Page 1

Symantec NetBackup™ Deduplication Guide
Release 7.0
20654102
Page 2

Symantec NetBackup™ Deduplication Guide
The softwaredescribed inthis bookis furnishedunder alicense agreementand maybe used
only in accordance with the terms of the agreement.
Documentation version 7.0
PN: 20654102
Legal Notice
Copyright © 2009 Symantec Corporation. All rights reserved.
Symantec, the Symantec Logo, Veritas, and NetBackup are trademarks or registered
trademarks of Symantec Corporation or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. Other
names may be trademarks of their respective owners.
The product described in this document is distributed under licenses restricting its use,
copying, distribution, and decompilation/reverse engineering. No part of this document
may be reproduced in any form by any means without prior written authorization of
Symantec Corporation and its licensors, if any.
THE DOCUMENTATIONISPROVIDED "ASIS" AND ALLEXPRESS ORIMPLIED CONDITIONS,
REPRESENTATIONS AND WARRANTIES, INCLUDING ANY IMPLIED WARRANTY OF
MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE OR NON-INFRINGEMENT,
ARE DISCLAIMED, EXCEPT TO THE EXTENT THAT SUCH DISCLAIMERS ARE HELD TO
BE LEGALLYINVALID. SYMANTEC CORPORATIONSHALL NOT BELIABLE FOR INCIDENTAL
OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES IN CONNECTION WITH THE FURNISHING,
PERFORMANCE, OR USE OF THIS DOCUMENTATION. THE INFORMATION CONTAINED
IN THIS DOCUMENTATION IS SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE.
The LicensedSoftware andDocumentation aredeemed tobe commercialcomputer software
as definedin FAR 12.212 and subject to restricted rights asdefined inFAR Section52.227-19
"Commercial Computer Software - Restricted Rights" and DFARS 227.7202, "Rights in
Commercial Computer Software or Commercial Computer Software Documentation", as
applicable, and any successor regulations. Any use, modification, reproduction release,
performance, displayor disclosure of the Licensed Software and Documentation bythe U.S.
Government shall be solely in accordance with the terms of this Agreement.
Page 3

Symantec Corporation
350 Ellis Street
Mountain View, CA 94043
http://www.symantec.com
Page 4

Technical Support
Symantec Technical Support maintains support centers globally. Technical
Support’s primary role is to respond to specific queries about product features
and functionality.The Technical Support group also creates contentfor our online
Knowledge Base. The Technical Support group works collaboratively with the
other functional areas within Symantec to answer your questions in a timely
fashion. Forexample, theTechnical Supportgroup works with Product Engineering
and SymantecSecurity Response to provide alerting services andvirus definition
updates.
Symantec’s maintenance offerings include the following:
■ A range of support options that give you the flexibility to select the right
amount of service for any size organization
■ Telephone and Web-based support that provides rapid response and
up-to-the-minute information
■ Upgrade assurance that delivers automatic software upgrade protection
■ Global support that is available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week
■ Advanced features, including Account Management Services
For information about Symantec’s Maintenance Programs, you can visitour Web
site at the following URL:
www.symantec.com/techsupp/
Contacting Technical Support
Customers with a current maintenanceagreement may access Technical Support
information at the following URL:
www.symantec.com/techsupp/
Before contacting Technical Support, make sure you have satisfied the system
requirements that are listed in your product documentation. Also, you should be
at thecomputer on which the problem occurred, incase itis necessaryto replicate
the problem.
When you contact Technical Support, please have the following information
available:
■ Product release level
■ Hardware information
■ Available memory, disk space, and NIC information
■ Operating system
Page 5

■ Version and patch level
■ Network topology
■ Router, gateway, and IP address information
■ Problem description:
■ Error messages and log files
■ Troubleshooting that was performed before contacting Symantec
■ Recent software configuration changes and network changes
Licensing and registration
If yourSymantec product requires registration or a licensekey, accessour technical
support Web page at the following URL:
www.symantec.com/techsupp/
Customer service
Customer service information is available at the following URL:
www.symantec.com/techsupp/
Customer Service is available to assist with the following types of issues:
■ Questions regarding product licensing or serialization
■ Product registration updates, such as address or name changes
■ General product information (features, language availability, local dealers)
■ Latest information about product updates and upgrades
■ Information about upgrade assurance and maintenance contracts
■ Information about the Symantec Buying Programs
■ Advice about Symantec's technical support options
■ Nontechnical presales questions
■ Issues that are related to CD-ROMs or manuals
Page 6

Maintenance agreement resources
If you want to contact Symantec regarding an existing maintenance agreement,
please contact the maintenance agreement administration team for your region
as follows:
Additional enterprise services
Symantec offers a comprehensive setof services that allow you to maximize your
investment in Symantec products and to develop your knowledge, expertise, and
global insight, which enable you to manage your business risks proactively.
Enterprise services that are available include the following:
customercare_apac@symantec.comAsia-Pacific and Japan
semea@symantec.comEurope, Middle-East, and Africa
supportsolutions@symantec.comNorth America and Latin America
Symantec EarlyWarning Solutions
Managed Security Services
Consulting Services
Educational Services
To access more information about Enterprise services, please visit our Web site
at the following URL:
www.symantec.com
Select your country or language from the site index.
These solutions provide early warning of cyber attacks, comprehensive threat
analysis, and countermeasures to prevent attacks before they occur.
These servicesremove theburden ofmanaging andmonitoring securitydevices
and events, ensuring rapid response to real threats.
Symantec Consulting Services provide on-site technical expertise from
Symantec andits trustedpartners. SymantecConsulting Servicesoffer avariety
of prepackaged and customizable options that include assessment, design,
implementation, monitoring,and managementcapabilities. Each is focused on
establishing andmaintaining the integrity and availability of your IT resources.
Educational Services provide a full array of technical training, security
education, security certification, and awareness communication programs.
Page 7

Contents
Technical Support ..... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ... 4
Chapter 1 Introducing NetBackup deduplication .. .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .. 11
About NetBackup deduplication ... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... ... 11
About NetBackup deduplication options ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... ... 12
How deduplication works ... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... 14
Chapter 2 Planning your deployment ... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . . 17
Planning your deduplication deployment .... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... .... . .... . ... 17
About the deduplication storage type . .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .. 19
About the NetBackup Media Server Deduplication Option .... . .... . .... . .... . 19
About deduplication servers ..... .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... 21
About deduplication nodes .... ..... .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ... 22
About deduplication server requirements ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... . 23
About media server deduplication limitations ..... .... . .... . .... ..... ..... 23
About NetBackup Client Deduplication .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .. 24
About client deduplication host requirements ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... 25
About client deduplication requirements ... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . ... 25
About client deduplication limitations . ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... 26
About NetBackup Deduplication Engine credentials ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ... 26
About the network interface for deduplication ... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .. 27
About firewalls and the deduplication hosts .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... 27
About scaling deduplication .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... . 27
About compression and encryption . .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... 28
About optimized duplication of deduplicated data . .... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... . 28
Optimized deduplication copy requirements ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... .. 28
Optimized deduplication copy limitations . ..... .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . 31
About deduplication performance . . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... . 32
How file size may affect the deduplication rate . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . ... 33
Replacing the PureDisk Deduplication Option with Media Server
Deduplication on the same host ... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... . 33
Migrating from PureDisk to the NetBackup Media Server
Deduplication option ... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... . 34
Migrating from another storage type to deduplication ... . .... ..... ..... .... . . 35
Page 8

Contents8
Chapter 3 Provisioning the storage ... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . 37
About provisioning the storage . . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . 37
About deduplication storage requirements .... .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . . 37
About deduplication storage capacity .... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . ... 38
About the deduplication storage paths ... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... ... 38
Chapter 4 Installing deduplication ... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... .... . .... . .... . . 41
About installing deduplication .... . .... . .... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . ... 41
About the deduplication license key .... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . . 42
Licensing NetBackup deduplication . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... 42
Replacing the deduplication storage server host computer ... . .... ..... ..... . 42
Uninstalling media server deduplication . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ... 44
Chapter 5 Configuring deduplication . ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... 47
Configuring deduplication ... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... ..... ..... 47
Configuring a deduplication storage server . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... ..... ..... 48
About deduplication pools . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .. 49
Configuring a deduplication pool . . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... .. 50
Media server deduplication pool properties ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... .... 50
Configuring a deduplication storage unit .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... .... 52
Deduplication storage unit properties . .... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... . 53
Deduplication storage unit recommendations ... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .. 54
Enabling client deduplication . ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ... 56
Configuring backups . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... . 56
Configuring optimized deduplication copy ... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ... 57
Configuring optimized deduplication copy behavior .... . .... . .... ..... ..... ... 57
Adding a load balancing server . . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . 58
About the deduplication configuration file . . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... ..... 60
Editing the deduplication configuration file .... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . 60
pd.conf file settings . .... . .... . .... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . 61
Reconfiguring the deduplication storage server and storage
paths ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... . 63
Chapter 6 Managing deduplication ... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... . 65
Managing deduplication servers . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... .... 65
Changing deduplication storage server properties ... ..... .... . .... . .... . . 66
Deleting a deduplication storage server . . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... ... 67
Determining the deduplication storage server state ... ..... .... . .... . .... 67
Getting the storage server configuration .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .. 68
Editing a storage server configuration file . . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . ... 68
Setting the storage server configuration .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... ..... .... 70
Page 9

Deleting a load balancing server configuration file . . .... . .... ..... ..... .. 70
Removing a load balancing server .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... ..... .. 70
Viewing deduplication storage servers . . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . ... 72
Viewing deduplication storage server attributes ... ..... ..... .... . .... . ... 72
Resetting the deduplication registry . ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .. 73
Managing NetBackup Deduplication Engine credentials .... . .... . .... ..... ... 74
Adding NetBackup Deduplication Engine credentials .... . .... . .... ..... . 74
Changing NetBackup Deduplication Engine credentials . . .... ..... ..... . 75
Deleting credentials from a load balancing server . ..... ..... .... . .... . ... 75
Determining which media servers have deduplication
credentials .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .. 76
Managing deduplication disk pools . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... . 76
Changing deduplication disk pool properties .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .. 76
Changing the deduplication pool state .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... . 77
Changing the deduplication disk volume state . . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . ... 77
Deleting a deduplication pool .... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . ... 78
Determining the deduplication pool state ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... . 78
Determining the deduplication disk volume state ... .... . .... . .... . .... ... 79
Viewing deduplication disk pools .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ... 79
Monitoring deduplication activity ... ..... .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... 80
Monitoring the deduplication rates ... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . 80
Viewing disk reports ... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .. 81
Monitoring deduplication processes ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . ... 83
Monitoring deduplication logs .... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... ... 83
Monitoring deduplication storage capacity and usage ... . .... . .... ..... ..... .. 87
About deduplication capacity and usage reporting .... ..... ..... .... . .... 87
About deduplication container files . ..... ..... .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . ... 89
Viewing capacity within deduplication container files . .... ..... ..... .... 89
Deleting backup images .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .. 90
Disabling deduplication for a client . ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... 90
About maintenance processing .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .. 90
9Contents
Chapter 7 Troubleshooting ... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... 93
Troubleshooting installation issues . .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... ..... 93
Installation on SUSE Linux fails .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... 93
Troubleshooting configuration issues . . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... ..... ..... . 94
Cannot configure deduplication storage server . ..... .... . .... . .... ..... ... 94
The disk pool wizard does not display a volume . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .. 95
Troubleshooting operational issues . .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... ..... 95
Verify that the server has sufficient memory . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . 95
Backup jobs fail ... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .. 96
Page 10

Contents10
Volume state changes to DOWN when volume is
unmounted .... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .. 96
Errors, delayed response, hangs . ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . ... 97
Viewing disk errors and events . ..... ..... .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... . 97
Deduplication event codes and messages ..... ..... .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . ... 97
Chapter 8 Disaster recovery . . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... .... 103
Preparing for disaster . . .... . .... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... . 103
Moving images off-site ... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ... 103
Recovering from a deduplication storage server disk failure . .... ..... ..... 104
Recovering from a permanent deduplication storage server
failure .... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . ... 105
Recovering the storage server after NetBackup catalog recovery . .... . ... 107
Chapter 9 Deduplication architecture ... .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... 109
Deduplication server components ... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . ... 109
Media server deduplication process . ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .. 111
Deduplication client components . ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . 114
Deduplication client backup process . .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... .. 114
About deduplication fingerprinting ... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . 117
Data removal process .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . ... 118
Index . . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .... ..... ..... .... . .... . .... . .. 119
Page 11

Chapter
Introducing NetBackup deduplication
This chapter includes the following topics:
■ About NetBackup deduplication
About NetBackup deduplication
The proprietary Symantec PureDisk deduplicationtechnology powersNetBackup
integrated deduplication.Symantec packagedPureDisk into modular components.
The components plug-in to NetBackup through the NetBackup OpenStorage
framework.
With thesecomponents, Symantec NetBackup provides the deduplication options
that let you deduplicate data everywhere, as close to the source of data as you
require.
Deduplication everywhere provides significant return on investment, as follows.
■ Reduce the amount of data that is stored.
1
■ Reduce backup bandwidth.
Reduced bandwidth can be especially important when you want to limit the
amount of data that a client sends over the network. Over the network can be
to a backup server or for image duplication between remote locations.
■ Reduce backup windows.
■ Reduce infrastructure.
Page 12

Deduplicate on NetBackup clients
Deduplicate on NetBackup media
servers
Deduplicate on disk appliances by
using the OpenStorage option
Deduplicate using NetBackup
PureDisk, including at remote
offices
Introducing NetBackup deduplication
12
About NetBackup deduplication
About NetBackup deduplication options
Deduplication everywhere lets you choose at which point in the backup process
to perform deduplication. NetBackup can manage your deduplication wherever
you implement it in the backup stream.
Figure 1-1 shows the options for deduplication.
Table 1-1 describes the options for deduplication.
Figure 1-1
NetBackup deduplication
Page 13

About NetBackup deduplication
13Introducing NetBackup deduplication
Table 1-1
NetBackup Client
Deduplication Option
NetBackup MediaServer
Deduplication Option
Appliance deduplication
NetBackup deduplication options
DescriptionType
With NetBackup client-side deduplication, clients deduplicate
their backup data and then send it directly to the storage
destination. A media server does not deduplicate the data.
NetBackup Client Deduplication is a useful deduplication
solution if a client host has unused CPU cycles or if the load
balancing servers are overloaded.
See “About NetBackup Client Deduplication” on page 24.
NetBackup clients send their backups to a NetBackup media
server, whichdeduplicates thebackup data.A NetBackupmedia
server hoststhe NetBackup DeduplicationEngine, which writes
the data to the storage and manages the deduplicated data.
NetBackup MediaServer Deduplicationis auseful deduplication
solution if a client does not have enough CPU cycles to
deduplicate its own data.
See “About the NetBackup Media Server DeduplicationOption”
on page 19.
The NetBackup OpenStorage option lets third-party vendor
appliances function as disk storage for NetBackup.
The disk appliance provides the storage and it manages the
storage. A disk appliance may provide deduplication
functionality. NetBackup backs up and restores client data and
manages the life cycles of the data.
Appliance deduplication is a storage optimization or reduction
strategy. It reduces the storage that you may require.
See “How deduplication works” on page 14.
Conversely, NetBackupintegrated deduplicationreduces storage
requirements and provides other benefits that a disk appliance
deduplication solution cannot.
See “About NetBackup deduplication” on page 11.
Page 14

A CB D E A QB D L
Client files
to back up
A CB D E Q L
File 1 File 2
Data written
to storage
Introducing NetBackup deduplication
14
About NetBackup deduplication
Table 1-1
PureDisk deduplication
How deduplication works
Deduplication is a method of retaining only one unique instance of backup data
on storage media. Redundant data is replaced with a pointer to the unique data
copy. Deduplication occurs on both a file level and a file segment level. When two
or more files are identical, deduplication stores only one copy of the file. When
two or more files share identical content, deduplication breaks the files into
segments and stores only one copy of each unique file segment.
Deduplication significantly reduces the amount of storage space that is required
for the NetBackup backup images.
Figure 1-2 is a diagram of file segments that are deduplicated.
NetBackup deduplication options (continued)
DescriptionType
NetBackup PureDisk is a deduplication solution for
bandwidth-optimized backups of data in remote offices. You
can use PureDisk to reduce the amount of backup data that is
stored in a datacenter by NetBackup.
You use PureDisk interfaces to install, configure, and manage
the PureDisk servers, storage pools, and client backups. You do
not use NetBackup to configure or manage the storage or
backups.
PureDisk has its own documentation set.
See the NetBackup PureDisk Getting Started Guide.
A PureDisk storage pool can be a storage destination for both
the NetBackup Client Deduplication Option and the NetBackup
Media Server Deduplication Option.
Figure 1-2
File deduplication
Page 15

About NetBackup deduplication
The following list describes how NetBackup derives unique segments to store:
■ The deduplication engine breaks file 1 into segments A, B, C, D, and E.
■ The deduplication engine breaks file 2 into segments A, B, Q, D, and L.
■ The deduplication engine stores file segments A, B, C, D, and E from file 1 and
file segments Q, and L fromfile 2. The deduplication engine does not store file
segments A, B, and D from file 2. Instead, it points to the unique data copies
of file segments A, B, and D that were already written from file 1.
More detailed information is available.
See “Media server deduplication process” on page 111.
15Introducing NetBackup deduplication
Page 16

Introducing NetBackup deduplication
16
About NetBackup deduplication
Page 17

Chapter
Planning your deployment
This chapter includes the following topics:
■ Planning your deduplication deployment
■ About the deduplication storage type
■ About the NetBackup Media Server Deduplication Option
■ About NetBackup Client Deduplication
■ About NetBackup Deduplication Engine credentials
■ About the network interface for deduplication
2
■ About firewalls and the deduplication hosts
■ About scaling deduplication
■ About compression and encryption
■ About optimized duplication of deduplicated data
■ About deduplication performance
■ Replacing thePureDisk Deduplication Option with Media Server Deduplication
on the same host
■ Migrating fromPureDisk to the NetBackup Media Server Deduplication option
■ Migrating from another storage type to deduplication
Planning your deduplication deployment
Table 2-1 provides an overview of planning your deployment of NetBackup
deduplication.
Page 18

