TDK Semiconductor Corporation 73K222AL-LP, 73K222AL-IH, 73K222AL-IGT Datasheet
73K222AL
V.22, V.21, Bell 212A, 103
Single-Chip Modem
April 2000
DESCRIPTION
The 73K222AL is a highly integrated single-chip
modem IC which provides the functions needed to
construct a CCITT V.22, V.21 and Bell 212A
compatible modem, capable of 1200 bit/s full-duplex
operation over dial-up lines. The 73K222AL is an
enhancement of the 73K212L/AL single-chip modem
which adds V.22 and V.21 modes to the Bell 212A and
103 operation of the 73K212AL. In Bell 212A mode,
the 73K222AL provides the normal Bell 212A and 103
functions and employs a 2225 Hz answer tone. The
73K222AL in V.22 mode produces either 550 or 1800
Hz guard tone, recognizes and generates a 2100 Hz
answer tone, and allows 600 bit/s V.22 or 0-300 bit/s
V.21 operation. The 73K222AL integrates analog,
digital, and switched-capacitor array functions on a
single substrate, offering excellent performance and a
high level of functional integration in a single 28-pin
DIP, PLCC and 44-pin TQFP configuration. The
73K222AL operates from a single +5V supply. The
73K222AL is a new version replacing the 73K222L.
The 73K222AL should be specified for all new
designs.
The 73K222AL includes the DPSK and FSK
modulator/demodulator functions, call progress and
handshake tone monitor and a tone generator capable
of tone required for European applications.
(continued)
FEATURES
• One-chip CCITT V.22, V.21, Bell 212A and Bell
103 standard compatible modem data pump
• Full-duplex operation at 0-300 bit/s (FSK) or 600
and 1200 bit/s (DPSK)
• Pin and software compatible with other TDK
Semiconductor Corporation K-Series 1-chip
modems
• Interfaces directly with standard
microprocessors (8048, 80C51 typical)
• Serial or parallel microprocessor bus for control
• Serial port for data transfer
• Both synchronous and asynchronous modes of
operation including V.22 extended overspeed
• Call progress, carrier, precise answer tone
(2100 or 2225 Hz), and long loop detectors
• DTMF, and 550 or 1800 Hz guard tone
generators
• Test modes available: ALB, DL, RDL, Mark,
Space, Alternating bit patterns
• Precise automatic gain control allows 45 dB
dynamic range
• CMOS technology for low power consumption
using 60 mW @ 5V
• Single +5 volt supply
• PLCC and PDIP packages
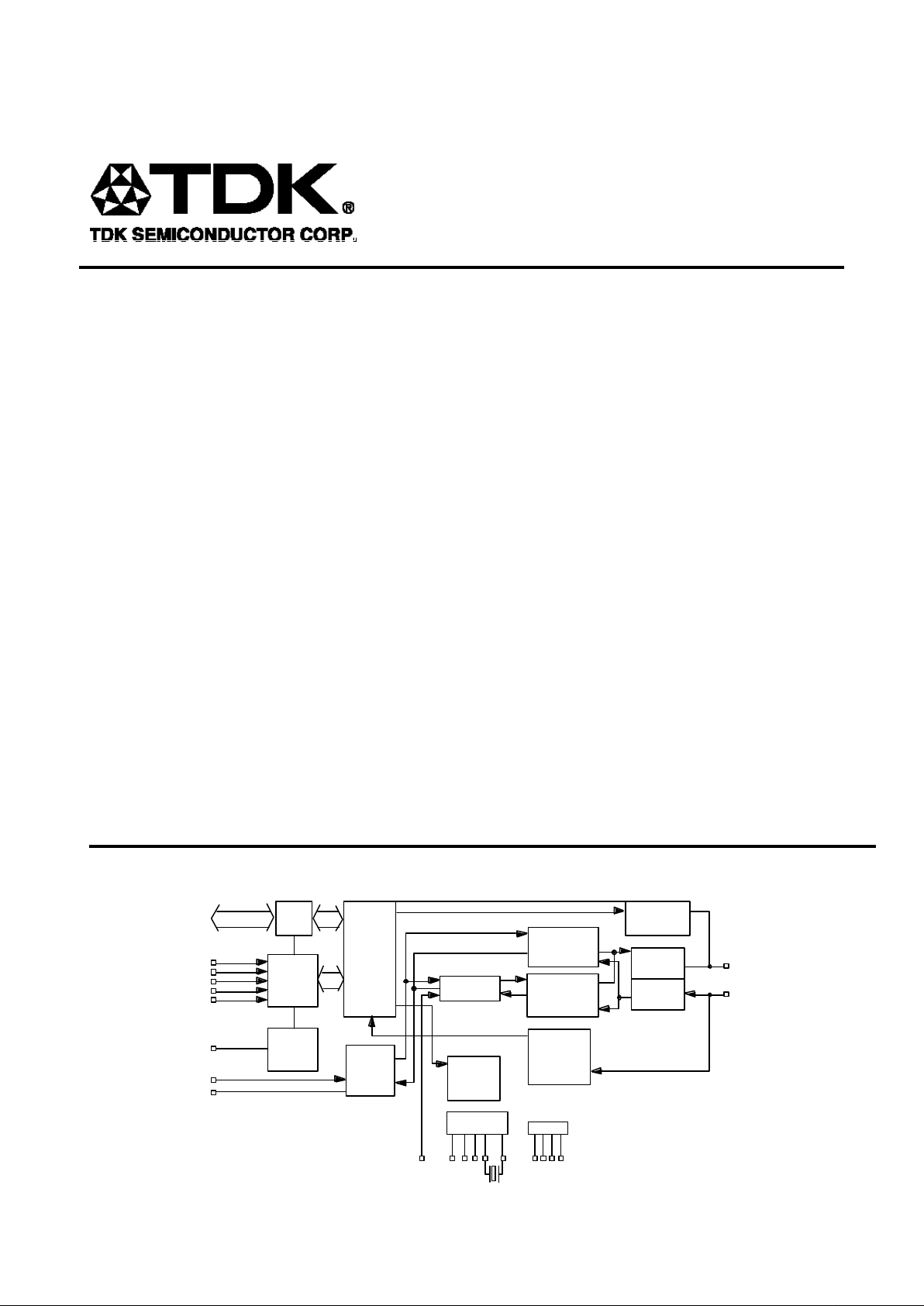
BLOCK DIAGRAM
DIGITAL
PROCESSING
DTMF &
TONE
GENERATORS
FSK
MODULATOR/
DEMODULATOR
PSK
MODULATOR/
DEMODULATOR
SMART
DIALING
&
DETECT
FUNCTIONS
POWER
TESTS:
ALB, DLB
RDLB
PATTERNS
TRANSMIT
FILTER
DATA
BUS
BUFFER
READ
WRITE
CONTROL
LOGIC
STATUS
AND
CONTROL
LOGIC
8-BIT
BUS
FOR
CONTROL
AND
STATUS
SERIAL
PORT
FOR
DATA
TXA
RXA
ISET
VDD
VREF
GND
RXCLK
CLOCK
GENERATOR
XTL2
XTL1
CLK
TXCLK
EXCLK
RD
WR
ALE
CS
RESET
INT
TXD
RXD
AD0-AD7
RECEIVE
FILTER

73K222AL
V.22, V.21, Bell 212A, 103
Single-Chip
2
DESCRIPTION (continued)
This device supports V.22 (except mode v) and V. 21
modes of operation, allowing both synchronous and
asynchronous communications. Test features such as
analog loop, digital loop, and remote digital loopback are
supported. Internal pattern generators are also included for
self-testing. The 73K222AL is designed to appear to the
systems designer as a microprocessor peripheral, and will
easily interface with popular one-chip microprocessors
(80C51 typical) for control of modem functions through its 8bit multiplexed address/data bus or serial control bus. An
ALE control line simplifies address demultiplexing. Data
communications occurs through a separate serial port only.
