Mode Selection
0:Disabled
1: Deviation D Control.
FWD Characteristic.
2: Feedback D Control
FWD Characteristic.
3: Deviation D Control
Reverse Characteristic.
4: Feedback D Control
Reverse Characteristic.
0 -
10-04
Feedback Gain Coefficient
0.00 ~ 10.00 1.00 % *1
10-05
Proportional Gain 0.0 ~ 10.0 1.0 % *1
10-06
Integral Time 0.0 ~ 100.0 10.0 s *1
10-07
Derivative Time 0.00 ~ 10.00 0.00 s *1
10-08
PID Offset
0: Positive
1: Negative
0 - *1
10-09
PID Offset Adjust 0 ~ 109 0 % *1
10-10
PID Output Lag Filter Time
0.0 ~ 2.5 0.0 s *1
10-11
Feedback Loss Detection
Mode
0: Disabled
1: Enabled - Drive Continues to
Operate After Feedback Loss
2: Enabled - Drive "STOPS"
After Feedback Loss
0 -
10-12
Feedback Loss Detection
Level
0 ~ 100
0 %
10-13
Feedback Loss Detection
Delay Time
0.0 ~25.5
1.0 s
10-14 Integration Limit Value
0 ~ 109
100 % *1
10-15
Integral Value Resets to Zero
when Feedback Signal Equals
the Target Value
0:Disabled
1: 1 Second
30: 30 Seconds (0 ~ 30)
0 -
10-16
Allowable Integration Error
Margin (units)(1unit = 1/8192)
0 ~ 100
0 -
10-17 PID Sleep Frequency Level
0.00~650.00
0.00 Hz
10-18
PID Sleep Function Delay
Time
0.0 ~25.5
0.0 s
10-19 PID Wake up frequency Level
0.00 ~ 650.00
0.00 Hz
10-20
PID Wake up function Delay
Time
0.0 ~ 25.5
0.0 s
10-21 Max PID Feedback Setting
0 ~999
100 - *1
10-22
Min PID Feedback Setting 0 ~999 0 - *1
Page 52

4-20
Group11- Performance Control functions
No. Description Range
Factory
Setting
unit Note
11-00
Reverse operation control
0: Reverse command is enabled
1: Reverse command is disabled
0 -
11-01
Carrier Frequency (kHz) 1~16 5 KHz
11-02
Carrier mode Selection
0: Mode0, 3phase PWM modulation
1: Mode1, 2phase PWM modulation
2: Mode2, 2phase random PWM
modulation
0 -
11-03
Carrier Frequency
Reduction by temperature
rise
0:disabled
1:enabled
0 -
11-04
S-Curve Acc 1 0.0 ~ 4.0 0.00 s
11-05
S-Curve Acc 2 0.0 ~ 4.0 0.00 s
11-06
S-Curve Dec 3 0.0 ~ 4.0 0.00 s
11-07
S-Curve Dec 4 0.0 ~ 4.0 0.00 s
11-08
Skip Frequency 1 0.00 ~ 650.00 0.00 Hz *1
11-09
Skip Frequency 2 0.00 ~ 650.00 0.00 Hz *1
11-10
Skip Frequency 3 0.00 ~ 650.00 0.00 Hz *1
11-11
Skip Frequency
Bandwidth (±)
0.00 ~ 30.00 0.00 Hz *1
Group12 Digital Display & Monitor functions
No. Description Range
Factory
Setting
Unit Note
00000 ~77777.
Each digit can be set to 0 to 7
0: Default display
(frequency¶meters)
1:Output Current
2:Output Voltage
3:DC voltage
4:Temperature
5:PID feedback
6:Analog Signal Input. (AVI)
12-00
Extended Display Mode
7:Analog Signal Input. (ACI)
00000 - *1
0: Integer (xxx)
1:One decimal Place (xx.x)
12-01
PID Feedback Display
format
2:Two Decimal Places (x.xx)
0 - *1
0:xxx-1:xxxpb (pressure)
12-02
PID Feedback Display
Unit Setting
2:xxxfl (flow)
0 - *1
12-03
Custom Units (Line
Speed) Value
0~65535 1500/1800 RPM *1
0:Drive Output Frequency is Displayed
1:Line Speed. Integer.(xxxxx)
2:Line Speed..One Decimal Place
(xxxx.x)
3:Line Speed.Two Decimal Places
(xxx.xx)
12-04
Custom Units (Line
Speed) Display Mode
4:Line Speed.Three Decimal Places
(xx.xxx)
0 - *1
Page 53

4-21
Group12 Digital Display & Monitor functions
No. Description Range
Factory
Setting
Unit Note
12-05
Inputs and output
Logic status display
( S1 to S5) & RY1
S1 S2 S3 S4 S5
RY1
----- - *4
Group 13 Inspection & Maintenance functions
No. Description Range
Factory
Setting
unit Note
13-00
Drive Horsepower
Code
---- - - *3
13-01
Software Version ---- - - *3*4
13-02
Fault Log
(Last 3 Faults)
---- - - *3*4
13-03
Accumulated Operation
Time1 1
0~23 - hour *3
13-04
Accumulated Operation
Time1 2
0~65535 ---- day *3
13-05
Accumulated Operation
Time Mode
0:Time Under Power
1:Run Mode Time Only
0 - *3
13-06
Parameter Lock
0: Enable all Functions
1: Preset speeds 05-01~05-08 cannot
be changed
2: All Functions cannot be changed
Except for Preset speeds
05-01~05-08
3: Disable All Function
0 -
13-07
Parameter Lock Code 00000~65535 00000 -
13-08
Reset Drive to Factory
Settings
1150: Reset to factory setting. 50Hz
system.
1160: Reset to factory setting. 60Hz
system.
00000 -
Page 54

4-22
4.3 Parameter Function Description
00- Basic parameter group
00- 01 Motor Direction Control
Range
【0】: Forward
【1】: Reverse
¾ 00 - 01 Is valid in key pad mode only.
Note※ : When Reverse function is disabled by parameter 11- 00=1 setting 00-01 to 1 .” LOC” will be
displayed
00- 02 Main Run Command Source selection
00- 03 Alternative Run Command Source selection
Range
【0】: Keypad
【1】: External Run/Stop Control
【2】: Communication
¾ Parameter 00 - 02/00- 03 sets the inverter operation command source. For switching between
00-02 and 00-03, use any of the external inputs S1 to S5 and set the relevant parameters
(03-00~03-04) to [12]. refer to parameter group3.
00- 04 Operation modes for external terminals
Range
【0】: Forward/stop-reverse/stop
【1】: Run/stop-forward/reverse
【2】: 3-wire control mode -run/stop
¾ 00-04 Is valid when Run command is set to External mode by 00- 02/00- 03 =1.
2-wire operation mode:
Set 00-04=【0/1】first, before setting (03-00,03-04) to[0] or [1]
00-04= 【0】Set external terminals (03-00 to 03-04) function to 0 for FWD/Stop or Set to 1 for
REV/Stop.
00-04= 【1】Set external terminals (03-00 to 03-04) function to 0 for Run/Stop or Set to 1 for
FWD/REV.
3-wire operation mode:
00-04 =【2】Terminals S1, S2, S3 are used in a combination to enable 3 wire run/stop mode.
Settings for 03-00, 03-01, 03–02 will not be effective. (refer to Group 03)
00- 05
Main Frequency Command Source Selection
00- 06 Alternative Frequency Command Source Selection
Range
【0】:UP/DOWN of Keypad
【1】:Potentiometer on Keypad
【2】:External AVI Analog Signal Input
【3】:External ACI Analog Signal Input
【4】:External Up/Down Frequency Control
【5】:Communication setting Frequency
【6】:PID Output frequency
¾ When 00-06 =[6], frequency command source is output of the PID.
00- 07 Main and Alternative Frequency Command Modes
Range
【0】:Main Or Alternative Frequency.
【1】:Main frequency + Alternative Frequency
¾ When 00-07=【0】, the frequency source is set by the Main frequency parameter 00-05 (Default)
or by the Alternative frequency parameter 00-06.
Use any of the external terminals S1 to S5 and set the relevant parameter 03-00 to 03-04 =【13】to
switch from main to Alternative source.
¾ When 00 - 07 =【1】The Frequency command will be the result of setting of Main & alternative
frequencies.
Page 55

4-23
00- 08 Communication Frequency Command
Range
【0.00~650.00】Hz
¾ This parameter can be used to set frequency command
¾ This parameter can be used to read the set frequency in communication mode
¾ This parameter is only effective in the communication mode.
00- 09 Frequency Command save on power down (Communication mode)
Range
【0】:disable
【1】:enable
¾ 00-09=【0】 Keypad frequency is saved.
¾ 00-09=【1】 Frequency set by communication is saved.
00-10 Initial Frequency Selection
Range
【0】:By Current Freq Command
【1】:By Zero Freq Command
【2】:By 00-11
00-11 Initial Frequency Setpoint
Range
【0.00~650.00】Hz
¾ This parameter is only effective in keypad mode..
¾ When 00-10=【0】,the initial frequency will be current frequency.
¾ When 00-10=【1】,the initial frequency will be 0.
¾ When 00-10=【2】,the initial frequency will be as set by parameter 00-11.
00-12 Frequency Upper limit
Range
【0.01~650.00】Hz
00-13 Frequency Lower limit
Range
【0.00~649.99】Hz
¾ When 00-13 and the command frequency are both set to 0.00, if RUN is pressed ” Stpo” is
displayed.
¾ When Frequency command is > than preset in 00-13 inverter output will ramp up from 0.00 to the
command frequency.
¾ When 00-13> 0, and the frequency command value ≤ 00-13, inverter output will ramp up from
preset in lower limit to the command frequency.
Frequency upper limit
Frequency Lower limit
0
Hz
T
Page 56

