
Synway SMG Series Analog Gateway
SMG1008
SMG1016
SMG1032
SMG1032A2
SMG1032A4
Analog Gateway
Version 1.6.4
Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
www.synway.net

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page i
Content
Content ................................................................................................i
Copyright Declaration...........................................................................iii
Revision History....................................................................................iv
Chapter 1 Product Introduction............................................................1
1.1 Typical Application......................................................................................... 1
1.2 Feature List....................................................................................................2
1.3 Hardware Description.................................................................................... 3
1.4 Alarm Info ......................................................................................................6
Chapter 2 Quick Guide..........................................................................7
Chapter 3 WEB Configuration............................................................12
3.1 System Login............................................................................................... 12
3.2 Operation Info.............................................................................................. 13
3.2.1 Sys
tem Info.............................................................................................................13
3.2.2 Channel S
tate .........................................................................................................14
3.2.3 Call Count
...............................................................................................................15
3.2.4 SIP
Message Count ................................................................................................16
3.3 Quick Config................................................................................................ 16
3.4 VoIP Settings............................................................................................... 19
3.4.1 SIP
..........................................................................................................................20
3.4.2 SIP
Compatibility.....................................................................................................21
3.4.3 SIP
Station..............................................................................................................24
3.4.4 SIP
Server ..............................................................................................................26
3.4.5 NA
T Setting.............................................................................................................28
3.4.6 Media
......................................................................................................................31
3.5 Advanced Settings....................................................................................... 33
3.5.1 FXS
.........................................................................................................................34
3.5.2 FXO
........................................................................................................................36
3.5.3 T
one Detector .........................................................................................................38
3.5.4 T
one Generator.......................................................................................................41
3.5.5 DTMF
......................................................................................................................42
3.5.6 Ringing Schem
e .....................................................................................................43
3.5.7 Fax
..........................................................................................................................44
3.5.8 Function Key
...........................................................................................................46
3.5.9 Dialing Rule
............................................................................................................48
3.5.10 Dialing T
imeout.......................................................................................................51
3.5.11 Cue Tone
................................................................................................................52
3.5.12 Color Ring
...............................................................................................................53
3.5.13 QoS
........................................................................................................................54
3.5.14 Action URL..............................................................................................................55
3.6 Port Settings................................................................................................ 55
3.6.1 FXS
.........................................................................................................................56
3.6.2 FXO
........................................................................................................................62

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page ii
3.6.3 Port Group ..............................................................................................................66
3.7 Route Settings............................................................................................. 71
3.7.1 Routing Param
eters................................................................................................71
3.7.2 IP
to Tel ...................................................................................................................71
3.7.3 T
el to IP...................................................................................................................74
3.8 Number Manipulation................................................................................... 76
3.8.1 IP
to Tel CallerID .....................................................................................................76
3.8.2 IP
to Tel CalleeID ....................................................................................................80
3.8.3 T
el to IP CallerID.....................................................................................................81
3.8.4 T
el to IP CalleeID....................................................................................................84
3.9 System Tools ............................................................................................... 85
3.9.1 Management
...........................................................................................................86
3.9.2 Network
..................................................................................................................87
3.9.3 Upgrade
..................................................................................................................88
3.9.4 Signaling Capture
...................................................................................................91
3.9.5 Call Log
..................................................................................................................91
3.9.6 Operation Log
.........................................................................................................92
3.9.7 Backup & Up
load ....................................................................................................93
3.9.8 Factory Res
et .........................................................................................................94
3.9.9 Sys
tem Monitor.......................................................................................................94
3.9.10 Centralized Manage
................................................................................................95
3.9.11 Acces
s Control........................................................................................................96
3.9.12 PING T
est ...............................................................................................................98
3.9.13 TRACER
T Test .......................................................................................................99
3.9.14 Change Password
................................................................................................100
3.9.15 Rest
art ..................................................................................................................100
Appendix A Technical Specifications...............................................101
Appendix B Troubleshooting............................................................102
Appendix C Technical/sales Support...............................................105

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page iii
Copyright Declaration
All rights reserved; no part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by
any means, electronic or mechanical, without prior written permission from Synway Information
Engineering Co., Ltd (hereinafter referred to as ‘Synway’).
Synway reserves all rights to modify this document without prior notice. Please contact Synway
for the latest version of this document before placing an order.
Synway has made every effort to ensure the accuracy of this document but does not guarantee
the absence of errors. Moreover, Synway assumes no responsibility in obtaining permission and
authorization of any third party patent, copyright or product involved in relation to the use of this
document.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page iv
Revision History
Version Date Comments
Version 1.0 2013-10 Initial publication
Version 1.3.0 2014-03 New revision
Version 1.3.1 2014-06 Add description on the new series SMG1032A2
Version 1.3.2 2014-07 New revision
Version 1.3.3 2014-09 New revision
Version 1.3.5 2014-10 New revision
Version 1.5.0 2014-12 Add description on the new series SMG1032A4
Version 1.5.1 2015-01 New revision
Version 1.5.2 2015-04 New revision
Version 1.5.3 2015-11 New revision
Version 1.6.0 2016-03 New revision
Version 1.6.3 2016-12 New revision
Version 1.6.4 2017-02 New revision
Note: Please visit our website http://www.synway.net to obtain the latest version of this document.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 1
Chapter 1 Product Introduction
Thank you for choosing Synway SMG Series Analog Gateway!
The Synway SMG series analog gateway products (hereinafter referred to as ‘SMG analog
gateway’) are mainly used for connecting traditional phone sets, fax machines and PBXes with
the IP telephony network or IP PBX. It provides a powerful, reliable and cost-effective VoIP
solution for such occasions as IP call centers and multi-branch agencies.
SMG series analog gateway has five modules:
SMG1008: 8 FXS/FXO
SMG1016: 16 FXS/FXO
SMG1032, SMG1032A2, SMG1032A4: 32 FXS/FXO
1.1 T ypical Application
Figure 1-1 Typical Application
Headquarter
SMG Gateway
Subscriber
Terminal
IP Phone
Tel TelFax
FXS
IP Phone
LAN
LAN
Router
SMG Gateway
FXO
FXO
Branch 1
SMG Gateway
Subscriber
Terminal
IP Phone
Tel TelFax
FXS
LAN
Router
IP Phone
FXO
Branch 2
SMG Gateway
Subscriber
Terminal
IP Phone
Tel TelFax
FXS
LAN
Router
IP Phone
FXO
FXO
Internet

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 2
1.2 Feature List
Basic Features Description
TDM Call
Call initiated from TDM to IP, via routing and number manipulation to obtain the
called IP address.
IP Call
Call initiated from IP to TDM, via routing and number manipulation to obtain the call
destination.
Number Manipulation
Peels off some digits of a phone number from left/right, or adds a prefix/suffix to a
phone number.
Call Forward Three options available: Unconditional, Busy and No Reply.
Call Waiting
When an FXS channel receives another call while it is in conversation, it will have
the newly received call keep waiting. Once the current call is finished, the new one
will ring the FXS channel and wait for its answer.
Auto Dial
If there is no dialing operation in a designated time period after pickup, the preset
auto dial number will be called.
Do Not Disturb Rejects all the incoming calls to the channel.
CID Displays the CallerID.
Echo Cancellation
Provides the echo cancellation feature for a call conversation over the FXS/FXO
channel.
TDM/VoIP Routing Sets a routing path: from IP to TDM or from TDM to IP.
Fax
Provides multiple fax parameters: fax mode, maximum fax rate, fax train mode,
error correction mode, etc.
Communication
without Power
Provides composite modules to enable a direct connection of the station which is
linked with the FXS port and the trunk which is linked with the FXO port to keep the
calls between the FXS port and PSTN uninterrupted during power outage.
Communication
without Network
Automatically routes a call to the proper port according to the configuration in case
of network failure or call timeout.
Send Polarity Reversal
Signal
Sends the polarity reversal signal to a corresponding FXS channel when the called
party pick-up behavior is detected.
Detect Polarity
Reversal Signal
Turns a corresponding channel into the talking state when the FXO port detects the
polarity reversal signal.
Simultaneous Register
to Multiple Servers
Registers the gateway to a master registrar server and a spare registrar server
simultaneously.
IMS Network Registers the gateway to a server under IMS network.
SIP Station Supports a SIP terminal to be registered to the gateway and become a SIP station.
Group Ringing Rings all the idle FXS ports in a port group.
Ringing by Turns
Rings the FXS ports in a port group by turns according to the Rule for Ringing by
Tur ns.
Preemptive Answer
When a channel in a port group is ringing, another channel in the same port group
can press the preemptive answer keyboard shortcut to transfer the call from the

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 3
ringing channel to the current channel.
Centralized Manage
The gateway can register to Synway DCMS platform and accept the management
of the platform.
Signaling & Protocol Description
SIP Signaling Supported protocol: SIP V1.0/2.0, RFC3261.
Voice
CODEC
G.711A, G.711U, G.729A/B, G.723, G.722, AMR, iLBC,
SILK(16K), OPUS(16K), SILK(8K), OPUS(8K)
DTMF Mode RFC2833, SIP INFO, INBAND
Network Description
Network Protocol
Supported protocol: TCP/UDP, HTTP, ARP/RARP, DNS, NTP, TFTP, TELNET,
STUN.
Static IP IP address modification support.
DHCP IP address dynamic allocation support.
PPPoE Virtual dial-up internet access support.
DNS Domain Name Service support.
Security Description
Admin Authentication Supports admin authentication to guarantee the resource and data security.
System Monitor Monitors the running status of the system and the server.
Maintain & Upgrade Description
WEB Configuration Support of configurations through the WEB user interface.
Language Chinese, English.
Software Upgrade
Support of user interface, gateway service, kernel and firmware upgrades based
on WEB.
Tracking Test Support of Ping and Tracert tests based on WEB.
SysLog Type Three options available: ERROR, WARNING, INFO.
1.3 Hardware Description
The SMG analog gateway features 1U rackmount design and integrates embedded LINUX
system within the POWERPC+DSP hardware architecture. It has 8/16/32 voice ports (FXS/FXO)
and 2 LANs on the chassis. Each voice port can be configured on demand to serve as an FXS or
FXO interface; however, the respective amount of FXS and FXO interfaces must be multiples of 2.
See below for product appearance.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 4
Figure 1-2 SMG1032 Front View
Figure 1-3 SMG1032 Rear View
Figure 1-4 SMG1032A2 Front View
Figure 1-5 SMG1032A2 Rear View
Figure 1-6 SMG1032A4 Front View
Console
Port
Channel
Indicator
Alarm Indicator
Reset Button
Power Indicator
Run Indicator
LAN2 Indicator
LAN1 Indicator
Power Key
220V AC
Grounding Stud
Console
Port
Channel
Indicator
Alarm Indicator
Reset Button
Power Indicato r
Run Indicator
LAN2 Indicator
LAN1 Indicator
Power Key
220V AC
Grounding
Stud
RJ21
Interfaces
LAN
Console Port
RJ11
Interfaces
Alarm Indicator
Reset Button
Power Indicator
Run Indicator
LAN

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 5
Figure 1-7 SMG1032A4 Rear View
Figure 1-8 Left View
The table below gives a detailed introduction to the interfaces, buttons and LEDs illustrated
above:
Interface Description
Amount: 2
Type: RJ-45
Bandwidth: 10/100Mbps
Self-Adaptive Bandwidth Supported
LAN
Auto MDI/MDIX Supported
Amount: 8/16/32
Type: RJ-11, RJ-21, RJ45
Maximum Transmission Distance: 1500m
FXS/FXO
Charge Mode: Negative Anti-billing Supported
Amount: 1
Type: RS-232
Baud Rate: 115200bps
Connector: RJ45 to DB-9 Connector
Data Bits: 8 bits
Stop Bit: 1 bit
Parity Unsupported
Console Port
Flow Control Unsupported
Button Description
Power Key Power on/off the SMG analog gateway.
Reset Button Restore the gateway to factory settings.
LED Description
Power Indicator
Indicates the power state. It lights up when the gateway starts up with the power
cord well connected
Run Indicator Indicates the running status. For more details, refer to 1.4 Alarm Info.
Alarm Indicator Alarms the device malfunction. For more details, refer to 1.4 Alarm Info.
Link Indicator The green LED on the left of LAN, indicating the network connection status.
Power Key
220V AC
Grounding
Stud
RJ45
Interface
LAN
Ventilation
Holes
Screw Holes for
Foot Bracket

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 6
ACT Indicator
The orange LED on the right of LAN, whose flashing tells data are being
transmitted.
Channel Indicator
FXS and FXO channels are respectively marked by green and red LED after power
on.
1. When the channel is idle, the LED Lights up;
2. When the channel is off-hook, the LED flashes slowly;
3. When the channel is ringing, the LED flashes fast.
For other hardware parameters, refer to Appendix A T echnical Specifications.
1.4 Alarm Info
The SMG analog gateway is equipped with two indicators denoting the system’s running status:
Run Indicator (green LED) and Alarm Indicator (red LED). The table below explains the states and
meanings of the two indicators.
LED State Description
Go out System is not yet started.
Light up and flash fast System is starting.
Run Indicator
Flash slowly System is normal.
Go out System is normal.
Light up
Upon startup: System is normal.
In runtime: System is abnormal.
Alarm Indicator
Flash System is abnormal.
Note:
The startup process consists of two stages: System Booting and Gateway Service
Startup. The system booting costs about 1 minute and once it succeeds, both the run
indicator and the alarm indicator light up. Then after the gateway service is successfully
started and the device begins to work normally, the run indicator flashes and the alarm
indicator goes out.
During runtime, if the alarm indicator lights up or flashes, it indicates that the device goes
abnormal. If you cannot figure out and solve the problem by yourself, please contact our
technicians for help. Go to Appendix C Technical/sales Support
to find the contact way.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 7
Chapter 2 Quick Guide
This chapter is intended to help you grasp the basic operations of the SMG analog gateway in the
shortest time.
Step 1: Confirm that your packing box contains all the following things.
SMG Series Analog Gateway *1
Angle Bracket *2, Rubber Foot Pad *4, Screw for Angle Bracket *8
220V Power Cord *1
Warranty Card *1
Installation Manual *1
Step 2: Properly fix the SMG analog gateway.
If you do not need to place the gateway on the rack, simply fix the 4 rubber foot pads. Otherwise,
you should first fix the 2 angle brackets onto the chassis and then place the chassis on the rack.
Step 3: Connect the power cord.
Make sure the device is well grounded before you connect the power cord. Check if the power
socket has the ground wire. If it doesn’t, use the grounding stud on the rear panel of the device
(See Figure 1-3) for earthing.
S
tep 4: Connect the network cable.
Step 5: Connect the telephone line. The line from PSTN should be connected to FXO port
(port with red LED flashing); the line from station should be connected to FXS port (port
with green LED flashing).
The connection for SMG1008, SMG1016, SMG1032 series products:
These series products provide RJ11 interfaces. You can use a common telephone line directly or
construct a telephone line by yourself according to Figure 2-1. Note that only the middle two cores
in the RJ1
1 jack are valid for use.
Figure 2-1 RJ11 Connection
The connection for SMG1032A2 series product:
SMG1032A2 adopts two RJ21 interfaces each of which accommodates 16 channels. One
corresponds to channels 1 through 16 and the other corresponds to 17 through 32. Each pin in
the RJ21 connector functions as follows.
Figure 2-2 RJ21 Pin Layout
The pins Ch1-a/b through Ch16-a/b on the RJ21 interface will be used respectively corresponding

