Page 1

FOREWORD CONTENTS
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL SERIAL NUMBER
Quad Raider 600
SERVICE MANUAL
Page 2

FOREWORD
Homepage
Contents
This service manual contains the technical data of each component inspection and
repair for the SANYANG QuadRaider 600 ATV. The manual is shown with
illustrations and focused on “Service Procedures”, “Operation Key Points”, and
“Inspection Adjustment”, providing technician with service guidelines.
If the style and construction of the ATV, QuadRaider 600, are different from the
photos, pictures shown in this manual, the actual vehicle shall prevail.
Specifications are subject to change without notice.
Service Department
SANYANG INDUSTRY CO., LTD.
Page 3

Homepage
Contents
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
This service manual describes basic information of different system parts and
system inspection & service for SANYANG QuadRaider 600ATV. In addition,
please refer to the manual contents in detailed for the model you serviced in
inspection and adjustment.
The first chapter covers general information and trouble diagnosis.
The second chapter covers service maintenance and special tools information.
The third to the 11th chapters cover engine and driving systems.
The 12th chapter is cooling system.
The 13th to the 16th chapter contain the parts set of assembly frame body.
The 17th chapter is electrical equipment.
The 18th chapter is wiring diagram.
Please see index of content to acquire the special parts and system information
quickly.
There are 4 buttons, “Foreword”, “Contents”, “How to use this manual” and
“Mechanism Illustrations” on the PDF version, and can be access to these items by
clicking on them.
If user wants to look for the content of each chapter, selecting the words of each
chapter on the contents can link to each chapter. There are two buttons,
“Homepage and contents, onto the top line of first page of the each chapter. Thus,
if the user needs to check other chapters, he can click the top buttons to back to
the homepage or contents. The content of each chapter can be selected too.
Therefore, when the user needs to check the content of the chapter, click the
content words of the chapter so that can back to the initial section of the content.
In addition, there is a “To this chapter contents” button on the top of the following
pages; clicking the button can back to the contents of this chapter.
Page 4

CONTENTS
Homepage
Page Content Index
1-1 ~ 1-17
GENERAL INFORMATION
1
2-1 ~ 2-17
MAINTENANCE INFORMATION
2
3-1 ~ 3-8
LUBRICATION SYSTEM
3
4-1 ~ 4-13
FUEL SYSTEM
4
5-1 ~ 5-6
ENGINE REMOVAL
5
6-1 ~ 6-17
CYLINDER HEAD/ VALVE
6
7-1 ~ 7-8
CYLINDER/ PISTON
7
8-1 ~ 8-17
“V” BELT DRIVING SYSTEM
8
9-1 ~ 9-14
TRANSMISSION
9
10-1 ~ 10-16
WHEEL DRIVE SHAFT/ PROPELLER SHAFT
10
11-1 ~ 11-11
A.C. GENERATOR/ STARTING CLUTCH
11
12-1 ~ 12-8
CRANKCASE/ CRANKSHAFT
12
13-1 ~ 13-14
COOLING SYSTEM
13
14-1 ~ 14-8
BODY COVER
14
15-1 ~ 15-12
FRONT BRAKE AND FRONT WHEEL
15
16-1 ~ 16-13
STEERING/ FRONT SUSPENSION
16
17-1 ~ 17-18
REAR BRAKE/ REAR WHEEL/ REAR CUSHION
17
18-1 ~ 18-21
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM
18
19-1 ~ 19-2
ELECTRICAL DIAGRAM
19
Page 5
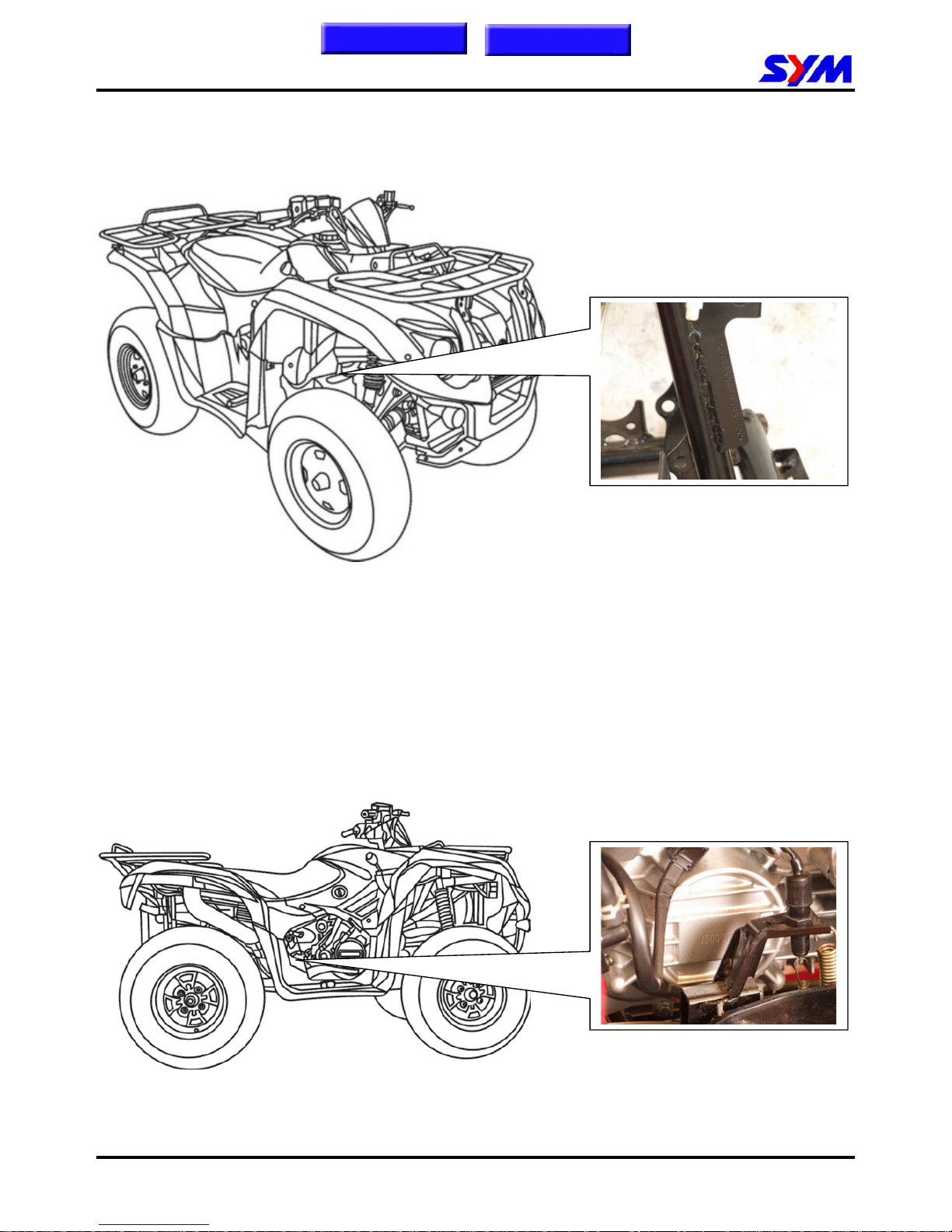
SERIAL NUMBER
Home page
Contents
Frame number
Engine number
Page 6

Homepage
Contents
1. GENERAL INFORMATION
Symbols and Marks............................. 1-1
Torque Values .................................... 1-10
Troubles Diagnosis............................ 1-12
Lubrication Points ............................. 1-17
General Safety ..................................... 1-2
Service Precautions ............................ 1-3
Specifications ...................................... 1-9
Symbols and Marks
Symbols and marks are used in this manual to indicate what and where the special service are needed, in
case supplemental information is procedures needed for these symbols and marks, explanations will be
added to the text instead of using the symbols or marks.
Warning
Means that serious injury or even death may result if procedures are not
followed.
Caution
Means that equipment damages may result if procedures are not followed.
Engine oil
Limits to use SAE 10W-30 API SG class oil. Warranty will not cover the
damage that caused by not apply with the limited engine oil.
(Recommended oil: KING MATE G-3 oil)
Grease King Mate G-3 is recommended.
Gear oil
King Mate gear oil serials are recommended. (Bramax HYPOID GEAR OIL
# 140)
Locking sealant
Apply sealant; medium strength sealant should be used unless otherwise
specified.
Oil seal
Apply with lubricant.。
Renew
Replace with a new part before installation.
Brake fluid
Use recommended brake fluid DOT3 or WELLRUN brake fluid.
Special tools
Special tools
Correct
Meaning correct installation.
Wrong
Meaning wrong installation.
Indication Indication of components.
Directions
Indicates position and operation directions
Components assembly directions each other.
Indicates where the bolt installation direction, --- means that bolt cross
through the component (invisibility).
1
1-1
Page 7
1. GENERAL INFORMATION
To this chapter contents
General Safety
Carbon monoxide
If you must run your engine, ensure the place is
well ventilated. Never run your engine in a closed
area. Run your engine in an open area, if you have
to run your engine in a closed area, be sure to use
an extractor.
Caution
Exhaust contains toxic gas, which may cause one
to lose consciousness and even result in death.
Gasoline
Gasoline is a low ignition point and explosive
material. Work in a well-ventilated place, no flame
or spark should be allowed in the work place or
where gasoline is being stored.
Caution
Gasoline is highly flammable, and may explode
under some conditions, keep it away from
children.
Used engine oil
Caution
Prolonged contact with used engine oil (or
transmission oil) may cause skin cancer although
it might not be verified.
We recommend that you wash your hands with
soap and water right after contacting. Keep the
used oil beyond reach of children.
Hot components
Caution
Components of the engine and exhaust system
can become extremely hot after engine running.
They remain very hot even after the engine has
been stopped for some time. When performing
service work on these parts, wear insulated
gloves and wait until cooling off.
Battery
Caution
• Battery emits explosive gases; flame is strictly
prohibited. Keeps the place well ventilated
when charging the battery.
• Battery contains sulfuric acid (electrolyte)
which can cause serious burns so be careful
do not be spray on your eyes or skin. If you
get battery acid on your skin, flush it off
immediately with water. If you get battery acid
in your eyes, flush it off immediately with
water and then go to hospital to see an
ophthalmologist.
• If you swallow it by mistake, drink a lot of
water or milk, and take some laxative such as
castor oil or vegetable oil and then go to see a
doctor.
• Keep electrolyte beyond reach of children.
Brake shoe
Do not use an air hose or a dry brush to clean
components of the brake system; use a vacuum
cleaner or the equivalent to avoid dust flying.
Caution
Inhaling brake shoe or pad ash may cause
disorders and cancer of the breathing system
Brake fluid
Caution
Spilling brake fluid on painted, plastic, or rubber
parts may cause damage to the parts. Place a
clean towel on the above-mentioned parts for
protection when servicing the brake system.
Keep the brake fluid beyond reach of children.
1-2
Page 8
1. GENERAL INFORMATION
To this chapter contents
Service Precautions
Always use with SANYANG genuine parts and
recommended oils. Using non-designed parts for
SANYANG ATV may damage the ATV.
Special tools are designed for remove and install
of components without damaging the parts being
worked on. Using wrong tools may result in parts
damaged.
When servicing this ATV, use only metric tools.
Metric bolts, nuts, and screws are not
interchangeable with the English system, using
wrong tools and fasteners may damage this
vehicle.
Clean the outside of the parts or the cover before
removing it from the ATV. Otherwise, dirt and
deposit accumulated on the part's surface may
fall into the engine, chassis, or brake system to
cause damage.
Wash and clean parts with high ignition point
solvent, and blow dry with compressed air. Pay
special attention to O-rings or oil seals because
most cleaning agents have an adverse effect on
them.
Never bend or twist a control cable to prevent
unsmooth control and premature worn out.
Rubber parts may become deteriorated when old,
and prone to be damaged by solvent and oil.
Check these parts before installation to make
sure that they are in good condition, replace if
necessary.
When loosening a component, which has
different sized fasteners, operate with a diagonal
pattern and work from inside out. Loosen the
small fasteners first. If the bigger ones are
loosen first, small fasteners may receive too
much stress.
Store complex components such as transmission
parts in the proper assemble order and tie them
together with a wire for ease of installation later.
Note the reassemble position of the important
components before disassembling them to
ensure they will be reassembled in correct
dimensions (depth, distance or position).
Components not to be reused should be
replaced when disassembled including gaskets
metal seal rings, O-rings, oil seals, snap rings,
and split pins.
1-3
Page 9

To this chapter contents
1. GENERAL INFORMATION
1-4
The length of bolts and screws for assemblies,
cover plates or boxes is different from one
another, be sure they are correctly installed. In
case of confusion, Insert the bolt into the hole to
compare its length with other bolts, if its length
out side the hole is the same with other bolts, it is
a correct bolt. Bolts for the same assembly
should have the same length.
Tighten assemblies with different dimension
fasteners as follows: Tighten all the fasteners
with fingers, then tighten the big ones with
special tool first diagonally from inside toward
outside, important components should be
tightened 2 to 3 times with appropriate
increments to avoid warp unless otherwise
indicated. Bolts and fasteners should be kept
clean and dry. Do not apply oil to the threads.
When oil seal is installed, fill the groove with
grease, install the oil seal with the name of the
manufacturer facing outside, and check the shaft
on which the oil seal is to be installed for
smoothness and for burrs that may damage the
oil seal.
Remove residues of the old gasket or sealant
before reinstallation, grind with a grindstone if the
contact surface has any damage.
The ends of rubber hoses (for fuel, vacuum, or
coolant) should be pushed as far as they can go
to their connections so that there is enough room
below the enlarged ends for tightening the
clamps.
Groove
Clamp
Connector
Rubber and plastic boots should be properly
reinstalled to the original correct positions as
designed.
Boots
The tool should be pressed against two (inner
and outer) bearing races when removing a ball
bearing. Damage may result if the tool is pressed
against only one race (either inner race or outer
race). In this case, the bearing should be
replaced. To avoid damaging the bearing, use
equal force on both races.
Manufacturer's name
Both of these examples can result in
bearing damage.
Page 10