The 73K222AL is ideal for use in either free standing or
integral system modem products where full-duplex 1200
bit/s data communications over the 2-wire switched
telephone network is desired. Its high functionality, low
power consumption and efficient packaging simplify
design requirements and increase system reliability. A
complete modem requires only the addition of the phone
line interface, a control microprocessor, and RS-232 level
converter for a typical system. The 73K222AL is part of
TDK Semiconductor Corporation's K-Series family of pin
and function compatible single-chip modem products.
These devices allow systems to be configured for higher
speeds and Bell or CCITT operation with only a single
component change.
OPERATION
ASYNCHRONOUS MODE
Data transmission for the DPSK mode requires that data
ultimately be transmitted in a synchronous fashion. The
73K222AL includes ASYNC/SYNC and SYNC/ASYNC
converters which delete or insert stop bits in order to
transmit data within a ±0.01% rate. In asynchronous mode
the serial data comes from the TXD pin into the
ASYNC/SYNC converter. The ASYNC/SYNC converter
accepts the data provided on the TXD pin which normally
must be 1200 or 600 bit/s +1.0%, -2.5%. The converter will
then insert or delete stop bits in order to output a signal
which is 1200 or 600 bit/s ± 0.01% (± 0.01% is required
synchronous data rate accuracy).
The serial data stream from the ASYNC/SYNC
converter is passed through the data scrambler and
onto the analog modulator. The data scrambler can be
bypassed under processor control when unscrambled
data must be transmitted. The ASYNC/SYNC
converter and the data scrambler are bypassed in all
FSK modes. If serial input data contains a break signal
through one character (including start and stop bits)
the break will be extended to at least 2 times N + 3 bits
long (where N is the number of transmitted
bits/character).
Serial data from the demodulator is passed first
through the data descrambler and then through
the SYNC/ASYNC converter. The SYNC/ASYNC
convertor will reinsert any deleted stop bits and
transmit output data at an intra-character rate (bitto-bit timing) of no greater than 1219 bit/s. An
incoming break signal (low through two
characters) will be passed through without
incorrectly inserting a stop bit.
The SYNC/ASYNC converter also has an
extended overspeed mode which allows selection
of an overspeed range of either +1% or +2.3%. In
the extended overspeed mode, stop bits are
output at 7/8 the normal width.
SYNCHRONOUS MODE
The CCITT V.22 standard defines synchronous
operation at 600 and 1200 bit/s. The Bell 212A
standard defines synchronous operation only at
1200 bit/s. Operation is similar to that of the
asynchronous mode except that data must be
synchronized to a provided clock and no variation
in data transfer rate is allowable. Serial input data
appearing at TXD must be valid on the rising edge
of TXCLK.
TXCLK is an internally derived signal in internal mode
and is connected internally to the RXCLK pin in slave
mode. Receive data at the RXD pin is clocked out on
the falling edge of RXCLK. The ASYNCH/SYNCH
converter is bypassed when synchronous mode is
selected and data is transmitted out at the same rate
as it is input.
DPSK MODULATOR/DEMODULATOR
The 73K222AL modulates a serial bit stream into
di-bit pairs that are represented by four possible
phase shifts as prescribed by the Bell 212A or
V.22 standards. The baseband signal is then
filtered to reduce intersymbol interference on the
bandlimited 2-wire telephone line. Transmission
occurs using either a 1200 Hz (originate mode) or
2400 Hz carrier (answer mode). Demodulation is
the reverse of the modulation process, with the
incoming analog signal eventually decoded into dibits and converted back to a serial bit stream. The
demodulator also recovers the clock which was
encoded into the analog signal during modulation.
Demodulation occurs using either a 1200 Hz
carrier (answer mode or ALB originate mode) or a

73K222AL
V.22, V.21, Bell 212A, 103
Single-Chip Modem
3
2400 Hz carrier (originate mode or ALB answer mode).
The 73K222AL uses a phase locked loop coherent
demodulation technique for optimum receiver
performance.
FSK MODULATOR/DEMODULATOR
The FSK modulator produces a frequency modulated
analog output signal using two discrete frequencies to
represent the binary data. In Bell 103, the standard
frequencies of 1270 and 1070 Hz (originate, mark and
space) or 2225 and 2025 Hz (answer, mark and space)
are used. V.21 mode uses 980 and 1180 Hz (originate,
mark and space), or 1650 and 1850Hz (answer, mark and
space). Demodulation involves detecting the received
frequencies and decoding them into the appropriate binary
value. The rate converter and scrambler/ descrambler are
bypassed in the 103 or V.21 modes.
PASSBAND FILTERS AND EQUALIZERS
High and low band filters are included to shape the
amplitude and phase response of the transmit and
receive signals and provide compromise delay
equalization and rejection of out-of-band signals in the
receive channel. Amplitude and phase equalization are
necessary to compensate for distortion of the
transmission line and to reduce intersymbol
interference in the bandlimited receive signal. The
transmit signal filtering approximates a 75% square
root of raised Cosine frequency response
characteristic.
AGC
The automatic gain control maintains a signal level at
the input to the demodulators which is constant to
within 1 dB. It corrects quickly for increases in signal
which would cause clipping and provides a total
receiver dynamic range of >45 dB.