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 8
to channels 1 through 16.
An RJ21 interface can be converted to 24 RJ11 interfaces through an RJ21-to-RJ11 adapter. See
Figure 2-3 for the connection. SMG103
2A2 needs two RJ21-to RJ11 adapters of which the first 16
slots will be used.
24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
Reverse Side of RJ21-to-RJ11 Adapter
Front Side of RJ21-to-RJ11 Adapter
Figure 2-3 RJ21-to-RJ11 Adapter Connection
Users can also use the RJ21 connecting cable directly.
SMG1032A4 has eight 8-pin RJ45 jacks each of which can be connected to four 2-pin RJ11 jacks
via a 4-way hub. Take the first RJ45 jack for example, the matching relationship among the
channel number, the pins of the RJ45 jack and the 4-way hub is shown in the table below.
Interface Channel Number Pins of the RJ45 Jack 4-way Hub
1 1st and 2nd pins 1st jack
2 3rd and 4th pins 2nd jack
3 5th and 6th pins 3rd jack
First RJ45
Jack
4 7
th
and 8th pins 4th jack
Table 2-1 Matching Relationship among Channel Number, Pins of RJ45 Jack and 4-way Hub
Step 6: Power on and start the gateway.
Step 7: Log in the gateway.
Enter the original IP address (LAN1: 192.168.1.101) of the SMG analog gateway in the browser to
go to the WEB interface of the gateway. The original username and password of the gateway are
both ‘admin’. For detailed instructions about login, refer to 3.1 System Login
. We suggest you
change the initial username and password via ‘System Tools Change Password’ on the WEB
interface as soon as possible after your first login. For detailed instructions about changing the
password, refer to 3.9.14 Change Password
. After changing the password, you are required to log

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 9
in again.
Step 8: Modify IP address of the gateway.
You can modify the IP address of the gateway via ‘System Tools Network’ on the WEB interface
to put it within your company’s LAN. Refer to 3.9.2 Network
for detailed instructions about IP
modification. After changing the IP address, you shall log in the gateway again using your new IP
address.
Step 9: Make phone calls.
Note: For your easy understanding and manipulation, all examples given in this step do not
involve registration, that is, SIP initiates calls in a point-to-point mode.
Situation 1: Call from a station to another (TelTel)
The gateway allows two FXS ports to call each other by default. Just use a station connected with
an FXS port to dial the number of the destination FXS port and you can make a TelTel call. The
default number of an FXS port is 80XX, among which XX represents the corresponding port
number. For example, the default number corresponding to Port 1 is 8001, and that corresponding
to Port 32 is 8032.
Actually a TelTel call on the gateway is accomplished via the routing of TelIPIPTe l . F o r
detailed introductions and configuration guide, refer to Q2
in Appendix B.
Situation 2: Call from a station to an IP phone (TelIP)
1. Go to ‘Advanced Settings Dialing Rule’ on the WEB interface and click the ‘Add New’
button to add a new dialing rule. Refer to 3.5.9 Dialing Rule
for detailed instructions. Enter
either a particular number or a string of ‘x’s to represent several random numbers. For
example, ‘xxx’ denotes 3 random numbers. You may use the default value of ‘Index’ and are
required not to leave ‘Description’ empty.
Example: Set Index to 99, fill in Description with test and configure Dial Rule to 123.
2. Go to ‘Port Settings Port Group’ on the WEB interface and click the ‘Add New’ button to
create a new port group and add FXS ports which are connected with stations to it. Refer to
3.6.3 Port Group
for detailed instructions. You may use the default values of other
configuration items and are required not to leave ‘Description’ empty.
Example: Provided the FXS port which is connected with a station is Port1, check the
checkbox before Port1, set Index to 1, fill in Description with test, and keep the default
values of other configuration items.
3. Go to ‘Route Settings TelIP’ on the WEB interface and click the ‘Add New’ button to add
a new routing rule. Refer to 3.7.3 TelIP
for detailed instructions. Select the port group
created in Step2 as ‘Source Port Group’ and fill in ‘Destination IP’ and ‘Destination Port’ with
the IP address and the Port number you plan to call. You may use the default values of other
configuration items and are required not to leave ‘Description’ empty.
Example: Provided the remote IP address intended to call is 192.168.0.111 and the port is
5060. Set Index to 63, Source Port Group to 1, fill in Description with test, configure
Destination IP to 192.168.0.111, Destination Port to 5060, and keep the default values of
other configuration items.
4. Pick up the station and dial the number set in Step1 to ring the remote IP phone. If you have
set a particular number in Step 1, only this number you can dial; if you have set a string of ‘x’s,
how many ‘x’s there are, how many random numbers you can dial.
Example: Pick up the station and dial 123. Then the IP phone with the IP address
192.168.0.111 and the port 5060 will ring.
Situation 3: Call from an IP phone to a station (IP Tel)
1. Go to ‘Port Settings Port Group’ on the WEB interface and click the ‘Add New’ button to
create a new port group and add FXS ports which are connected with stations to it. Refer to

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 10
3.6.3 Port Group for detailed instructions. You may use the default values of other
configuration items and are required not to leave ‘Description’ empty.
Example: Provided the FXS port which is connected with a station is Port1, check the
checkbox before Port1, set Index to 1, fill in Description with test, and keep the default
values of other configuration items.
2. Go to ‘Route Settings IPTel’ on the WEB interface and click the ‘Add New’ button to add
a new routing rule. Refer to 3.7.2 IPTe
l for detailed instructions. Fill in ‘Source IP’ with the
IP address which initiates the call and select the port group created in Step1 as ‘Destination
Port Group’. You may use the default values of other configuration items and required not to
leave ‘Description’ empty.
Example: Provided the IP address of the IP phone which initiates the call is 192.168.0.111.
Set Index to 63, Destination Port Group to 1, fill in Description with test, configure Source
IP to 192.168.0.111, and keep the default values of other configuration items.
3. Pick up the IP phone and call the IP address and port of the SMG analog gateway to ring the
station.
Example: Provided the IP address of the SMG analog gateway is 192.168.0.101 and the port
is 5060, use the IP phone to call the IP address 192.168.0.101 and the station connected with
Port1 will ring.
Step 10: Enable the auto dial feature. (Skip this step if not necessary.)
Go to the Port Settings interface to enable the auto dial feature and set the parameters ‘Auto Dial
Number’ and ‘Wait Time b efore Auto Dial’. If there is no dialing operation in a time period (i.e. Wait
Time before Auto Dial) after pickup, the port will automatically call the preset number (i.e. Auto
Dial Number). Refer to 3.6.1 FXS
for detailed instructions.
Step 11: Enable the DND (do not disturb) feature. (Skip this step if not necessary.)
Go to the Port Settings interface to enable the DND feature. Then, the FXS port will reject all
incoming calls. Refer to 3.6.1 FXS
for detailed instructions.
Step 12: Enable the call waiting feature. (Skip this step if not necessary.)
Go to the Port Settings interface to enable the call waiting feature. Then the corresponding FXS
port while in conversation can accept another call from IP and keep it in the waiting state. Once
the current conversation is finished and the station hangs up, the call in the waiting state will ring
the station and wait for answer . During the time in the waiting st ate, it will always hear the ringback
tone from the FXS port. Refer to 3.6.1 FXS
for detailed instructions.
Step 13: Perform call forwarding. (Skip this step if not necessary.)
Situation 1: Hook-flash operation
Figure 2-4 Call Forward via Hook-flash
As shown above, Remote A initiates and establishes a call with Station. Then by a hook-flash
operation, that is, a rapid clap on the hook or pressing the ‘flash’ button on the phone set, Station
can forward the call to Remote B.
Once a flash is generated, Station will go into the dialing state ( the FXS port sends it dialing tones)
before it dials the forwarding number.
Station
IP call in
Recover the call with Remote A/
Switch the call to Remote A or
Remote B
Call Forwarding
Go into a talk once Station hangs up
Remote A
Remote B

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 11
If the dialing succeeds, the FXS port will send ringback tones to S t ation. Provided Remote B picks
up the call, at this time Station can:
a) Directly talk with Remote B;
b) Perform another hook-flash operation to switch the call to either Remote A or Remote B.
c) Hang up to make Remote A and Remote B go into a direct talk with each other.
If the dialing fails, the FXS port will send busy tones to Station. At this time Station can:
a) Hang up to go back to the ringing state; then pick up the call again to recover the talk
with Remote A.
b) Perform the hook-flash operation again without hanging up the call to recover the talk
with Remote A.
Once Station recovers the call with Remote A, it can forward the call again by a new hook-flash
operation.
Situation 2: Automatic call forward
Go to the port setting interface to enable the automatic call forward feature and fill in a forward
number. According to what you set, the SMG analog gateway can automatically forward the
incoming calls on three conditions: unconditional, busy, no reply. Note that this feature is
applicable only to a single port, but not to a port group consisting of more than one port. Refer to
3.6.1 FXS
for detailed instructions.
Special Instructions:
The chassis of the SMG analog gateway must be grounded for safety reasons,
according to standard industry requirements. A simple way is earthing with the third pin
on the plug or the grounding studs on the machine. No or improper grounding may cause
instability in operation as well as decrease in lightning resistance.
As the device will gradually heat up while being used, please maintain good ventilation to
prevent sudden failure, ensuring that the ventilation holes (see Figure 1-8) are never
jammed.
During runtime, if the alarm indicator lights up or flashes, it indicates that the device goes
abnormal. If you cannot figure out and solve the problem by yourself, please contact our
technicians for help. Otherwise it may lead to a drop in performance or unexpected
errors.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 12
Chapter 3 WEB Configuration
3.1 System Login
Type the IP address into the browser and enter the login interface. See Figure 3-1.
Figure 3-1 Login Interface
The gateway only serves one user, whose original username and password are both ‘admin’. You
can change the username and the password via ‘System Tools Change Password’ on the WEB
interface. For detailed instructions, refer to 3.9.14 Change Password
.
After login, you can see the main interface as below.
Figure 3-2 Main Interface

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 13
3.2 Operation Info
Operation Info includes four parts: System Info, Channel State, Call Count and SIP Message
Count, showing the current running status of the gateway. See Figure 3-3.
Figure 3-3 Operation Info
3.2.1 System Info
Figure 3-4 System Info Interface
See Figure 3-4 for the system info interface. You can click Refresh to obtain the latest system
information. The table below explains the items shown in Figure 3-4.
Item Description
MAC Address MAC address of LAN 1 or LAN 2 (disabled by default).
IP Address
The three parameters from left to right are IP address, subnet mask and default
gateway of LAN 1 or LAN 2 (disabled by default).
DNS Server DNS server address of LAN 1 or LAN 2 (disabled by default).

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 14
Receive Packets
The amount of receive packets after the gateway’s startup, including three
categories: All, Error and Drop.
Transmit Packets
The amount of transmit packets after the gateway’s startup, including three
categories: All, Error and Drop.
Current Speed The current speed of data receiving and transmitting.
Work Mode
The work mode of the network, including four options: 10 Mbps Half Duplex, 10
Mbps Full Duplex, 100 Mbps Half Duplex, 100 Mbps Full Duplex.
Runtime
Time of the gateway keeping running normally after startup, which will be
automatically updated.
WEB Current version of the WEB interface.
Gateway Current version of the gateway service.
Serial No. Unique serial number of an SMG analog gateway.
U-boot Current version of Uboot.
Kernel
Current version of the system kernel on the gateway.
Note: The kernel version for the gateways with RJ45/RJ21 interface is different
from that for the gateways with RJ11 interface.
Product Type The type of the analog gateway.
3.2.2 Channel State
Figure 3-5 Channel State Interface
See Figure 3-5 for the channel state interface where shows the channel type, the voltage and the
channel state for each channel on the gateway. The table below explains the items shown in
Figure 3-5.
Item Description
Channel Channel number on the device.
Type
Type of the channel on the device: FXS or FXO. If this item shows ---, it means this
channel is unavailable, that is, the corresponding module to this channel is not
inserted or damaged.
Note: If the FXO port is unconnected, the channel is unavailable too.
Number The number corresponding to the port.
Voltage Line voltage on the channel, calculated by volt (V).
State Displays the channel state in real time. You can move the mouse onto the channel