1. GENERAL INFORMATION
To this chapter contents
Lubricate the rotation face with specified
lubricant on the lubrication points before
assembling.
Check if positions and operation for installed
parts is in correct and properly.
Make sure service safety each other when
conducting by two persons.
Note that do not let parts fall down.
Before battery removal operation, it has to
remove the battery negative (-) cable firstly.
Notre tools like open-end wrench do not contact
with body to prevent from circuit short and create
spark.
After service completed, make sure all
connection points is secured.
Battery positive (+) cable should be connected
firstly.
And the two posts of battery have to be greased
after connected the cables.
Make sure that the battery post caps are located
in properly after the battery posts had been
serviced.
If fuse burned, it has to find out the cause and
solved it. And then replace with specified
capacity fuse.
Capacity
verification
1-5
Page 11
1. GENERAL INFORMATION
To this chapter contents
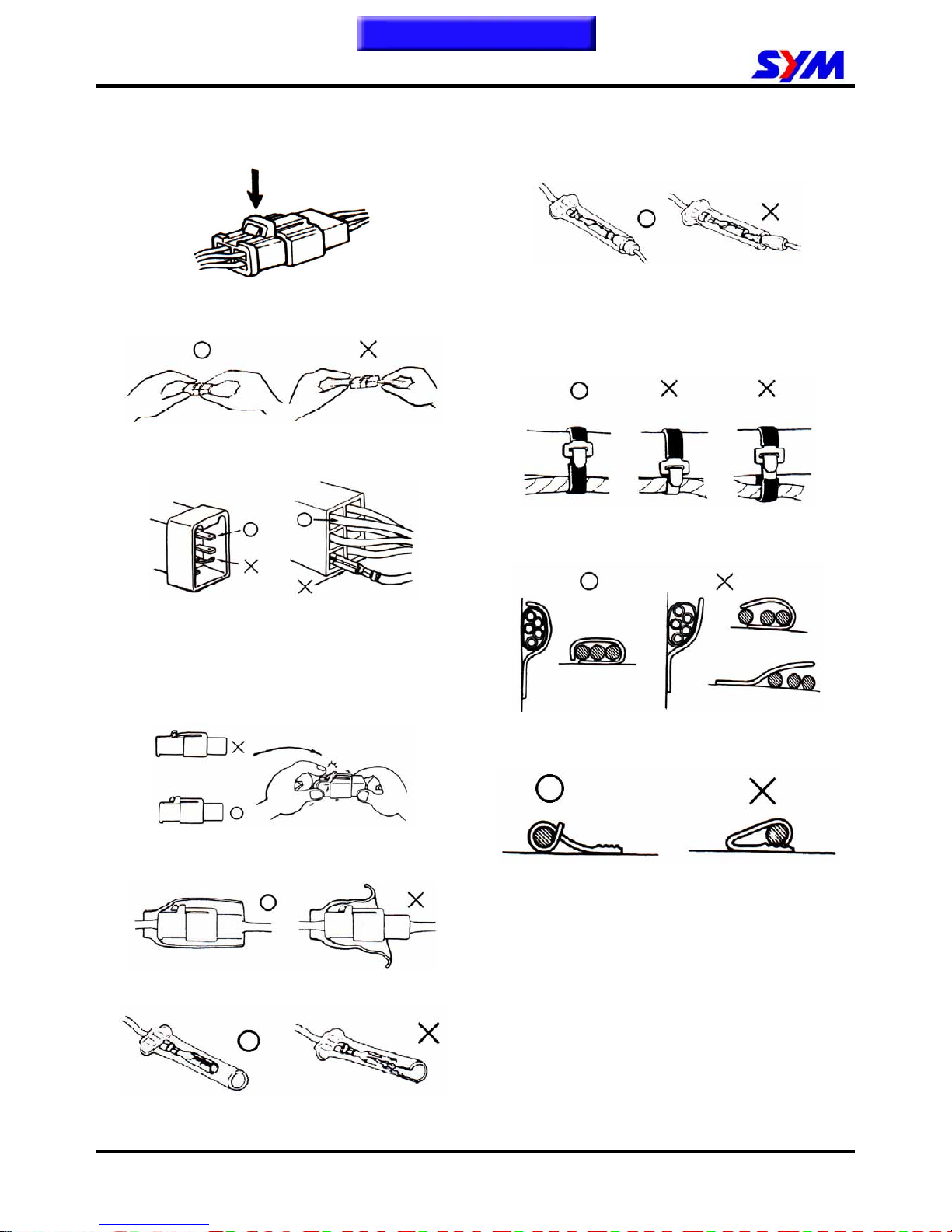
When separating a connector, it locker has to
be unlocked firstly. Then, conduct the service
operation.
Do not pull the wires as removing a connector
or wires. Hold the connector body.
Make sure if the connector pins are bent,
extruded or loosen.
Insert the connector completely.
If there are two lockers on two connector sides,
make sure the lockers are locked in properly.
Check if any wire loose.
Check if the connector is covered by the twin
connector boot completely and secured properly.
Before terminal connection, check if the boot is
crack or the terminal is loose.
Insert the terminal completely.
Check if the boot covers the terminal.
Do not let boot open facing up.
Secure wires and wire harnesses to the frame
with respective wire bands at the designated
locations. Tighten the bands so that only the
insulated surfaces contact the wires or wire
harnesses.
Wire band and wire harness have to be clamped
secured properly.
Do not squeeze wires against the weld or its
clamp.
1-6
Page 12
1. GENERAL INFORMATION
To this chapter contents
Do not let the wire harness contact with rotating,
moving or vibrating components as routing the
harness.
Keep wire harnesses far away from the hot
parts.
Route wire harnesses to avoid sharp edges or
corners and also avoid the projected ends of
bolts and screws.
Route harnesses so that they neither pull too
tight nor have excessive slack.
Protect wires or wire harnesses with electrical
tape or tube if they contact a sharp edge or
corner. Thoroughly clean the surface where
tape is to be applied.
Secure the rubber boot firmly as applying it on
wire harness.
Never Touch
Never use wires or harnesses which insulation
has been broken. Wrap electrical tape around
the damaged parts or replace them.
Never clamp or squeeze the wire harness as
installing other components.
Never clamp or
squeeze the wire
harness
Never too tight
1-7
Page 13

To this chapter contents
1. GENERAL INFORMATION
Do not let the wire harness been twisted as
installation.
Wire harnesses routed along the handlebar
should not be pulled too tight or have excessive
slack, be rubbed against or interfere with
adjacent or surrounding parts in all steering
positions.
Before operating a test instrument, operator
should read the operation manual of the
instrument. And then, conduct test in
accordance with the instruction.
With sand paper to clean rust on connector
pins/terminals if found. And then conduct
connection operation later.
Clean rust
Do you know how to set the
instrument to its
measurement position and
the insert locations of its
two probes?
1-8
Page 14
1. GENERAL INFORMATION
To this chapter contents
Specifications
MAKER SANYANG MODEL UA60A-6
Overall Length 2110 mm Front Double arm
Overall Width 1150 mm
Suspension
System
Rear Unit Swing
Overall Height 1220 mm Front AT25x8-12 (off road)
Wheel Base 1300 mm
Tire Specifications
Rear AT25x8-12 (off road)
Front 900 mm Rim Aluminum
Dimension
Wheel tread
Rear 895 mm Front Disk (ψ220mm)
Front 180 kg
Brake System
Rear Disk (ψ180mm)
Rear 165 kg Max. Speed Above 80 km/hr
Curb Weight
Total 345 kg
Performance
Climb Ability Below 25°
Passengers/Weight Two /150 kg
Front 215 kg
Primary
Reduction
Belt
Rear 280 kg
Weight
Total Weight
Total 495 kg
Secondary
Reduction
Gear / Sprocket
Type 4-Stroke Engine Clutch Centrifugal, dry type
Installation and
arrangement
Vertical, below center,
incline
Reduction
Transmission
C.V.T., auto speed
change
Fuel Used Above 92 unleaded Speedometer 0 ~ 100 km/hr
Cycle/Cooling 4-stroke/water cooled Horn 93~112 dB/A
Bore Ø92 mm Muffler
Expansion & Pulse
Type
Stroke 85 mm
Exhaust Pipe Position and
Direction
Left side, and
Backward
Cylinder
Number/Arrange
ment
Single Cylinder Lubrication System
Forced circulation &
splashing
Displacement 565cc Solid Particulate
Compression Ratio 10.2 CO Below 7.0 g/ km
Max. HP 20.4ps / 6000rpm HC Below 1.5g/ km
Max. Torque 3.6 Kg m / 2750rpm
Exhaust
Concentration
Nox Below 0.4g/ km
Ignition Full Transistor Ignition E.E.C. ―
Starting System Electrical Starter P.C.V. ―
Engine
Air filtration Sponge
Catalytic reaction control
system
―
1-9
Page 15

1. GENERAL INFORMATION
To this chapter contents
To this chapter contents
Torque Values
The torque values listed in above table are for more important tighten torque values. Please see standard
values for not listed in the table.
Standard Torque Values for Reference
Type Tighten Torque Type Tighten Torque
5 mm bolt、nut
0.45~0.6kgf-m 5 mm screw 0.35~0.5kgf-m
6 mm bolt、nut
0.8~1.2kgf-m
6 mm screw、SH nut
0.7~ 1.1kgf-m
8 mm bolt、nut
1.8~2.5kgf-m
6 mm bolt、nut
1.0 ~1.4kgf-m
10 mm bolt、nut
3.0~4.0kgf-m
8 mm bolt、nut
2.4 ~3.0kgf-m
12 mm bolt、nut
5.0~6.0kgf-m
10 mm bolt、nut
3.5~4.5kgf-m
Engine Torque Values
Item Q’ty Thread Dia. (mm) Torque Value(kgf-m) Remarks
Cylinder stud bolt 4 10 1.0~1.4
Cylinder head nut 4 8 3.6~4.0
Cylinder head right bolt 2 8 2.0~2.4
Cylinder head side cover bolt 2 6 1.0~1.4
Cylinder head cover bolt 4 6 1.0~1.4
Cylinder head stud bolt (inlet pipe) 2 6 1.0~1.4
Cylinder head stud bolt (EX. pipe) 2 8 2.4~3.0
Air inject pipe bolt 4 6 1.0~1.4
Air inject reed valve bolt 2 3 0.07~0.09
Tappet adjustment screw nut 4 5 0.7~1.1 Apply oil to thread
Spark plug 1 10 1.0~1.2
Tensioner lifter bolt 2 6 1.0~1.4
Carburetor insulator bolt 2 6 0.7~1.1
Oil pump screw 2 3 0.1~0.3
Water pump impeller 1 7 1.0~1.4
Engine left cover bolt 9 6 1.1~1.5
Engine oil draining bolt 1 12 3.5~4.5
Engine oil strainer cap 1 30 1.3~1.7
Mission draining bolt 1 8 1.1~1.5
Mission filling bolt 1 12 3.5~4.5
Shift drum fixing bolt 1 14 3.5~4.5
Clutch driving plate nut 1 28 5.0~6.0
Clutch outer nut 1 14 5.0~6.0
Drive face nut 1 14 8.5~10.5
ACG. Flywheel nut 1 14 5.0~6.0
Crankcase bolts 7 6 0.8~1.2
Mission case bolt 7 8 2.6~3.0
1-10
Page 16

1. GENERAL INFORMATION
To this chapter contents
Frame Torque Values
Item Q’ty Thread Dia. (mm) Torque Value(kgf-m) Remarks
Handlebar upper holder bolt
4 6 2.40
Steering shaft nut
1 10 5.00
Steering tie-rod nut
4 10 5.00
Knuckle nut
2 10 5.00
Steering shaft holder bolt
2 8 3.40
Tie rod lock nut
4 10 3.60
Handlebar under holder nut
2 8 4.00
Front wheel nut
8 10 2.40
Front axle castle nut
2 14 5.00
Rear axle castle nut
2 14 5.00
Rear wheel nut
8 10 2.40
Engine hanger nut
4 12 8.50
Rear axle holder bolt
4 12 9.20
Drive gear bolt
2 10 4.6
Driven gear nut
4 10 4.6
Swing arm pivot bolt
1 14 9.20
Front suspension arm nut 4 10 5.00
Front / Rear cushion mounting bolt 6 10 4.60
Brake lever nut
2 6 1.00
Brake hose bolt
13 10 3.50
Brake caliper bolt
6 6 3.25
Brake disk mounting bolt
11 8 4.25
Air-bleed valve
3 5 0.50
Exhaust muffler mounting bolt
2 8 3.00
Exhaust muffler connection nut
2 7 1.20
1-11
Page 17

To this chapter contents
1. GENERAL INFORMATION
Troubles Diagnosis
A. Engine hard to start or can not be started
Check and adjustment Fault condition Probable causes
Cylinder compression
pressure normal
Loosen carburetor drain bolt to
check if there is gasoline inside
the carburetor
Fuel supplied tom
carburetor sufficient
No fuel is supplied to
carburetor
Remove spark plug, install it
into spark plug cap, and perform
a spark test against engine
g
round.
Perform cylinder compression
pressure test.
Check if sparks Weak sparks, no spark at
all
Low compression
pressure or no pressure
Re-start by following the starting
procedures
No ignition
There are some signs of
ignition; nut engine can
Remove the spark plug again
and check it.
Remove carburetor after 30
minutes and connect a hose
onto fuel rich circuit. Then blow
the hose with air
Dry spark plug Wet spark plug
Blowing in normal Blowing clogged
No fuel in fuel tank
Check if the pipes, fuel tank to carburetor
and intake vacuum, are clogged.
Float valve clogged
Lines in fuel tank evaporation system
clogged
Malfunction of fuel pump
Loosen or damaged fuel pump vacuum
hose
Fuel filter clogged
Malfunction of spark plug
Spark plug foul
Malfunction of CDI set
Malfunction of AC generator
Ignition coil is in open or short circuit
Ignition coil leads open or short circuit
Malfunction of main switch
Piston ring seized
Malfunction of cylinder valves
Worn cylinder and piston ring
Cylinder gasket leak
Sand hole in compression parts
Malfunction of throttle valve operation
Air sucked into intake manifold
Incorrect ignition timing
Fuel level in carburetor too high
Malfunction of throttle valve operation
Throttle valve opening too wide
Malfunction of automatic by- starter
1-12
Page 18

