Page 1

SQL Remote™User’s Guide
Part number: DC38133-01-0902-01
Last modified: October 2004
Page 2

Copyright ©1989–2004 Sybase, Inc. Portions copyright © 2001–2004 iAnywhere Solutions, Inc. All rights reserved.
No part of thispublication may be reproduced, transmitted, or translated in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, manual, optical, or
otherwise, without the priorwritten permission of iAnywhereSolutions, Inc. iAnywhere Solutions, Inc. is a subsidiary of Sybase, Inc.
Sybase, SYBASE (logo), AccelaTrade, ADAWorkbench,Adaptable Windowing Environment,Adaptive Component Architecture, Adaptive Server,
Adaptive Server Anywhere, Adaptive Server Enterprise, Adaptive Server Enterprise Monitor,Adaptive Server Enterprise Replication, Adaptive
Server Everywhere, Adaptive Server IQ, Adaptive Warehouse, AnswerBase, Anywhere Studio, Application Manager, AppModeler,
APT Workbench, APT-Build,APT-Edit, APT-Execute,APT-Library, APT-Translator, ASEP, AvantGo, AvantGo Application Alerts, AvantGo
Mobile Delivery, AvantGo Mobile Document Viewer, AvantGo Mobile Inspection, AvantGo Mobile Marketing Channel, AvantGo Mobile Pharma,
AvantGo Mobile Sales, AvantGoPylon, AvantGo Pylon Application Server, AvantGo Pylon Conduit, AvantGo Pylon PIM Server,AvantGo
Pylon Pro, Backup Server, BayCam, Bit-Wise, BizTracker, Certified PowerBuilder Developer, Certified SYBASE Professional, Certified SYBASE
Professional Logo, ClearConnect, ClientServices, Client-Library, CodeBank, Column Design, ComponentPack, Connection Manager, Convoy/DM,
Copernicus, CSP, Data Pipeline, Data Workbench,DataArchitect, DatabaseAnalyzer, DataExpress, DataServer, DataWindow, DB-Library,
dbQueue, Developers Workbench, Direct Connect Anywhere, DirectConnect, Distribution Director, Dynamic Mobility Model, Dynamo, e-ADK,
E-Anywhere, e-Biz Integrator, EC Gateway, ECMAP, ECRTP,eFulfillment Accelerator, Electronic Case Management, Embedded SQL, EMS,
Enterprise Application Studio, EnterpriseClient/Server, Enterprise Connect, Enterprise Data Studio, Enterprise Manager, Enterprise Portal (logo),
Enterprise SQL Server Manager, Enterprise Work Architecture, Enterprise Work Designer, Enterprise Work Modeler, eProcurement Accelerator,
eremote, Everything WorksBetter WhenEverything Works Together, EWA, E-Whatever, Financial Fusion, Financial Fusion (and design), Financial
Fusion Server, Formula One, Fusion Powered e-Finance,Fusion PoweredFinancial Destinations,Fusion PoweredSTP, Gateway Manager,
GeoPoint, GlobalFIX, iAnywhere, iAnywhere Solutions, ImpactNow, Industry WarehouseStudio, InfoMaker, Information Anywhere, Information
Everywhere, InformationConnect, InstaHelp, Intelligent Self-Care, InternetBuilder, iremote, iScript, Jaguar CTS, jConnect for JDBC,
KnowledgeBase, Logical Memory Manager, Mail Anywhere Studio, MainframeConnect, Maintenance Express, Manage Anywhere Studio, MAP,
M-Business Channel, M-Business Network,M-Business Server, MDI Access Server,MDI DatabaseGateway,media.splash, MessageAnywhere
Server, MetaWorks, MethodSet, ML Query, MobiCATS, My AvantGo, My AvantGo Media Channel, My AvantGo Mobile Marketing, MySupport,
Net-Gateway, Net-Library,New Era of Networks,Next Generation Learning, Next Generation Learning Studio, O DEVICE, OASiS, OASiS logo,
ObjectConnect, ObjectCycle, OmniConnect, OmniSQLAccess Module, OmniSQL Toolkit, Open Biz, Open Business Interchange, Open Client,
Open Client/Server, Open Client/Server Interfaces, Open ClientConnect, Open Gateway, Open Server, Open ServerConnect, Open Solutions,
Optima++, Orchestration Studio, Partnershipsthat Work, PB-Gen,PC APT Execute, PC DB-Net, PC Net Library, PhysicalArchitect, Pocket
PowerBuilder, PocketBuilder, Power Through Knowledge, power.stop, Power++, PowerAMC, PowerBuilder, PowerBuilderFoundation Class
Library, PowerDesigner, PowerDimensions, PowerDynamo,Powering the New Economy, PowerJ, PowerScript, PowerSite, PowerSocket,
Powersoft, Powersoft Portfolio, Powersoft Professional, PowerStage, PowerStudio, PowerTips, PowerWareDesktop, PowerWare Enterprise,
ProcessAnalyst, QAnywhere, Rapport, Relational Beans, RepConnector, Replication Agent, Replication Driver, Replication Server, Replication
Server Manager, Replication Toolkit, Report Workbench, Report-Execute, Resource Manager, RW-DisplayLib, RW-Library, S.W.I.F.T. Message
Format Libraries, SAFE, SAFE/PRO, SDF, Secure SQL Server,Secure SQL Toolset, Security Guardian, SKILS, smart.partners, smart.parts,
smart.script, SQL Advantage, SQL Anywhere, SQL Anywhere Studio, SQL Code Checker, SQL Debug,SQL Edit, SQL Edit/TPU,
SQL Everywhere, SQL Modeler, SQL Remote, SQL Server, SQLServer Manager, SQL Server SNMP SubAgent, SQL Server/CFT,
SQL Server/DBM, SQL SMART, SQL Station, SQL Toolset, SQLJ, Stage III Engineering, Startup.Com, STEP, SupportNow, Sybase Central,
Sybase Client/Server Interfaces, Sybase Development Framework, SybaseFinancial Server, Sybase Gateways, Sybase Learning Connection,
Sybase MPP, Sybase SQL Desktop, Sybase SQL Lifecycle, Sybase SQL Workgroup, Sybase Synergy Program,Sybase User Workbench, Sybase
Virtual Server Architecture, SybaseWare, Syber Financial, SyberAssist, SybMD, SyBooks, System 10, System 11, System XI (logo), SystemTools,
Tabular Data Stream, The EnterpriseClient/Server Company, TheExtensible SoftwarePlatform, The Future Is Wide Open, The Learning
Connection, The Model ForClient/Server Solutions, The Online Information Center, The Power of One, TotalFix, TradeForce,Transact-SQL,
Translation Toolkit, Turning Imagination Into Reality, UltraLite, UltraLite.NET, UNIBOM, Unilib, Uninull,Unisep, Unistring, URK Runtime Kit
for UniCode, Versacore, Viewer, VisualWriter, VQL, Warehouse Control Center, Warehouse Studio, Warehouse WORKS, WarehouseArchitect,
Watcom,Watcom SQL, Watcom SQL Server, Web DeploymentKit, Web.PB, Web.SQL, WebSights, WebViewer, WorkGroup SQL Server,
XA-Library, XA-Server, and XP Server are trademarks of Sybase, Inc. or its subsidiaries.
Certicom, MobileTrust, and SSL Plus are trademarks and Security Builder is aregistered trademarkof CerticomCorp. Copyright © 1997–2001
Certicom Corp. Portions are Copyright © 1997–1998, Consensus Development Corporation, a wholly owned subsidiary of Certicom Corp. All
rights reserved. Contains an implementation of NR signatures, licensed under U.S. patent 5,600,725. Protected by U.S. patents 5,787,028;
4,745,568; 5,761,305. Patents pending.
All other trademarks areproperty of their respective owners.
ii
Page 3

Contents
About This Manual ix
SQL Anywhere Studio documentation . . . . . . . . . . . . . x
Documentation conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xiii
The Adaptive Server Anywhere sample database . . . . . . . xv
Finding out more and providing feedback . . . . . . . . . . . xvi
I Introduction to SQL Remote 1
1 Welcome to SQL Remote 3
About SQL Remote . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
About this manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
2 SQL Remote Concepts 7
SQL Remote components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Publications and subscriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
SQL Remote features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Some sample installations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
3 Setting Up SQL Remote 19
Setup overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Preparing your Adaptive Server Enterprise server . . . . . . 21
Upgrading SQL Remote for Adaptive Server Enterprise . . . 25
Uninstalling SQL Remote . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
4 Tutorials for Adaptive Server Anywhere Users 27
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Tutorial: Adaptive ServerAnywherereplication using Sybase
Central . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Tutorial: Adaptive Server Anywhere replication using Interac-
tive SQL and dbxtract . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Start replicating data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
A sample publication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
5 A Tutorial for Adaptive Server Enterprise Users 53
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Tutorial: Adaptive Server Enterprise replication . . . . . . . . 57
Start replicating data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
iii
Page 4

II Replication Design for SQL Remote 71
6 Principles of SQL Remote Design 73
Design overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
How statements are replicated . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
How data types are replicated . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Who gets what? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Replication errors and conflicts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
7 SQL Remote Design for Adaptive Server Anywhere 91
Design overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Publishing data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Publication design for Adaptive Server Anywhere . . . . . . . 102
Partitioning tables that do not contain the subscription ex-
pression . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Sharing rows among several subscriptions . . . . . . . . . . 112
Managing conflicts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
Ensuring unique primary keys . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
Creating subscriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
8 SQL Remote Design for Adaptive Server Enterprise 141
Design overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 142
Creating publications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 143
Publication design for Adaptive Server Enterprise . . . . . . . 147
Partitioning tables that do not contain the subscription column 149
Sharing rows among several subscriptions . . . . . . . . . . 157
Managing conflicts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 165
Ensuring unique primary keys . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 175
Creating subscriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 181
III SQL Remote Administration 183
9 Deploying and Synchronizing Databases 185
Deployment overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 186
Test before deployment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 187
Synchronizing databases . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 189
Using the extraction utility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 191
Synchronizing data over a message system . . . . . . . . . . 198
10 SQL Remote Administration 199
Management overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 200
Managing SQL Remote permissions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 201
Using message types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 210
iv
Page 5

Running the Message Agent . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 223
Tuning Message Agent performance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 228
Encoding and compressing messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . 235
The message tracking system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 237
11 Administering SQL Remote for Adaptive Server Anywhere241
Running the Message Agent . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 242
Error reporting and handling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 245
Transaction log and backup management . . . . . . . . . . . 249
Using passthrough mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 260
12 Administering SQL Remote for Adaptive Server Enterprise263
How the Message Agent for Adaptive Server Enterprise works 264
Running the Message Agent . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 269
Error reporting and handling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 271
Adaptive Server Enterprise transaction log and backup man-
agement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 272
Making schema changes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 275
Using passthrough mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 276
13 Using SQL Remote with Replication Server 277
When you need to use the SQL Remote Open Server . . . . 278
Architecture for Replication Server/SQL Remote installations 279
Setting up SQL Remote Open Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . 282
Configuring Replication Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 285
Other issues . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 287
IV Reference 289
14 Utilities and Options Reference 291
The Message Agent . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 292
The Database Extraction utility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 302
The SQL Remote Open Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 312
SQL Remote options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 315
SQL Remote event-hook procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 320
15 System Objects for Adaptive Server Anywhere 325
SQL Remote system tables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 326
SQL Remote system views . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 333
16 System Objects for Adaptive Server Enterprise 337
SQL Remote system tables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 338
SQL Remote system views . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 346
v
Page 6

Stable Queue tables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 350
17 Command Reference for Adaptive Server Anywhere 353
ALTER REMOTE MESSAGE TYPE statement . . . . . . . . 355
CREATE PUBLICATION statement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 356
CREATE REMOTE MESSAGE TYPE statement . . . . . . . 357
CREATE SUBSCRIPTION statement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 358
CREATE TRIGGER statement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 359
DROP PUBLICATION statement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 361
DROP REMOTE MESSAGE TYPE statement . . . . . . . . . 362
DROP SUBSCRIPTION statement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 363
GRANT CONSOLIDATE statement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 364
GRANT PUBLISH statement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 365
GRANT REMOTE statement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 366
GRANT REMOTE DBA statement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 367
PASSTHROUGH statement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 368
REMOTE RESET statement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 369
REVOKE CONSOLIDATE statement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 370
REVOKE PUBLISH statement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 371
REVOKE REMOTE statement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 372
REVOKE REMOTE DBA statement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 373
SET REMOTE OPTION statement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 374
START SUBSCRIPTION statement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 375
STOP SUBSCRIPTION statement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 376
SYNCHRONIZE SUBSCRIPTION statement . . . . . . . . . 377
UPDATE statement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 378
18 Command Reference for Adaptive Server Enterprise 379
sp_add_article procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 381
sp_add_article_col procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 383
sp_add_remote_table procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 384
sp_create_publication procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 386
sp_drop_publication procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 387
sp_drop_remote_type procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 388
sp_drop_sql_remote procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 389
sp_grant_consolidate procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 390
sp_grant_remote procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 393
sp_link_option procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 396
sp_modify_article procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 398
sp_modify_remote_table procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 400
sp_passthrough procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 402
sp_passthrough_piece procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 403
sp_passthrough_stop procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 405
sp_passthrough_subscription procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . 406
vi
Page 7

sp_passthrough_user procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 407
sp_populate_sql_anywhere procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . 408
sp_publisher procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 409
sp_queue_clean procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 410
sp_queue_confirmed_delete_old procedure . . . . . . . . . . 411
sp_queue_confirmed_transaction procedure . . . . . . . . . 412
sp_queue_delete_old procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 413
sp_queue_drop procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 414
sp_queue_dump_database procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . 415
sp_queue_dump_transaction procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . 416
sp_queue_get_state procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 417
sp_queue_log_transfer_reset procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . 418
sp_queue_read procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 419
sp_queue_reset procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 420
sp_queue_set_confirm procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 421
sp_queue_set_progress procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 422
sp_queue_transaction procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 423
sp_remote procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 424
sp_remote_option procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 425
sp_remote_type procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 427
sp_remove_article procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 428
sp_remove_article_col procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 429
sp_remove_remote_table procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 430
sp_revoke_consolidate procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 431
sp_revoke_remote procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 432
sp_subscription procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 433
sp_subscription_reset procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 434
V Appendices 435
A SQL Remote for Adaptive Server Enterprise and Adaptive
Server Anywhere: Differences 437
Types of difference . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 438
Differences in functionality . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 439
Differences in approach . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 440
Limitations for Enterprise to Enterprise replication . . . . . . 442
B Supported Platforms and Message Links 445
Supported message systems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 446
Supported operating systems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 447
Index 449
vii
Page 8

viii
Page 9

About This Manual
Subject This book describes all aspects of the SQL Remote data replication system
for mobile computing, which enables sharing of data between a single
Adaptive Server Anywhere or Adaptive Server Enterprise database and
many Adaptive Server Anywhere databases using an indirect link such as
e-mail or file transfer.
Audience This book is for users of Adaptive Server Anywhere and Adaptive Server
Enterprise who wish to add SQL Remote replication to their information
systems.
Before you begin ☞ For a comparison of SQL Remote with other replication technologies,
see “ Introducing Replication Technologies” [Introducing SQL Anywhere
Studio, page 21].
ix
Page 10