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 15
state icon for detailed state information.
State Icon Description
Idle The channel is available.
Off-hook The channel picks up the call.
Wait Answer
The channel receives the ringback tone and is waiting
for the called party to pick up the phone.
Ringing The channel is in the ringing state.
Talking The channel is in a conversation.
Dialing The channel is dialing.
Pending The channel is in the pending state.
Internal State Internal state of the channel.
Unusable The channel is unavailable.
Direction Displays the direction of the call on channel.
CallerID Displays the CallerID of the call on channel.
CalleeID Displays the CalleeID of the call on channel.
Reg Status Displays the registration status of the port.
Polarity Reversal
Count
The counts of the polarity reversal detected by the FXO port.
3.2.3 Call Count
Figure 3-6 Call Count Interface
See Figure 3-6 for the call count Interface. The above list shows the detailed information about all
the calls counted from the startup of the gateway service to the latest open or refresh of this
interface. You can click Refresh to obtain the current call count information. The table below
explains the items shown in Figure 3-6.
Item Description
Call Direction A condition for call count, two options available: IPTel and TelIP.
Total Calls Total number of calls in a specified call direction.
Successful Calls Total number of successful calls in conversation.
Busy
Total number of calls which fail as the called party has been occupied and replies a
busy message.
No Answer
Total number of calls which fail as the called party does not pick up the call in a long
time or the calling party hangs up the call before the called party picks it up.
Call Forward Total number of calls which have been forwarded.
Routing Failure Total number of calls which fail because no routing rules are matched.
Dialing Failure
Total number of calls which fail as the called party number does not conform to the
dialing rule or due to dialing timeout.
Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 16
Unknown Failure Total number of calls which fail due to unknown reasons.
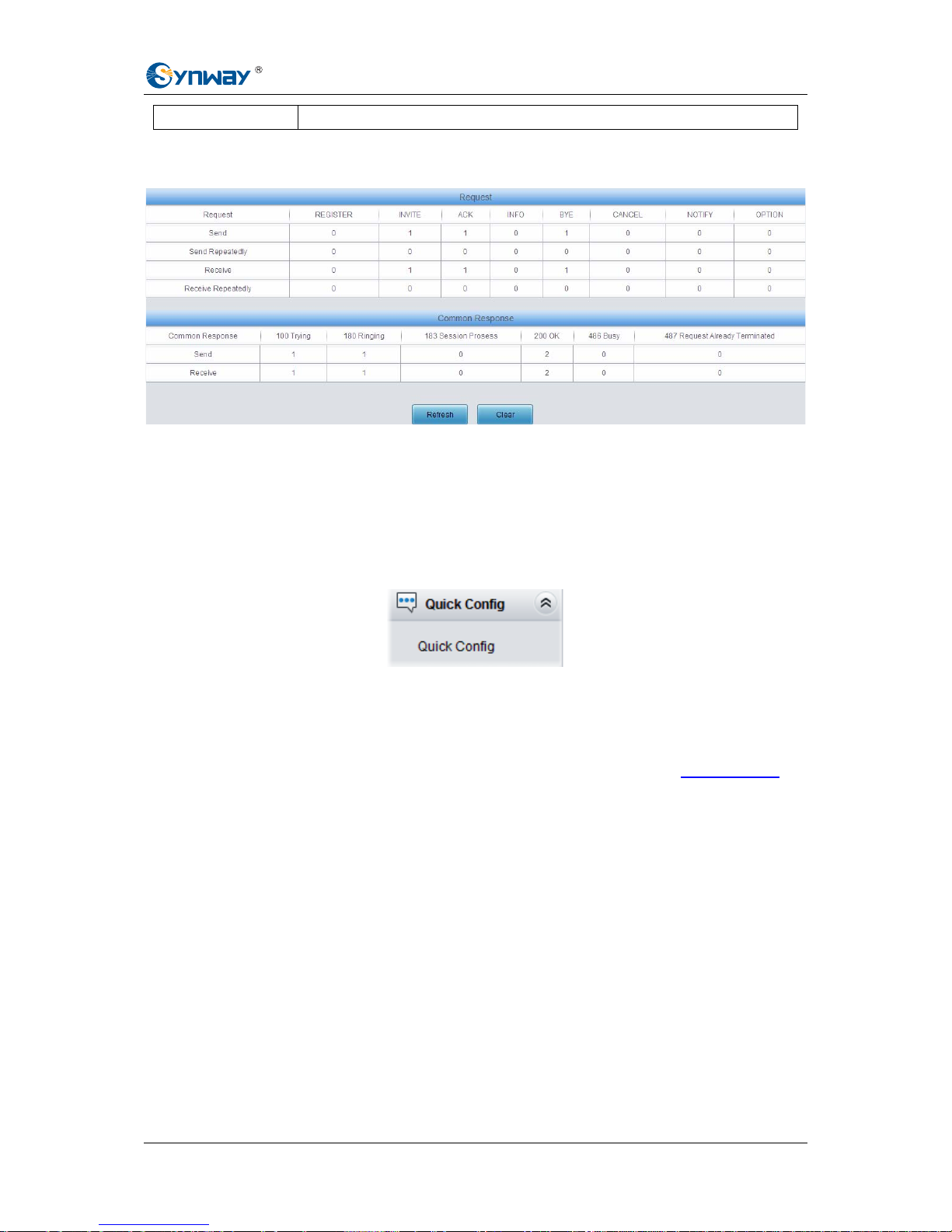
3.2.4 SIP Message Count
Figure 3-7 SIP Message Count Interface
See Figure 3-7 for the SIP Message Count interface. This is used to record the amount of the
normal SIP messages that are sent/received or repeatedly sent/received during the period from
the startup of the gateway service to the latest open or refresh of the interface. Click Refresh to
refresh the count of SIP messages, or click Clear to clear the current count of SIP messages.
3.3 Quick Config
Figure 3-8 Quick Config Interface
See Figure 3-8 for the Quick Config interface. Follow the gateway Quick Configuration wizard and
you can easily complete the settings on network, SIP and FXS/FXO. The gateway can work
normally after configuration.
See Figure 3-9 for the Quick Config-Netw
ork Settings interface. Refer to 3.9.2 Network for
detailed settings. After configuration, click Next to enter the SIP Settings interface.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 17
Figure 3-9 Quick Config-Network Settings Interface
See Figure 3-10 for the Quick Config-SIP Settings interface. The configuration items on this
interface are the same as those on the SIP
interface. Refer to 3.4.1 SIP for detailed settings. You
are required to fill with the information about the registrar if the gateway must be registered. After
configuration, click Back to go back to the Network Settings interface; click Next to enter the FXS
Settings interface.
Figure 3-10 Quick Config-SIP Settings Interface
See Figure 3-11 for the FXS Settings interface. The configuration items on this interface are the
same as those on the FXS interface. Refer to
9 3.6.1 FXS for detailed settings. After configuration,
click Back to go back to the SIP Settings interface; click Next to enter the FXO Settings interface.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 18
Figure 3-11 FXS Settings Interface
See Figure 3-12 for FXO Settings Interface. The configuration items on this interface are the
same as those on the FXO interface. Refer to 3.6.2 FXO
for detailed settings. After configuration,
click Back to back to the FXS Settings interface; click Next to enter the Quick Config-Completion
interface, see Figure 3-13.
Figure 3-12 FXO Settings Interface
Figure 3-13 Quick Config-Completion Interface
Click Back to go back to the FXO Settings interface; click Finish to finish the Quick Config wizard
and now the gateway can work normally with basic configuration.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 19
3.4 VoIP Settings
VoIP Settings includes six parts: SIP, SIP Compatibility, SIP Station, SIP Server, NAT Setting
and Media. See Figure 3-14. SIP is used to configure th
e general SIP parameters, SIP
Compatibility is used to set which SIP servers and SIP messages will the ga teway be comp atible
with, SIP Station is to set the basic information of the SIP station, SIP Server is to set the basic
information of the SIP server, NAT Setting is used to configure the parameters for NAT, and
Media Settings is to set the RTP port and the payload type.
Figure 3-14 VoIP Settings
Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 20
3.4.1 SIP
Figure 3-15 SIP Settings Interface
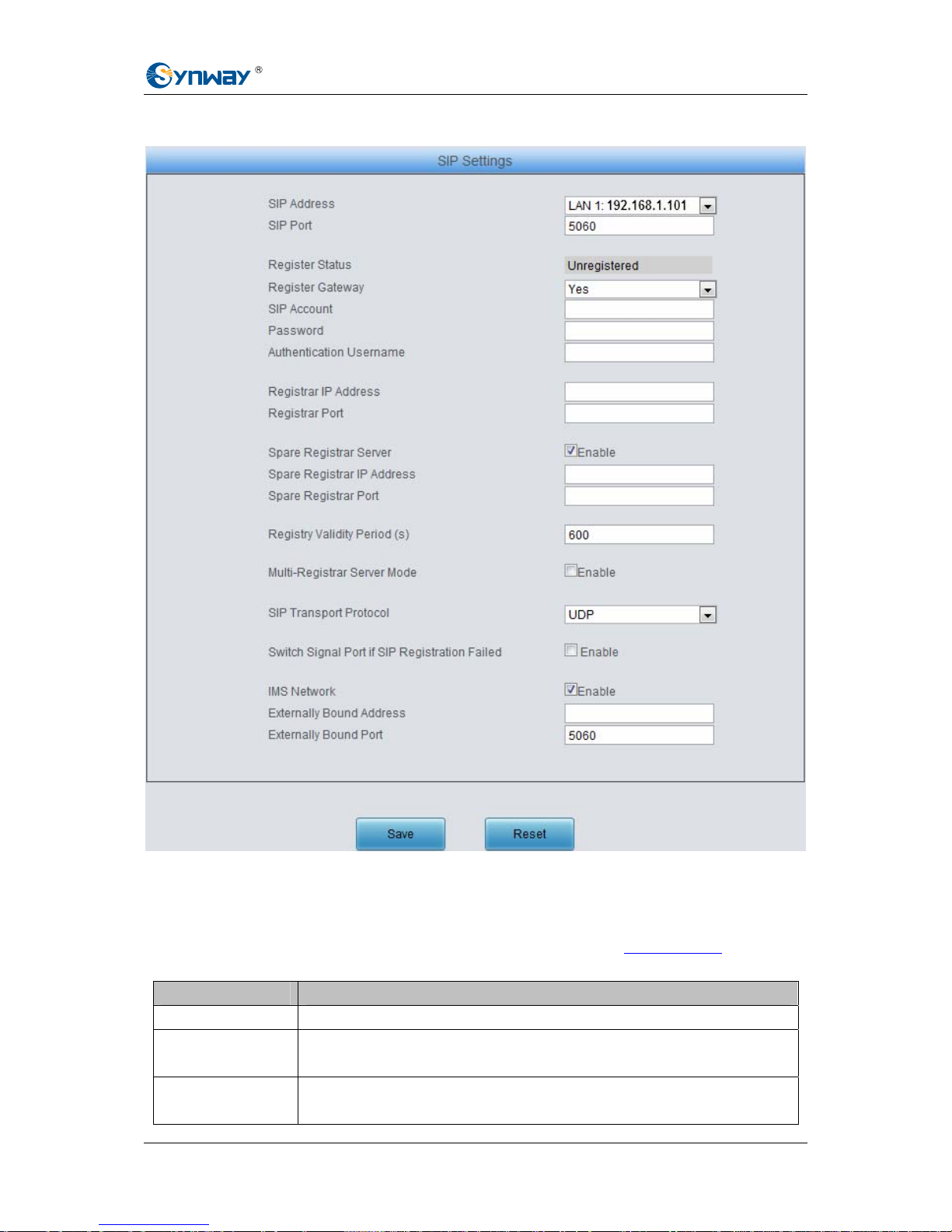
See Figure 3-15 for the SIP settings interface where you can configure the general SIP
parameters. After configuration, click Save to save your settings into the gateway or click Reset to
restore the configurations. If a dialog box pops up after you save your settings asking you to
restart the service, do it immediately to apply the changes. Refer to 3.9.15 Restart
for detailed
instructions. The table below explains the items shown in Figure 3-15.
Item Description
SIP Address IP address of SIP signaling, using LAN 1 by default.
SIP Port
Monitoring port of SIP signaling. The value range of it must be grater than 1024 and
less than 65535, with the default value of 5060.
Register Status
Registration status of the gateway. When Register Gateway is set to No, the value
of this item is Unregistered; when Register Gateway is set to Yes, the value of this

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 21
item is either Failed or Registered.
Register Gateway
Sets whether to register the gateway as a whole. The default value is No. Only
when this configuration is set to Yes can you see the configuration items SIP
Account and Password.
SIP Account
When the gateway initiates a call to SIP, this item corresponds to the username of
SIP.
Password
Registration password of the gateway. To register the gateway to SIP, both
configuration items SIP Account and Password should be filled in.
Authentication
Username
Authentication username for registration.
Registrar IP Address Address of the registry server for the gateway to register.
Registrar Port Signaling port of the registry server.
Spare Registrar
Server
Check the enable checkbox to enable the spare registrar server. By default, it is
disabled.
Spare Registrar IP
Address
Address of the spare registry server for the gateway to register. The gateway will
enable the spare registrar server if the master registrar server has no reply, or the
master server is detected with no response in case the item Detection Server
Cycle is enabled.
Spare Registrar Port Signaling port of the spare registry server.
Registry Validity
Period
Validity period of the SIP registry. Once the registry is overdue, the gateway should
be registered again. This configuration item is valid only when Register Gateway is
set to Yes. Range of value: 10~3600, calculated by s, with the default value of 600.
Multi-Registrar
Server Mode
Tick the checkbox before to enable the multi-registrar server mode. By default, it is
disabled.
SIP Transport
Protocol
There are two modes UDP and TCP available for running the SIP protocol. The
default value is UDP.
Switch Signal Port if
SIP Registration
Failed
If the SIP registration fails, the SIP signaling port N will switch to N+1 for a new
registration. It will continue until the registration succeeds. The default value is
disabled.
IMS Network
Once this feature is enabled, the gateway will send signaling messages to the
corresponding externally bound address and port when it registers to the server. By
default, this feature is disabled. Only when this feature is enabled will these items
Externally Bound Address, Externally Bound Port and Authentication
Username be shown.
Externally Bound
Address
Externally bound IP address for registration.
Externally Bound
Port
Externally bound port for registration.
3.4.2 SIP Compatibility
See Figure 3-16 for the SIP Compatibility interface where you can configure the SIP parameters
to determine which SIP servers and SIP messages will the gateway be compatible with. After
configuration, click Save to save your settings into the gateway or click Reset to restore the

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 22
configurations.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 23
Figure 3-16 SIP Compatibility Setting Interface
The table below explains the items shown in Figure 3-16.
Item Description
Obtain CalleeID
from
There are two optional ways to obtain the called party number: from “To” Field and
from “Request” Field. The default value is “Request” Field.
Set CallerID Position
There are two options to set the position of the calling party number: “Displayname
of From Field” and “Username of From Field”. The default value is “Username of
From Field”.
Obtain CallerID from
There are two optional ways to obtain the calling party number: from “Displayname
of From Field” and from “Username of From Field”. The default value is “Username
of From Field”.
Use Contact
Address
Sets whether to send the request message according to the content of Contact, with
the default setting of disabled. As it is disabled, if the Contact field indicates an IP
address within the LAN, the request message will be sent according t o the source
address; if the Contact field indicates an IP address belonging to the WAN, the
request message will be sent according to this IP address.
Call Transfer Mode
There are two optional ways to deal with call transfer: Internal Handling and
Platform to Handle SIP Info. The default value is Internal Handling.
Call Flash Mode
There are two optional ways to deal with call flash: Internal Handling and Platform to
Handle SIP Info. The default value is Internal Handling.
Hold Music Source
Sets the source of the hold music, with the default value of Remote, This feature
gets valid only when you choose the mode Platform to Handle SIP Info.
Two Stage Dialing
for SIP Incoming
Call
Once this feature is enabled, the incoming call from SIP should perform the two
stage dialing operation. By default this feature is disabled.
Maximum Wait
Answer Time
Sets the maximum time for the SIP channel to wait for the answer from the called
party of the outgoing call it initiates. If the call is not answered within the specified
time period, it will be canceled by the channel automatically. The default value is 60,
calculated by s.
SIP Station
Supported
Once this feature is enabled, a SIP terminal can be registered to the gate way and
becomes a SIP station. By default this feature is disabled.
Set SIP Identifying
Sets the SIP identifying content in the SIP call message. The default setting is
Gateway.
Maximum Wait RTP
Time
Sets the maximum time for the SIP channel to wait for the RTP packet. If no RTP
packet is received within the specified time period, the channel will enter the
pending state automatically and release the call. The default value is 15, calculated
by s.
Call Abnormal
Hangup Detection
Cycle
Sets the interval between checks of the remote end’s abnormal hangup, with the
default value of 0 (feature disabled), calculated by s. It is suggested to set to 10s if
this feature is necessary to be used.
Server Status
Detection Cycle
The interval of sending a heartbeat packet to detect the master registrar server
status, with the default value of 0 (feature disabled), calculated by s. It is suggested

