Page 1
n
n
Schattenbahnhofsteuerung
Shadow-station Control
Art.-Nr. 21-01-043
Art.-Nr. 22-01-043
Art.-Nr. 21-01-044
Art.-Nr. 22-01-044
n
n
n
n
Anleitung
n
Manual
n
n
n
Page 2
Deutsch 3
English 33
© 01/2007 Tams Elektronik GmbH
Alle Rechte, insbesondere das Recht der
Vervielfältigung und Verbreitung sowie der
Übersetzung vorbehalten. Vervielfältigungen
und Reproduktionen in jeglicher Form
bedürfen der schriftlichen Genehmigung
durch die Tams Elektronik GmbH.
Technische Änderungen vorbehalten.
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
© 01/2007 Tams Elektronik GmbH
All rights reserved. No part of this
publication may be reproduced or
transmitted in any form or by any means,
electronic or mechanical, including
photocopying, without prior permission in
writing from Tams Elektronik GmbH.
Subject to technical modification.
n
n
n
n
n
Page 3

SBS-1 English
Table of contents
How to use this manual 34
Intended use 34
Safety instructions 35
EMC declaration 36
Operation overview 37
Technical specifications 38
Choosing the power supply 38
Checking the package contents 38
Required tools and consumables 39
Safe and correct soldering 39
Assembling the kit 41
Performing a visual check 45
Display and operating elements of the modules 46
Operation of the modules 47
Connecting the modules and performing functional tests 49
Tracks within the reach of the shadow-station control 55
Connecting the shadow-station control 55
FAQ 58
Manufacturer's note 59
Certification 59
Conditional warranty 60
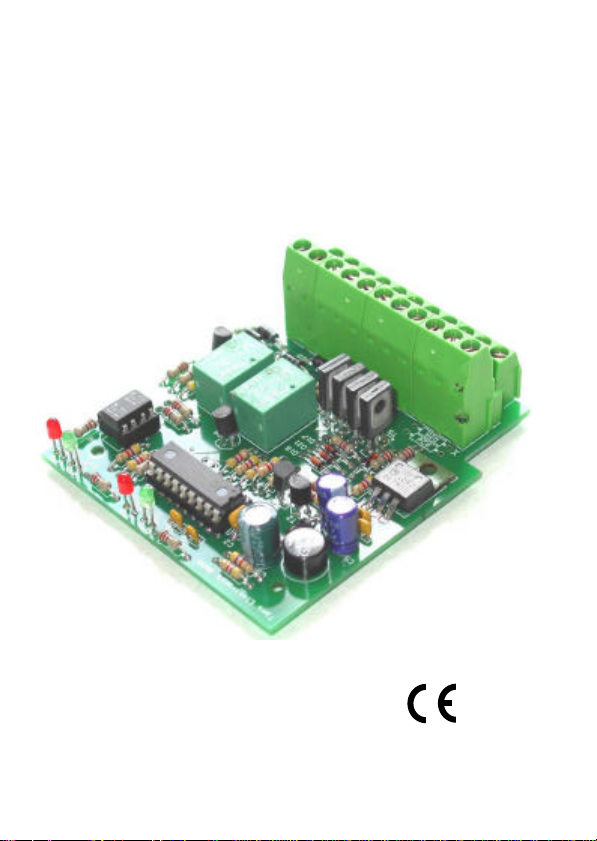
SBS-GZ-1: Parts list and Printed Circuit Board (PCB) layout (Fig. 1.1) I
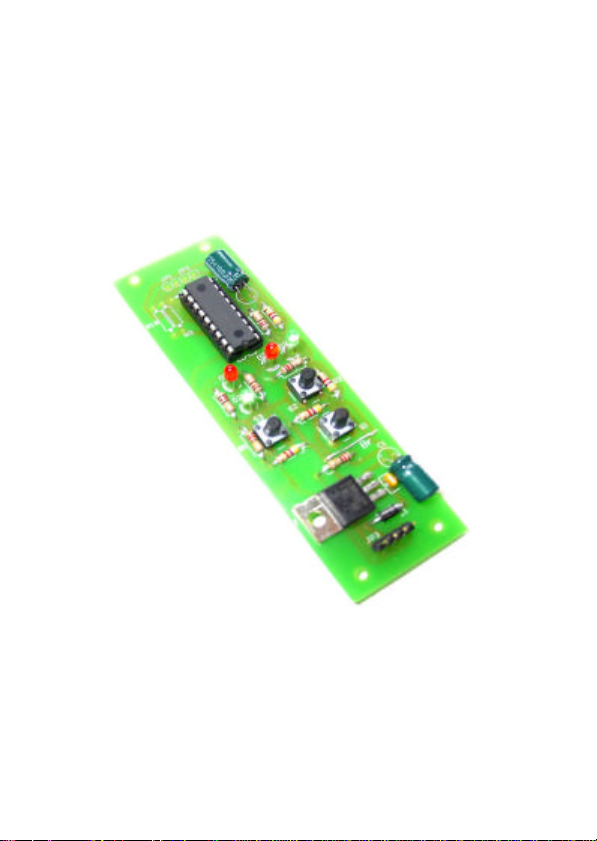
SBS-AB-1: Parts list and Printed Circuit Board (PCB) layout (Fig. 1.2) II
SBS-GZ-1: Circuit Diagram (Fig. 2.1) III
SBS-AB-1: Circuit Diagram (Fig. 2.2) IV
Connections testing assembly (Fig. 3) V
Connections (Fig. 4) VI
Connection of the track sections (Fig. 5) VII
(Pages I to VII in the centre of this handbook are removeable.)
Page 33
Page 4
English SBS-1
!
How to use this manual
If you have no specialist technical training, this manual gives step-bystep instructions for safe and correct assembly of the kit(s) or fitting of
the ready-built module(s), and operation. Before you start, we advise
you to read the whole manual, particularly the chapter on safety
instructions and the FAQ chapter. You will then know where to take
care and how to prevent mistakes which take a lot of effort to correct.
Keep this manual safely so that you can solve problems in the future. If
you pass the kit(s) or the module(s) on to another person, please pass on
the manual with it.
Intended use
Caution:
Integrated circuits are very sensitive to static electricity. Do not touch
components without first discharging yourself. Touching a radiator or
other grounded metal part will discharge you.
The kit(s) or the ready-built module(s) can be assembled or fitted using
this manual. They are designed for use in model railways.
The shadow-station control allows you to supervize and to control up to
32 railway sidings and one thoroughfare rail. The shadow-station
control is of modular design. It is composed of:
§ one central module with an integrated rail module to control two
railway sidings and one thoroughfare rail,
§ one display and operating module,
§ up to 15 further rail modules (optional).
The kit(s) and the ready-built module(s) are not suitable for children
under the age of 14.
Reading, understanding and following the instructions in this manual
are mandatory for the user.
Any other use of the kit is inappropriate and invalidates any guarantees.
Page 34
Page 5