4-24
00-14 Acceleration time 1
Range
【0.1~3600.0】 s
00-15 Deceleration time 1
Range
【0.1~3600.0】s
00-16 Acceleration time 2
Range
【0.1~3600.0】s
00-17 Deceleration time 2
Range
【0.1~3600.0】s
¾ Preset Acceleration and Deceleration times by above parameters are the time taken for the
output frequency to ramp up or ramp down between the Upper and the lower frequency limits.
¾ Actual acceleration and deceleration time is calculated as follows:
Maximum output Frequency
Set frequency
Acc-time 00-14
Dec-time 00-15
Actual acc-time
Actual dec-time
Hz
T0
The minimum starting
frequency
00-18
Jog Frequency
Range
【1.00~25.00】Hz
00-19
Jog Acceleration Time
Range
【0.1~3600.0】s
00-20
Jog Deceleration Time
Range
【0.1~3600.0】s
¾ The JOG function is operational by using the multi-function input terminals S1 to S5 and setting
the relevant parameters 03-00~03-04 to 【6】JOG FWD or【7】JOG REV. Refer to parameter
group 3.
Page 57

4-25
01-V/F command group
01- 00
Volts/Hz Patterns (V/F)
Range
【1~7】
¾ Set 01-00 to one of the following preset V/f selections 【1~6】according to the required
application.
¾ Parameters 01-02~01-09 are not applicable.
¾ Six fixed V/f patterns are shown below.【1~3】for 50 Hz systems and 【4~6】for 60 Hz.
TYPE 50Hz 60Hz
Function
01-00 V/F pattern 01-00 V/F pattern
General Use
=【1】
100
B
C
12.5 50
(V)%
Hz650
=【4】
100
B
C
13.0 50
(V)%
Hz650
High start torque
=【2】
100
B
C
12.5 50
(V)%
Hz650
=【5】
100
B
C
13.0 50
(V)%
Hz650
Decreasing torque
=【3】
100
B
C
125 50
(V)%
Hz650
=【6】
100
B
C
13050
(V)%
Hz650
¾ (V) 100% is the maximum output voltage. B, C point preset % settings will be as table below:-
01- 00 B(Xb) C(Xc)
1/4
10% 8%
2/5
15% 10.5%
3/6
25% 7.7%
¾ Setting 01-00 =[7] provides a flexible V/F curve which can be selected by experienced users by
setting parameters (01-02~01-09).
Page 58

4-26
01- 01 v/f Maximum voltage
Range
200:【198.0~256.0】V
400:【323.0~528.0】V
01- 02 Maximum Frequency
Range
【0.20 ~ 650.00】Hz
01- 03 Maximum Frequency Voltage Ratio
Range
【0.0 ~ 100.0】%
01- 04 Medium Frequency 2
Range
【0.10 ~ 650.00】Hz
01- 05 Medium Frequency Voltage Ratio 2
Range
【0.0 ~ 100.0】%
01- 06 Medium Frequency 1
Range
【0.10 ~ 650.00】Hz
01- 07 Medium Frequency Voltage Ratio 1
Range
【0.0 ~ 100.0】%
01- 08 Minimum Frequency
Range
【0.10 ~ 650.00】Hz
01- 09 Minimum Frequency Voltage Ratio
Range
【0.0 ~ 100.0】%
¾ Max output frequency depends on parameter 01-00 , for 01-00=【7】It can be set by parameter
01-02.
¾ For 01-00 ≠【7】, the maximum output frequency will depending on parameter 00-12, frequency
upper limit.
01-03 (Vmax)
01-05 (Vmid2)
01-07 (Vmid1)
01-09 (Vmin)
01-08 01-06 01-04 01-02
(V)%
Hz
650.00
01-10 Volts/Hz Curve Modification (Torque Boost)
Range
【0 ~ 10.0】%
¾ Inverter output V / F curve settings for points B, C can be adjusted by parameter 01-10 to
improve the output torque.
¾ Calculation of B, C point voltage: B point voltage = Xb × maximum output voltage, C point
voltage = Xc × maximum output voltage (Xb, Xc see Page 4-26). When 01-10 = 0, the torque
improvement is disabled.
100
B
C
1 2.5/3.0 50/60
(V)%
Hz
01-10
Page 59

4-27
01-11 V/F start Frequency
Range
【0.00 ~10.00】Hz
02- Motor parameter group
02- 00 Motor no load current
Range
----
02- 01 Motor Rated Current
Range
----
02- 02 Motor rated Slip Compensation
Range
【0.0 ~ 100.0】(%)
02- 03 Motor Rated Speed
Range
----
02- 04 Motor Rated Voltage
Range
----
¾ When the load causes the actual motor speed to be reduced below the speed set by inverter
output frequency (Slip) , parameter 02-02 Slip compensation can be used to correct the
speed.
Motor slip = Motor synchronous speed- Motor Rated Speed
※Note: 02- 00/02- 01 differs with the inverter capacities (13- 00),It should be regulated according
to actual conditions.
03- External digital inputs & Realy Output functions
03- 00 Multifunction Input Term. S1
03- 01 Multifunction Input Term. S2
03- 02 Multifunction Input Term. S3
03- 03 Multifunction Input Term. S4
03- 04 Multifunction Input Term. S5
Range
【0】:Forward/Stop Command-------------------(Parameters 00- 02/00-03=1 & 00-04)
Page 60

4-28
【1】:Reverse/Stop Command---------------------(Parameters 00-02/00-03=1 & 00-04)
【2】:Preset Speed 1 (5- 02)--------------------- (Parameter Group5)
【3】:Preset Speed 2 (5- 03)----------------------(Parameter Group5)
【4】:Preset Speed 4 (5- 05) ---------------------(Parameter Group5)
【6】:JOG Forward Command-------------------(Parameters 00-18~00-20)
【7】:JOG Reverse Command------------------ (Parameters 00-18~00-20)
【8】:Up Command------------------------------- (Parameters 00- 05/00- 06=4& 03-06/03-07)
【9】:Down Command--------------------------- (Parameters 00- 05/00- 06=4& 03-06/03-07)
【10】: 2
nd
Acc/Dec times
【11】: Disable Acc/Dec
【12】: Main/ Alternative run source Select-----------------(Parameters 00- 02/00- 03)
【13】: Main/Alternative Frequency Command Select----(Parameters 00- 05/00- 06)
【14】: Rapid Stop (controlled deceleration stop)
【15】: Base Block (
Coast to stop)
【16】: Disable PID Function.----------------------------------(Parameter Goup10)
【17】: Reset
【18】: Enable Auto Run Mode--------------------------------(Parameter Group 6)
Various example settings and descriptions for Parameters 03-00 to 03-04 are noted in the
following pages seconds from 1 to 13.
1) For setting parameters 03- 00~03- 04 to【0, 1】External Run/Stop Control, refer to 00- 04.
2-wire method. Mode 1.
Example: FWD/STOP and REV/STOP from two inputs ( S1&S2)
Set 00- 04=【0】, S1: 03- 00=【0】(FWD/STOP) , S2: 03- 01=【1】(REV/STOP);
L 510
S1
S2
COM
(FWD/STOP)
(REV/STOP)
S1 ON OFF
FWD
REV
ONOFF
S2
Hz
T
※ Note: If both forward and reverse commands are ON, it will be treated as a STOP.
Page 61

4-29
2-wire method. Mode 2.
Example: RUN/STOP and REV/FWD from two inputs ( S1&S2)
Set 00- 04=【1】; S1: 03- 00=【0】(RUN/STOP); S2:03- 01=【1】(REV/FWD);
L 510
S1
S2
COM
(RUN /STOP)
(REV/FWD)
S1 ON OFF
FWD
REV
S2
T
Hz
ON
OFF
3-wire method.
Example:- Two separate push buttons for RUN & STOP and a two position switch for
FWD/ REV
Set 00- 04 =2.( 3 wire control mode), then terminals S1, S2 and S3 are dedicated to this function and
Preset selections for parameters 03-00, 03-01 and 03-02.are not relevant.
L510
S1(RUN)
S2(STOP)
S3(FWD/REV)
COM
S1
OFF
FWD
REV
S2
S3
ON
ON
ON
Hz
T
OFF
ON
Page 62

4-30
2) Parameters 03- 00~03- 04=【2, 3, 4】Preset speed selections.
Combination of any three terminals from S1~ S5 can be used to select preset speeds 0 to 7
according to the table below.
Preset speed 0-7 and the related acceleration/decelerating times should be set in parameter group 5.
For example timing diagram refer to Group 5 description.
Function setting and state of any
three (A,B,C) of terminal S1~S5
Preset
speed
terminal A=2 terminal B =3 terminal C =4
Frequency Acc-time Dec-time
speed 0
OFF OFF OFF
05- 01 05- 17 05-18
speed 1
OFF OFF
ON
05- 02 05- 19 05-20
speed 2
OFF
ON OFF
05- 03 05- 21 05-22
speed 3
OFF
ON ON
05- 04 05- 23 05-24
speed 4
ON OFF OFF
05- 05 05- 25 05-26
speed 5
ON OFF ON
05- 06 05- 27 05-28
speed 6
ON ON OFF
05- 07 05- 29 05-30
speed 7
ON ON ON
05- 08 05- 31 05-32
3) 03- 00~03- 04=【6 ,7】Forward/ Reverse JOG
When an input terminal is set to function【6】and is turned on, inverter will work in jog forward mode.
When an input terminal is set to function【7】and is turned on, inverter will work in jog reverse mode.
Note: If jog forward and jog reverse function is enabled at the same time, inverter will enter stop
mode.
4) 03- 00~03- 04=【8, 9】UP/DOWN
When an input terminal is set to function【8】and is turned on ,frequency command is increased
according to the UP/DOWN , increment/decrement step set in parameter 03-06.
If the input is kept on continuously, the frequency command increases accordingly until the upper
frequency limit is reached.
When an input terminal is set to function【9】and is turned on , frequency command decreases
according to the UP/DOWN increment/decrement step set in parameter 03-06.
If the input is kept on continuously, the frequency command decreases accordingly and in relation to
settings for parameter 03-06 and 3-07 until Zero speed is reached.
Refer to group 3 parameter description.
5) 03- 00~03- 04=【10】 2nd Acc/Dec time
When an input terminal is set to function【10】and is turned on ,the actual acceleration and
deceleration time will be according to the time for 2
nd
Accel/Decel set in parameters 00-16 and 00-17.
if the input is turned off, the acceleration and deceleration times will be according to the default
accel/decal 1 set in parameters 00-14 & 00-15.
6) 03- 00~03- 04=【11】 Disable Acc/Dec function
When an input terminal is set to function【11】and is turned on, acceleration and deceleration function
will be disabled and the frequency at the time is maintained. (constant speed mode)
If the input is turned off, acceleration and deceleration function is enabled again.
For an example see the following diagram.
Accel/Decel & Enable/Disable timing diagram using terminal S1 and parameter 03-00 = 11.
Page 63

