Page 1

tams elektronik
Manual
PZS-2
Item no. 51-02025 | 51-02026 | 51-02027
Shuttle-train control
for analogue d.c. model railway layouts
tams elektronik
n n n
Page 2

tams elektronik
English PZS-2
Table of contents
1. Getting started............................................................................3
2. Safety instructions.......................................................................5
3. Safe and correct soldering...........................................................7
4. Operation overview.....................................................................9
5. Technical specifications..............................................................13
6. Assembling the kit.....................................................................14
7. Functional test..........................................................................23
8. Connecting the PZS-2................................................................24
8.1. Schema............................................................................24
8.2. Dividing the shuttle-train section into parts.........................25
8.3. Connecting the power supply.............................................25
8.4. Connecting the shuttle-train section to the PZS-2................27
9. Operation.................................................................................30
10. Programming the PZS-2.............................................................33
11. Check list for troubleshooting.....................................................36
12. Guarantee bond........................................................................38
13. EU declaration of conformity......................................................39
14. Declarations conforming to the WEEE directive...........................39
© 01/2015 Tams Elektronik GmbH
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced or
transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical,
including photocopying, without prior permission in writing from Tams
Elektronik GmbH.
Subject to technical modification.
Page 2
Page 3

tams elektronik
!
PZS-2 English
1. Getting started
How to use this manual
This manual gives step-by-step instructions for safe and correct
assembly of the kit and fitting and connecting of the ready-built
module, and operation. Before you start, we advise you to read the
whole manual, particularly the chapter on safety instructions and the
checklist for trouble shooting. You will then know where to take care
and how to prevent mistakes which take a lot of effort to correct.
Keep this manual safely so that you can solve problems in the future. If
you pass the kit or the ready-built module on to another person, please
pass on the manual with it.
Intended use
The shuttle-train control PZS-2 is designed to be operated according to
the instructions in this manual in model building, especially with model
railways. Any other use is inappropriate and invalidates any guarantees.
The PZS-2 should not be assembled or mounted by children under the
age of 14.
Reading, understanding and following the instructions in this manual
are mandatory for the user.
Caution:
The PZS-2 contains integrated circuits. These are very sensitive to
static electricity. Do not touch components without first discharging
yourself. Touching a radiator or other grounded metal part will
discharge you.
Page 3
Page 4

tams elektronik
English PZS-2
Checking the package contents
Please make sure that your package contains:
one kit, containing the components listed in the parts list
( page 20) and one PCB or
one ready-built module or
one ready-built module in a housing (complete unit),
a CD (containing the manual and further information).
Required materials
For assembling the kit you need:
an electronic soldering iron (max. 30 Watt) or a regulated soldering
iron with a fine tip and a soldering iron stand,
a tip-cleaning sponge,
a heat-resistant mat,
a small side cutter and wire stripper,
as necessary a pair of tweezers and long nose pliers,
electronic tin solder (0,5 mm. diameter).
For testing the module you need an electric light bulb.
In order to connect the module you need wire. Recommended
diameters: > 0.25 mm² for all connections.
It is recommended to connect two push-buttons when programming
the module (e.g. push-buttons item no. 85-5212x, x=1,2,3,6,7).
When connecting points at terminus station 2, you need for switching
the points:
a bistable relay 12 V (e.g. item no. 84-61111) or
a relay print RL-2 (e.g. 72-00055 as a kit or 72-00056 as a ready-
built module).
Page 4
Page 5

tams elektronik
PZS-2 English
2. Safety instructions
Mechanical hazards
Cut wires can have sharp ends and can cause serious injuries. Watch
out for sharp edges when you pick up the PCB.
Visibly damaged parts can cause unpredictable danger. Do not use
damaged parts: recycle and replace them with new ones.
Electrical hazards
Touching powered, live components,
touching conducting components which are live due to malfunction,
short circuits and connecting the circuit to another voltage than
specified,
impermissibly high humidity and condensation build up
can cause serious injury due to electrical shock. Take the following
precautions to prevent this danger:
Never perform wiring on a powered module.
Assembling and mounting the kit should only be done in closed,
clean, dry rooms. Beware of humidity.
Only use low power for this module as described in this manual and
only use certified transformers.
Connect transformers and soldering irons only in approved mains
sockets installed by an authorised electrician.
Observe cable diameter requirements.
After condensation build up, allow a minimum of 2 hours for
dispersion.
Use only original spare parts if you have to repair the kit or the
ready-built module.
Page 5
Page 6

tams elektronik
!
English PZS-2
Fire risk
Touching flammable material with a hot soldering iron can cause fire,
which can result in injury or death through burns or suffocation.
Connect your soldering iron or soldering station only when actually
needed. Always keep the soldering iron away from inflammable
materials. Use a suitable soldering iron stand. Never leave a hot
soldering iron or station unattended.
Thermal danger
A hot soldering iron or liquid solder accidentally touching your skin can
cause skin burns. As a precaution:
use a heat-resistant mat during soldering,
always put the hot soldering iron in the soldering iron stand,
point the soldering iron tip carefully when soldering, and
remove liquid solder with a thick wet rag or wet sponge from the
soldering tip.
Dangerous environments
A working area that is too small or cramped is unsuitable and can cause
accidents, fires and injury. Prevent this by working in a clean, dry room
with enough freedom of movement.
Other dangers
Children can cause any of the accidents mentioned above because they
are inattentive and not responsible enough. Children under the age of
14 should not be allowed to work with this kit or the ready-built
module.
Caution:
Little children can swallow small components with sharp edges, with
fatal results! Do not allow components to reach small children.
Page 6
Page 7

