Page 1

INVERTER
E510
INSTRUCTION MANUAL
230V Class 1~
IP66/NEMA 4X
0.4 - 2.2 kW / 0.5 - 3 HP
Read all operating instructions before installing,
connecting (wiring), operating, servicing, or inspecting
the inverter.
Ensure that this manual is made available to the end user of
the inverter.
Store this manual in a safe, convenient location.
230V Class 3~
IP66/NEMA 4X
0.4 - 15 kW / 0.75 - 20 HP
460V 460V Class 3~
IP66/NEMA 4X
0.45- 18.5 kW / 1 - 25 HP
The manual is subject to change without prior notice.
T
DOCUMENT - TECO-E510IM
Ver 01: 2015.08
Page 2

**** STATEMENT ****
Table of Contents
Preface (English) ........................................................................................................................................... 0-1
Preface (Français) ....................................................................................................................................... 0-2
1 Safety Precautions (English) .................................................................................................................... 1-1
1.1 Before Supplying Power to the Inverter .................................................................................................... 1-1
1.2 Wiring ........................................................................................................................................................ 1-2
1.3 Before Operation ....................................................................................................................................... 1-3
1.4 Parameters Setting ................................................................................................................................... 1-3
1.5 Operation .................................................................................................................................................. 1-4
1.6 Maintenance, Inspection and Replacement .............................................................................................. 1-5
1.7 Disposal of the Inverter ............................................................................................................................. 1-5
1 Consignes de sécurité (Français) ............................................................................................................ 1-6
1.1 Avant d'alimenter le disque dur ................................................................................................................. 1-6
1.2 Câblage ..................................................................................................................................................... 1-6
1.3 Avant l'opération........................................................................................................................................ 1-7
1.4 Configuration Paramètre ........................................................................................................................... 1-7
1.5 Opération .................................................................................................................................................. 1-8
1.6 Entretien, Inspection et remplacement ..................................................................................................... 1-8
1.7 Mise au rebut du variateur ........................................................................................................................ 1-9
2 Model Description ...................................................................................................................................... 2-1
2.1 Nameplate Data ........................................................................................................................................ 2-1
2.2 Inverter Models – Motor Power Rating ..................................................................................................... 2-2
3 Environment and Installation .................................................................................................................... 3-1
3.1 Environment .............................................................................................................................................. 3-1
3.2 Warning Labels ......................................................................................................................................... 3-2
Page 3

3.3 Removing the Front Cover and Keypad.................................................................................................... 3-3
3.4 Inverter Exterior ......................................................................................................................................... 3-5
3.5 Wire Gauges, Tightening Torque and Short Circuit Rating ...................................................................... 3-8
3.6 Wiring Peripheral Power Devices ............................................................................................................. 3-9
3.7 General Wiring Diagram .......................................................................................................................... 3-11
3.8 User Terminals ........................................................................................................................................ 3-12
3.9 Power Terminals ..................................................................................................................................... 3-15
3.10 Inverter Wiring ....................................................................................................................................... 3-17
3.11 Input Power and Motor Cable Length ................................................................................................... 3-19
3.12 Cable Length vs, Carrier Frequency ..................................................................................................... 3-19
3.13 Installing an AC Line Reactor ............................................................................................................... 3-19
3.14 Power Input Wire Size and NFB ........................................................................................................... 3-20
3.15 Control Circuit Wiring ............................................................................................................................ 3-20
3.16 Inverter Specifications ........................................................................................................................... 3-21
3.17 General Specifications .......................................................................................................................... 3-24
3.18 Inverter De-rating Based on Carrier Frequency .................................................................................... 3-26
3.19 Inverter Dimensions .............................................................................................................................. 3-27
4. Keypad and Programming Functions ..................................................................................................... 4-1
4.1 LED Keypad .............................................................................................................................................. 4-1
4.2 Parameters ................................................................................................................................................ 4-8
4.3 Description of Parameters ...................................................................................................................... 4-27
5. Check Motor Rotation and Direction ....................................................................................................... 5-1
6. Speed Reference Command Configuration............................................................................................ 6-1
6.1 Reference from the Keypad ...................................................................................................................... 6-1
6.2 Reference from an Analog Signal (0-10V / 4-20mA) / Speed Pot ............................................................ 6-2
6.3 Reference from Serial Communication RS485 ......................................................................................... 6-4
6.4 Reference from Pulse Input ...................................................................................................................... 6-6
6.5 Change Frequency Unit from Hz to rpm ................................................................................................... 6-7
Page 4

7. Operation Method Configuration (Run / Stop) ....................................................................................... 7-1
7.1 Run / Stop from the Keypad ...................................................................................................................... 7-1
7.2 Run / Stop from External Switch / Contact or Pushbutton ........................................................................ 7-2
7.3 Run / Stop from Serial Communication RS485 ........................................................................................ 7-4
8. Motor and Application Specific Settings ................................................................................................ 8-1
8.1 Set Motor Nameplate Data ....................................................................................................................... 8-1
8.2 Acceleration and Deceleration Time ......................................................................................................... 8-2
8.3 Volt/Hz Curve Modification (Torque Boost)............................................................................................... 8-3
8.4 Rapid Stop ................................................................................................................................................ 8-4
8.5 Forward and Reverse Jog ......................................................................................................................... 8-5
8.6 Analog Output Setup ................................................................................................................................. 8-6
9. Using PID Control for Constant Flow / Pressure Applications ............................................................ 9-1
9.1 What is PID Control ................................................................................................................................... 9-1
9.2 Connect Transducer Feedback Signal .................................................................................................... 9-3
9.3 Engineering Units ...................................................................................................................................... 9-4
9.4 Sleep / Wakeup Function .......................................................................................................................... 9-5
10 Troubleshooting, Fault Diagnostics and Maintenance ...................................................................... 10-1
10.1 General ................................................................................................................................................. 10-1
10.2 Fault Detection Function ....................................................................................................................... 10-1
10.3 General Troubleshooting ...................................................................................................................... 10-6
10.4 Routine and Periodic Inspection ........................................................................................................... 10-7
10.5 Routine Maintenance .......................................................................................................................... 10-10
Appendix A: UL Instructions........................................................................................................................ A1
Page 5

IMPORTANT
For Advanced Installation, Wiring and Programming of the E510 inverter
refer to the E510 Instruction Manual.
Warning
Failure to ignore the information indicated by the warning symbol may result in
death or serious injury.
Caution
Failure to ignore the information indicated by the caution symbol may result in
minor or moderate injury and/or substantial property damage.
Preface (English)
The E510 product is an inverter designed to control a three-phase induction motor. Please read this manual
carefully to ensure correct operation, safety and to become familiar with the inverter functions.
The E510 inverter is an electrical / electronic product and must be installed and handled by qualified service
personnel.
Improper handling may result in incorrect operation, shorter life cycle, or failure of this product as well as the
motor.
All E510 documentation is subject to change without notice.
Available Documentation:
1. E510 Start-up and Installation Manual
2. E510 Instruction Manual
Read this Start-up and Installation Manual in conjunction with E510 Instruction Manual thoroughly before
proceeding with installation, connections (wiring), operation, or maintenance and inspection. Ensure you have
sound knowledge of the device and familiarize yourself with all safety information and precautions before
proceeding to operate the inverter. Read E510 Instruction Manual for detailed description on parameters.
Ensure you have sound knowledge of the inverter and familiarize yourself with all safety information and
precautions before proceeding to operate the inverter.
Please pay close attention to the safety precautions indicated by the warning and caution symbol.
0-1
Page 6
Avertissement
ignorer les informations indiquées par le symbole d'avertissement peut
entraîner la mort ou des blessures graves.
Attention
ignorer les informations indiquées par le symbole de mise en garde peut
entraîner des blessures mineures ou modérées et / ou des dommages
matériels importants.
Préface (Français)
Le produit est un lecteur conçu pour commander un moteur à induction triphasé. lire attentivement ce
manuel pour garantir le bon fonctionnement, la sécurité et pour se familiariser avec les fonctions
d'entraînement.
Le lecteur est un appareil électrique / électronique et doit être installé et géré par un personnel qualifié
Une mauvaise manipulation peut entraîner un fonctionnement incorrect, cycle de vie plus court, ou l'échec
de ce produit ainsi que le moteur.
Tous les documents sont sujets à changement sans préavis. Soyez sûr d'obtenir les dernières éditions de
l'utilisation ou visitez notre site Web
Lire le manuel d'instructions avant de procéder à l'installation, les connexions (câblage), le fonctionnement
ou l'entretien et l'inspection.
Vérifiez que vous avez une bonne connaissance de l'entraînement et de vous familiariser avec les
consignes de sécurité et les précautions avant de procéder à fonctionner le lecteur.
prêter attention aux consignes de sécurité indiquées par l'avertissement et symbole Attention .
0-2
Page 7

1. Safety Precautions (English)
Warning
The main circuit must be correctly wired. For single phase supply use input terminals (R/L1, T/L3) and for
three phase supply use input terminals (L1(L), L2, L3(N)). Terminals T1, T2, T3 must only be used to
connect the motor. Connecting the input supply to any of the T1, T2 or T3 terminals will cause damage to
the inverter.
Caution
To avoid the front cover from disengaging or other physical damage, do not carry the inverter by
its cover. Support the unit by its heat sink when transporting. Improper handling can damage the
inverter or injure personnel, and should be avoided.
To avoid the risk of fire, do not install the inverter on or near flammable objects. Install on
nonflammable objects such as metal surfaces.
If several inverters are placed inside the same control panel, provide adequate ventilation to
maintain the temperature below 40°C/104°F (50°C/122°F without a dust cover) to avoid
overheating or fire.
When removing or installing the digital operator, turn off the power first, and then follow the
instructions in this manual to avoid operator error or loss of display caused by faulty connections.
Warning
This product is sold subject to IEC 61800-3. In a domestic environment this product may cause radio
interference in which case the user may need to apply corrective measures.
1.1 Before supplying Power to the Inverter
1-1
Page 8
1.2 Wiring
Warning
Always turn OFF the power supply before attempting inverter installation and wiring of the user
terminals.
Wiring must be performed by a qualified personnel / certified electrician.
Make sure the inverter is properly grounded. (230V Class: Grounding impedance shall be less
than 100Ω. 460V Class: Grounding impedance shall be less than 10Ω.)
Please check and test emergency stop circuits after wiring. (Installer is responsible for the correct
wiring.)
Never touch any of the input or output power lines directly or allow any input of output power lines to
come in contact with the inverter case.
Do not perform a dielectric voltage withstand test (megger) on the inverter this will result in inverter
damage to the semiconductor components.
Caution
The line voltage applied must comply with the inverter’s specified input voltage. (See product
nameplate section 2.1)
Use wire gauge recommendations and torque specifications. (See Wire Gauge and Torque
Specification section 3.7)
Never connect input power to the inverter output terminals T1, T2, T3.
Do not connect a contactor or switch in series with the inverter and the motor.
Do not connect a power factor correction capacitor or surge suppressor to the inverter output.
Ensure the interference generated by the inverter and motor does not affect peripheral devices.
1-2
Page 9
1.3 Before Operation
Warning
Make sure the inverter capacity matches the parameters 13-00.
Reduce the carrier frequency (parameter 11-01) If the cable from the inverter to the motor is
greater than 80 ft (25m). A high-frequency current can be generated by stray capacitance
between the cables and result in an overcurrent trip of the inverter, an increase in leakage
current, or an inaccurate current readout.
Be sure to install all covers before turning on power. Do not remove any of the covers while power to
the inverter is on, otherwise electric shock may occur.
Do not operate switches with wet hands, otherwise electric shock may result.
Do not touch inverter terminals when energized even if inverter has stopped, otherwise electric shock
may result.
Caution
Do not connect a load to the motor while performing a rotational auto-tune.
Make sure the motor can freely run and there is sufficient space around the motor when
performing a rotational auto-tune.
1.4 Parameter Setting
1-3
Page 10
1.5 Operation
Warning
Be sure to install all covers before turning on power. Do not remove any of the covers while power to
the inverter is on, otherwise electric shock may occur.
Do not connect or disconnect the motor during operation. This will cause the inverter to trip and
may cause damage to the inverter.
Operations may start suddenly if an alarm or fault is reset with a run command active. Confirm that no
run command is active upon resetting the alarm or fault, otherwise accidents may occur.
Do not operate switches with wet hands, otherwise electric shock may result.
It provides an independent external hardware emergency switch, which emergently shuts down the
inverter output in the case of danger.
If automatic restart after power recovery (parameter 07-00) is enabled, the inverter will start
automatically after power is restored.
Make sure it is safe to operate the inverter and motor before performing a rotational auto-tune.
Do not touch inverter terminals when energized even if inverter has stopped, otherwise electric shock
may result.
Do not check signals on circuit boards while the inverter is running.
After the power is turned off, the cooling fan may continue to run for some time.
Caution
Do not touch heat-generating components such as heat sinks and braking resistors.
Carefully check the performance of motor or machine before operating at high speed, otherwise
Injury may result.
Note the parameter settings related to the braking unit when applicable.
Do not use the inverter braking function for mechanical holding, otherwise injury may result.
Do not check signals on circuit boards while the inverter is running.
1-4
Page 11

1.6 Maintenance, Inspection and Replacement
Warning
Wait a minimum of five minutes after power has been turned OFF before starting an inspection. Also
confirm that the charge light is OFF and that the DC bus voltage has dropped below 25Vdc.
Never touch high voltage terminals in the inverter.
Make sure power to the inverter is disconnected before disassembling the inverter.
Only authorized personnel should perform maintenance, inspection, and replacement operations.
(Take off metal jewelry such as watches and rings and use insulated tools.)
Caution
The Inverter can be used in an environment with a temperature range from 14° -104°F (-10-40°C)
and relative humidity of 95% non-condensing.
The inverter must be operated in a dust, gas, mist and moisture free environment.
Caution
Please dispose of this unit with care as an industrial waste and according to your required local
regulations.
The capacitors of inverter main circuit and printed circuit board are considered as hazardous
waste and must not be burned.
The Plastic enclosure and parts of the inverter such as the top cover board will release harmful
gases if burned.
1.7 Disposal of the Inverter
1-5
Page 12
1. Consignes de sécurité (Français)
Avertissement
Le circuit principal doit être correctement câblée. Pour les terminaux monophasés d'approvisionnement
de l'utilisation des intrants (R/L1, T/L3) et de trois bornes d'entrée de l'utilisation de l'offre de phase (R/L1,
S/L2, T/L3). U/T1, V/T2, W/T3 ne doivent être utilisés pour connecter le moteur. Raccordement de
l'alimentation d'entrée à l'un des U/T1, V/T2 W/T3 ou bornes risque d'endommager le lecteur.
Attention
Pour éviter que le couvercle ne se désengage ou de tout autre dommage physique, ne portez pas le
lecteur par son couverture. Soutenir le groupe par son dissipateur de chaleur lors du transport. Une
mauvaise manipulation peut endommager le lecteur ou blesser le personnel, et doit être évitée.
Pour éviter que les risques d'incendie, ne pas installer le lecteur sur ou à proximité d'objets inflammables.
Installer sur des objets ininflammables comme les surfaces métalliques.
Si plusieurs disques sont placés dans le même panneau de contrôle, fournir une ventilation adéquate pour
maintenir la température en dessous de 40 ° C/104 ° F (50 ° C/122 ° F sans housse de protection) pour
éviter la surchauffe ou incendie.
Lors d'un retrait ou d'installation de l'opérateur numérique, éteignez-le d'abord, puis de suivre les
instructions de ce manuel pour éviter les erreurs de l'opérateur ou de la perte de l'affichage causé par des
connexions défectueuses.
Avertissement
Lors d'un retrait ou d'installation de l'opérateur numérique, éteignez-le d'abord, puis de suivre les
instructions de ce manuel pour éviter les erreurs de l'opérateur ou de la perte de l'affichage causé par des
connexions défectueuses....
Avertissement
Coupez toujours l'alimentation électrique avant de procéder à l'installation d'entraînement et le câblage
des terminaux utilisateurs.
Le câblage doit être effectué par un personnel qualifié / électricien certifié.
Assurez-vous que le lecteur est correctement mis à la terre. (220V Classe: impédance de mise à la terre
doit être inférieure à 100Ω Classe 440V:. Impédance de mise à la terre doit être inférieure à 10Ω.)
vérifier et tester mes circuits d'arrêt d'urgence après le câblage. (L’Installateur est responsable du
câblage.)
Ne touchez jamais de l'entrée ou de lignes électriques de sortie permettant directement ou toute entrée ou
de lignes de puissance de sortie à venir en contact avec le boîtier d'entraînement.
Ne pas effectuer un test de tenue en tension diélectrique (mégohmmètre) sur le disque dur ou cela va
entraîner des dommages de lecture pour les composants semi-conducteurs.
1.1 Avant d'alimenter le disque dur
1.2 Câblage
1-6
Page 13
Attention
La tension d'alimentation appliquée doit se conformer à la tension d'entrée spécifiée par le lecteur. (Voir
la section signalétique du produit)
Raccorder la résistance de freinage et de l'unité de freinage sur les bornes assignées.
Ne pas brancher une résistance de freinage directement sur les bornes CC P (+) et N (-), sinon risque
d'incendie.
Utilisez des recommandations de la jauge de fil et les spécifications de couple. (Voir Wire Gauge et la
section de spécification de couple)。
Ne jamais brancher l'alimentation d'entrée aux bornes onduleur de sortie U/T1, V/T2, W/T3.
Ne pas brancher un contacteur ou interrupteur en série avec le variateur et le moteur.
Ne branchez pas un facteur condensateur de correction de puissance ou suppresseur de tension à la
sortie du variateur。
S'assurer que l'interférence générée par l'entraînement et le moteur n'a pas d'incidence sur les
périphériques.
Avertissement
Assurez-vous que la capacité du disque correspond aux paramètres de notation avant d'alimenter.
Réduire le paramètre de la fréquence porteuse si le câble du variateur au moteur est supérieure à 80 pi
(25 m). Un courant de haute fréquence peut être générée par la capacité parasite entre les câbles et
entraîner un déclenchement de surintensité du variateur, une augmentation du courant ou d'une lecture
actuelle inexactes.
Veillez à installer tous les couvercles avant de l'allumer. Ne retirez pas les capots pendant que
l'alimentation du lecteur est allumé, un choc électrique peut se produire autrement.
Ne pas actionner d'interrupteurs avec les mains mouillées, un choc électrique pourrait survenir autrement.
Ne touchez pas les bornes d'entraînement lorsqu'il est alimenté, même si le lecteur est arrêté, un choc
électrique pourrait survenir autrement.
Attention
Ne branchez pas une charge pour le moteur tout en effectuant un auto-tune.
Assurez-vous que le moteur peut fonctionner librement et il y a suffisamment d'espace autour du moteur
lors de l'exécution d'un auto-tune rotation.
1.3 Avant l'opération
1.4 Configuration Paramètre
1-7
Page 14
1.5 Opération
Avertissement
Veillez à installer tous les couvercles avant de l'allumer. Ne retirez pas les capots pendant que
l'alimentation du lecteur est allumé, un choc électrique peut se produire autrement.
Ne pas brancher ou débrancher le moteur pendant le fonctionnement. Le variateur pourrai se déclencher
et ainsi endommager le lecteur.
Les opérations peuvent commencer soudainement si une alarme ou un défaut est réarmé avec un ordre
de marche active. Assurez-vous qu'un ordre de marche est actif lors de la réinitialisation de l'alarme ou
de défaut, autrement des accidents peuvent se produire.
Ne pas actionner d'interrupteurs avec les mains mouillées, un choc électrique pourrait survenir.
Un interrupteur d'urgence externe indépendant est fourni, qui s'arrête en urgence vers le bas la sortie de
l'onduleur en cas de danger.
Si le redémarrage automatique après une récupération d'énergie est activée, le variateur démarrera
automatiquement après le rétablissement du courant.
Assurez-vous qu'il est sûr de faire fonctionner le variateur et le moteur avant d'effectuer un auto-tune
rotation.
Ne touchez pas les bornes d'entraînement lorsqu'il est alimenté même si l’onduleur s'est arrêté, un choc
électrique pourrait survenir .
Ne pas contrôler les signaux sur les circuits pendant que le lecteur est en marche.
Après la mise hors tension, le ventilateur de refroidissement peut continuer à fonctionner pendant un
certain temps.
Attention
Ne touchez pas les composants générant de la chaleur tels que radiateurs et des résistances de
freinage.
Vérifiez soigneusement la performance du moteur ou de la machine avant d'utiliser à grande vitesse,
sous peine de blessure.
Notez les réglages des paramètres liés à l'unité de freinage lorsque applicable.
Ne pas utiliser la fonction de freinage d'entraînement pour un maintien mécanique, sous peine de
blessure.
Ne pas contrôler les signaux sur les circuits pendant que le lecteur est en marche.
Avertissement
Attendre un minimum de 5 minutes après que l'alimentation a été débranchée avant de commencer une
inspection. Vérifiez également que le voyant de charge est éteint et que la tension du bus cc a chuté
au-dessous de 25Vdc.
Ne jamais toucher les bornes à haute tension dans le lecteur.
Assurez-vous que l'alimentation du lecteur est débranché avant de démonter le lecteur.
Seul le personnel autorisé peuvent faire l'entretien, l'inspection et les opérations de remplacement.
(Enlevez les bijoux en métal tels que les montres et les bagues et utiliser des outils isolés.)
1.6 Entretien, Inspection et remplacement
1-8
Page 15
Attention
Le variateur peut être utilisé dans un environnement avec une gamme de température allant de
14 ° -104 ° F (10-40 ° C) et l'humidité relative de 95% sans condensation.
Le variateur doit être utilisé dans un environnement sans poussière, gaz, vapeur et humidité.
Attention
jeter cet appareil avec soin comme un déchet industriel et selon les réglementations locales nécessaires.
Les condensateurs du circuit principal d'entraînement et circuits imprimés sont considérés comme des
déchets dangereux et ne doivent pas être brûlés.
The Plastic enclosure and parts of the drive such as the top cover board will release harmful gases if
burned.
1.7 Mise au rebut du variateur
1-9
Page 16
Product Name and Motor Rating
Input Power Specifications
Output Power Specifications
Series No
UL and CE Marks
PRODUCT: E510-401-H3N4 MOTOR RATING: 1HP/0.75kW
INPUT : AC 3PH 50/60Hz 380-480V (+10%,-15%) 4.2A
OUTPUT : AC 3PH 0-650Hz 0-480V 2.3A IP66
MODEL : E510-401-H3N4
P/N BARCODE S/N BARCODE
C
E510 Inverter Series
E510 - 2 010 - H 1 F N4S
2:
4:
230V
460V
Voltage Rating
Motor Rating
H: Standard Type
Operator Type
1:
Blank:
3:
1Ph
1Ph or 3Ph
3Ph
Input
Blank:
F:
No EMC
EMC Filter
Noise Filter
200V Class P5: 0.5 HP
01: 1 HP
02: 2 HP
03: 3 HP
05: 5 HP
08: 8 HP
10: 10 HP
15: 15 HP
20: 20 HP
400V Class 01: 1 HP
02: 2 HP
03: 3 HP
05: 5 HP
08: 8 HP
10: 10 HP
15: 15 HP
20: 20 HP
25: 25 HP
N4:
N4R
N4S
IP66
IP66/Built-in VR
IP66/Built-in VR + Switch
Enclosure
2. Model Description
2.1 Nameplate Data
It is essential to verify the E510 inverter nameplate and make sure that the E510 inverter has the correct rating so
it can be used in your application with the proper sized AC motor.
Unpack the E510 inverter and check the following:
(1) The E510 inverter and start-up and installation manual (this document) are contained in the package.
(2) The E510 inverter has not been damaged during transportation there should be no dents or parts missing.
(3) The E510 inverter is the type you ordered. You can check the type and specifications on the main nameplate.
(4) Check that the input voltage range meets the input power requirements.
(5) Ensure that the motor HP matches the motor rating of the inverter.
(1HP = 0.746 kW)
Model Identification
2-1
Page 17
Model
Supply
voltage
(Vac)
HP
(kW)
Filter
VR
Switch
Frame
Size
V X V X V
X
E510-2P5-H1FN4S
1 Phase
200~240V
+10%-15%
50/60Hz
0.5
0.4 ◎ ◎ ◎ 1 E510-201-H1FN4S
1
0.75 ◎ ◎ ◎ 1 E510-202-H1FN4S
2
1.5 ◎ ◎ ◎ 2 E510-203-H1FN4S
3
2.2 ◎ ◎ ◎
2
E510-2P5-HN4R
1 & 3 Phase
200~240V
+10%-15%
50/60Hz
0.5
0.4
◎
◎
◎ 1
E510-201-HN4R
1
0.75
◎
◎
◎ 1
E510-202-HN4R
2
1.5
◎
◎
◎ 2
E510-203-HN4R
3
2.2
◎
◎
◎ 2
E510-205-H3N4
3 Phase
200~240V
+10%-15%
50/60Hz
5
3.7
◎ ◎ ◎ 2
E510-208-H3N4
7.5
5.5
◎ ◎ ◎ 3
E510-210-H3N4
10
7.5
◎ ◎ ◎ 3
E510-215-H3N4
15
11
◎ ◎ ◎ 3
E510-220-H3N4
20
15
◎ ◎ ◎ 3
E510-401-H3FN4S
3 Phase
380~480V
+10%-15%
50/60Hz
1
0.75 ◎ ◎ ◎
1
E510-401-H3N4
1
0.75
◎ ◎ ◎ 1
E510-402-H3FN4S
2
1.5 ◎ ◎ ◎ 1 E510-402-H3N4
2
1.5
◎ ◎ ◎ 1
E510-403-H3FN4S
3
2.2 ◎ ◎ ◎ 2 E510-403-H3N4
3
2.2
◎ ◎ ◎ 2
E510-405-H3FN4S
5
3.7 ◎ ◎ ◎
2
E510-405-H3N4
5
3.7
◎ ◎ ◎ 2
E510-408-H3FN4S
7.5
5.5 ◎ ◎ ◎ 3 E510-408-H3N4
7.5
5.5
◎ ◎ ◎ 3
E510-410-H3FN4S
10
7.5 ◎ ◎ ◎ 3 E510-410-H3N4
10
7.5
◎ ◎ ◎ 3
E510-415-H3FN4S
15
11 ◎ ◎ ◎
3
E510-415-H3N4
15
11
◎ ◎ ◎ 3
E510-420-H3N4
20
15
◎ ◎ ◎ 3
E510-425-H3N4
25
18.5
◎ ◎ ◎ 3
2.2 Inverter Models – Motor Power
IP66 / NEMA 4X Type
V: Built-in
X: None
2-2
Page 18
3. Environment and Installation
Protection
Protection Class
IP66 / NEMA 4X (Depending on models)
Operating
Temperature
IP66 / NEMA 4X type: -10°C - +50°C (14-122 °F)
If several inverters are placed in the same control panel, provide a heat
removal means to maintain ambient temperatures below 40°C
Storage
Temperature
-20°C - +60°C (-4 -140 °F)
Humidity:
95% non-condensing
Relative humidity 5% to 95%, free of moisture.
(Follow IEC60068-2-78 standard)
Altitude:
< 1000m (3,281 ft.)
Installation Site:
Avoid exposure to rain or moisture.
Avoid direct sunlight.
Avoid oil mist and salinity.
Avoid corrosive liquid and gas.
Avoid dust, lint fibers, and small metal filings.
Keep away from radioactive and flammable materials.
Avoid electromagnetic interference (soldering machines, power machines).
Avoid vibration (stamping, punching machines etc.).
Add a vibration-proof pad if the situation cannot be avoided.
Shock
Maximum acceleration: 1G (9.8m/s²), for <20Hz
Maximum acceleration: 0.6G (5.88m/s²), for 20 - 50Hz (IEC60068-2-6 standard)
3.1 Environment
The environment will directly affect the proper operation and the life span of the inverter. To ensure
that the inverter will give maximum service life, please comply with the following environmental
conditions:
3-1
Page 19