4-31
RUN Command
S1
RUN
STOP
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
T
Hz
7) 03- 00~03- 04=【12】Main/ Alternative run source select.
When an input terminal is set to function【12】and is turned on, the run command source is according
to parameter 00-03(Alternative Run source).If the Input is off it will be according to 00-02 ( Main run
source).
8) 03- 00~03- 04=【13】Main/ Alternative Frequency source Select
When an input terminal is set to function【13】and is turned on, the frequency source is according to
parameter 00-06(Alternative Frequency source).If the Input is off it will be according to 00-05 ( Main
Frequency source).
9) 03- 00~03- 04=【14】 Rapid Stop (controlled deceleration stop)
When an input terminal is set to function【14】and is turned on , inverter decelerates to stop.
10) 03- 00~03- 04=【15】Base Block (Coast to stop)
When an input terminal is set to function【15】and is turned on, inverter output is turned off.
11) 03- 00~03- 04=【16】Disable PID Function.
When an input terminal is set to function【16】and is turned on, PID functions is disabled, if it is turned
off , PID function is enabled again.
12) 03- 00~03- 04=【17】Reset
When a failure that can be manually reset occurs, turn on a terminal with function 【17】, the failure
will be reset. (Same function as the Reset button on keypad).
13) 03- 00~03- 04=【18】Auto _ Run Mode
When an input terminal is set to function【18】, the programmable auto- sequencer function is enabled,
Refer to description of parameter group 6.
03- 06 Up/Down frequency step
Range
【0.00~5.00】Hz
Example:S1:03- 00=【8】Up frequency command, S2:03- 01=【9】Down frequency command,
03- 06=【△】Hz
Mode1:If UP or DOWN input terminals are turned on for less than 2 seconds, for every On operation
frequency changes by △ Hz.
Page 64

4-32
S1
S2
ON ON ON
Hz
T
△Hz
Actual output
frequency
ON ON ON
△Hz
Mode 2:If UP or DOWN input terminals are turned on for more than 2Seconds, the original
UP/DOWN mode is restored Output frequency Ramps up or down as long as the input is
kept ON.
As shown in the diagram below.
S1
S2
ON ON
ON
>2Sec
OFF
OFF
>2Sec
T
Hz
ON
03- 07 Up/Down keep Frequency status after a stop command
Range
【0】: After a stop command in Up/Down mode, the preset frequency is held as
the inverter stops, and the UP/Down function is disabled.
【1】: After a stop command in Up/Down mode, the preset frequency is reset to
0 Hz as the inverter stops.
【2】: After a stop command in Up/Down mode, the preset frequency is held as
the inverter stops, and the UP/Down function remains enabled.
¾ 03 - 07 =【0】,【2】When run signal is removed (Stop Command), the output frequency is
stored in parameter 05-01( Key pad Frequency).
¾ 03 - 07 =【0】 In stop mode since frequency can not be increased or decreased from
Up/Down terminals then keypad can be used to change the frequency by modifying
parameter 05-01.
¾ 03 - 07 =【1】In Up/down frequency mode inverter will ramp up from 0Hz on Run command
and Ramp down to 0 Hz on stop command.
Page 65

4-33
03- 08 Multifunction terminals S1~S5 scan time
Range
【1~200】 1m s
¾ Multifunction input terminal On/Off periods will be scanned for the number of cycles according to
the set value in parameter 03-08. If the signal status for On or off period is less than the set
period it will be treated as noise.
¾
Scan period unit is 1ms.
¾ Use this parameter if unstable input signal is expected, however setting long scan time periods
results in slower response times.
03- 09 s1~s5 Input type selection NO & NC
Range
【xxxx0】:S1 NO 【xxxx1】:S1 NC
【xxx0x】:S2 NO 【xxx1x】:S2 NC
【xx0xx】:S3 NO 【xx1xx】:S3 NC
【x0xxx】:S4 NO 【x1xxx】:S4 NC
【0xxxx】:S5 NO 【1xxxx】:S5 NC
¾ (NO) Normally open, (NC) Normally closed. Select as required.
¾ For selecting Normally Open (NO) or Normally Closed(NC) set the relevant digit in
parameter 03-09 to 0 or 1 as required.
¾ Set Parameter 03-09 first before you use the Parameters 00-02/00-03=1 to set the
inverter run mode to External multifunction inputs.
03-11 Multifunction Output Relay RY1 functions. ( Terminals RB, RA )
Range
【0】:Run
【1】:Fault
【2】:Setting Frequency Agree -------------------------------( refer to 03-14)
【3】:Frequency Agree (3-13±3-14) -------------------------( refer to 03-13/03-14)
【4】:Output Frequency Detection 1 (> 03-13) ----------( refer to 03-13)
【5】:Output Frequency Detection 2 (< 03-13) ----------( refer to 03-13)
【6】:Auto-Restart
【7】:Momentary AC Power Loss----------------------------( refer to 07-00)
【8】:Rapid Stop ( Decelerate to Stop)
【9】:Base Block
【10】:Motor Overload Protection (OL1)
【11】:Drive Overload Protection (OL2)
【12】:Reserved
【13】:Output Current Agree---------------------------------(refer to 03-15/03-16)
【14】:Brake Control--------------------------------------------(refer to 03-17/03-18)
03-13 Frequency Detection Level
Range
【0.00~650.00】 Hz
03-14 Frequency Detection Width
Range
【0.00~30.00】 Hz
Output relay RY1. function descriptions:
1) 03-11 =【0】. RY1 will be ON with Run signal.
2) 03-11 =【1】. RY1 will be ON with inverter Faults.
3) 03-11 =【2】. RY1 will be ON when Output Frequency reached Setting Frequency.
Page 66

4-34
Example:Setting Freq. =30, and Frequency Detection Width (03-14) =5,
Relay will be ON when output frequency reached 25Hz to 30Hz and Run Command
is on (Allowable tolerance ±0.01).
4) 03-11=【3】RY1 will be ON when Setting Freq. and Output Frequency reached Frequency Agree
(03-13 +/- 03-14).
Example:
Frequency Detection Level (03-13) =30, and Frequency Detection Width (03-14) =5 cause
Frequency Detection Range upper limit = 35, and Frequency Detection Range lower limit =
25. So RY1 will be on when Setting Freq. and Output Freq. are both under these limits; on
the other hand, RY1 will be off when Setting Freq. and Output Freq. are not under these
limits either.
Page 67

4-35
5) 03-11=【4】. RY1 will be on while Output Freq. > Frequency Detection Level (03-13).
6) 03-11=【5】. RY1 will be on while Output Freq. < Frequency Detection Level (03-13).
03-15 Output Current Agree Setting
Range
【0.1~15.0】 A
03-16 Current Agree Delay Time
Range
【0.1~10.0】Sec
¾ 03-11=【13】.RY1 will be on as soon as the output current value > current agree setting
(03-15).
¾ 03-15: Setting range (0.1~15.0 Amps) as required according to the rated motor current.
¾ 03-16: Setting range (0.1~10.0) unit: seconds.
Page 68

4-36
03-16
Fixed
Value
100msec
03-15
03-11
ON
I load
100%
T
03-17
Brake Release Level
Range
【0.00~20.00】 Hz
03-18
Brake Engage Level
Range
【0.00~20.00】 Hz
¾ If 03-11 =【14】
¾ In accelerating mode. RY1 will be ON as soon as the actual output frequency reaches the
external Brake release level set in parameter 03-17.
¾ In decelerating mode, RY1 will be OFF as soon as the actual output frequency reaches the
external Brake engage level set in parameter 03-18.
Timing diagram for 03-17 < 03-18 is shown below:
03-17
03-18
03-11=14
RUN command
Hz
T
ON OFF
RUN STOP
Page 69

4-37
Timing diagram for 03-17 > 03-18 is shown below:
03- 19 Relay Output Status type
Range
【0】:A (Normally open)
【1】:B (Normally close)
04- External analog signal input / output functions
04- 00 Analog Voltage & Current input selections
Range
AVI ACI
【0】:0~10V 0~20mA
【1】:0~10V 4~20mA
【2】:2~10V 0~20mA
【3】:2~10V 4~20mA
¾ Analog Input Scaling formulas:-
AVI (0~10V), ACI (0~20mA)
V(v)
AVI(0~10V) F Hz (00 12)
10(v)
×−: ()=
;
I(mA)
ACI(0~20mA) F H z (00 12)
20(mA )
×−: ()=
AVI (2~10V), ACI (4~20mA)
V2(v)
AVI(2~10V) F Hz (00 12), V >=2
10 2(v)
−
×−
−
: ()= ;
I4(mA)
ACI(4~20mA) F Hz (00 12),I>=4
20 4( mA )
−
×−
−
: ()=
;
Page 70