Planning your deployment
18
Planning your deduplication deployment
Table 2-1
Determine the storage type
Determine which type of
deduplication to use
Determine the requirements for
deduplication hosts
Determine the credentials for
deduplication
Deployment overview
Where to find the informationDeployment task
See “About the deduplication storage type”
on page 19.
See “Aboutthe NetBackupMedia ServerDeduplication
Option” on page 19.
See “About NetBackup Client Deduplication”
on page 24.
See “About deduplication servers” on page 21.
See “About deduplication server requirements”
on page 23.
See “About client deduplication host requirements”
on page 25.
See “About the network interface for deduplication”
on page 27.
See “About firewalls and the deduplication hosts”
on page 27.
See “About scaling deduplication” on page 27.
See “About deduplication performance” on page 32.
See “About NetBackup Deduplication Engine
credentials” on page 26.
encryption recommendation
Determine the requirements for
optimized duplication
Determine the storage
requirements and provision the
storage
See “About compression and encryption” on page 28.Read the compression and
See “About optimized duplication of deduplicated
data” on page 28.
See “About provisioning the storage” on page 37.
See “About deduplication storage requirements”
on page 37.
See “About deduplication storage capacity”
on page 38.
See “About the deduplication storage paths”
on page 38.
Page 19

About the deduplication storage type
19Planning your deployment
Table 2-1
Replace a PDDO host or migrate
from PDDO to NetBackup
deduplication
Migrate from other storage to
NetBackup deduplication
Deployment overview (continued)
Where to find the informationDeployment task
See “Replacing the PureDisk Deduplication Option
with Media Server Deduplication on the same host”
on page 33.
See “Migratingfrom PureDiskto theNetBackup Media
Server Deduplication option” on page 34.
See “Migrating from another storage type to
deduplication” on page 35.
About the deduplication storage type
The deduplication storage type depends on the destination for the deduplicated
data, as follows:
■ The disk storage that is attached to a NetBackup media server.
If you use this destination, use this guide to plan, implement, configure, and
manage deduplicationand the storage. When you configure the storage server,
select Media Server Deduplication Pool as the storage type.
■ A PureDisk storage pool.
If you use a PureDisk storage pool, use the PureDisk documentation to plan,
implement, configure, and manage the storage.
NetBackup deduplication requires that PureDisk be at release 6.6 or later.
See the NetBackup PureDisk Getting Started Guide.
After you configure the storage, use this guide to configure backups and
deduplication in NetBackup. When you configure the storage server, select
PureDisk Deduplication Pool as the storage type.
You can use one or both of the destinations for NetBackup deduplication.
About the NetBackup Media Server Deduplication Option
NetBackup MediaServer DeduplicationOption existsin theSymantec OpenStorage
framework. A storage server writes data to the storage and reads data from the
storage; the storage server must be a NetBackup media server. The storageserver
hosts the core components of deduplication. Thestorage server also deduplicates
the backup data. It is known as a deduplication storage server.
Page 20

Planning your deployment
20
About the NetBackup Media Server Deduplication Option
For a backup, the NetBackup client software creates the image of backed up files
as for a normal backup. The client sends the backup image to the deduplication
storage server, which deduplicates the data. The deduplication storage server
writes the data to disk.
See “About deduplication servers” on page 21.
The NetBackup Media Server Deduplication Option is integrated into NetBackup.
It uses the NetBackup administration interfaces, commands, and processes for
configuring andexecuting backups and for configuring and managing the storage.
Deduplication occurswhen NetBackup backs up a client toa deduplicationstorage
destination. You do not have to use the separate PureDisk interfaces to configure
and use deduplication.
The NetBackup Media Server Deduplication Option integrates with NetBackup
application agentsthat are optimized for theclient streamformat. Agents include
but are not limited to Microsoft Exchange and Microsoft SharePoint Agents.
Figure 2-1shows NetBackupmedia serverdeduplication. The deduplication storage
server isa mediaserver onwhich thededuplication corecomponents areenabled.
Page 21

PureDisk
Plug-in
PureDisk
Plug-in
NetBackup
client
NetBackup
Deduplication
Engine
PureDisk
Plug-in
NetBackup
client
NetBackup
client
NetBackup
client
PureDisk
deduplication
pool
Media server
deduplication
pool
Deduplication storage
server
Load
balancing
servers
PureDisk
Plug-in
About the NetBackup Media Server Deduplication Option
21Planning your deployment
Figure 2-1
NetBackup media server deduplication
More detailed information is available.
See “Deduplication server components” on page 109.
See “Media server deduplication process” on page 111.
About deduplication servers
Table 2-2 describes the servers that are used for NetBackup deduplication.
Page 22

Planning your deployment
22
About the NetBackup Media Server Deduplication Option
Table 2-2
Deduplication storage
server
Load balancing server
NetBackup deduplication servers
DescriptionHost
One hostfunctions asthe storageserver for a deduplication node;
that host must be a NetBackup media server. The storage server
does the following:
■ Writes the data to and reads data from the disk storage.
■ Manages that storage.
The storage server also deduplicates data. Therefore, one host
both deduplicates the data and manages the storage.
Only one storage server exists for each NetBackup deduplication
node.
You can use NetBackup deduplication with one mediaserver host
only: the media server that is configured as the deduplication
storage server.
You can configure other NetBackup media servers to help
deduplicate data. They perform file fingerprint calculations for
deduplication, and they send the unique results to the storage
server. These helper media servers are called load balancing
servers.
See “About deduplication fingerprinting” on page 117.
You configure load balancing servers when you configure the
deduplication storage server. Also, you can add a deduplication
server later to a deduplication node.
Load balancingservers alsoperform restoreand duplicationjobs.
Symantec recommends that you add load balancing servers only
after the storage server reaches maximum CPU utilization. For
more information about how to use load balancing servers, see
the following Symantec tech note:
http://entsupport.symantec.com/docs/338123
About deduplication nodes
A mediaserver deduplication node is a deduplication storageserver, loadbalancing
servers (ifany), the clients that arebacked up,and the storage. Each nodemanages
its own storage. Deduplication within each node is supported; deduplication
between nodes is not supported.
Multiple mediaserver deduplication nodes can exist. Nodes cannot share servers,
storage, or clients.
Page 23

About the NetBackup Media Server Deduplication Option
About deduplication server requirements
All hosts that are used for deduplication must be NetBackup 7.0 or later. Hosts
include the master server, the media servers, and the clients.
The computer’sCPU andmemory constrainhow manyjobs canrun concurrently.
23Planning your deployment
Table 2-3
Deduplication server minimum requirements
RequirementHardware
CPU
Operating system
CPU speed is the mostimportant factor for performance. Minimum
CPU speed should be 2.2 GHz.
The deduplication storage server should have a minimum of 4 CPU
cores. Symantec recommends eight cores.
Symantec recommends Intel, AMD, and Sun SPARC processors (in
order of effectiveness).
Symantec recommends 4 GBs of memory minimum.RAM
The operatingsystem mustbe a supported 64-bit operating system.
For supported systems, see the NetBackup Release Notes.
Note: Symantec recommends that you do not use the master server as a
deduplication storageserver. Master server activity and media server deduplication
activity on the same host degrades performance.
Note: Symantec recommends that you do not use an existing media server for
deduplication. Similarly, Symantec recommends that you do not repurpose older
host hardware for deduplication.
About media server deduplication limitations
NetBackup media server deduplication and Symantec Backup Exec deduplication
cannot reside on the same host. If you use both NetBackup and Backup Exec
deduplication, each product must reside on a separate host.
NetBackup deduplicationcomponents cannotreside onthe same host as a PureDisk
Deduplication Option (PDDO) agent. Therefore, you cannot use the same media
server for both NetBackup deduplication and as a PDDO host.
You cannot upgrade to NetBackup 7.0 or later a NetBackup media server that
hosts a PDDO agent. If the NetBackup 7.0 installation detects the PDDO agent,
Page 24

Planning your deployment
24
About NetBackup Client Deduplication
the installation fails. To upgrade a NetBackup media server that hosts a PDDO
agent, you must first remove the PDDO agent.
See the NetBackup PureDisk Deduplication Option (PDDO) Guide.
Deduplication within each media server deduplication node is supported; global
deduplication between nodes is not supported.
About NetBackup Client Deduplication
With normal deduplication, the client sends the full backup data stream to the
media server.The deduplication engine on the media serverprocesses the stream,
saving only the unique segments.
With NetBackup Client Deduplication, the client hosts the PureDisk plug-in that
duplicates the backup data. The NetBackup client software creates the image of
backed up files as for a normal backup. Next, the PureDisk plug-in breaks the
backup image into segments and compares them to all of the segments that are
stored inthat deduplicationnode. The plug-in then sends only theunique segments
to the NetBackup Deduplication Engine on the storage server. The engine writes
the data to a media server deduplication pool.
Client deduplication does the following:
■ Reduces network traffic. The client sends only unique file segments to the
storage server. Duplicate data is not sent over the network.
■ Distributes some deduplication processing load from the storage server to
clients. (NetBackup does not balance load between clients; each client
deduplicates its own data.)
Figure 2-2shows client deduplication. The deduplicationstorage serveris a media
server on which the deduplication core components are enabled.
Page 25

PureDisk
Plug-in
NetBackup
deduplication
client
NetBackup
PureDisk
Deduplication
Engine
PureDisk
Plug-in
PureDisk
deduplication pool
Media server
deduplication pool
PureDisk
Plug-in
NetBackup
deduplication
client
PureDisk
Plug-in
NetBackup
deduplication
client
Deduplication storage
server
About NetBackup Client Deduplication
25Planning your deployment
Figure 2-2
NetBackup client deduplication
About client deduplication host requirements
About client deduplication requirements
More detailed information is available.
See “Deduplication client components” on page 114.
See “Deduplication client backup process” on page 114.
The operating system must be a supported 64-bit operating system.
For supported systems, see the NetBackup Release Notes.
All hosts that are used for client deduplication must be NetBackup 7.0 or later.
A media server deduplication pool or a PureDisk deduplication pool must be
configured. Storage units must be configured for the deduplication pool.
Page 26

Planning your deployment
26
About NetBackup Deduplication Engine credentials
About client deduplication limitations
Client deduplication does not support multiple copies per job. For the jobs that
specify multiple copies, the backupimages are sent to the storage server and may
be deduplicated there.
Client deduplication does not support encryption.
Client deduplicationis not tolerant of high latency networkconnections. Therefore,
Symantec recommendsthat youuse NetBackupPureDisk forremote officebackups.
About NetBackup Deduplication Engine credentials
The NetBackup Deduplication Engine requires credentials. The deduplication
components use the credentials when they communicate with the NetBackup
Deduplication Engine.The credentials are for the engine, notfor the host on which
it runs.
You enter the NetBackup Deduplication Engine credentials when you configure
the storage server.
The following are the rules for the credentials:
■ For user names and passwords, you can use characters in the printable ASCII
range (0x20-0x7E) except for the following characters:
■ Asterisk (*)
■ Backward slash (\) and forward slash (/)
■ Double quote (")
■ Left parenthesis [(] and right parenthesis [)]
■ The user name can be up to 127 characters in length. The password can be up
to 100 characters in length.
■ Leading and trailing spaces and quotes are ignored.
■ The user name and password cannot be empty or all spaces.
Record and save the credentials in case you need them in the future.
Caution: You cannot change the NetBackup Deduplication Engine credentialsafter
you enter them. Therefore, carefully choose and enter your credentials. If you
must change the credentials, contact your Symantec support representative.
Page 27

About the network interface for deduplication
About the network interface for deduplication
If the server host has more than one network interface, by default the host
operating system determines which network interface to use. However, you can
specify which interface NetBackup should use for the deduplication traffic.
To use a specific interface, enter that interface name when you configure the
deduplication storage server.
Caution: You cannot change the network interface after NetBackup configures
the deduplication storage server. Therefore, carefully enter the properties.
About firewalls and the deduplication hosts
If firewalls exist between the various deduplication hosts, open ports 10082 and
10102 between those hosts. Deduplication hosts are the deduplication storage
server, the load balancing servers, and theclients that deduplicate their owndata.
About scaling deduplication
27Planning your deployment
You can scale deduplication processing to improve performance by using load
balancing servers or client deduplication or both.
If youconfigure load balancing servers, those servers also perform deduplication.
The deduplication storage server still functions as both a deduplication server
and as a storage server. NetBackup uses standard load balancing criteria to select
a load balancing server for each job. However, deduplication fingerprint
calculations are not part of the load balancing criteria.
To completelyremove the deduplication storage server from deduplicationduties,
do the following for every storage unit that uses the deduplication disk pool:
■ Select Only use the following media servers.
■ Select all of the load balancing servers but do not select the deduplication
storage server.
The deduplication storage server performs storage server tasks only: storing and
managing the deduplicated data, file deletion, and optimized duplication.
If youconfigure client deduplication, the clientsdeduplicate their own data. Some
of the deduplication load is removed from the deduplication storage server and
loading balancing servers.
Symantec recommends the following strategies to scale deduplication:
Page 28

Planning your deployment
28
About compression and encryption
■ For theinitial full backups of yourclients, use the deduplication storageserver.
For subsequent backups, use load balancing servers.
Do not expect the deduplication storage server to be the media server that is
used for restores to that client. If a media server deduplicates a client backup,
your restoresettings may require that the media serveralso beused for restores
to that client.
■ Enable client-side deduplication gradually.
If a client cannot tolerate thededuplication processing workload, be prepared
to move the deduplication processing back to a server.
See “About deduplication performance” on page 32.
About compression and encryption
For compression or encryption, Symantec recommends that you enable them so
they occurduring theNetBackup deduplication process. If you compress orencrypt
the data before it is deduplicated, deduplication rates are low.
See “About the deduplication configuration file” on page 60.
See “Editing the deduplication configuration file” on page 60.
See “pd.conf file settings” on page 61.
About optimized duplication of deduplicated data
Optimized duplication of deduplicated data reduces the amount of data that is
transmitted over your network. Therefore, you can use optimized duplication for
off-site storage of data for disaster recovery. It can improve recovery times and
minimize the use of off-site tape storage.
Only the unique data segments are transferred.
See “Configuring optimized deduplication copy” on page 57.
Optimized deduplication copy requirements
Figure 2-3 shows a source deduplication node and a destination deduplication
node for optimized deduplication copy. The requirements description follows the
figure.
Page 29

Host A
PureDisk
Plug-in
NetBackup
Deduplication
Engine
PureDisk
Plug-in
Deduplication node A (source)
Deduplication node B
(destination)
PureDisk
Plug-in
Host B Host C
NetBackup
Deduplication
Engine
PureDisk
Plug-in
Host D
Host D is configured as a load balancing server for
node A
PureDisk
Plug-in
Host E
About optimized duplication of deduplicated data
29Planning your deployment
Figure 2-3
Optimized duplication copy example
The following are the requirements for optimized duplication:
■ The source images must be on a NetBackup media server deduplication pool.
■ The destinationdisk storage can be another MediaServer Deduplication Pool
or aPureDisk Deduplication Pool. The destination storage unit cannot be the
same as the source storage unit.
If thedestination is a PureDiskDeduplicationPool, thePureDisk environment
must be at release level 6.6 or later.
■ At least one media server must be common between the source deduplication
node and the destination, as follows:
■ If the destination is another Media ServerDeduplication Pool: Configure
a server in the destination deduplication node as a load balancing server
for the source storage server.
For example, Figure 2-3 shows two deduplication nodes. Host D from the
destination node is configured as a load balancing server for the source
node. It is the common host. The following Storage Server Configuration
Wizard screen shows the load balancing servers that are configured for
deduplication node A:
Page 30

Planning your deployment
30
About optimized duplication of deduplicated data
■ If the destination is a PureDisk Deduplication Pool: Configure a media
server that accesses the PureDisk Storage Pool Authority host as a load
balancing server for the source storage server.
To use more than one media server for the optimized copy operation, each
additional one must be common between them .If you select more than one,
NetBackup balances the optimized copy job load among them.
■ All of the media servers that are selected in the destination storage unit must
be common with the source storage server.
In the storage unit for the destination disk pool, select Only usethe following
mediaservers. Then, select the media server or media serversthat arecommon
to both the source storage server and the destination storage server.
For example, the following figure shows the destination storage unit media
server selection for the optimized duplication that is show inFigure 2-3. Host
D is the only common host, so it is selected in the destination storage unit.
Page 31