SQL Anywhere Studio documentation
This book is part of the SQL Anywhere documentation set. This section
describes the books in the documentation set and how you can use them.
The SQL Anywhere
Studio documentation
The SQL Anywhere Studio documentation is available in a variety of forms:
in an online form that combines all books in one large help file; as separate
PDF files for each book; and as printed books that you can purchase. The
documentation consists of the following books:
♦ Introducing SQL Anywhere Studio This book provides an overview of
the SQL Anywhere Studio database management and synchronization
technologies. It includes tutorials to introduce you to each of the pieces
that make up SQL Anywhere Studio.
♦ What’s New in SQL Anywhere Studio This book is for users of
previous versions of the software. It lists new features in this and
previous releases of the product and describes upgrade procedures.
♦ Adaptive Server Anywhere Database Administration Guide This
book covers material related to running, managing, and configuring
databases and database servers.
♦ Adaptive Server Anywhere SQL User’s Guide This book describes
how to design and create databases; how to import, export, and modify
data; how to retrieve data; and how to build stored procedures and
triggers.
♦ Adaptive Server Anywhere SQL Reference Manual This book
provides a complete reference for the SQL language used by Adaptive
Server Anywhere. It also describes the Adaptive Server Anywhere
system tables and procedures.
♦ Adaptive Server Anywhere Programming Guide This book describes
how to build and deploy database applications using the C, C++, and Java
programming languages. Users of tools such as Visual Basic and
PowerBuilder can use the programming interfaces provided by those
tools. It also describes the Adaptive Server Anywhere ADO.NET data
provider.
♦ Adaptive Server Anywhere SNMP Extension Agent User’s Guide
This book describes how to configure the Adaptive Server Anywhere
SNMP Extension Agent for use with SNMP management applications to
manage Adaptive Server Anywhere databases.
♦ Adaptive Server Anywhere Error Messages This book provides a
complete listing of Adaptive Server Anywhere error messages together
with diagnostic information.
x
Page 11

♦ SQL Anywhere Studio Security Guide This book provides
information about security features in Adaptive Server Anywhere
databases. Adaptive Server Anywhere 7.0 was awarded a TCSEC
(Trusted Computer System Evaluation Criteria) C2 security rating from
the U.S. Government. This book may be of interest to those who wish to
run the current version of Adaptive Server Anywhere in a manner
equivalent to the C2-certified environment.
♦ MobiLink Administration Guide This book describes how to use the
MobiLink data synchronization system for mobile computing, which
enables sharing of data between a single Oracle, Sybase, Microsoft or
IBM database and many Adaptive Server Anywhere or UltraLite
databases.
♦ MobiLink Clients This book describes how to set up and synchronize
Adaptive Server Anywhere and UltraLite remote databases.
♦ MobiLink Server-Initiated Synchronization User’s Guide This book
describes MobiLink server-initiated synchronization, a feature of
MobiLink that allows you to initiate synchronization from the
consolidated database.
♦ MobiLink Tutorials This book provides several tutorials that walk you
through how to set up and run MobiLink applications.
♦ QAnywhere User’s Guide This manual describes MobiLink
QAnywhere, a messaging platform that enables the development and
deployment of messaging applications for mobile and wireless clients, as
well as traditional desktop and laptop clients.
♦ iAnywhere Solutions ODBC Drivers This book describes how to set
up ODBC drivers to access consolidated databases other than Adaptive
Server Anywhere from the MobiLink synchronization server and from
Adaptive Server Anywhere remote data access.
♦ SQL Remote User’s Guide This book describes all aspects of the
SQL Remote data replication system for mobile computing, which
enables sharing of data between a single Adaptive Server Anywhere or
Adaptive Server Enterprise database and many Adaptive Server
Anywhere databases using an indirect link such as e-mail or file transfer.
♦ SQL Anywhere Studio Help This book includes the context-sensitive
help for Sybase Central, Interactive SQL, and other graphical tools. It is
not included in the printed documentation set.
♦ UltraLite Database User’s Guide This book is intended for all
UltraLite developers. It introduces the UltraLite database system and
provides information common to all UltraLite programming interfaces.
xi
Page 12

♦ UltraLite Interface Guides A separate book is provided for each
UltraLite programming interface. Some of these interfaces are provided
as UltraLite components for rapid application development, and others
are provided as static interfaces for C, C++, and Java development.
In addition to this documentation set, PowerDesigner and InfoMaker include
their own online documentation.
Documentation formats SQL Anywhere Studio provides documentation in the following formats:
♦ Online documentation The online documentation contains the
complete SQL Anywhere Studio documentation, including both the
books and the context-sensitive help for SQL Anywhere tools. The online
documentation is updated with each maintenance release of the product,
and is the most complete and up-to-date source of documentation.
To access the online documentation on Windows operating systems,
choose Start ➤ Programs ➤ SQL Anywhere 9 ➤ Online Books. You can
navigate the online documentation using the HTML Help table of
contents, index, and search facility in the left pane, as well as using the
links and menus in the right pane.
To access the online documentation on UNIX operating systems, see the
HTML documentation under your SQL Anywhere installation.
♦ PDF books The SQL Anywhere books are provided as a set of PDF
files, viewable with Adobe Acrobat Reader.
The PDF books are accessible from the online books, or from the
Windows Start menu.
xii
♦ Printed books The complete set of books is available from Sybase
sales or from eShop, the Sybase online store, at
http://eshop.sybase.com/eshop/documentation
.
Page 13

Documentation conventions
This section lists the typographic and graphical conventions used in this
documentation.
Syntax conventions The following conventions are used in the SQL syntax descriptions:
♦ Keywords All SQL keywords appear in upper case, like the words
ALTER TABLE in the following example:
ALTER TABLE [ owner.]table-name
♦ Placeholders Items that must be replaced with appropriate identifiers
or expressions are shown like the words
following example:
ALTER TABLE [ owner.]table-name
♦ Repeating items Lists of repeating items are shown with an element of
the list followed by an ellipsis (three dots), like
following example:
ADD column-definition [ column-constraint, .. . ]
One or more list elements are allowed. In this example, if more than one
is specified, they must be separated by commas.
♦ Optional portions Optional portions of a statement are enclosed by
square brackets.
RELEASE SAVEPOINT [ savepoint-name ]
owner
and
column-constraint
table-name
in the
in the
These square brackets indicate that the
square brackets should not be typed.
♦ Options When none or only one of a list of items can be chosen,
vertical bars separate the items and the list is enclosed in square brackets.
[ ASC | DESC ]
For example, you can choose one of ASC, DESC, or neither. The square
brackets should not be typed.
♦ Alternatives When precisely one of the options must be chosen, the
alternatives are enclosed in curly braces and a bar is used to separate the
options.
[ QUOTES { ON | OFF } ]
If the QUOTES option is used, one of ON or OFF must be provided. The
brackets and braces should not be typed.
savepoint-name
is optional. The
xiii
Page 14

Graphic icons The following icons are used in this documentation.
API
♦ A client application.
♦ A database server, such as Sybase Adaptive Server Anywhere.
♦ A database. In some high-level diagrams, the icon may be used to
represent both the database and the database server that manages it.
♦ Replication or synchronization middleware. These assist in sharing data
among databases. Examples are the MobiLink Synchronization Server
and the SQL Remote Message Agent.
♦ A programming interface.
xiv
Page 15

The Adaptive Server Anywhere sample database
fin_code
code char(2) <pk>
type char(10)
description char(50)
product
id integer <pk>
name char(15)
description char(30)
size char(18)
color char(6)
quantity integer
unit_price numeric (15,2)
asademo.db
contact
id integer <pk>
last_name char(15)
first_name char(15)
title char(2)
street char(30)
city char(20)
state char(2)
zip char(5)
phone char(10)
fax char(10)
customer
id integer <pk>
fname char(15)
lname char(20)
address char(35)
city char(20)
state char(2)
zip char(10)
phone char(20)
company_name char(35)
fin_data
year char(4) <pk>
quarter char(2) <pk>
code char(2) <pk,fk>
amount numeric(9)
sales_order
id integer <pk>
cust_id integer <fk>
order_date date
fin_code_id char(2) <fk>
region char(7)
sales_rep integer <fk>
sales_order_items
id integer <pk,fk>
line_id smallint <pk>
prod_id integer <fk>
quantity integer
ship_date date
department
dept_id integer <pk>
dept_name char(40)
dept_head_id integer <fk>
Employee
emp_id integer <pk>
manager_id integer
emp_fname char(20)
emp_lname char(20)
dept_id integer <fk>
street char(40)
city char(20)
state char(4)
zip_code char(9)
phone char(10)
status char(1)
ss_number char(11)
salary numeric(20,3)
start_date date
termination_date date
birth_date date
bene_health_ins char(1)
bene_life_ins char(1)
bene_day_care char(1)
sex char(1)
id = prod_id
id = cust_id
id = id
emp_id = sales_rep
emp_id = dept_head_id
code = fin_code_id
dept_id = dept_id
code = code
Many of the examples throughout the documentation use the Adaptive
Server Anywhere sample database.
The sample database is held in a file named
your SQL Anywhere directory.
The sample database represents a small company. It contains internal
information about the company (employees, departments, and finances) as
well as product information and sales information (sales orders, customers,
and contacts). All information in the database is fictional.
The following figure shows the tables in the sample database and how they
relate to each other.
asademo.db
, and is located in
xv
Page 16

Finding out more and providing feedback
Finding out more Additional information and resources, including a code exchange, are
available at the iAnywhere Developer Network at
http://www.ianywhere.com/developer/
If you have questions or need help, you can post messages to the iAnywhere
Solutions newsgroups listed below.
When you write to one of these newsgroups, always provide detailed
information about your problem, including the build number of your version
of SQL Anywhere Studio. You can find this information by typing dbeng9
-v at a command prompt.
.
The newsgroups are located on the
newsgroups include the following:
♦ sybase.public.sqlanywhere.general
♦ sybase.public.sqlanywhere.linux
♦ sybase.public.sqlanywhere.mobilink
♦ sybase.public.sqlanywhere.product_futures_discussion
♦ sybase.public.sqlanywhere.replication
♦ sybase.public.sqlanywhere.ultralite
♦ ianywhere.public.sqlanywhere.qanywhere
Newsgroup disclaimer
iAnywhere Solutions has no obligation to provide solutions, information
or ideas on its newsgroups, nor is iAnywhere Solutions obliged to provide
anything other than a systems operator to monitor the service and ensure
its operation and availability.
iAnywhere Solutions Technical Advisors as well as other staff assist on the
newsgroup service when they have time available. They offer their help
on a volunteer basis and may not be available on a regular basis to provide
solutions and information. Their ability to help is based on their workload.
forums.sybase.com
news server. The
Feedback We would like to receive your opinions, suggestions, and feedback on this
documentation.
You can e-mail comments and suggestions to the SQL Anywhere
documentation team at iasdoc@ianywhere.com. Although we do not reply
to e-mails sent to that address, we read all suggestions with interest.
xvi
Page 17

In addition, you can provide feedback on the documentation and the
software through the newsgroups listed above.
xvii
Page 18

xviii
Page 19

PART I
INTRODUCTION TO SQL
REMOTE
This part describes the concepts, architecture, and features of SQL Remote.
The material in this part refers to both SQL Remote for Adaptive Server
Anywhere and SQL Remote for Adaptive Server Enterprise.
Page 20

Page 21

CHAPTER 1
Welcome to SQL Remote
About this chapter This chapter introduces SQL Remote and the documentation.
Contents
Topic: page
About SQL Remote 4
About this manual 5
3
Page 22

About SQL Remote
SQL Remote is a data-replication technology designed for two-way
replication between a consolidated data server and large numbers of remote
databases, typically including many mobile databases.
SQL Remote replication is message based, and requires no direct
server-to-server connection. An occasional dial-up or e-mail link is
sufficient.
Administration and resource requirements at the remote sites are minimal.
The time lag between the consolidated and remote databases is configurable,
and can range from minutes to hours or days.
Sybase SQL Remote technology is provided in two forms:
♦ SQL Remote for Adaptive Server Anywhere Enables replication
between a consolidated Adaptive Server Anywhere database and a large
number of remote databases.
♦ SQL Remote for Adaptive Server Enterprise Enables replication
between a consolidated Adaptive Server Enterprise database and a large
number of remote Adaptive Server Anywhere databases.
This book describes both of these technologies.
In a SQL Remote installation, you must have properly licensed SQL Remote
software at each participating database.
☞ For a detailed introduction to SQL Remote concepts and features, see
“SQL Remote Concepts” on page 7.
☞ For a list of supported operating systems and message links, see
“Supported Platforms and Message Links” on page 445.
4
Page 23

About this manual
This manual describes how to design, build, and maintain SQL Remote
installations.
The manual includes the following parts.
♦ Introduction to SQL Remote Replication concepts and features of
SQL Remote.
♦ Replication Design for SQL Remote Designing SQL Remote
installations.
♦ SQL Remote Administration Deploying SQL Remote databases and
administering a running SQL Remote setup.
♦ Reference SQL Remote commands, system tables, and other reference
material.
Product installation
This section describes installation of SQL Remote for Adaptive Server
Enterprise. If you obtained SQL Remote as part of another product, consult
the installation instructions for the product you purchased.
Chapter 1. Welcome to SQL Remote
❖ To install the SQL Remote software ( Windows )
1. Insert the CD-ROM into your CD-ROM drive.
2. If the installation program does not start automatically, start the
application on the CD-ROM.
3. Follow the instructions in the installation program.
❖ To install the SQL Remote software ( UNIX )
1. Consult the instructions for your operating system in the
Anywhere Read Me First
If you are using SQL Remote for Adaptive Server Enterprise, you must
install SQL Remote into any database you wish to replicate.
booklet.
Adaptive Server
☞ For information about installing SQL Remote into a database, see
“Setting Up SQL Remote” on page 19.
setup
5
Page 24