4-38
04- 01 AVI signal verification Scan Time
Range
【1~200】1m s
04- 02 AVI Gain
Range
【0 ~ 1000】%
04- 03 AVI Bias
Range
【0~ 100】%
04- 04 AVI Bias Selection
Range
【0】: Positive 【1】: Negative
04- 05 AVI Slope
Range
【0】: Positive 【1】: Negative
04- 06 ACI signal verification Scan Time
Range
【1~200】1m sec
04- 07 ACIGain
Range
【0 ~ 1000】%
04- 08 ACI Bias
Range
【0 ~ 100】%
04- 09 ACI Bias Selection
Range
【0】: Positive 【1】: Negative
04-10 ACI Slope
Range
【0】: Positive 【1】: Negative
¾ Set 04- 01 and 04- 06 for Analog signal verification.
Inverter reads the average values of A/D signal once per (04- 01/04- 06 x 1ms).
Set scan intervals according to the application and with consideration for signal instability or
interference effects on the signal by external sources. Long scan times will result in slower
response time.
AVI. Analog Voltage input scaling examples by adjusting Gain, Bias & Slope parameters (04-02~04-05).
(1) Positive Bias type (04-04= 0) and effects of modifying Bias amount by parameter 04-03 and
Slope type with parameter 04-05 are shown in Fig 1&2.
Figure 1. Figure 2.
04- 02 04- 03 04- 04 04- 05 04- 02 04- 03 04- 04 04- 05
A 100% 50% 0 0 C 100% 50% 0 1
B 100% 0% 0 0 D 100% 0% 0 1
60Hz
30Hz
0Hz
0V 5V 10VHzV
04-03
Bias
100%
50%
0%
Upper
Frequency
A
B
60Hz
30Hz
0Hz
0V 5V 10VHzV
100%
50%
0%
C
D
04-03
Bias
Page 71

4-39
(2) Negative Bias type and effects of modifying Bias amount by parameter 04-03 and Slope type
with parameter 04-05 are shown in Fig 3&4.
Figure3: Figure4:
04- 02 04- 03 04- 04 04- 05 04- 02 04- 03 04- 04 04- 05
E 100% 20% 1 0 F 100% 50% 1 1
60Hz
30Hz
0Hz
2V 5V 10VHzV
04-03
Bias
-100%
-50%
-0%
E
Upper
Frequency
60Hz
30Hz
0Hz
5V 10VHzV
04-03
Bias
-100%
-50%
-0%
F
Upper
Frequency
(3) Offset bias set to 0% (04-03) and effect of modifying Analog Gain ( 04-02), Bias type ( 04-04)
and slope type( 04-05) are shown in shown Fig 5&6.
Figure 5 Figure 6
04- 02 04- 03 04- 04 04- 05 04- 02 04- 03 04- 04 04- 05
A' 50% 0% 0/1 0 C' 50% 0% 0/1 1
B' 200% 0% 0/1 0 D' 200% 0% 0/1 1
60Hz
30Hz
0Hz
0V 5V 10VHzV
Upper
Frequency
B'
A'
60Hz
30Hz
0Hz
0V 5V 10VHzV
Upper
Frequency
D'
C'
(4) Various other examples of analog input scaling and modification are shown in following
figures 7,8,9 & 10.
Figure7 Figure 8
04- 02 04- 03 04- 04 04- 05 04- 02 04- 03 04- 04 04- 05
a 50% 50% 0 0 c 50% 50% 0 1
b 200% 50% 0 0 d 200% 50% 0 1
Page 72

4-40
60Hz
30Hz
0Hz
0V 5V 10VHzV
04-03
bias
100%
50%
0%
Upper
Frequency
b
a
37.5Hz
60Hz
30Hz
0Hz
0V 5V 10VHzV
04-03
bias
100%
50%
0%
Upper
Frequency
c
d
37.5Hz
Figure 9 Figure 10
04- 02 04- 03 04- 04 04- 05 04- 02 04- 03 04- 04 04- 05
e 50% 20% 1 0 g 50% 50% 1 1
f 200% 20% 1 0 h 200% 0% 0 1
60Hz
18.26Hz
0Hz
1V 4V 10VHzV
04-03 bias
-100%
-50%
-0%
Upper
Frequency
e
f
60Hz
1.81Hz
0Hz
2V 10VHzV
04-03
bias
-100%
-50%
-0%
Upper
Frequency
h
5V
g
04-11 Analog Output (AO) function selection.
Range
【0】:Output frequency
【1】:Frequency Setting
【2】:Output voltage
【3】:DC Bus Voltage
【4】:Output current
Example: Set 04-11 required according to the following table.
04-11 A
Xmax
【0】
Output frequency
upper frequency limit
【1】
Frequency Setting
upper frequency limit
【2】
Output voltage
Motor Rated Voltage
【3】
DC Bus Voltage
220V: 0~400V
【4】
Output current
2 times rated current
of inverter
Page 73

4-41
04-12 AO Gain
Range
【0 ~ 1000】%
04-13 AO Bias
Range
【0 ~ 100】%
04-14 AO Bias Selection
Range
【0】: Positive 【1】: Negative
04-15 AO Slope
Range
【0】: Positive 【1】: Negative
¾ Select the Analog output type for the multifunction analog output on terminal (TM2)
as required by parameter 04-11. Output format is 0-10V dc.
The output voltage level can be scaled and modified by parameters 04-12 to 04-15 If
necessary.
¾ The modification format will be same as the examples shown previously for Analog Voltage
Input (AVI) parameters 4-02 to 4-05.
Note: the max output voltage is 10V due to the hardware of the circuit.
Use external devices that require a maximum of 10V dc signal.
05- Preset Frequency Selections.
05- 00 Preset Speed Control mode Selection
Range
【0】:Common Accel / Decel.
【1】: Individual Accel/Decel for each preset speed 0-7.
05- 01 Preset Speed 0 (Keypad Freq)
05- 02 Preset Speed 1
05- 03 Preset Speed 2
05- 04 Preset Speed 3
05- 05 Preset Speed 4
05- 06 Preset Speed 5
05- 07 Preset Speed 6
05- 08 Preset Speed 7
Range
【0.00 ~ 650.00】 Hz
05-17 Preset Speed 0 Acceleration time
05-18 Preset Speed 0 Deceleration time
05-19 Preset Speed 1 Acceleration time
05- 20 Preset Speed 1 Deceleration time
05- 21 Preset Speed 2 Acceleration time
05- 22 Preset Speed 2 Deceleration time
05- 23 Preset Speed 3 Acceleration time
05- 24 Preset Speed 3 Deceleration time
05- 25 Preset Speed 4 Acceleration time
05- 26 Preset Speed 4 Deceleration time
05- 27 Preset Speed 5 Acceleration time
05- 28 Preset Speed 5 Deceleration time
05- 29 Preset Speed 6 Acceleration time
05- 30 Preset Speed 6 Deceleration time
05- 31 Preset Speed 7Acceleration time
05- 32 Preset Speed 7 Deceleration time
Page 74

4-42
Range
【0.1 ~ 3600.0】s
¾ When 05- 00 =【0】Accel /Decl 1 or 2 set by parameters 00-14/00-15 or 00-16/00-17 apply to all
speeds.
¾ When 05- 00 =【1】Individual Accel/Decel apply to each preset speed 0-7. Parameters 05-17 to
05-32.
¾ Formula for calculating acceleration and deceleration time:
Actual Acc time=
Time of Accel1 or 2 x Preset Frequency
Max Frequency
Actual Dec time=
Time of Accel1 or 2 x Preset Frequency
Max Frequency
¾ Maximum output frequency = parameter 01-02 when programmable V/F is selected by 01- 00=
【7】.
¾ Maximum output frequency = 50.00 hz or 60.00 hz when preset V/F patterns are selected.
01-
00≠【7】.
¾ Multi speed run/stop cycles with Individual accel/decal times. 05-00=【1】
¾ Two modes are shown below:-
¾ Mode1 = On/Off run command
¾ Mode2= Continuous run command
Mode1 Example: 00- 02=【1】(External Run/Stop Control).
00- 04=【1】(Operation Mode:Run/stop-forward/reverse).
S1: 03- 00=【0】(RUN/STOP );
S2: 03- 01=【1】(Forward/Reserve);
S3: 03- 02=【2】(Preset speed 1);
S4: 03- 03=【3】(Preset speed 2);
S5: 03- 04=【4】(Preset speed 4);
Page 75

4-43
abcde f
RUN RUN RUN
ON
ON
STOP STOP STOP
OFF
OFF
RUN
command
S2
S3
S4
05-01
05-02
05-03
Preset
speed0
Preset
speed1
Preset
speed2
Hz
T
FWD
ON
OFF
When the run command is On/Off, acceleration and deceleration times for each cycle can be
calculated as below:- time unit is in seconds’.
a=
(05 17) (05 01)
01 02
−× −
−
, b =
(05 18) (05 01)
01 02
−× −
−
,c=
(05 19) (05 02)
01 02
−× −
−
,d =
(05 20) (05 02)
01 02
−×−
−
……
¾ Mode2 Example. Continuous run command.
¾ Set S1 for Continuous Run
¾ Set S2 For Forward /Revise direction selection
¾ Set multi function terminals S3,S4 & S5 for setting three different preset speeds
05-01
05-02
05-03
05-04
05-06
05-05
ON
OFF ON
OFF ON
OFF
abcde
f
g
hi
FWD
T
Hz
S2
S3
S4
S5
RUN
command
Preset
speed0
Preset
speed1
Preset
speed2
Preset
speed3
Preset
speed4
Preset
speed5
RUN
STOP
ON
OFF
OFF
OFF OFF
OFF
OFF
ON
ON
ON
ON
OFF
OFF
OFF OFF
OFF
ON
When the run command is continuous, acceleration and deceleration times for each segment can be
calculated as below:-
Page 76