About optimized duplication of deduplicated data
If you use your destination storage unit to back up clients, you can create a
different storage unit for those jobs. In that storage unit,select all of the hosts
in that node that you want to use for deduplication.
If you select the common server from the destination node in the source node
storage unit, NetBackup uses i5 for deduplication. Therefore, do not select it in
the storage unit for source node (unless you want to use it for the source node).
For example, for the storage unit for the backup jobs for node A in Figure 2-3, do
not select Host D (shown in the following figure):
31Planning your deployment
Optimized deduplication copy limitations
The following are limitations for optimized deduplication copy:
■ NetBackup doesnot supporta PureDisk storage pool as the sourcefor optimized
duplication. Therefore,you cannotuse optimizedduplication from a PureDisk
storage pool to a media server deduplication pool or to another PureDisk
storage pool.
■ If an optimized duplication job fails, NetBackup does not run the job again.
See “Configuring optimized deduplication copy behavior” on page 57.
Page 32
Planning your deployment
32
About deduplication performance
About deduplication performance
Many factorsaffect performance, especially the server hardware andthe network
capacity.
Table 2-4 provides information about performance during backup jobs for a
deduplication storage server. The deduplication storage server conforms to the
minimum host requirements. Client deduplication or load balancing servers are
not used.
See “About deduplication server requirements” on page 23.
Table 2-4
Initial
seeding
Normal
operation
Deduplication job load performance for a deduplication storage
server
DescriptionWhen
Initial seeding is when all clients are first backed up.
Approximately 15 to 20 jobs can run concurrently under the following
conditions:
■ The hardware meets minimum requirements. (More capable hardware
improves performance.)
■ No compression.If datais compressed,the CPU usage increases quickly,
which reduces the number of concurrent jobs that can be handled.
■ The deduplication rate is between 50% to 100%. The deduplication rate
is the percentage of data already stored so it is not stored again.
■ The amount of data that is stored is less than 30% of the capacity of the
storage.
Normal operation is when all clients have been backed up once.
Approximately 15to 20jobs canrun concurrentlyand with high performance
under the following conditions:
■ The hardware meets minimum requirements. (More capable hardware
improves performance.)
■ No compression.If datais compressed,the CPU usage increases quickly,
which reduces the number of concurrent jobs that can be handled.
■ The deduplication rate is between10% and 50%. The deduplication rate
is the percentage of data already stored so it is not stored again.
■ The amount of data thatis stored is between 30% to 90% ofthe capacity
of the storage.
Page 33
Replacing the PureDisk Deduplication Option with Media Server Deduplication on the same host
33Planning your deployment
Table 2-4
Clean up
periods
Storage
approaches
full capacity
Deduplication job load performance for a deduplication storage
server (continued)
DescriptionWhen
Clean upis whenthe NetBackupDeduplication Engine performs maintenance
such as deleting expired backup image data segments.
NetBackup maintainsthe samenumber ofconcurrent backupjobs asduring
normal operation.However, theaverage time to complete the jobs increases
significantly.
NetBackup maintainsthe samenumber ofconcurrent backupjobs asduring
normal operation under the following conditions:
■ The hardware meets minimum requirements. (More capable hardware
improves performance.)
■ The amount of data thatis stored is between 85% to 90% ofthe capacity
of the storage.
However, the average time to complete the jobs increases significantly.
How file size may affect the deduplication rate
The small file sizes that are combined with large file segment sizes may result in
low initial deduplication rates. However, after the deduplication engine performs
file fingerprint processing, deduplication rates improve. For example, a second
backup of a client shortly after the first does not show high deduplication rates.
But the deduplication rate improves if the second backup occurs after the file
fingerprint processing.
How long it takes the NetBackup Deduplication Engine to process the file
fingerprints varies.
Replacing the PureDisk Deduplication Option with
Media Server Deduplication on the same host
You can replace a PureDisk Deduplication Option agent from its media server
host with a NetBackup PureDisk plug-in on the same host. The storage remains
the PureDisk storage pool, and NetBackup maintains access to all of the valid
backup images in the PureDisk storage pool.
Note: The PureDisk storage pool must be part of a PureDisk 6.6 or later
environment.
Page 34
Planning your deployment
34
Migrating from PureDisk to the NetBackup Media Server Deduplication option
Table 2-5
Ensure that no activity
occurs on the host
Remove the PDDO plug-in
Upgrade the media server to
7.0 or later
Configure the host
Activate yourbackup policies
Replacing a PDDO host with a media server deduplication host
ProcedureTask
Deactivate all backup policies that use the host.
See the NetBackup Administrator's Guide for UNIX and
Linux, Volume I
See the NetBackup Administrator's Guide for Windows,
Volume I..
NetBackup deduplication components cannot resideon the
same hostas aPureDisk DeduplicationOption (PDDO)agent.
Therefore, remove the PDDO plug-in from the host.
See the NetBackup PureDisk Deduplication Option Guide.
If themedia server runs a version of NetBackup earlier than
7.0, upgrade that server to NetBackup 7.0 or later.
See the NetBackup Installation Guide for UNIX and Linux.
See the NetBackup Installation Guide for Windows.
In the Storage Server Configuration Wizard, select
PureDisk Deduplication Pool and enter the name of the
Storage Pool Authority.
See “Configuringa deduplicationstorage server”on page48.
See the NetBackup Administrator's Guide for UNIX and
Linux, Volume I
See the NetBackup Administrator's Guide for Windows,
Volume I..
Migrating from PureDisk to the NetBackup Media
Server Deduplication option
NetBackup cannot use the storage hardware while PureDisk uses it for storage.
The structureof the PureDisk storage isdifferent than the structure of the storage
for integrated NetBackup deduplication. The disk systems cannot be used
simultaneously by both NetBackup and PureDisk. The PureDisk images on the
storage cannot be transferred to the deduplication storage server storage.
Therefore, to migrate from NetBackup PureDisk to the NetBackup Media Server
Deduplication Option, Symantec recommends that you age the PureDisk storage
pool backups until they expire.
Page 35
Migrating from another storage type to deduplication
35Planning your deployment
Table 2-6
To migrate from PureDisk to NetBackup deduplication
ProcedureTask
Install and configure
NetBackup
deduplication
Redirect your backup
jobs
Uninstall PureDisk
See the NetBackup Installation Guide for UNIX and Linux.
See the NetBackup Installation Guide for Windows.
See “Configuring deduplication” on page 47.Configure NetBackup
Redirect your backup jobs to the NetBackup media server
deduplication pool.
See the NetBackup Administrator's Guide for UNIX and Linux,
Volume I.
See the NetBackup Administrator's Guide for Windows, Volume I.
After the PureDisk backup images expire, uninstall PureDisk.
See your NetBackup PureDisk documentation.
Migrating from another storage type to deduplication
To migrate from another NetBackup storage type to deduplication storage,
Symantec recommends that you age the backupimages on the other storageuntil
they expire.Symantec recommends that you age the backup images ifyou migrate
from disk storage or tape storage.
You should not use the same disk storage for NetBackup deduplication while you
use it for other storage such as AdvancedDisk, BasicDisk, or SharedDisk. Each
type managesthe storage differently and each requires exclusiveuse ofthe storage.
Also, the NetBackup Deduplication Engine cannot read the backup images that
another NetBackup storage type created. Therefore, you should age the data so
it expiresbefore you repurpose the storage hardware. Untilthat data expires, two
storage destinations exist: the media server deduplication pool and the other
storage. After the images on the other storage expire and are deleted, you can
repurpose it for other storage needs.
Table 2-7
deduplication
Migrating to NetBackup deduplication
ProcedureTask
See “Configuring deduplication” on page 47.Configure NetBackup
Page 36
Planning your deployment
36
Migrating from another storage type to deduplication
Table 2-7
Redirect your backup
jobs
Repurpose the storage
Migrating to NetBackup deduplication (continued)
ProcedureTask
Redirect your backup jobs to the media server deduplication
pool storage unit. To do so, change the backup policy storage
destination to the storage unit for the deduplication pool.
See the NetBackup Administrator's Guide for UNIX and Linux,
Volume I.
See the NetBackupAdministrator's Guide for Windows, Volume
I.
After all of the backup images that are associated with the
storage expire, repurpose that storage.
If it is disk storage, you cannotadd itto anexisting media server
deduplication pool. You can use it as storage for another, new
deduplication node.
Page 37

Chapter
Provisioning the storage
This chapter includes the following topics:
■ About provisioning the storage
■ About deduplication storage requirements
■ About deduplication storage capacity
■ About the deduplication storage paths
About provisioning the storage
3
How toprovision the storage is beyond the scope of theNetBackup documentation.
For help, consult the storage vendor's documentation.
What youchoose as your storage destination affects how you provisionthe storage.
NetBackup requirements also may affect how you provision the storage.
See “About the deduplication storage type” on page 19.
About deduplication storage requirements
The storagefor the NetBackup Media ServerDeduplication Optionis diskstorage.
The storage must be attached to the NetBackup media server that functions as
the storage server. Attached means a file system mount on the storage. You must
provision the storage such that a file system is mounted on the media server.
The storage can be SAN storage or network attached storage. The minimum
requirement is for the disk storage that is capable of read and write performance
of 130 MB/sec.
The storage must be configured and operational before you can configure
deduplication in NetBackup.
Page 38

Provisioning the storage
38
About deduplication storage capacity
NetBackup requires exclusive use of the disk resources. If the storage is used for
purposes other than backups, NetBackup cannot manage disk pool capacity or
manage storage lifecycle policies correctly. Therefore, NetBackup must be the
only entity that uses the storage.
See “About the deduplication storage paths” on page 38.
About deduplication storage capacity
Storage capacity for a deduplication node (deduplication storage server and
storage) is 32TB.
The deduplication database consumes approximately 10 percent of the storage
capacity. Therefore, approximately 90 percent of the storage capacity is usable
space forunique backup data. The actual percentages varydepending onthe data.
For performance optimization, Symantec recommends that you use a separate
disk, volume, partition, or spindle for the catalog database.
If your storage requirements exceed the capacity of a media server deduplication
node, do one of the following:
■ Use more than one media server deduplication node.
■ Use aPureDisk deduplication pool as the deduplication destination.A PureDisk
deduplication pool provides larger storage capacity. It also provides global
deduplication.
About the deduplication storage paths
When you configure the deduplication storage server, you must enter the path
name to the storage. The storage path is the directory in which NetBackup stores
the raw backup data.
Because the storage requires a directory path, do not use only a root node (/) or
drive letter (G:\) as the storage path.
You also can specify a different location for the deduplication database. The
database path is the directory in which NetBackup stores and maintains the
structure of the stored deduplicated data.
For performance optimization, Symantec recommends that you use a separate
disk, volume, partition, or spindle for the deduplication database.
If the directory or directories do notexist, NetBackup creates them andpopulates
them with the necessary subdirectory structure. If the directory or directories
exist, NetBackup populates them with the necessary subdirectory structure.
Page 39

About the deduplication storage paths
The path names must use ASCII characters only.
The NetBackupMedia ServerDeduplication Optiondoes not support NFS mounted
file systems.
Caution: You cannot changethe paths after NetBackup configures the deduplication
storage server. Therefore, carefully decide during the planning phase where and
how you want the deduplicated backup data stored.
39Provisioning the storage
Page 40

Provisioning the storage
40
About the deduplication storage paths
Page 41

Chapter
Installing deduplication
This chapter includes the following topics:
■ About installing deduplication
■ About the deduplication license key
■ Licensing NetBackup deduplication
■ Replacing the deduplication storage server host computer
■ Uninstalling media server deduplication
4
About installing deduplication
The NetBackupdeduplication componentsare installedby default on the supported
host systems. However, you must enter a license key to enable deduplication.
Before you try to install or upgrade to a NetBackup version that supports
deduplication, be aware of the following:
■ NetBackup supports deduplication on specific 64-bit host operating systems.
If you intend to upgrade an existing media server and use it for deduplication,
that host must be supported.
For the supported systems, see the NetBackup Release Notes.
■ NetBackup deduplication components cannot reside on the same host as a
PureDisk Deduplication Option agent.
To usea PDDO agent host for NetBackup deduplication, first removethe PDDO
agent from that host.
See the NetBackup PureDisk Deduplication Option (PDDO) Guide.
Then, upgrade that host to NetBackup 7.0 or later.
Finally, configure that host as a deduplication storage server or as a load
balancing server.
Page 42

Installing deduplication
42
About the deduplication license key
About the deduplication license key
NetBackup deduplication is licensed separately from base NetBackup.
The NetBackup Deduplication Option license key enables both NetBackup Media
Server Deduplication and NetBackup Client Deduplication. The license is a
front-end capacity license. It is based on the size of the data to be backed up, not
on the size of the deduplicated data.
You may have a single license key that activates both NetBackup and optional
features. Alternatively, you may have one license key that activates NetBackup
and another key that activates deduplication.
If you remove the NetBackup Deduplication Option license key or if it expires,
you cannotcreate new deduplication disk pools. you alsocannot create the storage
units that reference NetBackup deduplication pools.
NetBackup does not delete the disk pools or the storage units that reference the
disk pools. You can use them again if you enter a valid license key.
Licensing NetBackup deduplication
If you installed the license key when you installed or upgraded NetBackup, you
do not need to perform this procedure.
Enter the license key on the NetBackup master server. The following procedure
describes how to use the NetBackup Administration Console to enter the license
key.
To license NetBackup deduplication
To add a license to a specific server, on the File menu select Change Server
1
and then select the server.
In the NetBackup License Keys dialog box, click New.
2
In the Add aNew License Key dialog box, enterthe license key and click Add
3
or OK.
Click Close.
4
Restart all the NetBackup services and daemons.
5
Replacing the deduplication storage server host computer
If you replace the deduplication storage server host computer, use these
instructions toinstall NetBackup and reconfigure the deduplication storageserver.
Page 43

Replacing the deduplication storage server host computer
For the new host, you must use the same host name. The new host cannot host a
deduplication storage server already.
Reasons to replace the host include a lease swap or perhaps the current
deduplication storageserver hostdoes notmeet your performance requirements.
Warning: The new host must use the same byte order as the old host. If it does
not, you cannot access the deduplicated data.
In computing,endianness describes the byte order that representsdata: bigendian
and little endian. For example, Sun SPARC processors and Intel processors use
different byte orders. Therefore, you cannot replace a Solaris SPARC host with a
host that has an Intel processor.
43Installing deduplication
Table 4-1
Change thedisk volumestate
and disk pool state to DOWN
Configure the new host so it
meets deduplication
requirements
host.
Install the NetBackup media
server software on the new
host
Delete the NetBackup
Deduplication Engine
credentials
Add the credentials to the
storage server
How to replace the deduplication storage server host
ProcedureTask
See “Changing the deduplication disk volume state”
on page 77.
See “Changing the deduplication pool state” on page 77.
See “About deduplication servers” on page 21.
See “About deduplication server requirements” onpage 23.
See the storage vendor's documentation.Move the storage to the new
See the NetBackup Installation Guide for UNIX and Linux.
See the NetBackup Installation Guide for Windows.
If you have load balancing servers, delete the NetBackup
Deduplication Engine credentials on those media servers.
On eachload balancingserver, run the following command:
See “Deleting credentials from a load balancing server”
on page 75.
Add theNetBackup Deduplication Enginecredentials tothe
storage server.
See “Adding NetBackup Deduplication Engine credentials”
on page 74.
Page 44

Installing deduplication
44
Uninstalling media server deduplication
Table 4-1
Get a configuration file
template
Configure the storageserver
Configure theload balancing
servers
Change configuration
settings
Change thedisk volumestate
and disk pool state to UP
How to replace the deduplication storage server host (continued)
ProcedureTask
If youdid notsave a storage server configurationfile before
the failure, get a template configuration file.
See “Getting the storage server configuration” on page 68.
See “Editinga storageserver configuration file” on page68.Edit the configuration file
Configure thestorage serverby uploadingthe configuration
from the file you edited. If you saved a configuration file
before the storage server failure, use that file.
See “Setting the storage server configuration” on page 70.
If you have load balancing servers, add them to the
configuration.
See “Adding a load balancing server” on page 58.
If you edited the deduplication configuration file, make the
same changes to that file.
See “Aboutthe deduplicationconfiguration file” on page 60.
See “Editing the deduplication configuration file”
on page 60.
See “Changing the deduplication disk volume state”
on page 77.
See “Changing the deduplication pool state” on page 77.
Change thedisk volumestate
and disk pool state to UP
Restart the backup jobs
See “Changing the deduplication disk volume state”
on page 77.
See “Changing the deduplication pool state” on page 77.
If any backup jobs failed, restart those jobs. Alternatively,
wait until the next scheduled backup, at which time the
backup jobs should succeed.
Uninstalling media server deduplication
The NetBackup deduplication components are uninstalled when you uninstall
NetBackup software.
However, youcan disablemedia server deduplication and remove the configuration
files and storage files from the media server. The following procedure disables
Page 45

Uninstalling media server deduplication
NetBackup mediaserver deduplicationcomponents and the deduplication storage.
The host remains a NetBackup media server.
This processassumes thatall backupimages thatreside onthe deduplicationdisk
storage have expired.
Caution: If you uninstall deduplication and valid NetBackup images reside on the
deduplication storage, data loss may occur.
45Installing deduplication
Table 4-2
Disable client deduplication
Delete the storage units that
use the disk pool
Stop the services on the
storage server
Delete thestorage directories
On Windows,delete accounts
and files
Disable media server deduplication
Remove the clients that deduplicate their own data from
the client deduplication list.
See “Disabling deduplication for a client” on page 90.
See the NetBackup Administrator's Guide for UNIX and
Linux, Volume I
See the NetBackup Administrator's Guide for Windows,
Volume I..
See “Deleting a deduplication pool” on page 78.Delete the disk pool
See the NetBackup Administrator's Guide for UNIX and
Linux, Volume I
See the NetBackup Administrator's Guide for Windows,
Volume I..
Delete the storage directory and database directory (if you
configured a database directory).
See the operating system documentation.
On Windows, delete the following:
■ The purediskdbuser account. The account is for the
deduplication database administration.
■ The purediskdbuser folder.
See the operating system documentation.
Page 46

Installing deduplication
46
Uninstalling media server deduplication
Table 4-2
Disable media server deduplication (continued)
On UNIX and Linux, remove
files
storage server
Remove the NetBackup
Deduplication license key.
Start theNetBackup services
on the media server
On UNIX and Linux systems, remove the following files:
■ etc/pdregistry.cfg
■ opt/pdag
■ opt/pdshared
■ The hostname.cfg file
The fileresides inthe /usr/openv/lib/ost-plugins
directory. Theservername is the name ofthe configured
deduplication storage server. If you entered a
fully-qualified domain name for the server, that is the
name used for servername.
See “Deleting a deduplication storage server” on page 67.Delete the deduplication
See the NetBackup Administrator's Guide for UNIX and
Linux, Volume I
See the NetBackup Administrator's Guide for Windows,
Volume I..
See the NetBackup Administrator's Guide for UNIX and
Linux, Volume I
See the NetBackup Administrator's Guide for Windows,
Volume I..
Page 47

