Page 1

Adaptive Server™ Anywhere
Reference
Last modified: November 2000
Part Number: MC0058
Page 2

Copyright © 2001 Sybase, Inc. All rights reserved.
Information in this manual may change without notice and does not represent a commitment on the part of
Sybase, Inc. and its subsidiaries.
Sybase, Inc. provides the software described in this manual under a Sybase License Agreement. The software may be
used only in accordance with the terms of the agreem ent.
No part of this publication may be reproduced, transmitted, or translated in any form or by any means, electronic,
mechanical, manual, optical, or otherwise, without the prior written permission of Sybase, Inc.
Sybase, SYBASE (logo), ADA Workbench, Adaptable Windowing Environment, Adaptive Component Architecture,
Adaptive Server, Adaptive Server Anywhere, Adaptive Server Enterprise, Adaptive Server Enterprise Monitor, Adaptive
Server Enterprise Replication, Adaptive Server Everywhere, Adaptive Server IQ, Adaptive Warehouse, AnswerBase,
Anywhere Studio, Application Manager, AppModeler, APT-Build, APT-Edit, APT-Execute, APT-FORMS, APT-Library,
APT-Translator, APT Workbench, ASEP, Backup Server, BayCam, Bit-Wise, Certified PowerBuilder Developer, Certified
SYBASE Professional, Certified SYBASE Professional (logo), ClearConnect, Client Services, Client-Library, CodeBank,
Cohesion, Column Design, ComponentPack, Connection Manager, CSP, Data Pipeline, Data Workbench, DataArchitect,
Database Analyzer, DataExpress, DataServer, DataWindow, DB-Library, dbQueue, Developers Workbench, Direct
Connect Anywhere, DirectConnect, Distribution Director, Dynamo, E-Anywhere, E-Whatever, Electronic Case
Management, Embedded SQL, EMS, Enterprise Application Server, Enterprise Application Studio, Enterprise
Client/Server, Enterprise Connect, Enterprise Data Studio, Enterprise Manager, Enterprise SQL Server Manager, Enterprise
Work Architecture, Enterprise Work Designer, E nterprise Work Modeler, EWA, Financial Fusion, First Impression,
Formula One, Gateway Manager, GeoPoint, ImpactNow, InfoMaker, Information Anywhere, Information Everywhere,
InformationConnect, InstaHelp, Intellidex, InternetBuilder, iScript, Jaguar CTS, jConnect for JDBC, KnowledgeBase,
Logical Memory Manager, MainframeConnect, Maintenance Express, MAP, MDI Access Server, MDI Database Gateway,
media.splash, MetaWorks, MethodSet, MobiCATS, MySupport, Net-Gateway, Net-Library, NetImpact, Next Generation
Learning, Next Generation Learning Studio, O DEVICE, OASiS, OASiS (logo), ObjectConnect, ObjectCycle,
OmniConnect, OmniSQL Access Module, OmniSQL Toolkit, Open Client, Open Client/Server, Open Client/Server
Interfaces, Open ClientConnect, Open Gateway, Open Server, Open ServerConnect, Open Solutions, Optima++,
Partnerships that Work, PB-Gen, PC APT Execute, PC DB-Net, PC Net Library, PhysicalArchitect, Power Through
Knowledge, Power++, power.stop, PowerAMC, PowerBuilder, PowerBuilder Foundation Class Library, PowerDesigner,
PowerDimensions, PowerDynamo, PowerJ, PowerScript, PowerSite, PowerSocket, Powersoft, Powersoft Portfolio,
Powersoft Professional, PowerStage, PowerStudio, PowerTips, PowerWare Desktop, PowerWare Enterprise,
ProcessAnalyst, Relational Beans, Replication Agent, Replication Driver, Replication Server, Replication Server Manager,
Replication Toolkit, Report Workbench, Report-Execute, Resource Manager, RW-DisplayLib, RW-Library, S-Designor,
S Designor, SAFE, SAFE/PRO, SDF, Secure SQL Server, Secure SQL Toolset, Security Guardian, SKILS, smart.partners,
smart.parts, smart.script, SQL Advantage, SQL Anywhere, SQL Anywhere Studio, SQL Code Checker, SQL Debug,
SQL Edit, SQL Edit/TPU, SQL Everywhere, SQL Modeler, SQL Remote, SQL Server, SQL Server Manager, SQL Server
SNMP SubAgent, SQL Server/CFT, SQL Server/DBM, SQL SMART, SQL Station, SQL Toolset, SQLJ, Startup.Com,
STEP, SupportNow, Sybase Central, Sybase Client/Server Interfaces, Sybase Development Framework, Sybase Financial
Server, Sybase Gateways, Sybase Learning Connection, Sybase SQL Desktop, Sybase SQL Lifecycle, Sybase SQL
Workgroup, Sybase Synergy Program, Sybase User Workbench, Sybase Virtual Server Architecture, Sybase MPP,
SybaseWare, Syber Financial, SyberAssist, SyBooks, System XI (logo), System 10, System 11, SystemTools, Tabular Data
Stream, The Enterprise Client/S erver Company, The Extensible Software Platform, The Future Is Wide Op en,
The Learning Con nection, The Mode l F o r Client/Server So l utio ns , The Online Infor m atio n Ce nter, Transact-S Q L,
Translation Toolkit, Turning Imagination Into Reality, UltraLite, UNIBOM, Unilib, Uninull, Unisep, Unistring,
URK Runtime Kit for UniCode, Viewer, Visual Components, VisualSpeller, VisualWriter, VQL, Warehouse Control
Center, Warehouse Studio, Warehouse WORKS, WarehouseArchitect, Watcom, Watcom SQL Server, Watcom SQL,
Web.PB, Web.SQL, Web Deployment Kit, WebSights, WebViewer, WorkGroup SQL Server, XA-Library, XA-Server,
and XP Server are trademarks of Sybase, Inc. or its subsidiaries.
All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.
Last modified: March 2000. Part Number: MC0058.
Page 3

Contents
About This Manual............................................................xi
Related documentation............................................................xii
Documentation conventions....................................................xiii
The sample database..............................................................xvi
1 File Locations and Installation Settings........................... 1
Installation directory structure...................................................2
How Adaptive Server Anywhere locates files ...........................4
Environment variables ..............................................................6
Registry entries and INI files...................................................10
2 The Database Server .......................................................13
The database server...............................................................14
3 Connection and Communication Parameters................ 45
Connection parameters...........................................................46
Network communications parameters ....................................65
4 Database Administration Utilities................................... 75
Administration utilities overvi e w..............................................77
The Backup utility....................................................................78
The Collation utility..................................................................82
The Compression utility...........................................................85
The Console utility...................................................................87
The Data Source utility ............................................................89
The Erase utility ......................................................................94
The Information utility..............................................................96
The Initialization utility.............................................................98
The Interactive SQL utility.....................................................106
The License utility.................................................................109
The Log Transfer Manager...................................................111
The Log Translation utility.....................................................117
The Ping utility.......................................................................122
The REBUILD utility..............................................................124
iii
Page 4

The Server Location utility ....................................................125
The Service Creation utility...................................................126
The Spawn utility...................................................................129
The Stop utility ......................................................................130
The Transaction Log utility....................................................132
The Uncompression utility.....................................................136
The Unload utility..................................................................138
The Upgrade utility................................................................145
The Validation utility..............................................................148
The Write File utility ..............................................................151
5 Database Options.......................................................... 155
Introduction to database options...........................................156
General database options.....................................................161
Transact-SQL and SQL/92 compatibility options..................163
Replication options................................................................166
Interactive SQL options.........................................................167
Alphabetical list of options ....................................................169
6 SQL Language Elements .............................................. 219
Keywords ..............................................................................220
Identifiers...............................................................................223
Strings...................................................................................224
Operators..............................................................................225
Expressions...........................................................................230
Search conditions .................................................................239
Special values.......................................................................247
Variables...............................................................................250
Comments .............................................................................259
NULL value ...........................................................................260
7 SQL Data Types............................................................. 263
Character data types.............................................................264
Numeric data types...............................................................268
Money data types..................................................................275
Bit data type..........................................................................276
Date and time data types......................................................277
Binary data types ..................................................................284
Domains................................................................................286
Java class data types............................................................288
Data type conversions ..........................................................293
Java / SQL data type conversion..........................................294
Year 2000 compliance ..........................................................297
iv
Page 5

8 SQL Functions............................................................... 303
Function types.......................................................................304
Alphabetical list of f unctions..................................................313
9 SQL Statements............................................................. 377
Using the SQL statement reference......................................378
ALLOCATE DESCRIPTOR statement [ESQL].....................381
ALTER DATABASE statement .............................................383
ALTER DBSPACE statement ...............................................385
ALTER EVENT statement.....................................................387
ALTER PROCEDURE statement..........................................389
ALTER SERVER statement..................................................390
ALTER TABLE statement.....................................................392
ALTER TRIGGER statement................................................398
ALTER VIEW statement .......................................................399
ALTER WRITEFILE statement .............................................400
BACKUP statement ..............................................................401
BEGIN statement ..................................................................404
BEGIN TRANSACTION statement.......................................407
CALL statement ....................................................................410
CASE statement....................................................................412
CHECKPOINT statement......................................................414
CLEAR statement [Interactive SQL] .....................................415
CLOSE statement [ESQL] [SP].............................................416
COMMENT statement...........................................................418
COMMIT statement...............................................................420
CONFIGURE statement [Interactive SQL]............................422
CONNECT statement [ESQL] [Interactive SQL]...................423
CREATE COMPRESSED DATABASE statement................426
CREATE DATABASE statement ..........................................427
CREATE DBSPACE statement ............................................431
CREATE DOMAIN statement...............................................433
CREATE EVENT statement..................................................435
CREATE EXISTING TABLE statement ................................441
CREATE EXTERNLOGIN statement....................................443
CREATE FUNCTION statement...........................................445
CREATE INDEX statement...................................................448
CREATE MESSAGE statement [T-SQL]..............................452
CREATE PROCEDURE statement.......................................453
CREATE PROCEDURE statement [T-SQL].........................460
CREATE SCHEMA statement..............................................462
CREATE SERVER statement...............................................464
CREATE TABLE statement..................................................466
CREATE TRIGGER statement.............................................477
CREATE TRIGGER statement [T-SQL] ...............................480
v
Page 6

CREATE VARIABLE statement............................................481
CREATE VIEW statement ....................................................482
CREATE WRITEFILE statement ..........................................484
DEALLOCATE DESCRIPTOR statement [ESQL]................485
Declaration section [ESQL]...................................................486
DECLARE statement ............................................................487
DECLARE CURSOR statement [ESQL] [SP].......................488
DECLARE CURSOR statement [T-SQL]..............................493
DECLARE LOCAL TEMPORARY TABLE
statement ..............................................................................495
DELETE statement ...............................................................496
DELETE (positioned) statement [ESQL] [SP].......................498
DESCRIBE statement [ESQL]..............................................500
DISCONNECT statement
[ESQL][Interactive SQL]........................................................504
DROP statement...................................................................505
DROP DATABASE statement...............................................507
DROP CONNECTION statement .........................................508
DROP EXTERNLOGIN statement........................................509
DROP OPTIMIZER STATISTICS statement ........................510
DROP SERVER statement...................................................511
DROP STATEMENT statement [ESQL] ...............................512
DROP VARIABLE statement ................................................513
EXECUTE statement [ESQL]................................................514
EXECUTE statement [T-SQL]...............................................516
EXECUTE IMMEDIATE statement [SP] ...............................518
EXIT statement [Interactive SQL] .........................................520
EXPLAIN statement [ESQL] .................................................521
FETCH statement [ESQL] [SP].............................................523
FOR statement......................................................................528
FORWARD TO statement.....................................................530
FROM clause........................................................................532
GET DATA statement [ESQL]...............................................535
GET DESCRIPTOR statement [ESQL] ................................537
GET OPTION statement [ESQL] ..........................................538
GOTO statement [T-SQL].....................................................539
GRANT statement.................................................................540
HELP statement [Interactive SQL]........................................544
IF statement..........................................................................545
IF statement [T-SQL] ............................................................547
INCLUDE statement [ESQL].................................................549
INPUT statement [Interactive SQL] ......................................550
INSERT statement................................................................554
INSTALL statement...............................................................556
LEAVE statement..................................................................558
LOAD TABLE statement.......................................................560
vi
Page 7

LOCK TABLE statement.......................................................565
LOOP statement ...................................................................567
MESSAGE statement ...........................................................568
OPEN statement [ESQL] [SP]...............................................570
OUTPUT statement [Interactive SQL]...................................573
PARAMETERS statement [Interactive SQL] ........................577
PREPARE statement [ESQL] ...............................................578
PREPARE TO COMMIT statement ......................................580
PRINT statement [T-SQL].....................................................581
PUT statement [ESQL] .........................................................582
RAISERROR statement [T-SQL]..........................................584
READ statement [Interactive SQL] .......................................586
READTEXT statement [T-SQL] ............................................587
RELEASE SAVEPOINT statement.......................................588
REMOVE statement..............................................................589
RESIGNAL statement ...........................................................590
RESTORE statement............................................................591
RESUME statement..............................................................592
RETURN statement ..............................................................593
REVOKE statement ..............................................................595
ROLLBACK statement ..........................................................597
ROLLBACK TO SAVEPOINT statement ..............................598
ROLLBACK TRIGGER statement.........................................599
SAVEPOINT statement.........................................................600
SELECT statement ...............................................................601
SET statement ......................................................................605
SET statement [T-SQL].........................................................607
SET CONNECTION statement
[Interactive SQL][ESQL]........................................................610
SET DESCRIPTOR statement [ESQL].................................611
SET OPTION statement .......................................................612
SET OPTION statement [Interactive SQL] ...........................615
SET SQLCA statement [ESQL] ............................................616
SETUSER statement ............................................................617
SIGNAL statement ................................................................619
START DATABASE statement .............................................620
START ENGINE statement [Interactive SQL].......................622
START JAVA statement .......................................................623
START LOGGING statement [Interactive SQL]....................624
STOP DATABASE statement...............................................625
STOP ENGINE statement.....................................................626
STOP JAVA statement .........................................................627
STOP LOGGING statement [Interactive SQL]......................628
SYSTEM statement [Interactive SQL]...................................629
TRIGGER EVENT statement................................................630
TRUNCATE TABLE statement.............................................631
vii
Page 8

UNION operation ..................................................................633
UNLOAD statement ..............................................................634
UNLOAD TABLE statement..................................................635
UPDATE statement...............................................................637
UPDATE (positioned) statement...........................................641
VALIDATE INDEX statement................................................643
VALIDATE TABLE statement ...............................................644
WHENEVER statement [ESQL]............................................646
WHILE statement [T-SQL]....................................................647
WRITETEXT statement [T-SQL]...........................................648
10 Database Error Messages............................................. 649
Error messages indexed b y Adapt i ve Ser ver
Anywhere SQLCODE ...........................................................650
Error messages indexed by SQLSTATE..............................669
Error messages indexed by Sybase error code....................687
Alphabetic list of error messages..........................................711
Internal errors (assertion failed)............................................929
11 SQL Preprocessor Error Messages.............................. 931
SQL Preprocessor error messages indexed by
error message value .............................................................932
SQLPP errors........................................................................936
12 Differences from Other SQL Dialects........................... 953
Adaptive Server Anywhere SQL features.............................954
13 Physical Limitations...................................................... 957
Size and number limitations..................................................958
14 System Procedures and Functions .............................. 961
System procedure overview..................................................962
System and catalog stored procedures ................................963
System extended stored procedures....................................981
Adaptive Server Enterprise system and catalog
procedures............................................................................988
15 System Tables............................................................... 991
System tables diagram .........................................................993
System table descriptions.....................................................995
DUMMY system table ...........................................................996
SYSARTICLE system table ..................................................997
viii
Page 9