tams elektronik
!
PZS-2 English
In schools, training centres, clubs and workshops, assembly must be
supervised by qualified personnel.
In industrial institutions, health and safety regulations applying to
electronic work must be adhered to.
3. Safe and correct soldering
Caution:
Incorrect soldering can cause dangers through fires and heat. Avoid
these dangers by reading and following the directions given in the
chapter Safety instructions.
Use a small soldering iron with max. 30 Watt or a regulated
soldering iron.
Only use electronic tin solder with flux.
When soldering electronic circuits never use soldering-water or
soldering grease. They contain acids that can corrode components
and copper tracks.
Insert the component connecting pins into the PCB´s holes as far as
possible without force. The components should be close to the
PCB`s surface.
Observe correct polarity orientation of the parts before soldering.
Solder quickly: holding the iron on the joints longer than necessary
can destroy components and can damage copper tracks or soldering
eyes.
Apply the soldering tip to the soldering spot in such a way that the
part and the soldering eye are heated at the same time.
Simultaneously add solder (not too much). As soon as the solder
becomes liquid take it away. Hold the soldering tip at the spot for a
few seconds so that the solder flows into the joint, then remove the
soldering iron.
Do not move the component for about 5 seconds after soldering.
Page 7
Page 8

tams elektronik
English PZS-2
To make a good soldering joint you must use a clean and unoxidised
soldering tip. Clean the soldering tip with a damp piece of cloth, a
damp sponge or a piece of silicon cloth.
Cut the wires after soldering directly above the soldering joint with a
side cutter.
After placing the parts, please double check for correct polarity.
Check the PCB tracks for solder bridges and short circuits created by
accident. This would cause faulty operation or, in the worst case,
damage. You can remove excess solder by putting a clean soldering
tip on the spot. The solder will become liquid again and flow from
the soldering spot to the soldering tip.
Page 8
Page 9

tams elektronik
PZS-2 English
4. Operation overview
Traffic between two terminus stations
The module controls the shuttle-train traffic between two terminus
stations of an analogue d.c. model railway layout. At the second
terminus station points can be connected. This allows the alternating
traffic of two trains on the shuttle-train section. One additional stop can
be added in each direction of traffic between the terminus stations.
The shuttle-train traffic runs automatically. The trains are slowed down
before reaching the terminus sections or the two stops as soon as a
track busy indicator integrated into the module indicates the train
coming into the respective section. The further course (braking, halting
and accelerating) is time controlled.
Extra halts
Independent of the automatically running shuttle-train traffic between
the terminus sections (and the two stops), extra halts can be
incorporated with external circuits at any time and place.
Settings for the automatic operation
The traffic
between the terminus stations
between the terminus stations and the stops
between the terminus stations, the stops and/or the extra halts
always runs in four phases: acceleration, normal speed, braking and
halt. The length of the phases acceleration, braking and halt can be
programmed
individually for each of the two terminus stations
individually for each of the two stops
jointly for all extra halts.
Page 9
Page 10

tams elektronik
English PZS-2
The length of the phases is adjusted at a trimmer, the settings are
saved in an IC.
Manual operation
The halt at the terminus stations, the stops and the extra halts can be
prolonged by connecting the corresponding input of the module to
earth. Then the train stops at the next station, stop or halt as long as
the input is connected to earth (at least so long as programmed for the
particular halt). This allows intervention in the automatic shuttle-train
traffic via a switch or an external extra circuit.
The already mentioned extra halts are released as soon as the
corresponding input of the module is connected to earth. This can be
done at any time, regardless in which position of the shuttle-train
section the train is. There are a whole range of applications for this,
e.g.:
effectuating extra halts along the shuttle-train section or
effectuating of signal stops or
triggering exact halts at defined positions (e.g. at the end of a
platform).
To trigger additional halts, several external circuits can be used, e.g.
manually released swiches, couplings with reed contacts or light
barriers or complex signal control circuits.
Overcurrent protection
A fuse integrated in the PZS-2 interrupts the current circuit with
overload or when a short circuit occurs on the rails and thus protects
the module from damage. The fuse is designed as a self-closing fuse
which heats with overload and re-activates the module automatically
after cooling.
Page 10
Page 11