4-44
06- Auto Run(Auto Sequencer) function
06- 00 Auto Run( sequencer) mode selection
Range
【0】:Disabled
【1】:Single cycle (Continues to run from the unfinished step if restarted).
【2】:Periodic cycle. (Continues to run from the unfinished step if restarted).
【3】:Single cycle, then holds the speed of final step to run.
(Continues to run from the unfinished step if restarted).
【4】:Single cycle. (Starts a new cycle if restarted).
【5】:Periodic cycle. (Starts a new cycle if restarted).
【6】:Single cycle, then hold the speed of final step to run.
(Starts a new cycle if restarted).
Frequency of the step 0 is set by parameter 05-01 keypad Frequency.
06- 01 Auto _ Run Mode Frequency Command 1
06- 02 Auto _ Run Mode Frequency Command 2
06- 03 Auto _ Run Mode Frequency Command 3
06- 04 Auto _ Run Mode Frequency Command 4
06- 05 Auto _ Run Mode Frequency Command 5
06- 06 Auto _ Run Mode Frequency Command 6
06- 07 Auto _ Run Mode Frequency Command 7
Range
【0.00 ~ 650.00】Hz
06- 16 Auto_ Run Mode Running Time Setting0
06- 17 Auto_ Run Mode Running Time Setting1
06- 18 Auto_ Run Mode Running Time Setting2
06- 19 Auto_ Run Mode Running Time Setting3
06- 20 Auto_ Run Mode Running Time Setting4
06- 21 Auto_ Run Mode Running Time Setting5
06- 22 Auto_ Run Mode Running Time Setting6
06- 23 Auto_ Run Mode Running Time Setting7
Range
【0.00 ~ 3600.0】Sec
06- 32 Auto_ Run Mode Running Direction0
06- 33 Auto_ Run Mode Running Direction1
06- 34 Auto_ Run Mode Running Direction2
06- 35 Auto_ Run Mode Running Direction3
06- 36 Auto_ Run Mode Running Direction4
Page 77

4-45
06- 37 Auto_ Run Mode Running Direction5
06- 38 Auto_ Run Mode Running Direction6
06- 39 Auto_ Run Mode Running Direction7
Range
【0】: STOP 【1】: Forward 【2】: Reverse
¾ Auto Run sequencer mode has to be enabled by using one of the multifunctional inputs S1 to S5
and setting the relevant parameter 03-00 to 03-04 to selection【18】.
¾ Various Auto Run (sequencer) modes can be selected by parameter (06-00) as listed above.
¾ 7 Auto Run (sequencer) modes can be selected by parameters (06-01~06-39)
¾ Auto Run frequency commands1 to 7 are set with Parameters (06-01 ~ 06-07),
¾ Sequence run times are set with parameters (06-17 ~ 06-23)
¾ FWD/REV Direction for each sequence can be set with parameters (06-33 ~ 06-39).
¾ Auto sequence 0, frequency is set from keypad by parameter 05-01, sequence run time and
direction are set by parameters 06-16 and 06-32.
Auto RUN (Auto Sequencer) examples are shown in the following pages:-
Example 1. Single Cycle (06- 00=1,4)
The inverter will run for a single full cycle based on the specified number of sequences, then it
will stop. In this example 4 sequences are set, three in forward direction and one in Reverse.
Auto Run Mode. 06- 00=【1】or【4】,
Frequency 05- 01=【15】Hz, 06- 01=【30】Hz, 06- 02=【50】Hz, 06- 03=【20】Hz
Sequence Run Time 06-16=【20】s, 06-17 =【25】s, 06-18=【30】s, 06-19=【40】s,
Direction 06-32=【1】FWD, 06-33 =【1】FWD, 06-34=【1】(FWD), 06-35=【2】(REV)
Unused Sequence Parameters 06-04~ 06-07=【0】Hz , 06-20~06-23=【0】s , 06-36~06-39=【0】
05-01
06-01
06-02
06-03
06-16
06-17
06-18
06-19
T
Hz
RUN command
RUN
ON
S1 to S5 auto
run enable
Page 78

4-46
Example 2. Periodic cycle Run.
Mode: 06- 00=【2】or【5】
The inverter will repeat the same cycle periodically.
All other Parameters are set same as Example 1. shown above.
05-01
06-01
06-02
06-03
05-01
06-01
06-02
06-03
06-16 06-17 06-18
06-19
06-16
06-17
06-18
06-19
T
Hz
RUN
Command
RUN
ON
S1 to S5 auto
Run enable
Example 3. Auto_Run Mode for Single Cycle 06-00=【3 or 6】
The speed of final step will be held to run.
Auto Run Mode. 06- 00 =【3】or【6】
Frequency 05- 01 =【15】Hz, 06- 01=【30】Hz, 06- 02=【50】Hz, 06- 07=【20】Hz,
Sequence Run Time 06-16 =【20】s, 06-17=【25】s, 06-18=【30】s, 06-23=【40】s,
Direction 06-32 =【1】FWD 06-33=【1】, 06-34 =【1】, 06-39=【1】,
Unused Sequence Parameters 06-03~06- 06=【0】Hz, 06-19~06-22=【0】s, 06-35~06-38 =【0】
05-01
06-01
06-02
06-16 06-17 06-18 06-23
Hz
06-07
T
RUN
Command
RUN
RUN
S1 to S5 auto
run enable
Page 79

4-47
Example 4&5 .
Auto Run Mode 06-00=【1~3】. After a restart continues to run from the unfinished step.
Auto Run Mode 06-00=【4~6】. After a restart, it will begin a new cycle.
06- 00
1~3 4~6
Output Frequency
time
Output
Frequency
Run
Command
Continue running from
unfinished step
stop runrun
time
Output
Frequency
Run
Command
begin a new cycle
stop runrun
¾ ACC/DEC time in Auto run mode will be according to the setting of 00-14/00-15 or 00-16/00-17.
¾ For Auto sequence 0.The run frequency will be according to keypad frequency set by parameter
05-01.Parameters 06-16 and 06-32 are used to set the sequence Run time and Run direction.
07- Start/Stop command setup
07- 00 Momentary power loss and restart
Range
【0】:Momentary Power Loss and Restart disable
【1】:Momentary power loss and restart enable
¾ If the input power supply due to sudden increase in supply demand by other equipment results in
voltage drops below the under voltage level, the inverter will stop its output at once.
¾ When 07-00 =【0】.On power loss, the inverter will not start.
¾ When 07-00 =【1】.Aafter a momentary power loss, inverter will restart with the same frequency
before power loss, and there is no limitation on number of restarts.
¾ On power loss, as long as the inverter CPU power is not completely lost, the momentary
power loss restart will be effective, restart will be according to setting of parameters 00-02 &
07-04 and status of External run switch.
Caution:- After any power loss if the Run mode is set to External by parameter 00-02=1 and if Direct
start on power up is also selected by parameter 07-04=0, please note that the inverter will run on
resumption of power.
To ensure safety of operators and to avoid any damages to the machinery, all necessary safety
measure must be considered, including disconnection of power to the inverter.
07- 01 Auto Restart Delay Time
Range
【0.0~800.0】Sec
07- 02 Number of Auto Restart Attempts
Range
【0~10】
¾ 07- 02=【0】: The inverter will not auto restart after trips due to fault.
¾ 07- 02>【0】, 07- 01=【0】.After a trip due to fault the inverter will run with the same frequency
before power loss, and restarts after an internal delay of 0.5 seconds.
¾ 07- 02>【0】, 07- 01>【0】, After a fault trip the inverter will run with the same frequency before
power loss, and restart with a delay according the preset in parameter 07-01.
¾ Note:- Auto restart after a fault will not function while DC injection braking or decelerating
to stop
Page 80

4-48
07- 03 Reset Mode Setting
Range
【0】:Enable Reset Only when Run Command is Off
【1】:Enable Reset when Run Command is On or Off
¾ 07-03=0 Once the inverter is detected a fault, please turn Run switch Off and then On again to
perform reset, otherwise restarting will not be possible.
07- 04 Direct Running on Power Up
Range
【0】:Enable Direct running after power up
【1】:Disable Direct running after power up
07- 05 Delay-ON Timer (Seconds)
Range
【1.0~300.0】Sec
¾ When direct run on power up is selected by 07-04=0 and the inverter is set to external run by
(00-02/00-03=1), if the run switch is ON as power is applied, the inverter will auto start.
It is recommend that the power is turned off and the run switch is also off to avoid possibility of
injury to operators and damage to machines as the power is reapplied.
Note: If this mode is required all safety measures must be considered including warning
labels.
¾ When direct run on power up is disabled by 07-04=1and if the inverter is set to external run by
(00-02/00-03=1), if the run switch is ON as power is applied, the inverter will not auto start and
the display will flash with STP1. It will be necessary to turn OFF the run switch and then ON
again to start normally.
07- 06 DC Injection Brake Start Frequency (Hz)
Range
【0.10 ~ 10.00】Hz
07- 07 DC Injection Brake Level (%)
Range
【0~ 20】%
07- 08 DC Injection Brake Time (Sec)
Range
【0.0 ~ 25.5】Sec
¾ 07- 08/07- 06 set the DC injection brake duration and the brake start frequency as shown below.
Frequency
T
07-08
07-06
RUN
Command
Run Stop
07- 09 Stopping Method
Range
【0】:Deceleration to stop.
【1】:Coast to stop.
¾ 07- 09 = 【0】: after receiving stop command, the motor will decelerate to stop according to
setting of 00-15, deceleration time 1.
¾ 07- 09 = 【1】: after receiving stop command, the motor will free-run (Coast) to stop.
Page 81