PARALLEL BUS INTERFACE
Four 8-bit registers are provided for control, option
select and status monitoring. These registers are
addressed with the AD0, AD1, and AD2 multiplexed
address lines (latched by ALE) and appear to a control
microprocessor as four consecutive memory locations.
Two control registers and the tone register are
read/write memory. The detect register is read only
and cannot be modified except by modem response to
monitored parameters.
SERIAL COMMAND INTERFACE
The serial command interface allows access to the
73K222AL control and status registers via a serial
command port (22-pin version only). In this mode the
A0, A1 and A2 lines provide register addresses for
data passed through the data pin under control of the
RD and WR lines. A read operation is initiated when
the RD line is taken low. The first bit is available after
RD is brought low and the next seven cycles of
EXCLK will then transfer out seven bits of the
selected address LSB first. A write takes place by
shifting in eight bits of data LSB first for eight
consecutive cycles of EXCLK. WR is then pulsed low
and data transferred into the addressed register
occurs on the rising edge of WR. This interface
mode is also supported in the 28-pin packages. See
serial control interface pin description.
SPECIAL DETECT CIRCUITRY
The special detect circuitry monitors the received
analog signal to determine status or presence of
carrier, call-progress tones, answer tone and weak
received signal (long loop condition). An
unscrambled mark request signal is also detected
when the received data out of the DPSK
demodulator before the descrambler has been high
for 165.5 ms ± 6.5 ms minimum. The appropriate
detect register bit is set when one of these conditions
changes and an interrupt is generated for all
purposes except long loop. The interrupts are
disabled (masked) when the enable interrupt bit is
set to 0.
DTMF GENERATOR
The DTMF generator will output one of 16 standard
tone pairs determined by a 4-bit binary value and TX
DTMF mode bit previously loaded into the tone
register. Tone generation is initiated when the DTMF
mode is selected using the tone register and the
transmit enable (CR0 bit D1) is changed from 0 to 1.
73K222AL
V.22, V.21, Bell 212A, 103
Single-Chip
4
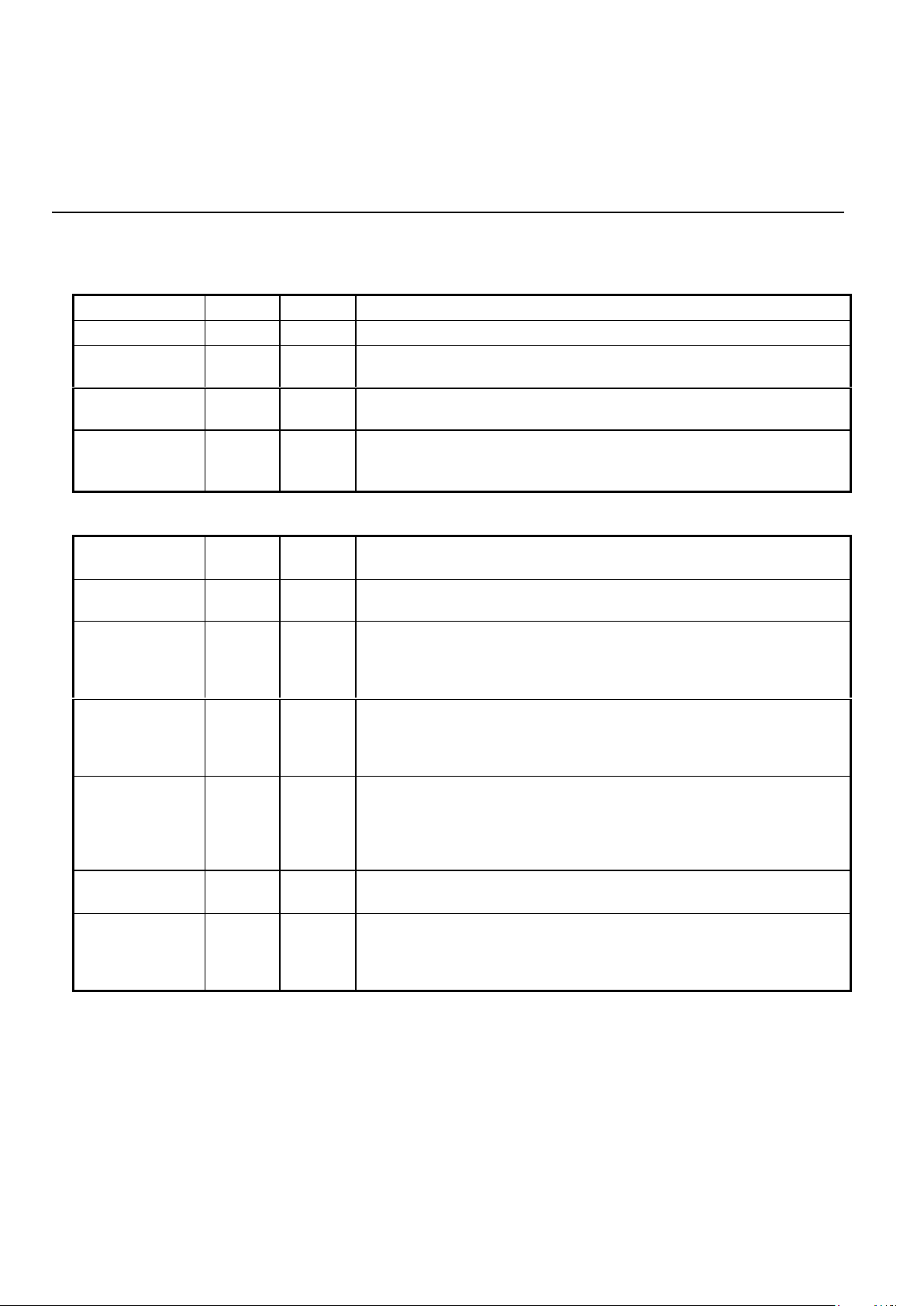
PIN DESCRIPTION
POWER
NAME 28-PIN TYPE DESCRIPTION
GND 28 I System Ground.
VDD 15 I
Power supply input, 5V ±10%. Bypass with 0.1 and 22 µF capacitors to
GND.
VREF 26 O An internally generated reference voltage. Bypass with 0.1 µF
capacitor to ground.
ISET 24 I Chip current reference. Sets bias current for op-amps. The chip
current is set by connecting this pin to VDD through a 2 MΩ resistor.
ISET should be bypassed to GND with a 0.1 µF capacitor.
