Page 1
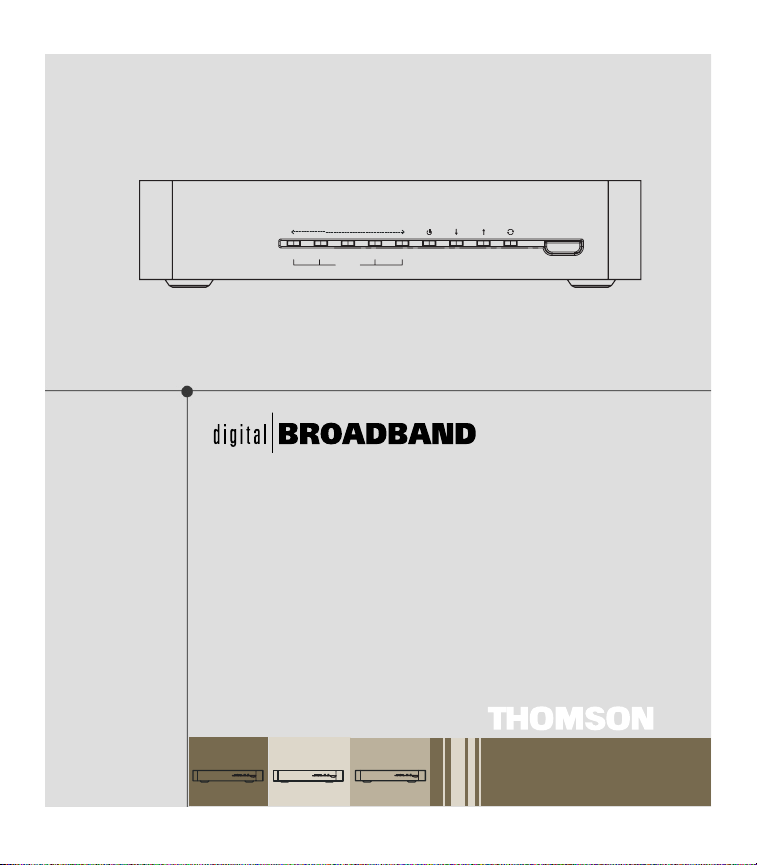
Internet On/Off
Eth2.
Eth3.
Eth1.
PC Link
PowerEth4. WLAN/USB DS
US
ONLINE
Wireless Cable Gateway
User’s Guide
Page 2
Safety Information
CAUTION
Disconnect power before
servicing.
CAUTION
To ensure reliable operation and to prevent overheating, provide
adequate ventilation for this modem and keep it away from
heat sources. Do not locate near heat registers or other heatproducing equipment. Provide for free air fl ow around the cable
modem and its power supply.
CABLE INSTALLER:
This reminder is provided to call your attention to Article 820-40 of the National Electrical Code
(Section 54 of the Canadian Electrical Code, Part 1) which provides guidelines for proper grounding
and, in particular, specifi es that the cable ground shall be connected to the grounding system of the
building as close to the point of cable entry as practical.
DOCSIS compliant
This product was designed according to Data Over Cable Service Interface Specifi cations.
It will operate on any DOCSIS-compliant Hybrid Fiber Coax (HFC) cable system and offers DOCSIS
Baseline Privacy to promote secure Internet transactions.
Power cord Requirement
This product must be operated with the supplied line cord or with a line cord meeting
IEC227 H03 VV-F or IEC227 H03 VVH2-F having conductors with a cross-sectional area
2
not less than .75mm
.
Operating Information
Operating Temperature:0˚ - 40˚ C (32˚ - 104˚ F)
Storage Temperature:-30˚ to 65˚ C
If you purchased this product at a retail outlet, please read the following:
Product Registration
Please fi ll out the product registration card that came with this product and return it immediately. Returning the card
allows us to contact you if needed.
Keep your sales receipt to obtain warranty parts and service and for proof of purchase. Attach it here and record the
serial and model numbers in case you need them. The num bers are located on the back of the product.
Model No. ____________________________________ Serial No _____________________________________________
Purchase Date: _________________________________ Dealer/Address/Phone: _______________________________
Page 3

Table of Contents
Chapter 1: Connections and Setup
Introduction ....................................................................................4
Wireless Cable Gateway Features .......................................................................... 4
What’s on the CD-ROM ............................................................................................. 5
Computer Requirements ........................................................................................... 6
Wireless Cable Gateway Overview ................................................ 6
Important Information .............................................................................................. 7
System Overview .............................................................................8
Understanding the Wireless Cable Gateway ...............................8
Your PC: Installing a PC Network Card ........................................9
Your PC: Installing a TCP/IP Stack ..............................................10
Your PC: Confi guring DHCP on a TCP/IP Stack on a PC ...........12
Confi guring Windows Me PCs .....................................................13
Confi guring Windows 2000 PCs .................................................14
Confi guring Windows XP PCs ......................................................14
Connecting Your Devices .............................................................15
Activating the Wireless Cable Gateway .....................................15
Initialization ...............................................................................................................15
Mandatory User Confi guration ...................................................16
Chapter 2: Networking
Communications ..........................................................................19
USB MAC Address .......................................................................27
MAC and IP Addresses Summary ................................................28
1
Page 4
Table of Contents
Chapter 3: Ad vanced Con fi g u ra tion
Advanced User Con fi g u ra tion ......................................................29
Status Web Page Group ...............................................................30
Software Web Page .................................................................................................30
Connection Web Page ..............................................................................................31
Password Web Page ................................................................................................32
Event Log Web Page ................................................................................................33
Diagnostics Web Page .............................................................................................33
Network Basic Web Page Group .................................................34
WAN Web Page ........................................................................................................34
LAN and Computers Web Pages ..........................................................................35
Advanced Web Page Group .........................................................36
Options Web Page ...................................................................................................36
IP Filtering Web Page .............................................................................................37
MAC Filtering Web Page ........................................................................................37
Port Filtering Web Page .........................................................................................38
Forwarding Web Page .............................................................................................39
Port Triggers Web Page ..........................................................................................40
DMZ Host Web Page ...............................................................................................41
Routing Information Protocol Setup Web Page ...............................................42
Firewall Web Pages Group ...........................................................43
Web Content Filter and Parental Control Web Pages ...................................43
Time of Day Access Filter Web Page ....................................................................44
Local Log and Remote Log Web Pages ................................................................45
2
Page 5

Table of Contents
Wireless Web Pages Group ..........................................................46
Performance ................................................................................................................46
Authentication ...........................................................................................................46
Privacy ..........................................................................................................................47
802.11b/g Basic Web Page ....................................................................................47
802.11b/g Privacy Web Page .................................................................................49
802.11b/g Advanced Web Page ............................................................................53
802.11b/g Access Control Web Page ...................................................................55
Determining WiFi MAC Address ............................................................................56
Bridging Web Page ...................................................................................................58
Chapter 4: Ad di tion al In for ma tion
Troubleshooting ............................................................................59
Front of the Unit ..........................................................................60
Back of the Unit ...........................................................................61
Description of Jacks .................................................................................................61
Detailed Explanation of Jacks ....................................................62
Care and Cleaning ........................................................................63
Service Information ......................................................................63
FCC Declaration of Conformity and Industry
Canada Information ....................................................................64
Product Specifi cations .................................................................65
3
Page 6

Chapter 1: Connections and Setup
Introduction
Wireless Cable Gateway Features
Thank you for purchasing the DCW725 Wireless Cable Gateway. This device delivers the highest
performance in data over cable technology. Ideal for home and small business users, this easyto-use communication device offers reliable connectivity as well as remarkable data transfer
rates – up to 600 times faster than a 56K dial-up modem. Once the DCW725 is activated, you are
online to enjoy real-time 3D animation, video conferencing, and perform other data intensive
tasks.
The Wireless Cable Gateway provides high-speed, reliable and secure transport capabilities and
is designed with DOCSIS upgrade ability for both DOCSIS 1.0, 1.1, and 2.0. The gateway offers
anti-spoofi ng functions, resulting in greater subscriber privacy and higher system availability.
Advanced features such as WLAN IEEE 802.11b/g, NAT, Firewall, VPN pass through and
CableHome are also available now and can be confi gured.
4 Chapter 1
Illustrations contained in this document are for representation only.
Page 7

Chapter 1: Connections and Setup
What’s on the CD-ROM
If you connect a PC using the USB port on your gateway, you’ll need the USB drivers found on the
CD-ROM.
CD-ROM Contents:
• Electronic copy of this user’s guide (.pdf format)
• Adobe Acrobat Reader — application you can load to read .pdf format, if you don’t have it
loaded already
• USB drivers — required if connecting by USB
Chapter 1 5
Page 8
Chapter 1: Connections and Setup
Computer Requirements
• USB 1.0 or 1.1 (PC only), Ethernet (10/100), 802.11b or g
• A TCP/IP network protocol for each machine
• A network cable with RJ-45 connector for Ethernet connection
• Microsoft Internet Explorer 4.0 or later, or Netscape Navigator 4.0 or later. (5.0 and 4.7 or
later, respectively, are strongly recommended.)
• Windows Me, 2000, or XP for USB
Wireless Cable Gateway Overview
Cable Internet Service Requirements
• cable company that offers DOCSIS-compliant Internet services
USB
Link/Act
Ready
Full/Col
Receive
HPNA
Power
100/10
Send
WLAN
Test
Link/Act Cable Modem
1 2 3 4
Computer
Wirelesss Cable Gateway Cable Company
Internet
What the Wireless Cable Gateway Does
The Digital Wireless Cable Gateway serves as a two-way high-speed bridge between your personal
computer and a cable Internet Service Provider (ISP). It converts information that originates from
the Internet or your computer into electronic messages that can be transported over the same
wires your cable company uses to transport video signals.
What the Wireless Cable Gateway Needs to Do Its Job
• The Right Cable Company: Make sure your cable company provides data services that use
cable TV industry-standard DOCSIS technology.
6 Chapter 1
Page 9