SBS-1 English
Safety instructions
Mechanical hazards
Cut wires can have sharp ends and can cause serious injuries. Watch
out for sharp edges when you pick up the PCB.
Visibly damaged parts can cause unpredictable danger. Do not use
damaged parts: recycle and replace them with new ones.
Electrical hazards
§ Touching powered, live components,
§ touching conducting components which are live due to malfunction,
§ short circuits,
§ connecting the circuit to a higher voltage than designed,
§ impermissibly high humidity,
§ condensation of water
can cause serious injury due to electrical shock. Take the following
precautions to prevent this danger:
§ Never perform wiring on a powered module.
§ Only use low power for this module as described in this manual and
only use certified transformers.
§ Connect transformers and soldering stations only in approved mains
sockets installed by an authorised electrician.
§ Observe cable diameter requirements.
§ After the condensation of water do not start working until after a
minimum of 2 hours of acclimatisation.
§ Mounting the module should only be done in closed, clean, dry
rooms. Beware of humidity.
§ Use only original spare parts if you have to repair the module.
Fire risk
Touching flammable material with a hot soldering iron can cause lifethreatening fire, burns and toxic smoke. Connect your soldering iron or
soldering station only when actually needed. Use the correct soldering iron
or station and never leave a hot soldering iron or station unattended.
Page 35
Page 6

English SBS-1
Thermal danger
A hot soldering iron or liquid solder accidentally touching your skin can
cause skin burns. As a precaution:
§ use a heat-resistant mat during soldering,
§ always put the hot soldering iron in the soldering iron stand,
§ point the soldering iron tip carefully when soldering, and
§ remove liquid solder with a thick wet rag or wet sponge.
Dangerous environments
A working area that is too small or cramped is unsuitable and can cause
accidents, fires and injury. Prevent this by working in a clean, dry room
with enough freedom of movement.
Other dangers
Children can cause any of the accidents mentioned above because they
are inattentive and not responsible enough. Children under the age of 14
should not be allowed to work with this kit or the ready-built module.
Little children can swallow small components with sharp edges. Life
threatening! Do not allow components to reach small children.
In schools, training centres, clubs and workshops, assembly must be
supervised by qualified personnel.
In industrial institutions, health and safety regulations applying to
electronic work must be adhered to.
EMC declaration
This product is developed in accordance with the European standards EN
55014 and EN 50082-1, tested corresponding to the EC - directive
89/336/EWG (EMVG of 09/11/1992, electromagnetic tolerance) and meets
legal requirements.
To guarantee the electromagnetic tolerance you must take the
following precautions:
§ Connect the transformer only to an approved mains socket installed
by an authorised electrician.
Page 36
Page 7

SBS-1 English
§ Make no changes to the original parts and accurately follow the
instructions, circuit diagram and PCB layout included with this manual.
§ Use only original spare parts if you have to repair the kit or the
ready-built module.
Operation overview
The shadow-station allows you to supervize and to control up to 32 railway
sidings and one thoroughfare rail. The modular design of the shadowstation allows it to be adapted to individual needs. It is composed of:
§ one central module with an integrated rail module to supervize
and to control two railway sidings and one thoroughfare rail,
§ one display and operating module,
§ up to 15 further rail modules (optional).
The following operating modes can be set:
§ first-in-first-out-operation
§ random operation or
§ manual operation.
The current operating mode is saved and is automatically set when the
model railway is started the next time.
The modules automatically control the connected points: As soon as a
train has arrived in a siding, the connected points turn to
"thoroughfare". When the train has departed out of the railway siding
and as soon as the module has detected the siding to be vacant (i.e.
there are no current consumers left on the siding) the connected points
are set to "entrance into railway siding".
If all railway sidings are occupied a further train coming into the
shadow-station is automatically guided on to the thoroughfare rail.
As soon as the departure of a train from a railway siding is initiated, the
siding will be provided with power supply for ca. 10 seconds. If a
current consumer is detected on the railway siding afterwards (e.g. a
torn-off carriage with lighting) the module indicates a malfunction. The
Page 37
Page 8