tams elektronik
PZS-2 English
Power supply
The module has to be supplied via a transformer not in use as driving
transformer. Note: Driving transformers providing an additional output
for further accessories are not suitable to supply both rails and module,
as they internally contain only one transformer. Note: It is possible to
supply the module via a transformer used to supply other accessories
as the rails (e.g. lighting).
When connecting the module to a transformer in use as driving
transformer, short circuits occur within the PZS-2 which may damage it
irreparably. The integrated fuse is without effect on these short circuits.
The seperate supply of module and rails has the advantage that the
driving voltage can be set individually. E.g. the maximum driving
voltage for the shuttle-train traffic (and the maximum speed with full
speed) can be (pre-) set individually.
Page 11
Page 12
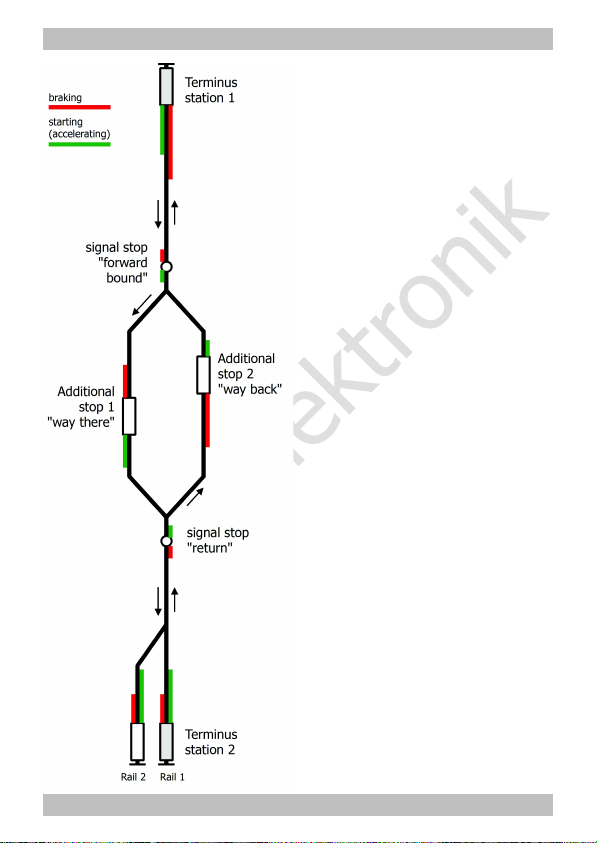
tams elektronik
English PZS-2
Example for a shuttle-train
traffic controlled by a PZS-2
In order to use the PZS-2 it is
sufficient to connect the two
terminus stations. All other
extensions are optional.
By connecting a second rail at
terminus station 2 it is possible to
run two trains alternatingly. In
order to switch between the two
rails an extra bistable relay (not
included in the package) has to be
mounted.
The additional stops 1 (outward
bound) and 2 (return) are
independent of each other. This
allows a different routeing for
outward and return journey (which
is not obligatory).
Extra halts (e.g. at signals or
further stops) can be mounted at
any point of the route. To release
the stop you need a switch or
another external circuit switching
against earth.
Page 12
Page 13
tams elektronik
!
PZS-2 English
5. Technical specifications
Caution:
The PZS-2 must not be supplied via a transformer in use as a driving
transformer! Further information see chapter 4. section "power
supply".
Supply voltage for the module 12 - 18 Volt d.c. or a.c. voltage
Supply voltage
for the shuttle-train section
d.c. driving transformer
Current consumption of the
module
approx. 30 mA
Max. current for the rails 1.000 mA
Predected to IP 00
Ambient temperature in use 0 ... +60 °C
Ambient temperature in storage -10 ... +80 °C
Comparative humidity allowed max. 85 %
Dimensions of the PCB
Dimensions including housing
approx. 72 x 82 mm
approx. 100 x 90 x 35 mm
Weight of the assembled board
Weight including housing
approx. 60 g
approx. 108 g
Page 13
Page 14

tams elektronik
English PZS-2
6. Assembling the kit
You can skip this part if you have purchased a ready-built module or device.
Preparation
Put the sorted components in front of you on your workbench.
The separate electronic components have the following special features
you should take into account in assembling:
Resistors
Resistors reduce current.
The value of resistors for smaller power ratings is indicated
through colour rings. Every colour stands for another
figure. Carbon film resistors have 4 colour rings. The 4th
ring (given in brackets here) indicates the tolerance of the
resistor (gold = 5 %).
Value: Colour rings:
120 brown - red - brown (gold)
1,5 k brown - green - red (gold)
4,7 k yellow - violet - red (gold)
330 k orange - orange - yellow (gold)
Trimm-potentiometers
Trimm-potentiometers (abrv. "trimm-pots") are resistors
which allow the value of resistance to be varied and that
way to be adapted to the particular demands. In the
middle they have a small slot into which a small
screwdriver can be put in order to vary the value of
resistance. The maximum value is printed on the housing.
Depending on the mounting situation trimmpots with a
lying or a standing package are used.
Page 14
Page 15

tams elektronik
PZS-2 English
Ceramic capacitors
Among other things ceramic capacitors are used for
filtering interference voltages or as frequency determining
parts. Ceramic capacitors are not polarized.
Normally they are marked with a three-digit number which
indicates the value coded.
The number 104 corresponds to the value 100 nF.
Electrolytic capacitors
Electrolytic capacitors are often used to store energy. In
contrast to ceramic capacitors they are polarized. The
value is given on the package.
Electrolytic capacitors are available with different voltage
sustaining capabilities. Using an electrolytic capacitor with
a voltage sustaining capability higher than required is
always possible.
Diodes
Diodes allow the current to pass through in one direction
only (forward direction), simultaneously the voltage is
reduced by 0,3 to 0,8 V. Exceeding of the limit voltage
always will destroy the diode, and allow current to flow in
the reverse direction.
The diode type is printed on the package.
Page 15
Page 16

tams elektronik
English PZS-2
Light emitting diodes (LEDs)
When operated in the forward direction the LEDs light.
They are available in several different versions (differing in
colour, size, form, luminosity, maximum current, voltage
limits).
Light emitting diodes should always be connected via a
series resistor which limits the current and prevents failure.
With circuits designed for the connection of LEDs the
series resistors are often integrated on the circuit board.
Rectifiers
Rectifiers convert alternating into direct voltage. They have
four pins: two for the input voltage (a.c. voltage) and two
for the output voltage (d.c. voltage). The pins for the
output voltage are polarized.
Transistors
Transistors are current amplifiers which convert low signals into
stronger ones. There are several types in different package forms
available. The type designation is printed on the component.
Transistors for a low power rating (e.g. BC types) have a
package in form of a half zylinder (SOT-package).
Transistors for a high power rating (e.g. BD types) have a
flat package (TO-package), which is in use in different
versions and sizes.
The three pins of bipolar transistors (e.g. BC and BD types)
are called basis, emitter and collector (abbreviated with the
letters B, E, C in the circuit diagram).
Page 16
Page 17