To this chapter contents
1. GENERAL INFORMATION
B. Engine run sluggish (Speed does not pick up, lack of power)
Check and adjustment Fault condition Probable causes
Try gradual acceleration and
check engine speed
Engine speed can be
increased.
Engine speed cannot be
increased.
Check ignition timing (Using
ignition lamp)
Check cylinder compression
pressure (using compression
Ignition timing correct Incorrect ignition timing
Compression pressure
correct
No compression pressure
Check if carburetor jet is
clogged
No clogged
Clogged
Remove spark plug
Check if engine over heat
No foul or discoloration
Fouled and discoloration
No knock
Knock
Air cleaner clogged
Poor fuel supply
Lines in fuel tank evaporation system
clogged
Exhaust pipe clogged
Fuel nozzle clogged in carburetor.
Fuel nozzle clogged in carburetor.
Malfunction of CDI
Malfunction of AC alternator
Cylinder & piston ring worn out
Cylinder gasket leaked
Sand hole in compression parts
Valve deterioration
Seized piston ring
Remove foreign
Remove dirt
Incorrect spark plug heat range
Piston and cylinder worn out
Lean mixture
Poor fuel quality
Too much carbon deposited in
combustion chamber
Ignition timing too advanced
Poor circuit on the cooling system
Normal
Engine overheat
Continually drive in acceleration
or high speed
Too much carbon deposited in
combustion chamber
Lean mixture
Poor fuel quality
Ignition timing too advanced
1-13
Page 19

To this chapter contents
1. GENERAL INFORMATION
C. Engine runs sluggish (especially in low speed and idling)
Check and adjustment Fault condition Probable causes
D. Engine runs sluggish (High speed)
Check ignition timing (using
ignition lamp)
Check for fuel supplying system
in automatic fuel cup
Check if carburetor clogged
Incorrect ignition timing (malfunction of
CDI or AC alternator)
Rich mixture (loosen the screw)
Lean mixture (tighten the screw)
Poor heat insulation gasket
Carburetor lock loose
Poor intake gasket
Poor carburetor O-ring
Vacuum hose crack
Spark plug fouled
Malfunction of CDI
Malfunction of AC generator
Malfunction of ignition coil
Open or short circuit in spark plug leads
Malfunction of main switch
Insufficient fuel in fuel tank
Fuel filter clogged
Restricted fuel tank vent
Good
A
bnormal
Good spark Poor
No air sucked
A
ir sucked
Good Poor
Normal
A
bnormal
A
ir sucked through carburetor
gasket
A
djust the airscrew of
carburetor
No clogged Clogged
Cleaning
Remove spark plug, install
spark plug into spark plug cap
and perform spark test against
engine ground
Check and adjustment Fault condition
Probable causes
Check ignition timing
Malfunction of CDI
Malfunction of AC alternator
A
bnormal Normal
1-14
Page 20

To this chapter contents
1. GENERAL INFORMATION
E. Clutch, driving and driving pulley
Clutch weights spring broken
Clutch outer stuck with clutch weights
Connection parts in clutch and shaft worn out or burned
Engine can be started but
motorcycle can not be moved.
FAULT CONDITIONS
PROBABLE CAUSES
Drive belt worn out or deformation
Weight roller worn out
Movable drive face shaft worn out
Driven pulley spring deformation
Driven pulley shaft worn out
Greased in drive belt and driven face.
Poor initial driving (Poor climbing
performance)
Engine running and misfire as
motorcycle initial forward moving or
j
umping suddenly (rear wheel
rotating as engine in running)
Drive belt worn out or deformation
Ramp plate of movable drive face damaged
Driving pulley spring broken
Clutch weights broken
Drive slide-shaft gear groove broken
Transmission gear damaged
F. Poor handling
Steering is heavy
FAULT CONDITIONS
PROBABLE CAUSES
One wheel is wobbling
Vehicle pulls to one side
Bent rim
Improperly installed wheel hub
Excessive wheel bearing play
Bent swing arm
Bent frame
Swing arm pivot bushing excessively
Worn
Bent tie-rod
Incorrect tie-rod adjustment
Rear tie air pressure incorrect
Improper wheel alignment
Bent frame
Damaged steering bearing
Damaged steering shaft bushing
1-15
Page 21

To this chapter contents
1. GENERAL INFORMATION
G. Loss power
Check and adjustment Fault condition Probable causes
Raise wheels off ground and
spin by hand
Brake dragging
Drive chain too tight
Damaged wheel bearing
Wheel bearing needs lubrication
Spin freely
A
bnormal
Punctured tire
Faulty tire valve
Fuel / air mixture ratio too rich or lean
Clogged in air cleaner
Clogged in muffler
Restricted fuel flow
Clogged fuel tank cap breather hole
Faulty pulse generator
Faulty CDI unit
Leaking head gasket
Worn cylinder and piston rings
Clean
Clean the spark plug
Spark plug is incorrect heat range
Excessive carbon deposited in
combustion chamber
Wrong type of fuel
Fuel / air mixture ratio is lean
Use of poor quality fuel
Worn piston and cylinder
Fuel / air mixture ratio is lean
Wrong type of fuel
Ignition timing too advanced
Excessive carbon deposited in
combustion chamber
Check tire pressure
Normal
A
bnormal
A
ccelerate lightly, engine speed
can be increase
Normal
A
bnormal
Check ignition timing
Normal
A
bnormal
Test cylinder compression
Normal
A
bnormal
Check carburetor
Normal Clogged
Check spark plug
Normal Fouled or discolored
Check for engine overheating
Normal Overheating
A
ccelerate or run at high speed
Knocks Normal
1-16
Page 22

1. GENERAL INFORMATION
Lubrication Points
Acceleration cable/ Front & rear brake/ Lever Pivot
To this chapter contents
Wheel bearing
1-17
Page 23

2. MAINTENANCE INFORMATION
2-1
Precautions in Operation ···················· 2-1
Periodical Maintenance Schedule ······ 2-2
Fuel Lines············································· 2-3
Acceleration Operation ······················· 2-3
Air Cleaner············································ 2-3
Spark Plug ············································ 2-4
Valve Clearance ··································· 2-4
Carburetor Idle Speed Adjustment····· 2-5
Ignition System ···································· 2-6
Cylinder Compression Pressure ········ 2-6
Drive Belt·············································· 2-7
Propeller Shaft ····································· 2-7
Front Differential ·································· 2-8
Rear Axle Gearbox······························· 2-8
Brake System ······································· 2-9
Brake Light Switch······························· 2-10
Headlight Beam Distance ···················· 2-11
Clutch Disc Wear ································· 2-11
Cushion················································· 2-11
Steering Handle···································· 2-12
Wheel/Tire············································· 2-12
Nuts, Bolts Tightness ·························· 2-12
Special Tools List ································ 2-13
Precautions in Operation
Specification
Fuel Tank Capacity 12000 c.c.
Capacity 1400 c.c.
Engine Oil
Change 1200 c.c.
Capacity 1300 c.c.
Transmission Gear oil
Change 1200 c.c.
Engine + radiator 850 c.c.
Capacity of coolant
Reservoir upper 420 c.c.
Clearance of throttle valve 1~3 mm
Type NGK CR8E
Spark plug
Gap 0.8 mm
“F” Mark in idling speed BTDC 10º / 1700 rpm
Full timing advanced BTDC 27º / 4000 rpm
Idling speed 1700±100 rpm
Cylinder compression pressure 12.0 ±2 kgf/cm²
Valve clearance IN: 0.10 ± 0.02 mm EX: 0.15 ± 0.02 mm
Front AT22x7-10
Tire dimension
Rear AT22x10-9
Tire pressure (cold) 3.8±2 psi
Battery 12V10Ah (MF battery) type: GTX12-BS
Home page
Contents
2
Page 24

2. MAINTENANCE INFORMATION
2-2
Periodical Maintenance Schedule
Maintenance
Code
Item
Every
300KM
1 Month
Every
3 month
Every
6 month
Every
1 year
Every
15 month
Every
1 Air cleaner
I C R
2 Fuel filter
I I R
3 Oil filter
C C
4 Engine oil change
R Replacement for every 1000 km
5 Tire pressure
I I
6 Battery inspection
I I
7 Brake & free ply check
I I
8 Steering handle check
I I
9 Cushion operation check
I I
10 Every screw tightening check
I I
11 Gear oil check for leaking
I I
12 Spark plug check or change
I I R
13 Gear oil change
R Replacement for every 12000 km
14 Frame lubrication
L
15 Exhaust pipe
I I
16 Ignition timing
I I
17 emission check in Idling
A I
18 Throttle operation
I I
19 Engine bolt tightening
I I
20 CVT driving device(belt)
I R
21 CVT driving device(roller)
C
22 Drive chain
I / L I / L
C
23
Lights/electrical
equipment/multi-meters
I I
24 Fuel lines
I I
25 Cam chain
I I
26 Valve clearance
I A
27
Lines & connections in cooling
I I
28 Coolant reservoir
I I
29 Coolant
I I R
Code: I ~ Inspection, cleaning, and adjustment R ~ Replacement
C ~ Cleaning (replaced if necessary) L ~ Lubrication
Have your ATV checked, adjusted, and recorded maintenance data periodically by your SYM Authorized Dealer to
maintain the ATV at the optimum condition
The above maintenance schedule is established by taking the monthly 1000 kilometers as a reference which ever
comes first.
Remarks: 1. Clean or replace the air cleaner element more often when the ATV is operated on dusty roads or in
the Heavily- polluted environment.
2. Maintenance should be performed more often if the ATV is frequently operated in high speed and
after the ATV has accumulated a higher mileage.
3. Preventive maintenance
a. Ignition system-Perform maintenance and check when continuous abnormal ignition, misfire,
after-burn, overheating occur.
b. Carbon deposit removal-Remove carbon deposits in cylinder head, piston heads, exhaust system
when power is obvious lower.
To this chapter contents
Page 25

2. MAINTENANCE INFORMATION
2-3
Fuel Lines
Remove the seat.
Loosen 2 screws and 2 bolts
Remove the tank cover.
Check all lines, and replace the lines when they
are deteriorated, damaged or leaking.
Warning
Gasoline is a low ignition material so any kind of
fire is strictly prohibited as dealing it.
Acceleration Operation
Have a wide open of throttle valve as handle in
any position and release it to let back original (full
closed) position.
Check handle if its operation is smooth.
Check acceleration cable and replace it if
deteriorated, twisted or damaged.
Lubricate the cable if operation is not smooth.
Measure the throttle lever free play in its flange
part.
Remove rubber boot, loosen fixing nut, and then
adjust it by turning the adjusting screw.
Tighten the fixing nut, and check acceleration
operation condition.
Free play: 1~3 mm.
Air Cleaner
Remove the seat.
Loosen 5 hooks from the air cleaner cover and
then remove the cover.
Loosen the clamp strip and 1 screw of air cleaner
element, and then remove the air cleaner element.
Clean the element with non-flammable or
high-flash point solvent and then squeeze it for
dry.
Caution
Never use gasoline or acid organized solvent to
clean the element.
Soap the element into cleaning engine oil and then
squeeze it out. Install the element onto the
element seat and then install the air cleaner cover.
Fuel tank
Fuel hose
Fuel filter
To this chapter contents
Lock nut
Throttle adjustment screw
Element
Clamp
Fuel valve
Carburetor
Screw
Page 26
2. MAINTENANCE INFORMATION
2-4
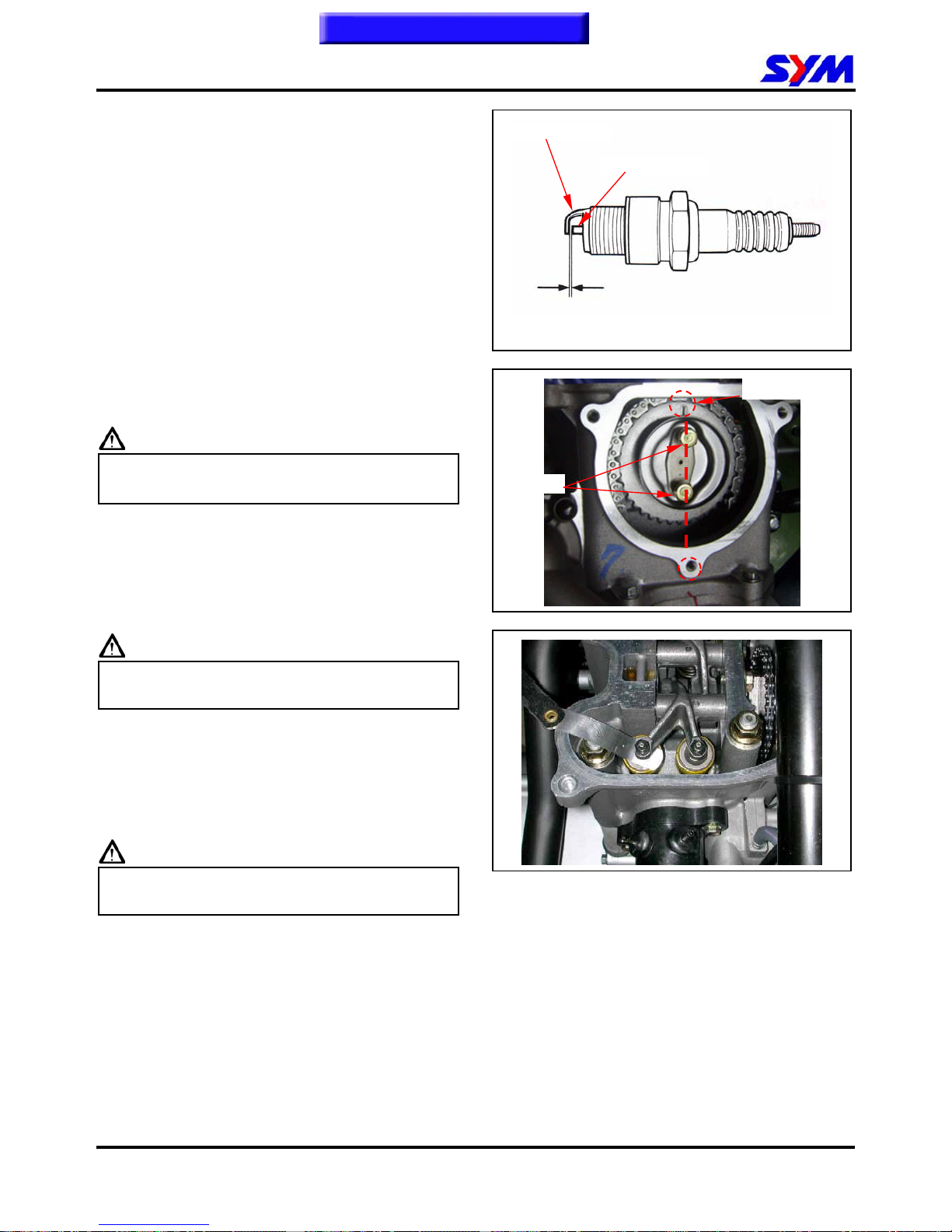
Spark Plug
Recommended spark plug: CR8E
Remove the spark plug cap.
Clean the dirt around the spark plug hole.
Remove the spark plug.
Measure the spark plug gap.
Spark plug gap:0.8 mm
Carefully bend ground electrode of the plug to
adjust the gap if necessary.
Hold the spark plug washer and install the spark
plug by screwing it.
Tighten the plug by turning 1/2 turn more with plug
socket after installed.
Tighten torque: 1.0~1.2kgf-m
Valve Clearance
Caution
Checks and adjustment must be performed when
the engine temperature is below 35℃.
Remove front fender, fuel tank cover and fuel tank.
Remove cylinder head cover.
Remove cylinder head side cover.
Turn camshaft bolt in C.W. direction and let the “T”
mark on the camshaft sprocket align with cylinder
head mark so that piston is placed at TDC position
in compression stroke.
Caution
Do not turn the bolt in C.C.W. direction to prevent
camshaft bolt looseness.
Valve clearance inspection and adjustment
Check & adjust valve clearance with feeler gauge.
Standard Value: IN 0.10 ± 0.02 mm
EX 0.15 ± 0.02 mm
Loosen fixing nut and turn the adjustment nut for
adjustment.
Caution
Re-check the valve clearance after tightened the
fixing nut.
To this chapter contents
2 bolts
Timing mark
0.8~0.9mm
Ground electrode
Central electrode
Page 27