PARALLEL MICROPROCESSOR INTERFACE
ALE 12 I Address latch enable. The falling edge of ALE latches the address on
AD0-AD2 and the chip select on CS .
AD0-AD7 4-11 I/O Address/data bus. These bidirectional tri-state multiplexed lines carry
information to and from the internal registers.
CS 20 I Chip select. A low on this pin during the falling edge of ALE allows a
read cycle or a write cycle to occur. AD0-AD7 will not be driven and no
registers will be written if CS (latched) is not active. The state of CS is
latched on the falling edge of ALE.
CLK 1 O Output clock. This pin is selectable under processor control to be either
the crystal frequency (for use as a processor clock) or 16 x the data
rate for use as a baud rate clock in DPSK modes only. The pin defaults
to the crystal frequency on reset.
INT 17 O Interrupt. This open drain output signal is used to inform the processor
that a detect flag has occurred. The processor must then read the
detect register to determine which detect triggered the interrupt. INT
will stay low until the processor reads the detect register or does a full
reset.
RD 14 I Read. A low requests a read of the 73K222AL internal registers. Data
cannot be output unless both RD and the latched CS are active or low.
RESET 25 I Reset. An active high signal on this pin will put the chip into an inactive
state. All control register bits (CR0, CR1, Tone) will be reset. The
output of the CLK pin will be set to the crystal frequency. An internal
pull down resistor permits power on reset using a capacitor to VDD.
73K222AL
V.22, V.21, Bell 212A, 103
Single-Chip Modem
5
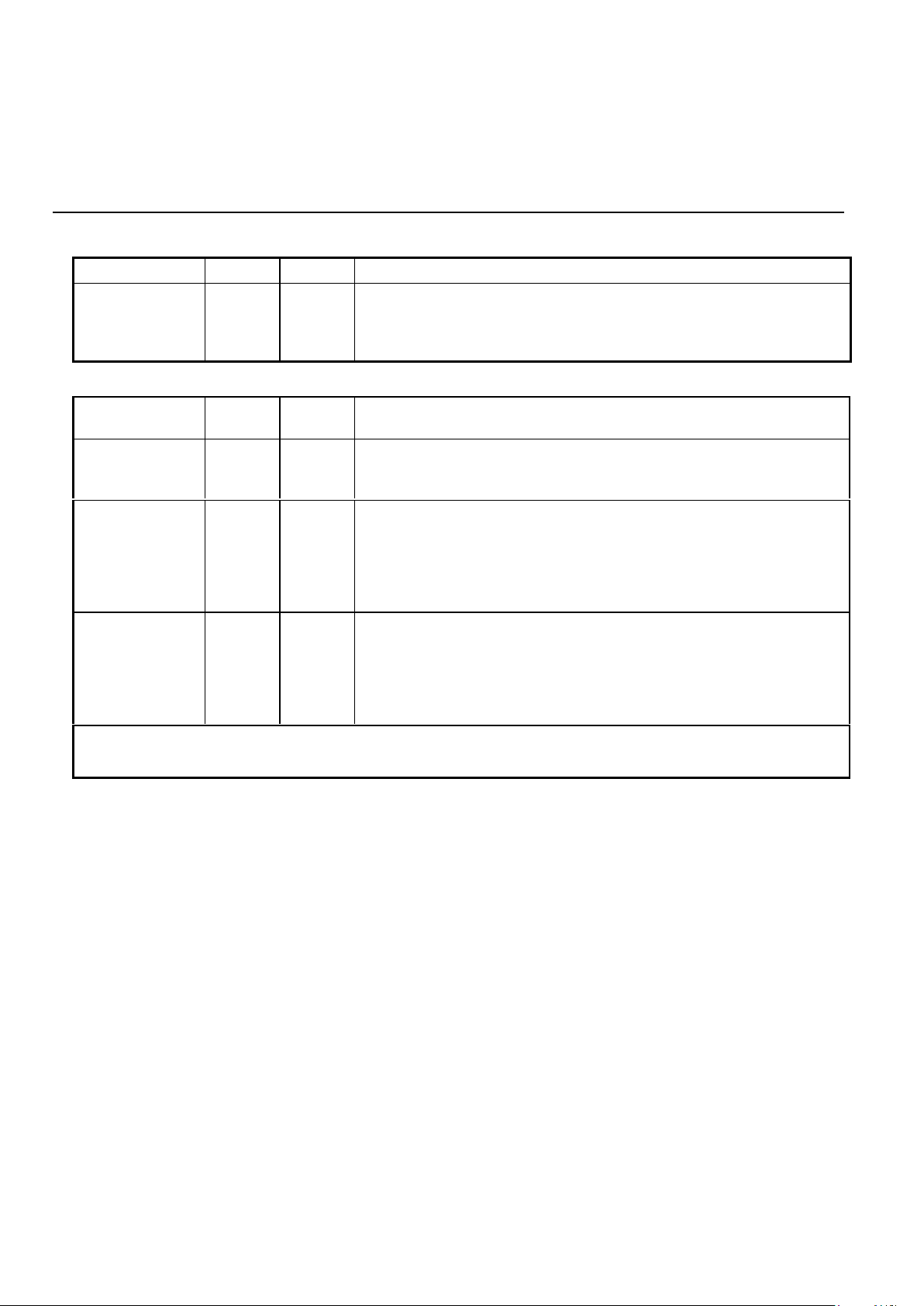
PARALLEL MICROPROCESSOR INTERFACE (continued)
NAME 28-PIN TYPE DESCRIPTION
WR 13 I
Write. A low on this informs the 73K222AL that data is available on
AD0-AD7 for writing into an internal register. Data is latched on the
rising edge of WR. No data is written unless both WR and the latched
CS are low.
SERIAL MICROPROCESSOR INTERFACE
A0-A2 - I Register Address Selection. These lines carry register addresses and
should be valid during any read or write operation.
DATA - I/O Serial Control Data. Data for a read/write operation is clocked in or out
on the falling edge of the EXCLK pin. The direction of data flow is
controlled by the RD pin. RD low outputs data. RD high inputs data.
RD - I Read. A low on this input informs the 73K222AL that data or status
information is being read by the processor. The falling edge of the RD
signal will initiate a read from the addressed register. The RD signal
must continue for eight falling edges of EXCLK in order to read all eight
bits of the referenced register. Read data is provided LSB first. Data
will not be output unless the RD signal is active.
WR - I Write. A low on this input informs the 73K222AL that data or status
information has been shifted in through the DATA pin and is available
for writing to an internal register. The normal procedure for a write is to
shift in data LSB first on the DATA pin for eight consecutive falling
edges of EXCLK and then to pulse WR low. Data is written on the
rising edge of WR.