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 24
to set to 15s if this feature is necessary to be used.
Send Cue Tone
Sets whether to send a cue tone once the server gets disconnected, with the default
setting of disabled.
SIP Encryption
Once this feature is enabled, you can encrypt the SIP signal following selecting an
encryption criterion and setting a key. By default it is disabled.
Encryption Criterion The criterion used to encrypt the SIP signal. At present only VOS1.1 is supported.
Identifier
The identifier field of the VOS encryption, which is used to obtain the key of the SIP
encryption.
Key The key to encrypt the SIP signal.
RTP Encryption
Once this feature is enabled, you can encrypt the RTP package. By default it is
disabled.
Ignore ACK
Once this feature is enabled, it is not necessary for the gateway to wait for the ACK
message after sending the 200OK message to establish a call. By default it is
disabled.
User-defined SIP
Code
Once this feature is enabled, you can define a SIP code for the corresponding SIP
status, with the default value of disabled.
Use Iptables
Once this feature is enabled, only the calls from the SIP registration server, the
source IP address of the route IP->TEL and these IP addressed set in Access
Control interface are permitted.
3.4.3 SI P Station
A SIP terminal can be registered to the gateway and becomes a SIP st ation. Enable the feature of
‘SIP Station Supported’ on 3.4.2 SIP Compatibility
interface, and you will see the item SIP
Station on the VoIP Settings menu. Click ‘SIP Station’ to go into the SIP Station interface. By
default, there is no available SIP station. See Figure 3-17 below.
Figure 3-17 SIP Station Setting Interface
Click Add New to add SIP stations manually. See Figure 3-18. You can configure basic SIP
station information on this interface. The bound port to a SIP station must be an FXO port and
unique. The username must be the same as that used to register the SIP terminal to the gateway.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 25
Figure 3-18 Add New SIP Station
The table below explains the items shown above:
Item Description
Number The logical number for a SIP station to register to the gateway.
Username The username used to register a SIP station to the gateway.
Password The password used to register a SIP station to the gateway.
Bound Port The FXO port which is bound to the SIP station.
Description It is user-defined, with the default value of default.
Batch Setting Used to set multiple SIP stations at the same time.
After configuration, click Save to save the above settings into the gateway or click Close to cancel
the settings. See Figure 3-19 for the applied SIP
station information.
Figure 3-19 SIP Station Interface
Click Modify in the above figure to modify the configuration of the SIP station. See Figure 3-20.
The configuration items on this interface are the same as those on the Add New SIP Station
interface.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 26
Figure 3-20 SIP Station Modification Interface
To delete a SIP station, check the checkbox before the corresponding index in Figure 3-19 and
click the Delete button. Check All means to select all available items on the current page;
Uncheck All means to cancel all selections on the current page; Inverse means to uncheck the
selected items and check the unselected. To clear all SIP stations at a time, click the Clear All
button in Figure 3-19.
3.4.4 SIP Server
The gateway supports the multi-registrar server feature. Enable the feature of ‘Multi-Registrar
Server Mode’ on the SIP
interface (see 3.4.1 SIP) and you will see the item SIP Server under the
VoIP Settings menu. Click ‘SIP Server’ to go into the SIP Server interface. By default, there is no
available SIP server. See Figure 3-21 below.
Figure 3-21 SIP Server Interface
Click Add New to add SIP servers manually. See Figure 3-22. You can configure basic SIP server
information on this interface.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 27
Figure 3-22 Add New SIP Server
All the items except Index and Description are the same as those on the SIP interface (3.4.1 SIP).
Item Description
Index The index of each SIP server. The gateway supports up to 8 SIP servers.
Description More information about each SIP server, with the default value of default.
After configuration, click Save to save the above settings into the gateway or click Cancel to
cancel the settings. See Figure 3-23 for the SIP server management interface.
Figure 3-23 SIP Server Management
Click Modify in the above figure to modify the configuration of the SIP server. See Figure 3-24.
The configuration items on this interface are the same as those on the Add New SIP Server
interface.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 28
Figure 3-24 SIP Server Modification Interface
To delete a SIP server, check the checkbox before the corresponding index in Figure 3-23 and
click the Delete button. Check All means to select all available items on the current page;
Uncheck All means to cancel all selections on the current page; Inverse means to uncheck the
selected items and check the unselected. To clear all SIP servers at a time, click the Clear All
button in Figure 3-23.
3.4.5 NAT Setting
See Figure 3-25 for the NAT setting interface where you can configure the parameters for NAT.
After configuration, click Save to save your settings into the gateway or click Reset to restore the
configurations.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 29
Figure 3-25 NAT Setting Interface
The table below explains the items shown in Figure 3-25.
Item Description
Auto Nat
Sets whether to enable the Auto Nat feature. Three options are available:
DisableAutoNat, Enable PMP and Enable UPNP, with the default value of Auto Nat.
Outer Network The address of the outer net work acquired automatically once the PMP or UPNP

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 30
Address feature is enabled.
STUN Server
Sets whether to enable the STUN server for NAT traversal. By default the STUN
server is disabled.
NAT Type
Detected NAT (Network Address Translation) type. The gateway will return the NAT
type automatically in case STUN Server is enabled. It includes 9 types: unknown;
no NAT; ConeNat; RestrictedNat; PortRestrictedNat; Symmetric NAT; Symmetric
NAT with firewall; can’t detect over (fail to send detect message) and fail to detect
(No reply from the stun server).
STUN Server
Address
Address of the server for STUN traversal.
Mapping Contact IP The IP filled in here will be used in the Contact field of the SIP message.
Mapping SDP IP The IP filled in here will be used in the SDP field of the SIP message.
Rport
When this feature is enabled, a corresponding Rport field will be added to the Vi a
message of SIP. The default value is enabled.
Auto Detect NAT IP
When this feature is enabled, the gateway will parse the corresponding address and
port in the message returned by Rport so as to use them for the following
communication. By default, this feature is disabled.
Note: This feature gets valid only when Rport is enabled.
RTP Self-adaption
When this feature is enabled, the RTP reception address or port carried by the
signaling message from the remote end, if not consistent with the actual state, will
be updated to the actual RTP reception address or port. By default, this feature is
disabled.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 31
3.4.6 Media
Figure 3-26 Media Settings Interface
See Figure 3-26 for the media settings interface where you can configure the RTP port and
payload type depending on your requirements. After configuration, click Save to save your
settings into the gateway or click Reset to restore the configurations. If a dialog box pops up after
you save your settings asking you to restart the service, do it immediately to apply the changes.
Refer to 3.9.15 Restart
for detailed instructions. The table below explains the items shown in
Figure 3-26.
Item Description

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 32
DTMF Transmit
Mode
Sets the transmit mode for the IP channel to send DTMF signals. The optional
values are RFC2833, In-band and Signaling, with the default value of RFC2833.
RFC2833 Payload
Payload of the RFC2833 formatted DTMF signals on the IP channel. Range of
value: 90~127, with the default value of 101.
RTP Port Range
Supported RTP port range for the IP end to establish a call conversation, with the
lower limit of 2000 and the upper limit of 60000 and the difference between larger
than 480. The default value is 6000-10000.
Silence
Suppression
Sets whether to send comfort noise packets to replace RTP packets or never to
send RTP packets to reduce the bandwidth usage when there is no voice signal
throughout an IP conversation. The optional values are Enable and Disable, with
the default value of Disable.
Auto Noise
Reduction
Once this feature is enabled, the volume of the noise accompanied with the line will
be reduced automatically. By default, the feature is disabled.
JitterMode
Sets the working mode of JitterMode. The optional values are Static Mode and
Adaptive Mode, with the default value of Static Mode.
JitterBuffer
Acceptable jitter for data packets transmission over IP, which indicates the buffering
capacity. A larger JitterBuffer means a higher jitter processing capability but as well
as an increased voice delay, while a smaller JitterBuffer means a lower jitter
processing capability but as well as a decreased voice delay. Range of value:
0~280, calculated by ms, with the default value of 100.
JitterUnderrunLead
Sets the initial delay of packets if they are received later than JitterBuffer. Range of
value: 0~280, calculated by ms, with the default value of 200,
Note: Only when JitterMode is set to Static Mode will this item be shown.
JitterOverrunLead
Sets the initial lead inserted if packets are received earlier than 300-JitterBuffer.
Range of value: 0~280, calculated by ms, with the default value of 200,
Note: Only when JitterMode is set to Static Mode will this item be shown.
JitterMin
Sets the minimum delay that can be set by the adaptive jitter function. It can not be
larger than the value set in JitterBuffer. Range of value: 0~280, calculated by ms,
with the default value of 10.
Note: Only when JitterMode is set to Adaptive Mode will this item be shown.
JitterDecreaseRatio
Sets the rate for delay reduction under the adaptive mode. It defines the maximum
percentage of silence that can be removed for delay reduction. Range of value:
0~100, with the default value of 50,
Note: Only when JitterMode is set to Adaptive Mode will this item be shown.
JitterIncreaseMax
Sets the maximum delay that can be increased during a silenc e period. Range of
value: 0~280, calculated by ms, with the default value of 50,
Note: Only when JitterMode is set to Adaptive Mode will this item be shown.
Voice Gain Output
from IP
Adjusts the gain of the voice output from IP. Range of value: -24~24, calculated by
dB, with the default value of 0.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 33
CODEC Priority
Supported CODECs and their corresponding priority for the IP end to establish a
call conversation. The table below explains the sub-items:
Sub-item Description
Priority
Priority for choosing the CODEC in an SIP conversation. The
smaller the value is, the higher the priority will be.
CODEC
Three optional CODECs are supported: G711A, G711U,
G729A/B, G723, G722, AMR, iLBC, SILK(16K), OPUS(16K),
SILK(8K) and OPUS(8K).
Packing Time Time interval for packing an RTP packet, calculated by ms.
Bit Rate
The number of thousand bits (excluding the packet header) that
are conveyed per second.
By default, all of the eleven CODECs are supported and ordered G711A, G711U,
G729A/B, G723, G722, AMR, iLBC, SILK(16K), OPUS(16K), SILK(8K) and
OPUS(8K) by priority from high to low.
The packing time and bit rate supported by different CODECs are listed in the table
below. Those values in bold face are the default values.
COEDC Packing Time (ms) Bit Rate (kbps)
G711A 5 / 10 / 20 / 30 / 40 / 50 / 60 64
G711U 5 / 10 / 20 / 30 / 40 / 50 / 60 64
G729A/B 20 8
G723 30 / 60 / 90 5.3 / 6.3
G722 5 / 10 / 20 / 30 / 40 64
AMR 20 / 40 / 60 / 80 / 100
4.75 / 5.15 / 5.90 / 6.70 / 7.40 /
7.95 / 10.20 / 12.20
20 / 40 15.2
30 13.3
iLBC
60 13.3 / 15.2
SILK(16K) 20 /40 / 60 20
OPUS(16K) 10 / 20 / 40 / 60 20
SILK(8K) 20 /40 / 60 12
OPUS(8K) 10 / 20 / 40 / 60 12
3.5 Advanced Settings
Advanced Settings includes fourteen parts: FXS, FXO, Tone Detector, Tone Generator, DTMF,
Ringing Scheme, Fax, Function Key, Dialing Rule, Dialing Timeout, Cue Tone, Color Ring,
QoS and Action URL. See Figure 3-27. FXS is used to configure the general properties of the
FXS port, FXO is used to configure the general properties of the analog voice ports, such as the
conditions for sending the caller party information. Tone Detector is used to configure some
properties of detected tones. Tone Generator is used to configure some properties of generated
tones. DTMF is used to set the properties related to DTMF. Ringing Scheme is used to set the
ringing scheme for the FXS port. Fax is used to configure multiple fax parameters. Function Key
is used to set a cluster of combination keys for you to query a related number. Dialing Rule and
Dialing Timeout are used to set the judging conditions for dialing. Cue Tone is used to set the
gateway language for playing voice and the voice file used for the two-stage dialing. Color Ring is
used to upload the color ring file which can be set as a ringback tone for an incoming call from IP