English SBS-1
malfunction will be automatically removed 5 to 6 seconds after the
current consumer has been taken off the rails.
The shadow-station control can be used in a.c. or d.c. systems as well
as in digital operation.
Technical specifications
Supply voltage 16 - 18 Volt a.c. voltage
Current consumption ca. 15 mA
Protected to IP 00
Ambient temperature in use 0 - + 60° C
Ambient temperature in storage -10 - + 80° C
Comparative humidity allowed max. 85 %
Dimensions (SBS-GZ-1) ca. 72 x 83 mm
Dimensions (SBS-AB-1) ca. 32 x 105 mm
Weight (SBS-GZ-1) ca. 70 g
Weight (SBS-AB-1) ca. 19 g
Choosing a power supply
The module is designed for connection to a model railway power
source, i.e. 16-18 Volt alternating (a.c.) voltage.
Checking the package contents
Check the contents of the package for completeness:
Basic pack shadow station control SBS-B-1
§ 1 kit "Central module" SBS-GZ-1, containing the components listed
in the parts list "Central module" and one PCB or
§ 1 ready-built central module,
§ 1 kit "Display and operating module" SBS-AB-1, containing the
components listed in the parts list and one PCB or
§ 1 ready-built display and operating module
§ 1 manual.
Page 38
Page 9

SBS-1 English
!
Addition pack rail module SBS-G-1
§ 1 kit " Rail module" SBS-GZ-1, containing the components listed in
the parts list "Rail module" and one PCB or
§ 1 ready-built rail module,
§ 1 manual.
Required tools and consumables
Make sure you have the following tools, equipment and materials ready
for use:
§ a heat-resistant mat
§ a soldering iron stand with tip-cleaning sponge
§ a small side cutter and wire stripper
§ a pair of tweezers and long nose pliers (not necessary for the
ready-built module)
§ an electronic soldering iron (max. 30 Watt) with a fine tip
§ tin solder (0,5 mm. diameter)
§ wire (diameter: > 0,22 mm² for all connections)
§ two lamps for testing the central / rail module
§ two points for testing the central / rail module
Safe and correct soldering
Caution:
Incorrect soldering can cause fires (through excessive heat). Avoid this
danger by reading the chapter Safety instructions again and
following the directions given.
If you have had training in soldering you can skip this chapter.
§ Use a small soldering iron with max. 30 Watt. Keep the soldering tip
clean so the heat of the soldering iron is applied to the solder point
effectively.
Page 39
Page 10

English SBS-1
§ When soldering electronic circuits never use soldering-water or
soldering grease. They contain acids that can corrode components
and copper tracks.
§ Only use electronic tin solder with flux.
§ Solder fast: long soldering can destroy components and copper
tracks, and damages through plated holes.
§ Observe correct polarity orientation of semi-conductors, LEDs
electrolytic capacitors and integrated circuits before soldering and
ensure that the solder time does not exceed 5 seconds, otherwise
components can be damaged.
§ Apply the soldering tip to the soldering spot in such a way that the
part and the soldering spot are heated at the same time.
Simultaneously add solder (not too much). As soon as the solder
becomes liquid take it away. Hold the soldering tip at the spot for a
few seconds so that the tin solder finds its way, then remove the
soldering iron.
§ Do not move the component for about 5 seconds after soldering.
§ To make a good soldering joint you must use a clean and
unoxidised soldering tip. Clean the soldering tip with a damp piece
of cloth, a damp sponge or a piece of silicon cloth.
§ Cut the wires after soldering directly above the PCB solder side with
a side cutter.
§ After placing the parts, please double check for correct polarity.
Check the PCB tracks for solder bridges, short circuits created by
accident. This would cause faulty operation or, in the worst case,
damage. You can remove excess solder by putting a clean soldering
tip on the spot. The solder will become liquid again and flow from
the soldering spot to the soldering tip.
Page 40
Page 11

SBS-1 English
Assembling the kit
You can skip this part if you have (a) ready-built module(s).
Preparation
Put the sorted components in front of you on your workbench. An
explanation of the separate electronic components follows:
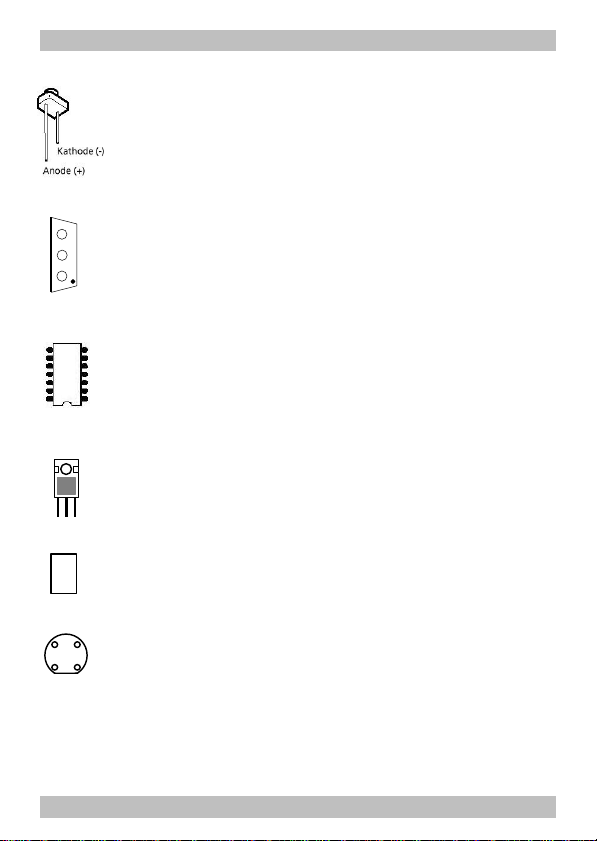
Resistors
A resistor will "brake" the current. Mounting orientation is of no
importance. Because resistors are very small there is no readable
information on them, but their value is given with colour rings.
Key:
Value Colour ring
120 Ω brown - red - brown (gold)
1,5 kΩ brown - green - red (gold)
4,7 kΩ yellow - violet - red (gold)
The colour ring in brackets indicates the tolerance of the
resistor and is of no importance here.
Capacitors
There is a difference between “normal” capacitors and
electrolytic capacitors which have to be placed in a certain
direction. They have a very bright line at one end marked with
the minus (-) sign. That end must always be connected to
minus.
Diodes
Diodes allow current to flow in one direction only and have to
be placed in that direction. The characteristic for a diode is
the ring at one end. Place them as drawn in the PCB layout.
Page 41
Page 12
English SBS-1
+
-
LEDs
LEDs are a special diode. When they are used in the current
direction they light up. They are available in diverse forms
(colour, shape, max. current, size, luminosity, etc. etc.). The
long wire of an LED is the anode (plus) side.
Transistors
Transistors are in fact power switches. They also have to be
placed in a certain direction. The PCB layout will help you to
place the transistor. The point in the PCB layout indicates the
lettered side of the transistor.
ICs
Depending on their type, ICs can take over different functions.
Some types are programmable and can be adjusted to special
requirements of a circuit. The notch on the IC shows the
mounting orientation. The PCB layout shows this marking.
Voltage regulator
Voltage regulators are ICs in a transistor housing. They
transform a varying uncontrolled input voltage into a
unvarying output voltage.
Relais
Relais are electronic change-over switches. The mounting
direction is preset by the order of the pins.
Rectifiers
Rectifiers convert alternating (a.c.) into direct (d.c.) voltage.
They should be inserted according to the polarity shown on
the PCB Layout.
Terminal strips
Terminal strips are solder-in screw-type terminals. They provide a
solder-free and safe connection of the cables to the circuit.
Page 42
Page 13