NOTE: The serial control mode is provided by tying ALE high and CS low. In this configuration AD7 becomes
DATA and AD0, AD1 and AD2 become the address only. See timing diagrams on page 20.
73K222AL
V.22, V.21, Bell 212A, 103
Single-Chip
6
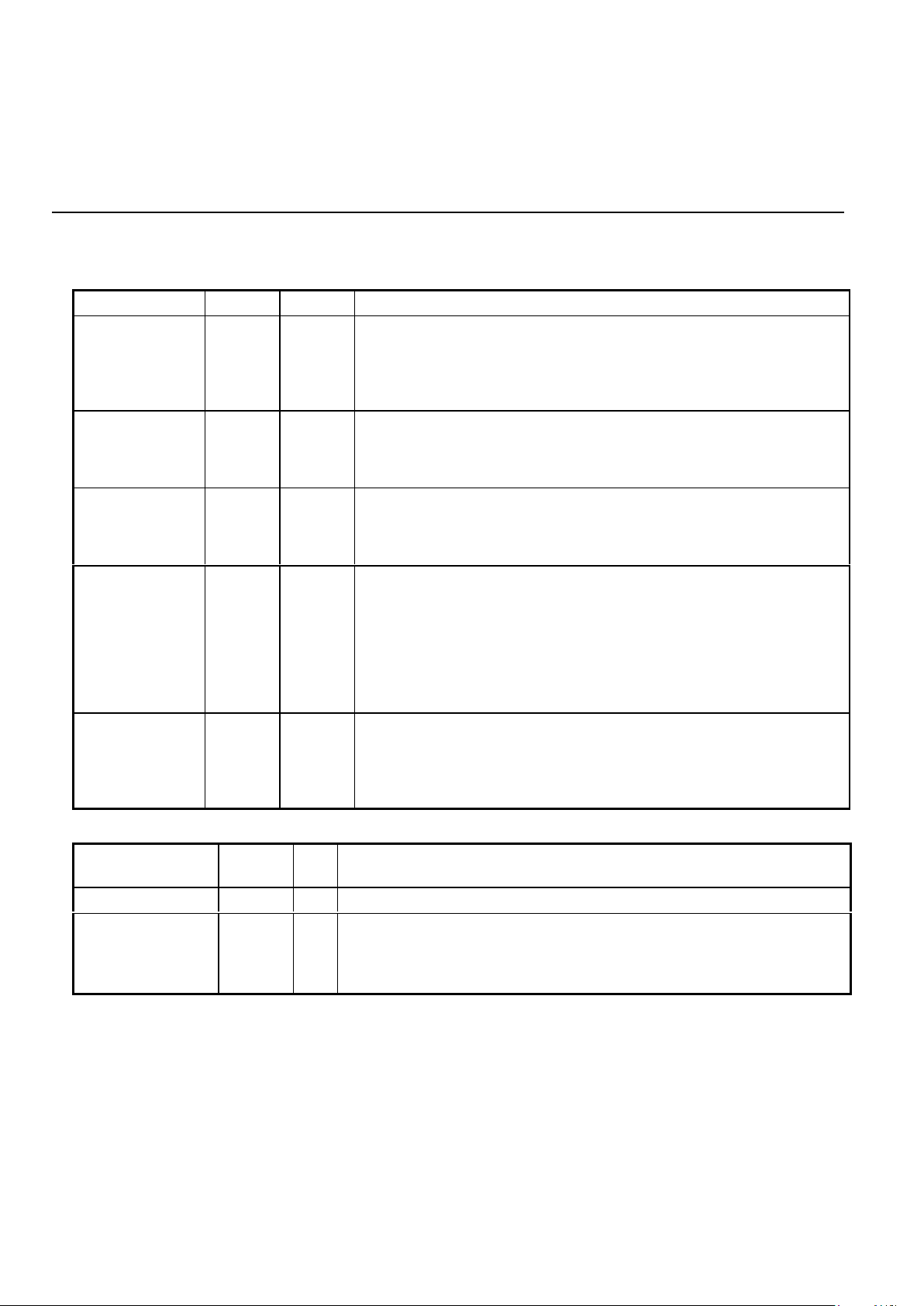
PIN DESCRIPTION (continued)
DTE USER
NAME 28-PIN TYPE DESCRIPTION
EXCLK 19 I
External Clock. This signal is used in synchronous transmission
when the external timing option has been selected. In the external
timing mode the rising edge of EXCLK is used to strobe synchronous
DPSK transmit data applied to on the TXD pin. Also used for serial
control interface.
RXCLK 23 O Receive Clock. The falling edge of this clock output is coincident with
the transitions in the serial received data output. The rising edge of
RXCLK can be used to latch the valid output data. RXCLK will be
valid as long as a carrier is present.
RXD 22 O/
Weak
Pull -up
Received Data Output. Serial receive data is available on this pin.
The data is always valid on the rising edge of RXCLK when in
synchronous mode. RXD will output constant marks if no carrier is
detected.
TXCLK 18 O Transmit Clock. This signal is used in synchronous transmission to
latch serial input data on the TXD pin. Data must be provided so that
valid data is available on the rising edge of the TXCLK. The transmit
clock is derived from different sources depending upon the
synchronization mode selection. In Internal Mode the clock is
generated internally. In External Mode TXCLK is phase locked to the
EXCLK pin. In Slave Mode TXCLK is phase locked to the RXCLK
pin. TXCLK is always active.
TXD 21 I Transmit Data Input. Serial data for transmission is applied on this pin.
In synchronous modes, the data must be valid on the rising edge of the
TXCLK clock. In asynchronous modes (1200/600 bit/s or 300 baud)
no clocking is necessary. DPSK data must be 1200/600 bit/s +1%,
-2.5% or +2.3%, -2.5 % in extended overspeed mode.
ANALOG INTERFACE AND OSCILLATOR
RXA 27 I Received modulated analog signal input from the telephone line
interface.
TXA 16 O Transmit analog output to the telephone line interface.
XTL1
XTL2
2
3
IIThese pins are for the internal crystal oscillator requiring a 11.0592 MHz
parallel mode crystal. Load capacitors should be connected from XTL1
and XTL2 to Ground. XTL2 can also be driven from an external clock.