4-49
08- Protection function group
08- 00 Trip Prevention Selection
Range
【xxxx0】:Enable Trip Prevention During Acceleration
【xxxx1】:Disable Trip Prevention During Acceleration
【xxx0x】:Enable Trip Prevention During Deceleration
【xxx1x】:Disable Trip Prevention During Deceleration
【xx0xx】:Enable Trip Prevention in Run Mode
【xx1xx】:Disable Trip Prevention in Run Mode
【x0xxx】:Enable over voltage Prevention in Run Mode
【x1xxx】:Disable over voltage Prevention in Run Mode
08- 01 Trip Prevention Level During Acceleration
Range
【50 ~ 200】%
¾ Trip prevention adjustment level during acceleration to prevent over current (OC-A) trips.
¾ If trip prevention during acceleration is enabled and an over current occurs due to the load, then
the acceleration is interrupted until the over current level is dropped below the setting in 08-01
then the acceleration is resumed.
08- 02 Trip Prevention Level During Deceleration
Range
【50 ~ 200】%
¾ Trip prevention adjustment level during deceleration to prevent over Voltage (OV-C) trips.
¾ If trip prevention during deceleration is enabled and an over voltage occurs during stopping due
to the load, then the deceleration is interrupted until the over voltage level is dropped below the
setting in 08-02 then the deceleration is resumed.
08- 03 Trip Prevention Level during continuous Run Mode
Range
【50 ~ 200】%
¾ Trip prevention adjustment level during continuous Run to prevent over current (OC-C) trips.
¾ If trip prevention during continuous Run is enabled and an over current occurs due the load such
as a sudden transient load, then the output frequency is reduced by decelerating to a lower
speed until the over current level is dropped below the preset in 08-03, then the output frequency
accelerates back to the normal running frequency.
08- 04 Over voltage Prevention Level during Run Mode
Range
200:【350~390】VDC
400:【700~780】VDC
¾ Over voltage prevention level can be set by parameter 08-04 when necessary.
When the DC bus voltage is higher than the level set in 08-04, the over voltage fault will occur.
08- 05 Electronic Motor Overload Protection Operation Mod (OL1)
Range
【0】:Enable Electronic Motor Overload Protection
【1】:Disable Electronic Motor Overload Protection
08- 06 Operation After Overload Protection is Activated
Range
【0】:Coast-to-Stop After Overload Protection is Activated
【1】:Drive Will Not Trip when Overload Protection is Activated (OL1)
¾ 08- 06 = 【0】: On overload condition the inverter coast to stop as the thermal relay detects the
overload and the display will flash OL1.To reset Press the ‘Reset’ key or use an external reset to
continue to run.
¾ 08- 06 = 【1】: On overload condition the inverter continues to run, display flash with OL1, until
the current falls below the overload level.
The heat sinking function will not be as effective when the motor run at low speed. So the thermal
action level will decline at the same time. (The curve 1 will change to curve 2)
Page 82

4-50
Minute
1.0
150
Current Precent (%)
(2)
(1)
5.0
123
113
103
08- 07 OH over heat Protection
Range
【0】:Auto (Depends on heat sink temp.)
【1】:Operate while in RUN mode
【2】:Always Run
【3】:Disabled
¾ 08- 07=【0】: Cooling fan runs as the inverter detects temperature rise.
¾ 08- 07=【1】: Cooling fan runs while the inverter is running.
¾ 08- 07=【2】: Cooling fan runs continuously.
¾ 08- 07=【3】: Cooling fan is Disabled.
08- 08 AVR function
Range
【0】:AVR function enable
【1】:AVR function disable
【2】:AVR function disable for stop
【3】:AVR function disable for Deceleration
【4】:AVR function disabled for stop & Deceleration from one speed to another
speed.
【5】:when VDC>(360V/740V), AVR function is disabled for stop and
Deceleration
¾ Automatic voltage regulator function provides a level of output voltage stability when there is
input voltage instability. So when 08-08=0, Input voltage fluctuations will not effect the output
voltage.
¾ 08-08=1. Input voltage fluctuations will cause fluctuations on output voltage.
¾ 08-08=2. AVR is disabled during stopping to avoid an increase in stopping time.
¾ 08-08=3. AVR is disabled only during deceleration from one speed to another speed. This will
avoid longer than required deceleration time.
08- 09 Input phase loss protection protection
Range
【0】:Disabled
【1】:Enabled
When 08-09=【1】:On phase loss warring message PF is displayed.
Page 83

4-51
09- Communication function group
09- 00 Assigned Communication Station Number
Range
【1 ~ 32】
¾ 09-00 sets the communication station number when there are more that one unit on the
communication network. Up to 32 Slave units can be controlled from one master controller such
as a PLC.
09- 01 RTU code /ASCII code Selection
Range
【0】:RTU
【1】:ASCII
09- 02 Baud Rate Setting (bps)
Range
【0】:4800
【1】:9600
【2】:19200
【3】:38400
09- 03 Stop Bit Selection
Range
【0】:1 stop bit
【1】:2 stop bit
09- 04 Parity Selection
Range
【0】:no parity
【1】:even parity
【2】:odd parity
09- 05 Data Format Selection
Range
【0】:8 bit data
【1】:7 bit data
¾ Set 09-01~09-05 to configure communication format before starting communication.
09- 06 Communication time-out detection time
Range
【0.0~25.5】Sec
09- 07 Communication time-out operation selection
Range
【0】:Stop in deceleration time 1 and show COT after communication timeout
【1】:Stop in free run mode and show COT after communication timeout
【2】:Stop in deceleration time 2 and show COT after communication timeout
【3】:Keep running and show COT after Communication timeout
¾ Time-out detection time: 00.0~25.5 seconds; setting 00.0 seconds: disables time-out function.
09- 08 Err6 fault tolerance times
Range
【1~20】
¾ When communication error time ≥ 09-08 setting,keypad display shows ERR6.
09- 09 Drive Transmit Wait Time
Range
【5~65】m s
¾ This parameter is used to set the converter to receive data from the sending date to the
beginning of the time.
Page 84

4-52
10-PID function Setup
PID block diagram
1? 2
3? 4
Positive
Negat ive
10-03
P(10-05)
I(10-06)
+
10-03
-
D
Target
10-00
Feedback
10-01
10-21
10-22
12-00, PID
Feedback Display
10-03=0
or external ter minal
prohibit or stop
I Limiter
1? 3
2? 4
D(10 -07)
+
+
Offset
(10-08
10-09)
+
Delay device
(10-10)
PID Communicatio n
Read
Sleep /Wake
Function
PID Freq.
Outp ut
2? 4
1? 3
10-03
I Reset
PID Li mit
10- 00 PID target value selection
Range
【0】:Potentiometer on Keypad
【1】:External AVI Analog Signal Input
【2】:External ACI Analog Signal Input
【3】:Target Frequency set by Communication method.
【4】:Set from keypad by parameter 10-02.
¾ 10-00 selections are only effective when frequency source selection is set to PID
by parameters 00 - 05 \ 00 - 06= 6.
10- 01
PID feedback value selection
Range
【0】:Potentiometer on Keypad
【1】:External AVI Analog Signal Input
【2】:External ACI Analog Signal Input
【3】:Communication setting Frequency
¾ !Note: 10-00 and 10-01 can not be set to the same value.
10- 02 PID keypad input
Range
【0.0~100.0】%
Page 85

4-53
10- 03 PID operation selection
【0】: PID Function disabled
【1】: FWD Characteristic.
Deviation is D-controlled
【2】: FWD Characteristic.
Feedback is D-controlled
【3】: REV Characteristic.
Deviation is D-controlled
Range
【4】: REV Characteristic.
Feedback is D-controlled
¾ 10- 03 =【1】.
Deviation (target - detected value) is derivative controlled in unit time set in parameter 10-07.
¾ 10- 03 =【2】
Feedback (detected value) is derivative controlled in unit time set in parameter 10- 07.
¾ 10- 03 =【3】
Deviation (target value - detected value) is derivative controlled in unit time set in parameter 10-
07. If the deviation is positive, the output frequency decreases, vice versa.
¾ 10- 03 =【4】
Feed back (detected value) is derivative controlled in unit time set in parameter 10- 07.
If the deviation is positive, the output frequency decreases, vice versa.
Note:-
For 10-03 = 1 or 2, If the deviation is positive, the output frequency increases and, vice versa.
For 10-03 = 3 or 4, If the deviation is positive, the output frequency decreases, vice versa.
10- 04
Feedback Gain coefficient
Range
【0.00 ~ 10.00】
¾ 10-04 is the calibration gain. Deviation = set point – (feedback signal×10-04)
10- 05
Proportional Gain
Range
【0.0 ~ 10.0】
¾ 10- 05: Proportion gain for P control.
10- 06
Integral Time
Range
【0.0 ~ 100.0】s
¾ 10- 06: Integration time for I control
10- 07
Derivative Time
Range
【0.00 ~ 10.00】s
¾ 10- 07: Differential time for D control
10- 08
PID Offset
Range
【0】: Positive Direction
【1】: Negative Direction
10- 09
PID Offset Adjust
Range
【0 ~ 109】%
¾ 10- 08 /10- 09: Calculated PID output is offset by 10-09 (the polarity of offset is according
to10-08)
10-10
PID Output Lag Filter Time
Range
【0.0 ~ 2.5】s
¾ 10-10: Update time for output frequency.
10-11
Feedback Loss Detection Mode
Range
【0】:Disable
【1】:
Enable – Drive Continues to Operate After Feedback Loss
【2】:
Enable – Drive “STOPS” After Feedback Loss
¾ 10-11= 【1】: On feed back loss detection, continue running, and display ‘PDER’;
¾ 10-11= 【2】: On feed back loss detection, stop, and display ‘PDER’。
Page 86

4-54
10-12
Feedback Loss Detection Level
Range
【0 ~ 100】
¾ 10-12 is the level for signal loss. Error = (Set point – Feedback value). When the error is
larger than the loss level setting, the feedback signal is considered lost.
10-13
Feedback Loss Detection Delay Time
Range
【0.0 ~25.5】s
¾ 10-13:The minimum time delay before feedback signal loss is determined.
10-14
Integration Limit Value
Range
【0 ~ 109】%
¾ 10-14: the Limiter to prevent the PID from saturating.
10-15
Integration Value Resets to Zero when Feedback Signal Equals the target
Value
Range
【0】:
Disabled
【1】: After 1 Sec
【30】: After 30 Sec ( Range:- 1 ~ 30 Sec)
¾ 10-15=0.As PID feedback value reaches the set point, the integral value will not be reset.
¾ 10-15=1~30.As PID feedback value reaches the set point, reset to 0 in 1~30 seconds and
inverter stops. The inverter will run again when the feedback value differs from the set point
value.
10-16
Allowable Integration Error Margin (Unit) (1 Unit = 1/8192)
Range
【0 ~ 100】%
¾ 10-16 = 0 ~ 100% unit value: Restart the tolerance after the integrator reset to 0.
10-17
PID Sleep Frequency Level
Range
【0.00~650.00】Hz
10-18
PID Sleep Function Delay Time
Range
【0.0 ~25.5】s
10-19
PID Wake up frequency Level
Range
【0.00 ~ 650.00】Hz
10-20
PID Wake up function Delay Time
Range
【0.0 ~ 25.5】s
¾ When PID output frequency is less than the sleep threshold frequency and exceeds the time
of sleep delay, the inverter will decelerate to 0 and enters PID sleep mode.
¾ When PID output frequency is larger than the Wake up threshold frequency inverter will
enter the PID mode again as shown in the timing diagram below.
10-18
Hz
T
10-19
10-17
10-20
Wake up
frequency
Sleep
frequency
PID output frequency
Actual output frequency
Page 87