SBS-1 English
!!!
!
Assembling the central / rail module
The PCBs for the central and the rail module are identical. The two kits
only differ with regard to the components.
Caution:
You must pay attention to the differences when mounting the PCBs. If
you don‘t then the module will not have the wanted function.
Start the assembly with the resistors and the diodes. First solder the
components on the solder side of the PCB and then cut the excess
wires with the side cutter as short as possible. Next solder the ICsockets. Continue with the capcitors, the LEDs and the transistors.
Caution:
Electrolytic capacitors, transistors, diodes, ICs and rectifiers must be
placed in the right direction! If you solder them the wrong way the
affected parts can be damaged when you connect the power. In the
worst case the whole circuit can be damaged. In any case, a wrongly
connected part will not function.
Continue with the rectifier and the voltage regulator IC2. Then solder
the relais and the terminal strips. Assemble the terminal strips before
mounting them. Finally, insert the ICs into the already soldered-in ICsocket. The ICs must be inserted as shown on the PCB.
Caution:
Do not touch the IC without first discharging yourself by touching a
radiator or other grounded metal parts. Do not bend the "legs" of the IC.
Caution:
All kits contain one IC PIC16F627 (IC-1). They are differently
programmed for the central module, the rail module and the display
and operating module. You should be careful not to mix up these Ics .
Page 43
Page 14

English SBS-1
!
!
!
Assembling the display and operating module SBS-AB-1
Start the assembly with the resistors and the diodes. First solder the
components on the solder side of the PCB and then cut the excess
wires with the side cutter as short as possible. Make the wire bridge Br
next. Use the cut-oof wires or the resistors. Then solder the socket for
the IC.
Continue with the capacitors, the LEDs and the voltage regulator IC2. If
you intend to mount the soldered PCB into a housing all elkos should be
soldered horizontal to the PCB. (You might have to extend the legs to
enable this.)
Caution:
Electrolytic capacitors, transistors, diodes, ICs and rectifiers must be
placed in the right direction! If you solder them the wrong way the affected
parts can be damaged when you connect the power. In the worst case the
whole circuit can be damaged. In any case, a wrongly connected part will
not function.
Continue with the push-button and the solder pin JP3. Finally, insert the
IC into the already soldered-in IC-socket. The ICs must be inserted as
shown on the PCB.
Caution:
Do not touch the IC without first discharging yourself by touching a
radiator or other grounded metal parts. Do not bend the "legs" of the IC.
Caution:
All kits contain one IC PIC16F627 (IC-1). They are differently
programmed for the central module, the rail module and the display
and operating module. Be careful not exchange these ICs otherwise
the modules will not operate correctly
There are some components shown on the PCB-layout of the display
and operating module which are not necessary for the basic version of
the display and operating module SBS-AB-1. These components are not
included in the basic pack:
Page 44
Page 15

SBS-1 English
!
§ resistors R9, R10
§ diode D3
§ socket pins JP1 and JP2
These components are to be used together with a LCD-display and are
part of the LCD-convertible pack.
Performing a visual check
Even if you have (a) ready-built module(s) you must perform a visual
check that screws, plugs and other fasteners are firm and tight to
exclude transport damage.
Caution:
Do not power up the module(s) yet.
Damaged material and/or incorrect handling of parts can always be a
danger. After assembling the kit, perform a visual inspection.
Check all nuts, pins and connections as well as the mechanical
connections for correct assembly.
Remove all loose parts, wire ends or drops of solder from the PCB.
Remove all sharp wire ends.
Check solder spots that are too close to each other for short circuits.
Check that all components are polarised correctly. When you have
taken all these precautions, go on to the next part.
Page 45
Page 16