SYSARTICLECOL system table...........................................998
SYSCAPABILITY system table.............................................999
SYSCAPABILITYNAME system table ................................1000
SYSCOLLATION system table...........................................1001
SYSCOLLATIONMAPPINGS system table ........................1002
SYSCOLPERM system table..............................................1003
SYSCOLUMN system table................................................1004
SYSDOMAIN system table.................................................1006
SYSEXTENT system table .................................................1007
SYSEXTERNLOGINS system table ...................................1008
SYSFILE system table ........................................................1009
SYSFKCOL system table....................................................1010
SYSFOREIGNKEY system table........................................1011
SYSGROUP system table ..................................................1013
SYSINDEX system table.....................................................1014
SYSINFO system table .......................................................1016
SYSIXCOL system table.....................................................1018
SYSJAR system table.........................................................1019
SYSJARCOMPONENT system table .................................1020
SYSJAVACLASS system table...........................................1021
SYSLOGIN system table ....................................................1023
SYSOPTION system table..................................................1024
SYSPROCEDURE system table.........................................1025
SYSPROCPARM system table...........................................1026
SYSPROCPERM system table...........................................1028
SYSPUBLICATION system table........................................1029
SYSREMOTEOPTION system table ..................................1030
SYSREMOTEOPTIONTYPE system table.........................1031
SYSREMOTETYPE system table.......................................1032
SYSREMOTEUSER system table......................................1033
SYSSERVERS system table ..............................................1035
SYSSQLSERVERTYPE system table ................................1036
SYSSUBSCRIPTION system table.....................................1037
SYSSYNC system table......................................................1038
SYSTABLE system table....................................................1039
SYSTABLEPERM system table..........................................1041
SYSTRIGGER system table...............................................1043
SYSTYPEMAP system table ..............................................1045
SYSUSERMESSAGES system table .................................1046
SYSUSERPERM system table ...........................................1047
SYSUSERTYPE system table............................................1049
16 System Views............................................................... 1051
SYSARTICLECOLS system view.......................................1053
SYSARTICLES system view...............................................1054
ix
Page 10

SYSCAPABILITIES system view........................................1055
SYSCATALOG system view...............................................1056
SYSCOLAUTH system view...............................................1057
SYSCOLUMNS system view..............................................1058
SYSFOREIGNKEYS system view......................................1059
SYSGROUPS system view.................................................1060
SYSINDEXES system view ................................................1061
SYSOPTIONS system view................................................1062
SYSPROCAUTH system view............................................1063
SYSPROCPARMS system view.........................................1064
SYSPUBLICATIONS system view......................................1065
SYSREMOTEOPTIONS system view ................................1066
SYSREMOTETYPES system views...................................1067
SYSREMOTEUSERS system view ....................................1068
SYSSUBSCRIPTIONS system view...................................1069
SYSTABAUTH system view ...............................................1070
SYSTRIGGERS system view .............................................1071
SYSUSERAUTH system view ............................................1072
SYSUSERLIST system view...............................................1073
SYSUSEROPTIONS system view......................................1074
SYSUSERPERMS system view .........................................1075
SYSVIEWS system view.....................................................1076
Views for Transact-SQL Compatibility................................1077
A Database Performance and Connection Properties...1081
Database performance statistics ........................................1082
Database properties............................................................1090
Index..............................................................................1103
x
Page 11

About This Manual
Subject
Audience
Contents
This manual provides reference material for all aspects of Adaptive Server
Anywhere, including SQL statements, administration utilities, error
messages, system tables, and so on.
While other manuals provide more motivation and co ntext for how to carry
out particular tasks, this manual is the place to look for complete listings of
available syntax, utility command-line options, and so on.
This manual is for all users of Adaptive Server Anywhere. It is to be used in
conjunction with other manuals in the documentation set.
Topic Page
Related documentation xii
Documentation conventions xiii
The sample database xvi
xi
Page 12

Related documentation
Adaptive Server Anywhere is a part of SQL Anywhere Studio. For an
overview of the different components of SQL Anywhere Studio, see
Introducing SQL Anywhere Studio.
The Adaptive Server Anywhere documentation consis ts of the following
books:
♦
Getting Started Intended for all users of Adaptive Server Anywhere,
this book describes the following:
♦ New features in Adaptive Server Anywhere
♦ Behavior change s from previous releases
♦ Upgrade procedures
♦ Introductory material for beginning users.
♦
Programming Interfaces Guide Intended for application developers
writing programs that directly access the ODBC, Embedded SQL, or
Open Client interfaces, this book describes how to develop applications
for Adaptive Server Anywhere.
This book is not required for users of Application Development tools
with built-in ODBC support, such as Sybase PowerBuilder.
♦
User’s Guide A comprehensive guide to using SQL, administerin g
databases, and using Adaptive Server Anywhere features.
xii
♦
Quick Reference A handy printed booklet with complete SQL syntax
and other key reference material in a concise format.
♦
Read Me First (UNIX only) A separate booklet is provided with UNIX
versions of Adaptive Server Anywhere, describing installation and
adding some UNIX-specific notes.
The format of these books (printed or online) may depend on the product in
which you o btained Adap tive Server A nywhere. Dep ending on which
package you have purchased, you may have additional books describing
other components of your product.
Page 13

Documentation conventions
This section lists the typographic and graphical conventions used in this
documentation.
Syntax conventions
The following conventions are used in the SQL syntax descriptions:
Keywords All SQL keywords are shown in UPPER CASE. However,
♦
SQL keywords are case insensitive, so you can enter keywords in any
case you wish; SELECT is the same as Select is the same as s e lect.
♦
Placeholders Items that must be replaced with appropriate identifiers
or expressions are shown in italics.
♦
Continuation Lines beginning with ... are a continuation of the
statements from the previous line.
♦
Repeating items Lists of repeating items appear with an element of
the list followed by an ellipsis (three dots). One or more list elements are
allowed. If you specify more than one, they must be separated by
commas.
♦
Optional portions Optional portions of a statement are enclosed by
square brackets. For example,
RELEASE SAVEPOINT [
savepoint-name
]
indicates that the savepoint-name is optional. Do not type the square
brackets.
♦
Options When none or only one of a list of items must be chosen, the
items are separated by vertical bars and the list enclosed in square
brackets. For example,
[ ASC | DESC ]
indicates that you can choose one of ASC, DESC, or neither. The square
brackets should not be typed.
♦
Alternatives When precisely one of the options must be chosen, the
alternatives are enclosed in curly braces. For example,
QUOTES { ON | OFF }
indicates that exactly one of ON or OFF must be provided. Do not type
the braces.
xiii
Page 14
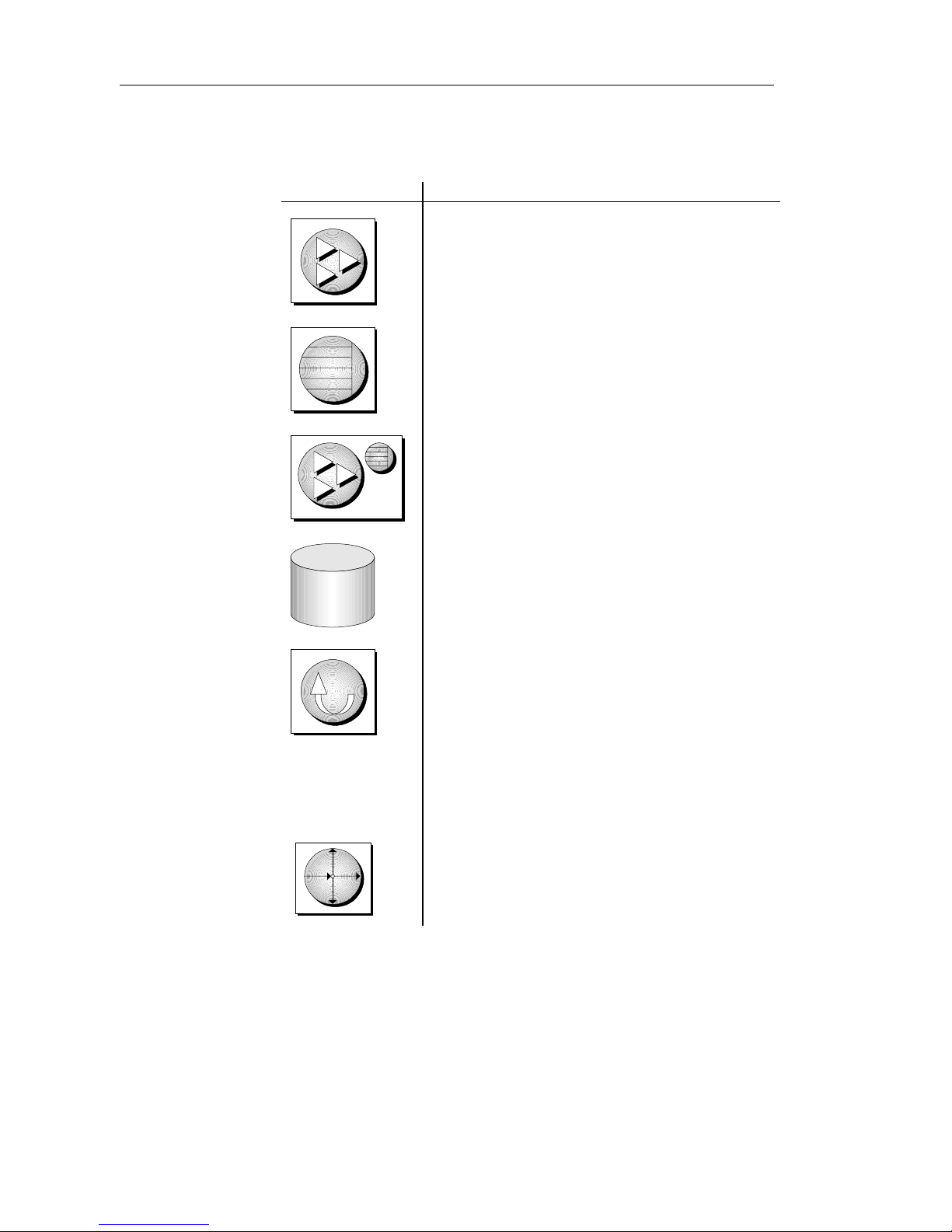
Graphic icons
The following icons are used in this docume ntation:
Icon Meaning
A client application.
If the icon is used to represent a particular application
or kind of application, the name is indicated in the
bottom right corner.
A database server, such as Sybase Adaptive Server
Anywhere or Adaptive Server Enterprise.
If the icon is used to represent a particular kind of
database server, such as Adaptive Server Anywhere,
the name is indicated in the bottom right corner.
An UltraLite application and database server.
In UltraLite, the database server and the application
are part of the same process.
A database.
In some high-level diagrams, the icon may be used to
represent both the database and the database server
that manages it.
xiv
Replication or synchronization middleware.
These pieces of software assist in sharing data among
databases. Examples include the MobiLink
Synchronization Server, the SQL Remote Message
Agent, and the Replication Agent (Log Transfer
Manager) for use with Replicat ion Server.
If the particular kind of middleware is not obvious
from the context of the diagram, the name is indicated
in the bottom right hand corner.
A Sybase Replication Server.
Page 15

Installed files
The following terms are used throughout the manual:
♦
Installation directory The directory into which you install Adaptive
Server Anywhere.
♦
Executable directory The executables and other files for each
operating system are held in an executable subdirectory of the
installation directory. This subdirectory has the following name:
♦
Windows NT and Windows 95/98 win32
♦
UNIX bin
♦
Windows 3.x win
♦
NetWare and Windows CE The executables are held in the
Adaptive Server Anywhere installation directory itself on these
platforms.
xv
Page 16
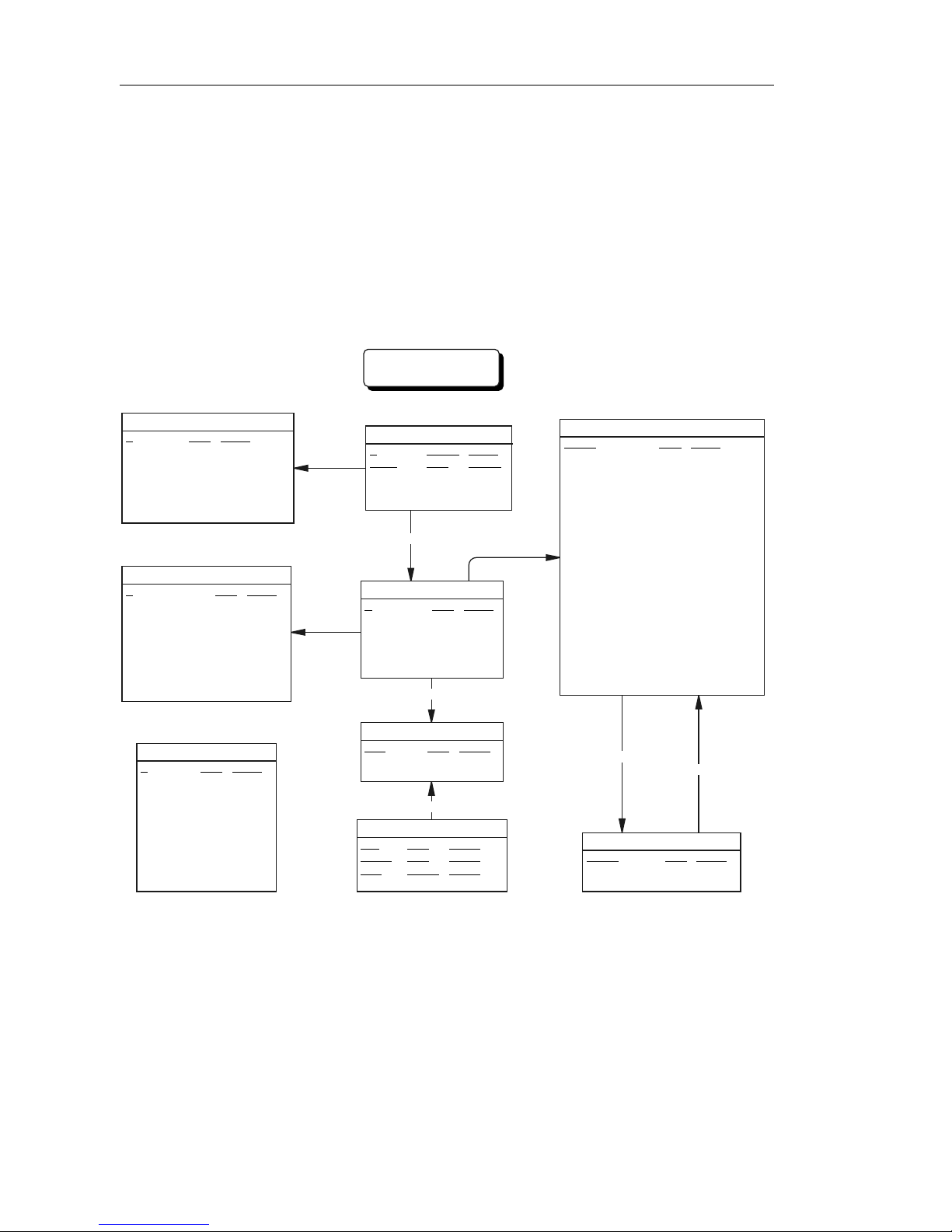
The sample database
There is a sample database included with Adaptive Server Anywhere. Many
of the examples throughout the documentation use this sample database.
The sample database represents a small company. It contains internal
information about the company (e mployees, departments, and financial data)
as well as product information (products), sales information (sales orders,
customers, and contacts), and financial information (fin_code, fin_data).
The following figure shows the tab les in the sample database and how they
are related to each other.
asademo.db
id <pk> integer
product
name char(15)
description char(30)
size char(18)
color char(6)
quantity integer
unit_price numeric(15,2)
customer
id <pk> integer
fname char(15)
lname char(20)
address char(35)
city char(20)
state char(2)
zip char(10)
phone char(12)
company_name char(35)
contact
id <pk> integer
last_name char(15)
first_name char(15)
title char(2)
street char(30)
city char(20)
state char(2)
zip char(5)
phone char(10)
fax char(10)
id = prod_id
id = cust_id
sales_order_items
id <pk,fk> integer
line_id <pk> smallint
prod_id <fk> integer
quantity integer
ship_date date
id = id
emp_id = sales_rep
sales_order
id <pk> integer
cust_id <fk> integer
order_date date
fin_code_id <fk> char(2)
region char(7)
sales_rep <fk> integer
code = fin_code_id
fin_code
code <pk> char(2)
type char(10)
description char(50)
code = code
fin_data
year <pk> char(4)
quarter <pk> char(2)
code <pk,fk> char(2)
amount numeric(9)
emp_id <pk> integer
employee
manager_id integer
emp_fname char(20)
emp_lname char(20)
dept_id <fk> integer
street char(40)
city char(20)
state char(4)
zip_code char(9)
phone char(10)
status char(1)
ss_number char(11)
salary numeric(20,3)
start_date date
termination_date date
birth_date date
bene_health_ins char(1)
bene_life_ins char(1)
bene_day_care char(1)
sex char(1)
dept_id = dept_id
emp_id = dept_head_id
department
dept_id <pk> integer
dept_name char(40)
dept_head_id <fk> integer
xvi
Page 17

The sample database is held in a file named
your installation directory.
asademo.db
, and is located in
xvii
Page 18

xviii
Page 19

CHAPTER 1
File Locations and Installation Settings
About this chapter
Contents
This chapter describes the installation and ope rating system settings used by
Adaptive Server Anywhere. Depending on the operating system, these
settings may be stored as environment variables, initialization file entries, or
registry entries.
Topic Page
Installation directory structure 2
How Adaptive Server Anywhere locates files 4
Environment variables 6
Registry entries and INI files 10
1
Page 20