Page 25

CHAPTER 2
SQL Remote Concepts
About this chapter This chapter introduces the concepts, design goals, and features of
SQL Remote.
Contents
Topic: page
SQL Remote components 8
Publications and subscriptions 11
SQL Remote features 13
Some sample installations 15
7
Page 26
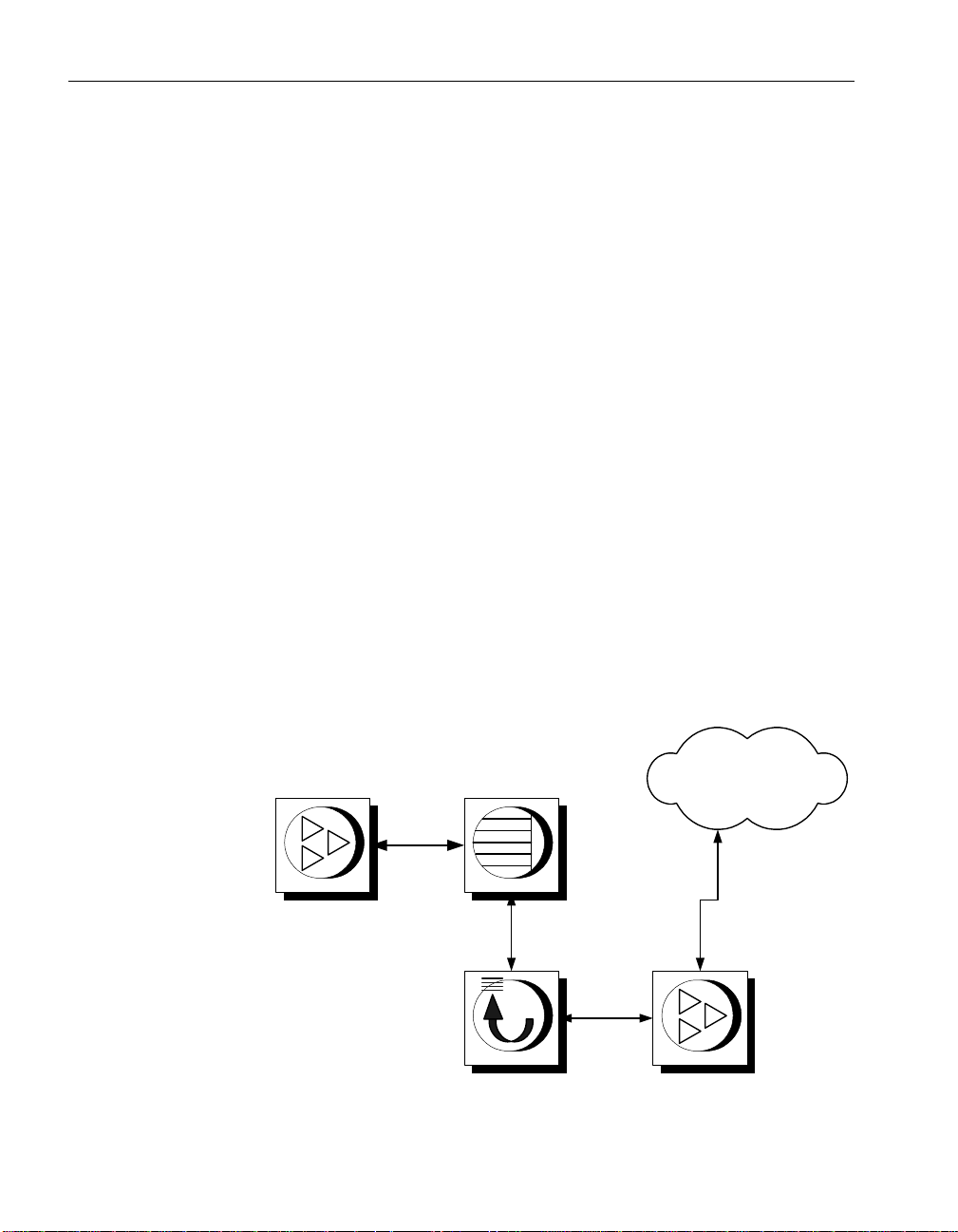
SQL Remote components
Message
system
transport
Data server
Message
Agent
Message
system client
The following components are required for SQL Remote:
♦ Data server An Adaptive Server Anywhere or Adaptive Server
Enterprise database-management system is required at each site to
maintain the data.
♦ Message Agent A SQL Remote Message Agent is required at the
consolidated site and at each remote site to send and receive SQL Remote
messages.
The Message Agent connects to the data server by a client/server
connection. It may run on the same machine as the data server or on a
different machine.
♦ Database extraction utility The extraction utility is used to prepare
remote databases from a consolidated database, during development and
testing, and also at deployment time.
♦ Message system client software SQL Remote uses existing message
systems to transport replication messages. A file-sharing “message
system” is provided, which does not require client software. Each
computer involved in SQL Remote replication using a message system
other than file sharing must have that message system installed.
♦ Client applications The applications that work with SQL Remote
databases are standard client/server database applications.
8
Page 27

The data server
Client applications
Chapter 2. SQL Remote Concepts
The data server may be an Adaptive Server Enterprise or an Adaptive Server
Anywhere server. At the remote site the data server is commonly an
Adaptive Server Anywhere personal server, but can also be an Adaptive
Server Enterprise or Adaptive Server Anywhere server.
Client applications work with the data in the database. Client applications
use one of the client/server interfaces supported by the data server:
♦ For Adaptive Server Anywhere, the client application may use ODBC,
Embedded SQL, or Sybase Open Client to work with Adaptive Server
Anywhere.
♦ For Adaptive Server Enterprise, the client application may use one of the
Sybase Client Server interfaces, ODBC, or Embedded SQL.
Client applications do not have to know if they are using a consolidated or
remote database. From the client application perspective, there is no
difference.
The Message Agent
The SQL Remote Message Agent sends and receives replication messages.
It is a client application that sends and receives messages from database to
database. The Message Agent must be installed at both the consolidated and
at the remote sites.
For Adaptive Server Anywhere, the Message Agent is a program called
dbremote.exe
For Adaptive Server Enterprise, the Message Agent is a program called
ssremote.exe
on PC operating systems, and
on PC operating systems, and
dbremote
ssremote
on UNIX.
on UNIX.
9
Page 28
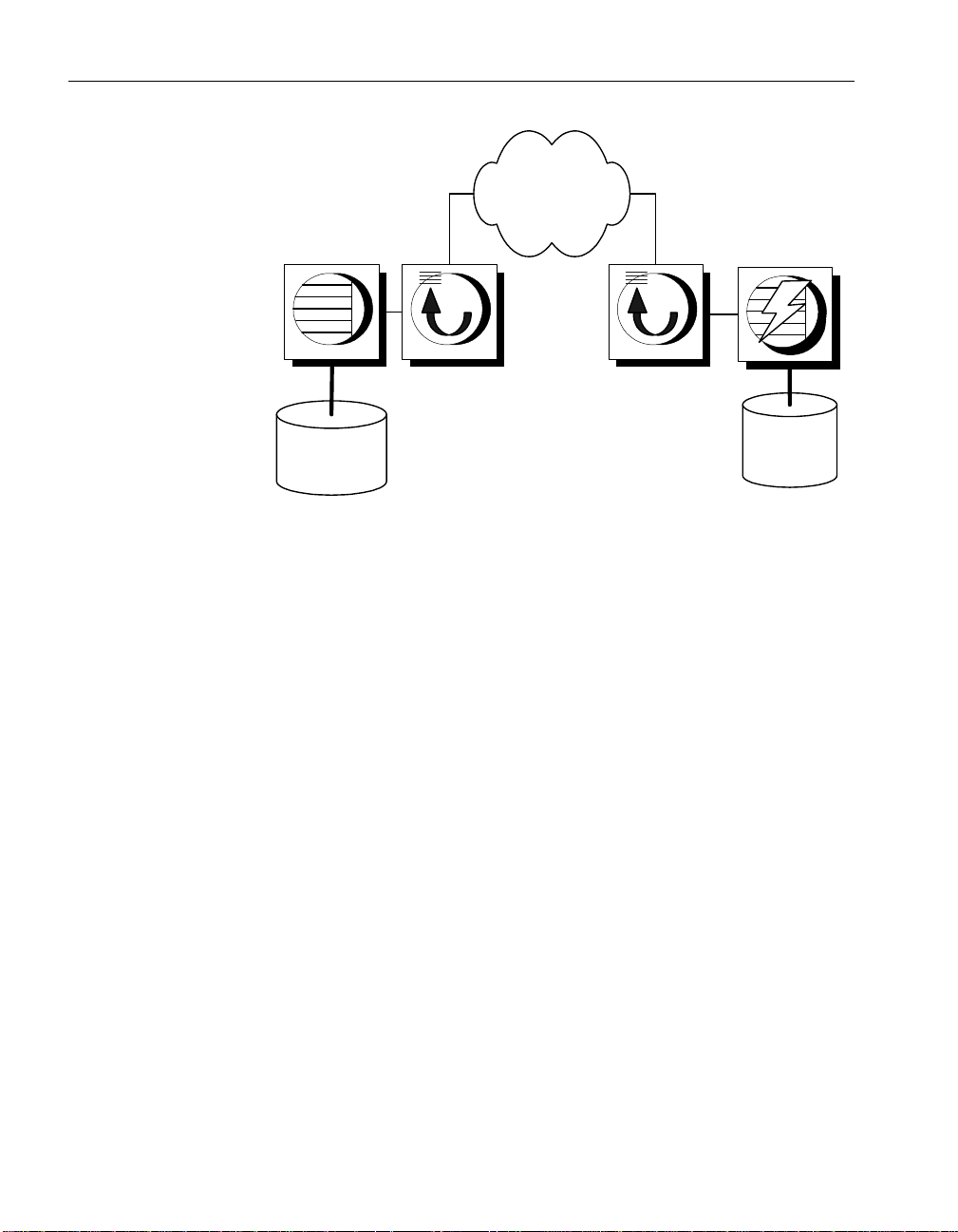
Remote
database
Consolidated
database
Message
System
Message Agent Message Agent
Message system client
If you are using a shared file message system, no message system client is
needed.
If you are using an e-mail or other message system, you must have a
message system for that client in order to send and receive messages.
10
Page 29
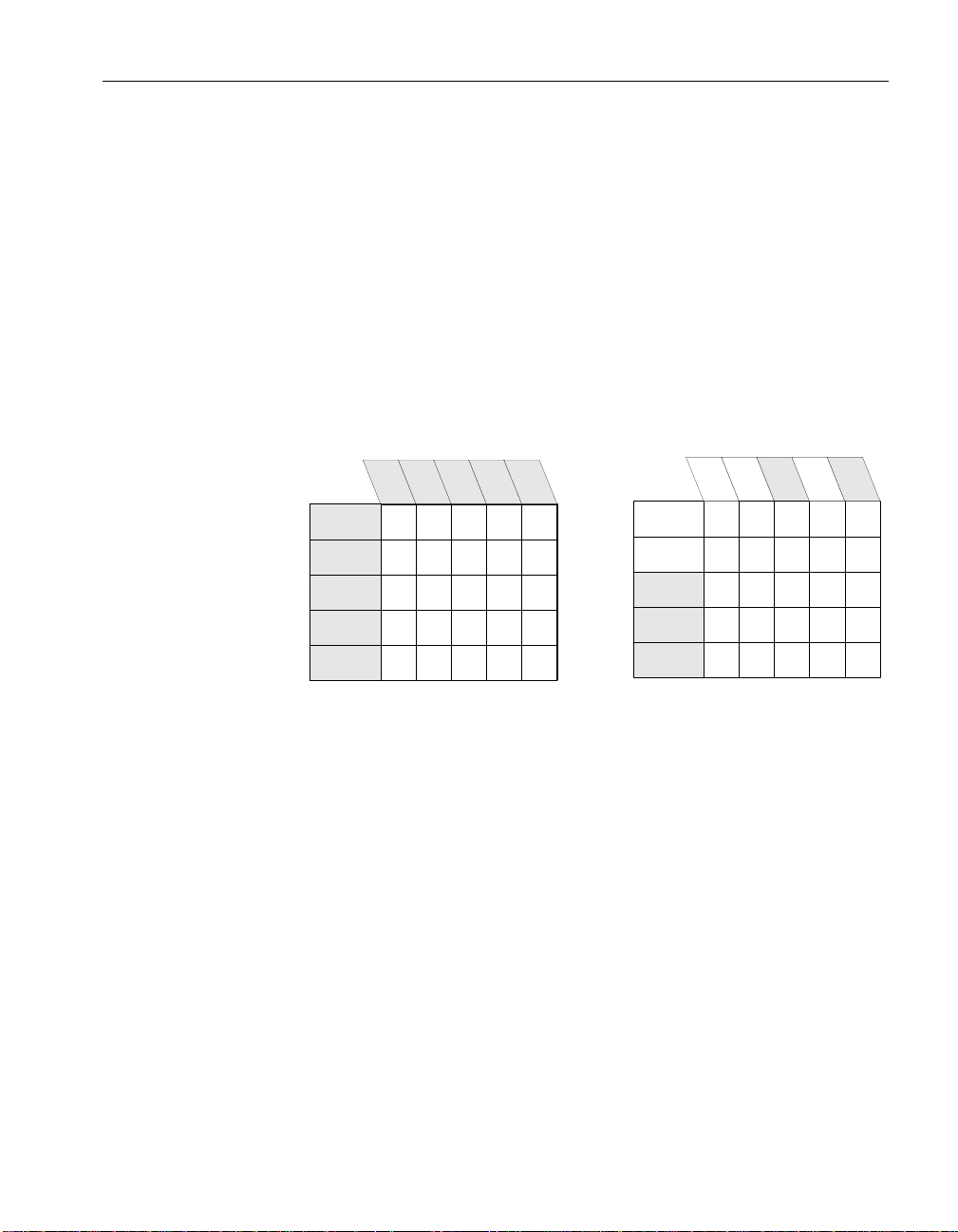
Publications and subscriptions
A two-table synchronization definition
Article 1: all of
table A
Article 2: some rows and
columns from table B
+
X
X
X
X
X
X
X X X X X
X X X X X
XXXXX
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
The data that is replicated by SQL Remote is arranged in publications. Each
database that shares information in a publication must have a subscription
to the publication.
Chapter 2. SQL Remote Concepts
Data is organized into
publications
The publication is a database object describing data to be replicated.
Remote users of the database who wish to receive a publication do so by
subscribing to a publication.
A publication may include data from several database tables. Each table’s
contribution to a publication is called an article. Each article may consist of
a whole table, or a subset of the rows and columns in a table.
Periodically, the changes made to each publication in a database are
replicated to all subscribers to that publication. These replications are called
publication updates.
Messages are always
sent both ways
Remote databases subscribe to publications on the consolidated database so
that they can receive data from the consolidated database. To do this, a
subscription is created at the consolidated database, identifying the
subscriber by name and by the publication they are to receive.
SQL Remote always involves messages being sent two ways. The
consolidated database sends messages containing publication updates to
remote databases, and remote databases also send messages to the
consolidated database.
For example, if data in a publication at a consolidated database is updated,
those updates are sent to the remote databases. And even if the data is never
updated at the remote database, confirmation messages must still be sent
back to the consolidated database, to keep track of the status of the
11
Page 30

replication.
Consolidated
database
Remote
database
Publish Subscribe
Publish
Subscribe
Data updates and
receipt confirmations
Data updates and
receipt confirmations
Both databases
subscribe
Messages must be sent both ways, so not only does a remote database
subscribe to a publication created at the consolidated database, but the
consolidated database must subscribe to a corresponding publication created
at the remote database.
When remote database users modify their own copies of the data, their
changes are replicated to the consolidated database. When the messages
containing the changes are applied at the consolidated database the changes
become part of the consolidated database’s publication, and are included in
the next round of updates to all remote sites (except the one it came from).
In this way, replication from remote site to remote site takes place via the
consolidated database.
Synchronizing a remote
database
12
When a subscription is initially set up, the two databases must be brought to
a state where they both have the same set of information, ready to start
replication. This process of setting up a remote database to be consistent
with the consolidated database is called synchronization. Synchronization
can be carried out manually, but the database extraction utility automates the
process. You can run the Extraction utility as a command-line utility or, if
you are using an Adaptive Server Anywhere consolidated database, from
Sybase Central.
The appropriate publication and subscription are created automatically at
remote databases when you use the SQL Remote database extraction utility
to create a remote database.
Page 31