English SBS-1
Display and operating elements
of the modules
This chapter is meant to familiarize you with the operating elements of
the modules. Before connecting the modules and setting them into
operation you must perform the required functional tests.
Operating elements of the display and operating module
By using the push-button S3 you can switch between programming and
operation mode. The attached diodes D23 and D24 show the set mode,
and indicate the following:
D23 (green) operation mode
D24 (red) programming mode
In the programming mode you can switch between the operating
modes with the push-buttons S1 (down) and S2 (up). The set operating
mode is shown by the diodes D25 and D26 as follows:
D25 (red) + D26 (green) manual operation
D25 (red) first in first out operation
D26 (green) random operation
Operating elements of the central module and the rail modules
The diodes D23 and D24 show the state of rail 1, and diodes D25 and
D26 that of rail 2, as indicated below:
D23 resp. D25 (green) Rail vacant, attached points set to
"entrance into railway siding"
D24 resp. D26 (red) Rail occupied, attached points set to
"thorougfare"
D23 (green) + D24 (red) /
D25 (green) + D26 (red)
light together
D23 (green) + D24 (red) /
D25 (green) + D26 (red)
flash by turns
Page 46
Departure of the train from the railway
siding
Malfunction on the rail (e.g. derailment)
Page 17

SBS-1 English
!
By pushing the buttons of the central or the rail module you can initiate
the following actions:
push-button between
X10 and X11
push-button between
X22 and X11
push-button between
X2 and X11
of the central module
Departure of the train from the railway
siding 1 (only in manual operation, in „first
in first out“ operation and in random
operation pushing the button has no effect.)
Departure of the train from the railway
siding 2 (only in manual operation, in „first
in first out“ operation and in random
operation pushing the button has no effect.)
Emergency stop. The central module and
all rail modules set the connected points
to "thorougfare". The shadow station
control can only be re-activated by
switching it off and on again.
Operation of the modules
This chapter is meant to familiarize you with the operation of the
modules. Before connecting the modules and setting them into
operation you should perform the required functional tests.
Caution:
Before switching on the shadow station control you should switch on
the power supply for the track, otherwise the data transferred to the
modules during the „rail occupied“ check is incorrect.
Operation of the display and operating module
When switched on, the display and operating module is set to the last
activated operation mode (the green LED D23 lights). The push-buttons
are kept blocked until as the diodes D23 and D24 have flashed twice.
This is the signal that the central modul has taken over the necessary
data and regular operation has started.
Page 47
Page 18

English SBS-1
Change of the operating mode
To change the operating mode you should switch to the programming
mode. Push the button S3. Now the red LED D23 and the green LED
D24 light together. Keep the button pushed until only the red LED
lights. By pushing the buttons S1 and S2 you an now switch between
the different operating modes.
Confirm the choice of the operating mode by pushing the button S2
again. Keep the button pushed until only the green LED lights. Next the
diodes D23 and D24 flash in turn three times. The first double flashlight
shows that the operating mode has been saved in the display and
operating module, the next two double flashlights confirm that the setting
of the operating mode has been transferred to the central module.
Initiating the departure of a train
in random operation and in „first in first out“ operation
In random operation and in „first in-first out“ operation you can
manually initiate the departure of a train. Push the buttons S1, S2 and
S3 one after the other and then push them simultaniously. As soon as
you release them the departure of the train is initiated.
Operation of the central module
When switched on, the central module first checks:
§ how many additional rail modules are connected
§ if the display and operating module are properly connected (if no
display and operating module is found the central module
automatically sets to manual operation)
§ which operating modus was active before switching off.
§ which rails are occupied.
As soon as the check is completed the LEDs D23 and D24 flash in turn
twice. Next the central module transfers the data to the display and
operating module. This confirms the data reception by double flashing
each of the LEDS D23 and D24 in turn. Then the central module checks
if the track sections connected to it are occupied and shows accordingly
Page 48
Page 19

SBS-1 English
!
the occupied state at the diode pairs D23/D24 and D25/D26. If
necessary it switches the connected points into the correct position.
Operation of the rail modules
When switched on, the rail modules check if the connected railway
sidings are occupied and indicate this at the diode pairs D23/D24 and
D25/D26. If necessary they switch the connected points into the correct
position.
While the central module checks the number of the connected rail modules
all four LEDs light at one rail module after the other. As soon as the check
is completed the occupied state of the railway sidings is shown again.
Connecting the modules and
performing functional tests
If you have purchased a ready-built module, please check all functions.
As transport damage can never be completely out ruled.
Caution:
The modules should not be connected to the powersupply when wiring
is being carried out!
Follow the connections diagramm Fig. 3!
First connect the connection points of the display and operating module
with the terminal strips on the central module as follows:
Display /operating module Central module
JP3/1 X11
JP3/2 X20
JP3/3 X13
JP3/4 X3
Continue with the following connections on the central module:
Central module Central module
X1 X7
X1 X18
Page 49
Page 20

English SBS-1
Next make the following connections for the testing assembly:
Central module Testing assembly
X9 and X12 lamp 1
X21 and X12 lamp 2
X4 testing points 1:
terminal for "thoroughfare"
X5 testing points 1:
Central (yellow) terminal
X6 testing points 1: terminal for "entrance
into railway siding"
X15 testing points 2:
terminal for "thoroughfare"
X16 testing points 2:
central (yellow) terminal
X17 testing points 2: terminal for "entrance
into railway siding"
X10 und X11 push-button for railway siding 1
X22 und X11 push-button for railway siding 2
Tip: The terminal strips X4 to X10 (lower row) are associated with
railway siding 1, the terminal strips X15 to X19, X21 and X22 (upper
row) with railway siding 2.
Explanation of the testing assembly
The lamps connected to the terminal strips X9 and X12 or X21 and X12
simulate two trains stopping on the attached railway sidings. As soon as
the departure of a train out of a railway siding is initiated, the attached
lamp lights. Approx. 10 seconds later the lamp goes off and a
malfunciton is shown for the railway siding (as the supposed train has
not left the railway siding). By disconnecting the lamps on the terminal
strips X9 or X21, the departure of a train out of the railway sidings 1 or
2 can be simulated and this way the malfunction is eliminated.
Page 50
Page 21