4-55
10-21
Max PID Feedback Level.
Range
【0 ~ 999】
10-22
Min PID Feedback Level.
Range
【0 ~ 999】
¾ Example: If 10-21=100 and 10-22=50 and the unit for the range from 0 to 999 will be defined
with the parameters setting of 12-02 , actual feedback value variation range, will be scaled to
50 and 100 only for display, as Shown below.
10-21=100
10-22=50
Min 0%
0V/0mA(or 2V/4mA)
Max 100%
(10V/20mA)
999
PID fback
Page 88

4-56
11 Performance control functions
11- 00 Prevention of Reverse operation
Range
【0】:Reverse command is enabled
【1】:Reverse command is disabled
¾ 11-00=1, the reverse command is disabled.
11- 01 Carrier Frequency
Range
【1~16】KHz
11- 02
Carrier mode selection
Range
【0】:Carrier mode0 3-phase PW M modulation
【1】:Carrier mode1 2-phase PW M modulation
【2】:Carrier mode2 2-phase randomized PW M modulation
¾ Mode 0: 3-phase PWM Modulation Three Output transistors on at the same time (Full Duty).
¾ Mode 1: 2-phase PWM Modulation Two output transistors on at the same time (2/3 Duty).
¾ Mode 2: Random PWM Modulation This modulation method will use 3-phase PWM and 2-phase
PWM modulation in a random mode.
Modes Name IGBT Duty
Heat
Losses
Torque
Performance
Waveform
Distortion
Motor
Noise
0 3-Phase PWM 100% High High Low Low
1 2-Phase PWM 66.6% Low Low High High
2 Randomized PWM Between mode0
& mode1
Mid Mid Mid Mid
(Leverage)
11- 03 Carrier Frequency auto reduction by temperature decreasing
Range
【0】:Disable
【1】:Enable
¾ When inverter (heatsink) temperature rises above 80°C the Carrier Frequency is reduced by 4K.
¾ When the temperature falls below less than 70°C, Carrier Frequency is reset to default.
¾ Temperature can be displayed by setting parameter 12-00=04000.
70℃
80℃
t1
t2
T0
Temperature
Carrier
Frequency
10K
4K
t1
t2
T0
Page 89

4-57
11- 04 S-Curve Acc 1
11- 05 S-Curve Acc 2
11- 06 S-Curve Dec 3
11- 07 S-Curve Dec 4
Range
【0.0 ~ 4.0】s
¾ Use S Curve parameters where a smooth acceleration or deceleration action is required,
this will prevent possible damage to driven machines by sudden acceleration/deceleration.
S1
S2
S3
S4
RUN command
Actual
output
frequency
RUN
T
Note:
¾ Regardless of the stall prevention period, actual acceleration and deceleration time =preset
acceleration / deceleration time + S curve time.
¾
Please set the required individual S curve times in the parameters (11-04~11-07).
¾
When S curve time (11-04~11-07) is set as 0, the S curve function is disabled.
¾
The calculation of S curve time is based on the Maximum output frequency of motor
(01-02), Please refer to the parameters (00-14/00-15/00-16/00-17).
¾
11- 08 Skip frequency 1
11- 09 Skip frequency 2
11-10 Skip frequency 3
Range
【0.00 ~ 650.00】Hz
11-11 Skip frequency range. (± frequency band)
Range
【0.00 ~ 30.00】Hz
Skip frequency parameters can be used to avoid mechanical resonance in certain applications.
Example: 11-08=10.00(Hz); 11-09=20.00(Hz); 11-10=30.00(Hz); 11-11=2.00(Hz).
±2Hz=8~12Hz
±2Hz=18~22Hz Skip frequency
±2Hz=28~32Hz
10Hz 20Hz 30Hz
11-11
11-10
11-09
11-08
Page 90

4-58
12 Monitor function group
12- 00 Display Mode
Range
0 0 0 0 0
MSD
LSD
00000~77777 Each digit can be set from 0 to 7 as listed below.
【0】:Disable display
【1】:output Current
【2】:output Voltage
【3】:DC voltage
【4】:Temperature
【5】:PID feedback
【6】:AVI
【7】:ACI
¾ MSD= Most significant digit. LSD= Least significant digit.
¾ Note: MSD of parameter 12-00 sets the power on display, other digits set user selected
displays. (refer to P4-4)
12- 01 PID Feedback Display Mode
Range
【0】:Displayed in Integer (xxx)
【1】:Displayed with One Decimal Place (xx.x)
【2】:Displayed with Two Decimal Places (x.xx)
12- 02 PID Feedback Display Unit Setting
Range
【0】:xxx--
【1】:xxxpb(pressure)
【2】:xxxfl(flow)
12- 03 Custom Units (Line Speed) Display Mode
Range
【0~65535】rpm
¾ Set motor rated RPM in this parameter if required then the display will show this value when
inverter output frequency reaches the motor name plate frequency. 50Hz or 60 Hz as
appropriate.
¾ The line speed display is linearly proportional to the output frequency 0 to 50Hz or 0-60 Hz
as appropriate. Motor synchronous speed = 120 x Rated frequency/Number of poles.
12- 04 Custom Units (Line Speed) Display Mode
Range
【0】:Drive Output Frequency is Displayed
【1】:Line Speed is Displayed in Integer (xxxxx)
【2】:Line Speed is Displayed with One Decimal Place (xxxx.x)
【3】:Line Speed is Displayed with Two Decimal Places (xxx.xx)
【4】:Line Speed is Displayed with Three Decimal Places (xx.xxx)
¾ 12- 04≠0, line speed is displayed while the inverter is running or stopped.
12- 05 Input and output terminal status display
Range Read only(Panel read only)
¾ When any of S1 ~ S5 is turned on, corresponding segments on the digital display digits will be
on.
¾ When relay output RY1 is on, the corresponding digit will be on as shown below.
¾ When no Digital input and no relay output, they will show - - - - - .
Page 91

4-59
Example 1: The following figure shows 12 - 05 display status,
when S1, S3, S5 Inputs are ON and S2, S4 and RY1 are OFF.
S1 S2 S3 S4 S5
Example 2: The following figure shows 12 - 05 display status
when S2, S3, S4 inputs are ON and S1, S5 are OFF but RY1 is ON.
RY1
13 Inspection & Maintenance functions
13- 00 Drive Horsepower Code
Range
----
Inverter Model: 13- 00 show Inverter Model: 13- 00 show Inverter Model: 13- 00 show
L510-1P2-XXX 1P2 L510-2P2-XXX 2P2 L510-401-XXX 401
L510-1P5-XXX 1P5 L510-2P5-XXX 2P5 L510-402-XXX 402
L510-101-XXX 101 L510-201-XXX 201 L510-403-XXX 403
L510-202-XXX 202
L510-203-XXX 203
13- 01 Software Version
Range
----
13- 02 Fault Log Display (Latest 3 faults)
Range
----
¾ Last three faults are stored in a stack and whenever there is a new fault the previous faults
are pushed down the stack. So the fault stored in 2.xxx will be transferred to 3.xxx, and the
one in 1.xxx to 2.xxx. The recent fault will be stored in the empty register 1.xxx.
¾ Use Up▲and Down▼ keys to scroll between the fault registers.
¾ Pressing reset key when parameter 13-02 is displayed then all three fault registers will be
cleared and the display for each register will change to 1. ---, 2. ---, 3. ---.
¾ E.g. fault log content is ‘1.OC-C’; this indicates the latest fault is OC-C, etc.
13- 03 Accumulated Inverter Operation Time 1
Range
【0~23】Hours
13- 04 Accumulated Inverter Operation Time 2
Page 92

4-60
Range
【0~65535】Days
13- 05 Accumulated Inverter Operation Time Mode
Range
【0】:Power on time
【1】:Operation time
¾ When the operation time recorded in accumulator 1(Parameter 13-03) reaches 24 hours
¾
The recorded value in accumulator 2 parameter 13-04 changes to 1 day and the value in
accumulator 1 is reset to 0000.
13- 06 Parameter lock
Range
【0】:Enable all Functions
【1】: Preset speeds 05- 01~05- 08 cannot be changed
【2】:All Functions cannot be changed Except for preset speeds set in 05-
01~05- 08
【3】:Disable All Function Except 13-06
¾ When the 13-07=00000 (not set a password), you can adjust the parameters 05-01~05-08 from
13-06.
13- 07 Parameter Lock Key Code
Range
【00000~65535】
¾ When a parameter lock key number is entered in parameter 13-07. For any parameter
modification the key number has to be entered.
See following Parameter lock key setting example:-
¾ Setting Parameter lock key number example:Step1:
1st entry
▲
▼
or
</ENT
</ENT
Step2:
2nd
entry
</ENT
▲ ▼
or
</ENT
Set Password successfully
Set Password failed
▲
▼
or
</ENT
Key code ( password) unlock
Page 93

4-61
Lifting
Password
</ENT
▲
▼
or
</ENT
Password successfully lifted
Password failed to lift
▲
▼
or
</ENT
13- 08 Reset Drive to Factory Settings
Range
【1150】:Reset to the 50Hz factory setting
【1160】:Reset to the 60Hz factory setting
¾ When a Parameter lock key number has been entered in parameter 13 – 07. This key
number must be entered first before parameter 13-08 cab be used.
Page 94