2. MAINTENANCE INFORMATION
2-5
Carburetor Idle Speed Adjustment
Caution
Inspection & adjustment for idle speed have to
be performed after all parts in engine that
needed adjustment have been adjusted.
Idle speed check and adjustment have to be
done after engine being warmed up. (It is
enough that operates engine from stop to
running for 10 minutes.)
Park the ATV warm up engine.
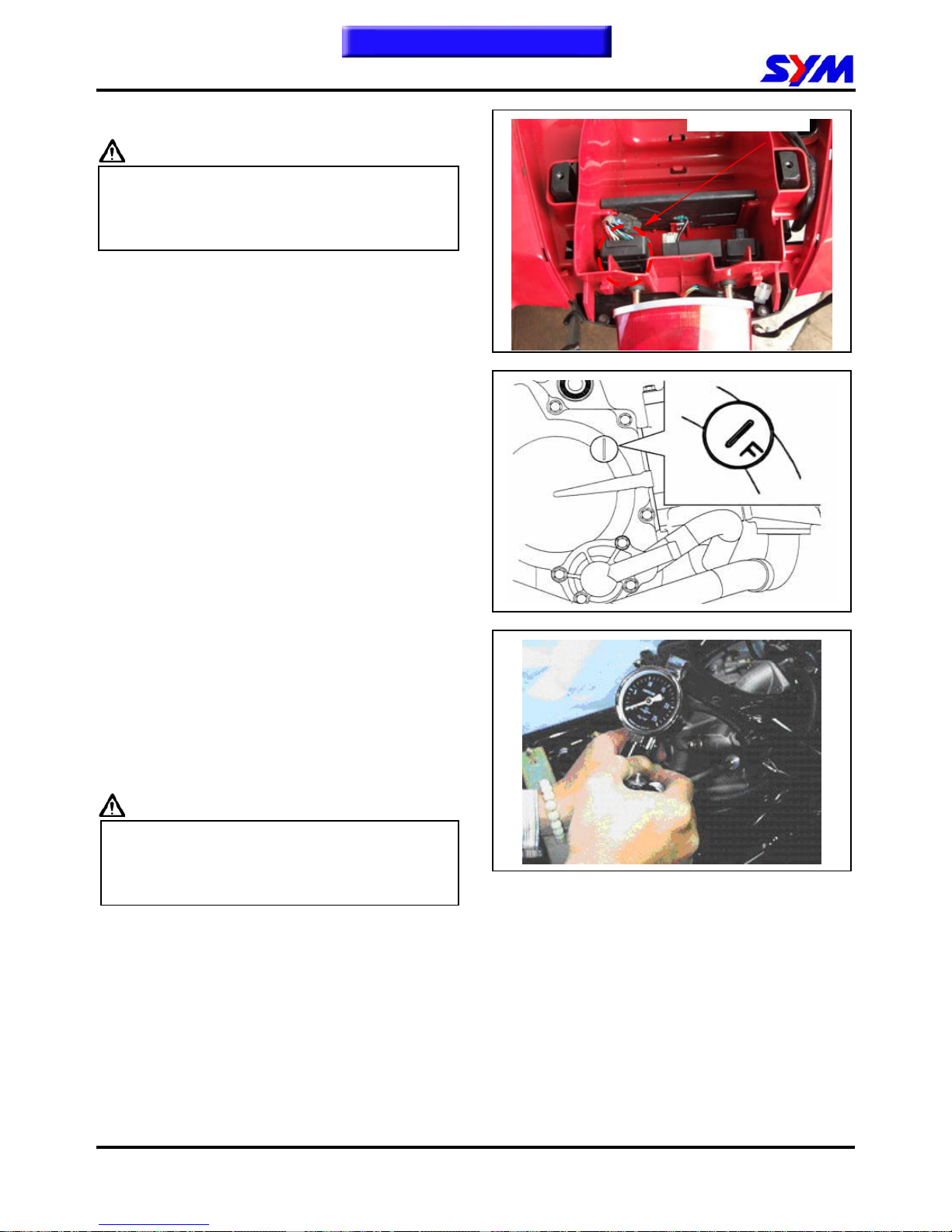
Connect tachometer (the wire clamp of tachometer
is connected to the high tension cable).
Turn the throttle valve stopper screw to specified
idle speed.
Specified idle speed: 1700 ± 100 rpm
Emission adjustment in idle speed
Warm up the engine for around 10 minutes and
then conduct this adjustment.
1. Connect the tachometer onto engine.
2. Adjust the throttle valve stopper screw and let
engine runs in 1600±100 rpm.
3. Insert the exhaust sampling pipe of exhaust
analyzer into the front section of exhaust pipe.
Adjust the air adjustment screw so that
emission value in idle speed is within standard.
4. Slightly accelerate the throttle valve and
release it immediately. Repeat this for 2~3
times.
5. Read engine RPM and value on the exhaust
analyzer. Repeat step 2 to step 4 procedures
until measured value within standard.
Emission standard CO: below 0,8~1.5%
HC: below 900ppm
Ignition coil
Idle speed adjust screw
To this chapter contents
Air/fuel adjusting screw
Page 28
2. MAINTENANCE INFORMATION
2-6
Ignition System
Caution
Full transistor ignition system is setup by the
manufacturer so it cannot be adjusted.
Ignition timing check procedure is for checking
whether ignition function is in normal or not.
Connect tachometer and ignition light.
Start engine.
As engine in idle speed: 1600 rpm, aim at the
mark “F” with the ignition light which means that
ignition timing is correct.
Increase engine speed to 6000 rpm to check
ignition advance degree. If indent is located within
the ignition advance degrees, it means that the
ignition advance degree is normal.
If ignition timing is incorrect, check the full
transistor ignition set, rotor and pulse generator.
Replace it if malfunction of these parts is found.
Cylinder Compression Pressure
Warm up engine.
Turn off the engine.
Remove the trunk.
Remove the central cover.
Remove spark plug cap and spark plug.
Install compression gauge.
Full open the throttle valve, and rotate the engine
by means of starter motor.
Caution
Rotate the engine until the reading in the gauge
no more increasing.
Usually, the highest-pressure reading will be
obtained in 4~7 seconds.
Compression pressure: 12 ± 2 Kg/cm²
Check following items if the pressure is too
low:
Incorrect valve clearance.
Valve leaking.
Cylinder head leaking, piston, piston ring and
cylinder worn out.
If the pressure is too high, it means carbon
deposits in combustion chamber or piston head.
To this chapter contents
Page 29
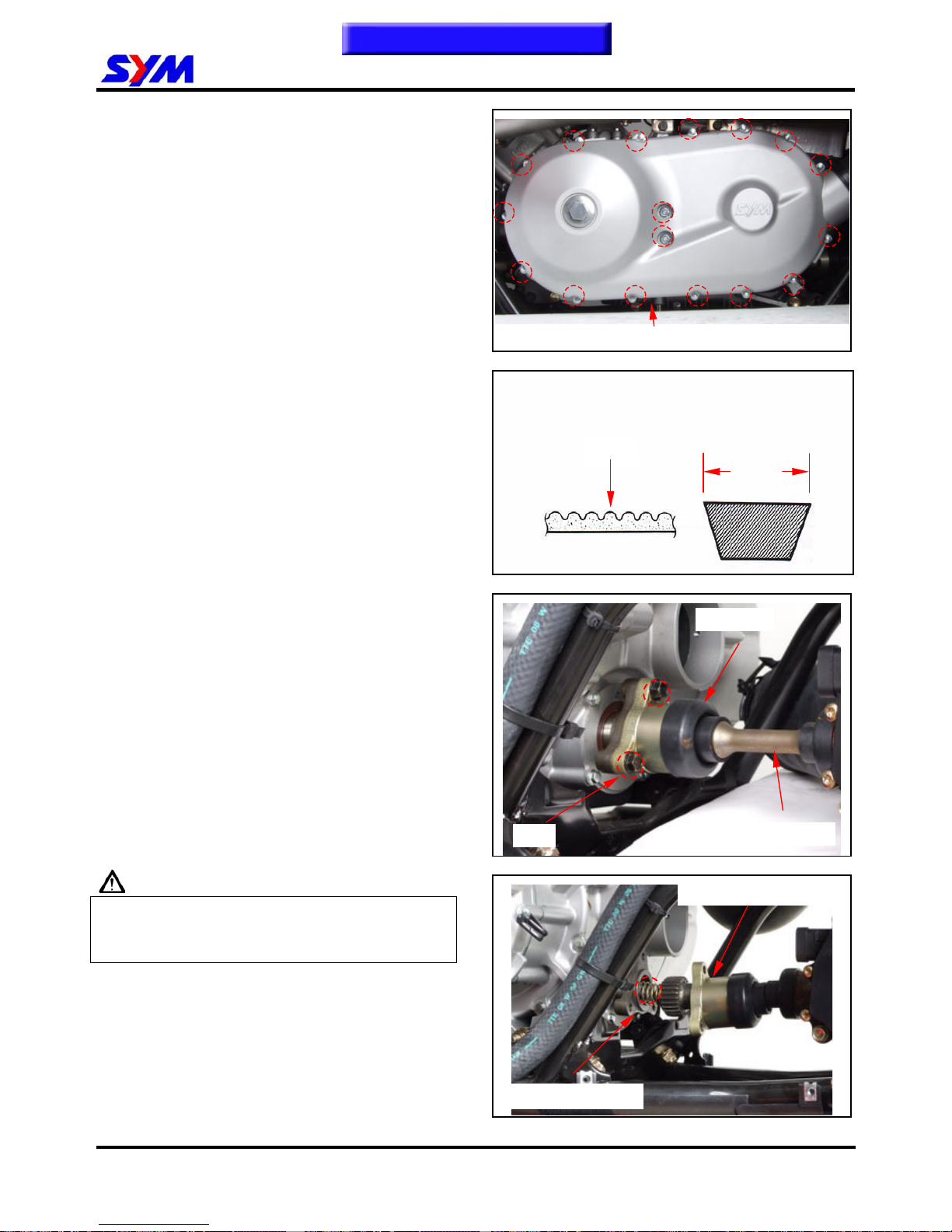
2. MAINTENANCE INFORMATION
2-7
Drive Belt
Loosen the 2 clamp strips of left crankcase cover,
and then remove the left crankcase cover
ventilation pipe.
Remove 17 bolts.
Remove the left crankcase cover.
Check if the belt is cracked or worn out.
Replace the belt if necessary or in accordance
with the periodical maintenance schedule to
replace it.
Width limit: 32.7 mm or above
Propeller Shaft
Remove 3 bolts from the propeller shaft connector.
Check the propeller shaft for any wear.
Check the rubber boots for any damage.
Caution
Don’t lose the propeller shaft spring.
Coat the propeller shaft gear with grease before
assembling the propeller shaft.
Teeth
Width
To this chapter contents
Propeller shaft spring
9 bolts
Propeller shaft connector
Front propeller shaft
3 bolts
Rubber boot
Page 30
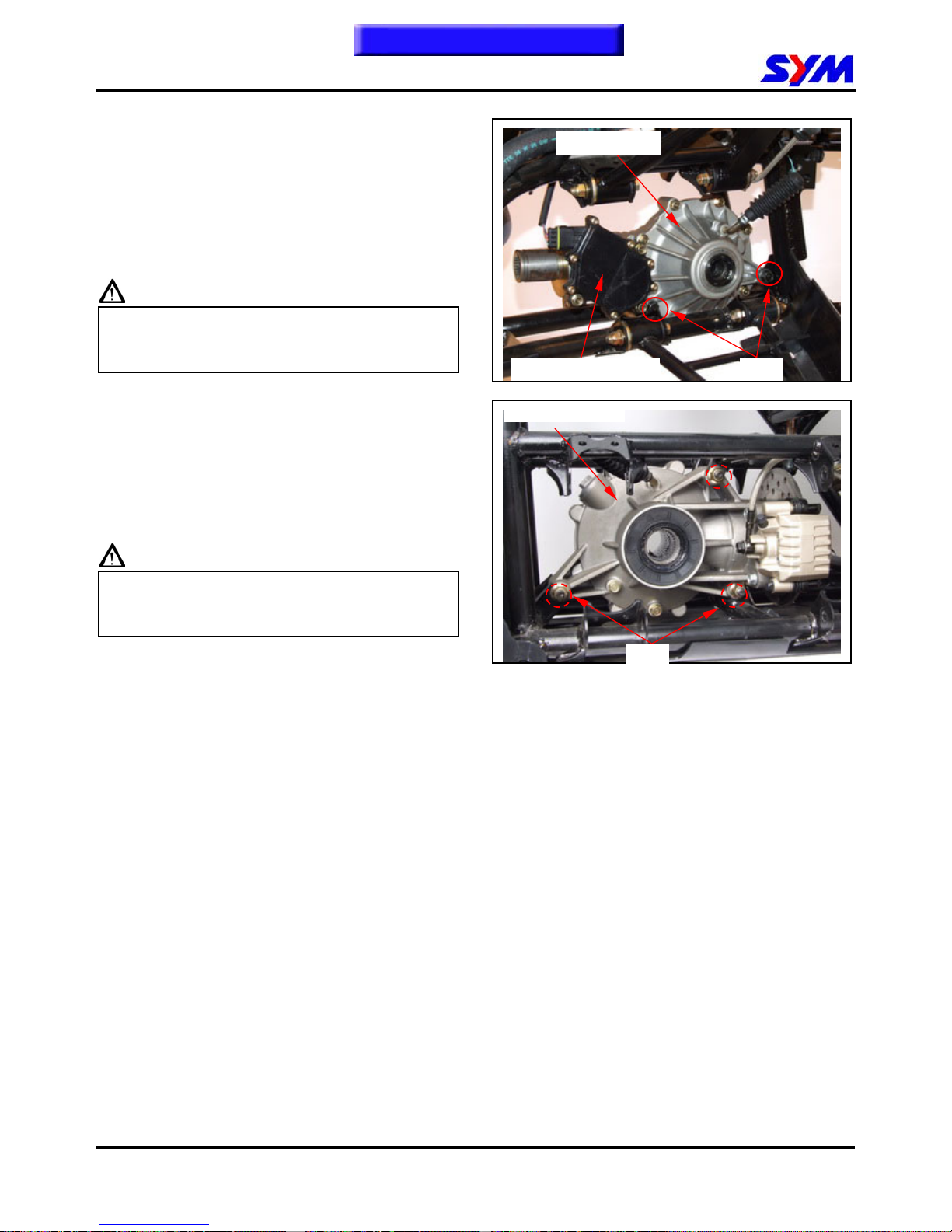
2. MAINTENANCE INFORMATION
2-8
Front Differential
Check the front differential for abnormal noise or
unsmooth rotation.
Caution
Do not attempt to disassemble the Front
Differential. Please exchange the whole
assembly if necessary.
Rear Axle Gearbox
Check the rear axle gearbox for abnormal noise or
unsmooth rotation.
Caution
Do not attempt to disassemble the Rear
Gear Box. Please exchange the whole
assembly if necessary.
2 bolts
Front differential
Differential control unit
3 bolts
Rear axle gearbox
To this chapter contents
Page 31