Chapter
Configuring deduplication
This chapter includes the following topics:
■ Configuring deduplication
■ Configuring a deduplication storage server
■ About deduplication pools
■ Configuring a deduplication pool
■ Configuring a deduplication storage unit
■ Enabling client deduplication
5
■ Configuring backups
■ Configuring optimized deduplication copy
■ Configuring optimized deduplication copy behavior
■ Adding a load balancing server
■ About the deduplication configuration file
■ Editing the deduplication configuration file
■ Reconfiguring the deduplication storage server and storage paths
Configuring deduplication
This guide describes how to configure deduplication in NetBackup.
Table 5-1 describes the configuration tasks.
The NetBackupadministrator's guidesdescribe how to configure a base NetBackup
environment.
Page 48
Configuring deduplication
48
Configuring a deduplication storage server
See the NetBackup Administrator's Guide for Windows, Volume I.
See the NetBackup Administrator's Guide for UNIX and Linux, Volume I.
Table 5-1
Configure a deduplication storage
server
Configure a disk pool
Configure a storage unit
Configure a backup policy
Configure optimized duplication
Deduplication configuration tasks
ProcedureTask
See “Configuring a deduplication storage server”
on page 48.
See “About deduplication pools” on page 49.
See “Configuring a deduplication pool”
on page 50.
See “Configuring a deduplication storage unit”
on page 52.
See “Enabling client deduplication” on page 56.Enable client-side deduplication
Use the deduplication storage unit as the
destination for the backup policy.
See the NetBackup Administrator's Guide for
Windows, Volume I.
See theNetBackup Administrator's Guide forUNIX
and Linux, Volume I.
See “Configuring optimized deduplication copy”
on page 57.
See “Configuring optimized deduplication copy
behavior” on page 57.
Optionally, specify advanced
deduplication settings
See “About the deduplication configuration file”
on page 60.
See “Editingthe deduplication configuration file”
on page 60.
See “pd.conf file settings” on page 61.
Configuring a deduplication storage server
Configure inthis context means to configure a NetBackup media serveras astorage
server for deduplication.
When youconfigure a storage server fordeduplication, you specify the following:
Page 49

About deduplication pools
■ The type of storage server.
For NetBackupmedia serverdeduplication, select Media Server Deduplication
Pool for the type of disk storage.
For a PureDisk deduplication pool, select PureDisk Deduplication Pool for
the type of disk storage.
■ The credentials for the deduplication engine.
See “About NetBackup Deduplication Engine credentials” on page 26.
■ The storage paths.
See “About the deduplication storage paths” on page 38.
■ The network interface.
See “About the network interface for deduplication” on page 27.
■ The load balancing servers, if any.
See “About deduplication servers” on page 21.
When you create the storage server, the wizard lets you create a disk pool and
storage unit also.
To configure a deduplication storage server in NetBackup
In the NetBackup Administration Console, expand Media and Device
1
Management > Configure Disk Storage Servers.
Follow the wizard screens to configure a deduplication storage server.
2
49Configuring deduplication
After NetBackupcreates the deduplication storage server,you can click Next
3
to continue to the Disk Pool Configuration Wizard.
About deduplication pools
Deduplication pools are the disk pools that are the storage destination for
deduplicated backup data. NetBackup media servers or NetBackup clients
deduplicate the backup data that is stored in a deduplication pool.
NetBackup deduplication disk pools are of type PureDisk.
NetBackup requires exclusive ownership of the disk resources that comprise the
disk pool.If you share those resources with otherusers, NetBackupcannot manage
disk pool capacity or storage lifecycle policies correctly.
Page 50

Configuring deduplication
50
Configuring a deduplication pool
Configuring a deduplication pool
When you create a deduplication storage server, you can launch the Disk Pool
Configuration Wizard after NetBackup creates the deduplication storage server.
If you created the disk pool already, you do not have to follow these instructions.
When you configure a disk pool for deduplication, you specify the following:
■ The type of disk pool (PureDisk).
■ The NetBackup deduplication storage server to query for the disk storage to
use for the pool.
■ The disk volume to include in the pool.
NetBackup exposes the storage as a single volume.
■ The disk pool properties.
See “Media server deduplication pool properties” on page 50.
Symantec recommends that disk pool names be unique across your enterprise.
To create a NetBackup disk pool
In the NetBackup Administration Console, select the Media and Device
1
Management node.
From the list of wizards in the Details pane, click Configure Disk Pool and
2
follow the wizard instructions.
For help, see the wizard help.
After NetBackupcreates the deduplication pool, you have theoption to create
3
a storage unit that uses the pool.
Media server deduplication pool properties
Table 5-2 describes the disk pool properties.
Table 5-2
Storage server
Media server deduplication pool properties
DescriptionProperty
The disk pool name.Name
The storage server name. The storage server is the same as the
NetBackup media server to which the storage is attached.
Page 51
Configuring a deduplication pool
51Configuring deduplication
Table 5-2
Disk volume
High water mark
Media server deduplication pool properties (continued)
DescriptionProperty
For a media server deduplication pool, all disk storage is exposed
as a single volume.
PureDiskVolume is a virtual name for the storage that is
contained withinthe directories you specified for the storage path
and the database path.
The amount of space available in the disk pool.Available space
The total raw size of the storage in the disk pool.Raw size
A comment that is associated with the disk pool.Comment
The high water mark is a threshold that indicates the
PureDiskVolume is full. When the PureDiskVolume is at the
high water mark, NetBackup fails any backup jobs that are
assigned to the disk pool storage unit.
NetBackup alsofails backup jobsif thePureDiskVolume does not
contain enough storage for its estimated space requirement.
NetBackup againassigns jobsto thestorage unitwhen thecapacity
of thePureDiskVolume drops below thehigh water mark.Capacity
is regained as backup images expire.
NetBackupdoes not assign backup jobs to the disk pool if used
space inthe PureDiskVolumeis greaterthan thehigh watermark.
The default is 98%.
Low water mark
The low water mark has no affect on the PureDiskVolume.
The lowwater mark setting cannot be greater than or equalto the
high water mark setting.
The default is 80%
Page 52

Configuring deduplication
52
Configuring a deduplication storage unit
Table 5-2
Limit I/O streams
per volume
Media server deduplication pool properties (continued)
DescriptionProperty
Select to limit the number of read andwrite streams (that is, jobs)
for each volume in the disk pool. A job may read backup images
or write backup images. By default, there is no limit. If you select
this property, also configure the number of streams to allow per
volume.
When the limit is reached, NetBackup chooses another volume
for write operations, if available. If not available, NetBackup
queues jobs until a volume is available.
Too many streams may degrade performance because of disk
thrashing. Disk thrashing is excessive swapping of data between
RAM and a hard disk drive. Fewer streams can improve
throughput, whichmay increasethe numberof jobsthat complete
in a specific time period.
Select or enter the number of read and write streams to allow per
volume.
Many factorsaffect theoptimal numberof streams.Factors include
but are not limited to disk speed, CPU speed, and the amount of
memory.
Configuring a deduplication storage unit
Create one or more storage units that reference the disk pool.
The Disk Pool Configuration Wizard lets you create a storage unit; therefore,
you may have created a storage unit when you created a disk pool. To determine
if storage units exist for the diskpool, see the NetBackupManagement > Storage
> Storage Units window of the Administration Console.
To configure a storage unit from the Actions menu
In theNetBackupAdministration Console, expand NetBackup Management
1
> Storage > Storage Units.
On the Actions menu, select New > Storage Unit.
2
Complete the fields in the New Storage Unit dialog box.
3
See “Deduplication storage unit properties” on page 53.
See “Deduplication storage unit recommendations” on page 54.
Page 53

Deduplication storage unit properties
The following are the configuration options for aPureDisk disk pool storage unit.
Configuring a deduplication storage unit
53Configuring deduplication
Table 5-3
Storageunitname
Disk type
Disk pool
Media server
Deduplication storage unit properties
DescriptionProperty
A unique name for the new storage unit. The name can describe the
type of storage. The storage unit name is the name used to specify a
storage unit for policies and schedules. Thestorage unitname cannot
be changed after creation.
Select Disk as the storage unit type.Storage unit type
Select PureDisk for the disk type for a media server deduplication
pool, a PureDisk deduplication pool, or a PureDisk Deduplication
Option storage pool.
Select the disk pool that contains the storage for this storage unit.
All disk pools of the specified Disk type appear in the Disk pool list.
If no disk pools are configured, no disk pools appear in the list.
The Mediaserver setting specifies the NetBackup media servers that
can move data to and from the disk pool for this storage unit. Only
the load balancing servers appear in the media server list.
Specify the media server or servers as follows:
■ To allow any server in the media server list to access the disk
storage (default), select Use any available media server.
■ To restrictthe media servers that can access the disk storage, select
Only use the following media servers. Then, select the media
servers to allow.
NetBackup selects the media server to use when the policy runs.
Maximum
fragment size
For normal backups, NetBackup breaks each backup image into
fragments so it does not exceed the maximum file size that the file
system allows. You can enter a value from 20 MBs to 51200 MBs.
Page 54
Configuring deduplication
54
Configuring a deduplication storage unit
Table 5-3
Maximum
concurrent jobs
Deduplication storage unit properties (continued)
DescriptionProperty
The Maximumconcurrent jobs settingspecifies themaximum number
of jobs that NetBackup can send to a disk storage unit at one time.
(Default: one job. The job count can range from 0 to 256.) This setting
corresponds to the Maximum concurrent write drives setting for a
Media Manager storage unit.
NetBackup queues jobs until the storage unit is available. If three
backup jobs are scheduled and Maximum concurrent jobs is set to
two, NetBackup starts the first two jobs and queues the third job. If a
job contains multiplecopies, each copyapplies toward theMaximum
concurrent jobs count.
Maximum concurrent jobs controls the traffic for backup and
duplication jobs but not restore jobs. The count applies to all servers
in the storage unit, not per server. If youselect multiplemedia servers
in the storage unit and 1 for Maximumconcurrent jobs, only one job
runs at a time.
The number to enter depends on the available disk space and the
server's ability to run multiple backup processes.
Warning: AMaximum concurrentjobs settingof 0disables thestorage
unit.
Deduplication storage unit recommendations
You can use storage unit properties to control how NetBackup performs.
Increase the Maximum concurrent jobs gradually
Symantec recommends that you increase the Maximum concurrent jobs value
gradually. The initial backup jobs (also known as initial seeding) require more
CPU and memory than successive jobs. After initial seeding, the storage server
can process more jobs concurrently. Gradually increase the jobs value over time.
Testing shows that the upper limit for a storage server with 8GB of memory and
4GB of swap space is 50 concurrent jobs.
Configure a client-to-server ratio
For a favorable client-to-server ratio, you can use one disk pool and configure
multiple storage units to separate your backup traffic. Because all storage units
use the same disk pool, you do not have to partition the storage.
Page 55

Configuring a deduplication storage unit
For example, assume that you have 100 important clients, 500 regular clients,
and four media servers. You can use two media servers to back up your most
important clients and two media servers to back up you regular clients.
The following example describes how to configure a favorable client-to-server
ratio:
■ Configure the media servers for NetBackup deduplication and configure the
storage.
■ Configure a disk pool.
■ Configure a storage unit foryour most important clients (such as STU-GOLD).
Select the disk pool. Select Only use the following media servers. Select two
media servers to use for your important backups.
■ Create a backup policy forthe 100 important clients and select the STU-GOLD
storage unit. The media servers that are specified in thestorage unit move the
client data to the deduplication storage server.
■ Configure another storage unit (such as STU-SILVER). Select the same disk
pool. Select Only usethe following mediaservers. Select the other two media
servers.
■ Configure abackup policy for the 500 regular clients and selectthe STU-SILVER
storage unit. The media servers that are specified in thestorage unit move the
client data to the deduplication storage server.
Backup traffic is routed to the wanted data movers by the storage unit settings.
55Configuring deduplication
Note: NetBackup uses storage units for media server selection for write activity
(backups andduplications) only. For restores, NetBackup chooses amongall media
servers that can access the disk pool.
Throttle traffic to the media servers
You can use the Maximum concurrent jobs settings on disk pool storage units to
throttle the traffic to the media servers.Effectively, this setting also directshigher
loads to specific media servers when you use multiple storage units for the same
disk pool. A higher number of concurrent jobs means that the disk can be busier
than if the number is lower.
For example, two storage units use the same set of media servers. One of the
storage units (STU-GOLD) has a higher Maximum concurrent jobs setting than
the other (STU-SILVER). More client backups occur for the storage unit with the
higher Maximum concurrent jobs setting.
Page 56

Configuring deduplication
56
Enabling client deduplication
Enabling client deduplication
To enable Client Deduplication, set an attribute in the NetBackup master server
Client Attributes host properties.
To specify the clients that deduplicate backups
In theNetBackupAdministration Console, expand NetBackup Management
1
> Host Properties > Master Servers.
In the details pane, select the master server.
2
On the Actions menu, select Properties.
3
On the Host Properties General tab, add the clients that use client direct to
4
the Clients list.
Select one of the following Deduplication Location options:
5
■ Always use the mediaserver disables client deduplication. By default, all
clients are configured with the Always use the media server option.
■ Prefer to use client-side deduplication uses client deduplication if the
PureDisk plug-in is active onthe client. If it isnot active, a normal backup
occurs; client deduplication does not occur.
■ Always use client-side deduplication uses client deduplication. If the
deduplication backup job fails, NetBackup retries the job.
You can override the Prefer to use client-side deduplication or Always use
client-side deduplication host property in the backup policies.
See Disableclient-side deduplicationin the NetBackup Administrator's Guide
for UNIX and Linux, Volume I.
See Disableclient-side deduplicationin the NetBackup Administrator's Guide
for Windows, Volume I.
Configuring backups
When you configure a backup policy, for the Policy storage select a storage unit
that uses a deduplication pool.
For a storage lifecycle policy, for the Storage unit select a storage unit that uses
a deduplication pool.
For VMware backups, select the Mapped full VM backup option when you
configure a VMware backup policy. The Mapped full VMbackup option provides
the best deduplication rates.
Page 57

Configuring optimized deduplication copy
NetBackup deduplicates the client data that it sends to a deduplication storage
unit.
Configuring optimized deduplication copy
You can configure optimized copy of deduplicated backups.
See “About optimized duplication of deduplicated data” on page 28.
To configure optimized duplication of deduplicated data
Ensure that all requirements are met.
1
See “Optimized deduplication copy requirements” on page 28.
Use one of the following methods to duplicate backup images:
2
■ A storage lifecycle policy to copy images automatically.
For the Backup destination Storage unit, select the storage unit for the
source media server deduplication pool. For the Duplication destination
Storage unit, select the storage unit for the destination disk pool. That
disk pool may be a media server deduplication pool or a PureDisk
deduplication pool.
See the NetBackup Administrator’s Guide for UNIX and Linux or the
NetBackup Administrator’s Guide for Windows.
■ A Vault policy to copy images automatically.
On the Profile dialog box ChooseBackups tab, choose the backup images
in thesource media server deduplication pool. For theDestination Storage
unit on the Duplication tab, select the storage unit for the destination
disk pool. That disk pool may be a media server deduplication pool or a
PureDisk deduplication pool.
See the NetBackup Vault Administrator’s Guide.
■ The NetBackup bpduplicate command to copy images manually.
Duplicate from the source media server deduplication pool to another
media server deduplication pool or to a PureDisk deduplication pool.
See NetBackup Commands.
You can apply separate retention periods to each copy. For example, you can
retain theprimary copy for three weeks and thedestination copy for a longer
period of time. If you delete the source image, the copy is not deleted.
57Configuring deduplication
Configuring optimized deduplication copy behavior
You can configure several optimized deduplication copy behaviors, as follows:
Page 58

Configuring deduplication
58
Adding a load balancing server
■ Optimized duplicationfailover. By default, if anoptimized duplication job fails,
NetBackup does not run the job again.
■ Number of optimized duplication attempts. You can specify the number of
times NetBackupretries anoptimized deduplicationjob before it fails the jobs.
■ Storage lifecyclepolicy retries. If the optimizeddeduplication job is configured
in a storage lifecycle policy, NetBackup retries the job three times.
Caution: These settings affect all optimized duplication jobs, not just optimized
deduplication copy jobs.
To configure NetBackup to revert to normal duplication if an optimized job fails
Add the following entry to the bp.conf file on the NetBackup master server:
◆
RESUME_ORIG_DUP_ON_OPT_DUP_FAIL = TRUE
On Windows systems, NetBackup configuration options are in the Windows
registry.
To configure the number of duplication attempts
Add an OPT_DUP_BUSY_RETRY_LIMIT entry in the NetBackup behavior file.
◆
For example, the following entry configures NetBackup to retry the job four
times before NetBackup fails the job:
OPT_DUP_BUSY_RETRY_LIMIT 4
The behavior file resides in the following directories:
■ UNIX: /usr/openv/netbackup/db/config/behavior
■ Windows: install_path\NetBackup\db\config\behavior.
To configure the number of storage lifecycle policy retries
Delay more retries by adding an IMAGE_EXTENDED_RETRY_PERIOD_IN_HOURS
◆
entry inthe NetBackup behavior file. The default forthis value is three hours.
Adding a load balancing server
You can add a load balancing server to an existing media server deduplication
node.
See “About deduplication servers” on page 21.
Page 59

Adding a load balancing server
To add a load balancing server
In the NetBackup Administration Console, expand Media and Device
1
Management > Credentials > Storage Server
Select the deduplication storage server.
2
On the Edit, select Change.
3
59Configuring deduplication
In the Change Storage Server dialog box, select the Media Servers tab
4
(Windows) or the Login Credentials tab (UNIX).
Select the media server or servers that you want to use as a load balancing
5
server. It must be a supported host.
The media servers that arechecked are configured as load balancing servers.
Click OK.
6
For all storage units in which Only use the following media servers is
7
configured, ensure that the new load balancing server is selected.
Page 60

Configuring deduplication
60
About the deduplication configuration file
About the deduplication configuration file
On eachhost that deduplicates data, a pd.conf file contains configuration settings
for the deduplication. You can edit thefile to configure advanced settingsfor that
host.
If you change the pd.conf file on a host, it changes the settings for that host only.
If you want the same settings for all of the hosts that deduplicate data, you must
change the pd.conf file on all of the hosts.
The pd.conf file resides in the following directories:
■ (UNIX) /usr/openv/lib/ost-plugins/
■ (Windows) install_path\Veritas\NetBackup\bin\ost-plugins
Editing the deduplication configuration file
The pd.conf file contains the configuration settings that control the operation
of deduplication on each host.
If you change the pd.conf file on a host, it changes the settings for that host only.
If you want the same settings for all of the hosts that deduplicate data, you must
change the pd.conf file on all of the hosts.
See “About the deduplication configuration file” on page 60.
To edit the pd.conf file
Use a text editor to open the pd.conf file.
1
The pd.conf file resides in the following directories:
■ (UNIX) /usr/openv/lib/ost-plugins/
■ (Windows) install_path\Veritas\NetBackup\bin\ost-plugins
See “About the deduplication configuration file” on page 60.
To activate a setting, remove the pound character (#) in column 1 from each
2
line that you want to edit.
To change a setting, specify a new value.
3
Note: The spaces to the left and right of the equal sign (=) in the file are
significant. Ensure that the space characters appear in the file after you edit
the file.
See “pd.conf file settings” on page 61.
Page 61