tams elektronik
PZS-2 English
Integrated circuits (ICs)
Depending on the type, ICs fulfil various tasks. The most
common housing form is the so-called "DIL"-housing, from
which 4, 6, 8, 14, 16, 18 or more "legs" (pins) are
arranged along the long sides.
ICs are sensitive to damage during soldering (heat,
electrostatic charging). For that reason in the place of the
ICs IC sockets are soldered in, in which the ICs are
inserted later.
Microcontrollers
Microcontrollers are ICs, which are individually programmed for the
particular application. The programmed controllers are only available
from the manufacturer of the circuit belonging to it.
Opto couplers
Opto couplers are ICs, which work similar to laser beam switches. They
combine in one housing a light emitting diode and a photo transistor. Their
task is the transmission of information without galvanic connection. They
are in a DIL-housing with at least 4 pins.
Voltage regulators
Voltage regulators are ICs, which convert a variable, non
regulated input voltage in a constant output voltage. They
are produced in transistor packages with three connecting
pins for input, output and earth.
The package forms of voltage regulators depend on their
type. In use are e.g. voltage regulators in flat TO
packages.
Page 17
Page 18

tams elektronik
English PZS-2
Fuses
Fuses interrupt a current circuit, when the current exceeds
a certain strength of current for a set time. In this way
they protect the circuit from damage due to overheating,
resulting from an excess current flowing for a longer
period. Excess current can be caused by overload or a
short circuit.
Terminal strips
Terminal strips are solder-in screw-type terminals. They provide a
solder-free and safe connection of the cables to the circuit, which can
still be separated any time.
Page 18
Page 19

tams elektronik
PZS-2 English
PCB layout and parts list
Page 19
Page 20

tams elektronik
English PZS-2
Resistors R21, R22, R33, R34 120
R3, R7, R12, R14, R15, R16 1,5 k
R2, R4, R5, R6, R8, R9, R10,
R11, R13
4,7 k
R17, R18, R19, R31, R32 330 k
Trimm-pots R1, R29, R30 470 k
Diodes D1- D20 1N400x, x=2...7
LEDs LED1 LED 3 mm
Rectifiers B1 B80C800
Ceramic
Capacitors
C1, C2, C3, C6, C7, C8, C10,
C11
100 nF
Electrolytic
capacitors
C12, C13, C14, C15 2,2 µF/25 V
C4, C5 100 µF/25 V
C9 220 µF/25 V
C16 470 µF/25 V
Transistors T1, T2 BC547
Q3, T3, T4, T5 BD679
Q1, Q2 BD680
ICs IC1 PIC 16F627 A-I/P
Opto couplers OK1, OK2 PC827
IC sockets IC1 18-pol.
OK1, OK2 8-pol.
Voltage
regulators
IC2 7805
Fuses F1 1 A
Terminal strips X1 2 x 9 poles
Page 20
Page 21

tams elektronik
!
PZS-2 English
Assembly
Proceed according to the order given in the list below. First solder the
components on the solder side of the PCB and then cut the excess
wires with the side cutter. Follow the instructions on soldering in
section 3.
Caution:
Several components have to be mounted according to their polarity.
When soldering these components the wrong way round, they can be
damaged when you connect the power. In the worst case the whole
circuit can be damaged. At the best, a wrongly connected part will not
function.
1. Resistors Mounting orientation of no importance.
2. Diodes Observe the polarity!
The negative end of the diodes is marked with
a ring. This is shown in the PCB layout.
3. Ceramic
Capacitors
Mounting orientation of no importance.
4. IC sockets Mount the sockets that way, the markings on
the sockets show in the same direction as the
markings on the PCB board.
5. Fuse Mounting orientation of no importance.
6. Transistors Observe the polarity!
The cross section of transistors for a low
power rating in SOT-packages is shown in the
PCB layout. With transistors for a high power
rating in TO packages (e.g. BD types) the
unlabelled back side is marked in the PCB
layout by a thick line.
Page 21
Page 22

tams elektronik
English PZS-2
7. Rectifier Observe the polarity! The pin connections are
printed on the housing. The longer connecting
pin is the positive pole.
8. Electrolytic
capacitors
Observe the polarity! One of the two leads
(the shorter one) is marked with a minus sign.
9. Voltage regulator Observe the polarity!
The cross section of voltage regulators in
SOT-packages is shown in the PCB layout.
With voltage regulators in TO-packages the
unlabelled back side is marked in the PCB
layout by a thick line.
10. Trimm-
potentiometers
The mounting orientation is preset by the
layout of the three pins.
11. Light emitting
diode (LED)
Observe the polarity!
With wired LEDs the longer lead is always the
anode (positive pole).
12. Terminal strips Put together the terminal strips before
mounting them.
13. ICs and
optocouplers in
DIL-housing
Insert the ICs into the soldered socket.
Do not touch the ICs without first discharging
yourself by touching a radiator or other
grounded metal parts.
Do not bend the "legs" when inserting them
into the sockets. Check that the markings on
the PCB, the socket and the IC show to the
same direction.
Page 22
Page 23