Chapter 1: Connections and Setup
• The Internet Service Provider (ISP): Your cable company provides you access to an Internet
Service Provider (ISP). The ISP is your gateway to the Internet. It provides you with a pipeline
to access Internet content on the World Wide Web (WWW).
Check with your cable company to make sure you have everything you need to begin; they’ll
know if you need to install special software or re-confi gure your computer to make your
cable Internet service work for you.
Contact Your Local Cable Company
You will need to contact your cable company to establish an Internet account before you can
use your gateway. You should have the following information ready (which you will fi nd on the
sticker on the gateway) :
• The serial number
• The model number
• The Media Access Control (MAC) address
Record your information here:
S.N.
XXXXXXXXXXXXXX
MODEL:
DCWXXX
MAC:
009064XXXXXX
Please verify the following with the cable company:
• The cable service to your home supports DOCSIS-compliant two-way modem access.
• Your Internet account has been set up.
• You have a cable outlet near your PC and it is ready for cable modem service.
Note: It is important to supply power to the modem at all times. Keeping your modem plugged in will keep it
connected to the Internet. This means that it will always be ready when you are. To disconnect your computer
from the Internet, use the ON/OFF button to put the modem in standby mode.
Important Information
Your cable company should always be consulted before installing a new cable outlet. Do not
attempt any rewiring without contacting your cable company fi rst.
Serial Number: __________________________
Model Number: _________________________
MAC Address: ___________________________
Chapter 1 7
Page 10
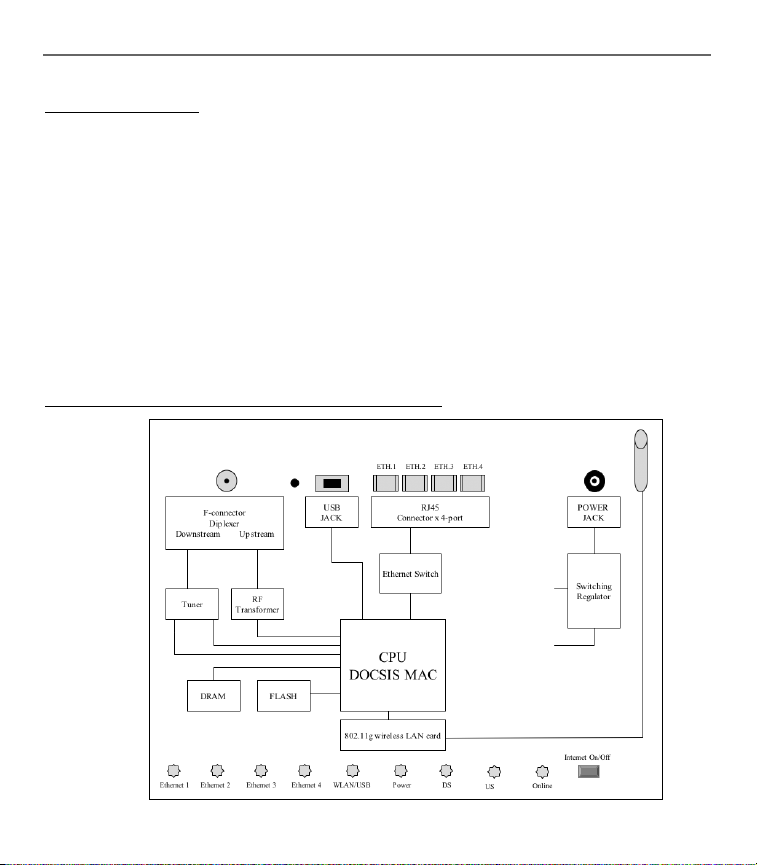
Chapter 1: Connections and Setup
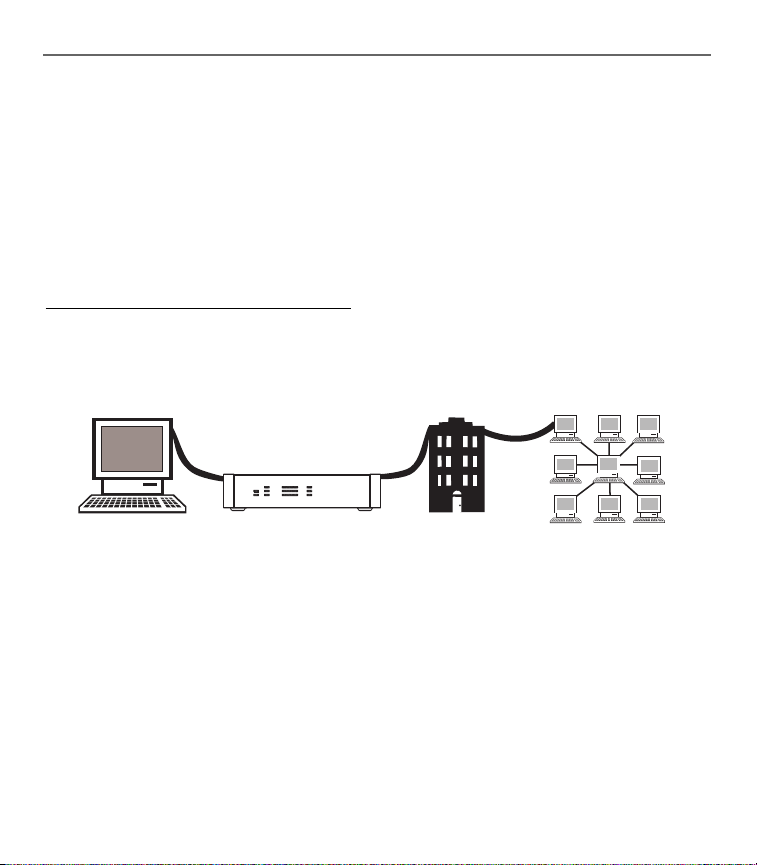
System Overview
The Wireless Cable Gateway is connected between your cable company and the PCs within your
home, as pictured previously in the Wireless Cable Gateway Overview. The connection to the cable
company is made by a coaxial cable, and is referred to as the WAN (Wide Area Network) side of
your Wireless Cable Gateway. The connections to your PCs are made by your choice of several
standard home networking methods: Ethernet, USB, or 802.11b Wireless, and are referred to as the
LAN (Local Area Network) side of your Wireless Cable Gateway. Multiple PCs can use any or all of
the LAN side connections simultaneously to share your single cable company connection, up to a
maximum of 254 PCs total.
Unlike a simple hub or switch, the gateway’s setup consists of more than simply plugging
hardware together. You’ll need to confi gure your networked PCs to accept the IP addresses the
gateway assigns them (if applicable), and you will also need to confi gure the gateway with
settings provided by your cable company.
Understanding the Wireless Cable Gateway
Connections
Fig. 1
8 Chapter 1
Page 11

Chapter 1: Connections and Setup
Your PC: Installing a PC Network Card
If your PC does not already support Ethernet or USB, you must install a network interface card.
Following is an example setup procedure:
1. Install an Ethernet card on your motherboard, following the card’s directions.
2. Power up your PC and follow the Add New Hardware Wizard’s instructions to install the
driver. When asked to restart your computer at the end of the installation, click Yes.
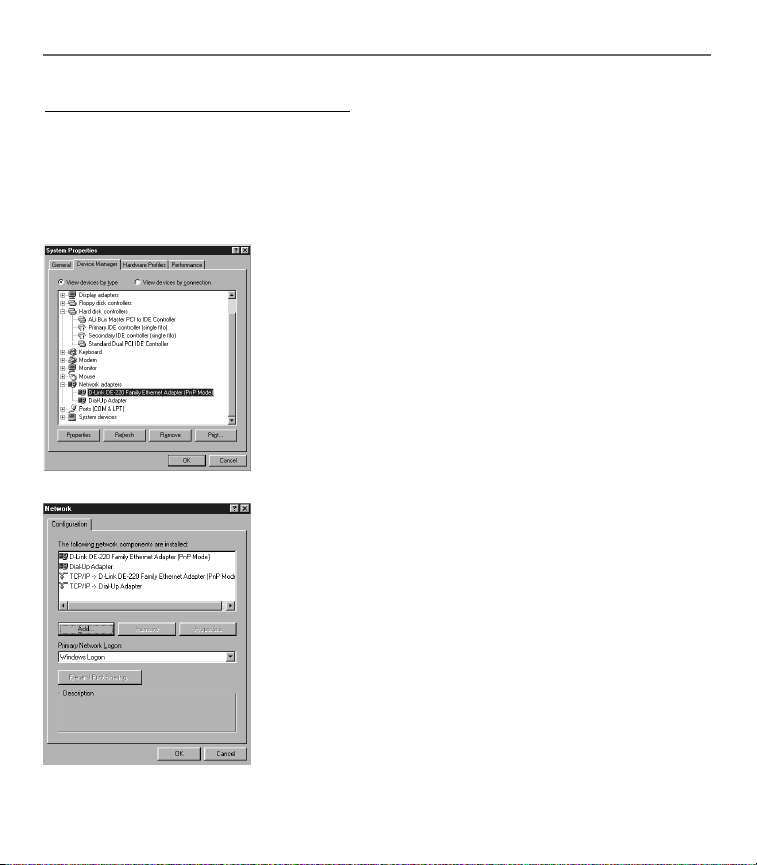
3. After restarting the system, right-click My Computer on the desktop, select Properties,
click the Device Manager tab, and then double-click Network adapters to confi rm that the
Ethernet driver is properly installed.
Chapter 1 9
Page 12
Chapter 1: Connections and Setup
Your PC: Installing a TCP/IP Stack
Follow these instructions to install the TCP/IP protocol stack on one of your PCs only after a
network card has been successfully installed inside the PC. These instructions are for Windows Me.
For TCP/IP setup under Windows NT, 2000, and XP, refer to your Windows documentation.
1. Click the Start button. Choose Settings and then Control Panel.
2. Double-click on the Network icon to bring up your
Network window. Select the Confi guration tab.
3. Click the Add button.
4. Double-click on Protocol.
Fig. 2
5. Highlight Microsoft under the list of manufacturers.
6. Find and double-click TCP/IP in the list to the right (see
Figure 3).
Fig. 3
10 Chapter 1
Page 13

Fig. 4
Fig. 5
Chapter 1: Connections and Setup
7. After a few seconds, the main Network window will appear.
The TCP/IP Protocol should now be listed.
8. Click the OK button again. Windows may ask you for the
original Windows installation disk or additional fi les. Supply
them by pointing to the correct fi le location, e.g., D:\win9x,
c:\windows\options\cabs, etc. (if “D” is the letter of your
CD-ROM drive).
9. Windows will ask you to restart the PC. Click the Yes
button.
The TCP/IP installation is now complete.
Chapter 1 11
Page 14