Save and close the file.
4
Restart theNetBackup Remote Manager and Monitor Service (nbrmms) on the
5
host.
pd.conf file settings
Table 5-4 describes the deduplication settings that you can configure.
Editing the deduplication configuration file
61Configuring deduplication
DEBUGLOG
Table 5-4
(Windows)
tmp/pdplugin.log
(UNIX)
pd.conf file values
Any pathC:\pdplugin.log
0 through 100LOGLEVEL
0 (off) or 1 (on)0COMPRESSION
0 (off) or 1 (on)0ENCRYPTION
ActionPossible valuesDefault valueSetting
Writes the log information to the specified file.
Uncomment theDEBUGLOG line that corresponds
to your operating system and then specify the
log filepath. Youcan specifya different location
and log file name.
Specifies the amount of information that is
written to the log file. The range is from 0 to 10,
with 10 being the most logging.
Note: Donot change this setting unless directed
to by a Symantec Technical Support
representative.
Specifies whether you want compression. By
default, files are not compressed. If you want
compression, change the value to 1.
See “About compression and encryption”
on page 28.
Specifies whether you want encryption. By
default files are not encrypted. If you want
encryption, change the value to 1.
See “About compression and encryption”
on page 28.
PREFETCH
This keyword is reserved for internal use.
Note: Donot change this setting unless directed
to by a Symantec Technical Support
representative.
Page 62

Configuring deduplication
62
Editing the deduplication configuration file
PDALIGN
Table 5-4
N/AOPTDUP_TIMEOUT
16MINFILE_KSIZE
pd.conf file values (continued)
ActionPossible valuesDefault valueSetting
This keyword is reserved for internal use.
Note: Donot change this setting unless directed
to by a Symantec Technical Support
representative.
The value expressed
in minutes
N/AN/ASEGKSIZE
Specifies the number of minutes before the
optimized duplication times out. Indicated in
minutes.
This keyword is reserved for internal use.
Warning: Changing this value can reduce
capacity and decrease performance. Modify this
setting only if directed to do so by Symantec
support representative.
From 1 to the
practical system
limit
Determines the smallest size file (in KBs) that
NetBackup segments. Files smaller than the
threshold are combined into a single large
segment to reduce the overhead of managing
many small segments. However, such segments
have less chance of being deduplicated.
Caution: Large numbers of files smaller than
the threshold may adversely affect backup
performance.
1 (on) or 0 (off)1MATCH_PDRO
Specifies that NetBackup should use the
PureDisk Remote Office Agent dynamic
segmentation deduplicationalgorithm. Enabling
it means that the data that is backed up is
globally deduplicatedwith eachother. Ifdisabled
(set to 0), PDDO uses a static 128KB
segmentation algorithm for deduplication.
Caution: Changing the default segmentation
algorithm most likely causes the next set of
backups to not deduplicate with the existing
storage pool data. Subsequent backups then
deduplicate using the PDRO algorithm.
0OPTDUP_BANDWITH
0 (no limit) to the
practical system
limit
Determines the maximum bandwidth that is
allowed for optimized duplication. The value is
specified in KBytes/second.
Page 63

Reconfiguring the deduplication storage server and storage paths
63Configuring deduplication
Table 5-4
0BANDWIDTH_LIMIT
pd.conf file values (continued)
ActionPossible valuesDefault valueSetting
1 (on) or 0 (off)1OPTDUP_ENCRYPTION
Any file extensionN/ADONT_SEGMENT_TYPES
0 (default - no limit)
to the practical
system limit
0 to 50,00050,000MAX_IMG_MBSIZE
Determines if the data to replicate is encrypted
before it is sent out over the network.
Allows a list of file name extensions to be
specified. Files in the backup stream that have
these extensions are given a single segment if
smaller than16MB. Largerfiles arededuplicated
using the maximum 16MB segment size.
Example:
DONT_SEGMENT_TYPES = mp3,avi
This settingprevents NetBackupfrom analyzing
and managing segments within the file types
that do not deduplicate globally.
Determines the maximum bandwidth that is
allowed when backing up or restoring data
between the media server andthe deduplication
pool. The value is specified in KBytes/second.
The default is no limit.
This keyword is reserved for internal use.
Note: Donot change this setting unless directed
to by a Symantec representative.
Reconfiguring the deduplication storage server and
storage paths
Only one deduplication storage path can exist on a media server. Therefore, you
cannot rerun the StorageServer Configuration Wizard. An activated NetBackup
Deduplication Enginerejects allconfiguration attempts that abandon its previously
defined storage and backup images. You must manually deactivate the engine
and physically delete the storage directory.
Two aspects to the configuration exist: the record of the deduplication storage in
the EMMdatabase andthe physical presence of the storage on disk (the populated
storage directory). Deleting the deduplication storage server does not alter the
contents of the storage on physical disk. To protect against inadvertent data loss,
NetBackup does not automatically delete the storage when you delete the storage
server.
Page 64
Configuring deduplication
64
Reconfiguring the deduplication storage server and storage paths
Warning: Deleting valid backup images may cause data loss.
Table 5-5
Ensure thatno deduplication
activity occurs
Expire backup images
Delete the storage units that
use the disk pool
Stop the services on the
media server
Disable media server deduplication
ProcedureTask
Deactivate allbackup policiesthat usededuplication storage.
See the NetBackup Administrator's Guide for UNIX and
Linux, Volume I
See the NetBackup Administrator's Guide for Windows,
Volume I..
Expire all backup images that reside on the deduplication
disk storage.
See the NetBackup Administrator's Guide for UNIX and
Linux, Volume I
See the NetBackup Administrator's Guide for Windows,
Volume I..
See the NetBackup Administrator's Guide for UNIX and
Linux, Volume I
See the NetBackup Administrator's Guide for Windows,
Volume I..
See “Deleting a deduplication pool” on page 78.Delete the disk pool
See the NetBackup Administrator's Guide for UNIX and
Linux, Volume I
See the NetBackup Administrator's Guide for Windows,
Volume I..
Delete thestorage directories
storage server
Start theNetBackup services
on the media server
Delete the storage directory and database directory (if you
configured a database directory).
See “Resetting the deduplication registry” on page 73.Reset the registry
See “Deleting a deduplication storage server” on page 67.Delete the deduplication
See the NetBackup Administrator's Guide for UNIX and
Linux, Volume I
See the NetBackup Administrator's Guide for Windows,
Volume I..
See “Configuring deduplication” on page 47.Reconfigure
Page 65

Chapter
Managing deduplication
This chapter includes the following topics:
■ Managing deduplication servers
■ Managing NetBackup Deduplication Engine credentials
■ Managing deduplication disk pools
■ Monitoring deduplication activity
■ Monitoring deduplication storage capacity and usage
■ Deleting backup images
6
■ Disabling deduplication for a client
■ About maintenance processing
Managing deduplication servers
After you configure deduplication, you can perform various tasks to manage
deduplication servers.
See “Changing deduplication storage server properties” on page 66.
See “Deleting a deduplication storage server” on page 67.
See “Determining the deduplication storage server state” on page 67.
See “Getting the storage server configuration” on page 68.
See “Editing a storage server configuration file” on page 68.
See “Setting the storage server configuration” on page 70.
See “Deleting a load balancing server configuration file” on page 70.
See “Removing a load balancing server” on page 70.
Page 66
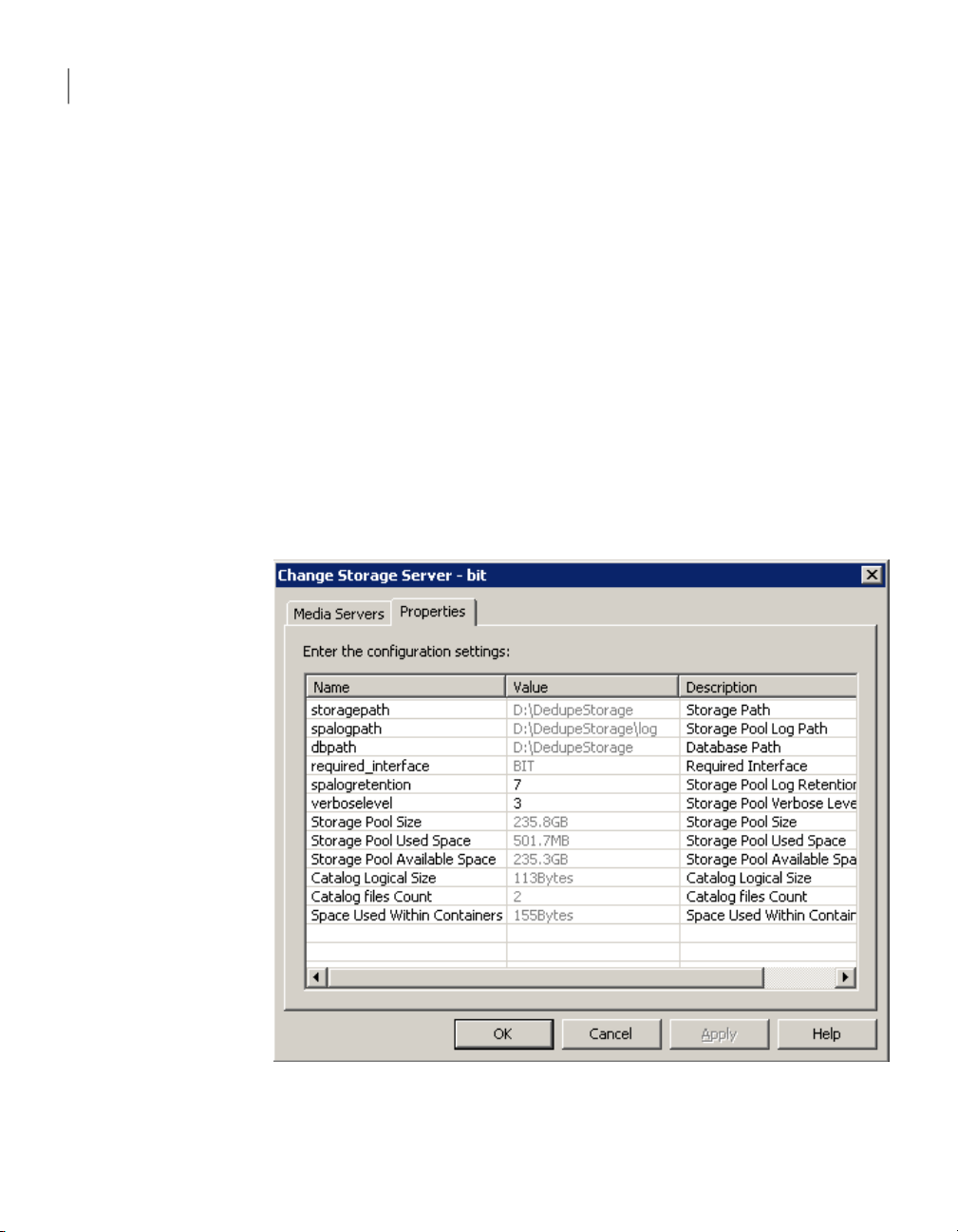
Managing deduplication
66
Managing deduplication servers
See “Viewing deduplication storage servers” on page 72.
See “Viewing deduplication storage server attributes” on page 72.
See “Resetting the deduplication registry” on page 73.
Changing deduplication storage server properties
You can change the retention period and logging level for the NetBackup
Deduplication Manager.
To change deduplication storage server properties
In the NetBackup Administration Console, expand Media and Device
1
Management > Credentials > Storage Server
Select the deduplication storage server.
2
On the Edit menu, select Change.
3
In the Change Storage Server dialog box, select the Properties tab.
4
For the property to change, select the value in the Value column.
5
Page 67

Change the value.
6
Click OK.
7
Deleting a deduplication storage server
If youdelete a deduplication storage server,NetBackup disablesthe deduplication
functionality and the storage server functionality on that media server.
NetBackup does not delete the media server from your configuration. To delete
the media server, use the NetBackup nbemmcmd command.
If a disk pool is configured from the disk volume that the deduplication storage
server manages, you cannot delete the deduplication storage server.
Warning: Do not delete a deduplication storage server if its storage contains
unexpired NetBackup images; if you do, data loss may occur.
To delete a deduplication storage server
In the NetBackup Administration Console, expand Media and Device
1
Management > Credentials > Storage Server
On the Edit menu, select Delete.
2
Click Yes in the confirmation dialog box.
3
Managing deduplication servers
67Managing deduplication
Determining the deduplication storage server state
Use theNetBackup nbdevquery command to determine the state of a deduplication
storage server. The state is either UP or DOWN.
Page 68

Managing deduplication
68
Managing deduplication servers
To determine deduplication storage server state
Run the following command on the NetBackup master server or a
◆
deduplication storage server:
UNIX: /usr/openv/netbackup/bin/admincmd/nbdevquery -liststs
-storage_server server_name -stype PureDisk –U
Windows: install_path\NetBackup\bin\admincmd\nbdevquery -liststs
-storage_server server_name -stype PureDisk –U
The following is example output:
Storage Server : bit
Storage Server Type : PureDisk
Storage Type : Formatted Disk, Network Attached
State : UP
This example output is shortened; more flags may appear in actual output.
Getting the storage server configuration
Symantec recommends that you get and save the storage server configuration.
Getting and saving the configuration can help you with recovery of your
environment.
If you get the configuration of a storage server that is unavailable because of a
disaster, NetBackup returns a template configuration file.
To get the storage server configuration
On the master server, enter the following command:
◆
UNIX: /usr/openv/netbackup/bin/admincmd/nbdevconfig -getconfig
-storage_server sshostname -stype PureDisk -configlist file.txt
Windows: install_path\NetBackup\bin\admincmd\nbdevconfig -getconfig
-storage_server sshostname -stype PureDisk -configlist file.txt
For sshostname, use the name of the storage server. For file.txt, use a file name
indicates its purpose.
Editing a storage server configuration file
In some very limited situations, you may need to create a storage server
configuration file that includes the configuration settings for your environment.
For example, for disaster recovery you may need to edit a template file to create
a configuration file for your environment.
Page 69

Managing deduplication servers
To edit the storage server configuration
If you did not save a storage server configuration file, get a storage server
1
configuration file.
See “Getting the storage server configuration” on page 68.
If you get the configuration of a storage server that is unavailable because of
a disaster, NetBackup returns a template configuration file. The following is
an example of a template configuration file:
V6.5.5 "storagepath" "none" string
V6.5.5 "spalogin" "n" string
V6.5.5 "spapasswd" " " string
V6.5.5 "dbpath" "db_path" string
V6.5.5 "required_interface" "" string
V6.5.5 "spalogretention" "7" int
V6.5.5 "verboselevel" "3" int
V6.5.5 represents the version of the input and output format not the
NetBackup release level. That version may differ on your system.
Use a text editor to enter or change values.
2
For a template configuration file, enter the appropriate information in the
second set of quotation marks in each line, replacing the default values. The
values shouldbe thesame asthose youused whenyou configuredthe storage
server initially.
The following are the values that are required:
■ storagepath.
69Managing deduplication
■ spalogin.
■ spapasswd.
■ dbpath.
If the database path is the same as the storage path, enter the same value
for storagepath and dbpath.
■ required_interface.
The required_interface is required only if you configured one initially;
if a specific interface is not required, leave it blank. The required interface
defaults to the computer's hostname.
Values for the other configuration parameters are optional and not
required for a recovery situation.
Page 70