Installation directory structure
Installation directory structure
When you install Adaptive Server Any where, several directories may be
created. Some of the files in these directories are essential, and others are
not. This section describes the directory structure.
Adaptive Server Anywhere software, whether you receive it as a product or
bundled as part of another product, is installed under a single installation
directory. The tools provided with the Adaptive Server Anywhere product,
however, are installed in other directories. This section describes only the
installation directory structure for Adaptive Server Anywhere itself.
The Adaptive
Server Anywhere
installation
directory
The Adaptive Server Anywhere installation d irectory itself holds several
items, including the followin g:
♦
The sample database The sample database is held in the file
asademo.db
♦
Read Me First A Read Me First file named
.
readme.txt
holds late-
breaking information.
For platforms other than Novell NetWare and Windows CE, there are several
directories under the installation directory:
Executable directories There is a separate directory for each
♦
operating syste m, which holds executables, dynamic link libraries, and
help files.
If you are using Windows 95/98, or NT, these files are installed in the
win32
directory. If you are using UNIX, they are installed in the
bin
directory. On NetWare, the executables are stored in the installation
directory itself.
You will not have all these directories on your machine; you will have
only the ones required for the operating system version you ins talled.
♦
Java directory Java base classes are stored in this directory.
♦
ProcDebug directory The stored procedure debugger is stor ed in this
directory.
♦
Scripts directory The scripts directory contains SQL scripts that are
used by the database administration utilities and as examples. With the
exception of specific scripts (
custom.sql, custmap.sql
), do not edit these
scripts. If the scripts directory is not present, the administration utilities
will not work.
♦
Examples directories There are separate directories for C (
Java (
2
jxmp
) examples.
cxmp
) and
Page 21

Chapter 1 File Locations and Installation Settings
h directory The h directory contains header files for ESQL and ODBC
♦
database development.
Novell NetWare file
locations
Windows CE file
locations
On Novell NetWare, all files are installed to a single directory on the server.
Throughout this documentation, when reference is made to files in
subdirectories of the installation directory, the file on NetWare is in the
installation directory itself.
On Windows CE, all files are installed to the installation directory, and no
subdirectories are created. The exception is that all DLLs are installed into
the
\Windows
the prefix
directory. To make identification easy, the DLL names all have
ASA_
.
3
Page 22

How Adaptive Server Anywhere locates files
How Adaptive Server Anywhere locates files
The client library and the database server need to locate files for two main
purposes:
♦ DLLs and initialization files are required to run Adaptive Server
Anywhere. If an incorrect DLL is located, there is the possibility of
version mismatch errors.
♦ Some files are specified in SQL statements and need to be located at run
time, such as INSTALL or LOAD TABLE.
Examples of SQL statements that use file names include the following:
♦
INSTALL statement The name of the file that holds Java classes.
LOAD TABLE and UNLOAD TABLE statements The name of the file
♦
from which data should be loaded or to which the data should be
unloaded.
♦
CREATE DATABASE statement A file name is needed for this
statement and similar statements that can create files (such as CREATE
WRITEFILE).
In some cases, Adaptive Server Anywhere uses a simple algorithm to locate
files. In other cases, a more extensive search is carried out.
Simple file
searching
Extensive file
searching
4
In many SQL statements (such as LOAD TABLE, or CREATE
DATABASE), the file name is interpreted as relative to the current working
directory of the database server.
Also, when a database server is started and a database file name (DBF
parameter) is supplied, the path is interpreted as relative to the current
working directory.
Adaptive Server Anywhere programs, including the database server and
administration utilities, carry out a more extensive search for required files,
such as DLLs or shared libraries. In these cases, Adaptive Server Anywhere
programs look for files in the following order:
1
Executable directory Holds the program executable file.
Related directories Holds directories with the following paths relative
2
to the program executable directory:
♦ Parent of the executable directory
♦ A child of the parent directory named
does not search in this location.
scripts
. The UNIX server
Page 23

Chapter 1 File Locations and Installation Settings
Current working directory When a program is started, it has a
3
current working directory (the directory from which it is started). This
directory is searched for required files.
4
Location registry entry On installation onto Windows 95/98, and NT,
Adaptive Server Anywhere adds a LOCATION registry entry. The
indicated directory is searched, followed by:
♦ A child named
♦ A child with the operating system name (
System specific directories This includes directories where common
5
operating system files are held, such as the
Windows\system
scripts
win32, win
Windows
, and so on)
directory and the
directory on Windows and Windows NT operating
systems.
6
CLASSPATH directories For Java files, directories listed in the
CLASSPATH environment variable are searched to locate files.
7
PATH directories Directories in the system path and the user’s path
are searched to locate files.
5
Page 24

Environment variables
Environment variables
Adaptive Server Anywhere uses a set of environment variables to store
various types of information. Not all variables need to be set in all
circumstances. These environment variables are listed in this section.
Setting environment variables
The way you set an environment variable depends on the operating system
you are using.
v To set an environment variable (Windows NT):
1 Right click on My Computer and select Properties from the popup menu.
2 Click the Environment tab. If the environment variable doe s not already
exist, type variable and its value in the spaces provided, and click Set.
If the variable does exist, select it from the list of System Variables or
User Variables, and make any modifications in the Value field. Click Set
to make the setting.
v To set an environment variable (UNIX):
♦ In one of your startup files (
variable.
In some shells (such as sh, bash, ksh) the line is as follows:
export VARIABLE=value
In other shells (such as csh, tsch) the line is as follows:
setenv VARIABLE value
ASTMP environment variable
Syntax
Default
Description
6
ASTMP=
None.
The database server checks the value of the ASTMP environment variable to
determine where to hold the temporary file. If the ASTMP environment
variable does not exist, then the first of the TMP, TMPDIR, and TEMP
environment variables to exist is used.
directory-name
.cshrc, .shrc, .login
), add a line that sets the
Page 25

Chapter 1 File Locations and Installation Settings
In many circumstances, ASTMP is not needed. It can be of use in securityconscious environments when running the database server as a service, to
enable you to hold the temporary file in a directory that cannot be accessed
by other programs.
LD_LIBRARY_PATH environment variable [UNIX]
Syntax
Description
LD_LIBRARY_PATH=
The LD_LIBRARY_PATH environment variable is used on UNIX only. It is
modified by the installation program to include the directories where
Adaptive Server Anywhere libraries are located.
The executables are located in the
directory (for example,
PATH environment variable
Syntax
Description
PATH=
installation_path
The PATH environment variable is modified by the installation program to
include the directories where Adaptive Server Anywhere executables are
located.
The executables are located in a subdirectory of the installation directory.
In addition, if you are using other Sybase app lications, the
SYBASE\dll
directories are added to your path.
On UNIX, each user must have the directory holding the executables
(
/opt/SYBSasa7/bin
SATMP environment variable
installation_path
lib
subdirectory of the installation
/opt/SYBSasa7/lib
) added to their path.
/lib
).
SYBASE\bin
and
Syntax
Description
SATMP=
temp_directory
The SATMP environment variable is used by UNIX versions of Adaptive
Server Anywhere to indicate a directory where temporary files are kept.
If more than one database server is running on a machine, each user needs
their own temporary directory. Typically, this is set to
/tmp/.userid
, so that
each user has their own directory and conflicts are avoided.
7
Page 26

Environment variables
SQLCONNECT environment variable
Syntax
Description
SQLCONNECT=
The SQLCONNECT environment variable is optional, and is not set by the
parameter#value
installation program.
SQLCONNECT specifies connection parameters that are used by several of
the database administration utilities when connecting to a database server.
This string is a list of parameter settings, of the form parameter=value,
delimited by semicolons.
The number sign "#" is an alternative to the equals sign, and should be used
if you are setting the connection parameters string in the SQLCONNECT
environment variable. Using "=" inside an environment variable setting is a
syntax erro r. The = sign is allowe d only in Wind ows NT.
$ For a description of the connection parameters, see "Connection
parameters" on page 64 of the book ASA User’s Guide.
SQLLOCALE environment variable
Syntax
See also
Description
SQLLOCALE= Charset=
"Setting the SQLLOCALE environment variable" on page 302 of the book
ASA User’s Guide
The SQLLOCALE environment variable is not set by the installation
program, and is required only in multi-character-set environments.
cslabel
; ...
;Language=
langlabel
;CollationLabel=
colabel
The SQLLOCALE environment variable is a single string that consists of
three semi-colon-separated assignments. The assignments set out the
character set, language, and collation of the environment.
$ For a list of supported character set labels, see "Setting the
SQLLOCALE environment variable" on page 302 of the book ASA User’s
Guide.
SQLPATH environment variable
Syntax
Description
8
SQLPATH=
path
;...
The SQLPATH environment variable is optional, and is not set by the
installation program.
Interactive SQL searches along SQLPATH for command files and Help files
before searching the system path.
Page 27

Chapter 1 File Locations and Installation Settings
SQLREMOTE environment variable
Syntax
Description
SQLREMOTE=
The SQLREMOTE environment variable is optio nal, and is not set by the
path
installation program.
Addresses for the FILE message link in SQL Remote are subdirectories of
the SQLREMOTE environment variable. This variable should point to a
shared directory.
On 32-bit Windows, an alternative to settin g the SQLREMOTE environment
variable is to set the
directory.
SYBASE environment variable
Syntax
Description
SYBASE=
The SYBASE variable marks the home directory for installation of some
Sybase applications, including Adaptive Server Enterprise and utilities such
as
dsedit
Anywhere together with other members of the Adaptive Server family.
path
. You need this variable only if you are using Adaptive Server
TEMP environment variable
Syntax
TMP=
path
TMPDIR=
TEMP=
path
path
SQL Remote\Directory
registry entry to the proper root
Description
The database server creates a temporary file for various operations such as
sorting and performing unions. Temporary files are placed in the directory
specified by the TMP, TMPDIR, or TEMP environment variable. Adaptive
Server Anywhere takes the first one of the three that it finds.
If none of the environment variables is defined, temporary files are placed in
the current working directory of the server.
On UNIX, the SATMP variable is used instead of the TEMP environment
variable.
9
Page 28

Registry entries and INI files
Registry entries and INI files
On Windows 95/98 and Windows NT operating systems, Adaptive Server
Anywhere uses several registry settings. On Windows 3.x, UNIX, and
Netware 3.11, these settings are held in initialization files instead.
These settings are made for you by the software, and in general operation
you should not need to access the registry. The settings are provided here for
those people who make modifications to their operating environment.
Current user and local machine settings
Some operating s ystems, such as Windows NT, hold two levels of system
settings. Some settings are specific to an individual user, and are used only
when that user is logged on; these settings are called current user settings.
Some settings are global to the machine, and are available no matter which
user is logged on; these are called local machine settings. You must have
administrator permissions on your machine to make local machine settings.
Adaptive Server Anywhere permits both current user and local machine
settings. For Windows NT, these are held in the HKEY_CURRENT_USER
registry and HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE registry, respectively.
Current user takes
precedence
When local
machine settings
are needed
10
If a setting is made in both current user and local machine registries, the
current user setting takes precedence over the local machine setting.
If you are running an Adaptive Server Anywhere program as a service under
Windows NT, you should ensure that the settings are made at the local
machine level.
Services can continue to run under a special account when you log off a
machine, as long as you do not shut the machine down entirely. They can be
made independent of individual accounts, and therefore need access to local
machine settings.
In addition to Adaptive Server Anywhere programs, some Web servers run
as services. You must set local machine se ttings in order for PowerDynamo
to work with such a Web server.
In general, the use of local machine settings is recommended.
Page 29

Registry structure
On Windows 95/98 and Windows NT, you can access the registry directly
with the registry editor. The Adaptive Server Anywhere registry entries are
held in either the HKEY_CURRENT_USER or
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE registries, in the followin g location:
Software
Sybase
Adaptive Server Anywhere
7.0
Sybase Central
4.0
Profiles
Providers
Registry settings on installation
The installation program makes the following registry settings in the Sybase
registry:
♦
Location In the
holds the installation directory location. For example:
Location "c:\sybase\asa7"
Chapter 1 File Locations and Installation Settings
Adaptive Server Anywhere\7.0
registry, this entry
♦ Language In the
Adaptive Server Anywhere\7.0
registry, this entry
holds a two-letter code indicating the current language for message s and
errors. For example:
Language "EN"
The default setting is English (EN). The installation program sets this
entry only if the software is installed for a langua ge other than English.
♦
Providers In the
Sybase Central\Providers
registry, this entry stores
the file names of installed plug-ins for Sybase Ce ntral. Adaptive Server
Anywhere has its own Sybase Central plug-in:
Adaptive Server Anywhere 7.0
"c:\sybase\asa7\win32\scasany7.dll"
11
Page 30

Registry entries and INI files
12
Page 31

CHAPTER 2
The Database Server
About this chapter
Contents
This chapter describes the command-line options for the Adaptive Server
Anywhere database server.
It also contains information for the command-line options of the client
executable (provided for compatibility with Version 5 software).
Topic Page
The database server 14
13
Page 32

The database server
The database server
Function
Syntax
NetWare syntax
Start a personal database server or network database server.
{ dbeng7 | dbsrv7 }
[
server-switches
load dbsrv7 [
Switch Description
@filename Read in switches from a configuration file. See "@filename
@environment-
variable
-?
-b
-c size Set initial cache size. See "–c command -line option" on page 2 1.
-ca 0
-ch size Set the cache size upper limit [Windows NT, Windows 95/98].
-cl
-cs
-ct
-d
-e
-ga
-gb level Set database process priority class to level [Windows NT]. See "–
-gc num Set maximum checkpoint timeout period to num minutes. See "–
server-switches
] [
database-file [ database-switches
] [
database-file [ database-switches
command-line option" on page 19.
Read in switches from an environ ment variable. See
"@environment-variable command-line option" on page 20.
Display usage information. See "–? command-line option" on
page 20.
Run in bulk operations mode. See "–b command-line option" on
page 20.
Disable dynamic cache sizing [Windows NT, Windows 95/98,
UNIX]. See "–ca command-line option" on page 22.
See "–ch command-line option" on page 23.
Set the cache size lower limit [Windows NT]. See "–cl
command-line option" on page 23.
Display cache usage in database server window. See "–cs
command-line option" on page 23.
Enable character-set translation [Not NetWare or Windows CE].
See "–ct command-line option" on page 24.
Disable asynchronous I/O [Wind ows NT, NetWare]. See "–d
command-line option" on page 24.
Enable packet encryption [network server]. See "–e command-
line option" on page 24.
Automatically unload the database after the last connection
closed. In addition, shut down after the last database is closed
[Not NetWare]. See "–ga command-line option" on page 24.
gb command-line option" on page 25.
gc command-line option" on page 25.
] ]*
] ]*
14
Page 33

Chapter 2 The Database Server
Switch Description
-gd level Set database starting permission. See "–gd command-line option"
on page 26.
-ge size Set the stack size for threads that run external functions [not
UNIX]. See "–ge command-line option" on page 27.
-gf
-gk level Set the permission required to stop the server. See "–gk
-gl level Set the permission required to load or unloa d da ta . See "–g l
-gm num Limit the maximum number of connections. See "–gm command-
-gn num Set the number of threads. See "–gn command- line option" on
-gp size Set the maximum page size to size bytes. See "–gp command-line
-gr minutes Set the maximum recovery time to num minutes. See "–gr
-gss size Set the thread stack size to size bytes [not applicable to
-gt num Sets the number of operating system threads allowed to run
-gu level Set the permission level for utility commands: utility_db, all,
-gx
-m
-n name Use name as the name of the database server. See "–n command-
-o filename Output messages to the specified file. See "–o command-line
-os size Limit the size of the log fil e fo r messages. See "–os command-
-p packet-size Set the maximum network packet size [n etwork server]. See "–p
-q
Disable firing of triggers. See "–gf command-line option" on
page 27.
command-line option" on page 27.
command-line option" on page 27.
line option" on page 28.
page 28.
option" on page 29.
command-line option" on page 29.
Windows]. See "–gss command-line option" on page 30.
concurrently. See "–gt command-line option" on page 30.
none, dba. See "–gu command-line option" on page 30.
Modify operating system threading [Windows 95/98 and
Windows NT]. See "–gx command-line option" on page 30.
Truncate the transacti on log after each checkpoint, for all
databases. See "–m command-line option" on page 31.
line option" on page 32.
option" on page 32.
line option" on page 32.
command-line option" on page 33.
Quiet mode—suppress output. See "–q command-line option" on
page 33.
15
Page 34