SBS-1 English
!
Switching on the shadow station control
Connect the central module to the power supply according to the
connection diagram fig. 3. The display and operating module is supplied
via the central modul.
Central module Power supply
X1 and X12 transformer
The LEDs D23 and D24 on the central module and the LEDs D23 and
D24 on the display and operating module should now flash several
times (see chapter "Operation of the modules"). The flashing of the
LEDs confirms that the power supply to the two modules and the data
transfer between the modules works. When this flashing stops the LEDs
should light as follows:
Central module D24 (red) and D26 (red)
à railway siding 1 and 2 are occupied
Display and operating module D23 (green) à operating mode
Display and operating
modulel
Testing the display and operating module
First perform a test of the display and operating module. Refer to the
chapters "Operating elements of the modules" and "Operation of the
modules".
Start with switching the programming mode (the red LED D24 must
light). Then switch between the operating modes
D25 (red) and D26 (green): optional
§ manual operation (the red LED D25 and the green LED D26 light
together)
§ first in first out operation (the red LED D25 lights) and
§ random operation (the green LED D26 ligths).
Caution:
If a component gets too hot, disconnect the central module from the
mains immediately. Possible short circuit! Check the assembly.
Page 51
Page 22

English SBS-1
!
Testing the central module
Refer to the chapters "Operating elements of the modules" and
"Operation of the modules".
Set the operating mode to first in first out operation at the display and
operating module and confirm the setting. Initiate the departure of a
train at the display and operating module.
One of the lamps connected to the central module should now light.
About 10 seconds later the lamp goes off. The pair of LEDs D23/D24 or
D25/D26 should flash in turn. Continue by disconnecting the lamp that
just lit, from X9 or X21. Five to six seconds later the attached green
LED D23 or D25 should light and the attached points should switch to
"entrance into railway siding".
Connect the lamp again. The red LED should light and the attached
points should switch to "thoroughfare".
Set the operating mode to manual operation at the display and
operating module. Perform the test as described before for the second
lamp and the second points. Initiate the departure of a train for the
appropriate railway siding by pushing the button between X10 and X11
or between X22 and X11 on the central module.
Caution:
If a component gets too hot, disconnect the central module from the
mains immediately. Possible short circuit! Check the assembly.
If you intend to test further rail modules after testing the central
module you should mount the resistor R29 according to the connection
diagram fig. 3. Otherwise correct data transmission between the
modules cannot be garranteed.
Testing the first rail module
First disconnect the central module from the power supply and if
necessary disconnect the lamps and the points connected to the central
module for the test. Connect the rail module to the central module,
according to the connection diagram Fig. 3 as follows:
Page 52
Page 23

SBS-1 English
Rail module Central module
X1 X1
X12 X12
X11 X11
X3 X3
X13 X13
Next make the following connections for the testing assembly:
Rail module
X9 and X12 lamp 1
X21 and X12 lamp 2
X4 testing points 1:
X5 testing points 1:
X6 testing points 1: terminal for "entrance into
X15 testing points 2:
X16 testing points 2:
X17 testing points 2: terminal for "entrance into
X10 und X11 push-button for railway siding 1
X22 und X11 push-button for railway siding 2
Connect the central module to the power supply. After checking if the
modules are ready for operation and the occupied state of the points on
the central module, the red diodes D24 and D26 on the rail module
should light. They show that both railway sidings are occupied.
Set the operating mode to manual operation on the display and
operating module. Perform the test for the two lamps and the two
points as described in the chapter "Testing the central module".
testing assembly
terminal for "thoroughfare"
central (yellow) terminal
railway siding"
terminal for "thoroughfare"
central (yellow) terminal
railway siding"
Page 53
Page 24

English SBS-1
!
!
Caution:
If a component gets too hot, disconnect the central module from the
mains immediately. Possible short circuit! Check the assembly.
Testing further rail modules
First disconnect the central module from the power supply and
disconnect if necessary the lamps and the points connected to a rail
module for the test. Connect the rail module according to the
connection diagram Fig. 3 to the respective last rail module as follows:
New rail module So far last rail module
X1 X1
X12 X12
X11 X11
X3 X3
X13 X14
Continue making the connections for the testing assembly as described
for the first additional rail module. Connect the central module to the
power supply. After checking if the modules are ready for operation and
the occupied state of the points at the central module, the red diodes
D24 and D26 on the rail module must light. They show that both
railway sidings are occupied.
Set the operating mode to manual operation at the display and
operating module. Perform the test for two lamps and two points as
described in the chapter "Testing the central module".
Caution:
If a component gets too hot, disconnect the central module from the
mains immediately. Possible short circuit! Check the assembly.
After performing successful function tests on all modules, disconnect
the central module from the power supply. Disconnect all connections
made for the test. Continue with the wiring up of the modules.
Page 54
Page 25

SBS-1 English
!
Tracks within the reach
of the shadow station control
The rails within the reach of the shadow station control must be divided
into three sections for each railway siding (see fig. 5). The entrance and
the departure rail as well as the thorougfare rail must be connected
electrically to the rest of the model railway. The other sections (part A
and part B of the railway siding should be cut off electrically from the
rest of the model railway. If the model railway is seperated into block
sections the complete shadow station must be one block section.
Section 1 = entrance rail with entrance points and departure rail with
departure points: These are parts of the model railway and are
powered constantly.
Section 2 = Part A of the railway siding: This section is also powered
constantly, but is supervized by the shadow station control. This section
must be as long as the longest train.
Section 3 = Part B of the railway siding: This section is not powered when a
train enters into the railway siding. When the departure is initiated the
section is powered for ca. 10 seconds and then disconnected again from the
power supply. When constructing this section you have to take care that the
incoming trains stop before reaching the next section. The required length
depends on the driving characteristics and the speed of the incoming
locomotives, and on the number and mass of the connected carriages.
Connecting the shadow station control
Caution:
Don’t connect the module to power until the wiring is complete!
Follow the connections diagramm Fig. 4!
Tip: The connections of the display and operating elements (push-
buttons and LEDs) can be extended according to the individual needs
and can be integrated into a „layout orientated“ switching desk.
Page 55
Page 26