Chapter 1: Connections and Setup
Your PC: Confi guring DHCP on a TCP/IP Stack on a PC
These instructions will help you confi gure each of your computers to be able to communicate
with the gateway to obtain an IP (or TCP/IP) address automatically (called DHCP, Dynamic Host
Confi guration Protocol).
Find out which operating system your computer is running by clicking the Start button and then
going to the Settings option. Then click Control Panel and double-click the System icon. If your
Start menu doesn’t have a Settings option, you’re running Windows XP. Click the Cancel button
when done.
You may need to do this for each computer you are connecting to the gateway.
Important: These instructions apply only to Windows Me, 2000, or XP machines. For TCP/IP setup
under Windows NT, see your Windows manual. By default Windows 2000, Me, and XP have TCP/IP
installed and set to obtain an IP address automatically.
The next few pages tell you, step by step, how to confi gure your network settings, based on the
type of Windows operating system you are using. Make sure that an Ethernet card or adapter has
been successfully installed in each PC you want to confi gure.
12 Chapter 1
Page 15
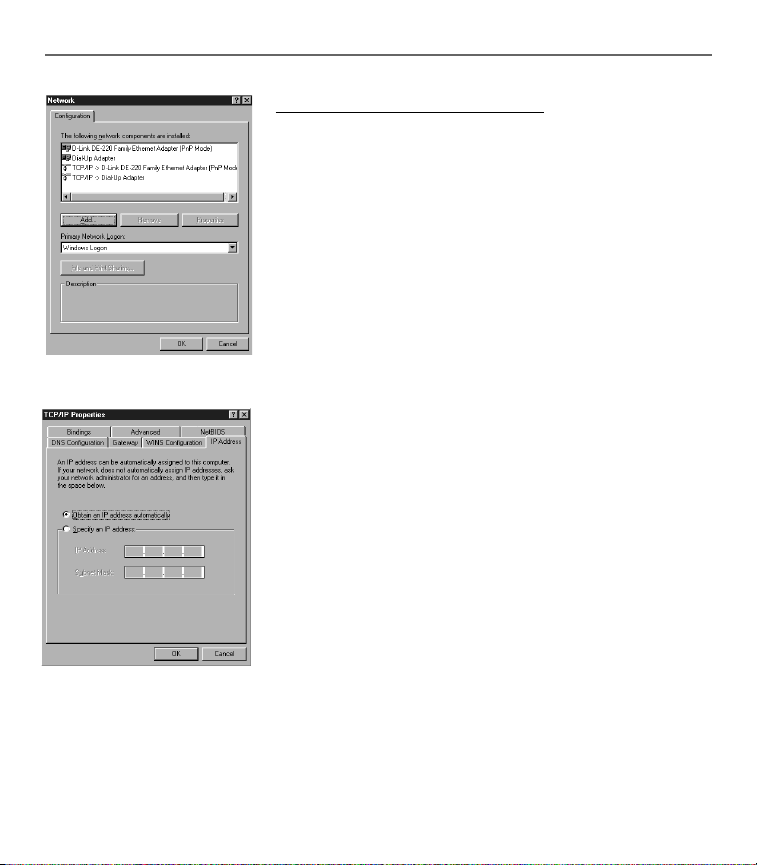
Fig. 6
Chapter 1: Connections and Setup
Confi guring Windows Me PCs
1. Go to the Network screen by clicking the Start button. Click
Settings and then Control Panel. From there, double-click
the Network icon.
2. On the Confi guration tab, select the TCP/IP line for the
applicable Ethernet adapter. Do not choose a TCP/IP entry
whose name mentions DUN, PPPoE, VPN, or AOL. If TCP/IP
appears by itself, select that line. (If there is no TCP/IP line
listed, you need to install a TCP/IP stack). Refer to Your PC:
Installing a TCP/IP Stack. Click the Properties button.
3. Click the IP Address tab. Select Obtain an IP address
automatically.
4. Now click the Gateway tab to ensure that the Installed
gateway fi eld is left blank. Click the OK button.
5. Click the OK button again. Windows may ask you for the
original Windows installation disk or additional fi les. Supply
them by pointing to the correct fi le location, e.g., D:\win9x,
c:\windows\options\cabs, etc. (if “D” is the letter of your
CD-ROM drive).
6. Windows may ask you to restart your PC. Click the Yes
button. If Windows does not ask you to restart, restart your
computer anyway.
Fig. 7
Chapter 1 13
Page 16

Chapter 1: Connections and Setup
Confi guring Windows 2000 PCs
1. Go to the Network screen by clicking the Start button. Click Settings and then Control Panel.
From there, double-click the Network and Dial-up Connections icon.
2. Select the Local Area Connection icon for the applicable Ethernet adapter (it’s usually
the fi rst Local Area Connection listed). Double-click the Local Area Connection. Click the
Properties button.
3. Select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), and click the Properties button.
4. Select Obtain an IP address automatically. Once the new window appears, click the OK
button. Click the OK button again to complete the PC confi guration.
5. Restart your computer.
Confi guring Windows XP PCs
The following instructions assume you are running Windows XP with the default interface. If you
are using the Classic interface (where the icons and menus look like previous Windows versions),
please follow the instructions for Windows 2000.
1. Go to the Network screen by clicking the Start button and then Control Panel. From there,
double-click the Network Internet Connections icon and then the Network Connections
icon.
2. Select the Local Area Connection icon for the applicable Ethernet adapter (it’s usually
the fi rst Local Area Connection listed). Double-click the Local Area Connection. Click the
Properties button.
3. Select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), and click the Properties button.
4. Select Obtain an IP address automatically. Once the new window appears, click the OK
button. Click the OK button again (or the Close button if any settings were changed) to
complete the PC confi guration.
5. Restart your computer.
14 Chapter 1
Page 17

Chapter 1: Connections and Setup
Connecting Your Devices
1. Before you begin, make sure that all of your hardware is powered off, including the gateway,
PCs, hubs, and switches.
2. Connect one end of an Ethernet cable to one of the LAN ports (labeled 1, 2, 3, or 4) on the
back of the gateway and the other end to a standard port on a network device, e.g., a PC,
print server, hub, or switch. Repeat the above step to connect more PCs or network devices to
the gateway.
3. Connect the coaxial cable from the wall to the CABLE jack on the back of the gateway.
4. Connect the power supply cable to the Power jack on the back of the gateway, then plug the
supplied power cable into an AC power outlet.
Activating the Wireless Cable Gateway
Initialization
1. Connect the power cable to the back of the gateway. For the fi rst few seconds of operation,
multiple LEDs will fl ash in unison while the gateway performs self-test diagnostics.
The Cable Modem section of the gateway proceeds with DOCSIS initialization. In this process,
the CM performs the following sequence of steps. For a newly-installed gateway, this can take as
much as 20 minutes to complete.
• Tuning - searching for a downstream DOCSIS CM signal
• Ranging - establishing 2-way communication with the cable company
• Connecting - obtaining the CM IP Address (for IP Stack 1)
• Confi guring - downloading and applying the cable company CM confi guration fi le
• Registering - establishing Internet access with the cable company
During this process, the LED indicators on the front of the unit indicate progress.
• DS – Flashing indicates Tuning; lit solid indicates Tuning step completed successfully.
• US – Flashing indicates Ranging; lit solid indicates Ranging step completed successfully.
• Online – Flashing indicates Connecting, Confi guring, Registering in progress; lit solid
indicates these steps completed successfully.
Chapter 1 15
Page 18

Chapter 1: Connections and Setup
When the Online LED is lit solid, all gateway initialization and startup steps have been
completed successfully, and the gateway should be capable of providing connectivity
between your PCs on the gateway LAN-side and your cable operator on the gateway
WAN-side.
Mandatory User Confi guration
This feature allows you to confi gure the gateway to function in your network and gain access
to the Internet through your cable company. Your ISP may require the use of a Host Name and
Domain Name. You will need to get the setup information from your ISP. If you do not have this
information, please contact your ISP before proceeding.
The instructions from your ISP will tell you how to set up your PC for Internet access.
Also, you must disable any Internet log-on software (such as Ivasion Winpoet or Enternet 300)
and any fi rewall software (such as ZoneAlarm and Watchdog) on all of your PCs.
To set up your gateway for internet access, you will use its built-in web pages feature. The
gateway includes a built-in HTTP server which can deliver many web-style pages of
information with which you can observe your current gateway settings and make changes.
1. Open your web browser. (It’s all right if you get an error
Fig. 8
message at this point. Continue following these directions).
Enter http://192.168.100.1 in the browser’s Address fi eld if
your gateway is in the CM Mode, or http://192.168.0.1 if it
is in the RG or CH Mode. Press the Enter key.
2. An Enter Network Password window appears (for Windows
XP users, the screen may look different). Leave the User
Name fi eld empty, and enter admin in lowercase letters in
the Password fi eld (admin is the default password). Then,
click the OK button.
Fig. 9
16 Chapter 1
Page 19

Chapter 1: Connections and Setup
3. This step is not required with most installations. However, based on setup instructions from
your cable company, you may need to enter the following information. To enter it, navigate
to the Network – WAN gateway web page by clicking Network at the top of the page, then
click WAN (on the left side of the page). Click the Apply button to save your settings.
Host Name and Domain Name: These fi elds allow you to provide a host name and domain
name for the gateway. These fi elds are usually left blank. If requested by your cable company,
complete these two fi elds.
Static IP Address and IP Mask: If your cable company says that you are connected through a
static or fi xed IP address, you should enter the fi eld of Default Gateway, Primary DNS and/or
Secondary DNS also.
Spoofed MAC Address: You can give a spoofed MAC Address to hide your gateway’s real MAC
address. However, this is NOT recommended, as this could cause an address confl ict, causing
your connection to the network to be rejected.
4. The gateway provides a Status Password webpage where you can change the web page’s
access password and restore factory default of the gateway. Also, you can change the default
“admin” password to the desired password. Click the Apply button to save your settings.
IMPORTANT: If you have previously enabled any Internet-Sharing Proxy server software on any of
your PCs, disable it.
Fig. 10
Chapter 1 17
Page 20

Chapter 1: Connections and Setup
Some examples of Internet-sharing software are Internet LanBridge, Wingate, ICS, and Sygate. To
disable your Internet-sharing software:
• If you are running Netscape Navigator: Click Edit >> Preference >> Advanced >> Proxies >,
and click Direct Connection to the Internet.
• If you are running Internet Explorer v5 or better, click Start >> Settings >> Control Panel >>
Internet Options >> Connections >> LAN Settings. Remove the checks from all three boxes.
Click OK to continue.
18 Chapter 1
Page 21

Chapter 2: Networking
Communications
Data communication involves the fl ow of packets of data from one device to another. These
devices include personal computers, Ethernet and USB hubs, cable modems, digital routers and
switches, and highly integrated devices that combine functions, like the Wireless Cable Gateway.
The gateway integrates the functionality often found in two separate devices into one. It’s both
a cable modem and an intelligent wireless gateway networking device that can provide a host
of networking features, such as NAT and fi rewall. Figure 2 illustrates this concept, with the cable
modem (CM) functionality on the left, and networking functionality on the right. In this fi gure,
the numbered arrows represent communication based on source and destination, as follows:
Type of Communication
1. Communication between the Internet and your PCs
Example: The packets created by your request for a page stored at a web site, and the
contents of that page sent to your PC.
2. Communication between your cable company and the cable modem side
Example: When your cable modem starts up, it must initialize with the cable company,
which requires the cable company to communicate directly with the cable modem itself.
3. Communication between your PCs and the networking side
Cable Modem Section
CM
WAN
2
Cable service
Fig. 11
Chapter 2 19
1
Illustrations contained in this document are for representation only.
CM IP
IP Stack 1
Networking Section
Networking
CPE IP
IP Stack 2
LAN
Connected to your PC via:
3
• Ethernet
• 802.11b/g
• USB
1
Page 22