tams elektronik
!
!
PZS-2 English
Performing a visual check
Perform a visual check after the assembly of the module and remove
faults if necessary:
Remove all loose parts, wire ends or drops of solder from the PCB.
Remove all sharp wire ends.
Check that solder contacts which are close to each other are not
unintentionally connected to each other. Risk of short circuit!
Check that all components are polarised correctly.
When you have remedied all faults, go on to the next part.
7. Functional test
It is recommended to test the basic functioning of the module before
installing it into the layout.
Connect a bulb to the connections 5 and 6 of the PZS-2.
Connect the driving transformer to the module, namely
the driving transformer´s earth connection to the connection 3 of
the PZS-2 and
the driving transformer´s "+" to the connection 11 of the PZS-2.
Turn on the controller of the driving transformer.
Connect the power supply for the shuttle-train control to the
connections 1 and 10 of the PZS-2 and switch it on.
Do not use the driving transformer for supplying the PZS-2.
The lamps should start to light up slowly. With it, the functional test is
completed. In case the lamp does not light up, check the connections.
Caution:
If a component gets too hot, disconnect the module from the power
supply mmediately. Possible short circuit! Check the assembly!
Page 23
Page 24

tams elektronik
English PZS-2
8. Connecting the PZS-2
8.1. Schema
1 Supplying transformer
PZS-2
10 Supplying transformer
PZS-2
2 Points, return line 11 Driving transformer "+"
3 Driving transformer "" 12 Switching input
"extra halt(s)"
4 Earth for switching and
programming inputs
13 Switching input
"prolonging the halting time"
5 Terminus station 2 "left" 14 Programming input "save"
6 Terminus station 1 "right" 15 Programming input "select"
7 Points, switching contact 1 16 Stop 1 and 2 ("left")
8 Points, switching contact 2 17 Stop 1 and 2 ("right")
9 Terminus station 1 "left" 18 Terminus station 2 "right"
N.B: The specifications "right" and "left" refer to the direction of travel"way there".
Page 24
Page 25

tams elektronik
!
!
PZS-2 English
8.2. Dividing the shuttle-train section into parts
The halts at the terminus stations and the two stops are initiated when
the train has come into the respective section and the accessory track
busy indicator has indicated the train coming in. The division of the
shuttle-train section should be done as follows:
At least into the parts: terminus station 1 and terminus station 2.
If neccessary into the additional parts: stop 1 and / or stop 2.
In order to define a new part you should cut the rail at that point where
the coming-in train has to start braking. Always cut the right rail – seen
in the train´s direction of travel. The other (left) rail should not be cut.
For the stop 1 and the terminus station 2 is the direction of travel "way
there" and for the stop 2 and the terminus station 2 the direction of
travel "way back" relevant.
Caution:
Dismount anti-interference capacitors possibly mounted to the rails of
the shuttle-train section. They can disturb the operation massively.
8.3. Connecting the power supply
You can use a d.c. or an a.c. transformer with 12 to 18 V as a power
supply for the PZS-2. The polarity is of no importance if you connect
the PZC-2 only.
Caution:
When connecting several devices to the same transformer, all
connections have to be polarized the same way as a rule. Otherwise a
short circuit could occur damaging connected devices.
Page 25
Page 26
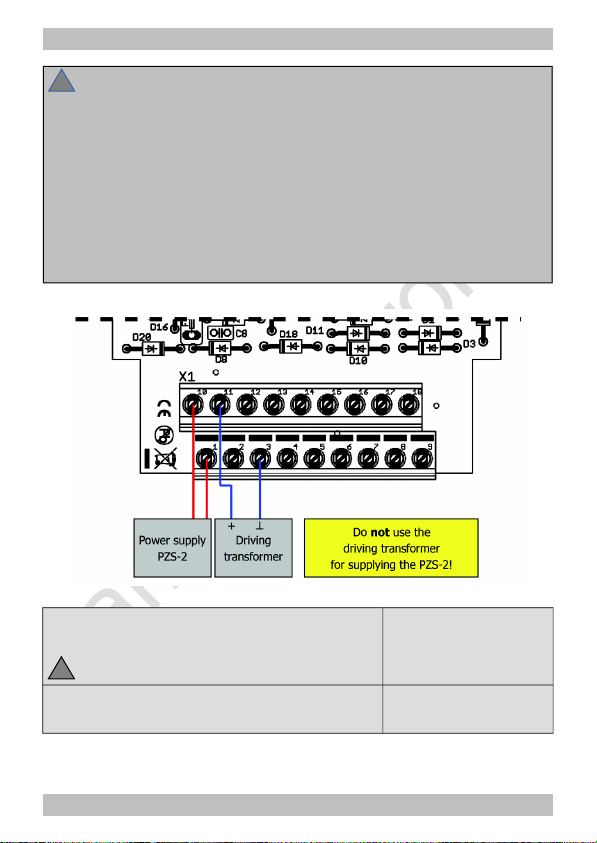
tams elektronik
!
!
English PZS-2
Caution:
Do not use the driving transformer for supplying the PZS-2!
When supplying the circuit via a transformer used as a driving
transformer as well, short circuits can occur and possibly damage the
circuit irreparably. The integrated fuse is without effect against short
circuits of this type.
Hint: Driving transformers with an additional output for further
accessories beside the driving controller are not suitable for supplying
both rails and PZS, as they internally consist of one trafo only.
Supplying transformer
(= power supply of the module)
Do not power the transformer yet!
1 and 10
Driving transformer
(= power supply for the shuttle-train section)
earth-connection: 3
connection "+": 11
Page 26
Page 27