Managing deduplication
70
Managing deduplication servers
Setting the storage server configuration
You can set the storage server configuration(that is, configure the storageserver)
by importingthe configuration from a file. Setting the configuration can help you
with recovery of your environment.
The file should be file of your configuration that you saved.
See “Preparing for disaster” on page 103.
Alternative, the file may be an edited configuration file.
See “Editing a storage server configuration file” on page 68.
To set the storage server configuration
On the master server, run the following command:
◆
UNIX: /usr/openv/netbackup/bin/admincmd/nbdevconfig -setconfig
-storage_server sshostname -stype PureDisk -configlist file.txt
Windows: install_path\NetBackup\bin\admincmd\nbdevconfig -setconfig
-storage_server sshostname -stype PureDisk -configlist file.txt
For sshostname, use the name of the storage server. For file.txt, use the name
of the file that contains the configuration.
Deleting a load balancing server configuration file
Each load balancing server for deduplication has a sshostname.cfg file. The
sshostname is the name of the configured deduplication storage server. The
sshostname is the fully qualified domain name if that was used to configure the
storage server.
You mayneed to delete the storage server configurationfile froma load balancing
server. For example, disaster recovery may require that you delete the
configuration file.
To delete the configuration file
Delete the file; it's location depends on the operating system type,as follows:
◆
UNIX: /usr/openv/lib/ost-plugins
Windows: install_path\Veritas\NetBackup\bin\ost-plugins
Removing a load balancing server
You can remove a load balancing server from a deduplication node. The media
server no longer deduplicates client data.
See “About deduplication servers” on page 21.
Page 71
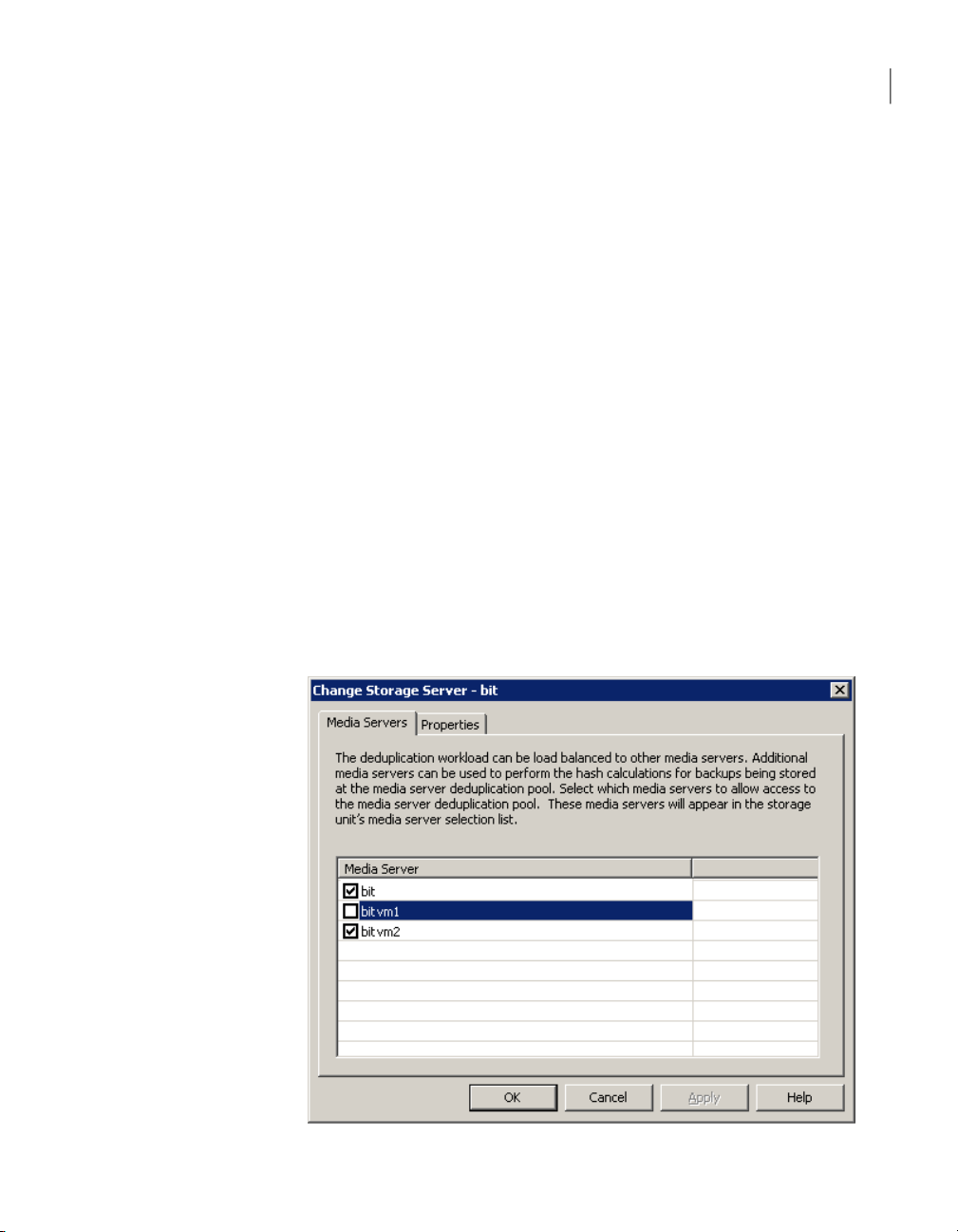
Managing deduplication servers
After you remove the load balancing server, restart the NetBackup Enterprise
Media Manager service. The NetBackup disk polling service may try to use the
removed server to query for disk status. Because the server is no longer a load
balancing server, it cannot query the disk storage. Consequently, NetBackup may
mark the disk volume as DOWN. When the EMM service restarts, it chooses a
different deduplication server to monitor the disk storage.
If thehost failed and is unavailable,you canuse the tpconfig device configuration
utility in menu mode to delete the server. However, you must run the tpconfig
utility on a UNIX or Linux NetBackup server.
For procedures, see the NetBackup Administrator’s Guide for UNIX and Linux,
Volume II.
To remove a media server from a deduplication node
For every storage unit that specifies the media server in Use one of the
1
following media servers, clear the checkbox that specifies the media server.
This step is not required if the storage unit is configured to use any available
media server.
In the NetBackup Administration Console, expand Media and Device
2
Management > Credentials > Storage Server.
Select the deduplication storage server, then select Edit > Change.
3
71Managing deduplication
Page 72

Managing deduplication
72
Managing deduplication servers
In the Change Storage Server dialog box, select the Media Servers tab
4
(Windows) or the Login Credentials tab (UNIX).
Clear the check box of the media server you want to remove.
5
Click OK.
6
Viewing deduplication storage servers
Use the NetBackup Administration Console to view a list ofdeduplication storage
servers already configured.
To view deduplication storage servers
In the NetBackup Administration Console, expand Media and Device
◆
Management > Credentials > Storage Server.
The All Storage Servers pane shows all configured deduplication storage
servers. deduplication storage servers show PureDisk in the Disk Type
column.
Viewing deduplication storage server attributes
Use theNetBackup nbdevquery command to view the deduplication storage server
attributes.
The server_nameyou usein the nbdevquery command must match the configured
name ofthe storage server. If thestorage server name is its fully-qualified domain
name, you must use that for server_name.
Page 73

Managing deduplication servers
To view deduplication storage server attributes
Run the following command on the NetBackup master server or a
◆
deduplication storage server:
UNIX: /usr/openv/netbackup/bin/admincmd/nbdevquery -liststs
-storage_server server_name -stype PureDisk –U
Windows: install_path\NetBackup\bin\admincmd\nbdevquery -liststs
-storage_server server_name -stype PureDisk –U
The following is example output:
Storage Server : bit
Storage Server Type : PureDisk
Storage Type : Formatted Disk, Network Attached
State : UP
Flag : OpenStorage
Flag : CopyExtents
Flag : AdminUp
Flag : InternalUp
Flag : LifeCycle
Flag : CapacityMgmt
Flag : FragmentImages
Flag : Cpr
Flag : FT-Transfer
73Managing deduplication
This example output is shortened; more flags may appear in actual output.
Resetting the deduplication registry
If you reconfigure your deduplication environment, one of the steps is to reset
the deduplication registry.
See “Reconfiguringthe deduplicationstorage server and storage paths” on page 63.
Warning: Only follow these procedures if you are reconfiguringyour storage server
and storage paths.
The procedure differs on UNIX and on Windows.
Page 74

Managing deduplication
74
Managing NetBackup Deduplication Engine credentials
To reset the deduplication registry file on UNIX and Linux
Enter thefollowing command on the storage server toreset the deduplication
◆
registry file:
cp -f /usr/openv/pdde/pdconfigure/cfg/userconfigs/pdregistry.cfg
/etc/pdregistry.cfg
To reset the deduplication registry on Windows
Delete the contents of the following keys in the Windows registry:
1
■ HKLM\SOFTWARE\Symantec\PureDisk\Agent\ConfigFilePath
■ HKLM\SOFTWARE\Symantec\PureDisk\Agent\EtcPath
Warning: Editing the Windows registry may cause unforeseen results.
Delete the storage path in the following key in the Windows key. That is,
2
delete everything after postgresql-8.3 -D in the key.
HKLM\SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Services\postgresql-8.3\ImagePath
For example, in the following example registry key, you would delete the
content of the key that is in italic type:
"C:\Program Files\Veritas\pdde\pddb\bin\pg_ctl.exe" runservice
-N postgresql-8.3 -D "D:\DedupeStorage\databases\pddb\data" -w
Managing NetBackup Deduplication Engine
credentials
You can manage existing credentials in NetBackup.
See “Adding NetBackup Deduplication Engine credentials” on page 74.
See “Changing NetBackup Deduplication Engine credentials” on page 75.
See “Deleting credentials from a load balancing server” on page 75.
See “Determiningwhich mediaservers have deduplication credentials” on page 76.
Adding NetBackup Deduplication Engine credentials
You mayneed toadd the NetBackup Deduplication Engine credentials to an existing
storage serveror load balancing server. For example, disasterrecovery mayrequire
that you add the credentials.
Page 75

Managing NetBackup Deduplication Engine credentials
Add the same credentials that you already use in your environment.
Another procedure exists to add a load balancing server to your configuration.
See “Adding a load balancing server” on page 58.
To add NetBackup Deduplication Engine credentials by using the tpconfig command
On thehost to which you want to addcredentials, runthe following command:
◆
UNIX: /usr/openv/volmgr/bin/tpconfig -add -storage_server
sshostname -stype PureDisk -sts_user_id UserID -password PassWord
Windows: install_path\Veritas\NetBackup\Volmgr\bin\tpconfig -add
-storage_server sshostname -stype PureDisk -sts_user_id UserID
-password PassWord
For sshostname, use the name of the storage server.
Changing NetBackup Deduplication Engine credentials
You cannot change the NetBackup Deduplication Engine credentials after you
enter them. If you must change the credentials, contact your Symantec support
representative.
See “About NetBackup Deduplication Engine credentials” on page 26.
75Managing deduplication
Deleting credentials from a load balancing server
You may need to delete the NetBackup Deduplication Engine credentials from a
load balancingserver. For example, disaster recovery may requirethat youdelete
the credentials on a load balancing server.
Another procedure exists to remove a load balancing serverfrom a deduplication
node.
See “Removing a load balancing server” on page 70.
To delete credentials from a load balancing server
On the load balancing server, run the following command:
◆
UNIX: /usr/openv/volmgr/bin/tpconfig -delete -storage_server
sshostname -stype PureDisk -sts_user_id UserID
Windows: install_path\Veritas\NetBackup\Volmgr\bin\tpconfig -delete
-storage_server sshostname -stype PureDisk -sts_user_id UserID
For sshostname, use the name of the storage server.
Page 76

Managing deduplication
76
Managing deduplication disk pools
Determining which media servers have deduplication credentials
You can determine which media servers have credentials configured for the
NetBackup DeduplicationEngine. The servers with credentials are load balancing
servers.
To determine if NetBackup Deduplication Engine credentials exist
In the NetBackup Administration Console, expand Media and Device
1
Management > Credentials > Storage Server.
Select the storage server, then select Edit > Change.
2
In the Change Storage Server dialog box, select the Media Servers tab
3
(Windows) or the Login Credentials tab (UNIX).
The media servers for which credentials are configured are checked.
Managing deduplication disk pools
After you configure NetBackup deduplication, you can perform various tasks to
manage your disk pools.
See “Changing deduplication disk pool properties” on page 76.
See “Changing the deduplication pool state” on page 77.
See “Changing the deduplication disk volume state” on page 77.
See “Deleting a deduplication pool” on page 78.
See “Determining the deduplication pool state” on page 78.
See “Determining the deduplication disk volume state” on page 79.
See “Viewing deduplication disk pools” on page 79.
Changing deduplication disk pool properties
You can change the properties of a deduplication disk pool.
To change disk pool properties
In the NetBackup Administration Console, expand Media and Device
1
Management > Devices > Disk Pools.
Select the disk pool you want to change in the details pane.
2
Page 77

On the Edit menu, select Change.
3
Managing deduplication disk pools
77Managing deduplication
In the Change Disk Pool dialog box, change properties.
4
See “Media server deduplication pool properties” on page 50.
Changing the deduplication pool state
Disk pool state is UP or DOWN.
To change the state to DOWN, the disk pool must not be busy. If backup jobs are
assigned to the disk pool, the state change fails. Cancel the backup jobs or wait
until the jobs complete.
To change deduplication pool state
In the NetBackup Administration Console, expand Media and Device
1
Management > Device Monitor.
Select the Disk Pools tab.
2
Select the disk pool.
3
Select either Actions > Up or Actions > Down.
4
Changing the deduplication disk volume state
The disk volume state is UP or DOWN.
Page 78

Managing deduplication
78
Managing deduplication disk pools
To change the state to DOWN, the disk pool in which the volume resides must not
be busy. If backup jobs are assigned to the disk pool, the state change fails. Cancel
the backup jobs or wait until the jobs complete.
To change the deduplication disk volume state
Determine the name of the disk volume. The following command lists all
1
volumes in the specified disk pool:
nbdevquery -listdv -stype PureDisk -dp disk_pool_name
The nbdevquery and the nbdevconfig commands reside in the following
directory:
■ UNIX: /usr/openv/NetBackup/bin/admincmd
■ Windows: install_path\NetBackup\bin\admincmd
To display the disk volumes in all disk pools, omit the -dp option.
Change the disk volume state; the following is the command syntax:
2
nbdevconfig -changestate -stype PureDisk -dp disk_pool_name –dv
vol_name -state state
The state is either UP or DOWN.
Deleting a deduplication pool
You can delete a disk pool if it does not contain valid NetBackup backup images
or image fragments. If it does, you must first expire and delete those images or
fragments.
If you delete a disk pool, NetBackup removes it from your configuration.
If a disk pool is the storage destination of a storage unit, you must first delete the
storage unit.
To delete a deduplication disk pool
In the NetBackup Administration Console, expand Media and Device
1
Management > Devices > Disk Pools.
Select a disk pool
2
On the Edit menu, select Delete.
3
In the Delete Disk Pool dialog box, verify that the disk pool is the one you
4
want to delete and then click OK.
Determining the deduplication pool state
Disk pool state is UP or DOWN.
Page 79

To determine disk pool state
In the NetBackup Administration Console, expand Media and Device
1
Management > Device Monitor.
Select the Disk Pools tab.
2
The state is displayed in the Status column.
3
Determining the deduplication disk volume state
Use the NetBackup nbdevquery command to determine the state of the volume
in a deduplication disk pool. The command shows the properties and attributes
of the PureDiskVolume.
To determine deduplication disk volume state
Display the volume state by using the following command:
◆
UNIX: /usr/openv/netbackup/bin/admincmd/nbdevquery -listdv -stype
PureDisk -U
Windows: install_path\NetBackup\bin\admincmd\nbdevquery -listdv
-stype PureDisk -U
Managing deduplication disk pools
79Managing deduplication
The state is either UP or DOWN.
The following is example output
Disk Pool Name : PD_Disk_Pool
Disk Type : PureDisk
Disk Volume Name : PureDiskVolume
Disk Media ID : @aaaab
Total Capacity (GB) : 49.98
Free Space (GB) : 43.66
Use% : 12
Status : UP
Flag : ReadOnWrite
Flag : AdminUp
Flag : InternalUp
Num Read Mounts : 0
Num Write Mounts : 1
Cur Read Streams : 0
Cur Write Streams : 0
Viewing deduplication disk pools
Use the NetBackup Administration Console to view configured disk pools.
Page 80

Managing deduplication
80
Monitoring deduplication activity
To view disk pools
In the NetBackup Administration Console, expand Media and Device
◆
Management > Devices > Disk Pools.
Monitoring deduplication activity
You can monitor deduplication activity.
See “Monitoring the deduplication rates” on page 80.
See “Viewing disk reports” on page 81.
See “Monitoring deduplication processes” on page 83.
See “Monitoring deduplication logs” on page 83.
Monitoring the deduplication rates
The deduplication rate is the percentage of data that was stored already. That
data is not stored again.
NetBackup reports the rate of deduplication as follows:
■ The Deduplication Rate column of the Activity Monitor Jobs tab.
■ The Job Details dialog box.
The Detailed Status tab shows detailed information, including the
deduplication rate.
The informationdepends onwhether itis media server deduplication or client
deduplication, as follows:
■ For media server deduplication, the Detailed Status tab shows the
deduplication rate on the server that performed the deduplication. The
following job details excerpt shows details for client1, for which
DedupeServer deduplicated the data:
10/6/2009 10:02:09 AM - Info DedupeServer(pid=30695)
StorageServer=PureDisk:DedupeServer; Report=PDDO Stats
for (DedupeServer): scanned: 30126998 KB, stream rate:
162.54 MB/sec, CR sent: 1720293 KB, dedup: 94.3%, cache
hits: 214717 (94.0%)
■ For client deduplication jobs, the Detailed Status tab shows two
deduplication rates. The first deduplication rate is always for the client
data. Thesecond duplication rate is forthe load balancing server. The client
sends the disk image header and True Image Restore information (if
Page 81

Monitoring deduplication activity
applicable) to a load balancing server for deduplication. Typically,
deduplication ratesfor that information are zeroor verylow. The following
job details excerpt is an example of the two rates:
10/8/2009 11:54:21 PM - Info DedupeServer(pid=2220)
Using OpenStorage client direct to backup from client
DedupeClient to DedupeServer
10/8/2009 11:58:09 PM - Info DedupeServer(pid=2220)
StorageServer=PureDisk:bitume; Report=PDDO Stats for
(DedupeServer): scanned: 3423425 KB, stream rate: 200.77
MB/sec, CR sent: 122280 KB, dedup: 96.4%, cache hits:
49672 (98.2%)
10/8/2009 11:58:09 PM - Info DedupeServer(pid=2220) Using
the media server to write NBU data for backup
DedupeClient_1254987197 to DedupeServer
10/8/2009 11:58:19 PM - Info DedupeServer(pid=2220)
StorageServer=PureDisk:DedupeServer; Report=PDDO Stats
for (DedupeServer): scanned: 17161 KB, stream rate: 1047.42
MB/sec, CR sent: 17170 KB, dedup: 0.0%, cache hits: 0 (0.0%)
the requested operation was successfully completed(0)
81Managing deduplication
■ The bpdbjobs command shows the deduplication rate if you configure a
COLDREFS entry for DEDUPRATIO in the bp.conf file on the media server on
which you run the command.
See the NetBackup Administrator's Guide for UNIX and Linux, Volume II.
Many factors affect deduplication performance.
See “About deduplication performance” on page 32.
See “About deduplication server requirements” on page 23.
See “About client deduplication host requirements” on page 25.
Viewing disk reports
The NetBackupdisk reports include information about the diskpools, disk storage
units, disk logs, images that are stored on disk media, and storage capacity.
Table 6-1 describes the disk reports available.
Page 82