Chapter 2: Networking
Example: The Wireless Cable Gateway offers a number of built-in web pages which you can
use to confi gure its networking side; when you communicate with the networking side, your
communication is following this path.
Each packet on the Internet addressed to a PC in your home travels from the Internet downstream on the cable company’s system to the WAN side of your Wireless Cable Gateway. There it
enters the Cable Modem section, which inspects the packet, and, based on the results, proceeds
to either forward or block the packet from proceeding on to the Networking section. Similarly,
the Networking section then decides whether to forward or block the packet from proceeding on
to your PC. Communication from your home device to an Internet device works similarly, but in
reverse, with the packet traveling upstream on the cable system.
Cable Modem (CM) Section
The cable modem (or CM) section of your gateway uses DOCSIS Standard cable modem technology. DOCSIS specifi es that TCP/IP over Ethernet style data communication be used between the
WAN interface of your cable modem and your cable company.
A DOCSIS modem, when connected to a Cable System equipped to support such modems,
performs a fully automated initialization process that requires no user intervention. Part of this
initialization confi gures the cable modem with a CM IP (Cable Modem Internet Protocol) address,
as shown in Figure 3, so the cable company can communicate directly with the CM itself.
Networking Section
The Networking section of your gateway also uses TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/ Internet
Protocol) for the PCs you connected on the LAN side. TCP/IP is a networking protocol that provides communication across interconnected networks, between computers with diverse hardware
architectures and various operating systems.
TCP/IP requires that each communicating device be confi gured with one or more TCP/IP stacks,
as illustrated by Figure 4. On a PC, you often use software that came with the PC or its network
interface (if you purchased a network interface card separately) to perform this confi guration. To
communicate with the Internet, the stack must also be assigned an IP (Internet Protocol) address.
192.168.100.1 is an example of an IP address. A TCP/IP stack can be confi gured to get this IP
20 Chapter 2
Page 23

Chapter 2: Networking
address by various means, including a DHCP server, by you directly entering it, or sometimes by a
PC generating one of its own.
Ethernet requires that each TCP/IP stack on the Wireless Cable Gateway also have associated with
it an Ethernet MAC (Media Access Control) address. MAC addresses are permanently fi xed into
network devices at the time of their manufacture. 00:90:64:12:B1:91 is an example of a MAC
address.
Data packets enter and exit a device through one of its network interfaces. The gateway offers
Ethernet, USB, and 802.11b/g wireless network interfaces on the LAN side and the DOCSIS
network interface on the WAN side.
When a packet enters a network interface, it is offered to all the TCP/IP stacks associated with the
device side from which it entered. But only one stack can accept it — a stack whose confi gured
Ethernet address matches the Ethernet destination address inside the packet. Furthermore, at a
packet’s fi nal destination, its destination IP address must also match the IP address of the stack.
Each packet that enters a device contains source MAC and IP addresses telling where it came
from, and destination MAC and IP addresses telling where it is going to. In addition, the packet
contains all or part of a message destined for some application that is running on the destination
device. IRC used in an Internet instant messaging program, HTTP used by a web browser, and
FTP used by a fi le transfer program are all examples of applications. Inside the packet, these
applications are designated by their port number. Port 80, the standard HTTP port, is an example
of a port number.
The Networking section of the router performs many elegant functions by recognizing different
packet types based upon their contents, such as source and destination MAC address, IP address,
and ports.
Three Networking Modes
Your gateway can be confi gured to provide connectivity between your cable company and your
home LAN in any one of three Networking Modes: CM, RG, and CH. This mode setting is under the
control of your cable company, who can select the mode to match the level of home networking
support for which you have subscribed. All units ship from the factory set for the RG mode,
but a confi guration fi le which the cable company sends the cable modem section during its
initialization can change it.
Chapter 2 21
Page 24

Chapter 2: Networking
Cable Modem (CM) Mode
Cable
Operator
Fig. 12
WAN
Internet
111.111.1.11
Wireless
Cable
Gateway
Cable
CM Mode
Wireless Cable Gateway
behaves as a bridge
RJ 45 USB
Wireless
CPE 1
111.111.2.11
CPE 2
111.111.2.12
LAN
CPE 3
111.111.2.13
CM/Networking
WAN
IP Stack 1
111.111.1.11
IP Stack 2
192.168.100.1
LAN
Fig. 13
22 Chapter 2
Page 25

Chapter 2: Networking
CM (Cable Modem) Mode provides basic home networking. In this mode, two IP stacks are active:
• IP Stack 1 - for use by the cable company to communicate with the cable modem section
only. This stack receives its IP address from the cable company during CM initialization. It uses
the MAC address printed on the label attached to the Wireless Cable gateway.
• IP Stack 2 - for use by you, the end user, to communicate with the cable modem and
Networking sections, to access the internal web page diagnostics and confi guration. This stack
uses a fi xed IP address: 192.168.100.1. It uses a MAC address of MAC label + 1 (the MAC label
is found on the bottom of the unit). E.g., if the MAC address is 00:90:64:12:B1:91, this MAC
address would be 00:90:64:12:B1:92.
With CM Mode, your cable company must provide one IP address for the CM section, plus one for
each PC you connect from their pool of available addresses. Your cable company may have you
or your installer manually enter these assigned addresses into your PC, or use a DHCP Server to
communicate them to your PCs, or use a method that involves you entering host names into your
PCs.
Note that in CM Mode, packets passing to the Internet to/from your PCs do not travel through
any of the IP stacks; instead they are directly bridged between the WAN and LAN sides.
Chapter 2 23
Page 26

Chapter 2: Networking
Residential Gateway (RG) Mode
Internet
WAN
Fig. 14
Cable
Operator
3360
Wireless
Cable
Gateway
Cable
RJ 45 USB
CPE 1
192.168.0.2
111.111.1.11
CM
IP Stack 1
WAN LAN
111.111.1.11
111.111.2.11
RG & CH Modes
Wireless Cable Gateway
behaves as a gateway
Wireless
CPE 2
192.168.0.3
LAN
Networking
IP Stack 3
IP Stack 5
192.168.0.1
192.168.0.4
CPE 3
Fig. 15
24 Chapter 2
Page 27

Chapter 2: Networking
RG (Residential Gateway) Mode provides basic home networking plus NAT (Network Address
Translation). In this mode, three IP stacks are active:
• IP Stack 1 - for use by the cable company to communicate with the Cable Modem section
only. This stack receives its IP address from the cable company during CM initialization. It uses
the MAC address printed on the label attached to the Wireless Cable Gateway.
• IP Stack 3 - for use by you to remotely (i.e. from somewhere on the WAN side, such as at your
remote workplace) communicate with the Cable Modem and Networking sections, to remotely
access the internal web page diagnostics and confi guration. This stack is also used by your
cable company to deliver packets between the Internet and the gateway’s networking section
so they can be routed to/from your PCs. This stack requires an IP address assigned by the
cable company from their pool of available addresses. Your cable company may have you or
your installer manually enter assigned addresses into your gateway, or use a DHCP Server to
communicate them, or use a method that involves you entering host names. This stack uses a
MAC address of MAC label + 2 (the MAC label is found on the bottom of the unit). E.g., if the
MAC address is 00:90:64:12:B1:91, this MAC address would be 00:90:64:12:B1:93.
• IP Stack 5 - for use by you to locally (i.e. from somewhere on the LAN side in your home)
communicate with the Cable Modem and Networking sections, to access the internal web
page diagnostics and confi guration. This stack is also used by the gateway’s networking
section to route packets between the gateway’s Networking section and your PCs. This stack
uses a fi xed IP address: 192.168.0.1. It uses a MAC address of MAC label + 4 (the MAC label
is found on the bottom of the unit). E.g., if the MAC address is 00:90:64:12:B1:91, this MAC
address would be 00:90:64:12:B1:95.
With RG Mode, your cable company must provide one IP address for the CM section, plus one
for the Networking section, from their pool of available addresses. With RG Mode, each PC you
connect gets an IP address from a DHCP Server that is part of the Networking section of the
gateway.
Chapter 2 25
Page 28

Chapter 2: Networking
CableHome (CH) Mode
CM
IP Stack 1
WAN LAN
Fig. 16
111.111.1.11
IP Stack 3
111.111.2.11
Networking
IP Stack 4
111.111.2.12
IP Stack 5
192.168.0.1
CH (CableHome) Mode provides all the functionality of RG mode and adds the ability of the cable
company to control the home networking confi guration of your Wireless Cable Gateway for you,
so you don’t need to perform the confi guration yourself. In this mode, four IP stacks are active:
• IP Stack 1 - for use by the cable company to communicate with the Cable Modem section
only. This stack receives its IP address from the cable company during CM initialization. It uses
the MAC address printed on the label attached to the Wireless Cable Gateway.
• IP Stack 3 - for use by your cable company to communicate with the Networking section
to help you confi gure and manage your home networking. This stack requires an IP address
assigned by the cable company from their pool of available addresses. Your cable company
may have you or your installer manually enter assigned addresses into your gateway, or use a
DHCP Server to communicate them, or use a method that involves you entering host names.
This stack uses a MAC address of MAC label + 2 (the MAC label is found on the bottom of the
unit). E.g., if the MAC address is 00:90:64:12:B1:91, this MAC address would be 00:90:64:12:
B1:93.
26 Chapter 2
Page 29