tams elektronik
PZS-2 English
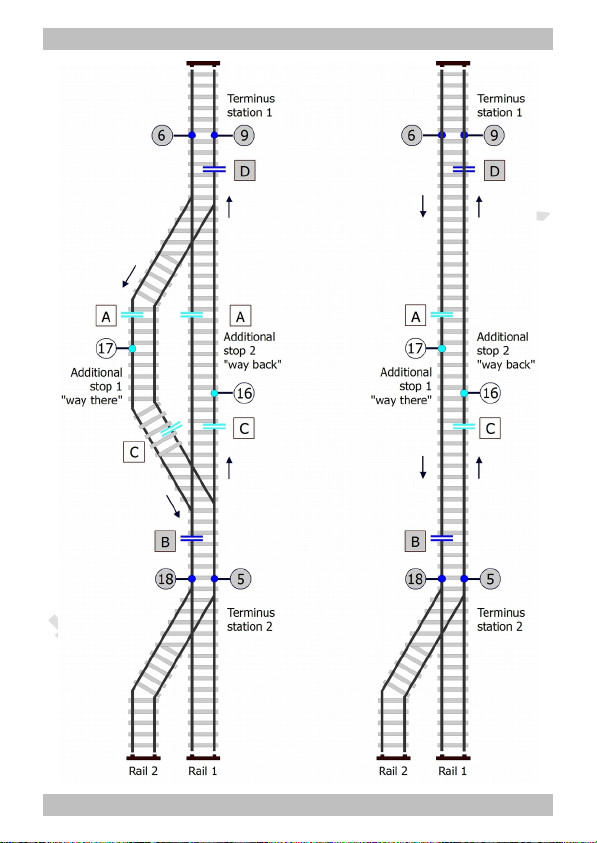
8.4. Connecting the shuttle-train section to the PZS-2
You must make at least the following connections (marked grey in the
list):
Supplying transformer for the PZS-2 (s. section 8.3)
Driving transformer (s. section 8.3)
Terminus station 1 and 2
The other connections should be made only if required.
Connecting the shuttle-train section
N.B: The specifications "right" and "left" refer to the
direction of travel"way there".
left right cutting
points
Terminus station 1 9 6 D
Terminus station 2 5 18 B
Stop 1 and stop 2 16 17 A, C
Stop 1 only (without stop 2) --- 17 A
Stop 2 only (without stop 1) 16 --- C
Additional connections
Points at terminus station 2
In case you do not use stop-points you should connect an
extra bistabile relais to the points (not included in the
package). See section "Connecting points".
return line: 2
switching contacts:
7,8
Switching input "prolonging the halting time" 13, earth: 4
Switching input "extra halts" 12, earth: 4
Programming input "save" 14, earth: 4
Programming input "select" 15, earth: 4
Page 27
Page 28
tams elektronik
English PZS-2
Page 28
Page 29
tams elektronik
PZS-2 English
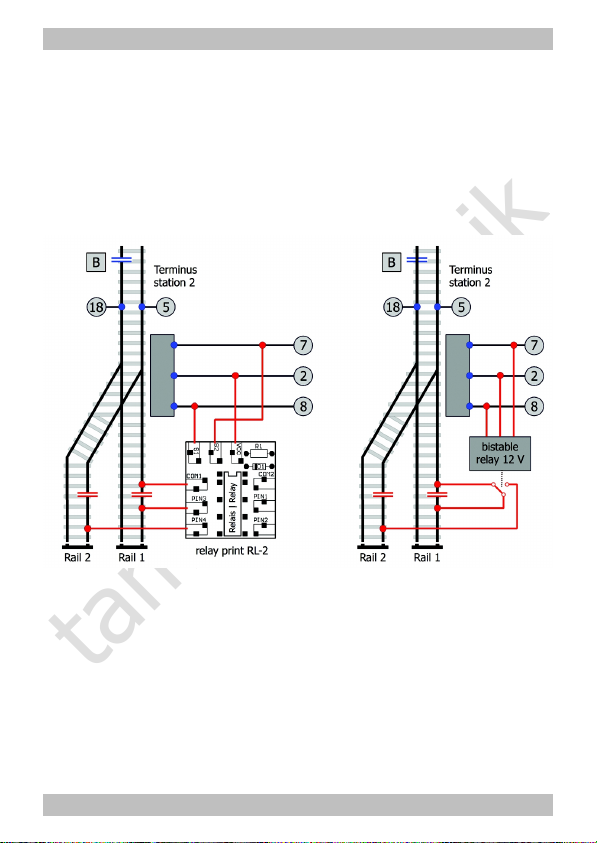
Connecting points
In case you do not use stop-points you should connect an extra
bistabile relais 12 V (or a relay circuit board RL-2) to the points. The
bistable relais switches on the power supply for the one rail in terminus
station 2 while switching off the power supply for the other rail. If
neither stop-points nor a bistabile relais are connected both rails are
constantly supplied with power.
Page 29
Page 30
tams elektronik
!
English PZS-2
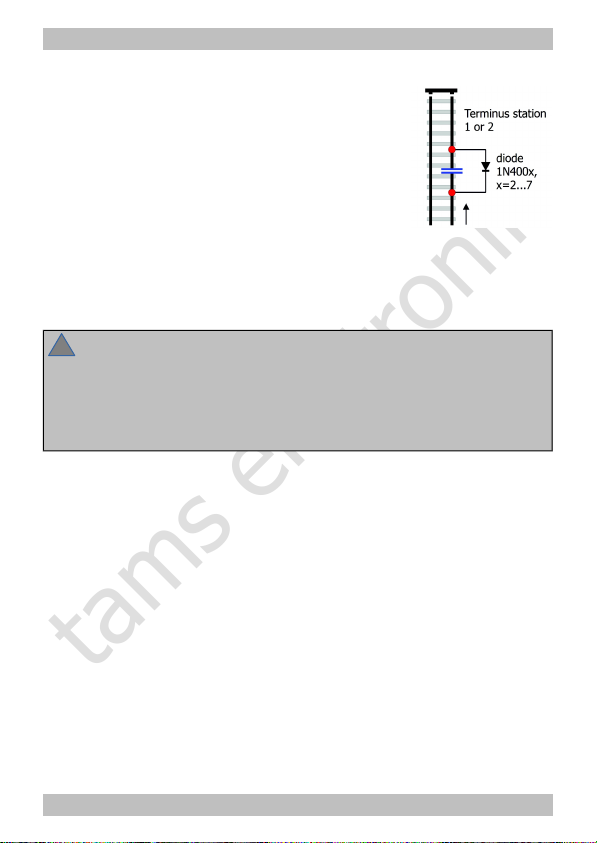
Connecting stop diodes
In order to prevent trains running beyond the
end of the rails in the terminus stations 1 and
2, you can install extra stop diodes.
Connect them to the right rail – seen in the
train´s direction of travel. Cut the rail that way
that all current collectors driving the motor
have passed the cut-off before the train
reaches the end of the rails.
9. Operation
Caution:
The maximum current of a train in the shuttle-train section should not
exceed 1 000 mA (including all loads as e.g. carriage lightings). When
exceeding the maximum current, the integrated fuse switches off the
circuit. In the worst case components on the circuit can be damaged.
Run
Immediately after switching on the power supply for the module, the
shuttle-train traffic starts with a train starting from the terminus station
1 in direction of travel "way there".
Between the halts the shuttle-train traffic always runs in four phases:
acceleration, normal speed, braking and halt. As soon as a braking
phase has been triggered (i.e. the locomotive has run into the
respective section) the phases braking, halt and acceleration are time
controlled. During the phase "normal speed" the train is supplied with
the voltage set at the driving transformer. The phase "normal speed" is
interupted by releasing a new braking phase.
Page 30
Page 31