SQL Remote features
The following features are key to SQL Remote’s design.
Support for many subscribers SQL Remote is designed to support
replication with many subscribers to a publication.
This feature is of particular importance for mobile workforce applications,
which may require replication to the laptop computers of hundreds or
thousands of sales representatives from a single office database.
Transaction log-based replication SQL Remote replication is based on
the transaction log. This enables it to replicate only changes to data, rather
than all data, in each update. Also, log-based replication has performance
advantages over other replication systems.
The transaction log is the repository of all changes made to a database.
SQL Remote replicates changes made to databases as recorded in the
transaction log. Periodically, all committed transactions in the consolidated
database transaction log belonging to any publication are sent to remote
databases. At remote sites, all committed transactions in the transaction log
are periodically submitted to the consolidated database.
By replicating only committed transactions, SQL Remote ensures proper
transaction atomicity throughout the replication setup and maintains a
consistency among the databases involved in the replication, albeit with
some time lag while the data is replicated.
Chapter 2. SQL Remote Concepts
Central administration SQL Remote is designed to be centrally
administered, at the consolidated database. This is particularly important for
mobile workforce applications, where laptop users should not have to carry
out database administration tasks. It is also important in replication
involving small offices that have servers but little in the way of
administration resources.
Administration tasks include setting up and maintaining publications,
remote users, and subscriptions, as well as correcting errors and conflicts if
they occur.
Economical resource requirements The only software required to run
SQL Remote in addition to your Adaptive Server Anywhere or Adaptive
Server Enterprise DBMS is the Message Agent, and a message system. If
you use the shared file link, no message system software is required as long
as each remote user ID has access to the directory where the message files
are stored.
Memory and disk space requirements have been kept moderate for all
components of the replication system, so that you do not have to invest in
13
Page 32

extra hardware to run SQL Remote.
Multi-platform support SQL Remote is provided on a number of
operating systems and message links.
☞ For a list of supported environments, see “Supported Platforms and
Message Links” on page 445.
14
Page 33

Chapter 2. SQL Remote Concepts
Laptop computer
Remote
database
Laptop computer
Remote
database
Office network
server
Consolidated
database
Laptop computer
Remote
database
Laptop computer
Remote
database
Some sample installations
While SQL Remote can provide replication services in many different
environments, its features are designed with the following characteristics in
mind:
♦ SQL Remote should be a solution even when no administration load can
be assigned to the remote databases, as in mobile workforce applications.
♦ Data communication among the sites may be occasional and indirect: it
need not be permanent and direct.
♦ Memory and resource requirements at remote sites are assumed to be at a
premium.
The following examples show some typical SQL Remote setups.
Server-to-laptop replication for mobile workforces
SQL Remote provides two-way replication between a database on an office
network and personal databases on the laptop computers of sales
representatives. Such a setup may use an e-mail system as a message
transport.
15
Page 34

The office server may be running a server to manage the company database.
The Message Agent at the company database runs as a client application for
that server.
At the laptop computers each sales representative has an Adaptive Server
Anywhere personal server to manage their own data.
While away from the office, a sales representative can make a single phone
call from their laptop to carry out the following functions:
♦ Collect new e-mail.
♦ Send any e-mail messages they have written.
♦ Collect publication updates from the office server.
♦ Submit any local updates, such as new orders, to the office server.
The updates may include, for example, new specials on the products the
sales representative handles, or new pricing and inventory information.
These are read by the Message Agent on the laptop and applied to the sales
rep’s database automatically, without requiring any additional action on the
sales representative’s part.
The new orders recorded by the sales representative are also automatically
submitted to the office without any extra action on the part of the sales
representative.
Server-to-server replication among offices
SQL Remote provides two-way replication between database servers at sales
offices or outlets and a central company office, without requiring database
administration experience at each sales office beyond the initial setup and
that required to maintain the server.
SQL Remote is not designed for up-to-the-minute data availability at each
site. Instead, it is appropriate where data can be replicated at periods of an
hour or so.
Such a setup may use an e-mail system to carry the replication, if there is
already a company-wide e-mail system. Alternatively, an occasional dial-up
system and file transfer software can be used to implement a FILE message
system.
16
Page 35

Chapter 2. SQL Remote Concepts
Central office
network server
Central office
database
More...
Office
database
Sales office server
More...
Sales office server
Desktop computerDesktop computer
Office
database
SQL Remote is easy to configure to allow each office to receive their own set
of data. Tables that are of office interest only (staff records, perhaps, if the
office is a franchise) may be kept private in the same database as the
replicated data.
Layers can be added to SQL Remote hierarchies: for example, each sales
office server could act as a consolidated database, supporting remote
subscribers who work from that office.
17
Page 36

Page 37

CHAPTER 3
Setting Up SQL Remote
About this chapter This chapter describes how to add SQL Remote capabilities to your
Adaptive Server Enterprise server.
Adaptive Server Enterprise users only
This chapter is required only for users of SQL Remote for Adaptive Server
Enterprise. SQL Remote capability is automatically installed into Adaptive
Server Anywhere databases.
This chapter assumes you have already installed the SQL Remote software
onto your machine.
Contents
Topic: page
Setup overview 20
Preparing your Adaptive Server Enterprise server 21
Upgrading SQL Remote for Adaptive Server Enterprise 25
Uninstalling SQL Remote 26
19
Page 38

Setup overview
We call the collection of databases exchanging information using
SQL Remote an installation. From a physical point of view, a SQL Remote
installation may consist of hundreds or even thousands of databases sharing
information; but as SQL Remote keeps the information in each physical
database loosely consistent at a transactional level with that in other physical
databases, you can also think of the whole installation as a single dispersed
database.
Deploying a large-scale SQL Remote installation can involve setting up
databases on many machines. While some changes to the design and setup
configuration can be made on a running installation, it is highly
recommended that you deploy only when you have completed a careful
analysis and test of your design.
Setup tasks Setup of a SQL Remote installation includes the following tasks:
♦ Preparing your server for SQL Remote You must take some steps to
configure your Adaptive Server Enterprise to act as a SQL Remote site.
These include installing the SQL Remote system objects and the stable
queue system objects.
♦ Selecting message types You must decide whether you want to
exchange information by file sharing, e-mail, some other message type,
or a combination.
All administration is at
the consolidated
database
20
♦ Ensuring proper permissions are set Each user in the installation
requires permissions on both their own database and on the consolidated
database.
♦ Extracting remote databases You must extract an initial copy of each
remote database from the consolidated database.
This chapter describes each of these tasks.
Like all SQL Remote administrative tasks, setup is carried out by a database
administrator or system administrator at the consolidated database.
The Sybase System Administrator should perform all SQL Remote
configuration tasks. See your Adaptive Server Enterprise documentation for
more information about the Adaptive Server Enterprise environment.
Page 39

Chapter 3. Setting Up SQL Remote
Preparing your Adaptive Server Enterprise server
Before you start This section assumes the following:
♦ You have installed an Adaptive Server Enterprise server that is to contain
the SQL Remote database.
♦ You have installed the SQL Remote software on your computer. To install
the SQL Remote software, run the setup program from the CD-ROM.
♦ You have created a database in the Adaptive Server Enterprise server that
will take part in your SQL Remote installation.
♦ You have system administrator permissions on the Adaptive Server
Enterprise server, and database owner permissions in the database.
Ensuring TEMPDB is large enough
SQL Remote uses the TEMPDB database for the following purposes:
♦ The database extraction utility used to create remote databases uses
TEMPDB to hold a temporary set of Adaptive Server Anywhere system
tables.
♦ The Message Agent creates a temporary table called #remote when it
connects to the server.
For these reasons, you should make TEMPDB larger than the 2 MB default
size. The size required depends on the number of tables and columns in your
SQL Remote installation, but a size of 10 MB is generally sufficient.
Installing the SQL Remote system objects
For a database in your Adaptive Server Enterprise server to take part in a
SQL Remote installation, you must install a number of SQL Remote system
tables, views, and stored procedures in your database.
❖ To install the SQL Remote system objects
1. Locate the SQL Remote initialization script
SQL Remote installation directory.
2. Make a backup copy of the
following two lines to the beginning of
use database_name
go
ssremote.sql
ssremote.sql
script file. Then add the
ssremote.sql
in your
:
21
Page 40

where
database_name
is the name of the database to take part in
SQL Remote replication.
These two lines set the current database to
SQL Remote tables are created in the
database_name
database_name
, so that the
database. The
SQL Remote tables are owned by the database owner.
3. Run the script against your Adaptive Server Enterprise server.
Change to the directory containing the script file and enter the following
command line (which should be entered all on one line) to run the script:
isql -S server-name -U login_id -P password -I ssremote.sql
where
login_id
permissions on the server who owns the database, and
of a log file to hold the log information from the script.
☞ The
Agent. For more information, see “The Message Agent and replication
security” on page 269.
4. Inspect the log file to confirm that the tables and procedures were created
without error.
The script creates a set of SQL Remote system objects in the database.
The SQL Remote system objects
The script creates the following objects in the database:
♦ SQL Remote system tables A set of tables used to maintain
SQL Remote information. These tables have names beginning with sr_.
♦ SQL Remote system views A set of views that hold the SQL Remote
information in a more understandable form. These views have names
beginning with sr_, and ending in s.
♦ SQL Remote system procedures A set of stored procedures used to
carry out SQL Remote configuration and administration tasks. These
procedures have names beginning with sp_, indicating their system
management roles.
-o logfile
server-name
and
password
login_id
is the name of the Adaptive Server Enterprise,
correspond to a user with system administrator
logfile
is the name
must correspond to the name used by the Message
22
Caution: Do not edit the SQL Remote system tables
Do not, under any circumstances, alter the SQL Remote system tables
directly. Doing so may corrupt the table and make it impossible for
SQL Remote to function properly. Use the SQL Remote system procedures
to carry out all system administration tasks.
Page 41

Command-line installation of the stable queue
The stable queue is a pair of database tables that hold transactions until they
are no longer needed by the replication system. Every Adaptive Server
Enterprise database participating in a SQL Remote installation needs a
stable queue.
☞ For detailed information about the stable queue, see “The stable queue”
on page 265.
The stable queue can exist in the same database as the database taking part
in SQL Remote, or in a separate database. Keeping the stable queue in a
separate database complicates the backup and recovery plan, but can
improve performance by putting the stable queue workload on separate
devices and/or a separate Adaptive Server Enterprise server.
❖ To install the stable queue
Chapter 3. Setting Up SQL Remote
1. Locate the stable queue initialization script
stableq.sql
in your
SQL Remote installation directory.
2. Make a backup copy of the
two lines to the beginning of
use database_name
go
where
database_name
stableq.sql
stableq.sql
script file. Then add the following
:
is the name of the database that will hold the stable
queue.
These two lines set the current database to
stable queue is created in the
database_name
database_name
, so that the
database. The stable queue
tables are owned by the database owner.
3. Run the script against your Adaptive Server Enterprise server.
Change to the directory holding the stable queue script, and enter the
following command line (which should be entered all on one line) to run
the script:
isql -S server-name -U login_id -P password -I stableq.sql -
where
login_id
permissions on the server who owns the database, and
o logfile
server-name
and
password
is the name of the Adaptive Server Enterprise,
correspond to a user with system administrator
logfile
is the name
of a log file to hold the log information from the script.
23
Page 42

☞ The
Agent. For more information, see “The Message Agent and replication
security” on page 269.
4. Inspect the log file to confirm that the tables and procedures were created
without error.
login_id
must correspond to the name used by the Message
24
Page 43

Chapter 3. Setting Up SQL Remote
Upgrading SQL Remote for Adaptive Server Enterprise
This section describes the procedure for upgrading SQL Remote for
Adaptive Server Enterprise.
As a SQL Remote installation may consist of a large number of databases, it
is generally not practical to upgrade software on all machines at the same
time. SQL Remote is designed so that upgrades can be carried out
incrementally. It is not important what order SQL Remote machines are
upgraded, as the message format is compatible with previous releases.
❖ To upgrade SQL Remote
1. Back up both the consolidated database and, if it is separate, the stable
queue database.
2. Install the new SQL Remote for Adaptive Server Enterprise software.
3. Run the script
SQL Remote system tables and procedures.
The
ssupdate.sql
4. Run the script
SQL Remote stable queue tables and procedures.
The
squpdate.sql
The software is now upgraded.
ssupdate.sql
script is held in your Sybase directory.
squpdate.sql
script is held in your Sybase directory.
at the consolidated database to upgrade the
at the stable queue database to upgrade the
25
Page 44

Uninstalling SQL Remote
This section describes how to uninstall the SQL Remote objects from a
database, and uninstall the stable queue from a database.
❖ To uninstall the SQL Remote objects from a database
1. Connect to the database containing the SQL Remote objects, as a user
with dbo permissions.
2. Run the sp_drop_sql_remote stored procedure to remove all
SQL Remote objects apart from the procedure itself. The
sp_drop_sql_remote procedure is installed along with the other
SQL Remote objects.
exec sp_drop_sql_remote
go
3. Drop the sp_drop_sql_remote procedure to complete the uninstall
procedure.
drop procedure sp_drop_sql_remote
go
❖ To uninstall the stable queue from a database
1. Connect to the database containing the stable queue, as a user with dbo
permissions.
26
2. Run the sp_queue_drop stored procedure to remove all stable queue
objects apart from the procedure itself. The sp_queue_drop procedure is
installed along with the other stable queue objects.
exec sp_queue_drop
go
3. Drop the sp_queue_drop procedure itself, to complete the uninstall
procedure.
drop procedure sp_queue_drop
go
Page 45

CHAPTER 4
Tutorials for Adaptive Server Anywhere Users
About this chapter This chapter guides you through setting up a simple replication system using
Adaptive Server Anywhere.
Contents
Topic: page
Introduction 28
Tutorial: AdaptiveServer Anywhere replicationusing Sybase Cen-
tral
Tutorial: Adaptive Server Anywhere replication using Interactive
SQL and dbxtract
Start replicating data 47
A sample publication 51
32
40
27
Page 46

Introduction
rep_key =
rep_key
SalesRep
rep_key char(5)
name char(40)
Customer
cust_key char(10)
name char(40)
rep_key char(5)
Goals
The database
These tutorials describe how to set up a simple SQL Remote replication
system using Adaptive Server Anywhere.
In the tutorials, you act as the system administrator of a consolidated
Adaptive Server Anywhere database, and set up a simple replication system.
The replication system consists of a simple sales database, with two tables.
The consolidated database holds all of the database, while the remote
database has all of one table, but only some of the rows in the other table.
The tutorials take you through the following steps:
♦ Creating a consolidated database on your Adaptive Server Anywhere
server.
♦ Creating a file-sharing replication system with a single Adaptive Server
Anywhere remote database.
♦ Replicating data between the two databases.
The tutorials use a simple two-table database. One table holds information
about sales representatives, and the other about customers. The tables are
much simpler than you would use in a real database; this allows us to focus
just on those issues important for replication.
Database schema The database schema for the tutorials is illustrated in the figure.
28
Features to note include the following:
♦ Each sales representative is represented by one row in the SalesRep table.
♦ Each customer is represented by one row in the Customer table.
♦ Each customer is assigned to a single sales representative, and this
assignment is built in to the database as a foreign key from the Customer
table to the SalesRep table. The relationship between the Customer table
and the SalesRep table is many-to-one.
Page 47

Chapter 4. Tutorials for Adaptive Server Anywhere Users
The tables in the
database
The tables are described in more detail as follows:
29
Page 48