Chapter 2: Networking
• IP Stack 4 - for use by you to remotely (i.e. from somewhere on the WAN side, such as at your
remote workplace) communicate with the Cable Modem and Networking sections, to remotely
access the internal web page diagnostics and confi guration. This stack is also used by your
cable company to deliver packets between the Internet and the Wireless Cable Gateway’s
Networking section so they can be routed to/from your PCs. This stack requires an IP address
assigned by the cable company from their pool of available addresses. Your cable company
may have you or your installer manually enter these assigned addresses into your gateway,
or use a DHCP Server to communicate them, or use a method that involves you entering host
names. This stack uses a MAC address of MAC label + 3 (the MAC label is found on the bottom
of the unit). E.g., if the MAC address is 00:90:64:12:B1:91, this MAC address would be 00:90:
64:12:B1:94.
• IP Stack 5 - for use by you to locally (i.e. from somewhere on the LAN side in your home)
communicate with the Cable Modem and Networking sections, to access the internal web
page diagnostics and confi guration. This stack is also used by the Wireless Cable Gateway
Networking section to route packets between the Wireless Cable Gateway’s Networking
section and your PCs. This stack uses a fi xed IP address: 192.168.0.1. It uses a MAC address of
MAC label+ 4 (the MAC label is found on the bottom of the unit). E.g., if the MAC address is
00:90:64:12:B1:91, this MAC address would be 00:90:64:12:B1:95.
With CH Mode, your cable company must provide one IP address for the CM section, plus two for
the Networking section, from their pool of available addresses. Each PC you connect gets an IP
address from a DHCP Server that is part of the Networking section of the gateway.
USB MAC Address
USB allows a single PC to be connected directly via your Wireless Cable Gateway USB port.
Other PCs can, of course, be connected to your other networking interfaces: wireless, HPNA, and
Ethernet. If you have a PC connected by USB, the following information is helpful.
The PCs you have connected by 802.11b/g Wireless, and Ethernet technologies associated with
your gateway all send and receive packets that contain the Ethernet-style MAC address associated
with that network interface. USB technology, however, uses a different addressing approach. In
this situation, your gateway modifi es the packets going to and from your USB-connected PC to
make them look Ethernet-style when passed between you and your cable company. To do this,
the gateway must effectively “loan” an Ethernet-style address for use in all these packets. For
this purpose, the gateway uses a MAC address of MAC label + 5 (the MAC label is found on the
bottom of the unit). E.g., if the MAC address is 00:90:64:12:B1:91, this MAC address would be 00:
90:64:12:B1:96.
Chapter 2 27
Page 30

Chapter 2: Networking
MAC and IP Addresses Summary
This table summarizes all the MAC and IP addresses that may be associated with the TCP/IP
communication stacks and USB handling in your Wireless Cable Gateway. The ones actually
used depend upon your gateway Operating Mode, as explained above. At minimum, your cable
company will need to know the MAC address associated with IP Stack 1, which is the MAC
address shown on the modem label.
Stack Name
IP Stack 1
IP Stack 2
IP Stack 3
IP Stack 4
IP Stack 5
---
MAC and IP Addresses
CM WAN access - all Modes
local management - CM Mode
only
CableHome remote management
- CH Mode only
end-user remote management,
LAN WAN access RG Mode only
WAN data access CH Mode only
local management RG, CH Modes only
LAN gateway
Purpose - Mode
MAC Address
per label on CM
CM label + 1
CM label + 2
CM label + 3
CM label + 4
CM label + 5
IP Address
assigned by cable company
during initialization
fi xed at 192.168.100.1
assigned by cable company
assigned by cable company
fi xed at 192.168.0.1
USB MAC
28 Chapter 2
Page 31

Chapter 3: Advanced Confi guration
Advanced User Confi guration
The Wireless Cable Gateway offers local management capability through a built in HTTP server
and a number of diagnostic and confi guration web pages. These pages are available from
http://192.168.0.1 in RG and CH modes, and http://192.168.100.1 in CM Mode. Not all pages are
available in some modes.
Some information on two of the following web pages MUST BE confi gured, as explained in
Mandatory User Confi guration.
In addition, more confi guration and diagnostics are possible through the following additional
web pages, most of which are aimed at controlling the advanced networking functions of the
gateway.
To navigate between pages, use the hyperlinks on the top of the page, and the side bar on the
left side of the page. For easy navigation, the pages are organized in groups, with group names
at the top of the pages. Individual page names within each group are provided in the sidebar. To
navigate to a page, click the group hyperlink at the top, then the page hyperlink on the sidebar.
Your cable company may not support the reporting of some items of information listed on your
gateway’s internal web pages. In such cases, the information fi eld appears blank. This is normal.
In the CM Mode, the simplest confi guration mode of the gateway, or in the CH Mode, where you
have subscribed to an outside service (your cable company or another party) to remotely manage
your home network confi guration, you will see only the Status and Wireless web page hyperlinks
in the sidebar, indicating only these page groups are available.
In the RG Mode, the mode where you manage your home network confi guration, you will see
web page hyperlinks to all fi ve page groups: Status, Basic, Advanced, Firewall, and Wireless. The
following section explains all of the available pages for all of the modes.
Note: Your gateway complies with DOCSIS standards regarding software upgrades. DOCSIS requires that any
software upgrade to a device that is connected to a cable system, like your gateway, must be "pushed" to the
gateway by the cable operator. Also, the features of the gateway, and the embedded web pages that control
those features, can vary by software version. Therefore, you may fi nd that your gateway's web pages and
features vary slightly from those shown here. This is normal, and is the result of a software upgrade your cable
operator has made to your gateway.
Chapter 3 29
Illustrations contained in this document are for representation only.
Page 32

Chapter 3: Advanced Confi guration
Status Web Page Group
Software Web Page (Fig. 17)
The Information section of this page provides hardware and software information about your
gateway that may be useful to your cable company. You can view your operating software version
but not change it. This is because your gateway adheres to the DOCSIS Cable Modem standard,
which requires that your cable company perform any software upgrade of the gateway from the
gateway WAN side.
The Status section of this page shows how long your gateway has operated since last being
powered up, and some key information the Cable Modem section received during the initialization
process with your cable company. If Network Access shows “Allowed,” then your cable company
has confi gured your gateway to have Internet connectivity. If Network Access shows otherwise,
you may not have Internet access, and should contact your cable company to resolve this.
Fig. 17
30 Chapter 3
Page 33

Chapter 3: Advanced Confi guration
Connection Web Page (Fig. 18)
This page reports diagnostic information about the initialization and operating status of your
gateway that can be useful at the time of installation. It can also be useful to your cable
company’s support technician if you’re having problems.
Fig. 18
Chapter 3 31
Page 34

Chapter 3: Advanced Confi guration
Password Web Page (Fig. 19)
This page is used to set a password that enables you to access all the gateway internal web pages.
The password can be a maximum of 8 characters and is case sensitive. In addition, this page can
be used to restore the gateway to its original factory settings. Use this with caution, as all the
settings you have made will be lost. To perform this reset, set Restore Factory Defaults to YES and
click Apply. This has the same effect as a factory reset using the rear panel reset switch, where
you hold in the switch for 15 seconds, then release.
Fig. 19
32 Chapter 3
Page 35

Chapter 3: Advanced Confi guration
Event Log Web Page (Fig. 20)
This page provides diagnostic information regarding the cable modem section of your gateway
that may be useful to your cable company if you are having startup or operation issues. As long
as your gateway startup and operational performance is normal, any messages contained in this
log can be ignored.
Diagnostics Web Page (Fig. 21)
This page verifi es you have IP connectivity from your gateway to other IP addresses on the LAN
side, such as when you want to confi rm you have successfully confi gured one of your PCs for
TCP/IP operation.
When you ping an Internet device, you send a packet to its TCP/IP stack, and it sends one back to
yours. Enter the IP address you want to ping, then click Start Test. Wait a few seconds, then click
your web browser’s refresh button. Success reported in the Results box means IP connectivity is
working from your CM TCP/IP stack to the target’s stack.
Note: Firewalls may cause pings to fail but still provide you TCP/IP access to selected devices behind them. Keep
this in mind when pinging a device that may be behind a fi rewall. Ping is most useful to verify connectivity with
PCs you know have no fi rewall, such as your own PCs on your LAN side.
Fig. 21Fig. 20
Chapter 3 33
Page 36

Chapter 3: Advanced Confi guration
Network Web Page Group
WAN Web Page (Fig. 22)
This page gives you the ability to enter some data your cable company may require, as explained
before in Mandatory User Confi guration. In addition, it enables you to view your WAN side IP
address and lease information.
Your gateway can provide NAT/PAT (Network and Port Address Translation) as an element of
security to prevent others from reaching your PCs when not authorized. To accomplish this, the
gateway watches packets you send from your PC to Internet sites. Each time you send to a site
(destination IP address) and application at that site (port), it translates your PC’s original IP and
source port to new ones, and adds a row to its Connection Table maintained internally. (Note the
different meaning of ‘connection’ here to describe an IP connection versus a physical cabling
connection). If and when that site/application replies, it looks up the connection and reverses the
IP/port process to direct the response to your PC.
The Connection Table manages itself, but you can also force this table to be cleared manually. To
do this, click the Renew NAT Lease button.
You can enter a spoofed MAC address that causes your gateway networking stack to use that
MAC address when communicating instead of the usual WAN MAC address (CM label + 2, as
explained in Chapter 2). Enter the desired MAC address and click Apply.
Caution: If you enter a MAC address in use by another party, it can cause an address confl ict on
the network that could affect both you and that party.
Fig. 22
34 Chapter 3
Page 37

Chapter 3: Advanced Confi guration
LAN and Computers Web Pages (Fig. 23 and 24)
These pages give you the ability to activate and deactivate the DHCP server function of your
gateway, and, if the DHCP server is activated, to see DHCP leases it has provided.
With this function activated, your cable company’s DHCP server provides one IP address for your
gateway, and your gateway’s DHCP server provides IP addresses, starting at the address you set in
IP Address on the LAN page, to your PCs. A DHCP server leases an IP address with an expiration
time.
To change the lowest IP address that your gateway will issue to your PCs, enter it into the IP
Address box and then click Apply.
To set the maximum number of PCs to which the gateway will issue IP addresses, enter it in the
Number of CPEs box and then click Apply. (CPE is another term sometimes used for PC.)
The Computers web page section shows leases the gateway DHCP server has made, including the
IP and MAC addresses of each PC’s TCP/IP stack. Since MAC addresses are unique and permanently
fi xed into hardware, you can identify any PC listed by its MAC address. The gateway provides
leases for 7 days, and has an automatic renewal mechanism that will keep extending a lease as
long as the associated PC remains active. If your PC is set to “obtain an IP address automatically,”
it is set to perform DHCP each time it is rebooted.
You can cancel an IP address lease by selecting it in the DHCP Client Lease Info list and then
clicking the Force Available button. If you do this, you may have to perform a DHCP Renew on
that PC, so it can obtain a new lease.
Fig. 23
Fig. 24
Chapter 3 35
Page 38

Chapter 3: Advanced Confi guration
Advanced Web Page Group
Options Web Page (Fig. 25)
This page allows you to enable/disable some features of the Wireless Cable Gateway. Check WAN
Blocking and then click Apply to prevent others on the WAN side from being able to ping your
gateway. With WAN Blocking on, your gateway will not respond to pings it receives, effectively
“hiding” your gateway.
Check Ipsec Pass Through and then click Apply to enable IpSec type packets to pass WAN <=>
LAN. IpSec (IP Security) is a security mechanism used in Virtual Private Networks (VPNs). E.g., your
employer may offer VPN connectivity to your offi ce network to provide security.
Check PPTP Pass Through and then click Apply to enable PPTP type packets to pass WAN <=>
LAN. PPTP (Point to Point Tunneling Protocol) is another mechanism sometimes used in VPNs.
Check Remote Confi g Management and then click Apply to make the confi guration web pages
in your gateway accessible from the WAN side. Then you could, for example, access your home
gateway confi guration from your workplace, if that location also had Internet connectivity.
Page access is limited to only those who know the gateway access password you set using the
Status...Password web page.
This function works only if your gateway is in the RG mode. When accessing your gateway from
a remote location, you must use HTTP port 8080 and your IP Stack 3 address. This is the "WAN IP
address" that appears at the Network...WAN page. For example, if this IP address were 157.254.5.7,
you would navigate to http://157.254.5.7:8080 to reach your gateway from a remote location.
Fig. 25
36 Chapter 3
Page 39