tams elektronik
PZS-2 English
Traffic with one train
Caution: When switching on the shuttle-train control, the train should
be standing in the terminus station 1. If it is standing in the terminus
station 2 it runs in direction of travel "way there" against the buffers.
Traffic with two trains
Caution: When switching on the shuttle-train control one train should
be standing in the terminus station 1. Check before switching on the
shuttle-train control if the points are set so that the train is runs freely
into the terminus station 2.
It is possible that the train starting at terminus station 1, after switching
on the shuttle-train control, runs back from terminus station 2 after the
set halting time, and not the train standing in terminus station 2. After
another "way there" of this train, the normal alternating traffic begins.
The points are switched automatically so that the trains alternatingly
start from rails 1 and 2.
Caution: The points´ position and the "track busy"-status of the two
rails in terminus station 2 are not controlled by the module. In case the
points´position is altered externally a coming-in train possibly runs into
occupied rails.
Prolonging the halting time
The halting phases for all stops can be prolonged individually by
connecting the switching input "prolonging the halting time" to earth.
The switching input can be connected either to a switch or an extra
circuit. Closing the earth contact affects the stop to be performed next
or the stop that actually is performed.
N.B: The halt at a terminus station, a stop or an extra halt takes at
least as long as programmed for the stop, even if the connection to
earth is interrupted earlier for the switching input.
Page 31
Page 32

tams elektronik
English PZS-2
Extra halts
By connecting the switching input "extra halts" to earth an extra halt is
released immediately and independent of the place where the train
momentarily is. In order to close the earth contact you can use
switches or external circuits (e.g. signal control circuits).
N.B: The length of the phases accelerating, halt and braking is set
jointly for all extra halts.
Page 32
Page 33

tams elektronik
PZS-2 English
10. Programming the PZS-2
Programming the length of the phases is done the same way for the
five different stops (two terminus stations, two stops, all extra halts).
Carry out the programming steps 1 to 3 for all stops you want to
program.
Programming step 1: Choosing a stop
Intermittently earth the programming input "select" (15) to point (4).
The LED on the module flashes and thus indicates the 1st stop is ready
to be programmed. By connecting the programming input once again to
earth you switch to the programming of the next stop. The number of
flashlights between the pauses indicates the one of the five stops
ready to be programmed.
If you do not want to program a stop you can skip this halt by
connecting the programming input once again to earth.
If you connect the programming input once again to earth after having
reached the programming of the 5th stop the module automatically
returns to standard operation.
Stop Number of flashlights Stop ready to be programmed
1 1 Terminus station 1
2 2 Stop 1
3 3 Terminus station 2 (both rails)
4 4 Stop 2
5 5 Extra halt(s)
Page 33
Page 34

tams elektronik
English PZS-2
Programming step 2: Setting the phases´length
By adjusting the trimmer you set the length of the phases accelerating,
halt and braking for the 5 stops. In state of delivery the phases are set
to the shortest possible length. Test the module with these settings
first. Choose the stop you want to program (see programming step 1)
and prolong the phases by turning the adjusting screw to the right.
N.B: The settings only take effect if you save them before choosing the
next stop for programming (see programming step 3).
Trimmer Phase Min. length (approx.)
Trimmer A R23 Accelerating 1 sec.
Trimmer B R20 Braking 1 sec.
Trimmer H R1 Halt 4-5 sec.
Page 34
Page 35