The database server
Switch Description
-r
-s
-sb [ 0 | 1 ] Specify how the server reacts to broadcasts. See "–sb command-
-sc
-ti minutes Client idle time before shutdown—default 240 minutes [network
-tl seconds Default liveness timeout for clients in seconds—default 120
-tmf
-tmt
millisecondst
-tq time Set quitting time [network server]. See "–tq time command-line
-u
-ud
-ut minutes Touch temporary files every min minutes [UNIX]. See "–ut
-v
-x list Comma-separated list of communication links to try. See "–x
-y
-z
-zo filename Redirect request-level logging information to a separate file. See
-zr { all | SQL |
none }
-zs size Limit the size of the log file used for request-level logging. See
Opens database in read-only mode. See "–r command-line
option" on page 33.
Set the syslog facility ID [UNIX]. See "–s command-line option"
on page 34.
line option" on page 34.
Disable the shared memory port , and enable Named Pipes.
[Windows NT]. See "–sc command-line option" on page 35.
server]. See "–ti command-line option" on page 35.
seconds. See "–tl command-line option" on page 35.
Force transaction manager recovery for distributed transaction s
[Windows NT]. See "–tmf command-line option" on page 36.
Set the reenlistment timeout for distributed transactions
[Windows NT]. See "–tmt command-line option" on page 36.
option" on page 36.
Use buffered disk I/O. See "–u command-line option" on
page 37.
Run as a daemon [UNIX]. See "–ud command-line option " on
page 37.
command-line option" on page 38.
Display database server version and stop. See "–v command-line
option" on page 38.
command-line option" on page 38.
Run as a Windows 95/98 service [Windows 95/98]. See "–y
command-line option" on page 40.
Provide diagnostic information on communication links [network
server]. See "–z command-line option" on page 40.
"–zo command-line option" on page 40.
Turn on logging of SQL operations. The default is NONE. See "–
zr command-line option" on page 40.
"–zs command-line option" on page 41.
16
Page 35

Chapter 2 The Database Server
Recovery
Database
Description
Cache size
Switch Description
-a filename Apply the named transaction log file. See "–a command-line
option" on page 41.
-f
Switch Description
-m
-n name Name the database. See "–n command-line option" on page 43.
-r
See also
Force the database to start without a transaction log. See "–f
command-line option " on page 41.
Truncate (delete) the tr ansaction log after each checkpo int. See "–
m command-line option" on page 42.
Read only mode. Database modifications not allowed. See "–r
command-line option" on page 33.
"Running the Database Server" on page 3 of the book ASA User’s Guide
"Network communications parameters" on page 65
The
dbeng7 command starts a personal database server. The dbsrv7
command starts a network database server.
The amount of cache memory available to the database server can be a key
factor in affecting performance. The database server takes an initial amount
of cache memory that is either specified by the -c command-line option or is
a default value. For information on the default cache size, see "–c command-
line option" on page 21.
Server differences
On Windows NT, Windows 95/98, and UNIX the database server
automatically takes more memory for use in the cache as needed, determined
by a heuristic algorithm
$ For more information, see "Using the cache to improve performance"
on page 807 of the book ASA User’s Guide.
You can use database command-line options to configure the upper limit: see
"–ch command-line option" on page 23. You can force the cache to remain at
its initial amount: see "–ca command -line option" on page 22.
The personal database server has a maximum of ten concurrent connections,
uses at most two CPUs for request processing, and does not support network
client/server connections.
In addition, there are other minor differences, such as the de fault permission
level that is required to start new databases, or the permissions required to
execute the CHECKPOINT statement.
17
Page 36

The database server
Platform availability
NetWare notes
Both personal and network database servers are supplied for each supported
operating system, with the followi ng exceptions:
♦
Novell NetWare Only the network server is supplied.
♦
Windows CE Only the network server is supplied. The support for
TCP/IP in the network server enables you to carry out tasks from your
desktop machine, incl ud in g datab ase mana ge me nt wi th Syba se Centr al.
In NetWare, the database file and the transaction log file must be on a
NetWare volume, and the paths must be fully specified. NetWare allows you
to have volumes that span two or mor e hard disks.
Adaptive Server Anywhere uses the Direct File System to maintain database
files. The Direct File System is built into NetWare 4.0 and 4.1, but not in
NetWare 3.12. Novell has provided a loadable module that contains the
DIRECTFS functions for version 3.12.
directfs.nlm
comes with Ad ap t i ve
Server Anywhere, and is installed during the installation if it is not found on
your NetWare server. The DIRECTFS module is automatically loaded if
necessary when you load
Novell has also provided an updated
dbsrv7
.
clib.nlm
for NetWare 3.11. This update
contains bug fixes that are necessary for Adaptive Server Anywhere to work
properly. It is installed during the installation of Adaptive Server Anywhere
if it is not already on your NetWare server.
Database file The database-file specifies the database filename. If
database-file is specified without a file extension, Adaptive Server
Anywhere looks first for database-file with extension
.db
followed by database-file with extension
.
.wrt
(a write file)
18
If you use a relative path, it is read relative to the current working directory.
You can supply a full path. Also, you can supply a path that conforms to the
Universal Naming Convention (UNC) format:
\\server\volume\path\file.ext
In addition, users of Novell NetWare version 4 and later can use NetWare
Directory Services (NDS) volumes, which have the following format:
\\treename\volume.org_unit.org\path\file.ext
where volume.org_unit.org is the name of an NDS volume object.
Caution
The database file must be on the same machine as the d atabase server.
Managing a database file that is located on a network drive can lead to
file corruption.
Page 37

Chapter 2 The Database Server
Suppressing
Windows NT event
log messages
If you run the database server as a Windows NT service, you can suppress
NT event log entries by setting a registry entry. The registry entry is
Software\Sybase\Adaptive Server Anywhere\7.0
To control event log entries, set the EventLogMask key, which is of type
REG_DWORD. The value is a bit mask containing the internal bit values for
the different types of event messages:
errors EVENTLOG_ERROR_TYPE 0x0001
warnings EVENTLOG_WARNING_TYPE 0x0002
information EVENTLOG_INFORMATION_TYPE 0x0004
For example, if the EventLogMask is set to zero, no messages appear at all.
A better setting would be 1, so that informational and warning message s do
not appear, but errors do. The default setting (no entry present) is for all
message types to appear.
Database server switches
These switches apply to the server as a whole, not just to an individual
database.
@filename command-line option
Function
Syntax
Applies to
Description
Examples
Read in command-line switches from the supplied file. Comments must be
preceded by the number sign (#).
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] @
filename
...
All operating systems and servers.
The command-line file may contain line breaks, and may contain any set of
command-line switches.
The following command file holds a set of command-line switches for a
server named myserver that starts with a cache size of 4 Mb and loads the
sample database:
-c 4096
-n myserver
c:\asa7\asademo.db
If this configuration file is saved as
c:\config.txt
, it can be used in a command
line as follows:
dbsrv7 @c:\config.txt
The following command file contains comments:
19
Page 38

The database server
#This is the server name:
-n MyServer
#These are the protocols:
-x tcpip
#This is the database file
my.db
@environment-variable command-line option
Function
Syntax
Applies to
Description
Read in command-line switches from the supplied environment variable.
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] @
All operating systems and servers.
The environment variable may contain any set of command line switches.
For example, the first statement sets an environment variable that holds
command line switches for a database server that starts with a cache size of
4Mb and loads the sample database. The second statement starts the database
server:
–? command-line option
Function
Syntax
Applies to
Display usage information.
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -?
All operating systems and servers.
env-var
set envvar=-c 4096 c:\asa6\asademo.db
dbsrv7 @envvar
...
Environment variable given priority
If you have both a file and an en vironment variable with the value of your
@ command-line switch, the environment variable is used.
Description
Display a short description of each command-line option. The database does
not carry out any other task.
–b command-line option
Function
Syntax
Applies to
Use bulk operation mode.
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -b ...
All operating systems and servers.
20
Page 39

Chapter 2 The Database Server
Description
This is useful for using the Interactive SQ L INP UT command to load large
quantities of data into a database.
The
load data.
When you use this option, the database server allows only one connection by
one application. It does not keep a rollback log or a transaction log, and the
multi-user locking mechanism is turned off.
When you first start the database server after loading data with the
switch, you should use a new log file .
Bulk operation mode does not disable the firing of triggers.
–c command-line option
Function
Set the initial memory reserved for caching database pages and other server
information.
Syntax
Applies to
Description
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -c [
All operating systems and servers.
The amount of memory available for use as a database server cache is one of
the key factors controlling performance. You can set the initial amount of
cache memory using the
The more cache memory that can be given the server, the better will be its
performance.
-b option should not be used if you are using LOAD TABLE to bulk
-b
integer
|
integer
K |
integer
M |
integer
P ] ...
-c command-line option
The units K and M can be either lower case or upper case. If K or M is not
supplied, any integer less than 10000 is assumed to be in kilobytes, and any
integer 10000 or greater is assumed to be in bytes. For example,
means 4096KB or 4 194 304 bytes. Whereas,
-c 200 000
means (an
-c 4096
unreasonably small) cache of 200 000 bytes.
The unit P is a percentage of the physical system memory, and if you use
this, the argument is a percentage. You can use % as an alternative to P, but
as most non-UNIX operating systems use % as an environment variable
escape character, you must escape the % character. To use 50 percent of the
physical system memory, you would use the following:
dbeng7 -c 50%% ...
If no -c option is provided, the database server computes the initial cache
allocation as follows:
1 I t uses the following operating-system-specific default cache sizes:
♦
Windows CE 600K
21
Page 40

The database server
Windows NT, Windows 95/98, NetWare 2 Mb
♦
♦
UNIX 8 Mb
2 I t computes a runtime-specific minimum default cache size, which is the
lesser of the following items:
♦ 25% of the machine’s physical memory
♦ The sum of the sizes of the main database files specified on the
command line. Additional dbspaces apart from the main database
files are not included in the calculation. If no files are specified, this
value is zero.
3 I t allocates the greater of the two values computed.
NetWare database server
There is a trade off between memory for the database server and memory
for the NetWare file system buffers. A larger database server cache will
improve database server performance at the expense of NetWare file
system performance. If the database server cache is too big, NetWare will
report an error that there is insufficient memory for cache buffers.
NetWare memory requirements increase with every new directory and file
on the file server. To track memory usage on the NetWare server, load
monitor.nlm
(if it is not already loaded) and select "Resource Utilization" .
Extra memory for your NetWare server computer could improve database
performance and/or file server performance dramatically.
See also
"–ch command-line option" on page 23
–ca command-line option
Function
When used as -ca 0, enforces a static cache size. The zero argument is
required.
Syntax
Applies to
Description
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -ca 0 ...
Windows NT, Windows 95/98, UNIX
Without setting
cache as needed. You can disable automatic cache increase due to high
server load by using -ca 0 on the command line. The cache size still increases
if the database server would otherwise run into the error
memory exhausted, or if the Java VM requires memory that would lead to a
fatal error.
This command-line option should be used only in the form
omitted, automatic cache growth is enabled.
22
-ca to 0, the database server automatically takes additional
Fatal Error: dynamic
-ca 0. If -ca is
Page 41

Chapter 2 The Database Server
See also
"–c command-line option" on page 21
"–ch command-line option" on page 23
–ch command-line option
Function
Syntax
Applies to
Description
Sets a maximum cache size, as a limit to automatic cache growth.
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -ch [
Windows NT, Windows 95/98
This option limits the cache that the datab a se server can take during
automatic cache growth. By default the upper limit is approximately the
lower of 256 Mb and 90% of the physical memory of the machine.
$ For the meaning and usage of the cache size arguments and the K, M,
and P characters, see "–c command-line option" on page 21.
See also
–cl command-line option
Function
Syntax
"–c command-line option" on page 21
"–ca command-line option" on page 22
"–cl command-line option" on page 23
Sets a minimum cache size, as a lower limit to automatic cache resizing.
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -cl [
integer
integer
|
|
integer
integer
K |
K |
integer
integer
M |
M |
integer
integer
P ] ...
P ] ...
Applies to
Description
Windows NT
This option sets a lower limits to the cache. The default minimum cache size
is the initial cache size.
$ For the meaning and usage of the cache size arguments and the K, M,
and P characters, see "–c command-line option" on page 21.
See also
–cs command-line option
Function
Syntax
Applies to
"–c command-line option" on page 21
"–ca command-line option" on page 22
"–ch command-line option" on page 23
Display cache size changes in the database server window.
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -cs...
All platforms with dynamic cache sizing.
23
Page 42

The database server
Description
For troubleshooting purposes, display cache information in the database
server window whenever the cache size changes.
–ct command-line option
Function
Syntax
Applies to
Description
Enable character set translation.
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -ct ...
All operating systems except NetWare and Windows CE.
Character set translation converting strings between character sets that
represent the same characters, but at different values. This is useful when the
client machine and the database use different character sets.
$ For more information, see "Starting a database server using character
set translation" on page 323 of the book ASA User’s Guide.
–d command-line option
Function
Syntax
Applies to
Description
Disable asynchronous I/O.
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -d ...
Windows NT, NetWare
Use synchronous I/O rather than async hronous I/O. Asynchro nous I/O is
generally the preferred option.
This option applies only to Wind ows NT and NetWare systems, which u se
asynchronous I/O by default.
–e command-line option
Function
Syntax
Applies to
Description
Encrypt all packets transmitted to and from all clients.
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -e...
All operating systems and servers.
By default, communication packets are not encrypted, thus posing a potential
security risk. If you are concerned about the security of network packets, use
the
–ga command-line option
Function
Unload database after last connection dropped.
24
-e switch. Encryption does marginally affect performance.
Page 43

Chapter 2 The Database Server
Syntax
Applies to
Description
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -ga ...
All operating systems except NetWare.
The meaning of this switch depends on whether you are running a personal
server or a network server.
♦
♦
–gb command-line option
Function
Syntax
Applies to
Description
Set the database process priority class.
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -gb [ idle | normal | high | maximum ] ...
Windows NT
Set the database process priority class. The value idle is provided for
completeness, and maximum may interfere with the running of your
computer. Normal and high are the commonly used settings.
Network server Specifying this switch on the network server causes
each database to be unloaded after the last connection to it is dropped.
The database server itself does not shut down.
Personal server In addition to unloading each d a tabase after the last
connection is dropped, the personal server shuts down when the last
database is stopped.
–gc command-line option
Function
Syntax
Applies to
Description
Set maximum desired interval between checkpoints.
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -gc
All operating systems and servers.
Set the maximum desired length of time in minutes that the database server
runs without doing a checkpoint on each database.
The default value is 60 minutes.
When a database server is running with multiple databases, the checkpoint
time specified by the first database started is used unless overridden by this
switch. If a value of 0 is entered, the default value of 60 minutes is used.
Checkpoints generally occur more frequentl y than the specified time. For
more information, see "How the database server decides when to checkpoint"
on page 671 of the book ASA User’s Guide.
See also
"CHECKPOINT_TIME option" on page 177.
integer
...
25
Page 44

The database server
"Checkpoints and the checkpoint log" on page 668 of the book ASA User’s
–gd command-line option
Guide
Function
Syntax
Applies to
Description
Example
Set permissions required to start a database.
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -gd [ dba | all | none ] ...
All operating systems and servers.
This is the permission required for a user to cause a new database file to be
loaded by the server. The level can be one of the following:
♦
dba Only users with DBA authority can start new databases.
♦
all All users can start new databases.
♦
none Starting new databases is not allowed.
The default setting is ALL for the personal database server and DBA for the
network database server. Both uppercase and lowercase syntax is acceptable.
The following set of steps illustrates how to use the
–gd option for the
network database server.
1 Enter a password in the
util_db.ini
file in your SQL Anywhere
win32
directory:
[UTILITY_DB]
pwd=mypwd
2 Start the network database server:
dbsrv7 -x tcpip -n myserver -gd dba
26
3 Connect to the utility database from Interactive SQL.
The following command assumes that myserver is the default database
server:
dbisql -c "uid=dba;pwd=mypwd;dbn=utility_db "
4 Start a d atabase:
start database asademo
on myserver;
5 Connect to the database you have started:
connect
to myserver
database asademo
user DBA identified by SQL
Page 45

–ge command-line option
Chapter 2 The Database Server
Function
Syntax
Applies to
Description
Set stack size for external functions.
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -ge
Windows 95/98, Windows NT, NetWare
Sets the stack size for threads running external functions, in bytes. The
default is 16384 (16K).
–gf command-line option
Function
Syntax
Applies to
Disable firing of triggers by the server.
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -gf...
All operating systems and servers.
–gk command-line option
Function
Syntax
Applies to
Description
Set the permission required to stop the database server and engine using
dbstop
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -gk [ dba | all | none ] ...
All operating systems and servers.
♦
integer
...
.
dba Only users with DBA authority can use
This is the default for the server.
dbstop
to stop the server.
♦
♦
Both uppercase and lower case syntax is acceptable.
–gl command-line option
Function
Set the permission required to load data using LOAD TABLE, and to unload
data using UNLOAD or UNLOAD TABLE.
Syntax
Applies to
Description
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -gl [ dba | all | none ] ...
All operating systems and servers.
Using the UNLOAD TABLE or UNLOAD statements places data in files on
the database server machine, and the LOAD TABLE statement reads files
from the database server machine.
all All users can use
dbstop
to stop the server. This is the default for
the standalone engine.
none The server cannot be stopped using
dbstop
.
27
Page 46