Chapter 3: Advanced Confi guration
Check Multicast Enable and then click Apply to enable multicast traffi c to pass WAN <=> LAN.
You may need to enable this to see some types of broadcast streaming and content on the
Internet, such as webcasting of a popular live event.
IP Filtering Web Page (Fig. 26)
This page enables you to enter the IP address ranges of PCs on your LAN that you don’t want to
have outbound access to the WAN. These PCs can still communicate with each other on your LAN,
but packets they originate to WAN addresses are blocked by the gateway.
MAC Filtering Web Page (Fig. 27)
This page enables you to enter the MAC address of specifi c PCs on your LAN that you wish to NOT
have outbound access to the WAN. As with IP fi ltering, these PCs can still communicate with each
other through the gateway, but packets they send to WAN addresses are blocked.
Fig. 26
Fig. 27
Chapter 3 37
Page 40

Chapter 3: Advanced Confi guration
Port Filtering Web Page (Fig. 28)
This page enables you to enter ranges of destination ports (applications) that you don’t want
your LAN PCs to send packets to. Any packets your LAN PCs send to these destination ports will
be blocked. For example, you could block access to worldwide web browsing (HTTP = port 80) but
still allow email service (SMTP port 25 and POP-3 port 110). To enable fi ltering, set Start Port and
End Port for each range, and click Apply. To block only one port, set both Start and End ports the
same.
Fig. 28
38 Chapter 3
Page 41

Chapter 3: Advanced Confi guration
Forwarding Web Page (Fig. 29)
For LAN <=> WAN communications, the gateway normally only allows you to originate an
IP connection with a PC on the WAN; it will ignore attempts of the WAN PC to originate a
connection onto your PC. This protects you from malicious attacks from outsiders. However,
sometimes you may wish for anyone outside to be able to originate a connection to a particular
PC on your LAN if the destination port (application) matches one you specify.
This page allows you to specify up to 10 such rules. For example, to specify that outsiders should
have access to an FTP server you have running at 192.168.0.5, create a rule with that address and
Start Port = 20 and End Port = 21 (FTP port ranges) and Protocol = TCP (FTP runs over TCP vs the
other transport protocol, UDP), and click Apply. This will cause inbound packets that match to
be forwarded to that PC rather than blocked. As these connections are not tracked, no entry is
made for them in the Connection Table. The same IP address can be entered multiple times with
different ports.
Fig. 29
Chapter 3 39
Page 42

Chapter 3: Advanced Confi guration
Port Triggers Web Page (Fig. 30)
Some Internet activities, such as interactive gaming, require that a PC on the WAN side of your
gateway be able to originate connections during the game with your game playing PC on the
LAN side. You could use the Advanced...Forwarding page to construct a forwarding rule during
the game, and then remove it afterwards (to restore full protection to your LAN PC) to facilitate
this. Port Triggering is an elegant mechanism that does this work for you, each time you play the
game.
Port Triggering works as follows. Imagine you want to play a particular game with PCs somewhere
on the Internet. You make a one time effort to set up a Port Trigger for that game, by entering
into Trigger Range the range of destination ports your game will be sending to, and entering into
Target Range the range of destination ports the other player (on the WAN side) will be sending
to (ports your PC’s game receives on). Application programs like games publish this information
in user manuals. Later, each time you play the game, the gateway automatically creates the
forwarding rule necessary (see Advanced...Forwarding discussion above). This rule is valid until
10 minutes after it sees game activity stop. After 10 minutes, the rule becomes inactive until the
next matched outgoing traffi c arrives.
For example, suppose you specify Trigger Range from 6660 to 6670 and Target Range from 113
to 113. An outbound packet arrives at the gateway with your game-playing PC source IP address
192.168.0.10, destination port 6666 over TCP/IP. This destination port is within the Trigger Range,
so the gateway automatically creates a forwarding rule to forward any inbound packets destined
for port 113 to your game-playing PC at 192.168.0.10.
You can specify up to 10 port ranges on which to trigger.
Fig. 30
40 Chapter 3
Page 43

Chapter 3: Advanced Confi guration
DMZ Host Web Page (Fig. 31)
Use this page to designate one PC on your LAN that should be left accessible to all PCs from the
WAN side, for all ports. For example, if you put an HTTP server on this machine, anyone will be
able to access that HTTP server by using your gateway IP address as the destination. A setting of
“0” indicates NO DMZ PC. “Host” is another Internet term for a PC connected to the Internet.
Fig. 31
Chapter 3 41
Page 44

Chapter 3: Advanced Confi guration
Routing Information Protocol Setup Web Page (Fig. 32)
This feature enables the gateway to be used in small business situations where more than one LAN
(local area network) is installed. The RIP protocol provides the gateway a means to "advertise"
available IP routes to these LANs to your cable operator, so packets can be routed properly in this
situation.
Your cable operator will advise you during installation if any setting changes are required here.
Fig. 32
42 Chapter 3
Page 45

Chapter 3: Advanced Confi guration
Firewall Web Pages Group
Web Content Filter and Parental Control Web Pages (Fig. 33 and 34)
These pages allow you to enable, disable, and confi gure a variety of fi rewall features associated
with web browsing, which uses the HTTP protocol and transports HTML web pages. On these
pages, you designate the gateway packet types you want to have forwarded or blocked. You can
activate settings by checking them and clicking Apply. Here are some of your choices on the
Parental Control page:
• Activate Keyword Blocking and specify some keywords in the Keyword List to cause blocking
of web pages on the WAN side with the specifi ed keyword in the content.
• Activate Domain Blocking and specify some Domain Names (e.g. disney.com) in the Domain
List.
Other types of web-related fi ltering features can be activated from the Web Content Filter page,
including Filter Proxy, Filter Cookies, Filter Java Applets, Filter ActiveX, Filter Popup Windows, and
Firewall Protection.
If you want the gateway to exclude your selected fi lters to certain computers on your LAN, enter
their MAC addresses in the Trusted Computers area of this page.
Fig. 33
Fig. 34
Chapter 3 43
Page 46

Chapter 3: Advanced Confi guration
Time of Day Access Filter Web Page (Fig. 35)
Use this page to set rules that will block specifi c LAN side PCs from accessing the Internet, but
only at specifi c days and times. Specify a PC by its hardware MAC address, then use the tools to
specify blocking time. Finally, click the Apply button to save your settings.
Fig. 35
44 Chapter 3
Page 47

Chapter 3: Advanced Confi guration
Local Log and Remote Log Web Pages (Fig. 36 and 37)
The gateway builds a log of fi rewall blocking actions that the Firewall has taken.
Using the Local Log page lets you specify an email address to which you want the gateway to
email this log. You must also tell the gateway your outgoing (i.e. SMTP) email server’s name, so
it can direct the email to it. Enable Email Alerts has the gateway forward email notices when
Firewall protection events occur. Click E-mail Log to immediately send the email log. Click Clear
Log to clear the table of entries for a fresh start.
The log of these events is also visible on the screen. For each blocking event type that has taken
place since the table was last cleared, the table shows Description, Count, Last Occurrence, Target,
and Source.
The Remote Log page allows you to specify the IP address where a SysLog server is located and
select different types of fi rewall events that may occur. Then, each time such an event occurs,
notifi cation is automatically sent to this log server.
Fig. 36 Fig. 37
Chapter 3 45
Page 48

Chapter 3: Advanced Confi guration
Wireless Web Pages Group
Important: Changes to the wireless web pages should be made from a PC that is hard wired to the gateway.
The Wireless web pages group enables a variety of settings that can provide secure and reliable
wireless communications for even the most demanding tech-savvy user.
The DCW725 gateway offers a choice of 802.1X, WPA and WPA-PSK authentication of your PCs
to the gateway, 64 and 128 bit WEP encryption of communication between the gateway and your
PCs to guaranty privacy, and an Access Control List function that enables you to restrict wireless
access to only your specifi c PCs.
The wireless function will probably work in your home as shipped from the factory, but without
the security features activated. In addition, the factory default wireless channel setting may not
provide optimum performance in your home due to interference from other wireless devices.
Therefore, the following minimum changes are recommended from the factory defaults, to secure
your wireless communications and provide optimum performance.
Performance
Because your wireless communication travels through the air, the factory default wireless channel
setting may not provide optimum performance in your home if you or your neighbors have
other interfering 2.4 GHz devices such as cordless phones. If your wireless PC is experiencing very
sluggish or dramatically slower communication compared with the speed you achieve on your
PC that is wired to the gateway, try changing the channel number. See the 802.11b/g Basic Web
Page discussion below for details.
Authentication
Authentication enables you to restrict your gateway from communicating with any remote
wireless PCs that aren’t yours. The following minimum authentication-related changes to factory
defaults are recommended. See the 802.11b/g Basic and Access Control Web Page discussions
below for details.
Network Name (SSID) – set to a unique name you choose
Network Type – set to Open
Access Control List - enter your wireless PCs' MAC addresses
46 Chapter 3
Page 49

Chapter 3: Advanced Confi guration
Privacy
Privacy secures or scrambles messages traveling through the air between your wireless PCs and
the gateway, so they can't be observed by others. The following minimum privacy-related setting
changes to factory defaults are recommended. See the 802.11b/g Privacy Web Page discussion
below for details.
Data Encryption – set to WEP (64-bit)
PassPhrase – use this feature to generate security keys
802.11b/g Basic Web Page (Fig. 38)
Use this page to confi gure the wireless 802.11b/g channel in the 2.4 GHz band you want to use
and the SSID you will use. These must match the settings you make on your wireless-equipped PC
you want to be a part of your LAN.
The SSID is your Network Name. Change the factory default to a name of your choice up to 32
characters long. The wireless radio in your gateway can be completely de-activated by changing
Interface to Disabled. Click the Apply button to save your settings.
The Network Type control is used to hide or reveal your network name to any remote, wireless
equipped PC in the area that may be scanning WiFi channels to fi nd available WiFi networks. The
gateway WiFi radio frequently transmits a beacon signal which can contain this network name
(SSID). If you set Network Type to Open, your SSID is included in that beacon, and is therefore
detectable by any nearby wireless equipped PCs in the area. The benefi t of using Open, is it can
speed your WiFi setup on some PCs. If you set Network Type to Closed, your SSID is not included
in the beacon. This hides your network name, but as a result may require a bit more effort on your
part to set up your wireless PCs.
Details of all settings on the 802.11b/g Basic Web Page are provided in Table 1.
Fig. 38
Chapter 3 47
Page 50