Table Description
SalesRep One row for each sales representative that works for the
company. The SalesRep table has the following columns:
♦ rep_key An identifier for each sales representative.
This is the primary key.
♦ name The name of each sales representative.
The SQL statement creating this table is as follows:
CREATE TABLE SalesRep (
rep_key CHAR(12) NOT NULL,
name CHAR(40) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (rep_key)
)
Customer One row for each customer that does business with the
company. The Customer table includes the following
columns:
♦ cust_key An identifier for each customer. This is the
primary key.
♦ name The name of each customer.
♦ rep_key Anidentifier for the salesrepresentative in a
sales relationship. This is a foreign key to the SalesRep
table.
The SQL statement creating this table is as follows:
CREATE TABLE Customer (
cust_key CHAR(12) NOT NULL,
name CHAR(40) NOT NULL,
rep_key CHAR(12) NOT NULL,
FOREIGN KEY ( rep_key )
REFERENCES SalesRep (rep_key
),
PRIMARY KEY (cust_key)
)
Replication goals
30
The goals of the replication design are to provide each sales representative
with the following information:
♦ The complete SalesRep table.
♦ Those customers assigned to them.
The tutorials describe how to meet this goal using SQL Remote.
Page 49

Chapter 4. Tutorials for Adaptive Server Anywhere Users
Sybase Central or command-line utilities
Use Sybase Central or
the command line
Where next?
The tutorial material is presented twice. One tutorial describes how to set up
the installation using the Sybase Central management utility. The second
tutorial describes how to set up the installation using command-line utilities:
this requires typing commands individually.
♦ To work through the tutorial using Sybase Central, go to “Tutorial:
Adaptive Server Anywhere replication using Sybase Central” on page 32.
♦ To work through the tutorial entering commands explicitly, go to
“Tutorial: Adaptive Server Anywhere replication using Interactive SQL
and dbxtract” on page 40.
31
Page 50

Tutorial: Adaptive Server Anywhere replication using Sybase Central
The following sections are a tutorial describing how to set up a simple
SQL Remote replication system in Adaptive Server Anywhere using Sybase
Central.
You do not need to enter SQL statements if you are using Sybase Central to
administer SQL Remote. A tutorial for those who do not have access to
Sybase Central, or who prefer to work with command-line utilities, is
presented in “Tutorial: Adaptive Server Anywhere replication using
Interactive SQL and dbxtract” on page 40. This tutorial contains the SQL
statements executed behind the scenes by Sybase Central.
In this tutorial you act as the DBA of the consolidated database, and set up a
simple replication system using the file-sharing message link. The simple
example is a primitive model for a sales-force automation system, with two
tables. One contains a list of sales representatives, and another a list of
customers. The tables are replicated in a setup with one consolidated
database and one remote database. You can install this example on one
computer.
This tutorial assumes that you have some familiarity with Sybase Central.
☞ For an introduction to Sybase Central, see “ Managing Databases with
Sybase Central” [Introducing SQL Anywhere Studio, page 241].
Preparing for the Sybase Central replication tutorial
This section describes the steps you need to take to prepare for the tutorial.
These steps include the following:
♦ Create the directories and databases required for the tutorial.
♦ Add the tables to the consolidated database.
❖ To prepare for the tutorial
1. Create a directory to hold the files you make during this tutorial; for
example
2. Create a subdirectory for each of the two user IDs in the replication
system, to hold their messages. Create these subdirectories using the
following statements at a system command line:
32
c:\tutorial
mkdir c:\tutorial
.
Page 51

Chapter 4. Tutorials for Adaptive Server Anywhere Users
mkdir c:\tutorial\HQ
mkdir c:\tutorial\field
3. Create the HQ database:
♦ Start Sybase Central.
♦ In the left pane, select the Adaptive Server Anywhere plug-in.
♦ In the right pane, click the Utilities tab.
♦ Double-click Create Database in the right pane.
The Create Database wizard appears.
♦ Create a database with filename
c:\tutorial\HQ.db
.
Use the default settings for this database.
An Adaptive Server Anywhere database is simply a file, which can be
copied to other locations and computers when necessary.
The next step is to add a pair of tables to the consolidated database.
❖ To add tables to the consolidated database
1. Connect to the HQ database from Sybase Central, with a user ID of DBA
and a password of SQL.
2. Select the Tables folder of the HQ database in the left pane.
3. From the File menu, choose New ➤ Table and create a table named
SalesRep using the Table Creation wizard.
4. Add the following columns to the table (you can add a column by
choosing File ➤ Add Column):
Key Column Data Type Size/Prec
Primary key Rep_key char 5
Name char 40
You do not need to use the Column property sheet.
5. Save the table by choosing File ➤ Save Table or pressing Ctrl+S.
6. From the File menu, choose New ➤ Table and create a table named
Customer with the following columns:
Key Column Data Type Size/Prec
Primary key Cust_key char 10
Name char 40
Rep_key char 5
33
Page 52

Again, you do not need to use the property sheets.
7. Save the table.
8. In the Tables folder in the left pane, select the Customer table, then click
the Foreign Keys tab in the right pane.
9. From the File menu, choose New ➤ Foreign Key. Using the wizard, add a
foreign key to the Rep_key column of the SalesRep table. You can use
the default settings for this foreign key.
You are now ready for the rest of the tutorial.
Setting up a consolidated database
This section of the tutorial describes how to prepare the consolidated
database of a simple replication system.
Preparing a consolidated database for replication involves the following
steps:
1. Create a message type to use for replication.
2. Grant PUBLISH permissions to a user ID to identify the source of
outgoing messages.
3. Grant REMOTE permissions to all user IDs that are to receive messages.
4. Create a publication describing the data to be replicated.
5. Create subscriptions describing who is to receive the publication.
You require DBA authority to carry out these tasks.
Add a SQL Remote message type
All messages sent as part of replication use a message type. A message type
description has two parts:
♦ A message link supported by SQL Remote. In this tutorial, we use the
FILE link.
♦ An address for this message link, to identify the source of outgoing
messages.
Adaptive Server Anywhere databases already have message types created,
but you need to supply an address for the message type you will use.
34
Page 53

Chapter 4. Tutorials for Adaptive Server Anywhere Users
field
hq
Database: hq
Publisher: hq_user
Remote user: field_user
Database: field
Publisher: field_user
Consolidated user:
hq_user
❖ To add an address to a message type
1. From Sybase Central, connect to the HQ database.
2. Open the SQL Remote Users folder for the HQ database.
3. In the right pane, click the Message Types tab.
4. In the right pane, right-click the FILE message type and choose
Properties from the popup menu.
5. Enter a publisher address to provide a return address for remote users.
Enter the directory you have created to hold messages for the
consolidated database (HQ).
The address is taken relative to the SQLRemote environment variable or
registry entry. As you have not set this value, the address is taken relative
to the directory from which the Message Agent is run. You should run the
Message Agent from your tutorial directory for the addresses to be
interpreted properly.
☞ For information about setting the SQLRemote value, see “Setting
message type control parameters” on page 214.
6. Click OK to save the message type.
Add the publisher and remote user to the database
In SQL Remote’s hierarchical replication system, each database may have
zero or one database immediately above it (the consolidated database) and
zero or more databases immediately below it (remote databases).
In this tutorial, the current database is the consolidated database of a
two-level system. It has no database above it, and only one remote database
below it.
The following diagram illustrates the two databases:
35
Page 54

For any database in a SQL Remote replication setup, there are three
permissions that may be granted to identify databases on the hierarchy:
♦ PUBLISH permission Identifies the current database in all outgoing
messages
♦ REMOTE permission Identifies each database receiving messages from
the current database that is below it on the hierarchy
♦ CONSOLIDATE permission Identifies a database receiving messages
from the current database that is directly above it on the hierarchy.
Permissions can only be granted by a user with DBA authority. To carry out
these examples you should connect from Sybase Central to the hq database
as user ID DBA, with password SQL.
Add a database
publisher user ID
Any database, consolidated or remote, that distributes changes to other
databases in the replication system is a publisher database. Each database in
the replication system is identified by a single user ID. You set that ID for
your database by adding a publisher to the database. This section describes
setting permissions for the consolidated hq database.
First create a user ID named hq_user, who will be the publisher user ID.
❖ To create a new user as the publisher
1. Select the Users & Groups folder.
2. From the File menu, choose New ➤ User.
The User Creation wizard appears.
3. Enter the name hq_user, with password hq_pwd, and click Finish.
4. Right-click the hq_user icon and choose Change to Publisher from the
popup menu.
A database can have only one publisher. You can find out who the
publisher is at any time by opening the Users & Groups folder.
Add a remote user Each remote database is identified in the consolidated database by a user ID
with REMOTE permissions. Whether the remote database is a personal
database server or a network server with many users, it needs a single user
ID to represent it to the consolidated database.
In a mobile workgroup setting, remote users may already be users of the
consolidated database, and so no new users would need to be added;
although they would need to be set as remote users.
36
When a remote user is added to a database, the message system they use and
their address under that message system need to be stored along with their
database user ID.
Page 55

Chapter 4. Tutorials for Adaptive Server Anywhere Users
❖ To add a remote user
1. Select the SQL Remote Users folder.
2. From the File menu, choose New ➤ SQL Remote User.
The Create a New Remote User wizard appears.
3. Create a remote user with user ID field_user with the following options:
♦ Enter the password field_pwd.
♦ Ensure that Remote DBA authority is selected, so that the user can run
the Message Agent.
♦ Select the message type FILE, and enter the address field.
As with the publisher address, the address of the remote user is taken
relative to the SQLREMOTE environment variable or registry entry.
As you have not set this value, the address is taken relative to the
directory from which the Message Agent is run. You should run the
Message Agent from your tutorial directory for the addresses to be
interpreted properly.
☞ For information about setting the SQLREMOTE value, see
“Setting message type control parameters” on page 214.
♦ Ensure that the Send Then Close option is selected.
(In many production environments you would not choose Send Then
Close, but it is convenient for this tutorial.)
4. When you have finished, click Finish to create the remote user.
You have now created the users who will use this system.
Add publications and subscriptions
This section describes how to add a publication to a database, and how to
add a subscription to that publication for a user. The publication replicates
all rows of the table SalesRep and some of the rows of the Customer table.
❖ To add a publication
1. Select the Publications folder in the left pane.
2. From the File menu, choose New ➤ Publication.
The Publication Creation wizard appears.
3. Name the publication SalesRepData.
4. On the Tables tab, select SalesRep from the list of Available Tables.
Click Add.
The table appears in the list of Selected Tables on the right.
37
Page 56

5. Select Customer from the list of Available Tables. Click Add.
6. On the SUBSCRIBE BY Restrictions tab, select the Customer table and
enter the expression rep_key.
7. Click Finish to create the publication.
Add a subscription Each user ID that is to receive changes to a publication must have a
subscription to that publication. Subscriptions can only be created for a
valid remote user. You need to add a subscription to the SalesRepData
publication for the remote database user field_user.
❖ To add a subscription
1. Open the Publications folder and select the SalesRepData publication in
the left pane.
2. Click the SQL Remote Subscriptions tab in the right pane.
3. From the File menu, choose New ➤ SQL Remote Subscription.
The SQL Remote Subscription Creation wizard appears.
4. Choose to subscribe field_user. Enter a Subscription value of rep1 and
click Finish.
The subscription value is an expression that matches the Subscribe By
expression in the publication. In a later step, the field_user user ID is
assigned a rep_key value of rep1.
You have now set up the consolidated database.
Set up the remote database in Sybase Central
The remote database needs to be created and configured in order to send and
receive messages and participate in a SQL Remote setup.
Like the consolidated database, the remote database needs a publisher (in
this case, the field_user user ID) to identify the source of outgoing
messages, and it needs to have hq_user identified as a user with
consolidated permissions. It needs the SalesRepData publication to be
created and needs a subscription created for the hq_user user ID.
The remote database also needs to be synchronized with the consolidated
database; that is, it needs to have a current copy of the data in order for the
replication to start. In this case, there is no data in the publication as yet.
The database extraction utility enables you to carry out all the steps needed
to create a remote database complete with subscriptions and required user
IDs.
38
Page 57

Chapter 4. Tutorials for Adaptive Server Anywhere Users
You need to extract a database from the consolidated database for remote
user field_user.
❖ To extract a database
1. Connect to the HQ database.
2. Right-click the database and choose Extract Database from the popup
menu.
3. Choose to extract the HQ database with the following options:
♦ Choose to extract at isolation level 3.
♦ Choose to Start Subscriptions Automatically, for user field_user.
♦ Choose Extract and Reload into a New Database.
♦ Leave the reload file location at its default setting.
♦ Choose to extract both structure and data.
♦ Choose not to extract fully-qualified publication definitions.
♦ Create the database as file
the remote database.
In a proper SQL Remote setup, the remote database field would need to be
loaded on to the computer using it, together with an Adaptive Server
Anywhere server and any client applications required. For this tutorial, we
leave the database where it is and use Interactive SQL to input and replicate
data.
c:\tutorial\field.db
, and click Finish to create
You should connect to the field database as DBA and confirm that all the
database objects are created. These include the SalesRep and Customer
tables, the SalesRepData publication, and the subscription for the
consolidated database.
What next? The system is now ready for replication.
☞ For the next step, inserting and replicating data, see the section “Start
replicating data” on page 47.
39
Page 58

Tutorial: Adaptive Server Anywhere replication using Interactive SQL and dbxtract
The following sections are a tutorial describing how to set up a simple
SQL Remote replication system for users who prefer to use command-line
tools or who want to know what Sybase Central is doing behind the scenes.
This tutorial describes the SQL statements for managing SQL Remote,
which can be run from Interactive SQL. It also describes how to run the
dbxtract
consolidated database.
In this tutorial you act as the DBA of the consolidated database, and set up a
simple replication system using the file-sharing message link. The simple
example is a primitive model for a sales-force automation system, with two
tables. One contains a list of sales representatives, and another a list of
customers. The tables are replicated in a setup with one consolidated
database and one remote database. You can install this example on one
computer.
Preparing for the replication tutorial
This section describes the steps you need to take to prepare for the tutorial.
These steps include the following:
♦ Create the directories and databases required for the tutorial.
command-line utility to extract remote databases from a
40
♦ Add a table to the consolidated database.
❖ To create the databases and directories for the tutorial
1. Create a directory to hold the files you make during this tutorial; for
example
2. The tutorial uses two databases: a consolidated database named
and a remote database named
and create these databases using the following statements at a command
prompt:
3. Create a subdirectory for each of the two user IDs in the replication
system. Create these subdirectories using the following statements at a
command prompt:
c:\tutorial
mkdir c:\tutorial
dbinit hq.db
dbinit field.db
.
field.db
. Change to the tutorial directory
hq.db
Page 59

Chapter 4. Tutorials for Adaptive Server Anywhere Users
mkdir c:\tutorial\hq
mkdir c:\tutorial\field
The next step is to add a pair of tables to the consolidated database.
❖ To add the tables to the consolidated database
1. Connect to
hq.db
password of SQL.
2. Execute the following CREATE TABLE statement to create the
SalesRep table:
CREATE TABLE SalesRep (
rep_key CHAR(12) NOT NULL,
name CHAR(40) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY ( rep_key )
);
3. Execute the following CREATE TABLE statement to create the
Customer table:
CREATE TABLE Customer (
cust_key CHAR(12) NOT NULL,
name CHAR(40) NOT NULL,
rep_key CHAR(12) NOT NULL,
FOREIGN KEY REFERENCES SalesRep,
PRIMARY KEY ( cust_key )
);
You are now ready for the rest of the tutorial.
Set up the consolidated database
This section of the tutorial describes how to set up the consolidated database
of a simple replication system.
from Interactive SQL with a user ID of DBA and a
You require DBA authority to carry out this task.
Create a SQL Remote message type
All messages sent as part of replication use a message type. A message type
description has two parts:
♦ A message link supported by SQL Remote. In this tutorial, we use the
FILE link.
♦ An address for this message link, to identify the source of outgoing
messages.
41
Page 60