English SBS-1
Tip: All modules are prepared for housing.
Connecting the display and operating module to the central
module
First connect the connecting points of the display and operating module
to the terminal strips of the central module as follows:
Display and operating module Central module
JP3/1 X11 (Ground)
JP3/2 X20 (+VCC)
JP3/3 X13 (Clock)
JP3/4 X3 (Data)
Connecting the central module
Tip: The terminal strips X4 to X10 (lower row) are associated with
raiway siding 1, the The terminal strips X15 to X19, X21 and X22 (upper
row) with railway siding 2.
First make the connection from the central module to the power supply.
Keep the module switched off!
Central module Power supply
X1 and X12 transformer
Next connect the points to the central module. (These connections are
identical to the rail module connections.)
Central / rail module Points
X4 points 1: terminal for "thoroughfare"
X5 points 1:
central (yellow) terminal
X6 points 1:
terminal for "entrance into railway siding"
X15 points 2: terminal for "thoroughfare"
X16 points 2: central (yellow) terminal
X17 points 2:
terminal for "entrance into railway siding"
Page 56
Page 27

SBS-1 English
Then connect the rails to the central module. (These connections are
identical to the rail module connections.) In 2-rail-d.c.-systems you
should pay attention to the polarity of the rails (see fig. 5).
Central / rail module Rails
X9 rail section 1 of the railway siding 1
X8 rail section 2 of the railway siding 1
X7 rail section 3 of the railway siding 1
X21 rail section 1 of the railway siding 2
X19 rail section 2 of the railway siding 2
X18 rail section 3 of the railway siding 2
Afterwards connect the push-buttons to the central module.
X10 and X11 push-button for railway siding 1
X22 and X11 push-button for railway siding 2
X2 and X11 push-button for emergency-stop
Connecting the first rail module
Tip: The terminal strips X4 to X10 (lower row) are associated with
raiway siding 1, the The terminal strips X15 to X19, X21 and X22 (upper
row) with railway siding 2.
First make the connection from the first rail module to the central
module. Keep the module switched off!
First rail module Central module
X1 X1
X12 X12
X11 X11
X3 X3
X13 X13
Then connect the points and the rails to the rail module. Proceed as
described in "Connecting the central module". Finally connect the pushbuttons to the rail module.
X10 and X11 push-button for railway siding 1
X22 and X11 push-button for railway siding 2
Page 57
Page 28

English SBS-1
!
If you intend to connect further rail modules beside the first rail module
you should mount the resistor R29 according to the connections
diagram fig. 4. Otherwise correct data transmission between the
modules cannot be garranteed Otherwise correct data transmission
between the modules cannot be garranteed.
Connecting further rail modules
You can connect up to 15 rail modules to the central module. This
allows to supervise and to control up to 32 railway sidings. Connect the
further rail modules to the existing previous rail module as follows:
New rail module Previous rail module
X1 X1
X12 X12
X11 X11
X3 X3
X14 X13
Then connect the points and the rails to the rail module. Proceed as
described in "Connecting the central module".
Finally connect the push-buttons as described in "Connecting the first
rail module".
The resistor R29 should be mounted on the last module according to
the connection diagram fig. 4. Otherwise correct data transmission
between the modules cannot be garranteed.
FAQ
§ Parts are getting too hot and/or start to smoke.
Disconnect the system from the mains immediately!
Possible cause: one or more components are soldered incorrectly.
à Perform a visual check.
§ The lamp(s) connected for the functional test of the module(s) does /
do not light.
Page 58
Page 29

SBS-1 English
Possible cause: One or more components are soldered incorrectly.
à Perform a visual check.
Possible cause: The power supply is interrupted.
à Check the connection from the central modul to the transformer.
Possible cause: The lamp(s) is / are defective.
à Check the lamp(s) by connecting it directly to the voltage supply.
§ After switching on the shadow station control and the diode pairs
D23/D24 on the central module have flashed, the diodes D23/D24
on the display and operating module do not flash.
Possible cause: The connections from the display and operating
module to the central module are incorrect.
à Check the connections.
§ After switching on the shadow station control and the diode pairs
D23/D24 on the central module have flashed, the diode pairs
D23/D24 and D25/D26 on the connected rail modules do not flash.
Possible cause: The connections from the rail modules to the
central module are incorrect.
à Check the connections.
If you cannot find the problem, please return the module for repair
(address on the cover page).
Manufacturer's note
According to DIN VDE 0869, the person who builds this kit or brings the
circuit into operation is the manufacturer of the product. If he sells the
product to another person he is responsible for passing on all the
relevant papers. Domestic appliances assembled from a kit are deemed
industrial products and must comply with health and safety regulations.
Certification
This product conforms with the EC- directive 89/336/EWG on
electromagnetic radiation and is therefore CE certified.
Page 59
Page 30