The database server
To control access to the file system using these statements, the
command-line option allows you to control the level of database permission
that is required to use these statements.
The allowed values are as follows:
♦
♦
♦
Both uppercase and lower case syntax is acceptable.
The default settings are all for personal database servers on non-Unix
operating systems, and dba for the network database server and the Unix
personal server. These settings reflect the fact that, on non-UNIX platforms,
the personal database server is running on the current machine, and so the
user already has access to the file system.
–gm command-line option
Function
Syntax
Applies to
Limit the number of concurrent connections to the server.
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -gm
All operating systems and servers.
–gl
dba Only users with DBA authority can load or unload data from the
database.
all All users can load or unload data from the database.
none Data cannot be unloaded or loaded.
integer
...
Description
If this number is greater than the number that is allowed under licensing and
memory constraints, it has no effect.
–gn command-line option
Function
Syntax
Applies to
Description
Set the number of execution threads.
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -gn
All operating systems and servers.
Set the number of execution threads to be used in the database server. Each
connection uses a thread for each request, and when the request is completed
the thread is returned to the pool for use by other connections. As no
connection can have more than one request in progress at one time, no
connection uses more than one thread at a time.
An exception to this rule is if a Java application uses threads. Each thread in
the Java application is a database server execution thread.
28
integer
...
Page 47

Chapter 2 The Database Server
The default is 20 threads for the network database server, and 10 threads for
the personal database server. The number of threads cannot be greater than
the number of server connections, so the maximum number of threads for the
personal database server is also 10.
You may want adj ust
Requests: Active and Requests: Unscheduled. I f the number of active
requests is always less than
requests (active + unscheduled) is often larger than
to increase
–gp command-line option
Function
Syntax
Applies to
Description
Set the maximum allowed database page size.
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -gp [ 1024 | 2048 | 4096 ] ...
All operating systems and servers.
Database files with a page size larger than the page size of the server cannot
be loaded. This switch explicitly sets the pa ge size of the server, in bytes.
If you do not use this switch, then the page size o f t he first d a tabase on the
command line is used.
The minimum page size on all UNIX platforms is 2048 bytes. You can still
use databases with smaller page sizes, but cache memory is used very
inefficiently. If you do not use this switch and start a server with no
databases loaded, the default value is 2048.
On all other platforms, if you do not use this switch and start a server with no
databases loaded, the default value is 1024.
-gn based on Performance Monitor readings for
-gn, you can lower -gn. If the number of total
-gn, then you might want
-gn.
–gr command-line option
Function
Set the maximum length of time (in minutes) for recovery from system
failure.
Syntax
Applies to
Description
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -gm
All operating systems and servers.
When a database server is running with multiple databases, the recovery time
that is specified by the first database started is used unles s o verridden by this
switch.
$ For more information, see "RECOVERY_TIME option" on page 208.
integer
...
29
Page 48

The database server
–gss command-line option
Function
Syntax
Applies to
Description
Set the stack size per internal execution thread in the server.
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -gss [
This option has no effect on Windows operating systems.
The number of internal execution threads is controlled by the
has a default value of 20. The default stack size per internal execution thread
is 16KB. The
database server in environments with li mited memory.
–gt command-line option
Function
Syntax
Applies to
Description
Sets the number of operating system threads allowed to run concurrently
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -gt
All operating systems and servers except NetWare.
By default, on Windows operating systems and NetWare, the network
database server uses all CPUs available on the machine, the personal
database server is limited to two processors, and the runtime database server
uses a single processor. On UNIX, all database servers use all available
processors by default.
This option should be left at the default setting on Windows op e rating
systems.
integer | integer
-gss option allows you to lo wer the memory usage of the
integer
...
K |
integerM
] ...
-gn option, and
–gu command-line option
Function
Syntax
Applies to
Description
Set permission levels for utility commands.
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -gu [ all | none | dba | utility_db ] ...
All operating systems and servers.
Sets permission levels for utilit y commands such as CREATE DATABASE
and DROP DATABASE. The level can be set to one of the following:
utility_db, all, none, dba.
The utility_db level restricts the use of these commands to only those users
who can connect to the utility database. The all, none, and dba levels permit
all users , no users, or users with dba authority to execute utility commands.
–gx command-line option
Function
Set the number of operating system threads.
30
Page 49

Chapter 2 The Database Server
Syntax
Applies to
Description
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -gx
Windows 95/98, Windows NT
By default, this is set to one more than the number of CP Us on the machine.
You may want to increase the option setting to reserve threads for external
tasks, separate from standa rd database tasks. For exa mple, you may want to
add an extra thread for each concurrent connection using remote data access,
or for connections using Java in the database to listen on an external port. In
other circumstances, this option should be left at the default value.
On UNIX, each task is executed in its own thread, so that the number of
tasks (
–m command-line option
Function
Syntax
Applies to
Description
Delete the transaction log when a checkpoint is d one.
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -m ...
All operating systems and servers.
This option deletes the transaction log when a checkpoint is done, either at
shutdown or as a result of a checkpoint scheduled by the server.
Caution
When this option is selected, there is no protection against media failure
on the device that contains the database files.
integer
...
-gn) also determines the number of threads.
This provides a way to automaticall y limit the growth of the transaction log.
Checkpoint fr equency is still controlled by the CHE CK POINT_TI ME and
RECOVERY_TIME options (which you can also set on the command line ).
This option is useful where hig h volume transactions that require fast
response times are being processed, and the contents of the transaction log
are not being relied upon for recovery or replication.
To avoid database file fragmentation, it is recommended that where this
option is used, the transaction log be placed on a separate device or partition
from the database itself.
Replicated databases
Do not use the -m optio n with databases that are being replicated.
Replication inherently relies on transaction log information.
31
Page 50

The database server
–n command-line option
Function
Syntax
Applies to
See also
Description
Set the name of the database server.
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -n
string
...
All operating systems and servers.
"Identifiers" on page 223
"EngineName connection parameter" on page 57
By default, the database server receives the name of the database file with
the path and extension removed. For example, if the server is started on the
c:\sybase\asa6\asademo.db
file
and no -n switch is specified, the name of
the server is asademo.
The server name is interpreted according to the character set of the machine,
as no database collation exists at startup time. It must be a valid identifier,
and long engine names are truncated to 40 characters. On NetBIOS, 16
characters is the maximum length.
The server name specifies the name to be used in the EngineName parameter
of client application connection strin gs or profiles. In all environments, there
is a default database server that will be used i f no server name is specified,
provided at least one database server is running on the computer.
There are two n switches
The -n switch is positional. If it appears after a database file name, it has
a different meaning.
$ For more information, see "–n command-line option" on page 43.
–o command-line option
Function
Syntax
Applies to
Description
–os command-line option
Function
Syntax
32
Print all server window output to a file.
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -o
All operating systems and servers.
Print all server message windo w ou tput to a file.
Limit the file size for the server window output.
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -os
filename
size
...
...
Page 51

Chapter 2 The Database Server
Applies to
Description
All operating systems and servers.
Limit the size of the log file used by the
and the value is in bytes.
See also
"–o command-line option" on p age 32
–p command-line option
Function
Syntax
Applies to
Description
Set the maximum size of communication packets.
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -p
All operating systems and servers.
The default is 1024 bytes. The minimum value is 300 bytes and the
maximum is 16000.
See also
"CommBufferSize connection parameter" on page 51
–q command-line option
Function
Syntax
Applies to
Do not display the server screen or its output.
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -q...
All operating systems and servers, except NetWare.
integer
–o switch. The default is no limit,
...
–r command-line option
Function
All databases started on the server are read-only. No changes to the
database(s) are allowed. The database file(s) and transaction log files are not
modified by the server. This option is position dependent.
Syntax
Applies to
Description
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -r ...
All operating systems and servers.
Opens all database files as read-only with the exceptio n of the temporary file.
You can make changes on temporary tables, but ROLLBACK has no effect,
since the transaction and rollback logs are disabled.
Databases distributed on CD-ROM devices, and compressed databases are
examples of database files that cannot be modified. You can either create a
write file to allow changes to the database outside the database file, or run in
read-only mode.
33
Page 52

The database server
If you attempt to modify the database, for example with an INSERT or
DELETE statement, a SQLSTATE_READ_ONLY_DATABASE error is
returned.
Databases that require recovery cannot be started in read-only mode. For
example, database files created using an online backup cannot be started in
read-only mode if there were any open transactions when the backup was
started, since these transactions would require recovery when the backup
copy is started.
Example
To open two databases in read-only mode
To open only the first of two databases in read-only mode.
–s command-line option
Function
Syntax
Applies to
Description
Set the user ID for syslog messages.
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -s { none | user |
UNIX
Sets the system user ID used in messages to the
is user, which uses the user ID for the database server process. A value of
none prevents any syslog messages from being logged.
–sb command-line option
Function
Syntax
Applies to
Description
Specify how the server reacts to broadcasts.
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -sb { 0 | 1}
TCP/IP
-sb 0 causes the server not to start up any TCP /UDP broadcast listeners. In
addition to forcing clients to use the DoBroadcast=NONE and HOST=
options to connect to the server, this op tion causes the server to be unlisted
when using dblocate.
dbeng7 -r database1.db database2.db
dbeng7 database1.db -r database2.db
login-id
...}
syslog facility. The default
-sb 1 causes the server to not respond to broadcasts from dblocate, while
leaving connection logic unaffected. You can connect to the server by
specifying LINKS=tcpip and ENG=<name>.
34
Page 53

–sc command-line option
Chapter 2 The Database Server
Function
Syntax
Applies to
Description
Disable the shared memory communications protocol and use Named Pipes.
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -sc...
Windows NT.
This option disables the shared memory communications protocol that is
used for same-machine communications, and starts the NamedPipes
protocol.
This option is implemented as p a rt of an initiative to obtain C2 security
certification. It is likely to be of general use only for customers wanting to
run in a C2-certified environment.
–ti command-line option
Function
Syntax
Applies to
See also
Description
Disconnect inactive connections.
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -ti
All operating systems and servers.
"sa_server_option system procedure" on page 971
Disconnect connections that have not submitted a request for minutes. The
default is 240 (4 hours). A client machine in the middle of a database
transaction holds locks until the transaction is ended or the connection is
terminated. The
freeing their locks.
minutes
-ti option is provided to disconnect inactive connections,
...
The
communications link.
Setting the value to zero disables checking of inactive connections, so that no
connections are disconnected.
–tl command-line option
Function
Syntax
Applies to
See also
Set the period at which to send liveness packets.
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -tl
All database servers usin g TCP/IP or SPX.
"sa_server_option system procedure" on page 971
-ti option does not disconnect clients that use the shared memory
seconds
...
35
Page 54

The database server
Description
A liveness packet is sent periodically across a client/server TCP/IP or SPX
communications protocol to confirm that a connection is intact. If the server
runs for a liveness timeout period (default 2 minutes) without detecting a
liveness packet, the communication is severed. The server drops any
connections associated with that client. UNIX non-threaded clients and TDS
connections do not do liveness checking.
The
not specify a live ness period.
Liveness packets are sent at an interval of the (liveness timeout)/4.
–tmt command-line option
Function
Syntax
Applies to
Description
To set a reenlistment timeout for participation in distrib uted transactions.
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -tmt [
Windows NT only.
Used during recovery of distributed transactions. The value specifies how
long the database server should wait to be reenlisted. By default there is no
timout (the database server waits indefinitely).
–tmf command-line option
-tl switch on the server sets the liveness timeout for all clients that do
milliseconds
]...
Function
Syntax
Applies to
Description
For recovery from distributed transactions in unusual circumstances.
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -tmf ...
Windows NT only.
Used during recovery of distributed transactions when the distributed
transaction coordinator is not available. It could also be used if starting a
database with distributed transactions in the tra nsaction log, on a platform
where the distributed transaction coordinator is not available.
Caution
If you use this option, distributed transactions are not recovered properly.
It is not for routine use.
–tq time command-line option
Function
Shut down the server at a specified time.
36
Page 55

Chapter 2 The Database Server
Syntax
Applies to
See also
Description
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -tq [
All operating systems and servers.
"sa_server_option system procedure" on page 971
This is useful for setting up automatic off-li ne backup procedures (see
"Backup and Data Recovery" on page 645 of the book ASA User’s Guide).
The format for the time is in hh:mm (24 hour clock), and can be preceded by
an optional date. If a date is specified, the date and time must be enclosed in
double quotes and be in the format YYYY/MM/DD HH:MM.
–u command-line option
Function
Syntax
Applies to
Description
Open files using the operating system disk cache.
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -u ...
Windows NT, Windows 95/98, Windows 2000, UNIX
Files are opened using the operating system disk cache in addition to the
database cache.
While the operating system disk cache may improve performance in some
cases, in general better performance is obtained without this switch, using the
database cache only.
If the server is running on a dedicated machine, you should not use the
option, as the database cache itself is generally more efficient. You may want
to use the
applications (so that a large database cache may interfere with other
applications) and yet IO-intensive tasks are run intermittently on the server
(so that a large cache will improve performance).
datetime
-u option if the server is running on a machine with several other
|
time
]...
-u
–ud command-line option
Function
Syntax
Applies to
Description
Run as a daemon.
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -ud ...
UNIX
Using this option lets you run the server so that it continues running after the
current operating system session ends.
37
Page 56

The database server
–ut command-line option
Function
Syntax
Applies to
Description
Touch temporary files.
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -ut
UNIX
This switch causes the server to touch temporary files at specified intervals.
–v command-line option
Function
Syntax
Applies to
Description
Display the software version.
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -v
All operating systems and servers.
Supplies the database server version in a message box, and then stops.
–x command-line option
Function
Syntax
Specify communications links.
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -x {
parmlist
minutes
all
| none
| { [ipx | namedpipes | netbios | spx | tcpip ]
} ...
:
{
keyword=value
;...}
...
parmlist
,... }
Applies to
See also
Description
38
All operating systems and servers.
"CommLinks connection parameter" on page 52
For example,
-x tcpip,spx
allows only TCP/IP and SPX communications.
A shared-memory protocol is provided for same-machine communications.
It is always made available for both network server and personal server.
The default set of communications links is to try all settings that are
supported by the database server that you are running on your operating
system, with the following exceptions:
♦ On Windows CE; the TCP/IP protocol is not started unless it is
explicitly requested.
Page 57

Chapter 2 The Database Server
♦ The IPX protocols is not started unless they are explicitly requested. It is
recommended that you use SPX instead of IPX.
The list is a comma-separated list of settings taken from the following caseinsensitive list:
♦
ALL Start all communications links that are supported on this platform
by the server that you are starting. This is the default.
♦
IPX Supported by NetWare, Windows NT, and Windows 95/98
network servers. This protocol is deprecated, and is not started by
default, as SPX provides a faster and more robust solution for IPX/SPX
communications.
♦
NamedPipes (NP) Supported on Windows NT, as an alternative
means of same-machine communication.
♦
NetBIOS Supported by Windows NT and Windows 95/98 network
database servers.
♦
NONE Do not start any communications links except for the shared
memory link.
♦
SPX Supported by NetWare, Windows NT, and Windows 95/98
network servers.
♦
TCPIP (TCP) Supported by the network server on all operating
systems. This communications link is also supported by the personal
database server for same-machine communications.
The database server always listens on port 2638, even if you specify a
different port using a network communica tion parameter. Hence,
applications can connect to the database server without specifying a port
number. For information, see "ServerPort parameter" on page 70.
An exception is the HP-UX operating system, on which the server does
not listen on port 2638 if it is started on another port.
For some protocols, additional parameters may be pro vided, in the format
-x tcpip(PARM1=value1;PARM2=value2;...)
For UNIX, quotation marks are required if more than one parameter is
supplied:
-x "tcpip(PARM1=value1;PARM2=value2;...)"
$ For a description of available parameters, see "Network
communications parameters" on page 65.
39
Page 58

The database server
–y command-line option
Function
Syntax
Applies to
Description
Run as a Windows 95/98 service.
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -y ...
Windows 95/98
If the server registered as a Windows 95/98 service, it continues to operate
whether users log on or off, and shutdown commands are ignored.
–z command-line option
Function
Syntax
Applies to
Description
Display communications operations on startup for troubleshooting purposes.
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -z ...
All operating systems and servers.
This should only be used when tracking problems. The information is
displayed in the database server window.
–zo command-li ne option
Function
Redirect request-level logging information to a file sep a rate from the regular
log file.
Syntax
Applies to
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -z ...
All operating systems and servers.
See also
"–zr command-line option" on page 40
"–zs command-line option" on page 41
Description
Request-level logging is turned o n using the
output from this file to a separate file from that specified on a
This switch also prevent s request-level logging from being displayed in the
console.
–zr command-line option
Function
Syntax
Applies to
See also
Enable request-level logging of operatio ns.
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -zr { all | sql | none }...
All operating systems and servers.
"sa_server_option system procedure" on page 971
40
–zr switch. You can direct the
–o switch.
Page 59