tams elektronik
PZS-2 English
Programming step 3: Saving the settings
After having set the phases´ length for a stop at the trimmer, connect
the programming input "save" (14) to earth (4) intermittently.
N.B: Before closing the earth contact make sure the LED on the module
flashes. If it does not the module is not in the programming mode and
you cannot save any settings. The number of the light pulses between
the pauses indicates for which stop the settings at the trimmer are
saved.
As long as the connection to earth is held the LED lights and indicates
that the settings are saved.
Tip
Especially if you use all possible connections of the module we advise
you to mount 2 push-button switches (not included in the package) into
the connections between the programming inputs and the earth
connection.
Page 35
Page 36

tams elektronik
!
English PZS-2
11. Check list for troubleshooting
Parts are getting too hot and/or start to smoke.
Disconnect the system from the mains immediately!
Possible cause: one or more components are soldered incorrectly.
I n case you have mounted the module from a kit, perform a
visual check ( section 6.) and if necessary, remedy the faults.
Otherwise send in the module for repair.
The train stops, restarts, stops again, and so forth.
Possible cause: The overload protection consistently switches on and
off the current circuit, due to overload or a short circuit. Check if
there is a short circuit on the rails or if the locomotive´s current
consumption exceeds 1.000 mA.
The train does not run. / Functional test: The lamp does not light.
Possible cause: The driving transformer has not been connected or
has been connected the wrong way around (connections "earth" and
"+" exchanged.) Check the connections.
The settings of the trimmer do not take any effect on phase length
of a stop.
Possible cause: The settings of the trimmer have not been saved or
have been saved for another stop. Program the phase length
anew for the stop concerned. See information on the programming
steps 1 and 3.
The train does not stop at a station or a stop.
Possible cause: The cuts are placed badly or the sections are
connected the wrong way. Check the placing of the cuts and the
connections of the sections.
Page 36
Page 37

tams elektronik
PZS-2 English
In a terminus station the train runs against a buffer.
Possible cause: The cuts are placed badly or the sections are
connected the wrong way. Check the placing of the cuts and the
connections of the sections.
Possible cause: When switching on the shuttle-train control the train
(or both trains) was (were) standing in terminus station 2.
Hotline: If problems with your module occur, our hotline is pleased to
help you (mail address on the last page).
Repairs: You can send in a defective module for repair (address on the
last page). In case of guarantee the repair is free of charge for you.
With damages not covered by guarantee, the maximum fee for the
repair is the difference between the price for the ready-built module
and the kit according to our valid price list. We reserve the right to
reject the repairing of a module when the repair is impossible for
technical or economic reasons.
Please do not send in modules for repair charged to us. In case of
warranty we will reimburse the forwarding expenses up to the flat rate
we charge according to our valid price list for the delivery of the
product. With repairs not covered by guarantee you have to bear the
expenses for sending back and forth.
Page 37
Page 38

tams elektronik
English PZS-2
12. Guarantee bond
For this product we issue voluntarily a guarantee of 2 years from the
date of purchase by the first customer, but in maximum 3 years after
the end of series production. The first customer is the consumer first
purchasing the product from us, a dealer or another natural or juristic
person reselling or mounting the product on the basis of selfemployment. The guarantee exists supplementary to the legal warranty
of merchantability due to the consumer by the seller.
The warranty includes the free correction of faults which can be proved
to be due to material failure or factory flaw. With kits we guarantee
the completeness and quality of the components as well as the function
of the parts according to the parameters in not mounted state. We
guarantee the adherence to the technical specifications when the kit
has been assembled and the ready-built circuit connected according to
the manual and when start and mode of operation follow the
instructions.
We retain the right to repair, make improvements, to deliver spares or
to return the purchase price. Other claims are excluded. Claims for
secondary damages or product liability consist only according to legal
requirements.
Condition for this guarantee to be valid, is the adherence to the
manual. In addition, the guarantee claim is excluded in the following
cases:
if arbitrary changes in the circuit are made,
if repair attempts have failed with a ready-built module or device,
if damaged by other persons,
if damaged by faulty operation or by careless use or abuse.
Page 38
Page 39

tams elektronik
PZS-2 English
13. EU declaration of conformity
This product conforms with the EC-directives mentioned below
and is therefore CE certified.
2004/108/EG on electromagnetic. Underlying standards: EN 55014-1
and EN 61000-6-3. To guarantee the electromagnetic tolerance in
operation you must take the following precautions:
Connect the transformer only to an approved mains socket installed
by an authorised electrician.
Make no changes to the original parts and accurately follow the
instructions, connection diagrams and PCB layout included with this
manual.
Use only original spare parts for repairs.
2011/65/EG on the restriction of the use of certain hazardous
substances in electrical and electronic equipment (ROHS). Underlying
standard: EN 50581.
14. Declarations conforming to the WEEE directive
This product conforms with the EC-directive 2012/19/EG on waste
electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE).
The Tams Elektronik GmbH is registered with the WEEE-no.
DE 37847206, according to. § 6 sect. 2 of the German
electro regulations from the responsible authority for the
disposal of used electro equipment.
Don´t dispose of this product in the house refuse, bring it to the next
recycling bay.
Page 39
DE 37847206
Page 40

tams elektronik
n
n
n
Information and tips:
n
http://www.tams-online.de
n
n
n
n
Warranty and service:
n
Tams Elektronik GmbH
n
Fuhrberger Straße 4
DE-30625 Hannover
n
fon: +49 (0)511 / 55 60 60
fax: +49 (0)511 / 55 61 61
n
e-mail: modellbahn@tams-online.de
n
n
DE 37847206
 Loading...
Loading...