3.2 Warning Labels
Important: Warning information located on the front cover must be read upon installation of the inverter.
3-2
Page 20
Caution
Before making any wiring connections to the inverter the front cover needs to be removed.
3.3 Removing the Front Cover and Keypad
IP66 / NEMA 4X
Step 1: Unscrew cover and place cover next to the inverter
3-3
Page 21
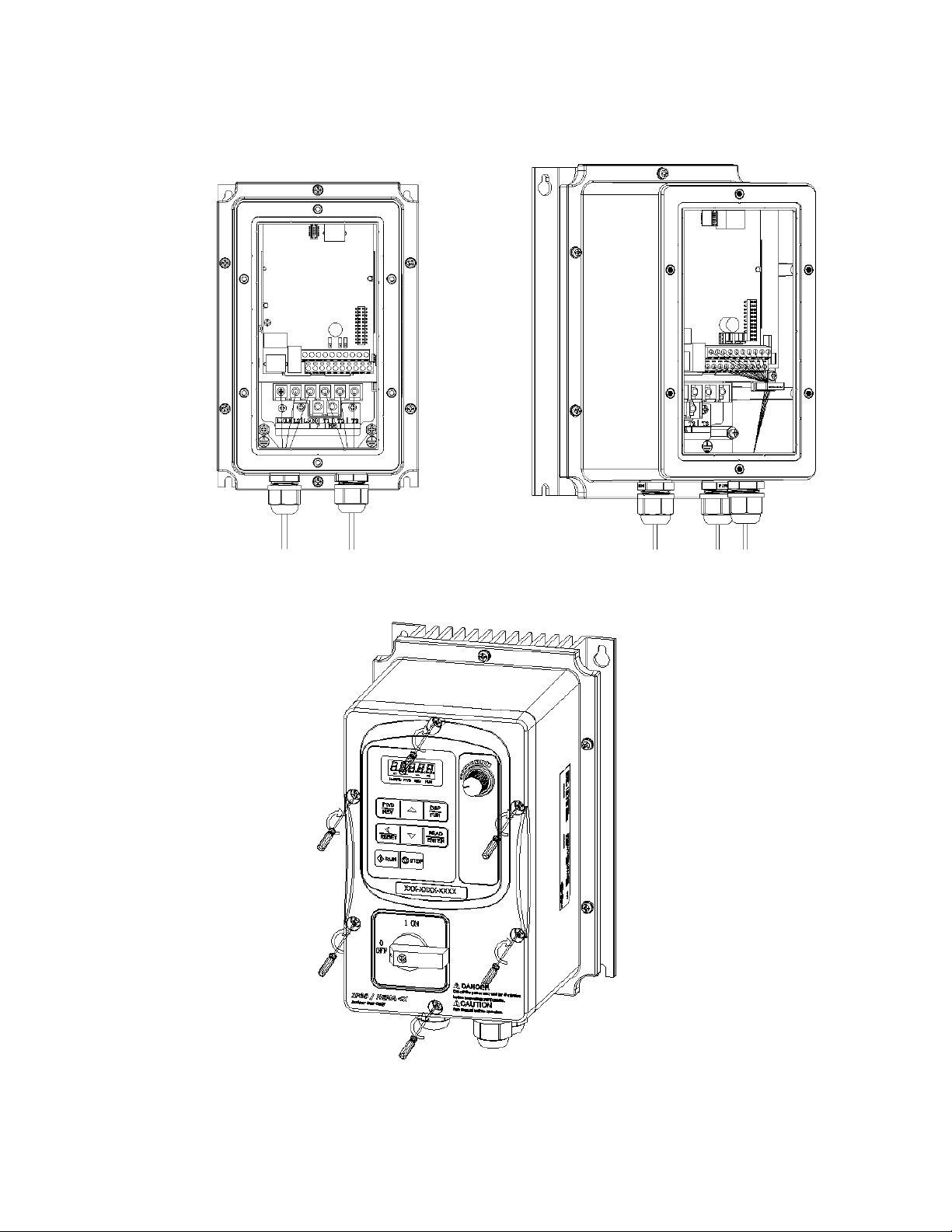
Step 2: Remove the rubber plugs and use the waterproof cable glands provided to connect cables.
Step 3: Connect power & motor cables through the cable glands to the correct terminals
Step 4: Connect power & motor cables through the cable glands to the correct terminals
3-4
Page 22
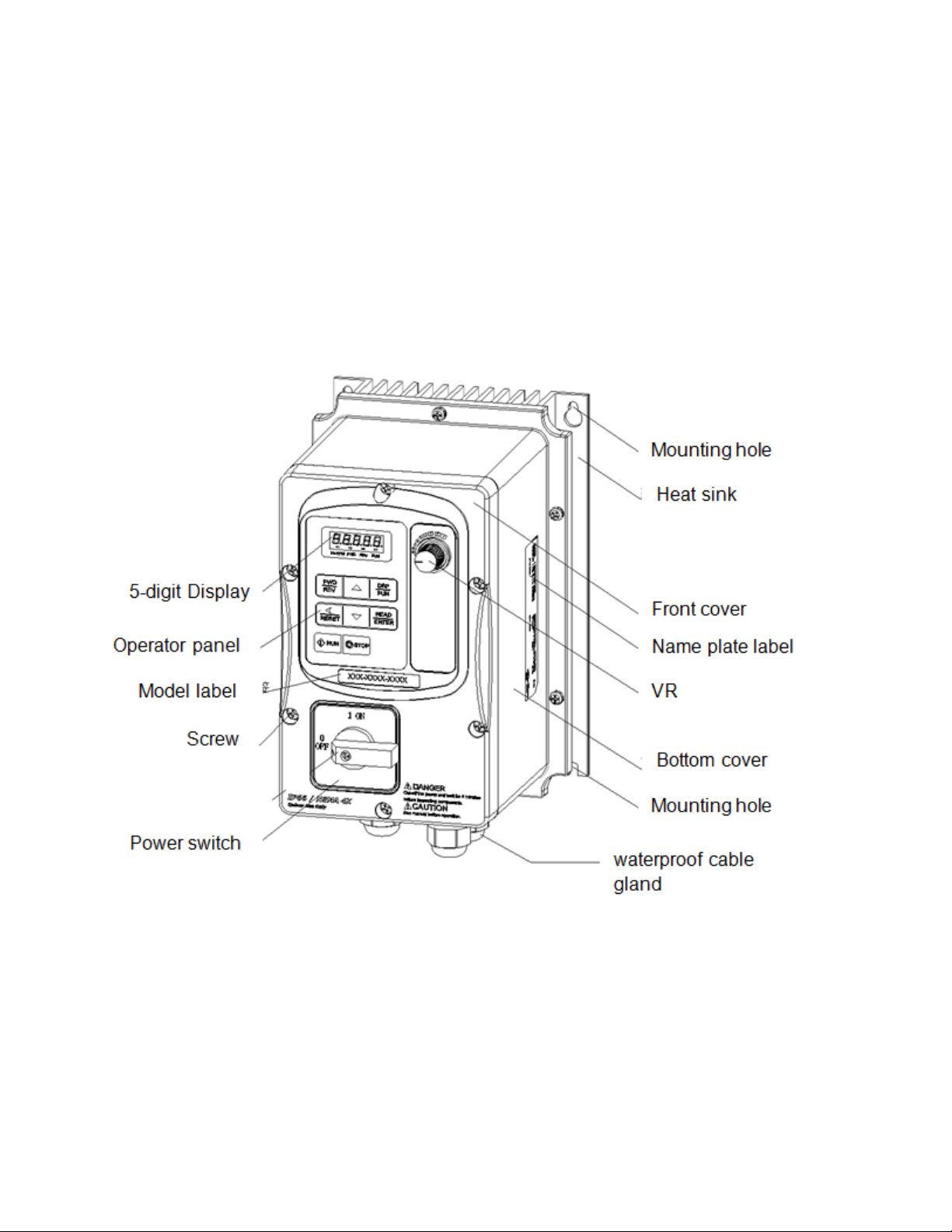
3.4 Inverter Exterior
IP66/NEMA4X
(a) Single/Three phase: 230V 0.5~1HP
Single phase: 230V 0.5~1HP
Three phase: 230V 2HP; 460V 1~2HP
E510-Frame 1 (IP66/NEMA 4X With/Without VR and disconnect switches depending on the model)
3-5
Page 23
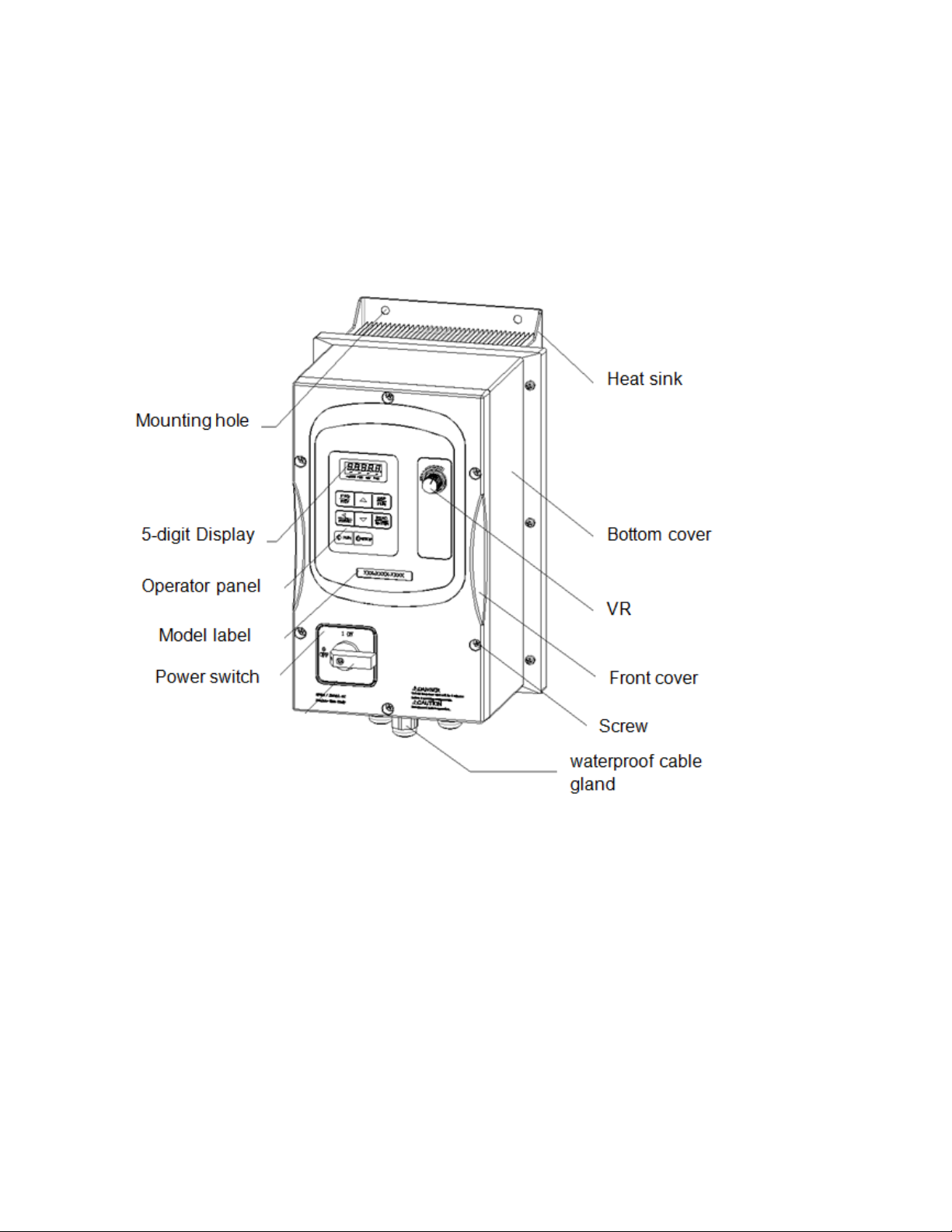
(b) Single/Three phase: 230V 2~3HP
Single phase: 230V 2~3HP
Three phase: 230V 5HP; 460V 3~5HP
E510-Frame 2 (IP66/NEMA 4X With/Without VR and disconnect switches depending on the model)
3-6
Page 24
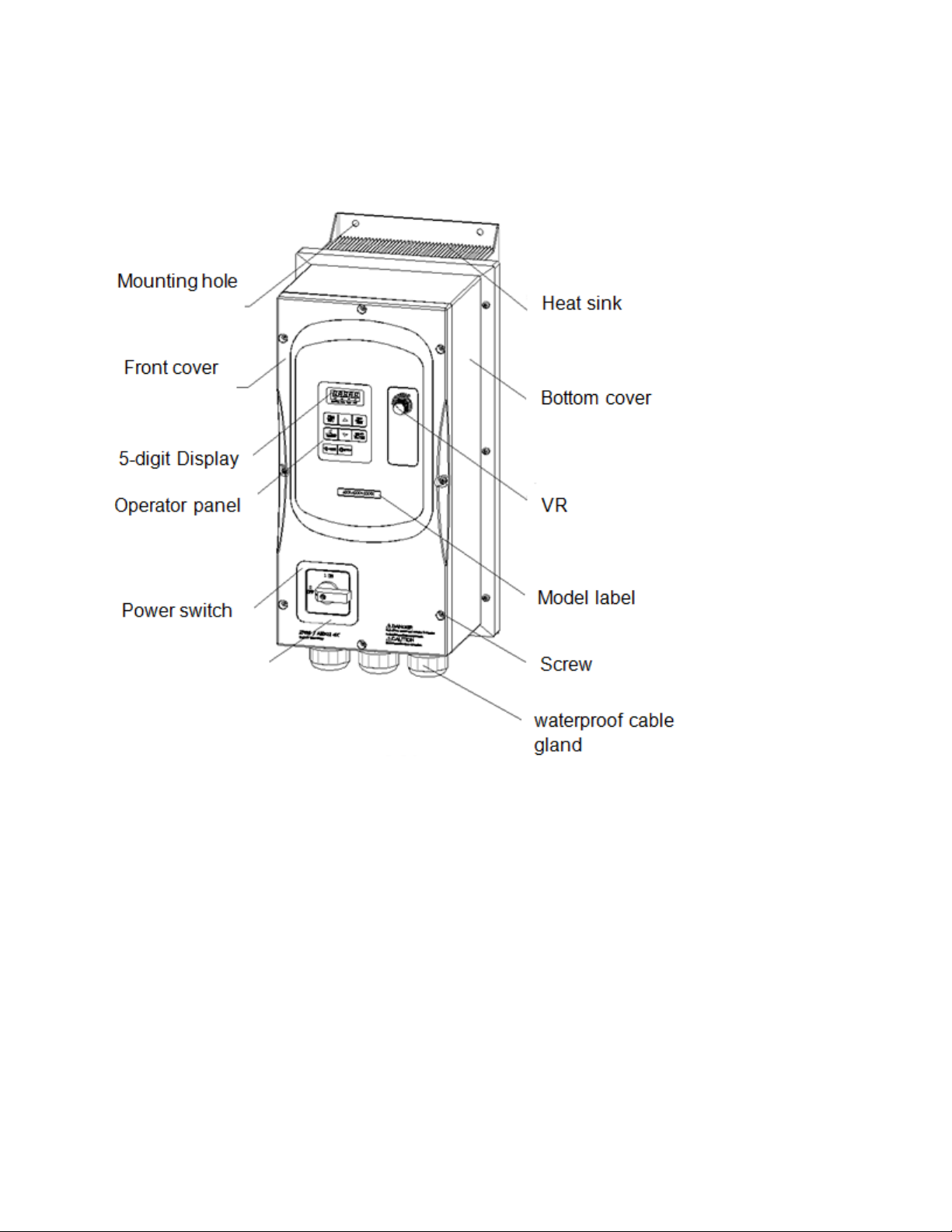
(c) Three phase: 230V 7.5~20HP; 460V 7.5~25HP
E510-Frame 3 (IP66/NEMA 4X With/Without VR and disconnect switches depending on the model)
3-7
Page 25
Model
TM1
TM2
Cable Size
Tightening torque
Cable Size
Tightening torque
AWG
mm²
kgf.cm
Ibf.in
Nm
AWG
mm²
kgf.cm
Ibf.in
Nm
Frame1
20~12
0.52~3.33
10.20
0.006
1.0
26~14
0.13~2.08
8.16
0.005
0.8
Frame2
18~8
0.81~8.37
18.35
0.010
1.8
Frame3
14~6
2.08~13.30
24.47
0.014
2.4
Frame4
4~3
21.15~26.67
Model
Horsepower
Power Specification
Voltage (Volt)
Current(A)
Frame1
0.5/1
200V~240V
600
20
1/2
380V~480V
Frame2
2/3/5
200V~240V
600
45
3/5
380V~480V
Frame 3/4
7.5/10/15/20
200V~240V
600
65
7.5/10/15/20/25
380V~480V
600
100
Device Rating
Short circuit
Rating(A)
Maximum
Voltage (Volt)
voltage
HP
230V
0.5~20
5,000
240
460V
1~25
5,000
480
3.5 Wire Gauges, Tightening Torque, Terminal and Short Circuit Ratings.
To comply with UL standards, use UL approved copper wires (rated 75° C) and round crimp terminals (UL
Listed products) as shown in table below when connecting to the main circuit terminals.
Terminals Electrical Rating
Short circuit rating
3-8
Page 26
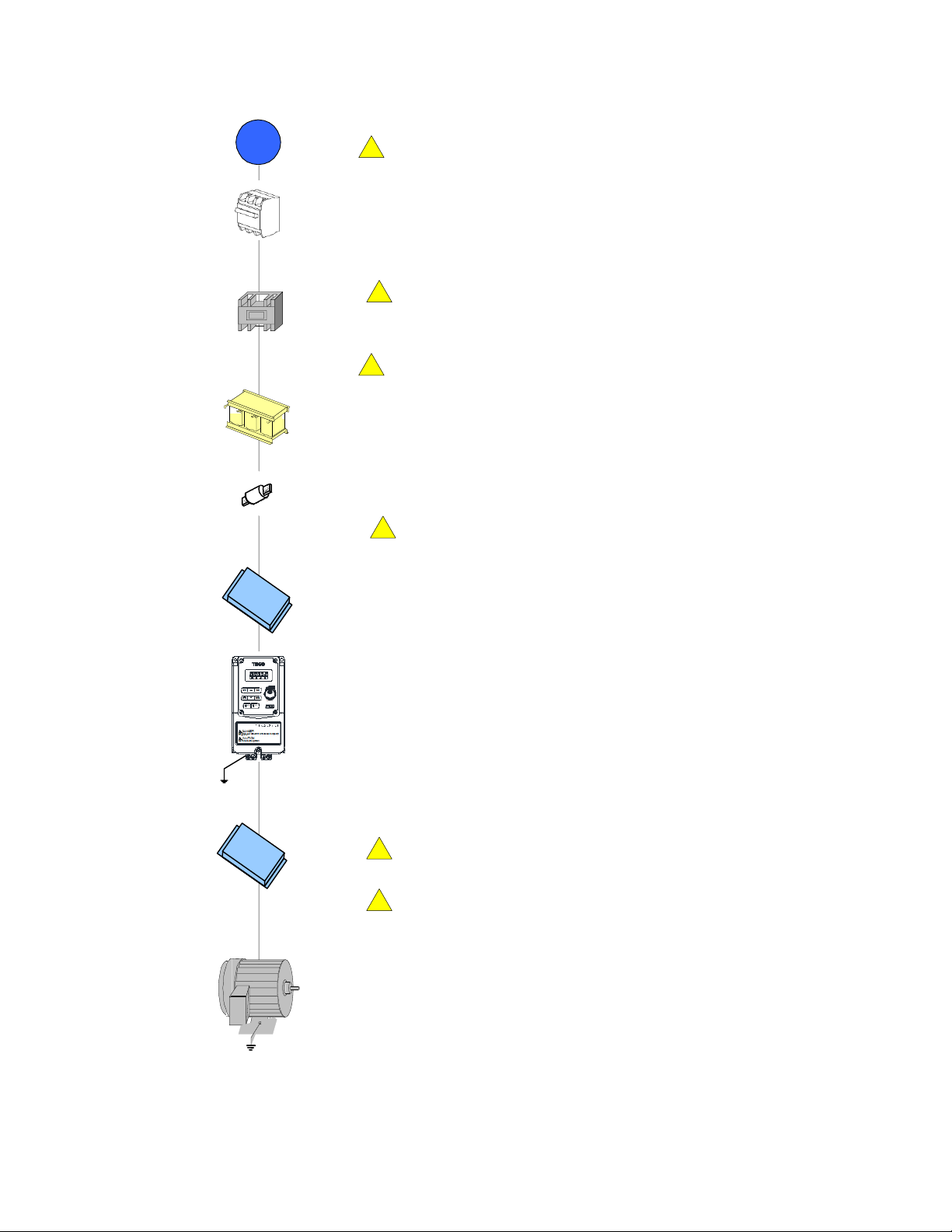
3.6 Wiring Peripheral Power Devices
Caution
After power is shut off to the inverter the capacitors will slowly discharge. Do NOT touch and of
the inverter circuitry or replace any components until the “CHARGE” indicator is off.
Do NOT wire or connect/disconnect internal connectors of the inverter when the inverter is
powered up or when powered off and the “CHARGE”” indicator is on.
Do NOT connect inverter output U, V and W to the supply power. This will result in damage to the
inverter.
The inverter must by properly grounded. Use terminal E to connect earth ground and comply with
local standards.
Do NOT perform a dielectric voltage withstand test (Megger) on the inverter this will result in inverter
damage to the semiconductor components.
Do NOT touch any of the components on the inverter control board to prevent damage to the inverter
by static electricity.
Caution
Refer to the recommended wire size table for the appropriate wire to use. The voltage between
the power supply and the input of the inverter may not exceed 2%.
Phase-to-phase voltage drop (V) = 3 ×resistance of wire (Ω/km) × length of line m) × current×10-3.
(km=3280 x feet) / (m=3.28 x feet )
Reduce the carrier frequency (parameter 11-01) If the cable from the inverter to the motor is
greater than 25m (82ft). A high-frequency current can be generated by stray capacitance
between the cables and result in an overcurrent trip of the inverter, an increase in leakage
current, or an inaccurate current readout.
To protect peripheral equipment, install fast acting fuses on the input side of the inverter. Refer to
section 11.6 for additional information.
3-9
Page 27
~
~
~
Power Supply
M
C
C
B
Molded
Circuit
Breaker
Magnetic
Contactor
AC
Reactor
Fast
Acting
Fuse
Input Noise
Filter
E510
Inverter
Ground
Induction
Motor
Ground
Output Noise
Filter
Power supply:
!
Make sure the correct voltage is applied to avoid damaging the
inverter.
Molded-case circuit breaker (MCCB) or fused disconnect:
A molded-case circuit breaker or fused disconnect must be installed
between the AC source and the inverter that conforms to the rated
voltage and current of the inverter to control the power and protect the
inverter.
!
Do not use the circuit breaker as the run/stop switch for the
inverter.
Ground fault detector / breaker:
!
Install a ground fault breaker to prevent problems caused by
current leakage and to protect personnel. Select current range up to
200mA, and action time up to 0.1 second to prevent high frequency
failure.
Magnetic contactor:
Normal operations do not need a magnetic contactor. When performing
functions such as external control and auto restart after power failure, or
when using a brake controller, install a magnetic contactor.
!
Do not use the magnetic contactor as the run/stop switch for
the inverter.
AC line reactor for power quality:
When inverters are supplied by a high capacity power source (>