2. MAINTENANCE INFORMATION
2-9
Brake System
Brake System Hose
Check the brake hoses for corrosion or leaking oil.
Brake Fluid
Check brake fluid level in the brake fluid
reservoir. If the level is lower than the LOWER
limit, add brake fluid to UPPER limit. Also check
brake system for leaking if low brake level found
Caution
In order to maintain brake fluid in the reservoir
in horizontal position, do not remove the cap
until handle stop.
Do not operate the brake lever after the cap
had been removed. Otherwise, the brake fluid
will spread out if operated the lever.
Do not mix non-compatible brake fluid together.
Filling Out Brake Fluid
Tighten the drain valve, and add brake fluid.
Operate the brake lever so that brake fluid
contents inside the brake system hoses.
Air Bleed Operation
Connect a transparent hose to draining valve.
Hold the brake lever and open air bleeding valve.
Perform this operation alternative until there is no
air inside the brake system hoses.
Caution
Before closing the air bleed valve, do not release
the brake lever.
Added Brake Fluid
Add brake fluid to UPPER limit lever.
Recommended brake fluid: DOT3 or DOT4 WELL
RUN brake fluid.
Caution
Never mix or use dirty brake fluid to prevent from
damage brake system or reducing brake
performance.
To this chapter contents
Transparent hose
Air bubble
Drain valve
Screws
Diaphragm plate
Upper
Diaphragm
Master cylinder cap
Page 32

2. MAINTENANCE INFORMATION
2-10
Brake Lining Wear
The indent mark on brake lining is the wear
limitation.
Replace the brake lining if the wear limit mark
closed to the edge of brake disc.
Caution
To check front brake lining must be remove
front wheel first.
It is not necessary to remove brake hose when
replacing the brake lining.
Brake Lining Replacement (refer chapter
14)
Make sure the brake lining condition. Replace
the lining if the brake lining wear limitation groove
close to the brake disc.
Caution
Do not operate the brake lever after the clipper
removed to avoid clipping the brake lining.
In order to maintain brake power balance, the
brake lining must be replaced with one set.
Brake Light Switch
The brake light switch is to light up brake light as
brake applied.
Make sure that electrical starter can be operated
only under brake applying.
Brake lining wear
limitation groove
Rear brake
To this chapter contents
Lining
Brake disk
Brake lining wear
limitation groove
Front brake
Brake switch
Brake switch
Page 33

2. MAINTENANCE INFORMATION
2-11
Headlight Beam Distance
Turn on main switch.
Turn the headlight adjusting screw to adjust
headlight beam height.
Caution
To adjust the headlight beam follows related
regulations.
Improper headlight beam adjustment will
make in coming driver dazzled or insufficient
lighting.
Clutch Weight
Run the ATV and increase throttle valve opening
gradually to check the clutch operation.
If the ATV is in forward moving and shaking, check
clutch disc condition. Replace it
Cushion
Front cushion
Press down the front cushion for several times to
check it operation.
Check if it is damage
Replace relative parts if damage found.
Tighten all nuts and bolts.
Rear Cushion
Press down the rear cushion for several times to
check it operation.
Check if it is damage
Replace relative parts if damage found.
Warning
Do not ride the ATV with poor cushion.
Looseness, wear or damage cushion will make
poor stability and drive-ability.
Adj
ustingscrew
Clutch weight
To this chapter contents
Page 34

2. MAINTENANCE INFORMATION
2-12
Steering Handle
Caution
Check all wires and cables if they are interfered
with the rotation of steering handle bar.
Lift the front wheel off ground.
Turn handle from right to left alternative and check
if turning is smoothly.
If handle turning is uneven and bending, or the
handle can be operated in vertical direction, then
check the handle top bearing.
Wheel/Tire
Caution
Tire pressure check should be done as cold
engine.
Check if tire surface is ticked with nails, stones or
other materials.
Appointed tire pressure
Tire size Front tire Rear tire
Tire pressure as cold
3.8±2
psi
Check if front and rear tires’ pressure is normal.
Measure tire thread depth from tire central surface.
Replace the tire if the depth is not come with
following specification:
Front tire: 1.5 mm
Rear tire: 2.0 mm
Nuts, Bolts Tightness
Perform periodical maintenance in accordance
with the Periodical Maintenance Schedule.
Check if all bolts and nuts on the frame are
tightened securely.
Check all fixing pins, snap rings, hose clamp, and
wire holders for security.
To this chapter contents
Page 35

2. MAINTENANCE INFORMATION
2-13
Special Tools List
NAME
Rocker arm pin puller
NAME
Tappet adjusting wrench
NAME
Tappet adjusting wrench
NO SYM-1445100 NO SYM-9001200 NO SYM-1472100
NAME
Tappet adjuster
NAME
Valve cotter remove &
assembly tool
NAME
AC.G. Flywheel puller
NO SYM-2301000-HMA NO SYM-1471110/20 NO SYM-3110000-HMA
NAME
KNUCKLE BODY BRG.
6006 driver
NAME
Drive shaft puller
NAME
Driveshaft BRG. 6228 driver
NO
SYM-5024000-REA 6006
NO SYM-2341120-REA NO
SYM-2341110-REA 6228
NAME
BEVEL GEAR HOUSHING
BRG 6306 driver
NAME
WHEEL DRIVE SHAFT
BALL SET tool
NAME
Countershaft OIL SEAL
20*40*5
NO SYM-2343700-REA A6306 NO SYM-4423500-REA NO SYM-9121000-REA
To this chapter contents
Page 36

2. MAINTENANCE INFORMATION
2-14
NAME
NEEDLE BRG. 2220C driver
NAME MDF. Fixer NAME Final shaft gear stopper
NO SYM-9100400-REA 2220 NO
SYM-2211000-REA
NO
SYM-2343100-REA
NAME
Driveshaft BRG. 6328 driver
NAME
OUTPUT SHAFT OIL SEAL
42*52*7
NAME
OUTPUT SHAFT OIL SEAL
38*52*7
NO SYM-9100500-REA A6328 NO SYM-9120900-REA NO SYM-9120800-REA
(12*28*7)
(6901)
NAME Water pump oil seal driver NAME
WATER PUMP BRG. 6001
driver
NAME
Water pump mechanical seal
driver
NO SYM-9120200-REA NO SYM-6001300-REA A6001 NO SYM-1721700-H9A
NAME
CLUTCH COVER BRG. 6207
driver
NAME
R COVER OIL SEAL GUIDE
NAME Lock nut driver
NO SYM-9610000- REA A6207 NO SYM-1133000-REA NO SYM-9020100
To this chapter contents
Page 37

2. MAINTENANCE INFORMATION
2-15
NAME Inner bearing puller NAME Inner bearing puller NAME
Outer bearing puller
NO SYM-6204002 NO SYM-6204022 NO SYM-6204001
NAME Universal holder NAME Clutch nut wrench NAME Crankcase tool
NO SYM-2210100 NO SYM-9020200 NO SYM-1120000-ALL
(55mm)
(55mm)
NAME Rear axle nut wrench NAME
Torque wrench
NAME
Rear axle nut torque wrench
NO SYM-HT06007 NO SYM-HT07004-RA1 NO
SYM-4230200
NAME ARM SUSPENSION NAME
WHEEL KNUCKLE BODY
SEAL 40*55*8 driver
NAME
WHEEL KNUCKLE BODY
SEAL 40*50*6.5 driver
NO SYM-2300000 NO SYM-9123200-REA NO SYM-9123000-REA
To this chapter contents
Page 38

2. MAINTENANCE INFORMATION
2-16
NAME
MAIN BRG. UP/LWR
40*44*20 driver
NAME NAME
PULLEY DRIVEN FACE
41*44*4 OIL SEAL GUIDE
NO SYM-9100110-REA NO SYM-9100400 G5A ADA NO SYM-9121100-REA
NAME
ENG L COVER RADIAL BALL
BRG. 6006 driver
NAME
FINAL SHAFT BRG 6307
driver
NAME
PULLEY DRIVEN FACE
expander
NO SYM-9615010-REA 6006 NO SYM-2343110-REA 6307 NO SYM-2321000-REA
NAME
CLUTCH COVER 35*55*8
OIL SEAL
NAME
DRIVEN PULLEY
Disassemble tool
NAME
PULLEY DRIVEN FACE
SEAL COLLER tool
NO SYM-9120300-REA NO SYM-2301000-REA NO SYM-2323700-REA
NAME
R CASE PARK GEAR
CLIP GUIDE & installer
NAME
Driveshaft oil seal driver
NAME
OUTPUT SHAFT BRG
6307 driver
NO SYM-9060200-REA NO SYM-9120600-REA NO SYM-2346000-REA A6307
To this chapter contents
Page 39

2. MAINTENANCE INFORMATION
2-17
NAME
MAIN BRG. UP/LWR
40*44*20 assemble tool
NAME
L COVER FR. BRG. 6302
driver
NAME Drive plate fixer
NO SYM-9100100-REA NO SYM-9615000-REA 6302 NO
SYM-2230000-REA
NAME
NAME
NAME
NO NO NO
NAME NAME NAME
NO NO NO
NAME
NAME
NAME
NO NO NO
To this chapter contents
Page 40

Home page
3. LUBRICATION SYSTEM
Contents
Mechanism Diagram·································3-1
Precautions in Operation ·························3-3
Troubleshooting ·······································3-3
Engine Oil··················································3-4
Engine Oil Strainer Clean·························3-4
Oil Filter Unit ·············································3-5
Oil Pump ····················································3-6
Mechanism Diagram
3
3-1
Page 41

To this chapter contents
3. LUBRICATION SYSTEM
Cam Shaft
Spray Lubrication
Spray Lubrication
Press-In Lubrication
Con-Rod
Oil Route
Valve Rocker Arm
Oil Route
3-2
Page 42

To this chapter contents
3. LUBRICATION SYSTEM
Precautions in Operation
General Information:
This chapter contains maintenance operation
for the engine oil pump and gear oil
replacement.
Specifications
Engine oil capacity Disassembly: 3000 c.c.
Replacement: 2400 c.c.
Replacement with oil filter replaced: 2700 c.c.
Oil viscosity SAE 10W-30 (Recommended
King serial oils)
Rear axle gear oil replacement: 100c.c.
Front differential gear oil replacement: 200c.c.
Gear oil viscosity SAE 80 or 90
(Recommended SYM Hypoid gear oil)
Items Standard (mm) Limit (mm)
Inner rotor clearance 0.15 0.20
Clearance between outer rotor and body 0.15~0.20 0.25
Oil pump
Clearance between rotor side and body 0.04~0.09 0.12
Torque value
Torque value oil strainer cap 1.3~1.7kgf-m
Engine oil drain bolt 3.5~4.5kgf-m
Gear oil drain bolt 1.1~1.5kgf-m
Gear oil join bolt 3.5~4.5kgf-m
Oil pump connection screw 0.1~0.3kgf-m
Troubleshooting
Low engine oil level
Oil leaking
Valve guide or seat worn out
Piston ring worn out
Low oil pressure
Low engine oil level
Clogged in oil strainer, circuits or pipes
Oil pump damage
Dirty oil
No oil change periodically
Cylinder head gasket damage
Piston ring worn out
3-3
Page 43

To this chapter contents
3. LUBRICATION SYSTEM
Engine Oil
Turn off engine, and park the ATV in flat surface.
Check oil level with oil dipstick.
Do not screw the dipstick into engine as
checking.
If oil level is nearly low level, fill out
recommended oil to upper level.
Oil Change
Caution
Drain oil as engine warmed up so that makes
sure oil can be drained smoothly and completely.
Place an oil pan under the ATV, and remove oil
drain bolt.
After drained, make sure washer can be re-used.
Install oil drain bolt.
Torque value:3.5~4.5kgf-m
Engine Oil Strainer Clean
Drain engine oil out.
Remove the oil strainer and spring.
Clean the oil strainer.
Check if the `O-ring can be re-used.
Install oil strainer and spring.
Install oil strainer cap.
Torque value:1.3~1.7kgf-m
Refill oil to crankcase (oil viscosity SAE 10W-30)
Recommended using King serial oil.
Engine oil capacity: 2400c.c. when replacing
Install dipstick, start the engine for running
several minutes.
Turn off engine, and check oil level again.
Check if engine oil leaks.
Drain bolt
Oil strainer cap
Oil strainer
3-4
Page 44