73K222AL
V.22, V.21, Bell 212A, 103
Single-Chip Modem
7
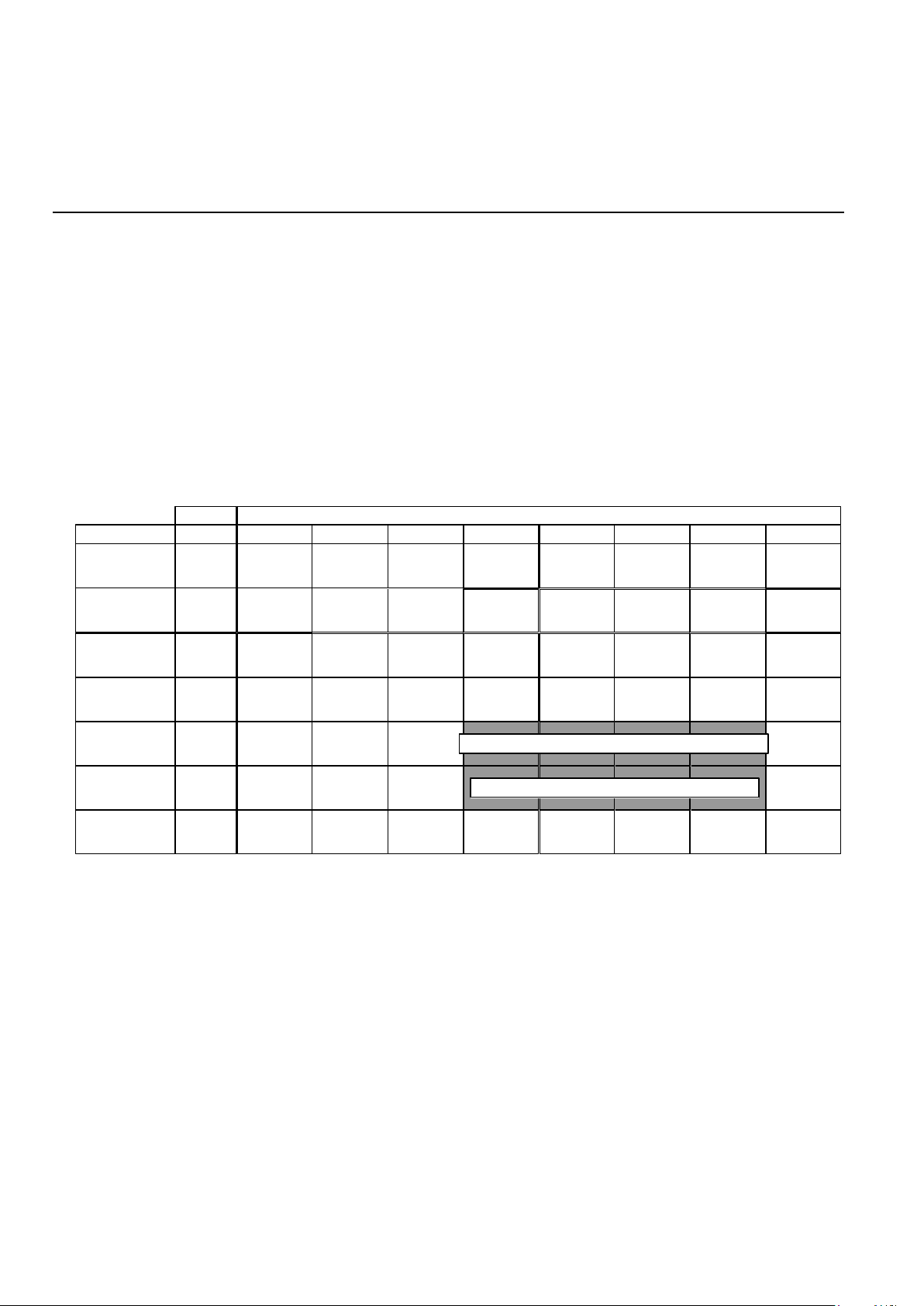
REGISTER DESCRIPTIONS
Four 8-bit internal registers are accessible for control
and status monitoring. The registers are accessed in
read or write operations by addressing the A0, A1
and A2 address lines in serial mode, or the AD0,
AD1 and AD2 lines in parallel mode. In parallel
mode the address lines are latched by ALE. Register
CR0 controls the method by which data is
transferred over the phone line. CR1 controls the
interface between the microprocessor and the
73K222AL internal state. DR is a detect register
which provides an indication of monitored
modem status conditions. TR, the tone control
register, controls the DTMF generator, answer
and guard tones and RXD output gate used in
the modem initial connect sequence. All
registers are read/write except for DR which is
read only. Register control and status bits are
identified below:
REGISTER BIT SUMMARY
NOTE: When a register containing reserved control
bits is written into, the reserved bits must be
programmed as 0's.
X = Undefined, mask in software
DTMF0/
GUARD/
ANS TONE
REGISTER
CONTROL
REGISTER
0
ID
REGISTER
CONTROL
REGISTER
3
CONTROL
REGISTER
1
DETECT
REGISTER
TONE
CONTROL
REGISTER
CONTROL
REGISTER
2
ID
CR3
CR2
CR1
DR
TR
ADDRESS
AD2 - AD0
110
101
100
011
010
001
000
D7
TRANSMIT
PATTERN
1
TRANSMIT
PATTERN
0
RXD
OUTPUT
CONTROL
D6 D5
ENABLE
DETECT
INTERRUPT
RECEIVE
DATA
TRANSMIT
ANSWER
TONE
TRANSMIT
MODE
2
TRANSMIT
DTMF
TRANSMIT
MODE
1
CLK
CONTROL
CARRIER
DETECT
DTMF3
DTMF1/
OVERSPEED
TRANSMIT
MODE
0
RESET
ANSWER
TONE
DTMF2
TRANSMIT
ENABLE
TEST
MODE
1
CALL
PROGRESS
ANSWER/
ORIGINATE
TEST
MODE
0
LONG
LOOP
D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
DATA BIT NUMBER
THESE REGISTER LOCATIONS ARE RESERVED FOR
USE WITH OTHER K-SERIES FAMILY MEMBERS
CR0
MODULATION
OPTION
ID
ID
TRANSMIT
GUARD
TONE
TRANSMIT
MODE
3
BYPASS
SCRAMBLER
UNSCR.