600KVA), an AC reactor can be connected to improve the power factor.
Install Fast Acting Fuse:
To protect peripheral equipment, install fast acting fuses in accordance
with the specifications in section 11 for peripheral devices.
Input Noise filter:
A filter must be installed when there are inductive loads affecting the
inverter. The inverter meets EN55011 Class A, category C3 when the
TECO special filter is used.
Inverter:
Output terminals T1, T2, and T3 are connected to U, V, and W terminals
of the motor. If the motor runs in reverse while the inverter is set to run
forward, swap any two terminals connections for T1, T2, and T3.
!
To avoid damaging the inverter, do not connect the output
terminals T1, T2, and T3 to AC input power.
!
Connect the ground terminal properly. (230V series: Rg <100;
460V series: Rg <10.)
Output Noise filter:
An output noise filter may reduce system interference and induced
noise. See section 11 for peripheral devices.
Motor:
If the inverter drives multiple motors the output rated current of the
inverter must be greater than the total current of all the motors.
3-10
Page 28
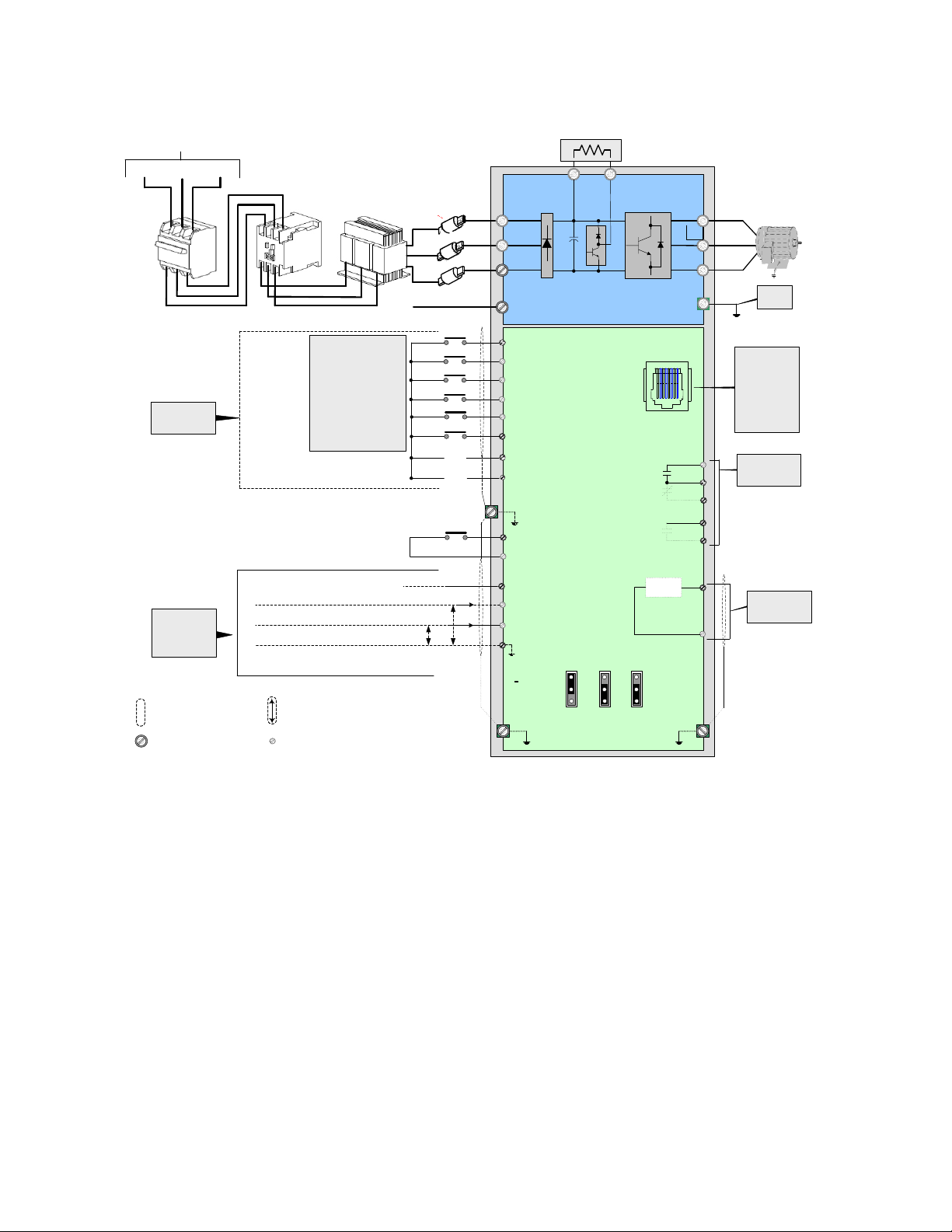
3.7 General Wiring Diagram
L1(L)
L2
L3(N)
T1
T2
T3
P
BR
3Ø Induction motor
E
+10V: Power for Analog Input
(max. 20mA)
AI1: Multi-Function Analog Input
AI2: Multi-Function Analog Input
S1
External
Analog
Inputs
Digital Input
Section
+
-
Ground
< 100Ω
Analog
Output
AO
AGND
Analog Outputs
0 – 10 VDC
S2
S3
S4
S5
E510
Multi-
Functional
Digital Inputs
Preset Speed 3
Preset Speed 2
Preset Speed 1
FWD / STOP
REV / STOP
Factory Default
L1(R)
L2(S)
L3(T)
Magnetic
Contactor
MCCB
AC
Reactor
Fast Acting
Fuses
AC Input Voltage
Braking Resistor
COM (NPN)
AGND: Analog Signal Common
0V
0 ~ 20mA
0 ~ 10V
P
P
(R1A)
(R1C)
(R1B)
NC
NO
Multi-Function
Relay Output
Contact rating:
250 VAC < 1.0A
30 VDC < 1.0A
R2A
R2B
*2
S6
Reset
+24V (PNP)
E (Ground)
E (Ground)
E (Ground)
NO
Relay Output
Relay Output
SF
SG
E
Output Disable
NPN
PNP
JP1
AI1
AV1
JP2
AI2
AV2
JP3
*3 *4
*5
*1
RS485
CON 2
Pin 1 to Pin 8
1:Data+
2:Data3:Data+
4:RXD0
5:TXD0
6:Data7:5V
8:GND
Twisted-pair shielded wire
P
Shielded wire
Control circuit
Main circuit
Notes:
*1: Use L1 (L) and L3 (N) for single phase input
*2: Use jumper JP1 to select between Sink (NPN, with 24VG common) or Source (PNP, with +24V
common) for multi-function digital input terminals S1~S6.
*3: Use jumper JP2 to switch between voltage and current input for Multi-function analog input 1 (AI1).
*4: Use jumper JP3 to switch between voltage and current input for Multi-function analog input 1 (AI2).
*5: Run Permissive input SF and SG is a normally open input. This input should be open to enable the
inverter output. To activate this input place a jumper wire between SF and SG.
3-11
Page 29
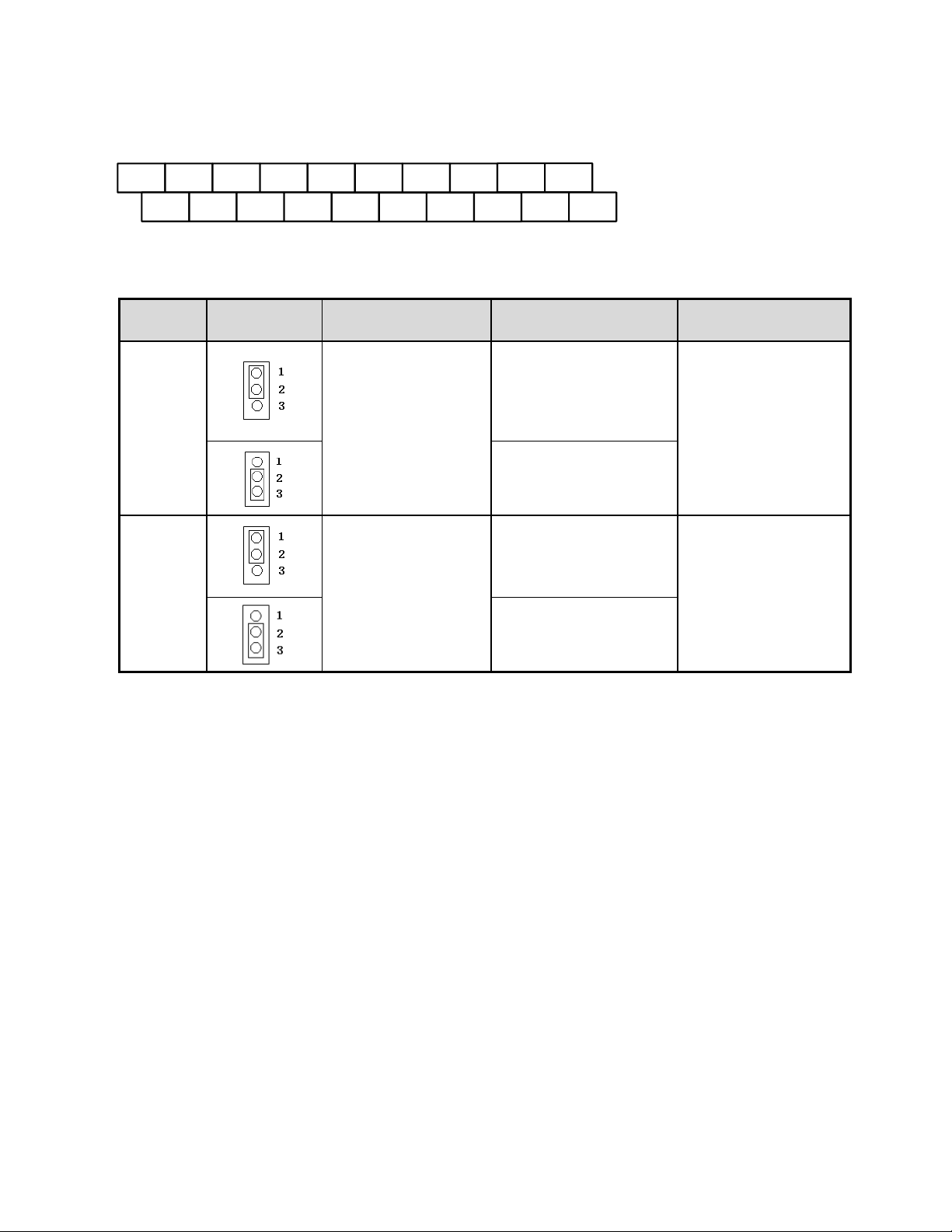
3.8 User Terminals (Control Circuit Terminals)
R2A R2B
COM
S1
S3 S5 SF 24V AI1 AI2
R1A R1B R1C S2 S4 S6 SG
AGND
10V AO
Jumper
Symbol
Function
Signal Reference
Note
JP1
NPN/PNP selectable
NPN Input
Factory default setting
PNP Input
JP2/JP3
External signal type
selection
0~20mA / 4~20mA
Analog signal
Set parameters
00-05/00-06
to 2 or 3 (external
analog input) to become
effective
0~10VDC / 2~10VDC
Analog signal
Jumper function descriptions
3-12
Page 30
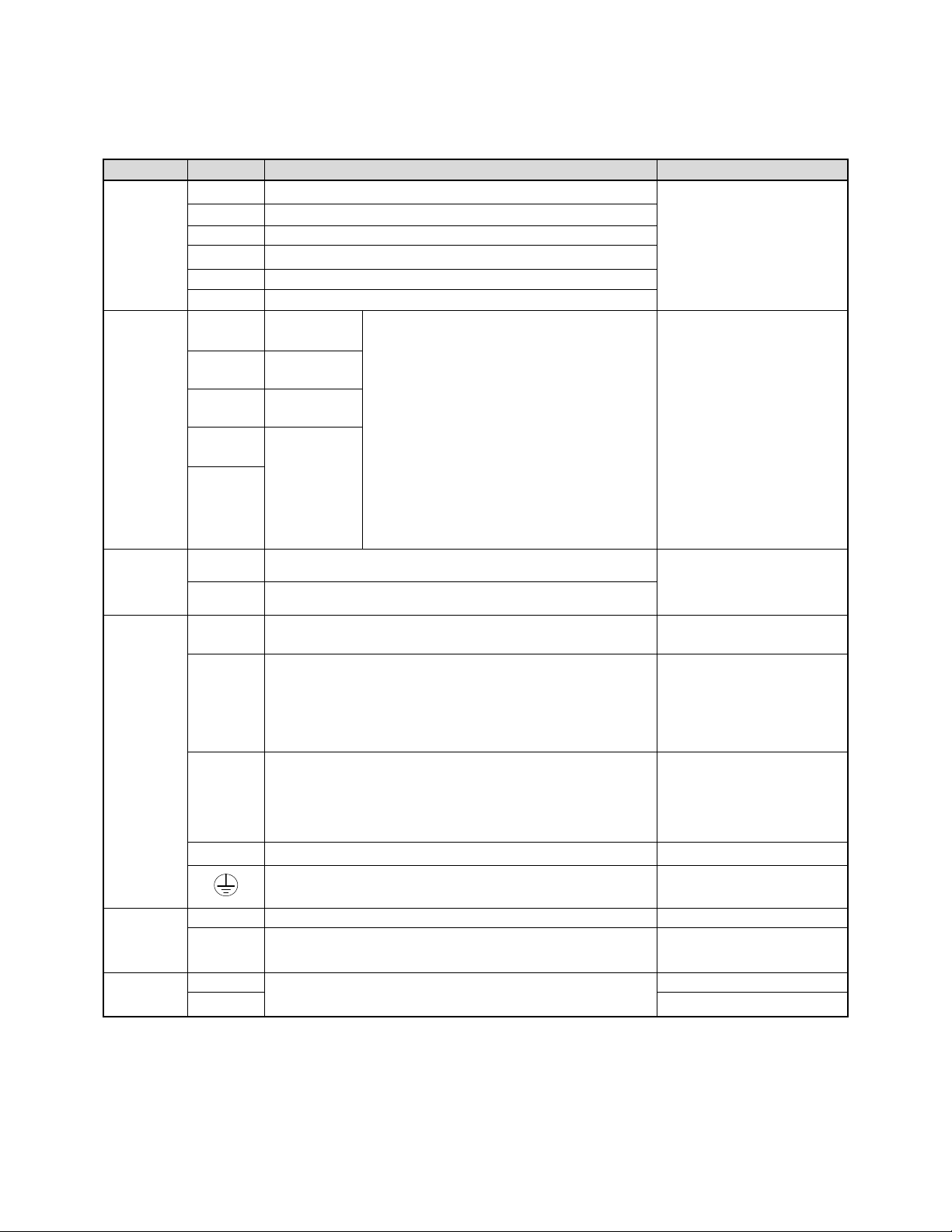
Description of User Terminals
Type
Terminal
Terminal function
Signal level
Digital
input
signal
S1
Forward- Stop (Preset), Multi-function input terminal
24 VDC, 8 mA, Optical
coupling isolation (Max,
voltage 30 VDC,
Input impedance 3.3kΩ)
S2
Reverse - Stop (Preset), Multi-function input terminal
S3
Preset Speed0(5-02),Multi-function input terminal
S4
Preset Speed1(5-03), Multi-function input terminal
S5
Preset Speed2(5-05), Multi-function input terminal
S6
Fault reset input, Multi-function input terminal
Relay
output
R1A
NO(Normally
open)
Multi-function output: Run, Fault, setting
Frequency ,Frequency Reached, Auto
Restart, Momentary AC Power Loss, Rapid
Stop ,Base Block Stop Mode, Motor
Overload Protection, Drive Overload
Protection, Over-torque Threshold Level、
Preset Current level Reached、Preset Brake
Frequency Reached, PID Feedback Signal
Loss, Final count value reached, Initial count
value reached, PLC Status Indicator ,PLC
control…
250VAC/1A(30VDC/1A)
R1B
NC(Normally
closed)
R1C
COMMON
R2A
R2B
24VPower
supply
COM
Digital signal common terminal (JP1 Switching NPN
position)
±15%,Max output current
60mA
24V
Digital signal common terminal (JP1 Switching PNP
position)
The
analog
input
signal
10V
Built in Power for an external speed potentiometer
10V(Max current:20mA)
AI1
Multifunctional analog input: JP2 selects voltage or current
input
Voltage: JP2 in AV1 position
Current: JP2 in AI1 position
0 ~ 10V,(Max
current:20mA)
(Input impedance: 153KΩ)
AI2
Multifunctional analog input: JP3 selects voltage or current
input
Voltage: JP3 in AV2 position
Current: JP3 in AI2 position
0 ~ 10V,0 ~20mA
(Input impedance: 153KΩ)
AGND
The analog common terminal
----
Shielding wire connecting terminal (The earth)
----
The
analog
output
signal
AO
Multifunctional analog output terminal*3
0 ~10V,(Max current:2mA)
AGND
The analog common terminal
----
Safety
switch
SF
Terminal SF is a safety input and can be used to disable
drive externally
SG
3-13
Page 31