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 34
to FXS port. QoS uses the differentiated services technology to increase the gateway’s service
quality. Action URL is used to designate the server path to report the on-hook or off-hook state of
the FXS channel.
Figure 3-27 Advanced Settings
3.5.1 FXS
Figure 3-28 FXS Configuration Interface
See Figure 3-28 for the FXS/FXO configuration interface. The table below explains the items
shown in the above figure.
Item Description
Tone Energy
Energy of the tone signal sent by the gateway. Range of value: -35~15, calculated
by dB, with the default value of -16.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 35
Hook-flash Detection
Sets whether to enable the hook-flash detection feature or not, with the default
setting of being disabled.
Minimum Time
Time length for judging a flash operation. Only a hook-flash operation which lasts a
time more than the value of this configuration item will be regarded as a valid flash
operation. Range of value: 80~ Maximum Time, calculated by ms, with the default
value of 80.
Note: This item appears only when Hook-flash Detection is enabled.
Maximum Time
Time length for judging a flash operation. Only a hook-flash operation which lasts a
time less than the value of this configuration item will be regarded as a valid flash
operation. Those lasting a time longer than the value of this configuration item will
be regarded as hangup operations. Range of value: 32~2000, calculated by ms,
with the default value of 700.
Note: This item appears only when the hook-flash detection is enabled.
Minimum Time
Length of On-hook
Detection
The minimum time length for detecting whether the phone is on-hook or not. Range
of value: 64~2000, calculated by ms, with the default value of 64.
Note: This item is valid only when Hook-flash Detection is disabled.
CID Transmit Mode
The mode adopted by the FXS port to send the CallerID. The optional values are
FSK and DTMF, with the default value of FSK.
Occasion to Send
FSK CallerID
Sets when to send the CallerID, before rings or after the 1st Ring. The default value
is after 1
st
Ring.
Send Polarity
Reversal Signal
Once this feature is enabled, the gateway will send the polarity reversal signal to a
corresponding FXS channel when it detects the called party pick-up behavior. By
default, this feature is disabled.
Off-hook Dither
Signal Duration
The minimum duration of the off-hook signal, calculated by millisecond (ms), which
must be the multiple of 16. The less value indicates the larger sensitivity. And the
default value is 64.
Hybrid Balance
Sets whether to enable the hybrid balance feature or not. The default setting is
being enabled.
Handling of Call from
Internal Station
Sets the handling mode for the calls from station to station, two options available:
Internal Handling and Platform Handling, with the default value of Platform
Handling.
Light Up Mode for
Voice Message
Sets the light up mode for leaving a voice message on the phone, two options
available: Not Light Up and Light Up by FSK, with the default value of Not Light Up.
After configuration, click Save to save your settings into the gateway or click Reset to restore the
configurations. If a dialog box pops up after you save your settings asking you to restart the
service, do it immediately to apply the changes. Refer to 3.9.15 Restart
for detailed instructions.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 36
3.5.2 FXO
Figure 3-29 FXO Configuration Interface
The table below explains the particular configuration items for FXO.
Item Description
Calling Party
Detection Time
The maximum waiting time for the detection of the calling party number from FXO
port. Range of value: 1~20, calculated by s, with the default value of 10.
Silence Detection
Used to detect whether the line is silent or not according to the energy threshold
and time threshold of silence. FXO will hang up the call automatically if these
conditions are satisfied. The default setting is being disabled.
Energy Threshold of
Silence
The energy threshold to judge whether the line is silent or not. The signal with the
energy less than this set value will be determined to be silence. Range of value:
-86~5, calculated by s, with the default value of -34.
Note: This item will be valid only when Silence Detection is enabled.
Time Threshold of
Silence
The time threshold to judge whether the line is silent or not, calculated by s, with the
default value of 60.
Note: This item will be valid only when Silence Detection is enabled.
Rapid Release
Once this feature is enabled, the FXO port will release the source rapidly and go to
the idle state when a call from PSTN to soft-terminal via FXO port is rejected by the
IP soft-terminal.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 37
FSK Standard
Standard for sending FSK formatted CallerID, which varies in different countries and
districts. The optional values are: ETSI (Europe), GR-30 (North America, China)
and NIT (Japan), with the default value of GR-30.
Reception Interval of
DTMF CallerID
The time interval between digits of the DTMF CallerID from FXO port, calculated by
ms, with the default value of 250.
Flash Time
Sets the time for generating a flash signal on the analog trunk. Range of value:
32~1000, calculated by ms, with the default value of 100.
Delay after Dial
Sets the delay to send the CalleeID to PBX after you pick up and dial. Range of
value: 200~2000, calculated by ms, with the default value of 1000.
FXO Pick-up Delay
after INVITE
Received at IP Side
Once this feature is enabled, the FXO port will be delayed to pick up the call after
the IP side receives the INVITE message.
Maximum Wait
Answer Time
The maximum time to wait the answer of the remote side for an outgoing call from
FXO port. This item is valid only when Polarity Reversal is enabled. It is calculated
by s, with the default value of 25.
Communication
without Network
Automatically routes a call to the proper port according to the configuration in case
of network failure or call timeout.
Communicate
without Network
Mode
Sets the mode for the communications without network, two options available: Auto
Search Idle Channel and Use Current Route Setting, with the default value of Auto
Search Idle Channel. In the mode of Auto Search Idle Channel, the gateway will
search an idle FXO port to route the call once the network is disconnected; in the
mode of Use Current Route Setting, the gateway will search an escaping channel
according to the settings of Tel->IP route.
Two Stages Dialing
Mode
Sets whether it is necessary to perform the two-stages dialing operation to call the
remote end via an FXO port. By default this feature is disabled.
Delay to Send 200
OK to IP Side
Once this feature is enabled, the gateway will delay to send 200 OK message to the
IP side. The default value is disabled.
Avoid Being
Detected as Flash
Signal by PBX
Once this feature is enabled, after hanging up a call, the FXO channel will be
compelled to stay idle for a while before making a new call outside, which helps
avoid the pick-up signal being detected as a flash signal by the PBX. The default
value is disabled.
Open Session In
Advance
Once this feature is enabled, the gateway will reply the 183 message when the FXO
port is making an outgoing call; otherwise, it will reply the 180 message. This item is
valid only when Polarity Reversal is enabled. The default value is enabled.
After configuration, click Save to save your settings into the gateway or click Reset to restore the
configurations. If a dialog box pops up after you save your settings asking you to restart the
service, do it immediately to apply the changes. Refer to 3.9.15 Restart
for detailed instructions.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 38
3.5.3 Tone Detector
Figure 3-30 Tone Parameters Setting Interface
See Figure 3-30 for the Tone Parameters setting interface. By default, there are three pieces of
tone parameters on the gateway. Click Add New to add tone parameters manually, see Figure
3-31.
Figure 3-31 Add New Tone Parameter Interface
The table below explains the items shown in the above figure.
Item Description
Index The unique index of each group of tone detectors.
Tone There are three options: Dial Tone, Busy Tone and Ringback Tone.
Type There are two options: Continuous Tone and Periodic Tone.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 39
The 1st
Mid-frequency
The 1st center frequency. Range of value: 300~3400, calculated by Hz. The default
value is 450.
The 2nd
Mid-frequency
The 2nd center frequency. Range of value: 0 or 300~3400, calculated by Hz. The
default value is 0.
Duration at ON State
The duration of tones at on state. The default setting: Dial Tone is 1500ms, Busy
Tone is 350ms, Ringback Tone is 1000ms.
Duration at OFF
State
The duration of tones at off state. The default setting: Dial T one is 0ms, Busy Tone is
350ms, Ringback Tone is 4000ms.
Period Count
Set the count of periods as the condition to determine a periodic tone. The default
setting: Dial Tone is 0, Busy Tone is 2, Ri ngback Tone is 1.
Accepted Frequency
Error
Allowable error of the center frequency. Range of value: 1~5, calculated by %, with
the default value of 5.
Duration Error at
ON/OFF State
The accepted maximum error at on/off state. Range of value: 0~100, calculated by
%, with the default value of 20.
After configuration, click Save to save the above settings into the gateway or click Close to cancel
the settings. If a dialog box pops up after you save your settings asking you to restart the service,
do it immediately to apply the changes. Refer to 3.9.15 Restart
for detailed instructions.
Click Modify in Figure 3-30 to modify the tone parameter. See Figure 3-32 for the tone parameter
modification interface.
The configuration items on this interface are the same as those on the Add
New Tone Parameter interface.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 40
Figure 3-32 Modify Tone Parameter
To delete a piece of tone, check the checkbox before the corresponding inde x in Figure 3-30 an d
click the ‘Delete’ button. Check All means to select all available items on the current page;
Uncheck All means to cancel all selections on the current page; Inverse means to uncheck the
selected items and check the unselected. To clear all tone at a time, click the Clear All button in
Figure 3-30.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 41
3.5.4 Tone Generator
Figure 3-33 Tone Generator Setting Interface
See Figure 3-33 for the Tone Generator Setting interface. By default, there are three tones on it:
Dial Tone—a continuous single tone with 450HZ frequency; Ringback Tone—a single tone with
450HZ frequency , repeatedly playing in the method of 1s play and 4s pause; Busy Tone—a single
tone with 450HZ frequency, repeatedly playing in the method of 350ms play and 350ms pause.
You can configure the tone generator manually. The exact explanation about the format and the
meaning is described on the right of the interface.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 42
3.5.5 DTMF
Figure 3-34 DTMF Detector Configuration Interface
See Figure 3-34 for the DTMF detector configuration. The table below explains the items shown in
the above figure.
Item Description
Energy Difference of
High-freq minus
Low-freq
The allowed difference in dB for the DTMF high frequenc y energy level to surpass
the low frequency energy level. Range of value: 0~24. The default value is 5.
Energy Difference of
Low-freq minus
High -freq
The allowed difference in dB for the DTMF low frequency energy level to surpass
the high frequency energy level. Range of value: 0~24. The default value is 9.
Minimum Duration
at ON
The shortest time that a valid tone has to last at ON state. Range of value: 10~
2000, calculated by ms. The default value is 50.
Maximum
Interruption at ON
The longest time for a valid tone to stay interrupted at ON state. Range of value: 0~
20, calculated by ms. The default value is 5.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 43
Center Frequency
Error
The error threshold of the center frequency at ON state in the DTMF tone, with the
default value of 1.
Lowest Energy
Threshold
The energy threshold to trigger the DTMF detection. Range of value: -40~-9,
calculated by dB. The default value is -30.
Minimum
Signal-to-noise
Ratio Threshold
The signal-to-noise ratio threshold to trigger the DT MF detection. Range of value:
-9~0, calculated by dB. The default value is -3.
DTMF Display via
Channel Status
Once this feature is enabled, the received/transmitted DTMF will be displayed as
you put the mouse on the icon of channel status.
ABCD Detection
Once this feature is enabled, the gateway can detect the DTMF digits A, B, C and D
(Case-insensitive). The default value is disabled.
DTMF Energy
Energy of the DTMF signal sent by the gateway. Range of value: -35~15, calculated
by dB, with the default value of -11.
Duration at ON
The duration of DTMF signal at on state. Range of value: 0~16383, calculated by
ms, with the default value of 100.
Duration at OFF
The duration of DTMF signal at off state. Range of value: 0~16383, calculated by
ms, with the default value of 32.
After configuration, click Save to save your settings into the gateway or click Reset to restore the
configurations. If a dialog box pops up after you save your settings asking you to restart the
service, do it immediately to apply the changes. Refer to 3.9.15 Restart
for detailed instructions.
3.5.6 Ringing Scheme

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 44
Figure 3-35 Ringing Scheme Configuration Interface
See Figure 3-35 for the Ringing Scheme interface. The gateway will execute different ringing
schemes according to the callerID or Alter-Info.
The table below explains the items shown in the above figure.
Item Description
CallerID
The gateway will match the CallerID set in this item to that of the incoming call. If
they are matched, the current ringing scheme will be executed; otherwise, the
default ringing scheme (1 sec on and 4 sec off) will work.
The rule to fill in the CallerID is the same as that of 3.5.9 Dialing Rule. Multiple
CallerIDs are supported; they should be separated by “,”
Alter-Info Value
The gateway will match the alter-info value set in this item to that of the incoming
call. If they are matched, the current ringing scheme will be executed; otherwise,
the default ringing scheme (1 sec on and 4 sec off) will work..
Ringing Scheme
The ringing scheme can be “1,X,Y” or “2,X,Y,M,N”, in which, the number 1 or 2
denotes one group or two groups; X, M denote the duration at on state while Y, N
denote the duration at off state.
Note: The duration at ON or OFF cannot be greater than 12000ms, the total
duration at ON and OFF cannot be greater than 16000ms, and N - the last duration
at OFF cannot be less than 1800ms if the item “Occasion to Send FSK CallerID” is
set to After the first ring.
After configuration, click Save to save the above settings into the gateway or click Reset to
restore the configurations.
3.5.7 Fax
Figure 3-36 Fax Configuration Interface (Disable by default)
See Figure 3-36 for the default fax mode configuration. The table below explains the items shown
in the above figure.
Item Description
Fax Mode
The real-time IP fax mode. The optional values are T. 38, Pass-through and Disable,
and the default value is Disable which means to disable both T.38 and
Pass-through.
See Figure 3-37 for the fax configuration under the T.38 mode.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 45
Figure 3-37 Fax Configuration Interface (T.38 Mode)
Users can configure the general fax parameters via this interface. After configuration, click Save
to save your settings into the gateway or click Reset to restore the configurations. If a dialog box
pops up after you save your settings asking you to restart the service, do it immediately to apply
the changes. Refer to 3.9.15 Restart
for detailed instructions. The table below explains the
configuration items in Figure 3-37.
Item Description
T38 Fax Port
The port for T.38 faxing, providing two options: Use Original Voice Port and Use
New Port. The default setting is Use Original Voice Port.
T38 Version
Version of T.38 which is defined by ITU-T. Range of value: 0~3, with the default
value of 0.
T38 Negotiation
The Negotiation mode of T.38, providing two options: Initiate Negotiation as Fax
Sender and Initiate Negotiation as Fax Receiver. The default value is Initiate
Negotiation as Fax Receiver.
Maximum Fax Rate
Sets the maximum faxing rate for both receiving and transmitting. Range of value:
14400, 9600 and 4800, calculated by bps, with the default value of 14400.
Fax Train Mode
Sets the train mode for T.38 fax. The optional values are transferredTCF and
localTCF, with the default value of transferredTCF.
Error Correction
Mode
Sets the error correction mode for T.38 fax. The optional values are
t38UDPRedundancy (Redundancy Error Correction) and t38UDPFEC (Forward
Error Correction), with the default value of t38UDPRedundancy.
T.30 ECM
Sets whether to enable the T.30 error correction mode. By default this f eature is
enabled.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 46
Min Duration of CNG
As stipulated in the standard FAX CNG, the minimum durat ion of CNG is 500ms
±
15%, calculated by ms, with the default value of 425.
Note: Usually there is no need to modify it; please contact our technicians if
necessary.
Min Duration of CED
As stipulated in the standard FAX CED, the minimum duration of CED is
2600~4000ms, calculated by ms, with the default value of 2600.
Note: Usually there is no need to modify it; please contact our technicians if
necessary.
If you set Fax Mode to Pass-through, you can see the interface shown as Figure 3-38.
Figure 3-38 Fax Configuration Interface (Pass-through Mode)
The table below explains the configuration item in the above figure.
Item Description
Pass-through
Payload
RTP Payload under the pass-through fax mode. Range of value: 96~127, with the
default value of 102.
3.5.8 Function Key
See Figure 3-39 for the function key configuration interface. Here you can set a cluster of
combination keys to query a related number.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 47
Figure 3-39 Function Key Configuration Interface
Click “Enable” to enable the corresponding function key. The gateway will use the default function
keys when the mode is set to default; and it will allow you to set new function keys when the mode
is set to user-defined. Click Save to save your settings into the gateway.
Note: Phone Test is used just to see if the phone can work normally. It requires you to hang up the
phone after dialing the corresponding combination keys. Then the gateway will ring the phone. At
that time, pick up the phone and you can hear the voice prompt played by the gateway (e.g. ‘Te s t
successful.’)
When the Blind Transfer feature is enabled, set a corresponding function key in the box behind.
After you transfer a call by rapidly clapping on the hook switch, dial the set function key for Blind
Transfer an d then the called party number. After that, hang up the call once hearing the howler
tone to let the subsequent call procedure go out of your control.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 48
3.5.9 Dialing Rule
Considering efficiency, it is not acceptable that the gateway reports to the PBX or relevant devices
every time it receives a number. Instead, we hope that the gateway can automatically judge the
received number to see if it meets the set rule, if it is complete and if it is qualified to make
outgoing calls. Therefore, a whole dialing plan, which consists of multiple dialing rules specifying
the auto judging conditions, is required. Each dialing rule has a priority, which is used to restrict
the sequence and avoid conflict.
Figure 3-40 Dialing Rule Configuration Interface (Standard)
See Figure 3-40 for the Dialing Rule Configuration interface under the standard mode. The list in
the above figure shows the dialing rules with their priorities and description, which can be added
by the Add New button on the bottom right corner. See Figure 3-41 for the dialing rule adding
interface.
Figure 3-41 Add New Dialing Rule

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 49
The table below explains the items shown in Figure 3-41.
Item Description
Index
The unique index of each dialing rule, which denotes its priority. A dialing rule with a
smaller index value has a higher priority and will be checked earlier while matching.
Description Remarks for the dialing rule. It can be any information, but can not be left empty.
Dialing Rule
Up to 100 dialing rules can be configured in the gateway, and the maximum length of
each dialing rule is 127 characters. See below for the meaning of each character in
the dialing rule. The gateway will do instant matching for your dialing number based
on the dialing rule and regard your dialing as finished upon receiving ‘#’ or dialing
timeout.
Character Description
“0”~”9” Digits 0~9.
“A”~”D” Letters A~D.
“x”
A random number. A string of ‘x’s represents several random
numbers. For example, ‘xxx’ denotes 3 random numbers.
“.”
‘.’ indicates a random amount (including zero) of characters
after it.
“[ ]”
‘[ ]’ is used to define the range for a number. Values within it only
can be digits ‘0~9’, punctuations ‘-‘ and ‘,’. For example,
[1-3,6,8] indicates any one of the numbers 1, 2, 3, 6, 8.
“-”
’-’ is used only in ‘[ ]’ between two numbers to indicates any
number between these two numbers.
“,”
’,’ is used to separate numbers or number ranges, representing
alternatives.
“*” Only represents symbol ”*”.
“#”
Only set it at the beginning of the string, representing symbol
“#”.
There are 19 dialing rules already configured on the gateway for easy use. See
below for detailed information.
Priority Dialing Rule Description
99 . Any number in any length.
98 01[3-5,7-8]xxxxxxxxx.
Any 12-digit number starting with 013,
014, 015, 017 or 018
97 010xxxxxxxx Any 11-digit number starting with 010
96 02xxxxxxxxx Any 11-digit number starting with 02
95 0[3-9]xxxxxxxxxx
Any 12-digit number starting with 03, 04,
05, 06, 07, 08 or 09
94 120 Number 120。
93 11[0,2-9]
Number 110, 112, 113, 1 14, 115, 116, 117,
118 or 119
92 111xx Any 5-digit number starting with 111
91 123xx Any 5-digit number starting with 123