MARKS
ID ID
0
X
X
X
X
X
X
X X X X
X
X
X X
73K222AL
V.22, V.21, Bell 212A, 103
Single-Chip
8
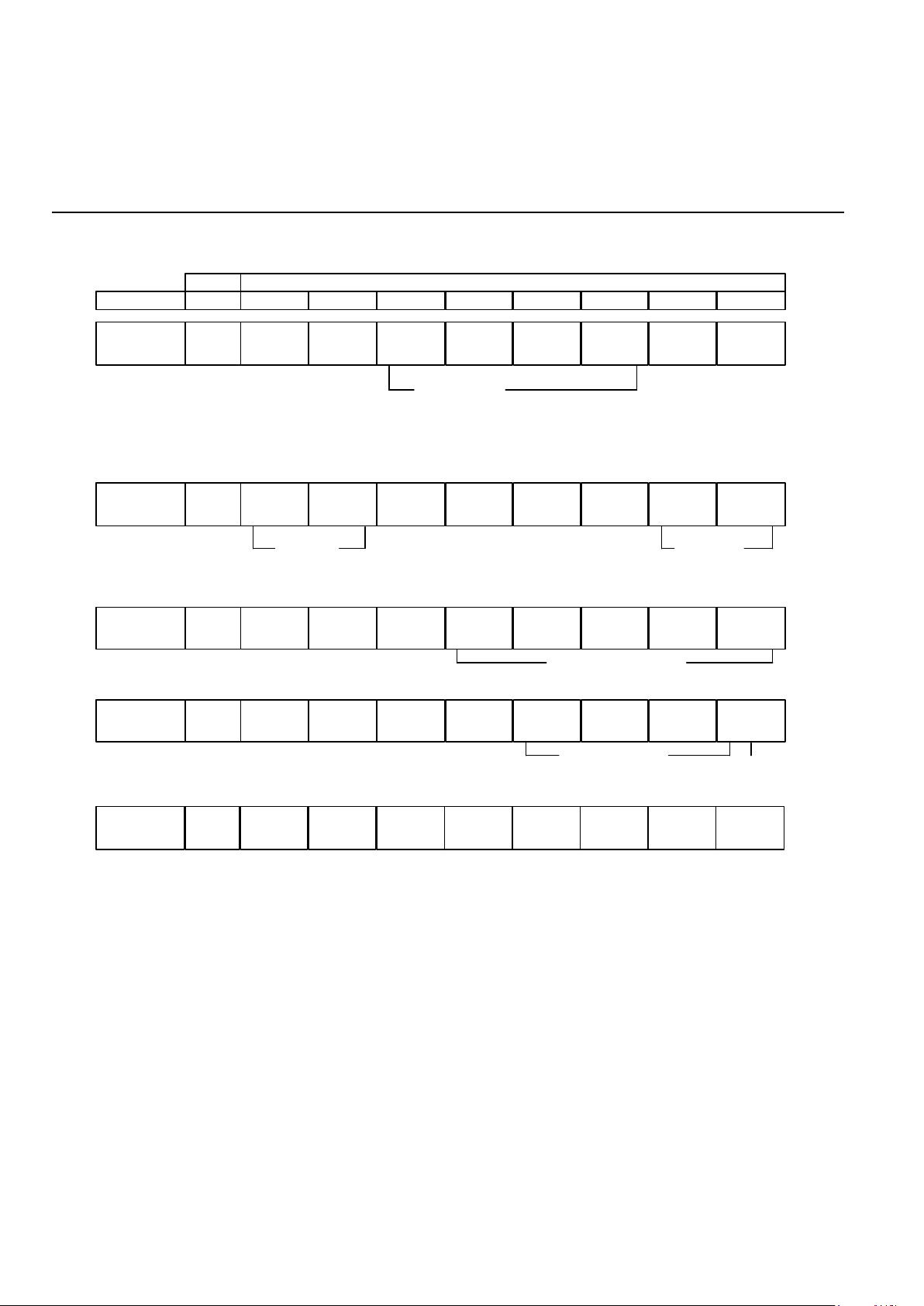
REGISTER ADDRESS TABLE
MODULATION
OPTION
00 = NORMAL
01 = ANALOG LOOPBACK
10 = REMOTE DIGITAL
LOOPBACK
11 = LOCAL DIGITAL
LOOPBACK
000
TRANSMIT
MODE
3
TRANSMIT
MODE
2
TRANSMIT
MODE
1
TRANSMIT
ENABLE
ORIGINATE/
ANSWER
DATA BIT NUMBER
AD2 - AD0REGISTER
ADDRESS
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
TEST
MODE
0
TEST
MODE
1
RESET
CLK
CONTROL
BYPASS
SCRAMBLER
ENABLE
DETECT
INTERRUPT
TRANSMIT
PATTERN
0
TRANSMIT
PATTERN
1
001CR1
LONG
LOOP
CALL
PROGRESS
ANSWER
TONE
CARRIER
DETECT
RECEIVE
DATA
010
DETECT
REGISTER
DR
DTMF0/
GUARD/
ANSWER/
TONE
DTMF1/
OVERSPEED
DTMF2DTMF3
TRANSMIT
DTMF
TRANSMIT
ANSWER
TONE
RXD
OUTPUT
CONTROL
011
TONE
CONTROL
REGISTER
TR
TRANSMIT
MODE
0
0000 = PWR DOWN
0001 = INT SYNCH
0010 = EXT SYNCH
0011 = SLAVE SYNCH
0100 = ASYNCH 8 BITS/CHAR
0101 = ASYNCH 9 BITS/CHAR
0110 = ASYNCH 10 BITS/CHAR
0111 = ASYNCH 11 BITS/CHAR
1100 = FSK
0 = DISABLE
TXA OUTPUT
1 = ENABLE
TXA OUTPUT
0 = ANSWER
1 = ORIGINATE
00 = TX DATA
01 = TX ALTERNATE
10 = TX MARK
11 = TX SPACE
0 = DISABLE
1 = ENABLE
0 = NORMAL
1 = BYPASS
SCRAMBLER
0 = XTAL
1 = 16 X DATA
RATE OUTPUT
AT CLK PIN IN
DPSK MODE
ONLY
0 = NORMAL
1 = RESET
OUTPUTS
RECEIVED
DATA STREAM
0 = CONDITION NOT DETECTED
1 = CONDITION DETECTED
RXD PIN
0 = NORMAL
1 = TRI STATE
0 = OFF
1 = ON
0 = DATA
1 = TX DTMF
4 BIT CODE FOR 1 OF 16
DUAL TONE COMBINATIONS
CR0
0 = 1200 BIT/S DPSK
1 = 600 BIT/S DPSK
0 = BELL 103 FSK
1 = V.21 FSK
TRANSMIT
GUARD/
TONE
0 = 2225 Hz A.T.
1800 Hz G.T.
1 = 2100 Hz A.T.
500 Hz G.T.
0 = OFF
1 = ON
UNSCR.