Notes:
Caution
Maximum output current capacity for terminal 12V is 20mA.
Multi-function analog output AO1 and AO2 are for use for an analog output meter. Do not use
these output for feedback control.
Control board’s 24V and ±12V are to be used for internal control only, Do not use the internal
power-supply to power external devices.
*1:Multi-function digital input can be referred to in this manual.
- Group 03: External Terminals Digital Input / Output Function Group.
*2:Multi-function analog input can be referred to in this manual..
- Group 04 - External Terminal Analog Signal Input (Output) Function Group.
*3:Multi-function analog output can be referred to in this manual.
- Group 04 - External Terminal Analog Signal Input (Output) Function Group.
3-14
Page 32

3.9 Power Terminals
Terminal
230V: 0.5 ~ 20HP
460V: 1 ~ 25HP
L1(L)
Input Power Supply (For single phase use terminals L1(L) and L3(N)
L2
L3(N)
P
Braking resistor connection terminal: For use in applications requiring a
high inertia load to stop rapidly. (Refer to specifications of the braking
resistor).
BR
T1
Inverter output, connect to U/V/W terminals of motor
T2
T3
Ground terminal
230V: 0.5 ~ 1HP (Single Phase)
230V: 0.5 ~ 1HP (Single/Three Phase)
230V 2HP, 460V 1~2HP (Three Phase)
3-15
Page 33

Frame 2
230V: 2 ~ 3HP (Single Phase)
230V: 2 ~ 3HP (Single / Three Phase)
230V: 5HP (Three Phase)
460V: 3 ~ 5HP (Three Phase)
Frame 3 & 4
230V: 7.5 ~ 20HP (Three Phase)
460V: 7.5 ~ 25HP (Three Phase)
Notes: For wire gauges and screw torques, please refer to the table in section 3.6.
3-16
Page 34

3.10 Inverter Wiring
Danger
!
Do NOT remove any protective covers or attempt any wiring while input power is
applied. Connect all wiring before applying input power. When making wiring
changes after power up, remove input power and wait a minimum of five minutes
after power has been turned off before starting. Also confirm that the charge lamp
is off and that DC voltage between terminals B1/P or (+) and (-) does not exceed
25V, otherwise electric shock may result.
Only authorized personnel should work on the equipment. (Take off metal jewelry
such as watches and rings and use insulated tools.), otherwise electric shock or
injury may result.
Inverter IM
Power
MCCB
Inverter IM
Machine
RFI
Filter
Power
MCCB
Inverter IM
Machine
Isolation transformer
Power
MCCB
Wiring Precautions
(A) Power input terminals
1. The Input power supply voltage can be connected in any phase sequence to power input terminals
R/L1, S/L2, or T/L3 on the terminal block.
2. DO NOT connect the AC input power source to the output terminals U/T1, V/T2 and. W/T3.
3. Connect the output terminals U/T1, V/T2, W/T3 to motor lead wires U/T1, V/T2, and W/T3,
respectively.
4. Check that the motor rotates forward with the forward run source. If it does not, swap any 2 of the
output cables to change motor direction.
5. DO NOT connect phase correcting capacitors or LC/RC noise filter to the output circuit.
Example power connections:
Inverter with dedicated power line
Install a Supply RFI filter or Isolation transformer when the power source is shared with other high power
electrical equipment as shown below.
3-17
Page 35

(B) Grounding
E510 E510
E510
E510 E510 E510
a) Correct
b) Correct
E510 E510 E510
c) Incorrect
Loop
1. Connect the ground terminal (E) to ground having a resistance of less than 100Ω.
2. Do not share the ground wire with other devices, such as welding machines or power tools.
3. Always use a ground wire that complies with the local codes and standards for electrical equipment
and minimize the length of ground wire.
4. When using more than one inverter, be careful not to loop the ground wire, as shown below in Fig. 3.11.1.
Fig. 3.11.1 Inverter Grounding
3-18
Page 36

3.11 Input Power and Motor Cable Length
Cable length between
the inverter and
Motor in m (ft.).
< 30m
(100)
30 – 50
(100 – 165)
50 – 100
(166 - 328)
> 100
(329)
Recommended carrier
frequency allowed
Parameter 11-01
16kHz
(max)
10 kHz
(max)
5 kHz
(max)
2 kHz
(max)
The length of the cables between the input power source and /or the motor and inverter can cause a
significant phase to phase voltage reduction due to the voltage drop across the cables. The wire size
shown in Tables 3.16.1 is based on a maximum voltage drop of 2%. If this value is exceeded, a wire size
having larger diameter may be needed. To calculate phase tot phase voltage drop, apply the following
formula:
Phase-to-phase voltage drop (V) = 3 ×resistance of wire (Ω/km) × length of line m) × current×10-3.
(km=3280 x feet)
(m=3.28 x feet )
3.12 Cable Length vs. Carrier Frequency
The allowable setting of the PWM carrier frequency is also determined by motor cable length and is
specified in the following Table 3.13.1.
Table 3.13.1 Cable Length vs. Carrier Frequency
3.13 Installing an AC Line Reactor
If the inverter is connected to a large-capacity power source (600kVA or more), install an optional AC
reactor on the input side of the inverter. This also improves the power factor on the power supply side.
3-19
Page 37

3.14 Power Input Wire Size, and NFB
Model
TM1
TM2
Cable Size
Tightening torque
Cable Size
Tightening torque
AWG
mm²
kgf.cm
Ibf.in
Nm
AWG
mm²
kgf.cm
Ibf.in
Nm
Frame1
20~12
0.52~3.33
10.20
0.006
1.0
26~14
0.13~2.08
8.16
0.005
0.8
Frame2
18~8
0.81~8.37
18.35
0.010
1.8
Frame3
14~6
2.08~13.30
24.47
0.014
2.4
Frame4
4~3
21.15~26.67
Shield
Twisted Pair
Wrap with insulating Tape
Ground Shield at Inverter
end
ONLY
DO NOT
Ground Shield at
this end
The following table shows the recommended wire size for each frame of the E510. It depends on the
application whether or not to install a circuit breaker. The NFB must be installed between the input power
supply and the inverter input (L1 (L), L2, L3 (N)).
Note: When using a ground protection make sure the current setting is above 200mA and trip delay time is
0.1 sec of higher.
Table 3.16.1 Wiring instrument for frame 1 ~ 4
3.15 Control Circuit Wiring
(1) Separate the wiring for control circuit terminals from main circuit wiring for terminals
T/L3, U/T1, V/T2, W/T3)
(2) Separate the wiring for control circuit terminals R1A-R1B-R1C or R2A, R2B (Relay outputs) from
wiring for terminals
(3) Use shielded twisted-pair cables (#24 - #14 AWG / 0.5 -2 mm2) shown in Fig. 3.17.1 for control
circuits to minimize noise problems. The maximum wiring distance should not exceed 50m (165 ft).
S1 – S6
.
, A0, AGND, +10V, AI1, AI2 and GND wiring.
(R/L1, S/L2,
Fig. 3.17.1 Shielded Twisted-Pair
3-20
Page 38

3.16 Inverter Specification
Model:E510-□□□- H1F(N4)(S)
2P5
201
202
203
Horse power (HP)
0.5 1 2
3
Suitable motor capacity (kW)
0.4
0.75
1.5
2.2
Rated output current (A)
3.1
4.5
7.5
10.5
Rated capacity (KVA)
1.2
1.7
2.90
4.00
Input voltage range(V)
Single Phase:200~240V,50/60Hz
Allowable voltage fluctuation
+10%-15%
Output voltage range(V)
Three phase: 0~240V
Input current (A)*
8.5
12
16
23.9
Inverter net weight (kg)
1.65
1.65
2.5
2.5
Allowable momentary power loss time (S)
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
Enclosure
IP66/NEMA4X
Model:E510-□□□- H(N4R)
2P5
201
202
203
Horse power (HP)
0.5 1 2
3
Suitable motor capacity (kW)
0.4
0.75
1.5
2.2
Rated output current (A)
3.1
4.5
7.5
10.5
Rated capacity (KVA)
1.2
1.7
2.90
4.00
Input voltage range(V)
Single/Three Phase:200~240V, 50/60Hz
Allowable voltage fluctuation
+10%-15%
Output voltage range(V)
Three phase: 0~240V
Input current (A)*
8.5/4.5
12/6.5
16/11
23.9/12.5
Inverter net weight (kg)
1.6
1.6
2.5
2.5
Allowable momentary power loss time (S)
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
Enclosure
IP66/NEMA4X
Product Specifications 230V class – Single Phase
Product Specifications 230V class – Single/Three Phase
3-21
Page 39

Product Specifications 230V class –Three Phase
Model: E510-□□□- H3(N4)
202
205
208
210
215
220
Horse power (HP)
2 5 7.5
10
15
20
Suitable motor capacity (kW)
1.5
3.7
5.5
7.5
11
15
Rated output current (A)
7.5
17.5
26
35
48
64
Rated capacity (KVA)
2.9
6.7
9.9
13.3
20.6
27.4
Input voltage range(V)
Three phase :200~240V,50/60HZ
Allowable voltage fluctuation
+10%-15%
Output voltage range(V)
Three phase: 0~240V
Input current (A)*
11
20.5
33
42
57
70
Inverter net weight (kg)
1.6
2.5
6.5
6.5
10.1
10.4
Allowable momentary power loss time (S)
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
Enclosure
IP66/NEMA4X
Model:E510-□□□- H3(F)(N4)(S)
401
402
403
405
Horse power (HP)
1 2 3
5
Suitable motor capacity (kW)
0.75
1.5
2.2
3.7
Rated output current (A)
2.3
3.8
5.2
8.8
Rated capacity (KVA)
1.7
2.9
4.0
6.7
Input voltage range(V)
Three phase: 380~480V,50/60Hz
Allowable voltage fluctuation
+10%-15%
Output voltage range(V)
Three phase:0~480V
Input current (A)*
4.2
5.6
7.3
11.6
Inverter net weight (kg)
1.7
1.7
2.5
2.5
Allowable momentary power loss time (S)
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
Enclosure
IP66/NEMA4X
Model:E510-□□□- H3(F)(N4)(S)
408
410
415
420
425
Horse power (HP)
7.5
10
15
20
25
Suitable motor capacity (kW)
5.5
7.5
11
15
18.5
Rated output current (A)
13.0
17.5
24
32
40
Rated capacity (KVA)
9.9
13.3
19.1
27.4
34
Input voltage range(V)
Three phase: 380~480V,50/60Hz
Allowable voltage fluctuation
+10%-15%
Output voltage range(V)
Three phase: 0~480V
Input current (A)*
17
23
31
38
48
Inverter net weight (kg)
6.7
6.7
6.7
13.7
13.7
Allowable momentary power loss time (S)
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.0
Enclosure
IP66/NEMA4X
Product Specifications 460V class –Three Phase
Product Specifications 460V class –Three Phase
3-22
Page 40

Product Specifications 460V class –Three Phase
Model: E510-□□□- H3(F)(PT)
420
425
Horse power (HP)
20
25
Suitable motor capacity ( kW )
15
18.5
Rated output current (A)
32
40
Rated capacity (KVA)
27.4
34
Input voltage range(V)
Three phase: 380~480V (+10%-15%),50/60Hz
Output voltage range(V)
Three phase: 0~480V
Input current (A)*
38
48
Allowable momentary power loss time (S)
2.0
2.0
Enclosure
IP66/NEMA4X
Notes:
*The input current is calculated value at full rated output current.
*N4S 460V series only up to 15HP.
N4: Protection class IP66, without built-in disconnect switches and VR.
N4R: Protection class IP66, with built-in VR, without disconnect switches
N4S: Protection class IP66, with built-in disconnect switches and VR
3-23
Page 41

General Specifications
Item
E510
Control Mode
V/F Control, Vector Control
Frequency
Output Frequency
0.01~650.00Hz
Starting Torque
150%/1Hz(Vector)
Speed Control Range
1:50
Setting resolution
Digital input: 0.01Hz
Analog input:0.06Hz/60Hz
Setting
Keypad: Set directly with▲▼ keys or the VR on the
keypad
External Input Terminals:
AI1(0/2~10V), AI2(0/4~20mA)input
Multifunction input up/down function(Group3)
Setting frequency by communication method.
Frequency limit
Lower and upper frequency limits,
3 skip frequency settings.
Run
Operation set
Keypad run, stop button
External terminals:
Multi- operation-mode2 / 3 wire selection
Jog operation
Run signal by communication method.
Main Control
Features
V / F curve setting
18 fixed curves and one customized curve
Carrier frequency
1~16KHz
Acceleration and
deceleration control
2 Acceleration / deceleration time parameters.
4 off S curve parameters.
Multifunction input
29 functions (refer to description on group3)
Multifunction output
21 functions (refer to description on group3)
Multifunction analog
output
5 functions (refer to description on group4)
Main features
Overload Detection,16 preset speeds, Auto-run, Acc/Dec
Switch (2 Stages),Main/Alt run Command select,
Main/Alt Frequency Command selection, PID control,
torque boost, V/F start Frequency, Fault reset, Firemode.
Display
LED
Display: parameter / parameter value / frequency / line
speed / DC voltage / output voltage / output current / PID
feedback / input and output terminal status / Heat sink
temperature / Program Version / Fault Log.
LED Status Indicator
Run / Stop / Forward / Reverse ,and etc.
Protective
Functions
Overload Protection
The relays to protect the motor and the inverter.
(150%/1min)
Over voltage
·220V: >410V ,380V: >820V
Under Voltage
·220V: <190V , 380V: <380V
Momentary Power Loss
Restart
Inverter auto-restart after a momentary power loss.
Stall Prevention
Stall prevention for Acceleration/ Deceleration/
Operation.
3-24
Page 42

Short-circuit output
terminal
Electronic Circuit Protection
Grounding Fault
Electronic Circuit Protection
Other protection
features
Protection for overheating of heat sink, The carrier
frequency decreases based on the temperature, Fault
output, Reverse prohibit, Prohibit for direct start after
power up and error recovery ,parameter lock up
All frames include brake transistor
Communication control
Standard built-in RS485 communication (Modbus), One
to one or One to many control.
Environment
Operating temperature
-10~50°C (Note1)
Storage temperature
-20~60°C
Humidity
95% RH or less (no condensation)
(Compliance with IEC 60068 - 2-78)
Shock
20Hz or less 1G(9.8m/s²)20~50Hz 0.6G(5.88m/s²)
(Compliance with IEC 60068 - 2-6)
Enclosure
IP66/NEMA4X
Note1:
IP66/NEMA 4X Type:
-10~50°C
3-25
Page 43

3.17 Inverter derating based on Carrier Frequency
100%
70%
85%
90%
50%
60%
2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16
Current Rating
Carrier Frequency(kHz)
Note:
De-rate curve for ambient temperature of 122°F (50°C).
De-rate curve for ambient temperature of 104°F (40°C).
Frame 1 / 2 / 3 / 4
Single phase: 230V: 0.5~3HP; Single /Three phase: 230V: 0.5~3HP;
Three phase: 230V: 2~20HP, 460V: 1~25HP)
3-26
Page 44

3.18 Inverter Dimensions
IP66 / NEMA 4X Dimensions
Frame 1 (IP66 / NEMA 4X)
Single phase: 230V 0.5~1HP
Single / Three phase: 230V 0.5~1HP
Three Phase: 230V 2HP; 460V 1~2HP
3-27
Page 45

Unit: mm(inch)
Model
Dimensions
N.W
(kg)
W
W1 H H1
H2 D D1
D2
D3
Q1
Q2
Q3
E510-2P5-HN4R
150.8
(5.94)
133.3
(5.25)
248.7
(9.79)
230.2
(9.06)
214.2
(8.43)
183
(7.20)
200
(7.87)
49.5
(1.95)
5.4
(0.21)
5.4
(0.21)
10.6
(0.42)
2.9
E510-2P5-H1FN4S
200
(7.87)
200
(7.87)
E510-201-HN4R
200
(7.87)
E510-201-H1FN4S
200
(7.87)
200
(7.87)
E510-401-H3N4
E510-401-H3FN4S
200
(7.87)
200
(7.87)
E510-402-H3N4
E510-402-H3FN4S
200
200
3-28
Page 46

Frame 2 (IP66 / NEMA 4X)
Single phase: 230V 2~3HP
Single / Three phase: 230V 2~3HP
Three Phase: 230V 5HP; 460V 3~5HP
3-29
Page 47