To this chapter contents
3. LUBRICATION SYSTEM
3-5
Oil Filter Unit
Remove the oil filter unit with special tool.
Special Service Tool:
Tool No: SYM-1445100
Install the oil filter unit by hand.
Lock the oil filter unit with special tool.
Special Service Tool:
Tool No: SYM-1445100
Torque value:1.3~1.7kgf-m
Drain bolt
Page 45

To this chapter contents
3. LUBRICATION SYSTEM
3-6
Oil Pump
Oil Pump Removal
Remove the recoil starter and the AC Generator.
(Refer to chapter 10) 。
Remove the cir clip and take out the oil pump
sprocket.
Make sure that pump shaft can be rotated freely.
Remove 3 screws on the oil pump, and then
remove the oil pump.
Oil Pump Disassembly
Remove the screws on oil pump cover and
remove the cover.
Remove the oil pump shaft roller and shaft.
Cir Clip
3 screws
1 screw
Roller Pin
Page 46

3. LUBRICATION SYSTEM
Oil Pump Inspection
Check the clearance between oil pump body and
outer rotor.
Limit: 0.25 mm
Check clearance between inner and outer rotors.
Limit: 0.20 mm
Check clearance between rotor side face and
pump body
Limit: 0.12 mm
Oil Pump Re-assembly
Install the inner and outer rotors into the pump
body.
Align the indent on driving shaft with that of inner
rotor.
Install the oil pump shaft and roller.
Install the oil pump cover and fixing pins properly.
Pins
To this chapter contents
3-7
Page 47

To this chapter contents
3. LUBRICATION SYSTEM
3-8
Tighten the oil pump screw.
Oil Pump Installation
Install the oil pump, and then tighten screws.
Torque value:0.1~0.3kgf-m
Make sure that oil pump shaft can be rotated
freely.
Install the oil pump sprocket, and then install cir
clip onto oil pump shaft.
1 screw
Roller
3 screws
Cir Clip
Page 48

To this chapter contents
3. LUBRICATION SYSTEM
Notes:
3-9
Page 49

Home page
Contents
4. FUEL SYSTEM
`
Vacuum Chamber ............................. 4-6
Float Chamber................................... 4-7
Adjustment of Idle Speed................. 4-9
Fuel Tank........................................... 4-10
Air Cleaner ........................................ 4-11
Mechanism Diagram ......................... 4-1
Precautions in Operation ................. 4-2
Trouble Diagnosis............................. 4-3
Carburetor Removal / Installation.... 4-4
Air Cut-off Valve................................ 4-5
Mechanism Diagram
UA60A-6
Fuel tank
Carburetor
Fuel valve
Fuel Strainer
4
Fuel tank cap
4-1
Page 50

4. FUEL SYSTEM
To this chapter contents
Precautions in Operation
General Information
Warning
Gasoline is a low ignition point and explosive materials, so always work in a well-ventilated place and
strictly prohibit flame when working with gasoline.
Cautions
Do not bend off throttle cable. Damaged throttle cable will make unstable drive-ability.
When disassembling fuel system parts, pay attention to O-ring position, replace with new one as
re-assembly
There is a drain screw in the float chamber for draining residual gasoline.
Do not disassemble air cut valve arbitrarily.
Specification
ITEM UA60A-6
Carburetor diameter 35 mm
I.D. number AG8
Fuel level 17 mm
Main injector #132
Idle injector #92
Idle speed 1700±100 rpm
Throttle handle clearance 1~3
Pilot screw 1 1/2
Tool
Special service tools
Vacuum/air pressure pump
Fuel level gauge
4-2
Page 51

To this chapter contents
4. FUEL SYSTEM
Trouble Diagnosis
Poor engine start
No fuel in fuel tank
Clogged fuel tube
Too much fuel in cylinder
No spark from spark plug(malfunction of ignition
system )
Clogged air cleaner
Malfunction of carburetor chock
Malfunction of throttle operation
Stall after started
Malfunction of carburetor chock
Incorrect ignition timing
Malfunction of carburetor
Dirty engine oil
Air existing in intake system
Incorrect idle speed
Rough idle
Malfunction of ignition system
Incorrect idle speed
Malfunction of carburetor
Dirty fuel
Intermittently misfire as acceleration
Malfunction of ignition system
Late ignition timing
Malfunction of ignition system
Malfunction of carburetor
Power insufficiency and fuel consuming
Fuel system clogged
Malfunction of ignition system
Mixture too lean
Clogged fuel injector
Vacuum piston stick and closed
Malfunction of float valve
Fuel level too low in float chamber
Clogged fuel tank cap vent
Clogged fuel filter
Obstructed fuel pipe
Clogged air vent hose
Air existing in intake system
Mixture too rich
Clogged air injector
Malfunction of float valve
Fuel level too high in float chamber
Malfunction of carburetor chock
Dirty air cleaner
4-3
Page 52

4. FUEL SYSTEM
To this chapter contents
Carburetor Removal / Installation
Removal
Remove the fuel tank.
Turn the fuel valve lever on off.
Remove 1 screw from throttle lever cap them
remove throttle lever cap.
Loosen throttle cable adjustment nut and remove
throttle cable
Remove the sleep adjustment wire.
Disconnect the fuel hose and by-starter and drain
tube
Release 2 clamps strip of air cleaner and inner
pipe.
Remove the carburetor.
Installation
Install in reverse order of removal procedures.
throttle cable
adjustment wire
By-starter
1 screw
Drain tube
Fuel hose
2 clamps
adjustment nut
4-4
Page 53

To this chapter contents
4. FUEL SYSTEM
4-5
Air Cut-Off Valve
Disassembly
Remove 2 screws.
Remove air cut-off valve cover, spring and valve.
Inspection
Check the valve is in normal.
If the valve is in normal, it will restrict air-flow.
If air-flow is no restricting, replace carburetor
assembly.
Check the vacuum pipe o-ring is in normal.
Assembly
Install in reverse order of removal procedures.
2 screws
O-ring
Air cut-off valve
Spring
Cover
Page 54

4. FUEL SYSTEM
To this chapter contents
Vacuum Chamber
Disassembly
Removal
Loosen drain screw, and drain out residual fuel in
float chamber.
Remove screws (4 screws) of vacuum chamber
cover and the cover.
Remove compress spring and vacuum piston.
.
Remove fuel needle seat, spring, and injector
needle.
Check if the vacuum piston for wear out, crack or
other damage.
Check if the diaphragm for damage or crack.
Cautions
vacuum chamber cover
Spring
Do not damage vacuum diaphragm.
needle
seat
needle
Spring
vacuum
piston
4 bolts
4-6
Page 55

To this chapter contents
4. FUEL SYSTEM
4-7
Float Chamber
Disassembly
Remove 4 mounting screws and remove float
chamber cover.
Remove the float pin, float and float valve.
Inspection
Check float valve and valve seat for damage,
blocking.
Check float valve for wearing, and check valve
seat face for wear, dirt.
Caution
In case of worn out or dirt, the float valve and
valve seat will not tightly close causing fuel level
to increase and as a result, fuel flooding. A worn
out or dirty float valve must be replaced with a
new a new one.
Float
PinFloat valve
Check for wear or damage
4 Screws
Pin
Float valve
Float
Page 56

To this chapter contents
4. FUEL SYSTEM
Remove main jet, needle jet holder, needle jet,
slow jet and air adjustment screw.
Caution
Take care not to damage jets and adjust screw.
Before removing adjustment screw, turn it all
the way down and note the number of turns.
Does not turn adjust screw forcefully to avoid
damaging valve seat face.
Clean jets with cleaning fluid. Then use
compressed air to blow the dirt off.
Blow carburetor body passages with compressed
air.
Assembly
Install main jet, needle jet holder, needle jet, slow
jet and air adjustment screw.
Caution
Set the air adjustment screw in according to
number of turns noted before it was removed.
Install the float valve, float, and float pin.
Checking fuel level
Caution
Check again to ensure float valve, float for
proper installation.
To ensure correct measurement, position the
float meter in such a way so that float chamber
face is vertical to the main jet.
Fuel level: 14.8mm
Installation of carburetor
Install carburetor in the reverse order of removal.
Following adjustments must be made after
installation.
˙Throttle cable adjustment.
˙Idle adjustment
Air adjustment screw
Float gauge
Needle jet Needle jet holder
Slow jet
Main jet
Lock nut
Rubbe
Throttle adjustment screw
4-8
Page 57

To this chapter contents
4. FUEL SYSTEM
4-9
Adjustment of Idle Speed
Caution
Air screw was set at factory, so no adjustment is
needed. Note the number of turns it takes to
screw it all the way in for ease of installation.
The parking brake must be used to stop the ATV
to perform the adjustments.
Use a tachometer when adjusting engine RPM.
Screw in air adjustment screw gently, then back up
to standard turns.
Standard turns: 2 turns
Warm up engine; adjust the throttle stopper wire of
throttle valve to standard RPM.
Idle speed rpm: 1700 ± 100 rpm
Connect the hose of exhaust analyzer to exhaust
front end. Press test key on the analyzer.
Adjust the pilot screw and read CO reading on the
analyzer
CO standard value: 0.5~1.0 %
Accelerate in gradual increments; make sure rpm
and CO value are in standard value after engine
running in stable. If rpm and CO value fluctuated,
repeat the procedures described above for
adjusting to standard value.
Air adjustment screw
Parking brake
Throttle valve stopper wire
Page 58

To this chapter contents
4. FUEL SYSTEM
4-10
Fuel Tank
Fuel tank removal
Open the seat.
Remove the front cover and front top center cover.
Remove the side covers and lower side covers.
Remove the front fender.
Remove fuel unit wire from tank.
(Covers remove please
refer chapter 13)
remove 2 fuel tubes from fuel valve.
Remove 4 bolts from tank rear side & front side
and then remove fuel tank.
.
Installation
Install the tank in the reverse order of removal.
Fuel unit
4 bolts
Fuel tube
FRONT REAR
Page 59

To this chapter contents
4. FUEL SYSTEM
4-11
Air Cleaner
Removal
Loosen the clamp strip of air cleaner and
carburetor, and then remove the vapor hose.
Loosen the clamp strip of air cleaner, and then
remove the air cleaner vapor hose.
Remove the air cleaner (4 bolts).
Installation
Install the tank in the reverse order of removal.
Cleaning air cleaner element
Remove the air cleaner cover (5 catch hooks).
Remove element mounting screw.
Loosen the clamp strip of air cleaner element.
Clamp
4 bolts
Clamp
Clamp
5 Catch hooks
Page 60

4. FUEL SYSTEM
To this chapter contents
Remove the air cleaner element.
Clean the element with non-flammable or
high-flash point solvent and then squeeze it for
dry.
Caution
Never use gasoline or acid organized solvent to
clean the element.
Soap the element into cleaning engine oil and then
squeeze it out. Install the element onto the
element seat and then install the air cleaner cover.
Element
4-12
Page 61

To this chapter contents
4. FUEL SYSTEM
4-13
Notes:
Page 62

Contents
Home page
5. ENGINE REMOVAL
Precautions in Operation...................... 5-1
Engine Removal .................................... 5-2
Engine Installation ................................ 5-6
Precautions in Operation
General Information
The engine has to be supported with special service tools that can be lifted or adjustable.
The following parts can be serviced as engine being mounted on frame:
Carburetor
Drive pulley, drive belt, clutch, and movable drive face assembly.
Start motor.
AC. Generator, oil pump and start one-way clutch.
Specification
Item Capacity
Replacement 2400 c.c.
Replacement with oil filter changed 2700 c.c.
Engine oil capacity
Disassembly 3000 c.c.
Rear axle gear oil capacity Replacement 100 c.c.
Front differential gear oil capacity Replacement 200 c.c.
Engine & radiator 1980 c.c.
Reservoir 420 c.c.
Coolant capacity
Total 2400 c.c.
5
Torque Value
Engine hanger bolt 7.5~9.5kgf-m
Exhaust muffler mounting bolt 2.8~3.2kgf-m
Exhaust muffler connection nut 1.0~1.4kgf-m
5-1
Page 63

To this chapter contents
5. ENGINE REMOVAL
Engine Removal
Negative
Remove the seat.
Positive
Remove the battery negative terminal (-).
Remove the battery positive (+) terminal.
Remove front fender and the footrest (refer
chapter 13).
Remove the starter motor wire.
Remove the spark plug cap.
Disconnect A.C. Generator wire couplers.
Spark plug cap
A.C.G wire couplers
Starter motor wire
5-2
Page 64

5. ENGINE REMOVAL
To this chapter contents
Remove the front left and rear left tires.
Remove the idle speed adjustment nut.
Remove 2 bolt on the muffler.
Remove the muffler.
Remove the throttle cable.
Remove 2 nuts and 1 bolt.
Remove the exhaust pipe.
Remove the choke cable and ventilation tube.
Remove 2 nuts, and then remove exhaust pipe.
Idle speed adjustment nut
Throttle cable
Choke cable
Ventilation tube
5-3
Page 65

To this chapter contents
5. ENGINE REMOVAL
5-4
Remove 2 manifold clamps.
Remove the carburetor.
Remove 4 bolts.
Remove the air cleaner.
Remove 2 bolts.
Remove the muffler.
Remove 2 nuts and 1 bolt.
Remove the exhaust pipe.
Manifold clamps
4 bolts
2 bolts
2 nuts
Bolt
Page 66

5. ENGINE REMOVAL
To this chapter contents
Remove the coolant drain bolt and drain out
coolant.
Remove the coolant inlet pipe from the water
pump cover and the outlet pipe from the
thermostat cover.
Remove the PCV pipe.
Remove 2 bolts.
Remove the starter motor.
Remove 3 bolts on the front propeller shaft
connector.
Remove the front propeller shaft.
Remove 3 bolts on the rear propeller shaft
connector.
Remove the rear propeller shaft.
Be careful not to do any damage to the rubber
boot.
PCV pipe
Coolant pipe
Starter motor
Rubber boot
2 bolts
3 bolts
3 bolts
Rubber boot
5-5
Page 67