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 50
90 95xxx Any 5-digit number starting with 95
89 100xx Any 5-digit number starting with 100
88 1[3-5,7-8]xxxxxxxxx
Any 11-digit number starting with 13, 14,
15, 17 or 18
87 [2-3,5-7]xxxxxxx
Any 8-digit number starting with 2, 3, 5, 6
or 7
86 8[1-9]xxxxxx
Any 8-digit number starting with 81, 82,
83, 84, 85, 86, 87, 88 or 89
85 80[1-9]xxxxx
Any 8-digit number starting with 801, 802,
803, 804, 805,.806, 807, 808 or 809
84 800xxxxxxx Any 10-digit number starting with 800
83 4[1-9]xxxxxx
Any 8-digit number starting with 41, 42,
43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48 or 49.
82 40[1-9]xxxxx
Any 8-digit number starting with 401, 402,
403, 404, 405, 406, 407, 408 or 409
81 400xxxxxxx Any 10-digit number starting with 400
After configuration, click Save to save the above settings into the gateway or click Close to cancel
the settings.
Click Modify in Figure 3-40 to modify the dialing rules. See Figure 3-42 for the dialing rule
modification interface.
The configuration items on this interface are the same as those on the Add
New Dialing Rule interface.
Figure 3-42 Modify Dialing Rule
To delete a dialing rule, check the checkbox before the corresponding index in Figure 3 -40 and
click the ‘Delete’ button. Check All means to select all available items on the current page;
Uncheck All means to cancel all selections on the current page; Inverse means to uncheck the
selected items and check the unselected. To clear all dialing rules at a time, click the Clear All
button in Figure 3-40.
See Figure 3-43 for the Dialing Rule Configuration interface under the Chara
cter mode. You can
edit the dialing rule list to add a new one or modify an old one. The exact meaning of each rule
element is described on the page.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 51
Figure 3-43 Dialing Rule Configuration Interface (Character)
3.5.10 Dialing Timeout
Figure 3-44 Dialing Timeout Info Interface
See Figure 3-44 for the dialing timeout info interface. The table below explains the items shown in
the above figure.
Item Description
Inter Digit Timeout
Sets the largest interval between two digits of a dialing number. Range of value:
1~10, calculated by s, with the default value of 6. In case your dialing rules do not
include “.”, the call will fail if there is no digit dialed or no dialing rule matched during
this interval; in case your dialing rules include “.”, the gat eway will wait until this
interval ends and match to the dialing rule “.” if there is no digit dialed or no other
dialing rule matched during this interval.
Description
More information about the configuration item Inter Digit Timeout, such as the
reason for adopting the current value.
Click Modify in Figure 3-44 to modify the dialing timeout info. See Figure 3-45 for the dialing
timeout info modification interface. The configuration items on this interface are the same as those
on the Dialing Timeout Info Interface.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 52
Figure 3-45 Modify Dialing Timeout Info
After configuration, click Save to save the above settings into the gateway or click Close to cancel
the settings.
3.5.11 Cue Tone
Figure 3-46 Cue Tone Interface
See Figure 3-46 for the Cue Tone interface. The table below explains the items shown in the
above figure.
Item Description
Upload a file of cue
tone
Uploads a user-defined cue tone file to the gateway, including two options: Cue
Tone for IVR and Cue Tone for Call Waiting.
Click Save to save the above settings into the gateway.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 53
3.5.12 Color Ring
Figure 3-47 Color Ring Interface
By default, there is no available color ring on the gateway. See Figure 3-47. Click Upload to
upload a new color ring manually. See Figure 3-48. You can upload the required color ring file to
the gatewa
y following this interface.
Figure 3-48 Color Ring Upload Interface
The table below explains the items shown above:
Item Description
Index The unique index of each color ring to be uploaded.
Description It is user-defined, with the default value of default.
Color Ring The file of the color Ring to be uploaded.
After configuration, click Upload to upload the color ring file to the gateway or click Return to
cancel the upload. After upload, the color ring will appear on the color ring manage interface, see
Figure 3-49.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 54
Figure 3-49 Color Ring Manage Interface
Click Modify in Figure 3-49 to modify the configuration of the color ring or tick the Upload
checkbox to change the old color ring file. See below for the color ring modification interface. The
configuration items on this interface are the same as those on the Color Ring Upload interface.
Figure 3-50 Color Ring Modification Interface
To delete a color ring, check the checkbox before the corresponding index in Figure 3-49 and click
the Delete button. Check All means to select all available items on the current page; Uncheck
All means to cancel all selections on the current page; Inverse means to uncheck the selected
items and check the unselected. To clear all color rings at a time, click the Clear All button in
Figure 3-50.
3.5.13 QoS
Figure 3-51 Differentiated Services Setting Interface
See Figure 3-51 for the Differentiated Services setting interface. Using this technology, the
gateway can meet various application requirements under a limited bandwidth and ensure neither
delay nor discard for important services so as to improve its quality of services.
The table below explains the items shown in the above figure.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 55
Item Description
QoS Sets whether to enable the OoS differentiated services. By default, it is disabled.
Media Premium QoS
Sets the priority of the media premium for QoS. A media premium QoS with a bigger
value has a higher priority. The value range is 0~63, with the default value of 46.
Control Premium QoS
Sets the priority of the control premium for QoS. A control premium QoS with a
bigger value has a higher priority. The value range is 0~63, with the default value of
26.
3.5.14 Action URL
Figure 3-52 Channel State Report Settings Interface
See Figure 3-52 for the Action URL interface, which is used to designate the server p atch to report
the on-hook or off-hook state of the FXS channel. You are allowed to designate two different
server paths. After setting, the state will be reported to the designated server once any of the FXS
channel hangs up or picks up a call. After configuration, click Save to save your settings into the
gateway or click Reset to restore the configurations.
3.6 Port Settings
Port Settings includes three parts: FXS, FXO and Port Group. See Figure 3-53.
Figure 3-53 Port Settings

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 56
3.6.1 FXS
Figure 3-54 FXS Settings Interface
See Figure 3-54 for the FXS settings interface. The list in the above figure shows the feature and
properties of each FXS port. Click Modify in Figure 3-54 to modify the properties of the
correspondi
ng port. See Figure 3-55 for the FXS modification interface.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 57
Figure 3-55 FXS Modification
The table below explains the configuration items on the FXS modification interface.
Item Description
Port Serial number of the FXS port on the device.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 58
Type Type of the port on the device (FXS). This item is not configurable.
Register Port
Sets whether to register the port to the SIP server.
When this item is set to No, the item Reg Status on the FXS settings interface
(Figure 3-54) shows Unr
egistered; when this item is set to Yes , the item Reg Status
shows Failed or Registered.
SIP Account
When the port initiates a call to SIP, this item correspon ds to the username of SIP.
The default SIP account is 80XX among which XX represents the corresponding
port number. For example, the default SIP account corresponding to Port 1 is 8001,
and that corresponding to Port 32 is 8032.
Display Name
Set the content of the displayname field of the SIP message. If it doesn’t set with
any value, the displayname field will by default display the content of callerid.
Password
Registration password of the port. To register a port to the SIP server, both items
SIP Account and Password must be filled in.
Authentication
Username
Authentication username of a port, used to register the port to the SIP server when
IMS network is enabled.
Note: This item appears only when IMS Network is enabled.
Display Name
Preferred
In case this feature is enabled and the port group or the whole gateway is
registered, if the display name set by the port are different from that set by the port
group, the displayname in the sent SIP message will be the one set by the port. In
case this feature is disabled, if the port group is registered, the displayname in the
sent SIP message will be the display name set by the port group; if the whole
gateway is registered, the displayname in the sent SIP message will be the
displayname of the gateway.
Server Index The index of the SIP server which will be qu oted by the current FXS port.
Auto Dial Number,
Wait Time before
Auto Dial
The FXS port will dial the Auto Dial Number if there is no dialing operation after
pickup within a designated time period (i.e. Wait Time before Auto Dial).
Input Gain, Output
Gain
Adjusts the gain of the voice input to/ output from the FXS port. The value must be
multiples of 3. Range of value: -24~24, calculated by dB, with the default value of 0.
Forbid Outgoing
Call
If this feature is enabled, the FXS port will be forbidden to call out. The default
setting is disabled.
CID
CallerID. If this feature is enabled, the FXS port will send the CallerID of the
incoming IP call together with the ringing tone to the corresponding station. The
default setting is enabled. CallerID displays digits only an d will filter out any other
characters if exist.
Call Waiting
If this feature is enabled, the FXS port in conversation can accept another call from
IP and keep it in the waiting state. Once the current conversation is finished and the
station hangs up, the call in the waiting state will ring the station and wait for
answer. The default setting is disabled.
DND
Do Not Disturb. If this feature is enabled, the FXS port will reply the 403 message to
reject all incoming calls. The default setting is disabled.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 59
Call Forward
The automatic call forward feature for the FXS port. Once this feature is enabled,
the FXS port will forward incoming IP calls according to FWD Type. Note: To
enable this feature, do not put the FXS port into a port group with other ports. The
default setting is disabled.
FWD Type
Forward conditions for the FXS port to forward incoming IP calls. The optional
values are:
Option Description
Unconditional
The FXS port will forward all incoming IP calls to the preset
FWD Num immediately when it receives them.
Busy
The FXS port will forward incoming IP calls to the preset FWD
Num if it is busy upon receiving them.
No Reply
The FXS port will forward incoming IP calls to the preset FWD
Num if the corresponding station does not answer them in a
designated time period (i.e. Time for No Reply Forward). Only
when this forward condition is selected does the configuration
item Time for No Reply Forward become valid.
This item is valid only when Call Forward is set to Enable.
FWD Num
The number to which the incoming IP call is forwarded. If the Call Forward feature
is enabled, this item can not be left empty.
Color Ring
Sets whether to enable the color ring feature or not, with the default setting of being
disabled.
Note: Only when there are available color rings will appear this item.
Color Ring Index The index of the color ring which will be quoted by the current FXS port.
Talkback
With this feature enabled and a number bound, the port can talkback to its bound
number. That is, they can start a call with each other as soon as picking up the
phone. The default setting is disabled.
Note: This feature is only used in the case of channel registration.
Bound Number Sets the bound number for talkback.
Ringing Parameter
Sets the ringing parameter for the FXS module. The default value is
RING_F25_75VRMS_0VDC_LPR_SIN
Note: Usually there is no need to modify it; please contact our technicians if
necessary.
Feed Voltage
Parameter
Sets the feed voltage parameter for the FXS module. The default value is
DCFEED_48V_20MA.
Note: Usually there is no need to modify it; please contact our technicians if
necessary.
Impedance
Parameter
Sets the impedance for the FXS module. The default value is
ZSYN_200_680_100_30_0.
Note: Usually there is no need to modify it; please contact our technicians if
necessary.
After configuration, click Modify to save the settings into the gateway, click Reset to restore the
configurations, or click Cancel to cancel the settings.
Or you can click Batch to modify several pieces of FXS settings at the same time. See Figure

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 60
3-56 below for the FXS batch modification interface. The configuration items on this interface are
the same as those on the FXS modification interface (Figure 3-55).

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 61

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 62
Figure 3-56 FXS Batch Modification
Some configuration items on this interface are the same as those on the FXS Modification
Interface. The others are described in the table below.
Item Description
Starting Port The starting serial number of the FXS port on the device in the batch setting.
Ending Port The ending serial number of the FXS port on the device in the batch setting.
Starting SIP Account The starting SIP account in the batch setting.
Starting Display Name The starting displayname in the batch setting.
Starting Authentication
Password
The starting authentication password in the batch setting.
Starting Authentication
Username
The starting authentication username in the batch setting.
SIP Account Batch Rule
The rule for batch setting the SIP account, including Increase and Decrease two
options.
SIP Account Batch Step
Size
Sets the increase or decrease step size of the SIP account in the batch setting.
Authentication Password
Batch Rule
The rule for batch setting the authentication password, including Increase and
Decrease two options.
Authentication Password
Batch Step Size
Sets the increase or decrease step size of the authentication password in the batch
setting.
Authentication Username
Batch Rule
The rule for batch setting the authentication username, including Increase and
Decrease two options.
Authentication Username
Batch Step Size
Sets the increase or decrease step size of the authentication username in the batch
setting.
After configuration, click Modify to save the settings into the gateway, or click Cancel to cancel
the settings.
3.6.2 FXO
Figure 3-57 FXO Settings Interface
See Figure 3-57 for the FXO settings interface. The list in the above figure shows the feature and
properties of each FXO port. Click Modify in Figure 3-57 to modify the properties of the

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 63
corresponding port. See Figure 3-58 for the FXO modification interface.
Figure 3-58 FXO Modification
The table below explains the configuration items on the FXO modification interface.
Item Description
Port Serial number of the FXO port on the device.
Type Type of the port on the device (FXO). This item is not configurable.
Register Port
Sets whether to register the port to the SIP server.
When this item is set to No, the item Reg Status on the FXO settings interface (Figure
3-57) s
hows Unregistered; when this item is set to Yes , the item Reg Status shows
Failed or Registered.
SIP Account
Registration account of an FXO port. The default SIP account is 80XX among which XX
represents the corresponding port number. For example, the default SIP account
corresponding to Port 1 is 8001, and that corresponding to Port 32 is 8032.
Display Name
Set the content of the displayname field of the SIP message. If it doesn’t set with any
value, the displayname field will by default display the content of callerid.
Password
Registration password of the port. To register a port to the SIP server, both items SIP
Account and Password must be filled in.
Authentication
Username
Authentication username of a port, used to register the port to the SIP server when IMS
network is enabled.
Note: This item appears only when IMS Network is enabled.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 64
Display Name
Preferred
In case this feature is enabled and the port group or the whole gateway is registered, if
the display names set by the port are different from that set by the port group, the
displayname in the sent SIP message will be the one set by the port. In case this feature
is disabled, if the port group is registered, the displayn ame in the sent SIP message will
be the display name set by the port group; if the whole gateway is registered, the
displayname in the sent SIP message will be the displayname of the gateway.
Server Index The index of the SIP server which will be quoted by the current FXO port.
Connection Method
FXO connection methods include:
Option Description
Static
Binding
Bind the number which corresponds to an FXS port to an FXO
port. The number will be listed in the Bound Number column. This
helps to achieve the corresponding binding between an FXO port
and an FXS port (two-way).
Two
Stages
Dialing
Mode
(default)
Under this mode, an incoming call from an FXO port will go into
the IVR system. Then IVR will play a speech prompt “Please dial
the extension number”. If you fail to input the correct target station
number before IVR finishes the third repeat of the prompt, the
FXO will hang up the call automatically; otherwise, the
corresponding station will ring.
Note: Both items Connection Method and Bound Number will be hidden if the SIP
Station feature is enabled on the SIP Settings interface.
Input Gain, Output
Gain
Adjusts the gain of the voice input to/ output from the FXO port. The value must be
multiples of 3. Range of value: -24~24, calculated by dB, with the default value of 0.
Echo Canceller
The echo cancellation feature for a call conversation over the FXO channel. By default,
this feature is enabled and the effect can reach 128ms.
Forbid Outgoing
Call
If this feature is enabled, the FXO port will be forbidden to call out. The default setting is
disabled.
Caller ID Detection
If this feature is enabled, the FXO port will detect the caller IDs from the incoming calls.
The default setting is enabled.
Polarity Reversal
Detection
Once this feature is enabled, only when the FXO port detects the polarity reversal signal
will the corresponding channel go into the talking state. The default setting is disabled.
Note: This feature and the Two Stages Dialing feature cannot be enabled at the same
time.
After configuration, click Modify to save the settings into the gateway, click Reset to restore the
configurations, or click Cancel to cancel the settings.
Or you can click Batch to modify several pieces of FXO settings at the same time. See Figure
3-59 b
elow for the FXO batch modification interface. The configuration items on this interface are
the same as those on the FXO modification interface (Figure 3-58).