Chapter 3: Advanced Confi guration
Setting Description Value List or Range Default
Network
Name
(SSID)
Network
Type
New
Channel
Interface
Table 1. Basic Settings Defi nitions
Sets the Network Name (also
known as SSID) of this network.
Selecting Closed hides the network
from active scans. Selecting Open
reveals the network to active scans.
Selects a particular channel on
which to operate.
Enables or disables the wireless
interface.
Up to 32-character string
containing ASCII characters
with codes between 0x20 and
0x7e
Open, Closed
1 - 11
Enabled, Disabled
THOMSON
Open
1
Enabled
48 Chapter 3
Page 51

Chapter 3: Advanced Confi guration
802.11b/g Privacy Web Page (Fig. 39)
The Privacy feature in the wireless section encrypts, i.e. effectively “scrambles,” all radio
communication between your gateway and remote wireless-connected PCs. This provides WiredEquivalent Privacy (WEP) on your wireless LAN. Use this page to activate encryption if desired,
and set the type to use, as well as the encryption keys.
An easy way to generate encryption keys for WEP is to use the Generate WEP Keys button on this
page. First, set Data Encryption to WEP (64) or WEp (129). Then, enter a word or phrase (up to 32
characters long) in the PassPhrase box. Finally, click the Generate WEP Keys button. The gateway
will generate digital encryption keys from the phrase and populate the Network Key 1, 2, 3 and 4
boxes with them. You may have to refresh the page in your web browser to see the results.
Advanced users may want to adjust additional security settings. Details of all available settings on
the 802.11b/g Privacy Web Page are provided in Tables 2, 3, and 4.
802.11b/g Advanced Web Page (Fig. 40)
Fig. 39
Chapter 3 49
Page 52

Chapter 3: Advanced Confi guration
Setting Description Value List or Range Default
Network
Authentication
WPA PreShared Key
WPA Group
Rekey Interval
RADIUS
Server
RADIUS Port
RADIUS KEY
Data
Encryption
Shared Key
Authentication
PassPhrase1
Network Key 1
thru Network
Key 4
Current
Network Key
Sets the network authentication method.
802.1X and WPA require that valid RADIUS
parameters be set. WPA-PSK requires a valid
WPA Pre-Shared Key to be set.
Sets the WPA Pre-Shared Key (PSK).
Sets the WPA Group Rekey Interval in
seconds. Set to zero to disable periodic
rekeying.
Sets the IP address of the RADIUS server
to use for authentication and dynamic key
derivation.
Sets the UDP port number of the RADIUS
server. The port number is usually 1812 or
1645 and depends upon the server.
Sets the shared secret for the RADIUS
connection.
Selecting Off disables data encryption.
Selecting WEP enables WEP data
encryption and requires that a valid
network key be set and selected unless
802.1X is enabled.
Sets whether shared key authentication is
required to associate. A valid network key
must be set and selected if required.
Sets the text to use for WEP keys
generation.
Enter 5 ASCII characters or 10
hexadecimal digits for a 64-bit key. Enter
13 ASCII characters or 26 hexadecimal
digits for a 128-bit key.
Selects which network key is used for
encrypting outbound data and/or
authenticating clients.
Table 2. Privacy Settings Defi nitions
Disabled, 802.1x, WPA,
WPA-PSK
Depends on Network
Authentication setting. See Table 3.
Depends on Network
Authentication setting.
See Table 3.
Depends on Network
Authentication setting.
See Table 3.
Depends on Network
Authentication setting.
See Table 3.
Depends on Network Authentication
setting. See Table 3.
Depends on Network
Authentication setting.
See Table 3.
Depends on Network
Authentication setting.
See Table 3.
Depends on Network Authentication
and Data Encryption settings. See
Table 3 and Table 4.
Depends on Network Authentication
and Data Encryption settings. See
Table 3 and Table 4.
Depends on Network Authentication
and Data Encryption settings. See
Table 3 and Table 4
Disabled
<NULL>
0
<NULL>
1812
<NULL>
Off (Disabled,
802.1x); TKIP
(WPA, WPPSK)
Optional
<NULL>
<NULL>
1
50 Chapter 3
Page 53

Chapter 3: Advanced Confi guration
Network
Authentication Disabled 802.1x WPA WPA-PSK
WPA Pre-Shared
Key
WPA Group
Rekey Interval
RADIUS Server
RADIUS Port
RADIUS Key
Data Encryption
Shared Key
Authentication
PassPhrase
Network Key 1
thru Network
Key 4
Current Network
Key
Disabled
(grayed out)
Disabled
(grayed out)
Disabled
(grayed out)
Disabled
(grayed out)
Disabled
(grayed out)
Off, WEP (64-bit),
WEP (128-bit)
Optional, Required
See Table 4.
See Table 4.
See Table 4.
Disabled
(grayed out)
Disabled
(grayed out)
IP v.4 address
0 to 65535
0 to 255 character
ASCII string
WEP (128-bit)
Disabled
(grayed out)
Disabled
(grayed out)
Disabled
(grayed out)
Disabled
(grayed out)
Disabled
(grayed out)
0 to 232-1
IP v.4 address
0 to 65535
0 to 255 character
ASCII string
TKIP, AES
Disabled
(grayed out)
Disabled
(grayed out)
Disabled
(grayed out)
Disabled
(grayed out)
Either a 64-digit
hexadecimal number
*or* an 8 to 63 character
ASCII string.
0 to 232-1
Disabled
(grayed out)
Disabled
(grayed out)
Disabled
(grayed out)
TKIP, AES
Disabled
(grayed out)
Disabled
(grayed out)
Disabled
(grayed out)
Disabled
(grayed out)
Table 3. Parameter Value List/Range Dependencies on Network Authentication Setting
Chapter 3 51
Page 54

Chapter 3: Advanced Confi guration
Data Encryption Off WEP (64-bit), WEP (128-bit)
Setting
PassPhrase
Disabled (grayed out)
Up to 32 character string
containing ASCII characters with
codes between 0x20 and 0x7e
Network Key 1 thru
Network Key 4
Current Network Key
Table 4. WEP-Specifi c Parameter Value List/Range Dependencies on Data Encryption Setting
Disabled (grayed out)
Disabled (grayed out)
5 or 13 ASCII characters or 10 or 26
hexadecimal digits
1 to 4
52 Chapter 3
Page 55

Chapter 3: Advanced Confi guration
This page enables some advanced 802.11b settings to be made. The factory default values should
provide good results in most cases. We don’t recommend you change these settings unless you
have technical knowledge of 802.11b wireless technology.
For expert users, details of all settings on the 802.11b/g Privacy Web Page are provided in Table 5.
Fig. 40
Chapter 3 53
Page 56

Chapter 3: Advanced Confi guration
Setting Description Value List or Range Default
54g™
Network Mode
54g™
Protection
Rate
Output Power
Beacon
Interval
DTIM Interval
Fragmentation
Threshold
RTS Threshold
Sets the network mode. Max
compatibility interoperates with the
widest variety of 54g and 802.11b
clients. 54g only accepts 54g clients.
Max performance provides the
highest throughout and accepts only
54g clients; nearby 802.11b networks
may have degraded performance.
In Auto mode, the AP will use RTS/CTS
to improve 802.11g performance in
mixed 802.11g/802.11b networks. Turn
protection Off to maximize 802.11g
throughput under most conditions.
Forces the transmission rate for the AP
to a particular speed.
Sets the output power relative to the
hardware's maximum capability.
Sets the beacon interval for the AP.
Sets the wakeup interval for clients in
power-save mode
Sets the fragmentation threshold.
Sets the RTS threshold.
Table 5. Advanced Settings Defi nitions
Max compatibility, 54g only, Max
performance
Off, Auto
Auto, 1 Mbps, 2 Mbps, 5.5 Mbps,
6 Mbps, 9 Mbps, 11 Mbps, 12 Mpbs,
18 Mbps, 24 Mbps, 36 Mbps,
48 Mbps, 54 Mbps
100%, 75%, 50%, 25%
1..65535
1..255
256..2346
1..2347
Max
compatibility
Auto
Auto
100%
100
3
2346
2347
54 Chapter 3
Page 57

Chapter 3: Advanced Confi guration
802.11b/g Access Control Web Page (Fig. 41)
The access control feature enables you to restrict wireless access to specifi c computers. Use this
feature to prevent outsider wireless PCs from connecting to your private network.
Fig. 41
Your Gateway identifi es wireless PCs by their WiFi MAC Address. This address consists of a string
of 6 pairs of numbers 0 – 9 and letters A - F, such as 00 90 4B F0 FF 50. It is usually printed on
the WiFi card of the device (e.g. the PCMCIA card in a laptop). It can also be determined from a
Windows DOS prompt as explained below.
The Connected Clients list on the Access Control Web Page always shows PCs that currently have
wireless connections to your Gateway.
Your Gateway default access control confi guration (MAC Restrict Mode Disabled) allows access
within reception range by any computer that has your same privacy (key) settings.
To restrict access to only specifi c computers:
1. Set MAC Restrict Mode to Allow.
2. Enter the WiFi MAC addresses of the PCs you want to have access.
3. Click on the Apply button.
To remove access privileges for a listed computer:
1. Select the MAC address in the list.
2. Press the DELETE key on your keyboard.
3. Click on the Apply button to make the changes effective.
More details of settings on the 802.11b/g Access Control Web Page are provided in Table 6.
Chapter 3 55
Page 58

Chapter 3: Advanced Confi guration
Determining WiFi MAC Address (Fig. 42)
If a printed WiFi MAC address for a PC cannot be found, it can be determined as follows from the
MS-DOS prompt in the MS Windows running on that computer:
1. Start MS-DOS. In Windows 98, this is “Start” ... “Run” ,,, [type in] “command” ... “OK”. In
Windows Me, 2k and XP, this is “Start” ... “Run” ... [type in] “cmd” ... OK.
2. List your installed interfaces, by typing “ipconfi g /all” and pressing ENTER.
3. Find the MAC address associated with the interface description that matches your wireless
card description. In this example, the phrase “802.11b PCMCIA” clearly identifi es the WiFi card
among the listed interfaces.
Fig. 42
56 Chapter 3
Page 59