❖ To create the message type
1. In Interactive SQL, create the file message type using the following
statement:
CREATE REMOTE MESSAGE
TYPE file
ADDRESS ’hq’
The address (hq) for a file link is a directory in which files containing the
message are placed. It is taken relative to the SQLRemote environment
variable or registry entry. As you have not set this value, the address is taken
relative to the directory from which the Message Agent is run. You should
run the Message Agent from your tutorial directory for the addresses to be
interpreted properly.
For information about setting the SQLRemote value, see
☞
message type control parameters” on page 214.
Grant PUBLISH and REMOTE at the consolidated database
In the hierarchical replication system supported by SQL Remote, each
database may have one consolidated database immediately above it in the
hierarchy and many databases immediately below it on the hierarchy
(remote databases).
PUBLISH permission identifies the current database for outgoing messages,
and the REMOTE permission identifies each database receiving messages
from the current database.
“Setting
GRANT PUBLISH to
identify outgoing
messages
42
Permissions can only be granted by a user with DBA authority. To carry out
these examples you should connect using the Interactive SQL utility to hq as
user ID DBA, with password SQL.
Each database that distributes its changes tootherdatabases in the replication
system is a publisher database. Each database in the replication system that
publishes changes to a database is identified by a single user ID. You set that
ID for your database using the GRANT PUBLISH statement. This section
describes setting permissions for the consolidated database (
hq.db
).
❖ To create a publisher for the database
1. Connect to the database using Interactive SQL, and type the following
statement:
GRANT CONNECT
TO hq_user
IDENTIFIED BY hq_pwd ;
GRANT PUBLISH TO hq_user ;
Page 61

Chapter 4. Tutorials for Adaptive Server Anywhere Users
You can check the publishing user ID of a database at any time using the
CURRENT PUBLISHER special constant:
SELECT CURRENT PUBLISHER
GRANT REMOTE for
each database to which
you send messages
Each remote database is identified using the GRANT REMOTE statement.
Whether the remote database is a personal server or a network server with
many users, it needs a single user ID to represent it to the consolidated
database.
In a mobile workgroup setting, remote users may already be users of the
consolidated database, and so this would require no extra action on the part
of the DBA.
The GRANT REMOTE statement identifies the message system to be used
when sending messages to the recipient, as well as the address.
❖ To add a remote user
1. Connect to the database using Interactive SQL, and execute the following
statements:
GRANT CONNECT TO field_user
IDENTIFIED BY field_pwd ;
GRANT REMOTE TO field_user
TYPE file ADDRESS ’field’ ;
The address string is the directory used to hold messages for field_user,
enclosed in single quotes. It is taken relative to the SQLRemote
environment variable or registry entry. As you have not set this value, the
address is taken relative to the directory from which the Message Agent
is run. You should run the Message Agent from your tutorial directory for
the addresses to be interpreted properly.
☞ For information about setting the SQLRemote value, see “Setting
message type control parameters” on page 214.
Create publications and subscriptions
A publication is created using a CREATE PUBLICATION statement. This is
a data definition language statement, and requires DBA authority. For the
tutorial, you should connect to the hq database as user ID DBA, password
SQL, to create a publication.
Set up a publication at
the consolidated
database
Create a publication named SalesRepData, which replicates all rows of the
table SalesRep, and some of the rows of the table Customer.
43
Page 62

❖ To create the publication
1. Connect to the database from Interactive SQL, and execute the following
statement:
CREATE PUBLICATION SalesRepData (
TABLE SalesRep,
TABLE Customer SUBSCRIBE BY rep_key
)
Set up a subscription Each user ID that is to receive changes to the publication must have a
subscription. The subscription can only be created for a user who has
REMOTE permissions. The GRANT REMOTE statement contains the
address to use when sending the messages.
❖ To create the subscription
1. Connect to the database from Interactive SQL, and execute the following
statement:
CREATE SUBSCRIPTION
TO SalesRepData (’rep1’)
FOR field_user ;
The value rep1 is the rep_key value we will give to the user field_user in
the SalesRep table.
The full CREATE SUBSCRIPTION statement allows control over the data
in subscriptions; allowing users to receive only some of the rows in the
publication. For more information, see “CREATE SUBSCRIPTION
statement” on page 358.
The CREATE SUBSCRIPTION statement identifies the subscriber and
defines what they receive. However, it does not synchronize data, or start the
sending of messages.
Set up the remote database
The remote database needs to be configured in order to send and receive
messages and participate in a SQL Remote setup. Like the consolidated
database, the remote database needs a CURRENT PUBLISHER to identify
the source of outgoing messages, and it needs to have the consolidated
database identified as a subscriber. The remote database also needs the
publication to be created and needs a subscription created for the
consolidated database. The remote database also needs to be synchronized
with the consolidated database; that is, it needs to have a current copy of the
data in order for the replication to start.
44
Page 63

Chapter 4. Tutorials for Adaptive Server Anywhere Users
The
dbxtract
utility enables you to carry out all the steps needed to create a
remote database complete with subscriptions and required user IDs.
Extract the remote database information
Leave the hq database running, and change to the tutorial directory.
Type the following command at the system command line (all on one line) to
extract a database for the user field_user from the consolidated database:
dbxtract -v -c "dbn=hq;uid=dba;pwd=sql" c:\tutorial field_user
The -v option produces more verbose output. This is useful during
development.
This command assumes the hq database is currently running on the default
server. If the database is not running, you should enter a database file
parameter in the connection string:
dbf=hq.db
instead of the dbn database name parameter.
☞ For details of the
utility” on page 303.
The
dbxtract
current directory and a data file in the
subscriptions to the remote user.
The next step is to load these files into the remote database.
Load the remote database information
❖ To load the database information
1. From the tutorial directory, connect to the remote database
Interactive SQL with a user ID of DBA and a password of SQL.
2. Run the
READ C:\tutorial\reload.sql
The
reload.sql
♦ Creates a message type at the remote database.
♦ Grants PUBLISH and REMOTE permissions to the remote and
consolidated database, respectively.
command creates a SQL command file named
reload.sql
command file carries out the following tasks:
dbxtract
utility and its options, see “The extraction
command file:
c:\tutorial
reload.sql
in the
directory. It also starts the
field.db
from
45
Page 64

♦ Creates the table in the database. If the table had contained any data
before extraction, the command file would fill the replicated table with a
copy of the data.
♦ Creates a publication to identify the data being replicated.
♦ Creates the subscription for the consolidated database, and starts the
subscription.
While connected to the field database as DBA, confirm that the tables are
created by executing the following statements:
SELECT*FROM SalesRep ;
SELECT*FROM Customer ;
What next? The system is now ready for replication.
☞ For the next step, inserting and replicating data, see the section “Start
replicating data” on page 47.
46
Page 65

Chapter 4. Tutorials for Adaptive Server Anywhere Users
Start replicating data
You now have a replication system in place. In this section, data is replicated
from the consolidated database to the remote database, and from the remote
to the consolidated database.
Enter data at the consolidated database
First, enter some data into the consolidated database.
❖ To enter data at the consolidated database
1. Connect to the consolidated database hq from the Interactive SQL utility
with a user ID of DBA and a password of SQL.
2. Insert two rows into the SalesRep table and commit the insertion by
executing the following statement:
INSERT INTO SalesRep (rep_key, name)
VALUES (’rep1’, ’Field User’) ;
INSERT INTO SalesRep (rep_key, name)
VALUES (’rep2’, ’Another User’) ;
COMMIT ;
3. Insert two rows into the Customer table and commit the insertion by
executing the following statement:
INSERT INTO Customer (cust_key, name, rep_key)
VALUES (’cust1’, ’Ocean Sports’, ’rep1’ ) ;
INSERT INTO Customer (cust_key, name, rep_key)
VALUES (’cust2’, ’Sports Plus’, ’rep2’ ) ;
COMMIT ;
4. Confirm that the data has been entered by executing the following
statements:
SELECT
FROM SalesRep;
SELECT
FROM Customer;
*
*
The next step is to send the relevant rows to the remote database.
Send data from the consolidated database
To send the rows to the remote database, you must run the Message Agent at
the consolidated database. The
Adaptive Server Anywhere.
dbremote
program is the Message Agent for
47
Page 66

❖ To send the data to the remote database
1. From a command prompt, change to your tutorial directory. For example,
> c:
> cd c:\tutorial
2. Enter the following statement at the command line to run the Message
Agent against the consolidated database:
dbremote -c "dbn=hq;uid=dba;pwd=sql"
This command line assumes that the hq database is currently running on
the default server. If the database is not running, you must supply a dbf
parameter with the database file name instead of the dbn parameter.
☞ For more information on
Agent” on page 292.
3. Click Shutdown on the Message Agent window to stop the Message
Agent when the messages have been sent. The Message Agent window
displays the message Execution completed when all processing is
complete.
Receive data at the remote database
To receive the insert statement at the remote database, you must run the
Message Agent,
dbremote
dbremote
options, see “The Message
, at the remote database.
48
❖ To receive data at the remote database
1. From a command prompt, change to your tutorial directory. For example,
> c:
> cd c:\tutorial
2. Enter the following statement at the command line to run the Message
Agent against the field database:
dbremote -c "dbn=field;uid=dba;pwd=sql"
This command line assumes that the field database is currently running
on the default server.
☞ For more information on
dbremote
options, see “The Message
Agent” on page 292.
3. Click Shutdown on the Message Agent window to stop the Message
Agent when the messages have been processed. The Message Agent
window displays the message Execution completed when all
processing is complete.
Page 67

Chapter 4. Tutorials for Adaptive Server Anywhere Users
The Message Agent window displays status information while running. This
information can be output to a log file for record keeping in a real setup. You
will see that the Message Agent first receives a message from hq, and then
sends a message. This return message contains confirmation of successful
receipt of the replication update; such confirmations are part of the
SQL Remote message tracking system that ensures message delivery even in
the event of message system errors.
Verify that the data has
arrived
You should now connect to the remote field database using Interactive SQL,
and inspect the SalesRep and Customer tables, to see which rows have been
received.
❖ To verify that the data has arrived
1. Connect to the field database using Interactive SQL.
2. Inspect the SalesRep table by executing the following statement:
SELECT*FROM SalesRep
You will see that the SalesRep table contains both rows entered at the
consolidated database. This is because the SalesRepData publication
included all the data from the SalesRep table.
3. Inspect the Customer table by executing the following statement:
SELECT*FROM Customer
You will also see that the Customer table contains only row (Ocean
Sports) entered at the consolidated database. This is because the
SalesRepData publication included only those customers assigned to the
subscribed Sales Rep.
Replicate from the remote database to the consolidated database
You should now try entering data at the remote database and sending it to the
consolidated database. Only the outlines are presented here.
❖ To replicate data from the remote database to the consolidated
database
1. Connect to the field database from Interactive SQL.
2. Insert a row at the remote database by executing the following statement:
INSERT INTO Customer (cust_key, name, rep_key)
VALUES (’cust3’, ’North Land Trading’, ’rep1’)
3. Commit the insertion by executing the following statement::
49
Page 68

COMMIT;
4. With the
field.db
database running, run the
dbremote
utility from a
command line to send the message to the consolidated database.
dbremote -c "dbn=field;uid=dba;pwd=sql"
5. With the
hq.db
database running, run the
dbremote
utility from a
command line to receive the message at the consolidated database:
dbremote -c "dbn=hq;uid=dba;pwd=sql"
6. Connect to the consolidated database. Display the Customer table by
executing the following statement:
SELECT
FROM Customer
cust_key name rep_key
cust1 Ocean Sports rep1
cust2 Sports Plus rep2
cust3 North Land Trading rep1
*
In this simple example, there is no protection against duplicate entries of
primary key values. SQL Remote does provide for such protection. For
information, see the chapters on SQL Remote Design.
50
Page 69

Chapter 4. Tutorials for Adaptive Server Anywhere Users
A sample publication
The command file
publication on the sample database. This publication illustrates several of
the points of the tutorials, in more detail.
❖ To add the publication to the sample database
1. Connect to the sample database from Interactive SQL.
2. In the SQL Statements pane, execute the following statement:
READ path\scripts\salespub.sql
where
path
The
salespub.sql
sample database, creates a publication and subscriptions, and also adds
triggers to resolve update conflicts that may occur.
salespub.sql
is your SQL Anywhere directory.
publication adds columns to some of the tables in the
contains a set of statements that creates a
51
Page 70

Page 71

CHAPTER 5
A Tutorial for Adaptive Server Enterprise Users
About this chapter This chapter presents a tutorial in which you set up a simple SQL Remote
replication system between an Adaptive Server Enterprise database and an
Adaptive Server Anywhere database, from scratch.
Contents
Topic: page
Introduction 54
Tutorial: Adaptive Server Enterprise replication 57
Start replicating data 66
53
Page 72

Introduction
rep_key =
rep_key
SalesRep
rep_key char(5)
name char(40)
Customer
cust_key char(10)
name char(40)
rep_key char(5)
Goals
The database
This chapter presents a tutorial to lead you through setting up a SQL Remote
installation. The installation replicates data between an Adaptive Server
Enterprise database (the consolidated database) and an Adaptive Server
Anywhere database (the remote database).
In the tutorial you act as the system administrator of a consolidated Adaptive
Server Enterprise database, and set up a simple replication system. The
replication system consists of a simple sales database, with two tables.
The consolidated database holds all of the database, while the remote
database has all of one table, but only some of the rows in the other table.
The tutorial takes you through the following steps:
♦ Creating a consolidated database on your Adaptive Server Enterprise
server.
♦ Creating a file-sharing replication system with a single Adaptive Server
Anywhere remote database.
♦ Replicating data between the two databases.
Database schema The database schema for the tutorial is illustrated in the figure.
54
The tutorial uses a simple two-table database. One table holds information
about sales representatives, and the other about customers. The tables are
much simpler than you would use in a real database; this allows us to focus
just on those issues important for replication.
Features to note include the following:
♦ Each sales representative is represented by one row in the SalesRep table.
♦ Each customer is represented by one row in the customer table.
♦ Each customer is assigned to a single Sales representative, and this
assignment is built in to the database as a foreign key from the Customer
Page 73

Chapter 5. A Tutorial for Adaptive ServerEnterprise Users
table to the SalesRep table. The relationship between the Customer table
and the SalesRep table is many-to-one.
The tables in the
database
The tables are described in more detail as follows:
Table Description
SalesRep One row for each sales representative that works for the
company. The SalesRep table has the following columns:
♦ rep_key An identifier for each sales representative.
This is the primary key.
♦ name The name of each sales representative.
The SQL statement creating this table is as follows:
CREATE TABLE SalesRep (
rep_key CHAR(12) NOT NULL,
name CHAR(40) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (rep_key)
)
Customer One row for each customer that does business with the
company. The Customer table includes the following
columns:
♦ cust_key An identifier for each customer. This is the
primary key.
♦ name The name of each customer.
♦ rep_key Anidentifier for the salesrepresentative in a
sales relationship. This is a foreign key to the SalesRep
table.
Replication goals
The SQL statement creating this table is as follows:
CREATE TABLE Customer (
cust_key CHAR(12) NOT NULL,
name CHAR(40) NOT NULL,
rep_key CHAR(12) NOT NULL,
FOREIGN KEY ( rep_key )
REFERENCES SalesRep (rep_key
),
PRIMARY KEY (cust_key)
)
The goals of the replication design are to provide each sales representative
with the following information:
55
Page 74