Unit: mm(inch)
Model
Dimensions
N.W
(kg)
W
W1 H H1
H2 D D1
D2
D3
Q1
Q2
E510-202-HN4R
198
(7.80)
115
(4.53)
335
(13.19)
315
(12.40)
337.9
(13.30)
218.4
(8.60)
235.2
(9.26)
79.8
(3.14)
7
(0.28)
7
(0.28)
5.98
E510-202-H1FN4S
235.2
(9.26)
235.2
(9.26)
E510-203-HN4R
235.2
(9.26)
E510-203-H1FN4S
235.2
(9.26)
235.2
(9.26)
E510-205-H3N4
E510-403-H3N4
E510-403-H3FN4S
235.2
(9.26)
235.2
(9.26)
E510-405-H3N4
E510-405-H3FN4S
235.2
(9.26)
235.2
(9.26)
3-30
Page 48

Frame 3 (IP66 / NEMA 4X)
Three Phase: 230V 7.5~20HP; 460V 7.5~25HP
3-31
Page 49

Unit: mm(inch)
Model
Dimensions
N.W
(kg)
W
W1 H H1
H2 D D1
D2
D3
Q1
Q2
E510-208-H3N4
222.8
(8.77)
140
(5.51)
460
(18.11)
440
(17.32)
466.3
(18.36)
246.6
(9.71)
96
(3.78)
7
(0.28)
7
(0.28)
12.68
E510-210-H3N4
E510-215-H3N4
E510-220-H3N4
E510-408-H3N4
E510-408-H3FN4S
266.5
(10.49)
263.5
(10.37)
E510-410-H3N4
E510-410-H3FN4S
266.5
(10.49)
263.5
(10.37)
E510-415-H3N4
E510-415-H3FN4S
266.5
(10.49)
263.5
(10.37)
E510-420-H3N4
E510-425-H3N4
3-32
Page 50

4. Keypad and Programming Functions
LED Display
Run Key
8 button
Membrane
Keypad
Stop Key
Forward Direction
Status Indicator
Reverse Direction
Status Indicator
Frequency
Potentiometer
DISPLAY
Description
5 Digit LED Display
Monitor inverter signals, view / edit parameters, fault / alarm display.
LED INDICATORS
Hz/RPM
LED ON when frequency or line speed is displayed.
FWD
LED ON when inverter is running in forward direction, flashing when stopping.
REV
On when inverter is running in reverse direction, flashing when stopping.
FUN
LED ON when parameters are displayed.
KEYS (8)
Description
RUN
RUN Inverter in Local Mode
STOP
STOP Inverter
▲
Parameter navigation Up, Increase parameter or reference value
▼
Parameter navigation down, decrease parameter or reference value
FWD/REV
FWD: Forward Run / REV: Reverse Run
DSP/FUN
DSP: Switch between available display modes
FUN: View/Edit parameter value
READ/ENTER
Used to display parameter settings and save parameter changed settings
< / RESET
Use to reset alarms or resettable faults
4.1 LED Keypad
4.1.1 Keypad Display and Keys
4-1
Page 51

4.1.2 Display Description
Actual
LED Display
Actual
LED Display
Actual
LED Display
Actual
LED Display
0 A L
Y
1 B n
-
2 C o
°
3 D P
_
4 E q
.
5 F r
6 G S
7 H t
8 I u
9 J V
Display output frequency
Frequency Reference
Set Frequency Reference
LED lights on
LED flashes
Flashing digit
◄
◄
◄
◄
◄
◄
◄
◄
At power-up the display will show the frequency reference setting, all LEDs are flashing. Press the ▲UP or
▼DOWN key to enter the frequency reference edit mode, use the ◄/ENT key to select which digit to edit
(flashing). Use the ▲UP or ▼DOWN key to modify the value. During run operation the display will show the
output frequency.
4-2
Page 52

LED display examples
Seven Segment display
Description
1. Displays the frequency reference at power-up
2. Display the actual output frequency in operation status.
Display parameter code
Display the setting value of parameter
Display input voltage
Display inverter current.
Display DC Bus Voltage
Display temperature
Display PID feedback value. The displayed digit is set by 12-01.
Error display, refer to Chapter 5 Troubleshooting and maintenance
Analog Current / Voltage AI1 / AI2. Range (0~1000)
4-3
Page 53

4.1.3 LED Status description
State
Description
Hz/RPM LED
Off
Display doesn’t show frequency or line speed
Illuminated
Display shows frequency or line speed
State
Description
FWD LED
Off
Inverter in reverse direction
Illuminated
Inverter is running in forward direction
Flashing
Forward direction active, no run command
State
Description
REV LED
Off
Inverter in forward direction
Illuminated
Inverter is running in reverse direction
Flashing
Reverse direction active, no run command
State
Description
FUN LED
Off
Display doesn’t show parameter
Illuminated
Display shows parameter
Flashing
Firemode Enabled
Hz/ RPM LED
Forward LED
Reverse LED
FUN LED
4-4
Page 54

4.1.4 Power-Up Monitor
DSP/
FUN
DSP/
FUN
After 2 sec.
Display at Power-up Frequency Reference Parameter Selection
12-00
Display selection
Range
Highest bit -> 0 0 0 0 0 <- Lowest bit
The setting range for each bit is 0 ~ 8 from the highest bit to the lowest bit.
0: No display 4: Temperature 8: Count value
1: Output current 5: PID feedback
2: Output voltage 6: AI1 value
3: DC voltage 7: AI2 value
DSP/
FUN
DSP/
FUN
After 2 sec.
Parameter Selection
Output Current
Frequency Reference
Display Voltage Class
at Power-up
DSP/
FUN
Power Up:
Change Monitor at Power-Up
Example: 12-00 = 10000
4-5
Page 55

Example: 12-00 = 12345
DSP/
FUN
DSP/
FUN
DSP/
FUN
DSP/
FUN
DSP/
FUN
DSP/
FUN
DSP/
FUN
After 2 sec.
Display Voltage Class
at Power-up
Output Current <1>
Parameter Selection
Output Voltage <2>
DC Voltage <3>
Heatsink Temperature <4>
PID Feedback <5>
Frequency Reference
Frequency
Short Press:
DSP/FUN
Once
Short Press:
</ENT Once
Short Press:
</RESET Twice
Short Press:
▲ Once
Short Press:
READ/ENTER
Once
Short Press:
▲ Once
Short Press:
READ/ENTER
Once
4.1.5 Modifying Parameters / Set Frequency Reference
4-6
Page 56

4.1.6 Operation Control
REV command
FWD command
RUN command
REV command
Stop command
FWD command
FWD
Indicator
REV
Indicator
REVREV
REV
FWDFWD FWD FWD FWD FWD FWD
REV
REV REV
REV
Power on
Output Frequency
Running StoppingStopped
FWD
REV
Stopped
4-7
Page 57

4.2 Parameters
Parameter group
Name
Group 00
Basic Parameters
Group 01
V/F Control Parameters
Group 02
Motor Parameters
Group 03
External Digital Input and Output Parameters
Group 04
External Analog Input and Output Parameters
Group 05
Preset-Speed Parameters
Group 06
Automatic Program Operation Parameters
Group 07
Start /Stop Parameters
Group 08
Protection Parameters
Group 09
Communication Parameters
Group 10
PID Parameters
Group 11
Performance Control Parameters
Group 12
Monitoring Parameters
Group 13
Maintenance Parameters
Group 14
PLC Parameters
Group 15
PLC Monitoring Parameters
Parameter Notes
*1
Parameter can be adjusted during running mode
*2
Cannot be modified in communication mode
*3
Does not change with factory reset
*4
Read only
*5
Available for above V1.1
*6
Available for above V1.3
*7
Available for above V1.7
4-8
Page 58

Group 00: Basic parameters
No.
Description
Range
Factory
Setting
Unit
Note
00-00
Control Mode Selection
0:V/F Mode
0 -
1:Vector Mode
00-01
Reserved
00-02
Main Run Command
Source Selection
0:Keypad
0 -
1:External Run/Stop Control
2:Communication
3:PLC
00-03
Alternative Run Command
Source Selection
0:Keypad
0 -
1:External Run/Stop Control
2:Communication
00-04
Operation Modes for
External Terminals
0:Forward/Stop-Reverse/Stop
0 -
1:Run/Stop- Reverse/Forward
2: 3 Wire Control Mode-Run/Stop
00-05
Main Frequency Command
Source Selection
0:UP/DOWM of Keypad
0
-
1:Potentiometer on Keypad
2:External AI1 Analog Signal Input
3:External AI2 Analog Signal Input
4:External Up/Down Frequency Control
5:Communication Setting Frequency
6:PID Ouput Frequency
7:Pulse Input
*6
00-06
Alternative Frequency
Command Source Selection
0:UP/DOWM of Keypad
4
-
1:Potentiometer on Keypad
2:External AI1 Analog Signal Input
3:External AI2 Analog Signal Input
4:External Up/Down Frequency Control
5:Communication Setting Frequency
6:PID Ouput Frequency
7:Pulse Input
*6
00-07
Main and Alternative
Frequency Command Modes
0:Main or Alternative Frequency
1:Main Frequency+ Alternative
Frequency
0 -
00-08
Communication
Frequency Command
0.00~650.00
60.00
Hz
*4
00-09
Frequency Command
Save on Power Down
0: Disable
0 -
1: Enable
00-10
Initial Frequency
Selection (keypad mode)
0:by Current Frequency Command
0 -
1:by 0 Frequency Command
2:by 00-11
00-11
Initial Frequency Setpoint
0.00~650.00
50.00/60.00
Hz
00-12
Frequency Upper Limit
0.01~650.00
50.00/60.00
Hz
00-13
Frequency Lower Limit
0.00~649.99
0.00
Hz
00-14
Acceleration Time 1
0.1~3600.0
10.0
Sec
*1
00-15
Deceleration Time 1
0.1~3600.0
10.0
Sec
*1
00-16
Acceleration Time 2
0.1~3600.0
10.0
Sec
*1
00-17
Deceleration Time 2
0.1~3600.0
10.0
Sec
*1
00-18
Jog Frequency
0.00~650.00
2.00
Hz
*1*7
00-19
Jog Acceleration Time
0.1~3600.0
0.5
Sec
*1*7
00-20
Jog Deceleration Time
0.1~3600.0
0.5
Sec
*1*7
4-9
Page 59

Group 01: V/F Control Parameters
No.
Description
Range
Factory
Setting
Unit
Note
01-00
Volts/Hz Patterns
0~18
0/9 -
01-01
V/F Max voltage
200V:170.0~264.0
400V:323.0~528.0
220.0/440.0
Vac
01-02
Max Frequency
0.20 ~ 650.00
50.00/60.00
Hz
01-03
Max Frequency Voltage Ratio
0.0 ~ 100.0
100.0 %
01-04
Mid Frequency 2
0.10 ~ 650.00
25.00/30.00
Hz
01-05
Mid Frequency Voltage Ratio 2
0.0 ~ 100.0
50.0 %
01-06
Mid Frequency 1
0.10 ~ 650.00
10.00/12.00
Hz
01-07
Mid Frequency Voltage Ratio 1
0.0 ~ 100.0
20.0 %
01-08
Min Frequency
0.10 ~ 650.00
0.50/0.60
Hz
01-09
Min Frequency Voltage Ratio
0.0 ~ 100.0
1.0 %
01-10
Volts/Hz Curve Modification
(Torque Boost)
0 ~ 10.0
0.0 % *1
01-11
V/F start Frequency
0.00~10.00
0.00
Hz
01-12
Slip compensation gain
0.05~10.00
0.10 S
01-13
V/F Mode Select
0 : Mode 0 1 : Mode 1
by models
-
Group 02: IM Motor parameters
No.
Description
Range
Factory
Setting
Unit
Note
02-00
Motor No Load Current
0~[(Patameter 02-01)-0.1]
-
Amps(AC)
*3
02-01
Motor Rated Current (OL1)
0.2~100 - A
*3
02-02
Motor rated Slip Compensation
0.0 ~ 200.0
0.0 % *1
02-03
Motor rated speed
0~39000
-
Rpm
*3
02-04
Motor rated voltage
200V: 170.0~264.0
400V: 323.0~528.0
220.0/440.0
V
02-05
Motor rated power
0.1~37.0
-
KW
02-06
Motor rated frequency
0~650.0
50.0/60.0
Hz
02-07
Motor pole number
2 ~16
4 -
02-08
~
02-13
Reserved
02-14
Auto Tune
0: Disable
0
1: Start Auto tune function.
02-15
Stator resistance gain
----
*3*4
02-16
Rotor resistance gain
----
*3*4
4-10
Page 60

Group 03: External Digital Inputs and Relay Output Functions
No.
Description
Range
Factory
Setting
Unit
Note
03-00
Multifunction Input Term. S1
0:Forward/Stop Command
0 -
03-01
Multifunction Input Term. S2
1:Reverse/Stop Command
1 -
03-02
Multifunction Input Term. S3
2:Speed Selection 1
2 -
03-03
Multifunction Input Term. S4
3:Speed Selection 2
3 -
03-04
Multifunction Input Term. S5
4:Speed Selection 3
4 -
03-05
Multifunction Input Term. S6
5:Speed Selection 4
17
6:Jog Forward Command
7:Jog Reverse Command
8:Up Command
9:Down Command
10:Acc/Dec 2
11:Acc/Dec Disabled
12:Main/Alternative run source
select
13:Main/ Alternative Frequency
Command select
14:Rapid Stop ( Decel to stop )
15:Base Block
16:Disabl PID Function
17:Fault Reset
18:Auto Run Mode Enable
19:Speed Search
20:Energy Saving (only V/F)
21:Reset PID integral value to Zero
22:Counter Input
23:Counter reset
24:PLC Input
25:Pulse Input-Width Measure (S3)
*6
26:Pulse Input-Frequency Measure (S3)
*6
27:Enable KEB Function
28:Fire mode function
*5
03-06
Up/Down frequency step
0.00~5.00
0.00
Hz
03-07
Up/Down Keep Frequency Status after
Stop Command
0:When Up/Down is used, the preset
frequency is held as the inverter stops,
and the UP/Down function is disabled
0
-
1:When Up/Down is used, the preset
frequency is reset to 0 Hz as the inverter
stops.
2:When Up/Down is used, the preset
frequency is held as the inverter stops,
and the UP/Down is available.
03-08
S1~S6 scan confirmation
1~200 Number of Scan cycles
10
2ms
03-09
S1~ S5 switch type select
xxxx0:S1 NO xxxx1:S1 NC
00000 -
xxx0x:S2 NO xxx1x:S2 NC
xx0xx:S3 NO xx1xx:S3 NC
x0xxx:S4 NO x1xxx:S4 NC
0xxxx:S5 NO 1xxxx:S5 NC
03-10
S6 switch type select
xxxx0:S6 NO xxxx1:S6 NC
00000 -
03-11
Output Relay RY1
0:Run
0
-
4-11
Page 61

Group 03: External Digital Inputs and Relay Output Functions
No.
Description
Range
Factory
Setting
Unit
Note
( Terminals R1A,R1B, R1C )
03-12
Output Relay RY2.
( Terminals R2A, R2B )
1:Fault
1
2:Setting Frequency Reached
3:Frequency Reached. Set by (3-13±3-14)
4:Output Frequency Detection1(> 3-13)
5:Output Frequency Detection2(< 3-13)
6:Auto Restart
7:Momentary AC Power Loss
8:Rapid Stop
9:Base Block
10:Motor Overload Protection(OL1)
11:Drive Overload Protection(OL2)
12:Over-torque Threshold Level
(OL3)
13:Preset Output Current Reached
(03-15~16)
14:Brake Control (03-17~18)
15:PID Feedback Signal Loss
16: Single pre-set count (3-22)
17: Dual pre-set count (3-22~23)
18:PLC Status Indicator (00-02)
19:PLC control
20:Zero Speed
*6
03-13
Frequency Reached Level
0.00~650.00
0.00
Hz
*1
03-14
Frequency Reached Detection Range
(±)
0.00~30.00
2.00
Hz
*1
03-15
Preset output current reached
0.1~15.0
0.1 A
03-16
Preset output Current detection delay
Time
0.1~10.0
0.1
Sec
03-17
Brake Release
level
0.00~20.00
0.00
Hz
03-18
Brake Engage
Level
0.00~20.00
0.00
Hz
03-19
Relay Output function type
0:A (Normally open)
1:B (Normally close)
0 -
03-20
Internal / external multi-function input
terminal selection
0~63 0 -
03-21
Action to set the internal multi-function
input terminals
0~63
0 -
03-22
Pre-set count 1
0~9999
0 -
03-23
Pre-set count 2
0~9999
0 -
03-24
Output under current detection
0:Disable
0 -
1:Enable
03-25
Output under current detection level
5%~100%
20% %
03-26
Output under current detection delay
time
0.0~50.0s
20.0
Sec
03-27
Pulse Frequency
0.01~0.20
0.1
kHz
*7
03-28
Pulse Frequency Gain
0.01~9.99
1.00 *6
※ “NO” indicates normally open, “NC” indicates normally closed.
4-12
Page 62

Group 04: External Analog Input and Output Parameters
No.
Description
Range
Factory
Setting
Unit
Note
04-00
Analog Input Signal Type
Select (AI1/AI2)
AI1 AI2
1 - *7
(0): 0~10V (0~20mA) 0~10V (0~20mA)
(1): 0~10V (0~20mA) 2~10V (4~20mA)
(2): 2~10V (4~20mA) 0~10V (0~20mA)
(3): 2~10V (4~20mA) 2~10V (4~20mA)
04-01
AI1 Signal Verification Scan Rate
1~200
50
2ms
04-02
AI1 Gain
0 ~ 1000
100 % *1
04-03
AI1 Bias
0 ~ 100
0 % *1
04-04
AI1 Bias Selection
0: Positive 1: Negative
0 - *1
04-05
AI1 Slope
0: Positive 1: Negative
0 - *1
04-06
AI2 Signal Verification Scan
Rate
1~200
50
2ms
04-07
AI2 Gain
0 ~ 1000
100 % *1
04-08
AI2 Bias
0 ~ 100
0 % *1
04-09
AI2 Bias Selection
0: Positive 1: Negative
0 - *1
04-10
AI2 Slope
0: Positive 1: Negative
0 - *1
04-11
Analog Output (AO) Mode
0: Output Frequency
1: Frequency Command
2: Output Voltage
3: DC Bus Voltage
4: Motor Current (100% rated current)
0 - *1
04-12
Analog Output (AO) Gain
0 ~ 1000
100 % *1
04-13
Analog Output (AO) Bias
0 ~ 100
0 % *1
04-14
AO Bias Selection
0: Positive 1: Negative
0 - *1
04-15
AO Slope
0: Positive 1: Negative
0 - *1
04-16
F-Gain Function
0: Invalid 1: Effective
0 - *1
4-13
Page 63

Group 05: Preset Speed Parameters
No.
Description
Range
Factory
Setting
Unit
Note
05-00
Preset Speed Control
Mode Selection
0: Common Accel/Decel
Accel/Decel 1 or 2 apply to all speeds
0 -
1: Individual Accel/Decel for each preset speed
0-15 apply to the selected preset speeds
(Acc0/Dec0~Acc15/Dec15)
05-01
Preset Speed 0
(Keypad Freq)
0.00 ~ 650.00
5.00
Hz
05-02
Preset Speed1 (Hz)
5.00
Hz
*1
05-03
Preset Speed2 (Hz)
10.00
Hz
*1
05-04
Preset Speed3 (Hz)
20.00
Hz
*1
05-05
Preset Speed4 (Hz)
30.00
Hz
*1
05-06
Preset Speed5 (Hz)
40.00
Hz
*1
05-07
Preset Speed6 (Hz)
50.00
Hz
*1
05-08
Preset Speed7 (Hz)
50.00
Hz
*1
05-09
Preset Speed8 (Hz)
0.00
Hz
*1
05-10
Preset Speed9 (Hz)
0.00
Hz
*1
05-11
Preset Speed10 (Hz)
0.00
Hz
*1
05-12
Preset Speed11 (Hz)
0.00
Hz
*1
05-13
Preset Speed12 (Hz)
0.00
Hz
*1
05-14
Preset Speed13 (Hz)
0.00
Hz
*1
05-15
Preset Speed14 (Hz)
0.00
Hz
*1
05-16
Preset Speed15 (Hz)
0.00
Hz
*1
05-17
Preset Speed0-Acctime
0.1 ~ 3600.0
10.0
Sec
*1
05-18
Preset Speed0-Dectime
10.0
Sec
*1
05-19
Preset Speed1-Acctime
10.0
Sec
*1
05-20
Preset Speed1-Dectime
10.0
Sec
*1
05-21
Preset Speed2-Acctime
10.0
Sec
*1
05-22
Preset Speed2-Dectime
10.0
Sec
*1
05-23
Preset Speed3-Acctime
10.0
Sec
*1
05-24
Preset Speed3-Dectime
10.0
Sec
*1
05-25
Preset Speed4-Acctime
10.0
Sec
*1
05-26
Preset Speed4-Dectime
10.0
Sec
*1
05-27
Preset Speed5-Acctime
10.0
Sec
*1
05-28
Preset Speed5-Dectime
10.0
Sec
*1
05-29
Preset Speed6-Acctime
10.0
Sec
*1
05-30
Preset Speed6-Dectime
10.0
Sec
*1
05-31
Preset Speed7-Acctime
10.0
Sec
*1
05-32
Preset Speed7-Dectime
10.0
Sec
*1
05-33
Preset Speed8-Acctime
10.0
Sec
*1
05-34
Preset Speed8-Dectime
10.0
Sec
*1
05-35
Preset Speed9-Acctime
10.0
Sec
*1
05-36
Preset Speed9-Dectime
10.0
Sec
*1
05-37
Preset Speed10-Acctime
10.0
Sec
*1
05-38
Preset Speed10-Dectime
10.0
Sec
*1
05-39
Preset Speed11-Acctime
10.0
Sec
*1
4-14
Page 64