Chapter 3: Advanced Confi guration
Setting Description Value List or Range Default
MAC
Restrict
Mode
MAC
Addresses
Connected
Clients
Table
Table 6. Access Control Settings Defi nitions
Selects whether clients with the
specifi ed MAC address are allowed
or denied wireless access.
Allows or denies wireless access to
clients with the specifi ed MAC addresses. Accepted input MAC address
formats are
XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX and
XX-XX-XX-XX-XX-XX. The display
format is
XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX.
Provides a list of all connected
wireless clients, including Host
Name, IP Address, and Client ID.
Clients with either dynamic or static
IP addresses are listed.
Disabled, Allow, Deny
16 addresses
Disabled
<NULL>
Chapter 3 57
Page 60

Chapter 3: Advanced Confi guration
Bridging Web Page (Fig. 43)
The Bridging page provides a location where settings can be adjusted related to the wireless WDS
(Wireless Distribution System) feature. The wireless gateway can be placed in a mode that allows
the gateway to communicate with other “extender” wireless access points either exclusively or
mixed with communications to local PCs. Use this page to designate the Remote Bridges the
gateway is allowed to communicate with, and to select the Wireless Bridging mode.
Fig. 43
58 Chapter 3
Page 61

Chapter 4: Additional Information
Troubleshooting
You can correct most problems you have with your product by consulting the troubleshooting list
that follows. If you need service, please contact your service provider.
Unit won’t turn on
• Make sure the unit is plugged in.
• Check the wall receptacle (or extension cord) to make sure it is “live” by plugging in
something else.
Gateway appears to be locked up
• First, try a power cycle, as this action preserves settings you have made in the gateway
confi guration: remove power to the gateway by disconnecting the power cord for 30
seconds, then reconnect it. Wait for the gateway startup steps to complete, then retry
operation.
• As a last resort, press and hold the RESET button on the back of the unit for 15 seconds, then
release. Wait for the gateway startup steps to complete and retry operation. Remember, the
Reset process returns all confi guration settings to the factory defaults.
No connection after more than 5 minutes
• Make sure all connections are secure and try connecting to your service provider again. Verify
the Internet On/Off button is set to ON (the Online LED will be lit solid). If you still have
problems connecting to the network, contact your service provider.
Chapter 4 59
Illustrations contained in this document are for representation only.
Page 62

Chapter 4: Additional Information
Internet On/Off
Eth2.
PC Link
Eth3.
PowerEth4. WLAN/USB DS
Eth1.
US
ONLINE
4213
Front of the Unit (from left to right)
1. The LAN indicators
Eth1 – Eth4 Indicates when an Ethernet interface is active.
WLAN/USB Indicates when either the wireless or USB interface is active.
2. Power Indicates when the unit is on.
3. The WAN indicators
DS (downstream) Flashes during the stage of DOCSIS startup when downstream
US (upstream) Flashes during a stage of DOCSIS startup when upstream connectivity is
ONLINE Flashes during later stages of DOCSIS startup, e.g. while the gateway is
connectivity is being established, e.g. while the gateway is scanning for a
DOCSIS downstream signal.
being established, e.g. while the gateway is fi rst transmitting to the cable
operator to join the network.
getting an IP address, downloading confi guration info, and completing
online registration. After completion of startup, indicates the state of the
Internet On/Off button.
4. Internet On/Off Provides secure, positive blocking of Internet connectivity to your LAN-side
button PCs with the press of a button. When Internet connectivity is On, the
Online LED is lit solid. When Internet connectivity is Off, the Online LED is
off.
60 Chapter 4
Page 63

Chapter 4: Additional Information
Cable
1
9-12VDC
2
Ethernet
USB
RESET
536
4
Back of the Unit
Description of Jacks and Switches (from left to right)
1. Antenna jack Connects to the 80 2.11b/g wireless antenna included with the gateway.
2. Power jack Connects to the AC power supply; requires 9-12 V AC. Important: Use only
3. Ethernet jacks Connect to LAN-side PCs, printers, etc. using Ethernet cables.
4. USB jack Connects to a LAN-side PC using a USB cable.
5. RESET switch Enables two types of gateway resets. Pressing and releasing the
5. CABLE jack Connects to the WAN-side coaxial cable jack from your cable company.
the power supply included with the gateway, otherwise you may damage
the unit.
button causes a reboot, e.g. the same as removing the power, and user
confi guration is retained. Pressing and holding the button for 15 seconds
resets the gateway to the factory defaults, including deleting all user
confi guration.
Chapter 4 61
Page 64

Chapter 4: Additional Information
Detailed Explanation of Jacks
The Wireless Cable Gateway provides the following data connections:
WAN Side:
Cable TV connection- connects to your cable service
LAN Side:
Ethernet RJ-45 jacks — connect up to four 10 or 100 Mbps Ethernet cables to PCs or to Ethernet
switches to connect more PCs. Each PC must be equipped with an Ethernet network interface, and
must have the TCP/IP protocol confi gured to operate over that interface.
USB- connects one USB cable to your PC. The PC must be equipped with a USB network interface.
In addition, the USB driver on the DCW725 CD-ROM must be installed on the connected PC, and
the PC must have the TCP/IP protocol confi gured to operate over that USB interface.
Wireless Card- utilizes the 2.4 GHz wireless 2-way technology built into the DCW725 to reach up
to 254 PCs in your home. Each PC must be equipped with an 802.11b/g Wireless Interface, and
must have the TCP/IP protocol confi gured to operate over that interface.
62 Chapter 4
Page 65

Chapter 4: Additional Information
Care and Cleaning
CAUTION: Unplug your unit before cleaning.
You can clean the unit as required, using a soft lint-free cloth. Be sure to occasionally dust the
ventilation slots in the cabinet to help assure adequate ventilation.
Never use strong cleaning agents, such as ammonia-based cleaners, or abrasive powder. These
types of cleaners will damage the unit.
Avoid placing drinks or vases with water on top of the unit. This could increase the risk of fi re or
shock hazard or damage to the unit.
Service Information
If you purchased or leased your Wireless Cable Gateway directly from your service provider, then
warranty service for the unit may be provided through your service provider or its authorized
representative. For information on 1) Ordering Service, 2) Obtaining Customer Support, or 3)
Additional Service Information, please contact your service provider.
Chapter 4 63
Page 66

Chapter 4: Additional Information
FCC Declaration of Conformity and Industry Canada Information
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions: (1) this device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept
any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
Trade Name: RCA Model: DCW725
Thomson Model: TCW720, TCW725
Equipment Classifi cation: Computing Device Accessory
Responsible Party: Thomson Inc.
10330 N. Meridian Street
Indianapolis, IN 46290
Telephone 580-634-0151
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can
radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions,
may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However there is no guarantee that
interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful
interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment
off and on, the user is encouraged to try and correct the interference by one or more of the
following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect this equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is
connected.
• Consult your service provider or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
FCC regulations state that unauthorized changes or modifi cations to this equipment may void the
user’s authority to operate it.
This Class B digital apparatus meets all requirements of the Canadian Interference Causing
Equipment Regulations.
64 Chapter 4
Page 67

Chapter 4: Additional Information
Product Specifi cations
WAN Cable Interface F type female 75 ohm
LAN 4 10/100 BASE-T 1 USB, 1.1 Connector Type B, 1 IEEE 802.11b/g (2.4
System Power 9-12V / 1A
EMI/EMC FCC Class B, CE Class B, VCCI Class B.
Operation Requirement Operating Temp. 0ºC to 40ºC (32ºF to 104ºF) Storage Temp. -20ºC to
Humidity 10% to 85% Non-Condensing Storage Humidity 5% to 90% Non-
Dimensions 186 x 155 x 63 (mm)
Main features:
Cable Modem Connection
• DOCSIS 1.0, 1.1, and 2.0 RFI compliant
• All DOCSIS 2.0 modulation types auto detection downstream
• All DOCSIS 2.0 modulation types auto detection upstream
• Fragmentation and concatenation enabling Quality of Service (QoS) features
• IP and LLC fi ltering
USB Interface
• USB 1.1 compliant full speed (12 Mbps) device interface for Windows 98SE, Windows 2000,
Windows Me, or Windows XP
GHz Unlicensed ISM radio band)
70ºC (-4ºF to 158ºF) Operating
Condensing
Chapter 4 65
Page 68

Chapter 4: Additional Information
Wireless Interface
• 11 Mbps IEEE 802.11b and 54 Mbps 802.11g Wireless LAN
• Frequency band: 2400-2497 MHz
• Supports 64/128 bit RC4 authentication and encryption
• Auto fallback to lower data rates as wireless gateway <=> PC distance increases
• Communicates with all Wi-Fi certifi ed wireless adapters
• Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) and WiFi Protected Access (WPA) security
Networking
• IEEE 802.1d compliant bridging
• DHCP Client
• DHCP Server
• DNS Relay
• ARP
• ICMP
• FTP/TFTP
• Telnet
Security and Firewall
• Password protected confi guration via web browser
• IP fi ltering; allows you to confi gure IP address fi lters
• MAC fi ltering; allows you to confi gure MAC address fi lters
• Port fi ltering; allows you to confi gure TCP/UDP port fi lters
• URL content fi ltering
• URL fi ltering blocks Proxy, Cookies, Java and ActiveX
• Traffi c and Security Event log
• PAP and CHAP authentication with PPP
66 Chapter 4
Page 69

Chapter 4: Additional Information
• Stateful Packet Inspection to protect against both Denial of Service and Distributed Denial of
Service attacks, including:
• Reassembly attacks
• SYN Attack (SYN Flood)
• ICMP Flood
• Ping of Death Attack
• Tear Drop Attack
• IP Spoofi ng Attack
• LAND Attack
• Jolt
• Winnuke Attack (Netbios out-of-bound)
• OverDrop
• BONK, BOINK
• Blind Spoofi ng
• Echo/Chargen
• Storm
• Smurf Attack
• Mime Flood
• De-Militarized Zone (DMZ) support, allowing a LAN side computer to expose all non-fi ltered
ports to the WAN
• URL keyword blocking for web access control
NAT
• With popular ALG support
• With port triggers
• With port forwarding, including support for:
Chapter 4 67
Page 70

Chapter 4: Additional Information
• FTP
• IRC
• H.323
• Quake
• Blizzard games
• Chat ALG
• Real Audio/Video
• CUSEEME
• Netmeeting
• MS Games (excluding game zone)
• DIABOLO II
• Activision Games
• PCAnywhere
• SSL
• NNTP
Virtual Private Network (VPN) Feature
• PPTP and IPSec pass-through can be enabled/disabled
68 Chapter 4
Page 71

Page 72

Please do not send any products to the Indianapolis address listed in this manual or
on the carton. This will only add delays in service for your product.
Thomson Inc.
10330 North Meridian Street
Indianapolis, IN 46290
© 2004 Thomson Inc.
Trademark(s) Registered
Marca(s) Registrada(s)
Printed in China
TOCOM 1644144A
THOMSON
 Loading...
Loading...