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 65
Figure 3-59 FXO Batch Modification
Some configuration items on this interface are the same as those on the FXO Modification
Interface. The others are described in the table below.
Item Description
Starting Port The starting serial number of the FXO port on the device in the batch setting.
Ending Port The ending serial number of the FXO port on the device in the batch setting.
Starting SIP Account The starting SIP account in the batch setting.
Starting Display Name The starting displayname in the batch setting.
Starting Authentication
Password
The starting authentication password in the batch setting.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 66
Starting Authentication
Username
The starting authentication username in the batch setting.
SIP Account Batch Rule
The rule for batch setting the SIP account, including Increase and Decrease two
options.
SIP Account Batch Step
Size
Sets the increase or decrease step size of the SIP account in the batch setting.
Authentication Password
Batch Rule
The rule for batch setting the authentication password, including Increase and
Decrease two options.
Authentication Password
Batch Step Size
Sets the increase or decrease step size of the authentication password in the batch
setting.
Authentication Username
Batch Rule
The rule for batch setting the authentication username, including Increase and
Decrease two options.
Authentication Username
Batch Step Size
Sets the increase or decrease step size of the authentication username in the batch
setting.
After configuration, click Save to save the settings into the gateway, or click Cancel to cancel the
settings.
3.6.3 Port Group
Figure 3-60 Port Group Setting Interface
See Figure 3-60 for the Port Group Settings interface. By default, there is no available port group
on the gateway . A port group is a set containing one or more than one port, having such properties
as Port Selection and Authentication Mode the same for all the ports in it. A new port group can
be added by the Add New button on the bottom right corner of the above list. See Figure 3-61 for
the port gro
up adding interface. Note that a port which has been occupied by one port group
cannot be chosen by others.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 67
Figure 3-61 Add New Port Group
The table below explains the items in the above figure.
Item Description
Index
The unique index of each port group, which is mainly used in the configuration of
routing rules and number manipulation rules to correspond to port groups.
Description More information about each port group, with default value of default.
Register Port Group
To register the port group to the SIP server. Only when this configuration item is set
to Yes can you see the configuration items SIP Account and Password.
SIP Account
When the port group initiates a call to SIP, this item corresponds to the username of
SIP.
Display Name
Set the content of the displayname field of the SIP message. If it doesn’t set with
any value, the displayname field will by default display the content of callerid.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 68
Password
Registration password of the port group. T o register the port group to the SIP server,
both configuration items SIP Account and Password should be filled in.
Authentication
Username
Authentication username of a port, used to register the port to the SIP server when
IMS network is enabled.
Note: This item appears only when IMS Network is enabled.
Server Index The index of the SIP server which will be qu oted by the current port group.
Authentication
Mode
Sets the way for SIP to make outgoing calls (TelIP) on the gateway.
Option Description
Do Not Register
(default)
SIP initiates a call in a point-to-point mode.
Register Gateway
SIP initiates a call with the registered SIP account and
password of the whole gateway. (Refer to 3.4.1 SIP
for
gateway registration.)
Register Port Group
SIP initiates a call with the registered SIP account and
password of the port group.
Register Port
SIP initiates a call with the registered SIP account and
password of the port.
Register Status
Registration status of the port group. When Register Port Group is set to No, the
value of this item is Unregistered; when Register Port Group is set to Yes, the
value of this item may be Failed or Registered.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 69
Port Select Mode
When the port group receives a call, it will choose a port based on the select mode
set by this configuration item to ring or to connect. The optional values and their
corresponding meanings are described in the table below.
Option Description
Increase (default)
Search for an idle port in the ascending order of the port
number, starting from the minimum. If no match is found,
search repeatedly until finding a port which is allowed to
enter the call waiting state.
Decrease
Search for an idle port in the descending order of the port
number, starting from the maximum. If no match is found,
search repeatedly until finding a port which is allowed to
enter the call waiting state.
Cyclic Increase
Provided Port N is the available port found last time.
Search for an idle port in the ascending order of the port
number, starting from Port N+1. If no match is found,
search repeatedly until finding a port which is allowed to
enter the call waiting state.
Cyclic Decrease
Provided Port N is the available port found last time.
Search for an idle port in the descending order of the port
number, starting from Port N-1. If no match is found,
search repeatedly until finding a port which is allowed to
enter the call waiting state.
Group Ringing Ring all the idle FXS ports in this port group.
Ringing by Turns
Ring the ports in this port group according to the Rule for
Ringing by Turns which can be user-defined. Refer to the
format of the rule in Figure 3-61. By default, the ringing
w
ill be carried out in the ascending order of the port
number. Timeout for Ringing by Turns is used to set the
overtime for ringing. Range of value: 15~60, calculated by
s, with the default value of 20.
Preemptive Answer
Keyboard Shortcut
When a channel in a port group is ringing, another channel in the same port group
can press the keyboard shortcut set by this item to transfer the call from the ringing
channel to the current channel.
Note: This item will become invalid if the gateway works under the port select mode
Group Ringing or Ringing by Turns.
Port Reused by
Multiple Groups
Once this feature is enabled, a port can be added to different port groups.
Port
The ports in the port group. If the checkbox before a port is grey , it indicates that the
port is not available or has been occupied. Once the feature “Port Reused by
Multiple Groups” is enabled, a port which has been occupied is still available for
other port groups. All selected ports for a port group will be displayed in the Ports
column in Figure 3-62. Note: When a port group contains multiple ports, the
automatic ca
ll forward feature is invalid.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 70
After configuration, click Save to save the settings into the gateway, click Reset to restore the
configurations, or click Cancel to cancel the settings. Check All means to select all available
ports on the current page; Inverse means to uncheck the selected items and check the
unselected. Check All FXO Ports means to select all available FXO ports on the current page;
Check All FXS Ports means to select all available FXS ports on the current page. See Figure
3-62 for the
port group list with saved configurations.
Figure 3-62 Port Group List
Click Modify at the end of the list in Figure 3-62 to modify the properties of a port group. See
Figure 3-63 for the port group modification interface.
The configuration items on this interface are
the same as those on the Add New Port Group interface.
Figure 3-63 Modify Port Group

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 71
To delete a port group, check the checkbox before the corresponding inde x in Figure 3-62 and
click the ‘Delete’ button. Check All means to select all available items on the current page;
Uncheck All means to cancel all selections on the current page; Inverse means to uncheck the
selected items and check the unselected. To clear all port groups at a time, click the Clear All
button in Figure 3-62.
3.7 Route Settings
Route Settings is used to specify the routing rules for calls on two directions: IPTel and TelIP.
See Figure 3-64.
Figure 3-64 Route Settings
3.7.1 Routing Parameters
Figure 3-65 Routing Parameters Configuration Interface
See Figure 3-65 for the routing parameters configuration interface. On this interface, you can set
the routing rules for calls respectively on two directions IPTel and TelIP to be routing before or
after number manipulation. The default value is Route before Number Manipulate.
After configuration, click Save to save the above settings into the gateway.
3.7.2 IP to Tel
Figure 3-66 IPTel Routing Rule Configuration Interface (Standard)
See Figure 3-66 for the IPTel routing rule configuration interface. By default, there is no
available routing rule on the gateway. The IPTel routing rule configuration has two modes:
Standard and Character.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 72
Under the Standard mode, click Add New to add them manually. See Figure 3-67. You may use
the default values of all the configuration items herein.
Figure 3-67 Add New Routing Rule (IPTel)
The table below explains the items shown in the above figure.
Item Description
Index
The unique index of each routing rule, which denotes its priority. A routing rule with
a smaller index value has a higher priority. If a call matches several routing rules, it
will be processed according to the one with the highest priority.
Description More information about each routing rule, with the default value of default.
Source IP
IP address from where the call is initiated. This item can be set to a specific IP
address or “*” which indicates any IP address
CallerID Prefix,
CalleeID Prefix
A string of characters at the beginning of the caller/called party number. It can be a
specific string consisting of digits 0~9, 、”[*]”, ”#" or character ranges defined by [ ].
‘[ ]’ represents a character within the range it defines. Values in [ ] only can be
characters ‘0~9’, ”[*]”, ”#", punctuations ‘-‘ and ‘,’. (’-’ is used between two
characters to indicates any character between these two characters. ’,’ is used to
separate characters or character ranges, representing alternatives.) For example,
057[1-3,6] represents the string 0571, 0572, 0573 or 0576. Also these items can be
set to “*” which indicates any string. These two configuration items together with
Source IP specify a routing rule for calls.
Note: “[*]” represents TFM symbol *, while “*” represents any string.
Route by Number
When this feature is enabled, the gateway will route a call from IP to a
corresponding port based on its number. And the number of the port which this call
will be routed to can be set via the item SIP Account on the FXS
or FXO settings
interface. In such case, the configuration item Call Destination goes invalid and

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 73
shows Route by Number on the routing rule configuration interface. The default
setting is disabled.
Call Destination Port group to which the call will be routed.
After configuration, click Save to save the settings into the gateway or click Close to cancel the
settings.
See Figure 3-68 for the IPT
el routing rule configuration interface after your configuration. There
is a rule displayed with Index 63 and Call Destination ‘Route by Number’, having no restriction on
Source IP, CallerID Prefix and CalleeID Prefix, which indicates the gateway will route a call from
any IP address to a corresponding port based on its number.
Press the Add New button on the bottom right corner of the list to add a new routing rule.
Figure 3-68 IPTel Routing Rule Configuration Interface
Click Modify in Figure 3-68 to modify a routing rule. The configuration items on the IPTel routing
rule modification interface are the same as those on the Add New Routing Rule (IP
Tel)
interface. Note that the item Index cannot be modified.
To delete a routing rule, check the checkbox before the corresponding index in Figure 3-68 an d
click the Delete button. Check All
means to select all available items on the current page;
Uncheck All means to cancel all selections on the current page; Inverse means to uncheck the
selected items and check the unselected. To clear all routing rules at a time, click the Clear All
button in Figure 3-68.
See Figure 3-69 for the IPT
el Routing Rule Configuration Interface under the Character mode.
You can edit the routing rule list to add a new one or modify an old one. The exact meaning of
each element of the rule is described on the page.
Figure 3-69 IPTel Routing Rule Configuration Interface (Character)

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 74
3.7.3 Tel to IP
Figure 3-70 TelIP Routing Rule Configuration Interface (Standard)
See Figure 3-70 for the TelIP routing rule configuration interface. By default, there is no
available routing rule on the gateway. The TelIP routing rule configuration has two modes:
Standard and Character.
Under the Standard mode, click Add New to add them manually. See Figure 3-71. You may use
the default values of all
the configuration items herein except for Destination IP and Destination
Port.
Figure 3-71 Add New Routing Rule (TelIP)
The table below explains the items shown in the above figure.
Item Description
Index
The unique index of each routing rule, which denotes its priority. A routing rule with
a smaller index value has a higher priority. If a call matches several routing rules, it
will be processed according to the one with the highest priority.
Description More information about each routing rule, with the default value of default.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 75
Source Port Group
(Call Initiator)
Port group from which the call is initiated. This item can be set to a specific port
group or ‘*’ which indicates any port group.
CallerID Prefix,
CalleeID Prefix
A string of characters at the beginning of the caller/called party number. It can be a
specific string consisting of digits 0~9, ”[*]”, ”#" or characters ranges defined by [ ].
‘[ ]’ represents a character within the range it defines. Values in [ ] only can be digits
‘0~9’, ”[*]”, ”#", punctuations ‘-‘ and ‘,’. (’-’ is used between two characters to
indicates any characters between these two characters. ’,’ is used to separate
characters or characters ranges, representing alternatives.) For example,
057[1-3,6] represents the string 0571, 0572, 0573 or 0576. Also these items can be
set to “*” which indicates any string. These two configuration items together with
Source Port Group (Call Initiator) specify a routing rule for calls.
Note: ”[*]” represents DTFM symbol *, while “*” represents any string.
Destination IP,
Destination Port
IP address and port number of the remote end to which the call will be routed.
After configuration, click Save to save the settings into the gateway or click Close to cancel the
settings.
See Figure 3-72 for the TelIP
routing rule configuration interface after your configuration. There
is a rule displayed with Index 63, Destination IP ‘192.168.1.101’ and Destination Port ‘5060’ (i.e.
default IP address and port of the gateway), having no restriction on Call Initiator, CallerID Prefix
and CalleeID Prefix, which indicates all the outgoing calls from Tel which conform to the dialing
rule will be routed to the gateway.
Figure 3-72 TelIP Routing Rule Configuration Interface
Click Modify in Figure 3-72 to modify a routing rule. The configuration items on the TelIP routing
rule modification interface are the same as those on the Add New Routing Rule (Tel
IP)
interface. Note that the item Index cannot be modified.
To delete a routing rule, check the checkbox before the corresponding index in Figure 3-72 an d
click the Delete button. Check All
means to select all available items on the current page;
Uncheck All means to cancel all selections on the current page; Inverse means to uncheck the
selected items and check the unselected. To clear all routing rules at a time, click the Clear All
button in Figure 3-72.
See Figure 3-73 for the TelIP
Routing Rule Configuration Interface under the Character mode.
You can edit the routing rule list to add a new one or modify an old one. The exact meaning of
each element of the rule is described on the page.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 76
Figure 3-73 TelIP Routing Rule Configuration Interface (Character)
3.8 Number Manipulation
Number Manipulation includes four parts: IPTel CallerID, IPTel CalleeID, TelIP CallerID
and TelIP CalleeID. See Figure 3-74.
Figure 3-74 Number Manipulation
3.8.1 IP to Tel CallerID
Figure 3-75 IPTel CallerID Manipulation Interface (Standard)
See Figure 3-75 for the IPTel CallerID manipulation interface under the Standard mode. A new
number manipulation rule can be added by the Add New button on the bottom right corn er of the
list in the above figure. See Figure 3-76 for the IPT
el CallerID manipulation rule adding interface.
You may use the default values of all the configuration items herein.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 77
Figure 3-76 Add IPTel CallerID Manipulation Rule
The table below explains the items shown in the above figure.
Item Description
Index
The unique index of each number manipulation rule, which denotes its priority. A
number manipulation rule with a smaller index value has a higher priority. If a call
matches several number manipulation rules, it will be proc essed according to the
one with the highest priority.
Description
More information about each number manipulation rule, with the default value of
default.
Call Initiator
IP address from where the call is initiated. This item can be set to a specific IP
address or “*” which indicates any IP address.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 78
CallerID Prefix,
CalleeID Prefix
A string of characters at the beginning of the caller/called party number. It can be a
specific string consisting of digits 0~9, ”[*]”, ”#" or character ranges defined by [ ]. ‘[ ]’
represents a character within the range it defines. Values in [ ] only can be digits
‘0~9’, “[*]”, ”#", punctuations ‘-‘ and ‘,’. (’-’ is used between two characters to
indicates any character between these two characters. ’,’ is used to separate
characters or character ranges, representing alternatives.) For example, 057[1-3,6]
represents the string 0571, 0572, 0573 or 0576. Also these items can be set to “*”
which indicates any string. These two configuration items together with Call
Initiator specify a number manipulation rule for calls.
Note: “[*]” represents DTFM symbol *, while “*” represents any string.
Stripped Digits from
Left
The amount of digits to be deleted from the left end of the number. If the value of
this item exceeds the length of the current number, the whole number will be
deleted. The default value is 0.
Stripped Digits from
Right
The amount of digits to be deleted from the right end of the number. If the value of
this item exceeds the length of the current number, the whole number will be
deleted. The default value is 0.
Reserved Digits
from Right
The amount of digits to be reserved from the right end of the number. Only w hen the
value of this item is less than the length of the current number will some digits be
deleted from left; otherwise, the number will not be manipulated. The default value
is 20.
Prefix to Add Designated information to be added to the left end of the current number.
Suffix to Add Designated information to be added to the right end of the current number.
Note: The number manipulation is performed in 5 steps by the order of the following
configuration items: Stripped Digits from Left, Stripped Digits from Right, Reserved Digits
from Right, Prefix to Add and Suffix to Add.
After configuration, click Save to save the settings into the gateway or click Close to cancel the
settings.
Click Modify in Figure 3-75 to modify a number manipulation rule. See Figure 3-77 for the IPTe
l
CallerID manipulation rule modification interface. The configuration items on this interface are the
same as those on the Add IP
Tel CallerID Manipulation Rule interface. Note that the item
Index cannot be modified.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 79
Figure 3-77 Modify IPTel CallerID Manipulation Rule
To delete a number manipulation rule, check the checkbox before the corresponding index in
Figure 3-75 and click the Delete button. Check All means to select all
available items on the
current page; Uncheck All means to cancel all selections on the current page; Inverse means to
uncheck the selected items and check the unselected. To clear all number manipulation rules at a
time, click the Clear All button in Figure 3-75.
See Figure 3-78 for the IPT
el CallerID Manipulation Interface under the Character mode. You
can edit the number manipulation rule list to add a new one or modify an old one. The exact
meaning of each element of the rule is described on the page.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 80
Figure 3-78 IPTel CallerID Manipulation Interface (Character)
3.8.2 IP to Tel CalleeID
The number manipulation process for IPTel CalleeID is almost the same as that for IPTel
CallerID; only the number to be manipulated changes from CallerID to CalleeID. See Figure 3-80
for IPT
el CalleeID manipulation interface. The configuration items on this interface are the same
as those on IP
Tel CallerID Manipulation Interface (Figure 3-75).
Figure 3-79 IPTel CalleeID Manipulation Interface(Standard)