Group 05: Preset Speed Parameters
No.
Description
Range
Factory
Setting
Unit
Note
05-40
Preset Speed11-Dectime
10.0
Sec
*1
05-41
Preset Speed12-Acctime
10.0
Sec
*1
05-42
Preset Speed12-Dectime
10.0
Sec
*1
05-43
Preset Speed13-Acctime
10.0
Sec
*1
05-44
Preset Speed13-Dectime
10.0
Sec
*1
05-45
Preset Speed14-Acctime
10.0
Sec
*1
05-46
Preset Speed14-Dectime
10.0
Sec
*1
05-47
Preset Speed15-Acctime
10.0
Sec
*1
05-48
Preset Speed15-Dectime
10.0
Sec
*1
Group 06: Automatic Program Operation Parameters
No.
Description
Range
Factory
Setting
Unit
Note
06-00
Auto Run Mode Selection
(Sequencer)
0: Disabled.
1: Single cycle.
(Continues to run from the Unfinished step if restarted).
2: Periodic cycle.
(Continues to run from the unfinished step if restarted).
3: Single cycle, then holds the speed Of final
step to run. (Continues to run from the
unfinished step if restarted).
4: Single cycle.
(Starts a new cycle if restarted).
5: Periodic cycle.
(Starts a new cycle if restarted).
6: Single cycle, then hold the speed of final step to run.
(Starts a new cycle if restarted).
0 -
06-01
Auto _ Run Mode
Frequency Command 1
0.00~650.00
0.00
Hz
*1
06-02
Auto _ Run Mode
Frequency Command 2
0.00
Hz
*1
06-03
Auto _ Run Mode
Frequency Command 3
0.00
Hz
*1
06-04
Auto _ Run Mode
Frequency Command 4
0.00
Hz
*1
06-05
Auto _ Run Mode
Frequency Command 5
0.00
Hz
*1
06-06
Auto _ Run Mode
Frequency Command 6
0.00
Hz
*1
06-07
Auto _ Run Mode
Frequency Command 7
0.00
Hz
*1
06-08
Auto _ Run Mode
Frequency Command 8
0.00
Hz
*1
4-15
Page 65

06-09
Auto _ Run Mode
Frequency Command 9
0 ~ 3600.0
0.00
Hz
*1
06-10
Auto _ Run Mode
Frequency Command10
0.00
Hz
*1
06-11
Auto _ Run Mode
Frequency Command 11
0.00
Hz
*1
06-12
Auto _ Run Mode
Frequency Command 12
0.00
Hz
*1
06-13
Auto _ Run Mode
Frequency Command 13
0.00
Hz
*1
06-14
Auto _ Run Mode
Frequency Command 14
0.00
Hz
*1
06-15
Auto _ Run Mode
Frequency Command 15
0.00
Hz
*1
06-16
Auto_ Run Mode Running
Time Setting 0
0.0
Sec
06-17
Auto_ Run Mode Running
Time Setting 1
0.0
Sec
06-18
Auto_ Run Mode Running
Time Setting 2
0.0
Sec
06-19
Auto_ Run Mode Running
Time Setting 3
0.0
Sec
06-20
Auto_ Run Mode Running
Time Setting 4
0.0
Sec
06-21
Auto_ Run Mode Running
Time Setting 5
0.0
Sec
06-22
Auto_ Run Mode Running
Time Setting 6
0.0
Sec
06-23
Auto_ Run Mode Running
Time Setting 7
0.0
Sec
06-24
Auto_ Run Mode Running
Time Setting 8
0.0
Sec
06-25
Auto_ Run Mode Running
Time Setting 9
0.0
Sec
06-26
Auto_ Run Mode Running
Time Setting 10
0.0
Sec
06-27
Auto_ Run Mode Running
Time Setting 11
0.0
Sec
06-28
Auto_ Run Mode Running
Time Setting 12
0.0
Sec
06-29
Auto_ Run Mode Running
Time Setting 13
0.0
Sec
06-30
Auto_ Run Mode Running
Time Setting 14
0.0
Sec
06-31
Auto_ Run Mode Running
Time Setting 15
0.0
Sec
4-16
Page 66

06-32
Auto_ Run Mode Running
Direction 0
0: Stop
1: Forward
2: Reverse
0 -
06-33
Auto_ Run Mode Running
Direction 1
0 -
06-34
Auto_ Run Mode Running
Direction 2
0 -
06-35
Auto_ Run Mode Running
Direction 3
0 -
06-36
Auto_ Run Mode Running
Direction 4
0 -
06-37
Auto_ Run Mode Running
Direction 5
0 -
06-38
Auto_ Run Mode Running
Direction 6
0 -
06-39
Auto_ Run Mode Running
Direction 7
0 -
06-40
Auto_ Run Mode Running
Direction 8
0 -
06-41
Auto_ Run Mode Running
Direction 9
0 -
06-42
Auto_ Run Mode Running
Direction10
0 -
06-43
Auto_ Run Mode Running
Direction 11
0 -
06-44
Auto_ Run Mode Running
Direction12
0 -
06-45
Auto_ Run Mode Running
Direction13
0 -
06-46
Auto_ Run Mode Running
Direction 14
0 -
06-47
Auto_ Run Mode Running
Direction 15
0 -
※ Frequency of the step 0 is set by parameter 05-01, keypad frequency.
4-17
Page 67

Group 07: Start/Stop Parameters
No.
Description
Range
Factory
Setting
Unit
Note
07-00
Momentary Power Loss and
Restart
0: Momentary Power Loss and Restart Disable
1: Momentary Power Loss and Restart Enable
0 -
07-01
Auto Restart Delay Time
0.0~800.0
0.0
Sec
07-02
Number of Auto Restart
Attempts
0~10 0 -
07-03
Reset Mode Setting
0: Enable Reset Only when Run Command is Off
1: Enable Reset when Run Command is On or Off
0 -
07-04
Direct Running on Power
Up
0: Enable Direct run on power up
1: Disable Direct run on power up
1 -
07-05
Delay-ON Timer
1.0~300.0
1.0
Sec
07-06
DC Injection Brake Start
Frequency
0.10 ~ 10.00
1.5
Hz
07-07
DC Injection Brake Level
(Current Mode)
0.0 ~ 150.0
50.0 %
07-08
DC Injection Brake Time
0.0 ~ 25.5
0.5
Sec
07-09
Stopping Method
0: Deceleration to stop
1: Coast to stop
0 -
07-10
Starting Methods
0: Normal Start 1: Speed Search
0 -
07-11
Starting method for auto
restart after fault
0: Speed Search 1: Normal start
0 -
07-12
Power Loss Ride Through
Time
0.0 ~ 2.0
0.5
Sec
07-13
Main Circuit Low Voltage
Detection Level
150.0~210.0 300.0~420.0
190.0/38
0.0
Vac
07-14
Kinetic Energy Back-up
Deceleration Time
0.0~25.0: KEB Deceleration Time
0.0
Sec
07-15
DC Injection Brake Mode
0 : Current Mode 1 : Voltage Mode
1 - *6
07-16
DC Injection Brake Level
(Voltage Mode)
0.0~10.0
4.0 % *6
4-18
Page 68

Group 08: Protection Parameters
No.
Description
Range
Factory
Setting
Unit
Note
08-00
Trip Prevention Selection
xxxx0: Enable Trip Prevention During
Acceleration
xxxx1: Disable Trip Prevention During
Acceleration
xxx0x: Enable Trip Prevention During
Deceleration
xxx1x: Disable Trip Prevention During
Deceleration
xx0xx: Enable Trip Prevention in Run
Mode
xx1xx: Disable Trip Prevention in Run
Mode
x0xxx: Enable Over Voltage Prevention
in Run Mode
x1xxx: Disable Over Voltage Prevention
in Run Mode
01000
-
*5
08-01
Trip Prevention Level
During Acceleration (%)
50 ~ 200
200
%1
08-02
Trip Prevention Level
During Deceleration (%)
50 ~ 200
200
08-03
Trip Prevention Level in
Run Mode (%)
50 ~ 200
200
08-04
Over Voltage Prevention
Level in Run Mode
350.0~390.0/700.0~780.0
380.0/7
60.0
VDC
08-05
Electronic Motor Overload
Protection Operation Mode
0: Disable
1: Enable
1 - *7
08-06
Operation After Overload
Protection is Activated
0: Coast-to-Stop After Overload Protection is Activated
1: Drive Will Not Trip when Overload Protection is
Activated (OL1)
0 -
08-07
Over Heat Protection
( cooling fan control)
0: Auto (Depends on temp.)
1: Operate while in RUN Mode
2: Always Run
3: Disabled
1 -
08-08
AVR Function
(Auto Voltage Regulation)
0: AVR Function is enabled
4 - *5
1: AVR Function is disabled
2: AVR Function is disabled for Stop
3: AVR Function is disabled for Deceleration.
4: AVR Function is disabled for Stop and Deceleration.
5: When VDC>360V, AVR Function is disabled for Stop
and Deceleration.
08-09
Input Phase Loss
Protection
0: Disable
1: Enable
0 -
08-10
Output Phase Losts
Protection
0: Disable
0 -
1: Enable
08-11
Motor Type Selection
0: Overload protection (Standard Motor)
0 -
1: Overload protection (Inverter Duty Motor)
08-12
Motor Overload Protection
Curve
0: Motor Overload Protection for General loads
(OL=103 %) (150% for 1 Minutes)
0 -
1: Motor Over load Protection for HVAC (Fan & Pump)
(OL=113%) (123% for 1 Minutes).
08-13
Over Torque Detection
Control
0: Over Torque Detection Disabled
0 -
1: Detected After the Setting Frequency
2: Detected When Running
1
Base on the percentage of inverter rated current.
4-19
Page 69

Group 08: Protection Parameters
No.
Description
Range
Factory
Setting
Unit
Note
08-14
Over torque protection
action
0: Stop Output After Over Torque Detection (Free Run to
Stop)
0 -
1: Continue Running After Over Torque Detection (Display
only OL3)
08-15
Over Torque Detection
Level
30~300
160 -
08-16
Over Torque Detection
Time
0.0~25.0
0.1 -
08-17
Fire Mode
0: Disable
0 - *5
1: Enable
08-18
Ground Fault Detection
0: Disable
0 *7
1: Enable
Notes: Fire mode function
Group 09: Communication Parameters
No.
Description
Range
Factory
Setting
Unit
Note
09-00
Assigned Communication
Station Number
1 ~ 32 1 -
*2*3
09-01
RTU/ASCII Code Selection
0:RTU Code
1:ASCII Code
0 - *2*3
09-02
Baud Rate Setting (bps)
0:4800
1:9600
2:19200
3:38400
2
bps
*2*3
09-03
Stop Bit Selection
0:1 Stop Bit
1:2 Stop Bits
0 - *2*3
09-04
Parity Selection
0:Without Parity
1:With Even Parity
2:With Odd Parity
0 - *2*3
09-05
Data Format Selection
0: 8-Bits Data
1: 7-Bits Data
0 - *2*3
09-06
Communication Time-Out
Detection Time
0.0 ~ 25.5
0.0
Sec
09-07
Communication Time Out
Operation Selection
0:Deceleration to Stop
(00-15: Deceleration Time 1)
1:Coast to Stop
2:Deceleration to Stop
(00-17: Deceleration Time 2)
3:Continue Operating
0 -
09-08
Comm. Fault Tolerance Count.
1 ~ 20
3
09-09
Wait Time of Inverter Transmission
5 ~ 65
5
ms
1. Before the firmware rev. 1.1, the fire mode is enabled when parameter 08-17 = 1
2. After the firmware 1.1, the firemode is enabled when any of parameters 03-00~03-05 is set to a value of 28
3. The keypad display will indicate FIrE
4. In fire mode the inverter will run at full speed
5. Parameter 08-18 is only displayed in the frame 3, 4 models
4-20
Page 70

Group 10: PID Parameters
No.
Description
Range
Factory
Setting
Unit
Note
10-00
PID Target Value Selection
(When 00-05\00-06=6 This Function is
Enabled)
0: Potentiometer on Keypad
1: Analog Signal Input. (AI1)
2: Analog Signal Input. (AI2)
3: Frequency Set by Communication
4: Keypad Frequency Parameter
10-02
1 - *1
10-01
PID Feedback Value Selection
0: Potentiometer on Keypad
1: Analog Signal Input. (AI1)
2: Analog Signal Input. (AI2)
3: Frequency Set by Communication
2 - *1
10-02
PID Target(Keypad Input)
0.0~100.0
50.0 % *1
10-03
PID Mode Selection
0: Disable
1: Deviation D Control.
FWD Characteristic.
2: Feedback D Control
FWD Characteristic.
3: Deviation D Control
Reverse Characteristic.
4: Feedback D Control
Reverse Characteristic.
0 -
10-04
Feedback Gain Coefficient
0.00 ~ 10.00
1.00 *1
10-05
Proportional Gain
0.0 ~ 10.0
1.0 *1
10-06
Integral Time
0.0 ~ 100.0
10.0
Sec
*1
10-07
Derivative Time
0.00 ~ 10.00
0.00
Sec
*1
10-08
PID Offset
0: Positive
1: Negative
0 - *1
10-09
PID Offset Adjust
0 ~ 109
0 % *1
10-10
PID Output Lag Filter Time
0.0 ~ 2.5
0.0
Sec
*1
10-11
Feedback Loss Detection
Mode
0: Disable
1: Enable - Drive Continues to
Operate After Feedback Loss
2: Enable - Drive "STOPS"
After Feedback Loss
0 -
10-12
Feedback Loss Detection
Level
0 ~ 100
0 %
10-13
Feedback Loss Detection
Delay Time
0.0 ~25.5
1.0
Sec
10-14
Integration Limit Value
0 ~ 109
100 % *1
10-15
Integral Value Resets to Zero
when Feedback Signal Equals
the Target Value
0: Disable
1: After 1 Second
30: After 30 Second (0~30)
0 -
10-16
Allowable Integral value Error
Margin (Units, 1 Unit = 1/8192)
0 ~ 100
0 -
10-17
PID Sleep Frequency Level
0.00~650.00
0.00
Hz
10-18
PID Sleep Function Delay Time
0.0 ~25.5
0.0
Sec
10-19
PID Wake up frequency Level
0.00 ~ 650.00
0.00
Hz
10-20
PID Wake up function Delay Time
0.0 ~ 25.5
0.0
Sec
10-21
Max PID Feedback Setting Level
0 ~999
100 - *1
4-21
Page 71

Group 10: PID Parameters
No.
Description
Range
Factory
Setting
Unit
Note
10-22
Min PID Feedback Setting Level
0 ~999
0 - *1
Group 11: Auxilary Parameters
No.
Description
Range
Factory
Setting
unit
Note
11-00
Reverse Operation Control
0: Reverse Command is Enabled
1: Reverse Command is Disabled
0 -
11-01
Carrier Frequency (kHz)
1~16
5
KHz
11-02
Carrier Mode Selection
0: Mode0, 3Phase PWM modulation
1: Mode1, 2Phase PWM modulation
2: Mode2, 2Phase Random PWM Modulation
0 -
11-03
Carrier Frequency
Reduction by Temperature Rise
0:Disable
1:Enable
0 -
11-04
S-Curve Acc 1
0.0 ~ 4.0
0.2
Sec
11-05
S-Curve Acc 2
0.0 ~ 4.0
0.2
Sec
11-06
S-Curve Dec 3
0.0 ~ 4.0
0.2
Sec
11-07
S-Curve Dec 4
0.0 ~ 4.0
0.2
Sec
11-08
Skip Frequency 1
0.00 ~ 650.00
0.00
Hz
*1
11-09
Skip Frequency 2
0.00 ~ 650.00
0.00
Hz
*1
11-10
Skip Frequency 3
0.00 ~ 650.00
0.00
Hz
*1
11-11
Skip Frequency Range
Bandwith (±)
0.00 ~ 30.00
0.00
Hz
*1
11-12
Energy Saving Gain (V/F Mode)
0 ~ 100
80 %
11-13
Regeneration Prevention Function
0:Disable
0 -
1:Enable
2:Enable (only during constant speed)
11-14
Regeneration Prevention Voltage
Level
200V:300.0~400.0
380.0
V
400V:600.0~800.0
760.0
11-15
Regeneration Prevention
Frequency Limit
0.00 ~ 15.00
3.00
Hz
11-16
Regeneration Prevention Voltage
Gain
0~200
100 %
11-17
Regeneration Prevention
Frequency Gain
0~200
100 %
4-22
Page 72

Group 12: Monitoring Parameters
No.
Description
Range
Factory
Setting
Unit
Note
12-00
Extended Display Mode
00000~88888
Each digit can be set from 0 to 8 as listed below.
00000
-
*1
0: Default Display
(Frequency and Parameters)
1:Output Current
2:Output Voltage
3:DC Voltage
4:Temperature
5:PID Feedback
6:Analog Signal Input. (AI1)
7:Analog Signal Input. (AI2)
8:Count Status
12-01
PID Feedback Display Format
0:Integer (xxx)
0 - *1
1:One Decimal Place (xx.x)
2:Two Decimal Places (x.xx)
12-02
PID Feedback Display Unit Setting
0:xxx--
0 - *1
1:xxxpb(pressure)
2:xxxfl(flow)
12-03
Custom Units (Line Speed) Value
0~65535
1500/1800
RPM
*1
12-04
Custom Units (Line Speed) Display
Mode
0:Drive Output Frequency is Displayed
0 - *1
1:Line Speed.Integer.(xxxxx)
2:Line Speed.One Decimal Place.
(xxxx.x)
3:Line Speed.Two Decimal Places
(xxx.xx)
4:Line Speed.Three Decimal Places
(xx.xxx)
12-05
Inputs and Output
Logic Status Display
( S1~S6, RY1 and RY2)
S1 S2 S3 S4 S5 S6
RY1
RY2
PLC
- - *4
12-06
Alarm Selections for Inverter
Components Life Expectancy
xxxx0:Life Alarm of Inrush Current Suppression
Circuit is Invalid
xxxx1:Life Alarm of Inrush Current
Suppression Circuit is Valid
00000
-
*1
xxx0x:Life Alarm of Control Circuit Capacitors is
Invalid
xxx1x:Life Alarm of Control Circuit
Capacitors is Valid
xx0xx:Life Alarm of Main Circuit Capacitors is
Invalid
xx1xx:Life Alarm of Main Circuit Capacitors is
Valid
12-07
Detect Main Circuit Capacitors
Reserved
4-23
Page 73

Group 12: Monitoring Parameters
No.
Description
Range
Factory
Setting
Unit
Note
12-08
Display of Inrush Current
Suppression Circuit
0~100
100 %
12-09
Display of Control Circuit
Capacitors
0~100
100 %
12-10
Reserved
12-11
Output Current when
Fault Appeared
---- 0 A
12-12
Output Voltage when
Fault Appeared
---- 0 Vac
12-13
Output Frequency when
Fault Appeared
---- 0 Hz
12-14
DC Bus Voltage when
Fault Appeared
---- 0 Vac
12-15
Frequency Command when Fault
Appeared
---- 0 Hz
Group 13: Maintenance Parameters
No.
Description
Range
Factory
Setting
unit
Note
13-00
Drive Horsepower Code
---- - -
*3
13-01
Software Version
---- - -
*3*4
13-02
Fault Log (Latest 3 Faults)
---- - -
*3*4
13-03
Accumulated Inverter
Operation Time 1
0~23
-
hour
*3
13-04
Accumulated Inverter
Operation Time 2
0~65535
----
day
*3
13-05
Accumulated Inverter
Operation Time Mode
0: Power On time
1: Operation time
0 - *3
13-06
Parameter Lock
0:Enable all Functions
1:Preset Speeds from 05-01 to 05-15 Can’t be
Changed
2:All Functions Can’t be Changed Except
for Preset speeds from 05-01 to 05-15
3:Disable All Functions Except 13-06
0 -
13-07
Parameter Lock Code
00000~65535
00000 -
13-08
Reset Drive to Factory
Settings
1150:Reset to Factory Setting(50Hz System)
1160:Reset to Factory Setting(60 Hz System)
1112:Reset PLC
00000 -
4-24
Page 74