Chapter 2 The Database Server
Description
This should only be used when tracking problems. The information is
displayed in the database server window or sent to the logging file.
–zs command-line option
Function
Syntax
Applies to
See also
Limit the size of the request-level logging file.
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -zs
All operating systems and servers.
"–zo command-line option" on page 40
"–zr command-line option" on page 40
Description
Request-level logging is turned o n using the
separate file using the
–zs switch.
By default there is no limit. The value is in b ytes.
Recovery switches
These switches are for use in recovery situations only.
–a command-line option
size
...
–zr switch, and redirected to a
–zo switch.. You can limit the size o f the file using the
Function
Syntax
Applies to
Description
Apply the named transaction log.
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -a
All operating systems and servers.
This is used to recover from media failure on the database file. When this
option is specified, the database server app lies the log and then terminates—
it will not continue to run.
$ For information on recovery, see "Backup and Data Recovery" on
page 645 of the book ASA User’s Guide.
–f command-line option
Function
Syntax
Applies to
Force the database server to start after the transaction log has b e en lost.
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] -f ...
All operating systems and servers.
log-filename
...
41
Page 60

The database server
Description
If there is no transaction log, the database server carries out a checkpoint
recovery of the database and then terminates—it does no t continue to run.
You can then restart the database server without the
operation.
If there is a transaction log in the same directory as the database, the database
server carries out a checkpoint recovery, and a recovery using the transaction
log, and then terminates—it does not continue to run. You can then restart
the database server without the
$ For more information see "Backup and Data Recovery" on page 645 of
the book ASA User’s Guide.
Database switches
These switches are entered after the database name, and apply only to that
database.
–m command-line option
Function
Syntax
Applies to
Truncate the transaction log when a checkpoint is done.
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] [ server-switches ].
All operating systems and servers.
-f option for normal
-f option for normal operation.
database-file
-m ..
Description
42
Truncate (delete) the transaction log when a checkpoint is done, either at
shutdown or as a result of a checkpoint scheduled by the server. This
provides a way to automatically li mit the growth of the transaction log.
Checkpoint fr equency is still controlled by the CHE CK POINT_TI ME and
RECOVERY_TIME options (which you can also define on the command
line).
The
-m option is useful where high volume transactions requiring fast
response times are being processed, and the contents of the transaction log
are not being relied upon for recovery or replication. When thi s o ption is
selected, there is no protection against media failure on the device that
contains the database files.
To avoid database file fragmentation, it is recommended that where this
option is used, the transaction log be placed on a separate device or partition
from the database itself.
This switch is the same as the
-m server switch, but applies only to the
current database or the database identified by the database-file command-
line variable.
Page 61

–n command-line option
Chapter 2 The Database Server
Replicated databases
Do not use the -m option with databases that are being replicated.
Replication inherently relies on transaction log information.
Function
Syntax
Applies to
Description
Set the name of the database.
[ dbsrv7 | dbeng7 ] [ server-switches ].
database-file
-n
string
..
All operating systems and servers.
Both database servers and databases can be named. Since a database server
can load several databases, the database name is used to distinguish the
different databases.
By default, the database receives the name of the database file with the path
and extension removed. For example, if the database is started on
c:\asa7\asademo.db
and no -n switch is specified, the name of the database
is asademo.
43
Page 62

The database server
44
Page 63

CHAPTER 3
Connection and Communication
Parameters
About this chapter
Contents
This chapter provides a reference for the parameters that establis h and
describe connections from client applications to a database.
Topic Page
Connection parameters 46
Network communications parameters 65
45
Page 64

Connection parameters
Connection parameters
This section describes each connection parameter. Connection parameters are
included in connection strings. They can be entered in the following places:
♦ In an application’s connection string. For more information, see
"Assembling a list of connection parameters" on page 69 of the book
ASA User’s Guide.
♦ In an ODBC data sour ce. For more information, see "Wo rking with
ODBC data sources" on page 49 of the book ASA User’s Guide.
♦ In the Adaptive Server Anywhere connection window. For more
information, see "Connecting from Adaptive Server Anywhere utilities"
on page 48 of the book ASA User’s Guide.
The ODBC configuration dialog and the Adaptive Server Anywhere
connection window for Windows operating systems share a common format.
Some of the parameters correspond to checkboxes and fields in these
windows, others can be entered in the text box at the end of the Advanced
tab.
Notes
♦ Connection parameters are case-insensitive.
♦ The Usage for each connection parameter describes the circumstances
under which the parameter is to be used. Common usage entries include
the following:
♦
Embedded databases When Adaptive Server Anywhere is used
as an embedded database, the connection starts a personal server
and loads the database. When the application disconnects from the
database, the database is unloaded and the server stops.
♦
Running local databases This refers to the case where an
Adaptive Server Anywhere personal server is already running, and
the database is already loaded on the server.
♦
Network servers When Adaptive Server Anywhere is used as a
network server, the client application must locate a server already
running somewhere on the network and connect to a database.
♦ You can use the dbping utility to test connection strings. For example, if
the database file
returns the message
dbping -d -c "dbf=c:\Databases\MyDB.db;astart=yes"
MyDB.db
is not currently running, the following string
Ping database successful:
The following command, however, returns the message Ping database
failed – Database server not running, because Adaptive Server
Anywhere is unable to find a server for
MyDB.db
:
46
Page 65

Chapter 3 Connection and Communication Parameters
dbping -d -c "dbf=c:\Databases\MyDB.db;astart=no"
$ For more information, see "The Ping utility" on page 122.
Agent connection parameter [Agent]
Function
Usage
Values
See also
Default
Description
To restrict the type of connections attempted by the client.
Anywhere
String. Must be one of the following:
♦ any
♦ engine or personal server.
♦ server or client
"CommLinks connection parameter" on page 52
No value
If you set the AGENT connection parameter to engine or personal server,
the application attempts to connect only to a da tabase server running on the
same machine as the client. It attempts the following connections:
♦ Shared memory connection
♦ Named Pipes co nnection, for Adaptive Server Anywhere ver sion 6
Windows 3.x applications running on Windows NT.
♦ TCP/IP connection to a database server running on the local machine.
This is useful only for Adaptive Server Anywhere version 6 Windows
3.x applications running on Windows 95/98.
For the application to attempt a Named Pipes o r TCP/IP connection, these
links must be specified in a CommLinks connection parameter. If a shared
memory link is available, it is always attempted first, even if CommLinks is
specified.
If you set the AGENT connection parameter to server or client, the client
attempts the following connection type s:
♦ TCP/IP
♦ IPX
♦ NetBIOS
♦ SPX
47
Page 66

Connection parameters
The database server may be running on the same machine, or on a different
machine. The client does not attempt to connect using shared memory,
Named Pipes, or DDE. The CommLinks connection parameter must specify
the appropriate protocol for it to be used.
AppInfo connection parameter [App]
Function
Usage
Default
Description
To assist administrators in identifying the origin of particular client
connections from a database server.
Anywhere
Empty string
This connection parameter is sent to the da tabase server from
Embedded SQL, ODBC, or OLE DB clients. It is not available from Open
Client or jConnect applications such as Interactive SQL or Sybase Central.
It consists of a generated string that hold s information about the client
process, such as the IP address of the client machine, the operating system it
is running on, and so on. The string is associated in the database server with
the connection, and you can retrieve it using the following statement:
select connection_property( ’appinfo’ )
Clients can also specify their own string, which is appended to the generated
string. The AppInfo property string is a sequence of semi-colon-delimited
key=value pairs. The valid keys are as follows:
♦
IP The IP address of the client machine (Unix and NetWare only)
♦
HOST The host name of the client machine
♦
OS The operating system name and version number (for example,
Windows NT 4.0, NetWare 3.12)
♦
PID The process ID of the client (Windows and Unix only)
48
♦
THREAD The thread ID of the client (Windows and Unix only)
EXE The name of the client executable (Windows and NetWare only)
♦
♦
VERSION The version of the connection protocol in use, including
major and minor values, and a build number (for example 7.0.00.3642)
♦
APPINFO If you specified APPINFO in the connection string, the
string entered.
If you specify a debug log file in your client connection parameters, the
APPINFO string is added to the file.
Page 67

Chapter 3 Connection and Communication Parameters
Examples
♦ Connect to the default database fro m the C++ version of
Interactive SQL:
dbisqlc -c uid=dba;pwd=sql
View the application information:
select connection_property(’appinfo’)
The result is as follows (in a single string):
HOST=
machine-name
OS=Windows NT 4.0;
PID=0x11b;
THREAD=0x102;
VERSION=7.0.00.3642
;
♦ Connect to the default database fro m the C++ version of
Interactive SQL, appending your own information to the AppInfo
property:
dbisqlc -c "uid=dba;pwd=sql;app=ISQL connection"
View the application information:
select connection_property(’appinfo’)
The result is as follows (in a single string):
HOST=
machine-name
OS=Windows NT 4.0;
PID=0x10e;
THREAD=0xe1;
VERSION=7.0.00.3642;
APPINFO=ISQL connection
;
AutoStart connection parameter [Astart]
Function
Usage
Default
Description
To prevent a local database server from being started if no connection is
found.
Anywhere
Yes
By default, if no server is found during a connection attempt, and a database
file is specified, then a database server is started on the same machine. You
can turn this behavior off b y settin g the AutoStart parameter to No or OFF in
the connection string.
49
Page 68

Connection parameters
AutoStop connection parameter [Astop]
Function
To prevent a database from being stopped as soon as there are no more open
connections.
Usage
Default
Description
Embedded databases
Yes
By default, any server that is started from a connection string is stopped
when there are no more connections to it. Also, any database that is loaded
from a connection string is unloaded as soon as there are no more
connections to it. This behavior is equivalent to Autostop=Yes.
If you s upply Autostop=No, any database that you start in that connection
remains running when there are no more connections to it. As a consequence,
the database server remains operational as well.
The AutoStop parameter is used only if you are connecting to a database that
is not currently running. It is ignored if the database is already started.
BroadcastListener parameter
Usage
Allowed values
Default
See also
TCP/IP, Server side
YES, NO
YES
"–sb command-line option" on page 34
Description
This option allows you to turn b roadcast listening OFF for this port.
BroadcastListener=0 is the same as
Examples
Start a server that accepts both TCP/IP and SPX connections, but require that
TCP/IP connections use DoBroadcast=NO:
dbsrv8 -x tcpip(BroadcastListener=NO),spx ...
CharSet connection parameter [CS]
Function
Usage
Default
50
To specify the character set to be used on this connection.
Anywhere
The local character set. For information on how this is determined, see
"Determining locale information" on page 320 of the book ASA User’s
Guide.
-sb 0.
Page 69

Chapter 3 Connection and Communication Parameters
Description
If you supply a value for CharSet, the specified character set is used for the
current connection.
$ For a list of valid character set values, see "Character set labels" on
page 300 of the book ASA User’s Guide.
CommBufferSize connection parameter [CBSize]
Function
Usage
Values
Default
Description
To set the maximum size of communication packets, in bytes.
Anywhere
Integer
1024
The CommBufferSize parameter specifies the size of communications
packets, in bytes. The minimum value of CommBufferSize is 300, and the
maximum is 16000. If the specified packet size is larger than that of the
database server, the server’s packet size is used.
The maximum size of a packet on a network is set by the protocol stack. If
you set CommBufferSize to be larger than that permitted by your network,
the largest buffers are broken up by the network software. You should set the
buffer size to be somewhat smaller than that allowed by your network,
because the network software may add information to each buffer before
sending it over the network.
Examples
A larger packet size improves performance for multi-row fetches and fetches
of larger rows. As each connection has its own pool of buffers, a large buffer
size increases the memory usage. The application side uses four default-sized
buffers per connection, and on the server side, there are two.
This corresponds to the SQL Anywhere Version 5
dbclient
–p command-line
switch.
The value is a global setting: the value is set on the first connection attempt
for a session, and that value is used for all connections until the client library
is closed down.
♦ To set the buffer size to 400 bytes:
...
CommBuffSize=400
...
Alternatively, you can set this parameter by entering its value in the Buffer
size text box of the Network tab of the connection wi ndow.
51
Page 70

Connection parameters
CommBufferSpace connection parameter [CBSpace]
Function
To specify the amount of space to allocate on startup for communication
buffers, in kilobytes.
Usage
Values
Default
Description
Anywhere
Integer
10
Specify amount of space to allocate on startup for communication buffers, in
kilobytes. The value is a global setting: the value is set on the first
connection attempt for a session, and that value is used for all connections
until the client library is closed down.
Examples
The following connection string fragment instr ucts the network lib rary to
allocate 200 kb for network buffers on startup.
CBSpace=200
You can set this parameter by entering its value in the Buffer space text box
of the Network tab of the connectio n window.
CommLinks connection parameter [Links]
Function
Usage
To specify network communications links.
Anywhere
Default
See also
Description
52
Use only the shared memory communications link to connect.
"Network communications parameters" on page 65
"Client/Server Communications" on page 85 of the book ASA User’s Guide
"–x command-line option" on page 38
If no CommLinks parameter is specified in a connection string, no search is
made for a server other than on the current machine, and only a shared
memory connection is attempted. T his b e havior is equivalent to
CommLinks=None.
The shared memory protocol is used for communication between a client and
server running under the same operating system on the same machine, as is
typical for applications connecting to the personal database server.
If a CommLinks parameter is supplied, the named communication links are
started and used when searching for a database server. The CommLinks
parameter is required for connections to a network server.
Page 71

Chapter 3 Connection and Communication Parameters
Available values of the CommLinks parameter are case insensitive, and are
as follows:
ALL Start all available communications links except IPX and
♦
NamedPipes.
♦
IPX Start the IPX communications link. The IPX protocol is currently
supported for Windows and NetWare clients. In a future version, IPX of
this software, IPX support will be dropped. It is recommended that you
use SPX instead.
♦
NamedPipes (NP) For C2 security purposes, connect from a
Windows NT client to a database server on the same machine that was
started with the
NetBIOS Start the NetBIOS communications li nk. NetBIOS is
♦
–sc command-line option.
supported on Windows operating systems.
♦
NONE Start no communications link s.
♦
SharedMemory (ShMem) Start the shared memory link for same-
machine communication.
♦
SPX Start the SPX communications link. The SPX protocol is
supported for Windows and NetWare clients.
♦
TCPIP (TCP) Start the TCP/IP communications link. TCP/IP is
supported on all operating systems.
Each of these values can have add itional network communications
parameters supplied.
$ For a list of parameters, see "Network communications parameters" on
page 65.
You may wish to use a specific protocol, as opposed to ALL, for the
following reasons:
♦ The network library starts slightly faster if unnecessary network links
are not started.
♦ Connecting to the database may be faster.
♦ If you wish to tune the broadcast behavior of a particular protocol by
providing additional networ k communications parameters, you must
specify the link explicitly.
Additional network communications parameters may be provided for each
link, to tune the broadcast behavior of the link.
The CommLinks parameter corresponds to the database server
command-line switch. The defa ult behavior of the network server is
equivalent to
-x ALL.
–x
53
Page 72

Connection parameters
Examples
♦ The following connection string fragment starts the TCP/IP protocol
only:
CommLinks=tcpip
♦ The following connection string fragment starts the TCP/IP and IPX
protocols, searching for the host kangaroo in addition to servers on the
immediate TCP/IP network:
CommLinks=ipx,tcpip(HOST=kangaroo)
ConnectionName connection parameter [CON]
Function
Usage
Default
Description
Examples
Names a connection, to make switching to it easier in multi-connection
applications.
Not available for ODBC.
No connection name.
An optional parameter, providing a name for the particular connection you
are making. You may leave this unspecified unless you are going to establish
more than one connection, and switch between them.
The connection name is not the same as the data source name.
♦ Connect, naming the connection FirstCon:
CON=First Con
DatabaseFile connection parameter [DBF]
Function
Usage
Default
Description
54
The database file to which you want to connect.
Embedded databases
There is no default setting.
To load and connect to a specific database file.
♦ If a database is loaded with a name that is the same as the DatabaseFile
parameter, but without the
.db
extension, the connection is made to that
database instead.
♦ If the filename does not include an e xten sio n, a file of name
looked for.
.db
is
Page 73