♦ The complete SalesRep table.
♦ Those customers assigned to them.
The tutorial describes how to meet this goal using SQL Remote.
56
Page 75

Chapter 5. A Tutorial for Adaptive ServerEnterprise Users
Tutorial: Adaptive Server Enterprise replication
The following sections are a tutorial describing how to set up a simple
SQL Remote replication system.
This tutorial describes the stored procedures used to configure and manage
SQL Remote. It also describes how to run the
remote databases from a consolidated database and the Message Agents to
send information between the databases in the replication system.
In this tutorial you act as the administrator of the consolidated database, and
set up a simple replication system using the file-sharing message link. The
simple example is a primitive model for a sales-force automation system,
with two tables. One contains a list of sales representatives, and another a
list of customers. The tables are replicated in a setup with one consolidated
database and one remote database. You can install this example on one
computer.
First steps
ssxtract
utility to extract
Create a login name and
password
Create a database Create a database named hq on your Adaptive Server Enterprise server with
To work through the tutorial, you must have system administrator privileges
on an Adaptive Server Enterprise server. The tutorial assumes that your
login name is the two-letter word sa and that your password is sysadmin.
The tutorial uses the Adaptive Server Enterprise
name and password as given above, you can connect to your Adaptive Server
Enterprise server using the following command line:
isql -S server-name -U sa -P sysadmin
where
server-name
which you connect.
Ensure that you have an appropriate login ID and can connect to your server
before starting this tutorial.
sufficient space to hold the tables and data required by the tutorial database.
A space of 4 MB is sufficient.
❖ To create a database
1. Using
2. Use the master database:
isql
privileges:
isql -S server-name -U sa -P sysadmin
is the name of the Adaptive Server Enterprise server to
, connect to the server as a user with system administrator
isql
utility. With the login
57
Page 76

use master
go
3. Create a database named hq. In this example, we use a 5 MB database
with a 5 Mb log, on two different devices:
create database hq
on database_device = 5
log on log_device = 5
go
☞ For more information on how to create databases and assign space to
them, see your Adaptive Server Enterprise documentation.
Install SQL Remote You need to install SQL Remote into the hq database.
❖ To install SQL Remote into the hq database
1. If the system administrator login name you are using does not have the
hq database as the default database, make a backup copy of the
ssremote.sql
two lines to the beginning of the script:
use hq
go
script from your installation directory, and add the following
Create directories for
messages
58
2. Change to the tutorial directory. Then, using
using the hq database, and run the
ssremote.sql
isql
, connect to the server
script from your
SQL Remote installation directory. The following command should be
entered all on one line:
isql -S server-name -U sa -P sysadmin -I ssremote.sql
3. If the system administrator login name you are using does not have the
hq database as the default database, make a backup copy of the
stableq.sql
script from your installation directory, and add the following
two lines to the beginning of the script:
use hq
go
4. Using
isql
stableq.sql
, connect to the server using the hq database, and run the
script from your SQL Remote installation directory. The
following command should be entered all on one line:
isql -S server-name -U sa -P sysadmin -I stableq.sql
Create a directory to hold the files from this tutorial. For example:
mkdir c:\tutorial
Page 77

Chapter 5. A Tutorial for Adaptive ServerEnterprise Users
You should create a directory for each of the two users of the replication
system under your parent directory for this tutorial:
mkdir c:\tutorial\hq
mkdir c:\tutorial\field
The next step is to add a pair of tables to the consolidated database.
❖ To add tables to the consolidated database
1. Connect to the hq database from
isql
, as a system administrator.
2. Use the hq database:
use hq
go
3. Create the SalesRep table with the following statement:
create table SalesRep (
rep_key char(12) not null,
name char(40) not null,
primary key (rep_key) )
go
4. Create the Customer table with the following statement:
create table Customer (
cust_key char(12) not null,
name char(40) not null,
rep_key char(12) not null,
primary key (cust_key) )
go
5. Alter the Customer table to add a foreign key to the SalesRep table:
alter table Customer
add foreign key
( rep_key ) references SalesRep
go
You are now ready for the rest of the tutorial.
Setting up the consolidated database
This section of the tutorial describes how to prepare the consolidated
database of a simple replication system.
Preparing a consolidated database for replication involves the following
steps:
1. Create a message type to use for replication.
59
Page 78

2. Grant PUBLISH permissions to a user ID to identify the source of
outgoing messages.
3. Grant REMOTE permissions to all user IDs that are to receive messages.
4. Create a publication describing the data to be replicated.
5. Create subscriptions describing who is to receive the publication.
You should have system administrator authority to carry out these tasks.
Create the message links and addresses
In this tutorial, messages are exchanged using the shared file link. You must
create a FILE message type supplying the address of the consolidated
database publisher.
❖ To create the message type
1. Execute the sp_remote_type stored procedure, using HQ as the address
of the consolidated database publisher:
sp_remote_type file, hq
go
The address (hq) for a file link is a directory in which files containing the
message are placed. It is taken relative to the SQLRemote environment
variable or registry entry. As you have not set this value, the address is
taken relative to the directory from which the Message Agent is run. You
should run the Message Agent from your tutorial directory for the
addresses to be interpreted properly.
☞ For information about setting the SQLRemote value, see “Setting
message type control parameters” on page 214.
With the message type defined, you can now make the necessary users.
Create the necessary users and permissions
A set of users and permissions are required for SQL Remote installations. In
this tutorial, the following are required:
♦ A remote user or subscriber, with name field_user.
♦ A publisher user name, called hq_user.
This section describes the steps you need to take to create each user and
assign them the necessary permissions.
60
Page 79

Chapter 5. A Tutorial for Adaptive ServerEnterprise Users
❖ To create the publisher
1. Add a login called hq_user, with hq as the default database and with
system administrator access:
exec sp_addlogin hq_user, hq_pwd, hq
go
exec sp_role ’grant’, sa_role, hq_user
go
2. Add the login name as a user to the HQ database:
use hq
go
exec sp_adduser hq_user
go
3. Make this user the publisher of the HQ database:
exec sp_publisher hq_user
go
Add a remote user Each remote database is identified in the consolidated database by a user ID
with REMOTE permissions. Whether the remote database is a single-user
server or a database server with many users, it needs a single user ID to
represent it to the consolidated database.
In a mobile workgroup setting, remote users may already be users of the
consolidated database, and so no new users would need to be added;
although they would need to be set as remote users.
When a remote user is added to a database, the message system they use and
their address under that message system need to be stored along with their
database user ID.
❖ To create the subscriber
1. If you do not have a login name that you can use for the remote user, add
a login:
exec sp_addlogin field_user, field_pwd, hq
go
2. Add a user to the hq database:
exec sp_adduser field_user
go
3. Grant the user remote permissions. Execute the sp_grant_remote stored
procedure, using field_user as the user name, file as the message type,
and the appropriate directory as the address:
61
Page 80

exec sp_grant_remote field_user, file, field
go
As with the publisher address, the address of the remote user (field) is a
directory relative to the SQLRemote environment variable or registry
entry. As you have not set this value, the address is taken relative to the
directory from which the Message Agent is run. You should run the
Message Agent from your tutorial directory for the addresses to be
interpreted properly.
☞ For information about setting the SQLRemote value, see “Setting
message type control parameters” on page 214.
Create the publication and subscription
The remaining task is to define the data to be replicated. To do this, you must
first create a publication, which defines the available data, and then create a
subscription for field_user, which defines the data that user is sharing.
In Adaptive Server Enterprise, they are created with the
sp_create_publication procedure, which creates an empty publication, and
the sp_add_article procedure, which adds articles to the procedure. Also,
each table must be marked for replication before it can be included in a
publication.
❖ To create the publication
62
1. Create an empty publication:
exec sp_create_publication SalesRepData
go
2. Mark both the SalesRep table and the Customer table for publication:
exec sp_add_remote_table SalesRep
go
exec sp_add_remote_table Customer
go
3. Add the whole SalesRep table to the SalesRepData publication:
exec sp_add_article SalesRepData, SalesRep
go
4. Add the Customer table to the SalesRepData publication, using the
rep_key column to partition the table. The following statement should be
typed all on one line, except for the go:
exec sp_add_article SalesRepData, Customer, NULL, ’rep_key’
go
Page 81

Chapter 5. A Tutorial for Adaptive ServerEnterprise Users
Add a subscription Each user ID that is to receive changes to a publication must have a
subscription to that publication. Subscriptions can only be created for a
valid remote user. You need to add a subscription to the SalesRepData
publication for the remote database user field_user.
❖ To create a subscription
1. Create a subscription to SalesRepData for field_user, with a
subscription value of rep1:
At this stage, the subscription is not started—that is, no data will be
exchanged. The subscription is started by the database extraction utility.
Extract the remote database
There are three stages to producing a remote Adaptive Server Anywhere
database:
♦ Extract the schema and data into a set of files. You do this using the
ssxtract
♦ Create an Adaptive Server Anywhere database.
♦ Load the schema and data into the database.
Extracting the schema
and data
With all the information included, the next step is to extract an Adaptive
Server Anywhere database for user field_user. The following command line
(entered all on one line, from the tutorial directory) carries out this
procedure:
ssxtract -v -c "eng=server-name; dbn=hq;uid=sa;pwd=sysadmin" C:\
The options have the following meaning.
exec sp_subscription ’create’, SalesRepData, field_user,
’rep1’
go
utility.
tutorial\field field_user
♦ -v Verbose mode. For development work, this provides additional
output.
♦ -c Connection string option. The connection string is supplied in double
quotes following the -c.
♦ eng=server-name Specifies the server to which the extraction utility is
to connect.
♦ dbn=hq Specifies the database on the server to use; in this case hq.
63
Page 82

♦ uid=sa The login ID to use to log on to the database.
♦ pwd=sysadmin The password to use to log on to the database.
♦ C:\tutorial\field The directory in which to place files holding the data.
♦ field_user The user ID for which to extract the database.
☞ For more information on extraction utility options, see “The extraction
utility” on page 303.
Running this command produces the following files:
Creating an Adaptive
Server Anywhere
database
Loading the data into the
database
♦ Reload script The reload script is named
reload.sql
, and is placed in
the current directory.
♦ Data files Files containing data to load into the database. In this case,
these files are empty.
You can create an Adaptive Server Anywhere database using the
dbinit
utility. A simple Adaptive Server Anywhere database is a file, unlike
Adaptive Server Enterprise databases.
You should create the Adaptive Server Anywhere database so that it is
compatible with Adaptive Server Enterprise database behavior, unless you
have set options in your Adaptive Server Enterprise server that are different
from the default.
❖ To create a database file named field.db
1. Enter the following command from the
dbinit -b -c -k field.db
c:\tutorial\field
directory:
The -b option forces use of blank padding in string comparisons. The -c
option enforces case sensitivity for string comparisons. The -k option
makes the system catalog more compatible with Adaptive Server
Enterprise.
You can load the data into the database using the Adaptive Server Anywhere
Interactive SQL utility or the
rtsql
utility.
rtsql
is an alternative to
Interactive SQL for batch processes only, and is provided for the runtime
database.
64
❖ To load the data into the database using Interactive SQL
1. Start an Adaptive Server Anywhere server running on the field database:
dbeng9 field.db
Page 83

Chapter 5. A Tutorial for Adaptive ServerEnterprise Users
2. Connect to the server using the Interactive SQL utility:
dbisql -c "eng=field;dbn=field;uid=DBA;pwd=SQL"
The user ID and password must be entered in upper case, as the Adaptive
Server Anywhere database was created as case-sensitive.
3. Load the data using the READ command:
READ C:\TUTORIAL\RELOAD.SQL
❖ To load the data into the database as a batch process
1. Start an Adaptive Server Anywhere server running on the field database:
dbeng9 field.db
2. Run the script from Interactive SQL:
dbisql -c "eng=field;dbn=field;uid=DBA;pwd=SQL" reload.sql
The user ID and password must be entered in upper case, as the Adaptive
Server Anywhere database was created as case-sensitive.
What next? The system is now ready for replication.
☞ For the next step, inserting and replicating data, see the section “Start
replicating data” on page 66.
65
Page 84

Start replicating data
You now have a replication system in place. In this section, data is replicated
from the consolidated database to the remote database, and from the remote
to the consolidated database.
Enter data at the consolidated database
In this section we enter data into the SalesRep and Customer tables at the
consolidated (Adaptive Server Enterprise) database, and replicate this data to
the Adaptive Server Anywhere database.
❖ To enter data at the Adaptive Server Enterprise database
1. Connect to the Adaptive Server Enterprise server from
isql -S server-name -U sa -P sysadmin
isql
:
2. Ensure you are using the hq database, and enter a series of rows:
use hq
go
insert into SalesRep (rep_key, name)
values (’rep1’, ’Field User’)
go
insert into SalesRep (rep_key, name)
values (’rep2’, ’Another User’)
go
insert into Customer (cust_key, name, rep_key)
values (’cust1’, ’Ocean Sports’, ’rep1’)
go
insert into Customer (cust_key, name, rep_key)
values (’cust2’, ’Sports Plus’, ’rep2’)
go
commit
go
Ocean Sports is assigned to Field User, and Sports Plus is assigned to
Another User. You must commit the changes, as SQL Remote replicates
only committed changes.
Having entered the data at the consolidated database, you now need to send
the relevant rows to the remote Adaptive Server Anywhere database.
Send data from the consolidated database
To send the rows to the remote database, you must run the Message Agent at
the consolidated database. The
Adaptive Server Enterprise.
66
ssremote
program is the Message Agent for
Page 85

Chapter 5. A Tutorial for Adaptive ServerEnterprise Users
❖ To replicate the data from Adaptive Server Enterprise
1. Enter the following statement (on a single line) at the command line to
run the Message Agent against the consolidated database:
ssremote -c "eng=server-name;dbn=hq;uid=sa;pwd=sysadmin"
2. Click Shutdown on the Message Agent window to stop the Message
Agent when the messages have been sent.
Receive data at the remote database
To receive the insert statement at the remote database, you must run the
Message Agent,
❖ To receive the data at Adaptive Server Anywhere
1. With the database server running, receive the data using the Message
Agent for Adaptive Server Anywhere:
dbremote -c "eng=field;dbn=field;uid=DBA;pwd=SQL"
dbremote
, at the remote database.
Verify that the data has
arrived
☞ For more information on
dbremote
options, see “The Message
Agent” on page 292.
2. Click Shutdown on the Message Agent window to stop the Message
Agent when the messages have been processed.
The Message Agent window displays status information while running. This
information can be output to a log file for record keeping in a production
setup.
The Message Agent first receives a message from hq, and then sends a
message. This return message contains confirmation of successful receipt of
the replication update; such confirmations are part of the SQL Remote
message tracking system that ensures message delivery even in the event of
message system errors.
You should now connect to the remote field database using Interactive SQL,
and inspect the SalesRep and Customer tables, to see which rows have been
received.
❖ To verify that the data has arrived
1. Connect to the field database using Interactive SQL.
2. Inspect the SalesRep table by typing the following statement:
SELECT*FROM SalesRep
67
Page 86