To this chapter contents
5. ENGINE REMOVAL
5-6
Remove the rear brake pedal.
Remove the coolant reserve tank.
Remove the front and rear side engine hanger
mounting nuts and bolts.
Remove left side engine hanger, and then remove
engine by left side.
Engine Installation
Check the bush of engine hanger parts for any
damage.
Install the engine in the reverse procedures of
removal.
Caution
Be careful when removing and installing the
engine.
Do not bend or twist the wires and tubes.
Cables wires have to be routed in accordance
with normal layout.
Engine hanger Bolt:
Torque value: 7.5~9.5kgf-m
3 bolts
2 bolts
Engine hanger
Page 68

6. CYLINDER HEAD/VALVE
6-1
Mechanism Diagram ··························· 6-1
Precautions in Operation ··················· 6-2
Troubleshooting·································· 6-3
Cylinder Head Removal······················ 6-4
Cylinder Head Inspection··················· 6-7
Valve Stem Replacement··················· 6-10
Valve Seat Inspection and Service ··· 6-11
Cylinder Head Reassembly··············· 6-13
Cylinder Head Installation················· 6-14
Valve Clearance Adjustment············· 6-16
Mechanism Diagram
6
0.7~1.1kgf-m
1.0~1.4kgf-m
1.0~1.4kgf-m
1.0~1.2kgf-m
3.6~4.0kgf-m
Home page
Contents
2.4~3.0kgf-m
1.0~1.4kgf-m
1.0~1.4kgf-m
1.0~1.4kgf-m
1.0~1.2kgf-m
Page 69

6. CYLINDER HEAD/VALVE
6-2
Precautions in Operation
General Information
This chapter is contained maintenance and service for cylinder head, valve, and camshaft as well as
rocker arm.
Cylinder head service can be carried out when engine is in frame.
Specification
Item Standard Limit
Compression pressure 12±2 kg/cm2 ---
Intake 36.478 36.458
Camshaft Height of cam lobe
Exhaust 36.847 36.832
ID of valve rocker arm 13.000~13.018 13.098
Rocker arm
OD of valve rocker arm shaft 12.991~13.009 11.936
Intake 4.975~4.990 4.900
OD of valve stem
Exhaust 4.955~4.970 4.900
ID of valve guide 5.000~5.012 5.030
Intake 0.010~0.037 0.080
Clearance between
valve stem and guide
Exhaust 0.025~0.062 0.100
Inner 33.700 30.100
Free length of valve
spring
outer 38.800 35.200
Valve seat width 1.600 ---
Intake 0.10±0.02mm ---
Valve
Valve clearance
Exhaust 0.15±0.02mm ---
Tilt angle of cylinder head --- 0.050
Torque Value
Cylinder head cover bolt 1.0~1.4kgf-m
Exhaust pipe stud bolt 2.4~3.0kgf-m
Cylinder head bolt 1.0~1.4kgf-m
Cylinder head Nut 3.6~4.0kgf-m
Sealing bolt of cam chain auto-tensioner 0.8~1.2kgf-m
Bolt of cam chain auto-tensioner 1.2~1.6kgf-m
Cylinder side cover bolt 1.0~1.4kgf-m
Cam sprocket bolt 1.0~1.4kgf-m
Tappet adjustment screw nut 0.7~1.1kgf-m
Spark plug 1.0~1.2kgf-m
Tools
Special service tools
Valve reamer: 5.0mm
Valve guide driver: 5.0mm
Valve spring compressor
To this chapter contents
Page 70

6. CYLINDER HEAD/VALVE
6-3
Troubleshooting
Engine performance will be affected by troubles on engine top parts. The trouble usually can be
determined or by performing cylinder compression test and judging the abnormal noise generated.
Low compression pressure
1. Valve
Improper valve adjustment
Burnt or bent valve
Improper valve timing
Valve spring damage
Valve carbon deposit.
2. Cylinder head
Cylinder head gasket leaking or damage
Tilt or crack cylinder
3. Piston
Piston ring worn out.
High compression pressure
Too much carbon deposit on combustion chamber or piston head
Noise
Improper valve clearance adjustment
Burnt valve or damaged valve spring
Camshaft wear out or damage
Chain wear out or looseness
Auto-tensioner wear out or damage
Camshaft sprocket
Rocker arm or rocker arm shaft wear out
To this chapter contents
Page 71

6. CYLINDER HEAD/VALVE
6-4
Cylinder Head Removal
Remove the engine from the frame. (Refer to
chapter 5)
Remove the inlet pipe (2 nuts).
Remove 2 thermostat bolts and then remove the
thermostat.
Remove the bolt and spring of the cam chain
tensioner.
Loosen 2 bolts, and then remove tensioner.
Remove thermostat (2 bolts).
Remove Air Injection system (AI) pipe mounting
bolts.
Remove the spark plug.
Loosen 4 bolts from the head cover then remove
head cover.
2 nuts
4 bolts
Tensioner bolts
Thermostat bolts
4 bolts
To this chapter contents
Page 72

6. CYLINDER HEAD/VALVE
6-5
Remove the side cover mounting blots of cylinder
head, and then remove the side cover.
Remove left crankcase cover, and turn the drive
face.
Align the timing mark on the cam sprocket with
that of cylinder head to make the piston at TDC
position.
Loosen 2 bolts from the cam sprocket.
Remove the cam sprocket disk and washer.
Remove the cam sprocket.
Special Service Tool:
Tool no: SYM-1445100
TOOL number: rocker arm and camshaft puller
Cam shafts
Timing Mark
To this chapter contents
3 bolts
Rocker arm shaft
and camshaft
p
uller
2 bolts
Cam sprocket disk
Page 73

6. CYLINDER HEAD/VALVE
6-6
Remove the 2 cylinder head mounting bolts from
cylinder head right side, and then remove 4 nuts
and washers from cylinder head upper side.
Remove the cylinder head.
Remove cylinder head gasket and 2 dowel pins.
Remove chain guide.
Clean up residues from the matching surfaces of
cylinder and cylinder head.
Caution
Do not damage the matching surfaces of
cylinder and cylinder head.
Avoid residues of gasket or foreign materials
falling into crankcase as cleaning.
Use a valve cotter remove & assembly tool to
press the valve spring, and then remove valves.
Caution
In order to avoid loosing spring elasticity, do not
press the spring too much. Thus, press length
is based on the valve cotter in which can be
removed.
Special Service Tool:
Tool no: SYM-1471110/20-4v
TOOL number: valve cotter remove &
assembly tool
4 Nuts
2 bolts
Spring retainer
Cotter
Exhaust valve
Dowel pins
Gasket
Chain guide
Valve cotter remove
and assembly tool
Inner spring
Outer spring
Inlet valve
To this chapter contents
Page 74

6. CYLINDER HEAD/VALVE
6-7
Remove the valve stem seals.
Clean carbon deposits in the combustion chamber.
Clean residues and foreign materials on cylinder
head matching surface.
Caution
Do not damage the matching surface of cylinder
head.
Cylinder Head Inspection
Check if spark plug and valve holes are cracked.
Measure cylinder head warp with a straightedge
and thickness gauge.
Service limit: 0.05 mm
Camshaft
Inspect cam lobe height for damaged.
Service Limit:
IN: Replacement when less than 34.860mm
EX: Replacement when less than 34.725mm
Inspect the camshaft bearing for looseness or
wear out. If any damage, replace whole set of
camshaft and bearing.
To this chapter contents
Valve stem seals
Page 75

6. CYLINDER HEAD/VALVE
6-8
Rocker Arm
Measure the cam rocker arm I.D., and wear or
damage, oil hole clogged?
Service Limit: Replace when it is less than
12.080 mm.
Rocker Arm Shaft
Measure the active O.D. of the cam rocker arm
shaft and cam rocker arm.
Service Limit: Replace when it is less than
11.936 mm.
Calculate the clearance between the rocker arm
shaft and the rocker arm.
Service Limit: Replace when it is less than 0.10
mm.
Valve spring free length
Measure the free length of intake and exhaust
valve springs.
Service limit:
Inner spring 35.20 mm
Outer spring 36.90 mm
Valve stem
Check if valve stems are bend, crack or burn.
Check the operation condition of valve stem in
valve guide, and measure & record the valve stem
outer diameter.
Service Limit: IN: 4.90 mm
EX: 4.90 mm
To this chapter contents
Page 76

6. CYLINDER HEAD/VALVE
6-9
Valve guide
Caution
Before measuring the valve guide, clean carbon
deposits with reamer.
Tool: 5.0 mm valve guide reamer
Measure and record each valve guide inner
diameters.
Service limit: 5.03 mm
The difference that the inner diameter of valve
guide deducts the outer diameter of valve stem is
the clearance between the valve stem and valve
guide.
Service Limit: IN→0.08 mm
EX→0.10 mm
Caution
If clearance between valve stem and valve guide
exceeded service limit, check whether the new
clearance that only replaces new valve guide is
within service limit or not. If so, replace valve
guide.
Correct it with reamer after replacement.
If clearance still exceeds service limit after
replaced valve guide, replace valve stem too.
Caution
It has to correct valve seat when replacing valve
guide.
5.0 mm valve guide reame
r
To this chapter contents
Page 77

6. CYLINDER HEAD/VALVE
6-10
Valve Stem Replacement
Heat up cylinder head to 100~150 ℃ with heated
plate or toaster.
Caution
Do not let torch heat cylinder head directly.
Otherwise, the cylinder head may be deformed
as heating it.
Wear on a pair of glove to protect your hands
when operating.
Hold the cylinder head, and then press out old
valve guide from combustion chamber side.
Tool: Valve guide driver: 5.0 mm
Caution
Check if new valve guide is deformation after
pressed it in.
When pressing in the new valve guide, cylinder
head still have to be kept in 100~150
℃.
Adjust the valve guide driver and let valve guide
height is in 13 mm.
Press in new valve guide from rocker arm side.
Tool: Valve guide driver: 5.0 mm
Wait for the cylinder head cooling down to room
temperature, and then correct the new valve guide
with reamer.
Caution
Using cutting oil when correcting valve guide
with a reamer.
Turn the reamer in same direction when it be
inserted or rotated.
Correct valve seat, and clean up all metal residues
from cylinder head.
Tool: Valve guide reamer: 5.0 mm
Valve guide driver
5.0 mm
Valve guide driver
5.0mm
Valve guide reamer 5.0 mm
To this chapter contents
Page 78

6. CYLINDER HEAD/VALVE
6-11
Valve Seat Inspection and Service
Clean up all carbon deposits onto intake and
exhaust valves.
Apply with emery slightly onto valve contact face.
Grind valve seat with a rubber hose or other
manual grinding tool.
Caution
Do not let emery enter into between valve stem
and valve guide.
Clean up the emery after corrected, and apply
with engine oil onto contact faces of valve and
valve seat.
Remove the valve and check its contact face.
Caution
Replace the valve with new one if valve seal is
roughness, wear out, or incomplete contacted
with valve seat.
Valve seat inspection
If the valve seat is too width, narrow or rough,
corrects it.
Valve seat width
Service limit: 1.6mm
Check the contact condition of valve seat.
Valve seat grinding
The worn valve seat has to be ground with valve
seat chamfer cutter.
Refer to operation manual of the valve seat
chamfer cutter.
Use 45° valve seat chamfer cutter to cut any rough
or uneven surface from valve seat.
Caution
After valve guide had been replaced, it has to be
ground with 45° valve seal chamfer cutter to
correct its seat face.
Use 32° cutter to cut a quarter upper parts out.
45°
Roughness
Old valve seat width
Valve seat width
32°
To this chapter contents
Page 79

6. CYLINDER HEAD/VALVE
6-12
Use 60° cutter to cut a quarter lower parts out.
Remove the cutter and check new valve seat.
Use 45° cutter to grind the valve seat to specified
width.
Caution
Make sure that all roughness and uneven faces
had been ground.
Grind valve seat again if necessary.
Coat the valve seat surface with red paint.
Install the valve through valve guide until the valve
contacting with valve seat, slightly press down the
valve but do not rotate it so that a seal track will be
created on contact surface.
Caution
The contact surfaces of valve and valve seat are
very important to the valve sealing capacity.
If the contact surface is too high, grind the valve
seat with 32° cutter.
Then, grind the valve seat to specified width.
If the contact surface is too low, grind the valve
seat with 60° cutter.
Then, grind the valve seat to specified width.
Old valve seat width
60°
1.0mm
60°
45°
32°
Old valve seat width
Contact surface too high
Old valve seat width
Contact surface too low
To this chapter contents
Page 80

6. CYLINDER HEAD/VALVE
6-13
After the valve seat being ground, coat the valve
seat surface with emery and then slightly press the
ground surface.
Clean up all emery coated onto the cylinder and
valve after grind.
Cylinder Head Reassembly
Lubricate the valve stem with engine oil, and then
insert the valve into valve guide.
Install the new valve stem oil seal.
Install the valve springs and retainers.
Caution
The closed coils of valve spring should face down
to combustion chamber.
Use a valve cotter remove & assembly tool to
press the valve spring, and then remove the
valves.
Caution
To avoid damaging the valve stem and the
cylinder head, in the combustion chamber place a
rag between the valve spring remover/installer as
compressing the valve spring directly.
Special Service Tool:
Valve cotter remove & assembly tool
Tap the valve stems gently with a plastic hammer
to make sure valve retainer and valve cotter is
settled.
Caution
Place and hold the cylinder head on working table
so that can prevent valve from being damaged.
Exhaust valve
Inlet valve
Valve stem seal
Valve spring
Valve spring retainer
V
alve cotter
To this chapter contents
Valve cotter remove
and assembly tool
Page 81

6. CYLINDER HEAD/VALVE
6-14
Cylinder Head Installation
Clean up all residues and foreign materials onto
the matching surfaces of both cylinder and
cylinder head.
Install chain guide, dowel pins and a new cylinder
head gasket onto the cylinder.
Caution
Do not damage the matching surfaces of cylinder
and cylinder head.
Prevent the residues of gasket or foreign
materials falling into crankcase as cleaning.
Install 4 washers and tighten 4 nuts on the cylinder
head upper side, and then tighten 2 cylinder head
mounting bolts of cylinder head right side.
Torque value:
Nut 3.6~4.0kgf-m
Bolt 1.0~1.4kgf-m
Install camshaft into cylinder head, and install
rocker arm, rocker arm shaft.
Install rocker arm pin mounting plate.
To this chapter contents
Dowel pins
Gasket
Chain guide
4 Nuts
2 bolts
Cam shaft setting plate
Page 82