Group 14: PLC Parameters
No.
Description
Range
Factory
Setting
unit
Note
14-00
Setting Value1 of T1
0~9999 0 -
14-01
Setting Value1 of T1 (mode 7)
0~9999 0 -
14-02
Setting Value1 of T2
0~9999 0 -
14-03
Setting Value1 of T2 (mode 7)
0~9999 0 -
14-04
Setting Value1 of T3
0~9999 0 -
14-05
Setting Value1 of T3 (mode 7)
0~9999 0 -
14-06
Setting Value1 of T4
0~9999 0 -
14-07
Setting Value1 of T4 (mode 7)
0~9999 0 -
14-08
Setting Value1 of T5
0~9999 0 -
14-09
Setting Value1 of T5 (mode 7)
0~9999
0
-
14-10
Setting Value1 of T6
0~9999
0
-
14-11
Setting Value1 of T6 (mode 7)
0~9999
0
-
14-12
Setting Value1 of T7
0~9999
0
-
14-13
Setting Value1 of T7 (mode 7)
0~9999
0
-
14-14
Setting Value1 of T8
0~9999
0
-
14-15
Setting Value1 of T8 (mode 7)
0~9999
0
-
14-16
Setting Value1 of C1
0~65535
0
-
14-17
Setting Value1 of C2
0~65535
0
-
14-18
Setting Value1 of C3
0~65535
0
-
14-19
Setting Value1 of C4
0~65535
0
-
14-20
Setting Value1 of C5
0~65535
0
-
14-21
Setting Value1 of C6
0~65535
0
-
14-22
Setting Value1 of C7
0~65535
0
-
14-23
Setting Value1 of C8
0~65535
0
-
14-24
Setting Value1 of AS1
0~65535
0
-
14-25
Setting Value2 of AS1
0~65535
0
-
14-26
Setting Value3 of AS1
0~65535
0
-
14-27
Setting Value1 of AS2
0~65535
0
-
14-28
Setting Value2 of AS2
0~65535
0
-
14-29
Setting Value3 of AS2
0~65535
0
-
14-30
Setting Value1 of AS3
0~65535
0
-
14-31
Setting Value2 of AS3
0~65535
0
-
14-32
Setting Value3 of AS3
0~65535
0
-
14-33
Setting Value1 of AS4
0~65535
0
-
14-34
Setting Value2 of AS4
0~65535
0
-
14-35
Setting Value3 of AS4
0~65535
0
-
14-36
Setting Value1 of MD1
0~65535
1
-
14-37
Setting Value2 of MD1
0~65535
1
-
14-38
Setting Value3 of MD1
1~65535
1
-
14-39
Setting Value1 of MD2
0~65535
1
-
14-40
Setting Value2 of MD2
0~65535
1
-
14-41
Setting Value3 of MD2
1~65535
1
-
14-42
Setting Value1 of MD3
0~65535
1
-
14-43
Setting Value2 of MD3
0~65535
1
-
14-44
Setting Value3 of MD3
1~65535
1
-
4-25
Page 75

14-45
Setting Value1 of MD4
0~65535
1
-
14-46
Setting Value2 of MD4
0~65535
1
14-47
Setting Value3 of MD4
1~65535
1
-
Group 15: PLC Monitoring Parameters
No.
Description
Range
Factory
Setting
unit
Note
15-00
Current Value of T1
0~9999 0 -
15-01
Current Value of T1(mode 7)
0~9999 0 -
15-02
Current Value of T2
0~9999 0 -
15-03
Current Value of T2(mode 7)
0~9999 0 -
15-04
Current Value of T3
0~9999 0 -
15-05
Current Value of T3(mode 7)
0~9999 0 -
15-06
Current Value of T4
0~9999 0 -
15-07
Current Value of T4(mode 7)
0~9999 0 -
15-08
Current Value of T5
0~9999 0 -
15-09
Current Value of T5(mode 7)
0~9999 0 -
15-10
Current Value of T6
0~9999 0 -
15-11
Current Value of T6(mode 7)
0~9999 0 -
15-12
Current Value of T7
0~9999 0 -
15-13
Current Value of T7(mode 7)
0~9999 0 -
15-14
Current Value of T8
0~9999 0 -
15-15
Current Value of T8(mode 7)
0~9999 0 -
15-16
Current Value of C1
0~65535
0
-
15-17
Current Value of C2
0~65535
0
-
15-18
Current Value of C3
0~65535
0
-
15-19
Current Value of C4
0~65535
0
-
15-20
Current Value of C5
0~65535
0
-
15-21
Current Value of C6
0~65535
0
-
15-22
Current Value of C7
0~65535
0
-
15-23
Current Value of C8
0~65535
0
-
15-24
Current Value of AS1
0~65535
0
-
15-25
Current Value of AS2
0~65535
0
-
15-26
Current Value of AS3
0~65535
0
-
15-27
Current Value of AS4
0~65535
0
-
15-28
Current Value of MD1
0~65535
0
-
15-29
Current Value of MD2
0~65535
0
-
15-30
Current Value of MD3
0~65535
0
-
15-31
Current Value of MD4
0~65535
0
-
15-32
Current Value of TD
0~65535
0
μs
4-26
Page 76

00 - Basic Parameters
00-00
Control Mode Selection
Range
【0】:V/F Mode
【1】:Vector Mode
00-02
Main Run Command Source Selection
00-03
Alternative Run Command Source Selection
Range
【0】:Keypad control
【1】:External terminal control
【2】:Communication control
【3】:PLC
Terminal S1
Terminal S2
Operation
Open
Open
Stop Inverter
Closed
Open
Run Forward
Open
Closed
Run Reverse
Closed
Closed
Stop Inverter, Display EF9 Alarm after 500ms
S1
S2
COM
Forward,
Run / Stop
Reverse
Run / Stop
4.3 Description of Parameters
To select the appropriate vector or V/F control mode according to the load characteristics.
If V/F mode is selected, please set parameters, group1 to comply with the load features.
Vector is best suited to control the general load or rapidly-changed torque load.
Note: To switch the command source between the setting of main (00-02) and alternative (00-03) assign one of
the DI (S1 to S6) to be the “Run Command Switch Over” (03-00~03-05=12).
00-02=0: Keypad Control
Use the keypad to start and stop the inverter and set direction with the forward / reverse key. Refer to section 4-1
for details on the keypad.
00-02=1: External Terminal Control
External terminals are used to start and stop the inverter and select motor direction. There are three different
types: 2-wire and 3-wire operation and 2-wire self holding (latching) mode.
■ 2-wire operation
For 2-wire operation, set 03-00 (S1 terminal selection) to 0 and 03-01 (S2 terminal selection) to 1
Figure 4.3.1 Wiring example of 2-wire
4-27
Page 77

S1
S2
S3
Forward/Reverse
selection
COM
Operation
(normally open
Momentary switch)
Stop
(Normally Close
Momentary
switch)
Stop Command
(Off: Stop)
Run Command
(On:Run)
Time
Time
Time
Time
Run Command
Stop Command
Forward/Reverse
Command
Motor Speed
Off
Off
(Stop)
Off
(forward)
On (Reversal)
Stop Forward Reverse Stop Forward
On
>= 50ms
■ 3-wire operation
Set parameter 00-04 to 2 for 3-wire program initialization, multi-function input terminal S1 is set to run operation,
S2 for stop operation and S3 for forward/reverse command.
Note: Terminal S1 must be closed for a minimum of 50ms to activate operation.
Figure 4.3.2 Wiring example of 3-wire
Figure 4.3.3 3-wire operation
00-03=2: Communication control
The inverter is controlled by the RS-485 port. Refer to parameter group 9 for communication setup.
4-28
Page 78

00-04
Operation Modes for External Terminals
Range
【0】:Forward/Stop-Reverse/Stop
【1】:Run/Stop- Reverse/ Forward
【2】:3 Wire Control Mode - Run/Stop
00-05
Main Frequency Command Source Selection
00-06
Alternative Frequency Source Selection
Range
【0】:Up/Down on Keypad
【1】:Potentiometer on Keypad
【2】:External AI1 Analog Signal Input
【3】:External AI2 Analog Signal Input
【4】:External Up/Down Frequency Control
【5】:Communication Setting Frequency
【6】:PID Output Frequency
【7】:Pulse Input
04-00
Analog Input Signal Type Select
(AI1/AI2)
AI1 AI2
(0): 0~10V (0~20mA) 0~10V (0~20mA)
(1): 0~10V (0~20mA) 2~10V (4~20mA) Factory Default
(2): 2~10V (4~20mA) 0~10V (0~20mA)
(3): 2~10V (4~20mA) 2~10V (4~20mA)
00-03=3: PLC control
The inverter is controlled by the inverter built-in PLC logic. Refer to section 4.3.
00-04 is valid when run command is set to external mode by 00-02/00-03 =1.
2 Wire Operation Mode,
Set 00-04=【0/1】first, before setting (03-00, 03-04) to【0】or【1】
00-04=【0】, Set external terminals (03-00 to 03-05) function to 0 for FWD/Stop or Set to 1 for REV/Stop..
00-04=【1】, Set external terminals (03-00 to 03-05) function to 0 for Run/Stop or Set to 1 for FWD/REV
3 Wire Operation Mode,
00-04 =【2】Terminals S1, S2, S3 are used in a combination to enable 3 wire run/stop mode.
Settings for 03-00, 03-01, and 03–02 will not be effective... (Refer to group 03)
00-05/00-06= 0: Keypad
Use the keypad to enter the frequency reference or by setting parameter 05-01 (frequency reference 1). Note that
once the frequency command is switched to alternative frequency reference and 00-06 is set to 0, the frequency
can be adjusted using parameter 05-01.
00-05/00-06= 1: Potentiometer on Keypad
Use the keypad potentiometer to set frequency reference
00-05/00-06= 2, 3: External Analog Input AI1 / External Analog Input AI2
Set any of the multi-function terminals (03-00~03-05) to 13, to switch between main and alternate frequency.
Use analog reference from analog input AI1 or AI2 to set the frequency reference (as shown in Figure 4.3.4).
Refer to parameter 04-00 to select the signal type.
4-29
Page 79

JP2/JP3
External signal type
selection
0~20mA / 4~20mA
Analog signal
0~10VDC / 2~10VDC
Analog signal
+ V
AGND
2K
Ω
AI1
AI2
Main Frequency
Reference Command
(voltage or current input)
10
Main Frequency
Reference Command
(voltage or current input)
Figure 4.3.4 Analog input as main frequency reference command
00-05/00-06= 4: Terminal UP / DOWN
The inverter accelerates with the UP command closed and decelerates with the DOWN command closed. Please
refer to parameter 03-00 ~ 03-05 for additional information.
Note: To use this function both the UP and DOWN command have to be set to any of the input terminals.
00-05/00-06= 5: Communication Control
The frequency reference command is set via the RS-485 communication port using the MODBUS RTU.
Refer to parameter group 9 for additional information.
00-05/00-06= 6: PID Output
Enables PID control, reference frequency is controlled by the PID function, refer to chapter 10 or parameter group
10 for PID setup.
00-05/00-06=7: Pulse Input
Frequency reference from an external pulse input. Can be used only with multi-function input terminal S3 (03-02 =
25 or 26). See parameter group 3 multi-function input selections 25 and 26.
4-30
Page 80

00-07
Main and Alternative Frequency Command Modes
Range
【0】:Main reference frequency
【1】:Main frequency + alternative frequency
00-08
Communication Frequency Command – READ ONLY
Range
【0.00~650.00】Hz
00-09
Communication Frequency Command Memory
Range
【0】:Do not store the communication frequency command at power down
【1】:Store communication frequency reference at power down
00-10
Initial Frequency Selection
Range
【0】:By Current Freq Command
【1】:By Zero Freq Command
【2】:By 00-11
00-11
Initial Frequency Setpoint
Range
【0.00~650.00】Hz
00-12
Upper Limit Frequency
Range
【0.01~650.00】Hz
00-13
Lower Limit Frequency
Range
【0.00~649.99】Hz
When set to 0 the reference frequency is set by the main reference frequency selection of parameter 00-05.
When set to 1 the reference frequency is sum of the main reference frequency (00-05) and alternative frequency
(00-06).
Note: The inverter will display the SE1 error when 00-07 = 1 and parameter 00-05 and 00-06 are set to the same
selection.
When parameter 00-06 is set to 0 (Keypad) the alternative frequency reference is set by parameter 05-01
(Frequency setting of speed-stage 0).
Display the frequency reference when 00-05 or 00-06 is set to communication control (3).
Note: This parameter is only effective when frequency reference is set via communication (00-05 / 00-06 = 3).
Notes:
- This parameter is only effective in keypad mode
- When 00-10=【0】, the initial frequency will be current frequency.
- When 00-10=【1】, the initial frequency will be 0.
- When 00-10=【2】, the initial frequency is set by parameter 00-11.
Set the maximum frequency reference. Maximum output frequency depends on motor selection.
Motor : Maximum frequency parameter 01-02.
4-31
Page 81

Frequency
Reference
Output
Frequency
650 Hz
00-12
00-13
650 Hz
00-14
Acceleration Time 1
Range
【0.1~3600.0】Sec
00-15
Deceleration Time 1
Range
【0.1~3600.0】Sec
00-16
Acceleration Time 2
Range
【0.1~3600.0】Sec
00-17
Deceleration Time 2
Range
【0.1~3600.0】Sec
(00-15)x(set frequency - the minimum starting frequency)
Actual acceleration time=
(00-14)x(set frequency - the minimum starting frequency)
Maximum output frequency
Actual deceleration time=
Maximum output frequency
Set the minimum frequency reference. Maximum output frequency depends on motor selection. Motor 1:
Maximum frequency is set by parameter 01-02.
Notes:
- When 00-13 and the command frequency are both set to 0.00, and RUN is pressed ” Stpo” is displayed.
- When Frequency command is higher than value in 00-13 inverter output will ramp up from 0.00 to the
command frequency.
- When 00-13> 0, and the frequency command value ≤ 00-13, inverter output will ramp up from preset to the
lower limit frequency.
Figure 4.3.5 Frequency reference upper and lower limits
Notes:
- Acceleration time is the time required to accelerate from 0 to 100% of maximum output frequency.
- Deceleration time is the time required to decelerate from 100 to 0% of maximum output frequency.
- Maximum frequency is set by parameter 01-02.
- If parameter 01-00=18, Maximum output frequency is set by parameter 01-02.
- If parameter 01-00≠18, Maximum output frequency = 50.00 or 60.00 depending on initialization mode.
Actual acceleration and deceleration time is calculated as follows:
4-32
Page 82

Maximum output
Frequency
Set frequency
Acc-time
00-14
Dec-time
00-15
Actual acc-time
Actual dec-time
Hz
T0
The minimum
starting
frequency
00-18
Jog Frequency
Range
【0.00~650.00】Hz
00-19
Jog Acceleration Time
Range
【0.1~3600.0】Sec
00-20
Jog Deceleration Time
Range
【0.1~3600.0】Sec
The JOG function is operational by using the multi-function input terminals S1 to S6 and setting the relevant
parameters 03-00~03-05 to 【6】JOG FWD or【7】JOG REV. Refer to parameter group 3.
Notes:
- To activate the JOG FWD function set any of the multi-function input terminals S1 to S6 to 6.
- To activate the JOG REV function set any of the multi-function input terminals S1 to S6 to 7.
- Jog acceleration time (00-19) is the time required to accelerate from 0 to 100% of maximum output frequency.
- Jog deceleration time (00-20) is the time required to decelerate from 100 to 0% of maximum output frequency.
- Maximum frequency is set by parameter 01-02.
- The inverter uses the Jog frequency (00-18, default 6.0 Hz) as its frequency reference when jog is active.
4-33
Page 83

01-V/F Control Parameters
01-00
Volts/Hz Patterns (V/F)
Range
【0~18】
01-03 (Vmax)
01-05 (Vmid2)
01-07 (Vmid1)
01-09 (Vmin)
01-08 01-06 01-04 01-02
(V)%
Hz
650.00
The V/F curve selection is enabled for V/F mode. Make sure to set the inverter input voltage parameter 01-14.
There are three ways to set V/F curve:
(1) 01-00 = 0 to 17: choose any of the 18 predefined curves (0 to 17).
(2) 01-00 = 18, use 01-02~01-09 and 01-12 ~ 01-13.
The default parameters (01-02 ~ 01-09 and 01-12 ~ 01-13) are the same when 01-00 is set to 18 and 01-00 is set
to 0 (50Hz) or 9 (60Hz) depending on the initialization mode.
Parameters 01-02 ~ 01-13 are automatically set when any of the predefined V/F curves are selected.
This parameter will be affected to reset by the initialization parameter (13-08).
Consider the following items as the conditions for selecting a V/F pattern.
(1) The voltage and frequency characteristic of motor.
(2) The maximum speed of motor.
4-34
Page 84

TYPE
50Hz
60Hz
Func
tion
01-00
V/F pattern
01-00
V/F pattern
General Use
=【0】
100
B
C
1.52.5 50
(V)%
Hz650
=【9】
100
B
C
1.5 3.0 60
(V)%
Hz650
High start torque
=【1】
100
B
C
1.32.5 50
(V)%
Hz650
=【10】
100
B
C
1.53.0 60
(V)%
650
=【2】
=【11】
=【3】
=【12】
Decreasing torque
=【4】
100
B
C
1.3 25 50
(V)%
Hz650
=【13】
100
B
C
1.5 30 60
(V)%
Hz650
=【5】
=【14】
Decreasing torque
=【6】
100
B
C
0.5 25 50
(V)%
Hz650
=【15】
100
B
C
0.6 30 60
(V)%
Hz650
=【7】
=【16】
=【8】
=【17】
4-35
Page 85

01-01
V/F Max Voltage
Range
【230V:170.0~264.0, 460V: 323.0~528.0】V
01-02
Maximum Frequency
Range
【0.20 ~ 650.00】Hz
01-03
Maximum Frequency Voltage Ratio
Range
【0.0 ~ 100.0】%
01-04
Medium Frequency 2
Range
【0.10 ~ 650.00】Hz
01-05
Medium Frequency Voltage Ratio 2
Range
【0.0 ~ 100.0】%
01-06
Medium Frequency 1
Range
【0.10 ~ 650.00】Hz
01-07
Medium Frequency Voltage Ratio 1
Range
【0.0 ~ 100.0】%
01-08
Minimum Frequency
Range
【0.10 ~ 650.00】Hz
01-09
Minimum Frequency Voltage Ratio
Range
【0.0 ~ 100.0】%
01-00
B (Xb)
C (Xc)
0 / 9
7.5%
4.5%
1 / 10
10.0%
7.0%
2
11.0%
8.5%
3
12.0%
9.5%
4
17.5%
4.0%
5
25.0%
5.0%
11
11.0%
8.0%
12
12.0%
9.0%
13
20.5%
7.0%
14
28.5%
8.0%
6 / 15
45.0%
1.0%
7 / 16
55.0%
1.0%
8 / 17
65.0%
1.0%
(V) 100% is the maximum output voltage. B, C point preset % settings will be as table below:
Notes:
- Max output frequency is set automatically when parameter 01-00 ≠ 18.
- Maximum output frequency is limited by 01-12, frequency upper limit when 01-00 ≠ 18.
- Maximum output frequency is set by parameter 01-02 when 01-00 = 18.
4-36
Page 86

01-10
Volts/Hz Curve Modification (Torque Boost)
Range
【0 ~ 10.0】%
100
B
C
1 2.5/3.0 50/60
(V)%
Hz
01-10
01-11
V/F Start Frequency
Range
【0.00 ~10.00】Hz
01-12
Slip Compensation Gain
Range
【0.05 ~10.00】s
01-13
V/F Mode Select
Range
【0】: Close Loop
【1】: Open Loop
Notes:
- Inverter output V / F curve settings for points B, C can be adjusted using parameter 01-10 to improve the
output torque.
- Calculation for point B and C voltage:
o B point voltage = Xb × maximum output voltage
o C point voltage = Xc × maximum output voltage
- When 01-10 = 0, torque boost is disabled.
Notes: VF Start Frequency can be used to when start frequency has to be greater than zero.
0: Uses current feedback to estimate motor speed and enhance speed control accuracy
1: No motor speed estimation used; open loop control based on set V/F curve.
4-37
Page 87

02-Motor Parameters
02-00
Motor No Load Current
Range
【0~【 (Parameter 02-01)-0.1】】
02-01
Motor Rated Current
Range
【0.2~100】
02-02
Motor Rated Slip Compensation
Range
【0.0 ~ 200.0】(%)
02-03
Motor Rated Speed
Range
【0~39000】
Slip compensation boost=
Output Current-(02-00)
(02-01)-(02-00)
X (02-02) X motor rated slip
(02-02)approximate Value=
Motor synchronization speed-Rated speed
Motor synchronization speed
120
Motor Poles
Motor synchronization speed(RPM)= x Motor rated frequency (50/60Hz)
02-04
Motor Rated Voltage
Range
【230V: 170.0~264.0 / 400V: 323.0~528.0】
02-05
Motor Rated Power
Range
【0.1~37.0】
02-06
Motor Rated Frequency
Range
【0~650.0】
02-07
Motor Pole Number
Range
【2~ 16】
02-14
Auto Tune
Range
【0】: Disable
【1】: Enable
When the load causes the actual motor speed to be reduced below the speed set by inverter output frequency (Slip),
parameter 02-02 Slip compensation can be used to adjust the speed.
Motor slip= Motor synchronization speed - Motor Rated Speed
Motor synchronization speed (Marked on the motor nameplate)
Example: 4 pole motor, 60 Hz, nominal motor speed is 120 ÷ 4 x 60 = 1800 RPM
Note: 02-00/02-01 default value based on inverter rating (13-00), make sure the data matches the motor
connected.
4-38
Page 88