5-1
Chapter 5 Troubleshooting and maintenance
5.1 Error display and corrective action
5.1.1 Manual Reset and Auto-Reset
Faults which can not be recovered manually
Display content Cause Corrective action
-oV-
Voltage too high
when stopped
Detection circuit malfunction Consult with the supplier
-LV-
Voltage too low
when stopped
1. Power voltage too low
2. Pre-charge resistor or fuse
burnt out.
3. Detection circuit malfunction
1.Check if the power voltage
is correct
2. failed resistor or fuse
3. Consult with the supplier
-oH-
The inverter is
overheated when
stopped
1. Detection circuit
malfunction
2. Ambient temperature too
high or bad ventilation
Improve the ventilation
conditions, if no result then
replace the inverter
CtEr
Current Sensor
detection error
Current sensor error or
circuit malfunction
Consult with the supplier
EPr
EEPROM
problem
Faulty EEPROM Consult with the supplier
Cot
Communication
error
Communications disruption Check the wiring
Faults which can be recovered manually and automatically
Display content Cause Corrective action
oC-A
Over-current at
acceleration
1.Acceleration time too short
2.The capacity of the motor
exceeds the capacity of
the inverter
3.Short circuit between the
motor coil and the case
4.Short circuit between
motor wiring and ground
5.IGBT module damaged
1.Set a longer acceleration
time
2.Replace inverter with one
that has the same rating as
that of the motor
3.Check the motor
4.Check the wiring
5. Consult with the supplier
oC-C
Over-current at
fixed speed
1. Transient load change
2. Transient power change
1.Increase the capacity of
the inverter
2.Install inductor on the
power supply input side
oC-d
Over-current at
deceleration
The preset deceleration time is
too short.
Set a longer deceleration time
oC-S
Over current at
start
1.Short circuit between the
motor coil and the case
2.Short circuit between motor
coil and ground
3.IGBT module damaged
1.Inspect the motor
2.Inspect the wiring
3. Consult with the supplier
Page 95

5-2
oV-C
Excessive Voltage
during operation/
deceleration
1.Deceleration time setting
too short or excessive load
inertia
2.Power voltage varies widely
(fluctuates)
1.Set a longer deceleration
time
2.Consider use of a brake
resistor and/or brake module
3.Consider use of a reactor at
the power input side
PF
Input phase Loss
Abnormal fluctuations in the
main circuit voltage
1.Check the main circuit
power supply wiring.
2.Check the power supply
voltage
Faults which can be recovered manually but not automatically
Display content Cause Corrective action
oC
Over-current
during stop
Detection circuit malfunction Consult with the supplier
oL1
Motor overload loading too large
Consider increasing the Motor
capacity
oL2
Inverter overload Excessive Load
Consider increasing the
inverter capacity
LV-C
Voltage too low
during operation
1.Power voltage too low
2.Power voltage varies widely
(fluctuates)
1.Improve power quality
2.Consider adding a reactor at
the power input side
5.1.2 Keypad Operation Error Instruction
Display content Cause Corrective action
LoC
1.Parameter
already locked
2.Motor direction
locked
3.Parameter
password (13-07)
enabled
1.Attempt to modify
frequency parameter while
13-06>0.
2.Attempt to reverse
direction when 11- 00=1。
3.Parameter (13 - 07)
enabled, set the correct
password will show LOC.
1.Adjust 13-06
2.Adjust 11-00
Err1
Keypad operation
error
1.Press ▲ or ▼while
00-05/00-06>0 or running
at preset speed.
2.Attempt to modify the
Parameter.Can not be
modified during operation
(refer to the parameter
list)
1.The ▲ or▼ is available for
modifying the parameter
only when 00-05/00-06=0
2.Modify the parameter in
STOP mode.
Err2
Parameter setting
error
1.00-13 is within the range
of (11-08 ±11-11) or
(11-09 ±11-11) or (11-10
±11-11)
2.00- 12≦00-13
1. Modify 11-08~11-10 or
11-11 Set 00-12>00-13
Err5
Modification of
parameter is not
available in
communication
1.Control command sent
during communication.
2.Attempt to modify the
function 09-02~ 09-05
during communication
1.Issue enable command
before communication
2.Set parameters 09-02~
09-05 function before
communication
Page 96

5-3
Err6
Communication
failed
1.Wiring error
2.Communication
parameter setting error.
3.Incorrect communication
protocol
1. Check hardware and wiring
2.Check Functions(09-00~
09- 05).
Err7
Parameter conflict
1.Attempt to modify the
function 13-00/13-08.
2. Voltage and current
detection circuit is
abnormal.
If reset is not possible, please
consult with the supplier.
5.1.3 Special conditions
Display Fault Description
StP0
Zero speed at stop Occurs when preset frequency <0.1Hz
StP1
Fail to start directly
On power up.
1. If the inverter is set for external terminal control mode
(00-02/00-03=1) and direct start is disabled (07-04=1)
2. The inverter cannot be started and will flash STP1.
3. The run input is active at power-up, refer to descriptions
of (07-04).
StP2
Keypad Stop
Operated when
inverter in external
Control mode.
1. If the Stop key is pressed while the inverter is set to
external control mode (00-02/00-03=1) then‘STP2’flashes
after stop.
2. Release and re-activate the run contact to restart the
inverter.
E.S.
External
Rapid stop
When external rapid stop input is activated the inverter will
decelerate to stop and the display will flash with E.S.
message.
b.b.
External base block
When external base block input is activated the inverter
stops immediately and then the display will flash with b.b.
message.
PdEr
PID feedback loss PID feedback loss is detected.
Page 97

5-4
5.2 General troubleshooting
Status Checking point Remedy
Is the wiring for the output
terminals correct?
Wiring must match U, V, and W terminals of the
motor.
Motor runs in
wrong
direction
Is the wiring for forward and
reverse signals correct?
Check for correct wiring.
Is the wiring for the analog
frequency inputs correct?
Check for correct wiring.
Is the setting of operation mode
correct?
Check the operation mode of the operator.
The motor
speed can
not be
regulated.
Is the load too excessive? Reduce the load.
Check the motor specifications
(poles, voltage…) correct?
Confirm the motor specifications.
Is the gear ratio correct? Confirm the gear ratio.
Motor
running
speed too
high or too
low
Is the setting of the highest output
frequency correct?
Confirm the highest output frequency
Is the load too excessive? Reduce the load.
Does the load vary excessively?
1.Minimize the variation of the load.
2.Consider increasing the capacities of the
inverter and the motor.
Consider adding an AC reactor at the power
input side if using single-phase power.
Motor speed
varies
unusually
Is the input power unstable or is
there a phase loss ?
2. Check wiring if using three-phase power
Is the power connected to the
correct L1, L2, and L3 terminals?
is the charging indicator lit ?
1 Is the power applied?
2.Turn the power OFF and then ON again.
3.Make sure the power voltage is correct.
4.Make sure screws are secured firmly.
Is there voltage across the output
terminals T1, T2, and T3?
Turn the power OFF and then ON again.
Is overload causing the motor to
stall?
Reduce the load so the motor will run.
Are there any abnormalities in the
inverter?
Is there a forward or reverse run
command ?
See error descriptions to check wiring and
correct if necessary.
Has the analog frequency signal
been input?
1.Is analog frequency input signal wiring correct?
2.Is voltage of frequency input correct?
Motor can
not run
Is the operation mode setting
correct?
Operate through the digital keypad
Page 98

5-5
5.3
Troubleshooting of the Inverter
5.3.1 Quick troubleshooting of the Inverter
INV Fault
Visually check controller
and Drive boards
*to next page
Check burnt and
damaged parts
Consult with the supplier
Replace fuse
Consult with the supplier
Consult with the supplier
Check according to
displayed fault messages
Replace the pre-charge
resistor
Check terminals and
wiring
Consult with the supplier
Perform detailed check and
consult with the supplier
Is fault known?
Symptoms other than burn
out, damage, or fuse
meltdown in the inverter?
Any Symptoms of burn
out and damage?
Is the main circuit DM
intact?
Fault signal?
Is the fuse intact?
Is the main circuit
I.G.B.T intact?
Any visual
abnormalities?
Are displays and
indicators of the
operating unit working
normally?
Is +5V control voltage
correct?
Is the DC input voltage
controlling the power
correct
Any fault display?
What the message ?
Is LED lit?
Replace control board
and digital operating unit
Is the error eliminated
after replacing control
board?
YES
NO
NO YES
NO
NO
NO
YES
YES
YES
YES
NO
NO
NO
YES
YES
YES
YES
NO
NO
YES
NO
YES
NO
YES
NO
YES
NO
Apply the power
Page 99

5-6
Check Inverter parameters
Replace the control
board
Perform parameter
initializations
Specify operation
control mode
Does the FWD or REV
LED light flash?
Is the frequency value
displayed on the display?
Are there voltage outputs at
terminals U, V and W
Is there any fault display?
Are output
currents of each
phase even?
The inverter is OK
Perform detailed check and
consult with the supplier.
Replace the control
board
Replace the control
board
Does the control Board
function after replacement
YES
YES
YES
NO
NO
YES
NO
NO
NO
YES
YES
NO
NO
From previous page
Set up frequency command
Connect the motor to run
Page 100

5-7
5.3.2 Troubleshooting for OC, OL error displays
The inverter displays OC, OL errors
The inverter output is OK
Is the output current of each
phase even?
Any fault values displayed?
Is there Voltage at U,V and W
output terminals?
Is the output frequency of the
operating unit displayed?
Is FWD LED illuminated?
Is the main circuit I.G.B.T
worki ng
Any visual abnormalities?
Is the current detector
OK?
Any abnormal indications?
Is the inverter operation OK
after board replacement ?
Replace the current
controller
Replace control board
Replace control board
Replace faulty circuit
board
Replace I.G.B.T
Replace control board
Replace control board
The inverter is faulted
(Perform detailed check)
YES
NO
YES
YES
NO
YES
NO
YES
YES
NO
YES
NO
NO
NO
YES
YES
NO
NO
Apply power
Input operation command
Input frequency command
Connect the motor to run
 Loading...
Loading...