Chapter 3 Connection and Communication Parameters
♦ The path of the file is relative to the working directory of the database
server. If you start the server from the command prompt, the working
directory is the directory that you are in when entering the command. If
you start the server from an icon or shortcut, it is the working directory
that the icon or shortcut specifies.
You can also use UNC filenames and Novell NetWare Directory Services
file names. For information, see "T he database server" on page 14.
Caution
The database file must be on the same machine as the database server.
Managing a database file that is located on a network drive can lead to
file corruption.
Example
♦ To load and connect to the sample database, installed in directo r y
c:\asa6
, use the following DBF parameter:
DBF=c:\asa7\asademo.db
DatabaseName connection parameter [DBN]
Function
Usage
Default
Description
Examples
Identifies a loaded database to which a connection needs to be made.
Running local databases or network servers.
There is no default setting.
Whenever a database is started on a server, it is assigned a database name.
The default database name is the name of the datab a se file with the extension
and path removed.
♦ Connect to a running database named Kitchener:
DBN=Kitchener
DatabaseSwitches connection parameter [DBS]
Function
Usage
To provide database-specific switches when starting a database.
Connecting to a running server when the database is not loaded.
Default
See also
No switches
"The database server" on page 14
"StartLine connection parameter" on page 63
55
Page 74

Connection parameters
Description
You should supply DatabaseSwitches only if you are connecting to a
database that is not currently running. When the server starts the database
specified by DatabaseFile, the server uses the supplied DatabaseSwitches
as command line options to determine startup options for the database.
Only database switches can be supplied using this parameter. Server
switches must be supplied using the START connection parameter.
Examples
♦ The following command, entered all on one line at the command
prompt, connects to the default database server, loads the database file
asademo.db
(DBF parameter), names it as my_db (DBS parameter) and
connects to the database of that name (DBN parameter).
dbcollat -c
"uid=dba;pwd=sql;dbf=asademo.db;dbn=my_db;dbs=-n
my_db" e:\temp\temp.col
DataSourceName connection parameter [DSN]
Function
Usage
Default
See also
Tells the ODBC driver manager or E mbedd ed SQL library where to look in
the
odbc.ini
file or registry to find ODBC data source information.
Anywhere
There is no default data source name.
"FileDataSourceName connection parameter" on page 59
Description
It is common practice for ODBC applications to send only a data source
name to ODBC. The ODBC driver manager and ODBC driver locate the data
source, which contains the remainder of the connection parameters.
In Adaptive Server Anywhere, Embedded SQL applications can also use
ODBC data sources to store connection parameters.
Examples
♦ The following parameter uses a data source name:
DSN=Dynamo Demo
Debug connection parameter [DBG]
Function
Usage
Default
See also
56
To provide diagnostic information on communications links on startup.
Anywhere
No diagnostic information
"Logfile connection parameter" on page 60
Page 75

Chapter 3 Connection and Communication Parameters
Description
If you are having trouble establishing a connectio n to a network server, set
the Debug connection parameter to Yes and the Logfile parameter to a log
file name. Diagnostic information is then placed in the log file.
The DEBUG connection parameter is connection-specific, so from a single
application you can set DEBUG=ON o n one connection and OFF on another,
or set DEBUG=ON on both but log to different files.
Examples
♦ The following data source fragment says to use t he Debug switc h, with
output to a file named
...
DBG=Yes;
Log=ERROR.LOG
...
error.log
.
DisableMultiRowFetch connection parameter [DMRF]
Function
Usage
Default
Description
To turn off multi-row fetches acro ss the network
Anywhere
No
By default, when the database server gets a simple fetch request, the
application asks for extra rows. You can disable this behavior by setting this
parameter to ON.
$ For more information, see "Using cursors in procedures and triggers"
on page 471 of the book ASA User’s Guide.
$ Setting the DisableMultiRowFetch parameter to ON is equivalent to
setting the PREFETCH option to OFF. Fo r more information, see
"Prefetching rows" on page 278 of the book ASA User’s Guide.
Examples
♦ The following connection string fragment prevents prefetching:
DMRF=Yes
EngineName connection parameter [ENG]
Function
Usage
Default
Synonym for ServerName. The name of a running database server to which
you want to connect.
Network servers or running personal servers.
The default local database server.
57
Page 76

Connection parameters
See also
"Identifiers" on page 223
"–n command-line option" on page 32
Description
EngineName is not needed if you wish to connect to the default local
database server.
You need to supp ly an EngineName only if more than one local database
server is running, or you wish to connect to a network server.
In the Sybase Central and Interactive SQL Connect dialog box, and in the
ODBC Administrator, this is the Server Name field.
The server name is interpreted according to the character set of the client
machine. It must be a valid identifier, and long engine names are truncated to
40 characters. On NetBIOS, 16 characters is the maximum length.
Examples
♦ Connect to a server named Guelph:
ENG=Guelph
EncryptedPassword connection parameter [ENP]
Function
Usage
Default
To provide a password, stored in an encrypted fashion in a data source.
Anywhere
None
Description
Data sources are stored on disk as a file or in the registry. Storing passwords
on disk may present a security problem. For this reason, when you enter a
password into a data source, it is stored in an encrypted form.
If both Password and EncryptedPassword are specified, Password takes
precedence.
Encryption connection parameter [ENC]
Function
Usage
Values
Default
Description
58
To encrypt packets sent between the client application and the server.
Anywhere
Boolean
No encryption
You can use this parameter if you are concerned about the security of
network packets. Encryption does affect performance marginally.
Page 77

Chapter 3 Connection and Communication Parameters
This parameter corresponds to the SQL Anywhere Version 5
command-line switch.
Using the
-e switch on the
dbsrv7
command line encrypts packets for all
clients regardless of whether the Encryption parameter is used at the client.
Similarly, if the client asks for encryption, the server will encrypt.
FileDataSourceName connection parameter [FileDSN]
Function
Usage
Default
See also
Description
The FileDataSourceName parameter tells the client library that there is an
ODBC file data source holding information about the database to which you
want to connect.
Both ODBC and Embedded SQL applications can use File data sources
Anywhere
There is no default name.
"DataSourceName connection parameter" on page 56
File data sources hold the same infor mation as ODBC data sources stored in
the registry. File data sources can be easily distributed to end users, so that
connection information does not have to be reco nstructed on each machine.
dbclient
–e
ForceStart connection parameter
Function
Usage
Default
See also
To start a server without attempting to connect to one.
Only with the db_start_engine function
No
"db_start_engine function" on page 61 of the book ASA Programming
Interfaces Guide
Integrated connection parameter [INT]
Function
Usage
Default
See also
Description
To use the integrated login facility.
Anywhere
No
"LOGIN_MODE option" on page 195
The Integrated parameter has the following settings:
59
Page 78

Connection parameters
Yes An integrated login is attempted. If the connection attempt fails
♦
and the LOGIN_MODE option is set to Mixed, a standard login is
attempted.
♦
No This is the default setting. No integrated login is attempted.
For a client application to use an integrated logi n, the server must be running
with the LOGIN_MODE database option set to Mixed or Integrated .
Examples
♦ The following data source fragment uses an integrated login:
INT=yes
LivenessTimeout connection parameter [LTO]
Function
Usage
Values
Default
Description
To control the termination of connections when they are no longer intact.
Network server only
Windows 95/98 and NT, NetWare and multi-threaded UNIX applications
only.
Integer
If no LivenessTimeout value is set, the liveness timeout is controlled b y the
setting on the server, which defaults to 120 seconds.
A liveness packet is sent periodically across a client/server TCP/IP, SPX,
IPX, or NetBIOS communications protocol to co nfirm that a connection is
intact. If the client runs for the liveness timeout period without detecting a
liveness packet, the communication is severed.
Liveness packets are sent at an interval of one quarter of the
LivenessTimeout value when the connection is idle; that is, there have been
no request or response packets sent back and forth for at least one quarter of
the LivenessTimeout value.
Examples
♦ The following sets a Liveness timeout value of 60 seconds
LTO=60
Alternatively, you can set this parameter by entering its value in the Liveness
timeout text box of the Network tab of the connection window.
Logfile connection parameter [LOG]
Function
Usage
60
To send client err or messages and d ebugging messages to a file.
Anywhere
Page 79

Chapter 3 Connection and Communication Parameters
Default
See also
Description
Example
No log file
"Debug connec tion parameter" on page 56
If you want to save client error messages and debugging messages in a file,
use the Logfile parameter.
If the file name includes a path, it is relative to the current working directory
of the client application.
The LogFile connection parameter is connection-specific, so from a single
application you can set different LogFile arguments for different
connections.
The following command line starts Interactive SQL connecting to the
ASA 7.0 Sample data source with a LogFile parameter:
dbisql -c "dsn=ASA 7.0 Sample;dbg=ON;log=d:\logs\test.txt"
Typical log file contents are as follows:
Tue May 30 2000 11:00
CONN: Starting remote ports
Trying to start TCPIP link ...
Loading wsock32.dll
Loading ws2_32.dll
TCP using Winsock version 2.0
My IP address is 172.31.140.75
My IP address is 127.0.0.1
TCPIP link started successfully
Password connection parameter [PWD]
Function
Usage
Default
See also
Description
To provide a password for the connection.
Anywhere
No password provided.
"EncryptedPassword connection parameter" on page 58
Every user of a database has a password. The password must be supplied for
the user to be allowed to connect to the database.
The password parameter is not encrypted. If you are storing passwords in a
data source, you should use the EncryptedPassword parameter. Sybase
Central and the Adaptive Server Anywhere ODBC configuration tool both
use encrypted parameters.
If both Password and EncryptedPassword are specified, Password takes
precedence.
61
Page 80

Connection parameters
Examples
♦ The following connection string fragment supplies the user ID
password
SQL.
uid=DBA;pwd=SQL
Alternatively, you can set these parameters in the User ID and Password
text boxes in t he connection window.
PrefetchBuffer connection parameter [PBUF]
Function
Usage
Default
Description
Example
Set the maximum amount o f memory for buffering rows, in kilobytes.
Anywhere
32
The PrefetchBuffer connection parameter controls the memory allocated on
the client to store prefetched rows. In some circumstances, increasing the
number of rows prefetched from the database server by the client can
improve query performance. You can increase the number of rows
prefetched using the PrefetchRows and PrefetchBuffer connection
parameters.
$ For more information, see "PrefetchRows connection p arameter" on
page 62.
♦ The following connection string fragment could be used to determine if
the PrefetchBuffer memory li mit is reducing the number of rows
prefetched.
…prefetchrows=100;debug=yes;logfile=c:\ client.txt
DBA and
The following string could be used to increase the memory limit to
256K:
…prefetchrows=100;prefetchbuffer=256
PrefetchRows connection parameter [PROWS]
Function
Usage
Default
Description
62
Set the maximum number of rows to prefetch when querying the database.
Anywhere
10
Increasing the number of rows prefetched from the database server by the
client can improve performance on cursors that do only fetch relative 0 or 1,
with either single row or wide fetches. Wide fetches include embedded SQL
array fetches and ODBC block fetches.
Page 81

Chapter 3 Connection and Communication Parameters
Improvements occur particularly under the following conditions:
♦ The application fetches many rows (several hundred or more) with very
few absolute fetches.
♦ The application fetches rows at a high rate, and the client and server are
on the same machine or connected by a fast network.
♦ Client/server communication is over a slow network, such as a dial-up
link or wide area network.
The number of rows prefetched is limited both by the PrefetchRows
connection parameter and the PrefetchBuffer parameter, which limits the
memory available for storing prefetched rows.
$ For more information, see "PrefetchBuffer connection parameter" on
page 62.
Example
♦ The following connection string fragment sets the number of prefetched
rows to 100:
…prefetchrows=100;…
ServerName connection parameter [ENG]
Synonym for "EngineName connection parameter" on page 57.
$ For more infor mation, see "EngineN ame connection parameter" on
page 57.
StartLine connection parameter [START]
Function
Usage
Default
Description
To start a database server running from an application.
Embedded databases
No StartLine parameter
You should supply a StartLine parameter only if you are connecting to a
database server that is not currently running. The StartLine parameter is a
command line to start a personal database server.
$ For a detailed description of available command line switches, see "The
database server" on page 14.
Examples
♦ The following data source fragment starts a personal database server
with a cache of 8 Mb.
StartLine=dbeng7 -c 8M asademo.db
63
Page 82

Connection parameters
Unconditional connection parameter [UNC]
Function
Usage
Default
See also
Description
To stop a server using
dbstop
Anywhere
No
"The dbstop command-line utility" on page 130
The
dbstop
specify
command-line utility shuts down a database server. If you
unc=Yes in the connection string, the server is shut down even if
there are active connections. If Unconditional is not set to Yes, then the
server is shut down only if there are no active connections.
Examples
♦ The following command line shuts down the server unconditionally:
dbstop -c "uid=dba;pwd=sql;eng=
Userid connection parameter [UID]
Function
Usage
Default
Description
Examples
The user ID with which you log on to the da tabase.
Anywhere
None
You must always supply a user ID when connecting to a database
♦ The following connection string fragment supplies the user ID
password
SQL:
uid=DBA;pwd=SQL
even when there are connections to the server.
server-name
;unc=yes"
DBA and
64
Page 83

Chapter 3 Connection and Communication Parameters
Network communications parameters
If you experience problems with c lient/server network communications,
there are a number of command line parameters for both the client and the
server. These parameters enable you to work around peculiarities of different
network protocol implementations.
You can supply the network communication parameters on the server
command line as in the following example:
dbsrv7 -x tcpip(PARM1=value1;PARM2=value2;. . .),IPX
From the client side, the communications parameters are entered as the
CommLinks communicat ion parameter:
CommLinks=tcpip(PARM1=value1;PARM2=value2;. . .),IPX
If there are spaces in a parameter, the network communication parameters
must be enclosed in quotation marks to be parsed properly by the system
command interpreter:
dbsrv7 -x "tcpip(PARM1=value 1;PARM2=value 2;...),IPX"
CommLinks="tcpip(PARM1=value 1;PARM2=value 2;...),IPX"
The quotation marks are required under UNIX if more than one parameter is
given, because UNIX interprets the semicolon as a command separator.
Boolean parameters are turned on with YES, ON, TRUE, or 1, and are turned
off with any of NO, OFF, FALSE, and 0. The parameters are caseinsensitive.
The examples provided should all be entered on a single line; you can also
include them in a configuration file and use the @ server command-line
switch to invoke the configuration file.
The parameters currently available are as follows.
ClientPort parameter [CPort]
Usage
Default
See also
TCP/IP. Client side only.
Assigned dynamically per-connection by the networking implementation. If
you do not have firewall restr i ctions, it is recommended that you do not use
this parameter.
"Host parameter" on page 68
"DoBroadcast parameter" on page 66
"ServerPort parameter" on page 70
"Connecting across a firewall" on page 96 of the book ASA User’s Guide
65
Page 84

Network communications parameters
Description
This option is provided for connections across firewalls, as firewall software
filters according to TCP/UDP port. It is recommended that you do not use
this parameter unless you need to for firewall reasons.
The ClientPort option designates the port number on which the client
application communicates using TCP/IP. You may specify a single port
number, or a combination of individual port numbers and ranges of port
numbers.
It is best to specify a list or a range of port numbers if you wish to make
multiple connections using a give n Data Source or given connect stri ng. If
you specify a single port number, then your application will be able to
maintain only one connection at a time. In fact, even after closing the one
connection, there is a short timeout period during which no new conne ction
can be made using the specified port. When you specify a list and/or range of
port numbers, the application keeps trying port numbers until it finds one to
which it can successfull y bind.
Examples
♦ The following string makes a connection from an application using port
6000 to a server named my_server using port 5000:
CommLinks=tcpip{ClientPort=6000;ServerPort=5000};
ServerName=my_server
♦ The following string makes a connection from an application that can
use ports 5050 through 5060, as well as ports 5040 and 5070 for
communicating with a server named my_server using the default server
port:
CommLinks=tcpip{ClientPort=5040,50505060,5070};ServerName=my_server
DoBroadcast parameter
Usage
Description
66
TCP/IP (all platforms)
IPX, SPX (all platforms except UNIX and CE)
DOBROADCAST=ALL (formerly DOBROADCAST=YES) a broadcast is
performed to search for a server. For IPX and SPX, the broadcast is only
performed if the server is not found in the bindery.
With DOBROADCAST=DIRECT (formerly DOBROADCAST= NO), no
broadcast is performed to search for a database server. In this case, you must
specify the server host with the HOST option.
Page 85