6. CYLINDER HEAD/VALVE
6-15
Install cam chain on to sprocket and align the
timing mark on the sprocket with the two sprocket
bolt holes and the lower bolt hole of the cylinder
side cover.
Align sprocket bolt hole with camshaft bolt hole.
Tighten the sprocket mounting bolts.
Caution
Make sure timing marks are matched.
Install the cylinder head side cover (3 bolts).
Install the thermostat (2 bolts).
Loosen auto tensioner adjustment bolt and
remove bolt and spring.
Install tensioner and install spring and adjustment
bolt.
Install cylinder head cover (4 bolts).
4 bolts
To this chapter contents
2 bolts Timing mark
3 bolts
Tensioner adjustment bolt
Thermostat bolts
Page 83

6. CYLINDER HEAD/VALVE
6-16
Install Air Injection system (AI) pipe. (4 bolts)
Install inlet pipe onto cylinder
Install and tighten spark plug
Torque value: 1.0~2.0kgf-m
Caution
This model is equipped with more precision
4-valve mechanism so its tighten torque can not
be exceeded standard value in order to avoid
causing cylinder head deformation, engine noise
and leaking so that vehicle performance be
affected.
Install the engine onto frame (refer chapter 5).
Valve Clearance Adjustment
Loosen Air Injection system (AI) pipe upper side
bolt (2 bolts).
Remove the cylinder head cover.
Remove the cylinder head side cover.
Remove left crankcase cover, and turn the drive
face, and align the timing mark on the cam
sprocket with that of cylinder head, piston is at
TDC position.
Loosen valve clearance adjustment nuts and bolts
located on valve rocker arm.
Measure and adjust valve clearance with feeler
gauge.
After valve clearance had been adjusted to
standard value, hold adjustment bolt and then
tighten the Adjustment nut.
Standard Value: IN 0.10 ± 0.02 mm
EX 0.15 ± 0.02 mm
Install the cylinder head side cover.
Start the engine and make sure that engine oil
flows onto the cylinder head.
Stop the engine after confirmed, and then install
the cylinder head cover and AI pipe.
Caution
If lubricant does not flow to cylinder head,
engine components will be worn out seriously.
Thus, it must be confirmed.
When checking lubricant flowing condition, run
the engine at idle speed. Do not accelerate
engine speed.
To this chapter contents
4 bolts
Timing mark
Page 84

6. CYLINDER HEAD/VALVE
6-17
Notes:
To this chapter contents
Page 85

Home page
Contents
7. CYLINDER/PISTON
Mechanism Diagram ···························· 7-1 Piston Ring Installation ··················· 7-6
Piston Installation ···························· 7-7
Cylinder Installation························· 7-7
Precautions in Operation ···················· 7-2
Trouble Diagnosis································ 7-2
Cylinder and Piston Removal ············· 7-3
Mechanism Diagram
1.0~1.4kgf-m
7
0.8~1.2kgf-m
7-1
Page 86

7. CYLINDER/PISTON
To this chapter contents
Precautions in Operation
General Information
Both cylinder and piston service cannot be carried out when engine mounted on frame.
UA25A
Specification Unit:mm
Item Standard Limit
ID 92.00 92.100
Cylinder
Bend - 0.050
Top ring 0.015~0.050 0.090
Clearance between piston
rings
2
nd
ring 0.015~0.050 0.090
Top ring 0.150~0.300 0.500
2nd ring 0.300~0.450 0.650
Ring-end gap
Oil ring side rail 0.200~0.700 -
OD of piston (2nd) 74.430~75.480 75.380
Clearance between piston and cylinder 0.010~0.040 0.100
Piston/
Piston ring
ID of piston pin boss 17.002~17.008 17.020
OD of piston pin 16.994~17.000 16.960
Clearance between piston and piston pin 0.002~0.014 0.020
ID of connecting rod small-end 17.016~17.034 17.064
Trouble Diagnosis
Low or Unstable Compression Pressure
Cylinder or piston ring worn out
Knock or Noise
Cylinder or piston ring worn out
Carbon deposits on cylinder head top-side
Piston pin hole and piston pin wear out
Smoking in Exhaust Pipe
Piston or piston ring worn out
Piston ring installation improperly
Cylinder or piston damage
Engine Overheat
Carbon deposits on cylinder head top side
Cooling pipe clogged or not enough in coolant
flow
7-2
Page 87

To this chapter contents
7. CYLINDER/PISTON
Cylinder and Piston Removal
Remove the cylinder head (refer to chapter 6).
Remove the coolant hose from cylinder.
Remove the cylinder.
Cover the holes of crankcase and cam chain with
a piece of cloth to prevent foreign material falling
into the crankcase.
Remove the piston pin clip, and then remove the
piston pin and piston.
Remove the cylinder gasket and dowel pin.
Clean up all residues or foreign materials from
the two contact surfaces of cylinder and
crankcase.
Caution
Wet the residues by solvent so that the
residues can be removed more easily.
Inspection
Check if the inner diameter of cylinder is worn out
or damaged.
In the 3 positions, top, center and bottom, of
cylinder, measure the X and Y values respective
in the cylinder.
Service limit: 75.100 mm
Dowel pins
Top
Center
Bottom
7-3
Page 88

To this chapter contents
7. CYLINDER/PISTON
7-4
Check cylinder if warp.
Service limit: 0.05 mm
Measure the clearance between piston rings and
grooves.
Service Limit: Top ring: 0.09 mm
2
nd
ring: 0.09 mm
Remove piston rings
Check if the piston rings are damaged or its
grooves are worn.
Caution
Pay attention to remove piston rings because
they are fragile.
Place piston rings respective into cylinder below
20 mm of cylinder top. In order to keep the piston
rings in horizontal level in cylinder, push the rings
with piston.
Service Limit: Top ring: 0.50 mm
2
nd
ring: 0.65 mm
Page 89

7. CYLINDER/PISTON
To this chapter contents
Measure the outer diameter of piston pin.
Service Limit: 16.96 mm
Measure the inner diameter of connecting rod
small end.
Service Limit: 17.064 mm
Measure the inner diameter of piston pin hole.
Service Limit: 17.02 mm
Calculate clearance between piston pin and its
hole.
Service Limit: 0.02 mm
Measure the piston outer diameter.
Caution
The measurement position is 10 mm distance
from piston bottom side, and 90° to piston pin.
Service limit:75.380 mm
Compare measured value with service limit to
calculate the clearance between piston and
cylinder.
7-5
Page 90

To this chapter contents
7. CYLINDER/PISTON
7-6
Piston Ring Installation
Clean up piston top, ring groove, and piston surface.
Install the piston ring onto piston carefully.
Place the openings of piston ring as diagram shown.
Caution
Do not damage piston and piston rings as installation.
All marks on the piston rings must be forwarded to up side.
Make sure that all piston rings can be rotated freely after installed.
Top ring
2
nd
ring
Oil ring
Top groove
2
nd
groove
Oil groove
Page 91

7. CYLINDER/PISTON
To this chapter contents
Clean up all residues and foreign materials on
the contact surface of crankcase. Pay attention to
not let these residues and foreign materials fall
into crankcase.
Caution
Wet the residues into solvent so that the residues
can be removed more easily.
Piston Installation
Install the piston and piston pin, and place the IN
marks on the piston topside forward to inlet valve.
Install new piston pin clip.
Caution
Do not let the opening of piston pin clip align
with the piston cutout.
Place a piece of cloth between piston and
crankcase in order to prevent snap ring from
falling into crankcase during servicing.
Cylinder Installation
Install dowel pins and new gasket.
IN mark
Clip end gap
Dowel pins
Cutout
7-7
Page 92

To this chapter contents
7. CYLINDER/PISTON
7-8
Coat some engine oil to inside of cylinder, piston
and piston rings.
Care to be taken when installing piston into
cylinder. Press piston rings in one by one as
installation.
Caution
Do not push piston into cylinder forcefully
because piston and piston rings will be
damaged.。
Install coolant hose onto cylinder.
Install cylinder head (refer to Chapter 6).
Coolant hose
Page 93

8. V-BELT DRIVING SYSTEM
8-1
Mechanism Diagram ··························· 8-1
Maintenance Description···················· 8-2
Trouble Diagnosis ······························· 8-2
Left Crankcase Cover ························· 8-3
Drive Belt ·············································· 8-3
Drive Plate ············································8-4
Movable Drive Face Disassembly······· 8-6
Driven Pulley Disassembly ·················8-13
Mechanism Diagram
Home page
Contents
8
5.0~6.0kgf-m
5.0~6.0kgf-m
5.0~6.0kgf-m
Page 94

8. V-BELT DRIVING SYSTEM
8-2
Maintenance Description
Precautions in Operation
General Information
Drive face, clutch outer, and driven pulley can be serviced on the vehicle.
Drive belt and drive pulley must be free of any grease.
Specification
Item Standard value Limit
Driving belt width 30.700 mm 29.200 mm
OD of movable drive face boss 35.970~35.990 mm 35.950 mm
ID of movable drive face 36.010~36.035 mm 36.055 mm
OD of weight roller 29.992~30.008 mm 29.950 mm
ID of clutch outer 140.000~140.200 mm 140.500 mm
Thickness of clutch weight 6.000 mm 3.000 mm
Free length of driven pulley spring 124.5 mm 119.500 mm
OD of driven pulley boss 40.965~40.985 mm 40.945 mm
ID of driven face 41.000~41.050 mm 41.070 mm
Weight of weight roller 19.700~20.300 g 19.200 g
Torque value
Drive face nut: 8.5~10.5kgf-m
Clutch outer nut: 5.0~6.0kgf-m
Drive plate nut: 5.0~6.0kgf-m
Special Service Tools
Clutch spring compressor: SYM-2301000
Inner bearing puller:
SYM-6204002
Clutch nut wrench 39 x 41 mm:
SYM-9020200
Universal holder:
SYM-2210100
Bearing driver:
SYM-9100100
Trouble Diagnosis
Engine can be started but vehicle can not
move
1. Worn drive Belt
2. Worn drive face
3. Worn or damaged clutch weight
4. Broken driven pulley
Shudder or misfire when driving
1. Broken clutch weight
2. Worn clutch weight
Insufficient horsepower or poor high
speed performance
1. Worn drive belt
2. Insufficient spring force of driven pulley
3. Worn roller
4. Driven pulley operation un-smoothly
To this chapter contents
Page 95

8. V-BELT DRIVING SYSTEM
8-3
Left Crankcase Cover
Left crankcase cover removal
Release 2 clamp strips of left crankcase cover
ducts, and then remove the ducts.
Remove left crankcase cover cap.
Remove left crankcase cover bolts (17bolts).
Remove 2 dowel pin and gasket.
Left crankcase cover installation
Install left crankcase cover in the reverse
procedure of removal.
Drive Belt
Loosen 1nut from the drive face with Special tool.
Tool name: Movable Drive Face Holder
Tool NO: SYM-2211000-REA
Remove the movable drive face.
To this chapter contents
15 bolts
L case cap
SYM-2211000-REA
2 bolts
Page 96

8. V-BELT DRIVING SYSTEM
8-4
Loosen 1nut from the driven pulley with Special
tool.
Tool name: Universal holder
Tool NO: SYM-2210100
Remove the drive pulley and belt.
Inspection
Check the drive belt for crack or wear. Replace it if
necessary.
Measure the width of drive belt as diagram shown.
Service Limit: 29.2 mm
Replace the belt if exceeds the service limit.
Caution
Using the genuine parts for replacement.
The surfaces of drive belt or pulley must be
free of grease.
Clean up all grease or dirt before installation.
Drive Plate
Remove the drive face.
Loosen 5 bolts from the CVT cooling plate then
remove it.
Drive face
SYM-2210100
Belt tooth
Width
To this chapter contents
Page 97

8. V-BELT DRIVING SYSTEM
8-5
Loosen 10 bolts from the clutch cover.
Remove the clutch cover.
Remove the clutch outer.
One-way Clutch Inspection
Check each roller for wear or damage.
Hold the clutch outer and turning the one way
clutch for right side. .
Loosen the drive plate nut with special tool.
Remove the drive plate.
Tool name: drive plate holder
Tool NO: SYM-2230000-REA
10 Belts
SYM-2230000-REA
To this chapter contents
Page 98

8. V-BELT DRIVING SYSTEM
8-6
Movable Drive Face Disassembly
Loosen 4 bolts form the drive face.
Remove the drive face plate
Remove the drive face plate
Remove the ramp plate and weight roller (8pcs).
Inspection
The weight rollers are to press movable drive face
by means of centrifuge force.
Thus, if weight rollers are worn out or damaged,
the centrifuge force will be affected.
Check if rollers are worn out or damaged.
Replace it if necessary.
Measure each roller’s outer diameter. Replace it if
exceed the service limit.
Service limit: 29.50 mm
To this chapter contents
Page 99

8. V-BELT DRIVING SYSTEM
8-7
Check if drive face boss is worn or damaged and
replace it if necessary.
Measure the outer diameter of movable drive face
boss, and replace it if it exceed service limit.
Service limit: 35.950 mm
Measure the inner diameter of movable drive face,
and replace it if it exceed service limit.
Service limit: 36.055 mm
Reassembly/installation
Install weight rollers.
Caution
The weight roller two end surfaces are not
certainly same. In order to lengthen the roller
life and prevented exceptionally wears the
occurrence, Please end surface of the closure
surface counter clockwise assembles onto
movable drive face.
Install ramp plate.
Movable drive face
Drive face boss
To this chapter contents
Page 100

8. V-BELT DRIVING SYSTEM
8-8
Left crankcase cover inspection
Remove cir clip with inner cir clip pliers
Check bearing on left crankcase cover.
Rotate bearing’s inner ring with fingers.
Check if bearings can be turned in smooth and
silent, and also check if bearing outer ring is
mounted on cover tightly.
If bearing rotation is uneven, noising, or loose
bearing mounted, then replace it.
Remove the bearing 6302 with inner bearing
puller.
Tools number: SYM-6204025
Tools name: INNER BEARING PULLER.
Remove the bearing 6006 with inner bearing
puller.
Tools number: SYM-6204025
Tools name: INNER BEARING PULLER.
Cir clip
To this chapter contents
SYM-6204025
SYM-6204025
 Loading...
Loading...