You will see that the SalesRep table contains both rows entered at the
consolidated database. This is because the SalesRepData publication
included all the data from the SalesRep table.
3. Inspect the Customer table by typing the following statement:
SELECT*FROM Customer
You will see that the Customer table contains only one row (Ocean
Sports) entered at the consolidated database. This is because the
SalesRepData publication included only those customers assigned to the
subscribed Sales Rep.
Replicate from the remote database to the consolidated database
You should now try entering data at the remote database and sending it to the
consolidated database. Only the outlines are presented here.
❖ To replicate data from the remote database to the consolidated
database
1. Connect to the field database from Interactive SQL.
2. INSERT a row at the remote database. For example
INSERT INTO Customer (cust_key, name, rep_key)
VALUES (’cust3’, ’North Land Trading’, ’rep1’)
68
3. COMMIT the row.
COMMIT;
4. With the
field.db
database running, run
dbremote
to send the message to
the consolidated database.
dbremote -c "eng=field;dbn=field;uid=DBA;pwd=SQL"
5. Run
ssremote
ssremote -c "eng=server-name;dbn=hq;uid=sa;pwd=sysadmin"
to receive the message at the consolidated database:
6. Connect to the consolidated database and display the Customer table.
This now has three rows:
SELECT
FROM Customer
*
Page 87
Chapter 5. A Tutorial for Adaptive ServerEnterprise Users
cust_key name rep_key
cust1 Ocean Sports rep1
cust2 Sports Plus rep2
cust3 North Land Trading rep1
In this simple example, there is no protection against duplicate entries of
primary key values. SQL Remote does provide for such protection. For
information, see the chapters on SQL Remote Design.
69
Page 88

70
Page 89

PART II
REPLICATION DESIGN FOR
SQL REMOTE
This part describes replication design issues for SQL Remote.
Page 90

Page 91

CHAPTER 6
Principles of SQL Remote Design
About this chapter This chapter describes general issues and principles for designing a
SQL Remote installation.
☞ For system-specific details, see the chapters “SQL Remote Design for
Adaptive Server Enterprise” on page 141 and “SQL Remote Design for
Adaptive Server Anywhere” on page 91.
Contents
Topic: page
Design overview 74
How statements are replicated 78
How data types are replicated 83
Who gets what? 86
Replication errors and conflicts 88
73
Page 92

Design overview
This chapter describes general publication design issues that you must
address when designing a SQL Remote installation. It also describes how
SQL Remote replicates data.
Design at the
consolidated database
Like all SQL Remote administrative tasks, design is carried out by a
database administrator or system administrator at the consolidated database.
The Adaptive Server Enterprise System Administrator or database
administrator should perform all SQL Remote configuration tasks.
Ensuring compatible databases
You should ensure that all databases participating in a SQL Remote
installation are compatible in terms of sort orders, character sets, and
database option settings.
If your installation includes both Adaptive Server Enterprise and Adaptive
Server Anywhere databases, you should ensure your Adaptive Server
Anywhere databases are created in an Adaptive Server
Enterprise-compatible fashion.
☞ For a full description of how to create Enterprise-compatible Adaptive
Server Anywhere databases, see “Creating a Transact-SQL-compatible
database” [ASA SQL User’s Guide, page 483]. This section provides a brief
description only.
❖ To create an Enterprise-compatible Adaptive Server Anywhere
database ( Sybase Central )
1. The Create Database wizard provides a button that sets each of the
available choices to emulate Adaptive Server Enterprise. This is the
simplest way to create a Transact-SQL-compatible database.
74
❖ To create an Enterprise-compatible Adaptive Server Anywhere
database ( Command line )
1. Ensure trailing blanks are ignored You can do this using the
option.
2. Ensure the dbo user ID is set If you have a database that already has a
user ID named dbo, then you can transfer the ownership of the Adaptive
Server Anywhere Transact-SQL system views to another user ID. You
can do this using the
3. Remove historical system views You can do this with the
option.
dbinit
-g option.
dbinit
dbinit
-b
-k
Page 93

Chapter 6. Principles of SQL Remote Design
4. Make the database case sensitive You can do this with the
option.
The following command creates a case-sensitive database named
the current directory, using the current dbo user, ignoring trailing blanks,
and removing historical system views:
dbinit -b -c -k test.db
Using compatible sort orders and character sets
The SQL Remote Message Agent does not perform any character set
conversions.
Character sets in
Adaptive Server
Anywhere installations
Character sets in
Adaptive Server
Enterprise installations
Character sets in mixed
installations
For an Adaptive Server Anywhere installation, the character set and
collation used by the consolidated database must be the same as the remote
databases. For information about supported character sets, see “International
Languages and Character Sets” [ASA Database Administration Guide, page 319].
The Open Client/Open Server libraries perform character set conversions
between SSREMOTE and Adaptive Server Enterprise whenever the
LOCALES.DAT character set is different from the Adaptive Server
Enterprise character set. Both character sets must be installed on the
Adaptive Server Enterprise server and conversion must be supported.
The
locales.dat
settings (which are used by all Open Client applications)
must match the remote Adaptive Server Anywhere settings.
dbinit
test.db
-c
in
The following table provides recommended matches between Adaptive
Server Enterprise and Adaptive Server Anywhere character sets. The
matches are not all complete.
Adaptive Server
Anywhere collation name
default cp850 dictionary_cp850 nocase_cp850
437LATIN1 cp437 dictionary_cp437 nocase_cp437
437ESP cp437 espdict_cp437 espnocs_cp437
437SVE cp437 bin_cp437 bin_cp437
819CYR iso_1 bin_iso_1 bin_iso_1
819DAN iso_1 bin_iso_1 bin_iso_1
Open Client /
Open Server
name
Open Client /
Open Server casesensitive sort order
Open Client
/ Open
Server caseinsensitive
sort order
75
Page 94
Adaptive Server
Anywhere collation name
Open Client /
Open Server
name
Open Client /
Open Server casesensitive sort order
Open Client
/ Open
Server caseinsensitive
sort order
819ELL iso_1 bin_iso_1 bin_iso_1
819ESP iso_1 espdict_iso_1 espnocs_iso_1
819ISL iso_1 bin_iso_1 bin_iso_1
819LATIN1 iso_1 dictionary_iso_1 nocase_iso_1
819LATIN2 iso_1 bin_iso_1 bin_iso_1
819NOR iso_1 bin_iso_1 bin_iso_1
819RUS iso_1 bin_iso_1 bin_iso_1
819SVE iso_1 bin_iso_1 bin_iso_1
819TRK iso_1 bin_iso_1 bin_iso_1
850CYR cp850 bin_cp850 bin_cp850
850DAN cp850 scandict_cp850 scannocp_-
cp850
850ELL cp850 bin_cp850 bin_cp850
76
850ESP cp850 espdict_cp850 espnocs_cp850
850ISL cp850 scandict_cp850 scannocp_-
cp850
850LATIN1 cp850 dictionary_cp850 nocase_cp850
850LATIN2 cp850 bin_cp850 bin_cp850
850NOR cp850 scandict_cp850 scannocp_-
cp850
850RUS cp850 bin_cp850 bin_cp850
850SVE cp850 scandict_cp850 scannocp_-
cp850
850TRK cp850 bin_cp850 bin_cp850
852LATIN2 cp852 bin_cp852 bin_cp852
852CYR cp852 bin_cp852 bin_cp852
Page 95
Chapter 6. Principles of SQL Remote Design
Adaptive Server
Anywhere collation name
Open Client /
Open Server
name
Open Client /
Open Server casesensitive sort order
Open Client
/ Open
Server caseinsensitive
sort order
855CYR cp855 cyrdict_cp855 cynocs_cp855
857TRK cp857 bin_cp857 bin_cp857
860LATIN1 cp860 bin_cp860 bin_cp860
866RUS cp866 rusdict_cp866 rusnocs_cp866
869ELL cp869 bin_cp869 bin_cp869
932JPN sjis bin_sjis bin_sjis
EUC_JAPAN eucjis bin_eucjis bin_eucjis
EUC_CHINA eucgb bin_eucgb bin_eucgb
EUC_TAIWAN eucb5 bin_big5 bin_big5
EUC_KOREA eucksc bin_eucksc bin_eucksc
UTF8 utf8 bin_utf8 bin_utf8
77
Page 96

How statements are replicated
SQL Remote replication is based on the transaction log, enabling it to
replicate only changes to data, rather than all data, in each update. When we
say that SQL Remote replicates data, we really mean that
replicates SQL statements that modify data
SQL Remote
.
Only committed
transactions are
replicated
Primary keys When an UPDATE or a DELETE is replicated, SQL Remote uses the
An UPDATE is not
always an UPDATE
SQL Remote replicates only statements in committed transactions, to ensure
proper transaction atomicity throughout the replication setup and maintain a
consistency among the databases involved in the replication, albeit with
some time lag while the data is replicated.
primary key columns to uniquely identify the row being updated or deleted.
All tables being replicated must have a declared primary key or uniqueness
constraint. A unique index is not sufficient. The columns of the primary key
are used in the WHERE clause of replicated updates and deletes. If a table
has no primary key, the WHERE clause refers to all columns in the table.
When a simple INSERT statement is entered at one database, it is sent to
other databases in the SQL Remote setup as an INSERT statement.
However, not all statements are replicated exactly as they are entered by the
client application. This section describes how SQL Remote replicates SQL
statements. It is important to understand this material if you are to design a
robust SQL Remote installation.
The Message Agent is the component that carries out the replication of
statements.
Replication of inserts and deletes
INSERT and DELETE statements are the simplest replication case.
SQL Remote takes each INSERT or DELETE operation from the transaction
log, and sends it to all sites that subscribe to the row being inserted or
deleted.
If only a subset of the columns in the table is subscribed to, the INSERT
statements sent to subscribers contains only those columns.
The Message Agent ensures that statements are not replicated to the user that
initially entered them.
Replication of updates
UPDATE statements are not replicated exactly as the client application
enters them. This section describes two ways in which the replicated
78
Page 97

Chapter 6. Principles of SQL Remote Design
Consolidated
ID Rep
Ann
21Marc
Dept
101
101
3
Ann
101
Ann
ID Rep
1 Ann
3 Ann
>
Marc
ID Rep
2 Marc
3 Marc
Marc
ID Rep
2
Marc
3
Marc
Ann
ID Rep
1
Ann
Consolidated
ID Rep
Ann
21Marc
Dept
101
101
3 Marc 101
UPDATE statement may differ from the entered UPDATE statement.
UPDATE statements
replicated as INSERTS
or DELETES
If an UPDATE statement has the effect of removing a row from a given
remote user’s subscription, it is sent to that user as a DELETE statement. If
an UPDATE statement has the effect of adding a row to a given remote
user’s subscription, it is sent to that user as an INSERT statement.
The figure illustrates a publication, where each subscriber subscribes by
their name:
An UPDATE that changes the Rep value of a row from Marc to Ann is
replicated to Marc as a DELETE statement, and to Ann as an INSERT
statement.
UPDATE conflict
detection
This reassignment of rows among subscribers is sometimes called territory
realignment, because it is a common feature of sales force automation
applications, where customers are periodically reassigned among
representatives.
An UPDATE statement changes the value of one or more rows from some
existing value to a new value. The rows altered depend on the WHERE
clause of the UPDATE statement.
When SQL Remote replicates an UPDATE statement, it does so as a set of
single-row updates. These single-row statements can fail for one of the
following reasons:
♦ The row to be updated does not exist Each row is identified by its
primary key values, and if a primary key has been altered by some other
user, the row to be updated is not found.
79
Page 98

In this case, the UPDATE does not update anything.
♦ The row to be updated differs in one or more of its columns If one
of the values expected to be present has been changed by some other user,
an update conflict occurs.
At remote databases, the update takes place regardless of the values in the
row.
At the consolidated database, SQL Remote allows conflict resolution
operations to take place. Conflict resolution operations are held in a
trigger or stored procedure, and run automatically when a conflict is
detected.
In Adaptive Server Anywhere, the conflict resolution trigger runs before
the update, and the update proceeds when the trigger is finished. In
Adaptive Server Enterprise, the conflict resolution procedure runs after
the update has been applied.
♦ A table without a primary key or uniqueness constraint refers to all
columns in the WHERE clause of replicated updates When two
users update the same row, replicated updates will not update anything
and databases will become inconsistent. All replicated tables should have
a primary key or uniqueness constraint and the columns in the constraint
should never be updated.
Replication of procedures
Any replication system is faced with a choice between two options when
replicating a stored procedure call:
♦ Replicate the procedure call A corresponding procedure is executed at
♦ Replicate the procedure actions The individual actions (INSERTs,
SQL Remote replicates procedures by replicating the actions of a procedure.
The procedure call is not replicated.
Replication of triggers
Trigger replication in SQL Remote is different for the Adaptive Server
Enterprise Message Agent and the Adaptive Server Anywhere Message
Agent.
Trigger replication from
Adaptive Server
Enterprise
80
From Adaptive Server Enterprise, trigger actions are replicated. You must
ensure that triggers are not fired in the remote Adaptive Server Anywhere
databases. If the trigger were fired, its actions would be executed twice.
the replicate site, or
UPDATEs, DELETEs and so on) of the procedure are replicated.
Page 99

Chapter 6. Principles of SQL Remote Design
The Adaptive Server Anywhere FIRE_TRIGGERS database option prevents
triggers from being fired. If you set this option for the user ID used by the
Message Agent, be careful to not use this user ID for other purposes.
An alternative approach to preventing trigger execution, available only for
Adaptive Server Anywhere, is to use the following condition around the
body of your triggers:
IF CURRENT REMOTE USER IS NULL
This make execution conditional on whether the current user is the Message
Agent.
Trigger replication from
Adaptive Server
Anywhere
An option to replicate
trigger actions
By default, the Message Agent for Adaptive Server Anywhere does not
replicate actions performed by triggers; it is assumed that the trigger is
defined remotely. This avoids permissions issues and the possibility of each
action occurring twice. There are some exceptions to this rule:
♦ Conflict resolution trigger actions The actions carried out by conflict
resolution, or RESOLVE UPDATE, triggers
are
replicated from a
consolidated database to all remote databases, including the one that sent
the message causing the conflict.
♦ Replication of BEFORE triggers Some BEFORE triggers can produce
undesirable results when using SQL Remote, and so BEFORE trigger
actions that modify the row being updated
are
replicated, before
UPDATE actions.
You must be aware of this behavior when designing your installation. For
example, a BEFORE UPDATE that bumps a counter column in the row
to keep track of the number of times a row is updated would double count
if replicated, as the BEFORE UPDATE trigger will fire when the
UPDATE is replicated. To prevent this problem, you must ensure that, at
the subscriber database, the trigger is not present or does not carry out the
replicated action. Also, a BEFORE UPDATE that sets a column to the
time of the last update will get the time the UPDATE is replicated as well.
The Adaptive Server Anywhere Message Agent has an option that causes it
to replicate all trigger actions when sending messages. This is the
-t option.
dbremote
If you use this option, you must ensure that the trigger actions are not carried
out twice at remote databases, once by the trigger being fired at the remote
site, and once by the explicit application of the replicated actions from the
consolidated database.
To ensure that trigger actions are not carried out twice, you can wrap an IF
CURRENT REMOTE USER IS NULL . .. END IF statement around the
81
Page 100

body of the triggers or you can set the Adaptive Server Anywhere
Fire_triggers option to OFF for the Message Agent user ID.
Replication of data definition statements
Data definition statements (CREATE, ALTER, DROP, and others that
modify database objects) are not replicated by SQL Remote unless they are
entered while in passthrough mode.
☞ For information about passthrough mode for Adaptive Server
Anywhere, see “Using passthrough mode” on page 260.
82
 Loading...
Loading...