Managing deduplication
82
Monitoring deduplication activity
Table 6-1
Images on Disk
Disk Logs
Disk Storage Unit
Disk reports
DescriptionReport
The Imageson Diskreport generates the image list present on the
disk storage units that are connected to the media server. The
report is a subset of the Images on Media report; it shows only
disk-specific columns.
The report provides a summary of the storage unit contents. If a
disk becomes bad or if a media server crashes, this report can let
you know what data is lost.
The Disk Logs report displays the media errors or the
informational messages that are recorded in the NetBackup error
catalog. The report is a subset of the Media Logs report; it shows
only disk-specific columns.
Either PureDisk or Symantec Deduplication Engine in the
description identifies a deduplication message. (The identifiers
are genericbecause thededuplication enginedoes notknow which
application consumesits resources.NetBackup, SymantecBackup
Exec, and NetBackup PureDisk are Symantec applications that
use deduplication.
The Disk Storage Unit Status report displays the state of disk
storage units in the current NetBackup configuration.
For disk pool capacity, see the disk pools window in Media and
Device Management > Devices > Disk Pools.
Multiple storage units can point to the same disk pool. When the
report query is by storage unit, the report counts the capacity of
disk pool storage multiple times.
Disk Pool Status
The Disk Pool Status report displays the state of disk pool and
usage information.
To view disk reports
In the NetBackup Administration Console, expand NetBackup Management
1
> Reports > Disk Reports.
Select the name of a disk report.
2
In the right pane, select the report settings.
3
Click Run Report.
4
Page 83

Monitoring deduplication processes
The following are the deduplication processes about which NetBackup reports:
■ NetBackup Deduplication Engine in the Administration Activity Monitor
Services tab on Windows systems. On UNIX, the NetBackup Deduplication
Engine appears as spoold on the Daemons tab.
■ NetBackup Deduplication Manager in the Activity Monitor Services tab on
Windows systems. On UNIX, the NetBackup Deduplication Manager appears
as spad on the Daemons tab.
■ The database processes (postgres) appear in the ActivityMonitor Processes
tab on Windows systems.
■ The NetBackup bpps command shows the spoold, spad, and postgres
processes.
See “Deduplication server components” on page 109.
Monitoring deduplication logs
The NetBackup deduplication components write information to various log files.
The following subsections describe the log files for each component.
Monitoring deduplication activity
83Managing deduplication
Deduplication configuration script log
The log file is in the storage_path/log/spoold directory. The log file name is
pdde-config.log.
NetBackup creates this log file during the configuration process. If your
configuration through the wizard succeeded, you do not need to examine the log
file. The only reason to look at the log file is if the configuration failed. If the
configuration process failed after it created and populated the storage directory,
this log file identifies when the configuration failed.
NetBackup Deduplication Engine log
The NetBackup Deduplication Engine writes several log files, as follows:
■ VxUL log files for the events and errors that NetBackup receives from polling.
See “About VxUL logs” on page 86.
■ Log files in the storage_path/log/spoold directory, as follows:
■ The spoold.log file is the main log file
■ The storaged.log file is for queue processing.
Page 84

Managing deduplication
84
Monitoring deduplication activity
■ A logfile for each connection tothe engine is stored ina directory structure.
The following describes the pathname to a log file for a connection:
IP
address/application/TaskName/FirstDigitofSessionID/sessionID-current_time_in_seconds.log
For example, the following is an example of a crcontrol connection log
pathname on a UNIX system:
/storage_path/log/spoold/127.0.0.1/crcontrol/Control/2/2916742631-1257956402.log
Usually, the only reason toexamine these connection log files is if a Symantec
support representative asks you to.
NetBackup Deduplication Manager logs
The log files are in the /storage_path/log/spad directory.
■ spad.log
■ sched_GarbageCollection.log
■ sched_QueueProcess.log
■ SchedClass.log
You canset the log level and retention periodin theChangeStorage Server dialog
box Properties tab.
See “Changing deduplication storage server properties” on page 66.
Deduplication database log
The deduplication database log file (postgresql.log) is in the
storage_path/databases/pddb directory.
You can configure log parameters. For more information, see the following:
http://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/static/runtime-config-logging.html
The default configuration for the PostgreSQL database does not add timestamps
to log entries on Windows systems. Therefore, Symantec recommends that you
edit the configuration file on Windows hosts so timestamps are added to the log
file.
To configure log file timestamps on Windows
Use a text edit to open the following file:
1
dbpath\databases\pddb\data\postgresql.conf
The database path may be the same as the configured storage path.
In the line that begins with log_line_prefix, change the value from %%t to
2
%t. (That is, remove one of the percent signs (%).)
Page 85

Monitoring deduplication activity
Save the file.
3
Run the following command:
4
install_path\Veritas\pdde\pddb\bin\pg_ctl reload -D
dbpath\databases\pddb\data
If the command output does not include server signaled, use Windows
Computer Management to restart the PostgreSQL Server 8.3 service.
PureDisk plug-in log
You can configure the location and name of the log file and the logging level. To
do so, edit the DEBUGLOG entry and the LOGLEVEL in the pd.conf file.
See “About the deduplication configuration file” on page 60.
See “Editing the deduplication configuration file” on page 60.
Client deduplication proxy plug-in log
The client deduplication proxy plug-in on the media server runs under bptm,
bpstsinfo, and bpbrm processes. Examine the log files for those processes for
proxy plug-in activity. The strings proxy or ProxyServer embedded in the log
messages identify proxy server activity.
They write log files to the following directories:
■ For bptm:
UNIX: /usr/openv/netbackup/logs/bptm
Windows: install_path\Veritas\NetBackup\logs\bptm
85Managing deduplication
■ For bpstsinfo:
Windows: /usr/openv/netbackup/logs/admin
UNIX: /usr/openv/netbackup/logs/bpstsinfo
Windows: install_path\Veritas\NetBackup\logs\admin
Windows: install_path\Veritas\NetBackup\logs\stsinfo
■ For bpbrm:
UNIX: /usr/openv/netbackup/logs/bpbrm
Windows: install_path\Veritas\NetBackup\logs\bpbrm
Client deduplication proxy server log
The deduplication proxy server nbostpxy on the client writes messages to files
in an eponymous directory, as follows:
UNIX: /usr/openv/netbackup/logs/nbostpxy
Page 86
Managing deduplication
86
Monitoring deduplication activity
Windows: install_path\Veritas\NetBackup\logs\nbostpxy.
About VxUL logs
Some NetBackup commands or processes write messages to their own log files.
Other processes use Veritas unified log (VxUL) files. VxUL uses a standardized
name and file format for log files. An originator ID (OID) identifies the process
that writes the log messages.
Table 6-2 shows the NetBackup logs for disk-related activity.
The messages that begin with a sts_ prefix relate to the interaction with the
storage vendorsoftware plug-in. Most interaction occurs on theNetBackup media
servers.
Table 6-2
restores
restores
Engine
configuration
configuration
configuration
configuration
NetBackup VxUL logs
Processes that use the IDVxUL OIDActivity
N/ABackups and
364Deduplication
178Device
202Device
230Device
Messages appear in the log files for the following
processes:
■ The bpbrm backup and restore manager
■ The bpdbm database manager
■ The bpdm disk manager
■ The bptm tape manager for I/O operations
The nbjm Job Manager.117Backups and
The NetBackup Deduplication Engine that runs on
the deduplication storage server.
The nbemm process.111Device
The Disk Service Manager process that runs in the
Enterprise Media Manager (EMM) process.
The storage server interface process that runs in the
Remote Manager and Monitor Service. RMMS runs
on media servers.
The Remote Disk Service Manager interface (RDSM)
that runsin theRemote Managerand MonitorService.
RMMS runs on media servers.
Page 87

Monitoring deduplication storage capacity and usage
To view and manage VxUL log files, you must use NetBackup log commands. For
information about how to use and manage logs on NetBackup servers, see the
NetBackup Troubleshooting Guide.
Monitoring deduplication storage capacity and usage
Several options exist to monitor your deduplication storage capacity and usage.
See “About deduplication capacity and usage reporting” on page 87.
See “About deduplication container files” on page 89.
See “Viewing capacity within deduplication container files” on page 89.
About deduplication capacity and usage reporting
Several factors may affect the expected usage results, as follows:
■ Expired backupsmay notchange the available size and the usedsize. Anexpired
backup may have no unique data segments. Therefore, the segments remain
valid for other backups.
■ NetBackup Deduplication Manager clean-up may not have run yet. The
Deduplication Manager performs clean up twice a day. Until it performs
clean-up, deleted image fragments remain on disk.
If you use operating system tools to examine storage space usage, their results
may not match the usage reported by NetBackup, as follows:
■ The operating system tools cannot report usage accurately. The storage
implementation uses container files. Deleted segments can leave free space
in container files, but the container file sizes do not change.
■ If otherapplications use the storage, NetBackup cannot report usage accurately.
NetBackup requires exclusive use of the storage.
Table 6-3 describes the options for monitoring capacity and usage.
87Managing deduplication
Table 6-3
Disk Pools window
Capacity and usage reporting
DescriptionOption
The Disk Pools window of the NetBackup Administration
Console displaysa valuethat wasstored whenNetBackup polled
the diskpools. Thevalue maynot beas currentas thevalue that
is displayed in the Storage Server window.
To displaythe window,expand Mediaand Device Management
> Devices > Disk Pools.
Page 88

Managing deduplication
88
Monitoring deduplication storage capacity and usage
Table 6-3
Storage Server window
Change Storage Server
dialog box
Disk Pool Status report
View container
command
The nbdevquery
command
Capacity and usage reporting (continued)
DescriptionOption
The Storage Server window of the NetBackup Administration
Console displays real-time values.
To displaythe window,expand Mediaand Device Management
> Credentials > Storage Servers.
The Change Storage Server dialog box Properties tab displays
storage capacity and usage.
See “Changing deduplication storage server properties”
on page 66.
The Disk Pool Status report displays the state of the disk pool
and usage information.
See “Viewing disk reports” on page 81.
A command that is installed with NetBackup provides a view of
storage capacity and usage within the deduplication container
files.
See “About deduplication container files” on page 89.
See “Viewing capacity within deduplication container files”
on page 89.
The nbdevquery command shows the state of the disk volume
and its properties and attributes. It also shows capacity, usage,
and percent used.
See “Determining the deduplication disk volume state”
on page 79.
License Keys dialog box
NetBackup OpsCenter
The summary of active capacity-based license features in the
NetBackupLicenseKeys dialog box. The summarydisplays the
storage capacity for which you are licensed and the capacity
used. It does not display the amount of physical storage space.
One theHelp menu in theNetBackupAdministrationConsole,
select License Keys.
The NetBackup OpsCenter also provides information about
storage capacity and usage.
See the NetBackup OpsCenter Administrator's Guide.
Page 89

Monitoring deduplication storage capacity and usage
About deduplication container files
The deduplicationstorage implementation allocates container files to holdbackup
data. Deleted segments can leave free space in containers files, but the container
file sizes do not change. Segments are deleted from containers when backup
images expire and the NetBackup Deduplication Manager performs clean-up.
Viewing capacity within deduplication container files
A command reports on storage usage within containers, as follows:
■ On UNIX and Linux systems, the path name of the command is
/usr/openv/pdde/pdcr/bin/crcontrol.
■ On Windows systems, the path name of the command is
install_path\Veritas\pdde\Crcontrol.exe.
The following is an example of the command usage on a Windows deduplication
storage server. The command shows the data store statistics (--dsstat option).
C:\Program Files\Veritas\pdde>Crcontrol.exe --dsstat 1
************ Data Store statistics ************
Data storage Size Used Avail Use%
68.4G 46.4G 22.0G 68%
Number of containers : 67
Average container size : 187441541 bytes (178.76MB)
Space allocated for containers : 12558583274 bytes (11.70GB)
Space used within containers : 12551984871 bytes (11.69GB)
Space available within containers: 6598403 bytes (6.29MB)
Space needs compaction : 508432 bytes (0.48MB)
Records marked for compaction : 3
Active records : 95755
Total records : 95758
89Managing deduplication
The NetBackupDeduplication Managerperiodically compactsthe spaceavailable
inside the container files. Therefore, space within a container is not available as
soon as it is free.. Various internal parameters control whether a container file is
compacted. Although space may be available within a container file, the file may
not be eligible for compaction. The NetBackup Deduplication Manager checks for
space every 20 seconds.
For help with the command options, enter crcontrol --help.
Page 90

Managing deduplication
90
Deleting backup images
Deleting backup images
Image deletionmay be time consuming. Therefore, if youdelete imagesmanually,
Symantec recommends the following approach.
See “Data removal process” on page 118.
To delete backup images manually
Expire all of the images by using the bpexpdate command and the
1
-notimmediate option. The -notimmediate option prevents bpexpdate from
calling the nbdelete command, which deletes the image.
Without this option, bpexpdate calls nbdelete to delete images. Each call to
nbdelete creates a job in the Activity Monitor, allocates resources, and
launches processes on the media server.
After youexpire the last image, delete all of the images by usingthe nbdelete
2
command with the –allvolumes option.
Only onejob is created in the Activity Monitor,fewer resources are allocated,
and fewer processes are started on the media servers. The entire process of
expiring images and deleting images takes less time.
Disabling deduplication for a client
If you remove a client from the list of clients that deduplicate their own data,
NetBackup backs up the client normally.
To disable client deduplication for a client
In the NetBackup Administration Console, expand NetBackup Management
1
> Host Properties > Master Servers.
In the details pane, select the master server.
2
On the Actions menu, select Properties.
3
On the Host Properties Client Attributes General tab, select the client that
4
deduplicates its own data.
In the Deduplication Location drop-down list, select Alwaysuse the media
5
server.
Click OK.
6
About maintenance processing
The following are background maintenance processes:
Page 91

About maintenance processing
■ NetBackup Deduplication Engine queue processing.
Operations that require database updates accumulate in a transaction queue.
Twice a day, the NetBackup Deduplication Manager directs the deduplication
engine to process the queue as one batch. The schedule is frequency-based.
By default, queue processing occurs every 12 hours, 20 minutes past the hour.
Queue processing is CPU-bound. The postgres database process usually
consumes 100% of the CPU cycles during queue processing.
■ NetBackup Deduplication Engine garbage collection.
In a few rare scenarios, some data segments may become orphaned. Garbage
collection cleans these segments up by removing them.
Garbage collection is an unobtrusive process; once a week the NetBackup
Deduplication Managerdirects the deduplication engine to collect andremove
garbage.
NetBackup cannot change the maintenance process schedules. Because these
processes do not block any other deduplication process, rescheduling should not
be necessary. However, it you must reschedule these processes, contact your
Symantec support representative.
See “NetBackup Deduplication Manager logs” on page 84.
91Managing deduplication
Page 92

Managing deduplication
92
About maintenance processing
Page 93

Troubleshooting
This chapter includes the following topics:
■ Troubleshooting installation issues
■ Troubleshooting configuration issues
■ Troubleshooting operational issues
■ Viewing disk errors and events
■ Deduplication event codes and messages
Chapter
7
Troubleshooting installation issues
The following sections may help you troubleshoot configuration issues.
See “Installation on SUSE Linux fails” on page 93.
Installation on SUSE Linux fails
The installation trace log shows an error when you install on SUSE:
....NetBackup and Media Manager are normally installed in /usr/openv.
Is it OK to install in /usr/openv? [y,n] (y)
Reading NetBackup files from /net/nbstore/vol/test_data/PDDE_packages/
suse/NB_FID2740_LinuxS_x86_20090713_6.6.0.27209/linuxS_x86/anb
/net/nbstore/vol/test_data/PDDE_packages/suse/NB_FID2740_LinuxS_x86_
20090713_6.6.0.27209/linuxS_x86/catalog/anb/NB.file_trans: symbol
lookup error: /net/nbstore/vol/test_data/PDDE_packages/suse/
NB_FID2740_LinuxS_x86_20090713_6.6.0.27209/linuxS_x86/catalog/anb/
NB.file_trans: undefined symbol: head /net/nbstore/vol/test_data/
Page 94

Troubleshooting
94
Troubleshooting configuration issues
PDDE_packages/suse/NB_FID2740_LinuxS_x86_20090713_6.6.0.27209/
linuxS_x86/catalog/anb/NB.file_trans failed. Aborting ...
Verify that your system is at patch level 2 or later, as follows:
cat /etc/SuSE-release
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 10 (x86_64)
VERSION = 10
PATCHLEVEL = 2
Troubleshooting configuration issues
The following sections may help you troubleshoot configuration issues.
See “Cannot configure deduplication storage server” on page 94.
See “The disk pool wizard does not display a volume” on page 95.
Cannot configure deduplication storage server
If you cannot configure a deduplication storage server or load balancing servers,
your network environment may not be configured for DNS reverse name lookup.
A configuration error message about license information failure indicates that
the NetBackup servers cannot communicate with each other.
You can edit the hosts file on the media servers that you use for deduplication.
Alternatively, youcan configure NetBackup so it does not use reversename lookup.
To prohibit reverse host name lookup by using the Administration Console
In theNetBackupAdministration Console, expand NetBackup Management
1
> Host Properties > Master Servers.
In the details pane, select the master server.
2
On the Actions menu, select Properties.
3
In the Master Server Properties dialog box, select the Network Settings
4
properties.
Select one of the following options:
5
■ Allowed
■ Restricted
■ Prohibited
For a description of these options, see the NetBackup online Help or the
administrator's guide.
Page 95

To prohibit reverse host name lookup by using the bpsetconfig command
Enter the following command on each media server that you use for
◆
deduplication:
echo REVERSE_NAME_LOOKUP = PROHIBITED | bpsetconfig -h host_name
The bpsetconfig command resides in the following directories:
UNIX: /usr/openv/netbackup/bin/admincmd
Windows: install_path\Veritas\NetBackup\bin\admincmd
The disk pool wizard does not display a volume
The Disk Pool Configuration Wizard does not display a disk volume for the
deduplication storage server.
First, restart all of the NetBackup daemons or services. The step ensures that the
NetBackup Deduplication Engine is up and ready to respond to requests.
Second, restart the NetBackup Administration Console. This step clears cached
information from the failed attempt to display the disk volume.
Troubleshooting operational issues
95Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting operational issues
The following sections may help you troubleshoot operational issues.
See “Verify that the server has sufficient memory” on page 95.
See “Backup jobs fail” on page 96.
See “Volume state changes to DOWN when volume is unmounted” on page 96.
See “Errors, delayed response, hangs” on page 97.
Verify that the server has sufficient memory
Insufficient memory on the storage server can cause operation problems. If you
have operation issues, you should verify that your storage server has sufficient
memory.
See “About deduplication server requirements” on page 23.
If the NetBackup deduplication processesdo no start on Red Hat Linux, configure
shared memory to be at least 128 MB (SHMMAX=128MB).
Page 96