02-15
Stator Resistance Gain
Range
----
02-16
Rotor Resistance Gain
Range
----
Notes:
- For vector mode, set parameter 00-00=【1】, next set the motor nameplate data in parameters 02-01,
02-03~02-06 and activate the auto tune function by setting parameter 02-14 = 1.
- The auto tuning function determines the best motor performance based on the motor connected.
- During the Auto tune. “AT” will be displayed on the inverter and auto tuning results (motor parameter)
will be stored in parameters 02-15~02-16.
- After a successful auto tune function the display will return to command frequency display.
- Auto tune function must be performed again when the motor is replaced.
4-39
Page 89

03-External Digital Inputs and Relay Output Functions
03-00
Multifunction Input Term. S1
03-01
Multifunction Input Term. S2
03-02
Multifunction Input Term. S3
03-03
Multifunction Input Term. S4
03-04
Multifunction Input Term. S5
03-05
Multifunction Input Term. S6
Range
【0】:Forward/Stop Command---------------- (Parameters 00-02/00-03=1& 00-04)
【1】:Reverse/Stop Command---------------- (Parameters 00-02/00-03=1& 00-04)
【2】:Speed Selection 1
【3】:Speed Selection 2
【4】:Speed Selection 3
【5】:Speed Selection 4
【6】:JOG Forward Command------------( Parameters 00-18~00-20)
【7】:JOG Reverse Command------------( Parameters 00-18~00-20)
【8】:Up Command---------( Parameters 00-05/00-06=4& 03-06/03-07)
【9】:Down Command-----( Parameters 00-05/00-06=4& 03-06/03-07)
【10】: 2nd Acc/Dec Times
【11】: Disable Acc/Dec
【12】: Main/ Alternative Run Source Select----( Parameters 00-02/00-03)
【13】: Main/ Alternative Frequency Command Select----( Parameters 00-05/00-06)
【14】: Rapid Stop (controlled deceleration stop)
【15】: Base Block (Coast to stop)
【16】: Disable PID Function ----------( Parameter Group 10)
【17】: Reset
【18】: Enable Auto Run Mode-----------( Parameter Group 6)
【19】: Speed Search
【20】: Energy Saving(V/F)
【21】: Reset PID integral value to Zero
【22】: Counter Input
【23】: Counter Reset
【24】: PLC Input
【25】: Pulse Input-Width Measure (S3)
【26】: Pulse Input-Frequency Measure (S3)
【27】: Enable KEB Function
【28】: Fire mode function (Valid for software issued after rev. 1.1 )
03-0X =【0】: 2-wire control: forward operation
03-0X =【1】: 2-wire control: reverse operation. Refer to the 2-wire operation mode
4-40
Page 90

E510
S1
S2
COM
(FWD/STOP)
(REV/STOP)
S1
ON OFF
FWD
REV
ONOFF
S2
Hz
T
E510
S1(RUN)
S2(STOP)
S3(FWD/REV)
COM
2-Wire control method
Example: FWD/STOP and REV/STOP from two inputs (S1 & S2)
Set 00-04=【0】; S1:03-00=【0】 (FWD/STOP); S2:03-01=【1】 (REV/STOP);
Note: If both forward and reverse commands are active the inverter treats this as a STOP command.
3-Wire control method
Example: Two separate push buttons for RUN & STOP and two position selector switch for FWD/REV
Set 00-04 =【2】, (3 wire control mode), to set terminals S1, S2 and S3 for 3-Wire control
When 3-Wire control mode is selected the setting for parameters 03-00, 03-01 and 03-02 are not active.
4-41
Page 91

S1
OFF
FWD
REV
S2
S3
ON
ON
ON
Hz
T
OFF
ON
Preset
speed
Function setting and state of any of the four inputs S1 ~ S6
Preset
Frequency
Acceleration
time
Deceleration
time
Speed
Select 4
(Sx=5)
Speed
Select 3
(Sx=4)
Speed
Select 2
(Sx=3)
Speed
Select 1
(Sx=2)
speed 0
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
05-01
05-17
05-18
speed 1
OFF
OFF
OFF
ON
05-02
05-19
05-20
speed 2
OFF
OFF
ON
OFF
05-03
05-21
05-22
speed 3
OFF
OFF
ON
ON
05-04
05-23
05-24
speed 4
OFF
ON
OFF
OFF
05-05
05-25
05-26
speed 5
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
05-06
05-27
05-28
speed 6
OFF
ON
ON
OFF
05-07
05-29
05-30
speed 7
OFF
ON
ON
ON
05-08
05-31
05-32
speed 8
ON
OFF
OFF
OFF
05-09
05-33
05-34
speed 9
ON
OFF
OFF
ON
05-10
05-35
05-36
speed 10
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
05-11
05-37
05-38
speed 11
ON
OFF
ON
ON
05-12
05-39
05-40
speed 12
ON
ON
ON
ON
05-13
05-41
05-42
speed 13
ON
ON
ON
ON
05-14
05-43
05-44
speed 14
ON
ON
ON
ON
05-15
05-45
05-46
speed 15
ON
ON
ON
ON
05-16
05-47
05-48
03-00~03-05 =【5, 4, 3, 2】Preset speed selections
Digital input S1 to S6 can be used to select between 16 different preset speeds (Preset speed 0 to 15).
Four speed selection bits are available and can be assigned to any of the digital input. The selected preset speed
is based on the combination of the speed selection bits shown in the table below.
Example: Input S3 set for speed selection 1 bit, [03-02] = 2, Input S4 set for speed select 2 bit, [03-03] = 3, Input
S5 set for speed select 3 bit, [03-04] = 4 and input S6 set for speed select 4 bit, [03-05] = 5.
4-42
UP Command
(Terminal S5)
Page 92

1 0 0
1
Down Command
(Terminal S6)
0 1 0
1
Operation
Accel
(UP)
Decel
(DWN)
Hold
Hold
S1 Forward Run / Stop (03-00 = 0)
COM
S5 Up Command (03-04=8)
S6 Down Command (03-04=9)
03-0X =【06】: Forward jog run command, uses jog frequency parameter 00-18.
Note:
Jog command has a higher priority than other frequency reference commands.
Jog command uses stop mode set in parameter 07-09 when Jog command is active > 500ms.
03-0X =【07】: Reverse jog run command, uses jog frequency parameter 00-18.
Note:
Jog command has a higher priority than other frequency reference commands.
Jog command uses stop mode set in parameter 07-09 when Jog command is active > 500ms.
Note: If Forward and Reverse Jog are active at the same time the inverter enters stop mode.
03-0X =【08】: UP frequency command; set parameter 00-05 Frequency command to 4 to activate. When ON
frequency reference increased by value set in parameter 03-06. If the input is kept on continuously, the frequency
command increases accordingly until the upper frequency limit is reached.
03-0X =【09】: Down frequency command; set parameter 00-05 Frequency command to 4 to activate. When ON
frequency reference decreased by value set in parameter 03-06. If the input is kept on continuously, the
frequency command decreases accordingly and in relation to settings for parameter 03-06 and 3-07 until zero
speed is reached.
03-00~03-05=【10】2nd Acc/Dec time
When active the acceleration and deceleration time will be set according to value set in parameter 00-16
(acceleration time 2) and 00-17 (deceleration time 2).
When not-active the acceleration and deceleration time will be set according to value set in parameter
00-14(acceleration time 1) and 00-15 (deceleration time 1).
4-43
Page 93

60Hz
0
10s
(accel time 1)
Hz
T
5s
(accel time 2)
S1 OffS1 On
RUN
Command
S1
RUN
STOP
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
T
Hz
Example:
00-12 (Frequency upper limit) =60Hz
03-00= 0 (Terminal S1 FWD/STOP)
00-14 (accelerating time 1) = 10 sec
00-16 (accelerating time 2) =5 sec
03-00~03-05=【11】Disable Acc/Dec function
When activated suspends the acceleration / deceleration operation and maintains the output frequency at current
level.
Accel/Decel & Enable/Disable timing diagram using terminal S1 and parameter 03-00 = 11.
03-00~03-05=【12】Main / Alternative Run Source Select
When active, the run command source is set by parameter 00-03(Alternative Run source). When Input is off run
command source is set by parameter 00-02 (Main run source).
4-44
Page 94

Count Input
Multi-function input
2ms
c0000 c0001 c0002 c0003 c0004 c0005 c0006 c0007
Count display set
by 12-00 = 8
03-00~03-05=【13】Main/ Alternative Frequency Source Select
When active the Alternative Frequency Source parameter 00-06 is used, otherwise Main Frequency Source is
used parameter 00-05.
03-00~03-05=【14】Rapid Stop (controlled deceleration stop)
When active inverter decelerates to stop using deceleration time 2.
03-00~03-05=【15】Base Block (Coast to stop)
When active the inverter output is turned off.
03-00~03-05=【16】Disable PID Function
When active PID function is disabled.
03-00~03-05=【17】Reset
When active inverter resets active fault (same function as the Reset button on the keypad).
03-00~03-05=【18】Auto _ Run Mode
When active the programmable auto- sequencer function is enabled, Refer to description of parameter group 6.
03-00~03-05=【19】Speed Search Stop
When active the inverter performs a speed-search by detecting the current speed of the motor and accelerating
from there to the target speed.
03-00~03-05=【20】Energy-saving operation
When active the inverter output voltage is gradually decreased to match the required torque demand and as a
result saves energy. Only for variable torque applications such as fans and pumps that require less torque when
operation speed is reached. When input is turned off the output voltage gradually increases again back to the
original output voltage.
Note: Acceleration and deceleration times in energy saving operation is identical to that of speed search
operation.
03-00~03-05=【21】Reset PID Integral value to Zero
When active resets the PID integral value zero.
03-00~03-05=【22】Counter Input
Input used as counter input, set related parameters 03-21 ~03-22.
Count status can be viewed by setting parameter 12-00 to 8
4-45
Page 95

03-00~03-05=【23】Counter Reset
When active resets counter to 0.
03-00~03-05=【24】PLC Input
Input used for PLC logic.
03-02=【25】Pulse Input-Width Measure (Available for S3 Input only)
When 03-02=25, S3 is used for pulse width measurement.
Related parameters:
00-05=7 (Pulsed Speed Control)
03-27= 0.01~0.20 kHz (Pulse Input Frequency)
03-28=0.01~9.99
Inverter Frequency = duty cycle x (00-12) x (03-28) Hz (Limited by the Frequency Upper limit)
To adjust speed through pulse input duty cycle, set parameters as follows:
00-05=7; 03-02=25; 03-27=pulse input frequency; 03-28=1 (as per actual need)
When pulse input frequency is 200Hz, set 03-27=0.20 (must be correct). Along with the duty cycle of this 200Hz
pulse input, inverter frequency is varied.
Example 1:
Pulse input frequency is 200Hz (03-27=0.20), duty cycle is 50%, frequency upper limit 50Hz (00-12=50.00), and
03-28=1. Inverter frequency is 50% x 50.00 x 1 = 25.00 Hz
Example 2:
Pulse input frequency is 100Hz (03-27=0.10), duty cycle is 30%, frequency upper limit 50Hz (00-12=50.00), and
03-28=2. Inverter frequency is 30% x 50.00 x 2 = 30.00 Hz
Example 3:
Pulse input frequency is 100Hz (03-27=0.10), duty cycle is 15%, frequency upper limit 650Hz (00-12=650.00),
and 03-28=5. Inverter frequency is 15% x 650.00 x 5 = 487.50 Hz
Notes:
- In this mode, pulse input frequency range is 0.01 kHz to 10.00 kHz.
- The examples above are based on a NPN input configuration. If PNP is used, the relationship between duty
cycle and inverter frequency is reversed, so a 20% duty cycle equals 80% inverter frequency
03-02=【26】Pulse Input-Frequency Measure (S3)
When 03-02=26, S3 is used for frequency measurement.
Related Parameters:
00-05=7 (Pulsed Speed Control)
03-02=26 (S3 is the pulse input- frequency measurement)
03-28=0.01~9.99
Inverter Frequency = f x (3-28) Hz, f: Pulse Input Frequency Hz (Limited by the Frequency Upper limit)
4-46
Page 96

Caution
The correct use of this function is the responsibility of the installer of the fire safety system. TWMC bares
no responsibility for direct or indirect damages or loss incurred as a result of using this function.
Warranty is void when inverter damage is caused by using Fire Mode.
Set the following parameters to use pulse input for speed command:
00-05=7
03-02=26
03-28=1 (adjust if required)
03-27: Not used.
Example 1:
Pulse input frequency is 20Hz, frequency upper limit is 50Hz (00-12=50.00), and 03-28=1.
Inverter frequency is 20.00Hz
Example 2:
Pulse input frequency is 45Hz, frequency upper limit is 50Hz (00-12=50.00), and 03-28=1.
Inverter frequency is 45.00Hz
Example 3:
Pulse input frequency is 55Hz, frequency upper limit is 50Hz (00-12=50.00), and 03-28=1.
Inverter frequency is 50.00Hz
Example 4:
Pulse input frequency is 2000Hz, frequency upper limit is 650Hz (00-12=650.00), and 03-28=0.2.
Inverter frequency is 2000 x 0.2 = 400.00Hz
Notes:
- In this mode, pulse input frequency range is 0.01 kHz to 200Hz.
- Pulse input can only be selected for terminal S3
- PLC common is COM terminal on TM2
03-00~03-05=【27】 Enable KEB Function
When active enables KEB (Kinetic Energy Braking) during acceleration. Refer to the parameter description of
07-14.
03-00~03-05=【28】Fire Mode Function
When active inverter runs at maximum speed (parameter 00-12) ignoring any protective functions. Fire Mode
function can be used for applications following a fire where it is necessary for a motor to continue running without
interruption.
Example: Smoke exhaust fans used in buildings for fire evacuation.
4-47
Page 97

03-06
Up/Down Frequency Step
Range
【0.00~5.00】Hz
S1
S2
ON ON ON
Hz
T
△Hz
Actual output
frequency
ON ON ON
Notes:
- To enable Fire Mode function set parameter 08-17 = 1
- The fire Mode function is activated by using one of the multifunction inputs S1 to S6 to a value of 28.
(Parameter 03-00~03-05).
- Fire mode can also be enabled by setting the functions of S1 to S6 via communication.
When Fire Mode is active:
- The keypad shows FIrE, and Fire Mode activation is recorded in the inverter fault log.
- The inverter will run up to the maximum frequency set in 00-12.
- The inverter will keep running unless main power is lost or the inverter breaks down.
- When Fire Mode is activated, all protection functions and alarms (e.g. ES, BB, OV, OC …), will be ignored.
- STOP key on the keypad is disabled during Fire Mode operation.
- To reset fire mode: turn power off, remove fire mode input signal, and power-up inverter.
Example: S1: 03-00=【8】Up frequency command, S2: 03-01=【9】Down frequency command,
03-06=【△】Hz
Mode1: UP or DOWN input terminals are turned on for less than 2 sec. The operation frequency changes by △
Hz (03-06) each time the input terminal is closed.
Mode 2: If UP or DOWN input terminals are closed for more than 2 sec, the original UP/DOWN mode is active
and the output frequency ramps up or down as long as the input is kept ON.
4-48
Page 98

S1
S2
ON
≥2Sec
OFF
OFF
ON
≥2Sec
T
Maximum
output
frequency
△H1
t1
△H2
t2
03-07
Up/Down Keep Frequency Status after Stop Command
Range
【0】: After a stop command in Up/Down mode, the preset frequency is held as the
inverter stops, and the UP/Down function is disabled.
【1】After a stop command in Up/Down mode, the preset frequency is reset to 0 Hz when
the inverter stops.
【2】: After a stop command in Up/Down mode,, the preset frequency is held when the
inverter stops and the UP/Down function remains active.
03-08
Multifunction terminals S1~S6 scan time
Range
【1~200】2ms
03-09
S1~S5 Input Type Selection NO & NC
Range
【xxxx0】:S1 NO 【xxxx1】:S1 NC
【xxx0x】:S2 NO 【xxx1x】:S2 NC
【xx0xx】:S3 NO 【xx1xx】:S3 NC
【x0xxx】:S4 NO 【x1xxx】:S4 NC
【0xxxx】:S5 NO 【1xxxx】:S5 NC
03-10
S6 Input Type Selection NO & NC
Range
【xxxx0】:S6 NO 【xxxx1】:S6 NC
03 - 07 =【0】, When run signal is removed (Stop Command), the output frequency is stored in parameter 05-01
(Keypad Frequency).
03 - 07 =【0】, When stopped the frequency reference is set by parameter 05-01.
03 - 07 =【1】, In Up/down frequency mode inverter will ramp up from 0Hz on Run command and Ramp down to
0 Hz on stop command.
Set the digital input CPU scan time. The digital input signal needs to be present for the minimum scan time to
qualify as a valid command.
Notes:
For noisy environments select scan time of 8ms (results in a slower response time).
Terminal SF is for safety switch, SF can cut off the inverter voltage output.
“NO”: Normally open, “NC”: Normally closed. . Select as required
For selecting Normally Open (NO) or Normally Closed (NC) set the relevant digit in parameter 03-09/03-10 to
0 or 1 as required.
In order to enable parameters 03-09/03-10, set 03-20 = 1 (internal control) beforehand.
Set Parameter 03-09 first before using parameters 00-02/00-03=1 (run mode from External input).
Example: To select S1, S2 as NC and S3, S4, S5 as NO, set 03-09 = 00011
4-49
Page 99

03-11
Multifunction Output Relay RY 1 functions. ( Terminals R1C,R1B, R1A )
03-12
Multifunction Output Relay RY 2 functions. ( Terminals R2B, R2A )
Range
【0】:Run
【1】:Fault
【2】:Set Frequency within the preset range. -------------------------------( refer to 03-14)
【3】:Set Frequency reached. As set by (3-13±3-14) -------------- ( refer to 03-13/03-14)
【4】:Output Frequency Detection 1 (> 03-13) ----------( refer to 03-13)
【5】:Output Frequency Detection 2 (< 03-13) ----------( refer to 03-13)
【6】:Auto-restart
【7】:Momentary AC Power Loss---------------------------------( refer to 07-00)
【8】:Rapid Stop ( Decelerate to Stop)
【9】:Base Block Stop Mode
【10】:Motor Overload Protection (OL1)
【11】:Drive Overload Protection (OL2)
【12】:Over Torque Threshold Level (OL3)
【13】:Preset Current level Reached -------------------------( refer to 03-15/03-16)
【14】:Preset Brake Frequency Reached -----(refer to 03-17/03-18)
【15】:PID Feedback Signal Loss
【16】:Single pre-set count (3-22)
【17】:Dual pre-set count (3-22~23)
【18】:PLC status indicator (00-02)
【19】:PLC control
【20】:Zero Speed
03-13
Frequency Reached Level
Range
【0.00~650.00】 Hz
03-14
Frequency Reached Detection Range (±)
Range
【0.00~30.00】 Hz
Output relay RY function descriptions:
03-11/03-12 =【0】: Run
Output is active when run command is ON or output frequency is greater than 0
03-11/03-12 =【1】: Fault
Output is active during fault condition.
03-11/03-12 =【2】Set Frequency within the preset range
Output is active when the output frequency falls within the frequency reference minus the frequency detection
width (03-14).
4-50
Page 100

FWD
REV
Preset Freq. Reached
Setting (03-13)
Preset Freq. Reached Detection Range (03-14)
When Output Freq. = Preset Freq. Reached Setting (03-13) –
Preset Freq.
Reached Detection Range (03-14), Relay Output will be ON
Output Freq.
ON ON
Relay Output
Hz
Time
0
RUN RUN
Run Command
(03-13) – (03-14)
Preset Freq. Reached
Detection Range, (03-14)
(03-13) - (03-14)
Preset Freq. Reached
Setting (03-13)
FWD
REV
Setting Freq. 2
Setting Freq. 1
Setting Freq. 1
Setting Freq. 2
2*Preset Freq. Reached Detection
Range (03-14)
Relay Output
ON
ON ON
RUN
RUN
RUN
RUN Command
FWD
Hz
Time
0
When, Freq. Detection Range Lower Limit<Setting Freq.<Freq. Detection Range Upper Limit
and Detection Range Lower Limit<Output Freq.<Freq. Detection Range Upper Limit
Relay output is ON(
Allowable tolerance ±0.01)
(03-13)
(03-13)+(03-14)
(03-13)-(03-14)
(03-13)
(03-13)-(03-14)
(03-13)+(03-14)
2*Preset Freq. Reached Detection
Range (03-14)
Freq. Detection Range Upper Limit
Freq. Detection Range Lower Limit
Example: Sets 03-13=30 and 03-14=5, Relay is ON when output frequency is >=25Hz and <= 30Hz.
03-11=【3】: Set Frequency reached
Output is active when the output frequency falls within the frequency detection width (03-14) of the set frequency
detection level (o3-13).
03-11=【4】: Output Frequency Detection 1
Output is active when the output frequency rises above the frequency detection level (03-13) and deactivates when
the output frequency falls below frequency detection level (03-13).
4-51
 Loading...
Loading...