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 81
Figure 3-80 IPTel CalleeID Manipulation Interface (Character)
3.8.3 Tel to IP CallerID
Figure 3-81 TelIP CallerID Manipulation Interface (Standard)
See Figure 3-81 for the TelIP CallerID manipulation interface under the Standard mode. A new
number manipulation rule can be added by the Add New button on the bottom right corn er of the
list in the above figure. See Figure 3-82 for the TelIP
CallerID manipulation rule adding interface.
You may use the default values of all the other configuration items herein.
Figure 3-82 Add TelIP CallerID Manipulation Rule
The table below explains the items shown in the above figure.
Item Description
Index
The unique index of each number manipulation rule, which denotes its priority. A
number manipulation rule with a smaller index value has a higher priority. If a call

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 82
matches several number manipulation rules, it will be proc essed according to the
one with the highest priority.
Description
More information about each number manipulation rule, with the default value of
default.
Source Port Group
(Call Initiator)
Port group from which the call is initiated. This item can be set to a specific port
group or ‘*’ which indicates any port group.
CallerID Prefix,
CalleeID Prefix
A string of characters at the beginning of the caller/called party number. It can be a
specific string consisting of digits 0~9, ”[*]”, ”#" or character ranges defined by [ ]. ‘[ ]’
represents a character within the range it defines. Values in [ ] only can be digits
‘0~9’, “[*]”, ”#", punctuations ‘-‘ and ‘,’. (’-’ is used between two characters to
indicates any character between these two characters. ’,’ is used to separate
characters or character ranges, representing alternatives.) For example, 057[1-3,6]
represents the string 0571, 0572, 0573 or 0576. Also these items can be set to “*”
which indicates any string. These two configuration items together with Call
Initiator specify a number manipulation rule for calls.
Note: “[*]” represents DTFM symbol *, while “*” represents any string.
Stripped Digits from
Left
The amount of digits to be deleted from the left end of the number. If the value of
this item exceeds the length of the current number, the whole number will be
deleted. The default value is 0.
Stripped Digits from
Right
The amount of digits to be deleted from the right end of the number. If the value of
this item exceeds the length of the current number, the whole number will be
deleted. The default value is 0.
Reserved Digits
from Right
The amount of digits to be reserved from the right end of the number. Only w hen the
value of this item is less than the length of the current number will some digits be
deleted from left; otherwise, the number will not be manipulated. The default value
is 20.
Prefix to Add Designated information to be added to the left end of the current number.
Suffix to Add Designated information to be added to the right end of the current number.
Note: The number manipulation is performed in 5 steps by the order of the following
configuration items: Stripped Digits from Left, Stripped Digits from Right, Reserved Digits
from Right, Prefix to Add and Suffix to Add.
After configuration, click Save to save the settings into the gateway or click Close to cancel the
settings.
Click Modify in Figure 3-81 to modify a number manipulation rule. See Figure 3-83 for the TelIP
CallerID manipulation rule modification interface. The configuration items on this interface are the
same as those on the Add Tel
IP CallerID Manipulation Rule interface. Note that the item
Index cannot be modified.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 83
Figure 3-83 Modify TelIP CallerID Manipulation Rule
To delete a number manipulation rule, check the checkbox before the corresponding index in
Figure 3-81 and click the Delete button. Check All means to select all
available items on the
current page; Uncheck All means to cancel all selections on the current page; Inverse means to
uncheck the selected items and check the unselected. To clear all number manipulation rules at a
time, click the Clear All button in Figure 3-81.
See Figure 3-84 for the TelIP
CallerID Manipulation Interface under the Character mode. You
can edit the number manipulation rule list to add a new one or modify an old one. The exact
meaning of each element of the rule is described on the page.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 84
Figure 3-84 TelIP CallerID Manipulation Interface (Character)
3.8.4 Tel to IP CalleeID
The number manipulation process for TelIP CalleeID is almost the same as that for TelIP
CallerID; only the number to be manipulated changes from CallerID to CalleeID. See Figure 3-85,
Figure 3-86 for the TelIP
CalleeID manipulation interface. The configuration items on this
interface are the same as those on Tel
IP CallerID Manipulation Interface (Figure 3-81).
Figure 3-85 TelIP CalleeID Manipulation Interface (Standard)

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 85
Figure 3-86 TelIP CalleeID Manipulation Interface (Character)
3.9 System Tools
System Tools is mainly for gateway maintenance. It provides such features as IP modification,
data backup and connectivity check. See Figure 3-87 for details.
Figure 3-87 System Tools

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 86
3.9.1 Management
Figure 3-88 Management Parameters Setting Interface
See Figure 3-88 for the Management Parameters Setting interface. The table below explains the
items shown in the above figure.
Item Description
WEB Port The port which is used to access the gateway via WEB. The default value is 80.
Access Setting
Sets the IP addresses which can access the gateway via WEB. By default, all IPs
are allowed. You can set an IP whitelist to allow all IPs within it to access the
gateway freely. Also can set an IP blacklist to forbid all IPs within it to access the
gateway.
SYSLOG
Sets whether to enable SYSLOG. It is required to fill in SYSLOG Server Address
and SYSLOG Level in case SYSLOG is enabled. By default, SYSLOG is disabled.
Server Address Sets the SYSLOG server address for log reception.
SYSLOG Level
Sets the SYSLOG level. There are three options: ERROR, WARNING and INFO.
The default value is INFO.
Send CDR
Sets whether to enable the feature of sending CDR. It is required to fill in Server
Address and Server Port in case Send CDR is enabled. By default, Send CDR is
disabled.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 87
Server Address The address of the server to receive CDR.
Server Port The port of the server to receive CDR.
NTP
Sets whether to enable the NTP time synchronization feature. It is required to fill in
NTP Server Address, Synchronizing Cycle and Time Zone in case NTP is
enabled. By default, NTP is disabled.
NTP Server Address Sets the Server address for NTP time synchronization.
Synchronizing Cycle Sets the cycle for NTP time synchronization. The default value is 3600.
Daily Restart
Sets whether to restart the gateway regularly every day at the preset Restart Time.
By default, this feature is disabled.
Restart Time Sets the time to restart the gateway regularly.
System Time
The system time. Check the checkbox before Modify and change the time in the
edit box.
Time Zone The time zone of the gateway.
3.9.2 Network
Figure 3-89 Network Settings Interface
See Figure 3-89 for the network settings interface. A gateway has two LANs, each of which can be
configured with independent network type, IP address, subnet mask, default gateway and DNS
server. Network Type has three options: Static, DHCP and PPPoE. If PPPoE is used, it is
necessary to enter the username and the password of the network. By default, LAN1 is enabled
and LAN2 is disabled.
Note:
1. The values of the IP address, Subnet Mask, Default Gateway and DNS Server shown in

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 88
Figure 3-89 are all factory settings. The IP Address for LAN 1 and that for LAN 2 cannot
be in the same segment.
2. LAN2 is disabled by default for the gateway Version 1.3.3 or above. If you want to use
LAN2, please log in the gateway through LAN1 first, and then modify the network
settings to enable LAN2.
After configuration, click Save to save the above settings into the gateway or click Reset to
restore the configurations. After changing the IP address, you shall log in th e gateway again using
your new IP address.
3.9.3 Upgrade
Figure 3-90 Upgrade Interface
See Figure 3-90 for the upgrade inte rface where you can upgrade the WEB, gateway service,
kernel and firmware to new versions. Select the upgrade package “*.tar.gz” (The gateway will do
MD5 verification before upgrading and will not start to upgrade until it passes the verification.) via
Browse… and click Update. Then the file uploading interface will appear. See Figure 3-91.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 89
Figure 3-91 File Uploading Interface
After a successful uploading of the file, the gateway will start to upgrade the system. See Figure
3-92 and you can learn the detailed upgrading information from the upgrade information box at
the bottom.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 90
Figure 3-92 System Upgrading Interface
Note that clicking Reset can only delete the selected update file but not cancel the operation of
Update.
Note: Please contact our technicians if you need to downgrade the gateway to an old version. An
improper operation may cause unexpected problems.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 91
3.9.4 Signaling Capture
Figure 3-93 Signaling Capture Interface
See Figure 3-93 for the Signaling Capture interface, including two parts: Packet Capture and Data
Recording. Packet capture contains Signaling Packet Capture and RTP Packet Capture. You can
select either of them to start the capture according to your requirement. Click Start to start
capturing packets. Click Stop to stop the capture and download the captured packets.
Data Recording will execute the recording task on the set port with the set recording time length.
You can choose ‘Recording of Connected IP Channels or ‘Recording before Echo Cancellation’.
Click Start to start recording data (consecutively recording 300 seconds at most) on the
corresponding port with the corresponding time length. Click Stop to stop the recording and click
Download File to download the recorded data.
3.9.5 Call Log
Figure 3-94 Call Log Interface

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 92
Figure 3-95 SIP Log Interface
See Figure 3-94, Figure 3-95 for the Call Log interface. Click the checkbox before Enable Call
Log to enable the call log feature, including Call Log and SIP Log. Call from IP Channel
displays the call log information generated on all IP channels, and Call from Port displays the call
log information generated on the port you select. All the SIP related information will be displayed
in SIP Log.
3.9.6 Operation Log
Figure 3-96 Operation Log Interface

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 93
See Figure 3-96 for the Operation Log interface, which is used to check the operation records on
WEB. Click Refresh to refresh the log; click Clear All to clear all the operation logs and click
Download to download the logs.
Note: The sign <@#> here means the configuration item is unconfigured.
3.9.7 Backup & Upload
Figure 3-97 Backup & Upload Interface
See Figure 3-97 for the backup and upload interface. To back up the configuration file to your PC,
just click Backup. To upload a configuration file, select it via Browse… and click Upload.
Figure 3-98 Backup & Upload & Prompt Interface
Click OK on the prompt box (Figure 3-98) to upload the configuration file to the gateway. Now the
prompt information ‘The gateway service is restarting, please do not leave this page’ appears.
See Figure 3-99. The gateway will overwrite the current configurations with the uploaded dat
a
after restart. Click Cancel to cancel this upload directly.

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 94
Figure 3-99 Configuration File Uploading Interface
3.9.8 Factory Reset
Figure 3-100 Factory Reset Interface
See Figure 3-100 for the factory reset interface. Click Reset to restore all configurations on the
gateway to factory settings.
3.9.9 System Monitor
Figure 3-101 System Monitor Configuration Interface
See Figure 3-101 for the System Monitor Configuration interface. Watchdog is a timing reset
system used to avoid application crash. You can set the dog feeding interval when this feature is
enabled. The feeding interval is calculated by s, with the value range of 1~15s. By default, this
feature is enabled with the default value of 5s. As the feature ‘Automatically restart the service if
undetected’ is enabled, the service application will restart automatically if it is not detected by the
gateway guard application. By default, this feature is enabled. Threshold to Judge Heartbeat Loss
for Service is used to judge whether the gateway receives the heartbeat packets from the service

Synway Information Engineering Co., Ltd
SMG Series Analog Gateway User Manual (Version 1.6.4) Page 95
during the set time, if not, it is considered that the gateway service has been disconnected. It is
calculated by s, with the value range of 20~120s and the default value of 60s.
3.9.10 Centralized Manage
Figure 3-102 Centralized Manage Setting Interface
See Figure 3-102 for the Centralized Manage S etting interface. The gateway can register to a
centralized management platform and accept the management of the platform. The table below
explains the items shown in above figures.
Item Description
Management
Platform
Select a management platform for the gateway to register, including two options:
DCMS and Others.
DCMS Server
Address
The address of the server in which the DCMS locates, It can be IP or a domain
name valid only when DCMS is selected.
Note: To configure the domain name, the DNS should be already configured an d
the corresponding domain name must be analyzable.
Company Name
The name used to register the gatew ay to Sy nway DC MS, valid only w hen DCMS is
selected.
Authorization Code
The authorization code is used for the connection verification. A device can connect
to the DCMS successfully only after it passes the verification. This item is valid only
when DCMS is selected.
 Loading...
Loading...