Troubleshooting
96
Troubleshooting operational issues
Backup jobs fail
If backup jobs fail with an Error 800: Disk Volume is Down message, examine
the disk error logs to determine why the volume was marked DOWN.
If the storage server is busy with jobs, it may not respond to master server disk
polling requests in a timely manner. A busy load balancing server also may cause
this error. Consequently, the query times out and the master server marks the
volume DOWN.
If the error occurs for an optimized duplication job: verify that source storage
server is configured as a load balancing server for the target storage server. Also
verify that the target storage server is configured as a load balancing server for
the source storage server.
See “Viewing disk errors and events” on page 97.
Volume state changes to DOWN when volume is unmounted
If a volume becomes unmounted, NetBackup changes the volume state to DOWN.
NetBackup jobs that require that volume fail.
To determine the volume state
Invoke the following command onthe master server or themedia server that
◆
functions as the deduplication storage server:
The following example output shows that the DiskPoolVolume is UP:
Disk Pool Name : PD_Disk_Pool
Disk Type : PureDisk
Disk Volume Name : PureDiskVolume
Disk Media ID : @aaaab
Total Capacity (GB) : 49.98
Free Space (GB) : 43.66
Use% : 12
Status : UP
Flag : ReadOnWrite
Flag : AdminUp
Flag : InternalUp
Num Read Mounts : 0
Num Write Mounts : 1
Cur Read Streams : 0
Cur Write Streams : 0
Page 97

To change the volume state to UP
Mount the file system
◆
After abrief period of time, thevolume state changes to UP. No furtheraction
is required.
Errors, delayed response, hangs
Insufficient memory or inadequate host capabilities may cause multiple errors,
delayed response, and hangs.
See “About deduplication server requirements” on page 23.
For virtual machines, Symantec recommends that you do the following:
■ Set the memory size of each virtual machine to double the physical memory
of the host.
■ Set the minimum and the maximum values of each virtual machine to the
same value (double the physical memory of the host). These memory settings
prevent the virtual memory from becoming fragmented on the disk because
it does not grow or shrink.
These recommendations may not be the best configuration for every virtual
machine. However, Symantec recommends that you try this solution first when
troubleshooting performance issues.
Viewing disk errors and events
97Troubleshooting
Viewing disk errors and events
You can view disk errors and events in several ways, as follows:
■ The Disk Logs report.
See “Viewing disk reports” on page 81.
■ The NetBackupbperror command with the-disk optionreports on disk errors.
The command resides in the following directories:
UNIX: /usr/openv/netbackup/bin/admincmd
Windows: install_path\Veritas\NetBackup\bin\admincmd
Deduplication event codes and messages
The following table shows the deduplication event codes and their messages.
Event codesappear inthe bperror command -disk output and in the diskreports
in the NetBackup Administration Console.
Page 98
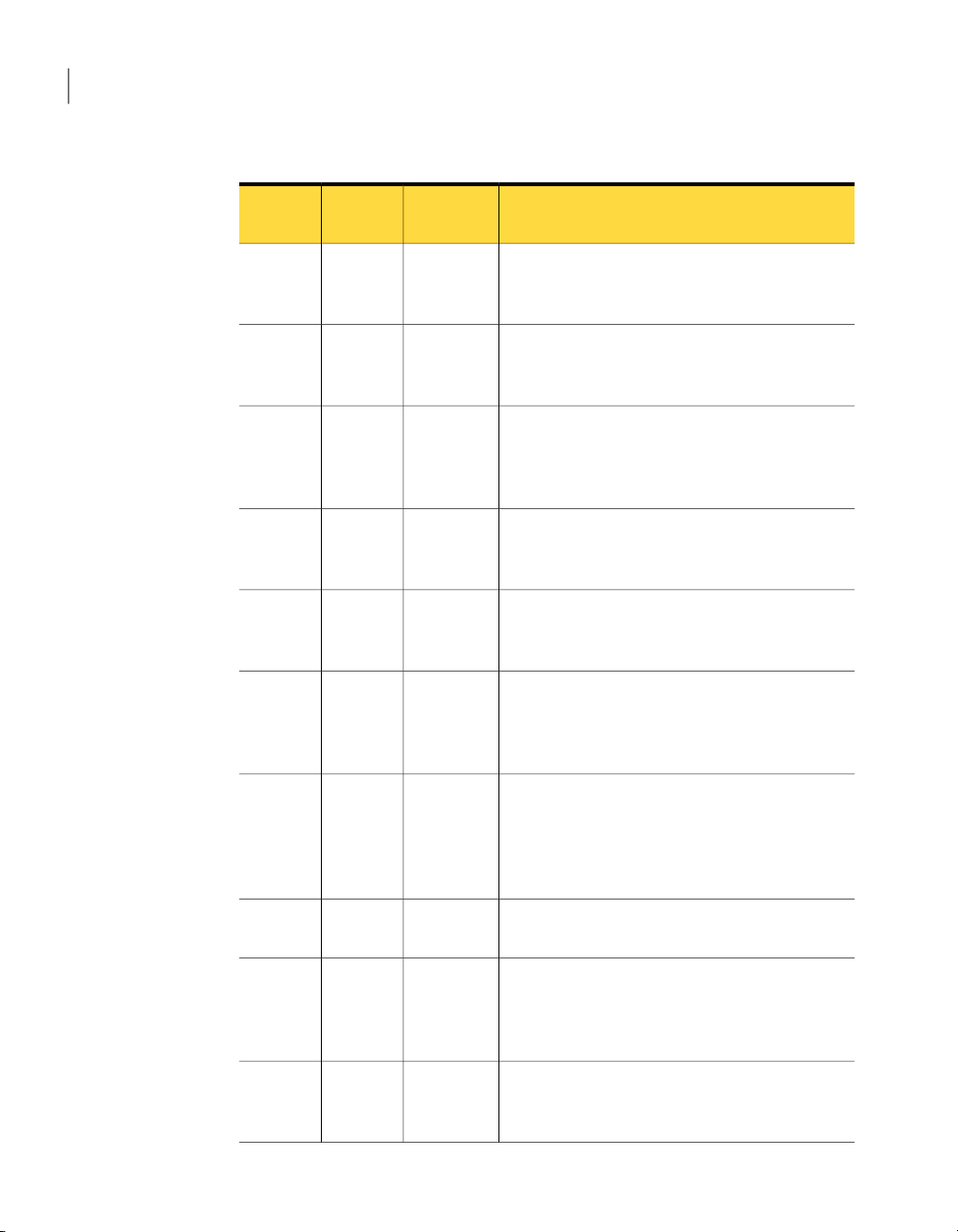
Troubleshooting
98
Deduplication event codes and messages
Table 7-1
Event #
Deduplication event codes and messages
Event
Severity
Severity
Error21000
Error21001
Warning41002
Error21003
Critical11004
Critical11013
Message exampleNetBackup
Operation configload/reload failed on
server PureDisk:server1.symantecs.orgon
host server1.symantecs.org.
Operation configload/reload failed on
server PureDisk:server1.symantecs.orgon
host server1.symantecs.org.
The open file limit exceeded in server
PureDisk:server1.symantecs.orgon host
server1.symantecs.org. Will attempt to
continue further.
A connection request was denied on the
server PureDisk:server1.symantecs.orgon
host server1.symantecs.org.
Network failure occurred in server
PureDisk:server1.symantecs.org on host
server1.symantecs.org.
Task session start request on server
PureDisk:server1.symantecs.org on host
server1.symantecs.org got an unexpected
error.
Error21008
Authorization81009
Error21010
Error21011
Task Aborted; An unexpected error
occurred during communication with
remote system in server
PureDisk:server1.symantecs.orgon host
server1.symantecs.org.
Authorization request from <IP> for
user <USER> denied (<REASON>).
Task initialization on server
PureDisk:server1.symantecs.org on host
server1.symantecs.org got an unexpected
error.
Task ended on server
PureDisk:server1.symantecs.org on host
server1.symantecs.org.
Page 99
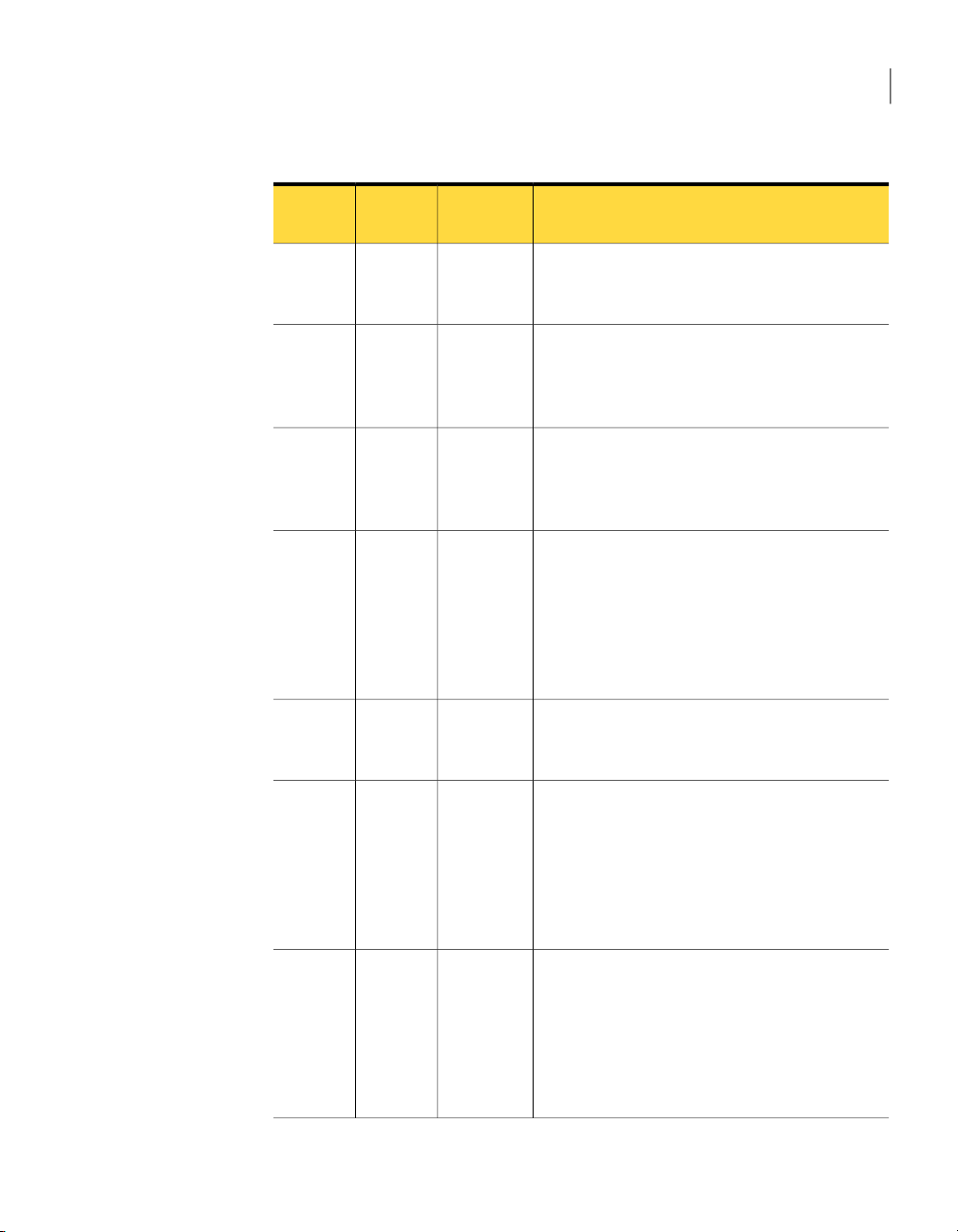
Deduplication event codes and messages
99Troubleshooting
Table 7-1
Event #
Deduplication event codes and messages (continued)
Event
Severity
Severity
Error21012
Critical11014
Critical11015
Critical11017
Message exampleNetBackup
A request for agent task was denied on
server PureDisk:server1.symantecs.orgon
host server1.symantecs.org.
Task session start request on server
PureDisk:server1.symantecs.orgon host
server1.symantecs.org got an unexpected
error.
Task creation failed, could not
initialize task class on server
PureDisk:server1.symantecs.orgon host
server1.symantecs.org.
Service Symantec DeduplicationEngine
exit on server
PureDisk:server1.symantecs.org on host
server1.symantecs.org. Please check the
server log for the probable cause of
this error. The application has
terminated.
Info161018
Critical11019
Critical11020
Startup of Symantec DeduplicationEngine
completed successfully on
server1.symantecs.org.
Service Symantec DeduplicationEngine
restart on server
PureDisk:server1.symantecs.orgon host
server1.symantecs.org. Please check the
server log for the probable cause of
this error. The application has
restarted.
Service Symantec Deduplication Engine
connection manager restart failed on
server PureDisk:server1.symantecs.org
on host server1.symantecs.org. Please
check the server log for the probable
cause of this error.The application has
failed to restart.
Page 100
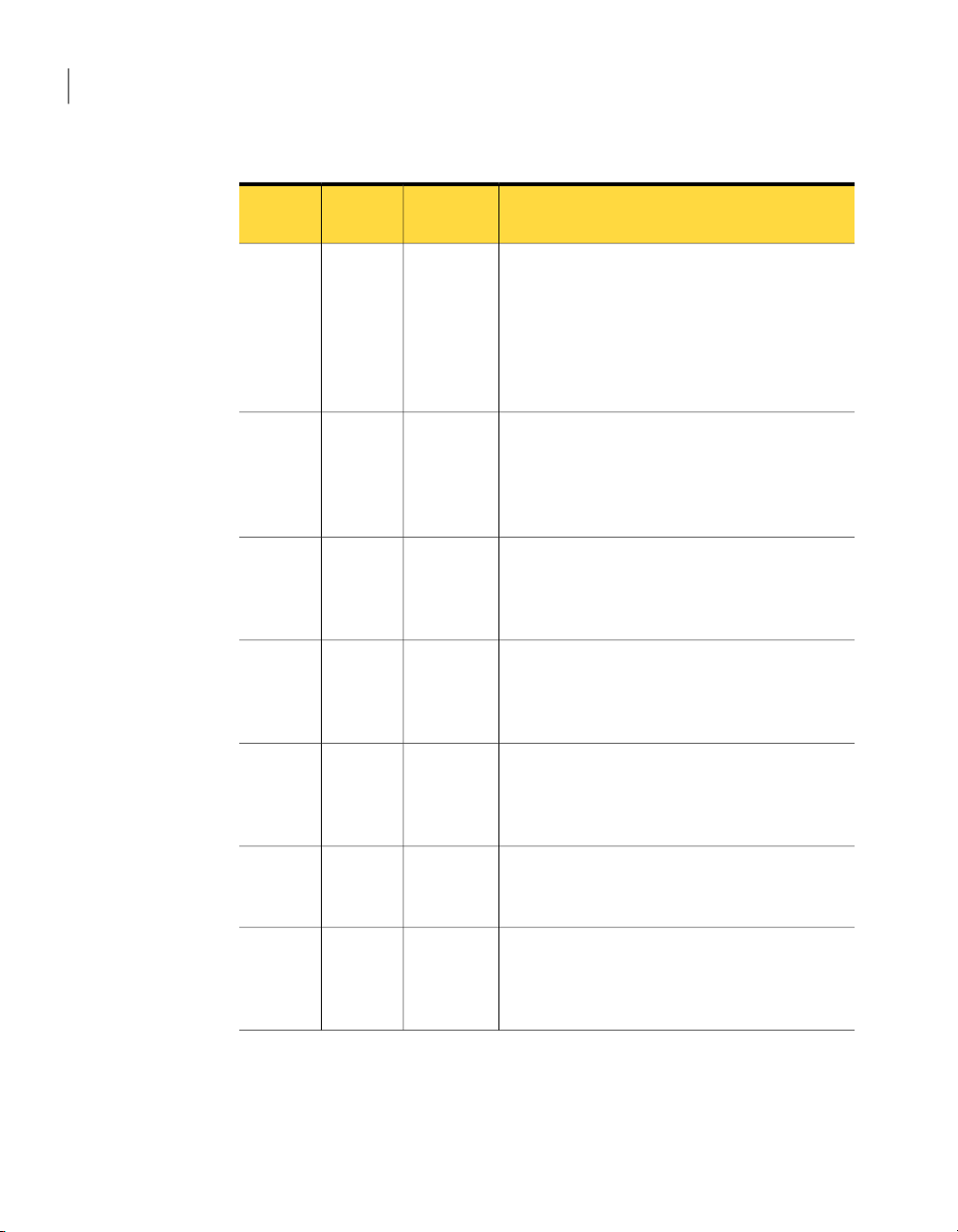
Troubleshooting
100
Deduplication event codes and messages
Table 7-1
Event #
Deduplication event codes and messages (continued)
Event
Severity
Severity
Critical11028
Critical11029
Critical11030
Critical11031
Message exampleNetBackup
Service Symantec DeduplicationEngine
abort on server
PureDisk:server1.symantecs.orgon host
server1.symantecs.org. Please check the
server log for the probable cause of
this error.The application has caught
an unexpected signal.
Double backend initialization failure;
Could not initialize storage backend
or cache failure detected on host
PureDisk:server1.symantecs.org in
server server1.symantecs.org.
Operation Storage Database
Initialization failed on server
PureDisk:server1.symantecs.org on host
server1.symantecs.org.
Operation Content router context
initialization failed on server
PureDisk:server1.symantecs.orgon host
server1.symantecs.org.
Critical11032
Warning41036
Warning41037
Operation log path creation/print
failed on server
PureDisk:server1.symantecs.orgon host
server1.symantecs.org.
Operation a transaction failed on
server PureDisk:server1.symantecs.org
on host server1.symantecs.org.
Transaction failed on server
PureDisk:server1.symantecs.orgon host
server1.symantecs.org. Transaction will
be retried.
 Loading...
Loading...