English SBS-1
Conditional warranty
This product is guaranteed for two years. The warranty includes free
repair if the problem is due to material failure or incorrect assembly of
the ready-built module by us. Because we have no control over the
assembly of the kit, we can only guarantee the quality of the
components and the completeness of the kit.
Other claims are excluded. By law, we are not responsible for damages
or secondary damages in connection with this product. We retain the
right to repair, make improvements, supply spare parts or return the
purchase price.
The following invalidate the warranty:
§ using an unsuitable soldering iron, solder containing liquid acids or
similar,
§ if the kit is assembled and soldered poorly, or if damage is caused
by not following the instructions in this manual or the circuit
diagram,
§ if the circuit has been altered and repair attempts have failed,
§ if arbitrary changes in the circuit are made,
§ if parts are stored incorrectly and if the wires to the switches, the
power resistors, etc. are made incorrectly,
§ if parts other then the original ones delivered with this kit are used,
§ if the copper tracks or soldering points are damaged,
§ if parts are placed incorrectly or the circuit is connected incorrectly,
§ if damage occurs due to an overload of the circuit,
§ if the wrong power or current is connected,
§ if damaged by other persons,
§ if damaged by the wrong use or abuse of the circuit,
§ if parts are damaged due to static because they were touched
before a discharge is performed.
Page 60
Page 31

SBS-1
Gleismodul / Zentralmodul
Rail module / Central module SBS-GZ-1
Stückliste - Parts list
Kondensatoren - Condensers
Dioden - Diodes
IC-Sockel - IC-sockets
Transistoren - Transitors
Widerstände - Resistors
Spannungsregler
Voltage regulator
Seite - Page I.1
C1, C2, C3, C6, C7 100 nF
(2)
C8
C4, C5 100 µF / 25 V
C9 220 µF / 25 V
D1 - D7 1N4002 *
D17 - D22 1N4148 *
D23, D25 grün - green
LEDs
D24, D26 rot - red
IC1 PIC 16F627
ICs
OK1 PC827
18-pol. 1 x
8-pol. 1 x
(1)
T1, T2
T7, T8 BC547B *
T3 - T6 BD679
(1)
R1, R2
R9 - R14, R17 R20, R29
(2)
R26
(1)
R3
R15, R16 1,5 kΩ
(1)
R4
R 5 - R8, R21 R24, R27, R28
(2)
R25
IC2 7805
100 nF
BC547B *
4,7 kΩ
4,7 kΩ
4,7 kΩ
1,5 kΩ
120 Ω
120 Ω
120 Ω
Page 32

Gleichrichter - Rectifier
Doppel-Anreihklemme
Double terminal strip
Taster - Button
* oder ähnlich - or similar
(1) nicht erforderlich beim Zentralmodul
not necessary for the central module
(2) nicht erforderlich beim Gleismodul
not necessary for the rail module
Bestückungsplan - PCB layout n n n Fig. 1.1
B1 B80 C1500
K1, K2 1xUm
Relais
X1 1 x 2-pol.
SBS-1
3 x 3-pol.
2 x
Seite - Page I.2
Page 33

SBS-1
Anzeige und Bedienmodul
Display and operating module SBS-AB-1
Stückliste - Parts list
Kondensatoren - Condensers
Dioden - Diodes
IC-Sockel - IC-socket
C1, C2 100 µF / 25V
C3 100 nF
D1 1N4004 *
D23, D26 grün - green
LEDs
D24, D25 rot - red
IC1 PIC16F627
ICs
18-pol. 1 x
Widerstände - Resistors
Spannungsregler
Voltage regulator
Stiftleisten - Solder pins
Taster - Button
R1, R4 - R8 120 Ω
R2, R3, R11, R12 4,7 kΩ
IC2 7805
JP3 4-pol.
S1 - S3 3 x
* oder ähnlich - or similar - ou équivalent - of gelijkwaardig
Seite - Page II.1
Page 34

SBS-1
Bestückungsplan
PCB layout n n n Fig. 1.2
Bitte beachten Sie:
Folgende auf dem Bestückungsdruck des Bedien- und Anzeigemoduls dargestellten Bauteile
werden für das Anzeige- und Bedienmodul SBS-AB-1 nicht benötigt und
sind in der Basispackung nicht
enthalten:
§ Widerstände R9, R10,
§ Diode D3,
§ Stiftleisten JP1 und JP2.
Die betreffenden Bauteile werden
bei Einsatz einer LCD-Anzeige
benötigt und sind im LCD-Umrüstsatz enthalten.
Please note:
There are some components shown
on the PCB-layout of the display and
operating module which are not
necessary for the basic version of
the display and operating module
SBS-AB-1. These components are
not included in the basic pack:
§ resistors R9, R10,
§ diode D3,
§ socket pins JP1 and JP2.
These components are to be used
together with a LCD-display and are
part of the LCD-convertible pack.
Seite - Page II.2
Page 35

SBS-1 SBS-1
Gleismodul / Zentralmodul
Rail module / Central module
SBS-GZ-1
Schaltplan - Circuit diagram
n n n Fig. 2.1
Seite - Page III Seite - Page III
Page 36

SBS-1 SBS-1
Anzeige- und Bedienmodul
Display and operating module
SBS-AB-1
Schaltplan - Circuit diagram
n n n Fig. 2.2
Seite - Page IV Seite - Page IV
Page 37

SBS-1 SBS-1
n n n Fig. 3: Anschlußplan Testaufbau - Connections testing assembly
Plan de raccordement pour les tests - Aansluitplan Testopbouw
Seite V Seite V
Page 38

SBS-1 SBS-1
n n n Fig. 4: Anschlußplan - Connections - Plan de raccordement - Aansluitplan
Seite VI Seite VI
Page 39

SBS-1 SBS-1
n n n Fig. 5: Anschluß der Gleisabschnitte - Connection of the track sections
Connexion des sections de voie - Aansluiten van de railstukken
Seite VII Seite VII
Page 40

n
n
n
n
Aktuelle Informationen und Tipps:
Information and tips:
http://www.tams-online.de n
Garantie und Service:
Warranty and service:
Tams Elektronik GmbH
Rupsteinstraße 10
D-30625 Hannover
fon: ++49 (0)511 / 55 60 60
fax: ++49 (0)511 / 55 61 61
e-mail: modellbahn@tams-online.de
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
 Loading...
Loading...