MARKS
ID
REGISTER
10 110
ID ID
ID ID
0
XX
X X X X
X = Undefined, mask in software
CONTROL
REGISTER
1
CONTROL
REGISTER
0
00XX = 73K212AL, 322L, 321L
01XX = 73K221AL, 302L
10XX = 73K222AL, 222BL
1100 = 73K224L
1110 = 73K324L
1111 = 73K224BL
1101 = 73K324BL
73K222AL
V.22, V.21, Bell 212A, 103
Single-Chip Modem
9
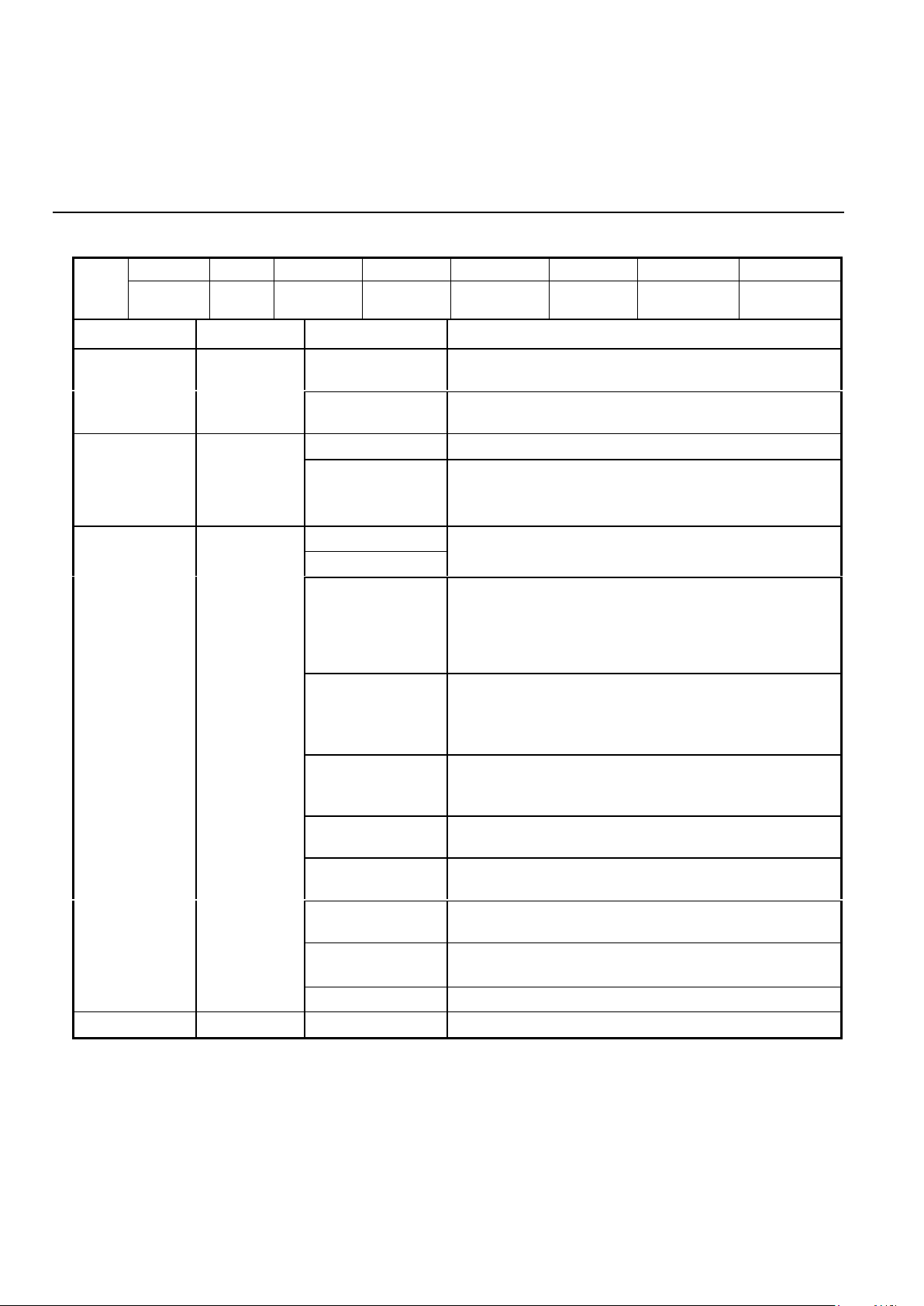
CONTROL REGISTER 0
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
CR0
000
MODUL.
OPTION
0 TRANSMIT
MODE 3
TRANSMIT
MODE 2
TRANSMIT
MODE 1
TRANSMIT
MODE 0
TRANSMIT
ENABLE
ANSWER/
ORIGINATE
BIT NO. NAME CONDITION DESCRIPTION
0
Selects answer mode (transmit in high band, receive
in low band).
D0 Answer/
Originate
1
Selects originate mode (transmit in low band, receive in
high band).
0
Disables transmit output at TXA.D1 Transmit
Enable
1
Enables transmit output at TXA.
Note: TX Enable must be set to 1 to allow Answer Tone
and DTMF Transmission.
D5 D4 D3 D2
0 0 0 0
Selects power down mode. All functions disabled except
digital interface.
0 0 0 1 Internal synchronous mode. In this mode TXCLK is an
internally derived 1200 Hz signal. Serial input data
appearing at TXD must be valid on the rising edge of
TXCLK. Receive data is clocked out of RXD on the
falling edge of RXCLK.
0 0 1 0 External synchronous mode. Operation is identical to
internal synchronous, but TXCLK is connected internally
to EXCLK pin, and a 1200 Hz ± 0.01% clock must be
supplied externally.
0 0 1 1 Slave synchronous mode. Same operation as other
synchronous modes. TXCLK is connected internally to
the RXCLK pin in this mode.
0 1 0 0 Selects PSK asynchronous mode - 8 bits/character
(1 start bit, 6 data bits, 1 stop bit).
0 1 0 1 Selects PSK asynchronous mode - 9 bits/character
(1 start bit, 7 data bits, 1 stop bit).
0 1 1 0 Selects PSK asynchronous mode - 10 bits/character
(1 start bit, 8 data bits, 1 stop bit).
0 1 1 1 Selects PSK asynchronous mode - 11 bits/character
(1 start bit, 8 data bits, Parity and 1 or 2 stop bits).
D5, D4,D3, D2 Transmit
Mode
1 1 0 0 Selects FSK operation.
D6 0 Not used; must be written as a “0.”
 Loading...
Loading...