Chapter 3 Connection and Communication Parameters
Specifying DoBroadcast=NONE causes no UDP or IPX broadcasts to be
used. This option is helpful if you are attempting to connect to a server that is
protected by a firewall, since many firewalls filter out UDP packets.
YES and NO arguments are still accepted.
Default
Example
ALL
♦ The following command starts a client without broadcasting to search
for a database server. Instead, the server is looked for only on the
computer named silver.
CommLinks=tcpip(DOBROADCAST=DIRECT;HOST=silver)
asademo
DLL parameter
Usage
Description
Default
Example
TCP/IP, SPX (Windows 95/98, Windows NT)
To support untested TCP/IP protocol stacks where the required networking
interface functions are in DLLs that differ from the default protocol stack.
The client or server looks for its required functionality in the na med DLLs.
♦ On Windows NT, the default is
♦ On Windows 95/98 the default is
♦ The following command starts a server using Winsock 1.1
dbsrv7 -x tcpip(dll=wsock32.dll) asademo
ExtendedName parameter
ws2_32.dll
wsock32.dll
(Winsock 2.0).
(Winsock 1.1).
:
Usage
Description
Default
IPX (platforms other than Windows 95/98 or NT)
According to the Novell standard for legal SAP names, the following
characters are not allowed:
\ / : ; , * ? + -
If you start a server named "asademo-1", the default behavior is to strip out
the - and try to start a server asademo1. By turning on ExtendedName, the
name is left untouched.
Caution
Users should be wary of using this option as it is contrary to the SAP
standard.
No.
67
Page 86

Network communications parameters
Example
♦ The following command starts a NetWare server with name asademo-1.
Host parameter [IP]
Usage
Where
See also
Description
TCP/IP, SPX, IPX (all platforms)
Server and client sides
"Debug connec tion parameter" on page 56
"ClientPort parameter" on page 65
HOST specifies additional machines outsid e the immediate network to be
searched by the client library. It also disables UDP broadcasts on TCP/IP
clients. On the server, the search is carried out to avoid starting a server with
a duplicate name.
For TCP/IP, the hostname or a dot-separated IP address may be used. For
SPX and IPX, an address of the form a:b:c:d:e:f/g:h:i:j is used, where
a:b:c:d:e:f is the node number (Ethernet card address) of the server, and
g:h:i:j is the network number. The server prints this addressing i nformation
during startup if the
information to its logfile if Debug is set to TRUE and LogFile is specified.
You can use a semicolon-separated list of addresses to search for more than
one machine. Also, you can append a port number to an IP address, using a
colon as separator. Alternatively, you can specify the host and server ports
explicitly, as in Host=a:b:c:d:e:f;ServerPort=k.
load dbsrv7.nlm -x ipx(ExtendedName=Yes) asademo-1
-Z switch is used. In additio n, the application writes this
IP is a synonym for HOST.
Default
Example
No additional machines.
♦ The following connection string fragment instructs the client to look on
MaxLANA parameter
Usage
68
NetBIOS
the machines "kangaroo" and 197.75.209.222 (port 2369) to find a
database server:
Links=tcpip(IP=kangaroo;IP=197.75.209.222:2369)
Page 87

Chapter 3 Connection and Communication Parameters
Description
Default
Example
MyIP parameter
Usage
Description
Each path through a NetBIOS protocol stack is assigned a LAN adapter
number. By default, the server looks through all possible numbers up to 255.
To speed up server startup, you can truncate the search for valid LAN
adapters at a specified value using the MAXLANA parameter.
255
♦ The following command line looks only at LAN adapters with numbers
less than 10 to identify active protocol stacks:
dbsrv7 -x netbios(MaxLANA=10) asademo
TCP/IP
The MyIP parameter is provided for machines with more than one network
adapter.
Each adapter has an IP address. By default, the database server uses the first
network card it finds. If you wish your database server to use more than one
network card, specify the address of each card in the MyIP parameter.
If the keyword NONE is supplied as the IP number, no attempt is made to
determine the addressing information. The NONE keyword is intended for
clients on machines where this operation is expensive, such as machines with
multiple network cards or remote access (RAS) software and a network card.
It is not intended for use on the server.
Example
Under Windows 95/98 or Windows NT, this option can be used multiple
times for machines with multiple IP addresses.
You can optionally append a port number to the IP address, separated by a
colon.
♦ The following command line (entered all on one line) instructs the
server to use two network cards, one with a specified port number.
dbsrv7 -x
tcpip(MyIP=192.75.209.12:2367,192.75.209.32)
c:\asa7\asademo.db
♦ The following connection string fragment instructs the client to make no
attempt to determine addressing information.
Links= tcpip(MyIP=NONE)
69
Page 88

Network communications parameters
ReceiveBufferSize parameter
Usage
Description
Default
TCP/IP
Sets the size for a buffer used by the TCP/IP protocol stack. You may want
to increase the value if blob performance over the network is important.
Machine-dependent.
RegisterBindery parameter [REGBIN]
Usage
Description
Default
IPX, SPX (Windows 95/98 and NT only). Server side only.
The database server attempts to register its name with any active binderies on
the network when loading the IPX link. To disable this name registration, set
RegisterBindery to NO, FALSE or 0. In this case, the client library must be
able to locate the database server over IPX by broadcasting packets.
TRUE
SearchBindery parameter [BINSEARCH]
Usage
Description
Default
IPX, SPX (Windows 95/98 and NT only)
With SEARCHBINDERY=NO, 0, or OFF no NetWare bindery is searched
for a database server.
Yes
SendBufferSize parameter
Usage
Description
Default
TCP/IP
Sets the size for a buffer used by the TCP/IP protocol stack. You may want
to increase the value if blob performance over the network is important.
Machine-dependent.
ServerPort parameter [PORT]
Usage
70
TCP/IP (all platforms)
Page 89

Chapter 3 Connection and Communication Parameters
Description
Default
Example
The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority has assigned the Adaptive Server
Anywhere database server port number 2638 to use for TCP/IP
communications. However, applications are not disallowed from using this
reserved port, and this may result in an addressing collision between the
database server and another application.
In the case of the database server, the ServerPort option designates the port
number on which to communicate using TCP/IP.
In a data source, the ServerPort option informs the client of the port or ports
on which database servers are listening for TCP /IP communication. The
client broadcasts to every port that is specified on the ServerPort parameter
to find the server.
The database server always listens on port 2638, even if you specify a
different port using a network communica tion parameter. Hence,
applications can connect to the database server without specifying a port
number. An exception is the HP-UX operating system, on which the server
does not listen on port 2638 if it is started on another port.
2638
1 Start a network database server:
dbsrv7 -x tcpip -n server1
Port number 2638 is now taken.
2 Attempt to start another database server:
dbsrv7 -x tcpip -n server2
Sessions parameter
Usage
Description
Default
NetBIOS. Server side only.
Sets the maximum number of clients that can communicate with the server at
one time through a single LAN adapter. The default setting is op eratingsystem specific. The value is an integer, with maximum value 254.
NetBIOS network software has a limit to the number of commands allowed
per machine. Adaptive Server Anywhere uses these NetBIOS commands,
and disallows further connections if the system has no more commands
available, even if this is less than the value of the Sessions parameter.
Operating system specific. On Windows NT, the default is 16.
The default port is currently allocated, and so the server starts on another
port.
71
Page 90

Network communications parameters
Example
♦ The following statement starts a server with a database named asademo,
TDS parameter
Usage
Description
Default
Example
TCP/IP, NamedPipes. Server side only.
To disallow TDS connections to a database server, set TDS to NO. If you
want to ensure that only encrypted connections are made to your server,
these port options are the only way to disallow TDS connections.
YES
♦ The following command starts a database server using the TCP/IP
Threads parameter
Usage
Description
IPX (Windows 95/98 and Windows NT)
THREADS specifies the number of threads that are used for reading network
communications. Integers from one to ten are allowed. It has been found that
two threads produces good performance, but the option is provided as a
performance parameter that you can tune.
allowing 200 NetBIOS connections.
dbsrv7 -x netbios(sessions=200) asademo.db
protocol, but disallowing connections from Open Client or jConnect
applications.
dbsrv7 -x tcpip(TDS=NO) ...
Default
Example
2
♦ The following command starts a database server to use the IPX protocol
only, using three threads.
dbsrv7 -x ipx(threads=3) c:\asa7\asademo.db
ThreadStats parameter [STATS]
Usage
Description
Default
72
IPX (Windows 95/98 and Windows NT only)
This option creates a file into which IPX thread statistics are written.
Currently, the only statistic written to the file is the number of packets
received by each executing IPX thread.
NULL
Page 91

Chapter 3 Connection and Communication Parameters
Example
♦ The following statement places the statistics in the file
current directory.
Timeout parameter [TO]
Usage
Description
Default
Example
TCP/IP, IPX, SPX (all platforms)
TIMEOUT specifies the length of time, in seconds, to wait for a response
when establishing communications. You may wish to try longer times if you
are having troub l e establishing TCP/IP communic ations.
5 seconds.
♦ The following data source fragment starts a TCP/IP communications
link only, with a timeout period of twenty seconds.
dbsrv7 -x ipx(threadstats=ipxstat.txt)
c:\asa7\asademo.db
...
CommLinks=tcpip(TO=20)
...
ipxstat.txt
in the
73
Page 92

Network communications parameters
74
Page 93

CHAPTER 4
Database Administration Utilities
About this chapter
Contents
Adaptive Server Anywhere includes a set of utility programs for backing up
databases and performing other database administration tasks. This chapter
provides reference information for each of the database administration
utilities.
Topic Page
Administration utilities overview 77
The Backup utility 78
The Collation utility 82
The Compression utility 85
The Console utility 87
The Data Source utility 89
The Erase utility 94
The Information utility 96
The Initialization utility 98
The Interactive SQL utility 106
The License utility 109
The Log Transfer Manager 111
The Log Translation utility 117
The Ping utility 122
The REBUILD utility 124
The Server Location utility 125
The Service Creation utility 126
The Spawn utility 129
The Stop utility 130
The Transaction Log utility 132
The Uncompression utility 136
75
Page 94

Administration utilities overview
The Unload utility 138
The Upgrade utility 145
The Validation utility 148
The Write File utility 151
76
Page 95

Chapter 4 Database Administration Utilities
Administration utilities overview
This chapter presents reference information on the programs and database
administration utilities that are part of Adaptive Server Anywhere. The
utilities can be accessed from Sybase Central, from Interactive SQL, or as
command-l i ne programs.
$ For comprehensive documentation on Sybase Central, see the Sybase
Central online Help. For an introduction to t he S yba se Central database
administration tool, see "Managing Databases with Sybase Central" on
page 35 of the book Introducing SQL Anywhere Studio.
The administration utilities use a set of system environment variables. These
variables are described in "Environment variables" on page 6.
Database file
administration
statements
A set of SQL statements are available that carry out some of the tasks that
the administration utilities carry out. These statements are listed in "SQL
Statements" on page 377.
77
Page 96

The Backup utility
The Backup utility
With the Backup utility, you can back up running databases, database files,
transaction logs, and write files.
You can access the Backup utility in the following ways:
♦ From Sybase Central
♦ From the system command line, using the
useful for incor porating backup procedures into batch or command files.
The Backup utility makes a backup copy of all the files for a single database.
A simple database consists of two files: the main database file and the
transaction log. More complicated databases can stor e tables in multiple
files, with each file as a separate dbspace. All backup filenames are the same
as the database filenames.
Running the Backup utility on a running database is equivalent to co pying
the database files when the database is not running. Thus, you can back up
the database while other applications or users are using it.
$ For a description of suggested backup procedures, see "Backup and
Data Recovery" on page 645 of the book ASA User’s Guide.
$ For more information about the backup utility, see " BACKUP
statement" on page 401.
Backing up a database from Sybase Central
v To back up a running database:
1 Connect to the database.
2 Right-click the database and choose Backup in the popup menu. The
Backup wizard appears.
dbbackup
utility. This is
78
3 Follow the instructions in the wizard.
v To back up a database file or a running database:
1 Open the Utilities folder in the left panel.
2 Double-click Backup Database in the right panel.
3 Follow the instructions in the wizard.
Page 97

$ For full information on backing up a database fro m S ybase Central, see
"Backup and Data Recovery" on page 645 of the book ASA User’s Guide.
For more information about options, see " Backup utility options" on p a ge 79
The dbbackup command-line utility
Chapter 4 Database Administration Utilities
Syntax
Description
dbbackup [
Switch Description
–c "keyword=value; ..." Supply database connection parameters
–d
–l file Live backup of the transaction log to a file
–n
–o filename Log output messages to a file
–q
–r
–t
–w
–x
–xo
–y
switches
]
directory
Only back up the main database file
Change the naming conventi on for the backup
transaction log
Quiet mode—do not print messages
Rename and start a new transaction log
Only back up the transaction log
Only back up the write file
Delete and restart the transaction log
Delete and restart the transaction log without
making a backup
Replace files without confirmation
If none of the s witches -d, -t, or -w are used, all database files are backed
up.
$ For more information about the command-line switches, see "Backup
utility options" on pa ge 79.
Backup utility options
Directory The directory to which the backup files are copied. If the
directory does not exist, it is created. However, the parent directory must
exist.
79
Page 98

The Backup utility
Connection parameters (–c) For a description of the connection
parameters, see "Connection parameters" on page 64 of the book ASA User’s
Guide. If the connection parameters are not specified, connection parameters
from the SQLCONNECT environment variable are used, if set. The user ID
must have DB A authority or RE MOTE DBA authority.
For example, the following command backs up the asademo database
running on the server sample_server, connecting as user ID
password
dbbackup -c "eng=sample_server;dbn=asademo;uid=DBA;pwd=SQL" asabackup
Backup main database only (–d) Back up the main database files only,
SQL, into the
asabackup
directory:
DBA with
without backing up the transaction log file or a write file, if one exists.
Live backup (–l lower-case L) This option is provided to enable a
secondary system to be brought up rapidly in the eve nt of a server crash. A
live backup does not terminate, but continues running while the server runs.
It runs until the primary server crashes. At that point, it is shut down, but the
backed up log file is intact and can be used to bring a secondary system up
quickly.
Change backup transaction log naming convention (–n) This option
is used in conjunction with
backup transaction log file to
to 99 and
yymmdd
represents the current year, month and day.
-r. It changes the naming convention of the
yymmddnn.log
, where nn is a number from 00
80
The backup copy of the transaction log file is stored in the directory specified
on the command line, and with the
yymmddnn.log
naming convention. This
allows backups of multiple versions of the transaction log file to be kep in
the same backup directory.
The two-digit year notation does not cause any year 2000 problems. The
names are used solely for identification, not for ordering.
Log output messages to file (–o) Write output messages to the named
file.
Operate quietly (–q) Do not display output messages. This option is
available only from the command-line utility.
Rename and start new transaction log (–r) This option forces a
checkpoint and the following three steps to occur:
♦
Step 1 The current working transaction log file is co pied and saved to
the directory specified in the command line.
Page 99

Chapter 4 Database Administration Utilities
Step 2 The current transaction log remains in its current directory, but
♦
is renamed usi ng the format
00 to 99 and
yymmdd
yymmdd
represents the current year, month and day. This
xx.
log
, where xx is a number from
file is then no longer the current transaction log.
♦
Step 3 A new transaction log file is ge nerated that contains no
transactions. It is given the name o f the file that was previously
considered the current transaction log, and is used by the database server
as the current transaction log.
Back up the transaction log file only (–t) This can be used as an
incremental backup since the transactio n log can be applied to the most
recently backed up copy of the database file(s).
Back up the database write file only (–w) For a description of database
write files, see "The Write File utility" on page 151.
Delete and restart the transaction log (–x) Back up the existing
transaction log, then delete the original log and start a new transaction log.
This option causes the backup to wait for a po int when all transactions from
all connections are committed.
Delete and restart the transaction log without a backup (–xo) Delete
the current transaction log and start a ne w one. This operation does not carry
out a backup; its purpose is to free up disk space in non-replication
environments.
Operate without confirming actions (–y) Choosing this option creates
the backup directory or the replacement of a previous backup file in the
directory without confirmation.
81
Page 100

The Collation utility
The Collation utility
With the Collation utility, you can extract a collation (sorting seque nce) into
a file suitable for creating a database using a custom collation.
The file that is produced can be modified and used with Sybase Central or
the
-z option of
You must change the label on the following line in the collation file. If you
do not, the custom collation will co nflict with the original collation on which
it is based.
Collation label (name)
$ For more information on custom collating sequences, see "Creating a
database with a custom collation" on page 326 of the book ASA User’s
Guide.
You can access the Collation utility in the following ways:
♦ From Sybase Central
dbinit
to create a new database with a custom collation.
♦ From the system command line, using the
Extracting a collation using Sybase Central
v To use the Collation utility from Sybase Central:
1 Open the Utilities folder in the left panel.
2 Double-click Create a Custom Collation in the right panel. The Custom
Collation wizard appears.
3 Follow the instructions in the wizard.
Tip
You can also access this wizard by clicking Tools➤Adaptive Server
Anywhere➤Create a Custom Collation.
The dbcollat command-line utility
Syntax
dbcollat [
switches
]
output-file
dbcollat
command-line utility
82
 Loading...
Loading...